Shoe: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Add: publisher, authors 1-1. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Spinixster | Category:Shoes | #UCB_Category 22/95 |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Footwear}} |
|||
{{otheruses}} |
|||
{{About|footwear}} |
|||
{{Redirect|Insole}} |
|||
{{pp|small=yes}} |
|||
[[File:Skor från 1700- till 1960-talet - Nordiska Museet - NMA.0056302.jpg|thumb|275px|alt=Three blue shelves on a black background. The top shelf displays a pair of pink high heels, a wedge sandal and a dance heel shoe. The middle shelf displays a variety of low-heeled, slipper-type shoes. The bottom shelf displays two antique heeled shoes and a pair of kid's shoes.|A variety of shoes displayed at the [[Nordic Museum]], including models from 1700 to the 1960s.]] |
|||
A '''shoe''' is an item of [[footwear]] |
A '''shoe''' is an item of [[footwear]] intended to protect and comfort the human [[foot]]. Though the human foot can adapt to varied terrains and climate conditions, it is vulnerable, and shoes provide protection. Form was originally tied to function, but over time, shoes also became fashion items. Some shoes are worn as safety equipment, such as [[steel-toe boots]], which are required footwear at industrial worksites. |
||
Additionally, shoes have often evolved into many different designs, such as [[High-heeled shoe|high heels]], which are most commonly worn by women during fancy occasions. Contemporary footwear varies vastly in style, complexity and cost. Basic [[sandal]]s may consist of only a thin [[sole (shoe)|sole]] and simple strap and be sold for a low cost. High fashion shoes made by famous [[Fashion design|designers]] may be made of expensive materials, use complex construction and sell for large sums of money. Some shoes are designed for specific purposes, such as [[boot]]s designed specifically for [[Mountaineering boot|mountaineering]] or [[Ski boot|skiing]], while others have more generalized usage such as [[sneakers]] which have transformed from a special purpose sport shoe into a general use shoe. |
|||
[[Image:Lotsofshoes.JPG|thumb|300px|Women's shoes on display in a shop window, [[July 2005]]]] |
|||
Traditionally, shoes have been made from [[leather]], [[wood]] or [[canvas]], but are increasingly being made from [[Synthetic rubber|rubber]], [[plastic]]s, and other [[petrochemical]]-derived materials.<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|last=Hoskins|first=Tansy E.|date=2020-03-21|title='Some soles last 1,000 years in landfill': the truth about the sneaker mountain|url=http://www.theguardian.com/fashion/2020/mar/21/some-soles-last-1000-years-in-landfill-the-truth-about-the-sneaker-mountain|access-date=2021-02-19|website=The Guardian|language=en}}</ref> Globally, the shoe industry is a $200 billion a year industry.<ref name=":0" /> 90% of shoes end up in landfills, because the materials are hard to separate, recycle or otherwise reuse.<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
==Parts of a shoe== |
|||
the sole of the shoe is the best way to get calcium which will use almost none of your health. |
|||
The bottom of a shoe is named the [[sole]]. It consists of several layers, and is usually a separate piece from the upper shoe (though not always, as in the case of wooden shoes). |
|||
==== Insole ==== |
|||
The insole is the interior bottom of the shoe, which sits directly beneath the foot. Many shoes have removable and replaceable insoles, and extra insoles are often added for comfort or health reasons (to control the shape, moisture, or smell of the shoe). |
|||
== History == |
|||
The outsole is the layer in direct contact with the ground. The material of the outsole depends on the function, dressiness, and quality of the shoe, but is generally very durable material, since it experiences the most stress. Dressier shoes have [[leather]] outsoles; casual or work-oriented shoes have outsoles made of natural [[rubber]] or a synthetic imitation or in the case of ballet shoes - cardboard. The outsole may comprise a single piece, or may comprise separate pieces of different materials. Often the heel of the sole is rubber for durability and traction, while the front is leather for style. Specialized shoes will often have modifications on this design: athletic [[cleats]] have spikes embedded in the outsole to grip the ground; many kinds of [[dancing]] shoes have much softer or harder soles. |
|||
=== |
=== Antiquity === |
||
The bottom rear part of a shoe is the heel. These come in a variety of sizes and are usually made to support the large stresses applied to the heel of the foot. They are often made of the same material as the sole of the shoe. |
|||
[[File:Chalcolithic leather shoe from Areni-1 cave.jpg|thumb|upright|The [[Areni-1 shoe|oldest known leather shoe]], about 5500 years old, found in [[Armenia]] ]] |
|||
=== Vamp, or upper === |
|||
[[File:Sandalias de esparto (29139609730).jpg|thumb|[[Esparto]] sandals from the [[6th millennium BC|6th]] or [[5th millennium BC]] found in [[Spain]] ]] |
|||
Any shoe has an upper part that helps hold the shoe onto the foot. In the simplest cases, such as [[sandal]]s or [[flip flop]]s, this may be nothing more than a few straps for holding the sole in place. Closed footwear, such as boots, sneakers and most men's shoes, will usually have a more complex upper.''''''also have been dien down since 100 b.c'''''' |
|||
[[File:Romanwallinscotl00macduoft raw 0263.png|thumb|right|Roman shoes: a man's,<ref>{{cite web|title=The Scottish Ten|url=https://www.engineshed.org/about-us/the-scottish-ten/sites/antonine-wall-scotland/|website=The Engine Shed|publisher=Centre for Digital Documentation and Visualisation LLP|access-date=14 October 2017}}</ref> a woman's<ref>{{cite web|title=Lady's Shoe, Bar Hill|url=https://vimeo.com/140404027|access-date=24 May 2018|date=2015-09-25}}</ref> and a child's<ref>{{cite web|title=Child's Shoe, Bar Hill|url=https://vimeo.com/140054166|access-date=24 May 2018|date=2015-09-22}}</ref> shoe from [[Bar Hill Fort|Bar Hill Roman Fort]], Scotland.]] |
|||
=== |
====Earliest evidence==== |
||
The earliest known shoes are sagebrush bark [[sandal]]s [[carbon dating|dating]] from approximately 7000 or 8000 BC, found in the [[Fort Rock Cave]] in the [[United States|US]] state of [[Oregon]] in 1938.<ref name="Connolly_Tom">{{cite web|last=Connolly|first=Tom|title=The World's Oldest Shoes|url=http://pages.uoregon.edu/connolly/FRsandals.htm|publisher=[[University of Oregon]]|access-date=July 22, 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120722013744/http://pages.uoregon.edu/connolly/FRsandals.htm|archive-date=July 22, 2012}}</ref> The world's [[Areni-1 shoe|oldest leather shoe]], made from a single piece of cowhide laced with a leather cord along seams at the front and back, was found in the [[Areni-1 cave complex]] in [[Armenia]] in 2008 and is believed to date to 3500 BC.<ref name="Ravilious_Kate">{{cite news|last=Ravilious|first=Kate|title=World's Oldest Leather Shoe Found—Stunningly Preserved|url=http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2010/06/100609-worlds-oldest-leather-shoe-armenia-science/|access-date=July 22, 2012|newspaper=[[National Geographic (magazine)|National Geographic]]|date=June 9, 2010|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120724020516/http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2010/06/100609-worlds-oldest-leather-shoe-armenia-science/|archive-date=July 24, 2012}}</ref><ref name="Petraglia_Michael">{{cite journal|last1=Petraglia|first1=Michael D.|author2=Pinhasi R|author3=Gasparian B|author4=Areshian G|author5=Zardaryan D|author6=Smith A|title=First Direct Evidence of Chalcolithic Footwear from the Near Eastern Highlands|journal=PLOS ONE|volume=5|pages=e10984|year=2010|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0010984|editor1-last=Petraglia|editor1-first=Michael D.|issue=6|pmid=20543959|pmc=2882957|display-authors=etal|bibcode=2010PLoSO...510984P|doi-access=free}} Reported in (among others) {{cite news|last=Belluck|first=Pam|title=This Shoe Had Prada Beat by 5,500 Years|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/06/10/science/10shoe.html|access-date=11 June 2010|newspaper=[[The New York Times]]|date=9 June 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100611103130/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/06/10/science/10shoe.html|archive-date=11 June 2010}}</ref> [[Ötzi the Iceman]]'s shoes, dating to 3300 BC, featured brown bearskin bases, deerskin side panels, and a bark-string net, which pulled tight around the foot.<ref name="Ravilious_Kate" /> The [[Jotunheimen shoe]] was discovered in August 2006: archaeologists estimate that this leather shoe was made between 1800 and 1100 BC,<ref name="Nesje Pilø Finstad Solli ">{{cite journal | last1=Nesje | first1=Atle | last2=Pilø | first2=Lars Holger | last3=Finstad | first3=Espen | last4=Solli | first4=Brit | last5=Wangen | first5=Vivian | last6=Ødegård | first6=Rune Strand | last7=Isaksen | first7=Ketil | last8=Støren | first8=Eivind N. | last9=Bakke | first9=Dag Inge | last10=Andreassen | first10=Liss M | title=The climatic significance of artefacts related to prehistoric reindeer hunting exposed at melting ice patches in southern Norway | journal=The Holocene | volume=22 | issue=4 | date=2011 | issn=0959-6836 | doi=10.1177/0959683611425552 | pages=485–496| s2cid=129845949 }}</ref><ref>[http://www.norwaypost.no/index.php/culture/13871 "Old Shoe- Even Older".] ''The Norway Post'', 2 May 2007. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160308201631/http://norwaypost.no/index.php/culture/13871 |date=8 March 2016 }}</ref> making it the oldest article of clothing discovered in Scandinavia. Sandals and other plant fiber based tools were found in [[Cueva de los Murciélagos]] in [[Albuñol]] in southern Spain in 2023, dating to approximately 7500 to 4200 BC, making them what are believed to be the oldest shoes found in Europe.<ref name="Science Advances">{{cite journal|title=The earliest basketry in southern Europe: Hunter-gatherer and farmer plant-based technology in Cueva de los Murciélagos (Albuñol)|journal=Science Advances|volume=9|issue=39|doi=10.1126/sciadv.adi3055|date=27 Sep 2023|author=Francisco Martínez-Sevilla|pages=eadi3055 |pmid=37756397 |pmc=10530072 |bibcode=2023SciA....9I3055M |display-authors=etal|doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
the string in the shoes |
|||
It is thought that shoes may have been used long before this, but because the materials used were highly perishable, it is difficult to find evidence of the earliest footwear.<ref name="Johnson_Olivia">{{cite news|last=Johnson|first=Olivia|title=Bones Reveal First Shoe-Wearers|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/4173838.stm|access-date=July 23, 2012|newspaper=[[BBC News]]|date=August 24, 2005|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120603011525/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/4173838.stm|archive-date=June 3, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
=== Tongue === |
|||
In some shoes and boots the tongue is a flap-like, usually flexible, part that goes underneath the laces. |
|||
[[Footprints]] suggestive of shoes or sandals due to having crisp edges, no signs of toes found and three small divots where leather tying laces/straps would have been attached have been at [[Garden Route National Park]], [[Addo Elephant National Park]] and [[Goukamma Marine Protected Area|Goukamma Nature Reserve]] in [[South Africa]].<ref name="Helm Lockley Cawthra De Vynck ">{{cite journal | last1=Helm | first1=Charles W. | last2=Lockley | first2=Martin G. | last3=Cawthra | first3=Hayley C. | last4=De Vynck | first4=Jan C. | last5=Dixon | first5=Mark G. | last6=Rust | first6=Renée | last7=Stear | first7=Willo | last8=Van Tonder | first8=Monique | last9=Zipfel | first9=Bernhard | title=Possible shod-hominin tracks on South Africa's Cape coast | journal=Ichnos | date=2023| volume=30 | issue=2 | issn=1042-0940 | doi=10.1080/10420940.2023.2249585 | pages=79–97| bibcode=2023Ichno..30...79H | s2cid=261313433 }}</ref> These date back to between 73,000 and 136,000 PB. Consistent with the existence of such shoe is the finding of [[Bone tool|bone awls]] dating back to this period that could have made simple footwear.<ref name="Helm Lockley Cawthra De Vynck " /> |
|||
== Accessories to shoes == |
|||
*[[shoe horn]] - can be used to insert a [[foot]] into a shoe by keeping the shoe open and providing a smooth surface for the foot to slide upon. |
|||
*[[shoe tree]] - placed inside the shoe when user is not wearing it, to help maintain the shoe's shape |
|||
*shoe polishing equipment - used for [[boot]]s also |
|||
:*shoe polish - a material spread on shoes to improve appearance, glossiness, and provide protection |
|||
:*polishing cloth - a piece of fabric used to apply polish to the shoe |
|||
*overshoes - a rubber covering placed over shoes for rain and snow protection |
|||
*orthotic insert - inserts for cushioning, improved fitting, or reduced abrasion. These include padding and inner linings. The insert may also be for the correction of foot problems |
|||
*shoe bag - a bag that protects the shoes against damage when packed in the bag |
|||
*[[shoe insert]]s |
|||
*shoe stretcher - a tool for making a shoe longer or wider or for reducing discomfort in areas of a shoe. |
|||
Another source of evidence is the study of the bones of the smaller toes (as opposed to the big toe), it was observed that their thickness decreased approximately 40,000 to 26,000 years ago. This led [[archaeologist]]s to deduce the existence of common rather than an occasional wearing of shoes as this would lead to less bone growth, resulting in shorter, thinner toes.<ref name="Trinkaus_Erik">{{cite journal|author1=Trinkaus, E. |author2=Shang, H. |title=Anatomical Evidence for the Antiquity of Human Footwear: Tianyuan and Sunghir|journal=Journal of Archaeological Science|date=July 2008|volume=35|issue=7|pages=1928–1933|doi=10.1016/j.jas.2007.12.002|bibcode=2008JArSc..35.1928T }}</ref> These earliest designs were very simple, often mere "foot bags" of leather to protect the feet from rocks, debris, and cold. |
|||
==Purpose of shoes== |
|||
Shoes fall into one of the following categories: dress, casual, work, snow, athletic and boots. |
|||
=== |
==== Americas ==== |
||
Many early natives in North America wore a similar type of footwear, known as the [[moccasin]]. These are tight-fitting, soft-soled shoes typically made out of leather or [[bison]] hides. Many moccasins were also decorated with various beads and other adornments. Moccasins were not designed to be waterproof, and in wet weather and warm summer months, most [[Indigenous peoples of the Americas|Native Americans]] went [[barefoot]].<ref name="Laubin_Laubin_Vestal">{{cite book|author1=Laubin, Reginald|author2=Laubin, Gladys|author3=Vestal, Stanley|title=The Indian Tipi: Its History, Construction, and Use|year=1977|publisher=University of Oklahoma Press|location=[[Norman, Oklahoma]]|isbn=978-0-8061-2236-6|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=koVdBGjlz8gC&pg=PA101|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180427210304/https://books.google.com/books?id=koVdBGjlz8gC&pg=PA101|archive-date=2018-04-27}}</ref> The leaves of the [[sisal]] plant were used to make [[twine]] for sandals in South America while the natives of Mexico used the [[Yucca]] plant.<ref name="Curtin_Cameron">{{cite book |last=Kippen |first=Cameron |title=The History of Footwear |publisher=Department of Podiatry, Curtin University of Technology |year=1999 |location=[[Perth]], [[Australia]]}}</ref><ref name="DeMello_Margo">{{cite book |last=DeMello |first=Margo |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5QdKSxajwP0C&pg=PA131 |title=Feet and Footwear: A Cultural Encyclopedia |publisher=ABC-CLIO, LLC |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-313-35714-5 |location=[[Santa Barbara, California]] |pages=20–24, 90, 108, 130–131, 226–230}}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Leather-Shoes.jpg|thumb|Casual shoes, made of leather]] |
|||
Dress shoes are categorized by smooth and supple leather uppers, leather soles, and narrow sleek shape. Casual shoes are characterized by sturdy leather uppers, non-leather outsoles, and wide profile. |
|||
==== Africa and Middle East ==== |
|||
Some designs of dress shoes can be worn by either sex. The majority of dress shoes have an upper covering, commonly made of leather, enclosing most of the lower foot, but not covering the ankles. This upper part of the shoe is often made without apertures or openings, but also made with openings or even a connected series of straps, e. g. an open toe feature in women's shoes. Shoes with ankle length (covering the ankles) upper bodies are also available. Such shoes often have zippers to open them. |
|||
As civilizations began to develop, thong sandals (precursors to the modern [[flip-flops|flip-flop]]) were worn. This practice dates back to pictures of them in [[ancient Egypt]]ian murals from 4000 BC. "Thebet" may have been the term used to describe these sandals in Egyptian times, possibly from the city [[Thebes, Egypt|Thebes]]. The [[Middle Kingdom of Egypt|Middle Kingdom]] is when the first of these thebets were found, but it is possible that it debuted in the [[Early Dynastic Period (Egypt)|Early Dynastic Period]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Egypt: The Birthplace of Flip Flops? – The Sheridan Libraries & University Museums Blog |date=21 July 2017 |url=https://blogs.library.jhu.edu/2017/07/ancient-egypt-the-birthplace-of-flip-flops/ |access-date=2022-05-20 |language=en-US}}</ref> One pair found in Europe was made of [[papyrus]] leaves and [[Carbon dating|dated]] to be approximately 1,500 years old. They were also worn in [[Jerusalem]] during the first century of the Christian era.<ref name="Kendzior_Russell">{{cite book|last=Kendzior|first=Russell J.|title=Falls Aren't Funny: America's Multi-Billion-Dollar Slip-and-Fall Crisis|publisher=www.govtinstpress.com/ Government Institutes|location=[[Lanham, Maryland]]|isbn=978-0-86587-016-1|page=117|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2TzSKEvGDIoC&pg=PA117|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170319011755/https://books.google.com/books?id=2TzSKEvGDIoC&pg=PA117|archive-date=2017-03-19|year=2010}}</ref> Thong sandals were worn by many civilizations and made from a vast variety of materials. Ancient Egyptian sandals were made from papyrus and palm leaves. The [[Maasai people|Masai]] of Africa made them out of [[rawhide (textile)|rawhide]]. In India they were made from wood. |
|||
[[Image:bristol.zoo.crocshoes.arp.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Shoes made from real [[crocodile]] skin, in a conservation exhibit at [[Bristol Zoo]], [[England]]]] |
|||
While thong sandals were commonly worn, many people in ancient times, such as the [[Ancient Egypt|Egyptians]], [[Hindus]] and [[Ancient Greece|Greeks]], saw little need for footwear, and most of the time, preferred being barefoot.<ref name="Frazine_Richard" /> The Egyptians and Hindus made some use of ornamental footwear, such as a soleless sandal known as a "Cleopatra",{{citation needed|date=January 2018}} which did not provide any practical protection for the foot. |
|||
====Men's shoes==== |
|||
Men's shoes can be categorized by how they are closed: |
|||
*[[Balmoral (shoe)|Balmorals]] - the vamp has a V-shaped slit to which the laces are attached; also known as "closed lacing." In England, the balmoral is known as the Oxford. The word "Oxford" is used by American clothing companies to market shoes that are not Oxfords, such as rubber-sole bluchers. |
|||
*[[Blücher]]s - the laces are tied to two pieces of leather independently attached to the vamp; also known as "open lacing." In England, the Blucher is known as the Derby shoe. |
|||
*Monk-straps - a buckle and strap instead of lacing |
|||
*Loafers - 'slip-on' shoes with no lacing |
|||
Various other closings exist but are less popular such as side-elastic closings. |
|||
==== Asia and Europe ==== |
|||
Men's shoes can also be decorated in various ways: |
|||
The ancient Greeks largely viewed footwear as self-indulgent, unaesthetic and unnecessary. Shoes were primarily worn in the theater, as a means of increasing stature, and many preferred to go barefoot.<ref name="Frazine_Richard">{{cite book|last=Frazine|first=Richard Keith|title=The Barefoot Hiker|year=1993|publisher=Ten Speed Press|isbn=978-0-89815-525-9|page=98|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=edsITVCd2G0C&q=barefoot+hiker}}</ref> Athletes in the [[Ancient Olympic Games]] participated barefoot—and naked.<ref name="ancient_olympics">{{cite news|title=Unearthing the First Olympics|url=https://www.npr.org/programs/re/archivesdate/2004/jul/nemea/|access-date=July 1, 2010|newspaper=[[NPR]]|date=July 19, 2004|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100728000414/http://www.npr.org/programs/re/archivesdate/2004/jul/nemea/|archive-date=July 28, 2010|df=mdy-all}}</ref> Even the [[Twelve Olympians|gods]] and heroes were primarily depicted barefoot, as well as the [[hoplite]] warriors. They fought battles in bare feet and [[Alexander the Great]] conquered his vast empire with barefoot armies. The runners of [[Ancient Greece]] had also been believed to have run barefoot.<ref name="Krentz_Peter">{{cite book|last=Krentz|first=Peter|title=The Battle of Marathon|year=2010|publisher=Yale University Press|location=New Haven and London|isbn=978-0-300-12085-1|pages=112–113|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ncT8JFn-ed8C&pg=PT112|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180427210304/https://books.google.com/books?id=ncT8JFn-ed8C&pg=PT112|archive-date=2018-04-27}}</ref> |
|||
*Plain-toes - have a sleek appearance and no extra decorations on the vamp. |
|||
*Cap-toes - has an extra layer of leather that 'caps' the toe. This is possibly the most popular decoration |
|||
*Wing-tips - The toe of the shoe is covered with a perforated panel, the wing-tip, which extends down either side of the shoe. Wing-tips can be found in both balmoral and blucher styles. In England this is called a brogue. |
|||
[[File:6 Schoen inheemse soldaat LegioIIAugusta BlackBox endeLimes fotoAvdOord.jpg|thumb|Footwear of Roman soldiers (reconstruction)]] |
|||
====Women's shoes==== |
|||
[[Image:MulticolorSandalette.jpg|thumb|250 px|Sandals.]] |
|||
*Heels - shoes with short, sturdy heels |
|||
*Flats - shoes with almost no heel at all |
|||
:*Ballerina shoes - mimicking the appearance of ballet shoes, [[pointe shoes]]. |
|||
*Medium height heels ("kitten" heels have less than 2 inches of height) |
|||
*[[High heels]] |
|||
:*[[Stiletto heel]]s - high, usually pointed, heels |
|||
:*Killer heels - very high, usually 4" or greater, heels, worn for their glamour- or sex-appeal |
|||
*Open-toed shoes - sometimes called "peep toe" |
|||
*[[Sandal (footwear)|Sandals]] - open shoes consisting of a sole and various straps |
|||
*[[Mary Jane (shoe)|Mary Janes]] |
|||
*[[Espadrilles]] - a casual sandal, with a canvas top and a rope sole |
|||
*[[Mule (footwear)]] - a close-toed, open-heeled slipper |
|||
The [[Ancient Rome|Romans]], who eventually conquered the Greeks and adopted many aspects of their culture, did not adopt the Greek perception of footwear and clothing. [[Clothing in ancient Rome|Roman clothing]] was seen as a sign of power, and footwear was seen as a necessity of living in a civilized world, although the slaves and paupers usually went barefoot.<ref name="Frazine_Richard" /> Roman soldiers were issued with [[chiral]] (left and right shoe different) footwear.<ref>'Greece and Rome at War' by Peter Connolly</ref> Shoes for soldiers had riveted insoles to extend the life of the leather, increase comfort, and provide better traction. The design of these shoes also designated the rank of the officers. The more intricate the insignia and the higher up the boot went on the leg, the higher the rank of the soldier.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Swann |first1=June |title=History of Footwear in Norway, Sweden and Finland: Prehistory to 1950 |date=2001|isbn=9789174023237|publisher=Kungl. Vitterhets, historie och antikvitets akademien}}</ref> There are references to shoes being worn in the [[Bible]].<ref>{{cite book|title=Genesis 14:23, Deuteronomy 25:9, Ruth 4:7-8, Luke 15:22}}</ref> In China and Japan, rice straws were used.{{Citation needed|date=June 2022}} |
|||
====Either sex==== |
|||
*[[Clog (shoe)|Clog]] |
|||
*[[Platform shoe]] - shoe with very thick soles and heels, mainly worn by women in the U.S. |
|||
*[[Moccasin (footwear)|Moccasin]] - originated by [[American Indians in the United States|American Indians]] |
|||
* Saddle shoe - leather shoe with a contrasting saddle-shaped band over the instep, typically white uppers with black "saddle" |
|||
* [[Loafers|Loafer]] - a dress or casual shoe without laces; often with tassels, buckles, or coin-holders (penny loafers) |
|||
Starting around 4 BC, the Greeks began wearing symbolic footwear. These were heavily decorated to clearly indicate the status of the wearer. Courtesans wore leather shoes colored with white, green, lemon or yellow dyes, and young woman betrothed or newly married wore pure white shoes. Because of the cost to lighten leather, shoes of a paler shade were a symbol of wealth in the upper class. Often, the soles would be carved with a message so it would imprint on the ground. Cobblers became a notable profession around this time, with Greek shoemakers becoming famed in the Roman empire.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Ledger |first1=Florence |title=Put Your Foot Down: A Treatise on the History of Shoes |date=1985|isbn=9780854751112 |publisher=C. Venton}}</ref> |
|||
===Athletic Shoes=== |
|||
[[Image:Zapato.jpg|right|frame|A shoe for right foot ]] |
|||
Men's and women's [[athletic shoe]]s and special function shoes often have less difference between the sexes than in dress shoes. In many cases these shoes can be worn by either sex. Emphasis tends to be more on function than style. |
|||
* [[Sneaker (footwear)|sneakers]]/trainers (also called ''gym shoes'' or ''tennis shoes'') - general purpose athletic shoes; made out of rubber, cloth, and/or plastic to be lightweight, flexible, and have good traction. Special varieties available for basketball or tennis. |
|||
* running shoes - very similar to above |
|||
* boating shoes - also similar to above. They have soft soles/heels to avoid marring or scratching a boat deck. |
|||
* [[track shoe]]s - lightweight; often with plastic or metal [[cleat]]s |
|||
* football shoes - with plastic or metal cleats |
|||
* [[golf]] shoes - with "spikes" for better grip in grass and wet ground. Originally the spikes or "cleats" were made of metal but replacable "soft spikes" made of synthetic plastic-like materials with prongs distributed radially around the edge of each spike are much more common today (and are required on many golf courses since they cause less damage to the greens) |
|||
* bowling shoes - intermediate style between ordinary dress shoes and athletic shoes. They have harder rubber soles/heels so as not to damage [[bowling]] alley floors. They are often rented or loaned at bowling alleys. |
|||
* hiking shoes or boots - usually have a high somewhat stiff upper with many lace eyelets, to provide ankle support on uneven terrain, with extra large traction on the sole. |
|||
* walking shoes - have a more flexible sole than the running shoe, lighter in weight than the hiking boot, may have air holes, may not be water proof. |
|||
* [[climbing shoe]]s |
|||
* orthopedic shoes - specially designed for people with foot problems. |
|||
* [[Skates|skating shoes]] - typically called ''skates''. They have various attachments for [[skating]] on the bottom of the shoe portion. |
|||
** ice skates |
|||
** roller skates |
|||
** inline skates |
|||
* [[ski boot]] - a large, thick plastic boot specially designed for attachment to the ski. |
|||
* skateboarding shoes- used for skateboarding but also worn by teenagers for fashion |
|||
* [[cycling shoe]]s are equipped with a metal cleat to interface with [[bicycle pedal#Clipless pedals|clipless pedals]], as well as a stiff sole to maximize power transfer and support the foot. |
|||
* [[sneaker boot]] and sneaker pump - a shoe that looks like an athletic shoe, but is equipped with a heel, making it a kind of novelty dress shoe |
|||
=== Middle Ages and early modern period === |
|||
===Categories=== |
|||
* shoes are any type of footwear worn on the foot, and to prevent further arguement, shoes include slippers, any type of heel shoes, uggs, and anything else you wear on your foot (not socks). |
|||
=== |
==== Asia and Europe ==== |
||
A common casual shoe in the [[Pyrenees]] during the Middle Ages was the [[espadrille]]. This is a sandal with braided jute soles and a fabric upper portion, and often includes fabric laces that tie around the ankle. The term is [[French language|French]] and comes from the [[esparto]] grass. The shoe originated in the [[Catalonia]]n region of [[Spain]] as early as the 13th century, and was commonly worn by [[peasant]]s in the farming communities in the area.<ref name="DeMello_Margo" /> |
|||
* dance shoes - special shoes made for tap, jazz, ballet or ballroom dancing. |
|||
* [[pointe shoes]] - shoes designed for professional ballet dancing. |
|||
* tango/flamenco dance shoes. |
|||
* dance sneakers (or dansneakers)- a combination of a sneaker and a dance shoe, with a block toe like a dance shoe |
|||
*Character shoes- special shoes usually used in plays and can be adapted into tap shoes |
|||
New styles began to develop during the Song dynasty in China, some of them resulting from the binding of women's feet, first used by the noble Han classes, but soon spreading throughout Chinese society. The practice allegedly started during the Shang dynasty, but it grew popular by {{Circa|AD 960}}.<ref name=":1">{{Cite web |title=The History of Foot Binding in China |url=https://www.thoughtco.com/the-history-of-foot-binding-in-china-195228 |access-date=2022-05-17 |website=ThoughtCo |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
===Work shoes=== |
|||
Work shoes are designed to stand heavy wear, to protect the wearer, and provide high traction. They are generally made from sturdy leather uppers and non-leather outsoles. Sometimes they are used for [[uniform]]s or comfort by [[nurse]]s, [[waitress]]es, [[police]], [[military]] personnel, etc. They are commonly used for protection in industrial settings, [[construction]], [[mining]], and other workplaces. Protective features may include [[steel-toe boots|steel-tipped toes]] and soles or [[ankle]] guards. |
|||
When the [[Mongols]] conquered China, they dissolved the practice in 1279, and the Manchus banned foot binding in 1644. The Han people, however, continued the practice without much government intervention.<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
===Snow shoes=== |
|||
[[Snowshoes]] are special shoes for walking in thick snow. In temperate climates, snowshoes are used for mostly recreational purposes in winter. |
|||
[[File:Walraversijde49.jpg|thumb|Dutch pattens, {{c.|1465}}. Excavated from the archeological site of [[Walraversijde]], near [[Ostend]], [[Belgium]]]] |
|||
===Boots=== |
|||
[[Boot]]s are special shoes that are used in times of bad weather, or simply as an alternate style of casual or dress wear. Styles include rubber boots and snow boots, as well as work boots and hiking boots. |
|||
In medieval times shoes could be up to two feet long, with their toes sometimes filled with hair, wool, moss, or grass.<ref>{{cite web |title=Getting To The Point Of Medieval Shoes |author=Ruth Hibbard |date=9 Jul 2015 |accessdate=4 Oct 2021 |website=Victoria & Albert Museum |url=https://www.vam.ac.uk/blog/museum-life/getting-to-the-point-of-medieval-shoes}}</ref> Many medieval shoes were made using the [[turnshoe]] method of construction, in which the upper was turned flesh side out, and was lasted onto the sole and joined to the edge by a seam.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Making Basic Viking-Age Men's Clothing|url=https://www.vikingsof.me/downloads/clothing-guide/male.html#shoes|access-date=2020-11-07|website=www.vikingsof.me}}</ref> The shoe was then turned inside-out so that the grain was outside. Some shoes were developed with toggled flaps or [[drawstring]]s to tighten the leather around the foot for a better fit. Surviving medieval turnshoes often fit the foot closely, with the right and left shoe being mirror images.<ref>'Shoes and Pattens: Finds from Medieval Excavations in London' (Medieval Finds from Excavations in London) by Francis Grew & Margrethe de Neergaard</ref> Around 1500, the turnshoe method was largely replaced by the welted rand method (where the uppers are sewn to a much stiffer sole and the shoe cannot be turned inside-out).<ref name="Blair_John">{{cite book|last=Blair|first=John|title=English Medieval Industries: Craftsmen, Techniques, Products|year=1991|publisher=Continuum International Publishing Group|location=[[London]]|isbn=978-0-907628-87-3|pages=309|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PDLPX7J8kW8C&q=turnshoe&pg=PA309|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160425002817/https://books.google.com/books?id=PDLPX7J8kW8C&pg=PA309&lpg=PA309&dq=turnshoe&source=bl&ots=VeX_KjBRBf&sig=qi6DCjKWfNRsg5Sg1R_uO5vqyXE&hl=en&sa=X&ei=VsoOUPTeI-rq0gGj_4CwBA&ved=0CEYQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=turnshoe&f=false|archive-date=2016-04-25}}</ref> The turn shoe method is still used for some [[dance shoe|dance]] and specialty shoes. |
|||
==Maintenance== |
|||
[[Image:Mandoe.JPG|thumb|right|An abandoned shoe, Kåre Sand, Wadden Sea, Denmark]] |
|||
*Breaking-in - Some shoes are made of hard but deformable material. After a person wears them multiple times, the material reforms to fit the wearer's feet. The person is said to have '''broken in''' the shoes. |
|||
*Polishing - for protection, water resistance (to some extent) and appearance, especially for leather shoes and [[boot]]s. |
|||
*Heel replacement - heels periodically wear out. Not all shoes are designed to enable this. |
|||
*Sole replacement - soles also wear out. Not all shoes can have their soles replaced. |
|||
*Shoelace replacement. |
|||
*When unfit for use, shoes can be treated as trash or [[municipal solid waste]] and disposed of. The exception can be with most athletic sneakers which can be recycled and turned into other raw materials. See [[Nike Grind]] as an example. |
|||
By the 15th century, [[Patten (shoe)|pattens]] became popular by both men and women in [[Europe]]. These are commonly seen as the predecessor of the modern [[high-heeled footwear|high-heeled shoe]],<ref name="high_heels">{{cite web|title=Dangerous Elegance: A History of High-Heeled Shoes|url=http://www.randomhistory.com/1-50/036heels.html|publisher=Random History|access-date=July 1, 2010|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100728002338/http://www.randomhistory.com/1-50/036heels.html|archive-date=July 28, 2010}}</ref> while the poor and lower classes in Europe, as well as slaves in the New World, were barefoot.<ref name="Frazine_Richard" /> In the 15th century, the [[Crakow (shoe)|Crakow]] was [[1400–1500 in fashion|fashionable]] in [[Europe]]. This style of shoe is named because it is thought to have originated in [[Kraków]], the capital of [[Poland]]. The style is characterized by the point of the shoe, known as the "polaine", which often was supported by a [[Baleen|whalebone]] tied to the knee to prevent the point getting in the way while walking.<ref name="polaine">{{cite book|title=The Encyclopaedia of the Renaissance|year=1988|publisher=Market House Books|isbn=978-0-7134-5967-8}}</ref> Also during the 15th century, [[chopine]]s were created in [[Spain]], and were usually {{cvt|7–8|in}} high.<ref>{{cite book | url=https://archive.org/details/hispaniccostume10000ande/page/229/mode/1up?view=theater | isbn=978-0-87535-126-1 | title=Hispanic costume, 1480-1530 | date=1979 | last1=Anderson | first1=Ruth Matilda | publisher=Hispanic Society of America }}</ref> These shoes became popular in [[Venice]] and throughout Europe, as a [[status symbol]] revealing wealth and social standing. During the 16th century, royalty, such as [[Catherine de Medici]] or [[Mary I of England]], started wearing high-heeled shoes to make them look taller or larger than life. By 1580, even men wore them, and a person with authority or wealth was often referred to as, "well-heeled".<ref name="high_heels" /> In 17th century France, heels were exclusively worn by aristocrats. [[Louis XIV of France]] outlawed anybody from wearing red high heels except for himself and his royal court.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Riello |first1=Giorgio |last2=McNeil |first2=Peter |title=Footprints from History |journal=History Today |date=March 2007 |volume=57 |issue=3 |url=https://www.historytoday.com/archive/footprints-history}}</ref> |
|||
Someone who makes or repairs shoes in a shop is called a ''cobbler''. |
|||
Eventually the modern shoe, with a sewn-on sole, was devised. Since the 17th century, most leather shoes have used a sewn-on sole. This remains the standard for finer-quality dress shoes today. Until around 1800, welted rand shoes were commonly made without differentiation for the left or right foot. Such shoes are now referred to as "straights".<ref name="Yue_Charlotte">{{cite book |last=Yue |first=Charlotte|title=Shoes: Their History in Words and Pictures|year=1997|publisher=Houghton Mifflin Company|location=New York City |isbn=978-0-395-72667-9 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/shoestheirhistor00yuec/page/46 46] |url=https://archive.org/details/shoestheirhistor00yuec |url-access=registration |quote=straights+shoes.}}</ref> Only gradually did the modern foot-specific shoe become standard. |
|||
== Shoe etiquette == |
|||
In most parts of the world (Asia, Eastern Europe, parts of the Middle East and Africa, much of Northern Europe and Canada, as well as Alaska) it is customary to remove shoes when entering a house. In some areas of the United States, especially the Midwest, it is expected that visitors remove their shoes unless a host specifically invites them to leave their shoes on. People do this to avoid bringing [[dirt]], [[mud]] or [[snow]] into the house. For some societies, including those in Asia, indoor footwear may be provided for guests. |
|||
=== Industrial era === |
|||
In the Middle East, parts of Africa, Korea and Thailand, it is considered rude to show the soles of the feet to others (even accidentally, such as by crossing the legs). In addition, in Thailand, it is an extreme insult for the foot, socks, or shoes to touch someone's head or be placed over it. Although feet touching heads is an extremely rare occurrence in any society, some [[Muay Thai]] boxers insult each other by "kicking" the opponent's head with their foot (most [[Muay Thai]] kicks are executed with the shin). |
|||
==== Asia and Europe ==== |
|||
See also [[dress code]]. |
|||
[[File:Shoemaker 1821.jpg|thumb|A [[shoemaker]] in the [[Georgian era]], from ''The Book of English Trades'', 1821.]] |
|||
[[Shoemaking]] became more commercialized in the mid-18th century, as it expanded as a [[cottage industry]]. Large [[warehouse]]s began to stock footwear, made by many small manufacturers from the area. |
|||
== Sizes == |
|||
{{main|Shoe size}} |
|||
Until the 19th century, shoemaking was a traditional handicraft, but by the century's end, the process had been almost completely mechanized, with production occurring in large factories. Despite the obvious economic gains of [[mass production]], the factory system produced shoes without the individual differentiation that the traditional shoemaker was able to provide. |
|||
*[[Units of measurement|Units]] for [[shoe size]]s vary widely around the world. European sizes are measured in '''Paris Points''', which are worth two-thirds of a [[centimetre]]. The UK and American units are approximately one-quarter of an [[inch]], starting at 8¼ inches. Men's and women's shoe sizes often have different scales. Shoes size is often measured using a [[Brannock Device]], which can determine both the width and length of the foot. |
|||
In the 19th century Chinese feminists called for an end to foot binding, and a ban in 1902 was implemented. The ban was soon repealed, but it was banned again in 1911 by the new Nationalist government. It was effective in coastal cities, but countryside cities continued without much regulation. Mao Zedong enforced the rule in 1949 and the practice is still forbidden. A number of women still have bound feet today.<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
==Shoe companies== |
|||
[[File:Woman's shoe, China, possibly Shanxi or Ningbo style, late 19th to early 20th century, satin, silk, cotton, gold thread, velvet - Redpath Museum - McGill University - Montreal, Canada - DSC08203.jpg|thumb|Woman's shoe, China, possibly Shanxi or Ningbo style, late 19th to early 20th century]] |
|||
See the category [[:Category:Shoe companies|shoe companies]] for a list of shoe companies. |
|||
The first steps towards mechanisation were taken during the [[Napoleonic Wars]] by the engineer, [[Marc Brunel]]. He developed machinery for the mass production of boots for the soldiers of the [[British Army]]. In 1812, he devised a scheme for making nailed-boot-making machinery that automatically fastened soles to uppers by means of metallic pins or nails.<ref name="Napol">{{cite web|url=http://staffscc.net/shoes1/?p=126|title=History of Shoemaking in Britain—Napoleonic Wars and the Industrial Revolution|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140202130102/http://staffscc.net/shoes1/?p=126|archive-date=2014-02-02}}</ref> With the support of the [[Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany|Duke of York]], the shoes were manufactured, and, due to their strength, cheapness, and durability, were introduced for the use of the army. In the same year, the use of screws and staples was patented by [[Richard Woodman (martyr)|Richard Woodman]]. Brunel's system was described by [[Sir Richard Phillips]] as a visitor to his factory in [[Battersea]] as follows: |
|||
[[File:Bottoming room.jpeg|thumb|left|By the late 19th century, the shoemaking industry had migrated to the factory and was increasingly mechanized. Pictured, the bottoming room of the B. F. Spinney & Co. factory in [[Lynn, Massachusetts]], 1872.]] |
|||
==Bibliography== |
|||
*''History of footwear in Norway, Sweden and Finland : prehistory to 1950'', ISBN 91-7402-323-3 |
|||
*''Patrick Cox: Wit, Irony, and Footwear'', Tamasin Doe (1998) ISBN 0-8230-1148-8 |
|||
*''Shoes : A Celebration of Pumps, Sandals, Slippers & More'', ISBN 0-7611-0114-4 |
|||
*''A Century of Shoes: Icons of Style in the 20th Century'', Angela Pattison ISBN 0-7858-0835-3 |
|||
*''Shoes '', Elizabeth Cotton (1999) ISBN 1-55670-894-7 |
|||
*''Shoes : A Lexicon of Style'', Valerie Steel ISBN 0-8478-2166-8 |
|||
*''Mad About Shoes'', Emma Bowd ISBN 1-84172-353-3 |
|||
*''Bootism : A Shoe Religion'', Penina Goodman, Michael Duranko (2003) ISBN 0-7407-3832-1 |
|||
*''The Perfect Fit: What Your Shoes Say about You'', Meghan Cleary, Sydney Van Dyke ISBN 0-8118-4501-X |
|||
BUM!! |
|||
<blockquote>In another building I was shown his manufactory of shoes, which, like the other, is full of ingenuity, and, in regard to subdivision of labour, brings this fabric on a level with the oft-admired manufactory of pins. Every step in it is affected by the most elegant and precise machinery; while, as each operation is performed by one hand, so each shoe passes through twenty-five hands, who complete from the hide, as supplied by the currier, a hundred pairs of strong and well-finished shoes per day. All the details are performed by the ingenious application of the mechanic powers; and all the parts are characterised by precision, uniformity, and accuracy. As each man performs but one step in the process, which implies no knowledge of what is done by those who go before or follow him, so the persons employed are not shoemakers, but wounded soldiers, who are able to learn their respective duties in a few hours. The contract at which these shoes are delivered to Government is 6s. 6d. per pair, being at least 2s. less than what was paid previously for an unequal and cobbled article.<ref>Richard Phillips, ''Morning's Walk from London to Kew'', 1817.</ref></blockquote> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
[[Image:Shopping for shoes.jpg|right|thumb|Shopping for shoes]] |
|||
However, when the war ended in 1815, [[manual labour]] became much cheaper, and the demand for military equipment subsided. As a consequence, Brunel's system was no longer profitable and it soon ceased business.<ref name="Napol" /> |
|||
*[[Footwear]] |
|||
*[[Shoelaces]] |
|||
==== Americas ==== |
|||
*[[Boot]] |
|||
Similar exigencies at the time of the [[Crimean War]] stimulated a renewed interest in methods of mechanization and mass-production, which proved longer lasting.<ref name="Napol" /> A shoemaker in [[Leicester]], Tomas Crick, patented the design for a riveting machine in 1853. His machine used an iron plate to push iron rivets into the sole. The process greatly increased the speed and efficiency of production. He also introduced the use of [[steam-power]]ed [[rolling-machine]]s for hardening leather and cutting-machines, in the mid-1850s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.british-history.ac.uk/report.aspx?compid=66568|title=FOOTWEAR MANUFACTURE|author=R. A. McKinley|year=1958|publisher=British History Online|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140203092232/http://www.british-history.ac.uk/report.aspx?compid=66568|archive-date=2014-02-03}}</ref> |
|||
*[[Imelda Marcos]] |
|||
*[[sandal (footwear)|Sandals]] |
|||
[[File:The Shoe for '96.jpg|thumb|Advertisement in an 1896 issue of ''[[McClure's]]'' for "The Regal".]] |
|||
*[[Slipper]]s |
|||
[[File:Attila Elina Linkopuu (16556987222).jpg|thumb|left|Attila, a former shoe factory from the 1910s in [[Tampere]], [[Finland]]]] |
|||
*[[Skates]] |
|||
*[[List of shoe designers]] |
|||
The sewing machine was introduced in 1846, and provided an alternative method for the mechanization of shoemaking. By the late 1850s, the industry was beginning to shift towards the modern factory, mainly in the US and areas of England. A shoe-stitching machine was invented by the American Lyman Blake in 1856 and perfected by 1864. Entering into a partnership with McKay, his device became known as the McKay stitching machine and was quickly adopted by manufacturers throughout [[New England]].<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XKiGgl36bkgC|title=American Inventors, Entrepreneurs, and Business Visionaries|author=Charles W. Carey|year=2009|publisher=Infobase Publishing|page=27|isbn=9780816068838}}</ref> As bottlenecks opened up in the production line due to these innovations, more and more of the manufacturing stages, such as pegging and finishing, became automated. By the 1890s, the process of mechanisation was largely complete. |
|||
*[[Foot odor]] |
|||
On January 24, 1899, Humphrey O'Sullivan of [[Lowell, Massachusetts]], was awarded a [[patent]] for a rubber heel for boots and shoes.<ref>{{cite book |last1=O'Sullivan |first1=Gary B |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CIDWbb-yOQ0C |title=The Oak and Serpent |publisher=Lulu |year=2007 |page=300 |isbn=978-0615155579 |access-date=2019-01-24 }}</ref> |
|||
==== Globalization ==== |
|||
A process for manufacturing stitchless, that is, glued, shoes—[[AGO system|AGO]]—was developed in 1910. Since the mid-20th century, advances in rubber, plastics, synthetic cloth, and industrial adhesives have allowed manufacturers to create shoes that stray considerably from traditional crafting techniques. Leather, which had been the primary material in earlier styles, has remained standard in expensive dress shoes, but athletic shoes often have little or no real leather. Soles, which were once laboriously hand-stitched on, are now more often machine stitched or simply glued on. Many of these newer materials, such as rubber and plastics, have made shoes less biodegradable. It is estimated that most mass-produced shoes require 1000 years to degrade in a [[landfill]].<ref name="Clark_Brian">{{cite news|last=Clark|first=Brian|title=Biodegradable... Shoes??|url=http://www.thedailygreen.com/living-green/blogs/recycling-design-technology/biodegradable-shoes-461009|access-date=July 23, 2012|newspaper=The Daily Green|date=October 24, 2009|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120920190620/http://www.thedailygreen.com/living-green/blogs/recycling-design-technology/biodegradable-shoes-461009|archive-date=September 20, 2012|df=mdy-all}}</ref> In the late 2000s, some shoemakers picked up on the issue and began to produce shoes made entirely from [[Cradle to Cradle Design|degradable materials]], such as the Nike Considered.<ref name="nike_considered">{{cite news|title=What is Nike Considered?|url=http://help-us.nike.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/13764/~/what-is-nike-considered%3F|access-date=July 23, 2012|newspaper=[[Nike, Inc.]]}}</ref><ref name="CSR">{{cite news|title=Ground-breaking Technology Brings World's First Biodegradable Midsole to Runners|url=http://www.csrwire.com/press_releases/15082-Brooks-R-Sports-Unveils-BioMoGo-Biodegradable-Shoe|access-date=July 23, 2012|newspaper=CSR Press Release|date=November 15, 2007|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120728232020/http://www.csrwire.com/press_releases/15082-Brooks-R-Sports-Unveils-BioMoGo-Biodegradable-Shoe|archive-date=July 28, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
In 2007, the global shoe industry had an overall market of [[United States Dollar|$]]107.4 billion, in terms of [[revenue]], and is expected to grow to $122.9 billion by the end of 2012. Shoe manufacturers in the [[People's Republic of China]] account for 63% of production, 40.5% of global exports and 55% of industry revenue. However, many manufacturers in [[Europe]] dominate the higher-priced, higher value-added end of the market.<ref name="PRWeb_ibisworld">{{cite news|title=Global Footwear Manufacturing Industry Market Research Report|url=http://www.prweb.com/releases/2012/6/prweb9580832.htm|access-date=July 24, 2012|newspaper=[[PRWeb]]|date=June 7, 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130313020222/http://www.prweb.com/releases/2012/6/prweb9580832.htm|archive-date=March 13, 2013}}</ref> |
|||
=== Culture and folklore === |
|||
{{See also|Tradition of removing shoes in home}} |
|||
[[File:Shoehouse.jpg|thumb|Haines Shoe House in [[Hallam, Pennsylvania]]]] |
|||
[[File:Shoes and Fruit (p365 20).jpg|thumb|Sports shoes in [[Hong Kong]]]] |
|||
[[File:Children's shoes at school in Ladakh.jpg|thumb|300px|Children's shoes at school in [[Ladakh]]]] |
|||
As an integral part of human culture and civilization, shoes have found their way into our culture, folklore, and art. A popular 18th-century [[nursery rhyme]] is ''[[There was an Old Woman Who Lived in a Shoe]]''. This story tells about an old woman living in a shoe with a lot of children. In 1948, [[Mahlon Haines]], a shoe salesman in [[Hallam, Pennsylvania]], built an actual house shaped like a [[boot|work boot]] as a form of advertisement. The [[Haines Shoe House]] was rented to newlyweds and the elderly until his death in 1962. Since then, it has served as an [[ice cream]] parlor, a [[bed and breakfast]], and a [[museum]]. It still stands today and is a popular roadside attraction.<ref name="Lake_Matt">{{cite book|author1=Lake, Matt|author2=Moran, Mark|author3=Sceurman, Mark|title=Weird Pennsylvania: Your Travel Guide to Pennsylvania's Local Legends and Best Kept Secrets|year=2005|publisher=Sterling Publishing Co.|location=[[New York City]]|isbn=978-1-4027-3279-9|pages=131|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bfaultPxl18C&q=haines+shoe+house&pg=PA131|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160306155239/https://books.google.com/books?id=bfaultPxl18C&pg=PA131&dq=haines+shoe+house&hl=en#v=onepage&q=haines%20shoe%20house&f=false|archive-date=2016-03-06}}</ref> |
|||
Shoes also play an important role in the [[fairy tales]] ''[[Cinderella]]'' and ''[[The Red Shoes (fairy tale)|The Red Shoes]]''. In the [[motion picture|movie]] adaption of the [[children's literature|children's book]] ''[[The Wonderful Wizard of Oz]]'', a pair of red ruby slippers play a key role in the plot. The 1985 comedy ''[[The Man with One Red Shoe]]'' features an eccentric man wearing one normal business shoe and one red shoe that becomes central to the plot. |
