Meråker Municipality: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Alter: url. URLs might have been anonymized. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by AManWithNoPlan | #UCB_CommandLine |
update population-area stats, add highest elevation, mayor info, sister bar, category, copy edit |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Infobox kommune |
{{Infobox kommune |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|native_name = |
|native_name = |
||
|native_name_lang = |
|native_name_lang = |
||
|other_name = |
|other_name = |
||
| |
|former_name = Meraaker herred |
||
|former_name1 = Meraker herred |
|||
|image_skyline = Meråkerdalen jan 2010.JPG |
|image_skyline = Meråkerdalen jan 2010.JPG |
||
|image_caption = View of the Meråker valley |
|image_caption = View of the Meråker valley |
||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
|capital = [[Midtbygda, Trøndelag|Midtbygda]] |
|capital = [[Midtbygda, Trøndelag|Midtbygda]] |
||
|established = 1 Jan 1874 |
|established = 1 Jan 1874 |
||
|preceded = [[Øvre |
|preceded = [[Øvre Stjørdalen Municipality]] |
||
|demonym = Meråkerbygg |
|demonym = Meråkerbygg |
||
|language = Bokmål |
|language = Bokmål |
||
|flag = |
|flag = |
||
|webpage = www.meraker.kommune.no |
|webpage = www.meraker.kommune.no |
||
|mayor = |
|mayor = Kari Anita Furunes |
||
|mayor_party = [[ |
|mayor_party = [[Centre Party (Norway)|Sp]] |
||
|mayor_as_of = |
|mayor_as_of = 2023 |
||
|elevation_max_m = 1441.36 |
|||
|highest_point_ref = <ref name="elev">{{Cite web |date=2024-01-16 |title=Høgaste fjelltopp i kvar kommune |url=https://www.kartverket.no/til-lands/fakta-om-norge/hoyeste-fjelltopp-i-kommunen |publisher=[[Kartverket]] |language=no}}</ref> |
|||
|area_rank = 80 |
|area_rank = 80 |
||
|area_total_km2 = 1273.94 |
|area_total_km2 = 1273.94 |
||
| Line 26: | Line 29: | ||
|area_water_km2 = 85.88 |
|area_water_km2 = 85.88 |
||
|area_water_percent = 6.7 |
|area_water_percent = 6.7 |
||
|population_as_of = |
|population_as_of = 2024 |
||
|population_rank = |
|population_rank = 259 |
||
|population_total = |
|population_total = 2454 |
||
|population_density_km2 = |
|population_density_km2 = 1.9 |
||
|population_increase = - |
|population_increase = -3.9 |
||
|coordinates = {{coord|63|26|17|N|11|50|58|E|region:NO|display=inline,title}} |
|coordinates = {{coord|63|26|17|N|11|50|58|E|region:NO|display=inline,title}} |
||
|utm_zone = 32V |utm_northing = 7037582 |utm_easting = 0642140 | geo_cat = adm2nd |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Meråker''' is a [[List of municipalities of Norway|municipality]] in [[Trøndelag]] [[Counties of Norway|county]], [[Norway]]. It is part of the [[Stjørdalen]] [[Districts of Norway|region]]. The [[administrative centre]] of the municipality is the village of [[Midtbygda, Trøndelag|Midtbygda]] which is about {{convert|20|km}} west of [[Storlien]] in [[Sweden]] and {{convert|46|km}} east of the town of [[Stjørdalshalsen]] in neighboring [[Stjørdal]] |
'''Meråker''' is a [[List of municipalities of Norway|municipality]] in [[Trøndelag]] [[Counties of Norway|county]], [[Norway]]. It is part of the [[Stjørdalen]] [[Districts of Norway|region]]. The [[administrative centre]] of the municipality is the village of [[Midtbygda, Trøndelag|Midtbygda]] which is about {{convert|20|km}} west of [[Storlien]] in [[Sweden]] and {{convert|46|km}} east of the town of [[Stjørdalshalsen]] in neighboring [[Stjørdal Municipality]]. Other villages in the municipality include [[Gudåa]], [[Kopperå]], and [[Stordalsvollen]]. |
||
| ⚫ | The {{convert|1274|km2|adj=on}} municipality is the 80th largest by area out of the 357 municipalities in Norway. Meråker is the 259th most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 2,454. The municipality's [[population density]] is {{convert|1.9|PD/km2}} and its population has decreased by 3.9% over the previous 10-year period.<ref name="ssb pop">{{Cite web |last=Statistisk sentralbyrå |author-link=Statistics Norway |title=Table: 06913: Population 1 January and population changes during the calendar year (M) |url=https://www.ssb.no/en/statbank/table/06913/ |language=Norwegian}}</ref><ref name="ssb area">{{Cite web |last=Statistisk sentralbyrå |author-link=Statistics Norway |title=09280: Area of land and fresh water (km²) (M) |url=https://www.ssb.no/en/statbank/table/09280/ |language=Norwegian}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The {{convert|1274|km2|adj=on}} municipality is the 80th largest by area out of the |
||
==General information== |
==General information== |
||
The municipality of Meråker was established on 1 January 1874 when the old |
The municipality of Meråker was established on 1 January 1874 when the old [[Øvre Stjørdalen Municipality]] was divided into two: [[Hegra Municipality]] (population: 3,409) in the east and Meråker Municipality (population: 1,861) in the west. The municipal borders have not changed since then.<ref name="Dag">{{Cite web |last=Jukvam |first=Dag |year=1999 |title=Historisk oversikt over endringer i kommune- og fylkesinndelingen |url=http://www.ssb.no/emner/00/90/rapp_9913/rapp_9913.pdf |publisher=[[Statistics Norway|Statistisk sentralbyrå]] |language=no |isbn=9788253746845}}</ref> On 1 January 2018, the municipality switched from the old [[Nord-Trøndelag]] county to the new [[Trøndelag]] county. |
||
===Name=== |
===Name=== |
||
The municipality (originally the [[prestegjeld|parish]]) is named after the old ''Meråker'' farm (spelled "Mørakre" around 1430) since the first [[Meråker Church]] was built there. The meaning of the first element is uncertain (maybe {{lang|non|merr}} which means "[[mare]]" or {{lang|non|mýrr}} which means "[[bog]]" or "[[marsh]]"). The last element is {{lang|non|akr}} which means "[[field (agriculture)|field]]" or "[[acre]]".<ref>{{Cite book |last=Rygh |first=Oluf |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_kFFxvxaufcC |title=Norske gaardnavne: Nordre Trondhjems amt |date=1903 |publisher=W. C. Fabritius & sønners bogtrikkeri |edition=15 |location=Kristiania, Norge |page=2 |language=no |authorlink=Oluf Rygh}}</ref> |
