Gonyosoma oxycephalum: Difference between revisions
GreenC bot (talk | contribs) Reformat 1 archive link. Wayback Medic 2.5 per WP:USURPURL and JUDI batch #20 |
|||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 21 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Species of reptile}} |
|||
{{italic title}}{{speciesbox |
|||
{{Italic title}} |
|||
{{Speciesbox |
|||
| name = Red-tailed green ratsnake |
| name = Red-tailed green ratsnake |
||
| image = Gonyosoma oxycephalum Oslo.JPG |
| image = Gonyosoma oxycephalum Oslo.JPG |
||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
| status = LC |
| status = LC |
||
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
||
| status_ref = <ref name= |
| status_ref = <ref name="iucn status 19 November 2021">{{cite iucn |author=Wogan, G. |author2=Vogel, G. |author3=Thy, N. |author4=Nguyen, T.Q. |author5=Demegillo, A. |author6=Diesmos, A.C. |author7=Gonzalez, J.C. |date=2012 |title=''Gonyosoma oxycephalum'' |volume=2012 |page=e.T183196A1732988 |doi=10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012-1.RLTS.T183196A1732988.en |access-date=19 November 2021}}</ref> |
||
| genus = Gonyosoma |
| genus = Gonyosoma |
||
| species = oxycephalum |
| species = oxycephalum |
||
| authority = ([[Friedrich Boie|F. Boie]], 1827) |
| authority = ([[Friedrich Boie|F. Boie]], 1827) |
||
| range_map = Gonyosoma oxycephalum distribution.png |
| range_map = Gonyosoma oxycephalum distribution.png |
||
| synonyms = ''Elaphe oxycephala'' <small>(Boie, 1827)</small> |
| synonyms = ''Elaphe oxycephala'' <small>(Boie, 1827)</small> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
It was first [[Scientific description|described]] by [[Friedrich Boie]] in 1827.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Boie, F. |year=1827 |title=Bemerkungen über Merrem's Versuch eines Systems der Amphibien, Erste Lieferung: Ophidier |journal=Isis von Oken |volume=20 |issue=VI |pages=508–566 |url=https://archive.org/details/isisvonoken1827oken/page/286}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | ''G. oxycephalum'' is a robust powerful snake, with wide smooth scales on its belly that are ideal for climbing trees and across branches. It has smaller, smooth scales on its back, which is usually bright green or light green and may have a black net-like pattern. A gray-colored morph with a yellow head exists in [[Panay]], in the Philippines. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
Image:Gonyosoma oxycephalum.jpg|''Gonyosoma oxycephalum'', [[Kaeng Krachan National Park]], Thailand |
Image:Gonyosoma oxycephalum.jpg|''Gonyosoma oxycephalum'', [[Kaeng Krachan National Park]], Thailand |
||
Image:Elaphe oxycephala.jpg|Gonyosoma oxycephalum |
Image:Elaphe oxycephala.jpg|''Gonyosoma oxycephalum'' |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
The female can reach a length of up to 2.4 m (almost 8 feet), while the male is generally a little bit smaller but brighter in coloration |
The female can reach a length of up to 2.4 m (almost 8 feet), while the male is generally a little bit smaller but brighter in coloration. |
||
== |
==Longevity== |
||
The average life span of ''G. oxycephalum'' in captivity is 20 years. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Reproduction== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
''G. oxycephalum'' reaches sexually maturity at 4 years of age, and its eggs have a hatching time from 13 to 16 weeks. The female lays on average between 3 and 8 eggs usually between September and January and the hatchlings are about 45 cm (18 inches) long. |
|||
== |
==Behavior== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==Diet== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Distribution== |
==Distribution== |
||
''G. oxycephalumm'' is found in the following countries: |
|||
*[[Indonesia]] (Bangka, Belitung, [[Java (island)|Java]], [[Kalimantan|Kalimantan/Borneo]], [[Karimata]], [[Legundi]], [[Lombok]], [[Mentawai islands]], [[Natuna islands]], [[Nias]], [[Panaitan]], [[Riau archipelago]], [[Sebuku (Sumatra)|Sebuku]], [[Sumatra]], [[Tambelan archipelago]]), |
*[[Indonesia]] ([[Bangka Island|Bangka]], Belitung, [[Java (island)|Java]], [[Kalimantan|Kalimantan/Borneo]], [[Karimata]], [[Legundi]], [[Lombok]], [[Mentawai islands]], [[Natuna islands]], [[Nias]], [[Panaitan]], [[Riau archipelago]], [[Sebuku (Sumatra)|Sebuku]], [[Sumatra]], [[Tambelan archipelago]]), |
