May 2003 lunar eclipse: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Total lunar eclipse 16 May 2003}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" align=right width=240 |
|||
{{Infobox lunar eclipse |
|||
! bgcolor=#e7dcc3 colspan=2|Total Lunar Eclipse<BR>May 16, 2003 |
|||
| type = total |
|||
| image = Lunar eclipse May 2003-TLR75.jpg |
|||
| caption = Totality as viewed from [[Minneapolis, MN]], 3:17 UTC |
|||
| date = May 16, 2003 |
|||
| gamma = 0.4123 |
|||
| magnitude = 1.1294 |
|||
| saros_ser = 121 |
|||
| saros_no = 54 of 82 |
|||
| totality = 51 minutes, 12 seconds |
|||
| partiality = 193 minutes, 53 seconds |
|||
| penumbral = 306 minutes, 31 seconds |
|||
| p1 = 1:06:53 |
|||
| u1 = 2:03:11 |
|||
| u2 = 3:14:26 |
|||
| greatest = 3:40:09 |
|||
| u3 = 4:05:51 |
|||
| u4 = 5:17:05 |
|||
| p4 = 6:13:24 |
|||
| previous = November 2002 |
|||
| next = November 2003 |
|||
}} |
|||
A total [[lunar eclipse]] occurred at the Moon’s [[Lunar node|descending node]] of orbit on Friday, May 16, 2003,<ref>{{cite web|title=May 15–16, 2003 Total Lunar Eclipse (Blood Moon)|url=https://www.timeanddate.com/eclipse/lunar/2003-may-15|publisher=timeanddate|access-date=12 November 2024}}</ref> with an umbral [[Magnitude of eclipse|magnitude]] of 1.1294. A lunar eclipse occurs when the [[Moon]] moves into the [[Earth's shadow]], causing the Moon to be darkened. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon's near side entirely passes into the Earth's umbral shadow. Unlike a [[solar eclipse]], which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the [[night]] side of Earth. A total lunar eclipse can last up to nearly two hours, while a total solar eclipse lasts only a few minutes at any given place, because the Moon's [[Umbra, penumbra and antumbra|shadow]] is smaller. Occurring only about 15 hours after [[Apsis|perigee]] (on May 15, 2003, at 11:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.<ref>{{cite web|title=Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England|url=https://www.timeanddate.com/astronomy/moon/distance.html?year=2003&n=136|publisher=timeanddate|access-date=12 November 2024}}</ref> |
|||
This lunar eclipse marks the beginning of a [[Tetrad (astronomy)|tetrad]], with four total lunar eclipses in series, the others being on [[November 2003 lunar eclipse|November 9, 2003]]; [[May 2004 lunar eclipse|May 4, 2004]]; and [[October 2004 lunar eclipse|October 28, 2004]]. The previous series was in 1985 and 1986, starting with the [[May 1985 lunar eclipse]]. The next series was in 2014 and 2015, starting with the [[April 2014 lunar eclipse]]. |
|||
== Visibility == |
|||
The eclipse was completely visible over eastern [[North America]], [[South America]], the [[Caribbean]], [[Antarctica]], and [[west Africa]], seen rising over western [[North America]] and the [[Pacific Ocean]] and setting over [[Europe]], [[west Asia]], and much of [[Africa]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Total Lunar Eclipse of 2003 May 16|url=https://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/LEplot/LEplot2001/LE2003May16T.pdf|publisher=NASA|access-date=12 November 2024}}</ref> |
|||
{| class=wikitable width=480 |
|||
|[[File:Lunar eclipse from moon-2003May16.png|240px]] |
|||
|[[File:Lunar eclipse chart close-03may16.png|240px]]<BR>Hourly motion shown right to left |
|||
|- align=center |
|||
|colspan=2| [[File:Lunar eclipse chart-03may16.png|250px]]<BR>The moon's path across the Earth's shadow near its descending node in [[Libra (constellation)|Libra]]. |
|||
|} |
|||
== Gallery == |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
Image:Lunar eclipse May 2003-TLR100.jpg|Wide Angle view from [[Minneapolis]] at 3:35 UTC, near greatest eclipse |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== Eclipse details == |
|||
Shown below is a table displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. It describes various parameters pertaining to this eclipse.<ref>{{cite web|title=Total Lunar Eclipse of 2003 May 16|url=https://eclipsewise.com/lunar/LEprime/2001-2100/LE2003May16Tprime.html|publisher=EclipseWise.com|access-date=12 November 2024}}</ref> |
|||
{|class="wikitable" align="{{{align|left}}}" style="margin:{{#ifeq:{{{align}}}|right|0 0 0.5em 1em|0 1em 0.5em 0}}" |
|||
|+May 16, 2003 Lunar Eclipse Parameters |
|||
! Parameter |
|||
! Value |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Penumbral Magnitude |
|||
| align=center colspan=2| [[Image:Lunar eclipse May 2003-TLR75.jpg|240px]]<BR>From [[Minneapolis, Minnesota]], 3:17 UTC |
|||
| 2.07649 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Umbral Magnitude |
|||
| align=center colspan=2| [[Image:Lunar eclipse chart close-03may16.png|240px]]<BR>The moon's path through the Earth's shadow. |
|||