The municipality (originally the [[prestegjeld|parish]]) is named after the old ''Meråker'' farm (spelled "Mørakre" around 1430) since the first [[Meråker Church]] was built there. The meaning of the first element is uncertain (maybe {{wikt-lang|non|merr}} which means "[[mare]]" or {{wikt-lang|non|mýrr}} which means "[[bog]]" or "[[marsh]]"). The last element is {{wikt-lang|non|akr}} which means "[[field (agriculture)|field]]" or "[[acre]]".<ref>{{Cite book |last=Rygh |first=Oluf |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_kFFxvxaufcC |title=Norske gaardnavne: Nordre Trondhjems amt |date=1903 |publisher=W. C. Fabritius & sønners bogtrikkeri |edition=15 |location=Kristiania, Norge |page=2 |language=no |authorlink=Oluf Rygh}}</ref> Historically, the name of the municipality was spelled ''Meraker''. On 3 November 1917, a [[royal decree|royal resolution]] changed the spelling of the name of the municipality to ''Meraaker''.<ref>{{Cite journal |year=1917 |title=Norsk Lovtidende. 2den Afdeling. 1917. Samling af Love, Resolutioner m.m |url=https://www.nb.no/items/URN:NBN:no-nb_digitidsskrift_2015102381014_001 |journal=[[Norsk Lovtidend]] |language=no |location=Kristiania, Norge |publisher=Grøndahl og Søns Boktrykkeri |pages=1057–1065}}</ref> On 21 December 1917, a [[royal decree|royal resolution]] enacted the [[Norwegian language conflict|1917 Norwegian language reforms]]. Prior to this change, the name was spelled ''Meraaker'' with the [[digraph (orthography)|digraph]] "[[Aa (digraph)|aa]]", and after this reform, the name was spelled ''Meråker'', using the letter [[å]] was instead.<ref>{{Cite journal |year=1917 |title=Norsk Lovtidende. 2den Afdeling. 1917. Samling af Love, Resolutioner m.m |url=https://www.nb.no/items/URN:NBN:no-nb_digitidsskrift_2015102381014_001 |journal=[[Norsk Lovtidend]] |language=no |location=Oslo, Norway |publisher=Grøndahl og Søns Boktrykkeri |page=1000}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |url=https://www.nb.no/items/7c810cb2510e5454433266c698b8808e |title=Den Nye rettskrivning : regler og ordlister |publisher=Den Mallingske Boktrykkeri |year=1918 |location=Kristiania, Norge |language=no}}</ref> |
||
===Coat of arms=== |
===Coat of arms=== |
||
The [[coat of arms]] was granted on 28 September 1990. The official [[blazon]] is ''"[[Gules]], a cart [[argent]]"'' ({{ |
The [[coat of arms]] was granted on 28 September 1990. The official [[blazon]] is ''"[[Gules]], a cart [[argent]]"'' ({{langx|no|I rødt en sølv vogn}}). This means the arms have a red [[field (heraldry)|field]] (background) and the [[charge (heraldry)|charge]] is a [[minecart|mining cart]]. The mining cart has a [[tincture (heraldry)|tincture]] of [[argent]] which means it is commonly colored white, but if it is made out of metal, then silver is used. This design was chosen to symbolize the fact that [[mining]] has traditionally played a major role in the area and has been of great economic importance for Meråker. The municipal flag has the same design as the coat of arms.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Civic heraldry of Norway - Norske Kommunevåpen |url=https://www.heraldry-wiki.com/heraldrywiki/index.php?title=Meråker |access-date=2023-02-15 |publisher=Heraldry of the World}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Meråker, Nord-Trøndelag (Norway) |url=https://www.crwflags.com/fotw/flags/no-17-11.html |access-date=2023-02-15 |website=Flags of the World}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=1990-12-09 |title=Godkjenning av våpen og flagg |url=https://lovdata.no/dokument/LF/forskrift/1990-09-28-821 |access-date=2023-02-15 |website=Lovdata.no |publisher=Norges kommunal- og arbeidsdepartementet |language=no}}</ref> {{See also|Coat of arms of Evje og Hornnes}} |
||
===Churches=== |
===Churches=== |
||
The [[Church of Norway]] has one parish ({{lang|no|sokn}}) within |
The [[Church of Norway]] has one parish ({{lang|no|sokn}}) within Meråker Municipality. It is part of the [[Stjørdal prosti]] ([[deanery]]) in the [[Diocese of Nidaros]]. |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
||
| Line 61: | Line 63: | ||
|[[Kopperå Chapel]]||[[Kopperå]]||1936 |
|[[Kopperå Chapel]]||[[Kopperå]]||1936 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Stordalen Chapel]]||[[ |
|[[Stordalen Chapel]]||[[Stordalsvollen]]||1863 |
||
|} |
|} |
||
==History== |
==History== |
||
===Meråker Smelter=== |
===Meråker Smelter=== |
||
In 1898, a [[carbide]] factory was opened at [[Kopperå]], later this factor was rebuilt as a [[silicon]] smelter. The [[smelter]] was in operation until June 2006. Its main product was [[microsilica]] which is used as an additive to [[cement]]. |
In 1898, a [[carbide]] factory was opened at [[Kopperå]], later this factor was rebuilt as a [[silicon]] smelter. The [[smelter]] was in operation until June 2006. Its main product was [[microsilica]] which is used as an additive to [[cement]]. |
||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
Meråker is a landlocked municipality in the central part of [[Trøndelag]] county. To the north is |
Meråker is a landlocked municipality in the central part of [[Trøndelag]] county. To the north is [[Verdal Municipality]], to the west is [[Stjørdal Municipality]], to the south is [[Selbu Municipality]] and [[Tydal Municipality]], and to the east is [[Åre Municipality]] in [[Sweden]]. |
||
