International Linguistics Olympiad: Difference between revisions
Tag: Reverted |
m Reverted edits by 193.223.71.33 (talk): addition of unsourced content to a biographical article (HG) (3.4.13) |
||
| (97 intermediate revisions by 37 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Use mdy dates|date=September 2012}} |
{{Use mdy dates|date=September 2012}} |
||
[[File:IOL Logo.png|thumb|The logo of the International Linguistics Olympiad]] |
|||
The '''International Linguistics Olympiad''' ('''IOL''') is one of the [[International Science Olympiad]]s for secondary school students. Its abbreviation IOL is deliberately chosen not to correspond to the name of the organization in any particular language, and member organizations are free to choose for themselves how to designate the competition in their own language.<ref name="ioling">{{Cite web|url=http://www.ioling.org/faq/|title=International Linguistics Olympiad FAQ|website=www.ioling.org|access-date=2019-11-10}}</ref> This olympiad furthers the fields of mathematical, theoretical, and descriptive linguistics. |
|||
The '''International Linguistics Olympiad''' ('''IOL''') is one of the [[International Science Olympiad]]s [[Student competition|for secondary school students]]. Its abbreviation IOL is deliberately chosen not to correspond to the name of the organization in any particular language, and member organizations are free to choose for themselves how to designate the competition in their own language.<ref name="ioling">{{Cite web|url=http://www.ioling.org/faq/|title=International Linguistics Olympiad FAQ|website=www.ioling.org|access-date=2019-11-10}}</ref> This olympiad furthers the fields of mathematical, theoretical, and descriptive linguistics. |
|||
==Format== |
==Format== |
||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
The concept of self-sufficient linguistics problems was formulated in the 1960s, in the intellectual environment of the recently-founded Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics (OTiPL) of the [[Moscow State University]]. |
The concept of self-sufficient linguistics problems was formulated in the 1960s, in the intellectual environment of the recently-founded ''Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics'' (OTiPL) of the [[Moscow State University]].<ref>{{cite web |title=Из истории кафедры и отделения структурной/теоретической и прикладной лингвистики (ОСиПЛ/ОТиПЛ): 1960-2000 |url=http://tipl.philol.msu.ru/index.php/department/history-1960-2000 |access-date=March 29, 2024}}</ref> Moscow linguists in this environment were specially interested in understanding and modelling the formal and mathematical aspects of the natural languages; they were hatching things like the [[meaning-text theory]], the [[Moscow School of Comparative Linguistics]] and the beginnings of what later became [[computational linguistics]].<ref>{{Cite thesis |title=Olimpíadas de linguística: mosaico de uma prática social baseada em problemas |last=Martins |first=Eduardo C. |date=2022-06-22 |degree=PhD Thesis |publisher=Universidade de Brasília |url=http://icts.unb.br/jspui/handle/10482/44028 |language=Portuguese |pages=}}</ref> |
||
In 1963, [[Andrey Zaliznyak]] published a book called ''Linguistics problems'' (Лингвистические задачи), explaining in the introduction: |
|||
Thus, in 1965, the first edition of the Moscow's ''Traditional Olympiad on Linguistics and Mathematics'' was held, with an Organizing Committee composed by Uspensky (president), [[Igor Miloslavsky]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://letopis.msu.ru/peoples/5411 |title=Милославский, Игорь Григорьевич |website=Летопись Московского университета}}</ref> [[Alexander Kibrik]] and {{interlanguage link|Anna Polivanova|ru|Поливанова, Анна Константиновна}}. The Problem Committee was composed by Zhurinsky (the author of most of the problems) and Zaliznyak, plus [[Boris Gorodetsky]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Памяти Б.Ю Городецкого |url=https://www.philol.msu.ru/faculty/in-memoriam/GorodetskyBY/ |website=Филологический факультет, МГУ имени М. В. Ломоносова |access-date=17 November 2022}}</ref> (president), [[Alexandra Raskina]]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://7iskusstv.com/Avtory/Raskina.php |title=Александра Раскина |access-date=17 November 2022}}</ref> and [[Victor Raskin]].<ref name="Martins">{{cite thesis |type=PhD |last=Martins |first=Eduardo C. |date=Jun 29, 2022 |title=Olimpíadas de Linguística: mosaico de uma prática social baseada em problemas |publisher=Universidade de Brasília|url=https://repositorio.unb.br/handle/10482/44028 |access-date=November 17, 2022}}</ref><ref name="HistUKLO">{{cite web|url=http://www.uklo.org/about/history/background|title=International history|date=June 3, 2011|publisher=United Kingdom Linguistics Olympiad|access-date=2013-08-09}}</ref> The Moscow Olympiad was held regularly until 1982 and resumed again in 1988, being still held nowadays.<ref name="Otipl">{{cite web|url=http://www.philol.msu.ru/~otipl/new/main/mol/sum-2003-en.php?page=0|title=First International Olympiad in Linguistics (2003)|publisher=Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, Moscow State University|access-date=September 8, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
<blockquote> |
|||
''Specially crafted problems can serve as an important tool for teaching the fundamental principles and methods of linguistics. In existing collections, the material used for problems is often drawn from the facts of students' native language or the most well-known European languages. While such tasks are undoubtedly beneficial, they often suffer from the disadvantage that it is challenging to separate the linguistic task itself (which requires nothing but understanding the basic linguistic principles) from testing specific knowledge of the language under consideration. The best (though not the only) way to get rid of that second element, which doesn't directly relate to general linguistics, is to create tasks based on material from languages unfamiliar to the students. Of course, it is more challenging to craft such problems, since all the essential specific facts necessary for solving the task must somehow be presented in the problem data. However, in this case, students only need an understanding of the properties of language in general.<ref name=Zaliz>Original quote: Важным средством обучения основным положениям и методам языкознания могут служить специально составленные задачи. В существующих сборниках в качестве материала для задач в большинстве случаев используются факты родного языка учащихся или наиболее известных европейских языков. Такие задачи, безусловно, полезны, но, к сожалению, они часто страдают тем недостатком, что в них трудно отделить собственно лингвистическое задание (не требующее ничего, кроме понимания основных лингвистических положений) от проверки знания конкретных фактов рассматриваемого языка. Наилучший (хотя отнюдь не единственный) способ избавиться от этого второго элемента задания, не имеющего прямого отношения к общему языкознанию, состоит в том, чтобы составлять задачи на материале языков, незнакомых учащемуся. Разумеется, составлять такие задачи труднее, поскольку все существенные для решения конкретные факты должны быть так или иначе представлены в исходных данных задачи, зато от учащегося в этом случае требуется только представление о свойствах языка вообще. (p. 8) {{cite book |last1=Зализняк |first1=Андрей Анатольевич |title=Лингвистические задачи |orig-date=1963 |date=2013 |publisher=МЦНМО |location=Москва |isbn=978-5-4439-0094-0 |pages=40}}</ref>''</blockquote> |
|||
Following the publication, the then student {{interlanguage link|Alfred Zhurinsky|ru|Журинский, Альфред Наумович}} proposed to the mathematics professor [[Vladimir Uspensky]] the creation of a high-school olympiad using such problems. |
|||
[[File:First-Linguistics-Olympiad-poster.jpg|thumb|Poster of the First Traditional Olympiad on Linguistics, Moscow 1965]] |
|||
Thus, in 1965, the first edition of the Moscow's ''Traditional Olympiad on Linguistics and Mathematics'' was held, with an Organizing Committee composed by Uspensky (president), [[Igor Miloslavsky]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://letopis.msu.ru/peoples/5411 |title=Милославский, Игорь Григорьевич |website=Летопись Московского университета}}</ref> [[Alexander Kibrik]] and {{interlanguage link|Anna Polivanova|ru|Поливанова, Анна Константиновна}}. The Problem Committee consisted of Zhurinsky (the author of most of the problems) and Zaliznyak, plus [[Boris Gorodetsky]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Памяти Б.Ю Городецкого |url=https://www.philol.msu.ru/faculty/in-memoriam/GorodetskyBY/ |website=Филологический факультет, МГУ имени М. В. Ломоносова |access-date=17 November 2022}}</ref> (president), [[Alexandra Raskina]]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://7iskusstv.com/Avtory/Raskina.php |title=Александра Раскина |access-date=17 November 2022}}</ref> and [[Victor Raskin]].<ref name="Martins">{{cite thesis |type=PhD |last=Martins |first=Eduardo C. |date=Jun 29, 2022 |title=Olimpíadas de Linguística: mosaico de uma prática social baseada em problemas |publisher=Universidade de Brasília |url=https://repositorio.unb.br/handle/10482/44028 |access-date=November 17, 2022 }}{{Dead link|date=September 2024 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref><ref name="HistUKLO">{{cite web|url=http://www.uklo.org/about/history/background|title=International history|date=June 3, 2011|publisher=United Kingdom Linguistics Olympiad|access-date=2013-08-09|archive-date=January 2, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140102051008/http://www.uklo.org/about/history/background|url-status=dead}}</ref> The Moscow Olympiad was held regularly until 1982 and resumed again in 1988, being still held nowadays.<ref name="Otipl">{{cite web|url=http://www.philol.msu.ru/~otipl/new/main/mol/sum-2003-en.php?page=0|title=First International Olympiad in Linguistics (2003)|publisher=Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, Moscow State University|access-date=September 8, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
In the next decades, olympiads using the format of self-sufficient linguistics problems started to appear in different regions: |
In the next decades, olympiads using the format of self-sufficient linguistics problems started to appear in different regions: |
||
* In 1984, professor [[Ruslan Mitkov]] founded the ''Bulgarian Olympiad of Mathematical Linguistics'', open for high-school students of the whole [[Bulgaria]].<ref name="Otipl"/> In this olympiad, each school could participate with 4 students, thus inspiring the format of the future IOL. From 2001, the Bulgarian Olympiad also started to feature a team competition.<ref name="Martins"/> |
* In 1984, professor [[Ruslan Mitkov]] founded the ''Bulgarian Olympiad of Mathematical Linguistics'', open for high-school students of the whole [[Bulgaria]].<ref name="Otipl"/> In this olympiad, each school could participate with 4 students, thus inspiring the format of the future IOL. From 2001, the Bulgarian Olympiad also started to feature a team competition.<ref name="Martins"/> |
||
* From 1988 to 2000, professor Thomas E. Payne, from the [[University of Oregon]] organized a program with linguistics problems for high-school students in the city of [[Eugene, Oregon]], United States. The format was very similar to the Moscow Olympiad, with which he had contact in 1986, when visiting the OTiPL in Moscow. From 2001 to 2006, the competition evolved into an online format, the ''Linguistics Challenge'', which stimulated local linguistics competitions in different U.S. cities. This movement culminated, in 2007, with the creation of the [[North American Computational Linguistics Open Competition]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.naclo.cs.cmu.edu/history.html|title=History of Linguistic Challenges|publisher=NACLO|access-date=September 8, 2012}}</ref><ref name="Martins"/> |
* From 1988 to 2000, professor Thomas E. Payne, from the [[University of Oregon]] organized a program with linguistics problems for high-school students in the city of [[Eugene, Oregon]], United States. The format was very similar to the Moscow Olympiad, with which he had contact in 1986, when visiting the OTiPL in Moscow. From 2001 to 2006, the competition evolved into an online format, the ''Linguistics Challenge'', which stimulated local linguistics competitions in different U.S. cities. This movement culminated, in 2007, with the creation of the [[North American Computational Linguistics Open Competition]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.naclo.cs.cmu.edu/history.html|title=History of Linguistic Challenges|publisher=NACLO|access-date=September 8, 2012}}</ref><ref name="Martins"/> |
||
* In 1995, a group of professors from the [[Saint Petersburg State University]] started to organize the ''Traditional Olympiad of Linguistics and Mathematics of Saint Petersburg'', following a format very similar to that of the Moscow Olympiad. Decades later, in the 2010s, the olympiads of Moscow and Saint Petersburg merged to form a Russian National Linguistics Olympiad.<ref name="Otipl"/><ref name="Martins"/> |
* In 1995, a group of professors from the [[Saint Petersburg State University]] started to organize the ''Traditional Olympiad of Linguistics and Mathematics of Saint Petersburg'', following a format very similar to that of the Moscow Olympiad. Decades later, in the 2010s, the olympiads of Moscow and Saint Petersburg merged to form a Russian National Linguistics Olympiad.<ref name="Otipl"/><ref name="Martins"/> |
||
| Line 33: | Line 43: | ||
* [[Czech Republic]], with a guest team. |
* [[Czech Republic]], with a guest team. |
||
== |
== Contests, year by year == |
||
=== IOL 2003 === |
=== IOL 2003 === |
||
The first edition of IOL then was realized from September 6 to 12, 2003, in the mountain resort [[Borovetz]], Bulgaria, chaired by [[Alexander Kibrik]] from [[Moscow State University]] (MSU) and with the participation of six countries: |
