Wikipedia:WikiProject Animal anatomy/Recognized content: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
updating recognized content |
updating recognized content |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Anatomical terms of location]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Anatomical terms of location]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Anatomy]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Anatomy]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Clitoris]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Clitoris]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Coral]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Coral]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Ear]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Ear]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Esophagus]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Esophagus]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:External morphology of Lepidoptera]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:External morphology of Lepidoptera]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Femoral gland]] |
|||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Foramen spinosum]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Foramen spinosum]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Gallbladder]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Gallbladder]] |
||
| Line 57: | Line 58: | ||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Heart]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Heart]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Lung]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Lung]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Lateral line]] |
|||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Limbs of the horse]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Limbs of the horse]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Pancreas]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Pancreas]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Prostate]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Prostate]] |
||
| Line 69: | Line 70: | ||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Venom]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Venom]] |
||
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Insect wing]] |
*{{icon|GA}} [[:Insect wing]] |
||
Total pages in content type is |
Total pages in content type is 28 |
||
=={{icon|DGA}} Former good articles== |
=={{icon|DGA}} Former good articles== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*{{icon|DGA}} [[:Love dart]] |
|||
*{{icon|DGA}} [[:Stem cell]] |
*{{icon|DGA}} [[:Stem cell]] |
||
Total pages in content type is |
Total pages in content type is 3 |
||
=={{icon|DYK}} ''Did you know?'' articles== |
=={{icon|DYK}} ''Did you know?'' articles== |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the '''[[ampullae of Lorenzini]]''' enable sharks to [[Electroreception and electrogenesis|sense electric fields]]? <small>(2022-10-10)</small> |
|||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the modern study of human '''[[anatomy]]''' is considered to have been founded by [[Andreas Vesalius]] ''(anatomical drawing pictured)'' in the sixteenth century? <small>(2013-07-27)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the modern study of human '''[[anatomy]]''' is considered to have been founded by [[Andreas Vesalius]] ''(anatomical drawing pictured)'' in the sixteenth century? <small>(2013-07-27)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that despite over a hundred years of scientific study, '''[[arthropod head problem|fierce debate]]''' still rages about how [[arthropod]]s' heads are [[segmentation (biology)|constructed]]? <small>(2007-07-16)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that despite over a hundred years of scientific study, '''[[arthropod head problem|fierce debate]]''' still rages about how [[arthropod]]s' heads are [[segmentation (biology)|constructed]]? <small>(2007-07-16)</small> |
||
