Swansea Airport: Difference between revisions
remove repeated info |
|||
| (250 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Use dmy dates|date=November 2022}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Use British English|date=May 2013}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{More citations needed|date=September 2009}} |
|||
| nativename = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| nativename-a = |
|||
| name = Swansea Airport<br />Fairwood Common |
|||
| nativename-r = |
|||
| |
| nativename = |
||
| |
| nativename-a = |
||
| |
| nativename-r = |
||
| |
| image = Swansea airport logo.svg |
||
| |
| image-width = 175 |
||
| image2 = Swansea Airport on Fairwood Common - geograph.org.uk - 33204.jpg |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| image2-width = 250 |
||
| |
| IATA = SWS |
||
| |
| ICAO = EGFH |
||
| |
| type = Public |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| elevation-f = 299 |
|||
| operator = Swansea Airport Stakeholders Alliance. |
|||
| elevation-m = 91 |
|||
| city-served = [[Swansea]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| location = {{nowrap|[[Fairwood Common]], Wales, UK}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| elevation-f = 299 |
||
| |
| elevation-m = 91 |
||
| |
| metric-elev = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| website = {{nowrap|{{URL|https://swansea-airport.co.uk}}}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| pushpin_map = Wales Swansea |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| pushpin_map_caption = Location in Swansea |
|||
| r2-number = 10/28 |
|||
| |
| pushpin_label = EGFH |
||
| |
| r1-number = 04/22 |
||
| |
| r1-length-f = 4,429 |
||
| |
| r1-length-m = 1,350 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| stat1-header = |
|||
| |
| metric-rwy = |
||
| |
| stat1-header = |
||
| |
| stat1-data = |
||
| |
| stat-year = |
||
| footnotes = Sources: UK [[Aeronautical Information Publication|AIP]] at [[National Air Traffic Services|NATS]]<ref name="aip">[http://www.nats-uk.ead-it.com/public/index.php%3Foption=com_content&task=blogcategory&id=142&Itemid=191.html Swansea – EGFH]</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| r2-surface = [[Asphalt concrete|Asphalt]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| stat2-data = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Swansea Airport''' {{Airport codes|SWS|EGFH}} is |
'''Swansea Airport''' ({{langx|cy|Maes Awyr Abertawe}}) {{Airport codes|SWS|EGFH}} is located in the middle of [[Fairwood Common]] on the [[Gower Peninsula]] {{convert|6|mi}} to the west of [[Swansea]], Wales. |
||
==Operations== |
==Operations== |
||
Swansea |
Swansea Airport has a [[United Kingdom Civil Aviation Authority|CAA]] Ordinary Licence (Number P867)<ref>[http://www.caa.co.uk/docs/375/srg_asd_ordinarylicences.pdf Civil Aviation Authority Aerodrome Ordinary Licences]</ref> (currently suspended) that allows flights for the public transport of passengers or for flying instruction as authorised by the licensee, fixed wing light aircraft experience flights and flying lessons are conducted by the Cambrian Flying Club, microlight flying lessons are also conducted by the Gower flight centre. The airport has two runways: 04/22 and 10/28. A part of the disused runway 15/33 is now used as [[taxiway]] Bravo. |
||
The airport is mainly used to handle |
The airport is mainly used to handle helicopters and privately owned aircraft. The [[Wales Air Ambulance]] used to operate from the airport but has now moved to a purpose-built site. |
||
The airport is also used by corporate aircraft as well as police, military and naval helicopters. |
|||
A flight training school is based at the airport offering training on light aircraft and helicopters. The flight school has a number of aircraft which are also used for practice and leisure. The flight school operates tours of the Gower and Wales from the air. |
|||
Several small [[general aviation]] companies such as [https://www.experienceflight.co.uk/ experience flight], Gower flight centre and Cambrian flying club conduct fixed-wing pilot training; and [[parachuting]] operations; from the airport. |
|||
A [[Parachuting|skydiving]] club - Skydive Swansea, affiliated to the [[British Parachute Association]], is based at the airport. |
|||
