Macedonian language: Difference between revisions
not a proofable source Tag: references removed |
No source was provided for this change. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{pp|small=yes}} |
|||
{{two other uses|the modern Slavic language|the ancient non-Slavic language|Ancient Macedonian language|other uses|Macedonian (disambiguation)}} |
|||
{{short description|South Slavic language spoken in North Macedonia}} |
|||
{{Infobox Language |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2024}} |
|||
|name = Macedonian |
|||
{{about|the modern South Slavic language|the extinct Hellenic language|Ancient Macedonian language}} |
|||
|nativename = {{lang|mk|Македонски јазик}} <br>''{{transl|mk|ALA|Makedonski jazik}}'' |
|||
{{Infobox language |
|||
|pronunciation = [maˈkɛdɔnski] |
|||
| |
| name = Macedonian |
||
| nativename = {{lang|mk|македонски}}<br>''{{transl|mk|ALA|makedonski}}'' |
|||
|familycolor = Indo-European |
|||
| pronunciation = {{IPA-mk|maˈkɛdɔnski|}} |
|||
|states = [[Macedonia]], [[Greece]], [[Australia]], [[Serbia]], [[Albania]], [[Germany]], [[France]], [[Italy]], [[United States]], [[Canada]], [[Turkey]] |
|||
| states = [[North Macedonia]], [[Albania]], [[Bulgaria]], [[Greece]], [[Romania]], [[Serbia]] |
|||
|region = [[Balkans|The Balkans]] |
|||
| region = [[Balkans]] |
|||
|speakers = 2.3<ref name="speakers"/> - 3 million<ref>[http://www.seelrc.org:8080/grammar/mainframe.jsp?nLanguageID=3]</ref> |
|||
| |
| ethnicity = [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonians]] |
||
| speakers = {{sigfig|1.641670|2}} million |
|||
|fam2=[[Balto-Slavic languages|Balto-Slavic]] |
|||
| |
| date = 2022 |
||
| |
| ref = e27 |
||
| |
| familycolor = Indo-European |
||
| fam2 = [[Balto-Slavic languages|Balto-Slavic]] |
|||
|script = [[Cyrillic alphabet|Cyrillic]] ([[Macedonian alphabet|Macedonian variant]]) |
|||
| fam3 = [[Slavic languages|Slavic]] |
|||
|nation = {{flagicon|Republic of Macedonia}} [[Republic of Macedonia]]<br>recognised as minority language in parts of:<br> {{ALB}}<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Hill|1999|p=?}}</ref><br> |
|||
| fam4 = [[South Slavic languages|South Slavic]] |
|||
|agency = [[Macedonian Language Institute "Krste Misirkov"]] at the [[Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje]] |
|||
| fam5 = [[Eastern South Slavic languages|Eastern South Slavic]] |
|||
|iso1 = mk |
|||
| |
| script = {{plainlist| |
||
*[[Cyrillic script|Cyrillic]] ([[Macedonian alphabet]]) |
|||
|map = [[Image:MapOfMacedonianSpeakers.png|center|315px]]<br/><center><small>Countries with significant Macedonian-speaking populations.<br/>(Click on image for the legend)</center></small> |
|||
*[[Macedonian Braille]]}} |
|||
| dia1 = [[Dialects of Macedonian|Macedonian dialects]] |
|||
| nation = {{flag|North Macedonia}} |
|||
| minority = {{plainlist| |
|||
*{{Flag|Albania|size=23px}} |
|||
*{{BIH}}<ref name="bih" /> |
|||
*{{ROU}}<ref name="rou" /> |
|||
*{{SRB}}<ref name="serbia" />}} |
|||
| agency = [[Macedonian Language Institute "Krste Misirkov"]] at the [[Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje]] |
|||
| iso1 = mk |
|||
| iso2b = mac |
|||
| iso2t = mkd |
|||
| iso3 = mkd |
|||
| glotto = mace1250 |
|||
| glottorefname = Macedonian |
|||
| lingua = 53-AAA-ha (part of 53-AAA-h) |
|||
| notice = IPA |
|||
| map = Idioma macedonio.PNG |
|||
| mapcaption = The Macedonian-speaking world:{{imagefact|date=September 2023}}{{Legend|#0080FF|regions where Macedonian is the language of the majority}}{{Legend|#88C4FF|regions where Macedonian is the language of a minority}} |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Macedonian''' ({{IPAc-en|ˌ|m|æ|s|ᵻ|ˈ|d|oʊ|n|i|ə|n}} {{respell|MASS|ih|DOH|nee|ən}}; {{lang|mk|македонски јазик}}, {{small|[[Romanization of Macedonian|translit.]]}} {{transl|mk|makedonski jazik}}, {{IPA-mk|maˈkɛdɔnski ˈjazik|pron|Mk-Makedonski jazik.ogg}}) is an [[Eastern South Slavic]] language. It is part of the [[Indo-European languages|Indo-European language family]], and is one of the [[Slavic languages]], which are part of a larger [[Balto-Slavic languages|Balto-Slavic branch]]. Spoken as a [[first language]] by around 1.6 million people, it serves as the official language of [[North Macedonia]].<ref name=e27/> Most speakers can be found in the country and [[Macedonian diaspora|its diaspora]], with a smaller number of speakers throughout the transnational [[Macedonia (region)|region of Macedonia]]. Macedonian is also a recognized [[minority language]] in parts of [[Albania]], [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]], [[Romania]], and [[Serbia]] and it is spoken by expatriate communities predominantly in [[Australia]], [[Canada]], and the [[United States]]. |
|||
'''Macedonian''' ({{audio|Mk-Makedonski jazik.ogg|македонски јазик}}, {{IPA2|maˈkɛdɔnski ˈjazik}}) is the official [[language]] of [[Republic of Macedonia]] and is a part of the Eastern group of [[South Slavic languages]]. Macedonian is closely related to and shares a high degree of [[mutual intelligibility]] with the [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]] and [[Serbian language|Serbian]] languages.<ref name="ucla">[http://www.lmp.ucla.edu/Profile.aspx?menu=004&LangID=42 Language profile Macedonian], UCLA International Institute</ref> |
|||
Macedonian developed out of the western [[dialect]]s of the Eastern South Slavic [[dialect continuum]], whose earliest recorded form is [[Old Church Slavonic]]. During much of its history, this dialect continuum was called "Bulgarian",<ref>{{cite book |last=Hupchick |first=Dennis P. |author-link=Dennis P. Hupchick |date=1995 |title=Conflict and Chaos in Eastern Europe |url= |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |page=143 |isbn=0312121164 |quote=The obviously plagiarized historical argument of the Macedonian nationalists for a separate Macedonian ethnicity could be supported only by linguistic reality, and that worked against them until the 1940s. Until a modern Macedonian literary language was mandated by the communist-led partisan movement from Macedonia in 1944, most outside observers and linguists agreed with the Bulgarians in considering the vernacular spoken by the Macedonian Slavs as a western dialect of Bulgarian}}</ref>{{Additional citation needed|date=September 2023|reason=Could use additional sources.}} although in the late 19th century, its western dialects came to be known separately as "Macedonian".{{cn|date=September 2023}} [[Standard Macedonian]] was codified in 1945 and has developed [[Macedonian literature#Modern literature|modern literature]] since.{{sfn|Thornburg|Fuller|2006|page=213}} As it is part of a dialect continuum with other [[South Slavic language]]s, Macedonian has a high degree of [[mutual intelligibility]] with [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]] and varieties of [[Serbo-Croatian]]. |
|||
The Macedonian language is a subject of controversy with Macedonia's neighbouring countries: [[Greece|Greeks]] challenge the [[Macedonian language naming dispute|legitimacy of its name]], while many [[Bulgaria]]ns deny its separateness from Bulgarian.<ref name=unity>{{cite book |author=Institute of Bulgarian Language |title=Единството на българския език в миналото и днес |publisher=[[Bulgarian Academy of Sciences]] |year=1978 |page=4 |language=Bulgarian |location=[[Sofia]] |oclc=6430481}}; {{cite book |title=Българска диалектология (Bulgarian dialectology)|last=Стойков (Stoykov)|first=Стойко |authorlink=Stoyko Stoykov |origyear=1962 |year=2002 |location=София |publisher=Акад. изд. "Проф. Марин Дринов" |language=Bulgarian |url=http://www.promacedonia.org/jchorb/st/index.htm |isbn=9544308466 |oclc=53429452}}</ref> [[Serbs]], on the other hand, acknowledge Macedonian language as distinct since 1945.<ref>http://www.kwintessential.co.uk/language/about/macedonian.html</ref> |
|||
Linguists distinguish 29 [[dialects of Macedonian]], with linguistic differences separating Western and Eastern groups of dialects. Some features of [[Macedonian grammar]] are the use of a dynamic [[Stress (linguistics)|stress]] that falls on the ante-penultimate syllable, three suffixed [[deixis|deictic articles]] that indicate noun position in reference to the speaker and the use of simple and complex [[verb tense]]s. [[Macedonian orthography]] is phonemic with a correspondence of one [[grapheme]] per [[phoneme]]. It is written using an adapted 31-letter version of the [[Cyrillic script]] with six original letters. Macedonian [[syntax]] is the same as of all other modern [[Slavic languages]], i.e. of the [[subject-verb-object]] (SVO) type and has flexible [[word order]].<ref>https://www.britannica.com/topic/Slavic-languages/Grammatical-characteristics</ref><ref>Siewierska, Anna, and Ludmila Uhlirova. "An overview of word order in Slavic languages." Empirical approaches to language typology 20 (1998): 105-150.</ref> |
|||
__TOC__ |
|||
{{-}} |
|||
Macedonian vocabulary has been historically influenced by [[Turkish language|Turkish]] and [[Russian language|Russian]]. Somewhat less prominent vocabulary influences also came from neighboring and [[prestige (linguistics)|prestige languages]]. The international consensus outside of [[Bulgaria]] is that Macedonian is an [[Autonomy and heteronomy (sociolinguistics)|autonomous language]] within the Eastern South Slavic dialect continuum, although since Macedonian and Bulgarian are mutually intelligible and are socio-historically related, a small minority of linguists are [[political views on the Macedonian language|divided in their views]] of the two as separate languages or as a single [[pluricentric language]].{{sfn|Reimann|2014|page=41}}{{sfn|Trudgill|1992}}<ref>Raúl Sánchez Prieto, Politics shaping linguistic standards: the case of Dutch in Flanders and Bulgaro-Macedonian in the Republic of Macedonia, in: Exploring linguistic standards in non-dominant varieties of pluricentric languages, {{ISBN|3631625839}}, pp.227-244; Peter Lang, with Carla Amoros Negre et al. as eds.</ref> |
