ʻEua: Difference between revisions
IdiotSavant (talk | contribs) →Ecology: - expand |
Mr. Lechkar (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Island in Tonga}} |
{{short description|Island in Tonga}} |
||
{{use dmy dates|date=March 2024}} |
|||
{{Infobox islands |
{{Infobox islands |
||
|name = |
|name = ʻEua |
||
|image_name = File:ʻEuaFromTheISS(Cropped).jpg |
|image_name = File:ʻEuaFromTheISS(Cropped).jpg |
||
|image_caption = |
|image_caption = |
||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
|elevation_m = 312 |
|elevation_m = 312 |
||
|country = Tonga |
|country = Tonga |
||
|country_admin_divisions_title = |
|country_admin_divisions_title = Vakaʻuta |
||
|country_admin_divisions =KVL |
|country_admin_divisions = KVL |
||
|country_largest_city = |
|country_largest_city = ʻOhonua |
||
|country_largest_city_population = |
|country_largest_city_population = |
||
|population = 4,903<ref name=MT2021Census>{{cite web |url=https://matangitonga.to/2021/12/24/tongas-population-drops-100209 |title=Tonga's population drops to 100,209 |publisher=Matangi Tonga |date=24 December 2021 |access-date=24 December 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211224045529/https://matangitonga.to/2021/12/24/tongas-population-drops-100209 |archive-date=24 December 2021}}</ref> |
|population = 4,903<ref name=MT2021Census>{{cite web |url=https://matangitonga.to/2021/12/24/tongas-population-drops-100209 |title=Tonga's population drops to 100,209 |publisher=Matangi Tonga |date=24 December 2021 |access-date=24 December 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211224045529/https://matangitonga.to/2021/12/24/tongas-population-drops-100209 |archive-date=24 December 2021}}</ref> |
||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
|density_km2 = 60.04 |
|density_km2 = 60.04 |
||
|ethnic_groups = Tongan (majority), European, Chinese, Pacific Islanders |
|ethnic_groups = Tongan (majority), European, Chinese, Pacific Islanders |
||
|image_map=Eua in Tonga.svg}} |
|||
}} |
|||
[[File:Eua in Tonga.svg|thumb|120px|Location of |
[[File:Eua in Tonga.svg|thumb|120px|Location of ʻEua District in Tonga]] |
||
[[File:ʻEua.gif|thumb|right|170px|Map of |
[[File:ʻEua.gif|thumb|right|170px|Map of ʻEua]] |
||
''' |
'''ʻEua''' {{IPA-to|ʔe.ˈu.a|}} is an island in the kingdom of [[Tonga]]. It is close to [[Tongatapu]], but forms a separate [[Administrative divisions of Tonga|administrative division]]. It has an area of {{convert|87.44|km2|2|abbr=on}}, and a population in 2021 of 4,903 people. The island leads in agriculture, tourism, and some of the forestry helps the island economically.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ʿEua |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Eua }}</ref> |
||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
ʻEua is a hilly island, the highest peaks are the ''Teʻemoa'' (chicken manure) 312 m, and the ''Vaiangina'' (watersprings) 305 m. The island is not volcanic, but was shaped by the rubbing of the [[Tonga Plate]] against the [[Pacific Plate]], pushing ʻEua up and leaving the {{convert|7|km|mi|adj=mid|-deep}} [[Tonga Trench]] on the bottom of the ocean, a short distance towards the east. The soil of ʻEua is volcanic, as is that of Tongatapu, but only the top layer, deposited by eruptions of nearby volcanoes ten thousands years ago. Under it are the solid rocks of pushed-up coral. ʻEua counts many huge caves and holes, not all of which have yet been explored. |
|||
ʻEua and [[Niuatoputapu]] are the only islands in Tonga that have [[stream]]s, and ʻEua had the only bridge in the kingdom until one was also built in [[Vavaʻu]].<ref>[https://www.britannica.com/place/Tonga Encyclopædia Britannica – Tonga]</ref> The stream drains into the harbour near the capital of the island, [[ʻOhonua]]. |