|||
One poem, written by Phebus Etienne with the title "Shoes", focuses on them. It describes religious messages and is 3 stanzas long. The first stanza is one line, whereas the second is 13 lines and the third being 14 lines. Throughout the poem the main character talks about their dead mother and their routine with her grave. Haitians are said to "not put shoes on the dead." as it makes spirits easier to "step over the offerings".<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Etienne |first=Phebus |date=2001 |title=Shoes |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/3300161 |journal=Callaloo |volume=24 |issue=3 |pages=738 |doi=10.1353/cal.2001.0137 |jstor=3300161 |s2cid=246284343 |issn=0161-2492}}</ref> |
|||
Athletic sneaker collection has also existed as a part of urban subculture in the United States for several decades.<ref name="Skidmore_Sarah">{{cite news|last=Skidmore|first=Sarah|title=Sneakerheads Love to Show Off Their Shoes|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/01/14/AR2007011400451.html|access-date=2 July 2011|newspaper=The Washington Post|date=15 January 2007|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121112215819/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/01/14/AR2007011400451.html|archive-date=12 November 2012}}</ref> Recent decades have seen this trend spread to European nations such as the [[Czech Republic]].<ref name="Czech">{{cite web|title=Czech 'Sneakerheads' Flaunt Their Best Trainers|url=http://www.ceskapozice.cz/en/news/society/czech-%E2%80%98sneakerheads%E2%80%99-flaunt-their-best-trainers|publisher=Czech Position|access-date=2 July 2011|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110620232159/http://www.ceskapozice.cz/en/news/society/czech-%E2%80%98sneakerheads%E2%80%99-flaunt-their-best-trainers|archive-date=20 June 2011}}</ref> A [[Sneakerhead]] is a person who owns multiple pairs of shoes as a form of collection and fashion. A contributor to the growth of sneaker collecting is the continued global popularity of the [[Air Jordan]] line of sneakers designed by [[Nike, Inc.|Nike]] for [[Basketball]] star [[Michael Jordan]]. |
|||
In the [[Bible]]'s [[Old Testament]], the shoe is used to symbolize something that is worthless or of little value. In the [[New Testament]], the act of removing one's shoes symbolizes servitude. [[Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples]] regarded the act of removing their shoes as a mark of reverence when approaching a sacred person or place.<ref name="Farbridge_Maurice">{{cite book|last=Farbridge|first=Maurice H.|author-link=Maurice H. Farbridge|title=Studies in Biblical & Semitic Symbolism 1923|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cDto8rWxKJcC&pg=PA274|year=2003|publisher=Kessinger Publishing|isbn=978-0-7661-3856-8|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161222034528/https://books.google.com/books?id=cDto8rWxKJcC&pg=PA274|archive-date=2016-12-22}}, pages=273–274</ref> In the [[Book of Exodus]], [[Moses]] was instructed to remove his shoes before approaching the burning bush: |
|||
{{blockquote|Put off thy shoes from off thy feet, for the place whereon thou standest [is] holy ground.<ref>{{bibleverse|Exodus|3:5|KJV}}</ref>}} |
|||
[[File:Salted Lake (Salt Crystal Shoes on a Frozen Lake).jpg|thumb|Salt Crystal Shoes, art installation at the [[Dead Sea]] by [[Israel]]i artist [[Sigalit Landau]]]] |
|||
The removal of the shoe also symbolizes the act of giving up a legal right. In [[Hebrew language|Hebrew]] custom, if a man chose not to [[Levirate marriage|marry his childless brother's widow]], the widow removed her brother-in-law's shoe to symbolize that he had abandoned his duty. In [[arab people|Arab]] custom, the removal of one's shoe also symbolized the dissolution of marriage.<ref name="Farbridge_Maurice" /> |
|||
In [[Arab culture]], showing the sole of one's shoe is considered an insult, and to [[Shoe tossing#Insult|throw a shoe]] and hit someone with it is considered an even greater insult. Shoes are considered to be dirty as they frequently touch the ground, and are associated with the lowest part of the body—the [[foot]]. As such, shoes are forbidden in [[mosque]]s, and it is also considered unmannerly to cross the legs and display the soles of one's shoes during conversation. This insult was demonstrated in Iraq, first when [[Saddam Hussein]]'s statue was toppled in 2003, Iraqis gathered around it and struck the statue with their shoes.<ref name="Gammell_Caroline">{{cite news|last=Gammell|first=Caroline|title=Arab Culture: The Insult of the Shoe |
|||
|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/iraq/3776970/Arab-culture-the-insult-of-the-shoe.html|access-date=July 24, 2012 |
|||
|newspaper=[[The Daily Telegraph]]|date=December 15, 2008|url-status=live |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120725033131/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/iraq/3776970/Arab-culture-the-insult-of-the-shoe.html|archive-date=July 25, 2012}}</ref> In 2008, United States President [[George W. Bush]] had a shoe [[George W. Bush shoeing incident|thrown at him]] by a journalist as a statement against the war in Iraq.<ref name="Asser_Martin">{{cite news|last=Asser|first=Martin |
|||
|title=Bush Shoe-ing Worst Arab Insult |
|||
|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/7783325.stm|access-date=July 24, 2012 |
|||
|newspaper=[[BBC News]]|date=December 15, 2008|url-status=live |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121016125313/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/7783325.stm|archive-date=October 16, 2012}}</ref> More generally, [[shoe-throwing]] or shoeing, showing the sole of one's shoe or using shoes to [[insult]] are forms of protest in many parts of the world. Incidents where shoes were thrown at political figures have taken place in Australia, India, Ireland, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Pakistan, the United Kingdom, the United States, and most notably the [[Arab world]].<ref name=Tel>[https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/iraq/3776970/Arab-culture-the-insult-of-the-shoe.html Arab culture: the insult of the shoe] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180312192122/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/iraq/3776970/Arab-culture-the-insult-of-the-shoe.html |date=2018-03-12 }}, ''[[The Daily Telegraph|The Telegraph]]'', 15 December 2008.</ref><ref name=BBC>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7783325.stm Bush shoe-ing worst Arab insult] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120530150415/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7783325.stm |date=2012-05-30 }}, BBC, 16 December 2008.</ref> |
|||
Empty shoes may also symbolize death. In [[Greece|Greek]] culture, empty shoes are the equivalent of the American funeral wreath. For example, empty shoes placed outside of a Greek home would tell others that the family's son has died in battle.<ref name="Reeve_Andru">{{cite book|last=Reeve|first=Andru J.|title=Turn Me On, Dead Man: The Beatles and the "Paul Is Dead" Hoax|year=2004|publisher=AuthorHouse|location=[[Bloomington, Indiana]]|isbn=978-1-4184-8294-7|pages=79|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=feRa_ol-CEgC&q=greek+empty+shoes&pg=PA79|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160427133401/https://books.google.com/books?id=feRa_ol-CEgC&pg=PA79&lpg=PA79&dq=greek+empty+shoes&source=bl&ots=ELuuyVAgwz&sig=LSVlExBoHi4aVg-SjLpfUFF6IM0&hl=en&sa=X&ei=KhoOUIXeH4-m8QSZzYDgDw&ved=0CDgQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=greek%20empty%20shoes&f=false|archive-date=2016-04-27}}</ref> At an observation memorializing the 10th anniversary of the [[September 11 attacks]], 3,000 pairs of empty shoes were used to recognize those killed.<ref name="Cohen_Sam">{{cite news|last=Cohen|first=Sam|title=Empty Shoes an Emotional Reminder of Those Who Died on 9/11|url=http://www.fox40.com/news/headlines/ktxl-empty-shoes-an-emotional-reminder-of-those-who-died-on-911-20110911,0,202292.story|access-date=July 23, 2012|newspaper=Fox 40|date=September 11, 2011}}{{Dead link|date=July 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> The [[Shoes on the Danube Bank]] is a memorial in [[Budapest]], [[Hungary]]. Conceived by film director [[Can Togay]], he created it on the east bank of the [[Danube River]] with sculptor [[Gyula Pauer]] to honor the Jews who were killed by fascist [[Arrow Cross Party|Arrow Cross]] militiamen in Budapest during [[World War II]]. They were ordered to take off their shoes and were shot at the edge of the water so that their bodies fell into the river and were carried away. The memorial represents their shoes left behind on the bank. |
|||
{{anchor|Shoe construction|Construction}} |
|||
== Construction == |
|||
{{Redirect|Insole}}{{Redirect|Shoe sole|the French pastry called shoe-soles|palmier}}{{See also|Shoe insert}} |
|||
The basic anatomy of a shoe is recognizable, regardless of the specific style of footwear. |
|||
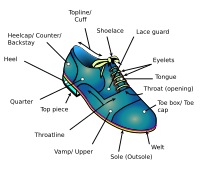
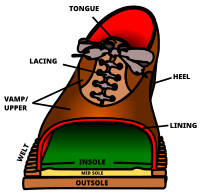
All shoes have a '''{{visible anchor|sole}}''', which is the bottom of a shoe, in contact with the ground. Soles can be made from a variety of materials, although most modern shoes have soles made from [[natural rubber]], [[polyurethane]], or [[polyvinyl chloride]] (PVC) compounds.<ref name="Karak_Niranjan">{{cite book|last=Karak|first=Niranjan|title=Fundamentals Of Polymers: Raw Materials To Finish Products|year=2009|publisher=PHI Learning Private Limited|location=[[New Delhi]]|isbn=978-81-203-3877-7|pages=263–264|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lUhf0y_fWYoC&q=shoe+vamp+welt&pg=PA263|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160513214125/https://books.google.com/books?id=lUhf0y_fWYoC&pg=PA263&lpg=PA263&dq=shoe+vamp+welt&source=bl&ots=ARiVAFESWK&sig=U21eLgu1lqxb7GpeqHT_F6og_pM&hl=en&sa=X&ei=5LIWUK32BueX6QGt0YCABQ&ved=0CFEQ6AEwBjgK#v=onepage&q=shoe%20vamp%20welt&f=false|archive-date=2016-05-13}}</ref> Soles can be simple—a single material in a single layer—or they can be complex, with multiple structures or layers and materials. When various layers are used, soles may consist of an insole, midsole, and an outsole.<ref name="Vonhof_John">{{cite book|last=Vonhof|first=John|title=Fixing Your Feet: Prevention and Treatments for Athletes|year=2011|publisher=Wilderness Press|location=[[Birmingham, Alabama]]|isbn=978-0-89997-638-9|pages=58–59|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7gpb8nlQjKkC&q=parts+of+a+shoe&pg=PA58|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160506020455/https://books.google.com/books?id=7gpb8nlQjKkC&pg=PA58&lpg=PA58&dq=parts+of+a+shoe&source=bl&ots=XUgXEhb16P&sig=GLDVufIYSRB9YrY15AUKOHAJ9oA&hl=en&sa=X&ei=gK8WUPmuAur50gHllIGgCw&ved=0CEoQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=parts%20of%20a%20shoe&f=false|archive-date=2016-05-06}}</ref> |
|||
The '''{{visible anchor|insole}}''' is the interior bottom of a shoe, which sits directly beneath the foot under the footbed (also known as sock liner). The purpose of the insole is to attach to the lasting margin of the upper, which is wrapped around the [[last]] during the closing of the shoe during the lasting operation. Insoles are usually made of cellulosic paper board or synthetic non woven insole board. Many shoes have removable and replaceable footbeds. Extra cushioning is often added for comfort (to control the shape, moisture, or smell of the shoe) or health reasons (to help deal with differences in the natural shape of the foot or positioning of the foot during standing or walking).<ref name="Vonhof_John" /> |
|||
The '''{{visible anchor|outsole}}''' is the layer in direct contact with the ground. Dress shoes often have leather or resin rubber outsoles; casual or work-oriented shoes have outsoles made of natural rubber or a synthetic material like polyurethane. The outsole may comprise a single piece or may be an assembly of separate pieces, often of different materials. On some shoes, the heel of the sole has a rubber plate for durability and traction, while the front is leather for style. Specialized shoes will often have modifications on this design: athletic or so-called cleated shoes like soccer, rugby, baseball and golf shoes have spikes embedded in the outsole to improve traction.<ref name="Vonhof_John" /> |
|||
The '''{{visible anchor|midsole}}''' is the layer in between the outsole and the insole, typically there for shock absorption. Some types of shoes, like running shoes, have additional material for [[shock absorption]], usually beneath the heel of the foot, where one puts the most pressure down. Some shoes may not have a midsole at all.<ref name="Vonhof_John" /> |
|||
The '''[[Heel (shoe)|heel]]''' is the bottom rear part of a shoe. Its function is to support the heel of the foot. They are often made of the same material as the sole of the shoe. This part can be high for fashion or to make the person look taller, or flat for more practical and comfortable use.<ref name="Vonhof_John" /> On some shoes the inner forward point of the heel is chiselled off, a feature known as a "gentleman's corner". This piece of design is intended to alleviate the problem of the points catching the bottom of trousers and was first observed in the 1930s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.oliversweeney.com/ShoeGlossary.html?article=260|title=Home Page—Oliver Sweeney|author=Oliver Sweeney Ltd|work=oliversweeney.com|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://archive.today/20141004213442/http://www.oliversweeney.com/ShoeGlossary.html?article=260|archive-date=2014-10-04}}</ref> A heel is the projection at the back of a shoe which rests below the [[Calcaneus|heel bone]]. The shoe heel is used to improve the balance of the shoe, increase the height of the wearer, alter posture or other decorative purposes. Sometimes raised, the [[High-heeled footwear|high heel]] is common to a form of shoe often worn by women, but sometimes by men too. See also [[stiletto heel]]. |
|||
The '''{{visible anchor|upper}}''' helps hold the shoe onto the foot. In the simplest cases, such as sandals or flip-flops, this may be nothing more than a few straps for holding the sole in place. Closed footwear, such as boots, trainers and most men's shoes, will have a more complex upper. This part is often decorated or is made in a certain style to look attractive. The upper is connected to the sole by a strip of leather, rubber, or plastic that is stitched between it and the sole, known as a [[welt (shoe)|welt]].<ref name="Vonhof_John" /> |
|||
Most uppers have a mechanism, such as laces, straps with buckles, zippers, elastic, velcro straps, buttons, or snaps, for tightening the upper on the foot. Uppers with laces usually have a tongue that helps seal the laced opening and protect the foot from abrasion by the laces. Uppers with laces also have eyelets or hooks to make it easier to tighten and loosen the laces and to prevent the lace from tearing through the upper material. An [[aglet]] is the protective wrapping on the end of the lace. |
|||
The '''{{visible anchor|vamp}}''' is the front part of the shoe, starting behind the toe, extending around the eyelets and tongue and towards back part of the shoe. |
|||
The '''{{visible anchor|medial}}''' is the part of the shoe closest to a person's center of symmetry, and the lateral is on the opposite side, away from their center of symmetry. This can be in reference to either the outsole or the vamp. Most shoes have [[shoelaces]] on the upper, connecting the medial and lateral parts after one puts their shoes on and aiding in keeping their shoes on their feet. In 1968, [[Puma SE]] introduced the first pair of sneakers with [[Velcro]] straps in lieu of shoelaces, and these became popular by the 1980s, especially among children and the elderly.<ref name="Suddath_Claire">{{cite news|last=Suddath|first=Claire|title=A Brief History of: Velcro|url=http://www.time.com/time/nation/article/0,8599,1996883,00.html|access-date=July 30, 2012|newspaper=[[Time (magazine)|Time]]|date=June 15, 2010|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120913155018/http://www.time.com/time/nation/article/0,8599,1996883,00.html|archive-date=September 13, 2012}}</ref><ref name="Frank_Robert">{{cite book|last=Frank|first=Robert H.|title=The Economic Naturalist: In Search of Explanations for Everyday Enigmas|year=2007|publisher=Basic Books|location=[[New York City]]|isbn=978-0-465-00217-7|pages=[https://archive.org/details/economicnaturali00fran_0/page/174 174]|url=https://archive.org/details/economicnaturali00fran_0|url-access=registration|quote=velcro laces.}}</ref> |
|||
The '''{{visible anchor|[[toe box]]}}''' is the part that covers and protects the toes. People with toe deformities, or individuals who experience toe swelling (such as [[long-distance running|long-distance runners]]) usually require a larger toe box.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Edelstein|first1=Joan E.|last2=Bruckner|first2=Jan|title=Orthotics: A Comprehensive Clinical Approach|year=2002|publisher=SLACK Incorporated|isbn=978-1-55642-416-8|pages=[https://archive.org/details/orthoticscompreh0000edel/page/21 21]|url=https://archive.org/details/orthoticscompreh0000edel/page/21}}</ref> |
|||
<gallery widths="200px" heights="200px"> |
|||
File:Shoe diagram.svg|Diagram of a typical dress shoe. The area labeled as the "Lace guard" is sometimes considered part of the quarter and sometimes part of the vamp. |
|||
File:Rhof-schuhmacher.ogv|A shoemaker making [[turnshoes]] at the [[Roscheider Hof Open Air Museum]]. English subtitles. |
|||
File:Shoe-parts-en.svg|Cutaway view of a typical shoe. |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== Types == |
|||
{{Advert|date=January 2024}} |
|||
Most types of shoes are designed for specific activities. For example, [[boot]]s are typically designed for work or heavy outdoor use. [[Athletic shoe]]s are designed for particular sports such as running, walking, or other sports. Some shoes are designed to be worn at more [[dress shoe|formal]] occasions, and others are designed for casual wear. There are also a vast variety of shoes designed for different types of dancing. Orthopedic shoes are special types of footwear designed for individuals with particular foot problems or special needs. Clinicians evaluate patient's footwear as a part of their clinical examination. However, it is often based on each individual's needs, with attention to the choice of footwear worn and if the shoe is adequate for the purpose of completing their activities of daily living.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Ellis |first1=Stephen |last2=Branthwaite |first2=Helen |last3=Chockalingam |first3=Nachiappan |title=Evaluation and optimisation of a footwear assessment tool for use within a clinical environment |journal=Journal of Foot and Ankle Research |date=December 2022 |volume=15 |issue=1 |pages=12 |doi=10.1186/s13047-022-00519-6|pmid=35144665 |pmc=8829975 |doi-access=free }}</ref> Other animals, such as [[dog]]s and [[horse]]s, may also wear special shoes to protect their feet as well. |
|||
Depending on the activity for which they are designed, some types of footwear may fit into multiple categories. For example, [[Cowboy boots]] are considered boots, but may also be worn in more formal occasions and used as [[dress shoe]]s. [[Hiking boots]] incorporate many of the protective features of boots, but also provide the extra flexibility and comfort of many [[athletic shoe]]s. [[Flip-flops]] are considered casual footwear, but have also been worn in formal occasions, such as visits to the [[White House]].<ref name="Ward_Julie">{{cite news|last=Ward|first=Julie|title=Next big step in team spirit: Flip-flops.|url=https://www.usatoday.com/sports/2005-09-13-flip-flops_x.htm|access-date=July 19, 2012|newspaper=[[USA Today]]|date=September 13, 2005|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110809113042/http://www.usatoday.com/sports/2005-09-13-flip-flops_x.htm|archive-date=August 9, 2011}}</ref><ref name="Lister_Richard">{{cite news|last=Lister|first=Richard|title=Flip-flop Diplomacy With the Dalai Lama|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8523248.stm|access-date=July 19, 2012|newspaper=[[BBC News]]|date=February 19, 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121016125254/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8523248.stm|archive-date=October 16, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
=== Athletic === |
|||
{{Main|Sneakers}} |
|||
[[File:Puma shoes.jpg|thumb|right|A pair of athletic running shoes]] |
|||
[[File:20230414 Bowling shoes in rack.jpg|thumb|Bowling centers maintain bowling shoes for rental to patrons, to prevent damage to lane approaches.]] |
|||
[[Athletic shoes]] are designed for various sports activities, focusing on maximizing [[friction]] between the foot and the ground. These shoes often utilize materials like [[Natural rubber|rubber]] to achieve this purpose.<ref name="McGinnis_Peter">{{cite book|last=McGinnis|first=Peter M.|title=Biomechanics of Sport and Exercise|year=2005|publisher=www.humankinetics.com|location=[[Champaign, Illinois]]|isbn=978-0-7360-5101-9|pages=26|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PrOKEcZXJ58C&q=athletic+shoes&pg=PA26|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160429115822/https://books.google.com/books?id=PrOKEcZXJ58C&pg=PA26&lpg=PA26&dq=athletic+shoes&source=bl&ots=dkFLbMtbgu&sig=ifnj5F7hHLK5d-hXDryKw00t6ZQ&hl=en&sa=X&ei=Xk42UPDfL46M0QGCk4DYDw&ved=0CEoQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=athletic%20shoes&f=false|archive-date=2016-04-29|edition=Second}}</ref> The earliest athletic shoes, dating to the mid-19th century, were [[track spikes]] with metal [[cleat (shoe)|cleats]] for increased traction. Over time, athletic shoe design evolved, with companies like [[Reebok]] and [[Adidas]] contributing to the development of modern athletic shoes. Notable innovations include rubber-soled athletic shoes and the introduction of specialized shoes for different sports, such as [[basketball]] and [[golf]]. More recently, minimalist shoes have gained popularity as [[barefoot running]] became popular by the late 20th and early 21st century, maintaining optimum flexibility and natural walking while also providing some degree of protection. Their purpose is to allow one's feet and legs to feel more subtly the impacts and forces involved in running, allowing finer adjustments in running style.<ref name="Dan Winters">{{cite news |last=Winters |first=Dan |date=November 2010 |title=Is Less More? |url=http://www.runnersworld.com/article/0,7120,s6-240-400--13691-F,00.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120728010633/http://www.runnersworld.com/article/0,7120,s6-240-400--13691-F,00.html |archive-date=July 28, 2012 |access-date=July 23, 2012 |magazine=[[Runner's World]] |df=mdy-all}}</ref><ref name="DeMello_Margo" /><ref name="Farrally_Cochran">{{cite book|author1=Farrally, Martin R. |author2=Cochran, Alastair J. |title=Science and Golf III: Proceedings of the 1998 World Scientific Congress of Golf|publisher=www.humankinetics.com|location=[[Champaign, Illinois]]|isbn=978-0-7360-0020-8|pages=568–569|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MnC60GN8PJ4C&q=golf+shoes&pg=PA569|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160518175144/https://books.google.com/books?id=MnC60GN8PJ4C&pg=PA569&lpg=PA569&dq=golf+shoes&source=bl&ots=p20uF2KOiQ&sig=PleJJIBWPb9r_ftziNEukm4W3Vw&hl=en&sa=X&ei=AWo2UKWvKceB0QHa7oHoAg&ved=0CEQQ6AEwAg#v=onepage&q=golf%20shoes&f=false|archive-date=2016-05-18|year=1999}}</ref> |
|||
The earliest rubber-soled athletic shoes date back to 1876 in the United Kingdom, when the New Liverpool Rubber Company made [[plimsolls]], or sandshoes, designed for the sport of [[croquet]]. Similar rubber-soled shoes were made in 1892 in the United States by Humphrey O'Sullivan, based on [[Charles Goodyear]]'s technology. The [[United States Rubber Company]] was founded the same year and produced rubber-soled and heeled shoes under a variety of brand names, which were later consolidated in 1916 under the name, [[Keds (shoes)|Keds]]. These shoes became known as, "sneakers", because the rubber sole allowed the wearer to sneak up on another person. In 1964, the founding of [[Nike, Inc.|Nike]] by [[Phil Knight]] and [[Bill Bowerman]] of the [[University of Oregon]] introduced many new improvements common in modern running shoes, such as rubber waffle soles, breathable [[nylon]] uppers, and cushioning in the mid-sole and heel. During the 1970s, the expertise of [[podiatrist]]s also became important in athletic shoe design, to implement new design features based on how feet reacted to specific actions, such as running, jumping, or side-to-side movement for men and women.<ref name="DeMello_Margo" /> |
|||
[[File:A classic Black pair of Converse All Stars resting on the Black & White Ed. Shoebox (1998-2002).JPG|left|thumb|upright|A pair of Converse All-Stars]] |
|||
Shoes specific to the sport of [[basketball]] were developed by [[Chuck Taylor (salesman)|Chuck Taylor]], and are popularly known as [[Chuck Taylor All-Stars]]. In 1969, Taylor was inducted into the [[Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame]] in recognition of this development, and in the 1970s, other shoe manufacturers, such as Nike, Adidas, Reebok, and others began imitating this style of athletic shoe.<ref name="Peterson_Hal">{{cite book|last=Peterson|first=Hal|title=Chucks!: The Phenomenon of Converse Chuck Taylor All Stars|year=2007|publisher=[[Skyhorse Publishing]]|location=[[New York City]]|isbn=978-1-60239-079-9|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ko_a_Ij3TRMC&q=converse+all-stars|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160511032858/https://books.google.com/books?id=ko_a_Ij3TRMC&printsec=frontcover&dq=converse+all-stars&source=bl&ots=yMn8WAJnK8&sig=GeSNFIYNAUgRGChnDqMfefDXuPY&hl=en&sa=X&ei=YIM2UK_vNIya8gT5iYDwBQ&ved=0CD4Q6AEwAQ#v=onepage&q=converse%20all-stars&f=false|archive-date=2016-05-11}}</ref> In April 1985, Nike introduced its own brand of basketball shoe which would become popular in its own right, the [[Air Jordan]], named after the then-rookie [[Chicago Bulls]] basketball player, [[Michael Jordan]]. The Air Jordan line of shoes sold $100 million in their first year.<ref name="Papson_Goldman">{{cite book|author1=Papson, Stephen|author2=Goldman, Robert|title=Nike Culture: The Sign of the Swoosh|year=1998|publisher=SAGE Publications|location=[[London]]|isbn=978-0-7619-6148-2|pages=47|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KYP03bw1mVIC&q=air+jordans&pg=PA47|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160517123717/https://books.google.com/books?id=KYP03bw1mVIC&pg=PA47&lpg=PA47&dq=air+jordans&source=bl&ots=2FUA00vpwr&sig=77efxA0aD2mdSqO5V5321Xv6TDI&hl=en&sa=X&ei=QoU2UN-6OpO08ASC3oGIDg&ved=0CFQQ6AEwBQ#v=onepage&q=air%20jordans&f=false|archive-date=2016-05-17}}</ref> |
|||
As [[barefoot running]] became popular by the late 20th and early 21st century, many modern shoe manufacturers have recently designed footwear that mimic this experience, maintaining optimum flexibility and natural walking while also providing some degree of protection. Some of these shoes include the [[Vibram FiveFingers]],<ref name="TrailSpace">{{cite news|title=Vibram FiveFingers Named A "Best Invention of 2007" by Time Magazine|url=http://www.trailspace.com/articles/2007/11/12/vibram-fivefingers-named-a-best-invention-of-2007-by-time-magazine.html|access-date=June 26, 2010|newspaper=trailspace.com|date=12 November 2007|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100513230848/http://www.trailspace.com/articles/2007/11/12/vibram-fivefingers-named-a-best-invention-of-2007-by-time-magazine.html|archive-date=13 May 2010}}</ref> [[Nike Free]],<ref name="Cortese_Amy">{{cite news|last=Cortese|first=Amy|title=Wiggling Their Toes at the Shoe Giants|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/30/business/30shoe.html|access-date=July 1, 2010|newspaper=[[The New York Times]]|date=August 29, 2009|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110404080819/http://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/30/business/30shoe.html|archive-date=April 4, 2011}}</ref> and [[Saucony]]'s Kinvara and Hattori.<ref name="Saucony">{{cite magazine |url=http://www.runnersworld.com/cda/shoefinder_detail/1,7161,s6-240-400-0-0-0-0-0-1861,00.html |title=Saucony Progrid Kinvara Running Shoe Review: Runner's World |magazine=Runner's World |date=February 15, 2008 |access-date=September 3, 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110911213001/http://www.runnersworld.com/cda/shoefinder_detail/1,7161,s6-240-400-0-0-0-0-0-1861,00.html |archive-date=September 11, 2011 |df=mdy-all }}</ref><ref name="Jhung_Lisa">{{cite news|last=Jhung|first=Lisa|title=Saucony Minimalism|url=http://gear.runnersworld.com/2011/05/saucony-minimalism.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110506145415/http://gear.runnersworld.com/2011/05/saucony-minimalism.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=2011-05-06|access-date=August 17, 2011|newspaper=Runner's World|date=May 2011}}</ref> Mexican [[Huarache (running shoe)|huaraches]] are also very simple running shoes, similar to the shoes worn by the [[Tarahumara]] people of northern Mexico, who are known for their distance running abilities.<ref name="McDougall_Christopher">{{cite book|last=McDougall|first=Christopher|title=Born to Run: A Hidden Tribe, Superathletes, and the Greatest Race the World Has Never Seen|year=2011|publisher=Vintage Books|location=[[New York City]]|isbn=978-0-307-27918-7|pages=[https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780307279187/page/168 168], 172|url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780307279187|url-access=registration|quote=born to run.}}</ref> [[Wrestling shoes]] are also very light and flexible shoes that are designed to mimic bare feet while providing additional traction and protection. |
|||
Many athletic shoes are designed with specific features for specific activities. One of these includes [[roller skates]], which have metal or plastic wheels on the bottom specific for the sport of roller skating. Similarly, [[ice skates]] have a metal blade attached to the bottom for locomotion across [[ice]]. [[Skate shoes]] have also been designed to provide a comfortable, flexible and durable shoe for the sport of [[skateboarding]].<ref name="Welinder_Whitley">{{cite book|author1=Welinder, Per|author2=Whitley, Peter|title=Mastering Skateboarding|year=2012|publisher=Human Kinetics|location=[[Champaign, Illinois]]|isbn=978-0-7360-9599-0|pages=8|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=n-sm3PHrfuMC&q=skate+shoes&pg=PA8|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160624133118/https://books.google.com/books?id=n-sm3PHrfuMC&pg=PA8&lpg=PA8&dq=skate+shoes&source=bl&ots=hHtSxS72qm&sig=r38MPQz6t7tiO5dgrvT6g3STjhg&hl=en&sa=X&ei=wos2ULXeD4T89gS6joGwCg&ved=0CEcQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=skate%20shoes&f=false|archive-date=2016-06-24}}</ref> [[Climbing shoe]]s are rubber-soled, tight-fitting shoes designed to fit in the small cracks and crevices for [[rock climbing]]. [[Cycling shoe]]s are similarly designed with rubber soles and a tight fit, but also are equipped with a metal or plastic cleat to interface with [[bicycle pedal#Clipless pedals|clipless pedals]], as well as a stiff sole to maximize power transfer and support the foot.<ref name="IPMBA">{{cite book|last=International Police Mountain Bike Association|title=The Complete Guide to Public Safety Cycling|year=2008|publisher=Jones & Bartlett Publishers|location=[[Sudbury, Massachusetts]]|isbn=978-0-7637-4433-5|pages=45|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OWeDspfAdKcC&q=cycling+shoes&pg=PA45|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160519050811/https://books.google.com/books?id=OWeDspfAdKcC&pg=PA45&lpg=PA45&dq=cycling+shoes&source=bl&ots=FRDs04HdY_&sig=H1Gf57RjKAVWzaYA6vMtKoHofN0&hl=en&sa=X&ei=YI02UKufII2o8gSAhIGwDA&ved=0CD4Q6AEwAQ#v=onepage&q=cycling%20shoes&f=false|archive-date=2016-05-19}}</ref> Some shoes are made specifically to improve a person's ability to [[weight training|weight train]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.yahoo.com/lifestyle/best-weightlifting-shoes-according-trainers-202200672.html|title=The Best Weightlifting Shoes, According to Trainers|website=Yahoo Life|first1=Ben|last1=Radding|date=November 15, 2018}}</ref> Sneakers that are a mix between an activity-centered and a more standard design have also been produced: examples include [[roller shoe]]s, which feature wheels that can be used to roll on hard ground, and [[Soap (shoes)|Soap shoes]], which feature a hard plastic sole that can be used for [[Grind (sport)|grinding]]. |
|||
=== Boot === |
|||
{{Main article|Boot}} |
|||
[[File:S3 safety footwear.jpg|thumb|right|A pair of [[Steel-toe boot|steel-toed]] safety boots]] |
|||
[[Boot]]s are a specialized type of footwear that covers the foot and extends up the leg. They serve both functional and fashion purposes, offering protection from elements like water, snow, and mud while also being a fashion statement. |
|||
Cowboy boots, for instance, are known for their distinctive style and are popular among cowboys in the [[western United States]]. [[Hiking boot]]s, on the other hand, are designed for comfort and support during long walks in rough terrains. [[Snow boot]]s are ideal for wet or snowy weather, providing warmth and protection against the elements. Additionally, boots are used in specialized activities like skiing, ice skating, and climbing due to their unique features tailored to these activities.<ref name="DeWeese_Daniel">{{cite news|last=DeWeese|first=G. Daniel|title=The Functional Side of Cowboy Boots|url=http://www.truewestmagazine.com/jcontent/living-the-dream/living-the-dream/fashion/2731-the-functional-side-of-cowboy-boots|access-date=August 10, 2012|newspaper=[[True West Magazine]]|date=June 29, 2010|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121016062459/http://www.truewestmagazine.com/jcontent/living-the-dream/living-the-dream/fashion/2731-the-functional-side-of-cowboy-boots|archive-date=October 16, 2012}}</ref><ref name="Chand_Elise">{{cite book|last=Chand|first=Elise Gaston|title=A Parent's Guide to Riding Lessons: Everything You Need to Know to Survive and Thrive With a Horse-Loving Kid|year=2009|publisher=Storey Publishing|location=[[North Adams, Massachusetts]]|isbn=978-1-60342-447-9|pages=91|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Iu2CzhW0g3YC&q=exotic+cowboy+boots&pg=PA91|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160510104233/https://books.google.com/books?id=Iu2CzhW0g3YC&pg=PA91&lpg=PA91&dq=exotic+cowboy+boots&source=bl&ots=o4vQGrMP6f&sig=qM8AFCqdgGZc_0dhQygyIq2UM6k&hl=en&sa=X&ei=cmAkUOTrNIag8gTctYG4Cw&ved=0CDYQ6AEwADgK#v=onepage&q=exotic%20cowboy%20boots&f=false|archive-date=2016-05-10}}</ref><ref name="Howe_Steve">{{cite news|last=Howe|first=Steve|title=Boots|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DOIDAAAAMBAJ&q=hiking+boots&pg=PA43|access-date=August 10, 2012|newspaper=Backpacker|date=March 2002|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130318234513/http://books.google.com/books?id=DOIDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA43&lpg=PA43&dq=hiking+boots&source=bl&ots=8CoJk-V0n9&sig=ZtaEOvkfB_S5S40bn7bAi7UF-3g&hl=en&sa=X&ei=amIkUMuJFI-g8gSE_IDYCA&ved=0CFAQ6AEwBTgK#v=onepage&q=hiking%20boots&f=false|archive-date=March 18, 2013}}</ref><ref name="Stimpert_Desiree">{{cite news|last=Stimpert|first=Desiree|title=What Makes a Boot a Snow Boot|url=http://shoes.about.com/od/boots/a/snow_boots.htm|access-date=August 10, 2012|newspaper=[[About.com]]|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120723171147/http://shoes.about.com/od/boots/a/snow_boots.htm|archive-date=July 23, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Boots may also be attached to [[snowshoe]]s to increase the distribution of weight over a larger [[surface area]] for walking in [[snow]]. [[Ski boots]] are a specialized snow boot which are used in [[alpine skiing|alpine]] or [[cross-country skiing]] and designed to provide a way to attach the skier to his/her [[ski]]s using [[ski binding]]s. The ski/boot/binding combination is used to effectively transmit control inputs from the skier's legs to the snow. [[Ice skate]]s are another specialized boot with a metal blade attached to the bottom which is used to propel the wearer across a sheet of [[ice]].<ref name="Bellis_Mary Ice">{{cite news|last=Bellis|first=Mary|title=History of Ice Skates|url=http://inventors.about.com/library/inventors/bliceskates.htm|archive-url=https://archive.today/20121205235844/http://inventors.about.com/library/inventors/bliceskates.htm|url-status=dead|archive-date=December 5, 2012|access-date=August 10, 2012|newspaper=[[About.com]]}}</ref> [[Inline skates]] are similar to ice skates but with a set of three to four wheels in lieu of the blade, which are designed to mimic ice skating on solid surfaces such as wood or concrete.<ref name="Olsen_Scott&Brennan">{{cite web|last=Olsen|first=Scott & Brennan|title=Inline-Skates|url=http://web.mit.edu/invent/iow/Inline.html|publisher=lemelson.mit.edu|access-date=August 10, 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060502164738/http://web.mit.edu/invent/iow/Inline.html|archive-date=May 2, 2006}}</ref> |
|||
Boots are designed to withstand heavy wear to protect the wearer and provide good traction. They are generally made from sturdy leather uppers and non-leather outsoles. They may be used for [[uniform]]s of the [[police]] or [[military]], as well as for protection in industrial settings such as [[mining]] and [[construction]]. Protective features may include [[steel-toe boots|steel-tipped toes]] and soles or [[ankle]] guards.<ref name="Construction_Materials">{{cite book|last1=Somaiya |first1=A. |last2=James |first2=E. |last3=Wieffering |first3=N. |title=Construction Materials|year=2008|publisher=Pearson Education South Africa|location=Forest Drive, Pinelands, [[Cape Town]]|isbn=978-1-77025-156-4|pages=36|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VIVr_oR3JowC&q=safety+boots&pg=PA36|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160508104957/https://books.google.com/books?id=VIVr_oR3JowC&pg=PA36&lpg=PA36&dq=safety+boots&source=bl&ots=hydz0hRuEA&sig=5OSk5uTUJBdFY4z2GJK-Rz6Arm8&hl=en&sa=X&ei=gFkkUM2KM4fM9QSvmIGwDA&ved=0CGUQ6AEwBzgK#v=onepage&q=safety%20boots&f=false|archive-date=2016-05-08}}</ref> |
|||
=== Dress and casual === |
|||
[[Dress shoe]]s are characterized by their smooth leather uppers, leather soles, and sleek design, suitable for formal occasions. In contrast, casual shoes have sturdier leather uppers, non-leather outsoles, and a wider profile for everyday wear. Some dress shoe designs are unisex, while others are specific to men or women. |
|||
==== Men's ==== |
|||
{{anchor|Open lacing|Closed lacing}} |
|||
[[File:Blucher (PSF).jpg|right|thumb|This male dress shoe, known as a [[derby shoe]], is distinguished by its open lacing.]] |
|||
Men's dress shoes include styles like Oxfords, Derbies, Monk-straps, and Slip-ons, each with its unique characteristics in terms of lacing, decoration, and formality. |
|||
==== Women's ==== |
|||
[[File:My Shoes.jpg|thumb|upright|High heel sandals]]Women's shoes cover a wide range of styles, including high heels, mules, slingbacks, ballet flats, and court shoes, with high-heeled footwear being a popular choice for formal occasions. |
|||
=== Unisex === |
|||
* [[Clog (shoe)|Clog]] |
|||
* [[Platform shoe]]: shoe with very thick soles and heels |
|||
* [[Sandal (footwear)|Sandals]]: open shoes consisting of a sole and various straps, leaving much of the foot exposed to air. They are thus popular for warm-weather wear, because they let the foot be cooler than a closed-toed shoe would. |
|||
* [[Saddle shoe]]: leather shoe with a contrasting saddle-shaped band over the instep, typically white uppers with black "saddle". |
|||
* [[Slip-on shoe]]: a dress or casual shoe without shoelaces or fasteners; often with tassels, buckles, or coin-holders (penny loafers). |
|||
* [[Boat shoe]]s, also known as "deck shoes": similar to a loafer, but more casual. Laces are usually simple leather with no frills. Typically made of leather and featuring a soft white sole to avoid marring or scratching a boat deck. The first boat shoe was invented in 1935 by [[Paul A. Sperry]]. |
|||
* [[Slipper]]s: For indoor use, commonly worn with [[pajamas]]. |
|||
=== Dance === |
|||
Dancers use a variety of footwear depending on the style of dance and the surface they will be dancing on. Pointe shoes, for instance, are designed for ballet dancing, featuring a stiffened toe box and hardened sole to allow dancers to stand on the tips of their toes. Ballet shoes, on the other hand, are soft, pliable shoes made of canvas or leather, providing flexibility and comfort for ballet dancing. Other dance shoe types include jazz shoes, tango, and flamenco shoes, ballroom shoes, tap shoes, character shoes, and foot thongs, each designed to meet the specific needs of different dance styles.<gallery mode="packed"> |
|||
File:PointeShoes.jpg|[[Pointe shoes]] |
|||
File:Ballet shoes in fifth position.jpg|[[Ballet shoes]] |
|||
File:AcroShoes.jpg|[[Jazz shoe]]s. This style is frequently worn by [[acro dance]]rs |
|||
File:Foot Thong.jpg|A ''foot thong'', viewed from the bottom |
|||
File:Ghillie.JPG|[[Ghillies (dance)|Ghillies]] |
|||
File:Ladies' ballroom shoes, Tango Shoes 2.jpg|Ladies' ballroom shoes |
|||
File:Mens' ballroom shoes, Eurodance CZ.jpg|Men's ballroom shoes |
|||
File:TapShoeSide.jpg|[[Tap shoe]]s |
|||
File:Pastalas.jpg|[[Kierpce]] |
|||
File:Barnskor - 1980.jpg|Children's shoe from the early 80s. |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
=== Orthopedic === |
|||
{{See also|Diabetic shoe}} |
|||
[[File:Orthopedic heavy duty black leather school uniform shoes.jpg|thumb|Orthopedic heavy duty black leather school uniform shoes]] |
|||
Orthopedic shoes are specially designed to alleviate discomfort associated with various foot and ankle disorders, such as [[blister]]s, bunions, calluses, and plantar fasciitis. They are also used by individuals with diabetes, [[unequal leg length]], or children with mobility issues.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Hill |first1=Matthew |last2=Healy |first2=Aoife |last3=Chockalingam |first3=Nachiappan |title=Key concepts in children's footwear research: a scoping review focusing on therapeutic footwear |journal=Journal of Foot and Ankle Research |date=December 2019 |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=25 |doi=10.1186/s13047-019-0336-z|pmid=31061678 |pmc=6487054 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Hill |first1=Matthew |last2=Healy |first2=Aoife |last3=Chockalingam |first3=Nachiappan |title=Effectiveness of therapeutic footwear for children: A systematic review |journal=Journal of Foot and Ankle Research |date=December 2020 |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=23 |doi=10.1186/s13047-020-00390-3|pmid=32404124 |pmc=7222438 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Hill |first1=Matthew |last2=Healy |first2=Aoife |last3=Chockalingam |first3=Nachiappan |title=Defining and grouping children's therapeutic footwear and criteria for their prescription: an international expert Delphi consensus study |journal=BMJ Open |date=August 2021 |volume=11 |issue=8 |pages=e051381 |doi=10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051381 |issn=2044-6055|pmid=34373314 |pmc=8354267 }}</ref> These shoes typically feature a low heel, wide toe box, and firm heel for added support. Some orthopedic shoes come with removable insoles or orthotics to provide extra arch support.<ref name="DeMello_Margo" /> |
|||
== Measures and sizes == |
|||
{{Main article|Shoe size}} |
|||
[[File:MarikinaRiverBankShoesjf9425 30.JPG|thumb|[[Giant shoes of Marikina|World's largest pair of shoes]], [[Riverbanks Center|Riverbank Center]], Philippines—5.29 metres (17.4 ft) long and 2.37 metres (7 ft 9 in) wide, equivalent to a French shoe size of 75.]] |
|||
Shoe sizes are indicated by a numerical value representing the length of the shoe, with different systems used globally. European sizes are measured in Paris Points, while the UK and American units are based on whole-number sizes spaced at one barleycorn (1/3 inch) with UK adult sizes starting at size 1 = {{cvt|8+2/3|in|cm|1}}. In the US, this is size 2. Men's and women's shoe sizes often use different scales{{citation needed|date=September 2020}}, and some systems are measured using a [[Brannock Device]] which considers the width and length size values of the feet. The Mondopoint system, introduced in the 1970s by International Standard ISO 2816:1973 "Fundamental characteristics of a system of shoe sizing to be known as Mondopoint" and ISO 3355:1975 "Shoe sizes – System of length grading (for use in the Mondopoint system)" includes measurements of both length and width of the foot.<ref>{{cite patent|country=US|number=1725334|title=Foot-measuring instrument|status=patent|pubdate=1929-08-20}}</ref><ref>R. Boughey. Size Labelling of Footwear. Journal of Consumer Studies & Home Economics. Volume 1, Issue 2. June 1977. DOI:10.1111/j.1470-6431.1977.tb00197.x</ref> |
|||
[[File:Toddler-Size Shoe.jpeg|thumb|right|Toddler-sized shoe.]] |
|||
== Accessories == |
|||
Various accessories are used to enhance the functionality and comfort of shoes. Crampons provide traction on icy terrain, foam taps adjust shoe fit, heel grips prevent slipping, and ice cleats enhance stability on slippery surfaces. Overshoes protect shoes from rain and snow, while shoe bags are used for storage. Shoe brushes and polishing cloths maintain shoe appearance, while shoe inserts offer additional comfort. |
|||
==Removal of shoes== |
|||
[[File:PLZZ REMOVE YOUR SHOES. Sign at entrance to stupa. Nubra, India.jpg|thumb|"Plzz REMOVE YOUR SHOES" sign at entrance to [[stupa]]. [[Nubra]], India]] |
|||
{{main article| Tradition of removing shoes in the home and houses of worship}} |
|||
In many places in the world, shoes are removed when moving from exteriors to interiors, particularly in homes<ref name="Kurzius 2023 p020">{{cite news | last=Kurzius | first=Rachel | title=The case for — and against — taking your shoes off in the house | newspaper=Washington Post | date=October 2, 2023 | url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/home/2023/10/02/take-shoes-off-indoors-house/ | access-date=February 14, 2024}}</ref><ref name="Nast Spier 2020 y674">{{cite web | last=Spier | first=Ally | title=Should You Take Your Shoes Off While Indoors? | website=Architectural Digest | date=April 24, 2020 | url=https://www.architecturaldigest.com/story/should-you-take-your-shoes-off-while-indoors | access-date=February 14, 2024}}</ref> and religious buildings.<ref name="Sood 2011 e867">{{cite web | last=Sood | first=Suemedha | title=Religious tourism etiquette | website=BBC Home | date=June 17, 2011 | url=https://www.bbc.com/travel/article/20110616-travelwise-religious-tourism-etiquette | access-date=February 14, 2024}}</ref> In many Asian countries, outdoor shoes are exchanged for indoor shoes or [[slipper]]s.<ref name="LaMotte 2023 u513">{{cite web | last=LaMotte | first=Sandee | title=The dirty truth about taking your shoes off at the door | website=CNN | date=December 7, 2023 | url=https://www.cnn.com/2023/12/07/health/remove-shoes-germs-wellness/index.html | access-date=February 14, 2024}}</ref> [[Fitness center]] etiquette encourages the exchange of outdoor shoes for indoor shoes, both to prevent dirt and grime from being transferred to the equipment and to ensure that participants are wearing the right shoes for their activities.<ref name="C.P.T 2023 s056">{{cite web | last=C.P.T | first=Lee Boyce | title=Gym Etiquette Code of Conduct: 12 Rules for Every Lifter | website=Men's Journal | date=2023-11-06 | url=https://www.mensjournal.com/health-fitness/gentlemans-guide-gym-etiquette#wear-indoor-shoes | access-date=February 14, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
== See also == |
|||
{{div col|colwidth=20em}} |
|||
* [[Foot binding]] |
|||
* [[:Category:Shoe companies|List of shoe companies]] |
|||
* [[List of shoe styles]] |
|||
* [[Locomotor effects of shoes]] |
|||
* [[Runner's toe]], injury from malfitting shoes |
|||
* [[Shoe dryer]] |
|||
* [[Shoe rack]] |
|||
* [[Shoe tossing]] |
|||
* [[Trousers]] |
|||
* [[Shoe fetish]] |
|||
{{div col end}} |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
== Bibliography == |
|||
* {{cite book | author=Bergstein, Rachelle | title=Women from the Ankle Down: The Story of Shoes and How They Define Us | location=New York | publisher=Harper Collins | year=2012 | type=Hardback | isbn=978-0-06-196961-4 | pages=[https://archive.org/details/womenfromankledo00berg/page/284 284 pages] | url=https://archive.org/details/womenfromankledo00berg/page/284 }} |
|||
* Doe, Tamasin (1998), ''Patrick Cox: Wit, Irony, and Footwear'', {{ISBN|0-8230-1148-8}}. |
|||
* Pattison, Angela, ''A Century of Shoes: Icons of Style in the 20th Century'', {{ISBN|0-7858-0835-3}}. |
|||
* Swann, June. ''History of Footwear in Norway, Sweden and Finland: Prehistory to 1950'', {{ISBN|91-7402-323-3}}. |
|||
== Further reading == |
|||
* Design Museum. ''[https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/30656443-fifty-shoes-that-changed-the-world Fifty Shoes That Changed the World]''. London: Conran Octopus, 2009. {{ISBN|978-1-84091-539-6}}. |
|||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{sister project links|Shoes}} |
|||
{{wiktionarypar|shoe}} |
|||
* [[Bata Shoe Museum]]'s online exhibits on the history and variety of footwear: {{cite web|url=http://www.allaboutshoes.ca/en/ |title=All About Shoes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20221005164952/http://www.allaboutshoes.ca/en/ |archivedate=2022-10-05 }} |
|||
* {{cite web|url=http://www.footwearhistory.com/ |title=Footwear History|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060813085112/http://www.footwearhistory.com/ |archive-date=2006-08-13 }} |
|||
* {{cite web|url=http://www.i18nguy.com/l10n/shoes.html |title=International Shoe Size Conversion Charts}}, from i18nguy's website, offers more information. |
|||
* {{cite web|url=http://www.schuh-lexikon.de/en/shoe-care.html |archive-url=https://archive.today/20121218002956/http://www.schuh-lexikon.de/en/shoe-care.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=2012-12-18 |title=Shoe Care}} |
|||
* Illustrated {{cite web|url=https://www.candefashions.com/about/glossary-of-shoe-terms/ |title=Glossary of Shoe Terms |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20220319083936/https://www.candefashions.com/about/glossary-of-shoe-terms/ |archivedate=2022-03-19 }} |
|||
* Map: {{cite web|url=https://www.google.com/maps/d/viewer?mid=1M-CQxxbfVfh7GtlSsNhZa5MTteiI2Dbb&ll=38.964142178237196%2C2.784477716013839&z=2 |title=Medieval shoes in museums}} |
|||
{{Footwear|state=collapsed}} |
|||
* [http://www.footwearhistory.com Footwear History] |
|||
{{Running Shoe Brands}} |
|||
* [http://www.i18nguy.com/l10n/shoes.html International Shoe Size Conversion Charts], from i18nguy's website, offers more information. |
|||
{{Clothing|state=collapsed}} |
|||
* [http://www.schuh-lexikon.de/en/shoe-care.html Shoe Care] |
|||
{{Prehistoric technology}} |
|||
* [http://podiatry.curtin.edu.au/shoo.html The History of Footwear], includes diagrams of parts |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
* [http://users.resist.ca/~kirstena/pageshoehistory.html The Political History of Shoes] |
|||
* [http://www.nbnorthshore.com NB North Shore - Online New Balance Shoe Store] |
|||
[[Category:Footwear]] |
|||
[[Category:Shoes|*]] |
|||
[[Category:Fashion]] |
|||
[[ |
[[Category:Shoes| ]] |
||
[[Category:Articles containing video clips]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:鞋]] |
|||
[[ |
[[Category:Footwear]] |
||
[[Category:Protective gear]] |
|||
[[da:Sko]] |
|||
[[de:Schuh]] |
|||
[[eo:Ŝuo]] |
|||
[[es:Zapato]] |
|||
[[fr:Chaussure]] |
|||
[[id:Sepatu]] |
|||
[[it:Scarpa]] |
|||
[[nl:Schoen]] |
|||
[[ja:靴]] |
|||
[[pl:But]] |
|||
[[pt:Sapato]] |
|||
[[ru:Ботинки]] |
|||
[[simple:Shoe]] |
|||
[[fi:Kenkä]] |
|||
[[sv:Skor]] |
|||
[[zh:鞋]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 13:28, 6 November 2024

