Cat: Difference between revisions
Reverted to revision 377948382 by Wolfkeeper; needs to be sourced, see WP:SOURCE. (TW) |
BhagyaMani (talk | contribs) →top: revised |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Small domesticated mammal}} |
|||
:''This article deals with the domestic feline. For other uses, see [[Cat (disambiguation)]] or [[Cats (disambiguation)]].'' |
|||
{{About|the species commonly kept as a pet|the cat family|Felidae|other uses|Cat (disambiguation)|and|Cats (disambiguation)}} |
|||
<!-- - per [[Wikipedia:Manual of Style (spelling)]], articles should conform to one overall spelling style of English, typically the one most linked to the article topic (if it is geographic based in some way) or the one it was created in. This article was created with American English. Please do not change the image in the infobox without prior discussion on the talk page. --> |
|||
{{Good article}} |
|||
{{Taxobox |
|||
{{pp-move|small=yes}} |
|||
| name = Domestic cat<ref name=msw3/> |
|||
{{pp-semi-indef|small=yes}} |
|||
| status = DOM |
|||
{{Use American English|date=October 2024}} |
|||
<!-- There has been extensive discussion about the choice of image in this infobox. Before replacing this image with something else, consider if it actually improves on the ENCYCLOPEDIC CRITERIA which led to this choice. See [[Talk:Cat]] and [[Talk:Cat/Lead photo]] and if in doubt, DISCUSS IT FIRST! --> |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2024}}<!-- Per MOS:ENGVAR and MOS:DATEVAR, articles should conform to one overall spelling of English and date format, typically the ones with which it was created when the topic has no strong national ties. This article was created with American English, using international date format (DD Month YYYY), and should continue to be written that way. If there is a compelling reason to change it propose a change on the talk page. --> |
|||
| image = Collage of Six Cats-02.jpg<!--please do not change without consensus, see talk page--> |
|||
{{Speciesbox |
|||
| image_width= 250px |
|||
|name=Cat |
|||
| image_caption = [[commons:Category:Felis silvestris catus|Cats]] |
|||
<!-- There has been extensive discussion about the choice of image in this infobox. Before replacing this image with something else, consider if it actually improves on the ENCYCLOPEDIC CRITERIA that led to this choice. See [[Talk:Cat]] and [[Talk:Cat/Lead photo]] and if in doubt, DISCUSS IT FIRST! --> |
|||
| regnum = [[Animal]]ia |
|||
|fossil_range= {{fossil range|0.0095|0}}<br/> [[Holocene]] to present (9,500 years ago) |
|||
| phylum = [[Chordate|Chordata]] |
|||
|image={{Multiple image |
|||
| classis = [[Mammal]]ia |
|||
|perrow=2/2/2 |
|||
| ordo = [[Carnivora]] |
|||
|total_width=275 |
|||
| familia = [[Felidae]] |
|||
|image1=Cat August 2010-4.jpg |
|||
| genus = ''[[Felis]]'' |
|||
|image2=Gustav chocolate.jpg |
|||
| species = '''''F. catus''''' |
|||
|image3=Orange tabby cat sitting on fallen leaves-Hisashi-01A.jpg |
|||
| binomial = ''Felis catus'' |
|||
|image4=Siam lilacpoint.jpg |
|||
| binomial_authority = ([[Carl Linnaeus|Linnaeus]], 1758)<ref name="Linaeus1758" /> |
|||
|image5=Felis catus-cat on snow.jpg |
|||
| synonyms = <small>''Felis catus domestica'' (invalid junior synonym)<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|image6=Sheba1.JPG |
|||
| url = http://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=727487 |
|||
|border=infobox |
|||
| title = ITIS Standard Report Page: Felis catus domestica |
|||
|footer=Various types of cats |
|||
| author = [[Integrated Taxonomic Information System|ITIS]]}}</ref><br /> |
|||
}} |
|||
''Felis silvestris catus''<ref name=Driscoll /></small> |
|||
|status=DOM |
|||
|genus=Felis |
|||
|species=catus<ref name="Linnaeus1758"/> |
|||
|authority=[[Carl Linnaeus|Linnaeus]], [[10th edition of Systema Naturae|1758]]<ref name="MSW3fc"/> |
|||
|synonyms=*''Catus domesticus'' {{small|[[Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben|Erxleben]], 1777}}<ref name=Erxleben>{{Cite book |last=Erxleben |first=J. C. P. |date=1777 |title=Systema regni animalis per classes, ordines, genera, species, varietates cvm synonymia et historia animalivm. Classis I. Mammalia |location=Lipsiae |publisher=Weygandt |pages=520–521 |chapter=Felis Catus domesticus |chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/iochristpolycerx00erxl/page/520}}</ref> |
|||
* ''F. angorensis'' {{small|[[Karl Christian Gmelin|Gmelin]], 1788}} |
|||
* ''F. vulgaris'' {{small|Fischer, 1829}} |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''cat''' ('''''Felis catus'''''), also referred to as the '''domestic cat''', is a small [[Domestication|domesticated]] carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated [[species]] of the family [[Felidae]]. Advances in [[archaeology]] and [[genetics]] have shown that the [[domestication of the cat]] occurred in the [[Near East]] around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a [[pet]] and [[farm cat]], but also ranges freely as a [[feral cat]] avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill [[vermin]]. Its retractable [[claw]]s are adapted to killing small prey species such as [[mice]] and [[rat]]s. It has a strong, flexible body, quick [[reflex]]es, and sharp teeth, and its [[night vision]] and [[sense of smell]] are well developed. It is a [[social species]], but a solitary hunter and a [[crepuscular]] [[predator]]. [[Cat communication]] includes vocalizations—including [[meow]]ing, [[purr]]ing, trilling, [[Wiktionary:hiss|hissing]], [[growling]], and [[Wiktionary:grunt|grunting]]—as well as [[cat body language|body language]]. It can hear sounds too faint or too high in [[frequency]] for human ears, such as those made by [[small mammal]]s. It secretes and perceives [[pheromone]]s. |
|||
The '''cat''' (''Felis catus''), also known as the '''domestic cat''' or '''housecat'''<ref>[http://education.yahoo.com/reference/dictionary/entry/housecat "Housecat" in the American Heritage Dictionary]</ref> to distinguish it from other [[felinae|felines]] and [[felidae|felids]], is a small [[Domestication|domesticated]] [[carnivore|carnivorous]] [[mammal]] that is valued by humans for its companionship and ability to hunt [[vermin]] and household pests. Cats have been associated with humans for at least 9,500 years,<ref name="9500 years">{{cite web | title = Oldest Known Pet Cat? 9500-Year-Old Burial Found on Cyprus | url = http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2004/04/0408_040408_oldestpetcat.html | accessdate = 2007-03-06 |date=2004-04-08 | publisher = National Geographic News}}</ref> and are currently the most popular pet in the world.<ref name=SciAm>{{cite web |url=http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=the-taming-of-the-cat |title=The Evolution of House Cats |publisher=Scientific American |author=Carlos A. Driscoll, Juliet Clutton-Brock, Andrew C. Kitchener and Stephen J. O'Brien |accessdate=26 August 2009}}</ref> Owing to their close association with humans, cats are now found almost everywhere on Earth. Their adaptability, rapid breeding rate, and predatory instincts make them effective hunters. In some locations, cats have affected indigenous animal populations; this has led them to be classified as an [[invasive species]] in some areas. Many problems are caused by the large number of [[feral cat]]s worldwide, with a population of up to 60 million of these animals in the United States alone.<ref name=Rochlitz/> Failure to control the breeding of pet cats by spaying and neutering and the abandonment of former household pets cause the development of such feral colonies. |
|||
Female domestic cats can have [[kitten]]s from [[Spring (season)|spring]] to late [[autumn]] in [[temperate zones]] and throughout the year in [[equatorial region]]s, with [[Litter (zoology)|litter]] sizes often ranging from two to five kittens. Domestic cats are bred and shown at events as registered [[pedigreed cat]]s, a hobby known as [[cat fancy]]. [[Animal population control]] of cats may be achieved by [[spaying]] and [[neutering]], but their proliferation and the abandonment of pets has resulted in large numbers of feral cats worldwide, contributing to the extinction of [[bird]], [[mammal]], and [[reptile]] species. |
|||
Cats are similar in anatomy to the other [[felid]]s, with strong, flexible bodies, quick reflexes, sharp retractable claws, and teeth adapted to killing small prey. As nocturnal predators, cats use their acute hearing and ability to see in near darkness to locate prey. Not only can cats hear sounds too faint for human ears, they can also hear sounds higher in frequency than humans can perceive. This is because cats' usual prey (particularly rodents such as mice) make high frequency noises, so cats' hearing has [[evolution|evolved]] to pinpoint these faint high-pitched sounds. Cats rely more on smell than taste, and have a vastly better sense of smell than humans. |
|||
{{As of|2017|post=,}} the domestic cat was the second most popular pet in the United States, with 95.6 million cats owned and around 42 million households owning at least one cat. In the United Kingdom, 26% of adults have a cat, with an estimated population of 10.9 million pet cats {{As of|2020|lc=y|post=.}} {{As of|2021|post=,}} there were an estimated 220 million owned and 480 million stray cats in the world. |
|||
Despite being solitary hunters, cats are a social species and use a variety of [[animal communication|vocalization]]s, [[pheromone]]s and types of [[Cat body language|body language]] for [[cat communication|communication]]. These include [[cat communication#Meowing|meow]]ing, [[purr]]ing, [[trill consonant|trilling]], [[hiss#Animals|hissing]], [[growling]], and grunting.<ref name=Moelk/> They are also bred and shown as [[Cat registry|registered]] pedigree pets. This hobby is known as [[animal fancy|cat fancy]]. |
|||
== Etymology and naming == |
|||
As ''[[The New York Times]]'' wrote in 2007, "Until recently the cat was commonly believed to have been domesticated in [[ancient Egypt]], where it was a [[Animal_cult#Cats|cult animal]]."<ref name="NYT">{{cite news |
|||
The origin of the English word ''cat'', [[Old English]] {{lang|ang|catt}}, is thought to be the [[Late Latin]] word {{lang|la|cattus}}, which was first used at the beginning of the 6th century.<ref>{{Cite book |last=McKnight |first=G. H. |title=English Words and Their Background |publisher=[[D. Appleton and Company]]|location=New York, London |date=1923 |chapter=Words and Archaeology |pages=293–311 |chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/englishwordsthei00mckn/page/300}}</ref> The Late Latin word may be derived from an unidentified [[Languages of Africa|African language]].<ref>{{cite book |last=Pictet |first=A. |date=1859 |title=Les origines indo-européennes ou les Aryas primitifs : essai de paléontologie linguistique |language=fr |volume=1 |location=Paris |publisher=Joël Cherbuliez |page=381}}</ref> The [[Nubian languages|Nubian]] word {{lang|nub|kaddîska}} 'wildcat' and [[Nobiin language|Nobiin]] {{lang|nub|kadīs}} are possible sources or cognates.<ref>{{cite book |last=Keller |first=O. |date=1909 |title=Die antike Tierwelt |language=de |volume=Säugetiere |location=Leipzig |page=75 |publisher=[[Walther von Wartburg]]}}</ref> |
|||
| url = http://www.nytimes.com/2007/06/29/science/29cat.html?em&ex=1183348800&en=46920e3fe2f7c649&ei=5087%0A |
|||
| title = Study Traces Cat's Ancestry to Middle East |
|||
| last = Wade |
|||
| first = Nicholas |
|||
| date=2007-06-29 |
|||
| work = [[The New York Times]] |
|||
| accessdate=2008-04-02}}</ref> A study that year found that the lines of descent of all house cats probably run through as few as five [[Self-domestication|self-domesticating]] [[African Wildcat]]s ''(Felis silvestris lybica)'' circa 8000 BC, in the [[Near East]].<ref name=Driscoll /> The earliest direct evidence of cat domestication is a kitten that was buried with its owner 9,500 years ago in [[Cyprus]].<ref>{{cite news | first= | last= |authorlink= | title=Meet Helen and Aphrodite, Cyprus's indigenous cats | date= | publisher= | url =http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/life/2009-11/03/content_8904093.htm | work =China Daily | pages = | accessdate = 2009-11-03 | language = }}</ref> |
|||
The forms might also have derived from an ancient Germanic word that was absorbed into Latin and then into Greek, Syriac, and Arabic.<ref>{{Cite book |first=J. |last=Huehnergard |chapter=Qitta: Arabic Cats |pages=407–418 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=n1_qqgNTsX8C&pg=PA407 |title=Classical Arabic Humanities in Their Own Terms: Festschrift for Wolfhart Heinrichs on his 65th Birthday |date=2008 |publisher=[[Brill (publisher)|Brill]] |location=Leiden, Boston |editor1-last=Gruendler |editor1-first=B. |editor2-last=Cooperson |editor2-first=M. |isbn=9789004165731 |access-date=25 October 2020 |archive-date=31 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210331062414/https://books.google.com/books?id=n1_qqgNTsX8C&pg=PA407 |url-status=live}}</ref> The word may be derived from Germanic and Northern European languages, and ultimately be borrowed from [[Uralic languages|Uralic]], {{Cf.}}[[Northern Sámi]] {{lang|se|gáđfi}}, 'female [[stoat]]', and [[Hungarian language|Hungarian]] {{lang|hu|hölgy}}, 'lady, female stoat'; from [[Proto-Uralic language|Proto-Uralic]] {{Lang|mis|*käďwä}}, 'female (of a furred animal)'.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Kroonen |first1=G. |title=Etymological Dictionary of Proto-Germanic |date=2013 |publisher=[[Brill Publishers]] |location=Leiden, Netherlands |isbn=9789004183407 |page=281f}}</ref> |
|||
== Nomenclature and etymology == |
|||
The word ''cat'' derives from [[Old English]] ''catt'', which belongs to a group of related words in [[Languages of Europe|European languages]], including Welsh ''cath'', Spanish ''gato'', French ''chat'' ({{IPA-fr|ʃɑ}}), Basque ''katu'', [[Byzantine Greek]] ''Κάτια'' ''kátia'', [[Old Irish]] ''cat'', [[Frisian language (disambiguation)|Frisian]] and [[Dutch language|Dutch]] ''kat'', [[German language|German]] ''Katze'', [[Armenian language|Armenian]] ''katu'', and [[Old Church Slavonic]] ''kotka''. The ultimate source of all these terms is [[Late Latin]] ''catus, cattus, catta'' "domestic cat", as opposed to ''feles'' "European wildcat". It is unclear whether the Greek or the Latin came first, but they were undoubtedly borrowed from an [[Afro-Asiatic languages|Afro-Asiatic]] language akin to [[Old Nubian language|Nubian]] ''kadís'' and [[Berber languages|Berber]] ''kaddîska'', both meaning "wildcat".<ref>{{cite web | title = Cat | url = http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=cat | work = [http://www.etymonline.com/index.php The Online etymology dictionary] | accessdate = 2007-05-15}}</ref><!-- This term was either [[cognate]] with or borrowed from [[Late Egyptian]] ''čaus'' "jungle cat, African wildcat" (later giving [[Coptic language|Coptic]] ''šau'' "tomcat"),<ref>Crum, Walter Ewing. ''A Coptic Dictionary]''. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1939: 601</ref> itself from earlier [[Ancient Egyptian language|Egyptian]] ''tešau'' "female cat"<ref>[http://www.chat-et-cie.fr/chat.htm "Le chat: origines et étymologie." ''Chat et compagnie''. 2006]</ref> (vs. ''miew'' "tomcat").<ref>SenenAnep Meritamen. "[http://www.ancientworlds.net/399761 English to Egyptian Dictionary]." posted August 29, 2004. ''Ancient Worlds''. AncientWorlds LLC, 2002.</ref>--> The term ''puss'' (as in pussycat) may come from [[Dutch language|Dutch]] ''poes'' or from [[Low German]] ''Puuskatte'', dialectal [[Swedish language|Swedish]] ''kattepus'', or [[Norwegian language|Norwegian]] ''pus'', ''pusekatt'', all of which primarily denote a woman and, by extension, a female cat.<ref>''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language''. New York: Gramercy Books, 1996: 1571.</ref> This name could be related to [[Turkish language|Turkish]] ''qadi.'' <ref>http://www.wordnik.com/words/cat/etymologies</ref> |
|||
The English ''[[wikt:puss#English|puss]]'', extended as ''pussy'' and ''pussycat'', is attested from the 16th century and may have been introduced from [[Dutch language|Dutch]] {{lang|nl|poes}} or from [[Low German]] {{lang|nds|puuskatte}}, related to [[Swedish language|Swedish]] {{lang|sv|kattepus}}, or [[Norwegian language|Norwegian]] {{lang|no|pus}}, {{lang|no|pusekatt}}. Similar forms exist in [[Lithuanian language|Lithuanian]] {{lang|lt|puižė}} and [[Irish language|Irish]] {{lang|ga|puisín}} or {{lang|ga|puiscín}}. The etymology of this word is unknown, but it may have [[Onomatopoeia|arisen from a sound]] used to attract a cat.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/155147#eid27609702 |title=Puss |work=The Oxford English Dictionary |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150903215025/http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/155147#eid27609702 |archive-date=3 September 2015 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Gramercy Unabridged">{{Cite book |title=Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language |chapter=puss |location=New York |publisher=[[Random House|Gramercy (Random House)]] |date=1996 |page=1571}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" 0" style="float:right; float:right; border:1.5px solid #bbb; margin:0.5em 0 0 0.5em;" |
|||
| colspan="4" style="text-align:center;"|'''Classification based on human interaction'''<ref name=Bradshaw1999/> |
|||
|- |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Population''' |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Food source''' |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Shelter''' |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Socialized''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| Pedigree |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| Fed by owner |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| Human homes |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| Yes |
|||
|- |
|||
| Pet |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| Fed by owner |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| Human homes |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| Yes |
|||
|- |
|||
| Semi-feral |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| General feeding |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| Buildings |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| Yes |
|||
|- |
|||
| Feral |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| General feeding/foraging |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| Buildings |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| No |
|||
|- |
|||
| Pseudo-wildcat |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| Foraging/hunting |
|||
|style="text-align:center;"| None |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| No |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
A male cat is called a ''tom'' or ''tomcat''<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/203100#eid18281825 |title=tom cat, tom-cat |work=The Oxford English Dictionary |publisher=Oxford University Press |access-date=1 October 2012 |url-access=subscription}}</ref> (or a ''gib'',<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/78103?rskey=Z7UU0G&result=1&isAdvanced=false#eid |title=gib, n.2 |work=The Oxford English Dictionary |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20180918111545/http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/78103?rskey=Z7UU0G&result=1&isAdvanced=false#eid |archive-date=18 September 2018 |url-status=live |url-access=subscription}}</ref> if [[Neutering|neutered]]). A female is called a ''queen''<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/156212?rskey=c2khr1&result=1&isAdvanced=false#eid27437294 |title=queen cat |work=The Oxford English Dictionary |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20150903215025/http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/156212?rskey=c2khr1&result=1&isAdvanced=false#eid27437294 |archive-date=3 September 2015 |url-status=live |url-access=subscription}}</ref><ref>Some sources wrote that ''queen'' refers to unspayed cats that are in an [[Estrous cycle|oestrus cycle]]. {{Cite web |last=Grosskopf |first=Shane |date=23 June 2022 |title=What is a Female Cat Called? A Guide to the Fascinating Terms |url=https://spotpet.com/blog/cat-tips/what-is-a-female-cat-called |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240411035905/https://spotpet.com/blog/cat-tips/what-is-a-female-cat-called |archive-date=11 April 2024 |access-date=1 May 2024 |website=Spot Pet Insurance}} {{Cite web |last=Scamporrino |first=Christina |date=12 December 2018 |title=Cat Parenting 101: Special Considerations for Your Female Cat |url=https://www.prettylitter.com/blog/cat-parenting-101-special-considerations-for-your-female-cat |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231001160548/https://www.prettylitter.com/blog/cat-parenting-101-special-considerations-for-your-female-cat |archive-date=1 October 2023 |access-date=1 May 2024 |website=PrettyLitter}}</ref> (or sometimes a ''molly'',<ref>{{Cite web |date=8 March 2020 |title=7 fascinating facts about female cats |url=https://www.cats.org.uk/cats-blog/7-facts-about-female-cats |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231216143959/https://www.cats.org.uk/cats-blog/7-facts-about-female-cats |archive-date=16 December 2023 |access-date=30 April 2024 |website=Cats Protection |language=en}}</ref> if [[Spaying|spayed]]). A juvenile cat is referred to as a ''[[kitten]]''. In [[Early Modern English]], the word ''kitten'' was interchangeable with the now-obsolete word ''catling''.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/28995?redirectedFrom=catling#eid |title=catling |work=The Oxford English Dictionary |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20150903215025/http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/28995?redirectedFrom=catling#eid |archive-date=3 September 2015 |url-status=live |url-access=subscription}}</ref> A group of cats can be referred to as a ''clowder'', a ''glaring'',<ref>{{cite web |url= http://oxforddictionaries.com/words/what-do-you-call-a-group-of |title=What do you call a group of ...? |work=[[Oxford Dictionaries Online]] |publisher=Oxford University Press |access-date=1 October 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121012112007/http://oxforddictionaries.com/words/what-do-you-call-a-group-of |archive-date=12 October 2012}}</ref> or a ''colony''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Terms we use for cats |url=https://www.humanesociety.org/resources/terms-we-use-cats |website=The Humane Society of the United States |access-date=2 August 2024}}</ref> |
|||
While ''[[wildcat]]s'' are the ancestral species from which domestic cats are descended, there are several intermediate stages between domestic pet and pedigree cats and these entirely wild cats. The semi-feral cat is a cat that is not owned by any one individual, but is generally friendly to people and may be fed by several households. [[Feral cat]]s are associated with human habitations and may be fed by people or forage in rubbish, but are wary of human interaction. Pseudo-wildcats are descended from domestic cats, but now tend to live entirely independently from people.<ref name=Bradshaw1999/> |
|||
== Taxonomy == |
|||
A group of cats is referred to as a "clowder", a male cat is called a "tom" (or a "gib", if neutered), and a female is called a "molly" or "queen". The male progenitor of a cat, especially a pedigreed cat, is its "sire", and its female progenitor is its "dam". An immature cat is called a "[[kitten]]" (which is also an alternative name for young [[rat]]s, [[rabbit]]s, [[hedgehog]]s, [[beaver]]s, [[squirrel]]s and [[skunk]]s). In [[England in the Middle Ages|medieval Britain]], the word ''kitten'' was interchangeable with the word ''catling''. A cat whose [[genealogy|ancestry]] is formally registered is called a [[pedigree (cat)|pedigreed cat]], [[purebred cat]], or a [[show cat]]. In strict terms, a purebred cat is one whose ancestry contains only individuals of the same breed. A pedigreed cat is one whose ancestry is recorded, but may have ancestors of different breeds. Cats of unrecorded mixed ancestry are referred to as [[domestic longhair cat|domestic longhairs]] and [[domestic shorthair cat|domestic shorthairs]] or commonly as random-bred, moggies, [[mongrel]]s, or mutt-cats. |
|||
The [[scientific name]] ''Felis catus'' was proposed by [[Carl Linnaeus]] in 1758 for a domestic cat.<ref name="Linnaeus1758">{{Cite book |last=Linnaeus |first=C. |title=Systema naturae per regna tria naturae: secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis |location=Holmiae |publisher=Laurentii Salvii |date=1758 |page=42 |chapter=Felis Catus |language=la |volume=1 |edition=10th reformed |chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/mobot31753000798865/page/42}}</ref><ref name="MSW3fc">{{MSW3 Wozencraft |id=14000031 |pages=534–535 |heading=Species ''Felis catus''}}</ref> ''Felis catus domesticus'' was proposed by [[Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben]] in 1777.<ref name="Erxleben" /> ''Felis daemon'' proposed by [[Konstantin Satunin]] in 1904 was a black cat from the [[Transcaucasus]], later identified as a domestic cat.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Satunin |first1=C. |title=The Black Wild Cat of Transcaucasia |journal=Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London |year=1904 |volume=II |pages=[https://archive.org/details/proceedingsofzoo19042zool/page/162 162]–163 |url= https://archive.org/details/proceedingsofzoo19042zool}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |editor1-last=Bukhnikashvili |editor1-first=A. |editor2-last=Yevlampiev |editor2-first=I. |title=Catalogue of the Specimens of Caucasian Large Mammalian Fauna in the Collection |publisher=[[National Museum of Georgia]] |location=Tbilisi |url= http://caucasian-large-mammalian.narod.ru/catalogue_english.pdf |access-date=19 January 2019 |archive-date=4 March 2016 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20160304073023/http://caucasian-large-mammalian.narod.ru/catalogue_english.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
In 2003, the [[International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature]] ruled that the domestic cat is a distinct species, namely ''Felis catus''.<ref name="ICZN">{{Cite journal |publisher=[[International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature]] |title=Opinion 2027 |journal=Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature |volume=60 |year=2003 |page=81−82 |url= https://archive.org/details/bulletinofzoolog602003int/page/81}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Gentry |first1=A. |last2=Clutton-Brock |first2=J. |last3=Groves |first3=C. P. |name-list-style=amp |year=2004 |title=The naming of wild animal species and their domestic derivatives |journal=Journal of Archaeological Science |volume=31 |issue=5 |pages=645–651 |doi=10.1016/j.jas.2003.10.006 |bibcode=2004JArSc..31..645G |url=http://www.rhinoresourcecenter.com/pdf_files/129/1297897712.pdf |access-date=19 January 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304052316/http://www.rhinoresourcecenter.com/pdf_files/129/1297897712.pdf |archive-date=4 March 2016 |url-status=live}}</ref> In 2007, the modern domesticated subspecies ''F. silvestris catus'' sampled worldwide was considered to have probably descended from the [[African wildcat]] (''F. lybica''), following results of [[phylogenetic]] research.<ref name="Driscoll">{{Cite journal |title=In the Light of Evolution III: Two Centuries of Darwin Sackler Colloquium: From Wild Animals to Domestic Pets – An Evolutionary View of Domestication |last1=Driscoll |first1=C. A. |last2=Macdonald |first2=D. W. |last3=O'Brien |first3=S. J. |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America |year=2009 |volume=106 |issue=S1 |pages=9971–9978 |pmid=19528637 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0901586106 |pmc=2702791 |bibcode=2009PNAS..106.9971D|doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name="MSW3fs">{{MSW3 Wozencraft |pages=536–537 |id=14000057 |heading=Species ''Felis silvestris''}}</ref>{{efn|{{harvnb|Driscoll|Macdonald|O'Brien|2009}} did not conclude a date for genetic divergence, noting from archaeological evidence that "the broadest range of dates for domestication to be from 11,000 to 4,000 B.P.".}} In 2017, the IUCN Cat Classification Taskforce followed the recommendation of the ICZN in regarding the domestic cat as a distinct species, ''Felis catus''.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Kitchener |first1=A. C. |last2=Breitenmoser-Würsten |first2=C. |last3=Eizirik |first3=E. |last4=Gentry |first4=A. |last5=Werdelin |first5=L. |last6=Wilting |first6=A. |last7=Yamaguchi |first7=N. |last8=Abramov |first8=A. V. |last9=Christiansen |first9=P. |last10=Driscoll |first10=C. |last11=Duckworth |first11=J. W. |last12=Johnson |first12=W. |last13=Luo |first13=S.-J. |last14=Meijaard |first14=E. |last15=O'Donoghue |first15=P. |last16=Sanderson |first16=J. |last17=Seymour |first17=K. |last18=Bruford |first18=M. |last19=Groves |first19=C. |last20=Hoffmann |first20=M. |last21=Nowell |first21=K. |last22=Timmons |first22=Z. |last23=Tobe |first23=S. |year=2017 |title=A revised taxonomy of the Felidae: The final report of the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN Cat Specialist Group |journal=Cat News |volume=Special Issue 11 |page=21 |url= https://repository.si.edu/bitstream/handle/10088/32616/A_revised_Felidae_Taxonomy_CatNews.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y |access-date=21 December 2018 |archive-date=17 January 2020 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20200117172708/https://repository.si.edu/bitstream/handle/10088/32616/A_revised_Felidae_Taxonomy_CatNews.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
== Taxonomy and evolution == |
|||
[[File:AfricanWildCat.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The wildcat ''[[Wildcat|Felis silvestris]]'' is a close relative of the domestic cat and possible ancestor.]] |
|||
The [[Felids]] are a rapidly evolving family of mammals that share a common ancestor only 10-15 million years ago,<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1007/PL00000060 |
|||
| volume = 44 |
|||
| issue = 0 |
|||
| pages = S98–S116 |
|||
| last = Johnson |
|||
| first = Warren |
|||
| title = Phylogenetic reconstruction of the felidae using 16S rRNA and NADH-5 mitochondrial genes |
|||
| journal = Journal of Molecular Evolution |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-27 |
|||
| date = 1997-01-01 |
|||
| last2 = O’brien |
|||
| first2 = Stephen J. |
|||
}}</ref> and include in addition to the domestic cat, lions, tigers, cougars, and many others. Within this family, domestic cats (''Felis catus'') are part of the [[genus]] ''[[Felis]]'', which is a group of small cats containing seven species.<ref name=msw3>{{MSW3 Wozencraft}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=180586 |title=ITIS Standard Report Page: Felis |publisher=Integrated Taxonomic Information System |accessdate=26 August 2009}}</ref> Members of the genus are found worldwide and include the [[Jungle Cat]] (''Felis chaus'') of southeast Asia, the [[African Wildcat]] (''Felis silvestris lybica''), the Chinese Mountain Cat (''Felis silvestris bieti'') and the Arabian [[Sand Cat]] (''Felis margarita'').<ref>{{Cite book |
|||
| publisher = Benchmark Books (NY) |
|||
| isbn = 0761415777 |
|||
| last = Stefoff |
|||
| first = Rebecca |
|||
| title = Cats |
|||
| date = 2003-11 |
|||
| page=34 |
|||
}}</ref> All the cats in this genus share a common ancestor that probably lived around 6-7 million years ago in Asia.<ref name=Johnson>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1126/science.1122277 |
|||
| volume = 311 |
|||
| issue = 5757 |
|||
| pages = 73–77 |
|||
| last = Johnson |
|||
| first = Warren E. |
|||
| title = The Late Miocene Radiation of Modern Felidae: A Genetic Assessment |
|||
| journal = Science |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-09-30 |
|||
| year = 2006 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/311/5757/73 |
|||
| pmid = 16400146 |
|||
| last1 = Johnson |
|||
| first1 = WE |
|||
| last2 = Eizirik |
|||
| first2 = E |
|||
| last3 = Pecon-Slattery |
|||
| first3 = J |
|||
| last4 = Murphy |
|||
| first4 = WJ |
|||
| last5 = Antunes |
|||
| first5 = A |
|||
| last6 = Teeling |
|||
| first6 = E |
|||
| last7 = O'brien |
|||
| first7 = SJ |
|||
}}</ref> Although the exact relationships within the Felidae are still uncertain,<ref name=Mattern/><ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1006/mpev.1996.0085 |
|||
| issn = 1055-7903 |
|||
| volume = 6 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 351–365 |
|||
| last = Masuda |
|||
| first = Ryuichi |
|||
| title = Molecular Phylogeny of Mitochondrial Cytochrome b and 12S rRNA Sequences in the Felidae: Ocelot and Domestic Cat Lineages |
|||
| journal = Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-09-30 |
|||
| date = 1996-12 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6WNH-45MGTSR-3/2/765f525a4abb24f13496d9339475c2a5 |
|||
| pmid = 8975691 |
|||
| last1 = Masuda |
|||
| first1 = R |
|||
| last2 = Lopez |
|||
| first2 = JV |
|||
| last3 = Slattery |
|||
| first3 = JP |
|||
| last4 = Yuhki |
|||
| first4 = N |
|||
| last5 = O'brien |
|||
| first5 = SJ |
|||
}}</ref> both the Chinese Mountain Cat and the African Wildcat are close relations of the domestic cat and are both classed as [[subspecies]] of the [[Wildcat]] ''Felis silvestris''.<ref name=Driscoll/><ref name=Mattern>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1111/j.1096-0031.2000.tb00354.x |
|||
| volume = 16 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| pages = 232–253 |
|||
| last = Mattern |
|||
| first = Michelle Y. |
|||
| title = Phylogeny and Speciation of Felids |
|||
| journal = Cladistics |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-27 |
|||
| year = 2000 |
|||
| last2 = McLennan |
|||
| first2 = Deborah A. |
|||
}}</ref> As domestic cats are little altered from wildcats, they can readily interbreed. This [[hybrid (biology)|hybridization]] may pose a danger to the genetic distinctiveness of wildcat populations, particularly in [[Scotland]] and [[Hungary]].<ref>{{cite journal |author=Oliveira R, Godinho R, Randi E, Alves PC |title=Hybridization versus conservation: are domestic cats threatening the genetic integrity of wildcats (Felis silvestris silvestris) in Iberian Peninsula? |journal=Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. |volume=363 |issue=1505 |pages=2953–61 |year=2008 |month=September |pmid=18522917 |doi=10.1098/rstb.2008.0052 |first1=R |first2=R |first3=E |first4=PC |issn=0962-8436 |pmc=2606743}}</ref> |
|||
== Evolution == |
|||
The domestic cat was first classified as ''Felis catus'' by [[Carolus Linnaeus]] in the tenth edition of his ''[[Systema Naturae]]'' of 1758.<ref name="Linaeus1758">{{cite book |last=Linnaeus |first=Carolus |authorlink=Carl Linnaeus |title=Systema naturae per regna tria naturae: secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis |publisher=Holmiae (Laurentii Salvii) |year=1766 |page=62 |url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k99004c/f62.chemindefer |accessdate=2008-04-02 |language={{la icon}} |volume=1 |edition = 12th |origyear = 1758}}</ref><ref name="MSW3-catus">{{MSW3 Wozencraft | pages = 534–535 | id = 14000031}}</ref> However, because of modern [[phylogenetics]], domestic cats are now usually regarded as another subspecies of the Wildcat ''Felis silvestris''.<ref name=Driscoll /><ref name="MSW3-catus" /><ref name="MSW3-silvestris">{{MSW3 Wozencraft | pages = 536–537 | id = 14000057}}</ref> This has resulted in mixed usage of the terms, as the domestic cat can be called by its subspecies name, ''Felis silvestris catus''.<ref name=msw3/><ref name=Driscoll/> Wildcats have also been referred to as various subspecies of ''F. catus'',<ref name="MSW3-silvestris" /> but in 2003 the [[International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature]] fixed the name for Wildcats as ''F. silvestris''.<ref name = ICZN>{{cite journal |
|||
{{Main|Felidae#Evolution|l1=Cat evolution}} |
|||
| author = ICZN |
|||
| title = Opinion 2027 |
|||
| journal = Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature |
|||
| volume = 60 |
|||
| publisher = [[International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature]] |
|||
| date = 2003-03-31 |
|||
| accessdate = 2008-04-02 |
|||
| url = http://www.iczn.org/BZNMar2003opinions.htm#opinion2027}}</ref> The most common name in use for the domestic cat remains ''F. catus'', following a [[Convention (norm)|convention]] for domesticated animals of using the earliest (the senior) [[synonym (taxonomy)|synonym]] proposed.<ref name = ICZN/> Sometimes the domestic cat is called ''Felis domesticus''<ref name=MacDonald/> or ''Felis domestica'',<ref name="MSW3-catus"/> the term coined by German naturalist [[Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben]] in 1777. These are not valid taxonomic names, and Linnaeus' binomial takes precedence.<ref>{{Cite book| edition = 4| publisher = Butterworth-Heinemann| isbn = 0750640693| last = Vella| first = Carolyn M.| coauthors = Lorraine M. Shelton, John J. McGonagle, Terry W. Stanglein | title = Robinson's Genetics for Cat Breeders and Veterinarians| year = 1999 |page=3}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Wild-domestic-hybrid cat skulls.png|thumb|Skulls of a wildcat (top left), a housecat (top right), and a hybrid between the two (bottom center)]] |
|||
Cats have either a [[Mutualism (biology)|mutualistic]] or [[commensalism|commensal]] relationship with humans. However, in comparison to [[dog]]s, cats have not undergone major changes during the domestication process, as the form and behavior of the domestic cat are not radically different from those of wildcats, and domestic cats are perfectly capable of surviving in the wild.<ref name=Lipinski>{{Cite journal |
|||
The domestic cat is a member of the Felidae, a [[Family (biology)|family]] that had a [[common ancestor]] about {{mya|10|15}}.<ref name="Johnson 1997">{{Cite journal |title=Phylogenetic Reconstruction of the Felidae Using 16S rRNA and NADH-5 Mitochondrial Genes |last1=Johnson |first1=W. E. |last2=O'Brien |first2=S. J. |journal=Journal of Molecular Evolution |year=1997 |volume=44 |issue=S1 |pages=S98–S116 |doi=10.1007/PL00000060 |pmid=9071018 |bibcode=1997JMolE..44S..98J |s2cid=40185850 |url= https://zenodo.org/record/1232587 |access-date=1 October 2018 |archive-date=4 October 2020 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20201004075723/https://zenodo.org/record/1232587 |url-status=live}}</ref> The [[evolutionary radiation]] of the Felidae began in Asia during the [[Miocene]] around {{mya|8.38|14.45}}.<ref name=Johnson2006>{{Cite journal |doi=10.1126/science.1122277 |volume=311 |issue=5757 |pages=73–77 |title=The late Miocene radiation of modern Felidae: A genetic assessment |journal=[[Science (journal)|Science]] |year=2006 |pmid=16400146 |last1=Johnson |first1=W. E. |last2=Eizirik |first2=E. |last3=Pecon-Slattery |first3=J. |last4=Murphy |first4=W. J. |last5=Antunes |first5=A. |last6=Teeling |first6=E. |last7=O'Brien |first7=S. J. |bibcode=2006Sci...311...73J |s2cid=41672825 |url= https://zenodo.org/record/1230866 |access-date=1 October 2018 |archive-date=4 October 2020 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20201004075725/https://zenodo.org/record/1230866 |url-status=live}}</ref> Analysis of [[mitochondrial DNA]] of all Felidae species indicates a radiation at {{mya|6.46|16.76}}.<ref name=Li_al2016>{{cite journal |author=Li, G. |author2=Davis, B. W. |author3=Eizirik, E. |name-list-style=amp |author4=Murphy, W. J. |year=2016 |title=Phylogenomic evidence for ancient hybridization in the genomes of living cats (Felidae) |journal=Genome Research |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages=1–11 |doi=10.1101/gr.186668.114 |pmid=26518481 |pmc=4691742}}</ref> The [[Genus (biology)|genus]] ''Felis'' [[Genetic divergence|genetically diverged]] from other Felidae around {{mya|6|7}}.<ref name=Johnson2006/> Results of [[phylogenetic]] research shows that the wild members of this genus evolved through [[sympatric speciation|sympatric]] or [[parapatric speciation]], whereas the domestic cat evolved through [[artificial selection]].<ref name="Mattern">{{cite journal |doi=10.1111/j.1096-0031.2000.tb00354.x |volume=16 |issue=2 |pages=232–253 |last1=Mattern |first1=M.Y. |last2=McLennan |first2=D.A. |title=Phylogeny and speciation of Felids |journal=Cladistics |year=2000 |pmid=34902955 |s2cid=85043293|doi-access=free }}</ref> The domestic cat and its closest wild ancestor are [[diploid]] and both possess 38 [[chromosome]]s<ref name="Nie 2002">{{cite journal |last1=Nie |first1=W. |last2=Wang |first2=J. |last3=O'Brien |first3=P. C. |title=The genome phylogeny of domestic cat, red panda and five Mustelid species revealed by comparative chromosome painting and G-banding |journal=Chromosome Research |volume=10 |issue=3 |pages=209–222 |year=2002 |pmid=12067210 |doi=10.1023/A:1015292005631|s2cid=9660694}}</ref> and roughly 20,000 genes.<ref name=Pontius2007>{{cite journal |last1=Pontius |first1=J. U. |last2=Mullikin |first2=J. C. |last3=Smith |first3=D. R. |author4=Agencourt Sequencing Team |collaboration=NISC Comparative Sequencing Program |title=Initial sequence and comparative analysis of the cat genome |journal=Genome Research |volume=17 |issue=11 |pages=1675–1689 |year=2007 |pmid=17975172 |pmc=2045150 |doi=10.1101/gr.6380007}}</ref> |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.10.009 |
|||
| issn = 0888-7543 |
|||
| volume = 91 |
|||
| issue = 1 |
|||
| pages = 12–21 |
|||
| last = Lipinski |
|||
| first = Monika J. |
|||
| title = The ascent of cat breeds: Genetic evaluations of breeds and worldwide random-bred populations |
|||
| journal = Genomics |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-28 |
|||
| date = 2008-01 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6WG1-4R8KT3B-3/2/3a963ce4b99082e9321dcb5a20204211 |
|||
| pmid = 18060738 |
|||
| month = January |
|||
| last1 = Lipinski |
|||
| first1 = MJ |
|||
| last2 = Froenicke |
|||
| first2 = L |
|||
| last3 = Baysac |
|||
| first3 = KC |
|||
| last4 = Billings |
|||
| first4 = NC |
|||
| last5 = Leutenegger |
|||
| first5 = CM |
|||
| last6 = Levy |
|||
| first6 = AM |
|||
| last7 = Longeri |
|||
| first7 = M |
|||
| last8 = Niini |
|||
| first8 = T |
|||
| last9 = Ozpinar |
|||
| first9 = H |
|||
| pmc = 2267438 |
|||
}}</ref><ref name=CameronBeaumont>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1046/j.1095-8312.2002.00028.x |
|||
| volume = 75 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 361–366 |
|||
| last = Cameron-Beaumont |
|||
| first = Charlotte |
|||
| title = Evidence suggesting pre-adaptation to domestication throughout the small Felidae |
|||
| journal = Biological Journal of the Linnean Society |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-09-29 |
|||
| year = 2002 |
|||
| url = http://www.neiu.edu/~jkasmer/Biol498R/Readings/essay1-06.pdf |
|||
|format=PDF| last2 = Lowe |
|||
| first2 = Sarah E. |
|||
| last3 = Bradshaw |
|||
| first3 = John W. S. |
|||
}}</ref> This limited evolution during domestication means that domestic cats tend to interbreed freely with feral cats, which distinguishes them from other domesticated animals.<ref name=Bradshaw1999>{{Cite journal |
|||
| title = Feral cats: their role in the population dynamics of Felis catus |
|||
| author = J. W. S Bradshawa, G. F. Horsfield, J. A. Allen and I. H. Robinson |
|||
| journal = Applied Animal Behaviour Science |
|||
| year = 1999 |
|||
| volume = 65 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 273–283 |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/S0168-1591(99)00086-6 |
|||
}}</ref> However, several natural behaviors and characteristics of Wildcats may have [[preadaptation|preadapted]] them for domestication as pets.<ref name=CameronBeaumont/> These traits include their small size, social nature, obvious body language, love of play and relatively high intelligence;<ref>{{harv|Fogle|1981|pp=12–17}}</ref> they may also have an inborn tendency towards tameness.<ref name=CameronBeaumont/> |
|||
{{clade gallery |main-caption=Phylogenetic relationships of the domestic cat as derived through analysis of |header1=nuclear DNA:<ref name=Johnson2006/><ref name=Li_al2016/> |header2=mitochondrial DNA:<ref name="DriscollMenotti-Raymond2007"/> |height=325px |
|||
There are two main models for how cats were domesticated. In one model, people deliberately tamed cats in a process of [[artificial selection]], as they were useful predators of vermin.<ref name=OConnor>{{Cite journal |
|||
|cladogram1={{clade |
|||
| doi = 10.1002/oa.913 |
|||
|label1=[[Felidae]] |
|||
| volume = 17 |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
| issue = 6 |
|||
|1=[[Pantherinae]] |
|||
| pages = 581–595 |
|||
|label2=[[Felinae]] |
|||
| last = O'Connor |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
| first = T. P. |
|||
|1=other Felinae [[Lineage (genetic)|lineages]] |
|||
| title = Wild or domestic? Biometric variation in the cat ''Felis silvestris'' Schreber |
|||
|label2=''[[Felis]]'' |
|||
| journal = International Journal of Osteoarchaeology |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-28 |
|||
|1=[[Jungle cat]] (''F. chaus'') [[File:Felis chaus - 1700-1880 - Print - Iconographia Zoologica - Special Collections University of Amsterdam -(White Background).jpg|79px]] |
|||
| year = 2007 |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
}}</ref> However, this model has been criticized as implausible, because there may have been little reward for such an effort: cats do not carry out commands and, although they do eat rodents, other species such as [[ferret]]s or [[terrier]]s may be better at controlling these pests.<ref name=Driscoll>{{cite journal |author=Driscoll CA, Macdonald DW, O'Brien SJ |title=In the Light of Evolution III: Two Centuries of Darwin Sackler Colloquium: From wild animals to domestic pets, an evolutionary view of domestication |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=106 |issue=S1 |pages=9971–9978 |year=2009 |month=June |pmid=19528637 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0901586106 |first1=CA |first2=DW |first3=SJ |issn=0027-8424 |pmc=2702791}}</ref> The alternative idea is that cats were simply tolerated by people and gradually diverged from their 'wild' relatives through [[natural selection]], as they adapted to hunting the vermin found around humans in towns and villages.<ref name=Driscoll/> |
|||
|1=[[Black-footed cat]] (''F. nigripes'') |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1=[[Sand cat]] (''F. margarita'') |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|1=[[Chinese mountain cat]] (''F. bieti'') |
|||
|2=[[African wildcat]] (''F. lybica'') |
|||
}} |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1=[[European wildcat]] (''F. silvestris'') [[File:Anatomie descriptive et comparative du chat (1845) Pl-I (white background & colourised).jpg|52px]] |
|||
|2='''Domestic cat''' <span style="{{MirrorH}}">[[File:202104 Cat.svg|60px]]</span> |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
|cladogram2={{clade |
|||
|label1=''[[Felis]]'' |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|1=[[Sand cat]] (''F. margarita'') |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1=[[Chinese mountain cat]] (''F. bieti'') |
|||
|2={{clade |
|||
|1=[[European wildcat]] (''F. silvestris'') [[File:Anatomie descriptive et comparative du chat (1845) Pl-I (white background & colourised).jpg|52px]] |
|||
|2={{clade <!--extra dummy clade--> |
|||
|label1=[[African wildcat]] |
|||
|1={{clade |
|||
|1=[[Southern African wildcat]] ''(F. l. cafra)'' |
|||
|2=[[Asiatic wildcat]] ''(F. l. ornata)'' |
|||
|3={{clade |
|||
|1=Near Eastern wildcat |
|||
|2='''Domestic cat''' <span style="{{MirrorH}}">[[File:202104 Cat.svg|60px]]</span> |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
=== Domestication === |
|||
==Genetics== |
|||
{{See also|Domestication of the cat|Cats in ancient Egypt}} |
|||
{{Main|Cat genetics}} |
|||
[[File:Tomb of Nakht (7).jpg|thumb|A cat eating a fish under a chair, a [[mural]] in an Egyptian tomb dating to the 15th century BC]] |
|||
[[File:WhiteCat.jpg|thumb|Blue-eyed cats with white fur have a high incidence of [[genetics|genetic]] [[Hearing impairment|deafness]].<ref name=Strain>{{cite journal |author=Strain GM |title=Aetiology, prevalence and diagnosis of deafness in dogs and cats |journal=Br. Vet. J. |volume=152 |issue=1 |pages=17–36 |year=1996 |month=January |pmid=8634862 |doi=10.1016/S0007-1935(96)80083-2 |first1=GM |issn=0007-1935}}</ref>]] |
|||
It was long thought that the [[domestication of the cat]] began in [[ancient Egypt]], where cats were venerated from around 3100 BC.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Cat in ancient Egypt, illustrated from the collection of cat and other Egyptian figures formed |publisher=Cambridge University Press |last1=Langton |first1=N. |last2=Langton |first2=M. B. |date=1940}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=The Cat in Ancient Egypt |publisher=[[University of Pennsylvania Press]] |last=Malek |first=J. |date=1997 |edition=Revised |location=Philadelphia}}</ref> However, the earliest known indication for the [[taming]] of an African wildcat was [[Excavation (archaeology)|excavated]] close by a human [[Neolithic]] grave in [[Shillourokambos]], southern [[Cyprus]], dating to about 7500–7200 BC. Since there is no evidence of native mammalian [[fauna]] on Cyprus, the inhabitants of this Neolithic village most likely brought the cat and other wild mammals to the island from the [[Middle East]]ern mainland.<ref name="Vigne_al2004">{{cite journal |last1=Vigne |first1=J. D. |last2=Guilaine |first2=J. |last3=Debue |first3=K. |last4=Haye |first4=L. |last5=Gérard |first5=P. |s2cid=28294367 |title=Early taming of the cat in Cyprus |journal=[[Science (journal)|Science]] |volume=304 |issue=5668 |page=259 |year=2004 |pmid=15073370 |doi=10.1126/science.1095335}}</ref> Scientists therefore assume that African wildcats were attracted to early human settlements in the [[Fertile Crescent]] by rodents, in particular the [[house mouse]] (''Mus musculus''), and were tamed by Neolithic farmers. This [[Mutualism (biology)|mutual]] relationship between early farmers and tamed cats lasted thousands of years. As [[agricultural practices]] spread, so did tame and domesticated cats.<ref name="DriscollMenotti-Raymond2007">{{Cite journal |title=The Near Eastern Origin of Cat Domestication |last1=Driscoll |first1=C. A. |last2=Menotti-Raymond |first2=M. |last3=Roca '|first3=A. L. |last4=Hupe |first4=K. |last5=Johnson |first5=W. E. |last6=Geffen |first6=E. |last7=Harley |first7=E. H. |last8=Delibes |first8=M. |last9=Pontier |first9=D. |last10=Kitchener |first10=A. C. |last11=Yamaguchi |first11=N. |last12=O'Brien |first12=S. J. |last13=Macdonald |first13=D. W. |journal=[[Science (journal)|Science]] |year=2007 |volume=317 |issue=5837 |pages=519–523 |pmid=17600185 |pmc=5612713 |doi=10.1126/science.1139518 |oclc=808298830 |bibcode=2007Sci...317..519D}}</ref><ref name="Driscoll_al2009">{{cite journal |last1=Driscoll |first1=C. A. |last2=Clutton-Brock |first2=J. |last3=Kitchener |first3=A. C. |last4=O'Brien |first4=S. J. |year=2009 |title=The taming of the cat |journal=Scientific American |volume=300 |issue=6 |pages=68–75 |doi=10.1038/scientificamerican0609-68 |doi-broken-date=1 November 2024 |pmid=19485091 |pmc=5790555 |bibcode=2009SciAm.300f..68D |jstor=26001382}}</ref> Wildcats of Egypt contributed to the maternal [[gene pool]] of the domestic cat at a later time.<ref name="OttoniVan Neer2017">{{cite journal |last1=Ottoni |first1=C. |last2=van Neer |first2=W. |last3=de Cupere |first3=B. |last4=Daligault |first4=J. |last5=Guimaraes |first5=S. |last6=Peters |first6=J. |last7=Spassov |first7=N. |last8=Prendergast |first8=M. E. |last9=Boivin |first9=N. |last10=Morales-Muñiz |first10=A. |last11=Bălăşescu |first11=A. |last12=Becker |first12=C. |last13=Benecke |first13=N. |last14=Boroneant |first14=A. |last15=Buitenhuis |first15=H. |last16=Chahoud |first16=J. |last17=Crowther |first17=A. |last18=Llorente |first18=L. |last19=Manaseryan |first19=N. |last20=Monchot |first20=H. |last21=Onar |first21=V. |last22=Osypińska |first22=M. |last23=Putelat |first23=O. |last24=Quintana Morales |first24=E.M. |last25=Studer |first25=J. |last26=Wierer |first26=U. |last27=Decorte |first27=R. |last28=Grange |first28=T. |last29=Geigl |first29=E. |s2cid=44041769 |title=The palaeogenetics of cat dispersal in the ancient world |journal=Nature Ecology & Evolution |volume=1 |issue=7 |year=2017 |page=0139 |doi=10.1038/s41559-017-0139 |bibcode=2017NatEE...1..139O |url= https://research.rug.nl/en/publications/the-paleogenetics-of-cat-dispersal-in-the-ancient-world(04942e78-fa48-4700-ad97-29fcdf9077a1).html |access-date=18 October 2021 |archive-date=7 March 2022 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20220307214831/https://research.rug.nl/en/publications/the-paleogenetics-of-cat-dispersal-in-the-ancient-world |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
The earliest known evidence for the occurrence of the domestic cat in [[Greece]] dates to around 1200 BC. Greek, [[Phoenicia]]n, [[Carthaginia]]n and [[Etrusca]]n traders introduced domestic cats to southern Europe.<ref name=Faure2009>{{cite journal |last1=Faure |first1=E. |last2=Kitchener |first2=A. C. |year=2009 |title=An archaeological and historical review of the relationships between Felids and people |journal=Anthrozoös |volume=22 |issue=3 |page=221−238 |doi=10.2752/175303709X457577|s2cid=84308532}}</ref> By the 5th century BC, they were familiar animals around settlements in [[Magna Graecia]] and [[Etruria]].<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Ragni |first1=B. |last2=Possenti |first2=M. |last3=Sforzi |first3=A. |last4=Zavalloni |first4=D. |last5=Ciani |first5=F. |year=1994 |title=The wildcat in central-northern Italian peninsula: a biogeographical dilemma |journal=Biogeographia |volume=17 |issue=1 |doi=10.21426/B617110417 |url= https://cloudfront.escholarship.org/dist/prd/content/qt1dz6x5xf/qt1dz6x5xf.pdf |doi-access=free |access-date=29 August 2019 |archive-date=26 July 2018 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20180726121432/https://cloudfront.escholarship.org/dist/prd/content/qt1dz6x5xf/qt1dz6x5xf.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> During the [[Roman Empire]], they were introduced to [[Corsica]] and [[Sardinia]] before the beginning of the 1st century AD.<ref name=Vigne1992>{{cite journal |last1=Vigne |first1=J.-D. |title=Zooarchaeology and the biogeographical history of the mammals of Corsica and Sardinia since the last ice age |year=1992 |journal=Mammal Review |volume=22 |issue=2 |pages=87–96 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2907.1992.tb00124.x}}</ref> By the end of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, the Egyptian domestic cat lineage had arrived in a [[Baltic Sea]] port in northern [[Germany]].<ref name="OttoniVan Neer2017" /> |
|||
The domesticated cat and its closest wild ancestor are both [[ploidy#Diploid|diploid]] organisms that possess 38 [[chromosome]]s<ref>{{cite journal |author=Nie W, Wang J, O'Brien PC |title=The genome phylogeny of domestic cat, red panda and five mustelid species revealed by comparative chromosome painting and G-banding |journal=Chromosome Res. |volume=10 |issue=3 |pages=209–22 |year=2002 |pmid=12067210 |doi=10.1023/A:1015292005631 |first1=W |first2=J |first3=PC |first4=B |first5=T |first6=MA |first7=F |issn=0967-3849}}</ref> and roughly 20,000 genes.<ref name="pmid17975172"/> About 250 heritable [[genetic disorder]]s have been identified in cats, many similar to human inborn errors.<ref name="O'Brien">{{cite journal |author=O'Brien SJ, Johnson W, Driscoll C, Pontius J, Pecon-Slattery J, Menotti-Raymond M |title=State of cat genomics |journal=Trends Genet. |volume=24 |issue=6 |pages=268–79 |year=2008 |month=June |pmid=18471926 |doi=10.1016/j.tig.2008.03.004 |first1=SJ |first2=W |first3=C |first4=J |first5=J |first6=M |issn=0168-9525}}</ref> The high level of similarity among the [[metabolism]]s of mammals allows many of these feline diseases to be diagnosed using [[genetic testing|genetic tests]] that were originally developed for use in humans, as well as the use of cats in the study of the human diseases.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Sewell AC, Haskins ME, Giger U |title=Inherited metabolic disease in companion animals: searching for nature's mistakes |journal=Vet. J. |volume=174 |issue=2 |pages=252–9 |year=2007 |month=September |pmid=17085062 |doi=10.1016/j.tvjl.2006.08.017 |first1=AC |first2=ME |first3=U |issn=1090-0233}}</ref><ref name=OBrien/> An interesting example of a [[mutation]] that is shared among all felines, including the big cats, is a mutant [[chemosensor]] in their [[taste bud]]s that prevents them from tasting sweetness, which may explain their indifference to fruits, berries, and other sugary foods.<ref name=sugar/> In some breeds of cats [[congenital deafness]] is very common, with most white cats (but not [[albino]]s) being affected, particularly if they also have blue eyes.<ref name=Strain/> The genes responsible for this defect are unknown, but the disease is studied in the hope that it may shed light on the causes of hereditary deafness in humans.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Saada AA, Niparko JK, Ryugo DK |title=Morphological changes in the cochlear nucleus of congenitally deaf white cats |journal=Brain Res. |volume=736 |issue=1-2 |pages=315–28 |year=1996 |month=October |pmid=8930338 |doi=10.1016/0006-8993(96)00719-6 |first1=AA |first2=JK |first3=DK |issn=0006-8993}}</ref> |
|||
The [[leopard cat]] (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') was [[tamed]] independently in China around 5500 BC. This line of partially domesticated cats leaves no trace in the domestic cat populations of today.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Earliest 'domestic' cats in China identified as leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') |journal=PLOS ONE |year=2016 |page=e0147295 |volume=11 |issue=1 |first1=J.-D. |last1=Vigne |first2=A. |last2=Evin |first3=T. |last3=Cucchi |first4=L. |last4=Dai |first5=C. |last5=Yu |first6=S. |last6=Hu |first7=N. |last7=Soulages |first8=W. |last8=Wang |first9=Z. |last9=Sun |pmid=26799955 |pmc=4723238 |bibcode=2016PLoSO..1147295V |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0147295 |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
Since a large variety of different coat patterns exist within the various cat breeds, the cat is an excellent animal to study the [[cat coat genetics|coat genetics]] of hair growth and coloration.<ref>{{cite book |author=Robinson, Roy; Vella, Carolyn M.; Lorraine Shelton; McGonagle, John J.; Carolyne Vella |title=Robinson's genetics for cat breeders and veterinarians |publisher=Butterworth-Heinemann |location=Oxford |year=1999 |isbn=0-7506-4069-3}}</ref> Several [[gene]]s interact to produce cats' hair color and coat patterns. Different combinations of these genes give different [[phenotype]]s. For example, the [[enzyme]] [[tyrosinase]] is needed to produce the dark pigment [[melanin]] and [[Burmese cats]] have a mutant form that is only active at low temperatures, resulting in color appearing only on the cooler ears, tail and paws.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Lyons LA, Imes DL, Rah HC, Grahn RA |title=Tyrosinase mutations associated with Siamese and Burmese patterns in the domestic cat (Felis catus) |journal=Anim. Genet. |volume=36 |issue=2 |pages=119–26 |year=2005 |month=April |pmid=15771720 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2052.2005.01253.x |first1=LA |first2=DL |first3=HC |first4=RA |issn=0268-9146}}</ref> A completely inactive gene for tyrosinase is found in albino cats, which therefore lack all pigment.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Imes DL, Geary LA, Grahn RA, Lyons LA |title=Albinism in the domestic cat (Felis catus) is associated with a tyrosinase (TYR) mutation |journal=Anim. Genet. |volume=37 |issue=2 |pages=175–8 |year=2006 |month=April |pmid=16573534 |pmc=1464423 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2052.2005.01409.x |first1=DL |first2=LA |first3=RA |first4=LA |issn=0268-9146 |format=Free full text}}</ref> Hair length is determined by the gene for [[FGF5|fibroblast growth factor 5]], with inactive copies of this gene causing long hair.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Kehler JS, David VA, Schäffer AA |title=Four independent mutations in the feline fibroblast growth factor 5 gene determine the long-haired phenotype in domestic cats |journal=J. Hered. |volume=98 |issue=6 |pages=555–66 |year=2007 |pmid=17767004 |doi=10.1093/jhered/esm072 |month=September |first1=JS |first2=VA |first3=AA |first4=K |first5=E |first6=DK |first7=SS |first8=SJ |first9=M |issn=0022-1503 |url=http://jhered.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17767004 |format=Free full text}}</ref> |
|||
During domestication, cats have undergone only minor changes in anatomy and behavior, and they are still capable of surviving in the wild. Several natural behaviors and characteristics of wildcats may have [[Preadaptation|pre-adapted]] them for domestication as pets. These traits include their small size, social nature, obvious body language, love of play, and high intelligence. Since they practice rigorous grooming habits and have an instinctual drive to bury and hide their urine and feces, they are generally much less messy than other domesticated animals. Captive ''[[Leopardus]]'' cats may also display affectionate behavior toward humans but were not domesticated.<ref name=CameronBeaumont>{{cite journal |title=Evidence suggesting pre-adaptation to domestication throughout the small Felidae |last1=Cameron-Beaumont |first1=C. |last2=Lowe |first2=S. E. |last3=Bradshaw |first3=J. W. S. |journal=Biological Journal of the Linnean Society |year=2002 |volume=75 |issue=3 |pages=361–366 |doi=10.1046/j.1095-8312.2002.00028.x |url= https://www.gwern.net/docs/catnip/2002-cameronbeaumont.pdf |doi-access=free |access-date=10 October 2019 |archive-date=10 October 2019 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20191010072239/https://www.gwern.net/docs/catnip/2002-cameronbeaumont.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> House cats often mate with feral cats.<ref name=Bradshaw1999>{{cite journal |title=Feral cats: Their role in the population dynamics of ''Felis catus'' |last1=Bradshaw |first1=J. W. S. |last2=Horsfield |first2=G. F. |last3=Allen |first3=J. A. |last4=Robinson |first4=I. H. |journal=Applied Animal Behaviour Science |year=1999 |volume=65 |issue=3 |pages=273–283 |doi=10.1016/S0168-1591(99)00086-6 |url=https://www.gwern.net/docs/catnip/1999-bradshaw.pdf |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20190130202509/https://www.gwern.net/docs/catnip/1999-bradshaw.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=30 January 2019}}</ref> [[Felid hybrid#Domestic cat and hybridization|Hybridization between domestic and other Felinae species]] is also possible, producing hybrids such as the [[Kellas cat]] in [[Scotland]].<ref name=Oliveira/><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Kitchener |first1=C. |last2=Easterbee |first2=N. |year=1992 |title=The taxonomic status of black wild felids in Scotland |journal=Journal of Zoology |volume=227 |issue=2 |pages=342–346 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7998.1992.tb04832.x}}</ref> |
|||
The Cat Genome Project, sponsored by the Laboratory of Genomic Diversity at the U.S. [[National Cancer Institute]] Frederick Cancer Research and Development Center in [[Frederick, Maryland]], aims to help the development of the cat as an [[animal model]] for human hereditary and [[infectious disease]]s, as well as contributing to the understanding of the evolution of mammals.<ref name=OBrien>{{cite journal |author=O'Brien SJ, Menotti-Raymond M, Murphy WJ, Yuhki N |title=The Feline Genome Project |journal=Annu. Rev. Genet. |volume=36 |issue= |pages=657–86 |year=2002 |pmid=12359739 |doi=10.1146/annurev.genet.36.060602.145553 |first1=SJ |first2=M |first3=WJ |first4=N |issn=0066-4197}}</ref> This effort led to the publication in 2007 of an initial draft of the genome of a [[Abyssinian (cat)|Abyssinian]] cat called Cinnamon.<ref name="pmid17975172">{{cite journal |author=Pontius JU, Mullikin JC, Smith DR |title=Initial sequence and comparative analysis of the cat genome |journal=Genome Res. |volume=17 |issue=11 |pages=1675–89 |year=2007 |month=November |pmid=17975172 |pmc=2045150 |doi=10.1101/gr.6380007 |first1=JU |first2=JC |first3=DR |first4=Team |first5=K |first6=S |first7=M |first8=J |first9=R |first11=N |last12=Schäffer |first12=AA |last13=Agarwala |first13=R |last14=Narfström |first14=K |last15=Murphy |first15=WJ |last16=Giger |first16=U |last17=Roca |first17=AL |last18=Antunes |first18=A |last19=Menotti-Raymond |first19=M |last20=Yuhki |first20=N |last21=Pecon-Slattery |first21=J |last22=Johnson |first22=WE |last23=Bourque |first23=G |last24=Tesler |first24=G |last25=Nisc Comparative Sequencing |first25=Program |last26=O'brien |first26=SJ |issn=1088-9051 |url=http://www.genome.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17975172 |format=Free full text}}</ref> The existence of a draft genome has led to the discovery of several cat disease genes,<ref name="pmid17975172"/> and even allowed the development of cat [[genetic fingerprinting]] for use in [[forensics]].<ref>{{cite journal |author=Menotti-Raymond M, David VA, Stephens JC, Lyons LA, O'Brien SJ |title=Genetic individualization of domestic cats using feline STR loci for forensic applications |journal=J. Forensic Sci. |volume=42 |issue=6 |pages=1039–51 |year=1997 |month=November |pmid=9397545 |first1=M |first2=VA |first3=JC |first4=LA |first5=SJ |issn=0022-1198 |url=http://www.scholaruniverse.com/ncbi-linkout?id=9397545 |format=Free full text}}</ref> |
|||
Development of [[cat breeds]] started in the mid 19th century.<ref>{{cite book |last=Wastlhuber |first=J. |date=1991 |chapter=History of domestic cats and cat breeds |pages=1–59 |title=Feline Husbandry: Diseases and management in the multiple-cat environment |editor1-last=Pedersen |editor1-first=N. C. |publisher=American Veterinary Publications |location=Goleta |isbn=9780939674299}}</ref> An analysis of the domestic cat [[genome]] revealed that the ancestral wildcat genome was significantly altered in the process of domestication, as specific [[mutation]]s were selected to develop cat breeds.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Montague |first1=M. J. |last2=Li |first2=G. |last3=Gandolfi |first3=B. |last4=Khan |first4=R. |last5=Aken |first5=B. L. |last6=Searle |first6=S. M. |last7=Minx |first7=P. |last8=Hillier |first8=L. W. |last9=Koboldt |first9=D. C. |last10=Davis |first10=B. W. |last11=Driscoll |first11=C. A. |year=2014 |title=Comparative analysis of the domestic cat genome reveals genetic signatures underlying feline biology and domestication |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=111 |issue=48 |pages=17230–17235 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1410083111 |pmid=25385592 |pmc=4260561 |doi-access=free |bibcode=2014PNAS..11117230M}}</ref> Most breeds are founded on random-bred domestic cats. [[Genetic diversity]] of these breeds varies between regions, and is lowest in purebred populations, which show more than 20 deleterious [[genetic disorder]]s.<ref name=Lipinski>{{cite journal |title=The ascent of cat breeds: Genetic evaluations of breeds and worldwide random-bred populations |last1=Lipinski |first1=M.J. |last2=Froenicke |first2=L. |last3=Baysac |first3=K. C. |last4=Billings |first4=N. C. |last5=Leutenegger |first5=C. M. |last6=Levy |first6=A. M. |last7=Longeri |first7=M. |last8=Niini |first8=T. |last9=Ozpinar |first9=H. |last10=Slater |first10=M.R. |last11=Pedersen |first11=N. C. |last12=Lyons |first12=L. A. |journal=Genomics |year=2008 |volume=91 |issue=1 |pages=12–21 |doi=10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.10.009 |pmid=18060738 |pmc=2267438}}</ref> |
|||
==Anatomy== |
|||
[[File:Scheme cat anatomy-en.svg|thumb|290px|Diagram of the general [[anatomy]] of a male cat.]] |
|||
== Characteristics == |
|||
Domestic cats are similar in size to the other members of the genus ''Felis'', typically weighing between {{convert|4|kg|lboz}} and {{convert|5|kg|lboz}}.<ref name=Mattern/> However, some [[Cat breed|breeds]], such as the [[Maine Coon]], can exceed 11 kilograms (25 lb). Conversely, very small cats (less than {{convert|1.8|kg|lboz}}) have been reported.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.messybeast.com/dwarfcats.html | title = Dwarf, Midget and Miniature cats | accessdate = 2007-03-06}}</ref> The world record for the largest cat is {{convert|21.297|kg|lboz}}.<ref>Cat World (2008). Cat World Records: Heaviest Cat. Retrieved on 2008-07-30 from [http://www.cat-world.com.au/CatRecords.htm Cat-world.com]</ref> The smallest adult cat ever officially recorded weighed around 1.36 kilograms (3 lb).<ref>[http://www.cat-world.com.au/CatRecords.htm Cat-world.com.au] retrieved on 2008/29/11</ref> Cats average about 23–25 centimeters (9–10 in) in height and 46 centimeters (18.1 in) in head/body length (males being larger than females), with tails averaging 30 centimeters (11.8 in) in length.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.seaworld.org/animal-info/Animal-Bytes/animalia/eumetazoa/coelomates/deuterostomes/chordata/craniata/mammalia/carnivora/domestic-cat.htm | title=Domestic Cat | publisher=[[SeaWorld]] | accessdate=2009-03-04}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Cat anatomy}} |
|||
=== Size === |
|||
Cats have 7 [[cervical vertebrae]] like almost all [[mammals]], 13 [[thoracic vertebrae]] (humans have 12), 7 [[lumbar vertebrae]] (humans have 5), 3 [[sacrum|sacral vertebrae]] like most mammals (humans have 5 because of their bipedal posture), and a variable number of [[caudal vertebrae]] in the tail (humans retain 3 to 5 caudal vertebrae, fused into an internal [[coccyx]]).<ref>{{harv|Walker|1982|p=11}}</ref> The extra lumbar and thoracic vertebrae account for the cat's spinal mobility and flexibility. Attached to the spine are 13 ribs, the shoulder, and the [[pelvis]].<ref>{{harv|Walker|1982|p=16}}</ref> Unlike human arms, cat forelimbs are attached to the shoulder by free-floating [[clavicle|clavicle bones]], which allow them to pass their body through any space into which they can fit their heads.<ref>{{cite web | title = Cat Skeleton | url = http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/zoolab/Table_of_Contents/Lab-9b/Cat_Skeleton_1/cat_skeleton_1.htm | archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20061206105542/http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/zoolab/Table_of_Contents/Lab-9b/Cat_Skeleton_1/cat_skeleton_1.htm | archivedate = 2006-12-06 | accessdate = 2006-12-12}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Scheme cat anatomy.svg|thumb|upright=1.35|Diagram of the general [[anatomy]] of a male domestic cat]] |
|||
The domestic cat has a smaller [[skull]] and shorter bones than the [[European wildcat]].<ref name="OConnor">{{cite journal |title=Wild or domestic? Biometric variation in the cat ''Felis silvestris'' |last=O'Connor |first=T. P. |journal=International Journal of Osteoarchaeology |year=2007 |volume=17 |issue=6 |pages=581–595 |doi=10.1002/oa.913 |url= http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/3700/1/OConnor_Cats-IJOA-submitted.pdf |access-date=20 January 2019 |archive-date=21 January 2019 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20190121010849/http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/3700/1/OConnor_Cats-IJOA-submitted.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> It averages about {{convert|46|cm|in|abbr=on}} in head-to-body length and {{convert|23|-|25|cm|in|abbr=on}} in height, with about {{convert|30|cm|in|abbr=on}} long tails. Males are larger than females.<ref name="WCoW">{{cite book |last1=Sunquist |first1=M. |last2=Sunquist |first2=F. |date=2002 |title=Wild Cats of the World |publisher=[[University of Chicago Press]] |isbn=9780226779997 |chapter=Domestic cat |pages=[https://archive.org/details/wildcatsofworld00sunq/page/99 99–112] |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=hFbJWMh9-OAC&pg=PA99 |url= https://archive.org/details/wildcatsofworld00sunq/page/99}}</ref> Adult domestic cats typically weigh {{convert|4|-|5|kg|lb|abbr=on}}.<ref name="Mattern" /> |
|||
=== Skeleton === |
|||
[[File:Cat skull.jpg|thumb|left|Skull of a domestic cat.]] |
|||
Cats have seven [[cervical vertebrae]] (as do most [[mammal]]s); 13 [[thoracic vertebrae]] (humans have 12); seven [[lumbar vertebrae]] (humans have five); three [[sacrum|sacral vertebrae]] (as do most mammals, but humans have five); and a variable number of [[caudal vertebrae]] in the tail (humans have only three to five vestigial caudal vertebrae, fused into an internal [[coccyx]]).<ref name="Walker">{{cite book |title=Study of the Cat with Reference to Human Beings |last=Walker |first=W.F. |edition=4th revised |date=1982 |publisher=[[Cengage|Thomson Learning/Cengage]] |isbn=9780030579141}}</ref>{{rp|11}} The extra lumbar and thoracic vertebrae account for the cat's spinal mobility and flexibility. Attached to the spine are 13 ribs, the shoulder, and the [[pelvis]].<ref name="Walker" />{{rp|16}} Unlike human arms, cat forelimbs are attached to the shoulder by free-floating [[clavicle]] bones which allow them to pass their body through any space into which they can fit their head.<ref name="Gillis 2002">{{cite web |title=Cat Skeleton |editor-last=Gillis |editor-first=R. |work=Zoolab |publisher=[[University of Wisconsin]] Press |location=La Crosse |year=2002 |url= http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/zoolab/Table_of_Contents/Lab-9b/Cat_Skeleton_1/cat_skeleton_1.htm |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20061206105542/http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/zoolab/Table_of_Contents/Lab-9b/Cat_Skeleton_1/cat_skeleton_1.htm |archive-date=6 December 2006 |access-date=7 September 2012}}</ref> |
|||
=== Skull === |
|||
The cat skull is unusual among mammals in having very large [[eye socket]]s and a powerful and specialized jaw.<ref name=Case>{{Harv|Case|2003|p=35}}</ref> Within the jaw, cats have [[tooth|teeth]] adapted for killing prey and tearing meat. When it overpowers its prey, a cat delivers a lethal neck bite with its two long [[canine tooth|canine teeth]], inserting them between two of the prey's [[vertebrae]] and severing its [[spinal cord]], causing irreversible [[paralysis]] and death.<ref name=Smith1992>{{Cite book |
|||
[[File:Cat skull.jpg|thumb|Cat skull|left]] |
|||
| publisher = Freund Publishing House Ltd. |
|||
[[File:Cat yawn with exposed teeth and claws.jpg|thumb|A cat with exposed teeth and claws]] |
|||
| isbn = 9652222704, 9789652222701 |
|||
The cat skull is unusual among mammals in having very large [[eye socket]]s and a powerful specialized jaw.<ref name="Case">{{cite book |title=The Cat: Its behavior, nutrition, and health |last=Case |first=Linda P. |date=2003 |publisher=[[Iowa State University]] Press |location=Ames |isbn=9780813803319}}</ref>{{rp|35}} Within the jaw, cats have teeth adapted for killing prey and tearing meat. When it overpowers its prey, a cat delivers a lethal neck bite with its two long [[Canine tooth|canine teeth]], inserting them between two of the prey's [[vertebra]]e and severing its [[spinal cord]], causing irreversible [[paralysis]] and death.<ref name="Smith1992">{{cite book |title=Structure, Function, and Evolution of Teeth |last1=Smith |first1=Patricia |last2=Tchernov |first2=Eitan |date=1992 |page=217 |publisher=Freund Publishing House |isbn=9789652222701}}</ref> Compared to other felines, domestic cats have narrowly spaced canine teeth relative to the size of their jaw, which is an adaptation to their preferred prey of small rodents, which have small vertebrae.<ref name="Smith1992" /> |
|||
| last = Smith |
|||
| first = Patricia |
|||
| coauthors = Eitan Tchernov |
|||
| title = Structure, function and evolution of teeth |
|||
| year = 1992 |
|||
| page = 217 |
|||
}}</ref> Compared to other felines, domestic cats have narrowly spaced canine teeth; which is an adaptation to their preferred prey of small rodents, which have small vertebrae.<ref name=Smith1992/> The [[premolar]] and [[molar (tooth)|first molar]] together compose the [[carnassial]] pair on each side of the mouth, which efficiently shears meat into small pieces, like a pair of [[scissors]]. These are vital in feeding, since cats' small [[molar (tooth)|molars]] cannot chew food effectively.<ref>{{Harv|Case|2003|p=37}}</ref> |
|||
The [[premolar]] and first [[Molar (tooth)|molar]] together compose the [[carnassial]] pair on each side of the mouth, which efficiently shears meat into small pieces, like a pair of scissors. These are vital in feeding, since cats' small [[molar (tooth)|molars]] cannot chew food effectively, and cats are largely incapable of mastication.<ref name="Case" />{{rp|37}} Cats tend to have better teeth than most humans, with decay generally less likely because of a thicker protective layer of [[Tooth enamel|enamel]], a less damaging saliva, less retention of food particles between teeth, and a diet mostly devoid of sugar. Nonetheless, they are subject to occasional tooth loss and infection.<ref name="Carr1978">{{cite book |first=William H. A. |last=Carr |title=The New Basic Book of the Cat |date=1 January 1978 |publisher=[[Scribner's]] |isbn=9780684155494 |page=[https://archive.org/details/newbasicbookofca00carr/page/174 174] |url= https://archive.org/details/newbasicbookofca00carr/page/174}}</ref> |
|||
Cats, like dogs, are [[digitigrade]]s. They walk directly on their [[toe]]s, with the [[bone]]s of their feet making up the lower part of the visible leg.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Lacquaniti F, Grasso R, Zago M |title=Motor Patterns in Walking |journal=News Physiol. Sci. |volume=14 |issue= 4|pages=168–174 |date=1 August 1999|pmid=11390844 |url=http://physiologyonline.physiology.org/cgi/content/full/14/4/168 |first1=F |first2=R |first3=M |issn=0886-1714}}</ref> Cats are capable of walking very precisely, because like all [[felinae|felines]] they directly register; that is, they place each hind paw (almost) directly in the print of the corresponding forepaw, minimizing noise and visible tracks. This also provides sure footing for their hind paws when they navigate rough terrain. Unlike most mammals, when cats walk, they use a "diagonal" [[gait]]; that is, they move the two legs on one side of the body before the legs on the other side. This trait is shared with [[camel]]s and [[giraffe]]s. As a walk speeds up into a trot, a cat's gait will change to be similar to other mammals: the diagonally opposite hind and forelegs will move simultaneously.<ref>{{cite book | title=Outwitting Cats | first=Wendy | last=Christensen | page=23 | publisher=Globe Pequot | year=2004 | isbn=1592282407 | url=http://books.google.com/?id=WmuQQXU6EtAC&pg=PA23&dq=cats+giraffes+camels+pace&q}}</ref> |
|||
=== Claws === |
|||
Like almost all members of the [[Felidae]] [[family (biology)|family]], cats have protractable [[claw]]s.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
[[File:Shed domestic cat claw sheaths.tiff|thumb|Shed claw sheaths]] |
|||
| doi = 10.1017/S0952836901000565 |
|||
Cats have protractible and retractable claws.<ref name="Kitchener2010">{{cite book |last1=Kitchener |first1=A. C. |last2=Van Valkenburgh |first2=B. |last3=Yamaguchi |first3=N. |date=2010 |chapter-url= https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266753114 |chapter=Felid form and function |title=Biology and Conservation of wild felids |editor1-first=D. |editor1-last=Macdonald |editor2-last=Loveridge |editor2-first=A. |publisher=Oxford University Press |pages=83–106 |access-date=10 October 2019 |archive-date=16 February 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210216135340/https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266753114_Felid_form_and_function |url-status=live}}</ref> In their normal, relaxed position, the claws are sheathed with the skin and fur around the paw's toe pads. This keeps the claws sharp by preventing wear from contact with the ground and allows for the silent stalking of prey. The claws on the forefeet are typically sharper than those on the hindfeet.<ref name="Armes 1900">{{cite journal |title=Outline of cat lessons |last=Armes |first=A.F. |journal=The School Journal |year=1900 |volume=LXI |page=659 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=-_gBAAAAYAAJ |access-date=5 June 2020 |archive-date=6 August 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210806133121/https://books.google.com/books?id=-_gBAAAAYAAJ |url-status=live}}</ref> Cats can voluntarily extend their claws on one or more paws. They may extend their claws in hunting or self-defense, climbing, [[kneading (cats)|kneading]], or for extra traction on soft surfaces. Cats shed the outside layer of their claw sheaths when scratching rough surfaces.<ref name="pmid19422432">{{cite journal |last1=Homberger |first1=D. G. |last2=Ham |first2=K. |last3=Ogunbakin |first3=T. |last4=Bonin |first4=J. A. |last5=Hopkins |first5=B. A. |last6=Osborn |first6=M. L. |display-authors=etal |title=The structure of the cornified claw sheath in the domesticated cat (''Felis catus''): Implications for the claw-shedding mechanism and the evolution of cornified digital end organs |journal=J Anat |year=2009 |volume=214 |issue=4 |pages=620–43 |pmid=19422432 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01068.x |pmc=2736126}}</ref> |
|||
| volume = 254 |
|||
| issue = 01 |
|||
| pages = 67–76 |
|||
| last = Russell |
|||
| first = Anthony P. |
|||
| title = Claw Retraction and Protraction in the Carnivora: The Cheetah (Acinonyx Jubatus) as an Atypical Felid |
|||
| journal = Journal of Zoology |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-28 |
|||
| year = 2001 |
|||
| url = http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=74235 |
|||
| last2 = Bryant |
|||
| first2 = Harold N. |
|||
}}</ref> In their normal, relaxed position the claws are sheathed with the [[skin]] and [[fur]] around the [[paw|toe pads]]. This keeps the claws sharp by preventing wear from contact with the ground and allows the silent stalking of prey. The claws on the forefeet are typically sharper than those on the hind feet.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Outline of Cat Lessons|journal=The School Journal|date=1900-12-22|first=Annetta F.|last=Armes|volume=LXI|issue=|page=659|id= |url=http://books.google.com/?id=-_gBAAAAYAAJ|format=|accessdate=2007-11-12|publisher=E.L. Kellogg & Co. }}</ref> Cats can voluntarily extend their claws on one or more paws. They may extend their claws in hunting or self-defense, climbing, "[[kneading (cats)|kneading]]", or for extra traction on soft surfaces. Most cats have five claws on their front paws, and four on their rear paws.<ref name=Danforth1947>{{cite journal |author=Danforth CH. |title=Heredity of Polydactyly in the Cat |journal=J. Hered. |volume=38 |pages=107–112 |year=1947 |url=http://jhered.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/reprint/38/4/107.pdf|format=PDF |pmid=20242531 |issue=4}}</ref> The fifth front claw (the [[dewclaw]]) is [[Anatomical terms of location|proximal]] to the other claws. More proximally, there is a protrusion which appears to be a sixth "finger". This special feature of the front paws, on the inside of the wrists, is the carpal pad, also found on the paws of [[big cat]]s and dogs. It has no function in normal walking, but is thought to be an anti-skidding device used while jumping. Some breeds of cats are prone to [[polydactyl cat|polydactylyism]], and may have eight or even ten toes.<ref name=Danforth1947/> These are particularly common along the North-East coast of [[North America]].<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1093/hmg/ddm370 |
|||
| issn = 1460-2083 |
|||
| volume = 17 |
|||
| issue = 7 |
|||
| pages = 978–985 |
|||
| last = Lettice |
|||
| first = Laura A |
|||
| title = Point mutations in a distant sonic hedgehog cis-regulator generate a variable regulatory output responsible for preaxial polydactyly |
|||
| journal = Human Molecular Genetics |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-27 |
|||
| date = 2008-04-01 |
|||
| pmid = 18156157 |
|||
| last1 = Lettice |
|||
| first1 = LA |
|||
| last2 = Hill |
|||
| first2 = AE |
|||
| last3 = Devenney |
|||
| first3 = PS |
|||
| last4 = Hill |
|||
| first4 = RE |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
Most cats have five claws on their front paws and four on their rear paws. The [[dewclaw]] is [[proximal]] to the other claws. More proximally is a protrusion which appears to be a sixth "finger". This special feature of the front paws on the inside of the wrists has no function in normal walking but is thought to be an antiskidding device used while jumping. Some cat breeds are prone to having extra digits ("[[Polydactyl cat|polydactyly]]").<ref name="Danforth1947">{{cite journal |last=Danforth |first=C. H. |title=Heredity of polydactyly in the cat |journal=The Journal of Heredity |volume=38 |issue=4 |pages=107–112 |year=1947 |pmid=20242531 |doi=10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a105701}}</ref> Polydactylous cats occur along North America's northeast coast and in Great Britain.<ref name="Lettice 2008">{{cite journal |last1=Lettice |first1=L. A. |last2=Hill |first2=A. E. |last3=Devenney |first3=P. S. |last4=Hill |first4=R. E. |title=Point mutations in a distant sonic hedgehog cis-regulator generate a variable regulatory output responsible for preaxial polydactyly |journal=Human Molecular Genetics |volume=17 |issue=7 |pages=978–985 |year=2008 |pmid=18156157 |doi=10.1093/hmg/ddm370 |doi-access=free|hdl=20.500.11820/76c18e1b-ba87-49c6-9da7-c837187646a5 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
==Physiology== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" 0" style="float:right; float:right; border:1.5px solid #bbb; margin:0.5em 0 0 0.5em;" |
|||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center;"|'''Normal physiological values'''<ref>{{harv|Kahn|Line|2007|p=330}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Body temperature]] |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 38.6°C (101.5°F) |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Heart rate]] |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 120-140 beats per minute |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Breathing rate]] |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 16-40 breaths per minute |
|||
|} |
|||
=== Ambulation === |
|||
As cats are familiar and easily kept animals, their physiology has been particularly well studied; it generally resembles that of other carnivorous mammals but displays several unusual features probably attributable to cats' descent from desert-dwelling species.<ref name=MacDonald/> For instance, cats are able to tolerate quite high temperatures: humans generally start to feel uncomfortable when their skin temperature passes about 44.5 °C (112 °F), but cats show no discomfort until their skin reaches around 52 °C (126 °F),<ref>{{Harv|Case|2003|p=46}}</ref> and can tolerate temperatures of up to 56 °C (133 °F) if they have access to water.<ref>{{cite book |author=Subcommittee on Dog and Cat Nutrition Co |title=Nutrient requirements of dogs and cats |publisher=National Academies Press |location=Washington, D.C |year=2006 |pages=292 |isbn=0-309-08628-0}}</ref> Cats conserve heat by reducing the flow of blood to their skin and lose heat by evaporation through their mouth. They do not sweat and pant only at very high temperatures.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Adams T, Morgan ML, Hunter WS, Holmes KR |title=Temperature regulation of the unanesthetized cat during mild cold and severe heat stress |journal=J Appl Physiol |volume=29 |issue=6 |pages=852–8 |year=1970 |month=December |pmid=5485356}}</ref> Unusually, a cat's body temperature does not vary throughout the day; this is part of cats' general lack of [[circadian rhythm]]s and may reflect their tendency to be active at both day and night.<ref>{{harv|Committee on Animal Nutrition|1986|p=1}}</ref> Cats' feces are usually dry and their urine is also highly concentrated, both of which are adaptations that allow cats to retain as much fluid as possible.<ref name=MacDonald/> Their kidneys are so efficient that cats can survive on a diet consisting only of meat, with no additional water,<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
The cat is [[digitigrade]]. It walks on the toes, with the bones of the feet making up the lower part of the visible leg.<ref name="Pocock1917">{{cite journal |last=Pocock |first=R. I. |year=1917 |title=VII — On the external characters of the Felidæ |url= https://archive.org/details/ser8annalsmagazi19londuoft |journal=The Annals and Magazine of Natural History; Zoology, Botany, and Geology |series=8 |volume=19 |issue=109 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/ser8annalsmagazi19londuoft/page/113 113–136] |doi=10.1080/00222931709486916}}</ref> Unlike most mammals, it uses a "pacing" [[gait]] and moves both legs on one side of the body before the legs on the other side. It registers directly by placing each hind paw close to the track of the corresponding fore paw, minimizing noise and visible tracks. This also provides sure footing for hind paws when navigating rough terrain. As it speeds up from walking to trotting, its gait changes to a "diagonal" gait: The diagonally opposite hind and fore legs move simultaneously.<ref name="Christensen 2004">{{Cite book |last=Christensen |first=W. |url= https://archive.org/details/outwittingcatsti0000chri/page/22 |title=Outwitting Cats |publisher=[[Globe Pequot]] |date=2004 |isbn=9781592282401 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/outwittingcatsti0000chri/page/22 22–45] |chapter=The physical cat |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=WmuQQXU6EtAC&pg=PA27}}</ref> |
|||
| volume = 196 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 625–632 |
|||
| last = Prentiss |
|||
| first = Phoebe G. |
|||
| title = Hydropenia in cat and dog. Ability of the cat to meet its water requirements solely from a diet of fish or meat |
|||
| journal = Am J Physiol |
|||
| pmid = 13627237 |
|||
| date = 1959-02-28 |
|||
| url = http://ajplegacy.physiology.org/cgi/content/abstract/196/3/625 |
|||
| first2 = AV |
|||
| first3 = HA |
|||
| issn = 0002-9513 |
|||
| author2 = W |
|||
| author3 = E |
|||
}}</ref> and can even rehydrate by drinking [[seawater]].<ref>{{harv|Committee on Animal Nutrition|1986|p=29}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| volume = 196 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 633–641 |
|||
| last = Wolf |
|||
| first = A. V. |
|||
| title = Potability of sea water with special reference to the cat |
|||
| journal = Am J Physiol |
|||
| pmid = 13627238 |
|||
| date = 1959-02-28 |
|||
| url = http://ajplegacy.physiology.org/cgi/content/abstract/196/3/633 |
|||
| first2 = PG |
|||
| first3 = LG |
|||
| first4 = RJ |
|||
| issn = 0002-9513 |
|||
| author2 = P |
|||
| author3 = D |
|||
| author4 = S |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
=== Balance === |
|||
[[File:Cat and mouse.jpg|thumb|upright|A cat carrying a [[house mouse]].]] |
|||
[[File:BIOASTRONAUTICS_RESEARCH_Gov.archives.arc.68700.ogv|thumb|thumbtime=4:00|right|start=3:38|end=4:11|Comparison of cat righting reflexes in [[gravity]] and zero gravity]] |
|||
Cats are generally fond of sitting in high places or ''perching''. A higher place may serve as a concealed site from which to hunt; domestic cats strike prey by pouncing from a perch such as a tree branch. Another possible explanation is that height gives the cat a better observation point, allowing it to survey its territory. A cat falling from heights of up to {{convert|3|m|ft|abbr=on}} can right itself and land on its paws.<ref name="Kent et al. 2010">{{Cite journal |last1=Kent |first1=Marc |last2=Platt |first2=Simon R. |date=September 2010 |title=The neurology of balance: Function and dysfunction of the vestibular system in dogs and cats |journal=The Veterinary Journal |volume=185 |issue=3 |pages=247–249 |doi=10.1016/j.tvjl.2009.10.029 |pmid=19944632}}</ref> |
|||
During a fall from a high place, a cat reflexively twists its body and rights itself to land on its feet using its acute sense of balance and flexibility. This reflex is known as the [[cat righting reflex]].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Gerathewohl |first1=S. J. |last2=Stallings |first2=H. D. |year=1957 |title=The labyrinthine posture reflex (righting reflex) in the cat during weightlessness |url= https://spacemedicineassociation.org/download/history/history_files_1957/28040345-1.pdf |journal=The Journal of Aviation Medicine |volume=28 |issue=4 |pages=345–355 |pmid=13462942 |access-date=27 April 2019 |archive-date=3 October 2020 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20201003155151/https://spacemedicineassociation.org/download/history/history_files_1957/28040345-1.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> A cat always rights itself in the same way during a fall, if it has enough time to do so, which is the case in falls of {{convert|90|cm|ft|abbr=on}} or more.<ref name="Nguyen 1998">{{cite web |last=Nguyen |first=H. D. |year=1998 |title=How does a cat always land on its feet? |url= http://helix.gatech.edu/Classes/ME3760/1998Q3/Projects/Nguyen/ |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20010410235503/http://helix.gatech.edu/Classes/ME3760/1998Q3/Projects/Nguyen/ |archive-date=10 April 2001 |access-date=15 May 2007 |series=Dynamics II (ME 3760) course materials |publisher=[[Georgia Institute of Technology]] |department=School of Medical Engineering}} {{tertiary source|date=December 2011}}</ref> How cats are able to right themselves when falling has been investigated as the "[[falling cat problem]]".<ref>{{cite journal |title=Falling cats, parallel parking, and polarized light |last=Batterman |first=R. |year=2003 |journal=Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part B: Studies in History and Philosophy of Modern Physics |volume=34 |issue=4 |pages=527–557 |url=http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/794/1/falling-cats.pdf |bibcode=2003SHPMP..34..527B |doi=10.1016/s1355-2198(03)00062-5 |access-date=13 September 2022 |archive-date=20 July 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180720140329/http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/794/1/falling-cats.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Cats are [[Carnivore#Obligate carnivores|obligate carnivore]]s: their [[physiology]] has evolved to efficiently process meat, and they have difficulty digesting plant matter.<ref name=MacDonald>{{cite journal |author=MacDonald ML, Rogers QR, Morris JG |title=Nutrition of the domestic cat, a mammalian carnivore |journal=Annu. Rev. Nutr. |volume=4 |issue= |pages=521–62 |year=1984 |pmid=6380542 |doi=10.1146/annurev.nu.04.070184.002513 |first1=ML |first2=QR |first3=JG |issn=0199-9885}}</ref> In contrast to [[omnivore]]s such as [[rat]]s, which only require about 4% protein in their diet, about 20% of a cat's diet must be protein.<ref name=MacDonald/> Cats are unusually dependent on a constant supply of the [[amino acid]] [[arginine]], and a diet lacking arginine causes marked weight loss and can be rapidly fatal.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Morris JG, Rogers QR |title=Arginine: an essential amino acid for the cat |journal=J. Nutr. |volume=108 |issue=12 |pages=1944–53 |date=1 December 1978|pmid=722344 |first1=JG |first2=QR |issn=0022-3166 |url=http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=722344 |format=Free full text }}</ref> Another unusual feature is that the cat also cannot produce the amino acid [[taurine]], with taurine deficiency causing [[macular degeneration]], where the cat's retina slowly degenerates, causing irreversible blindness.<ref name=MacDonald/> Since cats tend to eat all of their prey, they obtain minerals by digesting animal bones, and a diet composed only of meat may cause [[calcium]] deficiency.<ref name=MacDonald/> |
|||
=== Coats === |
|||
A cat's [[gastrointestinal tract|digestive tract]] is also adapted to meat eating, being much shorter than that of omnivores and having low levels of several of the [[digestive enzyme]]s that are needed to digest carbohydrates.<ref name=Zoran/> These traits severely limits the cat's ability to digest and use plant-derived nutrients, as well as certain [[fatty acid]]s.<ref name=Zoran>{{cite journal |author=Zoran DL |title=The carnivore connection to nutrition in cats |journal=J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. |volume=221 |issue=11 |pages=1559–67 |year=2002 |month=December |pmid=12479324 |doi= 10.2460/javma.2002.221.1559|url=http://www.rawessentials.co.nz/media/documents/website%20-zorans_article.pdf |format=PDF|first1=DL |issn=0003-1488}}</ref> Despite the cat's meat-oriented physiology, several vegetarian or vegan cat foods have been marketed that are supplemented with [[chemical synthesis|chemically synthesized]] taurine and other nutrients, in attempts to produce a complete diet. However, some of these products still fail to provide all the nutrients that cats require,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Gray CM, Sellon RK, Freeman LM |title=Nutritional adequacy of two vegan diets for cats |journal=J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. |volume=225 |issue=11 |pages=1670–5 |year=2004 |month=December |pmid=15626215 |doi=10.2460/javma.2004.225.1670 |first1=CM |first2=RK |first3=LM |issn=0003-1488}}</ref> and diets containing no animal products pose the risk of causing severe nutritional deficiencies.<ref name=Zaghini>{{cite journal |author=Zaghini G, Biagi G |title=Nutritional peculiarities and diet palatability in the cat |journal=Vet. Res. Commun. |volume=29 Suppl 2 |issue= |pages=39–44 |year=2005 |month=August |pmid=16244923 |doi=10.1007/s11259-005-0009-1 |first1=G |first2=G |issn=0165-7380}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Cat coat genetics}} |
|||
[[File:Nursing Cat 01.jpg|thumb|Mother cat with her different-colored offspring]] |
|||
The cat family (Felidae) can pass down many colors and patterns to their offspring. The domestic cat genes ''MC1R'' and ''ASIP'' allow color variety in their coats. The feline ''ASIP'' gene consists of three coding exons.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Eizirik |first1=Eduardo |last2=Yuhki |first2=Naoya |last3=Johnson |first3=Warren E. |last4=Menotti-Raymond |first4=Marilyn |last5=Hannah |first5=Steven S. |last6=O'Brien |first6=Stephen J. |date=4 March 2003 |title=Molecular Genetics and Evolution of Melanism in the Cat Family |journal=Current Biology |volume=13 |issue=5 |pages=448–453 |doi=10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00128-3 |pmid=12620197 |s2cid=19021807 |issn=0960-9822|doi-access=free|bibcode=2003CBio...13..448E }}</ref> Three novel [[microsatellite]] markers linked to ''ASIP'' were isolated from a domestic cat BAC clone containing this gene to perform [[linkage analysis]] on 89 domestic cats segregated for [[melanism]]. The domestic cat family demonstrated a cosegregation between the ''ASIP'' allele and coat black coloration.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Eizirik |first1=Eduardo |last2=Yuhki |first2=Naoya |last3=Johnson |first3=Warren E. |last4=Menotti-Raymond |first4=Marilyn |last5=Hannah |first5=Steven S. |last6=O'Brien |first6=Stephen J. |date=4 March 2003 |title=Molecular Genetics and Evolution of Melanism in the Cat Family |url=https://www.cell.com/current-biology/pdf/S0960-9822(03)00128-3.pdf |journal=Cell Press |volume=13 |issue=5 |pages=448–453 |doi=10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00128-3 |pmid=12620197 |bibcode=2003CBio...13..448E |access-date=26 March 2024 |archive-date=26 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240326122953/https://www.cell.com/current-biology/pdf/S0960-9822(03)00128-3.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
==Senses== |
== Senses == |
||
{{Main|Cat senses}} |
{{Main|Cat senses}} |
||
[[File:Catpupil03042006.jpg|upright|thumb|Cat's eye. Cats have extremely sensitive vision, particularly in dim light.]] |
|||
=== Vision === |
|||
Cats have excellent [[night vision]] and can see at only one-sixth the light level required for human vision.<ref>{{Harv|Case|2003|p=43}}</ref> This is partly the result of cat eyes having a [[tapetum lucidum]], which reflects any light that passes through the [[retina]] back into the eye, thereby increasing the eye's sensitivity to dim light.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
[[Image:TapetumLucidum.JPG|thumb|right|Reflection of camera flash from the ''[[tapetum lucidum]]'']] |
|||
| doi = 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2004.00318.x |
|||
[[File:Tabby cat with visible nictitating membrane.jpg|alt=A tabby cat with a third, translucent eyelid covering part of either eye|thumb|A cat's nictitating membrane shown as it blinks]] |
|||
| volume = 7 |
|||
Cats have excellent [[night vision]] and can see at one sixth the light level required for human vision.<ref name="Case" />{{rp|43}} This is partly the result of cat eyes having a ''[[tapetum lucidum]]'', which reflects any light that passes through the [[retina]] back into the eye, thereby increasing the eye's sensitivity to dim light.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Comparative morphology of the ''Tapetum Lucidum'' (among selected species) |last1=Ollivier |first1=F. J. |last2=Samuelson |first2=D. A. |last3=Brooks |first3=D. E. |last4=Lewis |first4=P. A. |last5=Kallberg |first5=M. E. |last6=Komaromy |first6=A. M. |s2cid=15419778 |journal=Veterinary Ophthalmology |year=2004 |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=11–22 |doi=10.1111/j.1463-5224.2004.00318.x |pmid=14738502}}</ref> Large pupils are an adaptation to dim light. The domestic cat has [[Pupil#In other animals|slit pupils]], which allow it to focus bright light without [[chromatic aberration]].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Malmström |first1=T. |last2=Kröger |first2=R. H. |title=Pupil shapes and lens optics in the eyes of terrestrial vertebrates |journal=Journal of Experimental Biology |volume=209 |issue=1 |pages=18–25 |year=2006 |pmid=16354774 |doi=10.1242/jeb.01959|doi-access=free|bibcode=2006JExpB.209...18M }}</ref> At low light, a cat's pupils expand to cover most of the exposed surface of its eyes.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Hammond |first1=P. |last2=Mouat |first2=G. S. V. |title=The relationship between feline pupil size and luminance |journal=Experimental Brain Research |year=1985 |volume=59 |issue=3 |pages=485–490 |doi=10.1007/BF00261338|pmid=4029324|s2cid=11858455}}</ref> The domestic cat has rather poor [[color vision]] and only two types of [[cone cell]]s, optimized for sensitivity to blue and yellowish green; its ability to distinguish between red and green is limited.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Cat color vision: The effect of stimulus size |last1=Loop |first1=M. S. |last2=Bruce |first2=L. L. |journal=[[Science (journal)|Science]] |volume=199 |issue=4334 |pages=1221–1222 |year=1978 |pmid=628838 |doi=10.1126/science.628838 |bibcode=1978Sci...199.1221L}}</ref> A response to middle wavelengths from a system other than the [[rod cell]]s might be due to a third type of cone. This appears to be an adaptation to low light levels rather than representing true [[Trichromacy|trichromatic]] vision.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Guenther |first1=E. |last2=Zrenner |first2=E. |title=The spectral sensitivity of dark- and light-adapted cat retinal ganglion cells |journal=Journal of Neuroscience |volume=13 |pages=1543–1550 |year=1993 |issue=4 |pmid=8463834 |pmc=6576706 |doi=10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01543.1993 }}</ref> Cats also have a [[nictitating membrane]], allowing them to blink without hindering their vision. |
|||
| issue = 1 |
|||
| pages = 11–22 |
|||
| last = Ollivier |
|||
| first = F. J. |
|||
| title = Comparative morphology of the tapetum lucidum (among selected species) |
|||
| journal = Veterinary Ophthalmology |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-21 |
|||
| year = 2004 |
|||
| pmid = 14738502 |
|||
| last2 = Samuelson |
|||
| first2 = DA |
|||
| last3 = Brooks |
|||
| first3 = DE |
|||
| last4 = Lewis |
|||
| first4 = PA |
|||
| last5 = Kallberg |
|||
| first5 = ME |
|||
| last6 = Komáromy |
|||
| first6 = AM |
|||
}}</ref> Another adaptation to dim light is the large pupils of cats' eyes. Unlike some big cats, such as [[tiger]]s, domestic cats have slit [[pupil]]s.<ref name=Malmstrom/> These slit pupils can focus bright light without [[chromatic aberration]], and are needed since the domestic cat's pupils are much larger, relative to their eyes, than the pupils of the big cats.<ref name=Malmstrom>{{cite journal |author=Malmström T, Kröger RH |title=Pupil shapes and lens optics in the eyes of terrestrial vertebrates |journal=J. Exp. Biol. |volume=209 |issue=Pt 1 |pages=18–25 |year=2006 |month=January |pmid=16354774 |doi=10.1242/jeb.01959 |first1=T |first2=RH |issn=0022-0949 |url=http://jeb.biologists.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16354774 |format=Free full text}}</ref> Indeed, at low light levels a cat's pupils will expand to cover most of the exposed surface of its eyes.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1007/BF00261338 |
|||
| volume = 59 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 485–490 |
|||
| last = Hammond |
|||
| first = P. |
|||
| title = The relationship between feline pupil size and luminance |
|||
| journal = Experimental Brain Research |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-21 |
|||
| year = 1985 |
|||
| last2 = Mouat |
|||
| first2 = G.S.V. |
|||
}}</ref> However, domestic cats have rather poor [[color vision]] and can only see two colors: blue and green, and are less able to distinguish between red and green,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Loop MS, Bruce LL |title=Cat color vision: the effect of stimulus size |journal=Science |volume=199 |issue=4334 |pages=1221–2 |year=1978 |month=March |pmid=628838 |doi=10.1126/science.628838 |first1=MS |first2=LL |issn=0036-8075}}</ref> although they can achieve this in some conditions.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Schneider H, Beller FK |title=The Spectral Sensitivity of Dark- and Light-adapted Cat Retinal Ganglion Cells |journal=Journal of Neuroscience|volume=13 |pages=1543–1550 |date=1 April 1993|url=http://www.jneurosci.org/cgi/reprint/13/4/1543 |issue=4 |pmid=8463834}}</ref> |
|||
=== Hearing === |
|||
[[File:Olhos de um gato-3.jpg|thumb|left|Cats' whiskers are highly sensitive to touch.]] |
|||
The domestic cat's hearing is most acute in the range of 500 Hz to 32 kHz.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Hearing range of the domestic cat |last=Heffner |first=R. S. |journal=Hearing Research |year=1985 |volume=19 |issue=1 |pages=85–88 |doi=10.1016/0378-5955(85)90100-5 |pmid=4066516 |s2cid=4763009 |url= https://www.utoledo.edu/al/psychology/pdfs/comphearaudio/HearingRangeOfTheDomesticCat_1985.pdf |access-date=10 October 2019 |archive-date=7 July 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210707001511/https://www.utoledo.edu/al/psychology/pdfs/comphearaudio/HearingRangeOfTheDomesticCat_1985.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> It can detect an extremely broad range of frequencies ranging from 55 Hz to 79 kHz, whereas humans can only detect frequencies between 20 Hz and 20 kHz. It can hear a range of 10.5 [[octave]]s, while humans and dogs can hear ranges of about 9 octaves.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Auditory awareness |last=Heffner |first=H. E. |journal=Applied Animal Behaviour Science |year=1998 |volume=57 |issue=3–4 |pages=259–268 |doi=10.1016/S0168-1591(98)00101-4}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Primate hearing from a mammalian perspective |last=Heffner |first=R. S. |s2cid=4991969 |journal=The Anatomical Record Part A: Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology |year=2004 |volume=281 |issue=1 |pages=1111–1122 |pmid=15472899 |doi=10.1002/ar.a.20117|doi-access=free}}</ref> Its hearing sensitivity is enhanced by its large movable outer ears, the [[Pinna (anatomy)|pinnae]], which amplify sounds and help detect the location of a noise. It can detect [[ultrasound]], which enables it to detect ultrasonic calls made by [[rodent]] prey.<ref name="Sunquist">{{cite book |last1=Sunquist |first1=M. |last2=Sunquist |first2=F. |date=2002 |title=Wild Cats of the World |publisher=University of Chicago Press |isbn=9780226779997 |chapter=What is a Cat? |pages=5–18 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hFbJWMh9-OAC&pg=PA3 |access-date=25 October 2020 |archive-date=19 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230719111036/https://books.google.com/books?id=hFbJWMh9-OAC&pg=PA3 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Blumberg |first=M. S. |title=Rodent ultrasonic short calls: Locomotion, biomechanics, and communication |journal=Journal of Comparative Psychology |year=1992 |volume=106 |issue=4 |pages=360–365 |pmid=1451418 |doi=10.1037/0735-7036.106.4.360}}</ref> Recent research has shown that cats have socio-spatial cognitive abilities to create mental maps of owners' locations based on hearing owners' voices.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Takagi |first1=S. |last2=Chijiiwa |first2=H. |last3=Arahori |first3=M. |last4=Saito|first4=A. |last5=Fujita |first5=K. |last6=Kuroshima |first6=H. |year=2021|title=Socio-spatial cognition in cats: Mentally mapping owner's location from voice |journal=PLOS ONE |volume=16 |issue=11 |page=e0257611 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0257611 |pmc=8580247 |pmid=34758043 |bibcode=2021PLoSO..1657611T |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
=== Smell === |
|||
Cats have excellent hearing and can detect an extremely broad range of frequencies. They can hear higher-pitched sounds than either dogs or humans, detecting frequencies from 55 [[Hertz|Hz]] up to 79 [[Hertz|kHz]], a range of 10.5 [[octave]]s; while humans can only hear from 31 Hz up to 18 kHz, and dogs hear from 67 Hz to 44 kHz, which are both ranges of about 9 octaves.<ref name=PMID15472899>{{Cite journal |
|||
Cats have an acute sense of smell, due in part to their well-developed [[olfactory bulb]] and a large surface of [[olfactory mucosa]], about {{convert|5.8|cm2|in2|abbr=on}} in area, which is about twice that of humans<!-- impossible logic and only 1.7-fold less than the average dog. -->.<ref name="Moulton 1967">{{cite journal |last=Moulton |first=David G. |date=1 August 1967 |title=Olfaction in mammals |url= https://academic.oup.com/icb/article/7/3/421/244992 |journal=American Zoologist |volume=7 |issue=3 |pages=421–429 |doi=10.1093/icb/7.3.421 |pmid=6077376 |issn=0003-1569 |doi-access=free |access-date=22 November 2019 |archive-date=6 August 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210806144530/https://academic.oup.com/icb/article/7/3/421/244992 |url-status=live}}</ref> Cats and many other animals have a [[Jacobson's organ]] in their mouths that is used in the behavioral process of [[Flehmen response|flehmening]]. It allows them to sense certain aromas in a way that humans cannot. Cats are sensitive to [[Cat pheromone|pheromones]] such as [[3-mercapto-3-methylbutan-1-ol]],<ref name="felinine">{{cite journal |last1=Miyazaki |first1=Masao |last2=Yamashita |first2=Tetsuro |last3=Suzuki |first3=Yusuke |last4=Saito |first4=Yoshihiro |last5=Soeta |first5=Satoshi |last6=Taira |first6=Hideharu |last7=Suzuki |first7=Akemi |date=October 2006 |title=A major urinary protein of the domestic cat regulates the production of felinine, a putative pheromone precursor |journal=Chemistry & Biology |volume=13 |issue=10 |pages=1071–1079 |doi=10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.08.013 |pmid=17052611 |doi-access=free}}</ref> which they use to communicate through [[urine spraying]] and marking with [[scent gland]]s.<ref name="Sommerville" /> Many cats also respond strongly to plants that contain [[nepetalactone]], especially [[catnip]], as they can detect that substance at less than one part per billion.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Grognet |first=Jeff |title=Catnip: Its uses and effects, past and present |journal=The Canadian Veterinary Journal |date=June 1990 |volume=31 |issue=6 |pages=455–456 |pmc=1480656 |pmid=17423611}}</ref> About 70–80% of cats are affected by nepetalactone.<ref>{{cite magazine |url= http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=experts-how-does-catnip-work-on-cats |title=How does catnip work its magic on cats? |date=29 May 2007 |last=Turner |first=Ramona |magazine=[[Scientific American]] |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20131022023257/http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=experts-how-does-catnip-work-on-cats |archive-date=22 October 2013}}</ref> This response is also produced by other plants, such as silver vine (''[[Actinidia polygama]]'') and the herb [[Valerian (herb)|valerian]]; it may be caused by the smell of these plants mimicking a pheromone and stimulating cats' social or sexual behaviors.<ref name="Tucker">{{cite journal |title=Catnip and the catnip response |last1=Tucker |first1=Arthur |last2=Tucker |first2=Sharon |journal=Economic Botany |year=1988 |volume=42 |issue=2 |pages=214–231 |doi=10.1007/BF02858923|bibcode=1988EcBot..42..214T |s2cid=34777592}}</ref> |
