Greater Rochester International Airport: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Domestic airport located in Rochester, New York, USA}} |
|||
{{For|the airport in Minnesota|Rochester International Airport}} |
|||
{{Use mdy dates|date=May 2014}} |
|||
{{more citations needed|date=May 2012}} |
|||
{{Infobox airport |
|||
| name = Frederick Douglass Greater Rochester International Airport |
|||
| image = Greater Rochester International Airport logo 2012.png |
|||
| image-width = 150 |
|||
| image2 = Greater_Rochester_International_Airport_May_2007_Aerial_View.jpg#file |
|||
| image2-width = 200 |
|||
| FAA = ROC |
|||
| IATA = ROC |
|||
| ICAO = KROC |
|||
| type = Public |
|||
| owner = [[Monroe County, New York|County of Monroe]] |
|||
| operator = Monroe County Airport Authority |
|||
| city-served = [[Rochester, New York]], U.S. |
|||
| location = |
|||
| elevation-m = 170 |
|||
| elevation-f = 559 |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|43|7|8|N|077|40|21|W|region:US-NY_type:airport|display=inline,title}} |
|||
| hub = [[Wiggins Airways]]<ref>{{Cite web|url = https://wiggins-air.com/route-map/|title = Route Map|date = July 4, 2017|access-date = December 22, 2020|archive-date = February 27, 2022|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220227232243/https://wiggins-air.com/route-map/|url-status = dead}}</ref> |
|||
| website = {{URL|https://rocairport.com/}} |
|||
| image_map = ROC - FAA airport diagram.png |
|||
| image_mapsize = 175 |
|||
| image_map_caption = FAA airport diagram |
|||
| mapframe = yes |
|||
| r1-number = 04/22 |
|||
| r1-length-m = 2,439 |
|||
| r1-length-f = 8,001 |
|||
| r1-surface = Asphalt |
|||
| r2-number = 07/25 |
|||
| r2-length-m = 1,219 |
|||
| r2-length-f = 4,000 |
|||
| r2-surface = Asphalt |
|||
| r3-number = 10/28 |
|||
| r3-length-m = 1,951 |
|||
| r3-length-f = 6,401 |
|||
| r3-surface = Asphalt |
|||
| stat-year = 2016, 2017 |
|||
| stat1-header = Aircraft operations (2017) |
|||
| stat1-data = 88,443 |
|||
| stat2-header = Based aircraft (2017) |
|||
| stat2-data = 83 |
|||
| stat3-header = Passengers (2017) |
|||
| stat3-data = 2.357 million |
|||
| footnotes = Sources: airport website,<ref name=Airport>[http://www.rocairport.com/ Greater Rochester International Airport], official site</ref> [[Federal Aviation Administration|FAA]],<ref name=FAA>{{FAA-airport|ID=ROC|use=PU|own=PU|site=16034.*A}}, effective November 28, 2024.</ref> [[Airports Council International|ACI]]<ref name="ACI">{{Cite web|url=http://www.aci-na.org/stats/stats_traffic|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080208130330/http://www.aci-na.org/stats/stats_traffic|url-status=dead|title=2010 North American final rankings|archive-date=February 8, 2008}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
'''[[Frederick Douglass]] Greater Rochester International Airport''' {{airport codes|ROC|KROC|ROC}} is a public airport located within the City of [[Rochester, New York|Rochester]], {{convert|3|mi|km|spell=in}} southwest of Downtown, in [[Monroe County, New York|Monroe County]], New York, United States.<ref name=FAA /> It is owned and operated by [[Monroe County, New York|Monroe County]]. The airport is home to the 642nd Aviation Support Battalion, part of the [[42nd Infantry Division (United States)|42nd Infantry Division]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://dmna.ny.gov/units/?unit=1227543460|title=642 Aviation Support Battalion (ASB) - Unit information|website=dmna.ny.gov|access-date=2018-05-15}}</ref> |
|||
==Airlines and nonstop destinations== |
|||
* [[Air Georgian]] dba [[Air Canada]] (Toronto) |
|||
==History== |
|||
* [[AirTran Airways]] (Atlanta, Baltimore/Washington, Fort Lauderdale/Hollywood, Orlando, and Tampa) |
|||
* [[American Airlines|American]] (Chicago/O'Hare and Dallas/Ft. Worth) |
|||
===Early history=== |
|||
* [[Chautauqua Airlines]] dba [[US Airways Express]] (Boston, New York/LaGuardia, and Washington/Reagan) |
|||
{{unreferenced section|date=May 2012}} |
|||
* [[Chautauqua Airlines]] dba [[United Express]] (Chicago/O'Hare and Washington/Dulles) |
|||
* [[Colgan Air]] dba [[US Airways Express]] (Hartford, New York/LaGuardia, and Pittsburgh) |
|||
====Baker Field==== |
|||
* [[Comair]] dba [[Delta Connection]] (Atlanta and Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky (Covington, KY)) |
|||
A 1910 newspaper article cited "a site near Scottsville Road", along with the Baker Farm in [[Genesee Valley Park]], as possible locations for "airships" to fly from Rochester to [[Toronto]].<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', June 8, 1910</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} The Baker Farm was located south of the original [[Genesee Valley Park]], and was donated to the Parks Department of the City of Rochester in 1908.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', January 31, 1908</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} The golf course at Genesee Valley Park was extended to include the Baker Farm in 1914.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', May 1, 1914</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} During World War I, the Baker Farm area of the park, renamed "Baker Field", was used for military purposes. The United States School of Aerial Photography had been created at [[Kodak Park]] in Rochester, and Baker Field was the airfield associated with the project.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', Dec. 25, 1918</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} Military use of the field ceased in 1918.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', April 9, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} Baker Field continued to be used as an airfield for a year or two thereafter,<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', June 19, 1919</ref><ref name="ReferenceA">''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', August 19, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} but flood conditions made it unsuitable for airfield use in the long run.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', August 2, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} Britton Field, located just west of Baker Field, became the primary airport for the Rochester area. |
|||
* [[Commutair]] dba [[Continental Connection]] (Albany, Elmira, and Westchester County) |
|||
* [[Continental Express]] (Cleveland and Newark) |
|||
====Britton Field==== |
|||
* [[Independence Air]] (Washington/Dulles) |
|||
The site of the Greater Rochester International Airport, originally known as Britton Field, was used for aviation purposes as early as 1919. The Rochester Aircraft Corporation launched its first passenger flight from Britton Field August 18, 1919. The [[Curtiss JN-4]] was piloted by Earl F. Beers. At the time, the only way to get to the field was either by car or by taking the Genesee Street trolley line to the end, and walking the remaining distance.<ref name="ReferenceA"/> Beers, a Rochester aviation pioneer, urged the local government to purchase Britton Field for a municipal airport.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'' (Beers obituary), July 30, 1927</ref><ref>''Medina Daily Journal'', July 27, 1927</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} In 1919, Beers offered passenger flights out of Britton Field, charging $1.00 per minute.<ref>''Geneva Daily Times'', November 7, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} |
|||
* [[Jetblue]] (New York/Kennedy) |
|||
* [[Mesa Air]] dba [[United Express]] (Chicago/O'Hare) |
|||
Britton Field hosted the United States Flying Circus, consisting of six planes, in September 1919.<ref>''Oswego Daily Palladium'', September 12, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} Dozens of planes landed in Britton Field as part of an aviation race across the United States<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'' October 9, 1919 and October 10, 1919</ref> and back again.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', October 11, 1919 and October 15, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} The race was won by Lt. B. W. Maynard, "The Flying Parson", who arrived in Rochester, from [[Buffalo, New York|Buffalo]], at 10:30 AM October 18, 1919. His flight from Buffalo's Curtiss Field to Britton Field, a distance of 70 miles, in 22 minutes. He continued to [[Binghamton]] before finishing the race at [[Mineola, New York|Mineola]] at 1:50 PM that afternoon.<ref>''Batavia Daily News'', October 18, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} Britton Field was the scene of more competition when a pair of Rochester fliers and two from [[Syracuse, New York|Syracuse]] raced between the two cities later in 1919, in a contest sponsored by the Rochester Aero Club and the Syracuse Aero Club. The Rochester newspaper reported that the two Rochester planes beat the combined flying time of the Syracuse pair by 15 seconds.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', November 29, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} |
|||
* [[MidAtlantic Airways]] dba [[US Airways Express]] (Washington/Reagan) |
|||
* [[Mesaba Airlines]] dba [[Northwest Airlink]] (Detroit and Minneapolis/St. Paul) |
|||
Purchase of the field as a "municipal aviation station" was authorized by the Rochester City Council in December 1919<ref>''The Fredonia Censor''; December 19, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}}<ref>''Monroe County Mail'', Dec. 25, 1919</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} The Rochester Aircraft Corporation proposed passenger service out of Britton Field across Lake Ontario to Toronto in 1920.<ref>''Buffalo Daily Palladium'', February 17, 1920</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} "Young" Sparks, of Bradford, PA., demonstrated the early art of parachuting, by leaping from a plane from 2,100 feet, in an aerial field day at Britton Field in 1921.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', September 25, 1921</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} The United States Army considered Britton Field as a possible site for an [[airship]] mooring mast in 1924.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', June 8, 1924</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} |
|||
* [[Piedmont Airlines]] dba [[US Airways Express]] (New York/LaGuardia, Philadelphia, and Pittsburgh) |
|||
* [[Pinnacle Airlines]] dba [[Northwest Airlink]] (Detroit) |
|||
In the 1920s [[Eastman Kodak Company]] and the United States Army used Britton Field as landing field for the testing of Kodak's aerial photography experiments.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', November 25, 1925</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} The Fokker monoplane "Josephine Ford", flown by Commander [[Richard E. Byrd|Richard Byrd]] over the North Pole, was exhibited at Britton Field in October 1926, part of a nationwide tour intended to stimulate interest in aviation. During the Rochester exhibition, an unlicensed pilot, Charles Teleska, crashed his own plane.<ref>''Corning Evening Leader'', October 12, 1926</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} |
|||
* [[PSA Airlines]] dba [[US Airways Express]] (New York/LaGuardia and Philadelphia) |
|||
* [[United Airlines]] (Chicago/O'Hare) |
|||
