Fluoroanion: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
added Category:Double salts using HotCat |
+image |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Negatively-charged ion containing a fluorine atom}} |
|||
A '''fluoroanion''' is an [[anion]] contain an element, and fluorine atoms. They are also known as '''complex fluorides'''. They can occur in salts, or in solution, but not as pure acids. They often contain elements in higher oxidation states. They mostly can be considered as fluorometalates which are a subclass of halometalates. |
|||
{{Chembox |
|||
|ImageFile = F-.svg |
|||
|ImageSize = 75px |
|||
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers |
|||
| ChEBI = 51527 |
|||
}} |
|||
|Section8={{Chembox Related |
|||
| OtherAnions = [[Chloroanion]]; [[Bromoanion]]; [[Iodoanion]]; [[Oxyanion]]; [[Thioanion]]; [[Selenoanion]] |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
In [[chemistry]], a '''fluoroanion''' or '''fluorometallate anion''' is a [[polyatomic anion]] that contains one or more [[fluorine]] atoms. The ions and salts form from them are also known as '''complex fluorides'''. They can occur in [[salts]], or in solution, but seldom as pure [[acid]]s. Fluoroanions often contain elements in higher [[oxidation state]]s. They mostly can be considered as fluorometallates, which are a subclass of halometallates.<ref>{{cite web |title=fluorometallate anion (CHEBI:51527) |url=https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI%3A51527 |website=www.ebi.ac.uk}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=fluorometallate anion - Ontology Browser - Rat Genome Database |url=https://rgd.mcw.edu/rgdweb/ontology/view.html?acc_id=CHEBI:51527 |website=rgd.mcw.edu}}</ref> |
|||
Anions that contain both fluorine and oxygen can be called "oxofluoroanions" (or rarely "fluorooxoanions"). |
|||
The following is a list of fluoroanions in [[atomic number]] order. |
The following is a list of fluoroanions in [[atomic number]] order. |
||
*[[trifluoroberyllate]] |
*[[trifluoroberyllate]] |
||
*[[tetrafluoroberyllate]] |
*[[tetrafluoroberyllate]] |
||
*[[tetrafluoroborate]] |
*[[tetrafluoroborate]] |
||
*[[magnesium tetrafluoride]] |
|||
*[[pentafluorocyclopentadienide]] |
|||
*[[trifluoroaluminate]] {{chem2|AlOF3(2−)}} |
|||
*[[tetrafluoroaluminate]] |
|||
*[[pentafluoroaluminate]] |
|||
*[[hexafluoroaluminate]] |
|||
*[[heptafluoroaluminate]] |
|||
*[[hexafluorosilicate]] |
*[[hexafluorosilicate]] |
||
*[[hexafluorophosphate]] |
*[[hexafluorophosphate]] |
||
*[[Sulfur trifluoride anion]] |
*[[Sulfur trifluoride anion]] |
||
*[[pentafluorosulfate]] aka pentafluorosulfite or Sulfur pentafluoride ion |
|||
*[[sulfur pentafluoride anion]] |
*[[sulfur pentafluoride anion]] |
||
*[[tetrafluorochlorate]] |
*[[tetrafluorochlorate]] |
||
*[[hexafluorotitanate]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[hexafluorovanadate(III)]] |
|||
*[[hexafluorovanadate(IV)]] |
|||
*[[hexafluorovanadate(V)]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[hexafluoromanganate(III)]] |
*[[hexafluoromanganate(III)]] |
||
*[[hexafluoromanganate(IV)]] |
*[[hexafluoromanganate(IV)]] |
||
*[[heptafluoromanganate]] IV |
|||
*[[Tetrafluoroferrate]] |
*[[Tetrafluoroferrate]] 1− and 2− |
||
*[[hexafluoroferrate]] 4− and 3− |
*[[hexafluoroferrate]] 4− and 3− |
||
*[[tetrafluorocobaltate]] II |
|||
