SA3 coupler: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Added date. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | Category:Soviet inventions | #UCB_Category 110/237 |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Automatic coupler for railway use}} |
{{Short description|Automatic coupler for railway use}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{more citations needed|date=September 2011}} |
{{more citations needed|date=September 2011}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{train topics}} |
{{train topics}} |
||
[[File:Diesel locomotive and power generator TGe-016 (3).jpg|280px|thumb|SA3 couplers]] |
[[File:Diesel locomotive and power generator TGe-016 (3).jpg|280px|thumb|SA3 couplers]] |
||
[[File:Scepka.GIF|thumb|280px|[[:Image:Sa3.gif|Click here for animation of coupling]]]] |
[[File:Scepka.GIF|thumb|280px|[[:Image:Sa3.gif|Click here for animation of coupling]]]] |
||
[[File:AutSA3 coup1.jpg|thumb|280px|SA3 details]] |
[[File:AutSA3 coup1.jpg|thumb|280px|SA3 details]] |
||
[[File:AuSA3 coupler2.jpg|thumb|280px|End view of coupler, with release lever to the left]] |
[[File:AuSA3 coupler2.jpg|thumb|280px|End view of SA3 coupler, with release lever to the left.|alt=End view of SA3 coupler, with release lever to the left.]] |
||
| ⚫ | '''SA3''' couplers (also known as СА3 or СА-3 couplers per the typical foundry stamp on top of these couplers, meaning "'''С'''оветская '''А'''втосцепка, '''3'''" in Russian or "'''S'''oviet '''A'''uto-latch '''3'''" in English) or '''Willison coupler''' and '''Russian coupler''' are [[railway coupling]]s used primarily in [[Russia]] and states influenced by the former [[Soviet Union]], such as Finland, Poland, and Mongolia.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railfaneurope.net/pix/de/misc/coupling/pix.html|title=Picture Gallery - Directory: /pix/de/misc/coupling|website=www.railfaneurope.net|accessdate=8 December 2022}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | '''SA3''' couplers (also known as СА3 or СА-3 couplers per the typical foundry stamp on top of these couplers, meaning "'''С'''оветская '''А'''втосцепка, '''3'''" in Russian or "'''S'''oviet '''A'''uto-latch '''3'''" in English) or '''Willison coupler''' and '''Russian coupler''' are [[railway coupling]]s used primarily in [[Russia]] and states |
||
Russian railways originally used [[buffers and chain coupler]]s during [[Russian Empire|Imperial era]], however these had several disadvantages: their draft load was limited, they were susceptible to buffer lock, and they were not semiautomatic like the North American [[Janney coupler]]s. Conversion to Janney couplers (as [[Japan]] and [[Australia]] had) was considered, as was development of a new design. The Willison coupler was patented in 1916 by [[John Willison (inventor)|John Willison]] from [[Derby, England]]. The [[Knorr-Bremse]] company bought |
Russian railways originally used [[buffers and chain coupler]]s during [[Russian Empire|Imperial era]], however these had several disadvantages: their draft load was limited, they were susceptible to buffer lock, and they were not semiautomatic like the North American [[Janney coupler]]s. Conversion to Janney couplers (as [[Japan]] and [[Australia]] had) was considered, as was development of a new design. The Willison coupler was patented in Germany (1914) and in US (1916) by English locksmith [[John Willison (inventor)|John Willison]] from [[Derby, England]]. The [[Knorr-Bremse]] company bought the invention in 1912 and it started to be used in Germany for some heavy trains and some suburban trains in Berlin and Paris. In the 1930s, the Soviets improved on this design and then decided to make this coupler standard across the Russian railway system. |
||
== Experimentation == |
== Experimentation == |
||
In the late 1920s, the [[Union Internationale des Chemins de Fer|UIC]] had established a working group for the replacement of the chain link coupler, which restricts the efficiency of freight railroads in a major way. Many railroads ran prototypes. In Germany, coal trains with [[Scharfenberg coupler]]s yielded unfavourable results in winter weather, other railroads did similar tests. But the UIC was not able to agree on one replacement. This failure of the UIC, which hampers freight operation in Europe even today, led to the decision by the Soviet Union to move forward without a standard being achieved in the talks. |