|||
A unique feature is the shore between |
A unique feature is the shore between ʻOhonua and [[Tufuvai]]. It is coral reef still close to the sea level. Many small tidal pools are found, named the ʻotumatafena. |
||
It is served by [[ʻEua Airport]], which has an unsealed coral runway. |
It is served by [[ʻEua Airport]], which has an unsealed coral runway. |
||
==Myths== |
==Myths== |
||
Together with [[ʻAta |
Together with [[ʻAta]], ʻEua was the first island to be created by Tangaloa, see ''Tangaloa And The Story Of How ʻEua Island Was Created''.<ref>{{cite web|title=Tangaloa <!-- BOT GENERATED TITLE -->|url=http://www.eua-island-tonga.com/Tangaloa.html|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110710204553/http://www.eua-island-tonga.com/Tangaloa.html|archivedate=2011-07-10|url-status=live|accessdate=2009-09-18}}</ref> |
||
==History== |
==History== |
||
ʻEua was put on the European maps by [[Abel Tasman]] who reached it and [[Tongatapu]] on 21 January 1643. He called it ''Middelburg Island'', after the Dutch city of [[Middelburg, Zeeland]]. He did not go on land, but proceeded to the [[Hihifo (Tongatapu)|Hihifo]] district of Tongatapu, which he named ''Amsterdam Island'' after the capital of the [[Netherlands]]. |
|||
ʻEua was considered by early missionaries as heathen as it was the rendezvous for whalers, a place that you can trade goods for guns, knives, axes and gunpowder. aka arsenal, or armory of Tonga, as well as its granary. |
|||
[[ |
[[James Cook]] visited the island in 1773 and 1777. On his map, it is named ''Eaoowe''.<ref name="Anne">{{cite book|last1=Salmond|first1=Anne|title=Aphrodite's Island|date=2010|publisher=University of California Press|location=Berkeley|isbn=9780520261143|pages=[https://archive.org/details/aphroditesisland00salm/page/291 291-292,417]|url-access=registration|url=https://archive.org/details/aphroditesisland00salm/page/291}}</ref> |
||
==Administration== |
==Administration== |
||
ʻEua is divided into two districts |
ʻEua is divided into two districts: |
||
* [[ |
* [[ʻEua Motuʻa]] (Old ʻEua), in the north, with six villages and population of 2,771. |
||
* [[ |
* [[ʻEua Foʻou]] (New ʻEua), in the south, with 2,132 inhabitants in nine villages. |
||
The nine villages of the southern district |
The nine villages of the southern district ʻEua Niuafoʻou (or ʻEua Foʻou for short) were founded by people who had to leave their island of Niuafoʻou in 1946 due to a volcanic eruption; they are all named after villages of Niuafoʻou. |
||
The northern district in contrast is Old |
The northern district in contrast is Old ʻEua. The southern village of [[Kolomaile]]'s inhabitants however are descendants of the former inhabitants of the island of [[ʻAta#History|ʻAta]], Tonga's southernmost island, evacuated after the island was targeted by [[slave ship|slavers]]. |
||
{{convert|3.8|km|1|abbr=off}} south-west of the southern tip of |
{{convert|3.8|km|1|abbr=off}} south-west of the southern tip of ʻEua (Lakufaʻanga) is the 35-acre island [[Kalau]]. |
||
==Demography== |
==Demography== |
||
| Line 70: | Line 71: | ||
|2021 |4,903 |
|2021 |4,903 |
||
|footnote=Sources:<ref name=1996Census>{{cite web |url=https://tonga-data.sprep.org/resource/1996-tonga-census-administrative-report |title=1996 Tonga Census Administrative Report |page=xii |publisher=Tonga Department of Statistics |access-date=30 December 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://tongastats.gov.to/census/ |title=Census |publisher=Tonga Statistics Department |date= |access-date=30 December 2021}}</ref><ref name=MT2021Census/>}} |
