Submandibular lymph nodes: Difference between revisions
link artery |
→Additional images: lowercase |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 32 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Lymph nodes near the jaw}} |
|||
{{Infobox |
{{Infobox lymph |
||
Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |
|||
| Name = Submandibular lymph nodes |
|||
| Latin = nodi lymphoidei submandibulares |
|||
GraySubject = 177 | |
|||
| Image = Illu quiz hn 03.jpg |
|||
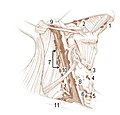
| ⚫ | | Caption = 1: [[Submental lymph nodes]]<br />2: Submandibular lymph nodes<br />3: [[Supraclavicular lymph nodes]]<br />4: [[Retropharyngeal lymph nodes]]<br />5: [[Buccinator lymph node]]<br />6: [[Superficial cervical lymph nodes]]<br />7: [[Jugular lymph nodes]]<br />8: [[Parotid lymph nodes]]<br />9: [[Retroauricular lymph nodes]] and [[occipital lymph nodes]] |
||
Image = Illu quiz hn 03.jpg | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| Source = [[Mandibular lymph node]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| DrainsTo = |
|||
DrainsTo = | |
|||
MeshName = | |
|||
MeshNumber = | |
|||
DorlandsPre = n_09 | |
|||
DorlandsSuf = 12577166 | |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''submandibular lymph nodes''' ('''submaxillary glands''' in older texts), |
The '''submandibular lymph nodes''' ('''submaxillary glands''' in older texts), are some 3-6 [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]] situated at the inferior border of the [[ramus of mandible]].<ref name=":023">{{Cite book |last=Fehrenbach |first=Margaret J. |title=Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck |last2=Herring |first2=Susan W. |date=2017 |publisher=Elsevier |isbn=978-0-323-39634-9 |edition=5th |location=St. Louis |pages=250}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
One gland, the ''middle gland of Stahr'', which lies on the [[external maxillary artery]] as it turns over the mandible, is the most constant of the series; small lymph glands are sometimes found on the deep surface of the [[submaxillary salivary glands]]. |
|||
They are situated just superficial to the submandibular salivary gland, and posterolateral to the anterior belly of either digastric muscle.<ref name=":023" /> |
|||
One gland, the ''middle gland of Stahr'', which lies on the [[facial artery]] as it turns over the mandible, is the most constant of the series; small lymph glands are sometimes found on the deep surface of the [[submandibular gland]].{{Citation needed|date=July 2023}} |
|||
=== Afferents === |
|||
''Efferent'' vessels from the facial and submental glands also enter the submaxillary glands. Their efferent vessels pass to the [[superior deep cervical glands]]. |
|||
They drain the upper lip, body of tongue, cheeks, anterior portion of the [[hard palate]], and most teeth with their associated periodontium and gingiva (except for the mandibular incisor teeth and third molar teeth).<ref name=":023" /> |
|||
The facial and [[submental lymph nodes]] may also drain into the submandibular glands.<ref name=":023" /> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Efferents === |
|||
They drain to the [[superior deep cervical lymph nodes|superior]]{{Citation needed|date=July 2023}} [[superior deep cervical lymph nodes|deep cervical lymph nodes]].<ref name=":023" /> |
|||
== Clinical significance == |
|||
The most common causes of enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes are infections of the head, neck, ears, eyes, nasal sinuses, pharynx, and scalp.<ref name=":023" /> |
|||
The lymph glands may be affected by metastatic spread of cancers of the oral cavity, anterior portion of the nasal cavity, soft tissues of the mid-face, and submandibular salivary gland.<ref name=":023" /> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:illu_lymph_chain02.jpg|Deep lymph nodes |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
== |
== References == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Gray's}} |
{{Gray's}} |
||
<references /> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
== External links == |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* https://web.archive.org/web/20080216031919/http://www.med.mun.ca/anatomyts/head/hnl3a.htm |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080517165214/http://www.bcm.edu/oto/studs/anat/neck.html Diagram] at [[Baylor College of Medicine]] |
|||
* [http://patient.info/health/non-hodgkins-lymphoma-leaflet http://www.patient.info/] |
|||
* http://www.aafp.org/afp/20021201/2103.html |
|||
* http://www.emedicine.com/ent/topic306.htm#section~anatomy_of_the_cervical_lymphatics |
|||
{{Lymphatics of head and neck}} |
{{Lymphatics of head and neck}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Submandibular Lymph Nodes}} |
|||
[[Category:Lymphatics of the head and neck]] |
|||
{{lymphatic-stub}} |
|||
{{Portal bar|Anatomy}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 15:19, 16 May 2024
| Submandibular lymph nodes | |
|---|---|
 1: Submental lymph nodes 2: Submandibular lymph nodes 3: Supraclavicular lymph nodes 4: Retropharyngeal lymph nodes 5: Buccinator lymph node 6: Superficial cervical lymph nodes 7: Jugular lymph nodes 8: Parotid lymph nodes 9: Retroauricular lymph nodes and occipital lymph nodes | |
 Superficial lymph glands and lymphatic vessels of head and neck. (Submaxillary glands labeled at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Source | Mandibular lymph node |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nodi lymphoidei submandibulares |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The submandibular lymph nodes (submaxillary glands in older texts), are some 3-6 lymph nodes situated at the inferior border of the ramus of mandible.[1]
Anatomy
[edit]They are situated just superficial to the submandibular salivary gland, and posterolateral to the anterior belly of either digastric muscle.[1]
One gland, the middle gland of Stahr, which lies on the facial artery as it turns over the mandible, is the most constant of the series; small lymph glands are sometimes found on the deep surface of the submandibular gland.[citation needed]
Afferents
[edit]They drain the upper lip, body of tongue, cheeks, anterior portion of the hard palate, and most teeth with their associated periodontium and gingiva (except for the mandibular incisor teeth and third molar teeth).[1]
The facial and submental lymph nodes may also drain into the submandibular glands.[1]
Efferents
[edit]They drain to the superior[citation needed] deep cervical lymph nodes.[1]
Clinical significance
[edit]The most common causes of enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes are infections of the head, neck, ears, eyes, nasal sinuses, pharynx, and scalp.[1]
The lymph glands may be affected by metastatic spread of cancers of the oral cavity, anterior portion of the nasal cavity, soft tissues of the mid-face, and submandibular salivary gland.[1]
Additional images
[edit]-
Deep lymph nodes
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 697 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 697 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
[edit]- Archived Diagram via umich.edu - rollover to see labels
- https://web.archive.org/web/20080216031919/http://www.med.mun.ca/anatomyts/head/hnl3a.htm
- Diagram at Baylor College of Medicine
- http://www.patient.info/
- http://www.aafp.org/afp/20021201/2103.html
- http://www.emedicine.com/ent/topic306.htm#section~anatomy_of_the_cervical_lymphatics