There are three major lakes in Meråker: [[Feren]], [[Fjergen]], and [[Funnsjøen]]. The river [[Stjørdalselva]] runs through the municipality towards the [[Trondheimsfjord]]. The river [[Rotla]] begins in the southern part of Meråker. The mountain [[Fongen]] |
There are three major lakes in Meråker: [[Feren]], [[Fjergen]], and [[Funnsjøen]]. The river [[Stjørdalselva]] runs through the municipality towards the [[Trondheimsfjord]]. The river [[Rotla]] begins in the southern part of Meråker. The highest point in the municipality is the {{convert|1441.36|m|adj=on}} tall mountain [[Fongen]], a [[tripoint]] on the border of Meråker Municipality, [[Selbu Municipality]], and [[Tydal Municipality]].<ref name="elev" /> |
||
==Government== |
==Government== |
||
Meråker Municipality is responsible for [[primary education]] (through 10th grade), outpatient [[Health care|health services]], [[old age|senior citizen]] services, [[welfare]] and other [[Social work|social services]], [[zoning]], [[economic development]], and municipal [[road]]s and utilities. The municipality is governed by a [[Municipal council (Norway)|municipal council]] of [[Direct election|directly elected]] representatives. The [[mayor]] is [[Indirect election|indirectly elected]] by a vote of the municipal council.<ref name="ks">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=kommunestyre |encyclopedia=[[Store norske leksikon]] |publisher=[[Kunnskapsforlaget]] |url=https://snl.no/kommunestyre |date=2022-09-20 |editor-last=Hansen |editor-first=Tore |language=Norwegian |editor2-last=Vabo |editor2-first=Signy Irene |accessdate=2022-10-14}}</ref> The municipality is under the jurisdiction of the [[Trøndelag District Court]] and the [[Frostating Court of Appeal]]. |
|||
===Municipal council=== |
===Municipal council=== |
||
The [[Municipal council (Norway)|municipal council]] ({{lang|no|Kommunestyre}}) of Meråker is made up of |
The [[Municipal council (Norway)|municipal council]] ({{lang|no|Kommunestyre}}) of Meråker is made up of 17 representatives that are elected to four year terms. The tables below show the current and historical composition of the council by political [[Political party|party]]. |
||
{{div col |
{{div col}} |
||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 2023 |
||
|end = 2027 |
|||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |title=Kommunestyrevalg 2023 - Trøndelag Trööndelage |url=https://valgresultat.no/valg/2023/ko/tr%C3%B8ndelag%20tr%C3%B6%C3%B6ndelage/meråker#seats |access-date=2024-01-09 |publisher=[[Valgdirektoratet]]}}</ref> |
|||
|collapsed = |
|||
|Total = 17 |
|||
|Arbeiderpartiet = 4 |
|||
|Rødt = 1 |
|||
|Senterpartiet = 5 |
|||
|Sosialistisk_Venstreparti = 1 |
|||
|otherparty = Meråker Cross-Party Local List<br /> |
|||
|otherparty_no = Meråker Tverrpolitiske Bygdeliste |
|||
|otherparty_number = 6 |
|||
|}} |
|||
{{Kommunestyre table |
|||
|name = Meråker |
|||
|start = 2019 |
|||
|end = 2023 |
|end = 2023 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |title=Tall for Norge: Kommunestyrevalg 2019 - Trøndelag |url=https://valgresultat.no/tr%C3%B8ndelag/ |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |title=Tall for Norge: Kommunestyrevalg 2019 - Trøndelag |url=https://valgresultat.no/valg/2019/ko/tr%C3%B8ndelag/mer%C3%A5ker#seats |access-date=2019-10-20 |publisher=Valg Direktoratet}}</ref> |
||
|collapsed = yes |
|||
|Total = 21 |
|Total = 21 |
||
|Arbeiderpartiet = 5 |
|Arbeiderpartiet = 5 |
||
| Line 97: | Line 114: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 2015 |
||
|end = 2019 |
|end = 2019 |
||
|reference = <ref name="ssb valg">{{Cite web |title=Table: 04813: Members of the local councils, by party/electoral list at the Municipal Council election (M) |url=https://www.ssb.no/en/statbank/table/04813/ |publisher=Statistics Norway |language=no}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref name="ssb valg">{{Cite web |title=Table: 04813: Members of the local councils, by party/electoral list at the Municipal Council election (M) |url=https://www.ssb.no/en/statbank/table/04813/ |publisher=Statistics Norway |language=no}}</ref> |
||
| Line 113: | Line 130: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 2011 |
||
|end = 2015 |
|end = 2015 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |title=Tall for Norge: Kommunestyrevalg 2011 - Nord-Trøndelag |url=https://valgresultat.no/nord-tr%C3%B8ndelag/ |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |title=Tall for Norge: Kommunestyrevalg 2011 - Nord-Trøndelag |url=https://valgresultat.no/valg/2011/ko/nord-tr%C3%B8ndelag/mer%C3%A5ker#seats |access-date=2019-10-20 |publisher=Valg Direktoratet}}</ref> |
||
|collapsed = yes |
|collapsed = yes |
||
|Total = 21 |
|Total = 21 |
||
| Line 130: | Line 147: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 2007 |
||
|end = 2011 |
|end = 2011 |
||
|reference = <ref name="ssb valg" /> |
|reference = <ref name="ssb valg" /> |
||
| Line 147: | Line 164: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 2003 |
||
|end = 2007 |
|end = 2007 |
||
|reference = <ref name="ssb valg" /> |
|reference = <ref name="ssb valg" /> |
||
| Line 163: | Line 180: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1999 |
||
|end = 2003 |
|end = 2003 |
||
|reference = <ref name="ssb valg" /> |
|reference = <ref name="ssb valg" /> |
||
| Line 179: | Line 196: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1995 |
||
|end = 1999 |
|end = 1999 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1996 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1995 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_c342.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo-Kongsvinger}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1996 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1995 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_c342.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo-Kongsvinger}}</ref> |