|||
| doi = 10.1002/ar.a.20117 |
|||
| issn = 1552-4884 |
|||
| volume = 281 |
|||
| issue = 1 |
|||
| pages = 1111–1122 |
|||
| last = Heffner |
|||
| first = Rickye S |
|||
| title = Primate hearing from a mammalian perspective |
|||
| journal = The Anatomical Record. Part A, Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 2004-11 |
|||
| url = http://psychology.utoledo.edu/images/users/74/Primate%20Hearing%20from%20a%20Mammalian%20Perspective.pdf |
|||
|format=PDF| pmid = 15472899 |
|||
| month = November |
|||
| last1 = Heffner |
|||
| first1 = RS |
|||
}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/S0168-1591(98)00101-4 |
|||
| issn = 0168-1591 |
|||
| volume = 57 |
|||
| issue = 3-4 |
|||
| pages = 259–268 |
|||
| last = Heffner |
|||
| first = Henry E. |
|||
| title = Auditory awareness |
|||
| journal = Applied Animal Behaviour Science |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 1998-05 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T48-3V4KMVW-7/2/8d870a338ffe3afc4aaf41122bf97bd6 |
|||
}}</ref> Cats do not use this ability to hear [[ultrasound]] for communication but it is probably important in hunting,<ref name=Sunquistp10>{{Harv|Sunquist|Sunquist|2002|p=10}}</ref> since many species of rodents make ultrasonic calls.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| issn = 0735-7036 |
|||
| volume = 106 |
|||
| issue = 4 |
|||
| pages = 360–365 |
|||
| last = Blumberg |
|||
| first = M S |
|||
| title = Rodent ultrasonic short calls: locomotion, biomechanics, and communication |
|||
| journal = Journal of Comparative Psychology |
|||
| year = 1992 |
|||
| pmid = 1451418 |
|||
| doi = 10.1037/0735-7036.106.4.360 |
|||
| month = December |
|||
}}</ref> Cats' hearing is also extremely sensitive and is among the best of any mammal,<ref name=PMID15472899/> being most acute in the range of 500 Hz to 32 kHz.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| issn = 0378-5955 |
|||
| volume = 19 |
|||
| issue = 1 |
|||
| pages = 85–88 |
|||
| last = Heffner |
|||
| first = R S |
|||
| title = Hearing range of the domestic cat |
|||
| journal = Hearing Research |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| year = 1985 |
|||
| url = http://psychology.utoledo.edu/images/users/74/Audiograms/HearingRangeOfTheDomesticCat_1985.pdf |
|||
|format=PDF| doi = 10.1016/0378-5955(85)90100-5 |
|||
| pmid = 4066516 |
|||
| last2 = Heffner |
|||
| first2 = HE |
|||
}}</ref> This sensitivity is further enhanced by the cat's large movable outer ears (their ''[[pinna (anatomy)|pinnae]]''), which both amplify sounds and help a cat sense the direction from which a noise is coming.<ref name=Sunquistp10/> |
|||
=== Taste === |
|||
Cats have an acute sense of smell, which is due in part to their well-developed [[olfactory bulb]] and also to a large surface of [[olfactory mucosa]], in cats this mucosa is about 5.8 cm<sup>2</sup> in area, which is about twice that of humans and only 1.7-fold less than the average dog.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
Cats have relatively few [[taste bud]]s compared to humans (470 or so, compared to more than 9,000 on the human tongue).<ref name="sch">{{cite web |title=Do cats have a sense of taste? |url= http://www.cathealth.com/nutrition/do-cats-have-a-sense-of-taste |website=CatHealth.com |last=Schelling |first=Christianne |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20160128163535/http://www.cathealth.com/nutrition/do-cats-have-a-sense-of-taste|archive-date=28 January 2016}}</ref> Domestic and wild cats share a [[Taste receptor#Loss of function|taste receptor gene mutation]] that keeps their sweet taste buds from binding to sugary molecules, leaving them with no ability to taste [[sweetness]].<ref>{{Citation |last1=Jiang |first1=Peihua |last2=Josue |first2=Jesusa |last3=Li |first3=Xia |last4=Glaser |first4=Dieter |last5=Li |first5=Weihua |last6=Brand |first6=Joseph G. |last7=Margolskee |first7=Robert F. |last8=Reed |first8=Danielle R. |last9=Beauchamp |first9=Gary K. |title=Major taste loss in carnivorous mammals |journal=PNAS |volume=13 |issue=109 |pages=4956–4961 |date=12 March 2012 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1118360109 |pmid=22411809 |pmc=3324019 |doi-access=free}}</ref> They, however, possess taste bud receptors specialized for [[acid]]s, [[amino acid]]s such as protein, and bitter tastes.<ref name="Bradshaw2006">{{cite journal |volume=136 |issue=7 |pages=1927S–1931 |last=Bradshaw |first=John W. S. |title=The evolutionary basis for the feeding behavior of domestic dogs (''Canis familiaris'') and cats (''Felis catus'') |journal=Journal of Nutrition |date=1 July 2006 |pmid=16772461 |doi=10.1093/jn/136.7.1927S |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
| doi = 10.1093/icb/7.3.421 |
|||
| volume = 7 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 421–429 |
|||
| last = Moulton |
|||
| first = David G. |
|||
| title = Olfaction in Mammals |
|||
| journal = Amer. Zool. |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 1967-08-01 |
|||
| url = http://icb.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/7/3/421 |
|||
}}</ref> Cats are very sensitive to [[cat pheromone|pheromones]] such as [[3-Mercapto-3-methylbutan-1-ol]],<ref name="felinine">{{cite journal |
|||
| author = M. Miyazaki, T. Yamashita, Y. Suzuki, Y. Saito, S. Soeta, H. Taira, and A. Suzuki |
|||
| year = 2006 |
|||
| month = October |
|||
| title = A major urinary protein of the domestic cat regulates the production of felinine, a putative pheromone precursor |
|||
| journal = Chem. Biol. |
|||
| volume = 13 |
|||
| issue = 10 |
|||
| pages = 1071–1079 |
|||
| pmid = 17052611 |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.08.013 |
|||
| format = PDF |
|||
| first1 = M |
|||
| first2 = T |
|||
| first3 = Y |
|||
| first4 = Y |
|||
| first5 = S |
|||
| first6 = H |
|||
| first7 = A |
|||
| issn = 1074-5521 |
|||
}}</ref> which they use to communicate through urine spraying and marking with scent glands.<ref name=Sommerville/> Cats also respond strongly to plants such as [[catnip]] which contains [[nepetalactone]], as they can detect this substance at less than one part per billion.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| volume = 31 |
|||
| issue = 6 |
|||
| pages = 455–456 |
|||
| last = Grognet |
|||
| first = Jeff |
|||
| title = Catnip: Its uses and effects, past and present |
|||
| journal = The Canadian Veterinary Journal |
|||
| date = 1990-06 |
|||
| pmc = 1480656 |
|||
}}</ref> This response is also produced by other plants, such as [[Actinidia polygama|Silver Vine]] and [[valerian (herb)|Valerian]], and may be caused by the smell of these plants mimicking a pheromone and stimulating cats' social or sexual behaviors.<ref name=Tucker>{{Cite journal |
|||
| unused_data = DUPLICATE DATA: doi = 10.1007/BF02858923 |
|||
| doi = 10.1007/BF02858923 |
|||
| volume = 42 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| pages = 214–231 |
|||
| last = Tucker |
|||
| first = Arthur |
|||
| coauthors = Sharon Tucker |
|||
| title = Catnip and the catnip response |
|||
| journal = Economic Botany |
|||
| year = 1988 |
|||
| doi_brokendate = 2010-06-20 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
Their taste buds possess the receptors needed to detect [[umami]]. However, these receptors contain molecular changes that make cat taste umami different from that of humans. In humans, they detect the [[amino acid]]s [[glutamic acid]] and [[aspartic acid]], but in cats, they instead detect [[inosine monophosphate]] and [[l-Histidine]].<ref name="McGrane Gibbs Hernangomez de Alvaro Dunlop">{{cite journal |last1=McGrane |first1=Scott J. |last2=Gibbs |first2=Matthew |last3=Hernangomez de Alvaro |first3=Carlos |last4=Dunlop |first4=Nicola |last5=Winnig |first5=Marcel |last6=Klebansky |first6=Boris |last7=Waller |first7=Daniel |title=Umami taste perception and preferences of the domestic cat (''Felis catus''), an obligate carnivore |journal=Chemical Senses |volume=48 |date=1 January 2023 |issn=0379-864X |doi=10.1093/chemse/bjad026 |pmid=37551788 |pmc=10468298}}</ref> These molecules are particularly enriched in [[tuna]].<ref name="McGrane Gibbs Hernangomez de Alvaro Dunlop" /> This, it has been argued, is why cats find tuna so [[Palatability|palatable]]: as put by researchers into cat taste, "the specific combination of the high IMP and free l-Histidine contents of tuna, which produces a strong umami taste synergy that is highly preferred by cats."<ref name="McGrane Gibbs Hernangomez de Alvaro Dunlop" /> One of the researchers in this research has stated, "I think umami is as important for cats as sweet is for humans."<ref name="Science Tuna Cat">{{cite journal |last=Grimm |first=David |title=Why do cats love tuna so much? |journal=[[Science (journal)|Science]] |volume=381 |date=1 October 2023 |issue=6661 |issn=0036-8075 |doi=10.1126/science.adk5725 |page=935|pmid=37651517 |bibcode=2023Sci...381..935G |s2cid=261395204}}</ref> |
|||
Cats have relatively few taste buds compared to humans. Owing to a mutation in an early cat ancestor, one of two genes necessary to taste [[sweetness]] may have been lost by the cat family.<ref name=sugar>{{cite journal | last = Li | first = Xia | title = Pseudogenization of a Sweet-Receptor Gene Accounts for Cats' Indifference toward Sugar | journal = PLOS Genetics | volume = 1 | issue = 1 | publisher = [[Public Library of Science]] | month = July | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pgen.0010003 | accessdate = 2006-11-08 | pages = e3 | pmid = 16103917 | last1 = Li | first1 = X | last2 = Li | first2 = W | last3 = Wang | first3 = H | last4 = Cao | first4 = J | last5 = Maehashi | first5 = K | last6 = Huang | first6 = L | last7 = Bachmanov | first7 = AA | last8 = Reed | first8 = DR | last9 = Legrand-Defretin | first9 = V | issn = 1553-7390 | url = http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0010003 | format = Free full text | pmc = 1183522}}</ref> Their [[taste bud]]s instead respond to amino acids, bitter tastes and acids.<ref name=Bradshaw2006>{{Cite journal |
|||
| volume = 136 |
|||
| issue = 7 |
|||
| pages = 1927S–1931 |
|||
| last = Bradshaw |
|||
| first = John W. S. |
|||
| title = The Evolutionary Basis for the Feeding Behavior of Domestic Dogs (Canis familiaris) and Cats (Felis catus) |
|||
| journal = J. Nutr. |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-25 |
|||
| date = 2006-07-01 |
|||
| url = http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/content/abstract/136/7/1927S |
|||
| pmid = 16772461 |
|||
| issn = 0022-3166 |
|||
}}</ref> To aid with navigation and sensation, cats have dozens of movable [[vibrissa]]e (whiskers) over their body, especially their face. These provide information on the width of gaps and on the location of objects in the dark, both by touching objects directly and by sensing air currents; they also trigger protective [[blink reflex]]es to protect the eyes from damage.<ref>{{Harv|Case|2003|p=47}}</ref> |
|||
Cats also have a distinct temperature preference for their food, preferring food with a temperature around {{convert|38|C|F|abbr=on}} which is similar to that of a fresh kill; some cats reject cold food (which would signal to the cat that the "prey" item is long dead and therefore possibly toxic or decomposing).<ref name="sch" /> |
|||
==Health== |
|||
{{Main|Cat health}} |
|||
In captivity, an average life expectancy for male indoor cats at birth is 12 to 14 years,<ref>[http://journals.cambridge.org/download.php?file=%2FPNS%2FPNS54_03%2FS002966519500067Xa.pdf&code=ca230b27d1cc39a5d298f403f4d38dc7 Some nutritional aspects of ageing in dogs and cats] |
|||
By E. J. Taylor, C. Adams and R. Neville, Proceedings of the Nutrition Society (1995), 54, 645-656</ref> with females usually living a year or two longer. However, there have been records of cats reaching into their 20s and 30s, with the oldest known cat, [[Creme Puff (cat)|Creme Puff]], dying at a verified age of 38.<ref>{{cite web | title = Me-wow! Texas woman says cat is 30 years old Although she can't hear or see very well, Caterack the cat is still purring | url = http://today.msnbc.msn.com/id/33094898/ns/today-today_pets_and_animals?GT1=43001 | accessdate = 2009-09-30}}</ref> Having a cat [[neutering|neutered]] or [[spaying|spayed]] confers some health benefits, since castrated males cannot develop [[testicular cancer]], spayed females cannot develop [[uterine cancer|uterine]] or [[ovarian cancer]], and both have a reduced risk of [[mammary tumor|mammary cancer]].<ref name="spay-neuter">{{cite web|url=http://www.aspca.org/pet-care/cat-care/spay-neuter.html|title=Cat care: Spay-neuter|year=2009|work=American Society for the Prevention of Cruelity to Animals|accessdate=2009-09-06}}</ref> The lifespan of feral cats is hard to determine accurately, although one study reported a [[median]] age of 4.7 years, with a range between 0 to 10 years.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Levy JK, Gale DW, Gale LA |title=Evaluation of the effect of a long-term trap-neuter-return and adoption program on a free-roaming cat population |journal=J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. |volume=222 |issue=1 |pages=42–6 |year=2003 |month=January |pmid=12523478 |url=http://www.collierferalcatcoalition.org/tnr%20sources/javma.2003.222.pdf |format=PDF|doi=10.2460/javma.2003.222.42 |first1=JK |first2=DW |first3=LA |issn=0003-1488}}</ref> |
|||
=== |
=== Whiskers === |
||
[[File:Kittyply edit1.jpg|thumb|right|The whiskers of a cat are highly sensitive to touch.]] |
|||
Cats can suffer from a wide range of health problems, including infectious diseases, parasites, injuries and chronic disease. [[Feline vaccination|Vaccinations]] are available for many of these diseases, and domestic cats are regularly given treatments to eliminate parasites such as worms and fleas. |
|||
To aid with navigation and sensation, cats have dozens of movable [[vibrissa|whiskers (vibrissae)]] over their body, especially their faces. These provide information on the width of gaps and on the location of objects in the dark, both by touching objects directly and by sensing air currents; they also trigger protective [[blink reflex]]es to protect the eyes from damage.<ref name="Case" />{{rp|47}} |
|||
== |
== Behavior == |
||
{{See also|Cat behavior}} |
|||
In addition to obvious dangers such as [[rodenticide]]s, [[insecticide]]s and [[herbicide|weed killer]]s, cats may be poisoned by many chemicals that are usually considered safe.<ref name="vetinfo"/> This is because their livers are less effective at some forms of [[detoxification]] than those of other animals, including humans and dogs.<ref name=MacDonald/><ref>{{cite journal |author=Williams RT |title=Species variations in the pathways of drug metabolism |journal=Environ. Health Perspect. |volume=22 |pages=133–8 |date=1 February 1978|pmid=417918 |pmc=1637137 |doi=10.2307/3428562 |issn=00916765 |first=R. T. |format=Free full text |url=http://jstor.org/stable/3428562 |publisher=Environmental Health Perspectives, Vol. 22}}</ref> Some of the most common causes of poisoning in cats are antifreeze and rodent baits.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Rowland J |title=Incidence of ethylene glycol intoxication in dogs and cats seen at Colorado State University Veterinary Teaching Hospital |journal=Vet Hum Toxicol |volume=29 |issue=1 |pages=41–4 |year=1987 |month=February |pmid=3824875 |first1=J |issn=0145-6296}}</ref> It has also been suggested that cats may be particularly sensitive to environmental pollutants.<ref name="vetinfo"/><ref name=Peters>{{cite journal |author=Potera C |title=Chemical exposures: cats as sentinel species |journal=Environ. Health Perspect. |volume=115 |issue=12 |pages=A580 |year=2007 |month=December |pmid=18087575 |pmc=2137107 |first1=C |issn=0091-6765 |doi=10.1289/ehp.115-a580a}}</ref> When a cat has a sudden or prolonged serious illness without any obvious cause, it is therefore possible that it has been exposed to a toxin. |
|||
[[File:Black and gray mackerel tabby cat at night in Tuntorp 7.jpg|thumb|An alert cat at night, with pupils dilated and ears directed at a sound]] |
|||
Outdoor cats are active both day and night, although they tend to be slightly more active at night.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Spatio-temporal Sharing between the European Wildcat, the Domestic Cat and their Hybrids |last1=Germain |first1=E. |last2=Benhamou |first2=S. |last3=Poulle |first3=M.-L. |journal=Journal of Zoology |year=2008 |volume=276 |issue=2 |pages=195–203 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7998.2008.00479.x|doi-access=free }}</ref> Domestic cats spend the majority of their time in the vicinity of their homes but can range many hundreds of meters from this central point. They establish [[Territory (animal)|territories]] that vary considerably in size, in one study ranging {{cvt|7|-|28|ha|acre}}.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Barratt |first=D. G. |title=Home Range Size, Habitat Utilisation and Movement Patterns of Suburban and Farm Cats ''Felis catus'' |journal=Ecography |year=1997 |doi=10.1111/j.1600-0587.1997.tb00371.x |jstor=3682838 |volume=20 |issue=3 |pages=271–280|bibcode=1997Ecogr..20..271B }}</ref> The timing of cats' activity is quite flexible and varied but being low-light predators, they are generally [[Crepuscular animal|crepuscular]], which means they tend to be more active near dawn and dusk. However, house cats' behavior is also influenced by human activity and they may adapt to their owners' sleeping patterns to some extent.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Circadian rhythms in food intake and activity in domestic cats |last1=Randall |first1=W. |last2=Johnson |first2=R. F. |last3=Randall |first3=S. |last4=Cunningham |first4=J. T. |journal=Behavioral Neuroscience |year=1985 |volume=99 |issue=6 |pmid=3843546 |doi=10.1037/0735-7044.99.6.1162 |pages=1162–1175}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Ling |first=Thomas |date=2 June 2021 |title=Why do cats sleep so much? |url=https://www.sciencefocus.com/nature/why-do-cats-sleep-so-much/ |access-date=3 April 2023 |website=BBC Science Focus Magazine |archive-date=3 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230403180235/https://www.sciencefocus.com/nature/why-do-cats-sleep-so-much/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Cats conserve energy by sleeping more than most animals, especially as they grow older. The daily duration of sleep varies, usually between 12 and 16 hours, with 13 and 14 being the average. Some cats can sleep as much as 20 hours. The term "cat nap" for a short rest refers to the cat's tendency to fall asleep (lightly) for a brief period. While asleep, cats experience short periods of [[rapid eye movement sleep]] often accompanied by muscle twitches, which suggests they are dreaming.<ref>{{Cite journal |doi=10.1016/0166-2236(79)90110-3 |volume=2 |pages=280–282 |last=Jouvet |first=M. |title=What Does a Cat Dream About? |journal=Trends in Neurosciences |year=1979|s2cid=53161799}}</ref> |
|||
Human medicines should never be given to cats. For example, the painkiller [[paracetamol]] (also called acetaminophen), sold under brand names such as [[Tylenol]] and [[Panadol]] is extremely toxic to cats: even very small doses can be fatal and need immediate treatment.<ref name="CanVetJ2003-Allen">{{cite journal | author = Allen AL | title = The diagnosis of acetaminophen toxicosis in a cat | journal = Canadian Veterinary Journal |date=1 June 2003| pages = 509–10 | volume = 44 | issue = 6 | pmid = 12839249 | pmc = 340185 | first1 = AL | issn = 0008-5286}}</ref><ref name="VetHumToxicol1998-Villar">{{cite journal | author = Villar D, Buck WB, Gonzalez JM | title = Ibuprofen, aspirin and acetaminophen toxicosis and treatment in Dogs and Cats | journal = Vet Hum Toxicol | year = 1998 | pages = 156–62 | volume = 40 | issue = 3 | pmid = 9610496 | month = June | first1 = D | first2 = WB | first3 = JM | issn = 0145-6296}}</ref> Even [[aspirin]], which is sometimes used to treat [[arthritis]] in cats, is much more toxic to them than to humans and must be administered cautiously.<ref name="vetinfo"/> Similarly, application of [[minoxidil]] (Rogaine) to the skin of cats, either accidentally or by well-meaning owners attempting to counter loss of fur, has sometimes been fatal.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Camille DeClementi | title = Suspected toxicosis after topical administration of minoxidil in 2 cats | journal = Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care | year = 2004 | month = December | pages = 287–292 | volume = 14 | issue = 4 | doi = 10.1111/j.1476-4431.2004.04014.x | accessdate= 2007-01-18 | last2 = Bailey | first2 = Keith L. | last3 = Goldstein | first3 = Spencer C. | last4 = Orser | first4 = Michael Scott}}</ref> [[Essential oil]]s can be toxic to cats and there have been reported cases of serious illnesses caused by [[tea tree oil]], and tea tree oil-based flea treatments and shampoos.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Bischoff K, Guale F |title=Australian tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia) oil poisoning in three purebred cats |journal=J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. |volume=10 |issue=2 |pages=208–10 |date=1 April 1998|pmid=9576358 |url=http://www.jvdi.org/cgi/reprint/10/2/208 |first1=K |first2=F |issn=1040-6387}}</ref> |
|||
A common misconception is that a cat's behavioral and personality traits correspond to its coat color. These traits instead depend on a complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors.<ref>{{cite journal | last1=Udell | first1=Monique | last2=Delgado | first2=Mikel | last3=Ekenstedt | first3=Kari | last4=Shoveller | first4=Anna Kate | last5=Croney | first5=Candace | title=CATastrophic myths part 2: Common misconceptions about the environmental, nutritional, and genetic management of domestic cats and their welfare implications | journal=The Veterinary Journal | volume=300-302 |year=2023 | doi=10.1016/j.tvjl.2023.106029 | page=106029| doi-access=free | pmid=37683762 }}</ref> |
|||
Other common household substances that should be used with caution around cats include [[mothball]]s and other [[naphthalene]] products.<ref name="vetinfo"/> [[Phenol]]-based products are often used for cleaning and disinfecting near cats' feeding areas or litter boxes: such as [[Pine-Sol]], [[Dettol]] (Lysol) or [[hexachlorophene]],<ref name="vetinfo">{{cite web | url = http://www.vetinfo.com/ctoxin.html | title = Toxic to Cats | accessdate = 2007-01-18 | publisher = Vetinfo4Cats}}</ref> but these can sometimes be fatal.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Rousseaux CG, Smith RA, Nicholson S | title = Acute Pinesol toxicity in a domestic cat | journal = Vet Hum Toxicol | year = 1986 | pages = 316–7 | volume = 28 | issue = 4 | pmid = 3750813 | month = August | first1 = CG | first2 = RA | first3 = S | issn = 0145-6296}}</ref> [[Ethylene glycol]], often used as an automotive [[antifreeze]], is particularly appealing to cats, and as little as a teaspoonful can be fatal.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.cfainc.org/articles/antifreeze.html | title = Antifreeze Warning | publisher = The Cat Fanciers' Association, Inc. |accessdate = 2007-05-15}}</ref> Some human foods are toxic to cats; for example [[theobromine]] in [[chocolate]] can cause [[theobromine poisoning]], although few cats will eat chocolate.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.aspcapro.org/animal-poison-control/documents/l-vettech_0301.pdf |format=PDF|title=Death by Chocolate? Methylxanthine Toxicosis |publisher=Veterinary Technician |month=March | year=2001 |accessdate=25 August 2009}}</ref> Large amounts of [[onion]]s or [[garlic]] are also poisonous to cats.<ref name="vetinfo"/> Many [[houseplant]]s are also dangerous,<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.cfainc.org/articles/plants.html | title = Plants and Your Cat | publisher = The Cat Fanciers' Association, Inc. | accessdate = 2007-05-15}}</ref> such as ''[[Philodendron]]'' species and the leaves of the [[Lilium longiflorum|Easter Lily]], which can cause permanent and life-threatening kidney damage.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| issn = 0003-1488 |
|||
| volume = 220 |
|||
| issue = 1 |
|||
| pages = 49–52, 36 |
|||
| last = Langston |
|||
| first = Cathy E |
|||
| title = Acute renal failure caused by lily ingestion in six cats |
|||
| journal = Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-25 |
|||
| date = 2002-01-01 |
|||
| pmid = 12680447 |
|||
| doi = 10.2460/javma.2002.220.49 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
== |
=== Sociability === |
||
The social behavior of the domestic cat ranges from widely dispersed individuals to [[Feral cat colony|feral cat colonies]] that gather around a food source, based on groups of co-operating females.<ref name="Crowell-davis2004">{{Cite journal |title=Social Organization in the Cat: A Modern Understanding |last1=Crowell-Davis |first1=S. L. |last2=Curtis |first2=T. M. |last3=Knowles |first3=R. J. |year=2004 |journal=Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery |volume=6 |issue=1 |pages=19–28 |doi=10.1016/j.jfms.2003.09.013 |pmid=15123163 |pmc=10822437 |s2cid=25719922 |url=http://zoopsy.free.fr/veille_biblio/social_organization_cat_2004.pdf |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110720231305/http://zoopsy.free.fr/veille_biblio/social_organization_cat_2004.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=20 July 2011}}</ref><ref name="Liberg_al2014">{{Cite book |last1=Liberg |first1=O. |last2=Sandell |first2=M. |last3=Pontier |first3=D. |last4=Natoli |first4=E. |chapter=Density, spatial organisation and reproductive tactics in the domestic cat and other felids |title=The domestic cat: the biology of its behaviour |location=Cambridge |publisher=Cambridge University Press |date=2000 |edition=2nd |isbn=9780521636483 |editor1-last=Turner |editor1-first=D. C. |editor2-last=Bateson |editor2-first=P. |pages=119–147 |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=GgUwg6gU7n4C&pg=PA119 |access-date=25 October 2020 |archive-date=31 March 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210331062218/https://books.google.com/books?id=GgUwg6gU7n4C&pg=PA119 |url-status=live}}</ref> Within such groups, one cat is usually dominant over the others.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Patterns of social interaction in cats (''Felis domestica'') |last1=Baron |first1=A. |last2=Stewart |first2=C. N. |last3=Warren |first3=J. M. |journal=Behaviour |date=1 January 1957 |doi=10.1163/156853956X00084 |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=56–66 |jstor=4532869}}</ref> Each cat in a colony holds a distinct territory, with sexually active males having the largest territories, which are about 10 times larger than those of female cats and may overlap with several females' territories. These territories are marked by [[urine spraying]], rubbing objects at head height with secretions from facial glands, and by [[defecation]].<ref name="Sommerville">{{Cite journal |doi=10.1016/S0168-1591(98)00102-6 |volume=57 |issue=3–4 |pages=269–286 |last=Sommerville |first=B. A. |title=Olfactory Awareness |journal=Applied Animal Behaviour Science |year=1998}}</ref> Between these territories are neutral areas where cats watch and greet one another without territorial conflicts. Outside these neutral areas, territory holders usually chase away stranger cats, at first by staring, hissing, and [[growling]], and, if that does not work, by short and violent, noisy attacks. Although cats do not have a social survival strategy or [[herd behavior]], they always hunt alone.<ref name="Bradshaw" /> |
|||
{{See also|Cat behavior|cat communication}} |
|||
{{listen | filename = Cat in front of open fire purring.ogg | title = "Cat purring" | description = A young female cat, purring in front of a warm open fire. | format = [[Ogg]]}} |
|||
Free-ranging cats are active both day and night, although they tend to be slightly more active at night.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2008.00479.x |
|||
| volume = 276 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| pages = 195–203 |
|||
| last = Germain |
|||
| first = E. |
|||
| title = Spatio-temporal sharing between the European wildcat, the domestic cat and their hybrids |
|||
| journal = Journal of Zoology |
|||
| year = 2008 |
|||
| last2 = Benhamou |
|||
| first2 = S. |
|||
| last3 = Poulle |
|||
| first3 = M.-L. |
|||
}}</ref><ref name=Barratt>{{Cite journal |
|||
| issn = 09067590 |
|||
| volume = 20 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 271–280 |
|||
| last = Barratt |
|||
| first = David G. |
|||
| title = Home Range Size, Habitat Utilisation and Movement Patterns of Suburban and Farm Cats Felis catus |
|||
| journal = Ecography |
|||
|date=1 June 1997 |
|||
| url = http://www.jstor.org/stable/3682838 |
|||
| doi = 10.1111/j.1600-0587.1997.tb00371.x |
|||
}}</ref> The timing of cats' activity is quite flexible and varied, which means that house cats may be more active in the morning and evening ([[crepuscular]] behavior), as a response to greater human activity at these times.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1037/0735-7044.99.6.1162 |
|||
| issn = 0735-7044 |
|||
| volume = 99 |
|||
| issue = 6 |
|||
| pages = 1162–1175 |
|||
| last = Randall |
|||
| first = Walter |
|||
| title = Circadian rhythms in food intake and activity in domestic cats. |
|||
| journal = Behavioral Neuroscience |
|||
| pmid = 3843546 |
|||
| year = 1985 |
|||
| month = December |
|||
| first2 = RF |
|||
| first3 = S |
|||
| first4 = JT |
|||
| last2 = Johnson |
|||
| last3 = Randall |
|||
| last4 = Cunningham |
|||
}}</ref> House cats have territories that vary quite a lot in size, in one study ranging from seven to {{convert|28|ha|acre|lk=in}}.<ref name=Barratt/> Although they spend the majority of their time in the vicinity of their home, they can range many hundreds of meters from this central point.<ref name=Barratt/> |
|||
Life in proximity to humans and other domestic animals has led to a symbiotic social adaptation in cats, and cats may express great affection toward humans or other animals. [[Ethology|Ethologically]], a cat's human keeper functions as a mother surrogate.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vrueZDfPUzoC&pg=PA518 |last1=Mills |first1=D. S. |last2=Marchant-Forde |first2=J. |date=2010 |title=Encyclopedia of Applied Animal Behaviour and Welfare |page=518 |isbn=9780851997247 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170407004417/https://books.google.com/books?id=vrueZDfPUzoC&pg=PA518 |archive-date=7 April 2017}}</ref> Adult cats live their lives in a type of extended kittenhood, a form of behavioral [[neoteny]]. Their high-pitched sounds may mimic the cries of a hungry human infant, making them particularly difficult for humans to ignore.<ref name="McComb 2009">{{Cite journal |last1=McComb |first1=K. |last2=Taylor |first2=A. M. |last3=Wilson |first3=C. |last4=Charlton |first4=B. D. |title=The Cry Embedded within the Purr |journal=Current Biology |volume=19 |issue=13 |pages=R507–508 |year=2009 |pmid=19602409 |doi=10.1016/j.cub.2009.05.033|s2cid=10972076 |doi-access=free|bibcode=2009CBio...19.R507M }}</ref> Some pet cats are poorly socialized. In particular, older cats show aggressiveness toward newly arrived kittens, which include biting and scratching; this type of behavior is known as feline asocial aggression.<ref name="Levine 2005">{{Cite journal |title=Intercat aggression in households following the introduction of a new cat |last1=Levine |first1=E. |last2=Perry |first2=P. |last3=Scarlett |first3=J. |last4=Houpt |first4=K. |journal=Applied Animal Behaviour Science |issue=3–4 |year=2005 |pages=325–336 |doi=10.1016/j.applanim.2004.07.006 |volume=90 |url=http://faculty.washington.edu/jcha/330_cats_introducing.pdf |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090326225932/http://faculty.washington.edu/jcha/330_cats_introducing.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=26 March 2009}}</ref> |
|||
Cats conserve energy by sleeping more than most animals, especially as they grow older. The daily duration of sleep varies, usually 12–16 hours, with 13–14 being the average. Some cats can sleep as much as 20 hours in a 24-hour period. The term ''[[wikt:cat nap|cat nap]]'' refers to the cat's ability to fall asleep (lightly) for a brief period and has entered the English lexicon—someone who nods off for a few minutes is said to be "taking a cat nap". During sleep cats experience short periods of [[rapid eye movement sleep]] accompanied by muscle twitches, which suggests that they are [[dream]]ing.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/0166-2236(79)90110-3 |
|||
| issn = 0166-2236 |
|||
| volume = 2 |
|||
| pages = 280–282 |
|||
| last = Jouvet |
|||
| first = Michel |
|||
| title = What does a cat dream about? |
|||
| journal = Trends in Neurosciences |
|||
| accessdate = 2010-02-11 |
|||
| year = 1979 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T0V-485RJ0M-4X/2/82ae75a3e2df00e9eb92989351aa4ebe |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
[[Redirected aggression]] is a common form of aggression which can occur in multiple cat households. In redirected aggression, there is usually something that agitates the cat: this could be a sight, sound, or another source of stimuli which causes a heightened level of anxiety or arousal. If the cat cannot attack the stimuli, it may direct anger elsewhere by attacking or directing aggression to the nearest cat, pet, human or other being.<ref name="Horwitz">{{cite news |last1=Horwitz |first1=Debra |title=Cat Behavior Problems - Aggression Redirected |url= https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/cat-behavior-problems-aggression-redirected#:~:text=What%20is%20redirected%20aggression%3F,cat%20out%20on%20the%20property |access-date=16 June 2022 |publisher=VCA Animal Hospitals |year=2022 |archive-date=19 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220319184510/https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/cat-behavior-problems-aggression-redirected#:~:text=What%20is%20redirected%20aggression%3F,cat%20out%20on%20the%20property |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Behaviorist">{{cite news |last1=Johnson |first1=Ingrid |title=Redirected Aggression in Cats: Recognition and Treatment Strategies |url= https://iaabc.org/cat/redirected-aggression-in-cats |access-date=16 June 2022 |publisher=International Association of Animal Behavior Consultants |date=17 May 2014 |archive-date=7 March 2022 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20220307001045/https://iaabc.org/cat/redirected-aggression-in-cats |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Sociability=== |
|||
[[File:Listen, do you want to know a secret.jpg|thumb|[[Social grooming]] in a pair of cats.]] |
|||
Although wildcats are solitary, the social behavior of domestic cats is much more variable and ranges from widely dispersed individuals to [[feral cat colony|feral cat colonies]] that form around a food source, based on groups of co-operating females.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/0376-6357(95)00070-4 |
|||
| issn = 0376-6357 |
|||
| volume = 37 |
|||
| issue = 1 |
|||
| pages = 85–88 |
|||
| last = Pontier |
|||
| first = Dominique |
|||
| coauthors = Eugenia Natoli |
|||
| title = Male reproductive success in the domestic cat (Felis catus L.): A case history |
|||
| journal = Behavioural Processes |
|||
| year = 1996 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T2J-497C79W-C/2/8dac343c3757c69ec2412aa80cfec5e3 |
|||
}}</ref><ref name=Crowell-davis2004>{{cite journal | author = Crowell-davis, S.L. | year = 2004 | title = Social organization in the cat: a modern understanding | journal = Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery | volume = 6 | issue = 1 | pages = 19–28 | url = http://zoopsy.free.fr/veille_biblio/social_organization_cat_2004.pdf |format=PDF| accessdate = 2008-05-21 | doi = 10.1016/j.jfms.2003.09.013 | pmid = 15123163 | month = February | last1 = Crowell-Davis | first1 = SL | last2 = Curtis | first2 = TM | last3 = Knowles | first3 = RJ | issn = 1098-612X}}</ref> Within such groups one cat is usually dominant over the others.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| issn = 00057959 |
|||
| volume = 11 |
|||
| issue = 1 |
|||
| pages = 56–66 |
|||
| last = Baron |
|||
| first = Alan |
|||
| title = Patterns of Social Interaction in Cats (Felis domestica) |
|||
| journal = Behaviour |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 1 January 1957 |
|||
| url = http://www.jstor.org/stable/4532869 |
|||
| doi = 10.1163/156853956X00084 |
|||
| first2 = . |
|||
| first3 = J. M. |
|||
| author3 = Warren |
|||
| last2 = Stewart |
|||
}}</ref> Each cat in a colony holds a distinct territory, with sexually active males having the largest territories, which are about ten times larger than those of female cats and may overlap with several females' territories.<ref name=Sommerville/> These territories are marked by urine spraying, by rubbing objects at head height with secretions from facial glands and by defecation.<ref name=Sommerville>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/S0168-1591(98)00102-6 |
|||
| issn = 0168-1591 |
|||
| volume = 57 |
|||
| issue = 3-4 |
|||
| pages = 269–286 |
|||
| last = Sommerville |
|||
| first = B. A. |
|||
| title = Olfactory awareness |
|||
| journal = Applied Animal Behaviour Science |
|||
| year = 1998 |
|||
}}</ref> Between these territories are neutral areas where cats watch and greet one another without territorial conflicts. Outside these neutral areas, territory holders usually chase away stranger cats, at first by staring, hissing, and growling, and if that does not work, by short but noisy and violent attacks. Despite some cats cohabiting in colonies, cats do not have a social survival strategy, or a [[herd behavior|pack mentality]] and always hunt alone.<ref name=Bradshaw/> |
|||
Domestic cats' [[scent rubbing]] behavior toward humans or other cats is thought to be a feline means of social bonding.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Soennichsen |first1=S. |last2=Chamove |first2=A. S. |year=2015 |title=Responses of cats to petting by humans |journal=Anthrozoös |volume=15 |issue=3 |pages=258–265 |doi=10.2752/089279302786992577|s2cid=144843766}}</ref> |
|||
Domestic cats use many vocalizations for [[cat communication|communication]], including [[purr]]ing, [[trill consonant|trilling]], [[hiss#Animals|hissing]], [[growling]], snarling and several different forms of [[cat communication#Meowing|meow]]ing.<ref name=Moelk>{{Cite journal |
|||
| issn = 00029556 |
|||
| volume = 57 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| pages = 184–205 |
|||
| last = Moelk |
|||
| first = Mildred |
|||
| title = Vocalizing in the House-Cat; A Phonetic and Functional Study |
|||
| journal = The American Journal of Psychology |
|||
| accessdate = 2010-03-04 |
|||
| date = 1944-04 |
|||
| url = http://www.jstor.org/stable/1416947 |
|||
| doi = 10.2307/1416947 |
|||
| publisher = The American Journal of Psychology, Vol. 57, No. 2 |
|||
}}</ref> In contrast, feral cats are generally silent.<ref>{{harv|Jensen|2009|p=208}}</ref> Their types of [[Cat body language|body language]], including position of ears and tail, relaxation of whole body, and kneading of paws, are all indicators of mood. The tail and ears are particularly important social signal in cats, with a raised tail acting as a friendly greeting.<ref name=behaviourguide/><ref name=Cafazzo/> Tail raising also indicates the cat's position in the group's [[social hierarchy]], with dominant individuals raising their tails less often than subordinate animals.<ref name=Cafazzo>{{cite journal |author=Cafazzo S, Natoli E |title=The social function of tail up in the domestic cat (Felis silvestris catus) |journal=Behav. Processes |volume=80 |issue=1 |pages=60–6 |year=2009 |month=January |pmid=18930121 |doi=10.1016/j.beproc.2008.09.008 |first1=S |first2=E |issn=0376-6357}}</ref> Nose-touching is also a common greeting and may be followed by [[social grooming]], which is solicited by one of the cats raising and tilting its head.<ref name=Crowell-davis2004/> However, some pet cats are poorly socialized. In particular older cats may show aggressiveness towards newly arrived kittens, which may include biting and scratching; this type of behavior is known as Feline Asocial Aggression.<ref>{{cite journal | url = http://faculty.washington.edu/jcha/330_cats_introducing.pdf | format = PDF | title = Intercat aggression in households following the introduction of a new cat | author = E. Levine | journal = Applied Animal Behaviour Science | issue = 90 | year = 2005 | pages = 325–336 | doi = 10.1016/j.applanim.2004.07.006 | volume = 90 | accessdate = 2009-04-08 | last2 = Perry | first2 = P | last3 = Scarlett | first3 = J | last4 = Houpt | first4 = K}}</ref> |
|||
=== Communication === |
|||
For cats, life in proximity with humans (and other animals kept by humans) amounts to a "symbiotic social adaptation". They may express great affection towards their human companions, especially if they [[imprinting (psychology)|imprint]] on them at a very young age and are treated with consistent affection. It has been suggested that, [[ethology|ethologically]], the human keeper of a cat functions as a sort of surrogate for the cat's mother, and that adult domestic cats live their lives in a kind of extended kittenhood, a form of behavioral [[neoteny]].<ref>[http://animal.discovery.com/guides/cats/body/maturity.html Cat Guide: Adolescence and Sexual Maturity] Animal Planet</ref> Conversely, the high-pitched purrs cats make to solicit food may mimic the cries of a hungry human infant, making them particularly hard for humans to ignore.<ref>{{cite journal |author=McComb K, Taylor AM, Wilson C, Charlton BD |title=The cry embedded within the purr |journal=Curr. Biol. |volume=19 |issue=13 |pages=R507–8 |year=2009 |month=July |pmid=19602409 |doi=10.1016/j.cub.2009.05.033}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Cat communication}} |
|||
{{Listen image |
|||
===Grooming=== |
|||
| main_image = Domestic Cat Face Shot.jpg |
|||
[[File:Cat tongue macro.jpg|thumb|The hooked papillae on a cat tongue act like a [[hairbrush]] to help clean and detangle fur.]] |
|||
| main_image_caption = Vocalizing domestic cat |
|||
Cats are known for their cleanliness, spending many hours licking their coats.<ref name=hairballs/> The cat's [[tongue]] has backwards-facing spines about 500 [[micrometre]]s long, which are called [[Filiform papilla|papillae]]. These are quite rigid, as they contain [[keratin]].<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| main_image_upright = 1 |
|||
| doi = 10.1159/000145583 |
|||
| filename = Meow domestic cat.ogg |
|||
| issn = 1422-6421 |
|||
| title = A meow |
|||
| volume = 114 |
|||
| description = |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| |
| plain = yes |
||
}} |
|||
| last = Boshel |
|||
| first = J. |
|||
| title = Filiform Papillae of Cat Tongue |
|||
| journal = Cells Tissues Organs |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-25 |
|||
| year = 1982 |
|||
| url = http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowAbstract&ArtikelNr=145583&Ausgabe=238501&ProduktNr=224197 |
|||
| pmid = 17728549 |
|||
| month = |
|||
| last1 = Mennel |
|||
| first1 = S |
|||
| last2 = Barbazetto |
|||
| first2 = I |
|||
| last3 = Meyer |
|||
| first3 = CH |
|||
| last4 = Peter |
|||
| first4 = S |
|||
| last5 = Stur |
|||
| first5 = M |
|||
}}</ref> These spines allow cats to groom themselves by licking their fur, with the rows of papillae acting like a hairbrush. Some cats, particularly longhaired cats, occasionally regurgitate [[hairball]]s of fur that have collected in their stomachs from grooming. These clumps of fur are usually sausage-shaped and about two to three centimeters long. Hairballs can be prevented with remedies that ease elimination of the hair through the gut, as well as regular grooming of the coat with a comb or stiff brush.<ref name=hairballs>{{cite web |url=http://www.vet.cornell.edu/FHC/news/hair.htm |title=When Hair Balls Aren't Harmless. |publisher=Cornell Feline Health Center |year=2006 |accessdate=25 August 2009}}</ref> |
|||
Domestic cats use many [[Animal communication|vocalizations]] for communication, including [[purr]]ing, [[Trill consonant|trilling]], hissing, growling/snarling, grunting, and several different forms of meowing.<ref name=Moelk1944>{{Cite journal |title=Vocalizing in the House-cat; A Phonetic and Functional Study |last=Moelk |first=M. |journal=The American Journal of Psychology |year=1944 |volume=57 |issue=2 |pages=184–205 |doi=10.2307/1416947 |jstor=1416947}}</ref> Their [[Cat body language|body language]], including position of ears and tail, relaxation of the whole body, and kneading of the paws, are all indicators of mood. The tail and ears are particularly important social signal mechanisms; a raised tail indicates a friendly greeting, and flattened ears indicate hostility. Tail-raising also indicates the cat's position in the group's [[social hierarchy]], with dominant individuals raising their tails less often than subordinate ones.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Cafazzo |first1=S. |last2=Natoli |first2=E. |title=The Social Function of Tail Up in the Domestic Cat (''Felis silvestris catus'') |journal=Behavioural Processes |volume=80 |issue=1 |pages=60–66 |year=2009 |pmid=18930121 |doi=10.1016/j.beproc.2008.09.008 |s2cid=19883549}}</ref> Feral cats are generally silent.<ref name="Jensen">{{Cite book |last=Jensen |first=P. |title=The Ethology of Domestic Animals |series="Modular Text" series |publisher=[[Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International]] |location=Wallingford, England |date=2009 |isbn=9781845935368}}</ref>{{rp|208}} Nose-to-nose touching is also a common greeting and may be followed by [[social grooming]], which is solicited by one of the cats raising and tilting its head.<ref name="Crowell-davis2004" /> |
|||
===Fighting=== |
|||
[[File:GAto.jpg|thumb|left|Cats intimidate opponents by arching their backs, raising their fur, turning sideways, and [[hiss#Animals|hissing]].]] |
|||
With domestic cats, males are more likely to fight than females.<ref name=Lindell>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/S0168-1591(97)00032-4 |
|||
| issn = 0168-1591 |
|||
| volume = 55 |
|||
| issue = 1-2 |
|||
| pages = 153–162 |
|||
| last = Lindell |
|||
| first = Ellen M. |
|||
| title = Intercat aggression: a retrospective study examining types of aggression, sexes of fighting pairs, and effectiveness of treatment |
|||
| journal = Applied Animal Behaviour Science |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 1997-12 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T48-3S53M4K-F/2/da92519b734addeef1e8f418610d1132 |
|||
}}</ref> With feral cats, the most common reason for [[Catfight (animal behavior)|cat fighting]] is when two males are competing to mate with a female: here most fights will be won by the heavier male.<ref>Akihiro Yamane, Teruo Doi and Yuiti Ono "Mating behaviors, courtship rank and mating success of male feral cat (Felis catus)" Journal of Ethology, Volume 14, Number 1, p35-44 (1996) doi:10.1007/BF02350090</ref> Another possible reason for fighting in domestic cats is when the cats have difficulties in establishing a territory within a small home.<ref name=Lindell/> Female cats will also fight over territory or to defend their kittens. Spaying females and neutering males will decrease or eliminate this behavior in many cases. |
|||
[[Purring]] may have developed as an evolutionary advantage as a signaling mechanism of reassurance between mother cats and [[Breastfeeding|nursing]] kittens, who are thought to use it as a care-soliciting signal.<ref name="bradshaw2012"/> Post-nursing cats also often purr as a sign of contentment: when being petted, becoming relaxed,<ref name="BruelKjaer">{{cite web |first1=E. |last1=von Muggenthaler |first2=B. |last2=Wright |url=http://www.bksv.com/catspurr |title=Solving the Cat's Purr Mystery Using Accelerometers |work=BKSV |publisher=[[Brüel & Kjær]] |access-date=11 February 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110722131617/http://www.bksv.com/catspurr |archive-date=22 July 2011}}</ref><ref name="IsnareCom">{{cite web |url= http://www.isnare.com/?aid=195293&ca=Pets |title=The Cat's Remarkable Purr |work=ISnare |access-date=6 August 2008 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110713063142/http://www.isnare.com/?aid=195293&ca=Pets |archive-date=13 July 2011}}</ref> or eating. Although purring is popularly interpreted as indicative of pleasure, it has been recorded in a wide variety of circumstances, most of which involve physical contact between the cat and another, presumably trusted individual.<ref name="bradshaw2012"/> Some cats have been observed to purr continuously when chronically ill or in apparent pain.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Beaver |first1=Bonnie V. G. |title=Feline behavior : a guide for veterinarians |date=2003 |publisher=Saunders |location=St. Louis, Missouri |isbn=9780721694986 |edition=2nd}}</ref> |
|||
When fighting, cats make themselves appear more impressive and threatening by raising their fur and arching their backs, thus increasing their apparent size.<ref name=behaviourguide>{{cite web |url=http://animal.discovery.com/guides/cats/behavior/bodylanguageintro.html |title=Cat Guide: Body Language |publisher=Animal Planet |accessdate=26 August 2009}}</ref> Often, the ears are pointed down and back to avoid damage to the inner ear and potentially listen for any changes behind them while focused forward. Attacks usually comprise powerful slaps to the face and body with the forepaws as well as bites, but serious damage is rare; usually the loser runs away with little more than a few scratches to the face, and sometimes the ears. Cats will also throw themselves to the ground in a defensive posture to rake their opponent's belly with their powerful hind legs.<ref>[http://www.hsus.org/pets/pet_care/our_pets_for_life_program/cat_behavior_tip_sheets/aggression_between_family_cats.html Aggression Between Family Cats] ''The Humane Society of the United States'' 2002</ref> |
|||
The exact mechanism by which cats purr has long been elusive, but it has been proposed that purring is generated via a series of sudden build-ups and releases of pressure as the [[glottis]] is opened and closed, which causes the [[vocal folds]] to separate forcefully. The [[Larynx|laryngeal muscles]] in control of the glottis are thought to be driven by a [[neural oscillation|neural oscillator]] which generates a cycle of contraction and release every 30–40 [[millisecond]]s (giving a frequency of 33 to 25 Hz).<ref name="bradshaw2012">{{cite book |last=Bradshaw |first=John W. S. |title=The Behaviour of the Domestic Cat |date=2012 |publisher=CABI |location=Wallingford |isbn=9781780641201 |pages=71–72 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=CMQdnrR0xEsC |access-date=6 July 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Remmers |first1=J. E. |last2=Gautier |first2=H. |title=Neural and mechanical mechanisms of feline purring |journal=Respiration Physiology |year=1972 |volume=16 |issue=3 |pages=351–361 |doi=10.1016/0034-5687(72)90064-3 |pmid=4644061}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Frazer Sissom |first1=D. E. |last2=Rice |first2=D. A. |last3=Peters |first3=G. |title=How cats purr |journal=Journal of Zoology |year=1991 |volume=223 |issue=1 |pages=67–78 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7998.1991.tb04749.x |s2cid=32350871}}</ref> |
|||
Normally, serious injuries from fighting will be limited to infections of scratches and bites, though these can occasionally kill cats if untreated. In addition, bites are probably the main route of transmission of [[feline immunodeficiency virus]] (FIV).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Pedersen NC, Yamamoto JK, Ishida T, Hansen H |title=Feline immunodeficiency virus infection |journal=Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. |volume=21 |issue=1 |pages=111–29 |year=1989 |month=May |pmid=2549690 |doi=10.1016/0165-2427(89)90134-7 |first1=NC |first2=JK |first3=T |first4=H |issn=0165-2427}}</ref> Sexually active males will usually be involved in many fights during their lives, and often have decidedly battered faces with obvious scars and cuts to the ears and nose. |
|||
Domestic cats observed in rescue facilities have 276 morphologically distinct [[facial expression]]s based on 26 facial movements; each facial expression corresponds to different social functions that are probably influenced by domestication.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Scott |first1=L. |last2=Florkiewicz |first2=B. N. |year=2023 |title=Feline Faces: Unraveling the Social Function of Domestic Cat Facial Signals |journal=Behavioural Processes |volume=213 |page=104959 |doi=10.1016/j.beproc.2023.104959|pmid=37858844 |s2cid=264176390}}</ref> Facial expressions have helped researchers detect pain in cats. The feline [[grimace scale]]'s five criteria—ear position, orbital tightening, muzzle tension, whisker change, and head position—indicated the presence of acute pain in cats.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Evangelista |first1=M. C. |last2=Watanabe |first2=R. |last3=Leung |first3=V. S. Y. |last4=Monteiro |first4=B. P. |last5=O'Toole |first5=E. |last6=Pang |first6=D. S. J. |last7=Steagall |first7=P. V. |year=2019 |title=Facial expressions of pain in cats: the development and validation of a Feline Grimace Scale |journal=Scientific Reports |language=en |volume=9 |issue=1 |pages=19128 |doi=10.1038/s41598-019-55693-8 |pmc=6911058 |pmid=31836868|bibcode=2019NatSR...919128E}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Monteiro |first1=B. P |last2=Lee |first2=N. H.Y. |last3=Steagall |first3=P. V. |year=2023 |title=Can cat caregivers reliably assess acute pain in cats using the Feline Grimace Scale? A large bilingual global survey |journal=Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery |volume=25 |issue=1 |pages=1098612X221145499 |doi=10.1177/1098612X221145499 |pmid=36649089|pmc=10812049 }}</ref> |
|||
===Hunting and feeding=== |
|||
Cats feed on small prey, primarily birds and rodents.<ref name=Woods/> Feral cats and house cats that are free-fed tend to consume many small meals in a single day, although the frequency and size of meals varies between individuals.<ref name=Bradshaw>{{cite journal |author=Bradshaw JW, Goodwin D, Legrand-Defrétin V, Nott HM |title=Food selection by the domestic cat, an obligate carnivore |journal=Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. |volume=114 |issue=3 |pages=205–9 |year=1996 |month=July |pmid=8759144 |doi=10.1016/0300-9629(95)02133-7 |first1=JW |first2=D |first3=V |first4=HM |issn=1096-4940}}</ref> Cats use two hunting strategies, either stalking prey actively, or waiting in ambush until an animal comes close enough to be captured. Although it is not certain, the type of strategy used may depend on the prey species in the area, with for example, cats waiting in ambush outside burrows, but tending to actively stalk birds.<ref name=Turner153>{{Harv|Turner|Bateson|2000|p=153}}</ref> |
|||
=== Grooming === |
|||
Most breeds of cat have a noted fondness for settling in high places, or perching. In the wild, a higher place may serve as a concealed site from which to hunt; domestic cats may strike prey by pouncing from such a perch as a tree branch, as does a [[leopard]].<ref>{{cite web | title=Why Do Cats Like High Places? | publisher = Dr. Holly Nash, DVM, MS | url =http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?c=1+1313&aid=1125 | archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20080102145008/http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?cls=1&cat=1313&articleid=1125 | archivedate=2008-01-02 | work = Drs. Foster & Smith, Inc.}}</ref> Other possible explanations include that height gives the cat a better observation point, allowing it to survey its territory. During a fall from a high place, a cat can reflexively twist its body and right itself using its acute [[equilibrioception|sense of balance]] and flexibility.<ref>{{cite web | title = Falling Cats | url = http://www.verrueckte-experimente.de/leseproben_e.html | archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20051026122408/http://www.verrueckte-experimente.de/leseproben_e.html | archivedate = 2005-10-26 | accessdate = 2005-10-24}}</ref> This is known as the cat's "[[cat righting reflex|righting reflex]]". It always rights itself in the same way, provided it has the time to do so, during a fall. The height required for this to occur is around 90 cm (3 feet). Cats without a tail also have this ability, since a cat mostly moves its hind legs and relies on conservation of [[angular momentum]] to set up for landing, and the tail is in fact little used for this feat.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://helix.gatech.edu/Classes/ME3760/1998Q3/Projects/Nguyen/ | title=How does a Cat always land on its feet? | author = Huy D. Nguyen | publisher = Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Medical Engineering | accessdate = 2007-05-15}}</ref> This leads to the proverb "a cat always lands on its feet." |
|||
[[File:Cat tongue macro.jpg|thumb|Cat tongue]] |
|||
Cats are known for spending considerable amounts of time licking their coats to keep them clean.<ref name="hairballs" /><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Noel |first1=A. C. |last2=Hu |first2=D. L. |title=Cats use hollow papillae to wick saliva into fur |journal=[[Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America]] |year=2018 |volume=115 |issue=49 |pages=12377–12382 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1809544115 |pmid=30455290 |pmc=6298077 |bibcode=2018PNAS..11512377N |doi-access=free}}</ref> The cat's tongue has backward-facing spines about 0.5 millimeter long, called [[lingual papilla]]e, which contain [[keratin]] making them rigid.<ref name="Boshel 1982">{{Cite journal |title=Filiform Papillae of Cat Tongue |last1=Boshel |first1=J. |last2=Wilborn |first2=W. H. |last3=Singh |first3=B. B. |last4=Peter |first4=S. |last5=Stur |first5=M. |s2cid=36216103 |journal=Acta Anatomica |year=1982 |volume=114 |issue=2 |pages=97–105 |doi=10.1159/000145583 |pmid=7180385}}</ref> The papillae act like a hairbrush, and some cats, particularly [[Domestic long-haired cat|long-haired cats]], occasionally regurgitate sausage-shaped {{cvt|2|–|3|cm}} long [[hairball]]s of fur that have collected in their stomachs from grooming. Hairballs can be prevented with remedies that ease elimination of the hair through the [[gut (anatomy)|gut]], as well as regular grooming of the coat with a comb or stiff brush.<ref name="hairballs">{{cite web |last=Hadzima |first=E. |title=Everything You Need to Know About Hairballs |year=2016 |url= http://www.dewintonvet.com/everything-you-need-know-about-hairballs/ |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20161006104436/http://www.dewintonvet.com/everything-you-need-know-about-hairballs/ |archive-date=6 October 2016 |access-date=23 August 2016}}</ref> |
|||
=== Fighting === |
|||
[[File:Cat-eating-prey.jpg|thumb|A domestic cat eating a [[House Sparrow]]]] |
|||
[[File:GAto.jpg|thumb|A domestic cat hissing and arching its back]] |
|||
Among domestic cats, males are more likely to fight than females.<ref name="Lindell">{{Cite journal |last=Lindell |first=E. M. |title=Intercat Aggression: A Retrospective Study Examining Types of Aggression, Sexes of Fighting Pairs, and Effectiveness of Treatment |journal=Applied Animal Behaviour Science |year=1997 |volume=55 |issue=1–2 |pages=153–162 |doi=10.1016/S0168-1591(97)00032-4 |doi-access=free}}</ref> Among feral cats, the most common reason for [[Catfight (animal behavior)|cat fighting]] is competition between two males to mate with a female. In such cases, most fights are won by the heavier male.<ref name="courtship">{{Cite journal |title=Mating Behaviors, Courtship Rank and Mating Success of Male Feral Cat (''Felis catus'') |first1=A. |last1=Yamane |first2=T. |last2=Doi |first3=Y. |last3=Ono |journal=Journal of Ethology |volume=14 |issue=1 |pages=35–44 |year=1996 |doi=10.1007/BF02350090 |s2cid=27456926}}</ref> Another common reason for fighting in domestic cats is the difficulty of establishing territories within a small home.<ref name="Lindell" /> Female cats also fight over territory or to defend their kittens. Neutering will decrease or eliminate this behavior in many cases, suggesting that the behavior is linked to [[sex hormone]]s.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Determining the Optimal age for Gonadectomy of Dogs and Cats |doi=10.2460/javma.231.11.1665 |year=2007 |last1=Kustritz |first1=M. V. R. |s2cid=4651194 |journal=Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association |volume=231 |issue=11 |pages=1665–1675 |pmid=18052800 |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
When cats become aggressive, they try to make themselves appear larger and more threatening by raising their fur, arching their backs, turning sideways, and hissing or spitting.<ref name="behaviourguide">{{cite web |year=2007 |title=Cat Behavior: Body Language |url=http://animal.discovery.com/guides/cats/behavior/bodylanguageintro.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090224154137/http://animal.discovery.com/guides/cats/behavior/bodylanguageintro.html |archive-date=24 February 2009 |access-date=7 September 2012 |work=AnimalPlanet}}</ref> Often, the ears are pointed down and back to avoid damage to the inner ear and potentially listen for any changes behind them while focused forward. Cats may also vocalize loudly and bare their teeth in an effort to further intimidate their opponents. Fights usually consist of grappling and delivering slaps to the face and body with the forepaws, as well as bites. Cats also throw themselves to the ground in a defensive posture to rake their opponent's belly with their hind legs.<ref>{{cite web |title=Aggression Between Family Cats and Feline Social Behavior |url=https://www.paws.org/resources/aggression/ |website=PAWS |access-date=6 September 2022 |archive-date=28 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220828003314/https://www.paws.org/resources/aggression/ |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
One poorly understood element of cat hunting behavior is the presentation of prey to human owners. [[Ethology|Ethologist]] Paul Leyhausen proposed that cats adopt humans into their social group, and share excess kill with others in the group according to the local [[pecking order]], in which humans are placed at or near the top.<ref>{{cite book |last=Leyhausen |first=Paul |title=Cat Behavior: The Predatory and Social Behavior of Domestic and Wild Cats |year=1978 |isbn=978-0824070175 |publisher=Garland STPM Press |location=New York}}</ref> However, anthropologist and animal scientist [[Desmond Morris]], in his 1986 book ''Catwatching'', suggests that when cats bring home mice or birds, they are teaching their human to hunt, or helping their human as if feeding "an elderly cat, or an inept kitten".<ref>{{Cite book |
|||
| publisher = Crown Pub |
|||
| last = Desmond |
|||
| first = Morris |
|||
| title = Catwatching Why Cats Purr and Everything Else You Ever Wanted to Know |
|||
| year = 1986 |
|||
}}</ref> However, this proposal is inconsistent with the fact that male cats also bring home prey, despite males having no involvement with raising kittens.<ref name=Turner153/> |
|||
Serious damage is rare, as the fights are usually short in duration, with the loser running away with little more than a few scratches to the face and ears. Fights for mating rights are typically more severe, and injuries may include deep puncture wounds and lacerations. Normally, serious injuries from fighting are limited to infections from scratches and bites, although these can occasionally kill cats if untreated. In addition, bites are probably the main route of transmission of the [[feline immunodeficiency virus]].<ref name="Pederson 1989">{{Cite journal |title=Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection |last1=Pedersen |first1=N. C. |last2=Yamamoto |first2=J. K. |last3=Ishida |first3=T. |last4=Hansen |first4=H. |journal=Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology |year=1989 |volume=21 |issue=1 |pages=111–129 |pmid=2549690 |doi=10.1016/0165-2427(89)90134-7}}</ref> Sexually active males are usually involved in many fights during their lives and often have decidedly battered faces with obvious scars and cuts to their ears and nose.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Whiteley |first=H. E. |date=1994 |chapter=Correcting misbehavior |title=Understanding and Training Your Cat or Kitten |publisher=Sunstone Press |location=Santa Fe |pages=146–147 |isbn=9781611390803}}</ref> Cats are willing to threaten animals larger than them to defend their territory, such as dogs and [[Red fox|foxes]].<ref>{{cite news |last1=Devlin |first1=Hannah |author-link=Hannah Devlin |title=Cat v fox: what made Downing Street's Larry so brave? |url=https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2022/oct/13/cat-v-fox-what-made-downing-streets-larry-so-brave |access-date=16 October 2022 |work=The Guardian |date=13 October 2022 |archive-date=16 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221016011130/https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2022/oct/13/cat-v-fox-what-made-downing-streets-larry-so-brave |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Domestic cats select food based on its temperature, smell and texture, strongly disliking chilled foods and responding most strongly to moist foods rich in amino acids, which are similar to meat.<ref name=Zaghini/><ref name=Bradshaw/> Cats may reject novel flavors (a response termed [[neophobia]]) and learn quickly to avoid foods that have [[taste aversion|tasted unpleasant]] in the past.<ref name=Bradshaw/> They may also avoid sugary foods and milk; since they are [[lactose intolerant]], these sugars are not easily digested and may cause soft stools or [[diarrhea]].<ref name=Bradshaw/><ref>{{cite journal |author=Kienzle E |title=Blood sugar levels and renal sugar excretion after the intake of high carbohydrate diets in cats |journal=J. Nutr. |volume=124 |issue=12 Suppl |pages=2563S–2567S |year=1994 |pmid=7996238 |url=http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/reprint/124/12_Suppl/2563S.pdf |format=PDF|month=December |first1=E |issn=0022-3166}}</ref> They can also develop odd eating habits. Some cats like to eat or chew on other things, most commonly wool, but also plastic, paper, string, or even coal. This condition is called [[pica (disorder)|pica]] and can threaten their health, depending on the amount and toxicity of the items eaten.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/S0168-1591(96)01136-7 |
|||
| issn = 0168-1591 |
|||
| volume = 52 |
|||
| issue = 3-4 |
|||
| pages = 373–379 |
|||
| last = Bradshaw |
|||
| first = John W. S. |
|||
| title = Factors affecting pica in the domestic cat |
|||
| journal = Applied Animal Behaviour Science |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 1997-04 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T48-3RH0C3B-J/2/eacc8602ebaecdd4a43f21fccd6bd59a |
|||
}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.vmth.ucdavis.edu/home/beh/feline_behavior/pica.html| title= Pica: The Un-finicky Feline|publisher=University of California School of Veterinary Medicine|accessdate=2009-09-06}}</ref> |
|||
=== |
=== Hunting and feeding === |
||
{{ |
{{See also|Cat food}} |
||
[[File:Kot z myszą.jpg|thumb|right|A domestic cat with its prey, a [[deermouse]]]] |
|||
Domestic cats, especially young kittens, are known for their love of play. This behavior mimics hunting and is important in helping kittens learn to [[predation|stalk, capture, and kill]] prey.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Poirier FE, Hussey LK |title=Nonhuman Primate Learning: The Importance of Learning from an Evolutionary Perspective |journal=Anthropology & Education Quarterly |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=133–148 |date=1 July 1982|url=http://www.jstor.org/pss/3216627 |doi=10.1525/aeq.1982.13.2.05x1830j |issn=01617761 |first=F. E. |first2=L. K.}}</ref> Cats will also engage in [[play fighting]], with each other and with humans. This behavior may be a way for cats to practice the skills needed for real combat, and might also reduce any fear they associate with launching attacks on other animals.<ref>{{cite book |author=Byers, John A.; Bekoff, Marc |title=Animal play: evolutionary, comparative, and ecological perspectives |publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]] |location=Cambridge, UK |year=1998 |page=135 |isbn=0-521-58656-9}}</ref> |
|||
The shape and structure of cats' cheeks is insufficient to allow them to take in liquids using suction. Therefore, when drinking, they lap with the tongue to draw liquid upward into their mouths. Lapping at a rate of four times a second, the cat touches the smooth tip of its tongue to the surface of the water, and quickly retracts it like a corkscrew, drawing water upward.<ref name="Reis 2010">{{cite journal |last1=Reis |first1=P. M. |last2=Jung |first2=S. |last3=Aristoff |first3=J. M. |last4=Stocker |first4=R. |s2cid=1917972 |title=How cats lap: Water uptake by ''Felis catus'' |journal=[[Science (journal)|Science]] |year=2010 |volume=330 |issue=6008 |pages=1231–1234 |doi=10.1126/science.1195421 |pmid=21071630 |bibcode=2010Sci...330.1231R |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name="Kim 2012">{{cite journal |last1=Kim |first1=W. |last2=Bush |first2=J.W.M. |title=Natural drinking strategies |journal=Journal of Fluid Mechanics |year=2012 |volume=705 |pages=7–25 |doi=10.1017/jfm.2012.122 |url= https://dspace.mit.edu/bitstream/1721.1/80405/2/Bush_Natural%20drinking%20strategies.pdf |bibcode=2012JFM...705....7K |hdl=1721.1/80405 |s2cid=14895835 |hdl-access=free |access-date=23 September 2019 |archive-date=7 March 2022 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20220307214820/https://dspace.mit.edu/bitstream/handle/1721.1/80405/Bush_Natural |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Feral cats and free-fed house cats consume several small meals in a day. The frequency and size of meals varies between individuals. They select food based on its temperature, smell, and texture; they dislike chilled foods and respond most strongly to moist foods rich in amino acids, which are similar to meat. Cats reject novel flavors (a response termed [[neophobia]]) and learn quickly to [[conditioned taste aversion|avoid foods that have tasted unpleasant]] in the past.<ref name="Bradshaw">{{cite journal |last1=Bradshaw |first1=J. W. |last2=Goodwin |first2=D. |last3=Legrand-Defrétin |first3=V. |last4=Nott |first4=H. M. |title=Food selection by the domestic cat, an obligate carnivore |journal=Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology – Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology |volume=114 |issue=3 |pages=205–209 |year=1996 |pmid=8759144 |doi=10.1016/0300-9629(95)02133-7}}</ref><ref name="Zaghini">{{cite journal |title=Nutritional peculiarities and diet palatability in the cat |last1=Zaghini |first1=G. |last2=Biagi |first2=G. |journal=Veterinary Res. Commun. |volume=29 |issue=Supplement 2 |pages=39–44 |year=2005 |pmid=16244923 |doi=10.1007/s11259-005-0009-1|s2cid=23633719}}</ref> It is also a common misconception that cats like milk/cream, as they tend to avoid sweet food and milk. Most adult cats are [[lactose intolerant]]; the sugar in milk is not easily digested and may cause soft stools or [[diarrhea]].<ref name="Kienzle 1994">{{cite journal |title=Blood sugar levels and renal sugar excretion after the intake of high carbohydrate diets in cats |last=Kienzle |first=E. |journal=Journal of Nutrition |year=1994 |volume=124 |issue=12 Supplement |pages=2563S–2567S |pmid=7996238 |doi=10.1093/jn/124.suppl_12.2563S |url= http://jn.nutrition.org/content/124/12_Suppl/2563S.full.pdf |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130903163949/http://jn.nutrition.org/content/124/12_Suppl/2563S.full.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=3 September 2013}}</ref> Some also develop odd eating habits and like to eat or chew on things such as wool, plastic, cables, paper, string, aluminum foil, or even coal. This condition, [[pica (disorder)|pica]], can threaten their health, depending on the amount and toxicity of the items eaten.<ref name="Bradshaw 1997">{{cite journal |title=Factors affecting pica in the domestic cat |last=Bradshaw |first=J. W. S. |journal=Applied Animal Behaviour Science |year=1997 |volume=52 |issue=3–4 |pages=373–379 |doi=10.1016/S0168-1591(96)01136-7}}</ref> |
|||
Owing to the close similarity between play and hunting, cats prefer to play with objects that resemble prey, such as small furry toys that move rapidly, but rapidly lose interest (they become [[habituation|habituated]]) in a toy they have played with before.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/S0168-1591(02)00153-3 |
|||
| issn = 0168-1591 |
|||
| volume = 79 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 263–271 |
|||
| last = Hall |
|||
| first = Sarah L. |
|||
| title = Object play in adult domestic cats: the roles of habituation and disinhibition |
|||
| journal = Applied Animal Behaviour Science |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 2002-11-01 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T48-46RKNW3-3/2/0ff8afc4f0383a2c0feef6ca70aeb6aa |
|||
}}</ref> Cats also tend to play with toys more when they are hungry.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/S0168-1591(97)00136-6 |
|||
| issn = 0168-1591 |
|||
| volume = 58 |
|||
| issue = 1-2 |
|||
| pages = 143–150 |
|||
| last = Hall |
|||
| first = Sarah L. |
|||
| title = The influence of hunger on object play by adult domestic cats |
|||
| journal = Applied Animal Behaviour Science |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 1998-06 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T48-3V4KMXK-T/2/0704d810349462cc333ce8b6714f404a |
|||
}}</ref> String is often used as a toy, but if it is eaten it can become caught at the base of the cat’s tongue and then move into the [[intestine]]s, a medical emergency which can cause serious illness and death.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1053/svms.2002.36606 |
|||
| issn = 1096-2867 |
|||
| volume = 17 |
|||
| issue = 4 |
|||
| pages = 178–183 |
|||
| last = MacPhail |
|||
| first = Catriona |
|||
| title = Gastrointestinal obstruction |
|||
| journal = Clinical Techniques in Small Animal Practice |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-20 |
|||
| date = 2002-11 |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B75BB-4JXPNDY-7/2/3d7e8fa2e709a02db0c8b5d4d3f2777e |
|||
| pmid = 12324686 |
|||
| month = October |
|||
| last1 = Norberg |
|||
| first1 = ST |
|||
| pmc = 2391006 |
|||
}}</ref> Owing to the risks posed by cats eating string, it is sometimes replaced with a [[laser pointer]]'s dot, which cats may chase.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.poconorecord.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=/20061210/NEWS01/612100320/-1/NEWS|title=Fat indoor cats need exercise|date=December 10, 2006|publisher=[[Pocono Record]]}}</ref> While concerns have been raised about the safety of these lasers, Professor John Marshall, an [[ophthalmologist]] at [[St Thomas' Hospital]], has stated that it would be "virtually impossible" to blind a cat with a laser pointer.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/34229.stm Eye expert challenges laser pen 'danger'] ''BBC News'' November 24, 1997</ref> |
|||
Cats hunt small prey, primarily birds and rodents,<ref name="Woods">{{cite journal |last1=Woods |first1=M. |last2=McDonald |first2=R. A. |last3=Harris |first3=S. |s2cid=42095020 |title=Predation of wildlife by domestic cats ''Felis catus'' in Great Britain |journal=Mammal Review |volume=23 |issue=2 |pages=174–188 |year=2003 |doi=10.1046/j.1365-2907.2003.00017.x}}</ref> and are often used as a form of pest control.<ref>{{cite book |title=Clones, Cats, and Chemicals: Thinking scientifically about controversial issues |page=9 |url-access=limited |url= https://archive.org/details/clonescatschemic00sles/page/n16 |first=I. L. |last=Slesnick |date=2004|publisher= NSTA Press |isbn=9780873552370}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |first=D. S. |last=Hill |date=2008 |title=Pests of Crops in Warmer Climates and their Control |publisher=Springer |edition=First |isbn=9781402067372 |page=120 |url= https://archive.org/details/pestscropswarmer00hill/page/n125 |url-access=limited}}</ref> Other common small creatures, such as lizards and snakes, may also become prey.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/cats-kill-reptiles-populations-australia-animals |title=Cats Have A Killer Impact on Reptiles: Experiments in Australia reveal that kitties are catching more than birds |first=Joshua Rapp |last=Learn |date=17 August 2018 |work=[[National Geographic Society|NationalGeographic]] |access-date=24 November 2023 |archive-date=24 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231124225514/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/cats-kill-reptiles-populations-australia-animals |url-status=live }}</ref> Cats use two hunting strategies, either stalking prey actively, or [[Ambush predator|waiting in ambush]] until an animal comes close enough to be captured.<ref name="How Cats Evolved to Win the Internet">{{cite news |last=Tucker |first=A. |title=How cats evolved to win the Internet |url= https://www.nytimes.com/2016/10/16/opinion/sunday/how-cats-evolved-to-win-the-internet.html |newspaper=[[The New York Times]] |year=2016 |access-date=13 November 2016|url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20161019204937/http://www.nytimes.com/2016/10/16/opinion/sunday/how-cats-evolved-to-win-the-internet.html |archive-date=19 October 2016}}</ref> The strategy used depends on the prey species in the area, with cats waiting in ambush outside burrows, but tending to actively stalk birds.<ref name="Turner 2000">{{cite book |editor-last1=Turner |editor-first1=D. C. |editor-last2=Bateson |editor-first2=P. |title=The Domestic Cat: The biology of its behaviour |date=2000 |edition=2nd |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=9780521636483}}</ref>{{rp|153}} Domestic cats are a major [[Cat predation on wildlife|predator of wildlife]] in the United States, killing an estimated 1.3 to 4.0 billion birds and 6.3 to 22.3 billion mammals annually.<ref name="NC012913">{{cite journal |last1=Loss |first1=S. R. |first2=T. |last2=Will |first3=P. P. |last3=Marra |title=The impact of free-ranging domestic cats on wildlife of the United States |journal=[[Nature Communications]] |year=2013 |volume=4 |page=1396 |doi=10.1038/ncomms2380 |pmid=23360987 |bibcode=2013NatCo...4.1396L |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
===Reproduction=== |
|||
[[File:Cats having sex in Israel.jpg|thumb|When cats mate, the male [[Tomcat|tom]] bites the scruff of the female's neck as she assumes a position conducive to [[mating]].]] |
|||
Female cats are seasonally [[polyestrous]], which means they may have many periods of heat over the course of a year, the season beginning in spring and ending in late autumn. Heat periods occur about every two weeks and last about 4 to 7 days.<ref name=compendium/> Multiple males will be attracted to a female in heat. The males will fight over her, and the victor wins the right to mate. At first, the female will reject the male, but eventually the female will allow the male to mate. The female will utter a loud yowl as the male pulls out of her. This is because a male cat's [[penis]] has a band of about 120-150 backwards-pointing spines, which are about one [[millimeter]] long;<ref>{{cite journal |author=Aronson LR, Cooper ML |title=Penile spines of the domestic cat: their endocrine-behavior relations |journal=Anat. Rec. |volume=157 |issue=1 |pages=71–8 |year=1967 |month=January |pmid=6030760 |doi=10.1002/ar.1091570111 |url=http://www.catcollection.org/files/PenileSpines.pdf |format=PDF|first1=LR |first2=ML |issn=0003-276X}}</ref> upon withdrawal of the penis, the spines rake the walls of the female's [[vagina]], which is a trigger for [[ovulation]]. This act also occurs to clear the vagina from other sperm in the context of a 2nd (or more) mating, thus giving the latter males a larger chance of conception.<br /> |
|||
After mating, the female will wash her [[vulva]] thoroughly. If a male attempts to breed with her at this point, the female will attack him. After about 20 to 30 minutes, once the female is finished grooming, the cycle will repeat.<ref name=compendium/> |
|||
Certain species appear more susceptible than others; in one English village, for example, 30% of house sparrow mortality was linked to the domestic cat.<ref name="Chucher 1987">{{cite journal |last1=Chucher |first1=P. B. |last2=Lawton |first2=J. H. |year=1987 |title=Predation by domestic cats in an English village |journal=Journal of Zoology, London |volume=212 |issue=3 |pages=439–455 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7998.1987.tb02915.x}}</ref> In the recovery of ringed robins (''[[Erithacus rubecula]]'') and dunnocks (''[[Prunella modularis]]'') in Britain, 31% of deaths were a result of cat predation.<ref name="Mead 1982 183–186">{{cite journal |title=Ringed birds killed by cats |last=Mead |first=C. J. |journal=Mammal Review |year=1982 |volume=12 |issue=4 |pages=183–186 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2907.1982.tb00014.x}}</ref> In parts of North America, the presence of larger carnivores such as [[coyote]]s, which prey on cats and other small predators, reduces the effect of predation by cats and other small predators such as [[opossum]]s and [[raccoon]]s on bird numbers and variety.<ref name="Crooks 1999">{{cite journal |title=Mesopredator release and avifaunal extinctions in a fragmented system |last1=Crooks |first1=K. R. |last2=Soul |first2=M. E. |journal=Nature |year=1999 |volume=400 |issue=6744 |pages=563–566 |doi=10.1038/23028 |bibcode=1999Natur.400..563C |s2cid=4417607 |archive-date=20 July 2011 |url-status=dead |url= http://www38.homepage.villanova.edu/jameson.chace/Urban%20Ecology/Crooks%26Soule_Mesopredator_release.pdf |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110720110246/http://www38.homepage.villanova.edu/jameson.chace/Urban%20Ecology/Crooks%26Soule_Mesopredator_release.pdf}}</ref> |
|||
Because ovulation is not always triggered by a single mating, females may not be impregnated by the first male with which they mate.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Wildt DE, Seager SW, Chakraborty PK |title=Effect of copulatory stimuli on incidence of ovulation and on serum luteinizing hormone in the cat |journal=Endocrinology |volume=107 |issue=4 |pages=1212–7 |year=1980 |month=October |pmid=7190893 |doi=10.1210/endo-107-4-1212 |first1=DE |first2=SW |first3=PK |issn=0013-7227}}</ref> Furthermore, cats are [[superfecundation|superfecund]]; that is, a female may mate with more than one male when she is in heat, with the result that different kittens in a litter may have different fathers.<ref name=compendium>{{cite web |url=http://vlsstore.com/Media/PublicationsArticle/PV_23_12_1049.pdf |format=PDF|title=Prolific Cats: The Estrous Cycle |publisher=Veterinary Learning Systems |accessdate=19 June 2009}}</ref> |
|||
Another poorly understood element of cat hunting behavior is the presentation of prey to human guardians. One explanation is that cats adopt humans into their social group and share excess kill with others in the group according to the [[dominance hierarchy]], in which humans are reacted to as if they are at or near the top.<ref name="Leyhausen 1978">{{cite book |title=Cat Behavior: The predatory and social behavior of domestic and wild cats |last=Leyhausen |first=P. |date=1978 |publisher=[[Garland STPM Press]] |location=New York |isbn=9780824070175}}</ref> Another explanation is that they attempt to teach their guardians to hunt or to help their human as if feeding "an elderly cat, or an inept kitten".<ref name="Morris Catwatching 1">{{cite book |title=Catwatching: Why cats purr and everything else you ever wanted to know |last=Desmond |first=M. |date=2002 |publisher=Ebury Press |edition=2nd |location=London |chapter=Why does a cat play with its prey before killing it? |pages=51–52 |isbn=9781409022213 |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=Q3ysT6xTJu4C&pg=PA51 |access-date=25 October 2020 |archive-date=31 March 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210331062240/https://books.google.com/books?id=Q3ysT6xTJu4C&pg=PA51 |url-status=live}}</ref> This hypothesis is inconsistent with the fact that male cats also bring home prey, despite males having negligible involvement in raising kittens.<ref name="Turner 2000" />{{rp|153}} |
|||
[[File:Youngkitten.JPG|thumb|left|A kitten with newly opened [[eye]]s.]] |
|||
[[File:Cat carrying kitten (cropped).jpg|thumb|Mother cats carry their kittens by the [[nape]] of the neck.]] |
|||
The [[gestation]] period for cats is between 64–67 days, with an average length of 66 days.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Tsutsui T, Stabenfeldt GH |title=Biology of ovarian cycles, pregnancy and pseudopregnancy in the domestic cat |journal=J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. |volume=47 |issue= |pages=29–35 |year=1993|pmid=8229938 |first1=T |first2=GH |issn=0449-3087}}</ref> The size of a [[litter (animal)|litter]] averages three to five kittens, with the first litter usually smaller than subsequent litters. Kittens are weaned at between six and seven weeks, and cats normally reach sexual maturity at 5–10 months (females) and to 5–7 months (males), although this can vary depending on breed.<ref name=compendium/> Females can have two to three litters per year, so may produce up to 150 kittens in their breeding span of around ten years.<ref name=compendium/> |
|||
=== Play === |
|||
Cats are ready to go to new homes at about 12 weeks old,<ref>{{cite book |title=The Complete Book of Cat Care: How to Raise a Happy and Healthy Cat |last=Behrend |first=Katrin |coauthors=Wegler, Monika; translated from German by Elizabeth D. Crawford. |year=1991 |publisher=Barron's Educational Series, Inc. |location=Hauppauge, NY |isbn=0-8120-4613-7 |page=28}}</ref> or when they are ready to leave their mother. Cats can be surgically [[Sterilization (surgical procedure)|sterilized]] (spayed or [[castration|castrated]]) as early as 7 weeks to limit unwanted reproduction.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Olson PN, Kustritz MV, Johnston SD |title=Early-age neutering of dogs and cats in the United States (a review) |journal=J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. |volume=57 |issue= |pages=223–32 |year=2001 |pmid=11787153 |first1=PN |first2=MV |first3=SD |issn=0449-3087}}</ref> This surgery also prevents undesirable sex-related behavior, such as aggression, [[spraying (animal behavior)|territory marking]] (spraying urine) in males and yowling (calling) in females. Traditionally, this surgery was performed at around six to nine months of age, but it is increasingly being performed prior to [[puberty]], at about three to six months.<ref>Margaret V. Root Kustritz "Determining the optimal age for gonadectomy of dogs and cats." J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2007 Dec 1;231(11):1665-75</ref> In the USA approximately 80% of household cats are neutered.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
{{Main|Cat play and toys}} |
|||
| doi = 10.2460/javma.234.8.1023 |
|||
[[File:Play fight between cats.webmhd.webm|thumbnail|thumbtime=4|alt=Play fight between kittens, age 14 weeks|Play fight between kittens aged 14 weeks]] |
|||
| issn = 0003-1488 |
|||
Domestic cats, especially young kittens, are known for their love of play. This behavior mimics hunting and is important in helping kittens learn to stalk, capture, and kill prey.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Poirier |first1=F. E. |last2=Hussey |first2=L. K. |title=Nonhuman Primate Learning: The Importance of Learning from an Evolutionary Perspective |journal=Anthropology and Education Quarterly |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=133–148 |year=1982 |doi=10.1525/aeq.1982.13.2.05x1830j |jstor=3216627|doi-access=free}}</ref> Cats also engage in [[Rough-and-tumble play|play fighting]], both with each other and with humans. This behavior may be a way for cats to practice the skills needed for real combat, and it might also reduce the fear that they associate with launching attacks on other animals.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hall |first=S. L. |chapter=Object play by adult animals |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=jkiTQ8dIIHsC&pg=PA45 |title=Animal Play: Evolutionary, Comparative, and Ecological Perspectives |editor1=Byers, J. A. |editor2=Bekoff, M. |publisher=Cambridge University Press |date=1998 |pages=45–60 |isbn=9780521586566 |access-date=25 October 2020 |archive-date=26 January 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210126043154/https://books.google.com/books?id=jkiTQ8dIIHsC&pg=PA45 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
| volume = 234 |
|||
| issue = 8 |
|||
| pages = 1023–1030 |
|||
| last = Chu |
|||
| first = Karyen |
|||
| title = Population characteristics and neuter status of cats living in households in the United States |
|||
| journal = Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-21 |
|||
| year = 2009 |
|||
| url = http://avmajournals.avma.org/doi/abs/10.2460/javma.234.8.1023 |
|||
| pmid = 19366332 |
|||
| month = April |
|||
| last1 = Chu |
|||
| first1 = K |
|||
| last2 = Anderson |
|||
| first2 = WM |
|||
| last3 = Rieser |
|||
| first3 = MY |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
Cats also tend to play with toys more when they are hungry.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Hall |first=S. L. |title=The Influence of Hunger on Object Play by Adult Domestic Cats |journal=Applied Animal Behaviour Science |year=1998 |volume=58 |issue=1–2 |pages=143–150 |doi=10.1016/S0168-1591(97)00136-6}}</ref> Owing to the close similarity between play and hunting, cats prefer to play with objects that resemble prey, such as small furry toys that move rapidly, but rapidly lose interest. They become [[habituation|habituated]] to a toy they have played with before.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Object Play in Adult Domestic Cats: The Roles of Habituation and Disinhibition |last=Hall |first=S. L. |journal=Applied Animal Behaviour Science |year=2002 |volume=79 |issue=3 |pages=263–271 |doi=10.1016/S0168-1591(02)00153-3}}</ref> String is often used as a toy, but if it is eaten, it can become caught at the base of the cat's tongue and then move into the [[intestine]]s, a medical emergency which can cause serious illness, even death.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=MacPhail |first=C. |title=Gastrointestinal obstruction |journal=Clinical Techniques in Small Animal Practice |year=2002 |volume=17 |issue=4 |pages=178–183 |doi=10.1053/svms.2002.36606 |pmid=12587284|s2cid=24977450}}</ref> |
|||
==Ecology== |
|||
===Habitats=== |
|||
Cats are a [[cosmopolitan species]] and are found across much of the world.<ref name=Lipinski/> They are extremely adaptable and are now present on all continents except [[Antarctica]], and on 118 of the 131 main groups of islands - even on sub-Antarctic islands such as the [[Kerguelen Islands]].<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1007/s003000100316 |
|||
| volume = 25 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| pages = 90–95 |
|||
| last = Say |
|||
| first = Ludovic |
|||
| title = Spatio-temporal variation in cat population density in a sub-Antarctic environment |
|||
| journal = Polar Biology |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-28 |
|||
| date = 2002-02-01 |
|||
}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1017/S1464793104006542 |
|||
| volume = 80 |
|||
| issue = 01 |
|||
| pages = 45–72 |
|||
| last = Frenot |
|||
| first = Yves |
|||
| title = Biological Invasions in the Antarctic: Extent, Impacts and Implications |
|||
| journal = Biological Reviews |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-28 |
|||
| year = 2005 |
|||
| url = http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=275546 |
|||
| last2 = Chown |
|||
| first2 = Steven L. |
|||
| last3 = Whinam |
|||
| first3 = Jennie |
|||
| last4 = Selkirk |
|||
| first4 = Patricia M. |
|||
| last5 = Convey |
|||
| first5 = Peter |
|||
| last6 = Skotnicki |
|||
| first6 = Mary |
|||
| last7 = Bergstrom |
|||
| first7 = Dana M. |
|||
}}</ref> Feral cats can live in forests, grasslands, tundra, coastal areas, agricultural land, scrublands, urban areas and wetlands.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=24&fr=1&sts=sss&lang=EN |title=Global Invasive Species Database: Ecology of Felis catus |publisher=Invasive Species Specialist Group |year=2006 |accessdate=31 August 2009}}</ref> Their habitats even include small oceanic islands with no human inhabitants.<ref name=Nogales/> This ability to thrive in almost any terrestrial habitat has led to the cat's designation as one of the world's worst [[invasive species]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.issg.org/booklet.pdf |format=PDF|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070927223530/http://www.issg.org/booklet.pdf |archivedate=2007-09-27 |title=100 of the World's Worst Invasive Alien Species: a Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database |publisher=The Invasive Species Specialist Group |year=2000 |accessdate=31 August 2009}}</ref> Despite this general adaptability, the close relatives of domestic cats, the [[African Wildcat]] (''Felis silvestris lybica'') and the Arabian [[Sand Cat]] (''Felis margarita'') both inhabit desert environments,<ref name=Driscoll/> and domestic cats still show similar adaptations and behaviors.<ref name=MacDonald/> |
|||
=== |
=== Reproduction === |
||
{{See also|Kitten}} |
|||
[[File:Feral-kitten-eating-adult-cottontail-rabbit.jpg|thumb|230px|right|Young feral cat eating a [[cottontail rabbit]].]] |
|||
[[File:Cats having sex in Israel.jpg|thumb|When cats mate, the tomcat (male) bites the scruff of the female's neck as she assumes a position conducive to [[mating]] known as [[lordosis behavior]].]] |
|||
To date, there are few scientific data available to assess the impact of cat predation on prey populations. Cat numbers in the UK are growing annually and their abundance is far above the ‘natural’ [[carrying capacity]], because their population sizes are independent of their prey’s dynamics – i.e. cats are ‘recreational’ hunters.<ref>{{cite journal|last=May|first=R.|year=1988|title= Control of feline delinquency|journal=Nature|volume=332|pages=392–393|doi=10.1038/332392a0}}</ref> Population densities can be as high as 2000 individuals per km<sup>2</sup><ref>{{cite journal|last=Liberg|first=O.|year=1982|title= Food habits and prey impact by feral and house-based domestic cats in a rural area in southern Sweden |journal= Journal of Mammalogy|volume=65|pages=424–432|doi=10.2307/1381089|url=http://jstor.org/stable/1381089|issue=3|publisher=Journal of Mammalogy, Vol. 65, No. 3}}</ref> and the current trend is an increase of 0.5 million cats annually. |
|||
The cat secretes and perceives [[pheromone]]s.<ref name="Bland1979">{{cite journal |last1=Bland |first1=K. P. |year=1979 |title=Tom-cat odour and other pheromones in feline reproduction |journal=Veterinary Science Communications |volume=3 |issue=1 |pages=125–136 |url= https://www.gwern.net/docs/catnip/1979-bland.pdf |doi=10.1007/BF02268958 |s2cid=22484090 |access-date=15 May 2019 |archive-date=30 January 2019 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20190130202521/https://www.gwern.net/docs/catnip/1979-bland.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> Female cats, called ''queens'', are [[polyestrous]] with several [[estrus]] cycles during a year, lasting usually 21 days. They are usually ready to mate between early February and August<ref name="Jemmett1977">{{cite journal |last1=Jemmett |first1=J. E. |last2=Evans |first2=J. M. |year=1977 |title=A survey of sexual behaviour and reproduction of female cats |journal=Journal of Small Animal Practice |volume=18 |issue=1 |pages=31–37 |doi=10.1111/j.1748-5827.1977.tb05821.x |pmid=853730}}</ref> in northern temperate zones and throughout the year in equatorial regions.<ref name="estrous_cycle">{{Cite book |title=Feline Reproduction |chapter=Feline Estrous Cycle |series=CABI Books |date=2022 |pages=11–22 |doi=10.1079/9781789247107.0002 |isbn=9781789247084 |editor-last1=Johnson |editor-first1=A.K |editor-last2=Kutzler |editor-first2=M.A |url=https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/9781789247107.0002 |access-date=18 August 2023 |archive-date=20 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220820105417/https://cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/9781789247107.0002 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Several males, called tomcats, are attracted to a female in heat. They fight over her, and the victor wins the right to mate. At first, the female rejects the male, but eventually, the female allows the male to mate. The female utters a loud yowl as the male pulls out of her because a male cat's [[penis]] has a band of about 120–150 backward-pointing [[penile spines]], which are about {{convert|1|mm|in|abbr=on}} long; upon withdrawal of the penis, the spines may provide the female with increased sexual stimulation, which acts to [[Induced ovulation (animals)|induce ovulation]].<ref name="Aronson 1967">{{Cite journal |title=Penile Spines of the Domestic Cat: Their Endocrine-behavior Relations |last1=Aronson |first1=L. R. |last2=Cooper |first2=M. L. |journal=The Anatomical Record |year=1967 |volume=157 |issue=1 |pages=71–78 |pmid=6030760 |doi=10.1002/ar.1091570111 |s2cid=13070242 |url= http://www.catcollection.org/files/PenileSpines.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20150319031546/http://www.catcollection.org/files/PenileSpines.pdf |archive-date=19 March 2015}}</ref> |
|||
Even well-fed domestic cats may hunt and kill, mainly catching small mammals, but also birds, amphibians, reptiles, fish and invertebrates.<ref name=Woods>{{cite journal |author=Woods M, McDonald RA, Harris S. |title=Predation of wildlife by domestic cats Felis catus in Great Britain |journal=Mammal Review |volume=23 |issue=2 |pages=174–188 |year=2003 |doi=10.1046/j.1365-2907.2003.00017 |url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/118839928/abstract |doi_brokendate=2009-09-06}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Robertson ID |title=Survey of predation by domestic cats |journal=Aust. Vet. J. |volume=76 |issue=8 |pages=551–4 |year=1998 |month=August |pmid=9741724 |doi=10.1111/j.1751-0813.1998.tb10214.x |first1=ID |issn=0005-0423}}</ref> Hunting by domestic cats may be contributing to the decline in the numbers of birds in [[urban area]]s, although the importance of this effect remains controversial.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Beckerman AP, Boots M, Gaston KJ. |title=Urban bird declines and the fear of cats |journal=Animal Conservation |volume=10 |issue=3 |pages=320–325 |year=2007 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-1795.2007.00115.x |url=http://img2.tapuz.co.il/forums/1_102419784.pdf|format=PDF}}</ref> In the wild, the introduction of feral cats during human settlement can threaten native species with extinction.<ref name=Nogales>{{cite journal |author=Nogales M, Martin A, Tershy BR, Donlan CJ, Veitch D, Uerta N, Wood B, Alonso J. |title=A Review of Feral Cat Eradication on Islands. |journal=Conservation Biology |volume=18 |issue=2 |year=2004 |doi=10.1111/j.1523-1739.2004.00442.x |page=310}}</ref> In many cases controlling or eliminating the populations of non-native cats can produce a rapid recovery in native animals.<ref name="pmid14558589">{{cite journal |author=Courchamp F, Chapuis JL, Pascal M |title=Mammal invaders on islands: impact, control and control impact |journal=Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc |volume=78 |issue=3 |pages=347–83 |year=2003 |month=August |pmid=14558589 |doi=10.1017/S1464793102006061 |first1=F |first2=JL |first3=M |issn=1464-7931}}</ref> However, the ecological role of introduced cats can be more complicated: for example, cats can control the numbers of rats, which also prey on birds' eggs and young, so in some cases eliminating a cat population can actually accelerate the decline of an endangered bird species in the presence of a mesopredator, controlled by cats.<ref name="pmid18083843">{{cite journal |author=Rayner MJ, Hauber ME, Imber MJ, Stamp RK, Clout MN |title=Spatial heterogeneity of mesopredator release within an oceanic island system |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=104 |issue=52 |pages=20862–5 |year=2007 |month=December |pmid=18083843 |pmc=2409232 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0707414105 |first1=MJ |first2=ME |first3=MJ |first4=RK |first5=MN |issn=0027-8424 |url=http://www.pnas.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18083843 |format=Free full text}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Radiography of a pregnant cat.jpg|thumb|upright|left|Radiography of a pregnant cat; the skeletons of two fetuses are visible on the left and right of the uterus.]] |
|||
In the [[Southern Hemisphere]], cats are a particular problem in landmasses such as Australasia, where cat species have never been native and there were few equivalent native medium-sized mammalian predators.<ref name=AusGovReport>{{cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/invasive/publications/cat-impacts/pubs/impacts-feral-cats.pdf |format=PDF|title=Overview of the Impacts of Feral Cats on Australian Native Fauna |publisher=Australian Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |author=Chris R. Dickman |year=1996 |accessdate=28 August 2009}}</ref> Native species such as the [[New Zealand]] [[Kakapo]] and the [[Australian]] [[Bettong]], for example, tend to be more ecologically vulnerable and behaviorally "naive" to predation by feral cats.<ref name="pmid12085522">{{cite journal |author=James H, Acharya AB, Taylor JA, Freak MJ |title=A case of bitten Bettongs |journal=J Forensic Odontostomatol |volume=20 |issue=1 |pages=10–2 |year=2002 |month=June |pmid=12085522 |first1=H |first2=AB |first3=JA |first4=MJ |issn=0258-414X}}</ref> Feral cats have had a major impact on these native species and have played a leading role in the endangerment and extinction of many animals.<ref name="pmid16094805">{{cite journal |author=Glen AS, Dickman CR |title=Complex interactions among mammalian carnivores in Australia, and their implications for wildlife management |journal=Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc |volume=80 |issue=3 |pages=387–401 |year=2005 |month=August |pmid=16094805 |doi=10.1017/S1464793105006718 |first1=AS |first2=CR |issn=1464-7931}}</ref> |
|||
After mating, the female cleans her [[vulva]] thoroughly. If a male attempts to mate with her at this point, the female attacks him. After about 20 to 30 minutes, once the female is finished grooming, the cycle will repeat.<ref name="compendium" /> Because ovulation is not always triggered by a single mating, females may not be impregnated by the first male with which they mate.<ref name="Wildt 1980">{{Cite journal |last1=Wildt |first1=D. E. |last2=Seager |first2=S. W. |last3=Chakraborty |first3=P. K. |title=Effect of Copulatory Stimuli on Incidence of Ovulation and on Serum Luteinizing Hormone in the Cat |journal=Endocrinology |year=1980 |volume=107 |issue=4 |pages=1212–1217 |pmid=7190893 |doi=10.1210/endo-107-4-1212}}</ref> Furthermore, cats are [[Superfecundation|superfecund]]; that is, a female may mate with more than one male when she is in heat, with the result that different kittens in a litter may have different fathers.<ref name="compendium">{{cite web |title=Prolific Cats: The Estrous Cycle |url= http://vlsstore.com/Media/PublicationsArticle/PV_23_12_1049.pdf |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20161209220101/http://vlsstore.com/Media/PublicationsArticle/PV_23_12_1049.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=9 December 2016 |publisher=Veterinary Learning Systems |access-date=19 June 2009}}</ref> |
|||
The [[morula]] forms 124 hours after conception. At 148 hours, early [[blastocyst]]s form. At 10–12 days, implantation occurs.<ref>{{Cite journal |journal=Biology of Reproduction |title=In Vivo Embryogenesis, Embryo Migration and Embryonic Mortality in the Domestic Cat |first1=W. F. |last1=Swanson |first2=T. L. |last2=Roth |first3=D. E. |last3=Wilt |doi=10.1095/biolreprod51.3.452 |pmid=7803616 |volume=51 |issue=3 |year=1994 |pages=452–464|doi-access=free}}</ref> The [[gestation]] of queens lasts between 64 and 67 days, with an average of 65 days.<ref name="Jemmett1977" /><ref name="Tsutsui 1993">{{Cite journal |last1=Tsutsui |first1=T. |last2=Stabenfeldt |first2=G. H. |title=Biology of Ovarian Cycles, Pregnancy and pseudopregnancy in the Domestic Cat |journal=Journal of Reproduction and Fertility |volume=Supplement 47 |pages=29–35 |year=1993 |pmid=8229938}}</ref> |
|||
===Impact on birds=== |
|||
The domestic cat is probably a significant predator of birds. Current UK assessments indicate that they may be accountable for an estimated 64.8 million bird deaths each year.<ref name=Woods/> Certain species appear more susceptible than others; for example, 30% of house sparrow mortality is linked to the domestic cat.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Chucher|first=P.B.| coauthors=Lawton, J.H.|year=1987|title= Predation by domestic cats in an English village. |journal= Journal of Zoology, London|volume=212|pages=439–455|doi=10.1111/j.1469-7998.1987.tb02915.x}}</ref> In the recovery of ringed [[Erithacus rubecula|robins]] and [[Prunella modularis|dunnocks]], it was also concluded that 31% of deaths were a result of cat predation.<ref name="Mead 1982 183–186">{{cite journal | last=Mead | first=C.J. | year=1982 |title= Ringed birds killed by cats |journal= Mammal Review | volume=12(4) | pages=183–186}}</ref> The presence of larger carnivores such as [[coyote]]s which prey on cats and other small predators reduces the effect of predation by cats and other small predators such as opossums and raccoons on bird numbers and variety.<ref>[http://www38.homepage.villanova.edu/jameson.chace/Urban%20Ecology/Crooks&Soule_Mesopredator_release.pdf "Mesopredator release and avifaunal extinctions in a fragmented system"] Crooks, K.R. & Soulé, M.E. 1999. Mesopredator release and avifaunal extinctions in a fragmented system. ''Nature'', 400, 563–566</ref> The proposal that cat populations will increase when the numbers of these top predators decline is called the [[mesopredator release hypothesis]]. |
|||
[[File:1dayoldkitten.JPG|thumb|A newborn kitten]] |
|||
On islands, birds can contribute as much as 60% of a cat’s diet.<ref>{{cite book | last=Fiztgerald | first=M.B.| coauthor =Turner, D.C. | title= Hunting behaviour of domestic cats and their impact on prey populations. In: The Domestic Cat: The biology of its behaviour, 2nd ed. Turner, D.C. and Bateson, P. (eds.),| pages= 151–175| publisher= Cambridge University Press | location=Cambridge}}</ref> In nearly all cases, however, the cat cannot be identified as the sole cause for reducing the numbers of island birds, and in some instances eradication of cats has caused a ‘[[mesopredator]] release’ effect;<ref>{{cite journal | last=Courchamp | first=F. | coauthors= Langlais, M. and Sugihara, G. | year=1999 |title=Cats protecting birds: modelling the mesopredator release effect |journal= Mammal Review | volume=12(4) | pages=183–186}}</ref> where the suppression of top carnivores creates an abundance of smaller predators that cause a severe decline in their shared prey. Domestic cats are, however, known to be a contributing factor to the decline of many species; a factor that has ultimately led, in some cases, to extinction. [[Turnagra capensis|The South Island Piopio]]; [[Rallus modestus|Chatham Islands Rail]];<ref name="Mead 1982 183–186"/> the [[Mergus australis|Auckland Islands Merganser]];<ref>{{cite book | last= Stattersfield | first=A.J.|coauthor = Crosby, M.J., Long, A.J. and Wege, D.C. | year=1998 | title= Endemic Bird Areas of the World: Priorities for Biodiversity Conservation. | publisher= BirdLife Conservation Series No.7. , Burlington Press | location=Cambridge. | isbn= 0946888337}}</ref> and the [[Pelecanoides urinatrix|common diving petrel]]<ref>{{cite book | last=Williams | first=A.J. | year=1984 | title= Status and Conservation of Seabirds at some Islands in the African Sector of the Southern Ocean. In: Status and Conservation of the World’s Seabirds, ed Croxall, J.P., Evans, P.G.H. & Schreiber, R.W. International Council for Bird Preservation. |pages=627–635| location=Cambridge.}}</ref> are a few from a long list, with the most extreme case being the flightless [[Xenicus lyalli|Stephen Island Wren]], which was driven to extinction only a few years after its discovery.<ref>{{cite book | last=Falla | first=R.A. | year=1955 | title= Zealand Bird Life past and present | publisher=Stiles.}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last=Galbreath | first=R. | coauthors= Brown, D. | year=2004 |title=The tale of the lighthouse-keeper’s cat: discovery and extinction of the Stephens Island wren (Traversia lyalli). |journal=Notornis | volume=51 | pages=193–200 |url=http://www.notornis.org.nz/free_issues/Notornis_51-2004/Notornis_51_4_193.pdf}}</ref> |
|||
Based on a study of 2,300 free-ranging queens conducted from May 1998 and October{{Nbsp}}2000, they had one to six kittens per [[Litter (animal)|litter]], with an average of three kittens. They produced a mean of 1.4 litters per year, but a maximum of three litters in a year. Of 169 kittens, 127 died before they were six months old due to a trauma caused in most cases by dog attacks and road accidents.<ref name="Nutter2004">{{cite journal |last1=Nutter |first1=F. B. |last2=Levine |first2=J. F. |last3=Stoskopf |first3=M. K. |s2cid=1903272 |year=2004 |title=Reproductive capacity of free-roaming domestic cats and kitten survival rate |journal=Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association |volume=225 |issue=9 |pages=1399–1402 |doi=10.2460/javma.2004.225.1399 |pmid=15552315 |citeseerx=10.1.1.204.1281}}</ref> The first litter is usually smaller than subsequent litters. Kittens are weaned between six and seven weeks of age. Queens normally reach sexual maturity at 5–10 months, and males at 5–7 months. This varies depending on breed.<ref name="compendium" /> Kittens reach [[puberty]] at the age of 9–10 months.<ref name="Jemmett1977" /> |
|||