A shoe is an item of footwear intended to protect and comfort the human foot. Though the human foot can adapt to varied terrains and climate conditions, it is vulnerable, and shoes provide protection. Form was originally tied to function, but over time, shoes also became fashion items. Some shoes are worn as safety equipment, such as steel-toe boots, which are required footwear at industrial worksites.
Additionally, shoes have often evolved into many different designs, such as high heels, which are most commonly worn by women during fancy occasions. Contemporary footwear varies vastly in style, complexity and cost. Basic sandals may consist of only a thin sole and simple strap and be sold for a low cost. High fashion shoes made by famous designers may be made of expensive materials, use complex construction and sell for large sums of money. Some shoes are designed for specific purposes, such as boots designed specifically for mountaineering or skiing, while others have more generalized usage such as sneakers which have transformed from a special purpose sport shoe into a general use shoe.
Traditionally, shoes have been made from leather, wood or canvas, but are increasingly being made from rubber, plastics, and other petrochemical-derived materials.[1] Globally, the shoe industry is a $200 billion a year industry.[1] 90% of shoes end up in landfills, because the materials are hard to separate, recycle or otherwise reuse.[1]
History
Antiquity



Earliest evidence
The earliest known shoes are sagebrush bark sandals dating from approximately 7000 or 8000 BC, found in the Fort Rock Cave in the US state of Oregon in 1938.[5] The world's oldest leather shoe, made from a single piece of cowhide laced with a leather cord along seams at the front and back, was found in the Areni-1 cave complex in Armenia in 2008 and is believed to date to 3500 BC.[6][7] Ötzi the Iceman's shoes, dating to 3300 BC, featured brown bearskin bases, deerskin side panels, and a bark-string net, which pulled tight around the foot.[6] The Jotunheimen shoe was discovered in August 2006: archaeologists estimate that this leather shoe was made between 1800 and 1100 BC,[8][9] making it the oldest article of clothing discovered in Scandinavia. Sandals and other plant fiber based tools were found in Cueva de los Murciélagos in Albuñol in southern Spain in 2023, dating to approximately 7500 to 4200 BC, making them what are believed to be the oldest shoes found in Europe.[10]
It is thought that shoes may have been used long before this, but because the materials used were highly perishable, it is difficult to find evidence of the earliest footwear.[11]
Footprints suggestive of shoes or sandals due to having crisp edges, no signs of toes found and three small divots where leather tying laces/straps would have been attached have been at Garden Route National Park, Addo Elephant National Park and Goukamma Nature Reserve in South Africa.[12] These date back to between 73,000 and 136,000 PB. Consistent with the existence of such shoe is the finding of bone awls dating back to this period that could have made simple footwear.[12]
Another source of evidence is the study of the bones of the smaller toes (as opposed to the big toe), it was observed that their thickness decreased approximately 40,000 to 26,000 years ago. This led archaeologists to deduce the existence of common rather than an occasional wearing of shoes as this would lead to less bone growth, resulting in shorter, thinner toes.[13] These earliest designs were very simple, often mere "foot bags" of leather to protect the feet from rocks, debris, and cold.
Americas
Many early natives in North America wore a similar type of footwear, known as the moccasin. These are tight-fitting, soft-soled shoes typically made out of leather or bison hides. Many moccasins were also decorated with various beads and other adornments. Moccasins were not designed to be waterproof, and in wet weather and warm summer months, most Native Americans went barefoot.[14] The leaves of the sisal plant were used to make twine for sandals in South America while the natives of Mexico used the Yucca plant.[15][16]
Africa and Middle East
As civilizations began to develop, thong sandals (precursors to the modern flip-flop) were worn. This practice dates back to pictures of them in ancient Egyptian murals from 4000 BC. "Thebet" may have been the term used to describe these sandals in Egyptian times, possibly from the city Thebes. The Middle Kingdom is when the first of these thebets were found, but it is possible that it debuted in the Early Dynastic Period.[17] One pair found in Europe was made of papyrus leaves and dated to be approximately 1,500 years old. They were also worn in Jerusalem during the first century of the Christian era.[18] Thong sandals were worn by many civilizations and made from a vast variety of materials. Ancient Egyptian sandals were made from papyrus and palm leaves. The Masai of Africa made them out of rawhide. In India they were made from wood.
While thong sandals were commonly worn, many people in ancient times, such as the Egyptians, Hindus and Greeks, saw little need for footwear, and most of the time, preferred being barefoot.[19] The Egyptians and Hindus made some use of ornamental footwear, such as a soleless sandal known as a "Cleopatra",[citation needed] which did not provide any practical protection for the foot.
Asia and Europe
The ancient Greeks largely viewed footwear as self-indulgent, unaesthetic and unnecessary. Shoes were primarily worn in the theater, as a means of increasing stature, and many preferred to go barefoot.[19] Athletes in the Ancient Olympic Games participated barefoot—and naked.[20] Even the gods and heroes were primarily depicted barefoot, as well as the hoplite warriors. They fought battles in bare feet and Alexander the Great conquered his vast empire with barefoot armies. The runners of Ancient Greece had also been believed to have run barefoot.[21]