|footnote=Sources:<ref name=1996Census>{{cite web |url=https://tonga-data.sprep.org/resource/1996-tonga-census-administrative-report |title=1996 Tonga Census Administrative Report |page=xii |publisher=Tonga Department of Statistics |access-date=30 December 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://tongastats.gov.to/census/ |title=Census |publisher=Tonga Statistics Department |date= |access-date=30 December 2021}}</ref><ref name=MT2021Census/>}} |
||
The villages of the original inhabitants of |
The villages of the original inhabitants of ʻEua are all in the north: [[Houma (ʻEua)|Houma]], [[Taʻanga]], [[ʻOhonua]], [[Pangai (ʻEua)|Pangai]], [[Tufuvai]]. |
||
[[ |
[[Haʻatuʻa]] and [[Kolomaile]] are from the original inhabitants from ʻAta, who were resettled there in 1863. The villages just north of that up to [[Angahā (ʻEua)|Angahā]], are from the inhabitants of [[Niuafoʻou]] who were resettled there in 1946. |
||
==Ecology== |
==Ecology== |
||
ʻEua is the only habitat of the [[maroon shining parrot|koki]] (''Prosopeia tabuensis'') in Tonga.<ref name=Saafi2002>{{cite thesis |url=http://hdl.handle.net/10179/12329 |title=Ecology and conservation of koki (Prosopeia tabuensis) in Tonga |type=MSc |date=2002 |publisher=Massey University |last=Saafi |first=Elizabeth Patisepa Kiteau |access-date=1 January 2022}}</ref>{{rp|4}} It supports 12 species of birds, nine of lizards, and two bats, the [[Insular flying fox]] and [[Pacific sheath-tailed bat]].<ref name=Saafi2002/>{{rp|9}} Bird species include the [[Buff-banded rail]], [[Pacific imperial pigeon]], [[Crimson-crowned fruit dove]], [[White-rumped swiftlet]], [[Collared kingfisher]], [[Polynesian starling]], [[Polynesian triller]] and [[Polynesian wattled honeyeater]].<ref name=Gill1987>{{cite journal |url=https://www.birdsnz.org.nz/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Notornis_34_3-1987pp217-223.pdf |title=NOTES ON THE BIRDS, REPTILES AND MAMMALS OF TONGATAPU AND 'EUA (TONGA) |last1=Gill |first1=B. J. |journal=Notornis |volume=34 |year=1987 |pages= |
ʻEua is the only habitat of the [[maroon shining parrot|koki]] (''Prosopeia tabuensis'') in Tonga.<ref name=Saafi2002>{{cite thesis |url=http://hdl.handle.net/10179/12329 |title=Ecology and conservation of koki (Prosopeia tabuensis) in Tonga |type=MSc |date=2002 |publisher=Massey University |last=Saafi |first=Elizabeth Patisepa Kiteau |hdl=10179/12329 |access-date=1 January 2022}}</ref>{{rp|4}} It supports 12 species of birds, nine of lizards, and two bats, the [[Insular flying fox]] and [[Pacific sheath-tailed bat]].<ref name=Saafi2002/>{{rp|9}} Bird species include the [[Buff-banded rail]], [[Pacific imperial pigeon]], [[Crimson-crowned fruit dove]], [[White-rumped swiftlet]], [[Collared kingfisher]], [[Polynesian starling]], [[Polynesian triller]] and [[Polynesian wattled honeyeater]].<ref name=Gill1987>{{cite journal |url=https://www.birdsnz.org.nz/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Notornis_34_3-1987pp217-223.pdf |title=NOTES ON THE BIRDS, REPTILES AND MAMMALS OF TONGATAPU AND 'EUA (TONGA) |last1=Gill |first1=B. J. |journal=Notornis |volume=34 |year=1987 |pages=217–223 |access-date=11 August 2022}}</ref> Reptiles include the [[Gehyra oceanica|Oceanic gecko]], [[Lepidodactylus lugubris|mourning gecko]] and [[Emoia cyanura|blue-tailed skink]].<ref name=Gill1987/> |
||
==Culture== |
==Culture== |
||
The 2014 film ''[[When the Man Went South]]'' was mostly filmed on ʻEua.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Tonga |url=http://whenthemanwentsouth.com/tonga/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160401075930/http://whenthemanwentsouth.com/tonga/ |archive-date=2016-04-01 |access-date=2024-03-02 |website=When the Man Went South}}</ref> |
|||
The 2014 film ''[[When the Man Went South]]'' was mostly filmed on ʻEua.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://whenthemanwentsouth.com/tonga/Put%20your%20own%20URL%20to%20the%20object%20here|title=Sample Article}}</ref> |