| 1.12938 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Gamma |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#c0d0e0| [[Saros cycle|Series (and member)]] || [[List of lunar eclipses in saros series 121|121]] (51 of 82) |
|||
| 0.41234 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Sun Right Ascension |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#c0d0e0| Date || 16 May 2003 |
|||
| 03h30m07.2s |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Sun Declination |
|||
!align=center bgcolor=#c0b0e0 colspan=2| Duration (hr:mn:sc) |
|||
| +18°59'20.2" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Sun Semi-Diameter |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#b0a0e0 | Totality || 51:25 |
|||
| 15'49.2" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Sun Equatorial Horizontal Parallax |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#c0a0e0 | Partial || 3:13:54 |
|||
| 08.7" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Moon Right Ascension |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#d0d0e0 | Penumbral || 5:06:31 |
|||
| 15h30m43.0s |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Moon Declination |
|||
!align=center bgcolor=#a0d0e0 colspan=2| Contacts |
|||
| -18°35'31.7" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Moon Semi-Diameter |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#d0d0e0 | P1 || 1:06:53 [[UTC]] |
|||
| 16'42.2" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Moon Equatorial Horizontal Parallax |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#c0a0e0 | U1 || 2:03:11 |
|||
| 1°01'18.2" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| ΔT |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#b0a0e0 | U2 || 3:14:26 |
|||
| 64.4 s |
|||
|- |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#a0a0e0| Greatest || 3:40:09 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#b0a0e0 | U3 || 4:05:51 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#c0a0e0 | U4 || 5:17:05 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align=center bgcolor=#d0d0e0 | P4 || 6:13:24 |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=center colspan=2| [[Image:Lunar eclipse chart-03may16.png|240px]]<BR>The moon's path across the Earth's shadow near its descending node in [[Libra (constellation)|Libra]]. |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
{{clear}} |
|||
== Eclipse season == |
|||
A '''total [[lunar eclipse]]''' took place on May 16, 2003, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2003, the other being on [[November 2003 lunar eclipse|November 9, 2003]]. |
|||
{{See also|Eclipse cycle}} |
|||
This eclipse is part of an [[eclipse season]], a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a [[fortnight]]. |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
This lunar eclipse is [[#Lunar year series|first of a ''tetrad'']], four total lunar eclipses in series. The previous series was in 1985 and 1986, starting with a [[May 1985 lunar eclipse]]. The next one was in [[Template:Lunar eclipse set 2013-2016|2014 and 2015]], starting with the April 15, 2014 lunar eclipse. |
|||
|+ Eclipse season of May 2003 |
|||
! [[May 2003 lunar eclipse|May 16]]<br/>Descending node (full moon)<br/> !! [[Solar eclipse of May 31, 2003|May 31]]<br/>Ascending node (new moon)<br/> |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[File:Lunar eclipse chart close-03may16.png|200px]] || [[File:SE2003May31A.png|200px]] |
|||
|- align=center |
|||
| [[Lunar eclipse#Types of lunar eclipse|Total lunar eclipse]]<br />Lunar Saros 121 || [[Total eclipse#Types|Annular solar eclipse]]<br />Solar Saros 147 |
|||
|} |
|||
== |
== Related eclipses == |
||
=== Eclipses in 2003 === |
|||
* '''A total lunar eclipse on May 16.''' |
|||
* [[Solar eclipse of May 31, 2003|An annular solar eclipse on May 31]]. |
|||
* [[November 2003 lunar eclipse|A total lunar eclipse on November 9]]. |
|||
* [[Solar eclipse of November 23, 2003|A total solar eclipse on November 23]]. |
|||
=== Metonic === |
|||
[[File:Lunar eclipse from moon-2003May16.png|320px]] |
|||
* Preceded by: [[July 1999 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of July 28, 1999]] |
|||
* Followed by: [[March 2007 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of March 3, 2007]] |
|||
== |
=== Tzolkinex === |
||
* Preceded by: [[April 1996 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of April 4, 1996]] |
|||
* Followed by: [[June 2010 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of June 26, 2010]] |
|||
=== Half-Saros === |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
* Preceded by: [[Solar eclipse of May 10, 1994]] |
|||
Image:Lunar eclipse May 2003-TLR100.jpg|From [[Minneapolis, Minnesota]], 3:35 UTC, wide angle, near greatest eclipse |
|||
* Followed by: [[Solar eclipse of May 20, 2012]] |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
=== Tritos === |
|||