The [[Colonial Air Transport]] Company, forerunner to [[American Airlines]], developed plans in 1926 to run daytime flights from Boston to Chicago, stopping at Albany, Syracuse, Rochester, Buffalo, and Cleveland. An intersecting route from New York City to Montreal would cross at Albany, allowing for passenger transfers. The new route would carry passengers, mail and merchandise. Night flights were planned as soon as lighted fields were available.<ref>''Buffalo Evening News'', September 29, 1926</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}}<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', November 25, 1926</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} The Rochester Flying Club was formed that Fall, intending to keep Britton Field open to all aviation, and to start construction of a hangar and other improvements.<ref>''Rochester Democrat and Chronicle'', November 28, 1926</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} |
|||
* [[US Airways]] (Charlotte, Philadelphia, and Washington/Reagan) |
|||
[[Charles Lindbergh]] flew ''[[The Spirit of St. Louis]]'' into Britton Field July 29, 1927, as part of an air tour of New York State. He was greeted by 75,000, according to newspaper reports. He stayed an hour and proceeded on to Buffalo.<ref>''Jamestown Evening Journal'', July 29, 1927 (Associated Press report)</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}}<ref>''Geneva Daily Times'', July 22, 1927</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} In the summer of 1927, the [[Rochester Community Players]] used Britton Field as one of the backdrops of their silent movie, "Fly Low Jack and The Game". The movie was written, directed, acted and produced by amateurs of the theater company, showcasing the new Cine-Kodak 16mm home movie system.<ref>''Rochester Evening Journal and Post Express'', June 30, 1927</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} |
|||
The first woman in Western New York to receive a pilot's license, Geraldine Grey of Buffalo, trained at Britton Field under the direction of William Dunlap in 1928.<ref>''Buffalo Courier Express'', February 18, 1928</ref>{{Title missing|date=September 2017}} |
|||
===Rochester Municipal Airport=== |
|||
The modern era of the Greater Rochester International Airport began in 1927, with the construction of Hangar No. 1 on a patch of land south of Rochester on Scottsville Road. The first scheduled passenger flights between New York City and Rochester were made that year. In 1928, the name was changed to Rochester Municipal Airport and more construction was completed, including improvements to the runways and drainage system, and Hangar No. 2. After the Second World War the airport saw a period of expansion as passenger volume, frequency of flights, and civilian pilot training increased. A flight training school, with nearly 1,000 students, was created. |
|||
On January 1, 1948, Monroe County took possession and control of the airport. The county made numerous improvements, including an instrumental runway {{convert|5000|ft|m|abbr=off|sp=us}} long, an extension of the north–south runway from {{convert|2,670|ft|m}} to {{convert|5000|ft|m|abbr=on}}, and administration facilities on [[New York State Route 204|Brooks Avenue]]. |
|||
===1953–1992 terminal=== |
|||
A new red-brick, single-level passenger terminal was opened on Brooks Avenue in 1953. It was expanded substantially in 1963, and expanded again in 1978 and 1980. The building had only one floor, until a small second floor was added for administrative offices as part of the 1980 expansion. At this time the airport was "Rochester Monroe County Airport." |
|||
After the 1963 expansion gave it its final layout, the terminal had ten gates in two concourses. A small three-gate concourse at the east end served [[American Airlines]], and a longer, angled concourse at the west end served [[Mohawk Airlines]] (four gates on the east side) and [[United Airlines]] (three gates on the west side). |
|||
Jet service began ROC in 1965 on American Airlines [[Boeing 727]]s, but the two longest runways, 10–28 ({{convert|5500|ft|m}}) and 1–19 ({{convert|5,000|ft|m|abbr=off|sp=us}}) were short for jets. In 1967 Monroe County built runway 4–22, initially {{convert|7,000|ft|m|abbr=off|sp=us}} and extended in 1969 to {{convert|8,002|ft|m}} (bypassing the {{convert|8,000|ft|m|abbr=off|sp=us}} threshold required for CAT III certification). 10–28 is still the crosswind runway. Runway 7–25, {{convert|4000|ft|m|abbr=off|sp=us}} long, is used by smaller aircraft. |
|||
In the late 1960s and early 1970s there was talk of building a Rochester-Buffalo airport in southeastern Niagara County, which would have taken over passenger traffic from Rochester-Monroe County and [[Buffalo Niagara International Airport|Greater Buffalo International Airport]] airports. This was never built. |
|||
The first jetways were added to gates 1 and 3 by American in 1977. As part of the 1978 expansion, new lounge space was built for [[Allegheny Airlines]] (successor to Mohawk) with three jetways. In about 1986 the airline (by then renamed [[USAir]]) added a fourth jetway. The 1980 expansion included two new lounge areas for United, each of which had one jetway. In 1987, [[Piedmont Airlines]], which had taken over the United lounge closest to the terminal, added a second jetway to it. In about 1985, USAir built an expansion to the end of the main concourse to house a USAir Club. |
|||
The large new low-fare carrier [[People Express Airlines (1980s)|People Express Airlines]] arrived at the airport in 1985. There was not room for them inside the terminal. A small ticket counter was built in office space in the northwest corner of the terminal, and a wooden peaked-roof shed was built on to house their outbound-baggage area, departure lounge, and baggage claim. No jetway was added. People's effect on fares was dramatic; ROC's enplanements increased 38% in 1985. When [[Continental Airlines]] took over People in 1987, they moved operations into the main terminal and shared gate space with American. The shed was removed. |
|||
In the mid-1980s, Monroe County Legislator Van Buren N. Hansford, Sr. (R-Pittsford) introduced successful legislation to have the airport's name changed to "Greater Rochester International Airport." By the end of the 1980s, The [[New York Air National Guard]] constructed a small hangar and office facility, and apron space, on the south side of the airport near the control tower. This facility has since been expanded. |
|||
===Present terminal building=== |
|||
==== 1988-1992 expansion project: new terminal ==== |
|||
[[File:Greater Rochester International Airport Aerial View of Terminal 05.jpg|thumb|left|ROC's passenger terminal seen from an approaching aircraft in December 2005]] |
|||
The terminal was outgrown by the mid-1980s, and debate began about expanding the airport. In 1985, the administration of Monroe County Executive Lucien A. Morin (R) proposed a complicated terminal expansion that would have had baggage claim carousels across the driveway in a separate building, which tugs would have reached by a tunnel, and passengers would have reached by second-floor bridge corridors. |
|||
The County got as far as building temporary parking lots to the west and closing the main parking lots to begin construction on a garage. However, in 1988 the new County Executive, Thomas R. Frey (D) and the County Legislature had doubts about the cost of the project, and it was abandoned before construction started in earnest. |
|||
In 1988 Monroe County approved a $109 million plan to replace the terminal with an entirely new two-level facility with a second-level approach road and parking garage. The new facilities were built in stages on the exact site, between 1989 and 1992 and designed by [[HNTB]] and built by Wilmorite, Inc.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.wilmorite.com/PortfolioInformation/?categoryID=9&portfolioID=30|title=Greater Rochester International Airport – Wilmorite: Portfolio|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140304035451/http://www.wilmorite.com/PortfolioInformation/?categoryID=9&portfolioID=30|archive-date=March 4, 2014|df=mdy-all}}</ref> Ticketing and departures are on the second floor, and baggage claim and ground transportation is on the first floor. The County Legislature authorized the creation of a "Monroe County Airport Authority" to issue the bonds for the construction. |
|||
This terminal has two angled concourses, each with 11 gates. Gate assignments are listed below. The eastern or B concourse opened in summer 1990. The eastern half of the main terminal opened in 1991. The western half of the main terminal, western or A concourse, and garage, all opened in 1992. A series of temporary prefabricated buildings were used to provide gate space and baggage claim space during the construction. |
|||
[[File:Greater Rochester International Airport Ticket Lobby 02.jpg|thumb|right|ROC's ticketing lobby, as seen in September 2002]] |
|||
==== 2006-2008 terminal improvements ==== |
|||
In 2006, Monroe County consolidated the separate security checkpoints at each concourse, to one central security checkpoint. Monroe County argued that this arrangement, although it would close the terminal's large concessions atrium and airfield views to non-passengers, would be more efficient and save money.<ref>{{cite news |publisher=Greater Rochester International Airport Newsletter |date=2005 |title=First Quarter Newsletter 2005 |url=http://www.monroecounty.gov/p/gria-Newsletter01.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061004102626/https://www.monroecounty.gov/p/gria-Newsletter01.pdf|archive-date=October 4, 2006}}</ref> The county replaced the lost public airfield view with a new viewing area at the west end of the terminal. |
|||
In 2008, renovations were undertaken to replace floors, carpets, and seating in the concourses, move explosives-scanning equipment from the ticketing lobby to the outbound baggage room, and replace T-shaped baggage claim carousels with four 360-degree walk-around carousels, which receive luggage from belts through the ceiling. These projects were completed by late 2009. |
|||
In January 2009, the airport began work on an extension of the three-story parking garage to the west, for additional capacity. By early 2010, that project was completed. |
|||
==== 2016-2018 terminal renovations ==== |
|||
[[File:GreaterRochesterInternationalAirportTerminalA.jpg|thumb|left|ROC's concourse B after terminal renovations]] |
|||
The concrete road decking of the departures level roadway was closed and repaired from April to July 2016. The Airport won the Governor Cuomo's Upstate Airport Economic and Revitalization Competition (UAERC) in 2016 and received nearly $40 million, for use to adapt and enhance the airport's facilities. A $54 million project was subsequently announced to create a high-tech smart facility that best serves the business and economic needs, while reducing barriers for passengers with disabilities, which broke ground in the spring of 2017. The UAERC sums were used to pay for a substantial portion of the project, with bonds and airport fees paying for remaining costs. By the fall, the total cost had ballooned to $79 million. |
|||
The security checkpoint was enlarged, now including two dedicated [[TSA PreCheck]] lanes in addition to four general lanes. A consolidated exit passageway, leading from the secure Food Court to non-secure Baggage Claim, eliminated two previous exits at either end of the concourse. The Food Court was renovated and revamped with new restaurants and additional seating. Bathrooms, interior lighting in addition to accessibility services and way-finding were overhauled throughout the terminal. |
|||
A new cell-phone lot was built with flight-display information and an electric vehicle charging station, and is located off the airport roadway, now before the terminal building instead of after. A canopy added over the departures-level roadway reduces winter maintenance costs, and features solar panels, colorful aesthetic lighting, and rainwater storage capabilities. The project was completed in October 2018. |
|||
=== Airport events at-large === |
|||