|||
5 May, the day when the government of [[Yugoslav Macedonia]] adopted the [[Macedonian alphabet]] as the official script of the republic, is marked as [[Macedonian Language Day]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=5 мај – Ден на македонскиот јазик |url=https://flf.ukim.mk/5-%D0%BC%D0%B0%D1%98-%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BD-%D0%BD%D0%B0-%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%BE%D1%82-%D1%98%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BA/ |access-date=7 January 2024 |website=Филолошки факултет "Блаже Конески" – Скопје |language=mk}}</ref> This is a [[Public holidays in North Macedonia|working holiday]], declared as such by the government of North Macedonia in 2019.<ref>{{Cite web |date=16 April 2019 |title=Од 130-тата седница на Владата на РСМ: 5 Мај прогласен за Ден на македонскиот јазик |url=https://vlada.mk/node/17590 |access-date=11 June 2023 |website=Влада на Република Северна Македонија |language=mk}}</ref> |
|||
==Classification and related languages== |
==Classification and related languages== |
||
[[File:Slavic languages tree.svg|thumb|left|upright=1.25|alt=Language-tree graph|Classification of Macedonian within the [[Balto-Slavic languages|Balto-Slavic]] branch of the Indo-European language family]] |
|||
{{Macedonian language}} |
|||
Macedonian belongs to the [[East South Slavic languages|eastern group]] of the [[South Slavic languages|South Slavic]] branch of [[Slavic languages]] in the [[Indo-European languages|Indo-European]] language family, together with [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]] and the extinct [[Old Church Slavonic]]. Some authors also classify the [[Torlakian dialects]] in this group. Macedonian's closest relative is Bulgarian followed by [[Serbo-Croatian]] and [[Slovene language|Slovene]], although the last is more distantly related.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=435}}{{sfn|Levinson|O'Leary|1992|p=239}} Together, South Slavic languages form a [[dialect continuum]].{{sfn|Dedaić|Mišković-Luković|2010|p={{pn|date=August 2021}}}}{{sfn|Kortmann|van der Auwera|2011|page=420}} |
|||
Macedonian, like the other Eastern South Slavic idioms has characteristics that make it part of the [[Balkan sprachbund]], a group of languages that share [[linguistic typology|typological]], grammatical and lexical features based on areal convergence, rather than genetic proximity.{{sfn|Topolinjska|1998|p=6}} In that sense, Macedonian has experienced convergent evolution with other languages that belong to this group such as Greek, [[Aromanian language|Aromanian]], [[Albanian language|Albanian]] and [[Romani language|Romani]] due to cultural and linguistic exchanges that occurred primarily through oral communication.{{sfn|Topolinjska|1998|p=6}} |
|||
Macedonian and Bulgarian are divergent from the remaining South Slavic languages in that they do not use [[noun case]]s (except for the [[vocative]], and apart from some traces of once productive inflections still found scattered throughout these two) and have lost the [[infinitive]].{{sfn|Fortson|2009|page=431}} They are also the only Slavic languages with any definite articles (unlike standard Bulgarian, which uses only one article, standard Macedonian as well as some south-eastern Bulgarian dialects{{sfn|Comrie|Corbett|2002|p=245}} have a set of three [[Deixis|deictic]] articles: unspecified, proximal and distal definite article). Macedonian, Bulgarian and Albanian are the only Indo-European languages that make use of the [[Inferential mood|narrative mood]].{{sfn|Campbell|2000|pp=274, 1031}} |
|||
==Geographical distribution== |
|||
{{see|Geographical distribution of the Macedonian Language}} |
|||
The population of the [[Republic of Macedonia]] was 2,022,547 in 2002, with 1,644,815 speaking Macedonian as the native language.<ref name="census">Popis na Naselenie, Domaćinstva i Stanovi vo Republika Makedonija, 2002 - Vkupno naselenie na Republika Makedonija spored majčin jazik.</ref> Outside of the Republic, there are Macedonians living in other parts of the [[Macedonia (region)|geographical area of Macedonia]]. There are [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|ethnic Macedonian]] minorities in neighbouring [[Albania]], in [[Bulgaria]] in [[Greece]] and in [[Serbia]]. According to the official Albanian census of 1989, 4,697 ethnic Macedonians reside in Albania.<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Artan|Gurraj|2001|p=219}}</ref> |
|||
According to Chambers and [[Peter Trudgill|Trudgill]], the question whether Bulgarian and Macedonian are distinct languages or dialects of a single language cannot be resolved on a purely linguistic basis, but should rather take into account sociolinguistic criteria, i.e., ethnic and linguistic identity.<ref>{{citation|first1=J.K.|last1=Chambers|first2=Peter|last2=Trudgill|year=1998| title=Dialectology (2nd ed., Cambridge Textbooks in Linguistics)|location=Cambridge|publisher=Cambridge University Press|doi=10.1017/CBO9780511805103|pages=169–170|isbn=9780521593786 }}</ref> This view is supported by [[Jouko Lindstedt]], who has suggested the reflex of the back [[yer]] as a potential boundary if the application of purely linguistic criteria were possible.<ref>Tomasz Kamusella, Motoki Nomachi, Catherine Gibson as ed., The Palgrave Handbook of Slavic Languages, Identities and Borders, Springer, 2016; {{ISBN|1137348399}}, p. 436.</ref><ref name=":0">{{cite book |last=Lindstedt |first=Jouko |title=The Palgrave Handbook of Slavic Languages, Identities and Borders |chapter=Conflicting Nationalist Discourses in the Balkan Slavic Language Area |year=2016 |chapter-url=https://www.academia.edu/10646592 |quote=Macedonian dialectology... considers the dialects of south-western Bulgaria to be Macedonian, despite the lack of any widespread Macedonian national consciousness in that area. The standard map is provided by Vidoeski.(1998: 32) It would be futile to tell an ordinary citizen of the Macedonian capital, Skopje, that they do not realise that they are actually speaking Bulgarian. It would be equally pointless to tell citizens of the southwestern Bulgarian town of Blagoevgrad that they (or at least their compatriots in the surrounding countryside) do not ‘really’ speak Bulgarian, but Macedonian. In other words, regardless of the structural and linguistic arguments put forth by a majority of Bulgarian dialectologists, as well as by their Macedonian counterparts, they are ignoring one, essential fact – that the present linguistic identities of the speakers themselves in various regions do not always correspond to the prevailing nationalist discourses. |pages=429–447|doi=10.1007/978-1-137-34839-5_21 |isbn=978-1-349-57703-3 }}</ref> |
|||
A large number of Macedonians live outside the traditional Balkan [[Macedonia (region)|Macedonian region]], with [[Australia]], [[Canada]] and the [[United States]] having the largest emigrant communities. According to a 1964 estimate, approximately 580,000 Macedonians live outside of the Macedonian Republic<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Topolinjska|1998|p=?}}</ref>, nearly 30% of the total population. The Macedonian spoken by communities outside the republic dates back to before the standardisation of the language{{Fact|date=February 2009}} and retains many dialectic though, overall, mutually intelligible variations. |
|||
{{Fact|date=February 2009}} |
|||
The Macedonian language has the status of official language only within [[Macedonia]], and is a recognised minority language in parts of [[Albania]]. There are provisions for learning the Macedonian language in Romania as Macedonians are an oficially recognised minority group. The language is taught in some universities in [[Australia]], [[Canada]], [[Croatia]], [[Italy]], [[Russia]], [[Serbia]], the [[United States]] and the [[United Kingdom]] among other countries. |
|||
As for the [[Slavic dialects of Greece]], Trudgill classifies the dialects in the east Greek Macedonia as part of the [[Bulgarian language]] area and the rest as [[Macedonian dialects]].<ref name="Trudgill">Trudgill P., 2000, "Greece and European Turkey: From Religious to Linguistic Identity". In: Stephen Barbour and Cathie Carmichael (eds.), Language and Nationalism in Europe, Oxford : Oxford University Press, p.259.</ref> According to [[Riki van Boeschoten]],<ref>Riki van Boeschoten is a retired professor of the [[University of Thessaly]] and director of the Laboratory of Social Anthropology and the Oral History Archive dialects in [[eastern Greek Macedonia]]. |
|||
===Macedonian Slavic in Greece===<!--[[Macedonian Slavic]] redirects here; please leave section heading intact.--> |
|||
{{main|Slavic dialects of Greece}} |
|||
{{Cite check|date=May 2009}} |
|||