Cats are ready to go to new homes at about 12 weeks of age, when they are ready to leave their mother.<ref>{{Cite book |title=The Complete Book of Cat Care: How to Raise a Happy and Healthy Cat |last1=Behrend |first1=K. |last2=Wegler |first2=M. |date=1991 |publisher=[[Barron's Educational Series]] |location=Hauppauge, New York |isbn=9780812046137 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/completebookofca00behr/page/28 28–29] |chapter=Living with a Cat |chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/completebookofca00behr/page/28}}</ref> They can be surgically [[neutering|sterilized]] (spayed or [[castration|castrated]]) as early as seven weeks to limit unwanted reproduction.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Early-age Neutering of Dogs and Cats in the United States (A Review) |last1=Olson |first1=P. N. |last2=Kustritz |first2=M. V. |last3=Johnston |first3=S. D. |journal=Journal of Reproduction and Fertility |year=2001 |volume=Supplement 57 |pages=223–232 |pmid=11787153}}</ref> This surgery also prevents undesirable sex-related behavior, such as aggression, [[spraying (animal behavior)|territory marking]] (spraying urine) in males, and yowling (calling) in females. Traditionally, this surgery was performed at around six to nine months of age, but it is increasingly being performed before [[puberty]], at about three to six months.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Determining the optimal age for gonadectomy of dogs and cats |last=Root Kustritz |first=M. V. |journal=Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association|year=2007 |volume=231 |issue=11 |pages=1665–1675 |doi=10.2460/javma.231.11.1665 |pmid=18052800 |s2cid=4651194 |url= http://www.imom.org/spay-neuter/pdf/kustritz.pdf |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20100713133619/http://www.imom.org/spay-neuter/pdf/kustritz.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=13 July 2010}}</ref> In the United States, about 80% of household cats are neutered.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Population characteristics and neuter status of cats living in households in the United States |last1=Chu |first1=K. |last2=Anderson |first2=W. M. |last3=Rieser |first3=M. Y. |s2cid=39208758 |journal=Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association|year=2009 |volume=234 |issue=8 |pages=1023–1030 |doi=10.2460/javma.234.8.1023 |pmid=19366332|doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
Some of the same factors that have promoted [[adaptive radiation]] of island [[Bird|avifauna]] over evolutionary time appear to promote vulnerability to non-native species in modern time. The susceptibility inherent of many island birds is undoubtedly due to evolution in the absence of mainland predators, competitors, diseases and parasites. In addition to lower reproductive rates and extended incubation periods.<ref name=dowd>{{cite journal | last=Dowding | first=J.E. | coauthors= Murphy, E.C. | year=2001 |title= The Impact of Predation be Introduced Mammals on Endemic Shorebirds in New Zealand: A Conservation Perspective. |journal= Biological Conservation | volume=99 | pages=47–64 | doi=10.1016/S0006-3207(00)00187-7}}</ref> The loss of flight, or reduced flying ability is also characteristic of many island endemics.<ref>{{cite journal | last=Whiting | first=M.F. | coauthors= Bradler, S. and Maxwell, T. | year=2003 |title= Loss and Recovery of Wings in Stick Insects |journal= Nature | volume=421 | pages=264–267 | doi=10.1038/nature01313 | pmid=12529642 | issue=6920}}</ref> These biological aspects have increased vulnerability to extinction in the presence of introduced species, such as the domestic cat.<ref>{{cite book | last=WCMC | first=. | year=1992 | title= World Conservation Monitoring Centre. | publisher= Chapman and Hall. |coauthor= McComb, J., Groombridge, B., Byford, E., Allan, C., Howland, J., Magin, C., Smith, H., Greenwood, V. and Simpson, L. | isbn=2831701562}}</ref> Equally, behavioural traits exhibited by island species, such as ‘predatory naivety’<ref>{{cite journal | last=Steadman | first=D.W. | coauthors= Martin, P.S. | year=2003 |title= The Late Quaternary Extinction and Future Resurrection of Birds on Pacific Islands |journal= Earth Science Reviews | volume=61 | pages=133–147 | doi=10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00116-2}}</ref> and ground-nesting,<ref name=dowd/> have also contributed to their susceptibility. |
|||
== Lifespan and health == |
|||
==Domesticated cats== |
|||
{{Main|Cat health|Aging in cats}} |
|||
Cats are a common [[companion animal]] in Europe and North America, and their worldwide population exceeds 500 million.<ref name="NYT"/> In 1998 there were around 43 million cats in [[Western Europe]], 33 million in [[Eastern Europe]], seven million in [[Japan]] and three million in [[Australia]].<ref>{{Harv|Turner|Bateson|2000|p=4}}</ref> A 2007 report stated that about 37 million US households owned cats, with an average of 2.2 cats per household giving a total population of around 82 million.<ref name=AMAstats>{{cite web |url=http://www.avma.org/reference/marketstats/ownership.asp |title=Market research statistics - U.S. pet ownership |publisher=American Veterinary Medical Association |accessdate=27 August 2009}}</ref> This is slightly more than the 72 million pet dogs in that country.<ref name=AMAstats/> Although cat ownership has commonly been associated with women,<ref name=Ellin>{{cite news |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2008/10/05/fashion/05cats.html |title=More Men Are Unabashedly Embracing Their Love of Cats |publisher=New York Times |author=Abby Ellin |accessdate=30 August 2009 | date=2008-10-05}}</ref> a 2007 [[Gallup poll]] reported that men and women were equally likely to own a cat.<ref name=Gallup>{{cite web |url=http://www.gallup.com/poll/102952/companionship-love-animals-drive-pet-ownership.aspx |title=Companionship and Love of Animals Drive Pet Ownership |publisher=Gallup, Inc |author=Jeffrey M. Jones |accessdate=30 August 2009}}</ref> The ratio of pedigree/purebred cats to random-bred cats varies from country to country. However, generally speaking, purebreds are less than ten percent of the total population.<ref>''ASPCA Complete Guide to Cats'' by James R. Richards,, DVM</ref> |
|||
The average lifespan of pet cats has risen in recent decades. In the early 1980s, it was about seven years,<ref name="Kraft1998">{{Cite journal |last=Kraft |first=W. |title=Geriatrics in canine and feline internal medicine |journal=European Journal of Medical Research |volume=3 |issue=1–2 |pages=31–41 |year=1998 |pmid=9512965}}</ref>{{rp|33}}<ref name="Nassar 1984">{{Cite journal |last1=Nassar |first1=R. |last2=Mosier |first2=J. E. |last3=Williams |first3=L. W. |title=Study of the feline and canine populations in the greater Las Vegas area |journal=American Journal of Veterinary Research |volume=45 |issue=2 |pages=282–287 |year=1984 |pmid=6711951}}</ref> rising to 9.4 years in 1995<ref name=Kraft1998/>{{rp|33}} and an average of about 13 years as of 2014 and 2023.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=O'Neill |first1=Dan G |last2=Church |first2=David B |last3=McGreevy |first3=Paul D |last4=Thomson |first4=Peter C |last5=Brodbelt |first5=David C |year=2014 |title=Longevity and mortality of cats attending primary care veterinary practices in England |journal=Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery |volume=17 |issue=2 |pages=125–133 |doi=10.1177/1098612X14536176 |pmid=24925771|doi-access=free |pmc=10816413 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Montoya |first1=M. |last2=Morrison |first2=J. A. |last3=Arrignon |first3=F. |last4=Spofford |first4=N. |last5=C. |first5=H. |last6=Hours |first6=M.-A. |last7=Biourge |first7=V. |year=2023 |title=Life expectancy tables for dogs and cats derived from clinical data |journal=Frontiers in Veterinary Science |volume=10 |pages=1082102 |doi=10.3389/fvets.2023.1082102 |doi-access=free |pmc=9989186 |pmid=36896289}}</ref> |
|||
Neutering increases life expectancy; one study found castrated male cats live twice as long as intact males, while spayed female cats live 62% longer than intact females.<ref name="Kraft1998" />{{rp|35}} Having a cat [[Neutering|neutered]] confers some health benefits, such as a greater life expectancy and a decreased incidence of reproductive [[neoplasia]].<ref name="Obesity1">{{cite journal | last1=Vendramini | first1=Thiago H. A. | last2=Amaral | first2=Andressa R. | last3=Pedrinelli | first3=Vivian | last4=Zafalon | first4=Rafael V. A. | last5=Rodrigues | first5=Roberta B. A. | last6=Brunetto | first6=Marcio A. | title=Neutering in dogs and cats: current scientific evidence and importance of adequate nutritional management | journal=Nutrition Research Reviews | publisher=Cambridge University Press (CUP) | volume=33 | issue=1 | date=14 January 2020 | issn=0954-4224 | doi=10.1017/s0954422419000271 | pages=134–144| pmid=31931899 }}</ref> However, neutering decreases metabolism<ref>{{cite journal | last1=Hoenig | first1=Margarethe | last2=Ferguson | first2=Duncan C. | title=Effects of neutering on hormonal concentrations and energy requirements in male and female cats | journal=American Journal of Veterinary Research | publisher=American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) | volume=63 | issue=5 | date=1 May 2002 | issn=0002-9645 | doi=10.2460/ajvr.2002.63.634 | pages=634–639| pmid=12013460 }}</ref><ref name="Obesity2">{{cite journal | last1=Harper | first1=E. J. | last2=Stack | first2=D. M. | last3=Watson | first3=T. D. G. | last4=Moxham | first4=G. | title=Effects of feeding regimens on bodyweight, composition and condition score in cats following ovariohysterectomy | journal=Journal of Small Animal Practice | publisher=Wiley | volume=42 | issue=9 | year=2001 | issn=0022-4510 | doi=10.1111/j.1748-5827.2001.tb02496.x | pages=433–438| pmid=11570385 }}</ref><ref name="Obesity3">{{cite journal | last1=Fettman | first1=M.J | last2=Stanton | first2=C.A | last3=Banks | first3=L.L | last4=Hamar | first4=D.W | last5=Johnson | first5=D.E | last6=Hegstad | first6=R.L | last7=Johnston | first7=S | title=Effects of neutering on bodyweight, metabolic rate and glucose tolerance of domestic cats | journal=Research in Veterinary Science | publisher=Elsevier BV | volume=62 | issue=2 | year=1997 | issn=0034-5288 | doi=10.1016/s0034-5288(97)90134-x | pages=131–136| pmid=9243711 }}</ref> and increases food intake,<ref name="Obesity3"/><ref name="Obesity4">{{cite journal | last1=Kanchuk | first1=Marc L. | last2=Backus | first2=Robert C. | last3=Morris | first3=James G. | last4=Rogers | first4=Quinton R. | last5=Calvert | first5=Christopher C. | title=Weight Gain in Gonadectomized Normal and Lipoprotein Lipase–Deficient Male Domestic Cats Results from Increased Food Intake and Not Decreased Energy Expenditure | journal=The Journal of Nutrition | publisher=Elsevier BV | volume=133 | issue=6 | year=2003 | issn=0022-3166 | doi=10.1093/jn/133.6.1866 | pages=1866–1874| doi-access=free | pmid=12771331 }}</ref> both of which can cause obesity in neutered cats.<ref name="Obesity5">{{cite journal | last1=Öhlund | first1=Malin | last2=Palmgren | first2=Malin | last3=Holst | first3=Bodil Ström | title=Overweight in adult cats: a cross-sectional study | journal=Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica | volume=60 | issue=1 | date=19 January 2018 | issn=1751-0147 | doi=10.1186/s13028-018-0359-7 | doi-access=free | page=5| pmid=29351768 | pmc=5775588 }}</ref> Pre-pubertal neutering (neutering at 4 months or earlier) was only recommended by 28% of American veterinarians in one study. Some concerns of early neutering were metabolic, retarded [[Epiphyseal plate|physeal closure]], and urinary tract disease related.<ref>{{cite journal | last1=Murray | first1=J. K. | last2=Skillings | first2=E. | last3=Gruffydd-Jones | first3=T. J. | title=Opinions of veterinarians about the age at which kittens should be neutered | journal=Veterinary Record | volume=163 | issue=13 |year=2008 | issn=0042-4900 | doi=10.1136/vr.163.13.381 | pages=381–385| pmid=18820325 }}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Domestic cat (Felix catus) fur skin.jpg|thumb|right|A cat [[fur|pelt]].]] |
|||
=== Disease === |
|||
According to the [[Humane Society of the United States]], as well as being kept as pets, cats are also used in the international [[fur trade]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.hsus.org/web-files/PDF/What-is-that-they-re-wearing_FurBooklet.pdf |title=What is that they’re wearing? |format=Pdf |publisher=Humane Society of the United States |accessdate=22 October 2009}}</ref> Cat fur is used in coats, gloves, hats, shoes, blankets and stuffed toys. About 24 cats are needed to make a cat fur coat.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6165786.stm |title=EU proposes cat and dog fur ban |publisher=BBC News |accessdate=22 October 2009 | date=2006-11-20}}</ref> This use has now been outlawed in several countries, including the United States, [[Australia]] and the [[European Union]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.hsus.org/about_us/humane_society_international_hsi/hsi_europe/dog_cat_fur/ |title=EU Announces Strict Ban on Dog and Cat Fur Imports and Exports |publisher=Humane Society International |accessdate=22 October 2009}}</ref> However, some cat furs are still made into blankets in [[Switzerland]] as [[traditional medicine|folk remedies]] that are believed to help [[rheumatism]].<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/switzerland-finds-a-way-to-skin-a-cat-for-the-fur-trade-and-high-fashion-815426.html |title=Switzerland finds a way to skin a cat for the fur trade and high fashion |publisher=The Independent |accessdate=23 October 2009 | location=London | first1=Tony | last1=Paterson | date=2008-04-25}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|List of feline diseases}} |
|||
About 250 heritable [[genetic disorder]]s have been identified in cats; many are similar to human [[inborn errors of metabolism]].<ref>{{Cite journal |title=State of Cat Genomics |last1=O'Brien |first1=S. J. |last2=Johnson |first2=W. |last3=Driscoll |first3=C. |last4=Pontius |first4=J. |last5=Pecon-Slattery |first5=J. |last6=Menotti-Raymond |first6=M. |journal=Trends in Genetics |volume=24 |issue=6 |pages=268–279 |year=2008 |pmid=18471926 |doi=10.1016/j.tig.2008.03.004|pmc=7126825}}</ref> The high level of similarity among the [[metabolism]] of mammals allows many of these feline diseases to be diagnosed using [[Genetic testing|genetic tests]] that were originally developed for use in humans, as well as the use of cats as [[animal model]]s in the study of the human diseases.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Inherited Metabolic Disease in Companion Animals: Searching for Nature's Mistakes |last1=Sewell |first1=A. C. |last2=Haskins |first2=M. E. |last3=Giger |first3=U. |journal=Veterinary Journal |volume=174 |issue=2 |pages=252–259 |year=2007 |pmid=17085062 |doi=10.1016/j.tvjl.2006.08.017 |pmc=3132193}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=O'Brien |first1=S. J. |last2=Menotti-Raymond |first2=M. |last3=Murphy |first3=W. J. |last4=Yuhki |first4=N. |title=The Feline Genome Project |journal=Annual Review of Genetics |volume=36 |pages=657–686 |year=2002 |pmid=12359739 |doi=10.1146/annurev.genet.36.060602.145553 |url=https://zenodo.org/record/1234973 |access-date=11 July 2019 |archive-date=5 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191005230324/https://zenodo.org/record/1234973 |url-status=live}}</ref> Diseases affecting domestic cats include acute infections, [[parasitic disease|parasitic infestation]]s, injuries, and chronic diseases such as [[Chronic kidney disease in cats|kidney disease]], [[thyroid disease]], and [[arthritis]]. [[Feline vaccination|Vaccinations]] are available for many infectious diseases, as are treatments to eliminate parasites such as worms, ticks, and fleas.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.petmd.com/blogs/thedailyvet/lhuston/2012/dec/veterinary-care-for-your-new-cat-29565 |title=Veterinary Care for Your New Cat |first=L. |last=Huston |work=PetMD |year=2012 |access-date=31 January 2017 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170508122739/http://www.petmd.com/blogs/thedailyvet/lhuston/2012/dec/veterinary-care-for-your-new-cat-29565 |archive-date=8 May 2017}}</ref> |
|||
== Ecology == |
|||
It has long been common for cats to be eaten in some parts of [[China]] and in some other [[Asia]]n countries. According to the Chengdu Business Daily, people in southern China's [[Guangdong]] province ate 10,000 cats a day.<ref>"[http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/28292558/ China protesters: Stop 'cooking cats alive']." Msnbc.com. December 18, 2008.</ref> Animal People estimates that 4 million cats are killed and consumed in Asia every year.<ref>"[http://www.animalpeoplenews.org/03/9/dogs.catseatenAsia903.html How many dogs and cats are eaten in Asia?]". Animalpeoplenews.org. September 2003.</ref> |
|||
=== Habitats === |
|||
[[File:Siamese cat of Altai shepherds.jpg|thumb|A [[Siamese cat]] living among the [[yurts]] of shepherds in the [[Altai Mountains]], Russia]] |
|||
The domestic cat is a [[cosmopolitan species]] and occurs across much of the world.<ref name="Lipinski" /> It is adaptable and now present on all continents except [[Antarctica]], and on 118 of the 131 main groups of islands, even on the isolated [[Kerguelen Islands]].<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Spatio-temporal variation in cat population density in a sub-Antarctic environment |last=Say |first=L. |journal=Polar Biology |year=2002 |volume=25 |issue=2 |pages=90–95 |doi=10.1007/s003000100316|bibcode=2002PoBio..25...90S |s2cid=22448763}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |title=Biological Invasions in the Antarctic: Extent, Impacts and Implications |last1=Frenot |first1=Y. |last2=Chown |first2=S. L. |last3=Whinam |first3=J. |last4=Selkirk |first4=P. M. |last5=Convey |first5=P. |last6=Skotnicki |first6=M. |last7=Bergstrom |first7=D. M. |s2cid=5574897 |journal=Biological Reviews |year=2005 |volume=80 |issue=1 |pages=45–72 |doi=10.1017/S1464793104006542 |pmid=15727038 |doi-access=free}}</ref> Due to its ability to thrive in almost any terrestrial habitat, it is among the world's most [[invasive species]].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Medina |first1=F. M. |last2=Bonnaud |first2=E. |last3=Vidal |first3=E. |last4=Tershy |first4=B. R. |author-link5=Erika Zavaleta |last5=Zavaleta |first5=E. |last6=Josh Donlan |first6=C. |last7=Keitt |first7=B. S. |last8=Le Corre |first8=M. |last9=Horwath |first9=S. V. |last10=Nogales |first10=M. |year=2011 |title=A global review of the impacts of invasive cats on island endangered vertebrates |journal=Global Change Biology |volume=17 |issue=11 |pages=3503–3510 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02464.x |citeseerx=10.1.1.701.4082 |bibcode=2011GCBio..17.3503M|s2cid=323316}}</ref> It lives on small islands with no human inhabitants.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=A Review of Feral Cat Eradication on Islands |last1=Nogales |first1=M. |last2=Martin |first2=A. |last3=Tershy |first3=B. R. |last4=Donlan |first4=C. J. |last5=Veitch |first5=D. |last6=Uerta |first6=N. |last7=Wood |first7=B. |last8=Alonso |first8=J. |journal=Conservation Biology |year=2004 |volume=18 |issue=2 |pages=310–319 |doi=10.1111/j.1523-1739.2004.00442.x |bibcode=2004ConBi..18..310N |hdl=10261/22249 |s2cid=11594286 |url= https://digital.csic.es/bitstream/10261/22249/1/CBL-2004-18-310.pdf |hdl-access=free |access-date=24 September 2019 |archive-date=6 December 2019 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20191206034647/https://digital.csic.es/bitstream/10261/22249/1/CBL-2004-18-310.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> Feral cats can live in forests, grasslands, tundra, coastal areas, agricultural land, scrublands, urban areas, and wetlands.<ref name="ISSG 2006">{{cite web |url= http://www.issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=24&fr=1&sts=sss |work=Global Invasive Species Database |title=Ecology of ''Felis catus'' |author=Invasive Species Specialist Group |publisher=[[IUCN Species Survival Commission|Species Survival Commission]], [[International Union for Conservation of Nature]] |year=2006 |access-date=31 August 2009 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20091027123405/http://www.issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=24&fr=1&sts=sss |archive-date=27 October 2009}}</ref> |
|||
The unwantedness that leads to the domestic cat being [[Cat predation on wildlife#Impact by location|treated as an invasive species]] is twofold. As it is little altered from the wildcat, it can readily interbreed with the wildcat. This [[hybrid (biology)|hybridization]] poses a danger to the genetic distinctiveness of some wildcat populations, particularly in [[Scotland]] and [[Hungary]], possibly also the [[Iberian Peninsula]], and where protected natural areas are close to human-dominated landscapes, such as [[Kruger National Park]] in [[South Africa]].<ref name="Kruger">{{cite journal |url= https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270912183 |title=Genetic analysis shows low levels of hybridization between African wildcats (Felis silvestris lybica) and domestic cats (F. s. catus) in South Africa |last1=Le Roux |first1=Johannes J. |last2=Foxcraft |first2=Llewellyn C. |last3=Herbst |first3=Marna |last4=Macfadyen |first4=Sandra |date=19 August 2014 |journal=Ecology and Evolution |volume=5 |issue=2 |pages=288–299 |doi=10.1002/ece3.1275 |pmid=25691958 |pmc=4314262 |access-date=14 November 2021 |archive-date=7 March 2022 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20220307214831/https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270912183_Genetic_analysis_shows_low_levels_of_hybridization_between_African_wildcats_Felis_silvestris_lybica_and_domestic_cats_F_s_catus_in_South_Africa |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Oliveira">{{Cite journal |last1=Oliveira |first1=R. |last2=Godinho |first2=R. |last3=Randi |first3=E. |last4=Alves |first4=P. C. |title=Hybridization Versus Conservation: Are Domestic Cats Threatening the Genetic Integrity of Wildcats (''Felis silvestris silvestris'') in Iberian Peninsula? |journal=Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences |volume=363 |issue=1505 |pages=2953–2961 |year=2008 |pmid=18522917 |doi=10.1098/rstb.2008.0052 |pmc=2606743}}</ref> However, its introduction to places where no native felines are present also contributes to the decline of native species.<ref name="contr-ext" /> |
|||
===Domesticated varieties=== |
|||
{{Main|Cat breed}} |
|||
[[File:Chocolate Persian.jpg|thumb|right|A [[purebred]] chocolate [[Persian (cat)|Persian]]]] |
|||
The concept of a cat breed appeared in Britain during the late 19th century.<ref>{{Harv|Mason|1984|p=224}}</ref> The current [[list of cat breeds]] is quite large: with the [[Cat Fanciers' Association]] recognizing 41 breeds, of which 16 are "natural breeds" that probably emerged before humans began breeding pedigree cats, while the others were developed over the latter half of the 20th century.<ref name=Lipinski/> The owners and breeders of show cats compete to see whose animal bears the closest resemblance to the "ideal" definition and standard of the breed (see [[selective breeding]]). Because of common crossbreeding in populated areas, many cats are simply identified as belonging to the homogeneous breeds of [[domestic longhaired cat|domestic longhair]] and [[domestic shorthaired cat|domestic shorthair]], depending on their type of fur. In the United Kingdom and Australasia, non-purebred cats are referred in slang as moggies (derived from "Maggie", short for Margaret, reputed to have been a common name for cows and calves in 18th century England and latter applied to housecats during the [[Victorian era]]).<ref>{{cite web |
|||
| url=http://www.worldwidewords.org/qa/qa-mog1.htm |
|||
| title=Moggie |
|||
| publisher=Worldwidewords.org |
|||
| accessdate=2007-05-15}}</ref> In the United States, a non-purebred cat is sometimes referred to in slang as a barn or alley cat, even if it is not a [[feral cat|stray]]. |
|||
=== Ferality === |
|||
Cats come in a variety of colors and patterns. These are physical properties and should not be confused with a breed of cat. Furthermore, cats may show the color and/or pattern particular to a certain breed without actually being of that breed. For example, cats may have seal point coloration, but not be [[Siamese (cat)|Siamese]]. |
|||
{{Main|Feral cat}} |
|||
[[File:Feral cat Virginia crop.jpg|right|thumb|upright|Feral [[farm cat]]]] |
|||
Feral cats are domestic cats that were born in or have reverted to a wild state. They are unfamiliar with and wary of humans and roam freely in urban and rural areas.<ref name="Rochlitz">{{Cite book |title=The Welfare of Cats |last=Rochlitz |first=I. |date=2007 |publisher=[[Springer Science+Business Media]] |isbn=9781402061431 |series="Animal Welfare" series |location=Berlin |pages=141–175 |oclc=262679891}}</ref> The numbers of feral cats is not known, but estimates of the United States feral population range from 25 to 60 million.<ref name="Rochlitz" /> Feral cats may live alone, but most are found in large [[feral cat colonies|colonies]], which occupy a specific territory and are usually associated with a source of food.<ref name="hsus-feral">{{cite web |url= http://www.hsus.org/pets/issues_affecting_our_pets/feral_cats/feral_cats_frequently_asked_questions.html#1_What_is_a_feral_cat |title=What is the difference between a stray cat and a feral cat? |date=2 January 2008 |work=HSUS.org |publisher=[[Humane Society of the United States]] |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20080501093143/http://www.hsus.org/pets/issues_affecting_our_pets/feral_cats/feral_cats_frequently_asked_questions.html#1_What_is_a_feral_cat |archive-date=1 May 2008}}</ref> Famous feral cat colonies are found in Rome around the [[Colosseum]] and [[Forum Romanum]], with cats at some of these sites being fed and given medical attention by volunteers.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.romancats.com/index_eng.php |title=Torre Argentina cat shelter. |access-date=17 June 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090122203413/http://www.romancats.com/index_eng.php |archive-date=22 January 2009}}</ref> |
|||
Public attitudes toward feral cats vary widely, from seeing them as free-ranging pets to regarding them as [[vermin]].<ref>{{Cite book |publisher=Humane Society of the United States |isbn=9780965894272 |editor-last1=Rowan |editor-first1=Andrew N. |editor-last2=Salem |editor-first2=Deborah J. |first1=Margaret R. |last1=Slater |first2=Stephanie |last2=Shain |title=The State of the Animals II: 2003 |date=November 2003 |chapter=Feral Cats: An Overview (4) |chapter-url= http://www.hsus.org/web-files/PDF/hsp/SOA_3-2005_Chap4.pdf |
|||
Some original cat breeds that have a distinct phenotype that is the main type occurring naturally as the dominant domesticated cat type in their region of origin are sometimes considered as subspecies and also have received names as such in nomenclature, although this is not supported by feline biologists. Some of these cat breeds are: |
|||
|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20061110230426/http://www.hsus.org/web-files/PDF/hsp/SOA_3-2005_Chap4.pdf |
|||
|archive-date=10 November 2006}}</ref> |
|||
=== Impact on wildlife === |
|||
* ''F. catus anura'' - the Manx - The Manx is a stocky, solid cat with a dense double [[Coat (animal)|coat]] (long or short), a compact [[body]], very short [[back]], hind legs that are visibly longer than the front legs, big [[bones]], a wide [[chest]], and greater depth of flank (sides of the cat nearest the rear) than other cats.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://fanciers.com/breed-faqs/manx-faq.html#description| title=Description|date=|accessdate= 2010-06-25}}</ref> A female Manx would not weigh more than 10 pounds and a male does not weigh over 12 pounds. Specific to this breed is the way their [[ears]] appear as a "cradle" when looked at from behind. A Manx cat is mainly recognized by its appearance as it does not have a [[tail]]. Although some of them may have a small tail, most Manx cats are tailless. Because of the genetic deformation of these cats they are susceptible of developing what is called Manx Syndrome, a condition that could be fatal for a kitten. Although the gene normally affects only the tail, there is the risk of causing damage to the [[spine]] such as fused vertebrae. |
|||
{{main|Cat predation on wildlife}} |
|||
* ''F. catus siamensis'' - the Siamese - Siamese cats are amongst the firstly recognized Oriental cats, a type of cat with a long body but an [[elegant]] [[posture]]. The length is the main characteristic based on which these cats are distinguished. Their body, legs and tail are all long and still Siamese cats are known for their grace. Also, they are famous because of their blue almond [[eyes]] and they are also called "people cats" because of the affection they show to their owners.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cfainc.org/breeds/profiles/siamese.html| title=Breed Profile: Siamese|date=|accessdate= 2010-06-25}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Causes of bird deaths.png|thumb|Outdoor cats are the largest human cause of bird mortality.]] |
|||
* ''F. catus cartusenensis'' - the Chartreux - The Chartreux is a natural French breed, which is easily recognized by its size, grayish color and double coat. These cats are also famous because of the paradox coming from the combination between a massively build body and smiling expression and sweet [[voice]]. |
|||
On islands, birds can contribute as much as 60% of a cat's diet.<ref name="Fitzgerald">{{Cite book |last1=Fitzgerald |first1=M. B. |last2=Turner |first2=Dennis C. |title=The Domestic Cat: The Biology of its Behaviour |editor-last1=Turner |editor-first1=Dennis C. |editor2-last=Bateson |editor2-first=Patrick P. G. |pages=151–175 |chapter=Hunting Behaviour of Domestic Cats and Their Impact on Prey Populations}}</ref> In nearly all cases, the cat cannot be identified as the sole cause for reducing the numbers of island birds, and in some instances, eradication of cats has caused a "[[mesopredator release]]" effect;<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Courchamp |first1=F. |last2=Langlais |first2=M. |last3=Sugihara |first3=G. |year=1999 |title=Cats protecting birds: Modelling the mesopredator release effect |journal=Journal of Animal Ecology |volume=68 |issue=2 |pages=282–292 |doi=10.1046/j.1365-2656.1999.00285.x |doi-access=free |bibcode=1999JAnEc..68..282C |s2cid=31313856}}</ref> where the suppression of top carnivores creates an abundance of smaller predators that cause a severe decline in their shared prey. Domestic cats are a contributing factor to the decline of several species, a factor that has ultimately led, in some cases, to extinction. [[Turnagra capensis|The South Island piopio]], [[Rallus modestus|Chatham rail]],<ref name="Mead 1982 183–186" /> and the [[New Zealand merganser]]<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Stattersfield |first1=A. J. |last2=Crosby |first2=M. J. |last3=Long |first3=A. J. |last4=Wege |first4=D. C. |title=Endemic Bird Areas of the World: Priorities for Biodiversity Conservation |date=1998 |publisher=Burlington Press |isbn=9780946888337 |series="BirdLife Conservation" series No. 7 |location=Cambridge, England}}</ref> are a few from a long list, with the most extreme case being the flightless [[Lyall's wren]], which was driven to extinction only a few years after its discovery.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Falla |first=R. A. |title=New Zealand Bird Life Past and Present |date=1955 |publisher=[[Cawthron Institute]]}}{{page needed|date=November 2014}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Galbreath |first1=R. |last2=Brown |first2=D. |year=2004 |title=The Tale of the Lighthouse-keeper's Cat: Discovery and Extinction of the Stephens Island Wren (''Traversia lyalli'') |url= http://www.notornis.org.nz/free_issues/Notornis_51-2004/Notornis_51_4_193.pdf |url-status=dead |journal=Notornis |volume=51 |pages=193–200 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20081017221501/http://www.notornis.org.nz/free_issues/Notornis_51-2004/Notornis_51_4_193.pdf |archive-date=17 October 2008}}</ref> One feral cat in New Zealand killed 102 [[New Zealand lesser short-tailed bat]]s in seven days.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Scrimgeour |first1=J. |last2=Beath |first2=A. |last3=Swanney |first3=M. |year=2012 |title=Cat predation of short-tailed bats (''Mystacina tuberculata rhyocobia'') in Rangataua Forest, Mount Ruapehu, Central North Island, New Zealand |journal=New Zealand Journal of Zoology |volume=39 |issue=3 |pages=257–260 |doi=10.1080/03014223.2011.649770 |doi-access=free}}</ref> In the United States, feral and free-ranging domestic cats kill an estimated 6.3–22.3 billion mammals annually.<ref name="NC012913" /> |
|||
* ''F. catus angorensis'' - the Turkish Angora |
|||
In Australia, one study found feral cats to kill 466 million reptiles per year. More than 258 reptile species were identified as being predated by cats.<ref>{{cite journal | last1=Woinarski | first1=J. C. Z. | last2=Murphy | first2=B. P. | last3=Palmer | first3=R. | last4=Legge | first4=S. M. | last5=Dickman | first5=C. R. | last6=Doherty | first6=T. S. | last7=Edwards | first7=G. | last8=Nankivell | first8=A. | last9=Read | first9=J. L. | last10=Stokeld | first10=D. | title=How many reptiles are killed by cats in Australia? | journal=Wildlife Research | publisher=CSIRO Publishing | volume=45 | issue=3 | year=2018 | issn=1035-3712 | doi=10.1071/wr17160 | page=247}}</ref> Cats have contributed to the extinction of the [[Navassa curly-tailed lizard]] and ''[[Chioninia coctei]].''<ref name="contr-ext">{{Cite journal |last1=Doherty |first1=T. S. |last2=Glen |first2=A. S. |last3=Nimmo |first3=D. G. |last4=Ritchie |first4=E. G. |last5=Dickman |first5=C. R. |year=2016 |title=Invasive predators and global biodiversity loss |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=113 |issue=40 |pages=11261–11265 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1602480113 |pmc=5056110 |pmid=27638204 |bibcode=2016PNAS..11311261D |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
====Coat patterns==== |
|||
[[Cat coat genetics]] can produce a variety of coat patterns. Some of the most common are: |
|||
== Interaction with humans == |
|||
[[File:Co-kbk-07-001.jpg|thumb|Blue (grey) and white bicolor cat.]] |
|||
{{Main|Human interaction with cats}} |
|||
; [[Bicolor cat|Bicolor, Tuxedo and Van]] :This pattern varies between the [[Bicolor cat#Tuxedo cats|tuxedo cat]] which is mostly black with a white chest, and possibly markings on the face and paws/legs, all the way to the ''Van'' pattern (so named after the [[Lake Van]] area in Turkey, which gave rise to the [[Turkish Van]] breed), where the only colored parts of the cat are the tail (usually including the base of the tail proper), and the top of the head (often including the ears). There are several other terms for amounts of white between these two extremes, such as ''Harlequin'' or ''[[jellicle]] cat''. Bicolor cats can have as their primary (non-white) color black, red, any dilution thereof, and tortoiseshell (see below for definition). |
|||
[[File:Mainecoon-lap.jpg|thumb|upright=.9|left|alt=A long-haired calico cat sat in the lap of a man who is sat cross-legged on the floor.|A cat lying on a man's lap]] |
|||
Cats are common [[pet]]s throughout the world, and their worldwide population as of 2007 exceeded 500 million.<ref name="NYT">{{Cite news |last=Wade |first=N. |year=2007 |title=Study Traces Cat's Ancestry to Middle East |url= https://www.nytimes.com/2007/06/29/science/29cat.html |work=The New York Times |access-date=2 April 2008 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090418082840/http://www.nytimes.com/2007/06/29/science/29cat.html |archive-date=18 April 2009}}</ref> {{As of|2017|post=,}} the domestic cat was the second most popular pet in the [[United States]], with 95.6 million cats owned<ref>{{cite web |title=Pet Industry Market Size & Ownership Statistics |url= https://www.americanpetproducts.org/press_industrytrends.asp |publisher=[[American Pet Products Association]] |access-date=25 February 2019 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20190225161902/https://www.americanpetproducts.org/press_industrytrends.asp |archive-date=25 February 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=The 5 Most Expensive Cat Breeds in America |url= https://www.moneytalksnews.com/the-5-most-expensive-cat-breeds-in-america/ |work=moneytalksnews.com |access-date=25 February 2019 |year=2017 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20190225103150/https://www.moneytalksnews.com/the-5-most-expensive-cat-breeds-in-america/ |archive-date=25 February 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> and around 42 million households owning at least one cat.<ref>{{Cite web|date=12 December 2020|title=61 Fun Cat Statistics That Are the Cat's Meow! (2022 UPDATE)|url= https://petpedia.co/cat-statistics/|access-date=18 February 2022 |archive-date=18 February 2022|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20220218184821/https://petpedia.co/cat-statistics/|url-status=live}}</ref> In the [[United Kingdom]], 26% of adults have a cat, with an estimated population of 10.9 million pet cats {{As of|2020|lc=y|post=.}}<ref>{{Cite web |title=How many pets are there in the UK? |url= https://www.pdsa.org.uk/get-involved/our-campaigns/pdsa-animal-wellbeing-report/uk-pet-populations-of-dogs-cats-and-rabbits |access-date=29 March 2021 |website=PDSA.org.uk |archive-date=3 March 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210303184319/https://www.pdsa.org.uk/get-involved/our-campaigns/pdsa-animal-wellbeing-report/uk-pet-populations-of-dogs-cats-and-rabbits |url-status=dead}}</ref> {{As of|2021|post=,}} there were an estimated 220 million owned and 480 million stray cats in the world.<ref>{{cite web |url= https://carocat.eu/statistics-on-cats-and-dogs/ |title=Statistics on cats |year=2021 |website=carocat.eu |access-date=15 February 2021 |archive-date=25 February 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210225150136/https://carocat.eu/statistics-on-cats-and-dogs/ |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Cats have been used for millennia to control rodents, notably [[Farm cat|around grain stores]] and [[Ship's cat|aboard ships]], and both uses extend to the present day.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Beadle|first=Muriel|title=Cat|publisher=Simon and Schuster|date=1979|isbn=9780671251901|pages=93–96}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Mayers |first=Barbara |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=q3LvHwAACAAJ |title=Toolbox: Ship's Cat on the Kalmar Nyckel|date=2007|publisher=Bay Oak Publishers |isbn=9780974171395 |access-date=17 July 2020 |archive-date=31 March 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210331062435/https://books.google.com/books?id=q3LvHwAACAAJ|url-status=live}}</ref> Cats are also used in the international [[fur trade]]<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.hsus.org/web-files/PDF/What-is-that-they-re-wearing_FurBooklet.pdf |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20061201153853/http://www.hsus.org/web-files/PDF/What-is-that-they-re-wearing_FurBooklet.pdf |archive-date=1 December 2006 |title=What Is That They're Wearing? |publisher=[[Humane Society of the United States]] |access-date=22 October 2009}}</ref> and leather industries for making coats, hats, blankets, stuffed toys,<ref>{{Cite book |title=A Primer on Animal Rights: Leading Experts Write about Animal Cruelty and Exploitation |editor-first=K. W. |editor-last=Stallwood |publisher=[[Lantern Books]] |date=2002}}</ref> shoes, gloves, and musical instruments.<ref>{{cite news|url= https://www.independent.co.uk/news/japan-finale-for-the-worlds-most-elegant-use-of-a-dead-cat-1294096.html |title=Japan: Finale for the world's most elegant use of a dead cat |date=15 November 1997 |work=[[The Independent]] |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20170621114633/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/japan-finale-for-the-worlds-most-elegant-use-of-a-dead-cat-1294096.html|archive-date=21 June 2017}}</ref> About 24 cats are needed to make a cat-fur coat.<ref>{{Cite news |url= http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6165786.stm |title=EU proposes cat and dog fur ban |work=[[BBC News]] |access-date=22 October 2009 |year=2006 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090102231651/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6165786.stm |archive-date=2 January 2009}}</ref> This use has been outlawed in the United States since 2000 and in the European Union (as well as the United Kingdom) since 2007.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.hsus.org/about_us/humane_society_international_hsi/hsi_europe/dog_cat_fur/ |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090217153420/http://www.hsus.org/about_us/humane_society_international_hsi/hsi_europe/dog_cat_fur/ |archive-date=17 February 2009 |title=EU Announces Strict Ban on Dog and Cat Fur Imports and Exports |year=2007 |first=C. |last=Ikuma |work=[[Humane Society International]] |access-date=14 December 2011}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Felis silvestris - July 2007-1.jpg|thumb|Mackerel tabby cat, showing the characteristic "M" on its forehead.]] |
|||
; [[Tabby]] :Striped, with a variety of patterns. The classic blotched tabby (or marbled) pattern is the most common and consists of butterflies and bullseyes. The mackerel or striped tabby is a series of vertical stripes down the cat's side (resembling the fish). This pattern broken into spots is referred to as a spotted tabby. Finally, the tabby markings may look like a series of ticks on the fur, thus the ticked tabby, which is almost exclusively associated with the Abyssinian breed of cats. The worldwide evolution of the cat means that certain types of tabby are associated with certain countries; for instance, blotched tabbies are quite rare outside NW Europe, where they are the most common type. |
|||
Cat pelts have been used for superstitious purposes as part of the practice of [[witchcraft]],<ref>{{Cite book |title=Witchcraft and Magic in Europe |volume=3: ''The Middle Ages'' |last1=Jolly |first1=K. L. |last2=Raudvere |first2=C. |last3=Peters |first3=E. |publisher=Athlone |date=2002 |isbn=9780567574466 |location=London |oclc=747103210}}</ref> and they are still made into blankets in [[Switzerland]] as [[traditional medicine]]s thought to cure [[rheumatism]].<ref>{{Cite news |url= https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/switzerland-finds-a-way-to-skin-a-cat-for-the-fur-trade-and-high-fashion-815426.html |title=Switzerland Finds a Way to Skin a Cat for the Fur Trade and High Fashion |last=Paterson |first=T. |year=2008 |work=The Independent |access-date=23 October 2009 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090707080420/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/switzerland-finds-a-way-to-skin-a-cat-for-the-fur-trade-and-high-fashion-815426.html |archive-date=7 July 2009 |location=London}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Curlycat02.jpg|thumb|Female tortoiseshell-and-white cat.]] |
|||
; [[Tortoiseshell cat|Tortoiseshell and calico]] |
|||
: This cat is also known as a calimanco cat or clouded tiger cat, and by the abbreviation 'tortie'. In the cat fancy, a tortoiseshell cat is patched over with ginger (or its dilute form, champagne) and black (or its dilute blue) mottled throughout the coat. Additionally, the cat may have white spots in its fur, which make it a 'tortoiseshell and white' cat; if there is a significant amount of white in the fur and the red and black colors form a patchwork rather than a mottled aspect, in North America the cat will be called a calico. All calicos are tortoiseshell (as they carry both black and red), but not all tortoiseshells are calicos (which requires a significant amount of white in the fur and patching rather than mottling of the colors). The calico is also sometimes called a tricolor cat. The Japanese refer to this pattern as ''mi-ke'' (meaning "triple fur"), while the Dutch call these cats ''lapjeskat'' (meaning "patches cat"). A true tricolor must consist of three colors: a reddish color, dark or light; white; and one other color, typically a brown, black, or blue.<ref>{{cite web | title=Torties, Calicos and Tricolor cats | url=http://www.fanciers.com/cat-faqs/tricolors.shtml| accessdate=2005-10-24 }}</ref> Both tortoiseshell and calico cats are typically female because the [[coat (animal)|coat]] pattern is the result of differential [[X chromosome]] [[x-inactivation|inactivation]] in [[female]]s (which, as with all normal female [[mammal]]s, have two X [[chromosome]]s). Conversely, cats where the overall color is ginger (orange) are commonly male (roughly in a 3:1 ratio). In a litter sired by a ginger tom, the females will be tortoiseshell or ginger. Male tortoiseshells can occur as a result of chromosomal abnormalities (often linked to sterility) or by a phenomenon known as [[mosaic (genetics)|mosaicism]], where two early stage embryos are merged into a single kitten. |
|||
[[File:Man holding Calico cat.jpg|thumb|A man holding a calico cat]] |
|||
[[File:Niobe050905-Siamese Cat.jpeg|thumb|upright|[[Siamese (cat)|Siamese cat]], classical colorpoint pattern.]] |
|||
A few attempts to build a cat census have been made over the years, both through associations or national and international organizations (such as that of the [[Canadian Federation of Humane Societies]]<ref name="Canadian">{{Cite news |url= https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/new-brunswick/humane-society-launches-national-cat-census-1.1185950 |title=Humane society launches national cat census |access-date=18 September 2012 |publisher=[[CBC News]] |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20121024184326/http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/new-brunswick/story/2012/07/17/nb-cat-census-1000.html |archive-date=24 October 2012}}</ref>) and over the Internet.<ref name="catsbe">{{cite web |url= http://www.catsbe.com |title=Cats Be |access-date=18 September 2012 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120922235823/http://www.catsbe.com/ |archive-date=22 September 2012}}</ref><ref name="SupremeCatCensus">{{cite web |url= http://www.supremecatcensus.co.za/ |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120316024409/http://www.supremecatcensus.co.za/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=16 March 2012 |title=The Supreme Cat Census |access-date=18 September 2012}}</ref> General estimates for the global population of domestic cats range widely from anywhere between 200 million to 600 million.<ref>{{cite web |title=About Pets |work=IFAHEurope.org |publisher=Animal Health Europe |url= http://www.ifaheurope.org/companion-animals/about-pets.html |access-date=3 October 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20141006074439/http://www.ifaheurope.org/companion-animals/about-pets.html|archive-date=6 October 2014}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Legay |first=J. M. |title=Sur une tentative d'estimation du nombre total de chats domestiques dans le monde |trans-title=Tentative estimation of the total number of domestic cats in the world |language=fr |journal=Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série III |volume=303 |issue=17 |pages=709–712 |year=1986 |id={{INIST|7950138}} |pmid=3101986}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=xYKqluO6c8UC&q=million%20cats%20worldwide&pg=PA157 |first1=S. D. |last1=Gehrt |first2=S. P. D. |last2=Riley |first3=B. L. |last3=Cypher |title=Urban Carnivores: Ecology, Conflict, and Conservation |date=2010 |publisher=[[Johns Hopkins University]] Press |access-date=3 October 2014 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20151231224128/https://books.google.com/books?id=xYKqluO6c8UC&lpg=PA157&pg=PA157&q=million%20cats%20worldwide |archive-date=31 December 2015 |isbn=9780801893896}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=0HmB3ix5IQ8C&q=million%20cats%20worldwide&pg=PA47 |first=I. |last=Rochlitz |title=The Welfare of Cats |date=2007 |publisher=[[Springer Science & Business Media]] |access-date=3 October 2014 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20151231224128/https://books.google.com/books?id=0HmB3ix5IQ8C&lpg=PA47&pg=PA47&q=million%20cats%20worldwide |archive-date=31 December 2015 |isbn=9781402032271}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Cats: Most interesting facts about common domestic pets |url= http://english.pravda.ru/society/family/09-01-2006/9478-cats-0/ |work=[[Pravda]] |access-date=3 October 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20141006105806/http://english.pravda.ru/society/family/09-01-2006/9478-cats-0/ |archive-date=6 October 2014 |date=9 January 2006}}</ref> [[Walter Chandoha]] made his career photographing cats after his 1949 images of ''Loco'', a stray cat, were published. He is reported to have photographed 90,000 cats during his career and maintained an archive of 225,000 images that he drew from for publications during his lifetime.<ref>{{cite news |last=Sandomir |first=R. |url= https://www.nytimes.com/2019/01/18/obituaries/walter-chandoha-dead.html?emc=edit_th_190119&nl=todaysheadlines&nlid=686341800119/ |title=Walter Chandoha, Photographer Whose Specialty Was Cats, Dies at 98 |work=The New York Times |date=18 January 2019 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20190119231032/https://www.nytimes.com/2019/01/18/obituaries/walter-chandoha-dead.html?emc=edit_th_190119&nl=todaysheadlines&nlid=686341800119%2FWalter |archive-date=19 January 2019 |url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
[[Pet humanization]] is a form of [[anthropomorphism]] in which cats are kept for companionship and treated more like human family members than traditional pets.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://static1.squarespace.com/enwiki/static/57f414e0b8a79bc04e0a2729/t/6081b71ec312977485a24fa4/1619113759478/CD-The+Rise+of+Pet+Humanization.pdf |title=The Rise of Pet Humanization |access-date=29 March 2024 |archive-date=2 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240402002609/https://static1.squarespace.com/enwiki/static/57f414e0b8a79bc04e0a2729/t/6081b71ec312977485a24fa4/1619113759478/CD-The+Rise+of+Pet+Humanization.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> This trend of [[pet culture]] involves providing cats with a higher level of care, attention and often even luxury, similar to the way humans are treated.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://advantagesolutions.net/news/the-humanization-of-pets/ |title=The Humanization of Pets |access-date=29 March 2024 |archive-date=6 December 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231206214159/https://advantagesolutions.net/news/the-humanization-of-pets/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
; [[Point (coat color)|Colorpoint]] |
|||
: The colorpoint pattern is most commonly associated with [[Siamese (cat)|Siamese]] cats, but may also appear in any domesticated cat. A colorpointed cat has dark colors on the face, ears, feet, and tail, with a lighter version of the same color on the rest of the body, and possibly some white. The exact name of the colorpoint pattern depends on the actual color, so there are seal points (dark brown), chocolate points (warm lighter brown), blue points (dark gray), lilac or frost points (silvery gray-pink), red or flame points (orange), and tortie (tortoiseshell mottling) points, among others. This pattern is the result of a [[Mutation#Special classes|temperature sensitive mutation]] in one of the [[enzyme]]s in the [[metabolic pathway]] from [[tyrosine]] to pigment, such as [[melanin]]; thus, little or no pigment is produced except in the extremities or points where the skin is slightly cooler. For this reason, colorpointed cats tend to darken with age as bodily temperature drops; also, the fur over a significant injury may sometimes darken or lighten as a result of temperature change. |
|||
=== Shows === |
|||
: The tyrosine pathway also produces [[neurotransmitter]]s, thus mutations in the early parts of that pathway may affect not only pigment, but also neurological development. This results in a higher frequency of [[strabismus|cross-eyes]] among colorpointed cats, as well as the [[White tiger#Genetics and albinism|high frequency of cross-eyes in white tigers]]. |
|||
{{main|Cat show}} |
|||
A [[cat show]] is a judged event in which the owners of cats compete to win titles in various cat-registering organizations by entering their cats to be judged after a breed standard.<ref name=":0">{{Cite news |url= https://animals.howstuffworks.com/pets/cat-show1.htm |title=All About Cat Shows |year=2008 |work=How Stuff Works |access-date=8 June 2018 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20180612143813/https://animals.howstuffworks.com/pets/cat-show1.htm |archive-date=12 June 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> It is often required that a cat must be healthy and vaccinated to participate in a cat show.<ref name=":0" /> Both [[Pedigree (cat)|pedigreed]] and non-[[purebred]] companion ("moggy") cats are admissible, although the rules differ depending on the organization. Competing cats are compared to the applicable breed standard, and assessed for temperament.<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
=== Infection === |
|||
; White cats |
|||
{{Main|Feline zoonosis}} |
|||
[[File:WhiteCatHarold.jpg|thumb|White cat.]] |
|||
Cats can be [[Cat predation on wildlife|infected]] or infested with [[virus]]es, [[pathogenic bacteria|bacteria]], [[fungus]], [[protozoans]], [[arthropod]]s or worms that can transmit diseases to humans.<ref name="Chomel2014" /> In some cases, the cat exhibits no [[symptoms]] of the disease.<ref name="Ohio2016">{{cite web |title=Cats |publisher=Ohio Department of Health|url= http://www.odh.ohio.gov/en/odhprograms/bid/zdp/animals/cats |access-date=26 November 2016 |date=21 January 2015 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20161127023823/https://www.odh.ohio.gov/en/odhprograms/bid/zdp/animals/cats|archive-date=27 November 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> The same disease can then become evident in a human.<ref name="Goldstein2015">{{cite journal |last1=Goldstein |first1=Ellie J. C. |last2=Abrahamian |first2=Fredrick M. |year=2015 |title=Diseases Transmitted by Cats |url=https://journals.asm.org/doi/epub/10.1128/microbiolspec.iol5-0013-2015 |journal=Microbiology Spectrum |volume=3 |issue=5 |doi=10.1128/microbiolspec.iol5-0013-2015 |pmid=26542039 |issn=2165-0497 |access-date=8 August 2023 |archive-date=10 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230810225116/https://journals.asm.org/doi/epub/10.1128/microbiolspec.iol5-0013-2015 |url-status=live }}</ref> The likelihood that a person will become diseased depends on the age and [[Immunocompetence|immune status]] of the person. Humans who have cats living in their home or in close association are more likely to become infected. Others might also acquire infections from cat [[feces]] and [[parasite]]s exiting the cat's body.<ref name="Chomel2014">{{Cite journal |last=Chomel |first=B. |title=Emerging and Re-Emerging Zoonoses of Dogs and Cats |journal=Animals |volume=4 |issue=3 |year=2014 |pages=434–445 |issn=2076-2615 |doi=10.3390/ani4030434 |pmid=26480316 |pmc=4494318|doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name="StullBrophy2015">{{Cite journal |last1=Stull |first1=J. W. |last2=Brophy |first2=J. |last3=Weese |first3=J. S. |title=Reducing the risk of pet-associated zoonotic infections |journal=Canadian Medical Association Journal |volume=187 |issue=10 |year=2015 |pages=736–743 |issn=0820-3946 |doi=10.1503/cmaj.141020 |pmid=25897046|pmc=4500695}}</ref> Some of the infections of most concern include [[salmonella]], [[cat-scratch disease]], and [[toxoplasmosis]].<ref name="Ohio2016" /> |
|||
: True albinism (a mutation of the tyrosinase gene) is quite rare in cats. Much more common is the appearance of white coat color that is caused by a lack of [[melanocyte]]s in the skin. A [[Melanin#Genetic disorders and disease states|higher frequency of deafness in white cats]] is due to a reduction in the population and survival of melanoblast stem cells, which in addition to creating pigment producing cells, develop into a variety of neurological cell types. White cats with one or two blue eyes have a particularly high likelihood of being deaf. |
|||
=== History and mythology === |
|||
; Smoke cats |
|||
{{Main|Cultural depictions of cats|Cats in ancient Egypt}} |
|||
: The bottom eighth of each hair is white or creamy-white, with the rest of the hair being a solid color. Genetically this color is a non-[[agouti signalling peptide|agouti]] cat with the dominant inhibitor gene; a non-agouti version of the silver [[tabby cat|tabby]]. Smoke cats will look solid colored until they move, when the white undercoat becomes apparent. It is mostly found in [[cat breed|pedigreed cat]]s (especially longhair breeds) but also present in some [[domestic longhaired cat]]s. |
|||
In [[ancient Egypt]], cats were [[animal worship|revered]], and the goddess [[Bastet]] often depicted in cat form, sometimes taking on the war-like aspect of a lioness. The Greek historian [[Herodotus]] reported that killing a cat was forbidden, and when a household cat died, the entire family mourned and shaved their eyebrows. Families took their dead cats to the sacred city of [[Bubastis]], where they were embalmed and buried in sacred repositories. Herodotus expressed astonishment at the domestic cats in Egypt, because he had only ever seen wildcats.<ref name="Malek1997">{{cite book |title=The Cat in Ancient Egypt |last=Malek |first=J. |date=1997 |publisher=University of Pennsylvania Press |isbn=9780812216325 |edition=Revised}}</ref> |
|||
Ancient Greeks and Romans kept [[weasel]]s as pets, which were seen as the ideal rodent-killers. The earliest unmistakable evidence of the Greeks having domestic cats comes from two coins from [[Magna Graecia]] dating to the mid-fifth century BC showing Iokastos and Phalanthos, the legendary founders of [[Reggio Calabria|Rhegion]] and [[Taranto|Taras]] respectively, playing with their pet cats. The usual ancient Greek word for 'cat' was {{lang|grc-Latn|ailouros}}, meaning 'thing with the waving tail'. Cats are rarely mentioned in [[ancient Greek literature]]. [[Aristotle]] remarked in his ''[[History of Animals]]'' that "female cats are naturally [[Promiscuity|lecherous]]". The Greeks later [[Interpretatio graeca|syncretized]] their own goddess [[Artemis]] with the Egyptian goddess Bastet, adopting Bastet's associations with cats and ascribing them to Artemis. In [[Ovid]]'s ''[[Metamorphoses]]'', when the deities flee to Egypt and take animal forms, the goddess [[Diana (mythology)|Diana]] turns into a cat.<ref name="Engels2001">{{Cite book |last=Engels |first=D. W. |title=Classical Cats: The Rise and Fall of the Sacred Cat |date=2001 |orig-year=1999 |publisher=Routledge |location=London |isbn=9780415261623 |chapter=Greece |pages=[https://archive.org/details/classicalcats00dona/page/48 48–87] |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=XAkeCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA68 |url= https://archive.org/details/classicalcats00dona/page/48}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Rogers |first=K. M. |title=Cat |date=2006 |publisher=Reaktion Books |location=London |isbn=9781861892928 |chapter=Wildcat to Domestic Mousecatcher |pages=7–48 |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=16ZsW4QLKlUC&pg=PA19 |access-date=5 June 2020 |archive-date=27 July 2020 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20200727182342/https://books.google.com/books?id=16ZsW4QLKlUC&pg=PA19 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
====Body types==== |
|||
Cats can also come in several body types, ranging between two extremes: |
|||
Cats eventually displaced [[weasel]]s as the pest control of choice because they were more pleasant to have around the house and were more enthusiastic hunters of mice. During the [[Middle Ages]], many of Artemis's associations with cats were grafted onto the [[Mary, mother of Jesus|Virgin Mary]]. Cats are often shown in icons of [[Annunciation]] and of the [[Holy Family]] and, according to [[Folklore of Italy|Italian folklore]], on the same night that Mary gave birth to [[Jesus]], a cat in [[Bethlehem]] gave birth to a kitten.<ref name="Beadle1977">{{Cite book |last=Beadle |first=M. |title=Cat |date=1977 |publisher=[[Simon & Schuster]] |location=New York |isbn=9780671224516 |chapter=Ups and Downs |pages=[https://archive.org/details/cathistorybiolog00bead/page/75 75–88] |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=tnjgqpNKYksC&pg=PA75 |url= https://archive.org/details/cathistorybiolog00bead/page/75}}</ref> Domestic cats were spread throughout much of the rest of the world during the [[Age of Discovery]], as [[Ship's cat|ships' cats]] were carried on [[sailing ship]]s to control shipboard rodents and as good-luck charms.<ref name="Faure2009" /> |
|||
; Oriental: Not a specific breed, but any cat with an elongated slender build, almond-shaped eyes, long nose, large ears (the [[Siamese (cat)|Siamese]] and [[Oriental Shorthair]] breeds are examples of this). |
|||
; Foreign: Less slender than the oriental type, but nevertheless a cat with a slight build and generally athletic look. Typical example breeds would be the [[Abyssinian (cat)|Abyssinian cat]] and the [[Turkish Angora]]. Some people consider the foreign and oriental body types as being the same, however. |
|||
; Semi-Foreign: More or less the middle range of body conformation types, this type of cat is less slender without being stocky. Example breeds would be the [[Devon Rex]] and the [[Egyptian Mau]]. |
|||
; Semi-Cobby: These cats look more rounded without looking too stocky. Example breeds would be the [[American Shorthair]] and [[British Shorthair]]. |
|||
; Cobby: Any cat with a short, muscular, compact build, roundish eyes, short nose, and small ears. [[Persian (cat)|Persian cat]]s and [[Exotic Shorthair|Exotic cat]]s are two prime examples of such a body type. |
|||
Several ancient religions believed cats are exalted souls, companions or guides for humans, that are all-knowing but mute so they cannot influence decisions made by humans. In Japan, the {{lang|ja-Latn|[[maneki neko]]}} cat is a symbol of good fortune.<ref>{{cite journal |url= http://www.darumamagazine.com/new/articles-excerpts/maneki-neko-feline-fact-fiction/ |title=Maneki Neko: Feline Fact & Fiction |first=A. |last=Pate |journal=Daruma Magazine |year=2008 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130314191210/http://www.darumamagazine.com/new/articles-excerpts/maneki-neko-feline-fact-fiction/ |archive-date=14 March 2013 |url-status=dead}}</ref> In [[Norse mythology]], [[Freyja]], the goddess of love, beauty, and fertility, is depicted as riding a chariot drawn by cats.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Faulkes |first=A. |date=1995 |title=Edda |page=24 |isbn=9780460876162}}</ref> In [[Legends of the Jews|Jewish legend]], the first cat was living in the house of the first man [[Adam]] as a pet that got rid of [[mice]]. The cat was once partnering with the first dog before the latter broke an oath they had made which resulted in enmity between the descendants of these two animals. It is also written that neither cats nor [[fox]]es are represented in the water, while every other animal has an incarnation species in the water.<ref name="Ginzberg">{{Cite book |last=Ginzberg |first=L. |date=1909 |title=The Legends of the Jews, Vol. I: The Sixth Day |url= http://www.swartzentrover.com/cotor/e-books/misc/Legends/Legends%20of%20the%20Jews.pdf |translator-first=H. |translator-last=Szold |location=Philadelphia |publisher=[[Jewish Publication Society]] |access-date=19 February 2018 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20180516120617/http://www.swartzentrover.com/cotor/e-books/misc/Legends/Legends%20of%20the%20Jews.pdf |archive-date=16 May 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> Although no species are sacred in Islam, [[Islam and cats|cats are revered by Muslims]]. Some Western writers have stated [[Muhammad]] had a favorite cat, ''[[Muezza]]''.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Geyer |first=G. A. |title=When Cats Reigned Like Kings: On the Trail of the Sacred Cats |publisher=[[Andrews McMeel Publishing]] |location=Kansas City, Missouri |date=2004 |isbn=9780740746970 |url= https://archive.org/details/whencatsreignedl00geor}}</ref> He is reported to have loved cats so much, "he would do without his cloak rather than disturb one that was sleeping on it".<ref name="Reeves">{{Cite book |first=M. |last=Reeves |title=Muhammad in Europe |publisher=[[New York University Press]] |page=[https://archive.org/details/muhammadineurope0000reev/page/52 52] |isbn=9780814775332 |date=2000 |url= https://archive.org/details/muhammadineurope0000reev/page/52}}</ref> The story has no origin in early Muslim writers, and seems to confuse a story of a later [[Sufi]] saint, [[Ahmed ar-Rifa'i]], centuries after Muhammad.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://library.islamweb.net/newlibrary/display_book.php?idfrom=5401&idto=5401&bk_no=60&ID=5263 |title=Biography of al-Rifai |last=Al-Thahabi |first=S. |work=سير أعلام النبلاء |language=ar |access-date=11 November 2014 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20141025030332/http://library.islamweb.net/newlibrary/display_book.php?idfrom=5401&idto=5401&bk_no=60&ID=5263 |archive-date=25 October 2014}}</ref> One of the companions of Muhammad was known as [[Abu Hurayrah]] ("father of the kitten"), in reference to his documented affection to cats.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://pictures-of-cats.org/abu-hurairah-and-cats.html |title=Abu Hurairah and Cats |date=13 January 2015 |first1=Michael |last1=Broad |work=Pictures-of-Cats.org |access-date=5 March 2018 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20180305203105/http://pictures-of-cats.org/abu-hurairah-and-cats.html |archive-date=5 March 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Effects on human health=== |
|||
Because of their small size, domesticated house cats pose little physical danger to adult humans. However, in the USA cats inflict about 400,000 bites per year, with 90% of these bites coming from provoked animals; this number represents about one in ten of all animal bites.<ref name=Kravetz/> Many cat bites will become infected,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Talan DA, Citron DM, Abrahamian FM, Moran GJ, Goldstein EJ |title=Bacteriologic analysis of infected dog and cat bites. Emergency Medicine Animal Bite Infection Study Group |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=340 |issue=2 |pages=85–92 |year=1999 |month=January |pmid=9887159 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199901143400202 |first1=DA |first2=DM |first3=FM |first4=GJ |first5=EJ |issn=0028-4793}}</ref> sometimes with serious consequences such as [[cat-scratch disease]], or, more rarely, [[rabies]].<ref name=Kravetz>{{cite journal |author=Kravetz JD, Federman DG |title=Cat-associated zoonoses |journal=Arch. Intern. Med. |volume=162 |issue=17 |pages=1945–52 |year=2002 |month=September |pmid=12230416 |doi=10.1001/archinte.162.17.1945 |first1=JD |first2=DG |issn=0003-9926 |url=http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12230416 |format=Free full text}}</ref> Cats may also pose a danger to pregnant women and [[immunosuppression|immunosuppressed]] individuals, since their feces can transmit [[toxoplasmosis]].<ref name=Torda>{{cite journal |author=Torda A |title=Toxoplasmosis. Are cats really the source? |journal=Aust Fam Physician |volume=30 |issue=8 |pages=743–7 |year=2001 |month=August |pmid=11681144 |first1=A |issn=0300-8495}}</ref> A large percentage of cats are infected with this parasite, with infection rates ranging from around 40 to 60% in both domestic and stray cats worldwide.<ref name="pmid9870370">{{cite journal |author=Svobodová V, Knotek Z, Svoboda M |title=Prevalence of IgG and IgM antibodies specific to Toxoplasma gondii in cats |journal=Vet. Parasitol. |volume=80 |issue=2 |pages=173–6 |year=1998 |month=December |pmid=9870370 |doi=10.1016/S0304-4017(98)00201-5 |first1=V |first2=Z |first3=M |issn=0304-4017}}</ref><ref name="pmid15303992">{{cite journal |author=Meireles LR, Galisteo AJ, Pompeu E, Andrade HF |title=Toxoplasma gondii spreading in an urban area evaluated by seroprevalence in free-living cats and dogs |journal=Trop. Med. Int. Health |volume=9 |issue=8 |pages=876–81 |year=2004 |month=August |pmid=15303992 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-3156.2004.01280.x |url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=1360-2276&date=2004&volume=9&issue=8&spage=876 |first1=LR |first2=Jr |first3=E |first4=Jr |issn=1360-2276 |format=Free full text}}</ref><ref name="pmid18707811">{{cite journal |author=De Craeye S, Francart A, Chabauty J |title=Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in Belgian house cats |journal=Vet. Parasitol. |volume=157 |issue=1-2 |pages=128–32 |year=2008 |month=October |pmid=18707811 |doi=10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.07.001 |first1=S |first2=A |first3=J |first4=V |first5=S |first6=I |first7=E |issn=0304-4017}}</ref> |
|||
{{Image frame|align=center|border=no|content=<gallery mode="packed"> |
|||
[[Allergy|Allergic]] reactions to cat [[dander]] and/or cat saliva are common.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Erwin EA, Woodfolk JA, Custis N, Platts-Mills TA |title=Animal danders |journal=Immunol Allergy Clin North Am |volume=23 |issue=3 |pages=469–81 |year=2003 |month=August |pmid=14524386 |doi=10.1016/S0889-8561(03)00004-3 |first1=EA |first2=JA |first3=N |first4=TA |issn=0889-8561}}</ref> Some humans who are [[cat allergy|allergic to cats]]—typically manifested by [[rhinitis#Hay fever|hay fever]], [[asthma]], or a skin [[rash]]—quickly acclimate themselves to a particular animal and live comfortably in the same house with it, while retaining an allergy to cats in general.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.animaltrustees.org/ATA_Web/pdfs/dealingwithcatallergies.pdf |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070604203854/http://www.animaltrustees.org/ATA_Web/pdfs/dealingwithcatallergies.pdf |archivedate=2007-06-04 |format=PDF| title=Dealing with cat allergies | work=animaltrustees.org}}</ref> Whether the risk of developing allergic diseases such as asthma is increased or decreased by cat ownership is uncertain.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Simpson A, Custovic A |title=Early pet exposure: friend or foe? |journal=Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol |volume=3 |issue=1 |pages=7–14 |year=2003 |month=February |pmid=12582308 |doi=10.1097/01.all.0000053261.39029.7a |first1=A |first2=A |issn=1528-4050 |doi_brokendate=2009-09-06}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Simpson A, Custovic A |title=Pets and the development of allergic sensitization |journal=Curr Allergy Asthma Rep |volume=5 |issue=3 |pages=212–20 |year=2005 |month=May |pmid=15842959 |doi=10.1007/s11882-005-0040-x |first1=A |first2=A |issn=1529-7322}}</ref> Some owners cope with this problem by taking allergy medicine, along with bathing their cats frequently, since weekly bathing will reduce the amount of dander shed by a cat.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
File:Louvre egyptologie 21.jpg|The ancient Egyptians [[Mummy|mummified]] dead cats out of respect in the same way that they mummified people.<ref name="Clutton-Brock1999">{{Cite book |title=A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals |last=Clutton-Brock |first=J. |publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]] |location=Cambridge, England<!--This is not redundant; there's a Cambridge, Massachusetts, also, with academic publishers.--> |date=1999 |isbn=9780521634953 |edition=2nd |pages=133–140 |chapter=Cats |oclc=39786571 |orig-year=1987 |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=cgL-EbbB8a0C&pg=PA133 |access-date=25 October 2020 |archive-date=22 January 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210122145647/https://books.google.com/books?id=cgL-EbbB8a0C&pg=PA133 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
| issn = 0091-6749 |
|||
File:Cat birds MAN Napoli Inv9993.jpg|Ancient [[Roman mosaic]] of a cat killing a [[partridge]] from the [[House of the Faun]] in [[Pompeii]] |
|||
| volume = 100 |
|||
File:PSM V37 D105 English tabby cat.jpg|A 19th-century drawing of a tabby cat |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
File:Black Cat (7983739954).jpg|Some cultures are superstitious about black cats, ascribing either good or bad luck to them. |
|||
| pages = 307–312 |
|||
</gallery>}} |
|||
| last = Avner |
|||
| first = D B |
|||
| title = Evaluation of different techniques for washing cats: quantitation of allergen removed from the cat and the effect on airborne Fel d 1 |
|||
| journal = The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-27 |
|||
| date = 1997-09 |
|||
| pmid = 9314341 |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/S0091-6749(97)70242-2 |
|||
| last2 = Perzanowski |
|||
| first2 = MS |
|||
| last3 = Platts-Mills |
|||
| first3 = TA |
|||
| last4 = Woodfolk |
|||
| first4 = JA |
|||
}}</ref> There have also been attempts to breed [[Cat allergy#Hypoallergenic cats|hypoallergenic cats]], which would be less likely to provoke an allergic reaction.<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1038/nbt0205-171 |
|||
| issn = 1087-0156 |
|||
| volume = 23 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| pages = 171–172 |
|||
| last = Miller |
|||
| first = Henry |
|||
| title = Cat and mouse in regulating genetic 'enhancement' |
|||
| journal = Nature Biotechnology |
|||
| accessdate = 2009-08-21 |
|||
| year = 2005 |
|||
| url = http://www.nature.com/index.html?file=/nbt/journal/v23/n2/full/nbt0205-171.html |
|||
| pmid = 15696141 |
|||
| month = February |
|||
| last1 = Miller |
|||
| first1 = H |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
=== Superstitions and rituals === |
|||
As well as posing health risks, interactions with cats may improve health and reduce physical responses to stress: for example the presence of cats may moderate increased [[blood pressure]].<ref>{{cite journal |author=Allen K, Blascovich J, Mendes WB |title=Cardiovascular reactivity and the presence of pets, friends, and spouses: the truth about cats and dogs |journal=Psychosom Med |volume=64 |issue=5 |pages=727–39 |year=2002 |pmid=12271103 |doi=10.1097/01.PSY.0000024236.11538.41 |month=September |first1=K |first2=J |first3=WB |issn=0033-3174 |url=http://www.psychosomaticmedicine.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12271103 |format=Free full text}}</ref> Cat ownership may also improve psychological health by providing emotional support and dispelling feelings of depression, anxiety and loneliness.<ref>{{harv|Fogle|1981|pp=23–56}}</ref> Their ability to provide companionship and friendship are common reasons given for owning a cat.<ref name=Gallup/> |
|||
[[File:The Love Potion.jpg|thumb|''[[The Love Potion]]'', a 1903 painting by [[Evelyn De Morgan]] depicting a [[witch]] with a black cat]] |
|||
Many cultures have negative [[superstition]]s about cats. An example would be the belief that encountering a [[black cat]] ("crossing one's path") leads to bad luck, or that cats are witches' [[familiar spirit]]s used to augment a witch's powers and skills. The killing of cats in Medieval [[Ypres]], [[Belgium]], is commemorated in the innocuous present-day [[Kattenstoet]] (cat parade).<ref>{{cite web |title=Are Black Cats Really Bad Luck? [Hoax] |url=http://socialnewsdaily.com/58901/are-black-cats-really-bad-luck-hoax/ |work=Social News Daily |first1= K. |last1=Adzo |date=2015 |access-date=19 December 2015 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151222141607/http://socialnewsdaily.com/58901/are-black-cats-really-bad-luck-hoax/ |archive-date=22 December 2015}}</ref> In mid-16th century France, [[Cat-burning|cats would allegedly be burnt alive]] as a form of entertainment, particularly during midsummer festivals. According to [[Norman Davies]], the assembled people "shrieked with laughter as the animals, howling with pain, were singed, roasted, and finally [[Carbonization|carbonized]]".<ref>{{Cite book |last=Davies |first=N. |title=Europe: A History |date=1996 |publisher=Oxford University Press |place=Oxford |isbn=9780198201717 |page=543 |url=https://archive.org/details/europehistory00davi_0/page/543}}</ref> The remaining ashes were sometimes taken back home by the people for good luck.<ref>{{Cite book |url=http://www.bartleby.com/196/164.html |title=The Golden Bough: A Study in Magic and Religion |last=Frazer |first=J. G. |publisher=Dover Publications |date=2002 |isbn=0486424928 |edition=Abridged |location=Mineola, New York |oclc=49942157 |orig-year=1922 |access-date=28 February 2017 |archive-date=8 December 2006 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061208190208/http://www.bartleby.com/196/164.html |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
According to a myth in many cultures, cats have multiple lives. In many countries, they are believed to have nine lives, but in Italy, Germany, Greece, Brazil and some Spanish-speaking regions, they are said to have seven lives,<ref>{{Cite news |title=Las vidas del gato |year=2010 |url= http://elcomercio.pe/impresa/notas/vidas-gato/20100307/423959 |access-date=19 March 2010 |first=N. |last=Sugobono |language=es |work=[[El Comercio (Peru)]] |location=Lima, Peru |url-status=dead |archive-date=27 January 2012 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120127052854/http://elcomercio.pe/impresa/notas/vidas-gato/20100307/423959}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Qual é a origem da lenda de que os gatos teriam sete vidas? |language=pt-BR |work=[[Mundo Estranho]] |publisher=[[Abril Media]] |location=São Paulo, Brazil |access-date=15 November 2015 |url= http://mundoestranho.abril.com.br/materia/qual-e-a-origem-da-lenda-de-que-os-gatos-teriam-sete-vidas |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151117031757/http://mundoestranho.abril.com.br/materia/qual-e-a-origem-da-lenda-de-que-os-gatos-teriam-sete-vidas |archive-date=17 November 2015}}</ref> while in Arabic traditions, the number of lives is six.<ref>{{Cite news |work=[[The Guardian]] |url=https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/gallery/2010/mar/18/guide-to-pets-pet-myths?picture=360591960 |access-date=15 November 2023 |first=T. |last=Dowling |title=Tall tails: Pet myths busted |date=2010 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130909160834/http://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/gallery/2010/mar/18/guide-to-pets-pet-myths?picture=360591960|archive-date=9 September 2013}}</ref> An early mention of the myth can be found in [[John Heywood]]'s ''The Proverbs of John Heywood'' (1546):<ref>{{cite book |first=J. |last=Heywood |author-link=John Heywood |editor-first=J. |editor-last=Sharman |url=https://archive.org/details/proverbsofjohnhe00heywrich/page/104/mode/2up |title=The Proverbs of John Heywood |date=1874 |page=104}}</ref> |
|||
From another point of view, cats are thought to be able to improve the general [[mood]] of their owners by alleviating the negative attitudes. According to a Swiss study carried out in 2003, cats may change the overall psychological state of their owner as their company's effect appears to be comparable to the one of a human partner.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://en.scientificcommons.org/20081280| title=Spouses and cats and their effects on human mood|date=|accessdate= 2010-06-25}}</ref> The researchers concluded that cats do not however promote optimistic moods but only alleviate the negative ones. |
|||
{{Poem quote|text=Husband, ([[:wikt:quoth#Verb 2|quoth]] she), ye studie, be merrie now, |
|||
And even as ye thinke now, so come to yow. |
|||
Nay not so, (quoth he), for my thought to tell right, |
|||
I thinke how you lay [[:wikt:groning#English|groning]], wife, all last night. |
|||
Husband, ''a groning horse and a groning wife'' |
|||
''Never faile their master'', (quoth she), for my life. |
|||
No wife, ''a woman [[:wikt:hath#English|hath]] nine lives like a cat''.}} |
|||
The myth is attributed to the natural suppleness and swiftness cats exhibit to escape life-threatening situations.<ref>{{cite web |title=Can Cats Cheat Death? |url=https://be.chewy.com/behavior-pet-facts-do-cats-really-have-nine-lives/ |website=BeChewy |date=6 October 2017 |access-date=25 September 2023 |archive-date=25 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230925171409/https://be.chewy.com/behavior-pet-facts-do-cats-really-have-nine-lives/ |url-status=live}}</ref> Also lending credence to this myth is the fact that falling cats often land on their feet, using an instinctive [[cat righting reflex|righting reflex]] to twist their bodies around. Nonetheless, cats can still be injured or killed by a high fall.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://cats.about.com/od/catsafety/a/highrisefalls.htm |title=The ASPCA Warns About High-rise Falls by Cats: High-rise Apartments, Windows, Terraces and Fire Escapes Pose Risk to Urban Cats |date=2005 |author=<!--staff writer(s)--> |publisher=[[American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals]] |via=About.com |access-date=6 June 2018 |location=New York |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120522014805/http://cats.about.com/od/catsafety/a/highrisefalls.htm |archive-date=22 May 2012}} (Press release.)</ref> |
|||
Several studies have shown that cats develop affection towards their owners. However, the effect of these pets on human health is closely related to the time and effort the cat owner is able to invest in it, in terms of bonding, playing and buying accessories for their pet.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.catadmirer.com/| title=Cat Supplies|date=|accessdate= 2010-06-25}}</ref> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
== |
== See also == |
||
{{Portal|Cats|Mammals|Animals}} |
|||
A natural behavior in cats is to periodically hook their front claws into suitable surfaces and pull backwards. This marks their territory and exercises their legs, in addition to cleaning and sharpening their claws.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Landsberg GM |title=Feline scratching and destruction and the effects of declawing |journal=Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. |volume=21 |issue=2 |pages=265–79 |year=1991 |month=March |pmid=2053250 |first1=GM |issn=0195-5616}}</ref> Indoor cats benefit from being provided with a [[scratching post]] so that they are less likely to use carpet or furniture which they can easily ruin.<ref>{{cite web | title=Scratching or clawing in the house | url=http://www.fabcats.org/behaviour/scratching/info.html|accessdate=2005-08-14 }}</ref> Commercial scratching posts typically are covered in carpeting or upholstery, but some authorities{{Who|date=October 2009}} advise against this practice, as not making it clear to the cat which surfaces are permissible and which are not; they suggest using a plain wooden surface, or reversing the carpeting on the posts so that the rougher texture of the carpet backing is a more attractive alternative to the cat than the floor covering. Scratching posts made of [[sisal]] rope or [[corrugated fiberboard|corrugated cardboard]] are also common. |
|||
{{div col|colwidth=22em}} |
|||
* [[Aging in cats]] |
|||
[[File:Cat claw closeup.jpg|thumb|Close-up of a cat's claw, with the quick clearly visible.]] |
|||
* [[Ailurophobia]] |
|||
Although scratching can serve cats to keep their claws from growing excessively long, their nails can be trimmed if necessary. Another response to indoor scratching is [[onychectomy]], commonly known as declawing. This is a surgical procedure to remove the claw and first bone of each digit of a cat's paws. Declawing is most commonly only performed on the front feet. A related procedure is [[tendonectomy]], which involves cutting a tendon needed for cats to extend their claws.<ref name=Swiderski>{{cite journal |author=Swiderski J |title=Onychectomy and its alternatives in the feline patient |journal=Clin Tech Small Anim Pract |volume=17 |issue=4 |pages=158–61 |year=2002 |month=November |pmid=12587280 |doi=10.1053/svms.2002.36604 |first1=J |issn=1096-2867}}</ref> Declawing is a major surgical procedure and can produce pain, infections and permanent lameness.<ref name=Swiderski/> |
|||
* [[Animal testing on cats]] |
|||
* [[Cancer in cats]] |
|||
Since this surgery is almost always performed for the benefit of owners, it is controversial and remains uncommon outside of North America.<ref name=AMAwelfare>[http://www.avma.org/reference/backgrounders/declawing_bgnd.pdf Welfare Implications of Declawing of Domestic Cats] ''American Veterinary Medical Association'' 09 April 2009</ref> In many countries, declawing is prohibited by [[animal welfare]] laws and it is ethically controversial within the veterinary community.<ref name="autogenerated1">{{cite journal |author=Patronek GJ |title=Assessment of claims of short- and long-term complications associated with onychectomy in cats |journal=J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. |volume=219 |issue=7 |pages=932–7 |year=2001 |pmid=11601788 |doi=10.2460/javma.2001.219.932 |month=October |first1=GJ |issn=0003-1488 |url=http://symptomresearch.nih.gov/chapter_1/index.htm |format=Free full text}}</ref> While both the [[Humane Society of the United States]] and the [[American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals]] strongly discourage or condemn the procedure,<ref>[http://www.pawproject.com/html/acknow.asp Paw Project Acknowledgements]</ref> the [[American Veterinary Medical Association]] supports the procedure under certain guidelines and finds "no scientific evidence that declawing leads to behavioral abnormalities when the behavior of declawed cats is compared with that of cats in control groups."<ref name=AVMA>{{cite web|url=http://www.avma.org/issues/policy/animal_welfare/declawing.asp|title=Declawing of Domestic Cats|work=American Veterinary Medical Association|accessdate=2010-07-30}}</ref> They further argue that many cats would be given up and euthanized were declawing not performed.<ref name=AMAwelfare/> |
|||
* [[Cat bite]] |
|||
* [[Cat café]] |
|||
===Waste=== |
|||
* [[Cat collar]] |
|||
[[File:Toilet Trained Cat 22 Aug 2005.jpg|thumb|upright|Toilet-trained house cat.]] |
|||
* [[Cat fancy]] |
|||
Cats bury their urine and feces. Indoor cats are usually provided with a [[litter box]] containing [[cat litter|litter]], typically [[bentonite]], but sometimes other absorbent material such as shredded paper or wood chips, or sometimes [[sand]] or similar material. It should be cleaned daily and changed often, depending on the number of cats in a household and the type of litter; if it is not kept clean, a cat may be fastidious enough to find other locations in the house for urination or defecation. This may also happen for other reasons; for instance, if a cat becomes [[constipation|constipated]] and defecation is uncomfortable, it may associate the discomfort with the litter box and avoid it in favor of another location. |
|||
Daily attention to the litter box also serves as a monitor of the cat's health. Bentonite or clumping litter is a variation which absorbs urine into clumps which can be sifted out along with feces, and thus stays cleaner longer with regular sifting, but has sometimes been reported to cause health problems in some cats.<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=8888544 |year=1996 |last1=Hornfeldt |first1=CS |last2=Westfall |title=Suspected bentonite toxicosis in a cat from ingestion of clay cat litter. |volume=38 |issue=5 |pages=365–6 |journal=Veterinary and human toxicology |author2=Westfall}}</ref> Those with toxoplasmosis-infected cats living in habitat areas of [[sea otter]]s<ref name=mag72>{{cite news|url=http://www.magazine.noaa.gov/stories/mag72.htm|title=Parasite in cats killing sea otters|publisher=[[National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration]]|date=2003-01-21|work=NOAA magazine|accessdate=2007-11-24}}</ref> may wish to dispose of droppings in the trash, rather than flushing them down the toilet.<ref>{{cite web|first=Darcy |last=Brown-Martin |url=http://www.viamagazine.com/top_stories/articles/seaotter_savior07.asp |title=Monterey Bay’s sea otter sleuth |publisher=Viamagazine.com |month=March | year=2007 |accessdate=2008-11-22}}</ref> Some cats can be trained to use the human toilet, eliminating the litter box and its attendant expense, unpleasant odor, and the need to use landfill space for disposal. Training may involve four to six weeks of incremental moves, such as moving and elevating the litter box until it is near the toilet, as well as employing an adapter such as a bowl or small box to suspend the litter above the toilet bowl.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.toilettrainedcat.com/toilet-train-cat.php |title=A Step-By-Step Guide on How To Train Your Cat to Use the Human Toilet |publisher=The Toilet Trained Cat |date= |accessdate=2009-02-15}}</ref> When training is complete, the cat uses the toilet by squatting on the toilet seat over the bowl. |
|||
==Feral cats== |
|||
{{Main|Feral cat}} |
|||
[[File:Feral cat Virginia crop.jpg|thumb|upright|American feral [[farm cat]].]] |
|||
[[Feral cat]]s are wild cats that are unfamiliar with humans and roam freely in urban or rural areas.<ref name=Rochlitz>{{cite book |author=Irene Rochlitz |title=The Welfare of Cats (Animal Welfare) |publisher=Springer |location=Berlin |year=2007 |pages=141–175 |isbn=1-4020-6143-9}}</ref> The numbers of feral cats are not known, but estimates of the US feral population range from 25 to 60 million.<ref name=Rochlitz/> Feral cats may live alone, but most are found in large groups called [[feral cat colony|feral colonies]], which occupy a specific territory and are usually associated with a source of food.<ref name=hsus-feral>[http://www.hsus.org/pets/issues_affecting_our_pets/feral_cats/feral_cats_frequently_asked_questions.html#1_What_is_a_feral_cat What is the difference between a stray cat and a feral cat?] Humane Society of the United States</ref> Famous feral cat colonies are found in [[Rome]] around the [[Colosseum]] and [[Forum Romanum]], with cats at some of these sites being fed and vetted by volunteers.<ref>[http://www.romancats.com/index_eng.php Torre Argentina cat shelter]. Retrieved 17 June 2009.</ref> |
|||
Public attitudes towards feral cats vary widely: ranging from seeing them as free-ranging pets, to regarding them as vermin.<ref>{{Cite book |
|||
| publisher = Humane Society Press |
|||
| isbn = 0965894274 |
|||
| last = Rowan |
|||
| first = Andrew N. |
|||
| coauthors = Deborah J. Salem |
|||
| title = The State of the Animals II: 2003 |
|||
| date = 2003-11 |
|||
| chapter = 4 |
|||
| url = http://www.hsus.org/web-files/PDF/hsp/SOA_3-2005_Chap4.pdf |
|||
|format=PDF}}</ref> One common approach to reducing the feral cat population is termed ''trap-neuter-return'', where the cats are trapped, [[neutering|neutered]], [[immunization|immunized]] against rabies and the [[feline leukemia virus]], and then released. Before releasing them back into their feral colonies, the attending veterinarian often nips the tip off one ear to mark the feral as neutered and inoculated, since these cats may be trapped again.<ref name=hsus-feral/> Volunteers continue to feed and give care to these cats throughout their lives, and not only is their lifespan greatly increased, but behavior and nuisance problems caused by competition for food are also greatly reduced.<ref name=hsus-feral/> |
|||
==History and mythology== |
|||
{{Main|Cultural depictions of cats|Cats in ancient Egypt}} |
|||
[[File:Egypte louvre 058.jpg|thumb|upright|Egyptian sculpture at the [[Louvre]].]] |
|||
Traditionally, historians tended to think that [[ancient Egypt]] was the site of cat domestication, owing to the clear depictions of house cats in Egyptian paintings about 3,600 years old.<ref name=Driscoll/> However, in 2004, a Neolithic grave was excavated in [[Shillourokambos]], Cyprus, that contained the skeletons, laid close to one another, of both a human and a cat. The grave is estimated to be 9,500 years old, pushing back the earliest known feline-human association significantly.<ref name="9500 years"/><ref>{{cite news |first=Hazel |last=Muir |
|||
|authorlink= |title=Ancient remains could be oldest pet cat |url=http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn4867.html |work= |publisher=[[New Scientist]] |date=2004-04-08 |accessdate=2007-11-23 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first=Marsha|last=Walton |authorlink= |title=Ancient burial looks like human and pet cat |url=http://edition.cnn.com/2004/TECH/science/04/08/cats.cyprus/index.html |work= |publisher=CNN|date= April 9, 2004|accessdate=2007-11-23 }}</ref> The cat specimen is large and closely resembles the [[African wildcat]] (''Felis silvestris lybica''), rather than present-day domestic cats. This discovery, combined with genetic studies, suggest that cats were probably domesticated in the Near East, in the [[Fertile Crescent]] around the time of the development of [[agriculture]] and then they were brought to Cyprus and Egypt.<ref name=Driscoll>{{cite journal |author=Driscoll CA, Menotti-Raymond M, Roca AL |title=The Near Eastern origin of cat domestication |journal=Science |volume=317 |issue=5837 |pages=519–23 |year=2007 |month=July |pmid=17600185 |doi=10.1126/science.1139518 |first1=CA |first2=M |first3=AL |first4=K |first5=WE |first6=E |first7=EH |first8=M |first9=D |first11=N |last12=O'brien |first12=SJ |last13=Macdonald |first13=DW |issn=0036-8075}}</ref> |
|||
In [[ancient Egypt]] cats were [[animal worship|sacred animal]]s, with [[Bast (goddess)|Bast]] often depicted in cat form, sometimes taking on the warlike aspect of a lioness.<ref>{{Harv|Mason|1984|p=220}}</ref> The [[Ancient Rome|Romans]] are often credited with introducing the domestic cat from Egypt to [[Europe]];<ref name=Mason223>{{Harv|Mason|1984|p=223}}</ref> in [[Gallia Aquitania|Roman Aquitaine]], a first or second century epitaph of a young girl holding a cat is one of two earliest depictions of the Roman domesticated cat.<ref>Paul Veyne, "The Household and its Freed Slaves", in Philippe Ariès and Georges Duby, eds, ''A History of Private Life !; FromPagan Rome to Byzantium'' 198781 and illustration (Bordeaux, Aquitaine Museum)</ref> However, it is possible that cats were already kept in Europe prior to the [[Roman Empire]], as they may have already been present in Britain in the late [[Iron Age]].<ref name=OConnor/> Domestic cats were spread throughout much of the rest of the world during the [[Age of Discovery]], as they were carried on [[sailing ship]]s to control shipboard rodents and as good-luck charms.<ref name=Mason223/> |
|||
[[File:Freya by Johannes Gehrts.jpg|thumb|left|upright|[[Freyja]] and her cats.]] |
|||
Several ancient religions believed that cats are exalted souls, companions or guides for humans, that they are all-knowing but are mute so they cannot influence decisions made by humans. In Japan, the [[Maneki Neko]] is a cat that is a symbol of good fortune. Although there are no sacred species in Islam, some writers have stated that [[Muhammad]] had a favorite cat, [[Muezza]].<ref>{{cite book | author = Geyer, Georgie Anne | year = 2004 | title = When Cats Reigned Like Kings: On the Trail of the Sacred Cats | isbn = 0740746979 | publisher = Andrews McMeel Pub. | location = Kansis City}}</ref> He is reported to have loved cats so much that "he would do without his cloak rather than disturb one that was sleeping on it".<ref name="Reeves">{{cite book | author = Minou Reeves | title = Muhammad in Europe | publisher = New York University (NYU) Press | page = 52 | isbn = 0814775330 | year = 2000}}</ref> |
|||
[[Freyja]]—the goddess of love, beauty, and fertility in [[Norse mythology]]—is depicted as riding a chariot drawn by cats. |
|||
Many cultures have negative [[superstition]]s about cats. An example would be the belief that a [[black cat]] "crossing your path" leads to bad [[luck]], or that cats are witches' [[familiar spirit|familiar]]s used to augment a witch's powers and skills. This led to the widespread extermination of cats in [[Europe]] in [[medieval]] times. The [[Black Plague]] was spread by [[flea]]s carried by infected rats, and the killing of cats ostensibly caused an increase in the rat population. The killing of cats in Medieval [[Ypres]] is commemorated in the innocuous present-day [[Kattenstoet]] (cat parade). |
|||
According to a myth in many cultures, cats have multiple lives. In many countries, they are believed to have nine lives, but in some Spanish-speaking regions they are said to have seven lives,<ref>{{cite news| url = http://elcomercio.pe/impresa/notas/vidas-gato/20100307/423959 | date=2010-03-07 | accessdate=2010-03-19 | author= Nora Sugobono | language= Spanish | title= Las vidas del gato | publisher= El Comercio }}</ref> while in Turkish and Arabic traditions the number of lives is six.<ref>{{cite news| publisher=The Guardian | url= http://www.guardian.co.uk/lifeandstyle/gallery/2010/mar/18/guide-to-pets-pet-myths?picture=360591960 | accessdate=2010-03-18 | author= Tim Dowling | title= Tall tails: Pet myths busted | location=London}}</ref> The myth is attributed to the natural suppleness and swiftness cats exhibit to escape life-threatening situations.<ref name=myth>{{cite web|url=http://www.best-cat-art.com/cat-myths.html |title=Cat Myths, Misinformation and Untruths |publisher=Best-cat-art.com |date= |accessdate=2008-11-22}}</ref> Also lending credence to this myth is that [[cat righting reflex|falling cats]] often land on their feet because of an inbuilt automatic twisting reaction and are able to twist their bodies around to land feet first, though they can still be injured or killed by a high fall.<ref>[http://cats.about.com/od/catsafety/a/highrisefalls.htm The ASPCA Warns About High-Rise Falls by Cats.] About.com</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{Portal|Cats}} |
|||
{{Wikipedia-Books}} |
|||
{{Colbegin}} |
|||
* [[Cat Fanciers' Association]] |
|||
* [[Cat flap]] |
|||
* [[Cat intelligence]] |
|||
* [[Cat lady]] |
* [[Cat lady]] |
||
* [[Cat food]] |
|||
* [[Cat meat]] |
* [[Cat meat]] |
||
* [[Cat |
* [[Cat repeller]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Cats and the Internet]] |
||
* [[Cats in Australia]] |
|||
* [[Kattenstoet]] (cat Parade in [[Ypres]], [[Belgium]]) |
|||
* [[ |
* [[Cats in New Zealand]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Cats in the United States]] |
||
* [[Cat–dog relationship]] |
|||
* [[List of most popular cat names]] |
|||
* [[ |
* [[Dog]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Dried cat]] |
||
* [[Feral cats in Istanbul]] |
|||
{{Colend}} |
|||
* [[List of cat breeds]] |
|||
* [[List of cat documentaries, television series and cartoons]] |
|||
==References==<!-- ZoolSci22:627. --> |
|||
* [[List of individual cats]] |
|||
{{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} |
|||
* [[List of fictional felines]] |
|||
* [[List of feline diseases]] |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
* [[Neko-dera]] |
|||
*{{cite book |last=Case |first=Linda P. |title=The cat: its behavior, nutrition, & health |publisher=Iowa State Press |location=Ames, Iowa |year=2003 |isbn=0-8138-0331-4|ref=harv }} |
|||
* [[Perlorian]] |
|||
*{{Cite book| edition = 2nd| publisher = National Academy Press| isbn = 0309074835| last = Committee on Animal Nutrition | title = Nutrient Requirements of Cats | year =1986 |url=http://www.nap.edu/catalog.php?record_id=910#toc| isbn-status = May be invalid - please double check|ref=harv }} |
|||
* [[Pet door]] |
|||
*{{Cite book | publisher = Charles C Thomas Pub Ltd | isbn = 0398041695 | last =Fogle | title = Interrelations Between People and Pets | year =1981 | author = edited by Bruce Fogle ; with a foreword by Andrew Edney.|ref=harv }} |
|||
* [[Pet first aid]] |
|||
*{{cite book |last=Jensen |first=Per |title=The Ethology of Domestic Animals (Modular Text) |publisher=CABI |location=Wallingford |year=2009 |isbn=1-84593-536-5|ref=harv }} |
|||
* [[Popular cat names]] |
|||
*{{Cite book| edition = 1| publisher = Merck| isbn = 0911910999 |last1= Kahn |first1=Cynthia M. |last2=Line |first2=Scott | title = The Merck/Merial Manual for Pet Health | year =2007| author = Joseph Lee Hollander, editor.|ref=harv }} |
|||
{{div col end}} |
|||
*{{Cite book| publisher = Prentice Hall Press| isbn = 0582460468| last = Mason| first = I.L.| title = Evolution of Domesticated Animals| year = 1984|ref=harv }} |
|||
*{{Cite book| edition = 1| publisher = Springer| isbn = 1402061439| last = Rochlitz| first = Irene| title = The Welfare of Cats| year = 2007|ref=harv }} |
|||
*{{Cite book| publisher = [[University of Chicago Press]]| isbn = 0226779998| last1=Sunquist| first1=Melvin E | last2 =Sunquist|first2=Fiona| title = Wild cats of the world| year =2002| author = Mel Sunquist and Fiona Sunquist ; with photographs by Terry Whittaker and others.|ref=harv }} |
|||
*{{cite book |last1=Turner |first1=D.C. | last2= Bateson |first2=P. |title=The Domestic Cat: The Biology of its Behaviour | publisher = Cambridge University Press |year=2000 | edition = 2 |isbn = 0521636485 |author=edited by Dennis C. Turner, Patrick Bateson.|ref=harv }} |
|||
*{{Cite book| edition = 4th Revised| publisher = Thomson Learning| isbn = 0030579147| last =Walker| first =Warren F.| title = Study of the Cat with Reference to Human Beings| year =1982|ref=harv }} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{Spoken Wikipedia-3|2007-05-13|En-Cat_(part_1).ogg|En-Cat_(part_2).ogg|En-Cat_(part_3).ogg|}} |
|||
{{Wiktionary|cat|kitty|meow}} |
|||
{{Wikiquote}} |
|||
{{Commons|Felis silvestris catus|Cat}} |
|||
{{Wikispecies|Felis sylvestris catus|Cat}} |
|||
{{Wikibooks|Animal Care}} |
|||
<!-- Please add the links and sources in alphabetical order. This is an encyclopedia. --> |
|||
;Anatomy |
|||
* [http://brainmaps.org/index.php?p=speciesdata&species=felis-catus High-Resolution Images of the Cat Brain] |
|||
== Notes == |
|||
;Articles |
|||
{{notelist}} |
|||
* [http://home.ncifcrf.gov/ccr/lgd/mammal%20pdfs/MS600_O%27Brien_SciAm.pdf The evolution of cats. Genomic paw prints in the DNA of the world's wild cats have clarified the cat family tree and uncovered several remarkable migrations in their past.] ''Scientific American'' |
|||
* [http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/name/Felis_catus Biodiversity Heritage Library bibliography] for ''Felis catus'' |
|||
* [http://www.catpert.com/ Catpert. The Cat Expert] - Cat articles |
|||
* [http://en.citizendium.org/wiki/Choosing_a_cat Choosing a cat] - article at ''[[Citizendium]]'' |
|||
* [[John Moisant|John Moisant's]] [http://www.flickr.com/photos/amphalon/2144454358/ famous cat Mademoiselle Paree dressed in funeral attire for his funeral after his death in a plane crash] |
|||
== References == |
|||
;Veterinary related |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
* [http://home.ncifcrf.gov/ccr/lgd/comparative_genome/catgenome/index_n.asp Cat Genome Project] at the US [http://www.cancer.gov/ The National Cancer Institute] |
|||
== External links == |
|||
<!-- {{Carnivora|Fe.}} --> |
|||
{{Spoken Wikipedia|date=13 May 2007|En-Cat_(part_1).ogg|En-Cat_(part_2).ogg|En-Cat_(part_3).ogg}} |
|||
* {{Wiktionary-inline|cat}} |
|||
* {{Wikispecies-inline|Felis catus|''Felis catus''}} |
|||
* {{Commons-inline}} |
|||
* {{Wikibooks inline|Animal Care}} |
|||
* {{Wikiquote-inline}} |
|||
* {{Cite Americana|wstitle=Cat, Domestic, The |short=x}} |
|||
* [https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/name/Felis_catus Biodiversity Heritage Library bibliography] for ''Felis catus'' |
|||
* View the [http://www.ensembl.org/Felis_catus/Info/Index/ cat genome] in [[Ensembl]] |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20190520030950/http://brainmaps.org/index.php?p=speciesdata&species=felis-catus High-resolution images of the cat's brain] |
|||
* ''[[Scientific American]]''. "[https://books.google.com/books?id=YIE9AQAAIAAJ&q=carbonic+oxide The Origin of the Cat]". 1881. p. 120. |
|||
{{Cat nav|state=uncollapsed}} |
|||
[[Category:Cats|Cats]] |
|||
{{Carnivora|Fe.}} |
|||
[[Category:Felines]] |
|||
{{Taxonbar|from=Q20980826}} |
|||
[[Category:Invasive animal species]] |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Cosmopolitan species]] |
|||
[[Category:Sequenced genomes]] |
|||
[[Category:Cats| ]] |
|||
{{Link GA|fr}} |
|||
[[Category:English words]] |
|||
{{Link GA|lt}} |
|||
[[Category:Mammals described in 1758]] |
|||
{{Link GA|lv}} |
|||
[[Category:Animal models]] |
|||
{{Link FA|ca}} |
|||
[[Category:Articles containing video clips]] |
|||
{{Link FA|el}} |
|||
[[Category:Felis]] |
|||
{{Link FA|eo}} |
|||
[[Category:Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus]] |
|||
{{Link FA|es}} |
|||
[[Category:Cosmopolitan mammals]] |
|||
{{Link FA|hu}} |
|||
{{Link FA|id}} |
|||
{{Link FA|ml}} |
|||
{{Link FA|pt}} |
|||
{{Link FA|sk}} |
|||
{{Link FA|sr}} |
|||
[[ace:Mië]] |
|||
[[af:Kat]] |
|||
[[als:Hauskatze]] |
|||
[[ang:Catte]] |
|||
[[ar:قط]] |
|||
[[an:Felis catus]] |
|||
[[frp:Chat]] |
|||
[[ast:Gatu]] |
|||
[[gn:Mbarakaja]] |
|||
[[ay:Phisi]] |
|||
[[az:Pişik]] |
|||
[[bm:Jakuma]] |
|||
[[bn:বিড়াল]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Niau]] |
|||
[[ba:Бесәй]] |
|||
[[be:Кот свойскі]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Кот]] |
|||
[[bar:Katz]] |
|||
[[bo:ཞི་མི།]] |
|||
[[bs:Mačka]] |
|||
[[br:Kazh]] |
|||
[[bg:Котка]] |
|||
[[ca:Gat]] |
|||
[[cv:Кушак]] |
|||
[[ceb:Iring]] |
|||
[[cs:Kočka domácí]] |
|||
[[sn:Kato]] |
|||
[[co:Ghjattu]] |
|||
[[cy:Cath]] |
|||
[[da:Kat]] |
|||
[[de:Hauskatze]] |
|||
[[nv:Mósí]] |
|||
[[et:Kass]] |
|||
[[el:Γάτα]] |
|||
[[eml:Gàt]] |
|||
[[myv:Катка]] |
|||
[[es:Felis silvestris catus]] |
|||
[[eo:Hejma kato]] |
|||
[[ext:Felis silvestris catus]] |
|||
[[eu:Katu]] |
|||
[[fa:گربه]] |
|||
[[fr:Chat]] |
|||
[[fy:Kat]] |
|||
[[fur:Gjat]] |
|||
[[ga:Cat]] |
|||
[[gd:Cat]] |
|||
[[gl:Gato]] |
|||
[[gan:貓]] |
|||
[[hak:Meu-é]] |
|||
[[xal:Мис]] |
|||
[[ko:고양이]] |
|||
[[haw:Pōpoki]] |
|||
[[hi:बिल्ली]] |
|||
[[hr:Domaća mačka]] |
|||
[[io:Kato]] |
|||
[[id:Kucing]] |
|||
[[ia:Catto]] |
|||
[[os:Гæды]] |
|||
[[zu:Ikati]] |
|||
[[is:Köttur]] |
|||
[[it:Felis silvestris catus]] |
|||
[[he:חתול הבית]] |
|||
[[jv:Kucing]] |
|||
[[kn:ಬೆಕ್ಕು]] |
|||
[[pam:Pusa]] |
|||
[[ka:შინაური კატა]] |
|||
[[csb:Kòt]] |
|||
[[sw:Paka-kaya]] |
|||
[[kv:Кань]] |
|||
[[ht:Chat]] |
|||
[[ku:Pisîk]] |
|||
[[la:Feles]] |
|||
[[lv:Kaķis]] |
|||
[[lb:Hauskaz]] |
|||
[[lt:Katė]] |
|||
[[ln:Nkɔ́ndɔkɔ́]] |
|||
[[jbo:mlatu]] |
|||
[[lmo:Gàt]] |
|||
[[hu:Macska]] |
|||
[[mk:Мачка]] |
|||
[[mg:Saka]] |
|||
[[ml:പൂച്ച]] |
|||
[[mt:Qattus]] |
|||
[[mr:मांजर]] |
|||
[[arz:قطه]] |
|||
[[mzn:بامشی]] |
|||
[[ms:Kucing]] |
|||
[[cdo:Mà]] |
|||
[[mn:Муур]] |
|||
[[nl:Kat (dier)]] |
|||
[[nds-nl:Kat]] |
|||
[[ne:बिरालो]] |
|||
[[ja:ネコ]] |
|||
[[no:Tamkatt]] |
|||
[[nn:Katt]] |
|||
[[nrm:Cat]] |
|||
[[oc:Felis silvestris catus]] |
|||
[[uz:Mushuk]] |
|||
[[pnb:بلی]] |
|||
[[km:ឆ្មា]] |
|||
[[pcd:Cot]] |
|||
[[nds:Katt]] |
|||
[[pl:Kot domowy]] |
|||
[[pt:Gato]] |
|||
[[ro:Pisică de casă]] |
|||
[[qu:Michi]] |
|||
[[ru:Кошка]] |
|||
[[sah:Куоска]] |
|||
[[se:Bussá]] |
|||
[[sco:Cat]] |
|||
[[stq:Kat]] |
|||
[[st:Katse]] |
|||
[[sq:Macja]] |
|||
[[scn:Jattu]] |
|||
[[si:බළලා]] |
|||
[[simple:Cat]] |
|||
[[sd:ٻلي]] |
|||
[[ss:Likati]] |
|||
[[sk:Mačka domáca]] |
|||
[[cu:Ко́тъ]] |
|||
[[sl:Domača mačka]] |
|||
[[szl:Kot]] |
|||
[[srn:Puspusi]] |
|||
[[sr:Мачка]] |
|||
[[fi:Kissa]] |
|||
[[sv:Katt]] |
|||
[[tl:Pusa]] |
|||
[[ta:பூனை]] |
|||
[[tt:Мәче]] |
|||
[[te:పిల్లి]] |
|||
[[th:แมว]] |
|||
[[to:Pusi]] |
|||
[[chr:ᏪᏌ]] |
|||
[[chy:Poeso]] |
|||
[[tr:Kedi]] |
|||
[[bug:Meong]] |
|||
[[uk:Кіт свійський]] |
|||
[[ur:بلی]] |
|||
[[ug:مۈشۈك]] |
|||
[[vec:Gato]] |
|||
[[vi:Mèo]] |
|||
[[fiu-vro:Kass]] |
|||
[[wa:Tchet]] |
|||
[[zh-classical:貓]] |
|||
[[war:Misay]] |
|||
[[wo:Muus]] |
|||
[[yi:קאץ]] |
|||
[[yo:Ológbò]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:貓]] |
|||
[[bat-smg:Katie]] |
|||
[[zh:猫]] |
|||
Revision as of 12:42, 25 December 2024
| Cat Temporal range:
Holocene to present (9,500 years ago) | |
|---|---|
Various types of cats | |
Domesticated
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Felinae |
| Genus: | Felis |
| Species: | F. catus[1]
|
| Binomial name | |
| Felis catus[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
The cat (Felis catus), also referred to as the domestic cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a pet and farm cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin. Its retractable claws are adapted to killing small prey species such as mice and rats. It has a strong, flexible body, quick reflexes, and sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat communication includes vocalizations—including meowing, purring, trilling, hissing, growling, and grunting—as well as body language. It can hear sounds too faint or too high in frequency for human ears, such as those made by small mammals. It secretes and perceives pheromones.
Female domestic cats can have kittens from spring to late autumn in temperate zones and throughout the year in equatorial regions, with litter sizes often ranging from two to five kittens. Domestic cats are bred and shown at events as registered pedigreed cats, a hobby known as cat fancy. Animal population control of cats may be achieved by spaying and neutering, but their proliferation and the abandonment of pets has resulted in large numbers of feral cats worldwide, contributing to the extinction of bird, mammal, and reptile species.
As of 2017,[update] the domestic cat was the second most popular pet in the United States, with 95.6 million cats owned and around 42 million households owning at least one cat. In the United Kingdom, 26% of adults have a cat, with an estimated population of 10.9 million pet cats as of 2020.[update] As of 2021,[update] there were an estimated 220 million owned and 480 million stray cats in the world.
Etymology and naming
The origin of the English word cat, Old English catt, is thought to be the Late Latin word cattus, which was first used at the beginning of the 6th century.[4] The Late Latin word may be derived from an unidentified African language.[5] The Nubian word kaddîska 'wildcat' and Nobiin kadīs are possible sources or cognates.[6]
The forms might also have derived from an ancient Germanic word that was absorbed into Latin and then into Greek, Syriac, and Arabic.[7] The word may be derived from Germanic and Northern European languages, and ultimately be borrowed from Uralic, cf. Northern Sámi gáđfi, 'female stoat', and Hungarian hölgy, 'lady, female stoat'; from Proto-Uralic *käďwä, 'female (of a furred animal)'.[8]
The English puss, extended as pussy and pussycat, is attested from the 16th century and may have been introduced from Dutch poes or from Low German puuskatte, related to Swedish kattepus, or Norwegian pus, pusekatt. Similar forms exist in Lithuanian puižė and Irish puisín or puiscín. The etymology of this word is unknown, but it may have arisen from a sound used to attract a cat.[9][10]
A male cat is called a tom or tomcat[11] (or a gib,[12] if neutered). A female is called a queen[13][14] (or sometimes a molly,[15] if spayed). A juvenile cat is referred to as a kitten. In Early Modern English, the word kitten was interchangeable with the now-obsolete word catling.[16] A group of cats can be referred to as a clowder, a glaring,[17] or a colony.[18]
Taxonomy
The scientific name Felis catus was proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for a domestic cat.[1][2] Felis catus domesticus was proposed by Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben in 1777.[3] Felis daemon proposed by Konstantin Satunin in 1904 was a black cat from the Transcaucasus, later identified as a domestic cat.[19][20]
In 2003, the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature ruled that the domestic cat is a distinct species, namely Felis catus.[21][22] In 2007, the modern domesticated subspecies F. silvestris catus sampled worldwide was considered to have probably descended from the African wildcat (F. lybica), following results of phylogenetic research.[23][24][a] In 2017, the IUCN Cat Classification Taskforce followed the recommendation of the ICZN in regarding the domestic cat as a distinct species, Felis catus.[25]
Evolution