[[File:Fredrick Douglass Greater Rochester International Airport (ROC) Signage Above Entrance.jpg|thumb|]][[Southwest Airlines]] replaced [[AirTran Airways|AirTran]]'s service at the airport after its acquisition by the airline in 2013. |
|||
In 2014, New York State Police established a base for its aviation unit at the Monroe County Regional Traffic Operations Center on airport property, already a station for that agency. At least two helicopters, previously based out of Batavia and Syracuse, were moved to consolidate operations and reduce costs. This unit services Western and Central New York, including Buffalo, Rochester and Syracuse.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2014-07-14|title=Syracuse's state police helicopter operations will move to Rochester|url=https://www.syracuse.com/news/2014/07/state_police_helicopter_operations_will_move_to_rochester.html|access-date=2020-06-18|website=syracuse|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
[[Allegiant Air]] started limited service out of Rochester, with flights to Orlando-Sanford that same year. |
|||
The Clock of Nations, previously at [[Midtown Plaza (Rochester, New York)|Midtown Plaza]] prior to 2007, was restored and moved to the airport Food Court in 2009. Planned to stay temporarily — until the clock's intended permanent home at the new Golisano Children's Hospital building was completed in 2014 — the hospital early in the design process opted to decline housing it, allotting the airport as an indefinite residence. It remained on display until 2017, before being disassembled and placed into storage before renovations started. The Clock of Nations will not be placed back in the terminal, as it can no longer occupy its previous location because of changes to the terminal layout. As of 2020, Monroe County has no plans for the clock's future home, which remains in storage. |
|||
In October 2018, [[Air Canada]] ended its service to Rochester from [[Toronto Pearson International Airport|Toronto]], leaving the airport without any international flights.<ref>{{cite web |title=Air Canada ends service to Rochester |url=https://www.whec.com/news/air-canada-ends-service-to-rochester-/5106213/ |website=WHEC News10NBC |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181012214057/https://www.whec.com/news/air-canada-ends-service-to-rochester-/5106213/ |archive-date=12 October 2018}}</ref> |
|||
In May 2021, [[Frontier Airlines]] started new service to [[Orlando International Airport|Orlando]] from Rochester.<ref>{{Cite web|last=NY|first=Monroe County|title=Frontier Airlines to Begin Flights at Frederick Douglass Greater Rochester International (ROC) {{!}} Monroe County, NY|url=https://www.monroecounty.gov/news-2021-04-07-frontier|access-date=2021-06-10|website=www.monroecounty.gov|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
=== Renaming efforts === |
|||
An online petition was started in July 2020 to rename the airport after [[Frederick Douglass]], possibly to "Frederick Douglass International Airport". Soon after, County Executive Adam Bello said that [[Monroe County, New York|Monroe County]] will begin to work with stakeholders - the FAA, Monroe County Legislature, among others - to examine and study a potential name change. Douglass lived in Rochester for much of his adult life and is buried at [[Mount Hope Cemetery (Rochester)|Mt. Hope Cemetery]]. |
|||
On August 12, 2020, [[Monroe County, New York|Monroe County]] legislators confirmed that the airport would be renamed in honor of Douglass.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.democratandchronicle.com/story/news/2020/08/12/rochester-ny-airport-renamed-frederick-douglass/3353030001/|title=Rochester airport to be renamed for Frederick Douglass|first=Sean|last=Lahman|work=[[Democrat and Chronicle]]}}</ref> |
|||
==Airfield== |
|||
The airport covers {{convert|1,136|acre|ha}} at an elevation of {{convert|559|ft|m}}. It has three [[runway]]s - a primary runway, a general aviation runway, and a crosswinds runway:<ref name=FAA /><ref>{{cite web|url=https://skyvector.com/airport/ROC/Frederick-Douglass-Greater-Rochester-International-Airport|title=ROC airport data at skyvector.com|website=skyvector.com|access-date=August 29, 2022}}</ref> |
|||
* 4/22: {{convert|8,001|x|150|ft|m|abbr=on}}, asphalt |
|||
* 7/25: {{convert|4,000|x|100|ft|m|abbr=on}}, asphalt |
|||
* 10/28: {{convert|6,402|x|150|ft|m|abbr=on}}, asphalt |
|||
Runways 4, 22 and 28 have [[Instrument Landing System]] (ILS); runway 4 has a Category II ILS. |
|||
In 2008 the airport completed two service roads around the end of Runway 28, near Interstate 390, in tunnels. The ground was graded upwards beyond the end of the runway to cover the tunnels. Earlier in the decade, a {{convert|500|ft|adj=on}} overrun area was added to the east (10) end of this runway, adjacent to railroad tracks and housing. An [[engineered materials arrestor system]] (EMAS) of about {{convert|200|ft}} was added to this extension. The EMAS consists of soft rubberized concrete into which an overrunning aircraft's wheels can sink, and the aircraft may be stopped safely before it veers onto the grass. |
|||
==Movements== |
|||
In 2017 the airport had 87,261 aircraft operations, average 239 per day: 44% [[general aviation]], 26% air carrier, 26% [[air taxi]] and 3% military. 86 aircraft are based at the airport: 48 single engine, 10 multi-engine, 17 jet and 11 military.{{citation needed|date=September 2021}} |
|||
==Terminal== |
|||
The Greater Rochester International Airport consists of a main terminal building with two angled concourses with 22 total passenger gates. The departures level includes a ticketing hall, a six lane security checkpoint, post-security food court and two passenger concourses. The arrivals level has four baggage claim carousels, airline baggage offices, visitor information and car rental offices. A three-level parking garage, designated for long-term parking and rental cars, sits across the roadway from the terminal building. Fairfield Inn & Suites has an on-site hotel across the street from the terminal, just east of the parking garage. |
|||
JetBlue, Spirit, American, Avelo and Southwest occupy Concourse A (also called [[Frederick Douglass]] Concourse) with gates A1-A11. United, Delta and Allegiant are in Concourse B (also known as [[Susan B. Anthony]] Concourse) with gates B1-B10. |
|||
==Airlines and destinations== |
|||
===Passenger=== |
|||
[[File:Fredrick Douglass Greater Rochester International Airport (ROC) Parked United Planes.jpg|thumb|right|Several [[United Airlines]] aircraft lined up at Concourse B]] |
|||
[[File:AirTran 737-700 at Greater Rochester International Airport 2007.jpg|thumb|right|[[Boeing 737-700]] of [[AirTran Airways]] and an [[Airbus A320]] of [[JetBlue Airways]] at Concourse A]] |
|||
{{Airport destination list |
|||
| [[Allegiant Air]] | '''Seasonal: ''' [[Punta Gorda Airport (Florida)|Punta Gorda (FL)]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[American Airlines]]| [[Charlotte Douglas International Airport|Charlotte]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[American Eagle (airline brand)|American Eagle]] | [[Logan International Airport|Boston]], [[O'Hare International Airport|Chicago–O'Hare]], [[Miami International Airport|Miami]], [[Philadelphia International Airport|Philadelphia]], [[Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport|Washington–National]] <br> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Avelo Airlines]] |[[Concord–Padgett Regional Airport|Charlotte/Concord]],<ref name="AveloUSA">{{cite web|url=https://www.wbtv.com/2024/07/24/avelo-airlines-expanding-concord-adding-6-nonstop-routes/|title=Avelo Airlines expanding to Concord, adding 6 nonstop routes |
|||
|website=wbtv|date=July 24, 2024|access-date=July 24, 2024}}</ref> [[Lakeland Linder International Airport|Lakeland]],<ref name="AveloLAL">{{cite web|title=Avelo Airlines announces 7 all-new nonstop routes from Lakeland|url=https://www.wfla.com/news/polk-county/avelo-airlines-launches-largest-expansion-in-history-at-lakeland-airport/ |
|||
|website=WFLA|date=July 24, 2024|access-date=July 24, 2024}}</ref> [[Nashville International Airport|Nashville]] (begins April 3, 2025),<ref name="AveloNew">{{cite web |last=Fox |first=Allison |title=Avelo Airlines Just Announced 7 New Routes — Including 2 to the Caribbean |url=https://www.travelandleisure.com/avelo-airlines-north-carolina-jamaica-dominican-republic-8756133 |website=Travel+Leisure|date=December 4, 2024|access-date=December 4, 2024}}</ref> [[Raleigh-Durham International Airport|Raleigh/Durham]],<ref name="AveloNewRDU">{{cite news |title=Avelo Airlines Grows its 5th Base in Raleigh-Durham with Second Aircraft, Three New Nonstop Destinations and More Jobs|url=https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/avelo-airlines-grows-its-5th-base-in-raleigh-durham-with-second-aircraft-three-new-nonstop-destinations-and-more-jobs-301772490.html |access-date=15 March 2023 |website=PRNewsWire}}</ref> [[Wilmington International Airport|Wilmington (NC)]] (begins April 4, 2025)<ref name="AveloNew" /> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Delta Air Lines]] |[[Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport|Atlanta]], [[Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport|Detroit]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Delta Connection]] |[[Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport|Detroit]], [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]], [[LaGuardia Airport|New York–LaGuardia]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[JetBlue]] | [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
|{{nowrap|[[Southwest Airlines]]}} | [[Baltimore–Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport|Baltimore]], [[Harry Reid International Airport|Las Vegas]],<ref>{{cite web | url=https://13wham.com/amp/news/local/southwest-airlines-adding-nonstop-service-between-rochester-and-las-vegas-airport-direct-flight-international-airport | title=Southwest Airlines adding nonstop service between Rochester and Las Vegas }}</ref> [[Orlando International Airport|Orlando]], [[Tampa International Airport|Tampa]] <br> '''Seasonal:''' [[Midway International Airport|Chicago–Midway]],<ref name="aeroroutes.com">{{cite web |title=Southwest Airlines 1Q25 Network Changes – 29JUL24 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240730-wn1q25 |website=Aeroroutes |access-date=30 July 2024}}</ref> [[Southwest Florida International Airport|Fort Myers]] (begins February 15, 2025)<ref name="aeroroutes.com">{{cite web |title=Southwest Airlines 1Q25 Network Changes – 29JUL24 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240730-wn1q25 |website=Aeroroutes |access-date=30 July 2024}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Spirit Airlines]] | [[Fort Lauderdale–Hollywood International Airport|Fort Lauderdale]],<ref>{{cite web |title=Spirit Airlines August 2024 Network Additions – 19MAY24 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240521-nkaug24us |website=Aeroroutes |access-date=21 May 2024}}</ref> [[Orlando International Airport|Orlando]] <br> '''Seasonal: ''' [[Myrtle Beach International Airport|Myrtle Beach]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[United Airlines]] | [[O'Hare International Airport|Chicago–O'Hare]], [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark]], [[Washington Dulles International Airport|Washington–Dulles]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[United Express]] | [[O'Hare International Airport|Chicago–O'Hare]], [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark]], [[Washington Dulles International Airport|Washington–Dulles]] |
|||
}} |
|||
{| class="collapsible collapsed" style="border:1px #aaa solid; width:50em; margin:0.2em auto" |
|||
! Destinations map |
|||
|- |
|||
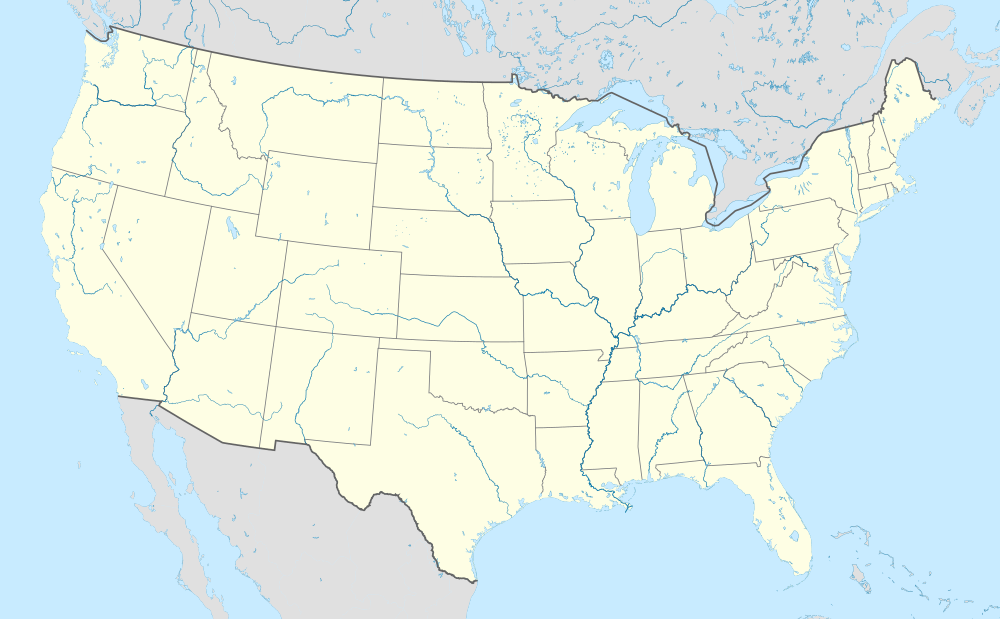
