G.992.5: Difference between revisions
m →top: removed second short desc template |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Technology for broadband Internet access}} |
|||
{{DSL technologies}} |
|||
{{refimprove|date=May 2024}} |
|||
'''ITU G.992.5''' is an ITU ([[International Telecommunication Union]]) standard, also referred to as '''ADSL2+''' or '''ADSL2Plus'''. <br />Commercially it is notable for its maximum theoretical speed of '''24 Mbit/s'''. |
|||
{{Infobox technology standard |
|||
| title = G.992.5 |
|||
| long_name = Asymmetric digital subscriber line 2 transceivers (ADSL2)- Extended bandwidth ADSL2 (ADSL2plus) |
|||
| image = ADSL modem Huawei MT882.jpg |
|||
| caption = |
|||
| status = In force |
|||
| year_started = 2003 |
|||
| version = 3.1 |
|||
| version_date = November 2010 |
|||
| preview = |
|||
| preview_date = |
|||
| organization = [[ITU-T]] |
|||
| committee = |
|||
| base_standards = |
|||
| related_standards = [[G.992.3]], [[G.992.5 Annex M]] |
|||
| abbreviation = |
|||
| domain = [[telecommunications]] |
|||
| license = Freely available |
|||
| website = [https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.992.5/ www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.992.5] |
|||
}} |
|||
'''G.992.5''' (also referred to as '''ADSL2+''', '''G.dmt.bis+''', and '''G.adslplus''')<ref>{{Cite web|title=G.992.5: Asymmetric digital subscriber line 2 transceivers (ADSL2)- Extended bandwidth ADSL2 (ADSL2plus)|url=https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.992.5|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210615115745/https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.992.5/|archive-date=2021-06-15|access-date=2021-06-15|website=www.itu.int}}</ref> is an [[ITU-T]] standard for [[asymmetric digital subscriber line]] (ADSL) [[broadband]] [[Internet access]]. The standard has a maximum theoretical downstream sync speed of 24 [[Mbit/s|megabits per second (Mbit/s)]]. Utilizing [[ITU G.992.5 Annex M|G.992.5 Annex M]] upstream sync speeds of 3.3 Mbit/s can be achieved. |
|||
==Technical information== |
==Technical information== |
||
ADSL2+ extends the capability of basic [[Asymmetric digital subscriber line|ADSL]] by doubling the number of [[downstream (computer science)|downstream]] [[communication channel|channels]]. The data rates can be as high as 24 Mbit/s downstream and up to 1.4 Mbit/s upstream depending on the distance from the [[digital subscriber line access multiplexer|DSLAM]] to the customer's premises. |
|||
[[Image:ADSL2 frequencies.png|frame|right]] |
|||
ADSL2+ extends the capability of basic [[Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line|ADSL]] by doubling the number of [[Downstream (computer science)|downstream]] bits. The data rates can be as high as 24 [[Mbit/s]] downstream and 1 Mbit/s upstream depending on the distance from the [[Digital subscriber line access multiplexer|DSLAM]] to the customer's home. |
|||
[[File:ADSL2 frequencies.png|left]] |
|||
ADSL2+ is capable of doubling the frequency band of typical ADSL connections from 1.1 MHz to 2.2 MHz. This doubles the downstream data rates of the previous [[ADSL2]] standard of up to 12 Mbit/s, but like the previous standards will degrade from its peak bitrate after a certain distance. |
|||
ADSL2+ is capable of doubling the frequency band of typical ADSL connections from 1.1 MHz to 2.2 MHz. This doubles the downstream data rates of the previous [[G.992.3|ADSL2]] standard (which was up to 12 Mbit/s), and like the previous standards will degrade from its peak bitrate after a certain distance. |
|||
Also ADSL2+ allows port bonding. This is where multiple ports are physically provisioned to the end user and the total bandwidth is equal to the sum of all provisioned ports. So if 2 lines capable of 24 Mbit/s were bonded the end result would be a connection capable of 48 Mbit/s. |
|||
ADSL2+ also allows [[port bonding]]. This is where multiple ports are physically provisioned to the end user and the total bandwidth is equal to the sum of all provisioned ports. So if 2 lines capable of 24 Mbit/s were bonded the result would be a connection capable of 48 Mbit/s download and twice the original upload speed. Not all DSLAM vendors have implemented this functionality. |