||
| Line 195: | Line 212: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1991 |
||
|end = 1995 |
|end = 1995 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1993 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1991 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_c057.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo-Kongsvinger}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1993 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1991 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_c057.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo-Kongsvinger}}</ref> |
||
| Line 208: | Line 225: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1987 |
||
|end = 1991 |
|end = 1991 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1988 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1987 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_b765.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo-Kongsvinger}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1988 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1987 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_b765.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo-Kongsvinger}}</ref> |
||
| Line 221: | Line 238: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1983 |
||
|end = 1987 |
|end = 1987 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1984 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1983 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_b450.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo-Kongsvinger}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1984 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1983 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_b450.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo-Kongsvinger}}</ref> |
||
| Line 234: | Line 251: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1979 |
||
|end = 1983 |
|end = 1983 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1979 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1979 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_b093.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1979 |title=Kommunestyrevalget 1979 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_b093.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 251: | Line 268: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1975 |
||
|end = 1979 |
|end = 1979 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1977 |title=Kommunevalgene 1975 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_a769.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1977 |title=Kommunevalgene 1975 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_a769.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 263: | Line 280: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1971 |
||
|end = 1975 |
|end = 1975 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1973 |title=Kommunevalgene 1972 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_a457.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1973 |title=Kommunevalgene 1972 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_a457.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 276: | Line 293: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1967 |
||
|end = 1971 |
|end = 1971 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1967 |title=Kommunevalgene 1967 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_a214.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo |volume=I}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1967 |title=Kommunevalgene 1967 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_a214.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo |volume=I}}</ref> |
||
| Line 289: | Line 306: | ||
{{Kommunestyre table |
{{Kommunestyre table |
||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|start = |
|start = 1963 |
||
|end = 1967 |
|end = 1967 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1964 |title=Kommunevalgene 1963 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_xii_138.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1964 |title=Kommunevalgene 1963 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_xii_138.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 302: | Line 319: | ||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|herad = yes |
|herad = yes |
||
|start = |
|start = 1959 |
||
|end = 1963 |
|end = 1963 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1960 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1959 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_xii_022.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1960 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1959 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_xii_022.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 315: | Line 332: | ||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|herad = yes |
|herad = yes |
||
|start = |
|start = 1955 |
||
|end = 1959 |
|end = 1959 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1957 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1955 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_xi_252.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1957 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1955 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_xi_252.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 327: | Line 344: | ||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|herad = yes |
|herad = yes |
||
|start = |
|start = 1951 |
||
|end = 1955 |
|end = 1955 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1952 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1951 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_xi_120.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1952 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1951 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_xi_120.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 339: | Line 356: | ||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|herad = yes |