[http://users.ha.uth.gr/boeschoten/index.php?page=cv Riki van Boeschoten - My CV.] '','' [http://users.ha.uth.gr/boeschoten/index.php?page=publications Her work] (2013)</ref> dialects in eastern Greek Macedonia (around [[Serres]] and [[Drama]]) are closest to Bulgarian, those in western Greek Macedonia (around [[Florina]] and [[Kastoria]]) are closest to Macedonian, while those in the centre ([[Edessa]] and [[Salonica]]) are intermediate between the two.<ref>Boeschoten, Riki van (1993): Minority Languages in Northern Greece. Study Visit to Florina, Aridea, (Report to the European Commission, Brussels) "The Western dialect is used in Florina and Kastoria and is closest to the language used north of the border, the Eastern dialect is used in the areas of Serres and Drama and is closest to Bulgarian, the Central dialect is used in the area between Edessa and Salonica and forms an intermediate dialect"</ref><ref>{{cite book|last1=Ioannidou |first1=Alexandra |title=Questions on the Slavic Dialects of Greek Macedonia |journal=Ars Philologica: Festschrift für Baldur Panzer zum 65. Geburstag. Karsten Grünberg, Wilfried Potthoff |date=1999 |pages=59, 63 |url=https://www.academia.edu/784444 |publisher=Peterlang |location=Athens |isbn=9783631350652|quote=In September 1993 ... the European Commission financed and published an interesting report by Riki van Boeschoten on the "Minority Languages in Northern Greece", in which the existence of a "Macedonian language" in Greece is mentioned. The description of this language is simplistic and by no means reflective of any kind of linguistic reality; instead it reflects the wish to divide up the dialects comprehensibly into geographical (i.e. political) areas. According to this report, Greek Slavophones speak the "Macedonian" language, which belongs to the "Bulgaro-Macedonian" group and is divided into three main dialects (Western, Central and Eastern) - a theory which lacks a factual basis.}}</ref> |
|||
Today the varieties spoken by the Slavophone minority in parts of [[northern Greece]], especially those in western and central [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]] are usually classified as part of the Macedonian language{{Fact|date=February 2009}} and in Eastern Macedonia, as for example [[Ser-Drama-Lagadin-Nevrokop dialect]], as transitional dialects between [[Macedonian]] and [[Bulgarian language]],{{Fact|date=February 2009}} though this identification is disputed by Bulgarian linguistics, which consider them to be a part of the [[Bulgarian dialects|Bulgarian diasystem]].<ref name="unity"/><ref name="Shklifov">Шклифов, Благой. Проблеми на българската диалектна и историческа фонетика с оглед на македонските говори, София 1995, с. 14.; Шклифов, Благой. Речник на костурския говор, Българска диалектология, София 1977, с. кн. VІІІ, с. 201-205,</ref> The codification of standard Macedonian has been in effect only in the Republic of Macedonia, and the varieties spoken in Greece are thus practically "roofless",<ref name="Trudgill2000">Trudgill P. (2000), "Greece and European Turkey: From Religious to Linguistic Identity". In: Stephen Barbour and Cathie Carmichael (eds.), Language and Nationalism in Europe, Oxford : Oxford University Press, p.259.</ref> with their speakers having little access to standard or written Macedonian. Estimates vary but it is thought that there are between 20,000 and 250,000 speakers in Greece.<ref>{{cite book |
|||
|title=Janua Linguarum — The Gateway to Language |
|||
|year=2004 |
|||
|publisher=Council of Europe |
|||
|isbn=9287153124 |
|||
|author=Michel Candelier, ed. ; Ana-Isabel Andrade ...}}, See Page 90, |
|||
[http://www.ecml.at/documents/pub121E2004Candelier.pdf (Full Document)]</ref><ref>{{citebook |
|||
|title = Macedonia and Greece: The Struggle to Define a New Balkan Nation |
|||
|first = Hugh |
|||
|last = Poulton |
|||
|isbn = 0786402288 |
|||
|publisher = McFarland |
|||
|year = 1997 |
|||
|page = 193 |
|||
}}</ref><ref name="Shea" /><ref name="ethnologue">[http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=mkd ethnologue]</ref> The largest group of speakers are concentrated in the [[Florina]], [[Kastoria]], [[Edessa]], [[Giannitsa]], [[Ptolemaida]] and [[Naousa, Imathia|Naousa]] regions. During the [[Greek Civil War]], the codified Macedonian language was taught in 87 schools with 10,000 students in areas of northern Greece under the control of Communist-led forces, until their defeat by the [[Hellenic Army|National Army]] in 1949.<ref>{{cite book |
|||
|title= Macedonia Its Disputed History |
|||
|last= Simpson |
|||
|first= Neil |
|||
|authorlink= |
|||
|coauthors= |
|||
|year= 1994 |
|||
|publisher= Aristoc Press |
|||
|location= Victoria |
|||
|isbn= 0646204629 |
|||
|pages= 101,102 & 91}} </ref> In recent years, there have been attempts to have the language recognised as a minority language. |
|||
==History== |
|||
[[File:Slogan NOF.JPG|thumb|right|200px|The use of the Macedonian and Greek languages together during the Greek Civil War, 1949]] |
|||
{{main|History of the Macedonian language}} |
|||
In Greece, although groups may be considered to be speaking dialects [[Heteronomous language|heteronomous]] with the standard Macedonian language, most do not identify their language with their national identity. Unlike in the Republic of Macedonia, many speakers of the language in Greece choose not to identify ethnically as "Macedonians", but as ethnic Greeks (''[[Slavophone Greeks]]'') or ''dopii'' (locals). The simple term "Macedonian" as a name for the Slavic language is often avoided in the Greek context, and vehemently rejected by most Greeks, for whom ''[[Macedonia (terminology)|Macedonian]]'' has very different connotations. Instead, the language is often called simply '''Slavic''' or '''Slavomacedonian''', with '''Macedonian Slavic''' often being used in English to distinguish the language from the [[Modern Greek#Varieties|Macedonian]] dialect of Greek. Speakers themselves variously refer to their language as ''makedonski'', ''makedoniski'' ("Macedonian"), ''slaviká'' ({{lang-el|σλαβικά}}, "Slavic"), ''dópia'' or ''entópia'' ({{lang-el|εντόπια}}, "local/indigenous [language]"),<ref name="eurac">[http://dev.eurac.edu:8085/mugs2/do/blob.html?type=html&serial=1044526702223 Greek Helsinki Monitor - Report about Compliance with the Principles of the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities]</ref>, ''bălgarski'', ''balgàrtzki'', ''bolgàrtski'' or ''bulgàrtski'' ("Bulgarian"), ''naši'' ("our own [language]"), or ''stariski'' ("the old [language]"). |
|||
[[File:Denasalization of yuses in the Macedonian recension of OCS.svg|left|thumb|Denasalization of [[Yus|yuses]] in the Macedonian recension of [[Old Church Slavonic|OCS]]]] |
|||
The [[Slavs|Slavic people]] who settled in the Balkans during the 6th century CE, spoke their own dialects and used different dialects or languages to communicate with other people.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=103}} The "canonical" Old Church Slavonic period of the development of Macedonian started during the 9th century and lasted until the first half of the 11th century. It saw translation of [[Greek language|Greek]] religious texts.<ref name="spasov">{{cite journal|last=Spasov|first=Ljudmil|title=Периодизација на историјата на македонскиот писмен јазик и неговата стандардизација во дваесеттиот век|journal=Filološki Studii|trans-title=Periodization of the history of the Macedonian literary language and its standardization in the twentieth century|publisher=[[St. Cyril and Methodius University]]|language=mk|year=2007|pages=229–235 |volume=5|issue=1|location=Skopje|issn=1857-6060}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Koneski|first=Blazhe |title=Историја на македонскиот јазик|trans-title=History of the Macedonian Language|publisher=Kultura |location=Skopje|date=1967|language=mk}}</ref><ref name="slavic">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Slavic languages |first1=Wayles|last1=Browne|first2=Vyacheslav|last2=Vsevolodovich Ivanov|encyclopedia=[[Encyclopædia Britannica Online]]|url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/Slavic-languages#ref604061|access-date=18 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200607110701/https://www.britannica.com/topic/Slavic-languages#ref604061 |archive-date=7 June 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> The [[Old Church Slavonic#Ohrid recension|Macedonian recension]] of Old Church Slavonic also appeared around that period in the [[First Bulgarian Empire|Bulgarian Empire]] and was referred to as such due to works of the [[Ohrid Literary School]].{{sfn|Lunt|2001|page=4}} Towards the end of the 13th century, the influence of Serbian increased as Serbia expanded its borders southward.{{sfn|Vidoeski|1999|page=12}} During the five centuries of [[Ottoman rule]], from the 15th to the 20th century, the vernacular spoken in the territory of current-day North Macedonia witnessed grammatical and linguistic changes that came to characterize Macedonian as a member of the Balkan sprachbund.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=436}}{{sfn|Usikova|2005|pages=103, 106}} This period saw the introduction of many [[Turkish language|Turkish]] loanwords into the language.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=438}} |
|||
[[File:Krste P. Misirkov.jpg|thumb|upright|[[Krste Petkov Misirkov]] (''pictured'') was one of the first to outline the distinctiveness of the Macedonian language in his book ''[[Za makedonckite raboti]]'' (''On the Macedonian Matters''), published in 1903.]] |
|||
The exact numbers of speakers in Greece is hard to ascertain. Jacques Bacid estimates in his 1983 book that "over 200,000 Macedonian speakers remained in Greece"<ref>Jacques Bacid, Ph.D. Macedonia Through the Ages. Columbia University, 1983.</ref>. Other sources put the numbers of speakers at 180,000<ref>[http://www.geocities.com/Athens/9479/makedonia.html GeoNative - Macedonia<!--Bot-generated title-->]</ref>{{Verify credibility|date=May 2009}} <ref>L. M. Danforth, The Macedonian Conflict: Ethnic Nationalism in a Transnational World 1995, Princeton University Press</ref>, 220,000<ref>Hill, P. (1999) "Macedonians in Greece and Albania: A Comparative study of recent developments". Nationalities Papers Volume 27, 1 March 1999, page 44(14)</ref> 250,000<ref>{{cite book |