The Romans, who eventually conquered the Greeks and adopted many aspects of their culture, did not adopt the Greek perception of footwear and clothing. Roman clothing was seen as a sign of power, and footwear was seen as a necessity of living in a civilized world, although the slaves and paupers usually went barefoot.[19] Roman soldiers were issued with chiral (left and right shoe different) footwear.[22] Shoes for soldiers had riveted insoles to extend the life of the leather, increase comfort, and provide better traction. The design of these shoes also designated the rank of the officers. The more intricate the insignia and the higher up the boot went on the leg, the higher the rank of the soldier.[23] There are references to shoes being worn in the Bible.[24] In China and Japan, rice straws were used.[citation needed]
Starting around 4 BC, the Greeks began wearing symbolic footwear. These were heavily decorated to clearly indicate the status of the wearer. Courtesans wore leather shoes colored with white, green, lemon or yellow dyes, and young woman betrothed or newly married wore pure white shoes. Because of the cost to lighten leather, shoes of a paler shade were a symbol of wealth in the upper class. Often, the soles would be carved with a message so it would imprint on the ground. Cobblers became a notable profession around this time, with Greek shoemakers becoming famed in the Roman empire.[25]
Middle Ages and early modern period
Asia and Europe
A common casual shoe in the Pyrenees during the Middle Ages was the espadrille. This is a sandal with braided jute soles and a fabric upper portion, and often includes fabric laces that tie around the ankle. The term is French and comes from the esparto grass. The shoe originated in the Catalonian region of Spain as early as the 13th century, and was commonly worn by peasants in the farming communities in the area.[16]
New styles began to develop during the Song dynasty in China, some of them resulting from the binding of women's feet, first used by the noble Han classes, but soon spreading throughout Chinese society. The practice allegedly started during the Shang dynasty, but it grew popular by c. AD 960.[26]
When the Mongols conquered China, they dissolved the practice in 1279, and the Manchus banned foot binding in 1644. The Han people, however, continued the practice without much government intervention.[26]