The first edition of IOL then was realized from September 6 to 12, 2003, in the mountain resort [[Borovetz]], [[Bulgaria]], chaired by [[Alexander Kibrik]] from [[Moscow State University]] (MSU) and with the participation of six countries: Bulgaria, [[Czech Republic]], [[Estonia]], [[Latvia]], [[Netherlands]], and [[Russia]].<ref name="IOL2003">{{cite web|url=http://www.ioling.org/2003/|title=IOL 2003|publisher=International Linguistics Olympiad official website|access-date=September 8, 2012|archive-date=June 30, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130630052613/http://www.ioling.org/2003/|url-status=dead}}</ref> The first International Jury was composed of four people: Ivan Derzhanski (president) ([[Institute of Mathematics and Informatics (Bulgarian Academy of Sciences)|Institute for Mathematics and Informatics]] of [[Bulgarian Academy of Sciences]]), Alexander Berdichevsky ([[Moscow State University|MSU]]), Boris Iomdin ([[Russian Language Institute]]) and Elena Muravenko (Department for Russian Language, [[Russian State University for the Humanities]]).<ref name="Otipl"/> The five problems at the individual contest concerned [[Jacob Linzbach]]'s "Transcendental algebra" writing system, [[Egyptian Arabic]] ([[Afroasiatic languages|Afroasiatic]]), Basque ([[Isolate language|Isolate]]), [[Adyghe language|Adyghe]] ([[Northwest Caucasian languages|Northwest Caucasian]]), and French ([[Indo-European languages|Indo-European]]). The team contest consisted of three problems, on [[Tocharian languages|Tocharian]] ([[Indo-European languages|Indo-European]]), the use of subscripts as indices, and on [[performative]] verbs. |
||
[[File:IOL 2004 logo.png|thumb|Logo of the Second International Linguistics Olympiad (2004), depicting a map of [[Moscow]] where each neighborhood (rayon) is marked with a letter in some writing system and the acronym МОЛ-2 (the Cyrillic acronym for 2nd IOL) follows the [[Moskva (river)|moskva river]]. |
|||
]] |
|||
=== IOL 2004 === |
=== IOL 2004 === |
||
The 2nd IOL was held from August 2 to 6, 2004, in the Russian State University for the Humanities (RSUH), in [[Moscow]], Russia.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.philol.msu.ru/~otipl/new/main/mol/index-en.php?page=1|title=Second International Linguistic Olympiad (2004)|publisher=Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, Moscow State University|access-date=September 8, 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.philol.msu.ru/~otipl/new/main/mol/index-en.php?page=4|title=Second International Linguistic Olympiad (2004)|publisher=Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, Moscow State University|access-date=August 14, 2023|archive-date=October 16, 2005|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051016043336/http://www.philol.msu.ru/~otipl/new/main/mol/index-en.php?page=4|url-status=bot: unknown}}</ref> Chaired by Vladimir Alpatov, it gathered seven countries, with the first participation of [[Poland]] and [[Serbia and Montenegro]]. The Problem Committee was chaired by Elena Muravenko; in addition to Berdichevsky, Derzhanski, and Iomdin, it also included Ksenia Gilyarova and Maria Rubinstein. The five problems at the individual contest were in [[Kayapo]], [[Latin]], English, [[Lakhota]] and [[Chuvash language|Chuvash]]. The team problem was in [[Armenian language|Armenian]]. |
|||
=== IOL 2005 === |
=== IOL 2005 === |
||
The 3rd IOL was held from August 8 to 12, 2005, in [[Leiden]], Netherlands.<ref>{{cite web |title=Internet Archive: Third International Linguistics Olympiad |url=http://www.ilo3.leidenuniv.nl:80/index.php3 |url-status=unfit |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060208130714/http://www.ilo3.leidenuniv.nl:80/index.php3 |archive-date=8 February 2006 |access-date=14 August 2023}}</ref> Organized by a Local Committee composed by [[Alexander Lubotsky]], Michiel de Vaan, Alwin Kloekhorst, Jesca Zweijtzer and Saskia Tiethoff, it had the participation of 13 teams from 9 countries, [[Finland]] and [[Romania]] for their first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Ksenia Gilyarova. The five problems at the individual contest were in [[Tzotzil language|Tzotzil]], [[Lango language (disambiguation)|Lango]], [[Mansi language|Mansi]], [[Yoruba language|Yoruba]] and [[Lithuanian language|Lithuanian]]. The team problem was in [[South Oran and Figuig Berber|Figuig]]. |
|||
=== IOL 2006 === |
=== IOL 2006 === |
||
The 4th IOL was held from August 1 to 6, 2006, at the [[University of Tartu]], [[Tartu]], Estonia.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.olympiaadid.ut.ee/ilo4/|title=Fourth International Linguistics Olympiad for Secondary School Students|access-date=September 8, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110720130341/http://www.olympiaadid.ut.ee/ilo4/|archive-date=July 20, 2011|url-status=dead}}</ref> Chaired by Renate Pajusalu, it received also 13 teams from 9 countries, with [[Lithuania]] sending a team for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Alexander Berdichevsky. The five problems at the individual contest were in [[Lakhota]] ([[Siouan languages|Siouan]]) syntax, [[Catalan language|Catalan]] ([[Romanic languages|Romanic]]) plural forms, [[Khmer language|Khmer]] ([[Austroasiatic languages|Austroasiatic]]) script, [[Udege language|Udihe]] ([[Tungusic languages|Tungusic]]) possessives and [[Ngoni language|Ngoni]] ([[Bantu languages|Bantu]]) syntax. The team problem was in [[American Sign Language]]. |
|||
=== IOL 2007 === |
=== IOL 2007 === |
||
The 5th IOL was held from July 31 to August 4, 2007, at the Hotel Gelios, [[Saint Petersburg]], Russia.<ref name="IOL5">{{cite web|url=http://www.ilolympiad.spb.ru/index.html|title=The Fifth International Linguistics Olympiad|access-date=September 8, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111005172941/http://ilolympiad.spb.ru/index.html|archive-date=October 5, 2011|url-status=dead}}</ref> Chaired by Stanislav Gurevich, it received 15 teams from 9 countries; [[Spain]], [[Sweden]] and [[USA]] came for the first time. In that year, it was decided that each country can send one or two teams, consisting of four students each, with the first team's costs fully covered by the host country. Also, the host country could send a third team.<ref name="IOL5"/> The Problem Committee was chaired by Dmitry Gerasimov. The five problems at the individual contest were in [[Braille]], [[Movima language|Movima]] ([[Language isolate|Isolate]]), [[Georgian language|Georgian]] ([[Kartvelian languages|Kartvelian]]), [[Ndom language|Ndom]] ([[Trans–New Guinea languages|Trans-New Guinea]]), and [[comparative method|correspondences]] between [[Turkish language|Turkish]] and [[Tatar language|Tatar]] ([[Turkic languages|Turkic]]). The team problem was in [[Hawaiian language|Hawaiian]] ([[Polynesian languages|Polynesian]]) and focused on [[genealogy|genealogical terms]]. |
|||
=== IOL 2008 === |
=== IOL 2008 === |
||
The 6th IOL was held from August 4 to 9, 2008, at the Sunny Beach Resort, [[Sunny Beach]], Bulgaria.<ref name="IOL6">{{cite web|url=http://iol6.linguistics-bg.com/index.php|title=6th International Linguistics Olympiad|access-date=September 8, 2012|archive-date=March 25, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120325002054/http://iol6.linguistics-bg.com/index.php|url-status=dead}}</ref> Chaired by Iliana Raeva, it gathered 16 teams from 11 countries, including the first time for Germany, Slovenia and [[South Korea]]. The Problem Committee was chaired by Ivan Derzhanski. The five individual problems were in [[Micmac language|Micmac]] ([[Algonquian languages|Algonquian]]), [[Old Norse]] ([[North Germanic languages|North Germanic]]) [[poetics|poetry]] (specifically, ''drottkvætt''), [[Drehu language|Drehu]] and [[Cemhui|Cemuhî]] correspondences ([[Oceanic languages|Oceanic]]), [[Zoque languages|Copainalá Zoque]] ([[Mixe–Zoquean languages|Mixe-Zoquean]]), and [[Inuktitut]] ([[Eskimo–Aleut languages|Eskimo-Aleut]]). The team problem was about correspondences between [[Standard Chinese|Mandarin]] and [[Cantonese]] ([[Sinitic languages|Sinitic]]) using the [[fanqie]] system. |
|||
=== IOL 2009 === |
=== IOL 2009 === |
||
The 7th IOL was held from July 26 to 31, 2009, at the [[University of Wrocław]], [[Wrocław]], Poland.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.math.uni.wroc.pl/~msliw/lingw/iol/index.php|title=7th International Olympiad in Linguistics|access-date=September 8, 2012}}</ref> Chaired by Michał Śliwiński, it received 23 teams from 17 countries, with Australia, United Kingdom, [[India]] and Ireland sending teams for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Todor Tchervenkov ([[University of Lyon]], France). The subject matter of the five individual problems covered: numerals in the [[Sulka language]] ([[Language isolate|Isolate]]), [[Maninka]] and [[Bambara language|Bamana]] ([[Mande languages|Mande]]) languages in the [[N'Ko script|N'Ko]] and Latin scripts, traditional [[Burmese language|Burmese]] ([[Sino-Tibetan languages|Sino-Tibetan]]) names and their relation with dates of birth, stress position in [[Old Indic]] ([[Indo-Aryan languages|Indo-Aryan]]) and the relation between grammar and morphology in classical [[Nahuatl]] ([[Uto-Aztecan languages|Uto-Aztecan]]). The team problem was in [[Vietnamese language|Vietnamese]] ([[Austroasiatic languages|Austroasiatic]]). |
|||
=== IOL 2010 === |
=== IOL 2010 === |
||
The 8th IOL was held from July 19 to 24, 2010, at Östra Real Hostel, [[Stockholm]], Sweden.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iol.nu|title=IOL10|access-date=September 8, 2012}}</ref> Chaired by Hedvig Skigård, it received 26 teams from 18 countries, including first time for [[Norway]] and Singapore. The Problem Committee was chaired by Alexander Piperski. The individual contest consisted of five problems covering: relations between various verb forms in [[Budukh language|Budukh]] ([[Northeast Caucasian languages|Northeast Caucasian]]), the [[Drehu language|Drehu]] ([[Oceanic languages|Oceanic]]) counting system, [[Blissymbols|Blissymbolics]], [[Messenger RNA|mRNA]] [[Genetic code|coding]], and the connection between Sursilvan and Engadine [[dialect]]s in [[Romansh language|Romansh]] ([[Western Romance languages|Western Romance]]). The team problem involved translating extracts from a monolingual [[Mongolian Language|Mongolian]] ([[Mongolic languages|Mongolic]]) dictionary. |
|||
=== IOL 2011 === |
=== IOL 2011 === |
||
The 9th IOL was held from July 25 to 30, 2011, at the [[Carnegie Mellon University]], [[Pittsburgh]], USA <ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ioling.org/venue/|title=IOL 2011: Venue|access-date=September 8, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180825102054/http://www.ioling.org/venue/|archive-date=August 25, 2018|url-status=dead}}</ref> - the first time outside of Europe. Chaired by Lori Levin, it received 27 teams from 19 countries, including [[Brazil]], Canada, [[United Arab Emirates]] and [[Vietnam]] for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Adam Hesterberg. The problems of the individual contest required reasoning about [[Faroese language|Faroese]] ([[Germanic languages|Germanic]]) orthography, [[Menominee language|Menominee]] ([[Algic]]) morphology, [[Vai language|Vai]] ([[Mande languages|Mande]]) syntax, [[Nahuatl]] ([[Uto-Aztecan]]) semantics and the structure of the [[barcode]] language [[EAN-13]]. The team contest involved the rules and structure of [[Sanskrit]] ([[Indo-Aryan languages|Indo-Aryan]]) poetry. |
|||
=== IOL 2012 === |
=== IOL 2012 === |
||
The 10th IOL was held from July 29 to August 4, 2012, at the [[University of Ljubljana]], [[Ljubljana]], Slovenia.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ioling.org/2012/|title=The 10th International Linguistics Olympiad|access-date=August 7, 2013|archive-date=June 30, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130630033349/http://www.ioling.org/2012/|url-status=dead}}</ref> Chaired by Mirko Vaupotic, it received 34 teams from 26 countries, first time for China, Greece, [[Hungary]], Israel and Japan. The Problem Committee was chaired by Ivan Derzhanski. The five problems at the individual contest were in [[Dyirbal language|Dyirbal]] ([[Pama-Nyungan]]) syntax, [[Umbu-Ungu]] ([[Trans-New Guinea]]) numbers, [[Basque language|Basque]] ([[Language isolate|Isolate]]) pronouns, [[Teop]] ([[Austronesian languages|Austronesian]]) syntax, and [[Rotuman language|Rotuman]] ([[Austronesian languages|Austronesian]]) semantics. The team problem involved recognizing country names in [[Lao language|Lao]] language ([[Tai-Kadai]]). |
|||
=== IOL 2013 === |
=== IOL 2013 === |
||
The 11th IOL was held from July 22 to 26, 2013, at the [[Manchester Grammar School]], [[Manchester]], UK.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.uklo.org/iol-2013|title=The International Linguistics Olympiad 2013|date=July 29, 2012|access-date=August 7, 2013|archive-date=August 29, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170829012205/http://www.uklo.org/iol-2013|url-status=dead}}</ref> Chaired by Neil Sheldon, it received 35 teams from 26 countries, including first time teams from [[Isle of Man]], [[Taiwan]] and [[Turkey]]. The Problem Committee was chaired by Stanislav Gurevich. The five problems at the individual contest were about [[Yidiny language|Yidiny]] ([[Pama-Nyungan]]) morphology, [[Tundra Yukaghir language|Tundra Yukaghir]] ([[Yukaghir languages|Yukhagir]]) semantics, [[Pirahã language|Pirahã]] ([[Mura language|Mura]]) phonology, [[Muna language|Muna]] ([[Austronesian languages|Austronesian]]) syntax, and [[telepathy]] based on [[English language|English]]. The team problem involved translating [[Martin Seymour-Smith]]'s list of the [[100 Most Influential Books Ever Written|100 most influential books]] from [[Georgian language|Georgian]] ([[Kartvelian languages|Kartvelian]]) written in the 9th century [[Nuskhuri]] script. |
|||
=== IOL 2014 === |
=== IOL 2014 === |
||
The 12th IOL was held from July 21 to 25, 2014, at the [[Beijing Language and Culture University]], [[Beijing]], China – for the first time on the [[Asian continent]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://ioling.itccc.org.cn/|title=The International Linguistics Olympiad 2014|access-date=July 27, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140731091609/http://ioling.itccc.org.cn/|archive-date=July 31, 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> Chaired by Jiang Yuqin, it received 39 teams from 28 countries, with [[Pakistan]] and [[Ukraine]] sending teams for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Tae Hun Lee. The five problems at the individual contest were about [[Benabena language|Benabena]] ([[Trans-New Guinea languages|Trans-New Guinea]]) morphology, [[Kiowa language|Kiowa]] ([[Tanoan languages|Tanoan]]) morphophonology, [[Tangut language|Tangut]] ([[Tibeto-Burman languages|Tibeto-Burman]]) kinship, [[Engenni language|Engenni]] ([[Niger-Congo languages|Niger-Congo]]) syntax, and [[Northwest Gbaya language|Gbaya]] ([[Niger-Congo languages|Niger-Congo]]). The team problem involved matching the articles of the [[Universal Declaration of Human Rights]] to their translations in [[Armenian language|Armenian]] ([[Indo-European languages|Indo-European]]). |
