Battle of Gulnabad: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
fixed links |
references already cover such as sword of persia |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| casualties2 = Unknown |
| casualties2 = Unknown |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{More citations needed|date=August 2021}} |
|||
{{Campaignbox Ashraf Hotak}} |
{{Campaignbox Ashraf Hotak}} |
||
The '''Battle of Gulnabad''' ({{Langx|ps|ده ګلونآبد جنګ|translit=Dh Gulonābād Džng}}; {{Langx|fa|نبرد گلونآباد|translit=Nabard-e Golūnābād}}) was fought between the [[military of Afghanistan#History|military forces]] from the [[Hotak dynasty]] and the army of the [[Safavid dynasty|Safavid Empire]] on Sunday, March 8, 1722. It further cemented the eventual fall of the [[Safavid dynasty]], which had been declining for decades. |
The '''Battle of Gulnabad''' ({{Langx|ps|ده ګلونآبد جنګ|translit=Dh Gulonābād Džng}}; {{Langx|fa|نبرد گلونآباد|translit=Nabard-e Golūnābād}}) was fought between the [[military of Afghanistan#History|military forces]] from the [[Hotak dynasty]] and the army of the [[Safavid dynasty|Safavid Empire]] on Sunday, March 8, 1722. It further cemented the eventual fall of the [[Safavid dynasty]], which had been declining for decades. |
||
Latest revision as of 12:24, 19 December 2024
| Hotaki-Safavid War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Hotaki-Safavid War | |||||||
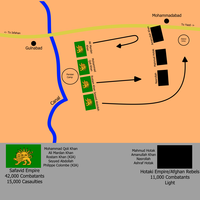 A diagram of the battle as well as casualties | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 5,000–15,000[4][7] | Unknown | ||||||
The Battle of Gulnabad (Pashto: ده ګلونآبد جنګ, romanized: Dh Gulonābād Džng; Persian: نبرد گلونآباد, romanized: Nabard-e Golūnābād) was fought between the military forces from the Hotak dynasty and the army of the Safavid Empire on Sunday, March 8, 1722. It further cemented the eventual fall of the Safavid dynasty, which had been declining for decades.
Aftermath
[edit]After the battle was won, the Hotak Afghans began slowly but surely to march on deeper into Persia, and eventually towards Isfahan, the Safavid Persian capital. Numbers and casualty figures of the Gulnabad battle are believed to be between 5,000 and 15,000 dead Safavid soldiers.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Axworthy (2006), p. 47.
- ^ Axworthy, Michael (2009). The Sword of Persia: Nader Shah, from tribal warrior to conquering tyrant, p. 75. I.B. Tauris
- ^ Malleson, George Bruce (1878). History of Afghanistan, from the Earliest Period to the Outbreak of the War of 1878. London: Elibron.com. p. 246. ISBN 1-4021-7278-8. Retrieved 2010-09-27.
- ^ a b "An Outline of the History of Persia During the Last Two CenturiesAN (A.D. 1722–1922)". Edward G. Browne. London: Packard Humanities Institute. p. 30. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
- ^ A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East, ed. Spencer C. Tucker, (ABC-CLIO, 2010), 726.
- ^ Axworthy, Michael(2009). The Sword of Persia: Nader Shah, from tribal warrior to conquering tyrant, p. 45. I.B. Tauris
- ^ Axworthy, Michael (2006). The Sword of Persia: Nader Shah, from Tribal Warrior to Conquering Tyrant. London: I.B. Tauris. p. 50. ISBN 1-85043-706-8. Retrieved 2010-09-27.
Further reading
[edit]- Axworthy, Michael (2006). The Sword of Persia: Nader Shah, from Tribal Warrior to Conquering Tyrant. I.B. Tauris, London. ISBN 1-85043-706-8
- Malleson, George Bruce. History of Afghanistan, from the Earliest Period to the Outbreak of the War of 1878. Elibron.com, London. ISBN 1-4021-7278-8
- J. P. Ferrier (1858). History of the Afghans. Publisher: Murray.
External links
[edit]- World Timelines – Battle of Gulnabad: Afghans defeat Safavids and take control of most of Persia
- Conflicts, some details on the battle
- Battle of Gulnabad, brief