The domestic cat is a member of the Felidae, a family that had a common ancestor about 10 to 15 million years ago.[26] The evolutionary radiation of the Felidae began in Asia during the Miocene around 8.38 to 14.45 million years ago.[27] Analysis of mitochondrial DNA of all Felidae species indicates a radiation at 6.46 to 16.76 million years ago.[28] The genus Felis genetically diverged from other Felidae around 6 to 7 million years ago.[27] Results of phylogenetic research shows that the wild members of this genus evolved through sympatric or parapatric speciation, whereas the domestic cat evolved through artificial selection.[29] The domestic cat and its closest wild ancestor are diploid and both possess 38 chromosomes[30] and roughly 20,000 genes.[31]
| nuclear DNA:[27][28] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| mitochondrial DNA:[32] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Domestication

It was long thought that the domestication of the cat began in ancient Egypt, where cats were venerated from around 3100 BC.[33][34] However, the earliest known indication for the taming of an African wildcat was excavated close by a human Neolithic grave in Shillourokambos, southern Cyprus, dating to about 7500–7200 BC. Since there is no evidence of native mammalian fauna on Cyprus, the inhabitants of this Neolithic village most likely brought the cat and other wild mammals to the island from the Middle Eastern mainland.[35] Scientists therefore assume that African wildcats were attracted to early human settlements in the Fertile Crescent by rodents, in particular the house mouse (Mus musculus), and were tamed by Neolithic farmers. This mutual relationship between early farmers and tamed cats lasted thousands of years. As agricultural practices spread, so did tame and domesticated cats.[32][36] Wildcats of Egypt contributed to the maternal gene pool of the domestic cat at a later time.[37]
The earliest known evidence for the occurrence of the domestic cat in Greece dates to around 1200 BC. Greek, Phoenician, Carthaginian and Etruscan traders introduced domestic cats to southern Europe.[38] By the 5th century BC, they were familiar animals around settlements in Magna Graecia and Etruria.[39] During the Roman Empire, they were introduced to Corsica and Sardinia before the beginning of the 1st century AD.[40] By the end of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, the Egyptian domestic cat lineage had arrived in a Baltic Sea port in northern Germany.[37]
The leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) was tamed independently in China around 5500 BC. This line of partially domesticated cats leaves no trace in the domestic cat populations of today.[41]
During domestication, cats have undergone only minor changes in anatomy and behavior, and they are still capable of surviving in the wild. Several natural behaviors and characteristics of wildcats may have pre-adapted them for domestication as pets. These traits include their small size, social nature, obvious body language, love of play, and high intelligence. Since they practice rigorous grooming habits and have an instinctual drive to bury and hide their urine and feces, they are generally much less messy than other domesticated animals. Captive Leopardus cats may also display affectionate behavior toward humans but were not domesticated.[42] House cats often mate with feral cats.[43] Hybridization between domestic and other Felinae species is also possible, producing hybrids such as the Kellas cat in Scotland.[44][45]
Development of cat breeds started in the mid 19th century.[46] An analysis of the domestic cat genome revealed that the ancestral wildcat genome was significantly altered in the process of domestication, as specific mutations were selected to develop cat breeds.[47] Most breeds are founded on random-bred domestic cats. Genetic diversity of these breeds varies between regions, and is lowest in purebred populations, which show more than 20 deleterious genetic disorders.[48]
Characteristics
Size