||
*[[Malaysia]] (Malaya and East Malaysia, Pulau Tioman ?), |
*[[Malaysia]] (Malaya and East Malaysia, Pulau Tioman ?), |
||
*[[Singapore]] Island, [[Penang Island]], |
*[[Singapore]] Island, [[Penang Island]], |
||
*[[India |
*[[India]] ([[Andaman Islands]]), |
||
*[[Myanmar]] |
*[[Myanmar]], |
||
*[[Thailand]] (incl. [[Phuket Province|Phuket]]), [[Cambodia]], [[Laos]], [[Vietnam]], |
*[[Thailand]] (incl. [[Phuket Province|Phuket]]), [[Cambodia]], [[Laos]], [[Vietnam]], |
||
*[[Philippine Islands]] (Balabac, Bohol, Catanduanes, Lubang, [[Luzon]], Negros, Palawan, Sulu Archipelago, Panay) |
*[[Philippine Islands]] (Balabac, Bohol, Catanduanes, Lubang, [[Luzon]], Negros, Palawan, Sulu Archipelago, Panay). |
||
[[Type locality (biology)|Type locality]] Indonesia: Java (Boie, 1827) |
The [[Type locality (biology)|Type locality]] is Indonesia: Java ([[Friedrich Boie|F. Boie]], 1827). |
||
==Population== |
|||
As of 2015, the Red-tailed Green Ratsnake was categorized as "Least Concern" by the IUCN due to its relatively healthy population estimated at 15,000-20,000 individuals across its range. However, recent data as of 2022 indicates a decline in its numbers, with an estimated population of around 10,000-15,000. Despite this decline, it still retains its "Least Concern" status. |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
* Boulenger, G.A. 1894 On the herpetological fauna of Palawan and Balabac. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. (6) 14: 81-90 |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* |
*[[George Albert Boulenger|Boulenger GA]] (1894). "On the Herpetological Fauna of Palawan and Balabac". ''Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist., Sixth Series'' '''14''': 81–90. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[John Edward Gray|Gray JE]] (1849). "Description of three new genera and species of snakes". ''Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist., Second Series'' '''4''': 246–248. |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* {{NRDB species|genus=Gonyosoma|species=oxycephalum|date=9 November|year=2010}} |
* {{Commons category-inline|Gonyosoma oxycephalum}} |
||
*{{NRDB species|genus=Gonyosoma|species=oxycephalum|date=9 November|year=2010}} |
|||
* |
*[http://www.herpFocus.com?HFID=HFV20080713-001 Video of ''Gonysoma oxycephalum'' drinking] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120212172406/http://www.herpfocus.com/?HFID=HFV20080713-001 |date=2012-02-12 }} |
||
* |
*{{usurped|1=[https://web.archive.org/web/20090226143243/http://www.ratsnakefoundation.org/modules/smartsection/item.php?itemid=123 ''Gonysoma oxycephalum'' Information sheet]}} |
||
{{Taxonbar|from=Q47945}} |
{{Taxonbar|from=Q47945}} |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Gonyosoma]] |
||
[[Category:Snakes of Southeast Asia]] |
[[Category:Snakes of Southeast Asia]] |
||
[[Category:Reptiles of Brunei]] |
[[Category:Reptiles of Brunei]] |
||
| Line 72: | Line 90: | ||
[[Category:Reptiles of Vietnam]] |
[[Category:Reptiles of Vietnam]] |
||
[[Category:Reptiles described in 1827]] |
[[Category:Reptiles described in 1827]] |
||
[[Category:Taxa named by Friedrich Boie]] |
|||
[[Category:Snakes of Vietnam]] |
|||
[[Category:Snakes of Asia]] |
|||
[[Category:Reptiles of Borneo]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 18:31, 21 December 2024
| Red-tailed green ratsnake | |
|---|---|

| |
| Red-tailed green ratsnake | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Colubridae |
| Genus: | Gonyosoma |
| Species: | G. oxycephalum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Gonyosoma oxycephalum (F. Boie, 1827)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Elaphe oxycephala (Boie, 1827) | |
Gonyosoma oxycephalum, known commonly as the arboreal ratsnake, the red-tailed green rat snake, and the red-tailed racer, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Southeast Asia.
It was first described by Friedrich Boie in 1827.[2]
Description
[edit]G. oxycephalum is a robust powerful snake, with wide smooth scales on its belly that are ideal for climbing trees and across branches. It has smaller, smooth scales on its back, which is usually bright green or light green and may have a black net-like pattern. A gray-colored morph with a yellow head exists in Panay, in the Philippines.