As of 1 October 2023, the landlord, the City and County of Swansea has initiated legal proceedings to reclaim the lease from Swansea Airport Ltd, with the Court Hearing listed for 16 September 2024, after the CAA suspended the operating license for systemic failure of safety rules.<ref>{{Cite news |date=2023-09-29 |title=Swansea Airport: Council's legal bid to take back control |language=en-GB |work=BBC News |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-wales-66964350 |access-date=2023-10-04}}</ref> The council have also been liaising with Swansea Airport Stakeholders Alliance, a group of operators and supporters regarding the interim operation of the airport to protect the locally based businesses.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Youle |first=Richard |date=2023-09-29 |title=Swansea Council intends to go to court to retake possession of airport |url=https://www.walesonline.co.uk/news/wales-news/swansea-airport-council-legal-action-27815792 |access-date=2023-10-04 |website=WalesOnline |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
==Facilities== |
|||
The airport's facilities date back to the early 1940s. There are 3 runways arranged in a triangular formation, of which only two are currently active. The main runway 04/22 is a little under 1,500m, aligned in a northeast/southwest configuration. It is operated as code 2 with a take of distance of 1,199m. Runway 10/28 is 800m long, aligned in a northwest/southeast configuration, crossing the main runway and allows code 1 operations. Runway 15/33 is inactive. |
|||
As of the 1st August 2024, the above High Court hearing has been vacated, as Swansea Airport Limited director R G D Thomas has agreed to vacate the lease, interim control will be taken over by Swansea Airport Stakeholder Alliance until a permanent operator can be found. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Council leader Rob Stewart said: "Our successful talks in this complex matter mean that we're now in a position to install a temporary new leaseholder - the Swansea Airport Stakeholders' Alliance. Its members are eager to make a success of the airport."<ref>{{Cite web |last=Youle |first=Richard |date=2024-08-01 |title=New operator to take over Swansea Airport after legal battle ends |url=https://www.walesonline.co.uk/news/wales-news/new-operator-take-over-swansea-29657625 |access-date=2024-08-09 |website=Wales Online |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
== |
==Facilities== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Swansea Airport was built on what was originally [[common land]] during [[World War |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The |
||
==History== |
|||
| ⚫ | The 1990s |
||
{{unreferenced section|date=June 2023}} |
|||
| ⚫ | Swansea Airport was built on what was originally [[common land]] during the [[Second World War]]. The aerodrome was declared operational on 15 June 1941 as [[RAF Fairwood Common]], after taking nearly a year to develop. It was built as a day and night fighter station within 10 Group RAF Fighter Command. The aerodrome became a sector station in October 1941, taking on the responsibility for the air defence of [[South Wales|South]] and [[West Wales]] including shipping in the [[Bristol Channel|Bristol]] and [[St George's Channel]]s. |
||
{{anchor|Swansea Corporation (Fairwood Common) Act 1956}} |
|||
The airport was, for a short time, the headquarters of [[Air Wales]] before they ceased all operations from the airport to focus on more popular routes from [[Cardiff International Airport]], although before their demise, the headquarters remained in Swansea, instead at a city centre location. |
|||
| ⚫ | The aerodrome fulfilled a variety of military roles during the Second World War, with the addition of an Armament Practice Camp in October 1943 which expanded into an Armament Practice Station in July 1945 following which it went into 'care and maintenance' in October 1946. Finally decommissioned by the [[Royal Air Force|RAF]] in spring 1949, private flying started in July 1949 with the formation of Swansea Flying Club at the renamed Fairwood Common Airfield. The airfield hosted a number of air races and motor/motorcycle races but it was not until 1957 that Swansea Corporation allowed Cambrian Airways to run the airport for them on a commercial basis. Renamed Swansea Airport, it was officially opened on 1 June 1957 with Cambrian Airways inaugural flight arriving from Jersey. Then in the following 12 years, a variety of airlines operated through the airport with varying degrees of success. Cambrian Airways operated services to [[Channel Islands|Jersey]] and [[Channel Islands|Guernsey]]; and [[Morton Air Services]] operated a service to [[London Gatwick Airport|Gatwick]]. Scheduled regular flights then ceased in 1969. During the 1970s and 1980s, mostly ''ad hoc'' and summer charter flights continued to operate, mainly by Dan Air/Skyways. However, for a period at the end of the 1970s Air Anglia flew a Piper PA-31 Navajo Chieftain on a year-round scheduled service linking Norwich and Newquay via Birmingham and Swansea. |
||