|{{Location map+ |United_States |width=1000 |float=center |
|||
|caption=Destinations from Greater Rochester International Airport <br /> {{font color | red | Red}} = Year-round destination <br />{{font color | green| Green }} = Seasonal destination <br />{{font color | blue | Blue }} = Future destination |
|||
|places= |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=43.1191 |long=-77.6719 |position=right |label=<div style="position:relative; top:-5px;"><small>'''Rochester'''</small></div>|caption=|mark=Airplane_silhouette.svg|marksize=15 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=33.6367|long=-84.4279|position=left|label='''<small>[[Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport|Atlanta]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat= 25.7959|long=-80.2871|position=bottom|label='''<small>[[Miami International Airport|Miami]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=42.3629 |long=-71.0064 |position=right |label='''<small>[[Logan International Airport|Boston]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=39.1757 |long=-76.6690 |position=top |label='''<small>[[Baltimore-Washington International Airport|Baltimore]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=35.2138 |long=-80.9491 |position=bottom |label='''<small>[[Charlotte Douglas International Airport|Charlotte]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=35.8778 |long=-78.7875 |position=right |label='''<small>[[Raleigh–Durham International Airport|Raleigh/Durham]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=38.8514 |long=-77.0377 |position=right |label='''<small>[[Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport|Washington-National]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=42.2124 |long=-83.3534 |position=left |label='''<small>[[Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport|Detroit-Metro]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=40.6925 |long=-74.1687 |position=left |label='''<small>[[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Red pog.svg |United_States |lat=26.0717 |long=-80.1497 |position=right |label='''<small>[[Fort Lauderdale-Hollywood International Airport|Fort Lauderdale]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=38.9474 |long=-77.4599 |position=left |label='''<small>[[Washington Dulles International Airport|Washington-Dulles]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=40.641173|long=-73.780532|position=right|label='''<small>[[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]]/[[LaGuardia Airport|LaGuardia]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |
|||
|marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=28.4294 |long=-81.3090 |position=right |label='''<small>[[Orlando International Airport|Orlando]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=41.9745 |long=-87.9066 |position=left |label='''<small>[[O'Hare International Airport|Chicago-O'Hare]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Green pog.svg |United_States |lat=26.9189 |long=-81.9909 |position=left |label='''<small>[[Punta Gorda Airport (Florida)|Punta Gorda]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=39.8721 |long=-75.2407 |position=right |label='''<small>[[Philadelphia International Airport|Philadelphia]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Red pog.svg |United_States |lat=27.9755 |long=-82.5333 |position=left |label='''<small>[[Tampa International Airport|Tampa]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |United_States |lat=41.786589|long=-87.752356|position=right|mark= Green pog.svg|label='''<small>[[Midway International Airport|Chicago–Midway]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Green pog.svg |United_States |lat=33.6822 |long=-78.9279 |position=bottom |label='''<small>[[Myrtle Beach International Airport|Myrtle Beach]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Red pog.svg |United_States |lat=36.0840|long=-115.1537 |position=top |label='''<small>[[Harry Reid International Airport|Las Vegas]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Red pog.svg |United_States |lat=35.3804|long=-80.7141 |position=left |label='''<small>[[Concord-Padgett Regional Airport|Concord]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Red pog.svg |United_States |lat=27.9945|long=-82.0143 |position=right |label='''<small>[[Lakeland Linder International Airport|Lakeland]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Blue pog.svg |United_States |lat= 26.5319|long=-81.7596 |
|||
|position=left |label='''<small>[[Southwest Florida International Airport|Fort Myers]]</small>''' |label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Blue pog.svg |United_States |lat=36.1249|long=-86.6762 |position=left |label='''<small>[[Nashville International Airport|Nashville]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
{{Location map~ |mark = Blue pog.svg |United_States |lat=34.2670|long=-77.9105 |position=right |label='''<small>[[Wilmington International Airport|Wilmington]]</small>'''|label_size=90 |marksize=7 }} |
|||
}} |
|||
|} |
|||
===Cargo=== |
|||
{{Airport destination list |
|||
| [[ABX Air]] | [[Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport|Cincinnati]], [[Bradley International Airport|Hartford]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Aeronaves TSM]] | [[Laredo International Airport|Laredo]], [[Louisville International Airport|Louisville]], [[Saltillo Airport|Saltillo]], [[Shreveport Regional Airport|Shreveport]], [[Toledo Express Airport|Toledo]], [[Willow Run Airport|Ypsilanti]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[FedEx Express]] |[[Baltimore Thurgood Marshall Airport|Baltimore]], [[Logan International Airport|Boston]], [[Chicago O'Hare International Airport|Chicago–O'Hare]], [[Rickenbacker International Airport|Columbus–Rickenbacker]], [[Indianapolis International Airport|Indianapolis]], [[Memphis International Airport|Memphis]], [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark]], [[Philadelphia International Airport|Philadelphia]], [[Washington Dulles International Airport|Washington–Dulles]]<br />'''Seasonal:''' [[Bradley International Airport|Hartford]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[FedEx Express#FedEx Feeder|FedEx Feeder]] | [[Elmira/Corning Regional Airport|Elmira]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Kalitta Charters]] | [[Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport|Cincinnati]], [[Bradley International Airport|Hartford]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Quest Diagnostics]] | [[Niagara Falls International Airport|Niagara Falls]], [[Syracuse Hancock International Airport|Syracuse]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[USA Jet Airlines]] | [[Laredo International Airport|Laredo]], [[Willow Run Airport|Ypsilanti]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
}} |
|||
==Airlines and terminal== |
|||
[[File:Continental Express ERJ-145 at ROC 2002.jpg|thumb|right|The East of Concourse B at ROC in September 2002]] |
|||
Greater Rochester International Airport has a two concourse terminal in the north of the airfield.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.airport-data.com/airport/ROC/maps.html|title = Greater Rochester International Airport (ROC) - Map, Aerial Photo, Diagram}}</ref> The terminal is owned and operated by The Monroe County Airport Authority (MCAA).<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.airport-technology.com/projects/greater-rochester-international-airport-expansion-rochester-new-york/|title = Greater Rochester International Airport Expansion, Rochester, New York - Airport Technology}}</ref> This terminal has two concourses, each with two stories. The top level of the terminal is home to shops, restaurants, bathrooms, and all gates. The bottom level is home to offices, ground service equipment, and US Customs and Immigration. The terminal has a total of twenty-one gates with ten gates in concourse A and eleven gates in concourse B. Both concourses have been named after somebody famous from Rochester. Concourse A is named after Frederick Douglass and concourse B is named after Susan B. Anthony.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.rocairport.com/map|title=Frederick Douglass Greater Rochester International Airport (ROC)}}</ref> The airport handles eight regularly scheduled airlines and one charter airline |
|||
Concourse A handles: |
|||
*[[American Airlines]] (A6, A8-A11) |
|||
*[[Avelo Airlines]] (A7) |
|||
*[[JetBlue Airways]] (A5) |
|||
*[[Southwest Airlines]] (A2, A4) |
|||
*[[Spirit Airlines]] (A1) |
|||
Concourse B handles: |
|||
*[[Allegiant Air]] (B9) |
|||
*[[Delta Airlines]] (B1, B3-B5, B7) |
|||
*[[United Airlines]] (B6, B8, B10) |
|||
==Cargo== |
|||
[[File:Greater Rochester International Airport Cargo Terminal 8-07.jpg|thumb|right|Two buildings of ROC's USAirports cargo terminal in August 2007]] |
|||
Greater Rochester International Airport has a cargo terminal in the northwest corner of the airfield. The terminal is operated by USAirports.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://usairports.com/fbo.html|title=FBO}}</ref> This terminal has three cargo buildings, two hangars, and USAirports' three-story headquarters administrative building. The company was founded in Rochester in the 1980s as Airport Systems and later changed its name to USAirports. The company operates cargo terminals at several airports in the United States. |
|||
This cargo terminal handles: |
|||
*Operators for [[DHL]] |
|||
*[[Quest Diagnostics]] |
|||
*Other non-FedEx cargo carriers |
|||
[[FedEx]] operates its own cargo terminal on the southeastern border of the airport off Scottsville Road. It handles: |
|||
*[[FedEx Express]] |
|||
*[[FedEx Feeder]] operated by [[Wiggins Airways]] & [[Mountain Air Cargo]] |
|||
==Statistics== |
|||
===Top destinations=== |
|||
[[File:Delta 722 at Greater Rochester International Airport 2002.jpg|thumb|right|Delta [[Boeing 727-200]] arriving from [[Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport]]]] |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size:95%;" |
|||
|+ Busiest domestic routes from ROC (October 2023 - September 2024)<ref name="transtats.bts.gov"> |
|||
{{cite web |
|||
| title = Rochester, NY: Greater Rochester International (ROC) |
|||
| url = https://www.transtats.bts.gov/airports.asp?20=E&Nv42146=ebP&Nv42146_anzr=e1pur56r4,%20al:%20T4rn6r4%20e1pur56r4%20V06r40n6v10ny&pn44vr4=SNPgf |
|||
| publisher = [[Bureau of Transportation Statistics]] |
|||
| date = December 2024 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
! Rank |
|||
! City |
|||
! Passengers |
|||
! Carriers |
|||
|- |
|||
| 1 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Maryland}} [[Baltimore/Washington International Airport|Baltimore, Maryland]] |
|||
| 156,930 |
|||
| Southwest |
|||
|- |
|||
| 2 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Illinois}} [[O'Hare International Airport|Chicago–O'Hare, Illinois]] |
|||
| 155,400 |
|||
| American, United |
|||
|- |
|||
| 3 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Georgia (U.S. state)}} [[Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport|Atlanta, Georgia]] |
|||
| 136,480 |
|||
| Delta |
|||
|- |
|||
| 4 |
|||
| {{flagicon|New York}} [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK, New York]] |
|||
| 130,860 |
|||
| Delta, JetBlue |
|||
|- |
|||
| 5 |
|||
| {{flagicon|North Carolina}} [[Charlotte Douglas International Airport|Charlotte, North Carolina]] |
|||
| 118,270 |
|||
| American |
|||
|- |
|||
| 6 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Florida}} [[Orlando International Airport|Orlando, Florida]] |
|||
| 94,880 |
|||
| Southwest, Spirit |
|||
|- |
|||
| 7 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Michigan}} [[Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport|Detroit, Michigan]] |