|||
=== IOL 2015 === |
=== IOL 2015 === |
||
The 13th IOL was held from July 20 to 24, 2015, at the [[American University in Bulgaria]], [[Blagoevgrad]], Bulgaria.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ioling.org|title= The International Linguistics Olympiad 2015|access-date=August 17, 2015}}</ref> Chaired by Aleksandar Velinov, it received 43 teams from 29 countries, with [[Bangladesh]], [[France]] and [[Kazakhstan]] sending teams for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by [[Bozhidar Bozhanov]]. The five problems at the individual contest were about [[Nahuatl]] ([[Uto-Aztecan languages|Uto-Aztecan]]) and [[Arammba language|Arammba]] ([[Trans-Fly–Bulaka River languages|South-Central Papuan]]) numbers, morphology in the [[Besleney]] dialect of [[Kabardian language|Kabardian]] ([[Northwest Caucasian languages|Abkhaz-Adyghe]]), [[Soundex]], [[Wambaya language|Wambaya]] ([[West Barkly languages|West Barkly]]) syntax and the rules of [[Somali language|Somali]] ([[Afroasiatic languages|Afroasiatic]]) poetry. The team problem involved using extracts from a monolingual [[Northern Sotho language|Northern Sotho]] ([[Bantu languages|Bantu]]) dictionary to build a grammar and lexicon of the language. |
|||
=== IOL 2016 === |
=== IOL 2016 === |
||
The 14th IOL was held from July 25 to 29, 2016, at the [[Infosys]] Development Center in [[Mysore]], [[India]].<ref>{{Cite web|title = International Olympiad for Linguists 2016|url = http://iol14.plo-in.org/|website = iol14.plo-in.org|access-date = 2016-01-06|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160112080851/http://iol14.plo-in.org/|archive-date = January 12, 2016|url-status = dead}}</ref> Chaired by Dr. Monojit Choudhury and Dr. Girish Nath Jha, it received 44 teams from 31 countries, with [[Nepal]] and [[Sri Lanka]] sending teams for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Boris Iomdin. The five problems at the individual contest were about spatial deictics in [[Aralle-Tabulahan language|Aralle-Tabulahan]] ([[Austronesian languages|Austronesian]]), [[Hieroglyphic Luwian|Luwian hieroglyphic script]] ([[Indo-European languages|Indo-European]]), [[Kenzi language|Kunuz Nubian]] ([[Eastern Sudanic languages|Eastern Sudanic]]) morphosyntax, [[Iatmül language|Iatmül]] ([[Sepik languages|Sepik]]) semantics and [[Jaqaru language|Jaqaru]] ([[Aymaran languages|Aymaran]]) morphology. The team problem involved matching over 100 utterances in [[Taa language|Taa]] ([[Tuu languages|Tuu]]) to their [[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA transcriptions]]. |
|||
=== IOL 2017 === |
=== IOL 2017 === |
||
The 15th IOL was held from July 31 to August 4, 2017, at [[Dublin City University]] in [[Dublin]], [[Ireland]].<ref name="ioling" /> Chaired by Dr. Cara Greene, it received 43 teams from 27 countries, with [[Canada]] sending a [[French Canadians|Francophone]] team for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Hugh Dobbs. The five problems at the individual content were about [[Berom language|Berom]] ([[Plateau languages|Plateau]]) numbers, [[Abui language|Abui]] ([[Timor-Alor-Pantar languages|Timor-Alor-Pantar]]) possessives and semantics, [[Kimbundu]] ([[Bantu languages|Bantu]]) morphosyntax, [[Jru' language|Jru']] ([[Austroasiatic languages|Austroasiatic]]) written in the [[Khom script (Ong Kommadam)|Khom script]] and [[Madak language|Madak]] ([[Meso-Melanesian languages|Meso-Melanesian]]) morphophonology. The team problem involved establishing correspondences between 87 [[emoji]]s and their descriptions in [[Indonesian language|Indonesian]] ([[Austronesian languages|Austronesian]]). |
|||
=== IOL 2018 === |
=== IOL 2018 === |
||
The 16th IOL was held from July 26 to 30, 2018, at the [[Czech University of Life Sciences Prague|Czech University of Life Sciences]] in [[Prague]], [[Czech Republic]].<ref>{{Cite web|title = International Linguistics Olympiad 2018|url = https://iol.ff.cuni.cz|website = iol.ff.cuni.cz|access-date = August 5, 2018}}</ref> Chaired by Vojtěch Diatka, it received 49 teams from 29 countries, with [[Malaysia]] and [[Denmark]] competing for the first time.<ref>{{cite web |title=IOL 2018 Participants |url=http://www.ioling.org/participants/2018/ |website=IOL |access-date=8 August 2018}}</ref> The Problem Committee was chaired by Maria Rubinstein. The five problems at the individual contest concerned [[Muscogee language|Creek]] ([[Muskogean languages|Muskogean]]) stress, [[Tangsa language|Hakhun]] ([[Sal languages|Sal]]) morphosyntax, [[Terêna language|Terêna]] ([[Arawakan languages|Arawakan]]) phonology, counting in [[Bukiyip language|Mountain Arapesh]] ([[Torricelli languages|Torricelli]]) and kinship in [[Akan language|Akan]] ([[Atlantic-Congo languages|Atlantic-Congo]]). The team problem examined phonological correspondences among the three [[Jê languages|Jê]] languages [[Kayapo language|Mẽbêngôkre]], [[Xavante language|Xavante]] and [[Timbira language|Krĩkatí]]. |
|||
=== IOL 2019 === |
=== IOL 2019 === |
||
The 17th IOL was held from July 29 to August 2, 2019 at the [[Hankuk University of Foreign Studies]] in [[Yongin]], [[South Korea]].<ref>{{cite web |title=IOL Yongin 2019 |url=https://iol2019.com/ |website=IOL 2019 |access-date=8 August 2018}}</ref> Chaired by Minkyu Kim and Yoojung Chae, it received 53 teams from 35 countries, with [[Hong Kong]], [[Uzbekistan]] and [[Colombia]] competing for the first time.<ref>{{cite web |title=IOL 2019 Participants |url=http://www.ioling.org/participants/2019/ |website=IOL |access-date=6 August 2019}}</ref> This year was also the first edition of the Asia Pacific Linguistics Olympiad (APLO).<ref>{{cite web |title=The Asia Pacific Linguistics Olympiad |url=https://aplo.asia/#about |access-date=14 August 2023}}</ref> The Problem Committee was chaired by Tae Hun Lee. The five problems at the individual contest concerned [[Yonggom language|Yonggom]] ([[Ok languages|Ok]]) morphosyntax, [[Yurok language|Yurok]] ([[Algic languages|Algic]]) colours, [[Middle Persian]] ([[Iranian languages|Iranian]]) written in [[Pahlavi scripts#Book Pahlavi|Book Pahlavi script]], [[Tarangan language|West Tarangan]] ([[Aru languages|Aru]]) [[reduplication]] and [[Nooni language|Nooni]] ([[Beboid languages|Beboid]]) morphosyntax and day names. The team problem involved the symbol notation used by judges in [[rhythmic gymnastics]]. |
|||
=== IOL |
=== IOL 2021 === |
||
The 18th IOL was scheduled to take place from July 20 to 24, 2020, in [[Ventspils]], [[Latvia]]. Due to the widespread [[COVID-19 pandemic]], the International Board of the IOL decided to postpone the event to July 19 to 23, 2021, on which it was successfully held. The competition was held remotely in the respective countries of each team, the first and so far only time that this mode of competition was adopted at the IOL.<ref name="2020 Cancellation"/> Chaired by Vladimir Litvinsky, it received 54 teams from 34 countries, with [[Azerbaijan]] competing for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by {{interlanguage link|Aleksejs Peguševs|et|Alexey Pegushev}}. The five problems at the individual contest concerned [[Ekari language|Ekari]] ([[Paniai Lakes languages|Paniai Lakes]]) numerals, [[Zuni language|Zuni]] ([[Isolate language|Isolate]]) semantics with special focus on food, [[Kilivila language|Kilivila]] ([[Oceanic languages|Oceanic]]) morphosyntax, [[Agbirigba]] (a [[Cant (language)|cant language]]) and its derivation from the Ogbakiri dialect of [[Ikwerre language|Ikwerre]] ([[Atlantic-Congo languages|Atlantic-Congo]]), and [[Rikbaktsa language|Rikbaktsa]] ([[Macro-Jê languages|Macro-Jê]]) morphology. The team problem involved matching sentences in passages written in [[Garifuna language|Garifuna]] ([[Arawakan languages|Arawakan]]) with its translations, as well as acknowledging the difference between the language's [[Garifuna language#Gender differences|male and female registers]] and establishing their relationships with [[Carib language|Kari'ña]] ([[Cariban languages|Cariban]]) and [[Arawak language|Lokono]] (Arawakan), respectively. |
|||
=== IOL 2022 === |
=== IOL 2022 === |
||
The 19th IOL was held from July 25 to 29, 2022 at [[King William's College]] in [[Castletown, Isle of Man|Castletown]], [[Isle of Man]].<ref>{{cite web |title=IOL Castletown 2022 |url=https://iol2022.org/ |website=IOL 2022 |access-date=1 August 2022 |archive-date=October 6, 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221006041808/https://iol2022.org/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> Chaired by Rob Teare, it received 46 teams from 32 countries, with [[Moldova]], [[Switzerland]] and [[Thailand]] competing for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Samuel Ahmed. The five problems at the individual contest concerned [[Ubykh language|Ubykh]] ([[Northwest Caucasian languages|Abkhaz-Adyghe]]) morphophonology, the semantics and morphophonology of [[Alabama language|Alabama]] ([[Muskogean languages|Muskogean]]) verbs, [[Nǁng language|Nǀuuki]] ([[Tuu languages|Tuu]]) syntax, [[Arabana language|Arabana]] ([[Pama-Nyungan languages|Pama-Nyungan]]) kinship, and phonological changes and [[tonogenesis]] in two daughter languages of [[Chamic languages|Proto-Chamic]], [[Cham language|Phan Rang Cham]] and [[Tsat language|Tsat]]. The team problem presented extracts in 17th and 18th century [[Manchu language|Manchu]] ([[Tungusic languages|Tungusic]]) from [[Nogeoldae|Cheong-eo Nogeoldae]] and the [[Kangxi Emperor]]'s [[Pentaglot Dictionary|Imperially Commissioned Mirror of the Manchu Language]] for analysis, with tasks involving matching sentences in Old and Modern Manchu to their respective translations as well as writing in the [[Manchu alphabet|Manchu script]]. |
|||
=== IOL 2023 === |
|||
The 20th IOL was held from July 24 to July 28, 2023 in [[Bansko]], [[Bulgaria]],<ref>{{cite web |title=IOL Bansko 2023 |url=https://iol2023.linguistic.bg/ |website=IOL 2023 |access-date=3 August 2023 }}{{Dead link|date=September 2024 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> for the fourth time in this country. Chaired by Aleks Velinov, it received 51 teams from 37 countries, with [[Philippines]] competing for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Milena Veneva. The five problems at the individual contest concerned [[Guazacapán language|Guazacapán Xinka]] (a language of Guatemala with now no living native speakers), [[Apurinã language|Apurinã]] ([[Maipurean|Arawak]]) morphosyntax, Coastal [[Marind language|Marind]] ([[Papuan language|Papuan]]) morphosyntax, [[Plains Cree language|Plains Cree]] ([[Algonquian languages|Algonquian]]) verb morphology and the numbering system of [[Supyire language|Supyire]] spoken in [[Mali]]. The team problem presented extracts from Chester S. Street's dictionary of [[Murrinh-Patha language|Murrin-patha]], an [[Australian Aboriginal language]] spoken by over 2,000 people in the Northern Territory. |
|||
=== IOL 2024 === |
|||
The 21st IOL was held from July 23 to July 31, 2024 at the [[Universidade de Brasília]], [[Brasília]], [[Brazil]], which was the first time the contest was held in the southern hemisphere. Chaired by Bruno L'Astorina, it received 206 contestants in 52 teams from 38 countries, with [[Iran]] and [[Malta]] competing for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Andrey Nikulin. The five problems at the individual contest concerned [[Koryak language|Koryak]] morphology, [[Hadza language|Hadza]] syntax and morphology, [[Kinship terminology|kinship terms]] in [[Kómnzo language|Kómnzo]], semantics in [[Dâw language|Dâw]], and male-female [[diglossia]] in [[Yanyuwa language|Yanyuwa]]. The team problem involved [[lexicostatistics]], [[Aharon Dolgopolsky|Dolgopolsky]]'s consonant classes, and the "StarlingNJ" algorithm to compute language family trees and stability indices based on lexicostatistical distance.<ref name="IOL2024">{{cite web |title=Brasília 2024 |url=https://ioling.org/2024/ |website=International Linguistics Olympiad |access-date=10 Aug 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240805163320/ioling.org/2024 |archive-date=5 Aug 2024}}</ref> |
|||
=== IOL 2025 === |
|||
The 22nd IOL is expected to be held in [[Taipei]], [[Taiwan]], from 21 to 26 of July 2025.<ref>{{cite web |title=Taipei 2025 |url=https://ioling.org/upcoming |website=International Linguistics Olympiad |access-date=10 August 2024}}</ref> |
|||
==Summary== |
==Summary== |
||
| Line 107: | Line 130: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||1 |
||1 |
||
| 2003 |
|||
| [[2003 International Linguistics Olympiad|2003]] |
|||
| [[Borovets]] |
| [[Borovets]] |
||
| {{BGR}} |
| {{BGR}} |
||
| Line 118: | Line 141: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||2 |
||2 |
||
| 2004 |
|||
| [[2004 International Linguistics Olympiad|2004]] |
|||
| [[Moscow]] |
| [[Moscow]] |
||
| {{RUS}} |
| {{RUS}} |
||
| Line 129: | Line 152: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||3 |
||3 |
||
| 2005 |
|||
| [[2005 International Linguistics Olympiad|2005]] |
|||
| [[Leiden]] |
| [[Leiden]] |
||
| {{NED}} |
| {{NED}} |
||
| Line 140: | Line 163: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||4 |
||4 |
||
| 2006 |
|||
| [[2006 International Linguistics Olympiad|2006]] |
|||
| [[Tartu]] |
| [[Tartu]] |
||
| {{EST}} |
| {{EST}} |
||
| Line 151: | Line 174: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||5 |
||5 |
||
| 2007 |
|||
| [[2007 International Linguistics Olympiad|2007]] |
|||
| [[Saint Petersburg]] |
| [[Saint Petersburg]] |
||
| {{RUS}} |
| {{RUS}} |
||
| Line 162: | Line 185: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||6 |
||6 |
||
| 2008 |
|||
| [[2008 International Linguistics Olympiad|2008]] |
|||
| [[Slantchev Bryag]] |
| [[Slantchev Bryag]] |
||
| {{BGR}} |
| {{BGR}} |
||
| Line 173: | Line 196: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||7 |
||7 |
||
| 2009 |
|||
| [[2009 International Linguistics Olympiad|2009]] |
|||
| [[Wrocław]] |
| [[Wrocław]] |