In the late 1920s, the [[Union Internationale des Chemins de Fer|UIC]] had established a working group for the replacement of the chain link coupler, which restricts the efficiency of freight railroads in a major way. Many railroads ran prototypes. In Germany, coal trains with [[Scharfenberg coupler]]s yielded unfavourable results in winter weather, other railroads did similar tests. But the UIC was not able to agree on one replacement. This failure of the UIC, which hampers freight operation in Europe even today, led to the decision by the Soviet Union to move forward without a standard being achieved in the talks. |
||
The coupler was developed in |
The coupler was developed in 1932 and named SA3 (abbreviation of Russian {{lang|ru|Советская автосцепка, 3-й вариант}}, Soviet Automatic-Coupler 3rd Variant) and was an improved version of the Willison coupler, with better design of lock parts and mechanics. Conversion of rolling stock began in 1935. The Second World War delayed the introduction, so that the conversion was completed only 1957. |
||
== Operation == |
== Operation == |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
In addition, the heavy iron ore trains on the Swedish [[Malmbanan]] began to use SA3 couplings in 1969 after problems with snapping chain couplers and a need for ever increasing capacity with higher train weights. Today, [[IORE]] locomotives haul trains of 68 [[hopper car]]s of {{convert|120|t|LT ST}} with a total weight of over {{convert|8000|t|LT ST}} over gradients of 1% in harsh weather conditions, from the [[LKAB]] mine in [[Kiruna]] to the ice-free harbour of [[Narvik]], [[Norway]] using couplings of the SA3 type without any problem. They tried out [[Janney coupler]]s, too, when moving beyond 8,000 tons because SA3 hasn't seen much use at such loads before that: in the Soviet Union, freight trains rarely exceeded 6,000 tons. The earlier [[SJ Dm3]] locomotives have buffers fitted; therefore, they can couple with rolling stock fitted with buffers and chain. |
In addition, the heavy iron ore trains on the Swedish [[Malmbanan]] began to use SA3 couplings in 1969 after problems with snapping chain couplers and a need for ever increasing capacity with higher train weights. Today, [[IORE]] locomotives haul trains of 68 [[hopper car]]s of {{convert|120|t|LT ST}} with a total weight of over {{convert|8000|t|LT ST}} over gradients of 1% in harsh weather conditions, from the [[LKAB]] mine in [[Kiruna]] to the ice-free harbour of [[Narvik]], [[Norway]] using couplings of the SA3 type without any problem. They tried out [[Janney coupler]]s, too, when moving beyond 8,000 tons because SA3 hasn't seen much use at such loads before that: in the Soviet Union, freight trains rarely exceeded 6,000 tons. The earlier [[SJ Dm3]] locomotives have buffers fitted; therefore, they can couple with rolling stock fitted with buffers and chain. |
||
The longest and heaviest train with SA3 couplings ran on 20 February 1986 from Ekibastuz to the Urals, Soviet Union. The composition consisted of 439 coal wagons and several diesel locomotives distributed along the train with a mass of 43,400 tonnes and the total length of {{convert|6.5|km|mi|abbr=on}}.<ref> |
The longest and heaviest train with SA3 couplings ran on 20 February 1986 from Ekibastuz to the Urals, Soviet Union. The composition consisted of 439 coal wagons and several diesel locomotives distributed along the train with a mass of 43,400 tonnes and the total length of {{convert|6.5|km|mi|abbr=on}}.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.railways.kz/en/node/509 |title=Kazakhstan railways |access-date=10 January 2015 |archive-date=10 January 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150110234809/http://www.railways.kz/en/node/509 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
=== Heaviest regular load === |