|||
| 87,440 |
|||
| Delta |
|||
|- |
|||
| 8 |
|||
| {{flagicon|New Jersey}} [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark, New Jersey]] |
|||
| 71,540 |
|||
| United |
|||
|- |
|||
| 9 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Washington, D.C.}} [[Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport|Washington–National]] |
|||
| 60,330 |
|||
| American |
|||
|- |
|||
| 10 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Illinois}} [[Midway International Airport|Chicago–Midway, Illinois]] |
|||
| 60,020 |
|||
| Southwest |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
===Airline market share=== |
|||
{{Bar graph |
|||
| title = Carrier shares for (October 2023 - September 2024)<ref name="transtats.bts.gov" /> |
|||
| bar_width = 33 |
|||
| width_units = em |
|||
| label_type = Carrier |
|||
| data_type = Passengers (arriving and departing) |
|||
| data_max = 997,000 <!-- highest of the data values below --> |
|||
| label1 = [[Southwest Airlines|Southwest]] |
|||
| data1 = 552,000 |
|||
| comment1 = 21.01% |
|||
| label2 = [[Endeavor Air|Endeavor]] |
|||
| data2 = 355,000 |
|||
| comment2 = 13.49% |
|||
| label3 = [[Delta Airlines|Delta]] |
|||
| data3 = 285,000 |
|||
| comment3 = 10.85% |
|||
| label4 = [[United Airlines|United]] |
|||
| data4 = 242,000 |
|||
| comment4 = 9.21% |
|||
| label5 = [[American Airlines|American]] |
|||
| data5 = 197,000 |
|||
| comment5 = 7.50% |
|||
| label6 = Other |
|||
| data6 = 997,000 |
|||
| comment6 = 37.94% |
|||
}} |
|||
=== Annual traffic === |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size: 95%; text-align:center" width= align= |
|||
! Year |
|||
! Total Passengers |
|||
! % Change |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2002<ref name="BTS Stats">{{cite web|url=http://www.transtats.bts.gov/airports.asp?pn=1&Airport=BUF&Airport_Name=Buffalo,%20NY:%20Buffalo%20Niagara%20International&carrier=FACTS|title=RITA – BTS – Transtats}}</ref> |
|||
| 2,055,000 |
|||
| {{steady}} |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2003<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,458,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 19.61% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2004<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,717,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 10.54% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2005<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| '''2,889,000''' |
|||
| {{increase}} 6.33% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2006<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,822,000 |
|||
| {{decrease}} 2.32% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2007<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,838,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 0.57% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2008<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,679,000 |
|||
| {{decrease}} 5.60% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2009<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,538,000 |
|||
| {{decrease}} 5.26% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2010<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,515,000 |
|||
| {{decrease}} 0.91% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2011<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,364,000 |
|||
| {{decrease}} 6.00% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2012<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,394,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 1.27% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2013<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,402,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 0.33% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2014<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,339,000 |
|||
| {{decrease}} 2.62% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2015<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,345,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 0.26% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2016<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,356,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 0.47% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2017<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,391,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 1.49% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2018<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,540,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 6.23% |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2019<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
| 2,544,000 |
|||
| {{increase}} 0.16% |
|||
|- |
|||
!!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2020<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
|831,000 |
|||
|{{decrease}} 67.33% |
|||
|- |
|||
!!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2021<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
|1,532,000 |
|||
|{{increase}} 84.36% |
|||
|- |
|||
!!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2022<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
|2,316,000 |
|||
|{{increase}} 51.17% |
|||
|- |
|||
!!style="height:20px;" scope="row"| 2023<ref name="BTS Stats"/> |
|||
|2,646,000 |
|||
|{{increase}} 14.25% |
|||
|} |
|||
==General aviation== |
|||
Greater Rochester International Airport has two [[fixed-base operator]]s supporting general aviation operations. USAirports and Avflight provide hangar, fuel, and maintenance support for general aviation aircraft. Both FBOs fuel and de-ice airline traffic.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://usairports.com/|title=HOME|website=usairports.com}}</ref> |
|||
==Incidents== |
|||
*[[Mohawk Airlines Flight 121]] crashed on takeoff July 2, 1963; seven died and 36 were injured. |
|||
*[[Allegheny Airlines]] Flight 453 crash-landed on July 9, 1978, while arriving from [[Boston Logan International Airport]]. The [[BAC-111]] aircraft was carrying 77 people. According to the NTSB report, the flight landed on Runway 28 at too high a speed, but with capability to reject the landing. The pilots chose to continue the landing, the aircraft skidded off the end of the runway, and its landing gear was sheared off by a ditch. There were no fatalities. The aircraft was written off.<ref>[http://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19780709-0 N1550 accident description] retrieved January 24, 2014</ref> |
|||
[[File:Allegheny Airlines BAC 1-11 N1132J 2.jpg|thumb|An [[Allegheny Airlines]] [[BAC-111]] similar to the one that crashed at the airport]] |
|||
*On December 22, 1984, a Cessna 402B operated by Falcon Air, N8064Q, was destroyed while returning to land after a cargo door had opened during takeoff. The pilot was killed, no passengers were aboard. The NTSB listed the cause of the accident as pilot error including inadequate pre-flight planning, failure to maintain airspeed, pilot attentiveness, and inability to recognize and avoid stall.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ntsb.gov/_layouts/ntsb.aviation/brief.aspx?ev_id=20001214X41877&key=1|title=NTSB Identification: NYC85FA047}}</ref> Contributing factors included high wind shear conditions and the baggage door opening upon takeoff. |
|||
*On November 14, 2002, a Cessna 210L, N2444S, was destroyed during a forced landing and collision with terrain while on approach to land. The accident site was 1 mile east of the airport {{coord|43|07|08.6|N|077|37|56.8|W|region:US_type:airport}}. The pilot was killed, no passengers were aboard. The NTSB determined the accident to be 'A loss of engine power for undetermined reasons.'<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ntsb.gov/_layouts/ntsb.aviation/brief2.aspx?ev_id=20021121X05502&ntsbno=NYC03FA020&akey=1|title=NTSB Identification: NYC03FA020}}</ref> |
|||
*On February 22, 2012, a [[United Express]] [[Embraer ERJ-145]] operated by [[Trans States Airlines]] from [[O'Hare International Airport|Chicago O'Hare]] skidded off the runway around 11:30 PM ET. Of the 45 people reported on board the flight, no one was injured.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://wxxinews.org/post/investigators-look-why-plane-skidded-runway|title=Investigators Look Into Why Plane Skidded off Runway|last=Agnew|first=LeShea|date=Feb 23, 2012|website=WXXI|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171201032756/https://wxxinews.org/post/investigators-look-why-plane-skidded-runway|archive-date=December 1, 2017|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
*On September 5, 2014, Socata TBM-700, with the registration N900KN,<ref>[http://registry.faa.gov/aircraftinquiry/NNum_Results.aspx?NNumbertxt=N900KN N900KN]</ref> departed Rochester bound for Naples, Florida, and lost contact with Air Traffic Control. It is believed the pilot suffered from [[Hypoxia (medical)|hypoxia]]. The aircraft crashed north of Jamaica, carrying Larry and Jane Glazer of Rochester, NY. They did not survive. |
|||
* On February 16, 2020, a Cessna 172M, with the registration N1126U,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://flightaware.com/resources/registration/N1126U|title=N1126U (1976 CESSNA 172M owned by SCHUBERT BROTHERS AVIATION INC) Aircraft Registration|website=FlightAware}}</ref> operated by Rochester Air Center LLC<ref name="WHAM">{{Cite news|url=https://13wham.com/news/local/small-plane-damaged-after-crashing-at-rochester-airport|title=Small plane damaged after crashing at Rochester airport|date=February 16, 2020|work=[[WHAM-TV]]}}</ref> crashed upon landing at runway 25. No one was injured, but the aircraft suffered substantial damage.<ref name="WHAM" /> |
|||
* On June 5, 2020, a [[Kalitta Charters]] 737-400 affiliated with DHL, with registration N733CK, went off Runway 4/22 near the intersection of Runway 10/28. The plane bound for Hartford rejected a takeoff attempt after experiencing a mechanical issue, before veering off the runway and into the grass. The two pilots were not injured. The plane experienced minimal damage and was towed away.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Hemmerdinger|first=Jon|title=Kalitta 737 freighter involved in Rochester runway incident|url=https://www.flightglobal.com/safety/kalitta-737-freighter-involved-in-rochester-runway-incident/138716.article|date=2020-06-05|access-date=2020-06-19|website=Flight Global|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=2020-06-05|title=Moore: 737 preparing to take off 'rolled off' runway|url=https://www.whec.com/rochester-new-york-news/fire-crews-737-off-the-runway-at-rochester-airport/5751801/|access-date=2020-06-19|website=WHEC News10NBC|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
* On August 1, 2021, [[United Express Flight 4583]] performed an emergency landing on Runway 4/22 after a fuel leak and the resulting fuel imbalance. There were no fatalities.<ref>{{cite news |title=Plane makes emergency landing at ROC Airport |url=https://13wham.com/news/local/plane-makes-emergency-landing-at-roc-airport |access-date=August 1, 2021 |date=August 1, 2021 |ref=13Wham}}</ref> |
|||
* On January 18, 2024, an [[American Eagle (airline brand)|American Eagle]]/[[Piedmont Airlines]] [[Embraer E145]] operating as Flight AA5811 from [[Philadelphia International Airport]] skidded off the runway after landing due to snowy conditions.<ref>[https://www.democratandchronicle.com/story/news/2024/01/18/american-airlines-plane-veers-off-runway-at-rochester-ny-airport/72273801007/ Passenger describes 'sudden shock' as plane veers off runway at Rochester airport], [[Democrat and Chronicle]], Jan. 18, 2024</ref><ref>[https://www.cbsnews.com/news/american-airlines-plane-slides-off-runway-rochester-airport-new-york/ American Airlines plane slides off runway at Rochester Airport], [[CBS News]], Jan. 18, 2024</ref> |