|||
The latter half of the 18th century saw the rise of modern literary Macedonian through the written use of [[Macedonian dialects]] referred to as "Bulgarian" by writers.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=436}} The first half of the 19th century saw the rise of nationalism among the South Slavic people in the Ottoman Empire.{{sfn|Kramer|1999|p=234}} This period saw proponents of creating a [[Bulgarian Exarchate|common church]] for Bulgarian and Macedonian Slavs which would use a common modern Macedo-Bulgarian literary standard.{{sfn|Kramer|1999|p=235}}{{sfn|Bechev|2009|page=134}} |
|||
| last = Shea |
|||
| first = John |
|||
| authorlink = |
|||
| coauthors = |
|||
| title = Macedonia and Greece - The Struggle to Define a New Balkan Nation |
|||
| publisher = McFarland |
|||
| date = 1997 |
|||
| location = |
|||
| pages = 180 |
|||
| url = 0786402288 |
|||
| doi = |
|||
| id = |
|||
| isbn = }}</ref> while Yugoslav sources vary, some putting the estimated number of "Macedonians in Greek Macedonia" at 150,000 - 200,000 and others at 300,000<ref>Poulton, H.(2000), "Who are the Macedonians?",C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, page 167, <blockquote>''As often occurs with Yugoslav sources, there appears to be confusion about the number of Macedonians in Greek Macedonia at present: some Yugoslav sources put the latter figure at 300,000, while more sober estimates put the number at 150,000 - 200,000''</blockquote></ref>. The Encyclopedia Britannica<ref>http://www.britannica.com/new-multimedia/pdf/wordat077.pdf</ref>{{Dead link|date=May 2009}} and the Reader's Digest World Guide both put the figure of [[Ethnic Macedonians]]{{Fact|date=May 2009}} in [[Greece]] at 1.8% or c.200,000 people, with the native language roughly corresponding with the figures. The UCLA also states that there is 200,000 Macedonian speakers in [[Greece]].<ref>[http://www.lmp.ucla.edu/Profile.aspx?LangID=42&menu=004 UCLA Language Materials Project: Language Profile<!--Bot-generated title-->]</ref><ref>[http://www.lmp.ucla.edu/Profile.aspx?LangID=37&menu=004 UCLA Language Materials Project: Language Profile<!--Bot-generated title-->]</ref>. A 2008 article in the Greek newspaper ''Eleftherotipia'' put the estimate at 20,000.<ref>Eletherotipia article[http://archive.enet.gr/online/online_text/c=110,dt=03.08.2008,id=62864592]</ref> |
|||
The period between 1840 and 1870, saw a struggle to define the dialectal base of the common language called simply "Bulgarian", with two opposing views emerging.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=438}}{{sfn|Kramer|1999|p=235}} One ideology was to create a Bulgarian literary language based on Macedonian dialects, but such proposals were rejected by the Bulgarian codifiers.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=436}}{{sfn|Kramer|1999|p=235}} That period saw poetry written in the [[Struga dialect]] with elements from [[Russian language|Russian]].{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=106}} Textbooks also used either spoken dialectal forms of the language or a mixed Macedo-Bulgarian language.{{sfn|Nihtinen|1999|page=51}} Subsequently, proponents of the idea of using a separate Macedonian language emerged.{{sfn|Nihtinen|1999|page=47}} |
|||
===Usage=== |
|||
[[Krste Petkov Misirkov]]'s book ''[[Za makedonckite raboti]]'' (''On Macedonian Matters'') published in 1903, was the first attempt to formalize a separate literary language.{{sfn|Kramer|1999|p=236}} With the book, the author proposed a Macedonian grammar and expressed the goal of codifying the language and using it in schools. The author postulated the principle that the [[Prilep-Bitola dialect]] be used as a dialectal basis for the formation of the Macedonian standard language; his idea however was not adopted until the 1940s.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=436}}{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=106}} On 2 August 1944 at the first [[Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia]] (ASNOM) meeting, Macedonian was declared an official language.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=436}}{{sfn|Pejoska-Bouchereau|2008|page=146}} With this, it became the last of the major Slavic languages to achieve a standard literary form.<ref name="slavic" /> As such, Macedonian served as one of the three official languages of Yugoslavia from 1945 to 1991.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://manu.edu.mk/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/%D0%9F%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B1%D0%B0-%D0%B7%D0%B0-%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%BE%D1%82-%D1%98%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BA.pdf|title=Повелба за македонскиот јазик|trans-title=Charter for the Macedonian language|publisher=[[Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts]]|language=mk|date=3 December 2019|location=Skopje|access-date=18 March 2020}}</ref> |
|||
The total number of Macedonian speakers is a highly disputed topic. |
|||
Of Macedonia's neighbours, Serbia and Albania recognize the Macedonian language whereas Greece and Bulgaria do not.<ref name="speakers">Although the precise number of speakers is unknown, figures of between 1.6 million (from [http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=mkd ethnologue]) and 2-2.5 million have been cited, see {{Harvcoltxt|Topolinjska|1998}} and {{Harvcoltxt|Friedman|1985}}. The general academic consensus is that there are approximately 2 million speakers of the Macedonian language, accepting that "it is difficult to determine the total number of speakers of Macedonian due to the official policies of the neighbouring Balkan states and the fluid nature of emigration" {{Harvcoltxt|Friedman|1985|p=?}}.</ref> According to the latest censuses and figures, the number of Macedonian-speakers is: |
|||
==Geographical distribution== |
|||
{|class="wikitable" |
|||
{{Further|Geographical distribution of Macedonian speakers|Slavic speakers of Greek Macedonia|Slavic dialects of Greece}} |
|||
! rowspan=2|State |
|||
Although the precise number of [[native language|native]] and [[second language]] speakers of Macedonian is unknown due to the policies of neighboring countries and emigration of the population, estimates ranging between 1.4 million and 3.5 million have been reported.<ref name="ethnologue">{{cite web|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=mkd |title=Ethnologue report for Macedonian |work=[[Ethnologue]] |date=19 February 1999 |access-date=7 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120901171251/http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=mkd |archive-date=1 September 2012 |url-status=live }}</ref>{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino |2001|page=435}} According to the 2002 census, the total population of [[North Macedonia]] was 2,022,547, with 1,344,815 citizens declaring Macedonian their [[First language|native language]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Попис на населението, домаќинствата и становите во Република Македонија, 2002|trans-title=Census of the population, households and dwellings in the Republic of Macedonia, 2002|work=Book X|publisher=Republic of Macedonia State Statistical Office|date=May 2005|location=Skopje|url=http://www.stat.gov.mk/Publikacii/knigaX.pdf |access-date=18 March 2020|language=mk, en|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190501180540/http://www.stat.gov.mk/publikacii/knigaX.pdf|archive-date=1 May 2019|url-status=live}}</ref> Macedonian is also studied and spoken to various degrees as a second language by all [[Demographics of North Macedonia#ethnic groups|ethnic minorities]] in the country.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=435}}<ref>{{cite web|title=Македонскиот јазик како втор и странски: терминолошки прашања|language=mk|trans-title=Macedonian as a foreign and second language: terminological questions |first1=Emilija|last1=Crvenkovska|first2=Elena|last2=Petroska|publisher=[[Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje]] |url=http://www.ffzg.unizg.hr/fisol/zbornik.pdf|access-date=18 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120616214059/http://www.ffzg.unizg.hr/fisol/zbornik.pdf|archive-date=16 June 2012|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
! colspan=2|Number |
|||