| ⚫ | The 1990s saw the arrival of Heli-air Wales to the airport, and so began the era of Helicopter Training in South Wales. In April 2000, Swansea entrepreneur Martin Morgan via his company Jaxx Landing Ltd., bought the remaining lease. Ambitious plans were put in place to upgrade the then run-down facilities. The airport changed ownership again in 2003, when the Morgans sold their interest in the airport to Swansea Airport Limited, owned by Air Wales owner and director Roy Thomas, who was appointed CEO of the airport company. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:Runway 04 at Swansea Airport - geograph.org.uk - 110787.jpg|thumb|left|Runway 04 from the cockpit of an aircraft about to land]] |
|||
| ⚫ | With the take over of the airport by Jaxx Landing, activity at the airport began to increase: the Welsh Air Ambulance service based a [[MBB Bö 105]] helicopter at the airport in March 2001. In August 2001, gliders of 636 VGS moved from [[Aberporth]] back to Swansea Airport. In March 2016 636 VGS was disbanded and the Wales Air Ambulance helicopter moved to a new base in Dafen, Llanelli at the end of May 2016 |
||
| ⚫ | [[Air Wales]] used the airport between October 2001 and October 2004, offering flights to Dublin, Cork, Amsterdam, Jersey and London. However, the venture was not successful. After 18 months of operation, Air Wales's owner Roy Thomas had invested more than £3.25 million of his personal fortune into the airport. The venture received only one tenth of the passengers needed to make the business viable. The final straw came when the [[United Kingdom Civil Aviation Authority]] demanded that the airport's landing lights be improved at a cost of £350,000. Roy Thomas decided to pull out of Swansea Airport and concentrate Air Wales's operations at [[Cardiff International Airport]] instead. |
||
| ⚫ | With the take over of the airport by Jaxx Landing, activity at the airport began to increase: the Welsh Air Ambulance service based a [[ |
||
| ⚫ | |||
From 2008 to 2011 the airport was the base for the Yak-52 formation aerobatic team 'Team Osprey'. In Spring 2014 a new formation aerobatic team was formed at the airport with Vans aircraft, Team Raven displaying in the 2014 and 2015 air show seasons with 5 aircraft increasing to 6 by mid-July 2016. |
|||
| ⚫ | [[Air Wales]] used |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The [[Welsh Assembly Government]] is{{when|date=June 2023}} conducting studies into improving the facilities at the airport as part of the transport infrastructure development strategy for the whole of Wales. These improvements may require some public sector support. Development proposals include: a new terminal building, new hangars, upgraded operating facilities, new fencing and a new access road.<ref>[http://new.wales.gov.uk/docrepos/40382/4038231141/403821125/403821125/639095/640175/report2_part1.pdf?lang=cy Welsh Assembly: Development of and Air Transport Strategy for Wales Stage 2 Part 1: Welsh Airports Infrastructure Appraisal]{{dead link|date=April 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref><ref>[http://wales.gov.uk/docrepos/40382/4038231141/403821125/403821125/639095/640175/report4.pdf?lang=en Welsh Assembly: Development of an Air Transport Strategy for Wales: Stage 4 – Strategies to Deliver intra Wales Air Services]{{dead link|date=April 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | There has been widespread local opposition against the idea of further development of the airport. The main concerns are: the impact on the internationally important [[Special Area of Conservation]] which almost surrounds the airport; noise from the increased number of flights at the airport; and the negative impact of the development of the airport on the local scenery, since Gower is a designated [[Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty]]. In addition, the undulating and boggy common land beyond the airport perimeter fence to the North East makes extension of the runway (Runway 04/22) difficult.{{citation needed|date=June 2023}} |
||
| ⚫ | The [[Welsh Assembly Government]] is |
||
The airport website does not rule out aircraft chartering to/from Swansea, although being an unlicensed aerodrome, this would be at the operators' own risk and subject to insurance conditions.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Swansea Airport {{!}} Your Gateway to Swansea City |url=https://swansea-airport.wales/index.html |access-date=2024-04-29 |website=Swansea Airport}}</ref> |
|||
===Opposition to the development=== |
|||
| ⚫ | There has been widespread local opposition against the idea of further development of the airport. |
||
==Statistics== |
|||
{{Airport-Statistics|iata=SWS}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 80: | Line 95: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Commons category-inline|Swansea Airport}} |
|||
*[http://www.swanseaairport.com/ Swansea Airport - official site] |
|||