|||
==References== |
|||
* Airport Operations Data: AirportIQ 5010: [http://www.gcr1.com/5010web/airport.cfm?Site=ROC&AptSecNum=2 AirportIQ 5010] FAA Source: [https://web.archive.org/web/20140809195730/http://www.gcr1.com/5010web/REPORTS/AFD07242014ROC.pdf Wayback Machine] |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Portal|New York (state)|Aviation}} |
|||
* [http://www.rocairport.com/ Greater Rochester International Airport Homepage] |
|||
{{Commons category|Greater Rochester International Airport}} |
|||
* {{cite web|url= https://www.dot.ny.gov/divisions/operating/opdm/aviation/repository/air_dir/roc.pdf |title=New York State DOT Airport Diagram }} |
|||
* {{FAA-diagram|00351}} |
|||
* {{FAA-procedures|ROC}} |
|||
{{US-airport|ROC}} |
|||
* [http://rocwiki.org/Greater_Rochester_International_Airport Rochester Wiki Airport page] |
|||
* [http://www.iaff1636.com Monroe County Airport Professional Firefighters – IAFF Local 1636] |
|||
* [https://www.youtube.com/user/USAF88TC?feature=mhee KROC Airport Spotter's YouTube page] |
|||
{{Airports in Upstate New York}} |
|||
{{City of Rochester, NY}} |
|||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Transportation in Rochester, New York]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Airports in New York (state)]] |
||
[[Category:Airports established in 1927]] |
|||
[[Category:Transportation buildings and structures in Monroe County, New York]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 12:03, 18 December 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2012) |
Frederick Douglass Greater Rochester International Airport | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | County of Monroe | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operator | Monroe County Airport Authority | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Rochester, New York, U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for | Wiggins Airways[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 559 ft / 170 m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 43°7′8″N 077°40′21″W / 43.11889°N 77.67250°W | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | rocairport | ||||||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||||||
 FAA airport diagram | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2016, 2017) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Frederick Douglass Greater Rochester International Airport (IATA: ROC, ICAO: KROC, FAA LID: ROC) is a public airport located within the City of Rochester, three miles (4.8 km) southwest of Downtown, in Monroe County, New York, United States.[3] It is owned and operated by Monroe County. The airport is home to the 642nd Aviation Support Battalion, part of the 42nd Infantry Division.[5]
History
[edit]Early history
[edit]Baker Field
[edit]A 1910 newspaper article cited "a site near Scottsville Road", along with the Baker Farm in Genesee Valley Park, as possible locations for "airships" to fly from Rochester to Toronto.[6][title missing] The Baker Farm was located south of the original Genesee Valley Park, and was donated to the Parks Department of the City of Rochester in 1908.[7][title missing] The golf course at Genesee Valley Park was extended to include the Baker Farm in 1914.[8][title missing] During World War I, the Baker Farm area of the park, renamed "Baker Field", was used for military purposes. The United States School of Aerial Photography had been created at Kodak Park in Rochester, and Baker Field was the airfield associated with the project.[9][title missing] Military use of the field ceased in 1918.[10][title missing] Baker Field continued to be used as an airfield for a year or two thereafter,[11][12][title missing] but flood conditions made it unsuitable for airfield use in the long run.[13][title missing] Britton Field, located just west of Baker Field, became the primary airport for the Rochester area.
Britton Field
[edit]The site of the Greater Rochester International Airport, originally known as Britton Field, was used for aviation purposes as early as 1919. The Rochester Aircraft Corporation launched its first passenger flight from Britton Field August 18, 1919. The Curtiss JN-4 was piloted by Earl F. Beers. At the time, the only way to get to the field was either by car or by taking the Genesee Street trolley line to the end, and walking the remaining distance.[12] Beers, a Rochester aviation pioneer, urged the local government to purchase Britton Field for a municipal airport.[14][15][title missing] In 1919, Beers offered passenger flights out of Britton Field, charging $1.00 per minute.[16][title missing]
Britton Field hosted the United States Flying Circus, consisting of six planes, in September 1919.[17][title missing] Dozens of planes landed in Britton Field as part of an aviation race across the United States[18] and back again.[19][title missing] The race was won by Lt. B. W. Maynard, "The Flying Parson", who arrived in Rochester, from Buffalo, at 10:30 AM October 18, 1919. His flight from Buffalo's Curtiss Field to Britton Field, a distance of 70 miles, in 22 minutes. He continued to Binghamton before finishing the race at Mineola at 1:50 PM that afternoon.[20][title missing] Britton Field was the scene of more competition when a pair of Rochester fliers and two from Syracuse raced between the two cities later in 1919, in a contest sponsored by the Rochester Aero Club and the Syracuse Aero Club. The Rochester newspaper reported that the two Rochester planes beat the combined flying time of the Syracuse pair by 15 seconds.[21][title missing]
Purchase of the field as a "municipal aviation station" was authorized by the Rochester City Council in December 1919[22][title missing][23][title missing] The Rochester Aircraft Corporation proposed passenger service out of Britton Field across Lake Ontario to Toronto in 1920.[24][title missing] "Young" Sparks, of Bradford, PA., demonstrated the early art of parachuting, by leaping from a plane from 2,100 feet, in an aerial field day at Britton Field in 1921.[25][title missing] The United States Army considered Britton Field as a possible site for an airship mooring mast in 1924.[26][title missing]
In the 1920s Eastman Kodak Company and the United States Army used Britton Field as landing field for the testing of Kodak's aerial photography experiments.[27][title missing] The Fokker monoplane "Josephine Ford", flown by Commander Richard Byrd over the North Pole, was exhibited at Britton Field in October 1926, part of a nationwide tour intended to stimulate interest in aviation. During the Rochester exhibition, an unlicensed pilot, Charles Teleska, crashed his own plane.[28][title missing]
The Colonial Air Transport Company, forerunner to American Airlines, developed plans in 1926 to run daytime flights from Boston to Chicago, stopping at Albany, Syracuse, Rochester, Buffalo, and Cleveland. An intersecting route from New York City to Montreal would cross at Albany, allowing for passenger transfers. The new route would carry passengers, mail and merchandise. Night flights were planned as soon as lighted fields were available.[29][title missing][30][title missing] The Rochester Flying Club was formed that Fall, intending to keep Britton Field open to all aviation, and to start construction of a hangar and other improvements.[31][title missing]
Charles Lindbergh flew The Spirit of St. Louis into Britton Field July 29, 1927, as part of an air tour of New York State. He was greeted by 75,000, according to newspaper reports. He stayed an hour and proceeded on to Buffalo.[32][title missing][33][title missing] In the summer of 1927, the Rochester Community Players used Britton Field as one of the backdrops of their silent movie, "Fly Low Jack and The Game". The movie was written, directed, acted and produced by amateurs of the theater company, showcasing the new Cine-Kodak 16mm home movie system.[34][title missing]
The first woman in Western New York to receive a pilot's license, Geraldine Grey of Buffalo, trained at Britton Field under the direction of William Dunlap in 1928.[35][title missing]
Rochester Municipal Airport
[edit]The modern era of the Greater Rochester International Airport began in 1927, with the construction of Hangar No. 1 on a patch of land south of Rochester on Scottsville Road. The first scheduled passenger flights between New York City and Rochester were made that year. In 1928, the name was changed to Rochester Municipal Airport and more construction was completed, including improvements to the runways and drainage system, and Hangar No. 2. After the Second World War the airport saw a period of expansion as passenger volume, frequency of flights, and civilian pilot training increased. A flight training school, with nearly 1,000 students, was created.
On January 1, 1948, Monroe County took possession and control of the airport. The county made numerous improvements, including an instrumental runway 5,000 feet (1,500 meters) long, an extension of the north–south runway from 2,670 feet (810 m) to 5,000 ft (1,500 m), and administration facilities on Brooks Avenue.
1953–1992 terminal
[edit]A new red-brick, single-level passenger terminal was opened on Brooks Avenue in 1953. It was expanded substantially in 1963, and expanded again in 1978 and 1980. The building had only one floor, until a small second floor was added for administrative offices as part of the 1980 expansion. At this time the airport was "Rochester Monroe County Airport."
After the 1963 expansion gave it its final layout, the terminal had ten gates in two concourses. A small three-gate concourse at the east end served American Airlines, and a longer, angled concourse at the west end served Mohawk Airlines (four gates on the east side) and United Airlines (three gates on the west side).
Jet service began ROC in 1965 on American Airlines Boeing 727s, but the two longest runways, 10–28 (5,500 feet (1,700 m)) and 1–19 (5,000 feet (1,500 meters)) were short for jets. In 1967 Monroe County built runway 4–22, initially 7,000 feet (2,100 meters) and extended in 1969 to 8,002 feet (2,439 m) (bypassing the 8,000 feet (2,400 meters) threshold required for CAT III certification). 10–28 is still the crosswind runway. Runway 7–25, 4,000 feet (1,200 meters) long, is used by smaller aircraft.
In the late 1960s and early 1970s there was talk of building a Rochester-Buffalo airport in southeastern Niagara County, which would have taken over passenger traffic from Rochester-Monroe County and Greater Buffalo International Airport airports. This was never built.
The first jetways were added to gates 1 and 3 by American in 1977. As part of the 1978 expansion, new lounge space was built for Allegheny Airlines (successor to Mohawk) with three jetways. In about 1986 the airline (by then renamed USAir) added a fourth jetway. The 1980 expansion included two new lounge areas for United, each of which had one jetway. In 1987, Piedmont Airlines, which had taken over the United lounge closest to the terminal, added a second jetway to it. In about 1985, USAir built an expansion to the end of the main concourse to house a USAir Club.
The large new low-fare carrier People Express Airlines arrived at the airport in 1985. There was not room for them inside the terminal. A small ticket counter was built in office space in the northwest corner of the terminal, and a wooden peaked-roof shed was built on to house their outbound-baggage area, departure lounge, and baggage claim. No jetway was added. People's effect on fares was dramatic; ROC's enplanements increased 38% in 1985. When Continental Airlines took over People in 1987, they moved operations into the main terminal and shared gate space with American. The shed was removed.