||
| {{POL}} |
| {{POL}} |
||
| Line 184: | Line 207: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||8 |
||8 |
||
| 2010 |
|||
| [[2010 International Linguistics Olympiad|2010]] |
|||
| [[Stockholm]] |
| [[Stockholm]] |
||
| {{SWE}} |
| {{SWE}} |
||
| Line 191: | Line 214: | ||
| 18 |
| 18 |
||
| 99 |
| 99 |
||
| [http://www.iol.nu/ Link] |
| [https://web.archive.org/web/20101010134547/http://www.iol.nu/ Link] |
||
| [http://www.ioling.org/problems/2010 Link] |
| [http://www.ioling.org/problems/2010 Link] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
||9 |
||9 |
||
| 2011 |
|||
| [[2011 International Linguistics Olympiad|2011]] |
|||
| [[Pittsburgh]] |
| [[Pittsburgh]] |
||
| {{USA}} |
| {{USA}} |
||
| Line 206: | Line 229: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||10 |
||10 |
||
| 2012 |
|||
| [[2012 International Linguistics Olympiad|2012]] |
|||
| [[Ljubljana]] |
| [[Ljubljana]] |
||
| {{SVN}} |
| {{SVN}} |
||
| Line 217: | Line 240: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||11 |
||11 |
||
| 2013 |
|||
| [[2013 International Linguistics Olympiad|2013]] |
|||
| [[Manchester]] |
| [[Manchester]] |
||
| {{GBR}} |
| {{GBR}} |
||
| Line 228: | Line 251: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||12 |
||12 |
||
| 2014 |
|||
| [[2014 International Linguistics Olympiad|2014]] |
|||
| [[Beijing]] |
| [[Beijing]] |
||
| {{CHN}} |
| {{CHN}} |
||
| Line 239: | Line 262: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||13 |
||13 |
||
| 2015 |
|||
| [[2015 International Linguistics Olympiad|2015]] |
|||
| [[Blagoevgrad]] |
| [[Blagoevgrad]] |
||
| {{BGR}} |
| {{BGR}} |
||
| Line 250: | Line 273: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
||14 |
||14 |
||
| 2016 |
|||
| [[2016 International Linguistics Olympiad|2016]] |
|||
| [[Mysore]] |
| [[Mysore]] |
||
| {{IND}} |
| {{IND}} |
||
| Line 261: | Line 284: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|15 |
|15 |
||
| 2017 |
|||
| [[2017 International Linguistics Olympiad|2017]] |
|||
| [[Dublin]] |
| [[Dublin]] |
||
| {{IRL}} |
| {{IRL}} |
||
| Line 272: | Line 295: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|16 |
|16 |
||
| 2018 |
|||
| [[2018 International Linguistics Olympiad|2018]] |
|||
| [[Prague]] |
| [[Prague]] |
||
| {{CZE}} |
| {{CZE}} |
||
| Line 283: | Line 306: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|17 |
|17 |
||
| 2019 |
|||
| [[2019 International Linguistics Olympiad|2019]] |
|||
| [[Yongin]] |
| [[Yongin]] |
||
| {{KOR}} |
| {{KOR}} |
||
| Line 300: | Line 323: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|18 |
|18 |
||
| 2021 |
|||
| [[2021 International Linguistics Olympiad|2021]] |
|||
| [[Ventspils]] |
| [[Ventspils]] |
||
| {{LVA}}{{ref|1a|1}} |
| {{LVA}}{{ref|1a|1}} |
||
| Line 308: | Line 331: | ||
| 216 |
| 216 |
||
| [https://iol2021.org Link]{{Dead link|date=February 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} |
| [https://iol2021.org Link]{{Dead link|date=February 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} |
||
| [http://www.ioling.org/problems/2021 Link] |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|19 |
|19 |
||
| 2022 |
|||
| [[2022 International Linguistics Olympiad|2022]] |
|||
| [[Castletown, Isle of Man|Castletown]] |
| [[Castletown, Isle of Man|Castletown]] |
||
| {{IMN}} |
| {{IMN}} |
||
| Line 318: | Line 341: | ||
| 32 |
| 32 |
||
| 185 |
| 185 |
||
| [https://iol2022.org/ Link] |
| [https://iol2022.org/ Link] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221006041808/https://iol2022.org/ |date=October 6, 2022 }} |
||
| [http://www.ioling.org/problems/2022 Link] |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|20 |
|20 |
||
| 2023 |
|||
| [[2023 International Linguistics Olympiad|2023]] |
|||
| [[Bansko]] |
| [[Bansko]] |
||
| {{BGR}} |
| {{BGR}} |
||
| July 24 |
| July 24 |
||
| July 28 |
| July 28 |
||
| |
| 37 |
||
| 204 |
| 204 |
||
| [https://iol2023.linguistics.bg/ Link] |
|||
| |
|||
| [http://www.ioling.org/problems/2023 Link] |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
|21 |
|||
| 2024 |
|||
| [[Brasília]] |
|||
| {{BRA}} |
|||
| July 23 |
|||
| July 31 |
|||
| 38 |
|||
| 206 |
|||
| [https://iol2024.org/ Link] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240804025837/https://iol2024.org/ |date=4 Aug 2024 }} |
|||
| [http://www.ioling.org/problems/2024 Link] |
|||
|- |
|||
|22 |
|||
| 2025 |
|||
| [[Taipei]] |
|||
| {{TWN}} |
|||
| July 21 |
|||
| July 26 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| [https://iol2024.org/upcoming/ Link] |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
|23 |
|||
| 2026 |
|||
| |
|||
| {{ROM}} |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| [https://iol2024.org/upcoming/ Link] |
|||
| |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
{{refbegin}} |
{{refbegin}} |
||
| Line 617: | Line 673: | ||
|align=left|2014 |
|align=left|2014 |
||
|[[Beijing]], China {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|[[Beijing]], China {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
||
|Milo Andrea Mazurkiewicz{{flagicon|POL |
|[[Milo Mazurkiewicz|Milo Andrea Mazurkiewicz]]{{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
||
Darryl Wu {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
Darryl Wu {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
||
Daniel Lovsted {{flagicon|CAN}} <br/> |
Daniel Lovsted {{flagicon|CAN}} <br/> |
||
| Line 634: | Line 690: | ||
Keisuke Yamada {{flagicon|Japan}} <br/> |
Keisuke Yamada {{flagicon|Japan}} <br/> |
||
Stanisław Wilczyński {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
Stanisław Wilczyński {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
||
Felicia Lane {{flagicon|Sweden}} <br/> |
|||
Deven Lahoti {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
Deven Lahoti {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
||
Xue Dailin {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
Xue Dailin {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
||
| Line 645: | Line 701: | ||
Dmitrii Zelenskii {{flagicon|RUS}} <br/> |
Dmitrii Zelenskii {{flagicon|RUS}} <br/> |
||
Annika Kluge {{flagicon|Estonia}} <br/> |
Annika Kluge {{flagicon|Estonia}} <br/> |
||
Jonathan Johansen {{flagicon|Sweden}} <br/> |
|||
Kevin Li {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
Kevin Li {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
||
Gleb Nikolaev {{flagicon|RUS}} <br/> |
Gleb Nikolaev {{flagicon|RUS}} <br/> |
||
| Line 675: | Line 731: | ||
Daniil Vedeneev {{flagicon|RUS}} <br/> |
Daniil Vedeneev {{flagicon|RUS}} <br/> |
||
Stanisław Frejlak {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
Stanisław Frejlak {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
||
Jin Xu {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|||
Julian Gau {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
Julian Gau {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
||
Dan Mircea Mirea {{flagicon|Romania}} <br/> |
Dan Mircea Mirea {{flagicon|Romania}} <br/> |
||
| Line 844: | Line 900: | ||
Ugrin Bálint József {{flagicon|HUN}} <br/> |
Ugrin Bálint József {{flagicon|HUN}} <br/> |
||
Emil Ingelsten {{flagicon|SWE}} <br/> |
Emil Ingelsten {{flagicon|SWE}} <br/> |
||
Klara Sapała-Niedzin {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
|||
Tung-Le Pan {{flagicon|Taiwan}} <br/> |
Tung-Le Pan {{flagicon|Taiwan}} <br/> |
||
Elena Keskinova {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
Elena Keskinova {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
||
| Line 986: | Line 1,042: | ||
Deyana Shevchenko {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
Deyana Shevchenko {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
||
Kunaal Chandrashekar {{flagicon|CAN}} <br/> |
Kunaal Chandrashekar {{flagicon|CAN}} <br/> |
||
Olivia Tennisberg {{flagicon|EST}} <br/> |
|||
Jeremy Zhou {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
Jeremy Zhou {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
||
Vedant Singh {{flagicon|IND}} <br/> |
Vedant Singh {{flagicon|IND}} <br/> |
||
| Line 1,044: | Line 1,100: | ||
Yelyzaveta Sherepenko {{flagicon|UKR}} <br/> |
Yelyzaveta Sherepenko {{flagicon|UKR}} <br/> |
||
Merlin Fischer {{flagicon|GER}} <br/> |
Merlin Fischer {{flagicon|GER}} <br/> |
||
Fernando César {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
Fernando César Gonçalves Filho {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
||
Toby Collins {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
Toby Collins {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
||
Siddhant Attavar {{flagicon|IND}} <br/> |
Siddhant Attavar {{flagicon|IND}} <br/> |
||
| Line 1,078: | Line 1,134: | ||
Rok Tadej Brunšek {{flagicon|SLO}} <br/> |
Rok Tadej Brunšek {{flagicon|SLO}} <br/> |
||
Józef Szymański {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
Józef Szymański {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
||
|- bgcolor=#D0E7FF align=left |
|||
|align=left|2023 |
|||
|[[Bansko]], Bulgaria {{flagicon|Bulgaria}} <br/> |
|||
| Tam Lok Hang {{flagicon|HKG}} <br/> |
|||
Ryusei Omiya {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Wonhyun Soh {{flagicon|KOR}} <br/> |
|||
Vlad-Ștefan Oros {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Daria Kryvosheieva {{flagicon|UKR}} <br/> |
|||
William Keith Thomson {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
|||
Artem Boyko <br/> |
|||
Kunaal Chandrashekar {{flagicon|CAN}} <br/> |
|||
Konstantin Georgiev {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Leonardo Torres {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
|||
Leonardo Paillo {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
|||
Eleonora Stepanova <br/> |
|||
| Elena Păvăloaia {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Panawat Tiacharoen {{flagicon|THA}} <br/> |
|||
Mihai-Alexandru Bratu {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Viktoriia Zubkova <br/> |
|||
Jordan Chi {{flagicon|AUS}} <br/> |
|||
Samantha Kao {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Zhang Yixuan {{flagicon|HKG}} <br/> |
|||
He Jianxing {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|||
Rei Kano {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Wong Tok Shing Henry {{flagicon|HKG}} <br/> |
|||
Wojciech Szot {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
|||
Daniel Titmas {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
|||
Alison Craig-Greene {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
|||
Matei Chirila {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Nestors Starostins {{flagicon|LAT}} <br/> |
|||
Sukrith Velmineti {{flagicon|CAN}} <br/> |
|||
Teodor Malchev {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Deeraj Pothapragada {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
|||
Eric Wu {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Bartłomiej Rozenberg {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
|||
Gyuhwa Lee {{flagicon|KOR}} <br/> |
|||
Faraz Ahmed Siddiqui {{flagicon|IND}} <br/> |
|||
Benjamin Móricz {{flagicon|HUN}} <br/> |
|||
Rami Hennawi {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
|Eleanor Borrel {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
|||
Chung Chi-En {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Teresa Lage {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
|||
Arul Kolla {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
|||
Jonasz Kościkiewicz {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
|||
Zori Schmidt {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
|||
Merlin Jonathan Fischer {{flagicon|GER}} <br/> |
|||
Everton Albuquerque De Oliveira {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
|||
Alexander Shlykov <br/> |
|||
Jiang Yiling {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|||
Perry Dai {{flagicon|CAN}} <br/> |
|||
Benjamin Yang {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
|||
Luiz Satoshi Yunomae Oikawa {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
|||
Darren Su {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
|||
Chen Nuo {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|||
Brest Lenarčič {{flagicon|Slovenia}} <br/> |
|||
Mihaela Anghel {{flagicon|Romania}} <br/> |
|||
Hiroto Yasui {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Gangrae Kim {{flagicon|KOR}} <br/> |
|||
Li Jiying {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|||
Wang Po-Hsiang {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Valeriia Pischchymukha {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Rando Lukk {{flagicon|EST}} <br/> |
|||
João Pedro Alves Ferreira {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
|||
Mikhail Iomdin {{flagicon|ISR}} <br/> |
|||
Nikolay Georgiev {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Carl Fredrik Constantin Lidberg Dimos {{flagicon|SWE}} <br/> |
|||
Satoshi Tsukada {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Hwang Yen-Hsi {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Matěj Čapka {{flagicon|CZE}} <br/> |
|||
Manoela Ferraz {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
|||
Bognár András Károly {{flagicon|HUN}} <br/> |
|||
|- bgcolor=#D0E7FF align=left |
|||
|align=left|2024 |
|||
|[[Brasília]], Brazil {{flagicon|Brazil}} <br/> |
|||
|Deeraj Pothapragada {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
|||
Devin Joe {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
|||
Alison Craig-Greene {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
|||
Yipeng Xu {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
|||
Tyson Lieu {{flagicon|AUS}} <br/> |
|||
Urszula Wąsiewicz {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
|||
Ryusei Omiya {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Luiza-Teodora Mihai {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Narongrith Artnarongrith {{flagicon|THA}} <br/> |
|||
Brest Lenarčič {{flagicon|SLO}} <br/> |
|||
Leonard Kottisch {{flagicon|GER}} <br/> |
|||
Varin Sikka {{flagicon|USA}} <br/> |
|||
Anna Bryłowska {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
|||
|Eric Wu {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Wong Tok Shing Henry {{flagicon|HKG}} <br/> |
|||
Marvin Mao {{flagicon|CAN}} <br/> |
|||
Mikhail Iomdin {{flagicon|GER}} <br/> |
|||
Matei Chirilă {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Nadežda Efremova <br/> |
|||
Matěj Čapka {{flagicon|CZE}} <br/> |
|||
