Developed country: Difference between revisions
| [pending revision] | [accepted revision] |
RV Vandalism |
GreenC bot (talk | contribs) Reformat 1 archive link. Wayback Medic 2.5 per WP:USURPURL and JUDI batch #20 |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Country with a developed economy and infrastructure}} |
|||
[[Image:HDImap current.png|thumb|right|300px|Coloured world map indicating [[Human Development Index]] (as of 2003). [[List of countries by Human Development Index|Countries]] coloured darker shades of green exhibit very high human development and are generally reckoned as developed countries.]]A '''developed country''' is one that enjoys a relatively high [[standard of living]] derived through an [[industrialisation|industrialised]], diversified economy. Countries with a very high [[Human Development Index]] (HDI) are generally considered developed countries. This usually coincides with countries that have a high [[gross domestic product]] (GDP) per capita; however, some countries have achieved a (usually temporarily) high GDP through [[natural resource]] exploitation (e.g., [[Nauru]] through phosphate extraction and [[Equatorial Guinea]]) without developing the diverse industrial and service-based economy necessary for "developed" status. |
|||
{{Redirect|Industrial nation|the magazine|Industrialnation{{!}}''Industrialnation''}} |
|||
{{Distinguish|Developing country}} |
|||
{{For|the investing classification|Developed market}} |
|||
{{Pp-pc1}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=May 2024}} |
|||
[[File:IMF advanced economies and UN least developed countries.svg|thumb|420x420px| |
|||
Synonyms include '''industrialised countries''', '''more economically developed countries''' (MEDC) and the '''[[First World]]'''. Other terms sometimes used to describe the developed/[[developing country]] dichotomy are First World/[[Third World]] (the term [[Second World]] refers to [[communist state]]s during and since the [[Cold War]]); [[The North|North]]/[[The South|South]]; and industrialised countries/non-industrialised countries. The term [[Western countries]] has a similar meaning, but its connotations restrict its usage, especially in Asia. |
|||
{{legend|#00b9fa|Developed countries ([[International Monetary Fund|IMF]])}} |
|||
{{legend|#ffb219|[[Developing countries]] (IMF)}} |
|||
{{legend|#ff562f|[[Least developed countries]] ([[United Nations|UN]])}} |
|||
{{legend|#b9b9b9|Data unavailable}}<br />World map showing country classifications per the [[International Monetary Fund|IMF]]<ref name="IMF1">{{cite web |title=World Economic and Financial Surveys World Economic Outlook Database—WEO Groups and Aggregates Information |url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2022/01/weodata/groups.htm |publisher=International Monetary Fund |access-date=2 June 2022 |archive-date=3 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230303145301/https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2022/01/weodata/groups.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> and the [[United Nations|UN]]<ref>[https://www.un.org/development/desa/dpad/wp-content/uploads/sites/45/publication/ldc_list.pdf Least Developed Countries] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110517090756/http://www.unohrlls.org/en/ldc/related/62/ |date=17 May 2011 }} ({{usurped|1=[https://web.archive.org/web/20191221185727/http://unohrlls.org/custom-content/uploads/2018/12/list-of-least-developed-countries-rev1.pdf 2018 list]}})</ref> (last updated April 2023). "Developed economies" according to this classification scheme are shown in blue. The map does not include classifications by the World Bank.]] |
|||
A '''developed country''', or '''advanced country''',<ref name="adv1">{{cite web |title=Fiscal Policy and Inclusive Growth in Advanced Countries: Their Experience and Implications for Asia |url=https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/150177/ewp-422.pdf |website=adb.org |publisher=[[Asian Development Bank]] |date=December 2014 |access-date=8 July 2021 |archive-date=26 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210726220914/https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/150177/ewp-422.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="adv2">{{cite web |title=Advanced Countries Will Benefit Most from Progress in Technology, with Lesser Benefits to Other Nations |url=https://www.rand.org/news/press/2006/06/01.html |website=rand.org |publisher=[[RAND Corporation]] |date=1 June 2006 |access-date=8 July 2021 |archive-date=21 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210821221948/https://www.rand.org/news/press/2006/06/01.html |url-status=live }}</ref> is a [[sovereign state]] that has a high [[quality of life]], [[developed economy]], and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are the [[gross domestic product]] (GDP), [[gross national product]] (GNP), the [[per capita income]], level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living.<ref>[http://www.investopedia.com/terms/d/developed-economy.asp#axzz1legO8olO Developed Economy Definition] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160322201145/http://www.investopedia.com/terms/d/developed-economy.asp |date=22 March 2016 }}. Investopedia (16 April 2010). Retrieved 12 July 2013.</ref> Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. Different definitions of developed countries are provided by the [[Developed country#IMF advanced economies|International Monetary Fund]] and the [[Developed country#High-income economies|World Bank]]; moreover, [[Developed country#Human Development Index (HDI)|HDI ranking]] is used to reflect the composite index of life expectancy, education, and income per capita. In [[Developed country#Comparative table (2024)|2024]], 40 countries fit all three criteria, while an additional 20 countries fit two out of three. |
|||
Different observers and theorists often see different reasons for why certain countries (and not others) enjoy a high level of [[economic development]]. Many argue that economic development requires some combination of representative government (or [[democracy]]), a [[free market]] economic model, and a general lack of [[political corruption|corruption]]. Some hold that rich countries grew wealthy by [[exploitation]] of poorer countries in the past, through [[imperialism]] and [[colonialism]], or in the present, through the process of [[globalization]]. |
|||
Developed countries have generally more advanced [[post-industrial society|post-industrial]] economies, meaning the [[tertiary sector of the economy|service sector]] provides more wealth than the [[secondary sector of the economy|industrial sector]]. They are contrasted with [[developing country|developing countries]], which are in the process of [[industrialisation]] or are pre-industrial and almost entirely [[agriculture|agrarian]], some of which might fall into the category of [[Least Developed Countries]]. {{As of|2023}}, advanced economies comprise 57.3% of global GDP based on [[real versus nominal value (economics)|nominal values]] and 41.1% of global GDP based on [[purchasing power parity|purchasing-power parity]] (PPP) according to the [[International Monetary Fund|IMF]].<ref name=":5">{{cite web |author=International Monetary Fund |title=World Economic Outlook Database, April 2023 |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/April |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |access-date=30 April 2023 |archive-date=13 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230413194731/https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/April |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
According to the [[United Nations]] [[United Nations Statistics Division|Statistics Division]]: |
|||
{{TOC level|3}} |
|||
:''In the United Nations system there is no established convention for the designation of "developed" and "developing" countries or areas. In common practice, [[Japan]] in [[Asia]], [[Canada]] and the [[United States]] in [[North America]], [[Australia]] and [[New Zealand]] in [[Oceania]], and [[Europe]] are considered "developed" regions or areas. In international trade statistics, the [[Southern African Customs Union]] is also treated as a developed region and [[Israel]] as a developed country; and countries of [[eastern Europe]] and the former [[Soviet Union|U.S.S.R.]] countries in Europe are not included under either developed or developing regions.'' |
|||
== Definition and criteria == |
|||
The UN [[HDI]] is a statistical measure that gauges a country's level of human development. [[List of countries by Human Development Index|Countries]] with an HDI of 0.8 or more — largely corresponding to what the conventional definition of being a 'developed' country is — exhibit high development, and those with an HDI between 0.5 and 0.8 (including many of the former Soviet and Eastern Bloc states) exhibit moderate development. |
|||
[[File:UNCTADclassificationofeconomies.png|thumb|334x334px|Economic classification of the world's countries and territories by UN Trade and Development: developed economies are highlighted in blue.<ref name="UNCTADstat"/><ref name="classfications">{{cite web|title=Classifications - UNCTAD Handbook of Statistics 2023|url=https://hbs.unctad.org/classifications/|publisher=unctad.org}}</ref>]] |
|||
Economic criteria have tended to dominate discussions. One such criterion is the income per capita; countries with the high [[gross domestic product]] (GDP) per capita would thus be described as developed countries. Another economic criterion is [[industrialisation]]; countries in which the [[tertiary sector of the economy|tertiary]] and [[quaternary sector of the economy|quaternary sectors of industry]] dominate would thus be described as developed. More recently, another measure, the [[Human Development Index]] (HDI), which combines an economic measure, national income, with other measures, indices for life expectancy and education has become prominent. This criterion would define developed countries as those with a very high (HDI) rating. The index, however, does not take into account several factors, such as the [[List of countries by wealth per adult|net wealth per capita]] or the relative [[Quality (business)|quality of goods]] in a country. This situation tends to lower the ranking of some of the most advanced countries, such as the [[Group of Seven|G7]] members and others.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=R2D0AAAAMAAJ|title=The Courier|date=1994|publisher=Commission of the European Communities|language=en|access-date=20 January 2021|archive-date=15 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200315205542/https://books.google.com/books?id=R2D0AAAAMAAJ|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/glossary/human-development-index/|title=Human development index|work=Economics Help|access-date=23 September 2018|language=en-GB|archive-date=17 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201217215047/https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/glossary/human-development-index/|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
According to the [[United Nations Statistics Division]]: |
|||
==Developed countries== |
|||
<blockquote>There is no established convention for the designation of "developed" and "developing" countries or areas in the [[United Nations]] system.<ref name="unstated.un.org">{{cite web |title=Millennium Development Indicators: World and regional groupings |url=https://unstats.un.org/unsd/mi/worldmillennium.htm |publisher=[[United Nations Statistics Division]] |date=2003 |at=Note b |access-date=13 May 2017 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050210031555/http://unstats.un.org/unsd/mi/worldmillennium.htm |archive-date=10 February 2005 }}</ref></blockquote> |
|||
And it notes that: |
|||
Organizations such as the [[World Bank]], the [[International Monetary Fund]] (IMF) and the [[Central Intelligence Agency]], generally agree that the group of developed countries include: |
|||
<blockquote>The designations "developed" and "developing" are intended for statistical convenience and do not necessarily express a judgement about the stage reached by a particular country or area in the development process.<ref name="unstats.un.org">{{cite web |title=Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49): Developed Regions |url=http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49.htm |publisher=[[United Nations Statistics Division]] |access-date=13 May 2017 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170711220015/https://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49.htm |archive-date=11 July 2017 }}</ref></blockquote> |
|||
Nevertheless, the [[UN Trade and Development]] considers that this categorization can continue to be applied: |
|||
The following [[European Union]] member states: |
|||
<blockquote>The developed economies broadly comprise Northern America and Europe, Israel, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Australia, and New Zealand.<ref name="UNCTADstat">{{cite web | url=https://unctadstat.unctad.org/EN/Classifications.html#:~:text=The%20developed%20economies%20broadly%20comprise,as%20Australia%20and%20New%20Zealand | title=UNCTADstat - Classifications | access-date=30 September 2022 | archive-date=6 October 2022 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221006081729/http://unctadstat.unctad.org/en/classifications.html#:~:text=The%20developed%20economies%20broadly%20comprise,as%20Australia%20and%20New%20Zealand | url-status=live }}</ref></blockquote> |