== Relation to other lunar eclipses == |
|||
* Preceded by: [[June 1992 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of June 15, 1992]] |
|||
* Followed by: [[April 2014 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of April 15, 2014]] |
|||
=== Saros |
=== Lunar Saros 121 === |
||
* Preceded by: [[May 1985 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of May 4, 1985]] |
|||
* Followed by: [[May 2021 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of May 26, 2021]] |
|||
=== Inex === |
|||
It is a member of [[Saros cycle]] [[List of lunar eclipses in saros series 121|121]]. |
|||
* Preceded by: [[June 1974 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of June 4, 1974]] |
|||
* Followed by: [[April 2032 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of April 25, 2032]] |
|||
=== |
=== Triad === |
||
* Preceded by: [[July 1916 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of July 15, 1916]] |
|||
* Followed by: [[March 2090 lunar eclipse|Lunar eclipse of March 15, 2090]] |
|||
It is also the second of four lunar year cycles, repeating every 354 days. |
|||
=== Lunar eclipses of 2002–2005 === |
|||
{{Lunar eclipse set 2002-2005}} |
{{Lunar eclipse set 2002-2005}} |
||
=== Metonic series === |
=== Metonic series === |
||
This eclipse is the second of four [[Metonic cycle]] lunar eclipses on the same date, 15–16 May, each separated by 19 years. |
|||
This eclipse is the second of four [[Metonic cycle]] lunar eclipses on the same date, May 15–16, each separated by 19 years. |
|||
{{Metonic lunar eclipse 1984-2041}} |
{{Metonic lunar eclipse 1984-2041}} |
||
=== Half-Saros cycle=== |
=== Half-Saros cycle === |
||
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a [[Saros_(astronomy)#Relationship_between_lunar_and_solar_saros_.28sar.29|half saros]]).<ref>Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, ''The half-saros''</ref> This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of [[Solar Saros 128]]. |
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a [[Saros_(astronomy)#Relationship_between_lunar_and_solar_saros_.28sar.29|half saros]]).<ref>Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, ''The half-saros''</ref> This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of [[Solar Saros 128]]. |
||
{| class=wikitable |
{| class=wikitable |
||
| Line 93: | Line 167: | ||
* [http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/LEsaros/LEsaros121.html NASA Saros series 121] |
* [http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/LEsaros/LEsaros121.html NASA Saros series 121] |
||
* [http://www.spaceweather.com/eclipses/gallery_15may03.html Lunar Eclipse Gallery] |
* [http://www.spaceweather.com/eclipses/gallery_15may03.html Lunar Eclipse Gallery] |
||
* [http://www.space.com/spacewatch/eclipse_post_030516.html Pictures of the May 15-16 Lunar Eclipse] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080724144145/http://www.space.com/spacewatch/eclipse_post_030516.html Pictures of the May 15-16 Lunar Eclipse] |
||
* [http://www.zam.fme.vutbr.cz/~druck/Eclipse/Ecll2003m/0-info.htm Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Czech Republic] |
* [http://www.zam.fme.vutbr.cz/~druck/Eclipse/Ecll2003m/0-info.htm Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Czech Republic] |
||
Latest revision as of 04:45, 11 December 2024
| Total eclipse | |||||||||||||||||
 Totality as viewed from Minneapolis, MN, 3:17 UTC | |||||||||||||||||
| Date | May 16, 2003 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 0.4123 | ||||||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 1.1294 | ||||||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 121 (54 of 82) | ||||||||||||||||
| Totality | 51 minutes, 12 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Partiality | 193 minutes, 53 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 306 minutes, 31 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
A total lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Friday, May 16, 2003,[1] with an umbral magnitude of 1.1294. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon's near side entirely passes into the Earth's umbral shadow. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. A total lunar eclipse can last up to nearly two hours, while a total solar eclipse lasts only a few minutes at any given place, because the Moon's shadow is smaller. Occurring only about 15 hours after perigee (on May 15, 2003, at 11:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.[2]
This lunar eclipse marks the beginning of a tetrad, with four total lunar eclipses in series, the others being on November 9, 2003; May 4, 2004; and October 28, 2004. The previous series was in 1985 and 1986, starting with the May 1985 lunar eclipse. The next series was in 2014 and 2015, starting with the April 2014 lunar eclipse.