The domestic cat has a smaller skull and shorter bones than the European wildcat.[49] It averages about 46 cm (18 in) in head-to-body length and 23–25 cm (9.1–9.8 in) in height, with about 30 cm (12 in) long tails. Males are larger than females.[50] Adult domestic cats typically weigh 4–5 kg (8.8–11.0 lb).[29]
Skeleton
Cats have seven cervical vertebrae (as do most mammals); 13 thoracic vertebrae (humans have 12); seven lumbar vertebrae (humans have five); three sacral vertebrae (as do most mammals, but humans have five); and a variable number of caudal vertebrae in the tail (humans have only three to five vestigial caudal vertebrae, fused into an internal coccyx).[51]: 11 The extra lumbar and thoracic vertebrae account for the cat's spinal mobility and flexibility. Attached to the spine are 13 ribs, the shoulder, and the pelvis.[51]: 16 Unlike human arms, cat forelimbs are attached to the shoulder by free-floating clavicle bones which allow them to pass their body through any space into which they can fit their head.[52]
Skull


The cat skull is unusual among mammals in having very large eye sockets and a powerful specialized jaw.[53]: 35 Within the jaw, cats have teeth adapted for killing prey and tearing meat. When it overpowers its prey, a cat delivers a lethal neck bite with its two long canine teeth, inserting them between two of the prey's vertebrae and severing its spinal cord, causing irreversible paralysis and death.[54] Compared to other felines, domestic cats have narrowly spaced canine teeth relative to the size of their jaw, which is an adaptation to their preferred prey of small rodents, which have small vertebrae.[54]
The premolar and first molar together compose the carnassial pair on each side of the mouth, which efficiently shears meat into small pieces, like a pair of scissors. These are vital in feeding, since cats' small molars cannot chew food effectively, and cats are largely incapable of mastication.[53]: 37 Cats tend to have better teeth than most humans, with decay generally less likely because of a thicker protective layer of enamel, a less damaging saliva, less retention of food particles between teeth, and a diet mostly devoid of sugar. Nonetheless, they are subject to occasional tooth loss and infection.[55]
Claws