|herad = yes |
||
|start = |
|start = 1947 |
||
|end = 1951 |
|end = 1951 |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1948 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1947 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_x_165.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1948 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1947 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_x_165.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 363: | Line 380: | ||
|name = Meråker |
|name = Meråker |
||
|herad = yes |
|herad = yes |
||
|start = |
|start = 1937 |
||
|end = 1941* |
|end = 1941* |
||
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1938 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1937 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_ix_133.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
|reference = <ref>{{Cite web |date=1938 |title=Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1937 |url=https://www.ssb.no/a/histstat/nos/nos_ix_133.pdf |access-date=2020-04-12 |publisher=Statistisk sentralbyrå |language=no |location=Oslo}}</ref> |
||
| Line 375: | Line 392: | ||
===Mayors=== |
===Mayors=== |
||
The |
The [[Mayor#Scandinavia|mayor]] ({{langx|no|ordfører}}) of Meråker is the political leader of the municipality and the chairperson of the municipal council. Here is a list of people who have held this position:<ref>{{Cite book |last=Krogstad |first=Bjørn R. |url=http://urn.nb.no/URN:NBN:no-nb_digibok_2014062606076 |title=Bygdebok for Meråker |publisher=Meråker kommune |year=1987 |volume=2 |language=no}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Straume |first=Kaurin |title=Meråker kommune 100 år 1874–1974. |publisher=Meråker kommune |year=1973 |page=7 |language=no}}</ref> |
||
{{div col|colwidth=20em}} |
{{div col|colwidth=20em}} |
||
*1874–1877: Christian Erlandsen |
*1874–1877: Christian Erlandsen |
||
| Line 398: | Line 415: | ||
*1995-2015: [[Bård Langsåvold]] ([[Labour Party (Norway)|Ap]]) |
*1995-2015: [[Bård Langsåvold]] ([[Labour Party (Norway)|Ap]]) |
||
*2015-2019: Kari Anita Furunes ([[Centre Party (Norway)|Sp]]) |
*2015-2019: Kari Anita Furunes ([[Centre Party (Norway)|Sp]]) |
||
* |
*2019–2023: Kjersti Kjenes ([[Bygdeliste|LL]]) |
||
*2023-present: Kari Anita Furunes ([[Centre Party (Norway)|Sp]])<ref>{{Cite news |date=2023-09-13 |title=Meråker: Senterpartiet får ordføreren |url=https://www.nrk.no/trondelag/meraker_-senterpartiet-far-ordforeren-1.16555453 |access-date=2024-01-07 |work=[[NRK]] |language=no}}</ref> |
|||
{{div col end}} |
{{div col end}} |
||
| Line 407: | Line 425: | ||
The newspaper ''[[Meråkerposten]]'' has been published in Meråker since 1982.<ref name="snl3">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Meråkerposten |encyclopedia=[[Store norske leksikon]] |publisher=[[Kunnskapsforlaget]] |url=https://snl.no/Mer%C3%A5kerposten |access-date=2018-03-24 |date=2016-12-01 |editor-last=Smith-Meyer |editor-first=Trond |language=no}}</ref> |
The newspaper ''[[Meråkerposten]]'' has been published in Meråker since 1982.<ref name="snl3">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Meråkerposten |encyclopedia=[[Store norske leksikon]] |publisher=[[Kunnskapsforlaget]] |url=https://snl.no/Mer%C3%A5kerposten |access-date=2018-03-24 |date=2016-12-01 |editor-last=Smith-Meyer |editor-first=Trond |language=no}}</ref> |
||
==Notable |
==Notable people== |
||
[[File:Bård Langsåvold.JPG|145px|thumb|Bård Langsåvold, 2013]] |
[[File:Bård Langsåvold.JPG|145px|thumb|Bård Langsåvold, 2013]] |
||
* [[Anton Johnson Fridrichsen]] (1888 in Meråker – 1953) a Swedish theologian |
* [[Anton Johnson Fridrichsen]] (1888 in Meråker – 1953), a Swedish theologian |
||
* [[Helge Ingstad]] (1899 in Meråker - 2001) [[author]], explorer and [[Archaeology|archeologist]] |
* [[Helge Ingstad]] (1899 in Meråker - 2001), an [[author]], explorer, and [[Archaeology|archeologist]] |
||
* [[Arne Braa Saatvedt]] (1922 in Meråker – 1945) a Norwegian police official and member of the [[Nasjonal Samling]] |
* [[Arne Braa Saatvedt]] (1922 in Meråker – 1945), a Norwegian police official and member of the [[Nasjonal Samling]]; executed in 1945 |
||
* [[Bård Langsåvold]] (born 1952) a Norwegian politician |
* [[Bård Langsåvold]] (born 1952), a Norwegian politician and Mayor of Meråker from 1995-2015 |
||
* [[Dag Lyseid]] (1954–2012) a footballer and politician |
* [[Dag Lyseid]] (1954–2012), a footballer and politician and deputy Mayor of Meråker from 1999-2008 |
||
* [[Vebjørn Selbekk]] (born 1969) a newspaper editor and author |
* [[Vebjørn Selbekk]] (born 1969), a newspaper editor and author who was brought up in Meråker |
||
=== Sport === |
=== Sport === |
||
* [[Magnar Lundemo]] (1938 in Meråker - 1987) a [[cross-country skiing (sport)|cross country skier]] and track and field athlete |
* [[Magnar Lundemo]] (1938 in Meråker - 1987), a [[cross-country skiing (sport)|cross country skier]] and track and field athlete who competed at the [[1960 Winter Olympics|1960]] and [[1964 Winter Olympics]] |
||
* [[Frode Estil]] (born 1972) a retired [[Cross-country skiing (sport)|cross country skier]] |
* [[Frode Estil]] (born 1972), a retired [[Cross-country skiing (sport)|cross country skier]] who lives in Meråker |
||
* [[Kine Beate Bjørnås]] (born 1980) a retired [[Cross-country skiing (sport)|cross country skier]] |
* [[Kine Beate Bjørnås]] (born 1980), a retired [[Cross-country skiing (sport)|cross country skier]] |
||
* [[Simen Raaen Sandmæl]] (born 1990 in Meråker) a Norwegian footballer with over 130 club caps |