| Line 87: | Line 91: | ||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that you can count lines in '''[[Dinosaur dental histology|dinosaur teeth]]''' to determine their age? <small>(2017-12-20)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that you can count lines in '''[[Dinosaur dental histology|dinosaur teeth]]''' to determine their age? <small>(2017-12-20)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that colour vision with resolution and clarity are the most prominent features of '''[[Eagle eyes|eagles' eyes]]''' ''(pictured)'', and hence the epithet given to sharp-sighted people is "eagle-eyed”? <small>(2012-11-12)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that colour vision with resolution and clarity are the most prominent features of '''[[Eagle eyes|eagles' eyes]]''' ''(pictured)'', and hence the epithet given to sharp-sighted people is "eagle-eyed”? <small>(2012-11-12)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that '''[[Electric organ (fish)|electric organs]]''' are composed of stacks of specialised cells that can generate electricity? <small>(2023-01-19)</small> |
|||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the human '''[[Embryological origins of the mouth and anus|mouth forms]]''' when the [[blastopore|opening]] that becomes the anus tunnels through the [[embryo]] and comes out the other side? <small>(2008-12-11)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the human '''[[Embryological origins of the mouth and anus|mouth forms]]''' when the [[blastopore|opening]] that becomes the anus tunnels through the [[embryo]] and comes out the other side? <small>(2008-12-11)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that '''[[Endochondral ossification]]''' is one of two types of [[bone]] formation and is the process responsible for much of the bone growth in [[vertebrate]] [[skeleton]]s? <small>(2004-12-24)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that '''[[Endochondral ossification]]''' is one of two types of [[bone]] formation and is the process responsible for much of the bone growth in [[vertebrate]] [[skeleton]]s? <small>(2004-12-24)</small> |
||
| Line 99: | Line 104: | ||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the '''[[largest body part]]s''' do not all belong to the [[largest organism|largest animal]], and that there are numerous [[Guinness World Records]] for the largest human body parts? <small>(2006-08-10)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the '''[[largest body part]]s''' do not all belong to the [[largest organism|largest animal]], and that there are numerous [[Guinness World Records]] for the largest human body parts? <small>(2006-08-10)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that some [[hermaphrodite]] [[snail]]s and [[slug]]s pierce each other with '''[[love dart]]s''' ''(pictured)'' during [[mating]]? <small>(2008-10-09)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that some [[hermaphrodite]] [[snail]]s and [[slug]]s pierce each other with '''[[love dart]]s''' ''(pictured)'' during [[mating]]? <small>(2008-10-09)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that, amongst the kidneys of the [[vertebrate]]s, only '''[[Mammalian kidney|those of mammals]]''' and birds can produce concentrated urine? <small>(2023-04-04)</small> |
|||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the [[epidermis]] of the '''[[Mantle (mollusc)|mantle]]''', an [[organ (anatomy)|organ]] in [[mollusk]]s, [[secretion|secretes]] the [[calcium carbonate]] that creates their [[shell]]? <small>(2005-01-28)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the [[epidermis]] of the '''[[Mantle (mollusc)|mantle]]''', an [[organ (anatomy)|organ]] in [[mollusk]]s, [[secretion|secretes]] the [[calcium carbonate]] that creates their [[shell]]? <small>(2005-01-28)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the anatomical term "'''[[Mesentery (zoology)|mesentery]]'''" is derived from the Greek ''mesos'', meaning "in the middle", and ''enteron'', "intestine"? <small>(2015-06-10)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the anatomical term "'''[[Mesentery (zoology)|mesentery]]'''" is derived from the Greek ''mesos'', meaning "in the middle", and ''enteron'', "intestine"? <small>(2015-06-10)</small> |
||
| Line 110: | Line 116: | ||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that while they are primarily [[Filter feeder|feeding]] structures, '''[[radiole]]s''' ''(pictured)'' also serve as [[Aquatic respiration|respiratory]] organs for certain [[Sessility (limnology)|sessile]] [[Marine (ocean)|marine]] [[Polychaeta|polychaetes]]? <small>(2010-05-09)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that while they are primarily [[Filter feeder|feeding]] structures, '''[[radiole]]s''' ''(pictured)'' also serve as [[Aquatic respiration|respiratory]] organs for certain [[Sessility (limnology)|sessile]] [[Marine (ocean)|marine]] [[Polychaeta|polychaetes]]? <small>(2010-05-09)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that a galloping [[horse]] must '''[[respiratory