As some of its common names indicate, the snake has a green body with a red tail, but is usually brown. It also has a dark line horizontally across the eye. On the sides of its black tongue there may be brown and blue colour. The top of the head may be dark green, yellow-green, or yellow in colour.
-
Gonyosoma oxycephalum, Kaeng Krachan National Park, Thailand
-
Gonyosoma oxycephalum
The female can reach a length of up to 2.4 m (almost 8 feet), while the male is generally a little bit smaller but brighter in coloration.
Longevity
[edit]The average life span of G. oxycephalum in captivity is 20 years.
Reproduction
[edit]G. oxycephalum reaches sexually maturity at 4 years of age, and its eggs have a hatching time from 13 to 16 weeks. The female lays on average between 3 and 8 eggs usually between September and January and the hatchlings are about 45 cm (18 inches) long.
Behavior
[edit]The red-tailed green ratsnake lives and spends its life in the trees and in cavities of trees. It seldom descends to the ground. When the snake is stressed, it may inflate a bag of air in its neck, making it appear larger in size.
In captivity, it has quite the "attitude" and may strike at or bite an unwary handler. Its temperament can be unpredictable and may change from time to time but an individual may become tame through proper handling.
Diet
[edit]G. oxycephalum feeds almost exclusively on birds, bird eggs, lizards, and bats. It catches them in mid-air while hanging amongst branches. In captivity, it can be trained to feed on rodents such as mice and rats.
Distribution
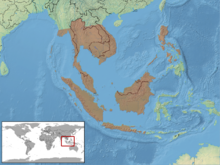
[edit]G. oxycephalumm is found in the following countries:
- Indonesia (Bangka, Belitung, Java, Kalimantan/Borneo, Karimata, Legundi, Lombok, Mentawai islands, Natuna islands, Nias, Panaitan, Riau archipelago, Sebuku, Sumatra, Tambelan archipelago),
- Malaysia (Malaya and East Malaysia, Pulau Tioman ?),
- Singapore Island, Penang Island,
- India (Andaman Islands),
- Myanmar,
- Thailand (incl. Phuket), Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam,
- Philippine Islands (Balabac, Bohol, Catanduanes, Lubang, Luzon, Negros, Palawan, Sulu Archipelago, Panay).
The Type locality is Indonesia: Java (F. Boie, 1827).
Population
[edit]As of 2015, the Red-tailed Green Ratsnake was categorized as "Least Concern" by the IUCN due to its relatively healthy population estimated at 15,000-20,000 individuals across its range. However, recent data as of 2022 indicates a decline in its numbers, with an estimated population of around 10,000-15,000. Despite this decline, it still retains its "Least Concern" status.
References
[edit]- ^ Wogan, G.; Vogel, G.; Thy, N.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Demegillo, A.; Diesmos, A.C.; Gonzalez, J.C. (2012). "Gonyosoma oxycephalum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012: e.T183196A1732988. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012-1.RLTS.T183196A1732988.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ Boie, F. (1827). "Bemerkungen über Merrem's Versuch eines Systems der Amphibien, Erste Lieferung: Ophidier". Isis von Oken. 20 (VI): 508–566.
Further reading
[edit]- Boulenger GA (1894). "On the Herpetological Fauna of Palawan and Balabac". Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist., Sixth Series 14: 81–90.
- Dowling, Herndon G. (1958). "A taxonomic study of the ratsnakes VI. Validation of the genera Gonyosoma Wagler and Elaphe Fitzinger". Copeia 1958 (1): 29–40.
- Gray JE (1849). "Description of three new genera and species of snakes". Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist., Second Series 4: 246–248.
External links
[edit] Media related to Gonyosoma oxycephalum at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Gonyosoma oxycephalum at Wikimedia Commons- Gonyosoma oxycephalum at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 9 November 2010.
- Video of Gonysoma oxycephalum drinking Archived 2012-02-12 at the Wayback Machine
- Gonysoma oxycephalum Information sheet[usurped]
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Gonyosoma
- Snakes of Southeast Asia
- Reptiles of Brunei
- Reptiles of Myanmar
- Reptiles of Cambodia
- Reptiles of India
- Reptiles of Indonesia
- Reptiles of Laos
- Reptiles of Malaysia
- Reptiles of the Philippines
- Reptiles of Singapore
- Reptiles of Thailand
- Reptiles of Vietnam
- Reptiles described in 1827
- Taxa named by Friedrich Boie
- Snakes of Vietnam
- Snakes of Asia
- Reptiles of Borneo