|||
==Deployment== |
|||
ADSL2+ port bonding is also known as ''G.998.x'' or ''G.Bond''. |
|||
===Belgium=== |
|||
ADSL2+ so far is only available in the major cities of Belgium and some smaller ones. |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
|||
[http://www.scarlet.be Scarlet] has ADSL2+ in its portfolio. The package is called Scarlet ADSL20. The download speed is capped at 20 Mbit/s and upload is as high as 1 Mbit/s.<br> |
|||
Monthly included bandwidth: 60 GByte. |
|||
[http://www.edpnet.be EDPNet] also offers ADSL2+. The Max24 Dyn and Max24 Fix subscriptions deliver speeds up to 24 Mbit/s downstream and 1 Mbit/s upstream.<br> |
|||
Monthly included bandwidth: 60 GByte. If 60 GByte is not enough, extra bandwidth is invoiced at 0.25 EUR/GByte.<br> |
|||
For all its ADSL products EDPNet is a wholeseller of Scarlet's ADSL network. |
|||
[http://www.belcenter.com Belcenter] : The Max2+ subscriptions deliver speeds up to 20 Mbit/s downstream and 1 Mbit/s upstream.<br> |
|||
Monthly included bandwidth: 60 GByte.<br> |
|||
For all its ADSL products Belcenter is a wholeseller of Scarlet's ADSL network. |
|||
[http://www.e-leven.be E-Leven] offers an ADSL2+ subscription at 20 Mbit/s downstream and 1 Mbit upstream with 30GB data volume included. For 9,90€ extra per month, the volume limit is lifted and a Fair Use Policy is applied. E-Leven's ADSL2+ offering is available only in areas where they have their own ADSL2+ [[Digital subscriber line access multiplexer|DSLAMs]]. |
|||
[http://www.dommel.com Dommel] offers 3 new ADSL2+ subscriptions, with speeds up to 24 Mbit/s downstream and 3 Mbit upstream. From mid-november 2007, these products will be available in Leuven. In the course of 2008 cityconnect products will become available in and around more belgian large cities (such as Gent, Hasselt, Genk, Oostende, Liege, Charleroi, Antwerp, Mons, Brussels and Kortrijk). |
|||
:{| class=wikitable |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! ITU-T Spec |
|||
! Internet Service!! Downstream !! Upstream !! Bandwidth Included !! Price |
|||
! Description |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| G.998.1 |
|||
| style="font-weight:bold;"| CityConnect Lite || 3,000 [[kbit]] || 512 [[kbit]] || 15 Gigabyte || 12,95 EUR |
|||
| ATM-based multi-pair bonding: A method for bonding of multiple DSL lines to transport an ATM payload beyond the rate/reach capability of a single DSL loop. This protocol allows the bonding of 2 to 32 pairs and supports dynamic removal and restoration of pairs without human intervention. |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| G.998.2 |
|||
| style="font-weight:bold;"| CityConnect|| 10,000 [[kbit]] || 1024 [[kbit]] || 40 Gigabyte || 19,95 EUR |
|||
| Ethernet-based multi-pair bonding: Provides a method for bonding of multiple DSL lines for Ethernet transport. This recommendation builds on the [[Ethernet in the first mile|IEEE 802.3ah-2004]] methods and extends Ethernet transport over other xDSL technologies, including ADSL. |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| G.998.3 |
|||
| style="font-weight:bold;"| CityConnect Pro || 24,000[[kbit]] || 3072 [[kbit]] || F.U.P. || 28,95 EUR |
|||
| Multi-pair bonding using time-division [[inverse multiplexer|inverse multiplexing]]: Details a method for bonding DSL lines using time-division inverse multiplexing (TDIM). This recommendation uses IEEE 802.3ah handshake for pair discovery, parameter negotiation, and setup. It also allows the hitless addition and removal of pairs and the fast removal of a pair upon pair failure. |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
All accounts will be delivered, by default, with fixed ip-addresses, no port-blocking at all and will use the adsl2+ annex a and annex m specifications. |
|||
== |
==See also== |
||
*[[ADSL]] |
|||
[http://www.launchnet.com LaunchNet] has deployed the service in 11 markets throughout the US with download speeds of 15.0 Mbit/s and upload speeds of 1.0 Mbit/s. |
|||
*[[List of interface bit rates]] |
|||
*[[VDSL#VDSL2]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