system of the horse|breathe with every stride]]''', due to the movement of the gut contents pushing forward and back on the [[Thoracic diaphragm|diaphragm]]? <small>(2007-08-02)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that a galloping [[horse]] must '''[[respiratory system of the horse|breathe with every stride]]''', due to the movement of the gut contents pushing forward and back on the [[Thoracic diaphragm|diaphragm]]? <small>(2007-08-02)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the [[amorphous solid|amorphous]] [[Phosphate minerals|phosphate mineral]] '''[[santabarbaraite]]''' was named after the [[Italy|Italian]] mining district Santa Barbara where it was discovered in 2003, but its name also honors [[Saint Barbara]], the [[patron saint]] of [[Mining|miners]]? <small>(2007-12-11)</small> |
|||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the [[Canine tooth|canine teeth]] of male [[baboon]]s—which can be up to four times as long as those of females—are an example of a '''[[Sexual dimorphism in non-human primates|sexual dimorphism]]'''? <small>(2008-06-01)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the [[Canine tooth|canine teeth]] of male [[baboon]]s—which can be up to four times as long as those of females—are an example of a '''[[Sexual dimorphism in non-human primates|sexual dimorphism]]'''? <small>(2008-06-01)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that a '''[[Siphon (mollusc)|siphon]]''' ''(example pictured)'' is used by some marine [[snail]]s for tasting, by some [[clam]]s for reproducing, and by [[octopus]]es for jet propulsion? <small>(2008-11-21)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that a '''[[Siphon (mollusc)|siphon]]''' ''(example pictured)'' is used by some marine [[snail]]s for tasting, by some [[clam]]s for reproducing, and by [[octopus]]es for jet propulsion? <small>(2008-11-21)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the chemicals responsible for the '''[[smell of freshly cut grass]]''' are a [[Plant defense against herbivory|plant defense mechanism]]? <small>(2023-08-19)</small> |
|||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that, in female [[bedbug]]s, the '''[[spermalege]]''' reduces the wounding costs caused by a male's [[traumatic insemination|needle-like penis]]? <small>(2011-02-06)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that, in female [[bedbug]]s, the '''[[spermalege]]''' reduces the wounding costs caused by a male's [[traumatic insemination|needle-like penis]]? <small>(2011-02-06)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that in [[1973]], an [[experiment]] successfully demonstrated that spiders can spin '''[[spider webs in space|webs in space]]'''? <small>(2007-01-29)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that in [[1973]], an [[experiment]] successfully demonstrated that spiders can spin '''[[spider webs in space|webs in space]]'''? <small>(2007-01-29)</small> |
||
| Line 123: | Line 131: | ||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the '''[[Weberian apparatus]]''', a set of modified bones that link the [[swim bladder]] and [[inner ear]] of some fishes, is a distinguishing characteristic of the [[superorder]] [[Ostariophysi]]? <small>(2009-01-27)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that the '''[[Weberian apparatus]]''', a set of modified bones that link the [[swim bladder]] and [[inner ear]] of some fishes, is a distinguishing characteristic of the [[superorder]] [[Ostariophysi]]? <small>(2009-01-27)</small> |
||
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that in [[rodent]]s, the position of the '''[[zygomatic plate]]''' varies from nearly horizontal to nearly vertical? <small>(2010-01-25)</small> |
*{{icon|DYK}} ... that in [[rodent]]s, the position of the '''[[zygomatic plate]]''' varies from nearly horizontal to nearly vertical? <small>(2010-01-25)</small> |
||
Total pages in content type is |
Total pages in content type is 54 |
||
=={{icon|FP}} Featured pictures== |
=={{icon|FP}} Featured pictures== |
||
<gallery mode=packed> |
<gallery mode=packed> |
||
| Line 143: | Line 151: | ||
=={{icon|GAN}} Good article nominees== |
=={{icon|GAN}} Good article nominees== |
||
*{{icon|GAN}} [[: |
*{{icon|GAN}} [[:Bilateria]] |
||
Total pages in content type is 1 |
Total pages in content type is 1 |
||
== Main page featured articles== |
== Main page featured articles== |
||
| Line 153: | Line 161: | ||
* [[:Toothcomb]] <small>(2012-09-27)</small> |
* [[:Toothcomb]] <small>(2012-09-27)</small> |
||
Total pages in content type is 6 |