Cats have protractible and retractable claws.[56] In their normal, relaxed position, the claws are sheathed with the skin and fur around the paw's toe pads. This keeps the claws sharp by preventing wear from contact with the ground and allows for the silent stalking of prey. The claws on the forefeet are typically sharper than those on the hindfeet.[57] Cats can voluntarily extend their claws on one or more paws. They may extend their claws in hunting or self-defense, climbing, kneading, or for extra traction on soft surfaces. Cats shed the outside layer of their claw sheaths when scratching rough surfaces.[58]
Most cats have five claws on their front paws and four on their rear paws. The dewclaw is proximal to the other claws. More proximally is a protrusion which appears to be a sixth "finger". This special feature of the front paws on the inside of the wrists has no function in normal walking but is thought to be an antiskidding device used while jumping. Some cat breeds are prone to having extra digits ("polydactyly").[59] Polydactylous cats occur along North America's northeast coast and in Great Britain.[60]
Ambulation
The cat is digitigrade. It walks on the toes, with the bones of the feet making up the lower part of the visible leg.[61] Unlike most mammals, it uses a "pacing" gait and moves both legs on one side of the body before the legs on the other side. It registers directly by placing each hind paw close to the track of the corresponding fore paw, minimizing noise and visible tracks. This also provides sure footing for hind paws when navigating rough terrain. As it speeds up from walking to trotting, its gait changes to a "diagonal" gait: The diagonally opposite hind and fore legs move simultaneously.[62]
Balance
Cats are generally fond of sitting in high places or perching. A higher place may serve as a concealed site from which to hunt; domestic cats strike prey by pouncing from a perch such as a tree branch. Another possible explanation is that height gives the cat a better observation point, allowing it to survey its territory. A cat falling from heights of up to 3 m (9.8 ft) can right itself and land on its paws.[63]
During a fall from a high place, a cat reflexively twists its body and rights itself to land on its feet using its acute sense of balance and flexibility. This reflex is known as the cat righting reflex.[64] A cat always rights itself in the same way during a fall, if it has enough time to do so, which is the case in falls of 90 cm (3.0 ft) or more.[65] How cats are able to right themselves when falling has been investigated as the "falling cat problem".[66]
Coats