* [[Simen Raaen Sandmæl]] (born 1990 in Meråker), a Norwegian footballer with over 130 club caps |
||
==Media gallery == |
==Media gallery == |
||
<gallery mode=packed> |
<gallery mode="packed" heights="140px"> |
||
Meråker, Norway - panoramio.jpg|Meråker, Norway |
Meråker, Norway - panoramio.jpg|Meråker, Norway |
||
Meråker smelteverk Kopperå 01.jpg|Meråker smelteverk Kopperå |
Meråker smelteverk Kopperå 01.jpg|Meråker smelteverk Kopperå |
||
| Line 431: | Line 449: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist |
{{reflist}} |
||
==External links== |
|||
{{commons category|Meråker}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{sister bar|auto=y|d=y|commonscat=y|voy=Trøndelag|wikt=Meråker}} |
|||
{{Trøndelag}} |
{{Trøndelag}} |
||
{{authority control}} |
{{authority control}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Meraaker}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Meraaker}} |
||
| Line 444: | Line 460: | ||
[[Category:Municipalities of Trøndelag]] |
[[Category:Municipalities of Trøndelag]] |
||
[[Category:1874 establishments in Norway]] |
[[Category:1874 establishments in Norway]] |
||
[[Category:Populated places established in 1874]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 03:25, 24 December 2024
Meråker Municipality
Meråker kommune | |
|---|---|
| Meraaker herred (historic name) Meraker herred (historic name) | |
 View of the Meråker valley | |
 Trøndelag within Norway | |
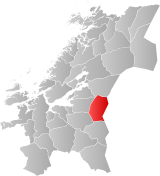 Meråker within Trøndelag | |
| Coordinates: 63°26′17″N 11°50′58″E / 63.43806°N 11.84944°E | |
| Country | Norway |
| County | Trøndelag |
| District | Stjørdalen |
| Established | 1 Jan 1874 |
| • Preceded by | Øvre Stjørdalen Municipality |
| Administrative centre | Midtbygda |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2023) | Kari Anita Furunes (Sp) |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,273.94 km2 (491.87 sq mi) |
| • Land | 1,188.06 km2 (458.71 sq mi) |
| • Water | 85.88 km2 (33.16 sq mi) 6.7% |
| • Rank | #80 in Norway |
| Highest elevation | 1,441.36 m (4,728.87 ft) |
| Population (2024) | |
• Total | 2,454 |
| • Rank | #259 in Norway |
| • Density | 1.9/km2 (5/sq mi) |
| • Change (10 years) | |
| Demonym | Meråkerbygg[2] |
| Official language | |
| • Norwegian form | Bokmål |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | NO-5034[4] |
| Website | Official website |
Meråker is a municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. It is part of the Stjørdalen region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Midtbygda which is about 20 kilometres (12 mi) west of Storlien in Sweden and 46 kilometres (29 mi) east of the town of Stjørdalshalsen in neighboring Stjørdal Municipality. Other villages in the municipality include Gudåa, Kopperå, and Stordalsvollen.
The 1,274-square-kilometre (492 sq mi) municipality is the 80th largest by area out of the 357 municipalities in Norway. Meråker is the 259th most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 2,454. The municipality's population density is 1.9 inhabitants per square kilometre (4.9/sq mi) and its population has decreased by 3.9% over the previous 10-year period.[5][6]
The municipality markets itself as a recreational area. The main areas of employment are in industry and agriculture. The municipality is noted for its characteristic dialect.
General information
[edit]The municipality of Meråker was established on 1 January 1874 when the old Øvre Stjørdalen Municipality was divided into two: Hegra Municipality (population: 3,409) in the east and Meråker Municipality (population: 1,861) in the west. The municipal borders have not changed since then.[7] On 1 January 2018, the municipality switched from the old Nord-Trøndelag county to the new Trøndelag county.
Name
[edit]The municipality (originally the parish) is named after the old Meråker farm (spelled "Mørakre" around 1430) since the first Meråker Church was built there. The meaning of the first element is uncertain (maybe merr which means "mare" or mýrr which means "bog" or "marsh"). The last element is akr which means "field" or "acre".[8] Historically, the name of the municipality was spelled Meraker. On 3 November 1917, a royal resolution changed the spelling of the name of the municipality to Meraaker.[9] On 21 December 1917, a royal resolution enacted the 1917 Norwegian language reforms. Prior to this change, the name was spelled Meraaker with the digraph "aa", and after this reform, the name was spelled Meråker, using the letter å was instead.[10][11]
Coat of arms
[edit]The coat of arms was granted on 28 September 1990. The official blazon is "Gules, a cart argent" (Norwegian: I rødt en sølv vogn). This means the arms have a red field (background) and the charge is a mining cart. The mining cart has a tincture of argent which means it is commonly colored white, but if it is made out of metal, then silver is used. This design was chosen to symbolize the fact that mining has traditionally played a major role in the area and has been of great economic importance for Meråker. The municipal flag has the same design as the coat of arms.[12][13][14]
Churches
[edit]The Church of Norway has one parish (sokn) within Meråker Municipality. It is part of the Stjørdal prosti (deanery) in the Diocese of Nidaros.
| Parish (sokn) | Church name | Location of the church | Year built |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meråker | Meråker Church | Midtbygda | 1874 |
| Kopperå Chapel | Kopperå | 1936 | |
| Stordalen Chapel | Stordalsvollen | 1863 |
History
[edit]Meråker Smelter
[edit]In 1898, a carbide factory was opened at Kopperå, later this factor was rebuilt as a silicon smelter. The smelter was in operation until June 2006. Its main product was microsilica which is used as an additive to cement.