Total pages in content type is 6 |
||
== Picture of the day pictures== |
=={{icon|potd}} Picture of the day pictures== |
||
<gallery mode=packed> |
<gallery mode=packed> |
||
File:Albino Macropus rufogriseus rufogriseus.jpg|Albino Macropus rufogriseus rufogriseus <small>(2009-12-08)</small> |
File:Albino Macropus rufogriseus rufogriseus.jpg|Albino Macropus rufogriseus rufogriseus <small>(2009-12-08)</small> |
||
| Line 171: | Line 179: | ||
Total pages in content type is 12 |
Total pages in content type is 12 |
||
<!-- End of content generated by JL-Bot --> |
<!-- End of content generated by JL-Bot --> |
||
[[Category:Wikipedia lists of recognized content|Animal anatomy]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 10:20, 21 December 2024
| This is a list of recognized content, updated weekly by JL-Bot (talk · contribs) (typically on Saturdays). There is no need to edit the list yourself. If an article is missing from the list, make sure it is tagged (e.g. {{WikiProject Animal anatomy}}) or categorized correctly and wait for the next update. See WP:RECOG for configuration options. |
 Featured articles
Featured articles
[edit]Total pages in content type is 5
 Former featured articles
Former featured articles
[edit]Total pages in content type is 1
 Good articles
Good articles
[edit] Adrenal gland
Adrenal gland Ampullae of Lorenzini
Ampullae of Lorenzini Anatomical terms of location
Anatomical terms of location Anatomy
Anatomy Clitoris
Clitoris Coral
Coral Ear
Ear Electric organ (fish)
Electric organ (fish) Esophagus
Esophagus External morphology of Lepidoptera
External morphology of Lepidoptera Femoral gland
Femoral gland Foramen spinosum
Foramen spinosum Gallbladder
Gallbladder Homology (biology)
Homology (biology) Heart
Heart Lung
Lung Lateral line
Lateral line Limbs of the horse
Limbs of the horse Pancreas
Pancreas Prostate
Prostate Sebaceous gland
Sebaceous gland Snake scale
Snake scale Sublingua
Sublingua Thymus
Thymus Thyroid
Thyroid Trachea
Trachea Venom
Venom Insect wing
Insect wing
Total pages in content type is 28
 Former good articles
Former good articles
[edit]Total pages in content type is 3
 Did you know? articles
Did you know? articles
[edit] ... that the ampullae of Lorenzini enable sharks to sense electric fields? (2022-10-10)
... that the ampullae of Lorenzini enable sharks to sense electric fields? (2022-10-10) ... that the modern study of human anatomy is considered to have been founded by Andreas Vesalius (anatomical drawing pictured) in the sixteenth century? (2013-07-27)
... that the modern study of human anatomy is considered to have been founded by Andreas Vesalius (anatomical drawing pictured) in the sixteenth century? (2013-07-27) ... that despite over a hundred years of scientific study, fierce debate still rages about how arthropods' heads are constructed? (2007-07-16)
... that despite over a hundred years of scientific study, fierce debate still rages about how arthropods' heads are constructed? (2007-07-16) ... that scientists first discovered the biological screw joint in the Papuan weevil Trigonopterus oblongus? (2011-08-07)
... that scientists first discovered the biological screw joint in the Papuan weevil Trigonopterus oblongus? (2011-08-07) ... that birds' eyes have three lids, including the nictitating membrane (pictured), which moves across the eyeball horizontally? (2008-07-16)
... that birds' eyes have three lids, including the nictitating membrane (pictured), which moves across the eyeball horizontally? (2008-07-16) ... that you started out as a blastula? (2013-05-04)
... that you started out as a blastula? (2013-05-04) ... that the casques of some large hornbill species (example pictured) can take up to six years to reach their full size? (2021-05-08)
... that the casques of some large hornbill species (example pictured) can take up to six years to reach their full size? (2021-05-08) ... that some hamsters hide their young in their cheek pouches to carry them when they fear danger? (2012-11-09)
... that some hamsters hide their young in their cheek pouches to carry them when they fear danger? (2012-11-09) ... that the cloven hoof is a characteristic of mountain goats, certain kosher foods and in some traditions, the Devil? (2007-12-07)
... that the cloven hoof is a characteristic of mountain goats, certain kosher foods and in some traditions, the Devil? (2007-12-07) ... that a corallite is a cup for a coral? (2015-05-05)
... that a corallite is a cup for a coral? (2015-05-05) ... that the black sea cucumber (pictured) can emit a mass of sticky cuvierian tubules to enmesh a potential predator? (2013-03-13)