|||
{| |
|||
=== Similar terms === |
|||
{{See also|Global North and Global South}} |
|||
Terms linked to the concept ''developed country'' include "advanced country", "industrialized country", "more developed country" (MDC), "more economically developed country" (MEDC), "[[North–South divide in the World|Global North]] country", "[[First World|first world]] country", and "post-industrial country". The term industrialized country may be somewhat ambiguous, as [[industrialisation]] is an ongoing process that is hard to define. The first industrialized country was the [[United Kingdom]], followed by [[Belgium]]. Later it spread further to [[Germany]], [[United States]], [[France]] and other [[Western Europe]]an countries. According to some [[economist]]s such as [[Jeffrey Sachs]], however, the current divide between the developed and [[Developing country|developing world]] is largely a phenomenon of the 20th century.<ref name="The End of Poverty">{{cite book |last=Sachs |first=Jeffrey |url=https://archive.org/details/endofpovertyecon0000sach |title=The End of Poverty |publisher=The Penguin Press |year=2005 |isbn=1-59420-045-9 |location=New York, New York |url-access=registration}}</ref> |
|||
[[Mathis Wackernagel]] calls the binary labeling of countries as "neither descriptive nor explanatory. It is merely a thoughtless and destructive endorsement of GDP fetish. In reality, there are not two types of countries, but over 200 countries, all faced with the same laws of nature, yet each with unique features."<ref name="Ecological Footprint: Managing Our Biocapacity Budget">{{cite book|last1=Wackernagel|first1=Mathis|url=https://www.newsociety.com/Books/E/Ecological-Footprint|title=Ecological Footprint: Managing Our Biocapacity Budget|last2=Beyers|first2=Bert|publisher=New Society Publishers|year=2019|isbn=978-0-86571-911-8|location=Gabriola Island, BC, Canada|page=132|author-link=Mathis Wackernagel|access-date=20 January 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191230123431/https://www.newsociety.com/Books/E/Ecological-Footprint|archive-date=30 December 2019|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
A 2021 analysis proposes the term ''emerged'' to describe markets, economies, or countries that have graduated from [[emerging market]] status, but have not yet reached the level equivalent to developed countries.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Lee|first1=Eun Su|last2=Liu|first2=Wei|last3=Yang|first3=Jing Yu|date=23 September 2021|title=Neither developed nor emerging: Dual paths for outward FDI and home country innovation in emerged market MNCs|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969593121001438|journal=International Business Review|volume=32 |issue=2 |language=en|page=101925|doi=10.1016/j.ibusrev.2021.101925|s2cid=244268711|issn=0969-5931}}</ref> Multinational corporations from these emerging markets present unique patterns of overseas expansion and knowledge acquisition from foreign countries. |
|||
== Economy lists by various criteria == |
|||
=== Human Development Index (HDI) === |
|||
{{Main|Human Development Index|List of countries by Human Development Index}} |
|||
[[File:2022-24 UN Human Development Report (multicolor).svg|thumb|The world map representing Human Development Index categories (based on 2022 data, published in 2024){{legend-col |
|||
|{{Legend|#008c00ff|Very high}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#ffcc00ff|High}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#ff6600ff|Medium}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#d40000ff|Low}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#b9b9b9ff|No data}} |
|||
}}|upright=1.9|alt=World map]] |
|||
[[File:HDI2022Incrimental.svg|thumb|World map of countries or territories by Human Development Index scores in increments of 0.050 (based on 2022 data, published in 2024){{legend-col |
|||
|thumb size=wide |
|||
|{{Legend|#001a00|≥ 0.950}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#003c00|0.900–0.950}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#007f00|0.850–0.899}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#00c400|0.800–0.849}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#00f900|0.750–0.799}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#d3ff00|0.700–0.749}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#ffee00|0.650–0.699}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#ffd215|0.600–0.649}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#ffa83c|0.550–0.599}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#ff852f|0.500–0.549}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#ff5b00|0.450–0.499}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#ff0000|0.400–0.449}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#a70000|≤ 0.399}} |
|||
|{{Legend|#C0C0C0|Data unavailable}} |
|||
}}|upright=1.9|alt=World map]] |
|||
The UN HDI is a statistical measure that gauges an economy's level of human development. While there is a strong correlation between having a high HDI score and being a prosperous economy, the UN points out that the HDI accounts for more than income or productivity. Unlike GDP per capita or per capita income, the HDI takes into account how income is turned "into education and health opportunities and therefore into higher levels of human development." |
|||
Since 1990, [[Norway]] (2001–2006, 2009–2019), [[Japan]] (1990–1991 and 1993), [[Canada]] (1992 and 1994–2000) and [[Iceland]] (2007–2008) have had the highest HDI score. |
|||
The following countries in the year 2022 are considered to be of "very high human development":<ref name="2022 components3">{{cite book |url=https://hdr.undp.org/content/human-development-report-2023-24 |title=Human Development Report 2023-24: Breaking the gridlock: Reimagining cooperation in a polarized world |date=13 March 2024 |publisher=United Nations Development Programme |access-date=16 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240317203048/https://hdr.undp.org/content/human-development-report-2023-24 |archive-date=17 March 2024 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
{{sticky header}}{{sort under}} |
|||
{| class="sortable wikitable sticky-header sort-under" {{right}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
<!-- Very High, High, Medium, and Low HDI labels should not be added due to accessibility and sorting issues, mainly [[WP:DTAB]]. See also [[Talk:List of countries by Human Development Index#Very High, High, Medium and Low HDI labels]] for more details. --> |
|||
| |
|||
! Rank |
|||
*[[Austria]] |
|||
! data-sort-type="number"| {{abbr|{{DELTA}}|Change since 2015}} |
|||
*[[Belgium]] |
|||
! style="width:17em;"| Country or territory |
|||
*[[Denmark]] |
|||
! HDI |
|||
*[[Finland]] |
|||
! data-sort-type="number"| % |
|||
*[[France]] |
|||
annual growth |
|||
| width=20 | |
|||
| |
|||
(2010-2022) |
|||
*[[Germany]] |
|||
*[[Greece]] |
|||
*[[Republic of Ireland|Ireland]] |
|||
*[[Italy]] |
|||
*[[Luxembourg]] |
|||
| width=20 | |
|||
| |
|||
*[[Netherlands]] |
|||
*[[Portugal]] |
|||
*[[Spain]] |
|||
*[[Sweden]] |
|||
*[[United Kingdom]] |
|||
|} |
|||
The following non-EU European countries: |
|||
{| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|1|| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Switzerland}} |
|||
*[[Andorra]] |
|||
|| 0.967 || {{sort|0.24|{{increase}} 0.24%}} |
|||
*[[Iceland]] |
|||
|- |
|||
*[[Liechtenstein]] |
|||
|2|| {{sort|-1|{{decrease}} (1)}} |
|||
*[[Monaco]] |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Norway}} |
|||
| width=20 | |
|||
|| 0.966 || {{sort|0.25|{{increase}} 0.25%}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
*[[Norway]] |
|||
|3|| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
*[[San Marino]] |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Iceland}} |
|||
*[[Switzerland]] |
|||
|| 0.959 || {{sort|0.28|{{increase}} 0.28%}} |
|||
*[[Vatican City]] |
|||
| |
|- |
||
|4|| {{sort|2|{{increase}} (2)}} |
|||
The following non-European countries: |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Hong Kong}} |
|||
{| |
|||
|| 0.956 || {{sort|0.38|{{increase}} 0.38%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 5|| {{sort|1|{{increase}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Denmark}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.952 || {{sort|0.35|{{increase}} 0.35%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Sweden}}|| {{sort|0.38|{{increase}} 0.38%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 7|| {{sort|8|{{increase}} (8)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Ireland}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.950 || {{sort|0.38|{{increase}} 0.38%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|-3|{{decrease}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Germany}}|| {{sort|0.19|{{increase}} 0.19%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|9|| {{sort|-1|{{decrease}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Singapore}} |
|||
|| 0.949 || {{sort|0.25|{{increase}} 0.25%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 10|| {{sort|1|{{increase}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Netherlands}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.946 || {{sort|0.26|{{increase}} 0.26%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|-1|{{decrease}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Australia}}|| {{sort|0.20|{{increase}} 0.20%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 12|| {{sort|2|{{increase}} (2)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Liechtenstein}} |
|||
| rowspan="3"| 0.942 || {{sort|0.23|{{increase}} 0.23%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Belgium}}|| {{sort|0.26|{{increase}} 0.26%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Finland}} |
|||
| {{sort|0.27|{{increase}} 0.27%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|15|| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|United Kingdom}} |
|||
|| 0.940 || {{sort|0.24|{{increase}} 0.24%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|16|| {{sort|-7|{{decrease}} (7)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|New Zealand}} |
|||
|| 0.939 || {{sort|0.13|{{increase}} 0.13%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|17|| {{sort|19|{{increase}} (19)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|United Arab Emirates}} |
|||
|| 0.937 || {{sort|1.04|{{increase}} 1.04%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|18|| {{sort|-5|{{decrease}} (5)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Canada}} |
|||
|| 0.935 || {{sort|0.22|{{increase}} 0.22%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|19|| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|South Korea}} |
|||
| 0.929 || {{sort|0.36|{{increase}} 0.36%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" |20 |
|||
| {{sort|-1|{{decrease}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Luxembourg}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" |0.927 |
|||
| {{sort|0.14|{{increase}} 0.14%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|-5|{{decrease}} (5)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|United States}}|| {{sort|0.10|{{increase}} 0.10%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 22|| {{sort|1|{{increase}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Slovenia}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.926 || {{sort|0.33|{{increase}} 0.33%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|-1|{{decrease}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Austria}}|| {{sort|0.21|{{increase}} 0.21%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|24 |
|||
| {{sort|-4|{{decrease}} (4)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Japan}} |
|||
|0.920 |
|||
| {{sort|0.16|{{increase}} 0.16%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 25|| {{sort|-1|{{decrease}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Israel}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.915 || {{sort|0.26|{{increase}} 0.26%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Malta}}|| {{sort|0.50|{{increase}} 0.50%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|27|| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Spain}} |
|||
|| 0.911 || {{sort|0.40|{{increase}} 0.40%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|28|| {{sort|-3|{{decrease}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|France}} |
|||
|| 0.910 || {{sort|0.28|{{increase}} 0.28%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|29|| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Cyprus}} |
|||
|| 0.907 || {{sort|0.45|{{increase}} 0.45%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|30|| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Italy}} |
|||
|| 0.906 || {{sort|0.24|{{increase}} 0.24%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|31|| {{sort|-2|{{decrease}} (2)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Estonia}} |
|||
|| 0.899 || {{sort|0.33|{{increase}} 0.33%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|32|| {{sort|-6|{{decrease}} (6)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Czech Republic}} |
|||
|| 0.895 || {{sort|0.22|{{increase}} 0.22%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|33|| {{sort|-3|{{decrease}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Greece}} |