The cat family (Felidae) can pass down many colors and patterns to their offspring. The domestic cat genes MC1R and ASIP allow color variety in their coats. The feline ASIP gene consists of three coding exons.[67] Three novel microsatellite markers linked to ASIP were isolated from a domestic cat BAC clone containing this gene to perform linkage analysis on 89 domestic cats segregated for melanism. The domestic cat family demonstrated a cosegregation between the ASIP allele and coat black coloration.[68]
Senses
Vision


Cats have excellent night vision and can see at one sixth the light level required for human vision.[53]: 43 This is partly the result of cat eyes having a tapetum lucidum, which reflects any light that passes through the retina back into the eye, thereby increasing the eye's sensitivity to dim light.[69] Large pupils are an adaptation to dim light. The domestic cat has slit pupils, which allow it to focus bright light without chromatic aberration.[70] At low light, a cat's pupils expand to cover most of the exposed surface of its eyes.[71] The domestic cat has rather poor color vision and only two types of cone cells, optimized for sensitivity to blue and yellowish green; its ability to distinguish between red and green is limited.[72] A response to middle wavelengths from a system other than the rod cells might be due to a third type of cone. This appears to be an adaptation to low light levels rather than representing true trichromatic vision.[73] Cats also have a nictitating membrane, allowing them to blink without hindering their vision.
Hearing
The domestic cat's hearing is most acute in the range of 500 Hz to 32 kHz.[74] It can detect an extremely broad range of frequencies ranging from 55 Hz to 79 kHz, whereas humans can only detect frequencies between 20 Hz and 20 kHz. It can hear a range of 10.5 octaves, while humans and dogs can hear ranges of about 9 octaves.[75][76] Its hearing sensitivity is enhanced by its large movable outer ears, the pinnae, which amplify sounds and help detect the location of a noise. It can detect ultrasound, which enables it to detect ultrasonic calls made by rodent prey.[77][78] Recent research has shown that cats have socio-spatial cognitive abilities to create mental maps of owners' locations based on hearing owners' voices.[79]
Smell
Cats have an acute sense of smell, due in part to their well-developed olfactory bulb and a large surface of olfactory mucosa, about 5.8 cm2 (0.90 in2) in area, which is about twice that of humans.[80] Cats and many other animals have a Jacobson's organ in their mouths that is used in the behavioral process of flehmening. It allows them to sense certain aromas in a way that humans cannot. Cats are sensitive to pheromones such as 3-mercapto-3-methylbutan-1-ol,[81] which they use to communicate through urine spraying and marking with scent glands.[82] Many cats also respond strongly to plants that contain nepetalactone, especially catnip, as they can detect that substance at less than one part per billion.[83] About 70–80% of cats are affected by nepetalactone.[84] This response is also produced by other plants, such as silver vine (Actinidia polygama) and the herb valerian; it may be caused by the smell of these plants mimicking a pheromone and stimulating cats' social or sexual behaviors.[85]
Taste
Cats have relatively few taste buds compared to humans (470 or so, compared to more than 9,000 on the human tongue).[86] Domestic and wild cats share a taste receptor gene mutation that keeps their sweet taste buds from binding to sugary molecules, leaving them with no ability to taste sweetness.[87] They, however, possess taste bud receptors specialized for acids, amino acids such as protein, and bitter tastes.[88]
Their taste buds possess the receptors needed to detect umami. However, these receptors contain molecular changes that make cat taste umami different from that of humans. In humans, they detect the amino acids glutamic acid and aspartic acid, but in cats, they instead detect inosine monophosphate and l-Histidine.[89] These molecules are particularly enriched in tuna.[89] This, it has been argued, is why cats find tuna so palatable: as put by researchers into cat taste, "the specific combination of the high IMP and free l-Histidine contents of tuna, which produces a strong umami taste synergy that is highly preferred by cats."[89] One of the researchers in this research has stated, "I think umami is as important for cats as sweet is for humans."[90]
Cats also have a distinct temperature preference for their food, preferring food with a temperature around 38 °C (100 °F) which is similar to that of a fresh kill; some cats reject cold food (which would signal to the cat that the "prey" item is long dead and therefore possibly toxic or decomposing).[86]
Whiskers

To aid with navigation and sensation, cats have dozens of movable whiskers (vibrissae) over their body, especially their faces. These provide information on the width of gaps and on the location of objects in the dark, both by touching objects directly and by sensing air currents; they also trigger protective blink reflexes to protect the eyes from damage.[53]: 47
Behavior

Outdoor cats are active both day and night, although they tend to be slightly more active at night.[91] Domestic cats spend the majority of their time in the vicinity of their homes but can range many hundreds of meters from this central point. They establish territories that vary considerably in size, in one study ranging 7–28 ha (17–69 acres).[92] The timing of cats' activity is quite flexible and varied but being low-light predators, they are generally crepuscular, which means they tend to be more active near dawn and dusk. However, house cats' behavior is also influenced by human activity and they may adapt to their owners' sleeping patterns to some extent.[93][94]
Cats conserve energy by sleeping more than most animals, especially as they grow older. The daily duration of sleep varies, usually between 12 and 16 hours, with 13 and 14 being the average. Some cats can sleep as much as 20 hours. The term "cat nap" for a short rest refers to the cat's tendency to fall asleep (lightly) for a brief period. While asleep, cats experience short periods of rapid eye movement sleep often accompanied by muscle twitches, which suggests they are dreaming.[95]
A common misconception is that a cat's behavioral and personality traits correspond to its coat color. These traits instead depend on a complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors.[96]
Sociability
The social behavior of the domestic cat ranges from widely dispersed individuals to feral cat colonies that gather around a food source, based on groups of co-operating females.[97][98] Within such groups, one cat is usually dominant over the others.[99] Each cat in a colony holds a distinct territory, with sexually active males having the largest territories, which are about 10 times larger than those of female cats and may overlap with several females' territories. These territories are marked by urine spraying, rubbing objects at head height with secretions from facial glands, and by defecation.[82] Between these territories are neutral areas where cats watch and greet one another without territorial conflicts. Outside these neutral areas, territory holders usually chase away stranger cats, at first by staring, hissing, and growling, and, if that does not work, by short and violent, noisy attacks. Although cats do not have a social survival strategy or herd behavior, they always hunt alone.[100]
Life in proximity to humans and other domestic animals has led to a symbiotic social adaptation in cats, and cats may express great affection toward humans or other animals. Ethologically, a cat's human keeper functions as a mother surrogate.[101] Adult cats live their lives in a type of extended kittenhood, a form of behavioral neoteny. Their high-pitched sounds may mimic the cries of a hungry human infant, making them particularly difficult for humans to ignore.[102] Some pet cats are poorly socialized. In particular, older cats show aggressiveness toward newly arrived kittens, which include biting and scratching; this type of behavior is known as feline asocial aggression.[103]
Redirected aggression is a common form of aggression which can occur in multiple cat households. In redirected aggression, there is usually something that agitates the cat: this could be a sight, sound, or another source of stimuli which causes a heightened level of anxiety or arousal. If the cat cannot attack the stimuli, it may direct anger elsewhere by attacking or directing aggression to the nearest cat, pet, human or other being.[104][105]
Domestic cats' scent rubbing behavior toward humans or other cats is thought to be a feline means of social bonding.[106]
Communication
 Vocalizing domestic cat | |
Domestic cats use many vocalizations for communication, including purring, trilling, hissing, growling/snarling, grunting, and several different forms of meowing.[107] Their body language, including position of ears and tail, relaxation of the whole body, and kneading of the paws, are all indicators of mood. The tail and ears are particularly important social signal mechanisms; a raised tail indicates a friendly greeting, and flattened ears indicate hostility. Tail-raising also indicates the cat's position in the group's social hierarchy, with dominant individuals raising their tails less often than subordinate ones.[108] Feral cats are generally silent.[109]: 208 Nose-to-nose touching is also a common greeting and may be followed by social grooming, which is solicited by one of the cats raising and tilting its head.[97]
Purring may have developed as an evolutionary advantage as a signaling mechanism of reassurance between mother cats and nursing kittens, who are thought to use it as a care-soliciting signal.[110] Post-nursing cats also often purr as a sign of contentment: when being petted, becoming relaxed,[111][112] or eating. Although purring is popularly interpreted as indicative of pleasure, it has been recorded in a wide variety of circumstances, most of which involve physical contact between the cat and another, presumably trusted individual.[110] Some cats have been observed to purr continuously when chronically ill or in apparent pain.[113]
The exact mechanism by which cats purr has long been elusive, but it has been proposed that purring is generated via a series of sudden build-ups and releases of pressure as the glottis is opened and closed, which causes the vocal folds to separate forcefully. The laryngeal muscles in control of the glottis are thought to be driven by a neural oscillator which generates a cycle of contraction and release every 30–40 milliseconds (giving a frequency of 33 to 25 Hz).[110][114][115]
Domestic cats observed in rescue facilities have 276 morphologically distinct facial expressions based on 26 facial movements; each facial expression corresponds to different social functions that are probably influenced by domestication.[116] Facial expressions have helped researchers detect pain in cats. The feline grimace scale's five criteria—ear position, orbital tightening, muzzle tension, whisker change, and head position—indicated the presence of acute pain in cats.[117][118]
Grooming

Cats are known for spending considerable amounts of time licking their coats to keep them clean.[119][120] The cat's tongue has backward-facing spines about 0.5 millimeter long, called lingual papillae, which contain keratin making them rigid.[121] The papillae act like a hairbrush, and some cats, particularly long-haired cats, occasionally regurgitate sausage-shaped 2–3 cm (0.79–1.18 in) long hairballs of fur that have collected in their stomachs from grooming. Hairballs can be prevented with remedies that ease elimination of the hair through the gut, as well as regular grooming of the coat with a comb or stiff brush.[119]
Fighting

Among domestic cats, males are more likely to fight than females.[122] Among feral cats, the most common reason for cat fighting is competition between two males to mate with a female. In such cases, most fights are won by the heavier male.[123] Another common reason for fighting in domestic cats is the difficulty of establishing territories within a small home.[122] Female cats also fight over territory or to defend their kittens. Neutering will decrease or eliminate this behavior in many cases, suggesting that the behavior is linked to sex hormones.[124]
When cats become aggressive, they try to make themselves appear larger and more threatening by raising their fur, arching their backs, turning sideways, and hissing or spitting.[125] Often, the ears are pointed down and back to avoid damage to the inner ear and potentially listen for any changes behind them while focused forward. Cats may also vocalize loudly and bare their teeth in an effort to further intimidate their opponents. Fights usually consist of grappling and delivering slaps to the face and body with the forepaws, as well as bites. Cats also throw themselves to the ground in a defensive posture to rake their opponent's belly with their hind legs.[126]
Serious damage is rare, as the fights are usually short in duration, with the loser running away with little more than a few scratches to the face and ears. Fights for mating rights are typically more severe, and injuries may include deep puncture wounds and lacerations. Normally, serious injuries from fighting are limited to infections from scratches and bites, although these can occasionally kill cats if untreated. In addition, bites are probably the main route of transmission of the feline immunodeficiency virus.[127] Sexually active males are usually involved in many fights during their lives and often have decidedly battered faces with obvious scars and cuts to their ears and nose.[128] Cats are willing to threaten animals larger than them to defend their territory, such as dogs and foxes.[129]
Hunting and feeding

The shape and structure of cats' cheeks is insufficient to allow them to take in liquids using suction. Therefore, when drinking, they lap with the tongue to draw liquid upward into their mouths. Lapping at a rate of four times a second, the cat touches the smooth tip of its tongue to the surface of the water, and quickly retracts it like a corkscrew, drawing water upward.[130][131]
Feral cats and free-fed house cats consume several small meals in a day. The frequency and size of meals varies between individuals. They select food based on its temperature, smell, and texture; they dislike chilled foods and respond most strongly to moist foods rich in amino acids, which are similar to meat. Cats reject novel flavors (a response termed neophobia) and learn quickly to avoid foods that have tasted unpleasant in the past.[100][132] It is also a common misconception that cats like milk/cream, as they tend to avoid sweet food and milk. Most adult cats are lactose intolerant; the sugar in milk is not easily digested and may cause soft stools or diarrhea.[133] Some also develop odd eating habits and like to eat or chew on things such as wool, plastic, cables, paper, string, aluminum foil, or even coal. This condition, pica, can threaten their health, depending on the amount and toxicity of the items eaten.[134]
Cats hunt small prey, primarily birds and rodents,[135] and are often used as a form of pest control.[136][137] Other common small creatures, such as lizards and snakes, may also become prey.[138] Cats use two hunting strategies, either stalking prey actively, or waiting in ambush until an animal comes close enough to be captured.[139] The strategy used depends on the prey species in the area, with cats waiting in ambush outside burrows, but tending to actively stalk birds.[140]: 153 Domestic cats are a major predator of wildlife in the United States, killing an estimated 1.3 to 4.0 billion birds and 6.3 to 22.3 billion mammals annually.[141]
Certain species appear more susceptible than others; in one English village, for example, 30% of house sparrow mortality was linked to the domestic cat.[142] In the recovery of ringed robins (Erithacus rubecula) and dunnocks (Prunella modularis) in Britain, 31% of deaths were a result of cat predation.[143] In parts of North America, the presence of larger carnivores such as coyotes, which prey on cats and other small predators, reduces the effect of predation by cats and other small predators such as opossums and raccoons on bird numbers and variety.[144]
Another poorly understood element of cat hunting behavior is the presentation of prey to human guardians. One explanation is that cats adopt humans into their social group and share excess kill with others in the group according to the dominance hierarchy, in which humans are reacted to as if they are at or near the top.[145] Another explanation is that they attempt to teach their guardians to hunt or to help their human as if feeding "an elderly cat, or an inept kitten".[146] This hypothesis is inconsistent with the fact that male cats also bring home prey, despite males having negligible involvement in raising kittens.[140]: 153
Play
Domestic cats, especially young kittens, are known for their love of play. This behavior mimics hunting and is important in helping kittens learn to stalk, capture, and kill prey.[147] Cats also engage in play fighting, both with each other and with humans. This behavior may be a way for cats to practice the skills needed for real combat, and it might also reduce the fear that they associate with launching attacks on other animals.[148]
Cats also tend to play with toys more when they are hungry.[149] Owing to the close similarity between play and hunting, cats prefer to play with objects that resemble prey, such as small furry toys that move rapidly, but rapidly lose interest. They become habituated to a toy they have played with before.[150] String is often used as a toy, but if it is eaten, it can become caught at the base of the cat's tongue and then move into the intestines, a medical emergency which can cause serious illness, even death.[151]
Reproduction

The cat secretes and perceives pheromones.[152] Female cats, called queens, are polyestrous with several estrus cycles during a year, lasting usually 21 days. They are usually ready to mate between early February and August[153] in northern temperate zones and throughout the year in equatorial regions.[154]
Several males, called tomcats, are attracted to a female in heat. They fight over her, and the victor wins the right to mate. At first, the female rejects the male, but eventually, the female allows the male to mate. The female utters a loud yowl as the male pulls out of her because a male cat's penis has a band of about 120–150 backward-pointing penile spines, which are about 1 mm (0.039 in) long; upon withdrawal of the penis, the spines may provide the female with increased sexual stimulation, which acts to induce ovulation.[155]

After mating, the female cleans her vulva thoroughly. If a male attempts to mate with her at this point, the female attacks him. After about 20 to 30 minutes, once the female is finished grooming, the cycle will repeat.[156] Because ovulation is not always triggered by a single mating, females may not be impregnated by the first male with which they mate.[157] Furthermore, cats are superfecund; that is, a female may mate with more than one male when she is in heat, with the result that different kittens in a litter may have different fathers.[156]
The morula forms 124 hours after conception. At 148 hours, early blastocysts form. At 10–12 days, implantation occurs.[158] The gestation of queens lasts between 64 and 67 days, with an average of 65 days.[153][159]

Based on a study of 2,300 free-ranging queens conducted from May 1998 and October 2000, they had one to six kittens per litter, with an average of three kittens. They produced a mean of 1.4 litters per year, but a maximum of three litters in a year. Of 169 kittens, 127 died before they were six months old due to a trauma caused in most cases by dog attacks and road accidents.[160] The first litter is usually smaller than subsequent litters. Kittens are weaned between six and seven weeks of age. Queens normally reach sexual maturity at 5–10 months, and males at 5–7 months. This varies depending on breed.[156] Kittens reach puberty at the age of 9–10 months.[153]
Cats are ready to go to new homes at about 12 weeks of age, when they are ready to leave their mother.[161] They can be surgically sterilized (spayed or castrated) as early as seven weeks to limit unwanted reproduction.[162] This surgery also prevents undesirable sex-related behavior, such as aggression, territory marking (spraying urine) in males, and yowling (calling) in females. Traditionally, this surgery was performed at around six to nine months of age, but it is increasingly being performed before puberty, at about three to six months.[163] In the United States, about 80% of household cats are neutered.[164]
Lifespan and health
The average lifespan of pet cats has risen in recent decades. In the early 1980s, it was about seven years,[165]: 33 [166] rising to 9.4 years in 1995[165]: 33 and an average of about 13 years as of 2014 and 2023.[167][168]
Neutering increases life expectancy; one study found castrated male cats live twice as long as intact males, while spayed female cats live 62% longer than intact females.[165]: 35 Having a cat neutered confers some health benefits, such as a greater life expectancy and a decreased incidence of reproductive neoplasia.[169] However, neutering decreases metabolism[170][171][172] and increases food intake,[172][173] both of which can cause obesity in neutered cats.[174] Pre-pubertal neutering (neutering at 4 months or earlier) was only recommended by 28% of American veterinarians in one study. Some concerns of early neutering were metabolic, retarded physeal closure, and urinary tract disease related.[175]
Disease
About 250 heritable genetic disorders have been identified in cats; many are similar to human inborn errors of metabolism.[176] The high level of similarity among the metabolism of mammals allows many of these feline diseases to be diagnosed using genetic tests that were originally developed for use in humans, as well as the use of cats as animal models in the study of the human diseases.[177][178] Diseases affecting domestic cats include acute infections, parasitic infestations, injuries, and chronic diseases such as kidney disease, thyroid disease, and arthritis. Vaccinations are available for many infectious diseases, as are treatments to eliminate parasites such as worms, ticks, and fleas.[179]
Ecology
Habitats

The domestic cat is a cosmopolitan species and occurs across much of the world.[48] It is adaptable and now present on all continents except Antarctica, and on 118 of the 131 main groups of islands, even on the isolated Kerguelen Islands.[180][181] Due to its ability to thrive in almost any terrestrial habitat, it is among the world's most invasive species.[182] It lives on small islands with no human inhabitants.[183] Feral cats can live in forests, grasslands, tundra, coastal areas, agricultural land, scrublands, urban areas, and wetlands.[184]
The unwantedness that leads to the domestic cat being treated as an invasive species is twofold. As it is little altered from the wildcat, it can readily interbreed with the wildcat. This hybridization poses a danger to the genetic distinctiveness of some wildcat populations, particularly in Scotland and Hungary, possibly also the Iberian Peninsula, and where protected natural areas are close to human-dominated landscapes, such as Kruger National Park in South Africa.[185][44] However, its introduction to places where no native felines are present also contributes to the decline of native species.[186]
Ferality

Feral cats are domestic cats that were born in or have reverted to a wild state. They are unfamiliar with and wary of humans and roam freely in urban and rural areas.[187] The numbers of feral cats is not known, but estimates of the United States feral population range from 25 to 60 million.[187] Feral cats may live alone, but most are found in large colonies, which occupy a specific territory and are usually associated with a source of food.[188] Famous feral cat colonies are found in Rome around the Colosseum and Forum Romanum, with cats at some of these sites being fed and given medical attention by volunteers.[189]
Public attitudes toward feral cats vary widely, from seeing them as free-ranging pets to regarding them as vermin.[190]
Impact on wildlife

On islands, birds can contribute as much as 60% of a cat's diet.[191] In nearly all cases, the cat cannot be identified as the sole cause for reducing the numbers of island birds, and in some instances, eradication of cats has caused a "mesopredator release" effect;[192] where the suppression of top carnivores creates an abundance of smaller predators that cause a severe decline in their shared prey. Domestic cats are a contributing factor to the decline of several species, a factor that has ultimately led, in some cases, to extinction. The South Island piopio, Chatham rail,[143] and the New Zealand merganser[193] are a few from a long list, with the most extreme case being the flightless Lyall's wren, which was driven to extinction only a few years after its discovery.[194][195] One feral cat in New Zealand killed 102 New Zealand lesser short-tailed bats in seven days.[196] In the United States, feral and free-ranging domestic cats kill an estimated 6.3–22.3 billion mammals annually.[141]
In Australia, one study found feral cats to kill 466 million reptiles per year. More than 258 reptile species were identified as being predated by cats.[197] Cats have contributed to the extinction of the Navassa curly-tailed lizard and Chioninia coctei.[186]
Interaction with humans

Cats are common pets throughout the world, and their worldwide population as of 2007 exceeded 500 million.[198] As of 2017,[update] the domestic cat was the second most popular pet in the United States, with 95.6 million cats owned[199][200] and around 42 million households owning at least one cat.[201] In the United Kingdom, 26% of adults have a cat, with an estimated population of 10.9 million pet cats as of 2020.[update][202] As of 2021,[update] there were an estimated 220 million owned and 480 million stray cats in the world.[203]
Cats have been used for millennia to control rodents, notably around grain stores and aboard ships, and both uses extend to the present day.[204][205] Cats are also used in the international fur trade[206] and leather industries for making coats, hats, blankets, stuffed toys,[207] shoes, gloves, and musical instruments.[208] About 24 cats are needed to make a cat-fur coat.[209] This use has been outlawed in the United States since 2000 and in the European Union (as well as the United Kingdom) since 2007.[210]
Cat pelts have been used for superstitious purposes as part of the practice of witchcraft,[211] and they are still made into blankets in Switzerland as traditional medicines thought to cure rheumatism.[212]

A few attempts to build a cat census have been made over the years, both through associations or national and international organizations (such as that of the Canadian Federation of Humane Societies[213]) and over the Internet.[214][215] General estimates for the global population of domestic cats range widely from anywhere between 200 million to 600 million.[216][217][218][219][220] Walter Chandoha made his career photographing cats after his 1949 images of Loco, a stray cat, were published. He is reported to have photographed 90,000 cats during his career and maintained an archive of 225,000 images that he drew from for publications during his lifetime.[221]
Pet humanization is a form of anthropomorphism in which cats are kept for companionship and treated more like human family members than traditional pets.[222] This trend of pet culture involves providing cats with a higher level of care, attention and often even luxury, similar to the way humans are treated.[223]
Shows
A cat show is a judged event in which the owners of cats compete to win titles in various cat-registering organizations by entering their cats to be judged after a breed standard.[224] It is often required that a cat must be healthy and vaccinated to participate in a cat show.[224] Both pedigreed and non-purebred companion ("moggy") cats are admissible, although the rules differ depending on the organization. Competing cats are compared to the applicable breed standard, and assessed for temperament.[224]
Infection
Cats can be infected or infested with viruses, bacteria, fungus, protozoans, arthropods or worms that can transmit diseases to humans.[225] In some cases, the cat exhibits no symptoms of the disease.[226] The same disease can then become evident in a human.[227] The likelihood that a person will become diseased depends on the age and immune status of the person. Humans who have cats living in their home or in close association are more likely to become infected. Others might also acquire infections from cat feces and parasites exiting the cat's body.[225][228] Some of the infections of most concern include salmonella, cat-scratch disease, and toxoplasmosis.[226]
History and mythology
In ancient Egypt, cats were revered, and the goddess Bastet often depicted in cat form, sometimes taking on the war-like aspect of a lioness. The Greek historian Herodotus reported that killing a cat was forbidden, and when a household cat died, the entire family mourned and shaved their eyebrows. Families took their dead cats to the sacred city of Bubastis, where they were embalmed and buried in sacred repositories. Herodotus expressed astonishment at the domestic cats in Egypt, because he had only ever seen wildcats.[229]
Ancient Greeks and Romans kept weasels as pets, which were seen as the ideal rodent-killers. The earliest unmistakable evidence of the Greeks having domestic cats comes from two coins from Magna Graecia dating to the mid-fifth century BC showing Iokastos and Phalanthos, the legendary founders of Rhegion and Taras respectively, playing with their pet cats. The usual ancient Greek word for 'cat' was ailouros, meaning 'thing with the waving tail'. Cats are rarely mentioned in ancient Greek literature. Aristotle remarked in his History of Animals that "female cats are naturally lecherous". The Greeks later syncretized their own goddess Artemis with the Egyptian goddess Bastet, adopting Bastet's associations with cats and ascribing them to Artemis. In Ovid's Metamorphoses, when the deities flee to Egypt and take animal forms, the goddess Diana turns into a cat.[230][231]
Cats eventually displaced weasels as the pest control of choice because they were more pleasant to have around the house and were more enthusiastic hunters of mice. During the Middle Ages, many of Artemis's associations with cats were grafted onto the Virgin Mary. Cats are often shown in icons of Annunciation and of the Holy Family and, according to Italian folklore, on the same night that Mary gave birth to Jesus, a cat in Bethlehem gave birth to a kitten.[232] Domestic cats were spread throughout much of the rest of the world during the Age of Discovery, as ships' cats were carried on sailing ships to control shipboard rodents and as good-luck charms.[38]
Several ancient religions believed cats are exalted souls, companions or guides for humans, that are all-knowing but mute so they cannot influence decisions made by humans. In Japan, the maneki neko cat is a symbol of good fortune.[233] In Norse mythology, Freyja, the goddess of love, beauty, and fertility, is depicted as riding a chariot drawn by cats.[234] In Jewish legend, the first cat was living in the house of the first man Adam as a pet that got rid of mice. The cat was once partnering with the first dog before the latter broke an oath they had made which resulted in enmity between the descendants of these two animals. It is also written that neither cats nor foxes are represented in the water, while every other animal has an incarnation species in the water.[235] Although no species are sacred in Islam, cats are revered by Muslims. Some Western writers have stated Muhammad had a favorite cat, Muezza.[236] He is reported to have loved cats so much, "he would do without his cloak rather than disturb one that was sleeping on it".[237] The story has no origin in early Muslim writers, and seems to confuse a story of a later Sufi saint, Ahmed ar-Rifa'i, centuries after Muhammad.[238] One of the companions of Muhammad was known as Abu Hurayrah ("father of the kitten"), in reference to his documented affection to cats.[239]
-
A 19th-century drawing of a tabby cat
-
Some cultures are superstitious about black cats, ascribing either good or bad luck to them.
Superstitions and rituals