... that the black sea cucumber (pictured) can emit a mass of sticky cuvierian tubules to enmesh a potential predator? (2013-03-13) ... that according to Traditional Chinese Medicine, deer penis is said to enchance virility in men, and was added to the list of banned substances during the 2008 Beijing Olympics? (2010-06-30)
... that according to Traditional Chinese Medicine, deer penis is said to enchance virility in men, and was added to the list of banned substances during the 2008 Beijing Olympics? (2010-06-30) ... that you can count lines in dinosaur teeth to determine their age? (2017-12-20)
... that you can count lines in dinosaur teeth to determine their age? (2017-12-20) ... that colour vision with resolution and clarity are the most prominent features of eagles' eyes (pictured), and hence the epithet given to sharp-sighted people is "eagle-eyed”? (2012-11-12)
... that colour vision with resolution and clarity are the most prominent features of eagles' eyes (pictured), and hence the epithet given to sharp-sighted people is "eagle-eyed”? (2012-11-12) ... that electric organs are composed of stacks of specialised cells that can generate electricity? (2023-01-19)
... that electric organs are composed of stacks of specialised cells that can generate electricity? (2023-01-19) ... that the human mouth forms when the opening that becomes the anus tunnels through the embryo and comes out the other side? (2008-12-11)
... that the human mouth forms when the opening that becomes the anus tunnels through the embryo and comes out the other side? (2008-12-11) ... that Endochondral ossification is one of two types of bone formation and is the process responsible for much of the bone growth in vertebrate skeletons? (2004-12-24)
... that Endochondral ossification is one of two types of bone formation and is the process responsible for much of the bone growth in vertebrate skeletons? (2004-12-24) ... that femoral pores are a part of a secretory gland found on the thighs of certain lizards which release pheromones to attract mates or mark territory? (2009-12-23)
... that femoral pores are a part of a secretory gland found on the thighs of certain lizards which release pheromones to attract mates or mark territory? (2009-12-23) ... that fins are used on artefacts and by aquatic animals such as killer whales (pictured) to generate thrust, to control motion, or to regulate temperature? (2012-11-29)
... that fins are used on artefacts and by aquatic animals such as killer whales (pictured) to generate thrust, to control motion, or to regulate temperature? (2012-11-29) ... that some species of fish undergo a genetically programmed sex change during their development? (2007-06-08)
... that some species of fish undergo a genetically programmed sex change during their development? (2007-06-08) ... that some species of waterfowl lose all their flight feathers (pictured) at once while moulting, rendering them incapable of flight? (2007-05-29)
... that some species of waterfowl lose all their flight feathers (pictured) at once while moulting, rendering them incapable of flight? (2007-05-29) ... that the ear's hair cells encode the information from the fluid waves of the cochlea for use by the auditory nerve? (2004-08-11)
... that the ear's hair cells encode the information from the fluid waves of the cochlea for use by the auditory nerve? (2004-08-11) ... that Hunter-Schreger bands strengthen the enamel of the incisor in rodents? (2010-01-24)
... that Hunter-Schreger bands strengthen the enamel of the incisor in rodents? (2010-01-24) ... that pit vipers and some boas and pythons have specialized facial pits for sensing infrared radiation? (2007-12-07)
... that pit vipers and some boas and pythons have specialized facial pits for sensing infrared radiation? (2007-12-07) ... that possible traces of interdigital webbing have been preserved in fossils of pakicetids, the ancestors of whales? (2009-12-29)
... that possible traces of interdigital webbing have been preserved in fossils of pakicetids, the ancestors of whales? (2009-12-29) ... that the largest body parts do not all belong to the largest animal, and that there are numerous Guinness World Records for the largest human body parts? (2006-08-10)
... that the largest body parts do not all belong to the largest animal, and that there are numerous Guinness World Records for the largest human body parts? (2006-08-10) ... that some hermaphrodite snails and slugs pierce each other with love darts (pictured) during mating? (2008-10-09)