*[[Hexafluorocobaltate]] III and IV<ref name="Klemm">{{cite journal|last1=Klemm|first1=W.|last2=Brandt|first2=W.|last3=Hoppe|first3=R.|title=Über Fluorocobaltate(III) und -(IV) und Fluoroniccolate(III)|journal=Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie|date=March 1961|volume=308|issue=1–6|pages=179–189|doi=10.1002/zaac.19613080119}}</ref> |
|||
*[[Heptafluorocobaltate]] IV<ref name="Klemm"/> |
|||
*[[Tetrafluoronickelate]] |
|||
*[[Hexafluoronickelate]] II, III and IV |
|||
*[[hexafluorocuprate]] |
*[[hexafluorocuprate]] |
||
*[[tetrafluorozincate]] |
*[[tetrafluorozincate]] |
||
| Line 23: | Line 55: | ||
*[[tetrafluorobromate]] |
*[[tetrafluorobromate]] |
||
*[[hexafluorobromate]] |
*[[hexafluorobromate]] |
||
*[[pentafluorozirconate]] |
*[[pentafluorozirconate]] {{chem2|ZrF5(-)}} |
||
*[[ |
*[[hexafluorozirconate]] |
||
*[[octafluorozirconate]] ( |
*[[octafluorozirconate]] {{chem2|ZrF8(4-)}} |
||
*[[hexafluoroniobate]] |
*[[hexafluoroniobate]] |
||
*[[heptafluoroniobate]] |
*[[heptafluoroniobate]] |
||
*[[octafluoromolybdate]] ( |
*[[octafluoromolybdate]] {{chem2|MoF8(2-)}} |
||
*[[tetrafluoropalladate]] |
*[[tetrafluoropalladate]] |
||
*[[hexafluororhodate]] |
*[[hexafluororhodate]] |
||
| Line 38: | Line 70: | ||
*[[hexafluoroiodate]] 1− |
*[[hexafluoroiodate]] 1− |
||
*[[octafluoroxenate]] |
*[[octafluoroxenate]] |
||
*[[tetrafluorolanthanate]] {{chem2|LaF4(-)}} |
|||
*[[pentafluorocerate]] IV |
|||
*[[Hexafluorocerate]] IV<ref name=doic/> |
|||
*[[Heptafluorocerate]] IV<ref name=doic/> |
|||
*[[octafluorocerate]] IV<ref name=doic>{{cite book|last1=Macintyre|first1=Jane E.|title=Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds|date=1992|publisher=CRC Press|isbn=9780412301209|page=2819|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9eJvoNCSCRMC&pg=PA2819|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
*[[pentafluorohafnate]] |
*[[pentafluorohafnate]] |
||
*[[hexafluorohafnate]] |
*[[hexafluorohafnate]] |
||
*[[heptafluorotantalate]] |
*[[heptafluorotantalate]] {{chem2|TaF7(-)}} |
||
*[[octafluorotantalate]] |
*[[octafluorotantalate]] |
||
*[[heptafluorotungstate]] |
*[[heptafluorotungstate]] |
||
*[[octafluorotungstate]] ( |
*[[octafluorotungstate]] {{chem2|WF8(2-)}} |
||
*[[octafluororhenate]] |
*[[octafluororhenate]] |
||
*[[hexafluoroplatinate]] |
*[[hexafluoroplatinate]] |
||
*[[tetrafluoroaurate]] {{chem2|AuF4(-)}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[hexafluoroaurate]] {{chem2|AuF6(-)}} |
|||
*[[hexafluorothallate(III)]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[hexafluorobismuthate]] |
|||
*[[hexafluorothorate]] |
|||
*[[hexafluorouranate(IV)]] |
|||
*[[hexafluorouranate(V)]] |
|||
*[[octafluorouranate(IV)]] |
|||
*[[octafluorouranate(V)]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
[[Category:Fluorine compounds]] |
[[Category:Fluorine compounds]] |
||
Latest revision as of 07:47, 10 December 2024
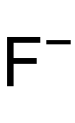
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Chloroanion; Bromoanion; Iodoanion; Oxyanion; Thioanion; Selenoanion |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
In chemistry, a fluoroanion or fluorometallate anion is a polyatomic anion that contains one or more fluorine atoms. The ions and salts form from them are also known as complex fluorides. They can occur in salts, or in solution, but seldom as pure acids. Fluoroanions often contain elements in higher oxidation states. They mostly can be considered as fluorometallates, which are a subclass of halometallates.[1][2]
Anions that contain both fluorine and oxygen can be called "oxofluoroanions" (or rarely "fluorooxoanions").