In medieval times shoes could be up to two feet long, with their toes sometimes filled with hair, wool, moss, or grass.[27] Many medieval shoes were made using the turnshoe method of construction, in which the upper was turned flesh side out, and was lasted onto the sole and joined to the edge by a seam.[28] The shoe was then turned inside-out so that the grain was outside. Some shoes were developed with toggled flaps or drawstrings to tighten the leather around the foot for a better fit. Surviving medieval turnshoes often fit the foot closely, with the right and left shoe being mirror images.[29] Around 1500, the turnshoe method was largely replaced by the welted rand method (where the uppers are sewn to a much stiffer sole and the shoe cannot be turned inside-out).[30] The turn shoe method is still used for some dance and specialty shoes.
By the 15th century, pattens became popular by both men and women in Europe. These are commonly seen as the predecessor of the modern high-heeled shoe,[31] while the poor and lower classes in Europe, as well as slaves in the New World, were barefoot.[19] In the 15th century, the Crakow was fashionable in Europe. This style of shoe is named because it is thought to have originated in Kraków, the capital of Poland. The style is characterized by the point of the shoe, known as the "polaine", which often was supported by a whalebone tied to the knee to prevent the point getting in the way while walking.[32] Also during the 15th century, chopines were created in Spain, and were usually 7–8 in (180–200 mm) high.[33] These shoes became popular in Venice and throughout Europe, as a status symbol revealing wealth and social standing. During the 16th century, royalty, such as Catherine de Medici or Mary I of England, started wearing high-heeled shoes to make them look taller or larger than life. By 1580, even men wore them, and a person with authority or wealth was often referred to as, "well-heeled".[31] In 17th century France, heels were exclusively worn by aristocrats. Louis XIV of France outlawed anybody from wearing red high heels except for himself and his royal court.[34]
Eventually the modern shoe, with a sewn-on sole, was devised. Since the 17th century, most leather shoes have used a sewn-on sole. This remains the standard for finer-quality dress shoes today. Until around 1800, welted rand shoes were commonly made without differentiation for the left or right foot. Such shoes are now referred to as "straights".[35] Only gradually did the modern foot-specific shoe become standard.
Industrial era
Asia and Europe