Outside North Macedonia, there are small [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|ethnic Macedonian]] minorities that speak Macedonian in neighboring countries including 4.697 in [[Albania]] (1989 census),<ref>{{cite book |author1=Artan Hoxha |author2=Alma Gurraj |chapter=Local Self-Government and Decentralization: Case of Albania. History, Reforms and Challenges |title=Local Self Government and Decentralization in South - East Europe |series=Proceedings of the workshop held in Zagreb, Croatia. 6 April 2001 |publisher=Friedrich Ebert Stiftung |place=Zagreb |year=2001 |page=219 |url=http://library.fes.de/pdf-files/bueros/kroatien/50257.pdf |access-date=7 August 2021}}</ref> 1,609 in [[Bulgaria]] (2011 census)<ref>{{cite web|title=Население по етническа група и майчин език|trans-title=Population per ethnic group and mother tongue|language=bg |year=2011|publisher=Bulgarian Census Bureau|access-date=18 March 2020 |url-status=live |url=https://censusresults.nsi.bg/Census/Reports/2/2/R9.aspx |archive-date=19 December 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151219105400/http://censusresults.nsi.bg/Census/Reports/2/2/R9.aspx}}</ref> and 12,706 in [[Serbia]] (2011 census).<ref>{{cite web |title=2011 Census – Mother tongue |url=http://webrzs.stat.gov.rs/WebSite/Public/ReportResultView.aspx?rptId=3690 |access-date=20 January 2015 |publisher=[[Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia]] |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://archive.today/20141023154939/http://webrzs.stat.gov.rs/WebSite/Public/ReportResultView.aspx?rptId=3690 |archive-date=23 October 2014}}</ref> The exact number of speakers of Macedonian in Greece is difficult to ascertain due to the country's policies. [[Slavic speakers of Greek Macedonia|Estimates of Slavophones]] ranging anywhere between 50,000 and 300,000 in the last decade of the 20th century have been reported.{{sfn|Hill|1999|page=19}}{{sfn|Poulton|2000|page=167}} Approximately 580,000 Macedonians live outside North Macedonia per 1964 estimates with [[Australia]], [[Canada]], and the [[United States]] being home to the largest emigrant communities. Consequently, the number of speakers of Macedonian in these countries include 66,020 (2016 census),<ref>{{cite web|title=Language spoken at home - Ranked by size |publisher=Profile ID |url=https://profile.id.com.au/australia/language|access-date=18 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181226071838/https://profile.id.com.au/australia/language|archive-date=26 December 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> 15,605 (2016 census)<ref>{{cite web|title=Data tables, 2016 Census |work=Statistics Canada |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/dt-td/Rp-eng.cfm?TABID=2&LANG=E&A=R&APATH=3&DETAIL=0&DIM=0&FL=A&FREE=0&GC=01&GL=-1&GID=1235625&GK=1&GRP=1&O=D&PID=110212&PRID=10&PTYPE=109445&S=0&SHOWALL=0&SUB=0&Temporal=2016&THEME=118&VID=0&VNAMEE=&VNAMEF=&D1=0&D2=0&D3=0&D4=0&D5=0&D6=0|date=2 August 2017|access-date=18 March 2020|url-status=live|archive-date=20 February 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200220044913/https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/dt-td/Rp-eng.cfm?TABID=2&LANG=E&A=R&APATH=3&DETAIL=0&DIM=0&FL=A&FREE=0&GC=01&GL=-1&GID=1235625&GK=1&GRP=1&O=D&PID=110212&PRID=10&PTYPE=109445&S=0&SHOWALL=0&SUB=0&Temporal=2016&THEME=118&VID=0&VNAMEE=&VNAMEF=&D1=0&D2=0&D3=0&D4=0&D5=0&D6=0}}</ref> and 22,885 (2010 census), respectively.<ref>{{cite web|title=Detailed Languages Spoken at Home and Ability to Speak English for the Population 5 Years and Over: 2009-2013|publisher=United States Census |url=https://www.census.gov/data/tables/2013/demo/2009-2013-lang-tables.html|access-date=18 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200412195838/https://www.census.gov/data/tables/2013/demo/2009-2013-lang-tables.html |archive-date=12 April 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> Macedonian also has more than 50,000 native speakers in countries of [[Western Europe]], predominantly in [[Germany]], [[Switzerland]] and [[Italy]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.mfa.gov.mk//Upload/ContentManagement/Files/Broj%20na%20makedonski%20iselenici%20vo%20svetot.doc |title=Броj на македонски иселеници во светот |trans-title=Number of Macedonian immigrants in the world |publisher=[[Ministry of Foreign Affairs (North Macedonia)]] |access-date=30 April 2020|language=mk|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080530070621/http://www.mfa.gov.mk//Upload/ContentManagement/Files/Broj%20na%20makedonski%20iselenici%20vo%20svetot.doc |archive-date=30 May 2008|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
The Macedonian language has the status of an official language only in North Macedonia, and is a recognized minority and official language in parts of Albania ([[Pustec]]),<ref name="Naumovski">{{cite news|url=http://balkans.courriers.info/article24081.html|title=Minorités en Albanie : les Macédoniens craignent la réorganisation territoriale du pays|last=Naumovski|first=Jaklina|language=fr|date=25 January 2014|publisher=Balkan Courriers|access-date=16 May 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140517121607/http://balkans.courriers.info/article24081.html|archive-date=17 May 2014|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="see">{{cite web|url=http://miris.eurac.edu/mugs2/do/blob.pdf?type=pdf&serial=1003744282130|title=On the Status of the Minorities in the Republic of Albania|publisher=Albanian [[Helsinki Committee]]|location=[[Sofia]]|year=2000|access-date=27 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303224002/http://miris.eurac.edu/mugs2/do/blob.pdf?type=pdf&serial=1003744282130|archive-date=3 March 2016|url-status=live}}</ref> [[Romania]], Serbia ([[Jabuka, Pančevo|Jabuka]] and [[Plandište]])<ref name="serbia">{{cite web|url=https://sitel.com.mk/makedoncite-vo-srbija-gi-uzhivaat-site-malcinski-prava-kako-i-srbite-vo-makedonija|title=Македонците во Србија ги уживаат сите малцински права, како и србите во Македонија|trans-title=Macedonians in Serbia have all the minority rights just as Serbians in Macedonia|language=mk|publisher=[[Sitel (TV channel)|Sitel]]|first=Valentin|last=Nikolovski|date=30 October 2016|access-date=26 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200326215220/https://sitel.com.mk/makedoncite-vo-srbija-gi-uzhivaat-site-malcinski-prava-kako-i-srbite-vo-makedonija|archive-date=26 March 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> and [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]].<ref name="bih">{{cite web|title=Reservations and Declarations for Treaty No.148 – European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages|url=http://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list/-/conventions/treaty/148/declarations?p_auth=63PpH3zN|publisher=[[Council of Europe]]|access-date=25 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208122308/http://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list/-/conventions/treaty/148/declarations?p_auth=63PpH3zN|archive-date=8 December 2015|url-status=live}}</ref> There are provisions to learn Macedonian in Romania as Macedonians are an officially recognized minority group.<ref name="rou">{{cite web |url=https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/search-on-treaties/-/conventions/treaty/148/declarations |title=European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages |publisher=Council of Europe |access-date=8 July 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151018085208/http://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/search-on-treaties/-/conventions/treaty/148/declarations |archive-date=18 October 2015 |url-status=live }}</ref> Macedonian is studied and taught at various universities across the world and research centers focusing on the language are found at universities across Europe ([[France]], [[Germany]], [[Austria]], [[Italy]], [[Russia]]) as well as Australia, Canada and the United States ([[Chicago]] and [[North Carolina]]).{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=105–106}} |
|||
==Dialects== |
|||
{{Main|Dialects of Macedonian}} |
|||
{{See also|Slavic dialects of Greece|Bulgarian dialects|Torlakian dialects}} |
|||
During the standardization process of the Macedonian language, the dialectal base selected was primarily based on the West-Central dialects, which spans the triangle of the communities [[Makedonski Brod]], [[Kičevo]], [[Demir Hisar (town)|Demir Hisar]], [[Bitola]], [[Prilep]], and [[Veles, North Macedonia|Veles]]. These were considered the most widespread and most likely to be adopted by speakers from other regions.{{sfn|Friedman|1998|p=33}} The initial idea to select this region as a base was first proposed in Krste Petkov Misirkov's works as he believed the Macedonian language should abstract on those dialects that are distinct from neighboring Slavic languages, such as Bulgarian and Serbian.{{sfn|Dedaić|Mišković-Luković|2010|page=13}} |
|||
{| class="infobox" width="400px" |
|||
| colspan="2" |[[File:Macedonian_Slavic_dialects.png|400x400px]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| colspan="2" |Dialect divisions of Macedonian per Macedonian dialectology.<ref name=":0" /><ref>After Z. Topolińska and B. Vidoeski (1984), Polski-macedonski gramatyka konfrontatiwna, z.1, PAN.</ref> |
|||
! Lower Range |
|||
! Higher Range |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|||
! Republic of Macedonia |
|||
; Northern |
|||
| 1,700,000<ref>[http://www.stat.gov.mk Macedonian census] {{Failed verification|date=March 2009}}</ref> |
|||
{{legend|#71889F|Lower Polog / Tetovo}} {{legend|#A6A8AA|Crna Gora}} {{legend|#DADDDF|Kumanovo / Kratovo ([[Torlakian dialects]])}} |
|||
| 2,022,547<ref>[http://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/kniga_13.pdf 2002 census]</ref> |
|||
; Western/Northwestern |
|||
{{legend|#FAf5E0|Central}} {{legend|#E0785E|Drimkol / Golo Brdo}} {{legend|#C58474|Reka}} {{legend|#E89580|Debar}} {{legend|#F8AD98|Small Reka / Galičnik}} {{legend|#EAB9AC|Upper Polog / Gostivar}} {{legend|#F8F594|Vevčani / Radοžda}} {{legend|#F5AA77|Upper Prespa / Ohrid}} |
|||
| |
|||
; Eastern |
|||
{{legend|#AAC84F|Mariovo / Tikveš}} {{legend|#B7E62B|Štip / Strumica}} {{legend|#D9F486|Maleševo / Pirin}} |
|||
; Southeastern |
|||
{{legend|#F8DA63|Solun / Voden}} {{legend|#D8CB64|Ser / Drama}} |
|||
; Southwestern |
|||