|||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
{{Gallery |
{{Gallery |
||
|File:Eua National Park.jpg|alt1= |
|File:Eua National Park.jpg|alt1=ʻEua National Park |ʻEua National Park, looking south, on the Eastern side of ʻEua |
||
|File:‘Ohonua&whales.jpg |alt2=Humpback whale off the coast of |
|File:‘Ohonua&whales.jpg |alt2=Humpback whale off the coast of ʻEua |[[Humpback whale]]s with Ohonua in the background |
||
|File:Regenwald auf Eua.jpg |alt3=Forest in |
|File:Regenwald auf Eua.jpg |alt3=Forest in ʻEua |Forest in ʻEua |
||
|File:Эуа, церковь.jpg | alt4=Church on |
|File:Эуа, церковь.jpg | alt4=Church on ʻEua |Church on ʻEua |
||
|File:Eua Island.jpg |alt5=Forested cliffs on |
|File:Eua Island.jpg |alt5=Forested cliffs on ʻEua |Forested cliffs on ʻEua |
||
}} |
}} |
||
==See also == |
==See also == |
||
* [[ |
* [[ʻEua National Park]] |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://www.eua-island-tonga.com/index.html eua-island-tonga.com] ([https://www. |
* [http://www.eua-island-tonga.com/index.html eua-island-tonga.com] ([https://archive.today/20130102160840/http://www.eua-island-tonga.com/index.html Archived] 2009-04-18) |
||
{{coord|21|23|15|S|174|56|02|W|region:TO_type:isle|display=title}} |
{{coord|21|23|15|S|174|56|02|W|region:TO_type:isle|display=title}} |
||
{{Divisions of Tonga}} |
{{Divisions of Tonga}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Eua}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Eua}} |
||
[[Category:ʻEua| ]] |
[[Category:ʻEua| ]] |
||
[[Category:History of Tonga]] |
|||
[[Category:Islands of Tonga]] |
[[Category:Islands of Tonga]] |
||
[[Category:Tongan mythology]] |
[[Category:Tongan mythology]] |
||
Latest revision as of 04:38, 5 September 2024
 | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 21°23′S 174°56′W / 21.383°S 174.933°W |
| Archipelago | Tonga Tapu Islands |
| Total islands | 2 |
| Major islands | 1 |
| Area | 87.44 km2 (33.76 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 312 m (1024 ft) |
| Highest point | Funga Fonua |
| Administration | |
Tonga | |
| Vakaʻuta | KVL |
| Largest settlement | ʻOhonua |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 4,903[1] (2021) |
| Pop. density | 60.04/km2 (155.5/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Tongan (majority), European, Chinese, Pacific Islanders |


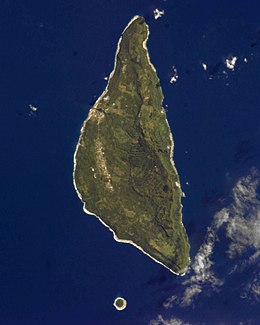
ʻEua [ʔe.ˈu.a] is an island in the kingdom of Tonga. It is close to Tongatapu, but forms a separate administrative division. It has an area of 87.44 km2 (33.76 sq mi), and a population in 2021 of 4,903 people. The island leads in agriculture, tourism, and some of the forestry helps the island economically.[2]
Geography
[edit]ʻEua is a hilly island, the highest peaks are the Teʻemoa (chicken manure) 312 m, and the Vaiangina (watersprings) 305 m. The island is not volcanic, but was shaped by the rubbing of the Tonga Plate against the Pacific Plate, pushing ʻEua up and leaving the 7-kilometre-deep (4.3 mi) Tonga Trench on the bottom of the ocean, a short distance towards the east. The soil of ʻEua is volcanic, as is that of Tongatapu, but only the top layer, deposited by eruptions of nearby volcanoes ten thousands years ago. Under it are the solid rocks of pushed-up coral. ʻEua counts many huge caves and holes, not all of which have yet been explored.
ʻEua and Niuatoputapu are the only islands in Tonga that have streams, and ʻEua had the only bridge in the kingdom until one was also built in Vavaʻu.[3] The stream drains into the harbour near the capital of the island, ʻOhonua.
A unique feature is the shore between ʻOhonua and Tufuvai. It is coral reef still close to the sea level. Many small tidal pools are found, named the ʻotumatafena.
It is served by ʻEua Airport, which has an unsealed coral runway.