[[Covad]] has deployed services across several cities in the [[United States]] and now operates the largest ADSL2+ network in the country. |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
[[BellSouth]] has deployed the service in limited areas of its 9 state region. |
|||
* [http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.992.5/en ITU-T Recommendation G.992.5: Asymmetric Digital SubscriberLine (ADSL) transceivers – Extended bandwidth ADSL2 (ADSL2+)] |
|||
* http://homehelphub.com/Tutorials/ADSL |
|||
{{DSL technologies}} |
|||
[[BCE Inc.|BCE inc.]] - [http://www.bell.ca Bell Canada] Service is expected to commence in Q2-2007 in selected areas of Ontario and Quebec. |
|||
{{ITU standards}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Itu G.992.5}} |
|||
[[TELUS]] in Alberta and British Columbia, Canada; have began the process of activating their networks (03/2007). |
|||
[[Category:Digital subscriber line]] |
|||
[http://www.gwi.net Great Works Internet] has deployed the service in areas of Maine and New Hampshire. |
|||
[http://www.colbanet.com ColbaNet] has deployed the service in the Montreal area of Quebec. |
|||
The independent telephone companies and rural carriers of North America probably have the highest total number of ADSL2+ subscribers collectively as they are currently using such technology to deliver the "[[triple play (telecommunications)|triple play]]" voice, video and data services in order to compete with the [[RBOC]]s and cable companies with their [[ILEC]] and [[CLEC]] footprint. |
|||
===United Kingdom=== |
|||
In the UK, various companies are deploying ADSL2+. |
|||
[[BT Group]], who own nearly all the [[POTS]] infrastructure across the country plan to launch ADSL2+ based services from early 2008 as part of its [[21CN]] program to upgrade of its core network. |
|||
Alternative operators currently use [[local loop unbundling]] to provide ADSL2+ lines. Therefore the availability is limited by the number of exchanges unbundled by each telecom operator in a certain area. |
|||
Such operators include: |
|||
•[[Be Unlimited]][http://www.bethere.co.uk] is rapidly expanding their service of up to 24 Mbit/s downstream and 2.5 Mbit/s upstream across the UK, and have recently overtaken Bulldog in number of unbundled exchanges.<br /> |
|||
•[[Bulldog Broadband]][http://www.bulldogbroadband.com] has extensively rolled out this service across the UK, though they only advertise up to 16 Mbit/s, 24 Mbit/s is possible.<br /> |
|||
•[[Easynet]] now owned and sold by [[BSkyB|Sky]][http://www.broadband.sky.com] is the largest ADSL2+ provider in the country with 942 exchanges unbundled as of April 2007.<br /> |
|||
•[[Cerberus Networks]][http://www.cerberusnetworks.co.uk/internet.html] are providers of business-class ADSL2+ services in the UK. Services have up to 24Mbps downstream line rates and 2.5Mbps upstream. |
|||
===India=== |
|||
[BSNL][http://www.bsnl.co.in] offers ADSL2+ Broadband under brand name DataOne with speeds up to 8 Mbps Download |
|||
===Ireland=== |
|||
[[Magnet Business]] [http://www.magnetbusiness.ie] has led the way with its ADSL2+ roll out over the incumbents (eircom) copper local loop. 10Mb Download and 1 Mb uploads represent the fastest Business Broadband available in the Irish market. Major cities initially (Limerick, Dublin, Waterford, Portlaoise, Cork, and Galway) as Magnet rolls out its unbundled exchange project. |
|||
===Greece=== |
|||
As of January 2007, most DSL providers started offering ADSL2+ from their proprietary Network. |
|||
These are: |
|||
<br />•On Telecoms ([http://www.ontelecoms.gr]) - Offers Triple Play Services - Up to 16 Mbit/s download |
|||
<br />•Vivodi ([http://www.vivodi.gr]) - Offers Triple Play Services - Up to 20 Mbit/s download |
|||
<br />•Forthnet ([http://www.forthnet.gr]) - Up to 24 Mbit/s download |
|||
<br />•Hellas On Line - ([http://www.hol.gr]) - Up to 12 Mbit/s download |
|||
<br />•ΟΤΕ & Otenet - ([http://www.ote.gr][http://www.otenet.gr]) - Up to 8 Mbit/s download<br /> |
|||
===Hungary=== |
|||
In Hungary, since mid-2006, multiple telecom companies have started offering ADSL2+ services. As of July 2007, T-Com, the biggest Hungarian ISP, is silently upgrading its customers' ADSL connections to ADSL2+, although with no speed changes. |