=== Heaviest regular load === |
||
* [[Mauritania railway]] hauls iron ore trains of about 21,000 tonnes. |
|||
The heaviest load for the SA3 in Ukraine is 12,000 tonnes.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://en.thepage.ua/economy/ukraines-switch-to-european-railway-gauge|title=Shmyhal reports complete switch of Ukraine to European railway gauge: Why this is impossible|website=The Page|accessdate=8 December 2022}}</ref> |
* The heaviest load for the SA3 in Ukraine is 12,000 tonnes.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://en.thepage.ua/economy/ukraines-switch-to-european-railway-gauge|title=Shmyhal reports complete switch of Ukraine to European railway gauge: Why this is impossible|website=The Page|date=26 May 2022 |accessdate=8 December 2022}}</ref> |
||
* [[Uzhhorod–Košice broad-gauge track]] iron ore trains of 4,200 tonnes. |
|||
== Developments == |
|||
[[File:Mittelpufferkupplung gekuppelt.JPG|alt=Unicoupler/Intermat/AK69e coupler on cargo train|thumb|Unicoupler/Intermat/AK69e coupler on cargo train]] |
|||
Based on the mechanical design of SA3 couplers has begun the development of a common European coupler under the umbrella of the [[International Union of Railways|UIC]] and the [[Organization for Cooperation of Railways|OSShD]]. For the latter was tasked the Waggonbau Bautzen ([[East Germany|GDR]]) and on the part of the UIC the [[Knorr-Bremse|Knorr Bremse]] ([[West Germany|FRG]]). The result were the fully tested and ready for production design [[Railway coupling#Unicoupler/Intermat|Unicoupler]]. Beside an installation for heavy ore trains in West Germany was no commercial application. |
|||
At the end of the 1980s a separate development in West Germany aimed to mitigate some issues of Unicoupler. It was known under the label [[Railway coupling#Z-AK|Z-AK]], but got no practical relevance. |
|||
[[File:J10 304 Kuppelkopf C-Ak.jpg|alt=Detailed View of a C-AKv Coupling Head|thumb|Detailed view of a C-AKv coupling head]] |
|||
| ⚫ | At the end of the 1990s [[SAB WABCO]] (now [[Faiveley Transport]] [[Witten]]) restarted development of a coupler on mechanical SA3 scheme. It was named [[C-AKv coupler|C-AKv]]<ref>[http://www.ba-bautzen.de/wirtschaftssenioren/amk/amkenglish/wabconeu_e.htm Automatic Center Coupler (C-AKv)] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090519233410/http://www.ba-bautzen.de/wirtschaftssenioren/amk/amkenglish/wabconeu_e.htm |date=19 May 2009}}</ref> and has different solutions for the problems of pneumatic and electric couplings. It also has vertical stability added, so that the coupling cannot fall down and damage the tracks or cause a derailment. It is compatible with the standard SA3 coupler and will have buffers needed for use with the standard [[buffers and chain coupler]]s. The electric plugs would be most useful with [[electronically controlled pneumatic brakes]]. The practical tests started in 2002 with heavy cargo trains in coal mining in Germany. The C-AKv was a strong candidate for a common European automatic coupler as a joining successor on the Eurasian continent. |
||
During the preparation for a common [[digital automatic coupling]] (DAC) in the [[European Union|EU]], there was another SA3-compatible coupler contributed by [[Construcciones y Auxiliar de Ferrocarriles|CAF]], but it was not chosen.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Bundesministerium für Verkehr und digitale Infrastruktur |date=2020-06-18 |title=Erstellung eines Konzeptes für die EU-weite Migration eines Digitalen Automatischen Kupplungssystems (DAK) für den Schienengüterverkehr. Schlussbericht. |url=https://www.bmvi.de/SharedDocs/DE/Anlage/E/schlussbericht-dak-studie.pdf?__blob=publicationFile |access-date=2024-01-07 |website=bmdv.bund.de |publisher=[[Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport|Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport (Germany)]] |page=77 |language=de |type=PDF}}</ref> |
|||
== Future == |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
== Usage == |
== Usage == |
||
| Line 62: | Line 71: | ||
* {{flag|Finland}}, [[Rail transport in Finland]] |
* {{flag|Finland}}, [[Rail transport in Finland]] |