{{legend|#C7814E|Lower Prespa}} {{legend|#AE9E62|Korča}} {{legend|#DBC985|Kostur}} {{legend|#EDED90|Nestram}} |
|||
|} |
|||
Based on a large group of features, Macedonian dialects can be divided into Eastern, Western and Northern groups. The boundary between them geographically runs approximately from [[Skopje]] and [[Skopska Crna Gora]] along the rivers [[Vardar]] and [[Crna River (Vardar)|Crna]].{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=103}} There are numerous [[isogloss]]es between these dialectal variations, with structural differences in phonetics, prosody (accentuation), morphology and syntax.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=103}} The Western group of dialects can be subdivided into smaller dialectal territories, the largest group of which includes the central dialects.{{sfn|Topolinjska|1998|p=7}} The linguistic territory where Macedonian dialects were spoken also span outside the country and within the [[Macedonia (region)|region of Macedonia]], including [[Pirin Macedonia]] into Bulgaria and [[Aegean Macedonia]] into Greece.{{sfn|Topolinjska|1998|p=6}} |
|||
Variations in consonant pronunciation occur between the two groups, with most Western regions losing the /x/ and the /v/ in intervocalic position ({{lang|mk|глава|italic=no}} (head): /ɡlava/ = /ɡla/: {{lang|mk|глави|italic=no}} (heads): /ɡlavi/ = /ɡlaj/) while Eastern dialects preserve it. Stress in the Western dialects is generally fixed and falls on the antepenultimate syllable while Eastern dialects have non-fixed stress systems that can fall on any syllable of the word,{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=111}} that is also reminiscent of Bulgarian dialects. Additionally, Eastern dialects are distinguishable by their fast tonality, [[elision]] of sounds and the suffixes for definiteness. The Northern dialectal group is close to South Serbian and Torlakian dialects and is characterized by 46–47 phonetic and grammatical isoglosses.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=104}} |
|||
In addition, a more detailed classification can be based on the modern reflexes of the [[Proto-Slavic]] reduced vowels ([[yer]]s), vocalic sonorants, and the back nasal *ǫ. That classification distinguishes between the following 6 groups:{{sfn|Comrie|Corbett|2002|p=247}} |
|||
{{tree list}} |
|||
* '''Macedonian''' |
|||
** Western dialects |
|||
*** '''Ohrid-Prespa Group''': [[Ohrid dialect]], [[Struga dialect]], [[Vevčani-Radožda dialect]], [[Upper Prespa dialect]] and [[Lower Prespa dialect]]. |
|||
*** '''Debar Group''': [[Debar dialect]], [[Reka dialect]], [[Drimkol-Golo Brdo dialect]], [[Galičnik dialect|Small Reka dialect]] (''Galičnik dialect''), [[Skopska Crna Gora dialect]] and [[Našinski|Gora dialect]] |
|||
*** '''Polog Group''': [[Gostivar dialect|Upper Polog dialect]] (''Gostivar dialect''), [[Tetovo dialect|Lower Polog dialect]] (''Tetovo dialect''), [[Prilep-Bitola dialect]], [[Kičevo-Poreče dialect]] and [[Skopje-Veles dialect]] |
|||
*** '''Kostur-Korča Group''': [[Korča dialect]], [[Kostur dialect]] and [[Nestram-Kostenar dialect]] |
|||
** Eastern dialects |
|||
*** '''Northern Group''': [[Kumanovo dialect]], [[Kratovo dialect]], [[Kriva Palanka dialect]] and [[Ovče Pole dialect]] |
|||
*** '''Eastern Group''': [[Štip - Kočani dialect]], [[Strumica dialect]], [[Tikveš-Mariovo dialect]], [[Maleševo-Pirin dialect]], [[Solun-Voden dialect]] and [[Ser-Drama-Lagadin-Nevrokop dialect]]. |
|||
{{tree list/end}} |
|||
==Phonology== |
|||
{{Listen |
|||
| type = speech |
|||
| header = |
|||
| filename = Prilep-Bitola dialect speech - Bitola.ogg |
|||
| title = Bitola dialect |
|||
| description = Spoken Macedonian in a folk story as spoken in the dialect of [[Bitola]] |
|||
| filename2 = Prilep-Bitola dialect speech - Topolčani.ogg |
|||
| title2 = Prilep dialect |
|||
| description2 = Spoken Macedonian in a folk story as spoken in the dialect of [[Prilep]] |
|||
}} |
|||
{{main|Macedonian phonology}} |
|||
The [[phonology|phonological]] system of Standard Macedonian is based on the Prilep-Bitola dialect. Macedonian possesses five [[vowels]], one [[semivowel]], three [[liquid consonants]], three [[nasal stops]], three pairs of [[fricative consonant|fricative]]s, two pairs of [[affricate]]s, a non-paired voiceless fricative, nine pairs of voiced and unvoiced consonants and four pairs of [[Stop consonant|stops]]. Out of all the Slavic languages, Macedonian has the most frequent occurrence of vowels relative to consonants with a typical Macedonian sentence having on average 1.18 consonants for every one vowel.<ref>{{cite book|title=Историческая типология славянских языков. Фонетика, слообразование, лексика и фразеология|trans-title=Historical typology of Slavic languages|language=uk|last1=Kolomiec|first1=V.T.|last2=Linik|first2=T.G.|last3=Lukinova|first3=T.V.|last4=Meljnichuk|first4=А.S.|last5=Pivtorak|first5=G.P.|last6=Sklyarenko|first6=V.G.|last7=Tkachenko|first7=V.A.|last8=Tkachenko|first8=O.B|year=1986|publisher=[[National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine]]|location=Kiev}}</ref> |
|||
===Vowels=== |
|||
The Macedonian language contains 5 [[vowel]]s which are /a/, /ɛ/, /ɪ/, /o/, and /u/. For the pronunciation of the middle vowels /''е''/ and /''о''/ by native Macedonian speakers, various vowel sounds can be produced ranging from [ɛ] to [ẹ] and from [o] to [ọ]. Unstressed vowels are not [[vowel reduction|reduced]], although they are pronounced more weakly and shortly than stressed ones, especially if they are found in a stressed syllable.{{sfn|Friedman|1998|p=252}}{{sfn|Friedman|2001}} The five vowels and the letter ''р'' (/r/) which acts as a vowel when found between two consonants (e.g. {{lang|mk|црква|italic=no}}, "church"), can be syllable-forming.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=111}} |
|||
The [[schwa]] is phonemic in many dialects (varying in closeness to {{IPAblink|ʌ}} or {{IPAblink|ɨ}}) but its use in the standard language is marginal.{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=10}} When writing a dialectal word and keeping the schwa for aesthetic effect, an [[apostrophe]] is used; for example, {{angbr|к’смет}}, {{angbr|с’нце}}, etc. When spelling words letter-by-letters, each consonant is followed by the schwa sound. The individual letters of [[acronyms]] are pronounced with the schwa in the same way: {{angbr|[[Macedonian Orthodox Church|МПЦ]]}} ({{IPA|[mə.pə.t͡sə]}}). The lexicalized acronyms {{angbr|[[USSR|СССР]]}} ({{IPA|[ɛs.ɛs.ɛs.ɛr]}}) and {{angbr|МТ}} ({{IPA|[ɛm.tɛ]}}) (a brand of cigarettes), are among the few exceptions. [[Vowel length]] is not phonemic. Vowels in stressed open syllables in disyllabic words with stress on the penultimate can be realized as long, e.g. {{angbr|Велес}} {{IPA-mk|ˈvɛːlɛs||Mk-Veles.ogg}} '[[Veles (city)|Veles]]'. The sequence {{IPA|/aa/}} is often realized phonetically as {{IPA|[aː]}}; e.g. {{angbr|саат}} {{IPA|/saat/}} {{IPA|[saːt]}} '''colloq.'' hour', {{angbr|змии}} - snakes. In other words, two vowels appearing next to each other can also be pronounced twice separately (e.g. {{lang|mk|пооди|italic=no}} - to walk).{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=111}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|+ Vowels{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=10}}{{sfn|Lunt|1952|pp=10–11}} |
|||
!Albania |
|||
! |
|||
|4,697<ref>[http://www.fes.hr/E-books/pdf/Local%20Self%20Government/09.pdf 1989 census]</ref> |
|||
! [[Front vowel|Front]] |
|||
|30,000<ref>[http://www.culturalpolicies.net/web/albania.php?aid=422 Albania : 4.2.2 Language issues and policies : Cultural Policies and Trends in Europe<!--Bot-generated title-->]</ref> |
|||
! [[Central vowel|Central]] |
|||
! [[Back vowel|Back]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! [[Close vowel|Close]] |
|||
!Bulgaria<ref>This people speak predominantly Bulgarian. See 2001 census data by mother tongue: [http://www.nsi.bg/Census/MotherTongue.htm]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPA link|i}} |
|||
|5,071<ref>[http://www.nsi.bg/Census/Ethnos.htm 2001 census by ethnos].</ref> |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPA link|u}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! [[Mid vowel|Mid]] |
|||
| {{IPA link|e̞|ɛ}} |
|||
| ({{IPA link|ə}}) |
|||
| {{IPA link|o̞|ɔ}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! [[Open vowel|Open]] |
|||
!Greece |
|||
| |
|||
|35,000 <ref>{{cite book |
|||
| {{IPA link|ä|a}} |
|||
|title=Janua Linguarum — The Gateway to Language |
|||
| |
|||
|year=2004 |
|||
|} |
|||
|publisher=Council of Europe |
|||
|isbn=9287153124 |
|||
===Consonants=== |
|||
|author=Michel Candelier, ed. ; Ana-Isabel Andrade ...}}, See Page 90, |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
[http://www.ecml.at/documents/pub121E2004Candelier.pdf (Full Document)]</ref><ref>Greek Helsinki Monitor March 18, 2002 Report [http://www.greekhelsinki.gr/bhr/english/organizations/ghm/ghm_18_03_02.rtf]</ref><ref>NATIONAL CONFLICT IN A TRANSNATIONAL WORLD: GREEKS AND MACEDONIANS AT THE CONFERENCE FOR SECURITY AND COOPERATION IN EUROPE [http://www.gate.net/~mango/Danforth_National_Conflict.htm] by [[Loring Danforth]] </ref><ref name="Shea">{{cite book |
|||
| total_width = |
|||
|title=The Real Macedonians |
|||
| align = right |
|||
|last=Shea |
|||
| image1 = LinguisticdivideinMacedonian1.png |
|||
|first=John |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
|year=1992 |
|||
| caption1 = |
|||
|publisher=Newcastle |
|||
| image2 = LinguisticdivideinMacedonian2.png |
|||
|isbn=0646105043 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
