North Anatolian Fault: Difference between revisions
completing reference |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| image_alt = The North Anatolian Fault and slip magnitudes of earthquakes in the 20th century |
| image_alt = The North Anatolian Fault and slip magnitudes of earthquakes in the 20th century |
||
| image_caption = The North Anatolian Fault and slip magnitudes of earthquakes in the 20th century |
| image_caption = The North Anatolian Fault and slip magnitudes of earthquakes in the 20th century |
||
| pushpin_map = |
| pushpin_map = |
||
| pushpin_map_width = |
| pushpin_map_width = |
||
| pushpin_map_caption = |
| pushpin_map_caption = |
||
| pushpin_map_alt = |
| pushpin_map_alt = |
||
| pushpin_relief = |
| pushpin_relief = |
||
| pushpin_map_label = |
| pushpin_map_label = |
||
| pushpin_label_position = |
| pushpin_label_position = |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| dip_angle = |
| dip_angle = |
||
| displacement = |
| displacement = |
||
| plate = [[Anatolian |
| plate = [[Anatolian sub-plate]], [[Eurasian plate]] |
||
| status = Active |
| status = Active |
||
| earthquakes = [[List of earthquakes in Turkey]] |
| earthquakes = [[List of earthquakes in Turkey]] |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''North Anatolian Fault''' ('''NAF''' |
The '''North Anatolian Fault''' ('''NAF'''; {{langx|tr| Kuzey Anadolu Fay Hattı}}) is an active right-lateral [[Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults|strike-slip fault]] in northern [[Anatolia]], and is the [[Transform fault|transform]] boundary between the [[Eurasian plate]] and the [[Anatolian sub-plate]]. The fault extends westward from a junction with the [[East Anatolian Fault]] at the [[Karliova triple junction]] in eastern [[Turkey]], across northern Turkey and into the [[Aegean Sea]] for a length of 1200<ref name="Sengor_etal_2005">{{Cite journal |last1= Şengör |first1=A.M.C. |last2=Tüysüz |first2=O. |last3=İmren |first3=C. |last4=Sakınç |first4=M. |last5=Eyidoğan |first5=H. |last6=Görür |first6=N. |last7=Le Pichon |first7=X. |last8=Rangin |first8=C. |year=2005 |title=The North Anatolian Fault: A new look |journal=Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences |volume=33 |pages=37–112 |doi=10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120415|bibcode=2005AREPS..33...37S }}</ref>−1500 kilometers.<ref>{{cite web |last=Caperton Morton |first=Mary |title=Closing Istanbul's seismic gap |url=http://www.earthmagazine.org/article/closing-istanbuls-seismic-gap |website=earthmagazine.org |date=8 March 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200808153559/http://www.earthmagazine.org/article/closing-istanbuls-seismic-gap |archive-date=2020-08-08 |access-date=2020-08-08 |quote="The North Anatolian Fault is a 1,500-kilometer-long east-west trending fault that runs across most of Turkey."}}</ref> It runs about 20 km south of [[Istanbul]]. |
||
The North Anatolian Fault is similar in many ways to the [[San Andreas Fault]] in California. Both are continental [[Transform fault|transforms]] with similar lengths and slip rates. The [[Sea of Marmara]] near [[Istanbul]] is an extensional basin similar to the [[Salton Trough]] in California, where a [[Transtension#Releasing bend|releasing bend]] in the strike |
The North Anatolian Fault is similar in many ways to the [[San Andreas Fault]] in California. Both are continental [[Transform fault|transforms]] with similar lengths and slip rates. The [[Sea of Marmara]] near [[Istanbul]] is an extensional basin similar to the [[Salton Trough]] in California, where a [[Transtension#Releasing bend|releasing bend]] in the strike slip system creates a [[pull-apart basin]]. |
||
==Significant earthquakes== |
==Significant earthquakes== |
||
{{see also|List of earthquakes in Turkey}} |
{{see also|List of earthquakes in Turkey}} |
||
Since the disastrous [[1939 Erzincan earthquake]], there have been seven [[earthquake]]s measuring over 7.0 in magnitude,<ref>USGS Worldwide Earthquake List. https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/map/</ref> each happening at a point progressively further west.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Progressive failure on the North Anatolian fault since 1939 by earthquake stress triggering|first1=R. S.|last1=Stein|author-link=Ross Stein|first2=A. A.|last2=Barka|author-link2=Aykut Barka|first3=J. H.|last3=Dieterich|year=1997|journal=[[Geophysical Journal International]]|volume=128|issue=3|pages=594–604|doi=10.1111/j.1365-246x.1997.tb05321.x|bibcode=1997GeoJI.128..594S |doi-access= |