||
* {{flag|Gabon}}, [[Trans-Gabon Railway]] (called Willison coupler) {{citation needed|date=January 2016}} |
* {{flag|Gabon}}, [[Trans-Gabon Railway]] (called Willison coupler) {{citation needed|date=January 2016}} |
||
* {{flag|Iran}}, [[ |
* {{flag|Iran}}, [[Islamic Republic of Iran Railways]] |
||
* {{flag|Iraq}}, [[Iraqi Republic Railways]] |
* {{flag|Iraq}}, [[Iraqi Republic Railways]] |
||
* {{flagicon|Mauritania}} [[Mauritania Railway]] operated by Société Nationale Industrielle et Minière |
* {{flagicon|Mauritania}} [[Mauritania Railway]] operated by Société Nationale Industrielle et Minière |
||
| Line 82: | Line 91: | ||
{{div col|colwidth=23em}} |
{{div col|colwidth=23em}} |
||
* [[C-AKv coupler]] |
* [[C-AKv coupler]] |
||
* [[Railway coupling# |
* [[Railway coupling#Draw gear|Draft gear]] |
||
* [[Gangway connection]] |
* [[Gangway connection]] |
||
* [[Janney coupler]]s used by heaviest trains up to {{convert|30000|ST|t LT|0|lk=on|abbr=on|disp=br()}}. |
* [[Janney coupler]]s, used by the heaviest trains up to {{convert|30000|ST|t LT|0|lk=on|abbr=on|disp=br()}}. |
||
* [[Intermat coupler]] |
* [[Intermat coupler]] |
||
* [[Longest trains]] of {{convert|2.5|km|mi|abbr=on}} |
* [[Longest trains]] of {{convert|2.5|km|mi|abbr=on}} |
||
| Line 96: | Line 105: | ||
== External == |
== External == |
||
* [https:// |
* [https://patents.google.com/patent/US4102459 Adapter piece between SA3 coupler] and [[Janney coupler]] |
||
{{Railway coupling}} |
{{Railway coupling}} |
||
Latest revision as of 23:08, 13 December 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2011) |
| Part of a series on |
| Rail transport |
|---|
 |
|
|
| Infrastructure |
|
|
| Service and rolling stock |
|
| Urban rail transit |
|
|
| Miscellanea |
|
|

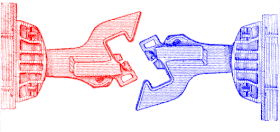


SA3 couplers (also known as СА3 or СА-3 couplers per the typical foundry stamp on top of these couplers, meaning "Советская Автосцепка, 3" in Russian or "Soviet Auto-latch 3" in English) or Willison coupler and Russian coupler are railway couplings used primarily in Russia and states influenced by the former Soviet Union, such as Finland, Poland, and Mongolia.[1]
Russian railways originally used buffers and chain couplers during Imperial era, however these had several disadvantages: their draft load was limited, they were susceptible to buffer lock, and they were not semiautomatic like the North American Janney couplers. Conversion to Janney couplers (as Japan and Australia had) was considered, as was development of a new design. The Willison coupler was patented in Germany (1914) and in US (1916) by English locksmith John Willison from Derby, England. The Knorr-Bremse company bought the invention in 1912 and it started to be used in Germany for some heavy trains and some suburban trains in Berlin and Paris. In the 1930s, the Soviets improved on this design and then decided to make this coupler standard across the Russian railway system.
Experimentation
[edit]In the late 1920s, the UIC had established a working group for the replacement of the chain link coupler, which restricts the efficiency of freight railroads in a major way. Many railroads ran prototypes. In Germany, coal trains with Scharfenberg couplers yielded unfavourable results in winter weather, other railroads did similar tests. But the UIC was not able to agree on one replacement. This failure of the UIC, which hampers freight operation in Europe even today, led to the decision by the Soviet Union to move forward without a standard being achieved in the talks.
The coupler was developed in 1932 and named SA3 (abbreviation of Russian Советская автосцепка, 3-й вариант, Soviet Automatic-Coupler 3rd Variant) and was an improved version of the Willison coupler, with better design of lock parts and mechanics. Conversion of rolling stock began in 1935. The Second World War delayed the introduction, so that the conversion was completed only 1957.
Operation
[edit]Helper locomotives at the end of the train are rarely used in the countries of the former Soviet Union. The load of the freight per train is not as heavy as on American railways.