Karina-Adriana Stăncescu {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Samantha Kao {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Gyuhwa Lee {{flagicon|KOR}} <br/> |
|||
Máté Gergely Virág {{flagicon|HUN}} <br/> |
|||
He Jianxing {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|||
Jiang Yiling {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|||
Nia Dimitrova {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Li-Bang Chen {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Ekaterina Churkina <br/> |
|||
Mihaela Anghel {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Animikha Dutta Dhar {{flagicon|IND}} <br/> |
|||
Keisuke Taeda {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Patricia Király {{flagicon|SLO}} <br/> |
|||
Gangrae Kim {{flagicon|KOR}} <br/> |
|||
Zhu Yucheng {{flagicon|China}} <br/> |
|||
Felipe Moraes Barros {{flagicon|BRA}} <br/> |
|||
Rudolf András Virág {{flagicon|HUN}} <br/> |
|||
|Tanupat Trakulthongchai {{flagicon|THA}} <br/> |
|||
Satoshi Tsukada {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Denys Tereshchenko {{flagicon|UKR}} <br/> |
|||
Po-Hsiang Wang {{flagicon|TWN}} <br/> |
|||
Kantetsu Oh {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Mixail Nikitin <br/> |
|||
Ji Shu Ching {{flagicon|HKG}} <br/> |
|||
Yuji Hokugo {{flagicon|JAP}} <br/> |
|||
Richard Dobíšek {{flagicon|CZE}} <br/> |
|||
Eleonora Stepanova <br/> |
|||
Ani Katelieva {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Shrilakshmi Venkatraman {{flagicon|IND}} <br/> |
|||
Choi John Nathaniel {{flagicon|HKG}} <br/> |
|||
Magdalena Vigenina {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Elena Păvăloaia {{flagicon|ROM}} <br/> |
|||
Nikolay Georgiev {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Faraz Ahmed Siddiqui {{flagicon|IND}} <br/> |
|||
Natalia Rewaj {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
|||
Rory Ambrosius {{flagicon|AUS}} <br/> |
|||
Sirma Karadjova {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Ostap Drushchak {{flagicon|UKR}} <br/> |
|||
Ivanimira Nedelcheva {{flagicon|BUL}} <br/> |
|||
Zachary Yen {{flagicon|UK}} <br/> |
|||
Nayoon Goo {{flagicon|KOR}} <br/> |
|||
Miroslav Havel {{flagicon|CZE}} <br/> |
|||
Adam Ahlberg {{flagicon|SWE}} <br/> |
|||
Olya Besova {{flagicon|ISR}} <br/> |
|||
Ignacy Jackl {{flagicon|POL}} <br/> |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
| Line 1,109: | Line 1,306: | ||
| 2005 |
| 2005 |
||
|[[Leiden]], The Netherlands |
|[[Leiden]], The Netherlands |
||
| Netherlands {{flagicon|NED}} |
| Netherlands {{flagicon|NED}} |
||
| Russia-Moscow {{flagicon|RUS}} |
| Russia-Moscow {{flagicon|RUS}} |
||
| Russia-StPetersburg {{flagicon|RUS}} |
| Russia-StPetersburg {{flagicon|RUS}} |
||
| Line 1,127: | Line 1,324: | ||
| USA-2 {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>Moscow {{flagicon|RUS}} |
| USA-2 {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>Moscow {{flagicon|RUS}} |
||
| Bulgaria-1 {{flagicon|BUL}}<br/>Bulgaria-2 {{flagicon|BUL}} |
| Bulgaria-1 {{flagicon|BUL}}<br/>Bulgaria-2 {{flagicon|BUL}} |
||
| None |
| None awarded |
||
| Estonia {{flagicon|EST}} |
| Estonia {{flagicon|EST}} |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 1,135: | Line 1,332: | ||
| USA-2 {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>Bulgaria-East {{flagicon|BUL}} |
| USA-2 {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>Bulgaria-East {{flagicon|BUL}} |
||
| Netherlands {{flagicon|NED}}<br/>USA-1 {{flagicon|USA}} |
| Netherlands {{flagicon|NED}}<br/>USA-1 {{flagicon|USA}} |
||
| None |
| None awarded |
||
| USA {{flagicon|USA}} |
| USA {{flagicon|USA}} |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 1,215: | Line 1,412: | ||
| USA-Blue {{flagicon|USA}} |
| USA-Blue {{flagicon|USA}} |
||
| USA-Red {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>Bulgaria 1 {{flagicon|BUL}} |
| USA-Red {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>Bulgaria 1 {{flagicon|BUL}} |
||
| Pões {{flagicon|BRA}}<br/>UK-U {{flagicon|UK}}<br/>Tým křivopřísežníků {{flagicon|CZE}} |
| Brazil Pões {{flagicon|BRA}}<br/>UK-U {{flagicon|UK}}<br/>Czechia Tým křivopřísežníků {{flagicon|CZE}} |
||
| USA-Blue {{flagicon|USA}} |
| USA-Blue {{flagicon|USA}} |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 1,241: | Line 1,438: | ||
| Japan Ninja {{flagicon|JAP}}<br/>USA Red {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>UK K {{flagicon|UK}} |
| Japan Ninja {{flagicon|JAP}}<br/>USA Red {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>UK K {{flagicon|UK}} |
||
| USA Red {{flagicon|USA}} |
| USA Red {{flagicon|USA}} |
||
|- |
|||
||20 |
|||
| 2023 |
|||
|[[Bansko]], Bulgaria |
|||
| United Kingdom {{flagicon|UK}} |
|||
| USA Red {{flagicon|USA}}<br/>Canada Anglophone {{flagicon|CAN}} |
|||
| Finland {{flagicon|FIN}}<br/>Hungary Uborka {{flagicon|HUN}}<br/>Poland Ę {{flagicon|POL}} |
|||
| Not awarded |
|||
|- |
|||
||21 |
|||
| 2024 |
|||
|[[Brasília]], Brazil |
|||
| Czechia {{flagicon|CZE}} |
|||
| Poland Świerszcze {{flagicon|POL}} |
|||
| Taiwan Black Bear {{flagicon|TWN}}<br/> Japan Samurai {{flagicon|JAP}}<br/> Slovenia {{flagicon|SLO}} |
|||
| United Kingdom {{flagicon|UK}} |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
==All-time medal table== |
==All-time medal table== |
||
Only countries with at least 1 gold medal are listed. The |
Only countries with at least 1 gold medal are listed. The list is accurate up to 2024.<ref>{{cite web |title=Results |url=https://ioling.org/results/by_year/ |access-date=7 October 2024 |website=International Linguistics Olympiad}}</ref> The rank is based on the number of gold medals. |
||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
||
! Rank !! Country !! Appearances !! Gold !! Silver !! Bronze !! Total !! Honorable Mentions |
! Rank !! Country !! Appearances !! Participants !! Gold !! Silver !! Bronze !! Total !! Honorable Mentions |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 1 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align="center" | 1 || align="left" | {{flag|United States}} || align="center" | 17 || align="center" | 140 || align="center" | 24 || align="center" | 39 || align="center" | 28 || align="center" | 91 || align="center" | 25 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 2 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align="center" | 2 || align="left" | {{flag|Bulgaria}} || align="center" | 21 || align="center" | 170 || align="center" | 22 || align="center" | 26 || align="center" | 41 || align="center" | 89 || align="center" | 24 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 3 ||align=left| {{flag|Russia}} || align=center| 18 ||align=center| 17 ||align=center| 31 ||align=center| 40 ||align=center| 88 ||align=center| 21 |
| align=center| 3 ||align=left| {{flag|Russia}} || align=center| 18 || align=center| 156 ||align=center| 17 || align="center" | 31 || align="center" | 40 || align="center" | 88 || align="center" | 21 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 4 ||align=left| {{flag|United Kingdom}} ||align=center| |
| align=center| 4 ||align=left| {{flag|United Kingdom}} ||align=center| 15 || align="center" | 92 || align="center" | 17 || align="center" | 14 || align="center" | 16 || align="center" | 47 || align="center" | 18 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 5 ||align=left| {{flag|Poland}} ||align=center| |
| align=center| 5 ||align=left| {{flag|Poland}} ||align=center| 20 || align="center" | 153 || align="center" | 12 || align="center" | 27 || align="center" | 23 || align="center" | 62 || align="center" | 38 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 6 ||align=left| {{flag|Japan}} ||align=center| |
| align=center| 6 ||align=left| {{flag|Japan}} ||align=center| 12 || align="center" | 84 || align="center" | 7 || align="center" | 5 || align="center" | 12 || align="center" | 24 || align="center" | 19 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 7 ||align=left| {{flag|Romania}} ||align=center| |
| align="center" | 7 || align="left" | {{flag|Romania}} || align="center" | 13 || align="center" | 59 || align="center" | 6 || align="center" | 10 || align="center" | 12 || align="center" | 28 || align="center" | 8 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 8 ||align=left| {{flag|India}} ||align=center| |
| align="center" | 8 || align="left" | {{flag|India}} || align="center" | 15 || align="center" | 92 || align="center" | 4 || align="center" | 9 || align="center" | 18 || align="center" | 31 || align="center" | 16 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 9 ||align=left| {{ |
| align="center" | 9 || align="left" | {{flagicon|KOR}} [[South Korea|Republic of Korea]]|| align="center" | 16 || align="center" | 128 || align="center" | 4 || align="center" | 6 || align="center" | 19 || align="center" | 29 || align="center" | 25 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 10 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align="center" | 10 || align="left" | {{flag|Brazil}} || align="center" | 11 || align="center" | 67 || align="center" | 3 || align="center" | 6 || align="center" | 9 || align="center" | 18 || align="center" | 12 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 11 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align="center" | 11 || align="left" | {{flag|Ukraine}} || align="center" | 10 || align="center" | 52 || align="center" | 3 || align="center" | 5 || align="center" | 9 || align="center" | 17 || align="center" | 12 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 12 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align=center| 12 ||align=left| {{flag|Netherlands}} ||align=center| 21 || align="center" | 91 || align="center" | 3 ||align=center| 3 ||align=center| 4 || align="center" | 10 || align="center" | 20 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 13 ||align=left| |
| align=center| 13 ||align=left| no country ||align=center| 2 ||align=center| 8 ||align=center| 3 ||align=center| 2 ||align=center| 3 ||align=center| 8 ||align=center| 0 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 14 ||align=left| {{flag|Taiwan}} ||align=center| |
| align=center| 14 ||align=left| {{flag|Taiwan}} ||align=center| 11 || align="center" | 67 || align="center" | 2 ||align=center| 14 || align="center" | 10 || align="center" | 26 || align="center" | 16 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 15 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align="center" | 15 || align="left" | {{flag|Czechia}} || align="center" | 14 || align="center" | 57 || align="center" | 2 || align="center" | 9 || align="center" | 7 || align="center" | 18 || align="center" | 11 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 16 ||align=left| {{ |
| align="center" | 16 || align="left" | {{flagicon|CAN}} [[Canada]] (Anglophone) || align="center" | 7 || align="center" | 28 || align="center" | 2 || align="center" | 5 || align="center" | 6 || align="center" | 13 || align="center" | 5 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 17 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align=center| 17 ||align=left| {{flag|Hong Kong}} ||align=center| 5 || align="center" | 24 || align="center" | 2 ||align=center| 6 || align="center" | 4 || align="center" | 12 || align="center" | 1 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 18 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align="center" | 18 || align="left" | {{flag|Australia}} || align="center" | 15 || align="center" | 93 || align="center" | 2 || align="center" | 3 || align="center" | 6 || align="center" | 11 || align="center" | 10 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 19 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align=center| 19 ||align=left| {{flag|China}} ||align=center| 11 || align="center" | 84 || align="center" | 1 ||align=center| 13 || align="center" | 15 ||align=center| 29 || align="center" | 23 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| align=center| 20 ||align=left| {{flag| |
| align="center" | 20 || align="left" | {{flag|Estonia}} || align="center" | 21 || align="center" | 95 || align="center" | 1 || align="center" | 7 || align="center" | 18 || align="center" | 26 || align="center" | 16 |
||
|- |
|||
| align="center" | 21 || align="left" | {{flag|Latvia}} || align="center" | 21 || align="center" | 92 || align="center" | 1 || align="center" | 5 || align="center" | 12 || align="center" | 18 || align="center" | 13 |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center" | 22 || align="left" | {{flag|Slovenia}} || align="center" | 16 || align="center" | 78 || align="center" | 1 || align="center" | 5 || align="center" | 10 || align="center" | 16 || align="center" | 12 |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center" | 23 || align="left" | {{flag|Germany}} || align="center" | 10 || align="center" | 52 || align="center" | 1 || align="center" | 3 || align="center" | 4 || align="center" | 8 || align="center" | 14 |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=center| 24 || align="left" | {{flag|Canada}}(before 2017)<ref>From 2017, Canada sent separate teams based on language: Canada Anglophone and Canada Francophone</ref> || align="center" | 6 ||align=center| 24 ||align=center| 1 ||align=center| 1 ||align=center| 4 ||align=center| 6 ||align=center| 9 |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center" | 25 || align="left" | {{flag|Thailand}} || align="center" | 3 || align="center" | 12 || align="center" | 1 || align="center" | 1 || align="center" | 2 || align="center" | 4 || align="center" | 2 |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
==Media coverage== |
==Media coverage== |
||
| Line 1,302: | Line 1,526: | ||
*[[Australian Computational and Linguistics Olympiad]] |
*[[Australian Computational and Linguistics Olympiad]] |
||
*[[Asia Pacific Linguistics Olympiad]] |
*[[Asia Pacific Linguistics Olympiad]] |
||
==Notes== |
|||
{{reflist|group=note}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Latest revision as of 12:18, 4 January 2025

The International Linguistics Olympiad (IOL) is one of the International Science Olympiads for secondary school students. Its abbreviation IOL is deliberately chosen not to correspond to the name of the organization in any particular language, and member organizations are free to choose for themselves how to designate the competition in their own language.[1] This olympiad furthers the fields of mathematical, theoretical, and descriptive linguistics.