Since the disastrous [[1939 Erzincan earthquake]], there have been seven [[earthquake]]s measuring over 7.0 in magnitude,<ref>USGS Worldwide Earthquake List. https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/map/</ref> each happening at a point progressively further west.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Progressive failure on the North Anatolian fault since 1939 by earthquake stress triggering|first1=R. S.|last1=Stein|author-link=Ross Stein|first2=A. A.|last2=Barka|author-link2=Aykut Barka|first3=J. H.|last3=Dieterich|year=1997|journal=[[Geophysical Journal International]]|volume=128|issue=3|pages=594–604|doi=10.1111/j.1365-246x.1997.tb05321.x|bibcode=1997GeoJI.128..594S |doi-access=}}</ref> [[Seismologist]]s studying this pattern believe that each earthquake may trigger the next.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/horizon/2003/earthquakestorms.shtml | title = Earthquake Storms | work = [[Horizon (BBC TV series)|Horizon]] | date = April 1, 2003 | access-date = 2007-05-02 }}</ref> By analyzing the stresses along the fault caused by each large earthquake, they were able to predict{{quantify|date=December 2021}}<!-- How far in advance and with what precision? [[Earthquake prediction]] says individual earthquakes aren't predictable. --> [[1999 İzmit earthquake|the shock]] that hit the town of [[İzmit]] with devastating effect in August 1999. It is thought that the chain is not complete, and that an earthquake will soon strike further west along the fault – perhaps near the heavily populated city of Istanbul. |
||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
! [[Moment magnitude scale|Moment magnitude]] |
! [[Moment magnitude scale|Moment magnitude]] |
||
! Casualties |
! Casualties |
||
|- |
|||
| [[1929 Suşehri earthquake|1929 Suşehri]] |
|||
| 6.3 |
|||
| 64 dead<ref name="Demirtaş">{{cite report |last1=Demirtaş |first1=Ramazan |title=Kuzey Anadolu Fay Sistemi Diri Fayları ve Deprem Etkinlikleri Paleosismolojik Çalışmalar ve Gelecek Deprem Potansiyelleri |trans-title=Northern Anatolian Fault System Active Faults and Earthquake Activities Paleoseismological Studies and Future Earthquake Potentials |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331772444 |date=2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210509141911/https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ramazan-Demirtas/publication/331772444_Kuzey_Anadolu_Fay_Sistemi_Diri_Faylari_ve_Deprem_Etkinlikleri_Paleosismolojik_Calismalar_ve_Gelecek_Deprem_Potansiyelleri/links/5c8b635792851c1df941bc74/Kuzey-Anadolu-Fay-Sistemi-Diri-Faylari-ve-Deprem-Etkinlikleri-Paleosismolojik-Calismalar-ve-Gelecek-Deprem-Potansiyelleri.pdf?origin=publication_detail |archive-date=9 May 2021 |language=tr |doi=10.13140/RG.2.2.36608.69125}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[1939 Erzincan earthquake|1939 Erzincan]] |
| [[1939 Erzincan earthquake|1939 Erzincan]] |
||
| Line 111: | Line 115: | ||
| [[1999 İzmit earthquake|1999 İzmit]] |
| [[1999 İzmit earthquake|1999 İzmit]] |
||
| 7.6 |
| 7.6 |
||
| |
| 18,373 dead and 43,953+ injured |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[1999 Düzce earthquake|1999 Düzce]] |
| [[1999 Düzce earthquake|1999 Düzce]] |
||
| Line 132: | Line 136: | ||
[[Category:Supershear earthquakes]] |
[[Category:Supershear earthquakes]] |
||
[[Category:Strike-slip earthquakes]] |
[[Category:Strike-slip earthquakes]] |
||
[[Category:Plate tectonics]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 18:34, 8 January 2025
| North Anatolian Fault | |
|---|---|
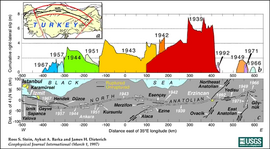 The North Anatolian Fault and slip magnitudes of earthquakes in the 20th century | |
 The North Anatolian and neighbouring faults covering most of Turkey | |
| Coordinates | 41°00′N 35°00′E / 41.000°N 35.000°E |
| Country | |
| Region | Marmara Region, Black Sea Region, Eastern Anatolia Region |
| Cities | Istanbul, Bursa, Bolu, Tokat, Erzincan, Erzurum |
| Characteristics | |
| Elevation | 3,937 metres (12,917 ft) |
| Top depth | 1,370 metres (4,495 ft) |
| Range | Pontic Mountains, Köroğlu Mountains |
| Length | 1,500 kilometres (900 mi) |
| Strike | E-W |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | Anatolian sub-plate, Eurasian plate |
| Status | Active |
| Earthquakes | List of earthquakes in Turkey |
| Type | strike-slip fault |
The North Anatolian Fault (NAF; Turkish: Kuzey Anadolu Fay Hattı) is an active right-lateral strike-slip fault in northern Anatolia, and is the transform boundary between the Eurasian plate and the Anatolian sub-plate. The fault extends westward from a junction with the East Anatolian Fault at the Karliova triple junction in eastern Turkey, across northern Turkey and into the Aegean Sea for a length of 1200[1]−1500 kilometers.[2] It runs about 20 km south of Istanbul. The North Anatolian Fault is similar in many ways to the San Andreas Fault in California. Both are continental transforms with similar lengths and slip rates. The Sea of Marmara near Istanbul is an extensional basin similar to the Salton Trough in California, where a releasing bend in the strike slip system creates a pull-apart basin.