Although the SA3 coupler is primarily used in the countries of the former Soviet Union, they are visible every day at the transshipping stations, at the eastern borders of the European Union (Poland, Slovakia and Hungary). Since bogie exchange technology has progressed, this allows for cars with SA3 couplers to regularly operate on the standard gauge tracks. A special converter car is inserted between standard and Russian gauge cars for this operation, with different couplers (SA3 and standard) on either end. Although these coupling freight cars have room for cargo, they are always operated empty.
If the vehicle fitted with the SA3 retains its buffers, then a special adapter allows that vehicle to couple to another vehicle fitted with buffers and chain, provided that the buffers have the same spacing or gauge. This appears to be done in Iran.
On the Uzhhorod–Košice broad-gauge track between Košice and Uzhhorod, Ukraine, of which the major part is on Slovakian territory, SA3 couplings are used exclusively. The railway is used for ore and coal transports from Kryvyi Rih, Ukraine to the US Steel mill in Košice and coal to the power plant of Vojany.
In addition, the heavy iron ore trains on the Swedish Malmbanan began to use SA3 couplings in 1969 after problems with snapping chain couplers and a need for ever increasing capacity with higher train weights. Today, IORE locomotives haul trains of 68 hopper cars of 120 tonnes (120 long tons; 130 short tons) with a total weight of over 8,000 tonnes (7,900 long tons; 8,800 short tons) over gradients of 1% in harsh weather conditions, from the LKAB mine in Kiruna to the ice-free harbour of Narvik, Norway using couplings of the SA3 type without any problem. They tried out Janney couplers, too, when moving beyond 8,000 tons because SA3 hasn't seen much use at such loads before that: in the Soviet Union, freight trains rarely exceeded 6,000 tons. The earlier SJ Dm3 locomotives have buffers fitted; therefore, they can couple with rolling stock fitted with buffers and chain.
The longest and heaviest train with SA3 couplings ran on 20 February 1986 from Ekibastuz to the Urals, Soviet Union. The composition consisted of 439 coal wagons and several diesel locomotives distributed along the train with a mass of 43,400 tonnes and the total length of 6.5 km (4.0 mi).[2]
Heaviest regular load
[edit]- Mauritania railway hauls iron ore trains of about 21,000 tonnes.
- The heaviest load for the SA3 in Ukraine is 12,000 tonnes.[3]
- Uzhhorod–Košice broad-gauge track iron ore trains of 4,200 tonnes.
Developments
[edit]
Based on the mechanical design of SA3 couplers has begun the development of a common European coupler under the umbrella of the UIC and the OSShD. For the latter was tasked the Waggonbau Bautzen (GDR) and on the part of the UIC the Knorr Bremse (FRG). The result were the fully tested and ready for production design Unicoupler. Beside an installation for heavy ore trains in West Germany was no commercial application.
At the end of the 1980s a separate development in West Germany aimed to mitigate some issues of Unicoupler. It was known under the label Z-AK, but got no practical relevance.

At the end of the 1990s SAB WABCO (now Faiveley Transport Witten) restarted development of a coupler on mechanical SA3 scheme. It was named C-AKv[4] and has different solutions for the problems of pneumatic and electric couplings. It also has vertical stability added, so that the coupling cannot fall down and damage the tracks or cause a derailment. It is compatible with the standard SA3 coupler and will have buffers needed for use with the standard buffers and chain couplers. The electric plugs would be most useful with electronically controlled pneumatic brakes. The practical tests started in 2002 with heavy cargo trains in coal mining in Germany. The C-AKv was a strong candidate for a common European automatic coupler as a joining successor on the Eurasian continent.