Myths
[edit]Together with ʻAta, ʻEua was the first island to be created by Tangaloa, see Tangaloa And The Story Of How ʻEua Island Was Created.[4]
History
[edit]ʻEua was put on the European maps by Abel Tasman who reached it and Tongatapu on 21 January 1643. He called it Middelburg Island, after the Dutch city of Middelburg, Zeeland. He did not go on land, but proceeded to the Hihifo district of Tongatapu, which he named Amsterdam Island after the capital of the Netherlands.
ʻEua was considered by early missionaries as heathen as it was the rendezvous for whalers, a place that you can trade goods for guns, knives, axes and gunpowder. aka arsenal, or armory of Tonga, as well as its granary.
James Cook visited the island in 1773 and 1777. On his map, it is named Eaoowe.[5]
Administration
[edit]ʻEua is divided into two districts:
- ʻEua Motuʻa (Old ʻEua), in the north, with six villages and population of 2,771.
- ʻEua Foʻou (New ʻEua), in the south, with 2,132 inhabitants in nine villages.
The nine villages of the southern district ʻEua Niuafoʻou (or ʻEua Foʻou for short) were founded by people who had to leave their island of Niuafoʻou in 1946 due to a volcanic eruption; they are all named after villages of Niuafoʻou.
The northern district in contrast is Old ʻEua. The southern village of Kolomaile's inhabitants however are descendants of the former inhabitants of the island of ʻAta, Tonga's southernmost island, evacuated after the island was targeted by slavers.
3.8 kilometres (2.4 miles) south-west of the southern tip of ʻEua (Lakufaʻanga) is the 35-acre island Kalau.
Demography
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1976 | 4,486 | — |
| 1986 | 4,393 | −2.1% |
| 1996 | 4,934 | +12.3% |
| 2006 | 5,206 | +5.5% |
| 2011 | 5,016 | −3.6% |
| 2016 | 4,945 | −1.4% |
| 2021 | 4,903 | −0.8% |
| Sources:[6][7][1] | ||
The villages of the original inhabitants of ʻEua are all in the north: Houma, Taʻanga, ʻOhonua, Pangai, Tufuvai.
Haʻatuʻa and Kolomaile are from the original inhabitants from ʻAta, who were resettled there in 1863. The villages just north of that up to Angahā, are from the inhabitants of Niuafoʻou who were resettled there in 1946.
Ecology
[edit]ʻEua is the only habitat of the koki (Prosopeia tabuensis) in Tonga.[8]: 4 It supports 12 species of birds, nine of lizards, and two bats, the Insular flying fox and Pacific sheath-tailed bat.[8]: 9 Bird species include the Buff-banded rail, Pacific imperial pigeon, Crimson-crowned fruit dove, White-rumped swiftlet, Collared kingfisher, Polynesian starling, Polynesian triller and Polynesian wattled honeyeater.[9] Reptiles include the Oceanic gecko, mourning gecko and blue-tailed skink.[9]
Culture
[edit]The 2014 film When the Man Went South was mostly filmed on ʻEua.[10]
Gallery
[edit]-
ʻEua National Park, looking south, on the Eastern side of ʻEua
-
Humpback whales with Ohonua in the background
-
Forest in ʻEua
-
Church on ʻEua
-
Forested cliffs on ʻEua
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Tonga's population drops to 100,209". Matangi Tonga. 24 December 2021. Archived from the original on 24 December 2021. Retrieved 24 December 2021.
- ^ "ʿEua".
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica – Tonga
- ^ "Tangaloa". Archived from the original on 10 July 2011. Retrieved 18 September 2009.
- ^ Salmond, Anne (2010). Aphrodite's Island. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 291-292, 417. ISBN 9780520261143.
- ^ "1996 Tonga Census Administrative Report". Tonga Department of Statistics. p. xii. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ "Census". Tonga Statistics Department. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ a b Saafi, Elizabeth Patisepa Kiteau (2002). Ecology and conservation of koki (Prosopeia tabuensis) in Tonga (MSc). Massey University. hdl:10179/12329. Retrieved 1 January 2022.
- ^ a b Gill, B. J. (1987). "NOTES ON THE BIRDS, REPTILES AND MAMMALS OF TONGATAPU AND 'EUA (TONGA)" (PDF). Notornis. 34: 217–223. Retrieved 11 August 2022.
- ^ "Tonga". When the Man Went South. Archived from the original on 1 April 2016. Retrieved 2 March 2024.
External links
[edit]- eua-island-tonga.com (Archived 2009-04-18)





