Longus capitis muscle: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
→External links: nothing useful at eMedicineDictionary |
YuniToumei (talk | contribs) Importing Wikidata short description: "Muscle of neck" |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Muscle of neck}} |
|||
{{Infobox muscle |
{{Infobox muscle |
||
| Name = Longus capitis muscle |
| Name = Longus capitis muscle |
||
| Latin = musculus longus capitis |
| Latin = musculus longus capitis |
||
| GraySubject = 113 |
|||
| GrayPage = 395 |
|||
| Image = Longus capitis.png |
| Image = Longus capitis.png |
||
| Caption = The anterior vertebral muscles. |
| Caption = The anterior vertebral muscles. |
||
| Image2 = |
| Image2 = |
||
| Caption2 = |
| Caption2 = |
||
| Origin = |
| Origin = Anterior tubercles of the [[transverse processes]] of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth [[cervical vertebræ]] |
||
| Insertion = [[ |
| Insertion = [[Basilar part of occipital bone|Basilar]] part of the [[occipital bone]] |
||
| Blood = |
| Blood = |
||
| Nerve = C1-C3/C4 |
| Nerve = C1-C3/C4 |
||
| Action = [[ |
| Action = [[Flexion]] of [[neck]] at [[atlanto-occipital joint]] |
||
| Antagonist = |
| Antagonist = |
||
| DorlandsPre = m_22 |
|||
| DorlandsSuf = 12549725 |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''longus capitis muscle''' (Latin for ''long muscle of the head'', alternatively '''rectus capitis anticus major''') |
The '''longus capitis muscle''' (Latin for ''long muscle of the head'', alternatively '''rectus capitis anticus major''') is broad and thick above, narrow below, and arises by four tendinous slips, from the anterior tubercles of the [[transverse processes]] of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth [[cervical vertebræ]], and ascends, converging toward its fellow of the opposite side, to be inserted into the inferior surface of the [[Basilar part of occipital bone|basilar]] part of the [[occipital bone]]. |
||
It is innervated by a branch of cervical plexus. |
It is innervated by a branch of cervical plexus. |
||
| Line 27: | Line 24: | ||
*rotate the head ipsilaterally |
*rotate the head ipsilaterally |
||
acting bilaterally: |
acting bilaterally: |
||
*flex the head and neck<ref>http://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=-1972699056</ref> |
*flex the head and neck<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=-1972699056|title=Longus capitis muscle (Anatomy) - General Practice Notebook}}</ref> |
||
==Additional images== |
==Additional images== |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Gray129.png|Occipital bone. Outer surface. |
File:Gray129.png|Occipital bone. Outer surface. |
||
File:Gray137.png|Left temporal bone. Outer surface. |
|||
File:Gray187.png|Base of skull. Inferior surface. |
File:Gray187.png|Base of skull. Inferior surface. |
||
File:Slide4ccc.JPG|Longus capitis muscle |
File:Slide4ccc.JPG|Longus capitis muscle |
||
| Line 43: | Line 39: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* {{cite web|url=http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s25420.000-1.html |title=Anatomy diagram: 25420.000-1 |work=Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator |publisher=Elsevier |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150226040726/http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s25420.000-1.html |archivedate=2015-02-26 |url-status=dead }} |
|||
* {{GPnotebook|-1972699056}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* {{RocheLexicon|25420.000-1}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Muscles_of_neck}} |
{{Muscles_of_neck}} |
||
{{Portal bar|Anatomy}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Muscles of the head and neck]] |
[[Category:Muscles of the head and neck]] |
||
Latest revision as of 09:38, 18 December 2024
| Longus capitis muscle | |
|---|---|
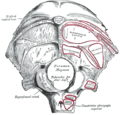
 The anterior vertebral muscles. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebræ |
| Insertion | Basilar part of the occipital bone |
| Nerve | C1-C3/C4 |
| Actions | Flexion of neck at atlanto-occipital joint |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus longus capitis |
| TA98 | A04.2.01.003 |
| TA2 | 2149 |
| FMA | 46308 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The longus capitis muscle (Latin for long muscle of the head, alternatively rectus capitis anticus major) is broad and thick above, narrow below, and arises by four tendinous slips, from the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebræ, and ascends, converging toward its fellow of the opposite side, to be inserted into the inferior surface of the basilar part of the occipital bone.
It is innervated by a branch of cervical plexus.
Longus capitis has several actions:
acting unilaterally, to:
- flex the head and neck laterally
- rotate the head ipsilaterally
acting bilaterally:
- flex the head and neck[1]
Additional images
[edit]-
Occipital bone. Outer surface.
-
Base of skull. Inferior surface.
-
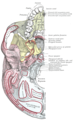
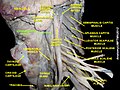
Longus capitis muscle
-
Longus capitis muscle
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 395 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 395 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
[edit]- "Anatomy diagram: 25420.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2015-02-26.
- PTCentral