Significant earthquakes
[edit]Since the disastrous 1939 Erzincan earthquake, there have been seven earthquakes measuring over 7.0 in magnitude,[3] each happening at a point progressively further west.[4] Seismologists studying this pattern believe that each earthquake may trigger the next.[5] By analyzing the stresses along the fault caused by each large earthquake, they were able to predict[quantify] the shock that hit the town of İzmit with devastating effect in August 1999. It is thought that the chain is not complete, and that an earthquake will soon strike further west along the fault – perhaps near the heavily populated city of Istanbul.
| Event | Moment magnitude | Casualties |
|---|---|---|
| 1929 Suşehri | 6.3 | 64 dead[6] |
| 1939 Erzincan | 7.8 | 32,700+ dead and 100,000+ injured |
| 1942 Niksar–Erbaa | 7.0 | ~3,000 dead |
| 1943 Tosya–Ladik | 7.2 | 2,824 dead |
| 1944 Bolu–Gerede | 7.2 | 3,959 dead |
| 1949 Karlıova | 6.7 | 320 dead |
| 1951 Kurşunlu | 6.9 | 50 dead and 3,354 injured |
| 1957 Abant | 7.1 | 52 dead |
| 1966 Varto | 6.9 | 2,394 dead and 1,489 injured |
| 1967 Mudurnu Valley | 7.1 | 86 dead, 332 injured |
| 1992 Erzincan | 6.7 | 498+ dead and 2,000+ injured |
| 1999 İzmit | 7.6 | 18,373 dead and 43,953+ injured |
| 1999 Düzce | 7.2 | 845+ dead and 4,948 injured |
| 2022 Düzce | 6.1 | 2 dead and 93 injured |
Notes
[edit]- ^ Şengör, A.M.C.; Tüysüz, O.; İmren, C.; Sakınç, M.; Eyidoğan, H.; Görür, N.; Le Pichon, X.; Rangin, C. (2005). "The North Anatolian Fault: A new look". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 33: 37–112. Bibcode:2005AREPS..33...37S. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120415.
- ^ Caperton Morton, Mary (8 March 2010). "Closing Istanbul's seismic gap". earthmagazine.org. Archived from the original on 2020-08-08. Retrieved 2020-08-08.
The North Anatolian Fault is a 1,500-kilometer-long east-west trending fault that runs across most of Turkey.
- ^ USGS Worldwide Earthquake List. https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/map/
- ^ Stein, R. S.; Barka, A. A.; Dieterich, J. H. (1997). "Progressive failure on the North Anatolian fault since 1939 by earthquake stress triggering". Geophysical Journal International. 128 (3): 594–604. Bibcode:1997GeoJI.128..594S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246x.1997.tb05321.x.
- ^ "Earthquake Storms". Horizon. April 1, 2003. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ Demirtaş, Ramazan (2019). Kuzey Anadolu Fay Sistemi Diri Fayları ve Deprem Etkinlikleri Paleosismolojik Çalışmalar ve Gelecek Deprem Potansiyelleri [Northern Anatolian Fault System Active Faults and Earthquake Activities Paleoseismological Studies and Future Earthquake Potentials] (PDF) (Report) (in Turkish). doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.36608.69125. Archived from the original on 9 May 2021.