During the preparation for a common digital automatic coupling (DAC) in the EU, there was another SA3-compatible coupler contributed by CAF, but it was not chosen.[5]
Usage
[edit]The former Soviet Union:
 Armenia, Armenian Railways
Armenia, Armenian Railways Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan Railways
Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan Railways Belarus, Belarusian Railway
Belarus, Belarusian Railway Estonia, Eesti Raudtee
Estonia, Eesti Raudtee Georgia, Georgian Railways
Georgia, Georgian Railways Kazakhstan, Kazakhstan Temir Zholy
Kazakhstan, Kazakhstan Temir Zholy Kyrgyzstan, Kyrgyz Railways
Kyrgyzstan, Kyrgyz Railways Latvia, Latvian Railways
Latvia, Latvian Railways Lithuania, Lithuanian Railways
Lithuania, Lithuanian Railways Moldova, Calea Ferată din Moldova
Moldova, Calea Ferată din Moldova Russia, Russian Railways
Russia, Russian Railways Turkmenistan, Türkmendemirýollary
Turkmenistan, Türkmendemirýollary Tajikistan, Rail transport in Tajikistan
Tajikistan, Rail transport in Tajikistan Ukraine, Ukrainian Railways
Ukraine, Ukrainian Railways Uzbekistan, Uzbek Railways
Uzbekistan, Uzbek Railways
Other countries with extensive usage
[edit] Cameroon, Camrail
Cameroon, Camrail Finland, Rail transport in Finland
Finland, Rail transport in Finland Gabon, Trans-Gabon Railway (called Willison coupler) [citation needed]
Gabon, Trans-Gabon Railway (called Willison coupler) [citation needed] Iran, Islamic Republic of Iran Railways
Iran, Islamic Republic of Iran Railways Iraq, Iraqi Republic Railways
Iraq, Iraqi Republic Railways Mauritania Railway operated by Société Nationale Industrielle et Minière
Mauritania Railway operated by Société Nationale Industrielle et Minière Mongolia, Rail transport in Mongolia
Mongolia, Rail transport in Mongolia Turkey, Rail transport in Turkey
Turkey, Rail transport in Turkey
Some usage
[edit] Australia; Miniature Willison used on some sugarcane tramways and underground colliery railways.
Australia; Miniature Willison used on some sugarcane tramways and underground colliery railways. Netherlands; Koninklijke Hoogovens (Tata Steel Europe): used on railways within the steel plant complex.[6]
Netherlands; Koninklijke Hoogovens (Tata Steel Europe): used on railways within the steel plant complex.[6] Norway and
Norway and  Sweden (Malmbanan/Ofotbanen); Used exclusively by heavy iron-ore trains.
Sweden (Malmbanan/Ofotbanen); Used exclusively by heavy iron-ore trains. Poland (Broad Gauge Metallurgy Line); The longest broad gauge railway line in Poland. It is used only for freight traffic, mainly iron ore and coal.
Poland (Broad Gauge Metallurgy Line); The longest broad gauge railway line in Poland. It is used only for freight traffic, mainly iron ore and coal. Slovakia (Uzhhorod–Košice broad-gauge track); Heavy iron-ore transports from Ukraine.
Slovakia (Uzhhorod–Košice broad-gauge track); Heavy iron-ore transports from Ukraine. United States; Willison Coupler used in mining and tunneling railroads.[7]
United States; Willison Coupler used in mining and tunneling railroads.[7]
See also
[edit]- C-AKv coupler
- Draft gear
- Gangway connection
- Janney couplers, used by the heaviest trains up to 30,000 short tons
(27,216 t; 26,786 long tons). - Intermat coupler
- Longest trains of 2.5 km (1.6 mi)
- Railway coupling by country
- Unicoupler/Intermat
- Unilink coupler
References
[edit]- ^ "Picture Gallery - Directory: /pix/de/misc/coupling". www.railfaneurope.net. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ "Kazakhstan railways". Archived from the original on 10 January 2015. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ^ "Shmyhal reports complete switch of Ukraine to European railway gauge: Why this is impossible". The Page. 26 May 2022. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ Automatic Center Coupler (C-AKv) Archived 19 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bundesministerium für Verkehr und digitale Infrastruktur (18 June 2020). "Erstellung eines Konzeptes für die EU-weite Migration eines Digitalen Automatischen Kupplungssystems (DAK) für den Schienengüterverkehr. Schlussbericht" (PDF). bmdv.bund.de (PDF) (in German). Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport (Germany). p. 77. Retrieved 7 January 2024.
- ^ Railvervoer Hoogovens - Nederlands • Great Railways. 1996. Event occurs at 8:56. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021.
- ^ "Couplers". Irwin Car and Equipment. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