The following is a list of fluoroanions in atomic number order.
- trifluoroberyllate
- tetrafluoroberyllate
- tetrafluoroborate
- magnesium tetrafluoride
- trifluoroaluminate AlOF2−3
- tetrafluoroaluminate
- pentafluoroaluminate
- hexafluoroaluminate
- heptafluoroaluminate
- hexafluorosilicate
- hexafluorophosphate
- Sulfur trifluoride anion
- pentafluorosulfate aka pentafluorosulfite or Sulfur pentafluoride ion
- sulfur pentafluoride anion
- tetrafluorochlorate
- hexafluorotitanate
- hexafluorovanadate(III)
- hexafluorovanadate(IV)
- hexafluorovanadate(V)
- trifluoromanganate MnF−3
- hexafluoromanganate(III)
- hexafluoromanganate(IV)
- heptafluoromanganate IV
- Tetrafluoroferrate 1− and 2−
- hexafluoroferrate 4− and 3−
- tetrafluorocobaltate II
- Hexafluorocobaltate III and IV[3]
- Heptafluorocobaltate IV[3]
- Tetrafluoronickelate
- Hexafluoronickelate II, III and IV
- hexafluorocuprate
- tetrafluorozincate
- Hexafluorogallate
- hexafluorogermanate
- hexafluoroarsenate
- tetrafluorobromate
- hexafluorobromate
- pentafluorozirconate ZrF−5
- hexafluorozirconate
- octafluorozirconate ZrF4−8
- hexafluoroniobate
- heptafluoroniobate
- octafluoromolybdate MoF2−8
- tetrafluoropalladate
- hexafluororhodate
- hexafluororuthenate(IV)
- hexafluororuthenate(V)
- hexafluoroindate
- hexafluorostannate
- fluoroantimonate
- hexafluoroiodate 1−
- octafluoroxenate
- tetrafluorolanthanate LaF−4
- pentafluorocerate IV
- Hexafluorocerate IV[4]
- Heptafluorocerate IV[4]
- octafluorocerate IV[4]
- pentafluorohafnate
- hexafluorohafnate
- heptafluorotantalate TaF−7
- octafluorotantalate
- heptafluorotungstate
- octafluorotungstate WF2−8
- octafluororhenate
- hexafluoroplatinate
- tetrafluoroaurate AuF−4
- hexafluoroaurate AuF−6
- hexafluorothallate(III)
- tetrafluorobismuthate BiF−4
- hexafluorobismuthate
- hexafluorothorate
- hexafluorouranate(IV)
- hexafluorouranate(V)
- octafluorouranate(IV)
- octafluorouranate(V)
References
[edit]- ^ "fluorometallate anion (CHEBI:51527)". www.ebi.ac.uk.
- ^ "fluorometallate anion - Ontology Browser - Rat Genome Database". rgd.mcw.edu.
- ^ a b Klemm, W.; Brandt, W.; Hoppe, R. (March 1961). "Über Fluorocobaltate(III) und -(IV) und Fluoroniccolate(III)". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 308 (1–6): 179–189. doi:10.1002/zaac.19613080119.
- ^ a b c Macintyre, Jane E. (1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 2819. ISBN 9780412301209.