|||
|| 0.893 || {{sort|0.18|{{increase}} 0.18%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|34|| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Bahrain}} |
|||
|| 0.888 || {{sort|0.80|{{increase}} 0.80%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|35|| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Andorra}} |
|||
| 0.884 || {{sort|0.20|{{increase}} 0.20%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|36 |
|||
| {{sort|-2|{{decrease}} (2)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Poland}} |
|||
|0.881 |
|||
| {{sort|0.35|{{increase}} 0.35%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" |37 |
|||
| {{sort|2|{{increase}} (2)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Latvia}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" |0.879 |
|||
| {{sort|0.51|{{increase}} 0.51%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|-2|{{decrease}} (2)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Lithuania}}|| {{sort|0.32|{{increase}} 0.32%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|39|| {{sort|6|{{increase}} (6)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Croatia}} |
|||
|| 0.878 || {{sort|0.53|{{increase}} 0.53%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 40|| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Qatar}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.875 || {{sort|0.45|{{increase}} 0.45%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|6|{{increase}} (6)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Saudi Arabia}} |
|||
| {{sort|0.70|{{increase}} 0.70%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| 42 || {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Portugal}} |
|||
| 0.874 || {{sort|0.42|{{increase}} 0.42%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|43 |
|||
| {{sort|-10|{{decrease}} (10)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|San Marino}} |
|||
|0.867 |
|||
| {{sort|-0.32|{{decrease}} 0.32%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|44|| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Chile}} |
|||
|| 0.860 || {{sort|0.47|{{increase}} 0.47%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 45|| {{sort|9|{{increase}} (9)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Turkey}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.855 || {{sort|1.10|{{increase}} 1.10%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|-5|{{decrease}} (5)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Slovakia}}|| {{sort|0.14|{{increase}} 0.14%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|47|| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Hungary}} |
|||
|| 0.851 || {{sort|0.22|{{increase}} 0.22%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|48|| {{sort|-6|{{decrease}} (6)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Argentina}} |
|||
|| 0.849 || {{sort|0.15|{{increase}} 0.15%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|49|| {{sort|0|{{steady}}}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Kuwait}} |
|||
|| 0.847 || {{sort|0.36|{{increase}} 0.36%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|50|| {{sort|1|{{increase}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Montenegro}} |
|||
|| 0.844 || {{sort|0.38|{{increase}} 0.38%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|51|| {{sort|-2|{{decrease}} (2)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Saint Kitts and Nevis}} |
|||
|| 0.838 || {{sort|0.49|{{increase}} 0.49%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|52|| {{sort|8|{{increase}} (8)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Uruguay}} |
|||
|| 0.830 || {{sort|0.47|{{increase}} 0.47%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|53|| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Romania}} |
|||
|| 0.827 || {{sort|0.14|{{increase}} 0.14%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|54|| {{sort|1|{{increase}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Antigua and Barbuda}} |
|||
|| 0.826 || {{sort|0.18|{{increase}} 0.18%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|55|| {{sort|-7|{{decrease}} (7)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Brunei}} |
|||
|| 0.823 || {{sort|-0.02|{{decrease}} 0.02%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|56|| {{sort|-3|{{decrease}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Russia}} |
|||
|| 0.821 || {{sort|0.25|{{increase}} 0.25%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 57|| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Bahamas}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.820 || {{sort|0.21|{{increase}} 0.21%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|5|{{increase}} (5)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Panama}}|| {{sort|0.47|{{increase}} 0.47%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|59 |
|||
| {{sort|-7|{{decrease}} (7)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Oman}} |
|||
|0.819 |
|||
| {{sort|0.22|{{increase}} 0.22%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 60|| {{sort|-3|{{decrease}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Trinidad and Tobago}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.814 || {{sort|0.30|{{increase}} 0.30%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|4|{{increase}} (4)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Georgia}}|| {{sort|0.54|{{increase}} 0.54%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|62|| {{sort|2|{{increase}} (2)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Barbados}} |
|||
|| 0.809 || {{sort|0.18|{{increase}} 0.18%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|63|| {{sort|6|{{increase}} (6)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Malaysia}} |
|||
| 0.807 || {{sort|0.41|{{increase}} 0.41%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|64 |
|||
| {{sort|5|{{increase}} (5)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Costa Rica}} |
|||
|0.806 |
|||
| {{sort|0.39|{{increase}} 0.39%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|65 |
|||
| {{sort|3|{{increase}} (3)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Serbia}} |
|||
|0.805 |
|||
| {{sort|0.39|{{increase}} 0.39%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|66|| {{sort|6|{{increase}} (6)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Thailand}} |
|||
|| 0.803 || {{sort|0.65|{{increase}} 0.65%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 67 || {{sort|-1|{{decrease}} (1)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Seychelles}} |
|||
| rowspan="2"| 0.802 || {{sort|0.30|{{increase}} 0.30%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{sort|-4|{{decrease}} (4)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Kazakhstan}}|| {{sort|0.38|{{increase}} 0.38%}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|69 |
|||
| {{sort|-11|{{decrease}} (11)}} |
|||
| {{left}} {{flag|Belarus}} |
|||
|0.801 |
|||
| {{sort|0.12|{{increase}} 0.12%}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|||
*[[Australia]] |
|||
*[[Canada]] |
|||
*[[Israel]] |
|||
*[[Japan]] |
|||
| width=20 | |
|||
| |
|||
*[[New Zealand]] |
|||
*[[United States]] |
|||
*[[Singapore]] |
|||
*[[South Korea]] |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
=== ''WESP'' developed economies === |
|||
==Other cases== |
|||
According to the [[United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs]]' ''World Economic Situation and Prospects'' report, the following 37 countries are classified as "developed economies" as of January 2024:<ref>{{cite web|title=World Economic Situation and Prospects 2024|url=https://www.un.org/development/desa/dpad/wp-content/uploads/sites/45/WESP_2024_Web.pdf|page=135 |publisher=United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
31 countries in Europe: |
|||
*Some organizations consider the remaining countries of the [[European Union]] — those which joined the body in [[2004]], especially [[Cyprus]], [[Malta]], and [[Slovenia]] — among the developed countries, but these mostly former-Communist countries are rather newly industrialised nations and some of them (such as [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]] and [[Poland]]) remain significantly less affluent than EU-15 countries. All European Union members, however, have a GDP per capita greater than the global average. |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Austria}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Belgium}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Bulgaria}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Croatia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Cyprus}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Czech Republic}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Denmark}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Estonia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Finland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|France}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Germany}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Greece}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Hungary}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Iceland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Ireland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Italy}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Latvia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Lithuania}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Luxembourg}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Malta}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Netherlands}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Norway}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Poland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Portugal}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Romania}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Slovakia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Slovenia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Spain}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Sweden}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Switzerland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|United Kingdom}} |
|||
}} |
|||
two countries in Northern America: |
|||
*[[Republic of China|Taiwan]], [[Hong Kong]] and [[Macau]] are considered developed by some organizations; however, the [[People's Republic of China]], a [[developing country]], claims the land of the first, and exercises sovereignty over the latter two. |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Canada}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|United States}} |
|||
}} |
|||
four countries in Asia and the Pacific: |
|||
*[[Mexico]], while a part of [[NAFTA]] and a member of the [[OECD]], remains much poorer than its northern neighbours. For this reason some authors consider Mexico a developing country rather than a developed one, though most properly Mexico lies between these two extremes as a [[newly industrialised country|NIC]], with its HDI just above 0.8 and possessing a booming upper middle-income economy. |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Australia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Japan}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|South Korea}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|New Zealand}} |
|||
}} |
|||
=== World Bank high-income economies=== |
|||
*[[South Africa]] and [[Turkey]] are considered developed by some sources; however their GDP per capita clearly places them among the developing countries (both have upper middle-income economies). |
|||
[[File:High income economies as classified by the World Bank.png|thumb|upright=1.6|High-income economies of the world as classified by the World Bank, 2023.]] |
|||
According to the [[World Bank]], the following 85 sovereign states and territories across are classified as [[World Bank high-income economy|high income economies]], having a [[List of countries by GNI (nominal) per capita|nominal GNI per capita]] in excess of $14,005 as of 2024:<ref>{{cite web|url=https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups|title=World Bank Country and Lending Groups|work=[[World Bank]]|access-date=25 July 2024}}</ref> |
|||
''Unsovereign Territories are denoted with an asterisk (*)''. |
|||
*[[Russia]] is also considered developed by some and belongs to the G8. This was mainly due to the fact it was once one of the world's leading superpowers, but it has recently faced many troubles such as rampant corruption. Like Turkey and South Africa their GDP per capita clearly places them among the developing countries and should not be considered developed. |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
*Despite their high per capita GDP, [[Brunei]] and the [[Middle East]]ern countries of [[Bahrain]], [[Kuwait]], [[Oman]], [[Qatar]], [[Saudi Arabia]] and the [[United Arab Emirates]] are generally not considered developed countries because their economies depend overwhelmingly on oil production and export. Some of these countries, especially Bahrain, have begun to diversify their economies and democratize. Similarly, the [[Bahamas]], [[Barbados]], [[Antigua and Barbuda]], [[Trinidad and Tobago]], and [[Saint Kitts and Nevis]] enjoy a high per capita GDP, but these economies depend overwhelmingly on the tourist industry. |
|||
* {{flag|American Samoa}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Andorra}} |