*[http://www.swansea-sport-flying.co.uk/index.html Swansea Sport Flying] |
|||
*[http://www.skydiveswansea.co.uk/ Skydive Swansea] |
|||
*[http://www.azworldairports.com/airports/p2720sws.htm A-Z World Airports Online - Swansea Airport] |
|||
*[http://www.airports-worldwide.com/uk/uk_swansea.html Airports Worldwide: Swansea Airport] |
|||
*[http://www.ggat.org.uk/cadw/historic_landscape/gower/english/Gower_075.htm CADW Historic Landscape Characterisation: Swansea Airport] |
|||
{{Airports in the United Kingdom}} |
|||
{{oscoor gbx|SS568914}} |
|||
{{ |
{{authority control}} |
||
{{Gower peninsula}} |
|||
[[Category:Airports in Wales]] |
[[Category:Airports in Wales]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Sports venues in Swansea]] |
|||
[[Category:Buildings and structures in Swansea]] |
|||
[[Category:Pennard (community)]] |
|||
[[Category:Transport in Swansea]] |
[[Category:Transport in Swansea]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[pms:Swansea Airport]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 23:39, 9 November 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2009) |
Swansea Airport Fairwood Common | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | Swansea Council | ||||||||||||||
| Operator | Swansea Airport Stakeholders Alliance. | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Swansea | ||||||||||||||
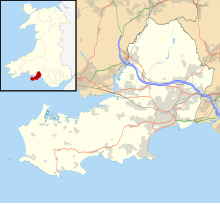
| Location | Fairwood Common, Wales, UK | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 299 ft / 91 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 51°36′19″N 004°04′04″W / 51.60528°N 4.06778°W | ||||||||||||||
| Website | swansea-airport | ||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Swansea Airport (Welsh: Maes Awyr Abertawe) (IATA: SWS, ICAO: EGFH) is located in the middle of Fairwood Common on the Gower Peninsula 6 miles (9.7 km) to the west of Swansea, Wales.
Operations
[edit]Swansea Airport has a CAA Ordinary Licence (Number P867)[2] (currently suspended) that allows flights for the public transport of passengers or for flying instruction as authorised by the licensee, fixed wing light aircraft experience flights and flying lessons are conducted by the Cambrian Flying Club, microlight flying lessons are also conducted by the Gower flight centre. The airport has two runways: 04/22 and 10/28. A part of the disused runway 15/33 is now used as taxiway Bravo.
The airport is mainly used to handle helicopters and privately owned aircraft. The Wales Air Ambulance used to operate from the airport but has now moved to a purpose-built site.
The airport is also used by corporate aircraft as well as police, military and naval helicopters.
Several small general aviation companies such as experience flight, Gower flight centre and Cambrian flying club conduct fixed-wing pilot training; and parachuting operations; from the airport.
As of 1 October 2023, the landlord, the City and County of Swansea has initiated legal proceedings to reclaim the lease from Swansea Airport Ltd, with the Court Hearing listed for 16 September 2024, after the CAA suspended the operating license for systemic failure of safety rules.[3] The council have also been liaising with Swansea Airport Stakeholders Alliance, a group of operators and supporters regarding the interim operation of the airport to protect the locally based businesses.[4]
As of the 1st August 2024, the above High Court hearing has been vacated, as Swansea Airport Limited director R G D Thomas has agreed to vacate the lease, interim control will be taken over by Swansea Airport Stakeholder Alliance until a permanent operator can be found.
Council leader Rob Stewart said: "Our successful talks in this complex matter mean that we're now in a position to install a temporary new leaseholder - the Swansea Airport Stakeholders' Alliance. Its members are eager to make a success of the airport."[5]
Facilities
[edit]Located on the eastern part of the site is the airport's only terminal building. The control tower is integrated into the terminal building. The airport has two hangars. The airport is covered by CAT1 fire cover.
The airport may be reached via the A4118, running through the Gower Peninsula. Being quite distant from any major routes and having to use mainly suburban roads, it takes approximately 20 minutes to reach from the nearest M4 junction.
History
[edit]Swansea Airport was built on what was originally common land during the Second World War. The aerodrome was declared operational on 15 June 1941 as RAF Fairwood Common, after taking nearly a year to develop. It was built as a day and night fighter station within 10 Group RAF Fighter Command. The aerodrome became a sector station in October 1941, taking on the responsibility for the air defence of South and West Wales including shipping in the Bristol and St George's Channels.