|||
===Norway=== |
|||
As of 2006, all major DSL providers in Norway offer ADSL2+, notable are Telenor, Tele2, Nextgentel and Ventelo. |
|||
===The Netherlands=== |
|||
As of October 2005 several wholesale DSL providers ([http://www.bbned.nl bbned], [[Tiscali]], [http://www.kpn-wholesale.com/ KPN Bitstream]) have ADSL2+ coverage on more than 50% of fixed phone lines in the Netherlands. |
|||
===Guatemala=== |
|||
Telefónica Guatemala is deploying ADSL2+ over many areas of Guatemala City and near zones, with 8 Mbit/s of download over this areas. |
|||
===Oceania=== |
|||
Telecom New Zealand is deploying its first ADSL2+ exchange in March 2007, and deploying more after consultation on locations. |
|||
Many of Australia's cities now have ADSL2+ enabled on their exchanges. ADSL2+ services are provided outside the regulated broadband requirement of the national provider [[Telstra]], so are enabled in areas primarily where there is high interest. Current service providers of ADSL2+ in Australia are: |
|||
*[[Total Peripherals Group]] (TPG) |
|||
*[[iiNet]] |
|||
*[[Optus]] |
|||
*[[Adam Internet]] |
|||
*[[Internode Systems|Internode]] |
|||
*[[Soul Pattinson Telecommunications]] |
|||
*Telstra [[BigPond]] |
|||
*[[Westnet]] |
|||
In 2006, [[Optus]] announced that it would sell its ADSL2+ network wholesale to other ISP providers. This is currently the most promising option for widespread coverage of ADSL2+ in Australia as the cost to service providers may be prohibitive with many ADSL2+ [[DSLAM]]s in each exchange. This move may provide a much wider coverage with cooperation from participating providers. |
|||
In 2007, [[OPEL Networks]] was awarded government funding to assist with a rollout of broadband in regional areas. Along with [[WiMAX|wireless broadband]], the project will see the rollout of further ADSL2+ [[DSLAM]]s to be made available on a wholesale basis.<ref>{{cite web | title = Broadband Access and Choice for rural and regional Australia | publisher = OPEL / Elders | date = [[2007-06-18]] | url = http://www.futuris.com.au/images/presentations/presentation_38.pdf | format = PDF | accessdate = 2007-07-14 }}</ref> |
|||
===Lebanon=== |
|||
Ogero has started to deploy ADSL2+ in Lebanon (the Middle East) in the spring of 2006, months after they deployed the first ADSL lines in the downtown of Beirut. The service by mid 2007 covers the capital Beirut and the second capital Tripoli in the North. The local incumbent telecom "Ogero" does not allow the use of splitters over the regular "voice" phone lines and requires that an additional separate copper pair has to be placed for the DSL link. The cost of installation is around 55,000 L.L and the standard internet fee is 35,000 L.L at 128 kbit/s. |
|||
===Egypt=== |
|||
TEdata is claiming the deployment of ADSL2+ lines through out the [[telecom Egypt]] telephone networks but there stil no signs of any speeds higher than 2 Mbit/s in any place in the country nor does it seem to be any package offers regarding that matter |
|||
===Brazil=== |
|||
ADSL2+ (Brasil Telecom) : Upload 400 kbit/s and Download speed up to 8 Mbit/s |
|||
===Germany=== |
|||
ADSL2+ (Deutsche Telekom AG) : Upload 1180 kbit/s and Download speed up to 16 Mbit/s |
|||
ADSL2+ (Arcor AG) : Upload up to 800 kbit/s , Download speed up to 16128 kbit/s f |
|||
ADSL2+ (Telefónica):Upload up to 1 MBit/s ,Download up to 16 MBit/s |
|||
===Turkey=== |
|||
ADSL2+ (TurboNet Broadband Co.) : Download speed up to 24 Mbit/s and Upload 1 Mbit/s for unlimited connection |
|||
[http://www.turbo.net.tr] |
|||
===Estonia=== |
|||
ADSL2+ together with a triple play solution is deployed on a large scale by [[Elion Enterprises Limited]]. |
|||
Download speed is 12mbit/s (8bmit/s when watching DTV) and upload speeds are up to 768kbit/s. |
|||
A [[map]] detailing the availability of ADSL2+ has been made available [http://tv.elion.ee/leviala.php here]. |
|||
===Iran=== |
|||
Only [http://www.shatel.ir Shatel] company provide ADSL2+ in Iran. |
|||
===Chile=== |
|||
[http://www.telsur.cl Telefonica del sur] Offers up to 20Mb/s, Video on demand, Digital Television and other products using ADSL2+ (G.992.5 Annex A). |