Shoemaking became more commercialized in the mid-18th century, as it expanded as a cottage industry. Large warehouses began to stock footwear, made by many small manufacturers from the area.
Until the 19th century, shoemaking was a traditional handicraft, but by the century's end, the process had been almost completely mechanized, with production occurring in large factories. Despite the obvious economic gains of mass production, the factory system produced shoes without the individual differentiation that the traditional shoemaker was able to provide.
In the 19th century Chinese feminists called for an end to foot binding, and a ban in 1902 was implemented. The ban was soon repealed, but it was banned again in 1911 by the new Nationalist government. It was effective in coastal cities, but countryside cities continued without much regulation. Mao Zedong enforced the rule in 1949 and the practice is still forbidden. A number of women still have bound feet today.[26]

The first steps towards mechanisation were taken during the Napoleonic Wars by the engineer, Marc Brunel. He developed machinery for the mass production of boots for the soldiers of the British Army. In 1812, he devised a scheme for making nailed-boot-making machinery that automatically fastened soles to uppers by means of metallic pins or nails.[36] With the support of the Duke of York, the shoes were manufactured, and, due to their strength, cheapness, and durability, were introduced for the use of the army. In the same year, the use of screws and staples was patented by Richard Woodman. Brunel's system was described by Sir Richard Phillips as a visitor to his factory in Battersea as follows:

In another building I was shown his manufactory of shoes, which, like the other, is full of ingenuity, and, in regard to subdivision of labour, brings this fabric on a level with the oft-admired manufactory of pins. Every step in it is affected by the most elegant and precise machinery; while, as each operation is performed by one hand, so each shoe passes through twenty-five hands, who complete from the hide, as supplied by the currier, a hundred pairs of strong and well-finished shoes per day. All the details are performed by the ingenious application of the mechanic powers; and all the parts are characterised by precision, uniformity, and accuracy. As each man performs but one step in the process, which implies no knowledge of what is done by those who go before or follow him, so the persons employed are not shoemakers, but wounded soldiers, who are able to learn their respective duties in a few hours. The contract at which these shoes are delivered to Government is 6s. 6d. per pair, being at least 2s. less than what was paid previously for an unequal and cobbled article.[37]
However, when the war ended in 1815, manual labour became much cheaper, and the demand for military equipment subsided. As a consequence, Brunel's system was no longer profitable and it soon ceased business.[36]
Americas
Similar exigencies at the time of the Crimean War stimulated a renewed interest in methods of mechanization and mass-production, which proved longer lasting.[36] A shoemaker in Leicester, Tomas Crick, patented the design for a riveting machine in 1853. His machine used an iron plate to push iron rivets into the sole. The process greatly increased the speed and efficiency of production. He also introduced the use of steam-powered rolling-machines for hardening leather and cutting-machines, in the mid-1850s.[38]