|pages=148}}, >{{cite book |
|||
| caption2 = |
|||
|title=Who are the Macedonians? |
|||
| footer = A 1962 map of the use of the intervocalic phonemes ''kj'' and ''gj'' in Macedonian. |
|||
|last=Poulton |
|||
}} |
|||
|first=Hugh |
|||
|year=1995 |
|||
The consonant inventory of the Macedonian language consists of 26 letters and distinguishes three groups of consonants ({{lang|mk|согласки|italic=no}}): [[voiced]] ({{lang|mk|звучни|italic=no}}), [[voicelessness|voiceless]] ({{lang|mk|безвучни|italic=no}}) and [[sonorant]] consonants ({{lang|mk|сонорни|italic=no}}).{{sfn|Friedman|2001}} Typical features and rules that apply to consonants in the Macedonian language include [[assimilation (phonology)|assimilation]] of voiced and voiceless consonants when next to each other, devoicing of vocal consonants when at the end of a word, double consonants and elision.{{sfn|Friedman|2001}}{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|p={{pn|date=August 2021}}}} At morpheme boundaries (represented in spelling) and at the end of a word (not represented in spelling), voicing opposition is [[Final-obstruent devoicing|neutralized]].{{sfn|Friedman|2001}} |
|||
|publisher=C. Hurst & Co. Publishers |
|||
|isbn=1850652384 |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
|||
|pages=167}}, [http://books.google.com/books?id=InyEqBVhH-EC&pg=PA6&dq=Shea,+John+(1992).+The+Real+Macedonians&client=firefox-a&sig=ACfU3U2cUU_AGM8ZpmUwRk32rSvECdi7ow#PPA125,M1 abstract from page 125]</ref><ref>2001 Country Report on Human Rights Practices published by the United States Department of State[http://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/hrrpt/2001/eur/8261.htm]</ref> |
|||
|+ Consonants{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=11}}{{sfn|Lunt|1952|pp=11–12}} |
|||
|200,000 <ref name="Shea" /><ref name="ethnologue"/> |
|||
! colspan="2" | |
|||
! [[Labial consonant|Labial]] |
|||
! [[Dental consonant|Dental]] |
|||
! [[Alveolar consonant|Alveolar]] |
|||
! [[Palatal consonant|Palatal]] |
|||
! [[Velar consonant|Velar]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan="2" | [[Nasal consonant|Nasal]] |
|||
!Serbia |
|||
| {{IPAlink|m}} |
|||
|14,355<ref>[http://webrzs.stat.gov.rs/axd/Zip/VJN3.pdf Serbian census]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|n̪}}{{ref|1|<sup>1</sup>}} |
|||
|30,000{{Fact|date=January 2009}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ɲ}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! rowspan="2" | [[Stop consonant|Plosive]] |
|||
!Rest of the Balkans |
|||
! {{small|[[voicelessness|voiceless]]}} |
|||
|15,939<ref>A combination of Balkan Censuses: [http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/26/42/39332415.xls], [http://www.dzs.hr/Eng/Census/Popis/E01_02_02/E01_02_02.html],[http://www.uni-koeln.de/jur-fak/ostrecht/minderheitenschutz/Vortraege/BiH/BiH_Marko_Railic.pdf 2005 census], [http://www.monstat.cg.yu/Popis/Popis01a.zip 2003 Census] and [http://www.stat.si/popis2002/si/rezultati/rezultati_red.asp?ter=SLO&st=7</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|p}} |
|||
|25,000 |
|||
| {{IPAlink|t̪}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|c}}{{ref|3|<sup>3</sup>}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|k}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! {{small|[[voice (phonetics)|voiced]]}} |
|||
!Canada |
|||
| {{IPAlink|b}} |
|||
|37,050{{Fact|date=January 2009}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|d̪}} |
|||
|150,000<ref name="autogenerated1">[http://www.mfa.gov.mk//Upload/ContentManagement/Files/Broj%20na%20makedonski%20iselenici%20vo%20svetot.doc Estimate from the MFA]</ref> |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ɟ}}{{ref|3|<sup>3</sup>}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ɡ}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! rowspan="2" | [[Affricate consonant|Affricate]] |
|||
!Australia |
|||
! {{small|[[voicelessness|voiceless]]}} |
|||
|71,994<ref>[http://www.abs.gov.au Australian government statistics]</ref> |
|||
| |
|||
|200,000<ref name="autogenerated1" /> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|t̪͡s̪}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|t͡ʃ}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! {{small|[[voice (phonetics)|voiced]]}} |
|||
!Germany |
|||
| |
|||
|62,295<ref>[http://www.destatis.de/jetspeed/portal/cms/Sites/destatis/Internet/DE/Content/Statistiken/Bevoelkerung/AuslaendischeBevoelkerung/Tabellen/Content100/AlterAufenthaltsdauer,property=file.xls 2006 figures]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|d̪͡z̪}} |
|||
|85,000<ref name="autogenerated1" /> |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|d͡ʒ}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! rowspan="2" | [[Fricative consonant|Fricative]] |
|||
!Italy |
|||
! {{small|[[voicelessness|voiceless]]}} |
|||
|50,000<ref>[http://www.mfa.gov.mk//Upload/ContentManagement/Files/Broj%20na%20makedonski%20iselenici%20vo%20svetot.doc Estimate from the Macedonian MFA]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|f}} |
|||
|74,162<ref>[http://demo.istat.it/str2006/query.php?lingua=eng&Rip=S0&paese=A12&submit=Tavola Italian government statistics]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|s̪}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ʃ}} |
|||
| x{{ref|2|<sup>2</sup>}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! {{small|[[voice (phonetics)|voiced]]}} |
|||
!United States of America |
|||
| {{IPAlink|v}} |
|||
|45,000<ref>[http://factfinder.census.gov American FactFinder<!--Bot-generated title-->]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|z̪}} |
|||
|200,000<ref name="autogenerated1" /> |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ʒ}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan="2" | [[Approximant consonant|Approximant]] |
|||
!Switzerland |
|||
| |
|||
|6,415<ref>[http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/01/22/publ.Document.52217.pdf Swiss government statistics]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ɫ̪}}{{ref|1|<sup>1</sup>}} |
|||
|60,362<ref>[http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/01/07/blank/key/01/01.Document.20578.xls Swiss government statistics]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|l}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|j}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan="2" | [[Trill consonant|Trill]] |
|||
!Rest of World |
|||
| |
|||
|101,600<ref name="autogenerated1"/> |
|||
| |
|||
|110,000<ref>[http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/extraction/retrieve/en/theme3/cens/cens_nscbirth?OutputDir=EJOutputDir_107&user=unknown&clientsessionid=977006CF24C55C1E56E251C52D2EDAE8.extraction-worker-1&OutputFile=cens_nscbirth.htm&OutputMode=U&NumberOfCells=4&Language=en&OutputMime=text%2Fhtml& 2001 census], [http://ecodata.mineco.fgov.be/mdn/Vreemde_bevolking.jsp 2001 census], [ftp://www.statistik.at/pub/neuerscheinungen/vzaustriaweb.pdf 2001 census ], [http://www.mfa.gov.mk//Upload/ContentManagement/Files/Broj%20na%20makedonski%20iselenici%20vo%20svetot.doc Population Estimate from the MFA], [http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/26/42/39332415.xls OECD Statistics], [http://www.dzs.hr/ 2002 census], [http://www.stat.si/popis2002/si/rezultati/rezultati_red.asp?ter=SLO&st=7 2002 census], [http://www.scb.se/statistik/_publikationer/BE0101_2006A01_BR_03_BE0107TAB.pdf 2006 census], [http://www.statbank.dk/statbank5a/default.asp?w=1024 2008 census], [http://www.statbank.dk/statbank5a/default.asp?w=1024 2008 census], [http://www.diplomatie.gouv.fr/fr/pays-zones-geo_833/macedoine-arym_442/presentation-macedoine-arym_991/donnees-generales_12144.html 2003 census], [http://www.uni-koeln.de/jur-fak/ostrecht/minderheitenschutz/Vortraege/BiH/BiH_Marko_Railic.pdf 2005 census], [http://www.stats.govt.nz/NR/rdonlyres/1C81F07B-28C6-4DDD-8EBA-80C592E8022A/0/20languagespokentotalresponse.xls 2006 census], [http://www.monstat.cg.yu/Popis/Popis01a.zip 2003 Census] and [http://www.recensamant.ro 2002 census]</ref> |
|||
| {{IPAlink|r}}{{ref|1|<sup>1</sup>}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| |
|||
!Total |
|||
| |
|||
|2,289,904 |
|||
|3,200,000 |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
<!-- {| class="standard" style="text-align: center;" --> |
|||
==Dialects== |
|||
{{note|1|1}} The alveolar trill ({{IPA|/r/}}) is [[Syllabic consonant|syllabic]] between two consonants; for example, {{angbr|прст}} {{IPA|[ˈpr̩st]}} 'finger'. The dental nasal ({{IPA|/n/}}) and dental lateral ({{IPA|/ɫ/}}) are also syllabic in certain foreign words; e.g. {{angbr|њутн}} {{IPA|[ˈɲutn̩]}} '[[Newton (unit)|newton]]', {{angbr|Попокатепетл}} {{IPA|[pɔpɔkaˈtɛpɛtɫ̩]}} '[[Popocatépetl]]', etc. The [[labiodental nasal]] {{IPA|[ɱ]}} occurs as an allophone of {{IPA|/m/}} before {{IPA|/f/}} and {{IPA|/v/}} (e.g. {{angbr|трамвај}} {{IPA|[ˈtraɱvaj]}} '[[tram]]').{{cn|date=March 2022}} The [[velar nasal]] {{IPA|[ŋ]}} similarly occurs as an allophone of {{IPA|/n/}} before {{IPA|/k/}} and {{IPA|/ɡ/}} (e.g. {{angbr|англиски}} {{IPA|[ˈaŋɡliski]}} 'English').{{sfn|Friedman|2001|page=11}} The latter realization is avoided by some speakers who strive for a clear, formal pronunciation.{{cn|date=March 2022}} |
|||
{{main|Dialects of Macedonian language}} |
|||