In the mid-1980s, Monroe County Legislator Van Buren N. Hansford, Sr. (R-Pittsford) introduced successful legislation to have the airport's name changed to "Greater Rochester International Airport." By the end of the 1980s, The New York Air National Guard constructed a small hangar and office facility, and apron space, on the south side of the airport near the control tower. This facility has since been expanded.
Present terminal building
[edit]1988-1992 expansion project: new terminal
[edit]
The terminal was outgrown by the mid-1980s, and debate began about expanding the airport. In 1985, the administration of Monroe County Executive Lucien A. Morin (R) proposed a complicated terminal expansion that would have had baggage claim carousels across the driveway in a separate building, which tugs would have reached by a tunnel, and passengers would have reached by second-floor bridge corridors.
The County got as far as building temporary parking lots to the west and closing the main parking lots to begin construction on a garage. However, in 1988 the new County Executive, Thomas R. Frey (D) and the County Legislature had doubts about the cost of the project, and it was abandoned before construction started in earnest.
In 1988 Monroe County approved a $109 million plan to replace the terminal with an entirely new two-level facility with a second-level approach road and parking garage. The new facilities were built in stages on the exact site, between 1989 and 1992 and designed by HNTB and built by Wilmorite, Inc.[36] Ticketing and departures are on the second floor, and baggage claim and ground transportation is on the first floor. The County Legislature authorized the creation of a "Monroe County Airport Authority" to issue the bonds for the construction.
This terminal has two angled concourses, each with 11 gates. Gate assignments are listed below. The eastern or B concourse opened in summer 1990. The eastern half of the main terminal opened in 1991. The western half of the main terminal, western or A concourse, and garage, all opened in 1992. A series of temporary prefabricated buildings were used to provide gate space and baggage claim space during the construction.

2006-2008 terminal improvements
[edit]In 2006, Monroe County consolidated the separate security checkpoints at each concourse, to one central security checkpoint. Monroe County argued that this arrangement, although it would close the terminal's large concessions atrium and airfield views to non-passengers, would be more efficient and save money.[37] The county replaced the lost public airfield view with a new viewing area at the west end of the terminal.
In 2008, renovations were undertaken to replace floors, carpets, and seating in the concourses, move explosives-scanning equipment from the ticketing lobby to the outbound baggage room, and replace T-shaped baggage claim carousels with four 360-degree walk-around carousels, which receive luggage from belts through the ceiling. These projects were completed by late 2009.
In January 2009, the airport began work on an extension of the three-story parking garage to the west, for additional capacity. By early 2010, that project was completed.
2016-2018 terminal renovations
[edit]
The concrete road decking of the departures level roadway was closed and repaired from April to July 2016. The Airport won the Governor Cuomo's Upstate Airport Economic and Revitalization Competition (UAERC) in 2016 and received nearly $40 million, for use to adapt and enhance the airport's facilities. A $54 million project was subsequently announced to create a high-tech smart facility that best serves the business and economic needs, while reducing barriers for passengers with disabilities, which broke ground in the spring of 2017. The UAERC sums were used to pay for a substantial portion of the project, with bonds and airport fees paying for remaining costs. By the fall, the total cost had ballooned to $79 million.
The security checkpoint was enlarged, now including two dedicated TSA PreCheck lanes in addition to four general lanes. A consolidated exit passageway, leading from the secure Food Court to non-secure Baggage Claim, eliminated two previous exits at either end of the concourse. The Food Court was renovated and revamped with new restaurants and additional seating. Bathrooms, interior lighting in addition to accessibility services and way-finding were overhauled throughout the terminal.
A new cell-phone lot was built with flight-display information and an electric vehicle charging station, and is located off the airport roadway, now before the terminal building instead of after. A canopy added over the departures-level roadway reduces winter maintenance costs, and features solar panels, colorful aesthetic lighting, and rainwater storage capabilities. The project was completed in October 2018.
Airport events at-large
[edit]
Southwest Airlines replaced AirTran's service at the airport after its acquisition by the airline in 2013.
In 2014, New York State Police established a base for its aviation unit at the Monroe County Regional Traffic Operations Center on airport property, already a station for that agency. At least two helicopters, previously based out of Batavia and Syracuse, were moved to consolidate operations and reduce costs. This unit services Western and Central New York, including Buffalo, Rochester and Syracuse.[38]
Allegiant Air started limited service out of Rochester, with flights to Orlando-Sanford that same year.
The Clock of Nations, previously at Midtown Plaza prior to 2007, was restored and moved to the airport Food Court in 2009. Planned to stay temporarily — until the clock's intended permanent home at the new Golisano Children's Hospital building was completed in 2014 — the hospital early in the design process opted to decline housing it, allotting the airport as an indefinite residence. It remained on display until 2017, before being disassembled and placed into storage before renovations started. The Clock of Nations will not be placed back in the terminal, as it can no longer occupy its previous location because of changes to the terminal layout. As of 2020, Monroe County has no plans for the clock's future home, which remains in storage.
In October 2018, Air Canada ended its service to Rochester from Toronto, leaving the airport without any international flights.[39]
In May 2021, Frontier Airlines started new service to Orlando from Rochester.[40]
Renaming efforts
[edit]An online petition was started in July 2020 to rename the airport after Frederick Douglass, possibly to "Frederick Douglass International Airport". Soon after, County Executive Adam Bello said that Monroe County will begin to work with stakeholders - the FAA, Monroe County Legislature, among others - to examine and study a potential name change. Douglass lived in Rochester for much of his adult life and is buried at Mt. Hope Cemetery.
On August 12, 2020, Monroe County legislators confirmed that the airport would be renamed in honor of Douglass.[41]
Airfield
[edit]The airport covers 1,136 acres (460 ha) at an elevation of 559 feet (170 m). It has three runways - a primary runway, a general aviation runway, and a crosswinds runway:[3][42]
- 4/22: 8,001 ft × 150 ft (2,439 m × 46 m), asphalt
- 7/25: 4,000 ft × 100 ft (1,219 m × 30 m), asphalt
- 10/28: 6,402 ft × 150 ft (1,951 m × 46 m), asphalt
Runways 4, 22 and 28 have Instrument Landing System (ILS); runway 4 has a Category II ILS.
In 2008 the airport completed two service roads around the end of Runway 28, near Interstate 390, in tunnels. The ground was graded upwards beyond the end of the runway to cover the tunnels. Earlier in the decade, a 500-foot (150 m) overrun area was added to the east (10) end of this runway, adjacent to railroad tracks and housing. An engineered materials arrestor system (EMAS) of about 200 feet (61 m) was added to this extension. The EMAS consists of soft rubberized concrete into which an overrunning aircraft's wheels can sink, and the aircraft may be stopped safely before it veers onto the grass.
Movements
[edit]In 2017 the airport had 87,261 aircraft operations, average 239 per day: 44% general aviation, 26% air carrier, 26% air taxi and 3% military. 86 aircraft are based at the airport: 48 single engine, 10 multi-engine, 17 jet and 11 military.[citation needed]
Terminal
[edit]The Greater Rochester International Airport consists of a main terminal building with two angled concourses with 22 total passenger gates. The departures level includes a ticketing hall, a six lane security checkpoint, post-security food court and two passenger concourses. The arrivals level has four baggage claim carousels, airline baggage offices, visitor information and car rental offices. A three-level parking garage, designated for long-term parking and rental cars, sits across the roadway from the terminal building. Fairfield Inn & Suites has an on-site hotel across the street from the terminal, just east of the parking garage.
JetBlue, Spirit, American, Avelo and Southwest occupy Concourse A (also called Frederick Douglass Concourse) with gates A1-A11. United, Delta and Allegiant are in Concourse B (also known as Susan B. Anthony Concourse) with gates B1-B10.
Airlines and destinations
[edit]Passenger
[edit]

| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Allegiant Air | Seasonal: Punta Gorda (FL) |
| American Airlines | Charlotte |
| American Eagle | Boston, Chicago–O'Hare, Miami, Philadelphia, Washington–National |
| Avelo Airlines | Charlotte/Concord,[43] Lakeland,[44] Nashville (begins April 3, 2025),[45] Raleigh/Durham,[46] Wilmington (NC) (begins April 4, 2025)[45] |
| Delta Air Lines | Atlanta, Detroit |
| Delta Connection | Detroit, New York–JFK, New York–LaGuardia |
| JetBlue | New York–JFK |
| Southwest Airlines | Baltimore, Las Vegas,[47] Orlando, Tampa Seasonal: Chicago–Midway,[48] Fort Myers (begins February 15, 2025)[48] |
| Spirit Airlines | Fort Lauderdale,[49] Orlando Seasonal: Myrtle Beach |
| United Airlines | Chicago–O'Hare, Newark, Washington–Dulles |
| United Express | Chicago–O'Hare, Newark, Washington–Dulles |
| Destinations map |
|---|
Cargo
[edit]Airlines and terminal
[edit]
Greater Rochester International Airport has a two concourse terminal in the north of the airfield.[50] The terminal is owned and operated by The Monroe County Airport Authority (MCAA).[51] This terminal has two concourses, each with two stories. The top level of the terminal is home to shops, restaurants, bathrooms, and all gates. The bottom level is home to offices, ground service equipment, and US Customs and Immigration. The terminal has a total of twenty-one gates with ten gates in concourse A and eleven gates in concourse B. Both concourses have been named after somebody famous from Rochester. Concourse A is named after Frederick Douglass and concourse B is named after Susan B. Anthony.[52] The airport handles eight regularly scheduled airlines and one charter airline
Concourse A handles:
- American Airlines (A6, A8-A11)
- Avelo Airlines (A7)
- JetBlue Airways (A5)
- Southwest Airlines (A2, A4)
- Spirit Airlines (A1)
Concourse B handles:
- Allegiant Air (B9)
- Delta Airlines (B1, B3-B5, B7)
- United Airlines (B6, B8, B10)
Cargo
[edit]
Greater Rochester International Airport has a cargo terminal in the northwest corner of the airfield. The terminal is operated by USAirports.[53] This terminal has three cargo buildings, two hangars, and USAirports' three-story headquarters administrative building. The company was founded in Rochester in the 1980s as Airport Systems and later changed its name to USAirports. The company operates cargo terminals at several airports in the United States.