|||
* {{flag|Antigua and Barbuda}} |
|||
* {{flag|Aruba}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Australia}} |
|||
* {{flag|Austria}} |
|||
* {{flag|The Bahamas}} |
|||
* {{flag|Bahrain}} |
|||
* {{flag|Barbados}} |
|||
* {{flag|Belgium}} |
|||
* {{flag|Bermuda}}* |
|||
* {{flag|British Virgin Islands}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Brunei}} |
|||
* {{flag|Bulgaria}} |
|||
* {{flag|Canada}} |
|||
* {{flag|Cayman Islands}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Channel Islands}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Chile}} |
|||
* {{flag|Croatia}} |
|||
* {{flag|Curaçao}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Cyprus}} |
|||
* {{flag|Czech Republic}} |
|||
* {{flag|Denmark}} |
|||
* {{flag|Estonia}} |
|||
* {{flag|Faroe Islands}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Finland}} |
|||
* {{flag|France}} |
|||
* {{flag|French Polynesia}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Germany}} |
|||
* {{flag|Gibraltar}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Greece}} |
|||
* {{flag|Greenland}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Guam}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Guyana}} |
|||
* {{flag|Hong Kong}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Hungary}} |
|||
* {{flag|Iceland}} |
|||
* {{flag|Ireland}} |
|||
* {{flag|Isle of Man}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Israel}} |
|||
* {{flag|Italy}} |
|||
* {{flag|Japan}} |
|||
* {{flag|South Korea}} |
|||
* {{flag|Kuwait}} |
|||
* {{flag|Latvia}} |
|||
* {{flag|Liechtenstein}} |
|||
* {{flag|Lithuania}} |
|||
* {{flag|Luxembourg}} |
|||
* {{flag|Macau}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Malta}} |
|||
* {{flag|Monaco}} |
|||
* {{flag|Nauru}} |
|||
* {{flag|Netherlands}} |
|||
* {{flag|New Caledonia}}* |
|||
* {{flag|New Zealand}} |
|||
* {{flag|Northern Mariana Islands}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Norway}} |
|||
* {{flag|Oman}} |
|||
* {{flag|Palau}} |
|||
* {{flag|Panama}} |
|||
* {{flag|Poland}} |
|||
* {{flag|Portugal}} |
|||
* {{flag|Puerto Rico}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Qatar}} |
|||
* {{flag|Romania}} |
|||
* {{flag|Russia}} |
|||
* {{flag|San Marino}} |
|||
* {{flag|Saudi Arabia}} |
|||
* {{flag|Seychelles}} |
|||
* {{flag|Singapore}} |
|||
* {{flag|Sint Maarten}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Slovakia}} |
|||
* {{flag|Slovenia}} |
|||
* {{flag|Spain}} |
|||
* {{flag|Saint Kitts and Nevis}} |
|||
* {{flag|Saint Martin}}* |
|||
* {{flag|Sweden}} |
|||
* {{flag|Switzerland}} |
|||
* {{flag|Taiwan}} |
|||
* {{flag|Trinidad and Tobago}} |
|||
* {{flag|Turks and Caicos Islands}}* |
|||
* {{flag|United Arab Emirates}} |
|||
* {{flag|United Kingdom}} |
|||
* {{flag|United States}} |
|||
* {{flag|Uruguay}} |
|||
* {{flag|United States Virgin Islands}}* |
|||
}} |
|||
=== Development Assistance Committee members === |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{See also|Development Assistance Committee}} |
|||
[[File:DAC members.svg|thumb|upright 1.2|Member nations of the [[Development Assistance Committee]] ]] |
|||
There are 29 [[OECD]] member countries and the [[European Union]]—in the [[Development Assistance Committee]] (DAC),<ref name="DAC">[http://www.oecd.org/dac/peer-reviews/peerreviewsofdacmembers.htm Peer reviews of DAC members – Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130527172525/http://www.oecd.org/dac/peer-reviews/peerreviewsofdacmembers.htm |date=27 May 2013 }}. Oecd.org. Retrieved 22 October 2013.</ref> a group of the world's major donor countries that discusses issues surrounding [[development aid]] and [[poverty reduction]] in [[developing country|developing countries]].<ref name="dac_dat">[http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/3/38/1896808.pdf DAC website >> "The DAC in Dates"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100215080158/http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/3/38/1896808.pdf |date=15 February 2010 }}, On the DAC's self-description, see the introductory letter. On other events, refer to the relevant section by date.</ref> The following OECD member countries are DAC members: |
|||
*[http://www.worldbank.org/data/countryclass/classgroups.htm#High_income World Bank] |
|||
*[http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/appendix/appendix-b.html The World Factbook] |
|||
*[http://unstats.un.org/unsd/cdb/cdb_dict_xrxx.asp?def_code=491 United Nations Statistics Division] (definition) |
|||
*[http://unstats.un.org/unsd/mi/developed_new.htm United Nations Statistics Division] (developed regions) |
|||
*[http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2005/01/data/groups.htm#1 IMF] |
|||
25 countries in Europe: |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Austria}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Belgium}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Czech Republic}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Denmark}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Estonia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Finland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|France}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Germany}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Greece}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Hungary}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Iceland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Ireland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Italy}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Lithuania}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Luxembourg}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Netherlands}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Norway}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Poland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Portugal}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Slovakia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Slovenia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Spain}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Sweden}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Switzerland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|United Kingdom}} |
|||
}} |
|||
two countries in the Americas: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* [[List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita]] |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Canada}} |
|||
* [[UN Human Development Index]] |
|||
* {{flagcountry|United States}} |
|||
* [[Developing country]] |
|||
}} |
|||
* [[Newly industrialized country]] |
|||
* [[Decolonisation]] |
|||
two countries in Asia: |
|||
* [[Economic development]] |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* [[Sustainable development]] |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Japan}} |
|||
* [[Industrialisation]] |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Republic of Korea}} |
|||
}} |
|||
two countries in Oceania: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Australia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|New Zealand}} |
|||
}} |
|||
=== IMF advanced economies === |
|||
[[File:IMF advanced economies 2008.svg|thumb|upright 1.2|{{legend|#0000FF|Countries described as Advanced Economies by the IMF}}]] |
|||
According to the [[International Monetary Fund]], 41 countries and territories are officially listed as "advanced economies",<!-- |
|||
START REF--><ref name="IMF1" /><ref name="IMF2">{{cite web |title=World Economic and Financial Surveys World Economic Outlook Database—All countries/Advanced economies (40 countries) |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2021/October/select-countries?grp=110&sg=All-countries/Advanced-economies |publisher=International Monetary Fund |access-date=13 October 2021 |archive-date=7 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211107153545/https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2021/October/select-countries?grp=110&sg=All-countries/Advanced-economies |url-status=live }}</ref><!--END REF |
|||
--> with the addition of 7 [[microstates]] and dependencies modified by the [[CIA]] which were omitted from the IMF version:<ref name="cia">{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/appendix/appendix-b.html|title=Appendix B. International Organizations and Groups.|work=[[World Factbook]].|author=CIA|year=2008|access-date=10 April 2008|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080409033504/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/appendix/appendix-b.html|archive-date=9 April 2008}}</ref> |
|||
29 countries and dependencies in [[Europe]] classified by the IMF, 6 others given by the CIA: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Andorra}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Austria}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Belgium}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Croatia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Cyprus}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Czech Republic}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Denmark}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Estonia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Finland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|France}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Germany}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Greece}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Iceland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Ireland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Italy}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Latvia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Lithuania}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Luxembourg}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Malta}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Netherlands}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Norway}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Portugal}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|San Marino}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Slovakia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Slovenia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Spain}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Sweden}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Switzerland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|United Kingdom}} |
|||
Plus<sup>d</sup> |
|||
* ''{{flagcountry|Faroe Islands}}'' |
|||
* ''{{flagcountry|Bailiwick of Guernsey|name=Guernsey}}'' |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Holy See}} |
|||
* ''{{flagcountry|Jersey}}'' |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Liechtenstein}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Monaco}} |
|||
}} |
|||
seven countries and territories in [[Asia]]: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* ''{{flagcountry|Hong Kong}}'' |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Israel}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Japan}} |
|||
* ''{{flagcountry|Macau}}'' |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Singapore}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Republic of Korea}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Taiwan}} |
|||
}} |
|||
three countries and territories in the [[Americas]] classified by the IMF, one territory given by the CIA : |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Canada}} |
|||
* ''{{flagcountry|Puerto Rico}}'' |
|||
* {{flagcountry|United States}} |
|||
* ''{{flagcountry|Bermuda}}'' <sup>d</sup> |
|||
}} |
|||
two countries in [[Oceania]]: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Australia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|New Zealand}} |
|||
}} |
|||
<sup>d</sup> The CIA has modified an older version of the IMF's list of 38 Advanced Economies, noting that the IMF's Advanced Economies list "would presumably also cover the following nine smaller countries of Andorra, Bermuda, Faroe Islands, Guernsey, Holy See, Jersey, Liechtenstein, Monaco, and San Marino[...]". San Marino (2012) and Andorra (2021) were later included in the IMF's list.<ref name=cia /> |
|||
=== Paris Club members === |
|||
[[File:Map of Paris Club.png|thumb|upright 1.2|Permanent members of the [[Paris Club]]]] |
|||
There are 22 permanent members in the [[Paris Club]] ({{langx|fr|Club de Paris}}), a group of officials from major creditor countries whose role is to find coordinated and sustainable solutions to the payment difficulties experienced by debtor countries. |
|||
15 countries in Europe: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Austria}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Belgium}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Denmark}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Finland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|France}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Germany}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Ireland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Italy}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Netherlands}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Norway}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Russia}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Spain}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Sweden}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Switzerland}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|United Kingdom}} |