Visibility
[edit]The eclipse was completely visible over eastern North America, South America, the Caribbean, Antarctica, and west Africa, seen rising over western North America and the Pacific Ocean and setting over Europe, west Asia, and much of Africa.[3]

|
 Hourly motion shown right to left |
 The moon's path across the Earth's shadow near its descending node in Libra. | |
Gallery
[edit]-
Wide Angle view from Minneapolis at 3:35 UTC, near greatest eclipse
Eclipse details
[edit]Shown below is a table displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. It describes various parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[4]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Penumbral Magnitude | 2.07649 |
| Umbral Magnitude | 1.12938 |
| Gamma | 0.41234 |
| Sun Right Ascension | 03h30m07.2s |
| Sun Declination | +18°59'20.2" |
| Sun Semi-Diameter | 15'49.2" |
| Sun Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 08.7" |
| Moon Right Ascension | 15h30m43.0s |
| Moon Declination | -18°35'31.7" |
| Moon Semi-Diameter | 16'42.2" |
| Moon Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 1°01'18.2" |
| ΔT | 64.4 s |
Eclipse season
[edit]This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
| May 16 Descending node (full moon) |
May 31 Ascending node (new moon) |
|---|---|
 |

|
| Total lunar eclipse Lunar Saros 121 |
Annular solar eclipse Solar Saros 147 |
Related eclipses
[edit]Eclipses in 2003
[edit]- A total lunar eclipse on May 16.
- An annular solar eclipse on May 31.
- A total lunar eclipse on November 9.
- A total solar eclipse on November 23.
Metonic
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of July 28, 1999
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of March 3, 2007
Tzolkinex
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of April 4, 1996
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of June 26, 2010
Half-Saros
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of May 10, 1994
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of May 20, 2012
Tritos
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of June 15, 1992
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of April 15, 2014
Lunar Saros 121
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of May 4, 1985
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of May 26, 2021
Inex
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of June 4, 1974
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of April 25, 2032
Triad
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of July 15, 1916
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of March 15, 2090
Lunar eclipses of 2002–2005
[edit]| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2002–2005 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros Photo |
Date View |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros Photo |
Date View |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 111 | 2002 May 26
|
penumbral
|
1.1759 | 116 | 2002 Nov 20
|
penumbral
|
−1.1127 | |
121
|
2003 May 16
|
total
|
0.4123 | 126
|
2003 Nov 09
|
total
|
−0.4319 | |
131
|
2004 May 04
|
total
|
−0.3132 | 136
|
2004 Oct 28
|
total
|
0.2846 | |
| 141 | 2005 Apr 24
|
penumbral
|
−1.0885 | 146
|
2005 Oct 17
|
partial
|
0.9796 | |
| Last set | 2002 Jun 24 | Last set | 2001 Dec 30 | |||||
| Next set | 2006 Mar 14 | Next set | 2006 Sep 07 | |||||
Metonic series
[edit]This eclipse is the second of four Metonic cycle lunar eclipses on the same date, 15–16 May, each separated by 19 years.
The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the Earth's shadow will be in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
|
|

|
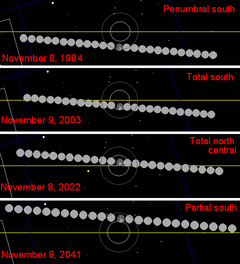
|
Half-Saros cycle
[edit]A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[5] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 128.
| May 10, 1994 | May 20, 2012 |
|---|---|

|

|
See also
[edit]- List of lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses
- November 2003 lunar eclipse
- October 2004 lunar eclipse
- May 2004 lunar eclipse
References
[edit]- ^ "May 15–16, 2003 Total Lunar Eclipse (Blood Moon)". timeanddate. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
- ^ "Total Lunar Eclipse of 2003 May 16" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
- ^ "Total Lunar Eclipse of 2003 May 16". EclipseWise.com. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
- ^ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
[edit]- Saros cycle 121
- 2003 May 16 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- NASA Saros series 121
- Lunar Eclipse Gallery
- Pictures of the May 15-16 Lunar Eclipse
- Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Czech Republic