Geography
[edit]Meråker is a landlocked municipality in the central part of Trøndelag county. To the north is Verdal Municipality, to the west is Stjørdal Municipality, to the south is Selbu Municipality and Tydal Municipality, and to the east is Åre Municipality in Sweden.
There are three major lakes in Meråker: Feren, Fjergen, and Funnsjøen. The river Stjørdalselva runs through the municipality towards the Trondheimsfjord. The river Rotla begins in the southern part of Meråker. The highest point in the municipality is the 1,441.36-metre (4,728.9 ft) tall mountain Fongen, a tripoint on the border of Meråker Municipality, Selbu Municipality, and Tydal Municipality.[1]
Government
[edit]Meråker Municipality is responsible for primary education (through 10th grade), outpatient health services, senior citizen services, welfare and other social services, zoning, economic development, and municipal roads and utilities. The municipality is governed by a municipal council of directly elected representatives. The mayor is indirectly elected by a vote of the municipal council.[15] The municipality is under the jurisdiction of the Trøndelag District Court and the Frostating Court of Appeal.
Municipal council
[edit]The municipal council (Kommunestyre) of Meråker is made up of 17 representatives that are elected to four year terms. The tables below show the current and historical composition of the council by political party.
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 4 | |
| Red Party (Rødt) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 5 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Meråker Cross-Party Local List (Meråker Tverrpolitiske Bygdeliste) | 6 | |
| Total number of members: | 17 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 5 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 7 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 1 | |
| Meråker Cross-Party Local List (Meråker Tverrpolitiske Bygdeliste) | 5 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 6 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 4 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Meråker Cross-Party Local List (Meråker Tverrpolitiske Bygdeliste) | 6 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 7 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 1 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 2 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Meråker Cross-Party Local List (Meråker Tverrpolitiske Bygdeliste) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 1 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 1 | |
| Meråker cross-party local list (Meråker tverrpolitiske bygdeliste) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 10 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 3 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Meråker Cross-party Local List (Meråker Tverrpolitiske Bygdeliste) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 10 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 4 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 1 | |
| Meråker Cross-party local list (Meråker Tverrpolitisk bygdeliste) | 4 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 10 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Meråker Cross-party local list (Meråker Tverrpolitiske bygdeliste) | 4 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 5 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 12 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 2 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 2 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 1 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 6 | |
| Joint list of the New People's Party and independent voters (Det Nye Folkepartiet og uavhengige velgere) |
1 | |
| Joint list of the Conservative Party (Høyre) and Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 1 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 3 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Joint list of the Conservative Party (Høyre), Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti), and Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 13 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 2 | |
| Socialist People's Party (Sosialistisk Folkeparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Local List(s) (Lokale lister) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 13 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 1 | |
| Socialist People's Party (Sosialistisk Folkeparti) | 3 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 15 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Joint List(s) of Non-Socialist Parties (Borgerlige Felleslister) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 13 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Joint List(s) of Non-Socialist Parties (Borgerlige Felleslister) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 13 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 3 | |
| Joint List(s) of Non-Socialist Parties (Borgerlige Felleslister) | 5 | |
| Total number of members: | 21 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 4 | |
| Joint List(s) of Non-Socialist Parties (Borgerlige Felleslister) | 5 | |
| Total number of members: | 20 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 5 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Total number of members: | 20 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 6 | |
| Joint List(s) of Non-Socialist Parties (Borgerlige Felleslister) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 20 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 12 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 4 | |
| Joint List(s) of Non-Socialist Parties (Borgerlige Felleslister) | 5 | |
| Total number of members: | 20 | |
| Note: Due to the German occupation of Norway during World War II, no elections were held for new municipal councils until after the war ended in 1945. | ||
Mayors
[edit]The mayor (Norwegian: ordfører) of Meråker is the political leader of the municipality and the chairperson of the municipal council. Here is a list of people who have held this position:[35][36]
- 1874–1877: Christian Erlandsen
- 1878–1885: John Johnsen
- 1886–1887: Iver Lie
- 1888–1893: Fredrik Rø (V)
- 1894–1897: O. Hugdahl
- 1898–1907: Fredrik Rø (V)
- 1908–1910: Carl Olaf Iversen (H)
- 1911–1913: Olav Stubban (Ap)
- 1914–1916: Ole E. Wollan (Ap)
- 1917–1922: Peder J. Myrmo (Ap)
- 1923–1925: Arne Bergsaas (Ap)
- 1926–1937: Kristian Rothaug (Ap)
- 1938–1939: Joar Eimhjellen (Ap)
- 1939–1941: Alf Karlsen (Ap)
- 1942-1942: Arild Solberg (NS)
- 1943–1945: Alf Hembre (NS)
- 1945–1966: Alf Karlsen (Ap)
- 1967–1973: Johnny Stenberg (Ap)
- 1973-1995: Svein Brækken (Ap)
- 1995-2015: Bård Langsåvold (Ap)
- 2015-2019: Kari Anita Furunes (Sp)
- 2019–2023: Kjersti Kjenes (LL)
- 2023-present: Kari Anita Furunes (Sp)[37]
Transportation
[edit]The European route E14 highway runs east to west through the municipality connecting to Trondheim Airport, Værnes about 40 kilometres (25 mi) to the west. The Meråker Line railway follows the E14 through the municipality also, with stops at Kopperå Station, Meråker Station, and Gudå Station.