|||
}} |
|||
three countries in the Americas: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Brazil}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Canada}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|United States}} |
|||
}} |
|||
three countries in Asia: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Israel}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Japan}} |
|||
* {{flagcountry|South Korea}} |
|||
}} |
|||
one country in Oceania: |
|||
{{columns-list|colwidth=18em| |
|||
* {{flagcountry|Australia}} |
|||
}} |
|||
== Comparative table (2024) == |
|||
[[File:Comparison of developed countries.png|thumb|upright=1.8|A comparison among the developed countries in the world]] |
|||
Comparative table of countries with a "very high" human development (0.800 or higher), according to [[United Nations Development Programme|UNDP]]; "advanced" economies, according to the [[International Monetary Fund|IMF]]; "high income" economies, according to the [[World Bank]]. |
|||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="margin-right:auto; margin-right: auto" |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |{{big|Developed countries}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! Countries !!HDI<ref name="UNDP2024">{{cite book |title=Human Development Report 2023/2024 Breaking the gridlock: Reimaging cooperation in a polarized world |author=United Nations |date=13 March 2024 |publisher=United Nations Development Programme |isbn=978-9-210-03102-8 |pages=279–282 |url=https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/country-insights |access-date=5 May 2024 |archive-date=4 May 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240504213447/https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/country-insights#/ranks |url-status=bot: unknown }}</ref>!! IMF<ref name=":1">{{cite web|url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/data/changes.htm|title=World Economic Outlook Database – Changes to the Database|website=International Monetary Fund|access-date=7 February 2019|archive-date=29 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171229080726/http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/data/changes.htm|url-status=live}}</ref>!! WB<ref name=":2">{{cite web|url=https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups|title=World Bank Country and Lending Groups – World Bank Data Help Desk|website=datahelpdesk.worldbank.org|access-date=20 January 2021|archive-date=28 October 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191028223324/https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2023'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Croatia}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2007|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2023|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2017 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2021'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|San Marino}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2021|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2000 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2020'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Andorra}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2003|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2020 || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1990 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2015'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Lithuania}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2005|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2015 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2014'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Latvia}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2005|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2014 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2011'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Estonia}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2003|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2011 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2006 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2009'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Slovakia}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2006|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2009 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2007 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Czech Republic}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2001|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2009 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2006 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2008'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Malta}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2003|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2008 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2002 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Liechtenstein}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2000|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2008 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1990 |
|||
|- |
|||
|style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Monaco}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990<ref>{{cite web|url=https://monacoestate.com/monaco-has-the-worlds-highest-score-on-the-u-n-human-development-index/ |
|||
|title=Monaco Has The World's Highest Score on the U.N. Human Development Index |work=Monaco Estate |date=29 November 2021 |access-date=8 June 2023|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230708062956/https://monacoestate.com/monaco-has-the-worlds-highest-score-on-the-u-n-human-development-index/ |archive-date= 8 July 2023 }}</ref> |
|||
|style="background:#98fb98; |Yes since 2008 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2007'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Slovenia}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1998|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2007 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1997 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2005'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Portugal}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2005|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1989<ref name="IMF1989">{{cite web|url=https://www.elibrary.imf.org/doc/IMF081/14573-9781451944433/14573-9781451944433/Other_formats/Source_PDF/14573-9781455235476.pdf|title=World Economic Outlook, October 1989|website=International Monetary Fund|page=12|access-date=8 May 2020|archive-date=28 June 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200628212104/https://www.elibrary.imf.org/doc/IMF081/14573-9781451944433/14573-9781451944433/Other_formats/Source_PDF/14573-9781455235476.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1994 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''2001'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Greece}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2001|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1989<ref name="IMF1989" /> |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1996 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|South Korea}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1999|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1997<ref name="IMF1997">{{cite book|title=International Monetary Fund Annual Report 1997|series=Annual Report of the Executive Board |date=October 1997|url=https://www.elibrary.imf.org/view/IMF011/00315-9781451945102/00315-9781451945102/ch01.xml?language=en|doi=10.5089/9781451945102.011|access-date=8 May 2020|publisher=International Monetary Fund|isbn=9781451945102|archive-date=25 June 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200625192202/https://www.elibrary.imf.org/view/IMF011/00315-9781451945102/00315-9781451945102/ch01.xml?language=en|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2001 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Cyprus}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2001|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2001 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1988 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |1999 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Singapore}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1999|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1997<ref name="IMF1997" /> |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''1997'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Israel}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1991|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1997<ref name="IMF1997"/> |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;"|{{flag2|Taiwan}}|| |N/A{{refn|group=Note|The [[Human Development Report|HDI annual report]] compiled by the [[UNDP]] does not include Taiwan because it is no longer a UN member state, and is neither included as part of the People's Republic of China by the UNDP when calculating data for China.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Nations |first=United |title=Data Reader's Guide |url=https://hdr.undp.org/reports-and-publications/2020-human-development-report/data-readers-guide |language=en |access-date=27 October 2022 |archive-date=28 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221028110944/https://hdr.undp.org/reports-and-publications/2020-human-development-report/data-readers-guide |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Directorate General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics|Taiwan's Statistical Bureau]] calculated its HDI to be 0.926 based on UNDP's 2010 methodology,<ref>{{Cite web |title=What is the human development index (HDI)? How are relevant data queried? |url=https://eng.stat.gov.tw/public/Data/1513164433IGBKG0IN.pdf |access-date=26 October 2022 |archive-date=12 June 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210612071634/https://eng.stat.gov.tw/public/Data/1513164433IGBKG0IN.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=人類發展指數 |url=https://win.dgbas.gov.tw/eyimc/ebook/SB/statistcs-brief_opf_files/pdfs/statistcs-brief__.pdf |access-date=26 October 2022 |language=zh |archive-date=14 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210414101606/https://win.dgbas.gov.tw/eyimc/ebook/SB/statistcs-brief_opf_files/pdfs/statistcs-brief__.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> which would place Taiwan well within the group of "Very high human development" at 19th globally in 2021 within the 2022 UNDP report.<ref>{{Cite web |title=National Statistics, Republic of China (Taiwan) - Statistical Tables |url=https://eng.stat.gov.tw/ct.asp?xItem=25280&ctNode=6032&mp=5 |access-date=27 October 2022 |website=eng.stat.gov.tw |archive-date=16 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221016192219/https://eng.stat.gov.tw/ct.asp?xItem=25280&ctNode=6032&mp=5 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=國情統計通報 |url=https://ws.dgbas.gov.tw/Download.ashx?u=LzAwMS9VcGxvYWQvMC9yZWxmaWxlLzExMDIwLzIyOTU5MS9iNDdhNmYyYy1jNjY2LTRjZDAtYmQ2Ni03OGEyYjMwMmM4MzkucGRm&n=TjExMTEwMTQucGRm&icon=.pdf |access-date=26 October 2022 |language=zh |archive-date=11 February 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230211120125/https://ws.dgbas.gov.tw/Download.ashx?u=LzAwMS9VcGxvYWQvMC9yZWxmaWxlLzExMDIwLzIyOTU5MS9iNDdhNmYyYy1jNjY2LTRjZDAtYmQ2Ni03OGEyYjMwMmM4MzkucGRm&n=TjExMTEwMTQucGRm&icon=.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref>}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1997<ref name="IMF1997" /> |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;"|Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''1996'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Ireland}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1996|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''1995'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Spain}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1995|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Italy}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1995|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''1994'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Finland}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1994|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''1993'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|France}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1993|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''1992'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|United Kingdom}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1992|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Austria}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1992|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Luxembourg}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1992|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''1991'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Denmark}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1991|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |''1987'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|New Zealand}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Iceland}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Sweden}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Australia}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Belgium}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Canada}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Germany}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Japan}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Netherlands}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|United States}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Norway}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Switzerland}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes before 1990|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1945 |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |{{big|In process}} |