... that some hermaphrodite snails and slugs pierce each other with love darts (pictured) during mating? (2008-10-09) ... that, amongst the kidneys of the vertebrates, only those of mammals and birds can produce concentrated urine? (2023-04-04)
... that, amongst the kidneys of the vertebrates, only those of mammals and birds can produce concentrated urine? (2023-04-04) ... that the epidermis of the mantle, an organ in mollusks, secretes the calcium carbonate that creates their shell? (2005-01-28)
... that the epidermis of the mantle, an organ in mollusks, secretes the calcium carbonate that creates their shell? (2005-01-28) ... that the anatomical term "mesentery" is derived from the Greek mesos, meaning "in the middle", and enteron, "intestine"? (2015-06-10)
... that the anatomical term "mesentery" is derived from the Greek mesos, meaning "in the middle", and enteron, "intestine"? (2015-06-10) ... that in Swabia, the length of a housefly's penis is an idiomatic expression for a very short length? (2013-08-31)
... that in Swabia, the length of a housefly's penis is an idiomatic expression for a very short length? (2013-08-31) ... that at least twelve different nomenclatures have been proposed for features of the molar in muroid rodents? (2010-03-15)
... that at least twelve different nomenclatures have been proposed for features of the molar in muroid rodents? (2010-03-15) ... that mushroom bodies have nothing to do with fungi, but are part of the brain anatomy of arthropods? (2004-03-17)
... that mushroom bodies have nothing to do with fungi, but are part of the brain anatomy of arthropods? (2004-03-17) ... that the spines of a sea urchin (two pictured) are connected to other ossicles by ball and socket joints? (2013-05-16)
... that the spines of a sea urchin (two pictured) are connected to other ossicles by ball and socket joints? (2013-05-16) ... that many rice rats have pits at the back of their palates recessed into a deep depression? (2010-01-23)
... that many rice rats have pits at the back of their palates recessed into a deep depression? (2010-01-23) ... that the hirola (pictured) is often referred to as the "four-eyed antelope" due to its large preorbital glands? (2012-05-30)
... that the hirola (pictured) is often referred to as the "four-eyed antelope" due to its large preorbital glands? (2012-05-30) ... that oysters deposit pseudofeces in such amounts that they can clean up an entire estuary? (2008-09-30)
... that oysters deposit pseudofeces in such amounts that they can clean up an entire estuary? (2008-09-30) ... that while they are primarily feeding structures, radioles (pictured) also serve as respiratory organs for certain sessile marine polychaetes? (2010-05-09)
... that while they are primarily feeding structures, radioles (pictured) also serve as respiratory organs for certain sessile marine polychaetes? (2010-05-09) ... that a galloping horse must breathe with every stride, due to the movement of the gut contents pushing forward and back on the diaphragm? (2007-08-02)
... that a galloping horse must breathe with every stride, due to the movement of the gut contents pushing forward and back on the diaphragm? (2007-08-02) ... that the amorphous phosphate mineral santabarbaraite was named after the Italian mining district Santa Barbara where it was discovered in 2003, but its name also honors Saint Barbara, the patron saint of miners? (2007-12-11)
... that the amorphous phosphate mineral santabarbaraite was named after the Italian mining district Santa Barbara where it was discovered in 2003, but its name also honors Saint Barbara, the patron saint of miners? (2007-12-11) ... that the canine teeth of male baboons—which can be up to four times as long as those of females—are an example of a sexual dimorphism? (2008-06-01)
... that the canine teeth of male baboons—which can be up to four times as long as those of females—are an example of a sexual dimorphism? (2008-06-01) ... that a siphon (example pictured) is used by some marine snails for tasting, by some clams for reproducing, and by octopuses for jet propulsion? (2008-11-21)
... that a siphon (example pictured) is used by some marine snails for tasting, by some clams for reproducing, and by octopuses for jet propulsion? (2008-11-21) ... that the chemicals responsible for the smell of freshly cut grass are a plant defense mechanism? (2023-08-19)
... that the chemicals responsible for the smell of freshly cut grass are a plant defense mechanism? (2023-08-19) ... that, in female bedbugs, the spermalege reduces the wounding costs caused by a male's needle-like penis? (2011-02-06)