Media
[edit]The newspaper Meråkerposten has been published in Meråker since 1982.[38]
Notable people
[edit]
- Anton Johnson Fridrichsen (1888 in Meråker – 1953), a Swedish theologian
- Helge Ingstad (1899 in Meråker - 2001), an author, explorer, and archeologist
- Arne Braa Saatvedt (1922 in Meråker – 1945), a Norwegian police official and member of the Nasjonal Samling; executed in 1945
- Bård Langsåvold (born 1952), a Norwegian politician and Mayor of Meråker from 1995-2015
- Dag Lyseid (1954–2012), a footballer and politician and deputy Mayor of Meråker from 1999-2008
- Vebjørn Selbekk (born 1969), a newspaper editor and author who was brought up in Meråker
Sport
[edit]- Magnar Lundemo (1938 in Meråker - 1987), a cross country skier and track and field athlete who competed at the 1960 and 1964 Winter Olympics
- Frode Estil (born 1972), a retired cross country skier who lives in Meråker
- Kine Beate Bjørnås (born 1980), a retired cross country skier
- Simen Raaen Sandmæl (born 1990 in Meråker), a Norwegian footballer with over 130 club caps
Media gallery
[edit]-
Meråker, Norway
-
Meråker smelteverk Kopperå
-
Elven Kopperåa i Kopperå, Meråker
-
Grønbergdammen in Meråker
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Høgaste fjelltopp i kvar kommune" (in Norwegian). Kartverket. 16 January 2024.
- ^ "Navn på steder og personer: Innbyggjarnamn" (in Norwegian). Språkrådet.
- ^ "Forskrift om målvedtak i kommunar og fylkeskommunar" (in Norwegian). Lovdata.no.
- ^ Bolstad, Erik; Thorsnæs, Geir, eds. (26 January 2023). "Kommunenummer". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget.
- ^ Statistisk sentralbyrå. "Table: 06913: Population 1 January and population changes during the calendar year (M)" (in Norwegian).
- ^ Statistisk sentralbyrå. "09280: Area of land and fresh water (km²) (M)" (in Norwegian).
- ^ Jukvam, Dag (1999). "Historisk oversikt over endringer i kommune- og fylkesinndelingen" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Statistisk sentralbyrå. ISBN 9788253746845.
- ^ Rygh, Oluf (1903). Norske gaardnavne: Nordre Trondhjems amt (in Norwegian) (15 ed.). Kristiania, Norge: W. C. Fabritius & sønners bogtrikkeri. p. 2.
- ^ "Norsk Lovtidende. 2den Afdeling. 1917. Samling af Love, Resolutioner m.m". Norsk Lovtidend (in Norwegian). Kristiania, Norge: Grøndahl og Søns Boktrykkeri: 1057–1065. 1917.
- ^ "Norsk Lovtidende. 2den Afdeling. 1917. Samling af Love, Resolutioner m.m". Norsk Lovtidend (in Norwegian). Oslo, Norway: Grøndahl og Søns Boktrykkeri: 1000. 1917.
- ^ Den Nye rettskrivning : regler og ordlister (in Norwegian). Kristiania, Norge: Den Mallingske Boktrykkeri. 1918.
- ^ "Civic heraldry of Norway - Norske Kommunevåpen". Heraldry of the World. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ^ "Meråker, Nord-Trøndelag (Norway)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ^ "Godkjenning av våpen og flagg". Lovdata.no (in Norwegian). Norges kommunal- og arbeidsdepartementet. 9 December 1990. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ^ Hansen, Tore; Vabo, Signy Irene, eds. (20 September 2022). "kommunestyre". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Retrieved 14 October 2022.
- ^ "Kommunestyrevalg 2023 - Trøndelag Trööndelage". Valgdirektoratet. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ^ "Tall for Norge: Kommunestyrevalg 2019 - Trøndelag". Valg Direktoratet. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ a b c d "Table: 04813: Members of the local councils, by party/electoral list at the Municipal Council election (M)" (in Norwegian). Statistics Norway.
- ^ "Tall for Norge: Kommunestyrevalg 2011 - Nord-Trøndelag". Valg Direktoratet. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ "Kommunestyrevalget 1995" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1996. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunestyrevalget 1991" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1993. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunestyrevalget 1987" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1988. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunestyrevalget 1983" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1984. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunestyrevalget 1979" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1979. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene 1975" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1977. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene 1972" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1973. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene 1967" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1967. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene 1963" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1964. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1959" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1960. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1955" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1957. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1951" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1952. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1947" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1948. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1945" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1947. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1937" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1938. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ Krogstad, Bjørn R. (1987). Bygdebok for Meråker (in Norwegian). Vol. 2. Meråker kommune.
- ^ Straume, Kaurin (1973). Meråker kommune 100 år 1874–1974 (in Norwegian). Meråker kommune. p. 7.
- ^ "Meråker: Senterpartiet får ordføreren". NRK (in Norwegian). 13 September 2023. Retrieved 7 January 2024.
- ^ Smith-Meyer, Trond, ed. (1 December 2016). "Meråkerposten". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Retrieved 24 March 2018.