Format
[edit]The setup differs from most of the other Science Olympiads, in that the olympiad contains both individual and team contests. The individual contest consists of 5 problems, covering the main fields of theoretical, mathematical and applied linguistics – phonetics, morphology, semantics, syntax, sociolinguistics, etc. – which must be solved in six hours.
The team contest has consisted of one extremely difficult and time-consuming problem since the 2nd IOL. Teams, which generally consist of four students, are given three to four hours to solve this problem.
Like nearly all International Science Olympiads, its problems are translated and completed in several languages and as such must be written free of any native language constraints. However, unlike other olympiads, the translations are provided by the multilingual Problem Committee, a body of experts independent of the delegates' team leaders. Because competitors could gain some advantage if they are familiar with one or more of the language groups which are the subject of some of the assignments, problems are increasingly based on some of the world's lesser known languages. Fortunately, with more than 6,000 languages spoken world-wide (not including so-called dead languages) there are plenty to choose from. The committee has a policy of not using artificial[contradictory] or fictional languages for its problems. The presence of an independent Problem Committee and Jury means that team leaders do not have to be experts in the field (though most are): they can (and often do) work closely with their teams, providing last-minute coaching throughout the week of the competition.
In any case, the most helpful ability is analytic and deductive thinking, as all solutions must include clear reasoning and justification.
History
[edit]The concept of self-sufficient linguistics problems was formulated in the 1960s, in the intellectual environment of the recently-founded Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics (OTiPL) of the Moscow State University.[2] Moscow linguists in this environment were specially interested in understanding and modelling the formal and mathematical aspects of the natural languages; they were hatching things like the meaning-text theory, the Moscow School of Comparative Linguistics and the beginnings of what later became computational linguistics.[3]
In 1963, Andrey Zaliznyak published a book called Linguistics problems (Лингвистические задачи), explaining in the introduction:
Specially crafted problems can serve as an important tool for teaching the fundamental principles and methods of linguistics. In existing collections, the material used for problems is often drawn from the facts of students' native language or the most well-known European languages. While such tasks are undoubtedly beneficial, they often suffer from the disadvantage that it is challenging to separate the linguistic task itself (which requires nothing but understanding the basic linguistic principles) from testing specific knowledge of the language under consideration. The best (though not the only) way to get rid of that second element, which doesn't directly relate to general linguistics, is to create tasks based on material from languages unfamiliar to the students. Of course, it is more challenging to craft such problems, since all the essential specific facts necessary for solving the task must somehow be presented in the problem data. However, in this case, students only need an understanding of the properties of language in general.[4]
Following the publication, the then student Alfred Zhurinsky proposed to the mathematics professor Vladimir Uspensky the creation of a high-school olympiad using such problems.

Thus, in 1965, the first edition of the Moscow's Traditional Olympiad on Linguistics and Mathematics was held, with an Organizing Committee composed by Uspensky (president), Igor Miloslavsky,[5] Alexander Kibrik and Anna Polivanova. The Problem Committee consisted of Zhurinsky (the author of most of the problems) and Zaliznyak, plus Boris Gorodetsky[6] (president), Alexandra Raskina[7] and Victor Raskin.[8][9] The Moscow Olympiad was held regularly until 1982 and resumed again in 1988, being still held nowadays.[10]
In the next decades, olympiads using the format of self-sufficient linguistics problems started to appear in different regions:
- In 1984, professor Ruslan Mitkov founded the Bulgarian Olympiad of Mathematical Linguistics, open for high-school students of the whole Bulgaria.[10] In this olympiad, each school could participate with 4 students, thus inspiring the format of the future IOL. From 2001, the Bulgarian Olympiad also started to feature a team competition.[8]
- From 1988 to 2000, professor Thomas E. Payne, from the University of Oregon organized a program with linguistics problems for high-school students in the city of Eugene, Oregon, United States. The format was very similar to the Moscow Olympiad, with which he had contact in 1986, when visiting the OTiPL in Moscow. From 2001 to 2006, the competition evolved into an online format, the Linguistics Challenge, which stimulated local linguistics competitions in different U.S. cities. This movement culminated, in 2007, with the creation of the North American Computational Linguistics Open Competition.[11][8]
- In 1995, a group of professors from the Saint Petersburg State University started to organize the Traditional Olympiad of Linguistics and Mathematics of Saint Petersburg, following a format very similar to that of the Moscow Olympiad. Decades later, in the 2010s, the olympiads of Moscow and Saint Petersburg merged to form a Russian National Linguistics Olympiad.[10][8]
- In 2001, a group connected to the Leiden University, including Ruslan Mitkov, the founder of the Bulgarian Olympiad, and two other former participants of the Moscow Olympiad (Alexander Lubotsky participated from 1973 to 1976; Leonid Kulikov participated from 1981 to 1988), founded a Linguistics Olympiad for the Netherlands.
After the foundation of the Bulgarian olympiad, teams of winners of the Moscow Linguistic Olympiad successfully competed in Bulgaria and vice versa, demonstrating good potential for international cooperation in the field. With the multiplication of initiatives, the organizers of the different olympiads decided to organize, in 2003, the First International Olympiad in Theoretical, Mathematical, and Applied Linguistics, with six participating countries:
- Russia, with one team from the Moscow Olympiad and another from the Saint Petersburg Olympiad;
- Bulgaria, also with two teams, both from the Bulgarian Olympiad;
- Netherlands, with a team selected from its newly formed olympiad;
- Estonia, with a team from the olympiad organized in the same year by Renate Pajusalu and other professors from Tartu University;
- Latvia, with a team of students from Riga's Secondary School No 40, the former school of Alexander Berdichevsky, then a master student at the OTiPL.
- Czech Republic, with a guest team.
Contests, year by year
[edit]IOL 2003
[edit]The first edition of IOL then was realized from September 6 to 12, 2003, in the mountain resort Borovetz, Bulgaria, chaired by Alexander Kibrik from Moscow State University (MSU) and with the participation of six countries: Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Estonia, Latvia, Netherlands, and Russia.[12] The first International Jury was composed of four people: Ivan Derzhanski (president) (Institute for Mathematics and Informatics of Bulgarian Academy of Sciences), Alexander Berdichevsky (MSU), Boris Iomdin (Russian Language Institute) and Elena Muravenko (Department for Russian Language, Russian State University for the Humanities).[10] The five problems at the individual contest concerned Jacob Linzbach's "Transcendental algebra" writing system, Egyptian Arabic (Afroasiatic), Basque (Isolate), Adyghe (Northwest Caucasian), and French (Indo-European). The team contest consisted of three problems, on Tocharian (Indo-European), the use of subscripts as indices, and on performative verbs.
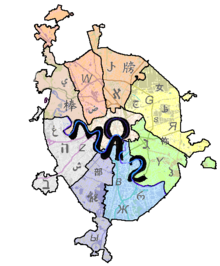
IOL 2004
[edit]The 2nd IOL was held from August 2 to 6, 2004, in the Russian State University for the Humanities (RSUH), in Moscow, Russia.[13][14] Chaired by Vladimir Alpatov, it gathered seven countries, with the first participation of Poland and Serbia and Montenegro. The Problem Committee was chaired by Elena Muravenko; in addition to Berdichevsky, Derzhanski, and Iomdin, it also included Ksenia Gilyarova and Maria Rubinstein. The five problems at the individual contest were in Kayapo, Latin, English, Lakhota and Chuvash. The team problem was in Armenian.
IOL 2005
[edit]The 3rd IOL was held from August 8 to 12, 2005, in Leiden, Netherlands.[15] Organized by a Local Committee composed by Alexander Lubotsky, Michiel de Vaan, Alwin Kloekhorst, Jesca Zweijtzer and Saskia Tiethoff, it had the participation of 13 teams from 9 countries, Finland and Romania for their first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Ksenia Gilyarova. The five problems at the individual contest were in Tzotzil, Lango, Mansi, Yoruba and Lithuanian. The team problem was in Figuig.
IOL 2006
[edit]The 4th IOL was held from August 1 to 6, 2006, at the University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia.[16] Chaired by Renate Pajusalu, it received also 13 teams from 9 countries, with Lithuania sending a team for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Alexander Berdichevsky. The five problems at the individual contest were in Lakhota (Siouan) syntax, Catalan (Romanic) plural forms, Khmer (Austroasiatic) script, Udihe (Tungusic) possessives and Ngoni (Bantu) syntax. The team problem was in American Sign Language.
IOL 2007
[edit]The 5th IOL was held from July 31 to August 4, 2007, at the Hotel Gelios, Saint Petersburg, Russia.[17] Chaired by Stanislav Gurevich, it received 15 teams from 9 countries; Spain, Sweden and USA came for the first time. In that year, it was decided that each country can send one or two teams, consisting of four students each, with the first team's costs fully covered by the host country. Also, the host country could send a third team.[17] The Problem Committee was chaired by Dmitry Gerasimov. The five problems at the individual contest were in Braille, Movima (Isolate), Georgian (Kartvelian), Ndom (Trans-New Guinea), and correspondences between Turkish and Tatar (Turkic). The team problem was in Hawaiian (Polynesian) and focused on genealogical terms.
IOL 2008
[edit]The 6th IOL was held from August 4 to 9, 2008, at the Sunny Beach Resort, Sunny Beach, Bulgaria.[18] Chaired by Iliana Raeva, it gathered 16 teams from 11 countries, including the first time for Germany, Slovenia and South Korea. The Problem Committee was chaired by Ivan Derzhanski. The five individual problems were in Micmac (Algonquian), Old Norse (North Germanic) poetry (specifically, drottkvætt), Drehu and Cemuhî correspondences (Oceanic), Copainalá Zoque (Mixe-Zoquean), and Inuktitut (Eskimo-Aleut). The team problem was about correspondences between Mandarin and Cantonese (Sinitic) using the fanqie system.
IOL 2009
[edit]The 7th IOL was held from July 26 to 31, 2009, at the University of Wrocław, Wrocław, Poland.[19] Chaired by Michał Śliwiński, it received 23 teams from 17 countries, with Australia, United Kingdom, India and Ireland sending teams for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Todor Tchervenkov (University of Lyon, France). The subject matter of the five individual problems covered: numerals in the Sulka language (Isolate), Maninka and Bamana (Mande) languages in the N'Ko and Latin scripts, traditional Burmese (Sino-Tibetan) names and their relation with dates of birth, stress position in Old Indic (Indo-Aryan) and the relation between grammar and morphology in classical Nahuatl (Uto-Aztecan). The team problem was in Vietnamese (Austroasiatic).
IOL 2010
[edit]The 8th IOL was held from July 19 to 24, 2010, at Östra Real Hostel, Stockholm, Sweden.[20] Chaired by Hedvig Skigård, it received 26 teams from 18 countries, including first time for Norway and Singapore. The Problem Committee was chaired by Alexander Piperski. The individual contest consisted of five problems covering: relations between various verb forms in Budukh (Northeast Caucasian), the Drehu (Oceanic) counting system, Blissymbolics, mRNA coding, and the connection between Sursilvan and Engadine dialects in Romansh (Western Romance). The team problem involved translating extracts from a monolingual Mongolian (Mongolic) dictionary.