The sewing machine was introduced in 1846, and provided an alternative method for the mechanization of shoemaking. By the late 1850s, the industry was beginning to shift towards the modern factory, mainly in the US and areas of England. A shoe-stitching machine was invented by the American Lyman Blake in 1856 and perfected by 1864. Entering into a partnership with McKay, his device became known as the McKay stitching machine and was quickly adopted by manufacturers throughout New England.[39] As bottlenecks opened up in the production line due to these innovations, more and more of the manufacturing stages, such as pegging and finishing, became automated. By the 1890s, the process of mechanisation was largely complete.
On January 24, 1899, Humphrey O'Sullivan of Lowell, Massachusetts, was awarded a patent for a rubber heel for boots and shoes.[40]
Globalization
A process for manufacturing stitchless, that is, glued, shoes—AGO—was developed in 1910. Since the mid-20th century, advances in rubber, plastics, synthetic cloth, and industrial adhesives have allowed manufacturers to create shoes that stray considerably from traditional crafting techniques. Leather, which had been the primary material in earlier styles, has remained standard in expensive dress shoes, but athletic shoes often have little or no real leather. Soles, which were once laboriously hand-stitched on, are now more often machine stitched or simply glued on. Many of these newer materials, such as rubber and plastics, have made shoes less biodegradable. It is estimated that most mass-produced shoes require 1000 years to degrade in a landfill.[41] In the late 2000s, some shoemakers picked up on the issue and began to produce shoes made entirely from degradable materials, such as the Nike Considered.[42][43]
In 2007, the global shoe industry had an overall market of $107.4 billion, in terms of revenue, and is expected to grow to $122.9 billion by the end of 2012. Shoe manufacturers in the People's Republic of China account for 63% of production, 40.5% of global exports and 55% of industry revenue. However, many manufacturers in Europe dominate the higher-priced, higher value-added end of the market.[44]
Culture and folklore



As an integral part of human culture and civilization, shoes have found their way into our culture, folklore, and art. A popular 18th-century nursery rhyme is There was an Old Woman Who Lived in a Shoe. This story tells about an old woman living in a shoe with a lot of children. In 1948, Mahlon Haines, a shoe salesman in Hallam, Pennsylvania, built an actual house shaped like a work boot as a form of advertisement. The Haines Shoe House was rented to newlyweds and the elderly until his death in 1962. Since then, it has served as an ice cream parlor, a bed and breakfast, and a museum. It still stands today and is a popular roadside attraction.[45]
Shoes also play an important role in the fairy tales Cinderella and The Red Shoes. In the movie adaption of the children's book The Wonderful Wizard of Oz, a pair of red ruby slippers play a key role in the plot. The 1985 comedy The Man with One Red Shoe features an eccentric man wearing one normal business shoe and one red shoe that becomes central to the plot.
One poem, written by Phebus Etienne with the title "Shoes", focuses on them. It describes religious messages and is 3 stanzas long. The first stanza is one line, whereas the second is 13 lines and the third being 14 lines. Throughout the poem the main character talks about their dead mother and their routine with her grave. Haitians are said to "not put shoes on the dead." as it makes spirits easier to "step over the offerings".[46]
Athletic sneaker collection has also existed as a part of urban subculture in the United States for several decades.[47] Recent decades have seen this trend spread to European nations such as the Czech Republic.[48] A Sneakerhead is a person who owns multiple pairs of shoes as a form of collection and fashion. A contributor to the growth of sneaker collecting is the continued global popularity of the Air Jordan line of sneakers designed by Nike for Basketball star Michael Jordan.
In the Bible's Old Testament, the shoe is used to symbolize something that is worthless or of little value. In the New Testament, the act of removing one's shoes symbolizes servitude. Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples regarded the act of removing their shoes as a mark of reverence when approaching a sacred person or place.[49] In the Book of Exodus, Moses was instructed to remove his shoes before approaching the burning bush:
Put off thy shoes from off thy feet, for the place whereon thou standest [is] holy ground.[50]

The removal of the shoe also symbolizes the act of giving up a legal right. In Hebrew custom, if a man chose not to marry his childless brother's widow, the widow removed her brother-in-law's shoe to symbolize that he had abandoned his duty. In Arab custom, the removal of one's shoe also symbolized the dissolution of marriage.[49]
In Arab culture, showing the sole of one's shoe is considered an insult, and to throw a shoe and hit someone with it is considered an even greater insult. Shoes are considered to be dirty as they frequently touch the ground, and are associated with the lowest part of the body—the foot. As such, shoes are forbidden in mosques, and it is also considered unmannerly to cross the legs and display the soles of one's shoes during conversation. This insult was demonstrated in Iraq, first when Saddam Hussein's statue was toppled in 2003, Iraqis gathered around it and struck the statue with their shoes.[51] In 2008, United States President George W. Bush had a shoe thrown at him by a journalist as a statement against the war in Iraq.[52] More generally, shoe-throwing or shoeing, showing the sole of one's shoe or using shoes to insult are forms of protest in many parts of the world. Incidents where shoes were thrown at political figures have taken place in Australia, India, Ireland, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Pakistan, the United Kingdom, the United States, and most notably the Arab world.[53][54]
Empty shoes may also symbolize death. In Greek culture, empty shoes are the equivalent of the American funeral wreath. For example, empty shoes placed outside of a Greek home would tell others that the family's son has died in battle.[55] At an observation memorializing the 10th anniversary of the September 11 attacks, 3,000 pairs of empty shoes were used to recognize those killed.[56] The Shoes on the Danube Bank is a memorial in Budapest, Hungary. Conceived by film director Can Togay, he created it on the east bank of the Danube River with sculptor Gyula Pauer to honor the Jews who were killed by fascist Arrow Cross militiamen in Budapest during World War II. They were ordered to take off their shoes and were shot at the edge of the water so that their bodies fell into the river and were carried away. The memorial represents their shoes left behind on the bank.
Construction
The basic anatomy of a shoe is recognizable, regardless of the specific style of footwear.
All shoes have a sole, which is the bottom of a shoe, in contact with the ground. Soles can be made from a variety of materials, although most modern shoes have soles made from natural rubber, polyurethane, or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) compounds.[57] Soles can be simple—a single material in a single layer—or they can be complex, with multiple structures or layers and materials. When various layers are used, soles may consist of an insole, midsole, and an outsole.[58]
The insole is the interior bottom of a shoe, which sits directly beneath the foot under the footbed (also known as sock liner). The purpose of the insole is to attach to the lasting margin of the upper, which is wrapped around the last during the closing of the shoe during the lasting operation. Insoles are usually made of cellulosic paper board or synthetic non woven insole board. Many shoes have removable and replaceable footbeds. Extra cushioning is often added for comfort (to control the shape, moisture, or smell of the shoe) or health reasons (to help deal with differences in the natural shape of the foot or positioning of the foot during standing or walking).[58]
The outsole is the layer in direct contact with the ground. Dress shoes often have leather or resin rubber outsoles; casual or work-oriented shoes have outsoles made of natural rubber or a synthetic material like polyurethane. The outsole may comprise a single piece or may be an assembly of separate pieces, often of different materials. On some shoes, the heel of the sole has a rubber plate for durability and traction, while the front is leather for style. Specialized shoes will often have modifications on this design: athletic or so-called cleated shoes like soccer, rugby, baseball and golf shoes have spikes embedded in the outsole to improve traction.[58]
The midsole is the layer in between the outsole and the insole, typically there for shock absorption. Some types of shoes, like running shoes, have additional material for shock absorption, usually beneath the heel of the foot, where one puts the most pressure down. Some shoes may not have a midsole at all.[58]
The heel is the bottom rear part of a shoe. Its function is to support the heel of the foot. They are often made of the same material as the sole of the shoe. This part can be high for fashion or to make the person look taller, or flat for more practical and comfortable use.[58] On some shoes the inner forward point of the heel is chiselled off, a feature known as a "gentleman's corner". This piece of design is intended to alleviate the problem of the points catching the bottom of trousers and was first observed in the 1930s.[59] A heel is the projection at the back of a shoe which rests below the heel bone. The shoe heel is used to improve the balance of the shoe, increase the height of the wearer, alter posture or other decorative purposes. Sometimes raised, the high heel is common to a form of shoe often worn by women, but sometimes by men too. See also stiletto heel.
The upper helps hold the shoe onto the foot. In the simplest cases, such as sandals or flip-flops, this may be nothing more than a few straps for holding the sole in place. Closed footwear, such as boots, trainers and most men's shoes, will have a more complex upper. This part is often decorated or is made in a certain style to look attractive. The upper is connected to the sole by a strip of leather, rubber, or plastic that is stitched between it and the sole, known as a welt.[58]
Most uppers have a mechanism, such as laces, straps with buckles, zippers, elastic, velcro straps, buttons, or snaps, for tightening the upper on the foot. Uppers with laces usually have a tongue that helps seal the laced opening and protect the foot from abrasion by the laces. Uppers with laces also have eyelets or hooks to make it easier to tighten and loosen the laces and to prevent the lace from tearing through the upper material. An aglet is the protective wrapping on the end of the lace.
The vamp is the front part of the shoe, starting behind the toe, extending around the eyelets and tongue and towards back part of the shoe.
The medial is the part of the shoe closest to a person's center of symmetry, and the lateral is on the opposite side, away from their center of symmetry. This can be in reference to either the outsole or the vamp. Most shoes have shoelaces on the upper, connecting the medial and lateral parts after one puts their shoes on and aiding in keeping their shoes on their feet. In 1968, Puma SE introduced the first pair of sneakers with Velcro straps in lieu of shoelaces, and these became popular by the 1980s, especially among children and the elderly.[60][61]
The toe box is the part that covers and protects the toes. People with toe deformities, or individuals who experience toe swelling (such as long-distance runners) usually require a larger toe box.[62]
-
Diagram of a typical dress shoe. The area labeled as the "Lace guard" is sometimes considered part of the quarter and sometimes part of the vamp.
-
A shoemaker making turnshoes at the Roscheider Hof Open Air Museum. English subtitles.
-
Cutaway view of a typical shoe.
Types
This article contains promotional content. (January 2024) |
Most types of shoes are designed for specific activities. For example, boots are typically designed for work or heavy outdoor use. Athletic shoes are designed for particular sports such as running, walking, or other sports. Some shoes are designed to be worn at more formal occasions, and others are designed for casual wear. There are also a vast variety of shoes designed for different types of dancing. Orthopedic shoes are special types of footwear designed for individuals with particular foot problems or special needs. Clinicians evaluate patient's footwear as a part of their clinical examination. However, it is often based on each individual's needs, with attention to the choice of footwear worn and if the shoe is adequate for the purpose of completing their activities of daily living.[63] Other animals, such as dogs and horses, may also wear special shoes to protect their feet as well.
Depending on the activity for which they are designed, some types of footwear may fit into multiple categories. For example, Cowboy boots are considered boots, but may also be worn in more formal occasions and used as dress shoes. Hiking boots incorporate many of the protective features of boots, but also provide the extra flexibility and comfort of many athletic shoes. Flip-flops are considered casual footwear, but have also been worn in formal occasions, such as visits to the White House.[64][65]
Athletic


Athletic shoes are designed for various sports activities, focusing on maximizing friction between the foot and the ground. These shoes often utilize materials like rubber to achieve this purpose.[66] The earliest athletic shoes, dating to the mid-19th century, were track spikes with metal cleats for increased traction. Over time, athletic shoe design evolved, with companies like Reebok and Adidas contributing to the development of modern athletic shoes. Notable innovations include rubber-soled athletic shoes and the introduction of specialized shoes for different sports, such as basketball and golf. More recently, minimalist shoes have gained popularity as barefoot running became popular by the late 20th and early 21st century, maintaining optimum flexibility and natural walking while also providing some degree of protection. Their purpose is to allow one's feet and legs to feel more subtly the impacts and forces involved in running, allowing finer adjustments in running style.[67][16][68]
The earliest rubber-soled athletic shoes date back to 1876 in the United Kingdom, when the New Liverpool Rubber Company made plimsolls, or sandshoes, designed for the sport of croquet. Similar rubber-soled shoes were made in 1892 in the United States by Humphrey O'Sullivan, based on Charles Goodyear's technology. The United States Rubber Company was founded the same year and produced rubber-soled and heeled shoes under a variety of brand names, which were later consolidated in 1916 under the name, Keds. These shoes became known as, "sneakers", because the rubber sole allowed the wearer to sneak up on another person. In 1964, the founding of Nike by Phil Knight and Bill Bowerman of the University of Oregon introduced many new improvements common in modern running shoes, such as rubber waffle soles, breathable nylon uppers, and cushioning in the mid-sole and heel. During the 1970s, the expertise of podiatrists also became important in athletic shoe design, to implement new design features based on how feet reacted to specific actions, such as running, jumping, or side-to-side movement for men and women.[16]

Shoes specific to the sport of basketball were developed by Chuck Taylor, and are popularly known as Chuck Taylor All-Stars. In 1969, Taylor was inducted into the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame in recognition of this development, and in the 1970s, other shoe manufacturers, such as Nike, Adidas, Reebok, and others began imitating this style of athletic shoe.[69] In April 1985, Nike introduced its own brand of basketball shoe which would become popular in its own right, the Air Jordan, named after the then-rookie Chicago Bulls basketball player, Michael Jordan. The Air Jordan line of shoes sold $100 million in their first year.[70]
As barefoot running became popular by the late 20th and early 21st century, many modern shoe manufacturers have recently designed footwear that mimic this experience, maintaining optimum flexibility and natural walking while also providing some degree of protection. Some of these shoes include the Vibram FiveFingers,[71] Nike Free,[72] and Saucony's Kinvara and Hattori.[73][74] Mexican huaraches are also very simple running shoes, similar to the shoes worn by the Tarahumara people of northern Mexico, who are known for their distance running abilities.[75] Wrestling shoes are also very light and flexible shoes that are designed to mimic bare feet while providing additional traction and protection.
Many athletic shoes are designed with specific features for specific activities. One of these includes roller skates, which have metal or plastic wheels on the bottom specific for the sport of roller skating. Similarly, ice skates have a metal blade attached to the bottom for locomotion across ice. Skate shoes have also been designed to provide a comfortable, flexible and durable shoe for the sport of skateboarding.[76] Climbing shoes are rubber-soled, tight-fitting shoes designed to fit in the small cracks and crevices for rock climbing. Cycling shoes are similarly designed with rubber soles and a tight fit, but also are equipped with a metal or plastic cleat to interface with clipless pedals, as well as a stiff sole to maximize power transfer and support the foot.[77] Some shoes are made specifically to improve a person's ability to weight train.[78] Sneakers that are a mix between an activity-centered and a more standard design have also been produced: examples include roller shoes, which feature wheels that can be used to roll on hard ground, and Soap shoes, which feature a hard plastic sole that can be used for grinding.
Boot

Boots are a specialized type of footwear that covers the foot and extends up the leg. They serve both functional and fashion purposes, offering protection from elements like water, snow, and mud while also being a fashion statement.
Cowboy boots, for instance, are known for their distinctive style and are popular among cowboys in the western United States. Hiking boots, on the other hand, are designed for comfort and support during long walks in rough terrains. Snow boots are ideal for wet or snowy weather, providing warmth and protection against the elements. Additionally, boots are used in specialized activities like skiing, ice skating, and climbing due to their unique features tailored to these activities.[79][80][81][82]
Boots may also be attached to snowshoes to increase the distribution of weight over a larger surface area for walking in snow. Ski boots are a specialized snow boot which are used in alpine or cross-country skiing and designed to provide a way to attach the skier to his/her skis using ski bindings. The ski/boot/binding combination is used to effectively transmit control inputs from the skier's legs to the snow. Ice skates are another specialized boot with a metal blade attached to the bottom which is used to propel the wearer across a sheet of ice.[83] Inline skates are similar to ice skates but with a set of three to four wheels in lieu of the blade, which are designed to mimic ice skating on solid surfaces such as wood or concrete.[84]
Boots are designed to withstand heavy wear to protect the wearer and provide good traction. They are generally made from sturdy leather uppers and non-leather outsoles. They may be used for uniforms of the police or military, as well as for protection in industrial settings such as mining and construction. Protective features may include steel-tipped toes and soles or ankle guards.[85]
Dress and casual
Dress shoes are characterized by their smooth leather uppers, leather soles, and sleek design, suitable for formal occasions. In contrast, casual shoes have sturdier leather uppers, non-leather outsoles, and a wider profile for everyday wear. Some dress shoe designs are unisex, while others are specific to men or women.
Men's
Men's dress shoes include styles like Oxfords, Derbies, Monk-straps, and Slip-ons, each with its unique characteristics in terms of lacing, decoration, and formality.
Women's

Women's shoes cover a wide range of styles, including high heels, mules, slingbacks, ballet flats, and court shoes, with high-heeled footwear being a popular choice for formal occasions.
Unisex
- Clog
- Platform shoe: shoe with very thick soles and heels
- Sandals: open shoes consisting of a sole and various straps, leaving much of the foot exposed to air. They are thus popular for warm-weather wear, because they let the foot be cooler than a closed-toed shoe would.
- Saddle shoe: leather shoe with a contrasting saddle-shaped band over the instep, typically white uppers with black "saddle".
- Slip-on shoe: a dress or casual shoe without shoelaces or fasteners; often with tassels, buckles, or coin-holders (penny loafers).
- Boat shoes, also known as "deck shoes": similar to a loafer, but more casual. Laces are usually simple leather with no frills. Typically made of leather and featuring a soft white sole to avoid marring or scratching a boat deck. The first boat shoe was invented in 1935 by Paul A. Sperry.
- Slippers: For indoor use, commonly worn with pajamas.
Dance
Dancers use a variety of footwear depending on the style of dance and the surface they will be dancing on. Pointe shoes, for instance, are designed for ballet dancing, featuring a stiffened toe box and hardened sole to allow dancers to stand on the tips of their toes. Ballet shoes, on the other hand, are soft, pliable shoes made of canvas or leather, providing flexibility and comfort for ballet dancing. Other dance shoe types include jazz shoes, tango, and flamenco shoes, ballroom shoes, tap shoes, character shoes, and foot thongs, each designed to meet the specific needs of different dance styles.
-
Jazz shoes. This style is frequently worn by acro dancers
-
A foot thong, viewed from the bottom
-
Ladies' ballroom shoes
-
Men's ballroom shoes
-
Children's shoe from the early 80s.
Orthopedic

Orthopedic shoes are specially designed to alleviate discomfort associated with various foot and ankle disorders, such as blisters, bunions, calluses, and plantar fasciitis. They are also used by individuals with diabetes, unequal leg length, or children with mobility issues.[86][87][88] These shoes typically feature a low heel, wide toe box, and firm heel for added support. Some orthopedic shoes come with removable insoles or orthotics to provide extra arch support.[16]
Measures and sizes

Shoe sizes are indicated by a numerical value representing the length of the shoe, with different systems used globally. European sizes are measured in Paris Points, while the UK and American units are based on whole-number sizes spaced at one barleycorn (1/3 inch) with UK adult sizes starting at size 1 = 8+2⁄3 in (22.0 cm). In the US, this is size 2. Men's and women's shoe sizes often use different scales[citation needed], and some systems are measured using a Brannock Device which considers the width and length size values of the feet. The Mondopoint system, introduced in the 1970s by International Standard ISO 2816:1973 "Fundamental characteristics of a system of shoe sizing to be known as Mondopoint" and ISO 3355:1975 "Shoe sizes – System of length grading (for use in the Mondopoint system)" includes measurements of both length and width of the foot.[89][90]

Accessories
Various accessories are used to enhance the functionality and comfort of shoes. Crampons provide traction on icy terrain, foam taps adjust shoe fit, heel grips prevent slipping, and ice cleats enhance stability on slippery surfaces. Overshoes protect shoes from rain and snow, while shoe bags are used for storage. Shoe brushes and polishing cloths maintain shoe appearance, while shoe inserts offer additional comfort.
Removal of shoes