Many cultures have negative superstitions about cats. An example would be the belief that encountering a black cat ("crossing one's path") leads to bad luck, or that cats are witches' familiar spirits used to augment a witch's powers and skills. The killing of cats in Medieval Ypres, Belgium, is commemorated in the innocuous present-day Kattenstoet (cat parade).[241] In mid-16th century France, cats would allegedly be burnt alive as a form of entertainment, particularly during midsummer festivals. According to Norman Davies, the assembled people "shrieked with laughter as the animals, howling with pain, were singed, roasted, and finally carbonized".[242] The remaining ashes were sometimes taken back home by the people for good luck.[243]
According to a myth in many cultures, cats have multiple lives. In many countries, they are believed to have nine lives, but in Italy, Germany, Greece, Brazil and some Spanish-speaking regions, they are said to have seven lives,[244][245] while in Arabic traditions, the number of lives is six.[246] An early mention of the myth can be found in John Heywood's The Proverbs of John Heywood (1546):[247]
Husband, (quoth she), ye studie, be merrie now,
And even as ye thinke now, so come to yow.
Nay not so, (quoth he), for my thought to tell right,
I thinke how you lay groning, wife, all last night.
Husband, a groning horse and a groning wife
Never faile their master, (quoth she), for my life.
No wife, a woman hath nine lives like a cat.
The myth is attributed to the natural suppleness and swiftness cats exhibit to escape life-threatening situations.[248] Also lending credence to this myth is the fact that falling cats often land on their feet, using an instinctive righting reflex to twist their bodies around. Nonetheless, cats can still be injured or killed by a high fall.[249]
See also
- Aging in cats
- Ailurophobia
- Animal testing on cats
- Cancer in cats
- Cat bite
- Cat café
- Cat collar
- Cat fancy
- Cat lady
- Cat food
- Cat meat
- Cat repeller
- Cats and the Internet
- Cats in Australia
- Cats in New Zealand
- Cats in the United States
- Cat–dog relationship
- Dog
- Dried cat
- Feral cats in Istanbul
- List of cat breeds
- List of cat documentaries, television series and cartoons
- List of individual cats
- List of fictional felines
- List of feline diseases
- Neko-dera
- Perlorian
- Pet door
- Pet first aid
- Popular cat names
Notes
- ^ Driscoll, Macdonald & O'Brien 2009 did not conclude a date for genetic divergence, noting from archaeological evidence that "the broadest range of dates for domestication to be from 11,000 to 4,000 B.P.".
References
- ^ a b Linnaeus, C. (1758). "Felis Catus". Systema naturae per regna tria naturae: secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. 1 (10th reformed ed.). Holmiae: Laurentii Salvii. p. 42.
- ^ a b Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Species Felis catus". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 534–535. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b Erxleben, J. C. P. (1777). "Felis Catus domesticus". Systema regni animalis per classes, ordines, genera, species, varietates cvm synonymia et historia animalivm. Classis I. Mammalia. Lipsiae: Weygandt. pp. 520–521.
- ^ McKnight, G. H. (1923). "Words and Archaeology". English Words and Their Background. New York, London: D. Appleton and Company. pp. 293–311.
- ^ Pictet, A. (1859). Les origines indo-européennes ou les Aryas primitifs : essai de paléontologie linguistique (in French). Vol. 1. Paris: Joël Cherbuliez. p. 381.
- ^ Keller, O. (1909). Die antike Tierwelt (in German). Vol. Säugetiere. Leipzig: Walther von Wartburg. p. 75.
- ^ Huehnergard, J. (2008). "Qitta: Arabic Cats". In Gruendler, B.; Cooperson, M. (eds.). Classical Arabic Humanities in Their Own Terms: Festschrift for Wolfhart Heinrichs on his 65th Birthday. Leiden, Boston: Brill. pp. 407–418. ISBN 9789004165731. Archived from the original on 31 March 2021. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
- ^ Kroonen, G. (2013). Etymological Dictionary of Proto-Germanic. Leiden, Netherlands: Brill Publishers. p. 281f. ISBN 9789004183407.
- ^ "Puss". The Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 3 September 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ "puss". Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language. New York: Gramercy (Random House). 1996. p. 1571.
- ^ "tom cat, tom-cat". The Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ "gib, n.2". The Oxford English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 18 September 2018. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ "queen cat". The Oxford English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 3 September 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ Some sources wrote that queen refers to unspayed cats that are in an oestrus cycle. Grosskopf, Shane (23 June 2022). "What is a Female Cat Called? A Guide to the Fascinating Terms". Spot Pet Insurance. Archived from the original on 11 April 2024. Retrieved 1 May 2024. Scamporrino, Christina (12 December 2018). "Cat Parenting 101: Special Considerations for Your Female Cat". PrettyLitter. Archived from the original on 1 October 2023. Retrieved 1 May 2024.
- ^ "7 fascinating facts about female cats". Cats Protection. 8 March 2020. Archived from the original on 16 December 2023. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ^ "catling". The Oxford English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 3 September 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ "What do you call a group of ...?". Oxford Dictionaries Online. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 12 October 2012. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ "Terms we use for cats". The Humane Society of the United States. Retrieved 2 August 2024.
- ^ Satunin, C. (1904). "The Black Wild Cat of Transcaucasia". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. II: 162–163.
- ^ Bukhnikashvili, A.; Yevlampiev, I. (eds.). Catalogue of the Specimens of Caucasian Large Mammalian Fauna in the Collection (PDF). Tbilisi: National Museum of Georgia. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- ^ "Opinion 2027". Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature. 60. International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: 81−82. 2003.
- ^ Gentry, A.; Clutton-Brock, J. & Groves, C. P. (2004). "The naming of wild animal species and their domestic derivatives" (PDF). Journal of Archaeological Science. 31 (5): 645–651. Bibcode:2004JArSc..31..645G. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2003.10.006. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- ^ Driscoll, C. A.; Macdonald, D. W.; O'Brien, S. J. (2009). "In the Light of Evolution III: Two Centuries of Darwin Sackler Colloquium: From Wild Animals to Domestic Pets – An Evolutionary View of Domestication". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (S1): 9971–9978. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.9971D. doi:10.1073/pnas.0901586106. PMC 2702791. PMID 19528637.
- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Species Felis silvestris". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 536–537. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Kitchener, A. C.; Breitenmoser-Würsten, C.; Eizirik, E.; Gentry, A.; Werdelin, L.; Wilting, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Abramov, A. V.; Christiansen, P.; Driscoll, C.; Duckworth, J. W.; Johnson, W.; Luo, S.-J.; Meijaard, E.; O'Donoghue, P.; Sanderson, J.; Seymour, K.; Bruford, M.; Groves, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Nowell, K.; Timmons, Z.; Tobe, S. (2017). "A revised taxonomy of the Felidae: The final report of the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN Cat Specialist Group" (PDF). Cat News. Special Issue 11: 21. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 January 2020. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- ^ Johnson, W. E.; O'Brien, S. J. (1997). "Phylogenetic Reconstruction of the Felidae Using 16S rRNA and NADH-5 Mitochondrial Genes". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 44 (S1): S98 – S116. Bibcode:1997JMolE..44S..98J. doi:10.1007/PL00000060. PMID 9071018. S2CID 40185850. Archived from the original on 4 October 2020. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ^ a b c Johnson, W. E.; Eizirik, E.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Murphy, W. J.; Antunes, A.; Teeling, E.; O'Brien, S. J. (2006). "The late Miocene radiation of modern Felidae: A genetic assessment". Science. 311 (5757): 73–77. Bibcode:2006Sci...311...73J. doi:10.1126/science.1122277. PMID 16400146. S2CID 41672825. Archived from the original on 4 October 2020. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ^ a b Li, G.; Davis, B. W.; Eizirik, E. & Murphy, W. J. (2016). "Phylogenomic evidence for ancient hybridization in the genomes of living cats (Felidae)". Genome Research. 26 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1101/gr.186668.114. PMC 4691742. PMID 26518481.
- ^ a b Mattern, M.Y.; McLennan, D.A. (2000). "Phylogeny and speciation of Felids". Cladistics. 16 (2): 232–253. doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.2000.tb00354.x. PMID 34902955. S2CID 85043293.
- ^ Nie, W.; Wang, J.; O'Brien, P. C. (2002). "The genome phylogeny of domestic cat, red panda and five Mustelid species revealed by comparative chromosome painting and G-banding". Chromosome Research. 10 (3): 209–222. doi:10.1023/A:1015292005631. PMID 12067210. S2CID 9660694.
- ^ Pontius, J. U.; Mullikin, J. C.; Smith, D. R.; Agencourt Sequencing Team; et al. (NISC Comparative Sequencing Program) (2007). "Initial sequence and comparative analysis of the cat genome". Genome Research. 17 (11): 1675–1689. doi:10.1101/gr.6380007. PMC 2045150. PMID 17975172.
- ^ a b Driscoll, C. A.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Roca ', A. L.; Hupe, K.; Johnson, W. E.; Geffen, E.; Harley, E. H.; Delibes, M.; Pontier, D.; Kitchener, A. C.; Yamaguchi, N.; O'Brien, S. J.; Macdonald, D. W. (2007). "The Near Eastern Origin of Cat Domestication". Science. 317 (5837): 519–523. Bibcode:2007Sci...317..519D. doi:10.1126/science.1139518. OCLC 808298830. PMC 5612713. PMID 17600185.
- ^ Langton, N.; Langton, M. B. (1940). The Cat in ancient Egypt, illustrated from the collection of cat and other Egyptian figures formed. Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Malek, J. (1997). The Cat in Ancient Egypt (Revised ed.). Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
- ^ Vigne, J. D.; Guilaine, J.; Debue, K.; Haye, L.; Gérard, P. (2004). "Early taming of the cat in Cyprus". Science. 304 (5668): 259. doi:10.1126/science.1095335. PMID 15073370. S2CID 28294367.
- ^ Driscoll, C. A.; Clutton-Brock, J.; Kitchener, A. C.; O'Brien, S. J. (2009). "The taming of the cat". Scientific American. 300 (6): 68–75. Bibcode:2009SciAm.300f..68D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0609-68 (inactive 1 November 2024). JSTOR 26001382. PMC 5790555. PMID 19485091.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ a b Ottoni, C.; van Neer, W.; de Cupere, B.; Daligault, J.; Guimaraes, S.; Peters, J.; Spassov, N.; Prendergast, M. E.; Boivin, N.; Morales-Muñiz, A.; Bălăşescu, A.; Becker, C.; Benecke, N.; Boroneant, A.; Buitenhuis, H.; Chahoud, J.; Crowther, A.; Llorente, L.; Manaseryan, N.; Monchot, H.; Onar, V.; Osypińska, M.; Putelat, O.; Quintana Morales, E.M.; Studer, J.; Wierer, U.; Decorte, R.; Grange, T.; Geigl, E. (2017). "The palaeogenetics of cat dispersal in the ancient world". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 1 (7): 0139. Bibcode:2017NatEE...1..139O. doi:10.1038/s41559-017-0139. S2CID 44041769. Archived from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ a b Faure, E.; Kitchener, A. C. (2009). "An archaeological and historical review of the relationships between Felids and people". Anthrozoös. 22 (3): 221−238. doi:10.2752/175303709X457577. S2CID 84308532.
- ^ Ragni, B.; Possenti, M.; Sforzi, A.; Zavalloni, D.; Ciani, F. (1994). "The wildcat in central-northern Italian peninsula: a biogeographical dilemma" (PDF). Biogeographia. 17 (1). doi:10.21426/B617110417. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 July 2018. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- ^ Vigne, J.-D. (1992). "Zooarchaeology and the biogeographical history of the mammals of Corsica and Sardinia since the last ice age". Mammal Review. 22 (2): 87–96. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2907.1992.tb00124.x.
- ^ Vigne, J.-D.; Evin, A.; Cucchi, T.; Dai, L.; Yu, C.; Hu, S.; Soulages, N.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z. (2016). "Earliest 'domestic' cats in China identified as leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis)". PLOS ONE. 11 (1): e0147295. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1147295V. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0147295. PMC 4723238. PMID 26799955.
- ^ Cameron-Beaumont, C.; Lowe, S. E.; Bradshaw, J. W. S. (2002). "Evidence suggesting pre-adaptation to domestication throughout the small Felidae" (PDF). Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 75 (3): 361–366. doi:10.1046/j.1095-8312.2002.00028.x. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2019. Retrieved 10 October 2019.
- ^ Bradshaw, J. W. S.; Horsfield, G. F.; Allen, J. A.; Robinson, I. H. (1999). "Feral cats: Their role in the population dynamics of Felis catus" (PDF). Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 65 (3): 273–283. doi:10.1016/S0168-1591(99)00086-6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 January 2019.
- ^ a b Oliveira, R.; Godinho, R.; Randi, E.; Alves, P. C. (2008). "Hybridization Versus Conservation: Are Domestic Cats Threatening the Genetic Integrity of Wildcats (Felis silvestris silvestris) in Iberian Peninsula?". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 363 (1505): 2953–2961. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0052. PMC 2606743. PMID 18522917.
- ^ Kitchener, C.; Easterbee, N. (1992). "The taxonomic status of black wild felids in Scotland". Journal of Zoology. 227 (2): 342–346. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1992.tb04832.x.
- ^ Wastlhuber, J. (1991). "History of domestic cats and cat breeds". In Pedersen, N. C. (ed.). Feline Husbandry: Diseases and management in the multiple-cat environment. Goleta: American Veterinary Publications. pp. 1–59. ISBN 9780939674299.
- ^ Montague, M. J.; Li, G.; Gandolfi, B.; Khan, R.; Aken, B. L.; Searle, S. M.; Minx, P.; Hillier, L. W.; Koboldt, D. C.; Davis, B. W.; Driscoll, C. A. (2014). "Comparative analysis of the domestic cat genome reveals genetic signatures underlying feline biology and domestication". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (48): 17230–17235. Bibcode:2014PNAS..11117230M. doi:10.1073/pnas.1410083111. PMC 4260561. PMID 25385592.
- ^ a b Lipinski, M.J.; Froenicke, L.; Baysac, K. C.; Billings, N. C.; Leutenegger, C. M.; Levy, A. M.; Longeri, M.; Niini, T.; Ozpinar, H.; Slater, M.R.; Pedersen, N. C.; Lyons, L. A. (2008). "The ascent of cat breeds: Genetic evaluations of breeds and worldwide random-bred populations". Genomics. 91 (1): 12–21. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.10.009. PMC 2267438. PMID 18060738.
- ^ O'Connor, T. P. (2007). "Wild or domestic? Biometric variation in the cat Felis silvestris" (PDF). International Journal of Osteoarchaeology. 17 (6): 581–595. doi:10.1002/oa.913. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 January 2019. Retrieved 20 January 2019.
- ^ Sunquist, M.; Sunquist, F. (2002). "Domestic cat". Wild Cats of the World. University of Chicago Press. pp. 99–112. ISBN 9780226779997.
- ^ a b Walker, W.F. (1982). Study of the Cat with Reference to Human Beings (4th revised ed.). Thomson Learning/Cengage. ISBN 9780030579141.
- ^ Gillis, R., ed. (2002). "Cat Skeleton". Zoolab. La Crosse: University of Wisconsin Press. Archived from the original on 6 December 2006. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ a b c d Case, Linda P. (2003). The Cat: Its behavior, nutrition, and health. Ames: Iowa State University Press. ISBN 9780813803319.
- ^ a b Smith, Patricia; Tchernov, Eitan (1992). Structure, Function, and Evolution of Teeth. Freund Publishing House. p. 217. ISBN 9789652222701.
- ^ Carr, William H. A. (1 January 1978). The New Basic Book of the Cat. Scribner's. p. 174. ISBN 9780684155494.
- ^ Kitchener, A. C.; Van Valkenburgh, B.; Yamaguchi, N. (2010). "Felid form and function". In Macdonald, D.; Loveridge, A. (eds.). Biology and Conservation of wild felids. Oxford University Press. pp. 83–106. Archived from the original on 16 February 2021. Retrieved 10 October 2019.
- ^ Armes, A.F. (1900). "Outline of cat lessons". The School Journal. LXI: 659. Archived from the original on 6 August 2021. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ Homberger, D. G.; Ham, K.; Ogunbakin, T.; Bonin, J. A.; Hopkins, B. A.; Osborn, M. L.; et al. (2009). "The structure of the cornified claw sheath in the domesticated cat (Felis catus): Implications for the claw-shedding mechanism and the evolution of cornified digital end organs". J Anat. 214 (4): 620–43. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01068.x. PMC 2736126. PMID 19422432.
- ^ Danforth, C. H. (1947). "Heredity of polydactyly in the cat". The Journal of Heredity. 38 (4): 107–112. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a105701. PMID 20242531.
- ^ Lettice, L. A.; Hill, A. E.; Devenney, P. S.; Hill, R. E. (2008). "Point mutations in a distant sonic hedgehog cis-regulator generate a variable regulatory output responsible for preaxial polydactyly". Human Molecular Genetics. 17 (7): 978–985. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm370. hdl:20.500.11820/76c18e1b-ba87-49c6-9da7-c837187646a5. PMID 18156157.
- ^ Pocock, R. I. (1917). "VII — On the external characters of the Felidæ". The Annals and Magazine of Natural History; Zoology, Botany, and Geology. 8. 19 (109): 113–136. doi:10.1080/00222931709486916.
- ^ Christensen, W. (2004). "The physical cat". Outwitting Cats. Globe Pequot. pp. 22–45. ISBN 9781592282401.
- ^ Kent, Marc; Platt, Simon R. (September 2010). "The neurology of balance: Function and dysfunction of the vestibular system in dogs and cats". The Veterinary Journal. 185 (3): 247–249. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2009.10.029. PMID 19944632.
- ^ Gerathewohl, S. J.; Stallings, H. D. (1957). "The labyrinthine posture reflex (righting reflex) in the cat during weightlessness" (PDF). The Journal of Aviation Medicine. 28 (4): 345–355. PMID 13462942. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 October 2020. Retrieved 27 April 2019.
- ^ Nguyen, H. D. (1998). "How does a cat always land on its feet?". School of Medical Engineering. Dynamics II (ME 3760) course materials. Georgia Institute of Technology. Archived from the original on 10 April 2001. Retrieved 15 May 2007. This tertiary source reuses information from other sources but does not name them.
- ^ Batterman, R. (2003). "Falling cats, parallel parking, and polarized light" (PDF). Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part B: Studies in History and Philosophy of Modern Physics. 34 (4): 527–557. Bibcode:2003SHPMP..34..527B. doi:10.1016/s1355-2198(03)00062-5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 July 2018. Retrieved 13 September 2022.
- ^ Eizirik, Eduardo; Yuhki, Naoya; Johnson, Warren E.; Menotti-Raymond, Marilyn; Hannah, Steven S.; O'Brien, Stephen J. (4 March 2003). "Molecular Genetics and Evolution of Melanism in the Cat Family". Current Biology. 13 (5): 448–453. Bibcode:2003CBio...13..448E. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00128-3. ISSN 0960-9822. PMID 12620197. S2CID 19021807.
- ^ Eizirik, Eduardo; Yuhki, Naoya; Johnson, Warren E.; Menotti-Raymond, Marilyn; Hannah, Steven S.; O'Brien, Stephen J. (4 March 2003). "Molecular Genetics and Evolution of Melanism in the Cat Family" (PDF). Cell Press. 13 (5): 448–453. Bibcode:2003CBio...13..448E. doi:10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00128-3. PMID 12620197. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 March 2024. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ Ollivier, F. J.; Samuelson, D. A.; Brooks, D. E.; Lewis, P. A.; Kallberg, M. E.; Komaromy, A. M. (2004). "Comparative morphology of the Tapetum Lucidum (among selected species)". Veterinary Ophthalmology. 7 (1): 11–22. doi:10.1111/j.1463-5224.2004.00318.x. PMID 14738502. S2CID 15419778.
- ^ Malmström, T.; Kröger, R. H. (2006). "Pupil shapes and lens optics in the eyes of terrestrial vertebrates". Journal of Experimental Biology. 209 (1): 18–25. Bibcode:2006JExpB.209...18M. doi:10.1242/jeb.01959. PMID 16354774.
- ^ Hammond, P.; Mouat, G. S. V. (1985). "The relationship between feline pupil size and luminance". Experimental Brain Research. 59 (3): 485–490. doi:10.1007/BF00261338. PMID 4029324. S2CID 11858455.
- ^ Loop, M. S.; Bruce, L. L. (1978). "Cat color vision: The effect of stimulus size". Science. 199 (4334): 1221–1222. Bibcode:1978Sci...199.1221L. doi:10.1126/science.628838. PMID 628838.
- ^ Guenther, E.; Zrenner, E. (1993). "The spectral sensitivity of dark- and light-adapted cat retinal ganglion cells". Journal of Neuroscience. 13 (4): 1543–1550. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01543.1993. PMC 6576706. PMID 8463834.
- ^ Heffner, R. S. (1985). "Hearing range of the domestic cat" (PDF). Hearing Research. 19 (1): 85–88. doi:10.1016/0378-5955(85)90100-5. PMID 4066516. S2CID 4763009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 July 2021. Retrieved 10 October 2019.
- ^ Heffner, H. E. (1998). "Auditory awareness". Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 57 (3–4): 259–268. doi:10.1016/S0168-1591(98)00101-4.
- ^ Heffner, R. S. (2004). "Primate hearing from a mammalian perspective". The Anatomical Record Part A: Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology. 281 (1): 1111–1122. doi:10.1002/ar.a.20117. PMID 15472899. S2CID 4991969.
- ^ Sunquist, M.; Sunquist, F. (2002). "What is a Cat?". Wild Cats of the World. University of Chicago Press. pp. 5–18. ISBN 9780226779997. Archived from the original on 19 July 2023. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
- ^ Blumberg, M. S. (1992). "Rodent ultrasonic short calls: Locomotion, biomechanics, and communication". Journal of Comparative Psychology. 106 (4): 360–365. doi:10.1037/0735-7036.106.4.360. PMID 1451418.
- ^ Takagi, S.; Chijiiwa, H.; Arahori, M.; Saito, A.; Fujita, K.; Kuroshima, H. (2021). "Socio-spatial cognition in cats: Mentally mapping owner's location from voice". PLOS ONE. 16 (11): e0257611. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1657611T. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0257611. PMC 8580247. PMID 34758043.
- ^ Moulton, David G. (1 August 1967). "Olfaction in mammals". American Zoologist. 7 (3): 421–429. doi:10.1093/icb/7.3.421. ISSN 0003-1569. PMID 6077376. Archived from the original on 6 August 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2019.
- ^ Miyazaki, Masao; Yamashita, Tetsuro; Suzuki, Yusuke; Saito, Yoshihiro; Soeta, Satoshi; Taira, Hideharu; Suzuki, Akemi (October 2006). "A major urinary protein of the domestic cat regulates the production of felinine, a putative pheromone precursor". Chemistry & Biology. 13 (10): 1071–1079. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.08.013. PMID 17052611.
- ^ a b Sommerville, B. A. (1998). "Olfactory Awareness". Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 57 (3–4): 269–286. doi:10.1016/S0168-1591(98)00102-6.
- ^ Grognet, Jeff (June 1990). "Catnip: Its uses and effects, past and present". The Canadian Veterinary Journal. 31 (6): 455–456. PMC 1480656. PMID 17423611.
- ^ Turner, Ramona (29 May 2007). "How does catnip work its magic on cats?". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 22 October 2013.
- ^ Tucker, Arthur; Tucker, Sharon (1988). "Catnip and the catnip response". Economic Botany. 42 (2): 214–231. Bibcode:1988EcBot..42..214T. doi:10.1007/BF02858923. S2CID 34777592.
- ^ a b Schelling, Christianne. "Do cats have a sense of taste?". CatHealth.com. Archived from the original on 28 January 2016.
- ^ Jiang, Peihua; Josue, Jesusa; Li, Xia; Glaser, Dieter; Li, Weihua; Brand, Joseph G.; Margolskee, Robert F.; Reed, Danielle R.; Beauchamp, Gary K. (12 March 2012), "Major taste loss in carnivorous mammals", PNAS, 13 (109): 4956–4961, doi:10.1073/pnas.1118360109, PMC 3324019, PMID 22411809
- ^ Bradshaw, John W. S. (1 July 2006). "The evolutionary basis for the feeding behavior of domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) and cats (Felis catus)". Journal of Nutrition. 136 (7): 1927S–1931. doi:10.1093/jn/136.7.1927S. PMID 16772461.
- ^ a b c McGrane, Scott J.; Gibbs, Matthew; Hernangomez de Alvaro, Carlos; Dunlop, Nicola; Winnig, Marcel; Klebansky, Boris; Waller, Daniel (1 January 2023). "Umami taste perception and preferences of the domestic cat (Felis catus), an obligate carnivore". Chemical Senses. 48. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjad026. ISSN 0379-864X. PMC 10468298. PMID 37551788.
- ^ Grimm, David (1 October 2023). "Why do cats love tuna so much?". Science. 381 (6661): 935. Bibcode:2023Sci...381..935G. doi:10.1126/science.adk5725. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 37651517. S2CID 261395204.
- ^ Germain, E.; Benhamou, S.; Poulle, M.-L. (2008). "Spatio-temporal Sharing between the European Wildcat, the Domestic Cat and their Hybrids". Journal of Zoology. 276 (2): 195–203. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2008.00479.x.
- ^ Barratt, D. G. (1997). "Home Range Size, Habitat Utilisation and Movement Patterns of Suburban and Farm Cats Felis catus". Ecography. 20 (3): 271–280. Bibcode:1997Ecogr..20..271B. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.1997.tb00371.x. JSTOR 3682838.
- ^ Randall, W.; Johnson, R. F.; Randall, S.; Cunningham, J. T. (1985). "Circadian rhythms in food intake and activity in domestic cats". Behavioral Neuroscience. 99 (6): 1162–1175. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.99.6.1162. PMID 3843546.
- ^ Ling, Thomas (2 June 2021). "Why do cats sleep so much?". BBC Science Focus Magazine. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ Jouvet, M. (1979). "What Does a Cat Dream About?". Trends in Neurosciences. 2: 280–282. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(79)90110-3. S2CID 53161799.
- ^ Udell, Monique; Delgado, Mikel; Ekenstedt, Kari; Shoveller, Anna Kate; Croney, Candace (2023). "CATastrophic myths part 2: Common misconceptions about the environmental, nutritional, and genetic management of domestic cats and their welfare implications". The Veterinary Journal. 300–302: 106029. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2023.106029. PMID 37683762.
- ^ a b Crowell-Davis, S. L.; Curtis, T. M.; Knowles, R. J. (2004). "Social Organization in the Cat: A Modern Understanding" (PDF). Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. 6 (1): 19–28. doi:10.1016/j.jfms.2003.09.013. PMC 10822437. PMID 15123163. S2CID 25719922. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2011.
- ^ Liberg, O.; Sandell, M.; Pontier, D.; Natoli, E. (2000). "Density, spatial organisation and reproductive tactics in the domestic cat and other felids". In Turner, D. C.; Bateson, P. (eds.). The domestic cat: the biology of its behaviour (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 119–147. ISBN 9780521636483. Archived from the original on 31 March 2021. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
- ^ Baron, A.; Stewart, C. N.; Warren, J. M. (1 January 1957). "Patterns of social interaction in cats (Felis domestica)". Behaviour. 11 (1): 56–66. doi:10.1163/156853956X00084. JSTOR 4532869.
- ^ a b Bradshaw, J. W.; Goodwin, D.; Legrand-Defrétin, V.; Nott, H. M. (1996). "Food selection by the domestic cat, an obligate carnivore". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology – Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 114 (3): 205–209. doi:10.1016/0300-9629(95)02133-7. PMID 8759144.
- ^ Mills, D. S.; Marchant-Forde, J. (2010). Encyclopedia of Applied Animal Behaviour and Welfare. p. 518. ISBN 9780851997247. Archived from the original on 7 April 2017.
- ^ McComb, K.; Taylor, A. M.; Wilson, C.; Charlton, B. D. (2009). "The Cry Embedded within the Purr". Current Biology. 19 (13): R507–508. Bibcode:2009CBio...19.R507M. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.05.033. PMID 19602409. S2CID 10972076.
- ^ Levine, E.; Perry, P.; Scarlett, J.; Houpt, K. (2005). "Intercat aggression in households following the introduction of a new cat" (PDF). Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 90 (3–4): 325–336. doi:10.1016/j.applanim.2004.07.006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 March 2009.
- ^ Horwitz, Debra (2022). "Cat Behavior Problems - Aggression Redirected". VCA Animal Hospitals. Archived from the original on 19 March 2022. Retrieved 16 June 2022.
- ^ Johnson, Ingrid (17 May 2014). "Redirected Aggression in Cats: Recognition and Treatment Strategies". International Association of Animal Behavior Consultants. Archived from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 16 June 2022.
- ^ Soennichsen, S.; Chamove, A. S. (2015). "Responses of cats to petting by humans". Anthrozoös. 15 (3): 258–265. doi:10.2752/089279302786992577. S2CID 144843766.
- ^ Moelk, M. (1944). "Vocalizing in the House-cat; A Phonetic and Functional Study". The American Journal of Psychology. 57 (2): 184–205. doi:10.2307/1416947. JSTOR 1416947.
- ^ Cafazzo, S.; Natoli, E. (2009). "The Social Function of Tail Up in the Domestic Cat (Felis silvestris catus)". Behavioural Processes. 80 (1): 60–66. doi:10.1016/j.beproc.2008.09.008. PMID 18930121. S2CID 19883549.
- ^ Jensen, P. (2009). The Ethology of Domestic Animals. "Modular Text" series. Wallingford, England: Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International. ISBN 9781845935368.
- ^ a b c Bradshaw, John W. S. (2012). The Behaviour of the Domestic Cat. Wallingford: CABI. pp. 71–72. ISBN 9781780641201. Retrieved 6 July 2022.
- ^ von Muggenthaler, E.; Wright, B. "Solving the Cat's Purr Mystery Using Accelerometers". BKSV. Brüel & Kjær. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 11 February 2010.
- ^ "The Cat's Remarkable Purr". ISnare. Archived from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 6 August 2008.
- ^ Beaver, Bonnie V. G. (2003). Feline behavior : a guide for veterinarians (2nd ed.). St. Louis, Missouri: Saunders. ISBN 9780721694986.
- ^ Remmers, J. E.; Gautier, H. (1972). "Neural and mechanical mechanisms of feline purring". Respiration Physiology. 16 (3): 351–361. doi:10.1016/0034-5687(72)90064-3. PMID 4644061.
- ^ Frazer Sissom, D. E.; Rice, D. A.; Peters, G. (1991). "How cats purr". Journal of Zoology. 223 (1): 67–78. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1991.tb04749.x. S2CID 32350871.
- ^ Scott, L.; Florkiewicz, B. N. (2023). "Feline Faces: Unraveling the Social Function of Domestic Cat Facial Signals". Behavioural Processes. 213: 104959. doi:10.1016/j.beproc.2023.104959. PMID 37858844. S2CID 264176390.
- ^ Evangelista, M. C.; Watanabe, R.; Leung, V. S. Y.; Monteiro, B. P.; O'Toole, E.; Pang, D. S. J.; Steagall, P. V. (2019). "Facial expressions of pain in cats: the development and validation of a Feline Grimace Scale". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 19128. Bibcode:2019NatSR...919128E. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-55693-8. PMC 6911058. PMID 31836868.
- ^ Monteiro, B. P; Lee, N. H.Y.; Steagall, P. V. (2023). "Can cat caregivers reliably assess acute pain in cats using the Feline Grimace Scale? A large bilingual global survey". Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. 25 (1): 1098612X221145499. doi:10.1177/1098612X221145499. PMC 10812049. PMID 36649089.
- ^ a b Hadzima, E. (2016). "Everything You Need to Know About Hairballs". Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 23 August 2016.
- ^ Noel, A. C.; Hu, D. L. (2018). "Cats use hollow papillae to wick saliva into fur". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 115 (49): 12377–12382. Bibcode:2018PNAS..11512377N. doi:10.1073/pnas.1809544115. PMC 6298077. PMID 30455290.
- ^ Boshel, J.; Wilborn, W. H.; Singh, B. B.; Peter, S.; Stur, M. (1982). "Filiform Papillae of Cat Tongue". Acta Anatomica. 114 (2): 97–105. doi:10.1159/000145583. PMID 7180385. S2CID 36216103.
- ^ a b Lindell, E. M. (1997). "Intercat Aggression: A Retrospective Study Examining Types of Aggression, Sexes of Fighting Pairs, and Effectiveness of Treatment". Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 55 (1–2): 153–162. doi:10.1016/S0168-1591(97)00032-4.
- ^ Yamane, A.; Doi, T.; Ono, Y. (1996). "Mating Behaviors, Courtship Rank and Mating Success of Male Feral Cat (Felis catus)". Journal of Ethology. 14 (1): 35–44. doi:10.1007/BF02350090. S2CID 27456926.
- ^ Kustritz, M. V. R. (2007). "Determining the Optimal age for Gonadectomy of Dogs and Cats". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 231 (11): 1665–1675. doi:10.2460/javma.231.11.1665. PMID 18052800. S2CID 4651194.
- ^ "Cat Behavior: Body Language". AnimalPlanet. 2007. Archived from the original on 24 February 2009. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ "Aggression Between Family Cats and Feline Social Behavior". PAWS. Archived from the original on 28 August 2022. Retrieved 6 September 2022.
- ^ Pedersen, N. C.; Yamamoto, J. K.; Ishida, T.; Hansen, H. (1989). "Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection". Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology. 21 (1): 111–129. doi:10.1016/0165-2427(89)90134-7. PMID 2549690.
- ^ Whiteley, H. E. (1994). "Correcting misbehavior". Understanding and Training Your Cat or Kitten. Santa Fe: Sunstone Press. pp. 146–147. ISBN 9781611390803.
- ^ Devlin, Hannah (13 October 2022). "Cat v fox: what made Downing Street's Larry so brave?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 16 October 2022. Retrieved 16 October 2022.
- ^ Reis, P. M.; Jung, S.; Aristoff, J. M.; Stocker, R. (2010). "How cats lap: Water uptake by Felis catus". Science. 330 (6008): 1231–1234. Bibcode:2010Sci...330.1231R. doi:10.1126/science.1195421. PMID 21071630. S2CID 1917972.
- ^ Kim, W.; Bush, J.W.M. (2012). "Natural drinking strategies" (PDF). Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 705: 7–25. Bibcode:2012JFM...705....7K. doi:10.1017/jfm.2012.122. hdl:1721.1/80405. S2CID 14895835. Archived from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 23 September 2019.
- ^ Zaghini, G.; Biagi, G. (2005). "Nutritional peculiarities and diet palatability in the cat". Veterinary Res. Commun. 29 (Supplement 2): 39–44. doi:10.1007/s11259-005-0009-1. PMID 16244923. S2CID 23633719.
- ^ Kienzle, E. (1994). "Blood sugar levels and renal sugar excretion after the intake of high carbohydrate diets in cats" (PDF). Journal of Nutrition. 124 (12 Supplement): 2563S – 2567S. doi:10.1093/jn/124.suppl_12.2563S. PMID 7996238. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2013.
- ^ Bradshaw, J. W. S. (1997). "Factors affecting pica in the domestic cat". Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 52 (3–4): 373–379. doi:10.1016/S0168-1591(96)01136-7.
- ^ Woods, M.; McDonald, R. A.; Harris, S. (2003). "Predation of wildlife by domestic cats Felis catus in Great Britain". Mammal Review. 23 (2): 174–188. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2907.2003.00017.x. S2CID 42095020.
- ^ Slesnick, I. L. (2004). Clones, Cats, and Chemicals: Thinking scientifically about controversial issues. NSTA Press. p. 9. ISBN 9780873552370.
- ^ Hill, D. S. (2008). Pests of Crops in Warmer Climates and their Control (First ed.). Springer. p. 120. ISBN 9781402067372.
- ^ Learn, Joshua Rapp (17 August 2018). "Cats Have A Killer Impact on Reptiles: Experiments in Australia reveal that kitties are catching more than birds". NationalGeographic. Archived from the original on 24 November 2023. Retrieved 24 November 2023.
- ^ Tucker, A. (2016). "How cats evolved to win the Internet". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 19 October 2016. Retrieved 13 November 2016.
- ^ a b Turner, D. C.; Bateson, P., eds. (2000). The Domestic Cat: The biology of its behaviour (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521636483.
- ^ a b Loss, S. R.; Will, T.; Marra, P. P. (2013). "The impact of free-ranging domestic cats on wildlife of the United States". Nature Communications. 4: 1396. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.1396L. doi:10.1038/ncomms2380. PMID 23360987.
- ^ Chucher, P. B.; Lawton, J. H. (1987). "Predation by domestic cats in an English village". Journal of Zoology, London. 212 (3): 439–455. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1987.tb02915.x.
- ^ a b Mead, C. J. (1982). "Ringed birds killed by cats". Mammal Review. 12 (4): 183–186. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2907.1982.tb00014.x.
- ^ Crooks, K. R.; Soul, M. E. (1999). "Mesopredator release and avifaunal extinctions in a fragmented system" (PDF). Nature. 400 (6744): 563–566. Bibcode:1999Natur.400..563C. doi:10.1038/23028. S2CID 4417607. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2011.
- ^ Leyhausen, P. (1978). Cat Behavior: The predatory and social behavior of domestic and wild cats. New York: Garland STPM Press. ISBN 9780824070175.
- ^ Desmond, M. (2002). "Why does a cat play with its prey before killing it?". Catwatching: Why cats purr and everything else you ever wanted to know (2nd ed.). London: Ebury Press. pp. 51–52. ISBN 9781409022213. Archived from the original on 31 March 2021. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
- ^ Poirier, F. E.; Hussey, L. K. (1982). "Nonhuman Primate Learning: The Importance of Learning from an Evolutionary Perspective". Anthropology and Education Quarterly. 13 (2): 133–148. doi:10.1525/aeq.1982.13.2.05x1830j. JSTOR 3216627.
- ^ Hall, S. L. (1998). "Object play by adult animals". In Byers, J. A.; Bekoff, M. (eds.). Animal Play: Evolutionary, Comparative, and Ecological Perspectives. Cambridge University Press. pp. 45–60. ISBN 9780521586566. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
- ^ Hall, S. L. (1998). "The Influence of Hunger on Object Play by Adult Domestic Cats". Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 58 (1–2): 143–150. doi:10.1016/S0168-1591(97)00136-6.
- ^ Hall, S. L. (2002). "Object Play in Adult Domestic Cats: The Roles of Habituation and Disinhibition". Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 79 (3): 263–271. doi:10.1016/S0168-1591(02)00153-3.
- ^ MacPhail, C. (2002). "Gastrointestinal obstruction". Clinical Techniques in Small Animal Practice. 17 (4): 178–183. doi:10.1053/svms.2002.36606. PMID 12587284. S2CID 24977450.
- ^ Bland, K. P. (1979). "Tom-cat odour and other pheromones in feline reproduction" (PDF). Veterinary Science Communications. 3 (1): 125–136. doi:10.1007/BF02268958. S2CID 22484090. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 January 2019. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ a b c Jemmett, J. E.; Evans, J. M. (1977). "A survey of sexual behaviour and reproduction of female cats". Journal of Small Animal Practice. 18 (1): 31–37. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5827.1977.tb05821.x. PMID 853730.
- ^ Johnson, A.K; Kutzler, M.A, eds. (2022). "Feline Estrous Cycle". Feline Reproduction. CABI Books. pp. 11–22. doi:10.1079/9781789247107.0002. ISBN 9781789247084. Archived from the original on 20 August 2022. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ Aronson, L. R.; Cooper, M. L. (1967). "Penile Spines of the Domestic Cat: Their Endocrine-behavior Relations" (PDF). The Anatomical Record. 157 (1): 71–78. doi:10.1002/ar.1091570111. PMID 6030760. S2CID 13070242. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 March 2015.
- ^ a b c "Prolific Cats: The Estrous Cycle" (PDF). Veterinary Learning Systems. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 December 2016. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ Wildt, D. E.; Seager, S. W.; Chakraborty, P. K. (1980). "Effect of Copulatory Stimuli on Incidence of Ovulation and on Serum Luteinizing Hormone in the Cat". Endocrinology. 107 (4): 1212–1217. doi:10.1210/endo-107-4-1212. PMID 7190893.
- ^ Swanson, W. F.; Roth, T. L.; Wilt, D. E. (1994). "In Vivo Embryogenesis, Embryo Migration and Embryonic Mortality in the Domestic Cat". Biology of Reproduction. 51 (3): 452–464. doi:10.1095/biolreprod51.3.452. PMID 7803616.
- ^ Tsutsui, T.; Stabenfeldt, G. H. (1993). "Biology of Ovarian Cycles, Pregnancy and pseudopregnancy in the Domestic Cat". Journal of Reproduction and Fertility. Supplement 47: 29–35. PMID 8229938.
- ^ Nutter, F. B.; Levine, J. F.; Stoskopf, M. K. (2004). "Reproductive capacity of free-roaming domestic cats and kitten survival rate". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 225 (9): 1399–1402. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.204.1281. doi:10.2460/javma.2004.225.1399. PMID 15552315. S2CID 1903272.
- ^ Behrend, K.; Wegler, M. (1991). "Living with a Cat". The Complete Book of Cat Care: How to Raise a Happy and Healthy Cat. Hauppauge, New York: Barron's Educational Series. pp. 28–29. ISBN 9780812046137.
- ^ Olson, P. N.; Kustritz, M. V.; Johnston, S. D. (2001). "Early-age Neutering of Dogs and Cats in the United States (A Review)". Journal of Reproduction and Fertility. Supplement 57: 223–232. PMID 11787153.
- ^ Root Kustritz, M. V. (2007). "Determining the optimal age for gonadectomy of dogs and cats" (PDF). Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 231 (11): 1665–1675. doi:10.2460/javma.231.11.1665. PMID 18052800. S2CID 4651194. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2010.
- ^ Chu, K.; Anderson, W. M.; Rieser, M. Y. (2009). "Population characteristics and neuter status of cats living in households in the United States". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 234 (8): 1023–1030. doi:10.2460/javma.234.8.1023. PMID 19366332. S2CID 39208758.
- ^ a b c Kraft, W. (1998). "Geriatrics in canine and feline internal medicine". European Journal of Medical Research. 3 (1–2): 31–41. PMID 9512965.
- ^ Nassar, R.; Mosier, J. E.; Williams, L. W. (1984). "Study of the feline and canine populations in the greater Las Vegas area". American Journal of Veterinary Research. 45 (2): 282–287. PMID 6711951.
- ^ O'Neill, Dan G; Church, David B; McGreevy, Paul D; Thomson, Peter C; Brodbelt, David C (2014). "Longevity and mortality of cats attending primary care veterinary practices in England". Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. 17 (2): 125–133. doi:10.1177/1098612X14536176. PMC 10816413. PMID 24925771.
- ^ Montoya, M.; Morrison, J. A.; Arrignon, F.; Spofford, N.; C., H.; Hours, M.-A.; Biourge, V. (2023). "Life expectancy tables for dogs and cats derived from clinical data". Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 10: 1082102. doi:10.3389/fvets.2023.1082102. PMC 9989186. PMID 36896289.
- ^ Vendramini, Thiago H. A.; Amaral, Andressa R.; Pedrinelli, Vivian; Zafalon, Rafael V. A.; Rodrigues, Roberta B. A.; Brunetto, Marcio A. (14 January 2020). "Neutering in dogs and cats: current scientific evidence and importance of adequate nutritional management". Nutrition Research Reviews. 33 (1). Cambridge University Press (CUP): 134–144. doi:10.1017/s0954422419000271. ISSN 0954-4224. PMID 31931899.
- ^ Hoenig, Margarethe; Ferguson, Duncan C. (1 May 2002). "Effects of neutering on hormonal concentrations and energy requirements in male and female cats". American Journal of Veterinary Research. 63 (5). American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA): 634–639. doi:10.2460/ajvr.2002.63.634. ISSN 0002-9645. PMID 12013460.
- ^ Harper, E. J.; Stack, D. M.; Watson, T. D. G.; Moxham, G. (2001). "Effects of feeding regimens on bodyweight, composition and condition score in cats following ovariohysterectomy". Journal of Small Animal Practice. 42 (9). Wiley: 433–438. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5827.2001.tb02496.x. ISSN 0022-4510. PMID 11570385.
- ^ a b Fettman, M.J; Stanton, C.A; Banks, L.L; Hamar, D.W; Johnson, D.E; Hegstad, R.L; Johnston, S (1997). "Effects of neutering on bodyweight, metabolic rate and glucose tolerance of domestic cats". Research in Veterinary Science. 62 (2). Elsevier BV: 131–136. doi:10.1016/s0034-5288(97)90134-x. ISSN 0034-5288. PMID 9243711.
- ^ Kanchuk, Marc L.; Backus, Robert C.; Morris, James G.; Rogers, Quinton R.; Calvert, Christopher C. (2003). "Weight Gain in Gonadectomized Normal and Lipoprotein Lipase–Deficient Male Domestic Cats Results from Increased Food Intake and Not Decreased Energy Expenditure". The Journal of Nutrition. 133 (6). Elsevier BV: 1866–1874. doi:10.1093/jn/133.6.1866. ISSN 0022-3166. PMID 12771331.
- ^ Öhlund, Malin; Palmgren, Malin; Holst, Bodil Ström (19 January 2018). "Overweight in adult cats: a cross-sectional study". Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica. 60 (1): 5. doi:10.1186/s13028-018-0359-7. ISSN 1751-0147. PMC 5775588. PMID 29351768.
- ^ Murray, J. K.; Skillings, E.; Gruffydd-Jones, T. J. (2008). "Opinions of veterinarians about the age at which kittens should be neutered". Veterinary Record. 163 (13): 381–385. doi:10.1136/vr.163.13.381. ISSN 0042-4900. PMID 18820325.
- ^ O'Brien, S. J.; Johnson, W.; Driscoll, C.; Pontius, J.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Menotti-Raymond, M. (2008). "State of Cat Genomics". Trends in Genetics. 24 (6): 268–279. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2008.03.004. PMC 7126825. PMID 18471926.
- ^ Sewell, A. C.; Haskins, M. E.; Giger, U. (2007). "Inherited Metabolic Disease in Companion Animals: Searching for Nature's Mistakes". Veterinary Journal. 174 (2): 252–259. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2006.08.017. PMC 3132193. PMID 17085062.
- ^ O'Brien, S. J.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Murphy, W. J.; Yuhki, N. (2002). "The Feline Genome Project". Annual Review of Genetics. 36: 657–686. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.36.060602.145553. PMID 12359739. Archived from the original on 5 October 2019. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
- ^ Huston, L. (2012). "Veterinary Care for Your New Cat". PetMD. Archived from the original on 8 May 2017. Retrieved 31 January 2017.
- ^ Say, L. (2002). "Spatio-temporal variation in cat population density in a sub-Antarctic environment". Polar Biology. 25 (2): 90–95. Bibcode:2002PoBio..25...90S. doi:10.1007/s003000100316. S2CID 22448763.
- ^ Frenot, Y.; Chown, S. L.; Whinam, J.; Selkirk, P. M.; Convey, P.; Skotnicki, M.; Bergstrom, D. M. (2005). "Biological Invasions in the Antarctic: Extent, Impacts and Implications". Biological Reviews. 80 (1): 45–72. doi:10.1017/S1464793104006542. PMID 15727038. S2CID 5574897.
- ^ Medina, F. M.; Bonnaud, E.; Vidal, E.; Tershy, B. R.; Zavaleta, E.; Josh Donlan, C.; Keitt, B. S.; Le Corre, M.; Horwath, S. V.; Nogales, M. (2011). "A global review of the impacts of invasive cats on island endangered vertebrates". Global Change Biology. 17 (11): 3503–3510. Bibcode:2011GCBio..17.3503M. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.701.4082. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02464.x. S2CID 323316.
- ^ Nogales, M.; Martin, A.; Tershy, B. R.; Donlan, C. J.; Veitch, D.; Uerta, N.; Wood, B.; Alonso, J. (2004). "A Review of Feral Cat Eradication on Islands" (PDF). Conservation Biology. 18 (2): 310–319. Bibcode:2004ConBi..18..310N. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1739.2004.00442.x. hdl:10261/22249. S2CID 11594286. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 December 2019. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ^ Invasive Species Specialist Group (2006). "Ecology of Felis catus". Global Invasive Species Database. Species Survival Commission, International Union for Conservation of Nature. Archived from the original on 27 October 2009. Retrieved 31 August 2009.
- ^ Le Roux, Johannes J.; Foxcraft, Llewellyn C.; Herbst, Marna; Macfadyen, Sandra (19 August 2014). "Genetic analysis shows low levels of hybridization between African wildcats (Felis silvestris lybica) and domestic cats (F. s. catus) in South Africa". Ecology and Evolution. 5 (2): 288–299. doi:10.1002/ece3.1275. PMC 4314262. PMID 25691958. Archived from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ a b Doherty, T. S.; Glen, A. S.; Nimmo, D. G.; Ritchie, E. G.; Dickman, C. R. (2016). "Invasive predators and global biodiversity loss". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (40): 11261–11265. Bibcode:2016PNAS..11311261D. doi:10.1073/pnas.1602480113. PMC 5056110. PMID 27638204.
- ^ a b Rochlitz, I. (2007). The Welfare of Cats. "Animal Welfare" series. Berlin: Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 141–175. ISBN 9781402061431. OCLC 262679891.
- ^ "What is the difference between a stray cat and a feral cat?". HSUS.org. Humane Society of the United States. 2 January 2008. Archived from the original on 1 May 2008.
- ^ "Torre Argentina cat shelter". Archived from the original on 22 January 2009. Retrieved 17 June 2009.
- ^ Slater, Margaret R.; Shain, Stephanie (November 2003). "Feral Cats: An Overview (4)" (PDF). In Rowan, Andrew N.; Salem, Deborah J. (eds.). The State of the Animals II: 2003. Humane Society of the United States. ISBN 9780965894272. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 November 2006.
- ^ Fitzgerald, M. B.; Turner, Dennis C. "Hunting Behaviour of Domestic Cats and Their Impact on Prey Populations". In Turner, Dennis C.; Bateson, Patrick P. G. (eds.). The Domestic Cat: The Biology of its Behaviour. pp. 151–175.
- ^ Courchamp, F.; Langlais, M.; Sugihara, G. (1999). "Cats protecting birds: Modelling the mesopredator release effect". Journal of Animal Ecology. 68 (2): 282–292. Bibcode:1999JAnEc..68..282C. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2656.1999.00285.x. S2CID 31313856.
- ^ Stattersfield, A. J.; Crosby, M. J.; Long, A. J.; Wege, D. C. (1998). Endemic Bird Areas of the World: Priorities for Biodiversity Conservation. "BirdLife Conservation" series No. 7. Cambridge, England: Burlington Press. ISBN 9780946888337.
- ^ Falla, R. A. (1955). New Zealand Bird Life Past and Present. Cawthron Institute.[page needed]
- ^ Galbreath, R.; Brown, D. (2004). "The Tale of the Lighthouse-keeper's Cat: Discovery and Extinction of the Stephens Island Wren (Traversia lyalli)" (PDF). Notornis. 51: 193–200. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 October 2008.
- ^ Scrimgeour, J.; Beath, A.; Swanney, M. (2012). "Cat predation of short-tailed bats (Mystacina tuberculata rhyocobia) in Rangataua Forest, Mount Ruapehu, Central North Island, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Zoology. 39 (3): 257–260. doi:10.1080/03014223.2011.649770.
- ^ Woinarski, J. C. Z.; Murphy, B. P.; Palmer, R.; Legge, S. M.; Dickman, C. R.; Doherty, T. S.; Edwards, G.; Nankivell, A.; Read, J. L.; Stokeld, D. (2018). "How many reptiles are killed by cats in Australia?". Wildlife Research. 45 (3). CSIRO Publishing: 247. doi:10.1071/wr17160. ISSN 1035-3712.
- ^ Wade, N. (2007). "Study Traces Cat's Ancestry to Middle East". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 18 April 2009. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- ^ "Pet Industry Market Size & Ownership Statistics". American Pet Products Association. Archived from the original on 25 February 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2019.
- ^ "The 5 Most Expensive Cat Breeds in America". moneytalksnews.com. 2017. Archived from the original on 25 February 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2019.
- ^ "61 Fun Cat Statistics That Are the Cat's Meow! (2022 UPDATE)". 12 December 2020. Archived from the original on 18 February 2022. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ "How many pets are there in the UK?". PDSA.org.uk. Archived from the original on 3 March 2021. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- ^ "Statistics on cats". carocat.eu. 2021. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ Beadle, Muriel (1979). Cat. Simon and Schuster. pp. 93–96. ISBN 9780671251901.
- ^ Mayers, Barbara (2007). Toolbox: Ship's Cat on the Kalmar Nyckel. Bay Oak Publishers. ISBN 9780974171395. Archived from the original on 31 March 2021. Retrieved 17 July 2020.
- ^ "What Is That They're Wearing?" (PDF). Humane Society of the United States. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 December 2006. Retrieved 22 October 2009.
- ^ Stallwood, K. W., ed. (2002). A Primer on Animal Rights: Leading Experts Write about Animal Cruelty and Exploitation. Lantern Books.
- ^ "Japan: Finale for the world's most elegant use of a dead cat". The Independent. 15 November 1997. Archived from the original on 21 June 2017.
- ^ "EU proposes cat and dog fur ban". BBC News. 2006. Archived from the original on 2 January 2009. Retrieved 22 October 2009.
- ^ Ikuma, C. (2007). "EU Announces Strict Ban on Dog and Cat Fur Imports and Exports". Humane Society International. Archived from the original on 17 February 2009. Retrieved 14 December 2011.
- ^ Jolly, K. L.; Raudvere, C.; Peters, E. (2002). Witchcraft and Magic in Europe. Vol. 3: The Middle Ages. London: Athlone. ISBN 9780567574466. OCLC 747103210.
- ^ Paterson, T. (2008). "Switzerland Finds a Way to Skin a Cat for the Fur Trade and High Fashion". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 7 July 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2009.
- ^ "Humane society launches national cat census". CBC News. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 18 September 2012.
- ^ "Cats Be". Archived from the original on 22 September 2012. Retrieved 18 September 2012.
- ^ "The Supreme Cat Census". Archived from the original on 16 March 2012. Retrieved 18 September 2012.
- ^ "About Pets". IFAHEurope.org. Animal Health Europe. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 3 October 2014.
- ^ Legay, J. M. (1986). "Sur une tentative d'estimation du nombre total de chats domestiques dans le monde" [Tentative estimation of the total number of domestic cats in the world]. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série III (in French). 303 (17): 709–712. PMID 3101986. INIST 7950138.
- ^ Gehrt, S. D.; Riley, S. P. D.; Cypher, B. L. (2010). Urban Carnivores: Ecology, Conflict, and Conservation. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 9780801893896. Archived from the original on 31 December 2015. Retrieved 3 October 2014.
- ^ Rochlitz, I. (2007). The Welfare of Cats. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9781402032271. Archived from the original on 31 December 2015. Retrieved 3 October 2014.
- ^ "Cats: Most interesting facts about common domestic pets". Pravda. 9 January 2006. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 3 October 2014.
- ^ Sandomir, R. (18 January 2019). "Walter Chandoha, Photographer Whose Specialty Was Cats, Dies at 98". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 19 January 2019.
- ^ "The Rise of Pet Humanization" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 April 2024. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ "The Humanization of Pets". Archived from the original on 6 December 2023. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ a b c "All About Cat Shows". How Stuff Works. 2008. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- ^ a b Chomel, B. (2014). "Emerging and Re-Emerging Zoonoses of Dogs and Cats". Animals. 4 (3): 434–445. doi:10.3390/ani4030434. ISSN 2076-2615. PMC 4494318. PMID 26480316.
- ^ a b "Cats". Ohio Department of Health. 21 January 2015. Archived from the original on 27 November 2016. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ^ Goldstein, Ellie J. C.; Abrahamian, Fredrick M. (2015). "Diseases Transmitted by Cats". Microbiology Spectrum. 3 (5). doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.iol5-0013-2015. ISSN 2165-0497. PMID 26542039. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ Stull, J. W.; Brophy, J.; Weese, J. S. (2015). "Reducing the risk of pet-associated zoonotic infections". Canadian Medical Association Journal. 187 (10): 736–743. doi:10.1503/cmaj.141020. ISSN 0820-3946. PMC 4500695. PMID 25897046.
- ^ Malek, J. (1997). The Cat in Ancient Egypt (Revised ed.). University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 9780812216325.
- ^ Engels, D. W. (2001) [1999]. "Greece". Classical Cats: The Rise and Fall of the Sacred Cat. London: Routledge. pp. 48–87. ISBN 9780415261623.
- ^ Rogers, K. M. (2006). "Wildcat to Domestic Mousecatcher". Cat. London: Reaktion Books. pp. 7–48. ISBN 9781861892928. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ Beadle, M. (1977). "Ups and Downs". Cat. New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 75–88. ISBN 9780671224516.
- ^ Pate, A. (2008). "Maneki Neko: Feline Fact & Fiction". Daruma Magazine. Archived from the original on 14 March 2013.
- ^ Faulkes, A. (1995). Edda. p. 24. ISBN 9780460876162.
- ^ Ginzberg, L. (1909). The Legends of the Jews, Vol. I: The Sixth Day (PDF). Translated by Szold, H. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 May 2018. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- ^ Geyer, G. A. (2004). When Cats Reigned Like Kings: On the Trail of the Sacred Cats. Kansas City, Missouri: Andrews McMeel Publishing. ISBN 9780740746970.
- ^ Reeves, M. (2000). Muhammad in Europe. New York University Press. p. 52. ISBN 9780814775332.
- ^ Al-Thahabi, S. "Biography of al-Rifai". سير أعلام النبلاء (in Arabic). Archived from the original on 25 October 2014. Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- ^ Broad, Michael (13 January 2015). "Abu Hurairah and Cats". Pictures-of-Cats.org. Archived from the original on 5 March 2018. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ Clutton-Brock, J. (1999) [1987]. "Cats". A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals (2nd ed.). Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. pp. 133–140. ISBN 9780521634953. OCLC 39786571. Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
- ^ Adzo, K. (2015). "Are Black Cats Really Bad Luck? [Hoax]". Social News Daily. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- ^ Davies, N. (1996). Europe: A History. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 543. ISBN 9780198201717.
- ^ Frazer, J. G. (2002) [1922]. The Golden Bough: A Study in Magic and Religion (Abridged ed.). Mineola, New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 0486424928. OCLC 49942157. Archived from the original on 8 December 2006. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- ^ Sugobono, N. (2010). "Las vidas del gato". El Comercio (Peru) (in Spanish). Lima, Peru. Archived from the original on 27 January 2012. Retrieved 19 March 2010.
- ^ "Qual é a origem da lenda de que os gatos teriam sete vidas?". Mundo Estranho (in Brazilian Portuguese). São Paulo, Brazil: Abril Media. Archived from the original on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 15 November 2015.
- ^ Dowling, T. (2010). "Tall tails: Pet myths busted". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 9 September 2013. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ Heywood, J. (1874). Sharman, J. (ed.). The Proverbs of John Heywood. p. 104.
- ^ "Can Cats Cheat Death?". BeChewy. 6 October 2017. Archived from the original on 25 September 2023. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ^ "The ASPCA Warns About High-rise Falls by Cats: High-rise Apartments, Windows, Terraces and Fire Escapes Pose Risk to Urban Cats". New York: American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals. 2005. Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 6 June 2018 – via About.com. (Press release.)
External links
 The dictionary definition of cat at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of cat at Wiktionary Data related to Felis catus at Wikispecies
Data related to Felis catus at Wikispecies Media related to Felis silvestris catus at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Felis silvestris catus at Wikimedia Commons Animal Care at Wikibooks
Animal Care at Wikibooks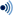 Quotations related to Cat at Wikiquote
Quotations related to Cat at Wikiquote- . Encyclopedia Americana. 1920.
- Biodiversity Heritage Library bibliography for Felis catus
- View the cat genome in Ensembl
- High-resolution images of the cat's brain
- Scientific American. "The Origin of the Cat". 1881. p. 120.







![The ancient Egyptians mummified dead cats out of respect in the same way that they mummified people.[240]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/87/Louvre_egyptologie_21.jpg/300px-Louvre_egyptologie_21.jpg)