|||
|- |
|||
!Countries |
|||
!HDI<ref name="UNDP2024" /> |
|||
!IMF<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
!WB<ref name=":2" /> |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Russia}} || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2013|| style="background:#ffa07a;" | No || style="background:#98fb98;" | Yes since 2023 |
|||
|- |
|||
|{{flag2|Uruguay}} |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2014 |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Chile}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2007|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Trinidad and Tobago}} || style="background:#98fb98;" | Yes since 2021 || style="background:#ffa07a;" | No || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2006 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Romania}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2013|| style="background:#ffa07a;" | No || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2021 |
|||
|- |
|||
|{{flag2|Panama}} |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2019 |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2021 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Bahamas}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2016|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Hungary}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2005|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2014 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Poland}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2003|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2009 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Kuwait}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2014|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Bahrain}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2001 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Oman}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2007 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Saudi Arabia}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2010|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2004 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|United Arab Emirates}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2004|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Brunei}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1999|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1990 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Qatar}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1996|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Saint Kitts and Nevis}} || style="background:#98fb98;" | Yes since 2011 || style="background:#ffa07a;" | No || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012 |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Seychelles}} || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2022|| style="background:#ffa07a;" | No || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2014 |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flag2|Antigua and Barbuda}} |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2007 |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012 |
|||
|- |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flag2|Barbados}} |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2016 |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2006 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="4" |{{big|Other recognitions}} |
|||
|- |
|||
!Countries |
|||
!HDI<ref name="UNDP2024" /> |
|||
!IMF<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
!WB<ref name=":2" /> |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Serbia}} || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2019|| style="background:#ffa07a;" | No || style="background:#ffa07a;" | No |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Costa Rica}} || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2019|| style="background:#ffa07a;" | No || style="background:#ffa07a;" | No |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Argentina}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2006|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Montenegro}} || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2013|| style="background:#ffa07a;" | No || style="background:#ffa07a;" | No |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Kazakhstan}} || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2015|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No || style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | {{flag2|Malaysia}} || style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2016|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No || style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" |{{flag2|Turkey}}|| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2015|| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No || style="background:#ffa07a;" | No |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flag2|Georgia}} |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2019 |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flag2|Belarus}} |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2012 |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
|- |
|||
|{{flag2|Bulgaria}} |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2023 |
|||
|- |
|||
|{{flag2|Guyana}} |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2022 |
|||
|- |
|||
|{{flag2|Thailand}} |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2021 |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" |No |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flag2|Nauru}} |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" | No |
|||
| style="background:#ffa07a;" | No |
|||
| style="background:#98fb98;" |Yes since 2019 |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
== See also == |
|||
{{col div|colwidth=20em}} |
|||
* [[Digital divide]] |
|||
* [[First World privilege]] |
|||
* [[First World problem]] |
|||
* [[Fourth World]] |
|||
* [[Globalization]] |
|||
* [[G8]] |
* [[G8]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[G7]] |
||
* [[List of countries by wealth per adult]] |
|||
* [[Multinational corporation]] |
|||
* [[Western Bloc]] |
|||
* [[Developed market]] |
|||
{{colend}} |
|||
== Notes == |
|||
{{reflist|group="Note"}} |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
== External links == |
|||
* {{Wikiquote-inline}} |
|||
* [https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2018/02/weodata/groups.htm#ae IMF] (advanced economies) |
|||
* [https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/appendix/appendix-b.html The World Factbook] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080409033504/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/appendix/appendix-b.html |date=9 April 2008 }} (developed countries) |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080327210253/http://unstats.un.org/unsd/cdb/cdb_dict_xrxx.asp?def_code=491 United Nations Statistics Division] (definition)<!-- archived --> |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20050511011954/http://unstats.un.org/unsd/mi/developed_new.htm List of countries, United Nations Statistics Division] (developed regions)<!-- archived --> |
|||
* [https://data.worldbank.org/income-level/high-income World Bank] (high-income economies) |
|||
{{GDP country lists}} |
|||
[[Category:Country classifications]] |
|||
{{Global economic classifications}} |
|||
{{Quality of life country lists}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Economic country classifications]] |
|||
[[ca:Països desenvolupats]] |
|||
[[Category:Human geography]] |
|||
[[de:Industrieland]] |
|||
[[Category:Economic geography]] |
|||
[[es:Países desarrollados]] |
|||
[[Category:International development|Country]] |
|||
[[fr:Pays développé]] |
|||
[[Category:Lists of countries]] |
|||
[[ko:선진국]] |
|||
[[Category:Imperialism studies]] |
|||
[[id:Negara maju]] |
|||
[[he:מדינה מפותחת]] |
|||
[[nl:Ontwikkelde landen]] |
|||
[[ja:先進国]] |
|||
[[no:Industriland]] |
|||
[[fi:Teollisuusmaa]] |
|||
[[sv:I-land]] |
|||
[[zh:已開發國家]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 23:51, 20 December 2024

World map showing country classifications per the IMF[1] and the UN[2] (last updated April 2023). "Developed economies" according to this classification scheme are shown in blue. The map does not include classifications by the World Bank.
A developed country, or advanced country,[3][4] is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are the gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living.[5] Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. Different definitions of developed countries are provided by the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; moreover, HDI ranking is used to reflect the composite index of life expectancy, education, and income per capita. In 2024, 40 countries fit all three criteria, while an additional 20 countries fit two out of three.
Developed countries have generally more advanced post-industrial economies, meaning the service sector provides more wealth than the industrial sector. They are contrasted with developing countries, which are in the process of industrialisation or are pre-industrial and almost entirely agrarian, some of which might fall into the category of Least Developed Countries. As of 2023[update], advanced economies comprise 57.3% of global GDP based on nominal values and 41.1% of global GDP based on purchasing-power parity (PPP) according to the IMF.[6]
Definition and criteria
[edit]
Economic criteria have tended to dominate discussions. One such criterion is the income per capita; countries with the high gross domestic product (GDP) per capita would thus be described as developed countries. Another economic criterion is industrialisation; countries in which the tertiary and quaternary sectors of industry dominate would thus be described as developed. More recently, another measure, the Human Development Index (HDI), which combines an economic measure, national income, with other measures, indices for life expectancy and education has become prominent. This criterion would define developed countries as those with a very high (HDI) rating. The index, however, does not take into account several factors, such as the net wealth per capita or the relative quality of goods in a country. This situation tends to lower the ranking of some of the most advanced countries, such as the G7 members and others.[9][10]
According to the United Nations Statistics Division:
There is no established convention for the designation of "developed" and "developing" countries or areas in the United Nations system.[11]
And it notes that:
The designations "developed" and "developing" are intended for statistical convenience and do not necessarily express a judgement about the stage reached by a particular country or area in the development process.[12]
Nevertheless, the UN Trade and Development considers that this categorization can continue to be applied:
The developed economies broadly comprise Northern America and Europe, Israel, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Australia, and New Zealand.[7]
Similar terms
[edit]Terms linked to the concept developed country include "advanced country", "industrialized country", "more developed country" (MDC), "more economically developed country" (MEDC), "Global North country", "first world country", and "post-industrial country". The term industrialized country may be somewhat ambiguous, as industrialisation is an ongoing process that is hard to define. The first industrialized country was the United Kingdom, followed by Belgium. Later it spread further to Germany, United States, France and other Western European countries. According to some economists such as Jeffrey Sachs, however, the current divide between the developed and developing world is largely a phenomenon of the 20th century.[13]
Mathis Wackernagel calls the binary labeling of countries as "neither descriptive nor explanatory. It is merely a thoughtless and destructive endorsement of GDP fetish. In reality, there are not two types of countries, but over 200 countries, all faced with the same laws of nature, yet each with unique features."[14]
A 2021 analysis proposes the term emerged to describe markets, economies, or countries that have graduated from emerging market status, but have not yet reached the level equivalent to developed countries.[15] Multinational corporations from these emerging markets present unique patterns of overseas expansion and knowledge acquisition from foreign countries.