In many places in the world, shoes are removed when moving from exteriors to interiors, particularly in homes[91][92] and religious buildings.[93] In many Asian countries, outdoor shoes are exchanged for indoor shoes or slippers.[94] Fitness center etiquette encourages the exchange of outdoor shoes for indoor shoes, both to prevent dirt and grime from being transferred to the equipment and to ensure that participants are wearing the right shoes for their activities.[95]
See also
- Foot binding
- List of shoe companies
- List of shoe styles
- Locomotor effects of shoes
- Runner's toe, injury from malfitting shoes
- Shoe dryer
- Shoe rack
- Shoe tossing
- Trousers
- Shoe fetish
References
- ^ a b c Hoskins, Tansy E. (2020-03-21). "'Some soles last 1,000 years in landfill': the truth about the sneaker mountain". The Guardian. Retrieved 2021-02-19.
- ^ "The Scottish Ten". The Engine Shed. Centre for Digital Documentation and Visualisation LLP. Retrieved 14 October 2017.
- ^ "Lady's Shoe, Bar Hill". 2015-09-25. Retrieved 24 May 2018.
- ^ "Child's Shoe, Bar Hill". 2015-09-22. Retrieved 24 May 2018.
- ^ Connolly, Tom. "The World's Oldest Shoes". University of Oregon. Archived from the original on July 22, 2012. Retrieved July 22, 2012.
- ^ a b Ravilious, Kate (June 9, 2010). "World's Oldest Leather Shoe Found—Stunningly Preserved". National Geographic. Archived from the original on July 24, 2012. Retrieved July 22, 2012.
- ^ Petraglia, Michael D.; Pinhasi R; Gasparian B; Areshian G; Zardaryan D; Smith A; et al. (2010). Petraglia, Michael D. (ed.). "First Direct Evidence of Chalcolithic Footwear from the Near Eastern Highlands". PLOS ONE. 5 (6): e10984. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...510984P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010984. PMC 2882957. PMID 20543959. Reported in (among others) Belluck, Pam (9 June 2010). "This Shoe Had Prada Beat by 5,500 Years". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 June 2010. Retrieved 11 June 2010.
- ^ Nesje, Atle; Pilø, Lars Holger; Finstad, Espen; Solli, Brit; Wangen, Vivian; Ødegård, Rune Strand; Isaksen, Ketil; Støren, Eivind N.; Bakke, Dag Inge; Andreassen, Liss M (2011). "The climatic significance of artefacts related to prehistoric reindeer hunting exposed at melting ice patches in southern Norway". The Holocene. 22 (4): 485–496. doi:10.1177/0959683611425552. ISSN 0959-6836. S2CID 129845949.
- ^ "Old Shoe- Even Older". The Norway Post, 2 May 2007. Archived 8 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Francisco Martínez-Sevilla; et al. (27 Sep 2023). "The earliest basketry in southern Europe: Hunter-gatherer and farmer plant-based technology in Cueva de los Murciélagos (Albuñol)". Science Advances. 9 (39): eadi3055. Bibcode:2023SciA....9I3055M. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adi3055. PMC 10530072. PMID 37756397.
- ^ Johnson, Olivia (August 24, 2005). "Bones Reveal First Shoe-Wearers". BBC News. Archived from the original on June 3, 2012. Retrieved July 23, 2012.
- ^ a b Helm, Charles W.; Lockley, Martin G.; Cawthra, Hayley C.; De Vynck, Jan C.; Dixon, Mark G.; Rust, Renée; Stear, Willo; Van Tonder, Monique; Zipfel, Bernhard (2023). "Possible shod-hominin tracks on South Africa's Cape coast". Ichnos. 30 (2): 79–97. Bibcode:2023Ichno..30...79H. doi:10.1080/10420940.2023.2249585. ISSN 1042-0940. S2CID 261313433.
- ^ Trinkaus, E.; Shang, H. (July 2008). "Anatomical Evidence for the Antiquity of Human Footwear: Tianyuan and Sunghir". Journal of Archaeological Science. 35 (7): 1928–1933. Bibcode:2008JArSc..35.1928T. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2007.12.002.
- ^ Laubin, Reginald; Laubin, Gladys; Vestal, Stanley (1977). The Indian Tipi: Its History, Construction, and Use. Norman, Oklahoma: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-2236-6. Archived from the original on 2018-04-27.
- ^ Kippen, Cameron (1999). The History of Footwear. Perth, Australia: Department of Podiatry, Curtin University of Technology.
- ^ a b c d e DeMello, Margo (2009). Feet and Footwear: A Cultural Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO, LLC. pp. 20–24, 90, 108, 130–131, 226–230. ISBN 978-0-313-35714-5.
- ^ "Egypt: The Birthplace of Flip Flops? – The Sheridan Libraries & University Museums Blog". 21 July 2017. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
- ^ Kendzior, Russell J. (2010). Falls Aren't Funny: America's Multi-Billion-Dollar Slip-and-Fall Crisis. Lanham, Maryland: www.govtinstpress.com/ Government Institutes. p. 117. ISBN 978-0-86587-016-1. Archived from the original on 2017-03-19.
- ^ a b c d Frazine, Richard Keith (1993). The Barefoot Hiker. Ten Speed Press. p. 98. ISBN 978-0-89815-525-9.
- ^ "Unearthing the First Olympics". NPR. July 19, 2004. Archived from the original on July 28, 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ Krentz, Peter (2010). The Battle of Marathon. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. pp. 112–113. ISBN 978-0-300-12085-1. Archived from the original on 2018-04-27.
- ^ 'Greece and Rome at War' by Peter Connolly
- ^ Swann, June (2001). History of Footwear in Norway, Sweden and Finland: Prehistory to 1950. Kungl. Vitterhets, historie och antikvitets akademien. ISBN 9789174023237.
- ^ Genesis 14:23, Deuteronomy 25:9, Ruth 4:7-8, Luke 15:22.
- ^ Ledger, Florence (1985). Put Your Foot Down: A Treatise on the History of Shoes. C. Venton. ISBN 9780854751112.
- ^ a b c "The History of Foot Binding in China". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 2022-05-17.
- ^ Ruth Hibbard (9 Jul 2015). "Getting To The Point Of Medieval Shoes". Victoria & Albert Museum. Retrieved 4 Oct 2021.
- ^ "Making Basic Viking-Age Men's Clothing". www.vikingsof.me. Retrieved 2020-11-07.
- ^ 'Shoes and Pattens: Finds from Medieval Excavations in London' (Medieval Finds from Excavations in London) by Francis Grew & Margrethe de Neergaard
- ^ Blair, John (1991). English Medieval Industries: Craftsmen, Techniques, Products. London: Continuum International Publishing Group. p. 309. ISBN 978-0-907628-87-3. Archived from the original on 2016-04-25.
- ^ a b "Dangerous Elegance: A History of High-Heeled Shoes". Random History. Archived from the original on July 28, 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ The Encyclopaedia of the Renaissance. Market House Books. 1988. ISBN 978-0-7134-5967-8.
- ^ Anderson, Ruth Matilda (1979). Hispanic costume, 1480-1530. Hispanic Society of America. ISBN 978-0-87535-126-1.
- ^ Riello, Giorgio; McNeil, Peter (March 2007). "Footprints from History". History Today. 57 (3).
- ^ Yue, Charlotte (1997). Shoes: Their History in Words and Pictures. New York City: Houghton Mifflin Company. pp. 46. ISBN 978-0-395-72667-9.
straights+shoes.
- ^ a b c "History of Shoemaking in Britain—Napoleonic Wars and the Industrial Revolution". Archived from the original on 2014-02-02.
- ^ Richard Phillips, Morning's Walk from London to Kew, 1817.
- ^ R. A. McKinley (1958). "FOOTWEAR MANUFACTURE". British History Online. Archived from the original on 2014-02-03.
- ^ Charles W. Carey (2009). American Inventors, Entrepreneurs, and Business Visionaries. Infobase Publishing. p. 27. ISBN 9780816068838.
- ^ O'Sullivan, Gary B (2007). The Oak and Serpent. Lulu. p. 300. ISBN 978-0615155579. Retrieved 2019-01-24.
- ^ Clark, Brian (October 24, 2009). "Biodegradable... Shoes??". The Daily Green. Archived from the original on September 20, 2012. Retrieved July 23, 2012.
- ^ "What is Nike Considered?". Nike, Inc. Retrieved July 23, 2012.
- ^ "Ground-breaking Technology Brings World's First Biodegradable Midsole to Runners". CSR Press Release. November 15, 2007. Archived from the original on July 28, 2012. Retrieved July 23, 2012.
- ^ "Global Footwear Manufacturing Industry Market Research Report". PRWeb. June 7, 2012. Archived from the original on March 13, 2013. Retrieved July 24, 2012.
- ^ Lake, Matt; Moran, Mark; Sceurman, Mark (2005). Weird Pennsylvania: Your Travel Guide to Pennsylvania's Local Legends and Best Kept Secrets. New York City: Sterling Publishing Co. p. 131. ISBN 978-1-4027-3279-9. Archived from the original on 2016-03-06.
- ^ Etienne, Phebus (2001). "Shoes". Callaloo. 24 (3): 738. doi:10.1353/cal.2001.0137. ISSN 0161-2492. JSTOR 3300161. S2CID 246284343.
- ^ Skidmore, Sarah (15 January 2007). "Sneakerheads Love to Show Off Their Shoes". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 12 November 2012. Retrieved 2 July 2011.
- ^ "Czech 'Sneakerheads' Flaunt Their Best Trainers". Czech Position. Archived from the original on 20 June 2011. Retrieved 2 July 2011.
- ^ a b Farbridge, Maurice H. (2003). Studies in Biblical & Semitic Symbolism 1923. Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7661-3856-8. Archived from the original on 2016-12-22., pages=273–274
- ^ Exodus 3:5
- ^ Gammell, Caroline (December 15, 2008). "Arab Culture: The Insult of the Shoe". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on July 25, 2012. Retrieved July 24, 2012.
- ^ Asser, Martin (December 15, 2008). "Bush Shoe-ing Worst Arab Insult". BBC News. Archived from the original on October 16, 2012. Retrieved July 24, 2012.
- ^ Arab culture: the insult of the shoe Archived 2018-03-12 at the Wayback Machine, The Telegraph, 15 December 2008.
- ^ Bush shoe-ing worst Arab insult Archived 2012-05-30 at the Wayback Machine, BBC, 16 December 2008.
- ^ Reeve, Andru J. (2004). Turn Me On, Dead Man: The Beatles and the "Paul Is Dead" Hoax. Bloomington, Indiana: AuthorHouse. p. 79. ISBN 978-1-4184-8294-7. Archived from the original on 2016-04-27.
- ^ Cohen, Sam (September 11, 2011). "Empty Shoes an Emotional Reminder of Those Who Died on 9/11". Fox 40. Retrieved July 23, 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Karak, Niranjan (2009). Fundamentals Of Polymers: Raw Materials To Finish Products. New Delhi: PHI Learning Private Limited. pp. 263–264. ISBN 978-81-203-3877-7. Archived from the original on 2016-05-13.
- ^ a b c d e f Vonhof, John (2011). Fixing Your Feet: Prevention and Treatments for Athletes. Birmingham, Alabama: Wilderness Press. pp. 58–59. ISBN 978-0-89997-638-9. Archived from the original on 2016-05-06.
- ^ Oliver Sweeney Ltd. "Home Page—Oliver Sweeney". oliversweeney.com. Archived from the original on 2014-10-04.
- ^ Suddath, Claire (June 15, 2010). "A Brief History of: Velcro". Time. Archived from the original on September 13, 2012. Retrieved July 30, 2012.
- ^ Frank, Robert H. (2007). The Economic Naturalist: In Search of Explanations for Everyday Enigmas. New York City: Basic Books. pp. 174. ISBN 978-0-465-00217-7.
velcro laces.
- ^ Edelstein, Joan E.; Bruckner, Jan (2002). Orthotics: A Comprehensive Clinical Approach. SLACK Incorporated. pp. 21. ISBN 978-1-55642-416-8.
- ^ Ellis, Stephen; Branthwaite, Helen; Chockalingam, Nachiappan (December 2022). "Evaluation and optimisation of a footwear assessment tool for use within a clinical environment". Journal of Foot and Ankle Research. 15 (1): 12. doi:10.1186/s13047-022-00519-6. PMC 8829975. PMID 35144665.
- ^ Ward, Julie (September 13, 2005). "Next big step in team spirit: Flip-flops". USA Today. Archived from the original on August 9, 2011. Retrieved July 19, 2012.
- ^ Lister, Richard (February 19, 2010). "Flip-flop Diplomacy With the Dalai Lama". BBC News. Archived from the original on October 16, 2012. Retrieved July 19, 2012.
- ^ McGinnis, Peter M. (2005). Biomechanics of Sport and Exercise (Second ed.). Champaign, Illinois: www.humankinetics.com. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-7360-5101-9. Archived from the original on 2016-04-29.
- ^ Winters, Dan (November 2010). "Is Less More?". Runner's World. Archived from the original on July 28, 2012. Retrieved July 23, 2012.
- ^ Farrally, Martin R.; Cochran, Alastair J. (1999). Science and Golf III: Proceedings of the 1998 World Scientific Congress of Golf. Champaign, Illinois: www.humankinetics.com. pp. 568–569. ISBN 978-0-7360-0020-8. Archived from the original on 2016-05-18.
- ^ Peterson, Hal (2007). Chucks!: The Phenomenon of Converse Chuck Taylor All Stars. New York City: Skyhorse Publishing. ISBN 978-1-60239-079-9. Archived from the original on 2016-05-11.
- ^ Papson, Stephen; Goldman, Robert (1998). Nike Culture: The Sign of the Swoosh. London: SAGE Publications. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-7619-6148-2. Archived from the original on 2016-05-17.
- ^ "Vibram FiveFingers Named A "Best Invention of 2007" by Time Magazine". trailspace.com. 12 November 2007. Archived from the original on 13 May 2010. Retrieved June 26, 2010.
- ^ Cortese, Amy (August 29, 2009). "Wiggling Their Toes at the Shoe Giants". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 4, 2011. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ "Saucony Progrid Kinvara Running Shoe Review: Runner's World". Runner's World. February 15, 2008. Archived from the original on September 11, 2011. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ Jhung, Lisa (May 2011). "Saucony Minimalism". Runner's World. Archived from the original on 2011-05-06. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ McDougall, Christopher (2011). Born to Run: A Hidden Tribe, Superathletes, and the Greatest Race the World Has Never Seen. New York City: Vintage Books. pp. 168, 172. ISBN 978-0-307-27918-7.
born to run.
- ^ Welinder, Per; Whitley, Peter (2012). Mastering Skateboarding. Champaign, Illinois: Human Kinetics. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-7360-9599-0. Archived from the original on 2016-06-24.
- ^ International Police Mountain Bike Association (2008). The Complete Guide to Public Safety Cycling. Sudbury, Massachusetts: Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-7637-4433-5. Archived from the original on 2016-05-19.
- ^ Radding, Ben (November 15, 2018). "The Best Weightlifting Shoes, According to Trainers". Yahoo Life.
- ^ DeWeese, G. Daniel (June 29, 2010). "The Functional Side of Cowboy Boots". True West Magazine. Archived from the original on October 16, 2012. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- ^ Chand, Elise Gaston (2009). A Parent's Guide to Riding Lessons: Everything You Need to Know to Survive and Thrive With a Horse-Loving Kid. North Adams, Massachusetts: Storey Publishing. p. 91. ISBN 978-1-60342-447-9. Archived from the original on 2016-05-10.
- ^ Howe, Steve (March 2002). "Boots". Backpacker. Archived from the original on March 18, 2013. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- ^ Stimpert, Desiree. "What Makes a Boot a Snow Boot". About.com. Archived from the original on July 23, 2012. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- ^ Bellis, Mary. "History of Ice Skates". About.com. Archived from the original on December 5, 2012. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- ^ Olsen, Scott & Brennan. "Inline-Skates". lemelson.mit.edu. Archived from the original on May 2, 2006. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- ^ Somaiya, A.; James, E.; Wieffering, N. (2008). Construction Materials. Forest Drive, Pinelands, Cape Town: Pearson Education South Africa. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-77025-156-4. Archived from the original on 2016-05-08.
- ^ Hill, Matthew; Healy, Aoife; Chockalingam, Nachiappan (December 2019). "Key concepts in children's footwear research: a scoping review focusing on therapeutic footwear". Journal of Foot and Ankle Research. 12 (1): 25. doi:10.1186/s13047-019-0336-z. PMC 6487054. PMID 31061678.
- ^ Hill, Matthew; Healy, Aoife; Chockalingam, Nachiappan (December 2020). "Effectiveness of therapeutic footwear for children: A systematic review". Journal of Foot and Ankle Research. 13 (1): 23. doi:10.1186/s13047-020-00390-3. PMC 7222438. PMID 32404124.
- ^ Hill, Matthew; Healy, Aoife; Chockalingam, Nachiappan (August 2021). "Defining and grouping children's therapeutic footwear and criteria for their prescription: an international expert Delphi consensus study". BMJ Open. 11 (8): e051381. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051381. ISSN 2044-6055. PMC 8354267. PMID 34373314.
- ^ US patent 1725334, "Foot-measuring instrument", published 1929-08-20
- ^ R. Boughey. Size Labelling of Footwear. Journal of Consumer Studies & Home Economics. Volume 1, Issue 2. June 1977. DOI:10.1111/j.1470-6431.1977.tb00197.x
- ^ Kurzius, Rachel (October 2, 2023). "The case for — and against — taking your shoes off in the house". Washington Post. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
- ^ Spier, Ally (April 24, 2020). "Should You Take Your Shoes Off While Indoors?". Architectural Digest. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
- ^ Sood, Suemedha (June 17, 2011). "Religious tourism etiquette". BBC Home. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
- ^ LaMotte, Sandee (December 7, 2023). "The dirty truth about taking your shoes off at the door". CNN. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
- ^ C.P.T, Lee Boyce (2023-11-06). "Gym Etiquette Code of Conduct: 12 Rules for Every Lifter". Men's Journal. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
Bibliography
- Bergstein, Rachelle (2012). Women from the Ankle Down: The Story of Shoes and How They Define Us (Hardback). New York: Harper Collins. pp. 284 pages. ISBN 978-0-06-196961-4.
- Doe, Tamasin (1998), Patrick Cox: Wit, Irony, and Footwear, ISBN 0-8230-1148-8.
- Pattison, Angela, A Century of Shoes: Icons of Style in the 20th Century, ISBN 0-7858-0835-3.
- Swann, June. History of Footwear in Norway, Sweden and Finland: Prehistory to 1950, ISBN 91-7402-323-3.
Further reading
- Design Museum. Fifty Shoes That Changed the World. London: Conran Octopus, 2009. ISBN 978-1-84091-539-6.
External links
- Bata Shoe Museum's online exhibits on the history and variety of footwear: "All About Shoes". Archived from the original on 2022-10-05.
- "Footwear History". Archived from the original on 2006-08-13.
- "International Shoe Size Conversion Charts"., from i18nguy's website, offers more information.
- "Shoe Care". Archived from the original on 2012-12-18.
- Illustrated "Glossary of Shoe Terms". Archived from the original on 2022-03-19.
- Map: "Medieval shoes in museums".