|||
==See also== |
|||
*[[Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line|ADSL]] |
|||
*[[VDSL2]] |
|||
*[[List of device bandwidths]] |
|||
==External links== |
|||
*[http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.992.5/en ITU-T Recommendation G.992.5: Asymmetric Digital SubscriberLine (ADSL) transceivers - Extended bandwidth ADSL2 (ADSL2+)] |
|||
*[http://www.dslprime.com/a/adsl21.pdf ADSL2 & ADSL2+ White Paper] ([[Portable Document Format|PDF]]) (Aware) |
|||
*[http://www.bethere.co.uk/showRollOutExchange.do Be There Current Coverage] |
|||
[[Category:Digital Subscriber Line]] |
|||
[[Category:ITU-T recommendations]] |
[[Category:ITU-T recommendations]] |
||
[[Category:ITU-T G Series Recommendations]] |
|||
[[Category:Telecommunications-related introductions in 2009]] |
|||
[[es:ADSL2+]] |
|||
[[Category:Telecommunication protocols]] |
|||
[[fr:ADSL 2+]] |
|||
[[it:ITU G.992.5]] |
|||
[[hu:ADSL2+]] |
|||
[[pt:ADSL2+]] |
|||
[[fi:ADSL2+]] |
|||
[[tr:ADSL2+]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 10:55, 1 July 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2024) |
| Asymmetric digital subscriber line 2 transceivers (ADSL2)- Extended bandwidth ADSL2 (ADSL2plus) | |
 | |
| Status | In force |
|---|---|
| Year started | 2003 |
| Latest version | 3.1 November 2010 |
| Organization | ITU-T |
| Related standards | G.992.3, G.992.5 Annex M |
| Domain | telecommunications |
| License | Freely available |
| Website | www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.992.5 |
G.992.5 (also referred to as ADSL2+, G.dmt.bis+, and G.adslplus)[1] is an ITU-T standard for asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) broadband Internet access. The standard has a maximum theoretical downstream sync speed of 24 megabits per second (Mbit/s). Utilizing G.992.5 Annex M upstream sync speeds of 3.3 Mbit/s can be achieved.
Technical information
[edit]ADSL2+ extends the capability of basic ADSL by doubling the number of downstream channels. The data rates can be as high as 24 Mbit/s downstream and up to 1.4 Mbit/s upstream depending on the distance from the DSLAM to the customer's premises.
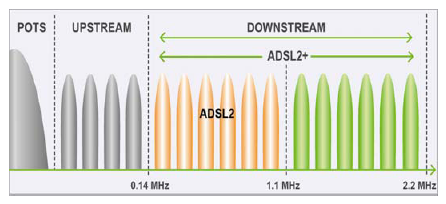
ADSL2+ is capable of doubling the frequency band of typical ADSL connections from 1.1 MHz to 2.2 MHz. This doubles the downstream data rates of the previous ADSL2 standard (which was up to 12 Mbit/s), and like the previous standards will degrade from its peak bitrate after a certain distance.
ADSL2+ also allows port bonding. This is where multiple ports are physically provisioned to the end user and the total bandwidth is equal to the sum of all provisioned ports. So if 2 lines capable of 24 Mbit/s were bonded the result would be a connection capable of 48 Mbit/s download and twice the original upload speed. Not all DSLAM vendors have implemented this functionality. ADSL2+ port bonding is also known as G.998.x or G.Bond.
| ITU-T Spec | Description |
|---|---|
| G.998.1 | ATM-based multi-pair bonding: A method for bonding of multiple DSL lines to transport an ATM payload beyond the rate/reach capability of a single DSL loop. This protocol allows the bonding of 2 to 32 pairs and supports dynamic removal and restoration of pairs without human intervention. |
| G.998.2 | Ethernet-based multi-pair bonding: Provides a method for bonding of multiple DSL lines for Ethernet transport. This recommendation builds on the IEEE 802.3ah-2004 methods and extends Ethernet transport over other xDSL technologies, including ADSL. |
| G.998.3 | Multi-pair bonding using time-division inverse multiplexing: Details a method for bonding DSL lines using time-division inverse multiplexing (TDIM). This recommendation uses IEEE 802.3ah handshake for pair discovery, parameter negotiation, and setup. It also allows the hitless addition and removal of pairs and the fast removal of a pair upon pair failure. |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "G.992.5: Asymmetric digital subscriber line 2 transceivers (ADSL2)- Extended bandwidth ADSL2 (ADSL2plus)". www.itu.int. Archived from the original on 2021-06-15. Retrieved 2021-06-15.