Economy lists by various criteria
[edit]Human Development Index (HDI)
[edit]
- Very high
- High
- Medium
- Low
- No data
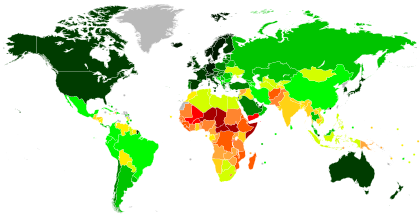
- ≥ 0.950
- 0.900–0.950
- 0.850–0.899
- 0.800–0.849
- 0.750–0.799
- 0.700–0.749
- 0.650–0.699
- 0.600–0.649
- 0.550–0.599
- 0.500–0.549
- 0.450–0.499
- 0.400–0.449
- ≤ 0.399
- Data unavailable
The UN HDI is a statistical measure that gauges an economy's level of human development. While there is a strong correlation between having a high HDI score and being a prosperous economy, the UN points out that the HDI accounts for more than income or productivity. Unlike GDP per capita or per capita income, the HDI takes into account how income is turned "into education and health opportunities and therefore into higher levels of human development."
Since 1990, Norway (2001–2006, 2009–2019), Japan (1990–1991 and 1993), Canada (1992 and 1994–2000) and Iceland (2007–2008) have had the highest HDI score.
The following countries in the year 2022 are considered to be of "very high human development":[16]
| Rank | Δ | Country or territory | HDI | %
annual growth (2010-2022) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.967 | |||
| 2 | 0.966 | |||
| 3 | 0.959 | |||
| 4 | 0.956 | |||
| 5 | 0.952 | |||
| 7 | 0.950 | |||
| 9 | 0.949 | |||
| 10 | 0.946 | |||
| 12 | 0.942 | |||
| 15 | 0.940 | |||
| 16 | 0.939 | |||
| 17 | 0.937 | |||
| 18 | 0.935 | |||
| 19 | 0.929 | |||
| 20 | 0.927 | |||
| 22 | 0.926 | |||
| 24 | 0.920 | |||
| 25 | 0.915 | |||
| 27 | 0.911 | |||
| 28 | 0.910 | |||
| 29 | 0.907 | |||
| 30 | 0.906 | |||
| 31 | 0.899 | |||
| 32 | 0.895 | |||
| 33 | 0.893 | |||
| 34 | 0.888 | |||
| 35 | 0.884 | |||
| 36 | 0.881 | |||
| 37 | 0.879 | |||
| 39 | 0.878 | |||
| 40 | 0.875 | |||
| 42 | 0.874 | |||
| 43 | 0.867 | |||
| 44 | 0.860 | |||
| 45 | 0.855 | |||
| 47 | 0.851 | |||
| 48 | 0.849 | |||
| 49 | 0.847 | |||
| 50 | 0.844 | |||
| 51 | 0.838 | |||
| 52 | 0.830 | |||
| 53 | 0.827 | |||
| 54 | 0.826 | |||
| 55 | 0.823 | |||
| 56 | 0.821 | |||
| 57 | 0.820 | |||
| 59 | 0.819 | |||
| 60 | 0.814 | |||
| 62 | 0.809 | |||
| 63 | 0.807 | |||
| 64 | 0.806 | |||
| 65 | 0.805 | |||
| 66 | 0.803 | |||
| 67 | 0.802 | |||
| 69 | 0.801 |
WESP developed economies
[edit]According to the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs' World Economic Situation and Prospects report, the following 37 countries are classified as "developed economies" as of January 2024:[17]
31 countries in Europe:
two countries in Northern America:
four countries in Asia and the Pacific:
World Bank high-income economies
[edit]
According to the World Bank, the following 85 sovereign states and territories across are classified as high income economies, having a nominal GNI per capita in excess of $14,005 as of 2024:[18]
Unsovereign Territories are denoted with an asterisk (*).
 American Samoa*
American Samoa* Andorra
Andorra Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda Aruba*
Aruba* Australia
Australia Austria
Austria The Bahamas
The Bahamas Bahrain
Bahrain Barbados
Barbados Belgium
Belgium Bermuda*
Bermuda* British Virgin Islands*
British Virgin Islands* Brunei
Brunei Bulgaria
Bulgaria Canada
Canada Cayman Islands*
Cayman Islands* Channel Islands*
Channel Islands* Chile
Chile Croatia
Croatia Curaçao*
Curaçao* Cyprus
Cyprus Czech Republic
Czech Republic Denmark
Denmark Estonia
Estonia Faroe Islands*
Faroe Islands* Finland
Finland France
France French Polynesia*
French Polynesia* Germany
Germany Gibraltar*
Gibraltar* Greece
Greece Greenland*
Greenland* Guam*
Guam* Guyana
Guyana Hong Kong*
Hong Kong* Hungary
Hungary Iceland
Iceland Ireland
Ireland Isle of Man*
Isle of Man* Israel
Israel Italy
Italy Japan
Japan South Korea
South Korea Kuwait
Kuwait Latvia
Latvia Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein Lithuania
Lithuania Luxembourg
Luxembourg Macau*
Macau* Malta
Malta Monaco
Monaco Nauru
Nauru Netherlands
Netherlands New Caledonia*
New Caledonia* New Zealand
New Zealand Northern Mariana Islands*
Northern Mariana Islands* Norway
Norway Oman
Oman Palau
Palau Panama
Panama Poland
Poland Portugal
Portugal Puerto Rico*
Puerto Rico* Qatar
Qatar Romania
Romania Russia
Russia San Marino
San Marino Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Seychelles
Seychelles Singapore
Singapore Sint Maarten*
Sint Maarten* Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia
Slovenia Spain
Spain Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Martin*
Saint Martin* Sweden
Sweden Switzerland
Switzerland Taiwan
Taiwan Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago Turks and Caicos Islands*
Turks and Caicos Islands* United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States Uruguay
Uruguay United States Virgin Islands*
United States Virgin Islands*
Development Assistance Committee members
[edit]
There are 29 OECD member countries and the European Union—in the Development Assistance Committee (DAC),[19] a group of the world's major donor countries that discusses issues surrounding development aid and poverty reduction in developing countries.[20] The following OECD member countries are DAC members:
25 countries in Europe:
two countries in the Americas:
two countries in Asia:
two countries in Oceania:
IMF advanced economies
[edit]
According to the International Monetary Fund, 41 countries and territories are officially listed as "advanced economies",[1][21] with the addition of 7 microstates and dependencies modified by the CIA which were omitted from the IMF version:[22]
29 countries and dependencies in Europe classified by the IMF, 6 others given by the CIA:
 Andorra
Andorra Austria
Austria Belgium
Belgium Croatia
Croatia Cyprus
Cyprus Czech Republic
Czech Republic Denmark
Denmark Estonia
Estonia Finland
Finland France
France Germany
Germany Greece
Greece Iceland
Iceland Ireland
Ireland Italy
Italy Latvia
Latvia Lithuania
Lithuania Luxembourg
Luxembourg Malta
Malta Netherlands
Netherlands Norway
Norway Portugal
Portugal San Marino
San Marino Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia
Slovenia Spain
Spain Sweden
Sweden Switzerland
Switzerland United Kingdom
United Kingdom
Plusd
seven countries and territories in Asia:
three countries and territories in the Americas classified by the IMF, one territory given by the CIA :
two countries in Oceania:
d The CIA has modified an older version of the IMF's list of 38 Advanced Economies, noting that the IMF's Advanced Economies list "would presumably also cover the following nine smaller countries of Andorra, Bermuda, Faroe Islands, Guernsey, Holy See, Jersey, Liechtenstein, Monaco, and San Marino[...]". San Marino (2012) and Andorra (2021) were later included in the IMF's list.[22]
Paris Club members
[edit]
There are 22 permanent members in the Paris Club (French: Club de Paris), a group of officials from major creditor countries whose role is to find coordinated and sustainable solutions to the payment difficulties experienced by debtor countries.