IOL 2011
[edit]The 9th IOL was held from July 25 to 30, 2011, at the Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, USA [21] - the first time outside of Europe. Chaired by Lori Levin, it received 27 teams from 19 countries, including Brazil, Canada, United Arab Emirates and Vietnam for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Adam Hesterberg. The problems of the individual contest required reasoning about Faroese (Germanic) orthography, Menominee (Algic) morphology, Vai (Mande) syntax, Nahuatl (Uto-Aztecan) semantics and the structure of the barcode language EAN-13. The team contest involved the rules and structure of Sanskrit (Indo-Aryan) poetry.
IOL 2012
[edit]The 10th IOL was held from July 29 to August 4, 2012, at the University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia.[22] Chaired by Mirko Vaupotic, it received 34 teams from 26 countries, first time for China, Greece, Hungary, Israel and Japan. The Problem Committee was chaired by Ivan Derzhanski. The five problems at the individual contest were in Dyirbal (Pama-Nyungan) syntax, Umbu-Ungu (Trans-New Guinea) numbers, Basque (Isolate) pronouns, Teop (Austronesian) syntax, and Rotuman (Austronesian) semantics. The team problem involved recognizing country names in Lao language (Tai-Kadai).
IOL 2013
[edit]The 11th IOL was held from July 22 to 26, 2013, at the Manchester Grammar School, Manchester, UK.[23] Chaired by Neil Sheldon, it received 35 teams from 26 countries, including first time teams from Isle of Man, Taiwan and Turkey. The Problem Committee was chaired by Stanislav Gurevich. The five problems at the individual contest were about Yidiny (Pama-Nyungan) morphology, Tundra Yukaghir (Yukhagir) semantics, Pirahã (Mura) phonology, Muna (Austronesian) syntax, and telepathy based on English. The team problem involved translating Martin Seymour-Smith's list of the 100 most influential books from Georgian (Kartvelian) written in the 9th century Nuskhuri script.
IOL 2014
[edit]The 12th IOL was held from July 21 to 25, 2014, at the Beijing Language and Culture University, Beijing, China – for the first time on the Asian continent.[24] Chaired by Jiang Yuqin, it received 39 teams from 28 countries, with Pakistan and Ukraine sending teams for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Tae Hun Lee. The five problems at the individual contest were about Benabena (Trans-New Guinea) morphology, Kiowa (Tanoan) morphophonology, Tangut (Tibeto-Burman) kinship, Engenni (Niger-Congo) syntax, and Gbaya (Niger-Congo). The team problem involved matching the articles of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights to their translations in Armenian (Indo-European).
IOL 2015
[edit]The 13th IOL was held from July 20 to 24, 2015, at the American University in Bulgaria, Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria.[25] Chaired by Aleksandar Velinov, it received 43 teams from 29 countries, with Bangladesh, France and Kazakhstan sending teams for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Bozhidar Bozhanov. The five problems at the individual contest were about Nahuatl (Uto-Aztecan) and Arammba (South-Central Papuan) numbers, morphology in the Besleney dialect of Kabardian (Abkhaz-Adyghe), Soundex, Wambaya (West Barkly) syntax and the rules of Somali (Afroasiatic) poetry. The team problem involved using extracts from a monolingual Northern Sotho (Bantu) dictionary to build a grammar and lexicon of the language.
IOL 2016
[edit]The 14th IOL was held from July 25 to 29, 2016, at the Infosys Development Center in Mysore, India.[26] Chaired by Dr. Monojit Choudhury and Dr. Girish Nath Jha, it received 44 teams from 31 countries, with Nepal and Sri Lanka sending teams for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Boris Iomdin. The five problems at the individual contest were about spatial deictics in Aralle-Tabulahan (Austronesian), Luwian hieroglyphic script (Indo-European), Kunuz Nubian (Eastern Sudanic) morphosyntax, Iatmül (Sepik) semantics and Jaqaru (Aymaran) morphology. The team problem involved matching over 100 utterances in Taa (Tuu) to their IPA transcriptions.
IOL 2017
[edit]The 15th IOL was held from July 31 to August 4, 2017, at Dublin City University in Dublin, Ireland.[1] Chaired by Dr. Cara Greene, it received 43 teams from 27 countries, with Canada sending a Francophone team for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Hugh Dobbs. The five problems at the individual content were about Berom (Plateau) numbers, Abui (Timor-Alor-Pantar) possessives and semantics, Kimbundu (Bantu) morphosyntax, Jru' (Austroasiatic) written in the Khom script and Madak (Meso-Melanesian) morphophonology. The team problem involved establishing correspondences between 87 emojis and their descriptions in Indonesian (Austronesian).
IOL 2018
[edit]The 16th IOL was held from July 26 to 30, 2018, at the Czech University of Life Sciences in Prague, Czech Republic.[27] Chaired by Vojtěch Diatka, it received 49 teams from 29 countries, with Malaysia and Denmark competing for the first time.[28] The Problem Committee was chaired by Maria Rubinstein. The five problems at the individual contest concerned Creek (Muskogean) stress, Hakhun (Sal) morphosyntax, Terêna (Arawakan) phonology, counting in Mountain Arapesh (Torricelli) and kinship in Akan (Atlantic-Congo). The team problem examined phonological correspondences among the three Jê languages Mẽbêngôkre, Xavante and Krĩkatí.
IOL 2019
[edit]The 17th IOL was held from July 29 to August 2, 2019 at the Hankuk University of Foreign Studies in Yongin, South Korea.[29] Chaired by Minkyu Kim and Yoojung Chae, it received 53 teams from 35 countries, with Hong Kong, Uzbekistan and Colombia competing for the first time.[30] This year was also the first edition of the Asia Pacific Linguistics Olympiad (APLO).[31] The Problem Committee was chaired by Tae Hun Lee. The five problems at the individual contest concerned Yonggom (Ok) morphosyntax, Yurok (Algic) colours, Middle Persian (Iranian) written in Book Pahlavi script, West Tarangan (Aru) reduplication and Nooni (Beboid) morphosyntax and day names. The team problem involved the symbol notation used by judges in rhythmic gymnastics.
IOL 2021
[edit]The 18th IOL was scheduled to take place from July 20 to 24, 2020, in Ventspils, Latvia. Due to the widespread COVID-19 pandemic, the International Board of the IOL decided to postpone the event to July 19 to 23, 2021, on which it was successfully held. The competition was held remotely in the respective countries of each team, the first and so far only time that this mode of competition was adopted at the IOL.[32] Chaired by Vladimir Litvinsky, it received 54 teams from 34 countries, with Azerbaijan competing for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Aleksejs Peguševs. The five problems at the individual contest concerned Ekari (Paniai Lakes) numerals, Zuni (Isolate) semantics with special focus on food, Kilivila (Oceanic) morphosyntax, Agbirigba (a cant language) and its derivation from the Ogbakiri dialect of Ikwerre (Atlantic-Congo), and Rikbaktsa (Macro-Jê) morphology. The team problem involved matching sentences in passages written in Garifuna (Arawakan) with its translations, as well as acknowledging the difference between the language's male and female registers and establishing their relationships with Kari'ña (Cariban) and Lokono (Arawakan), respectively.
IOL 2022
[edit]The 19th IOL was held from July 25 to 29, 2022 at King William's College in Castletown, Isle of Man.[33] Chaired by Rob Teare, it received 46 teams from 32 countries, with Moldova, Switzerland and Thailand competing for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Samuel Ahmed. The five problems at the individual contest concerned Ubykh (Abkhaz-Adyghe) morphophonology, the semantics and morphophonology of Alabama (Muskogean) verbs, Nǀuuki (Tuu) syntax, Arabana (Pama-Nyungan) kinship, and phonological changes and tonogenesis in two daughter languages of Proto-Chamic, Phan Rang Cham and Tsat. The team problem presented extracts in 17th and 18th century Manchu (Tungusic) from Cheong-eo Nogeoldae and the Kangxi Emperor's Imperially Commissioned Mirror of the Manchu Language for analysis, with tasks involving matching sentences in Old and Modern Manchu to their respective translations as well as writing in the Manchu script.
IOL 2023
[edit]The 20th IOL was held from July 24 to July 28, 2023 in Bansko, Bulgaria,[34] for the fourth time in this country. Chaired by Aleks Velinov, it received 51 teams from 37 countries, with Philippines competing for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Milena Veneva. The five problems at the individual contest concerned Guazacapán Xinka (a language of Guatemala with now no living native speakers), Apurinã (Arawak) morphosyntax, Coastal Marind (Papuan) morphosyntax, Plains Cree (Algonquian) verb morphology and the numbering system of Supyire spoken in Mali. The team problem presented extracts from Chester S. Street's dictionary of Murrin-patha, an Australian Aboriginal language spoken by over 2,000 people in the Northern Territory.
IOL 2024
[edit]The 21st IOL was held from July 23 to July 31, 2024 at the Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, which was the first time the contest was held in the southern hemisphere. Chaired by Bruno L'Astorina, it received 206 contestants in 52 teams from 38 countries, with Iran and Malta competing for the first time. The Problem Committee was chaired by Andrey Nikulin. The five problems at the individual contest concerned Koryak morphology, Hadza syntax and morphology, kinship terms in Kómnzo, semantics in Dâw, and male-female diglossia in Yanyuwa. The team problem involved lexicostatistics, Dolgopolsky's consonant classes, and the "StarlingNJ" algorithm to compute language family trees and stability indices based on lexicostatistical distance.[35]
IOL 2025
[edit]The 22nd IOL is expected to be held in Taipei, Taiwan, from 21 to 26 of July 2025.[36]
Summary
[edit]The different editions of IOL can be summarized on the following table:
| No. | Year | Location | Country | Dates | Countries | Participants | Webpage | Problems | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2003 | Borovets | September 6 | September 12 | 6 | 33 | Link | Link | |
| 2 | 2004 | Moscow | July 31 | August 2 | 7 | 43 | Link | Link | |
| 3 | 2005 | Leiden | August 8 | August 12 | 9 | 50 | Link | Link | |
| 4 | 2006 | Tartu | August 1 | August 6 | 9 | 51 | Link | Link | |
| 5 | 2007 | Saint Petersburg | July 31 | August 4 | 9 | 61 | Link | Link | |
| 6 | 2008 | Slantchev Bryag | August 4 | August 9 | 11 | 63 | Link Archived March 25, 2012, at the Wayback Machine | Link | |
| 7 | 2009 | Wrocław | July 26 | July 31 | 17 | 86 | Link | Link | |
| 8 | 2010 | Stockholm | July 19 | July 24 | 18 | 99 | Link | Link | |
| 9 | 2011 | Pittsburgh | July 24 | July 30 | 19 | 102 | Link Archived June 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine | Link | |
| 10 | 2012 | Ljubljana | July 29 | August 4 | 26 | 131 | Link Archived June 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine | Link | |
| 11 | 2013 | Manchester | July 22 | July 26 | 26 | 138 | Link Archived August 29, 2017, at the Wayback Machine | Link | |
| 12 | 2014 | Beijing | July 21 | July 25 | 28 | 152 | Link | Link | |
| 13 | 2015 | Blagoevgrad | July 20 | July 24 | 29 | 166 | Link Archived May 19, 2017, at the Wayback Machine | Link | |
| 14 | 2016 | Mysore | July 25 | July 29 | 31[37] | 167 | Link | Link | |
| 15 | 2017 | Dublin | July 31 | August 4 | 29 | 180 | Link | Link | |
| 16 | 2018 | Prague | July 25 | July 31 | 29 | 192 | Link | Link | |
| 17 | 2019 | Yongin | July 29 | August 2 | 35 | 209 | Link | Link | |
| – | 2020 | Ventspils | Cancelled due to the COVID-19 pandemic[32] | ||||||
| 18 | 2021 | Ventspils | July 19 | July 23 | 34 | 216 | Link[permanent dead link] | Link | |
| 19 | 2022 | Castletown | July 25 | July 29 | 32 | 185 | Link Archived October 6, 2022, at the Wayback Machine | Link | |
| 20 | 2023 | Bansko | July 24 | July 28 | 37 | 204 | Link | Link | |
| 21 | 2024 | Brasília | July 23 | July 31 | 38 | 206 | Link Archived 4 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine | Link | |
| 22 | 2025 | Taipei | July 21 | July 26 | Link | ||||
| 23 | 2026 | Link | |||||||
- a The competition was held remotely.