... that, in female bedbugs, the spermalege reduces the wounding costs caused by a male's needle-like penis? (2011-02-06) ... that in 1973, an experiment successfully demonstrated that spiders can spin webs in space? (2007-01-29)
... that in 1973, an experiment successfully demonstrated that spiders can spin webs in space? (2007-01-29) ... that prosimian primates like lemurs and slow lorises have a "second tongue" called a sublingua, which they use to clean their toothcomb? (2012-02-22)
... that prosimian primates like lemurs and slow lorises have a "second tongue" called a sublingua, which they use to clean their toothcomb? (2012-02-22) ... that some plants have tentacles, but octopuses have none (they have arms)? (2004-04-10)
... that some plants have tentacles, but octopuses have none (they have arms)? (2004-04-10) ... that one method of preparing a tiger penis for consumption is to place it dried, with testicles still attached, into a bottle of French cognac, whiskey or Chinese wine and let it soak for many weeks? (2010-07-05)
... that one method of preparing a tiger penis for consumption is to place it dried, with testicles still attached, into a bottle of French cognac, whiskey or Chinese wine and let it soak for many weeks? (2010-07-05) ... that lemurs, lorises, and galagos have a special dental structure called a toothcomb (example pictured), which they use to comb their fur during grooming? (2012-03-19)
... that lemurs, lorises, and galagos have a special dental structure called a toothcomb (example pictured), which they use to comb their fur during grooming? (2012-03-19) ... that in rice rats living in the water, the tufts of hair at the base of the claws are reduced? (2010-04-08)
... that in rice rats living in the water, the tufts of hair at the base of the claws are reduced? (2010-04-08) ... that the deep water barreleye fish (pictured) is so named because of its unusual visual system which uses barrel-shaped, telescopic eyes that are generally directed upwards? (2011-10-04)
... that the deep water barreleye fish (pictured) is so named because of its unusual visual system which uses barrel-shaped, telescopic eyes that are generally directed upwards? (2011-10-04) ... that some water birds use their webbed feet (illustration shown) as an aid in elaborate courtship displays? (2019-02-21)
... that some water birds use their webbed feet (illustration shown) as an aid in elaborate courtship displays? (2019-02-21) ... that the Weberian apparatus, a set of modified bones that link the swim bladder and inner ear of some fishes, is a distinguishing characteristic of the superorder Ostariophysi? (2009-01-27)
... that the Weberian apparatus, a set of modified bones that link the swim bladder and inner ear of some fishes, is a distinguishing characteristic of the superorder Ostariophysi? (2009-01-27) ... that in rodents, the position of the zygomatic plate varies from nearly horizontal to nearly vertical? (2010-01-25)
... that in rodents, the position of the zygomatic plate varies from nearly horizontal to nearly vertical? (2010-01-25)
Total pages in content type is 54
 Featured pictures
Featured pictures
[edit]-
Albino Macropus rufogriseus rufogriseus
-
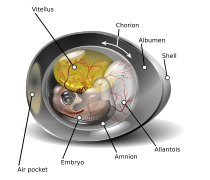
BirdBeaksA
-
Chicken egg diagram
-
Colias dimera copulating
-
Coral Outcrop Flynn Reef
-
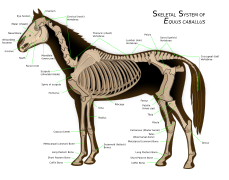
Horse anatomy
-
Inachis io top detail MichaD
-
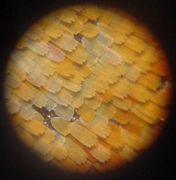
Microphoto-butterflywing
-
SEM image of a Peacock wing, slant view 1
-
SEM image of a Peacock wing, slant view 2
-
SEM image of a Peacock wing, slant view 3
-
SEM image of a Peacock wing, slant view 4
Total pages in content type is 12
 Good article nominees
Good article nominees
[edit]Total pages in content type is 1
Main page featured articles
[edit]- Cerebellum (2005-09-16)
- Chromatophore (2006-07-30)
- Flight feather (2007-12-25)
- Hippocampus (2009-07-28)
- Immune system (2007-03-01)
- Toothcomb (2012-09-27)
Total pages in content type is 6
 Picture of the day pictures
Picture of the day pictures
[edit]-
Albino Macropus rufogriseus rufogriseus (2009-12-08)
-
BirdBeaksA (2007-11-03)
-
Chicken egg diagram (2021-02-10)
-
Colias dimera copulating (2021-06-07)
-
Coral Outcrop Flynn Reef (2015-09-11)
-
Horse anatomy (2022-02-23)
-
Inachis io top detail MichaD (2012-02-06)
-
Microphoto-butterflywing (2012-02-06)
-
SEM image of a Peacock wing, slant view 1 (2012-02-06)
-
SEM image of a Peacock wing, slant view 2 (2012-02-06)
-
SEM image of a Peacock wing, slant view 3 (2012-02-06)
-
SEM image of a Peacock wing, slant view 4 (2012-02-06)
Total pages in content type is 12