This cargo terminal handles:
- Operators for DHL
- Quest Diagnostics
- Other non-FedEx cargo carriers
FedEx operates its own cargo terminal on the southeastern border of the airport off Scottsville Road. It handles:
- FedEx Express
- FedEx Feeder operated by Wiggins Airways & Mountain Air Cargo
Statistics
[edit]Top destinations
[edit]
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 156,930 | Southwest | |
| 2 | 155,400 | American, United | |
| 3 | 136,480 | Delta | |
| 4 | 130,860 | Delta, JetBlue | |
| 5 | 118,270 | American | |
| 6 | 94,880 | Southwest, Spirit | |
| 7 | 87,440 | Delta | |
| 8 | 71,540 | United | |
| 9 | 60,330 | American | |
| 10 | 60,020 | Southwest |
Airline market share
[edit]| Carrier | Passengers (arriving and departing) |
|---|---|
| Southwest | |
| Endeavor | |
| Delta | |
| United | |
| American | |
| Other |
Annual traffic
[edit]| Year | Total Passengers | % Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2002[55] | 2,055,000 | |
| 2003[55] | 2,458,000 | |
| 2004[55] | 2,717,000 | |
| 2005[55] | 2,889,000 | |
| 2006[55] | 2,822,000 | |
| 2007[55] | 2,838,000 | |
| 2008[55] | 2,679,000 | |
| 2009[55] | 2,538,000 | |
| 2010[55] | 2,515,000 | |
| 2011[55] | 2,364,000 | |
| 2012[55] | 2,394,000 | |
| 2013[55] | 2,402,000 | |
| 2014[55] | 2,339,000 | |
| 2015[55] | 2,345,000 | |
| 2016[55] | 2,356,000 | |
| 2017[55] | 2,391,000 | |
| 2018[55] | 2,540,000 | |
| 2019[55] | 2,544,000 | |
| 2020[55] | 831,000 | |
| 2021[55] | 1,532,000 | |
| 2022[55] | 2,316,000 | |
| 2023[55] | 2,646,000 |
General aviation
[edit]Greater Rochester International Airport has two fixed-base operators supporting general aviation operations. USAirports and Avflight provide hangar, fuel, and maintenance support for general aviation aircraft. Both FBOs fuel and de-ice airline traffic.[56]
Incidents
[edit]- Mohawk Airlines Flight 121 crashed on takeoff July 2, 1963; seven died and 36 were injured.
- Allegheny Airlines Flight 453 crash-landed on July 9, 1978, while arriving from Boston Logan International Airport. The BAC-111 aircraft was carrying 77 people. According to the NTSB report, the flight landed on Runway 28 at too high a speed, but with capability to reject the landing. The pilots chose to continue the landing, the aircraft skidded off the end of the runway, and its landing gear was sheared off by a ditch. There were no fatalities. The aircraft was written off.[57]

- On December 22, 1984, a Cessna 402B operated by Falcon Air, N8064Q, was destroyed while returning to land after a cargo door had opened during takeoff. The pilot was killed, no passengers were aboard. The NTSB listed the cause of the accident as pilot error including inadequate pre-flight planning, failure to maintain airspeed, pilot attentiveness, and inability to recognize and avoid stall.[58] Contributing factors included high wind shear conditions and the baggage door opening upon takeoff.
- On November 14, 2002, a Cessna 210L, N2444S, was destroyed during a forced landing and collision with terrain while on approach to land. The accident site was 1 mile east of the airport 43°07′08.6″N 077°37′56.8″W / 43.119056°N 77.632444°W. The pilot was killed, no passengers were aboard. The NTSB determined the accident to be 'A loss of engine power for undetermined reasons.'[59]
- On February 22, 2012, a United Express Embraer ERJ-145 operated by Trans States Airlines from Chicago O'Hare skidded off the runway around 11:30 PM ET. Of the 45 people reported on board the flight, no one was injured.[60]
- On September 5, 2014, Socata TBM-700, with the registration N900KN,[61] departed Rochester bound for Naples, Florida, and lost contact with Air Traffic Control. It is believed the pilot suffered from hypoxia. The aircraft crashed north of Jamaica, carrying Larry and Jane Glazer of Rochester, NY. They did not survive.
- On February 16, 2020, a Cessna 172M, with the registration N1126U,[62] operated by Rochester Air Center LLC[63] crashed upon landing at runway 25. No one was injured, but the aircraft suffered substantial damage.[63]
- On June 5, 2020, a Kalitta Charters 737-400 affiliated with DHL, with registration N733CK, went off Runway 4/22 near the intersection of Runway 10/28. The plane bound for Hartford rejected a takeoff attempt after experiencing a mechanical issue, before veering off the runway and into the grass. The two pilots were not injured. The plane experienced minimal damage and was towed away.[64][65]
- On August 1, 2021, United Express Flight 4583 performed an emergency landing on Runway 4/22 after a fuel leak and the resulting fuel imbalance. There were no fatalities.[66]
- On January 18, 2024, an American Eagle/Piedmont Airlines Embraer E145 operating as Flight AA5811 from Philadelphia International Airport skidded off the runway after landing due to snowy conditions.[67][68]
References
[edit]- Airport Operations Data: AirportIQ 5010: AirportIQ 5010 FAA Source: Wayback Machine
- ^ "Route Map". July 4, 2017. Archived from the original on February 27, 2022. Retrieved December 22, 2020.
- ^ Greater Rochester International Airport, official site
- ^ a b c FAA Airport Form 5010 for ROC PDF, effective November 28, 2024.
- ^ "2010 North American final rankings". Archived from the original on February 8, 2008.
- ^ "642 Aviation Support Battalion (ASB) - Unit information". dmna.ny.gov. Retrieved May 15, 2018.
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, June 8, 1910
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, January 31, 1908
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, May 1, 1914
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, Dec. 25, 1918
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, April 9, 1919
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, June 19, 1919
- ^ a b Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, August 19, 1919
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, August 2, 1919
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle (Beers obituary), July 30, 1927
- ^ Medina Daily Journal, July 27, 1927
- ^ Geneva Daily Times, November 7, 1919
- ^ Oswego Daily Palladium, September 12, 1919
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle October 9, 1919 and October 10, 1919
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, October 11, 1919 and October 15, 1919
- ^ Batavia Daily News, October 18, 1919
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, November 29, 1919
- ^ The Fredonia Censor; December 19, 1919
- ^ Monroe County Mail, Dec. 25, 1919
- ^ Buffalo Daily Palladium, February 17, 1920
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, September 25, 1921
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, June 8, 1924
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, November 25, 1925
- ^ Corning Evening Leader, October 12, 1926
- ^ Buffalo Evening News, September 29, 1926
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, November 25, 1926
- ^ Rochester Democrat and Chronicle, November 28, 1926
- ^ Jamestown Evening Journal, July 29, 1927 (Associated Press report)
- ^ Geneva Daily Times, July 22, 1927
- ^ Rochester Evening Journal and Post Express, June 30, 1927
- ^ Buffalo Courier Express, February 18, 1928
- ^ "Greater Rochester International Airport – Wilmorite: Portfolio". Archived from the original on March 4, 2014.
- ^ "First Quarter Newsletter 2005" (PDF). Greater Rochester International Airport Newsletter. 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 4, 2006.
- ^ "Syracuse's state police helicopter operations will move to Rochester". syracuse. July 14, 2014. Retrieved June 18, 2020.
- ^ "Air Canada ends service to Rochester". WHEC News10NBC. Archived from the original on October 12, 2018.
- ^ NY, Monroe County. "Frontier Airlines to Begin Flights at Frederick Douglass Greater Rochester International (ROC) | Monroe County, NY". www.monroecounty.gov. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ Lahman, Sean. "Rochester airport to be renamed for Frederick Douglass". Democrat and Chronicle.
- ^ "ROC airport data at skyvector.com". skyvector.com. Retrieved August 29, 2022.
- ^ "Avelo Airlines expanding to Concord, adding 6 nonstop routes". wbtv. July 24, 2024. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- ^ "Avelo Airlines announces 7 all-new nonstop routes from Lakeland". WFLA. July 24, 2024. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- ^ a b Fox, Allison (December 4, 2024). "Avelo Airlines Just Announced 7 New Routes — Including 2 to the Caribbean". Travel+Leisure. Retrieved December 4, 2024.
- ^ "Avelo Airlines Grows its 5th Base in Raleigh-Durham with Second Aircraft, Three New Nonstop Destinations and More Jobs". PRNewsWire. Retrieved March 15, 2023.
- ^ "Southwest Airlines adding nonstop service between Rochester and Las Vegas".
- ^ a b "Southwest Airlines 1Q25 Network Changes – 29JUL24". Aeroroutes. Retrieved July 30, 2024.
- ^ "Spirit Airlines August 2024 Network Additions – 19MAY24". Aeroroutes. Retrieved May 21, 2024.
- ^ "Greater Rochester International Airport (ROC) - Map, Aerial Photo, Diagram".
- ^ "Greater Rochester International Airport Expansion, Rochester, New York - Airport Technology".
- ^ "Frederick Douglass Greater Rochester International Airport (ROC)".
- ^ "FBO".
- ^ a b "Rochester, NY: Greater Rochester International (ROC)". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. December 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v "RITA – BTS – Transtats".
- ^ "HOME". usairports.com.
- ^ N1550 accident description retrieved January 24, 2014
- ^ "NTSB Identification: NYC85FA047".
- ^ "NTSB Identification: NYC03FA020".
- ^ Agnew, LeShea (February 23, 2012). "Investigators Look Into Why Plane Skidded off Runway". WXXI. Archived from the original on December 1, 2017.
- ^ N900KN
- ^ "N1126U (1976 CESSNA 172M owned by SCHUBERT BROTHERS AVIATION INC) Aircraft Registration". FlightAware.
- ^ a b "Small plane damaged after crashing at Rochester airport". WHAM-TV. February 16, 2020.
- ^ Hemmerdinger, Jon (June 5, 2020). "Kalitta 737 freighter involved in Rochester runway incident". Flight Global. Retrieved June 19, 2020.
- ^ "Moore: 737 preparing to take off 'rolled off' runway". WHEC News10NBC. June 5, 2020. Retrieved June 19, 2020.
- ^ "Plane makes emergency landing at ROC Airport". August 1, 2021. Retrieved August 1, 2021.
- ^ Passenger describes 'sudden shock' as plane veers off runway at Rochester airport, Democrat and Chronicle, Jan. 18, 2024
- ^ American Airlines plane slides off runway at Rochester Airport, CBS News, Jan. 18, 2024
External links
[edit]- "New York State DOT Airport Diagram" (PDF).
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective December 26, 2024
- FAA Terminal Procedures for ROC, effective December 26, 2024
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KROC
- ASN accident history for ROC
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KROC
- FAA current ROC delay information
- Rochester Wiki Airport page
- Monroe County Airport Professional Firefighters – IAFF Local 1636
- KROC Airport Spotter's YouTube page