The aerodrome fulfilled a variety of military roles during the Second World War, with the addition of an Armament Practice Camp in October 1943 which expanded into an Armament Practice Station in July 1945 following which it went into 'care and maintenance' in October 1946. Finally decommissioned by the RAF in spring 1949, private flying started in July 1949 with the formation of Swansea Flying Club at the renamed Fairwood Common Airfield. The airfield hosted a number of air races and motor/motorcycle races but it was not until 1957 that Swansea Corporation allowed Cambrian Airways to run the airport for them on a commercial basis. Renamed Swansea Airport, it was officially opened on 1 June 1957 with Cambrian Airways inaugural flight arriving from Jersey. Then in the following 12 years, a variety of airlines operated through the airport with varying degrees of success. Cambrian Airways operated services to Jersey and Guernsey; and Morton Air Services operated a service to Gatwick. Scheduled regular flights then ceased in 1969. During the 1970s and 1980s, mostly ad hoc and summer charter flights continued to operate, mainly by Dan Air/Skyways. However, for a period at the end of the 1970s Air Anglia flew a Piper PA-31 Navajo Chieftain on a year-round scheduled service linking Norwich and Newquay via Birmingham and Swansea.
The 1990s saw the arrival of Heli-air Wales to the airport, and so began the era of Helicopter Training in South Wales. In April 2000, Swansea entrepreneur Martin Morgan via his company Jaxx Landing Ltd., bought the remaining lease. Ambitious plans were put in place to upgrade the then run-down facilities. The airport changed ownership again in 2003, when the Morgans sold their interest in the airport to Swansea Airport Limited, owned by Air Wales owner and director Roy Thomas, who was appointed CEO of the airport company.

With the take over of the airport by Jaxx Landing, activity at the airport began to increase: the Welsh Air Ambulance service based a MBB Bö 105 helicopter at the airport in March 2001. In August 2001, gliders of 636 VGS moved from Aberporth back to Swansea Airport. In March 2016 636 VGS was disbanded and the Wales Air Ambulance helicopter moved to a new base in Dafen, Llanelli at the end of May 2016
Air Wales used the airport between October 2001 and October 2004, offering flights to Dublin, Cork, Amsterdam, Jersey and London. However, the venture was not successful. After 18 months of operation, Air Wales's owner Roy Thomas had invested more than £3.25 million of his personal fortune into the airport. The venture received only one tenth of the passengers needed to make the business viable. The final straw came when the United Kingdom Civil Aviation Authority demanded that the airport's landing lights be improved at a cost of £350,000. Roy Thomas decided to pull out of Swansea Airport and concentrate Air Wales's operations at Cardiff International Airport instead. Since 29 October 2004, there have been no scheduled flights operating from the airport.
From 2008 to 2011 the airport was the base for the Yak-52 formation aerobatic team 'Team Osprey'. In Spring 2014 a new formation aerobatic team was formed at the airport with Vans aircraft, Team Raven displaying in the 2014 and 2015 air show seasons with 5 aircraft increasing to 6 by mid-July 2016.
Development of the airport
[edit]The Welsh Assembly Government is[when?] conducting studies into improving the facilities at the airport as part of the transport infrastructure development strategy for the whole of Wales. These improvements may require some public sector support. Development proposals include: a new terminal building, new hangars, upgraded operating facilities, new fencing and a new access road.[6][7]
There has been widespread local opposition against the idea of further development of the airport. The main concerns are: the impact on the internationally important Special Area of Conservation which almost surrounds the airport; noise from the increased number of flights at the airport; and the negative impact of the development of the airport on the local scenery, since Gower is a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. In addition, the undulating and boggy common land beyond the airport perimeter fence to the North East makes extension of the runway (Runway 04/22) difficult.[citation needed]
The airport website does not rule out aircraft chartering to/from Swansea, although being an unlicensed aerodrome, this would be at the operators' own risk and subject to insurance conditions.[8]
Statistics
[edit]Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
References
[edit]- ^ Swansea – EGFH
- ^ Civil Aviation Authority Aerodrome Ordinary Licences
- ^ "Swansea Airport: Council's legal bid to take back control". BBC News. 29 September 2023. Retrieved 4 October 2023.
- ^ Youle, Richard (29 September 2023). "Swansea Council intends to go to court to retake possession of airport". WalesOnline. Retrieved 4 October 2023.
- ^ Youle, Richard (1 August 2024). "New operator to take over Swansea Airport after legal battle ends". Wales Online. Retrieved 9 August 2024.
- ^ Welsh Assembly: Development of and Air Transport Strategy for Wales Stage 2 Part 1: Welsh Airports Infrastructure Appraisal[permanent dead link]
- ^ Welsh Assembly: Development of an Air Transport Strategy for Wales: Stage 4 – Strategies to Deliver intra Wales Air Services[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Swansea Airport | Your Gateway to Swansea City". Swansea Airport. Retrieved 29 April 2024.
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Swansea Airport at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Swansea Airport at Wikimedia Commons