15 countries in Europe:
three countries in the Americas:
three countries in Asia:
one country in Oceania:
Comparative table (2024)
[edit]
Comparative table of countries with a "very high" human development (0.800 or higher), according to UNDP; "advanced" economies, according to the IMF; "high income" economies, according to the World Bank.
| Developed countries | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Countries | HDI[23] | IMF[24] | WB[25] |
| 2023 | |||
| Yes since 2007 | Yes since 2023 | Yes since 2017 | |
| 2021 | |||
| Yes since 2021 | Yes since 2012 | Yes since 2000 | |
| 2020 | |||
| Yes since 2003 | Yes since 2020 | Yes since 1990 | |
| 2015 | |||
| Yes since 2005 | Yes since 2015 | Yes since 2012 | |
| 2014 | |||
| Yes since 2005 | Yes since 2014 | Yes since 2012 | |
| 2011 | |||
| Yes since 2003 | Yes since 2011 | Yes since 2006 | |
| 2009 | |||
| Yes since 2006 | Yes since 2009 | Yes since 2007 | |
| Yes since 2001 | Yes since 2009 | Yes since 2006 | |
| 2008 | |||
| Yes since 2003 | Yes since 2008 | Yes since 2002 | |
| Yes since 2000 | Yes since 2008 | Yes since 1990 | |
| Yes before 1990[26] | Yes since 2008 | Yes before 1990 | |
| 2007 | |||
| Yes since 1998 | Yes since 2007 | Yes since 1997 | |
| 2005 | |||
| Yes since 2005 | Yes since 1989[27] | Yes since 1994 | |
| 2001 | |||
| Yes since 2001 | Yes since 1989[27] | Yes since 1996 | |
| Yes since 1999 | Yes since 1997[28] | Yes since 2001 | |
| Yes since 2001 | Yes since 2001 | Yes since 1988 | |
| 1999 | |||
| Yes since 1999 | Yes since 1997[28] | Yes since 1987 | |
| 1997 | |||
| Yes since 1991 | Yes since 1997[28] | Yes since 1987 | |
| N/A[Note 1] | Yes since 1997[28] | Yes since 1987 | |
| 1996 | |||
| Yes since 1996 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| 1995 | |||
| Yes since 1995 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes since 1995 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| 1994 | |||
| Yes since 1994 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| 1993 | |||
| Yes since 1993 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| 1992 | |||
| Yes since 1992 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes since 1992 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes since 1992 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| 1991 | |||
| Yes since 1991 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| 1987 | |||
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes before 1990 | Yes since 1945 | Yes since 1987 | |
| In process | |||
| Countries | HDI[23] | IMF[24] | WB[25] |
| Yes since 2013 | No | Yes since 2023 | |
| Yes since 2014 | No | Yes since 2012 | |
| Yes since 2007 | No | Yes since 2012 | |
| Yes since 2021 | No | Yes since 2006 | |
| Yes since 2013 | No | Yes since 2021 | |
| Yes since 2019 | No | Yes since 2021 | |
| Yes since 2016 | No | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes since 2005 | No | Yes since 2014 | |
| Yes since 2003 | No | Yes since 2009 | |
| Yes since 2014 | No | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes since 2012 | No | Yes since 2001 | |
| Yes since 2012 | No | Yes since 2007 | |
| Yes since 2010 | No | Yes since 2004 | |
| Yes since 2004 | No | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes since 1999 | No | Yes since 1990 | |
| Yes since 1996 | No | Yes since 1987 | |
| Yes since 2011 | No | Yes since 2012 | |
| Yes since 2022 | No | Yes since 2014 | |
| Yes since 2007 | No | Yes since 2012 | |
| Yes since 2016 | No | Yes since 2006 | |
| Other recognitions | |||
| Countries | HDI[23] | IMF[24] | WB[25] |
| Yes since 2019 | No | No | |
| Yes since 2019 | No | No | |
| Yes since 2006 | No | No | |
| Yes since 2013 | No | No | |
| Yes since 2015 | No | No | |
| Yes since 2016 | No | No | |
| Yes since 2015 | No | No | |
| Yes since 2019 | No | No | |
| Yes since 2012 | No | No | |
| No | No | Yes since 2023 | |
| No | No | Yes since 2022 | |
| Yes since 2021 | No | No | |
| No | No | Yes since 2019 | |
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ The HDI annual report compiled by the UNDP does not include Taiwan because it is no longer a UN member state, and is neither included as part of the People's Republic of China by the UNDP when calculating data for China.[29] Taiwan's Statistical Bureau calculated its HDI to be 0.926 based on UNDP's 2010 methodology,[30][31] which would place Taiwan well within the group of "Very high human development" at 19th globally in 2021 within the 2022 UNDP report.[32][33]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "World Economic and Financial Surveys World Economic Outlook Database—WEO Groups and Aggregates Information". International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 3 March 2023. Retrieved 2 June 2022.
- ^ Least Developed Countries Archived 17 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine (2018 list[usurped])
- ^ "Fiscal Policy and Inclusive Growth in Advanced Countries: Their Experience and Implications for Asia" (PDF). adb.org. Asian Development Bank. December 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 July 2021. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ "Advanced Countries Will Benefit Most from Progress in Technology, with Lesser Benefits to Other Nations". rand.org. RAND Corporation. 1 June 2006. Archived from the original on 21 August 2021. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ Developed Economy Definition Archived 22 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Investopedia (16 April 2010). Retrieved 12 July 2013.
- ^ International Monetary Fund. "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2023". International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 13 April 2023. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ a b "UNCTADstat - Classifications". Archived from the original on 6 October 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- ^ "Classifications - UNCTAD Handbook of Statistics 2023". unctad.org.
- ^ The Courier. Commission of the European Communities. 1994. Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ "Human development index". Economics Help. Archived from the original on 17 December 2020. Retrieved 23 September 2018.
- ^ "Millennium Development Indicators: World and regional groupings". United Nations Statistics Division. 2003. Note b. Archived from the original on 10 February 2005. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ^ "Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49): Developed Regions". United Nations Statistics Division. Archived from the original on 11 July 2017. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ^ Sachs, Jeffrey (2005). The End of Poverty. New York, New York: The Penguin Press. ISBN 1-59420-045-9.
- ^ Wackernagel, Mathis; Beyers, Bert (2019). Ecological Footprint: Managing Our Biocapacity Budget. Gabriola Island, BC, Canada: New Society Publishers. p. 132. ISBN 978-0-86571-911-8. Archived from the original on 30 December 2019. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ Lee, Eun Su; Liu, Wei; Yang, Jing Yu (23 September 2021). "Neither developed nor emerging: Dual paths for outward FDI and home country innovation in emerged market MNCs". International Business Review. 32 (2): 101925. doi:10.1016/j.ibusrev.2021.101925. ISSN 0969-5931. S2CID 244268711.
- ^ Human Development Report 2023-24: Breaking the gridlock: Reimagining cooperation in a polarized world. United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024. Retrieved 16 March 2024.
- ^ "World Economic Situation and Prospects 2024" (PDF). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. p. 135.
- ^ "World Bank Country and Lending Groups". World Bank. Retrieved 25 July 2024.
- ^ Peer reviews of DAC members – Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Archived 27 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Oecd.org. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ^ DAC website >> "The DAC in Dates" Archived 15 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine, On the DAC's self-description, see the introductory letter. On other events, refer to the relevant section by date.
- ^ "World Economic and Financial Surveys World Economic Outlook Database—All countries/Advanced economies (40 countries)". International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 7 November 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ a b CIA (2008). "Appendix B. International Organizations and Groups". World Factbook. Archived from the original on 9 April 2008. Retrieved 10 April 2008.
- ^ a b c United Nations (13 March 2024). Human Development Report 2023/2024 Breaking the gridlock: Reimaging cooperation in a polarized world. United Nations Development Programme. pp. 279–282. ISBN 978-9-210-03102-8. Archived from the original on 4 May 2024. Retrieved 5 May 2024.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ a b c "World Economic Outlook Database – Changes to the Database". International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 29 December 2017. Retrieved 7 February 2019.
- ^ a b c "World Bank Country and Lending Groups – World Bank Data Help Desk". datahelpdesk.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 28 October 2019. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ "Monaco Has The World's Highest Score on the U.N. Human Development Index". Monaco Estate. 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 8 July 2023. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ a b "World Economic Outlook, October 1989" (PDF). International Monetary Fund. p. 12. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 June 2020. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ^ a b c d International Monetary Fund Annual Report 1997. Annual Report of the Executive Board. International Monetary Fund. October 1997. doi:10.5089/9781451945102.011. ISBN 9781451945102. Archived from the original on 25 June 2020. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ^ Nations, United. "Data Reader's Guide". Archived from the original on 28 October 2022. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- ^ "What is the human development index (HDI)? How are relevant data queried?" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 June 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2022.
- ^ "人類發展指數" (PDF) (in Chinese). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2022.
- ^ "National Statistics, Republic of China (Taiwan) - Statistical Tables". eng.stat.gov.tw. Archived from the original on 16 October 2022. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- ^ "國情統計通報" (PDF) (in Chinese). Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 February 2023. Retrieved 26 October 2022.
External links
[edit] Quotations related to Developed country at Wikiquote
Quotations related to Developed country at Wikiquote- IMF (advanced economies)
- The World Factbook Archived 9 April 2008 at the Wayback Machine (developed countries)
- United Nations Statistics Division (definition)
- List of countries, United Nations Statistics Division (developed regions)
- World Bank (high-income economies)