Participant countries
[edit]
Individual medalists
[edit]| Year | Location | Gold | Silver | Bronze |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | Borovets, Bulgaria |
Alexandra Petrova |
Mirjam Plooij |
Polina Oskolskaya |
| 2004 | Moscow, Russia |
Ivan Dobrev |
Maria Mamykina |
Alexandra Zabelina Xenia Kuzmina |
| 2005 | Leiden, Netherlands |
Ivan Dobrev |
Eleonora Glazova |
Nikita Medyankin |
| 2006 | Tartu, Estonia |
Maria Kholodilova |
Yordan Mehandzhiyski Eleonora Glazova |
Yuliya Taran |
| 2007 | Saint Petersburg, Russia |
Adam Hesterberg |
Kira Kiranova Mihail Minkov |
Anna Shlomina |
| 2008 | Slanchev Bryag, Bulgaria |
Alexander Daskalov |
Anand Natarajan Maciej Janicki |
Guy Tabachnick Joon Kyu Kang |
| 2009 | Wrocław, Poland |
Diana Sofronieva |
Vitaly Pavlenko Andrey Nikulin |
Deyana Kamburova Szymon Musioł |
| 2010 | Stockholm, Sweden |
Vadim Tukh |
Martin Camacho Tian-Yi Damien Jiang |
Mirjam Parve Miroslav Manolov |
| 2011 | Pittsburgh, USA |
Morris Alper |
Wesley Jones Allen Yuan |
Min Kyu Kim Elena Rykunova |
| 2012 | Ljubljana, Slovenia |
Anton Sokolov Alexander Wade |
Darryl Wu Allan Sadun |
Pedro Neves Lopes Erik Andersen |
| 2013 | Manchester, UK |
Alexander Wade Anton Sokolov |
Omri Faraggi Yash Sinha |
Nilai Sarda Vesko Milev |
| 2014 | Beijing, China |
Milo Andrea Mazurkiewicz Darryl Wu |
Ada Melentieva Catherine Wu |
Anindya Sharma Elena Chaparova |
| 2015 | Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria |
James Wedgwood Samuel Ahmed |
Kevin M Li Ying Ming Poh |
Bálint Ugrin Nilai Sarda |
| 2016 | Mysore, India |
Jaeyeong Yang James Wedgwood |
Margarita Misirpashayeva Ioana Bouroș |
Tsuyoshi Kobayashi Elena Shukshina |
| 2017 | Dublin, Ireland |
Samuel Ahmed Przemysław Podleśny |
Andrew Tockman Takumi Yoshino |
Ekaterina Voloshinova Emil Indzhev |
| 2018 | Prague, Czech Republic |
Przemysław Podleśny Liam McKnight |
Jakub Petr Chih-Chun Wang |
David Avellan-Hultman Vlada Petrusenko |
| 2019 | Yongin, Republic of Korea |
Ken Jiang Wesley Zhang |
Diego Król João Henrique Fontes |
Tatiana Romanova Kövér Blanka |
| 2021 | Ventspils, Latvia |
Roman Shabanov Daria Kryvosheieva |
Aleksandra Limonova Tam Lok Hang |
Lili Probojcsevity Shao-Chi Ou |
| 2022 | Castletown, Isle of Man |
Artem Borisov Jun Hyeong Yook |
Tam Lok Hang Kunaal Chandrashekar |
Anita Dalma Páhán Hyunsoo Park |
| 2023 | Bansko, Bulgaria |
Tam Lok Hang Ryusei Omiya |
Elena Păvăloaia Panawat Tiacharoen |
Eleanor Borrel Chung Chi-En |
| 2024 | Brasília, Brazil |
Deeraj Pothapragada Devin Joe |
Eric Wu Wong Tok Shing Henry |
Tanupat Trakulthongchai Satoshi Tsukada |
Team medals
[edit]| Nbr | Year | Location | Team Gold | Team Silver | Team Bronze | Winning team in individual competition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2003 | Borovets, Bulgaria | Netherlands |
Russia-StPetersburg |
Russia-Moscow |
Netherlands |
| 2 | 2004 | Moskva, Russia | Russia-StPetersburg |
Latvia |
Bulgaria-1 |
Bulgaria-1 |
| 3 | 2005 | Leiden, The Netherlands | Netherlands |
Russia-Moscow |
Russia-StPetersburg |
Bulgaria-1 |
| 4 | 2006 | Tartu, Estonia | Bulgaria-2 |
Netherlands |
Poland-1 |
Bulgaria-1 |
| 5 | 2007 | Sankt-Peterburg, Russia | USA-2 Moscow |
Bulgaria-1 Bulgaria-2 |
None awarded | Estonia |
| 6 | 2008 | Slantchev Bryag, Bulgaria | USA-2 Bulgaria-East |
Netherlands USA-1 |
None awarded | USA |
| 7 | 2009 | Wrocław, Poland | USA-Red |
Korea-1 |
Russia-Moscow |
Russia-Moscow |
| 8 | 2010 | Stockholm, Sweden | Latvia |
Russia-Moscow |
Poland-2 |
USA-Blue |
| 9 | 2011 | Pittsburgh, USA | USA-Red |
Russia-StPetersburg |
Russia-Moscow |
USA-Red |
| 10 | 2012 | Ljubljana, Slovenia | USA-Blue |
Netherlands |
Poland-2 |
Russia-StPetersburg |
| 11 | 2013 | Manchester, UK | USA-Red |
Russia-StPetersburg |
Bulgaria-1 Romania |
USA-Red |
| 12 | 2014 | Beijing, China | USA-Red |
Russia-StPetersburg |
Russia-Moscow |
USA-Red |
| 13 | 2015 | Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria | UK-West |
USA-Red |
Poland-White Netherlands |
USA-Red |
| 14 | 2016 | Mysore, India | Sweden |
Australia-1 |
UK |
USA-Red |
| 15 | 2017 | Dublin, Ireland | Taiwan-TaiTWO |
Poland-Ą |
Slovenia |
UK-K |
| 16 | 2018 | Prague, Czech Republic | USA-Blue |
USA-Red Bulgaria 1 |
Brazil Pões UK-U Czechia Tým křivopřísežníků |
USA-Blue |
| 17 | 2019 | Yongin, Republic of Korea | Slovenia |
China KUN Russia Strelka |
Poland Bóbr Russia Belka Malaysia A |
USA Red |
| 18 | 2021 | Ventspils, Latvia | Ukraine і |
USA Red |
India Saffron Canada Moose |
Hong Kong EAT |
| 19 | 2022 | Castletown, Isle of Man | Korea Mal |
Taiwan Blue Magpie Japan Samurai |
Japan Ninja USA Red UK K |
USA Red |
| 20 | 2023 | Bansko, Bulgaria | United Kingdom |
USA Red Canada Anglophone |
Finland Hungary Uborka Poland Ę |
Not awarded |
| 21 | 2024 | Brasília, Brazil | Czechia |
Poland Świerszcze |
Taiwan Black Bear Japan Samurai Slovenia |
United Kingdom |
All-time medal table
[edit]Only countries with at least 1 gold medal are listed. The list is accurate up to 2024.[38] The rank is based on the number of gold medals.
| Rank | Country | Appearances | Participants | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total | Honorable Mentions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17 | 140 | 24 | 39 | 28 | 91 | 25 | |
| 2 | 21 | 170 | 22 | 26 | 41 | 89 | 24 | |
| 3 | 18 | 156 | 17 | 31 | 40 | 88 | 21 | |
| 4 | 15 | 92 | 17 | 14 | 16 | 47 | 18 | |
| 5 | 20 | 153 | 12 | 27 | 23 | 62 | 38 | |
| 6 | 12 | 84 | 7 | 5 | 12 | 24 | 19 | |
| 7 | 13 | 59 | 6 | 10 | 12 | 28 | 8 | |
| 8 | 15 | 92 | 4 | 9 | 18 | 31 | 16 | |
| 9 | 16 | 128 | 4 | 6 | 19 | 29 | 25 | |
| 10 | 11 | 67 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 18 | 12 | |
| 11 | 10 | 52 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 17 | 12 | |
| 12 | 21 | 91 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 10 | 20 | |
| 13 | no country | 2 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 0 |
| 14 | 11 | 67 | 2 | 14 | 10 | 26 | 16 | |
| 15 | 14 | 57 | 2 | 9 | 7 | 18 | 11 | |
| 16 | 7 | 28 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 13 | 5 | |
| 17 | 5 | 24 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 12 | 1 | |
| 18 | 15 | 93 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 11 | 10 | |
| 19 | 11 | 84 | 1 | 13 | 15 | 29 | 23 | |
| 20 | 21 | 95 | 1 | 7 | 18 | 26 | 16 | |
| 21 | 21 | 92 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 18 | 13 | |
| 22 | 16 | 78 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 16 | 12 | |
| 23 | 10 | 52 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 14 | |
| 24 | 6 | 24 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 9 | |
| 25 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
Media coverage
[edit]- Newspaper article in The Age "It may be semantics, but linguistics can be a team event". July 27, 2012.[40]
See also
[edit]- International Science Olympiad
- North American Computational Linguistics Open competition
- United Kingdom Linguistics Olympiad
- Panini Linguistics Olympiad
- Bulgarian National Olympiad in Linguistics
- Australian Computational and Linguistics Olympiad
- Asia Pacific Linguistics Olympiad
References
[edit]- ^ a b "International Linguistics Olympiad FAQ". www.ioling.org. Retrieved November 10, 2019.
- ^ "Из истории кафедры и отделения структурной/теоретической и прикладной лингвистики (ОСиПЛ/ОТиПЛ): 1960-2000". Retrieved March 29, 2024.
- ^ Martins, Eduardo C. (June 22, 2022). Olimpíadas de linguística: mosaico de uma prática social baseada em problemas (PhD Thesis thesis) (in Portuguese). Universidade de Brasília.
- ^ Original quote: Важным средством обучения основным положениям и методам языкознания могут служить специально составленные задачи. В существующих сборниках в качестве материала для задач в большинстве случаев используются факты родного языка учащихся или наиболее известных европейских языков. Такие задачи, безусловно, полезны, но, к сожалению, они часто страдают тем недостатком, что в них трудно отделить собственно лингвистическое задание (не требующее ничего, кроме понимания основных лингвистических положений) от проверки знания конкретных фактов рассматриваемого языка. Наилучший (хотя отнюдь не единственный) способ избавиться от этого второго элемента задания, не имеющего прямого отношения к общему языкознанию, состоит в том, чтобы составлять задачи на материале языков, незнакомых учащемуся. Разумеется, составлять такие задачи труднее, поскольку все существенные для решения конкретные факты должны быть так или иначе представлены в исходных данных задачи, зато от учащегося в этом случае требуется только представление о свойствах языка вообще. (p. 8) Зализняк, Андрей Анатольевич (2013) [1963]. Лингвистические задачи. Москва: МЦНМО. p. 40. ISBN 978-5-4439-0094-0.
- ^ "Милославский, Игорь Григорьевич". Летопись Московского университета.
- ^ "Памяти Б.Ю Городецкого". Филологический факультет, МГУ имени М. В. Ломоносова. Retrieved November 17, 2022.
- ^ "Александра Раскина". Retrieved November 17, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Martins, Eduardo C. (June 29, 2022). Olimpíadas de Linguística: mosaico de uma prática social baseada em problemas (PhD). Universidade de Brasília. Retrieved November 17, 2022.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "International history". United Kingdom Linguistics Olympiad. June 3, 2011. Archived from the original on January 2, 2014. Retrieved August 9, 2013.
- ^ a b c d "First International Olympiad in Linguistics (2003)". Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, Moscow State University. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "History of Linguistic Challenges". NACLO. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "IOL 2003". International Linguistics Olympiad official website. Archived from the original on June 30, 2013. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "Second International Linguistic Olympiad (2004)". Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, Moscow State University. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "Second International Linguistic Olympiad (2004)". Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, Moscow State University. Archived from the original on October 16, 2005. Retrieved August 14, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Internet Archive: Third International Linguistics Olympiad". Archived from the original on February 8, 2006. Retrieved August 14, 2023.
- ^ "Fourth International Linguistics Olympiad for Secondary School Students". Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ a b "The Fifth International Linguistics Olympiad". Archived from the original on October 5, 2011. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "6th International Linguistics Olympiad". Archived from the original on March 25, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "7th International Olympiad in Linguistics". Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "IOL10". Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "IOL 2011: Venue". Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "The 10th International Linguistics Olympiad". Archived from the original on June 30, 2013. Retrieved August 7, 2013.
- ^ "The International Linguistics Olympiad 2013". July 29, 2012. Archived from the original on August 29, 2017. Retrieved August 7, 2013.
- ^ "The International Linguistics Olympiad 2014". Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved July 27, 2014.
- ^ "The International Linguistics Olympiad 2015". Retrieved August 17, 2015.
- ^ "International Olympiad for Linguists 2016". iol14.plo-in.org. Archived from the original on January 12, 2016. Retrieved January 6, 2016.
- ^ "International Linguistics Olympiad 2018". iol.ff.cuni.cz. Retrieved August 5, 2018.
- ^ "IOL 2018 Participants". IOL. Retrieved August 8, 2018.
- ^ "IOL Yongin 2019". IOL 2019. Retrieved August 8, 2018.
- ^ "IOL 2019 Participants". IOL. Retrieved August 6, 2019.
- ^ "The Asia Pacific Linguistics Olympiad". Retrieved August 14, 2023.
- ^ a b "Ventspils 2021". Retrieved April 7, 2020.
- ^ "IOL Castletown 2022". IOL 2022. Archived from the original on October 6, 2022. Retrieved August 1, 2022.
- ^ "IOL Bansko 2023". IOL 2023. Retrieved August 3, 2023.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Brasília 2024". International Linguistics Olympiad. Archived from the original on August 5, 2024. Retrieved August 10, 2024.
- ^ "Taipei 2025". International Linguistics Olympiad. Retrieved August 10, 2024.
- ^ "Participants". IOL 2016. Archived from the original on July 9, 2016. Retrieved July 9, 2016.
- ^ "Results". International Linguistics Olympiad. Retrieved October 7, 2024.
- ^ From 2017, Canada sent separate teams based on language: Canada Anglophone and Canada Francophone
- ^ "It may be semantics, but linguistics can be a team event". The Age. Australia. July 26, 2012. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
External links
[edit]- IOL official website
- Borovetz, 2003 – Official website
- Moscow, 2004 – Official website
- Leiden, 2005 – Official website
- Tartu, 2006 – Official website
- St. Petersburg, 2007 – Official website Archived September 15, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- Slanchev Bryag, 2008 – Official website Archived March 24, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- Wrocław, 2009 – Official website
- Stockholm, 2010 – Official website
- Pittsburgh, 2011 – Official website Archived June 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- Ljubljana, 2012 – Official website Archived June 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- Manchester, 2013 – Official website Archived August 29, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- Beijing, 2014 – Official website
- Blagoevgrad, 2015 – Official website Archived May 19, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- Mysore, 2016 – Official website
- Dublin, 2017 – Official website
- Prague, 2018 - Official website
- Yongin, 2019 - Official website
- Latvia, 2021 (previously, 2020) - Official website Archived May 12, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