{{note|2|2}} Inherited Slavic {{IPA|/x/}} was lost in the Western dialects of Macedonian on which the standard is based, having become zero initially and mostly {{IPA|/v/}} otherwise. {{IPA|/x/}} became part of the standard language through the introduction of new foreign words (e.g. {{lang|mk|хотел|italic=no}}, hotel), [[toponym]]s ({{lang|mk|Пехчево|italic=no}}, [[Pehčevo]]), words originating from Old Church Slavonic ({{lang|mk|дух|italic=no}}, ghost), newly formed words ({{lang|mk|доход|italic=no}}, income) and as a means to disambiguate between two words ({{lang|mk|храна|italic=no}}, food vs. {{lang|mk|рана|italic=no}}, wound). This explains the rarity of Х in the Macedonian language.{{sfn|Friedman|2001|page=11}} |
|||
{|class="infobox" width="400px" |
|||
{{note|3|3}} They exhibit different pronunciations depending on dialect. They are dorso-palatal stops in the standard language and are pronounced as such by some native speakers.{{sfn|Friedman|2001|page=11}} |
|||
===Stress=== |
|||
The [[Stress (linguistics)|word stress]] in Macedonian is {{linktext|antepenultimate}} and dynamic (expiratory). This means that it falls on the third from last [[syllable]] in words with three or more syllables, and on the first or only syllable in other words. This is sometimes disregarded when the word has entered the language more recently or from a foreign source.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=109–110}} To note which syllable of the word should be accented, Macedonian uses an apostrophe over its vowels. [[Disyllabic]] words are stressed on the second-to-last syllable: ''дéте'' ({{IPA|[ˈdɛtɛ]}}: child), ''мáјка'' ({{IPA|[ˈmajka]}}: mother) and ''тáтко'' ({{IPA|[ˈtatkɔ]}}: father). [[Trisyllabic]] and [[polysyllabic]] words are stressed on the third-to-last syllable: ''плáнина'' ({{IPA|[ˈpɫanina]}}: mountain) ''планѝната'' ({{IPA|[pɫaˈninata]}}: the mountain) ''планинáрите'' ({{IPA|[pɫaniˈnaritɛ]}}: the mountaineers).{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=109–110}} There are several exceptions to the rule and they include: [[Participle|verbal adverbs]] (i.e. words suffixed with ''-ќи''): e.g. ''викáјќи'' ({{IPA|[viˈkajci]}}: shouting), ''одéјќи'' ({{IPA|[ɔˈdɛjci]}}: walking); adverbs of time: ''годинáва'' ({{IPA|[godiˈnava]}}: this year), ''летóво'' ({{IPA|[leˈtovo]}}: this summer); foreign [[loanword]]s: e.g. ''клишé'' ({{IPA|[kliˈʃɛ:]}} cliché), ''генéза'' ({{IPA|[ɡɛˈnɛza]}} genesis), ''литератýра'' ({{IPA|[litɛraˈtura]}}: literature), ''Алексáндар'' ({{IPA|[alɛkˈsandar]}}, [[Alexander]]).{{sfn|Friedman|2001|page=13}} |
|||
Linking occurs when two or more words are pronounced with the same stress. Linking is a common feature of the Macedonian language. This linguistic phenomenon is called ''акцентска целост'' and is denoted with a [[Tie_(typography)|spacing tie]] ([[Tie_(typography)#Encoding|‿]]) sign. Several words are taken as a single unit and thus follow the rules of the stress falling on the antepenultimate syllable. The rule applies when using [[clitics]] (either enclitics or proclitics) such as the negating particle ''не'' with verbs (''тој нé‿дојде'', he did not come) and with short pronoun forms. The future particle ''ќе'' can also be used in-between and falls under the same rules (''не‿му‿јá‿даде'', did not give it to him; ''не‿ќé‿дојде'', he will not come).{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} Other uses include the [[imperative form]] accompanied by short pronoun forms (''дáј‿ми'': give me), the expression of possessives (''мáјка‿ми''), prepositions followed by a noun (''зáд‿врата''), question words followed by verbs (''когá‿дојде'') and some compound nouns (''сувó‿грозје'' - raisins, ''киселó‿млеко'' - yoghurt) among others.{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
==Grammar== |
|||
{{Main|Macedonian grammar}} |
|||
Macedonian grammar is markedly [[Analytic language|analytic]] in comparison with other Slavic languages, having lost the common Slavic [[case system]]. The Macedonian language shows some special and, in some cases, unique characteristics due to its central position in the Balkans. Literary Macedonian is the only South Slavic literary language that has three forms of the definite article, based on the degree of proximity to the speaker, and a perfect tense formed by means of an [[auxiliary verb]] "to have", followed by a [[past tense|past]] participle in the [[Neuter gender|neuter]], also known as the [[verbal adjective]]. Other features that are only found in Macedonian and not in other Slavic languages include the antepenultimate accent and the use of the same vocal ending for all verbs in first person, present simple (''глед-'''a'''-м'', ''јад-'''а'''-м'', ''скок-'''а'''-м'').{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|page=43}} Macedonian distinguishes at least 12 major [[part of speech|word classes]], five of which are modifiable and include nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numbers and verbs and seven of which are invariant and include [[adverb]]s, prepositions, [[conjunction (grammar)|conjunction]]s, [[interjection]]s, [[Grammatical particle|particles]] and [[Linguistic modality|modal words]].{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|p={{pn|date=August 2021}}}} |
|||
===Nouns=== |
|||
Macedonian [[noun]]s (''именки'') belong to one of three [[Grammatical gender|genders]] (masculine, feminine, and neuter) and are [[Inflection|inflected]] for [[Grammatical number|number]] (singular and plural), and marginally for [[grammatical case|case]]. The gender opposition is not distinctively marked in the plural.{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=40}} Masculine nouns usually end in a consonant or a vowel (''-a'', ''-o'' or ''-e'') and neuter nouns end in a vowel (''-o'' or ''-e''). Virtually all feminine nouns end in the same vowel, ''-a''.{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
The vocative of nouns is the only remaining case in the Macedonian language and is used to address a person directly. The vocative case always ends with a vowel, which can be either an -у (''јунаку'': hero vocative) or an -e (''човече'': man vocative) to the root of masculine nouns. For feminine nouns, the most common final vowel ending in the vocative is -o (''душо'', sweetheart vocative; ''жено'', wife vocative). The final suffix -e can be used in the following cases: three or polysyllabic words with the ending ''-ица'' (''мајчице'', mother vocative), female given names that end with ''-ка'': ''Ратка'' becomes ''Ратке'' and ''-ја'': ''Марија'' becomes ''Марије'' or ''Маријо''. There is no vocative case in neuter nouns. The role of the vocative is only facultative and there is a general tendency of vocative loss in the language since its use is considered impolite and dialectal.{{sfn|Friedman|2001|page=23}} The vocative can also be expressed by changing the tone.{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}}<ref>{{cite book|last=Minova Gjurkova|first=Liljana |year=1994|title=Синтакса на македонскиот стандарден јазик|trans-title=Syntax of the standard Macedonian language|language=mk}}</ref> |
|||
There are three different types of plural: regular, counted and [[collective noun|collective]]. The first plural type is most common and used to indicate regular plurality of nouns: ''маж - мажи'' (a man - men), ''маса - маси'' (a table - table), ''село - села'' (a village - villages). There are various suffixes that are used and they differ per gender; a linguistic feature not found in other Slavic languages is the use of the suffix ''-иња'' to form plural of neuter nouns ending in ''-е'': ''пиле - пилиња'' (a chick - chicks).{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|page=43}} Counted plural is used when a number or a [[quantifier (linguistics)|quantifier]] precedes the noun; suffixes to express this type of plurality do not correspond with the regular plurality suffixes: ''два молива'' (two pencils), ''три листа'' (three leaves), ''неколку часа'' (several hours). The collective plural is used for nouns that can be viewed as a single unit: ''лисје'' (a pile of leaves), ''ридје'' (a unit of hills). Irregular plural forms also exist in the language: ''дете - деца'' (child - children).{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
====Definiteness==== |
|||
{|class="wikitable floatright" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|+The definite articles |
|||
|colspan="2"|[[Image:Macedonian Slavic dialects.png|400px]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
!rowspan="2" | |
|||
|colspan="2"|Dialect divisions of Macedonian<ref>After Z. Topolińska and B. Vidoeski (1984), Polski-macedonski gramatyka konfrontatiwna, z.1, PAN.</ref> |
|||
!colspan="3" | Singular |
|||
!colspan="3" | Plural |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
!Masculine |
|||
| |
|||
!Feminine |
|||
;Northern |
|||
!Neuter |
|||
{{legend|#71889F|Lower Polog}} |
|||
!Masculine |
|||
{{legend|#A6A8AA|Crna Gora}} |
|||
!Feminine |
|||
{{legend|#DADDDF|Kumanovo / Kratovo}} |
|||
!Neuter |
|||
;Western/Northwestern |
|||
|- |
|||
{{legend|#FAf5E0|Central}} |
|||
!Unspecified |
|||
{{legend|#EAB9AC|Upper Polog}} |
|||
| ''маж'''от''''' |
|||
{{legend|#C58474|Reka}} |
|||
| ''жена'''та''''' |
|||
{{legend|#F8AD98|Mala Reka / Galičnik}} |
|||
| ''дете'''то''''' |
|||
{{legend|#E89580|Debar}} |
|||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center;"| ''мажи'''те'''''/''жени'''те''''' |
|||
{{legend|#E0785E|Drimkol / Golo Brdo}} |
|||
| ''деца'''та''''' |
|||
{{legend|#F8F594|Vevčani / Radοžda}} |
|||
|- |
|||
{{legend|#F5AA77|Upper Prespa / Ohrid}} |
|||
!Proximate |
|||
{{legend|#C7814E|Lower Prespa}} |
|||
| ''маж'''ов''''' |
|||
| |
|||
| ''жена'''ва''''' |
|||
;Eastern |
|||
| ''дете'''вo''''' |
|||
{{legend|#AAC84F|Mariovo / Tikveš}} |
|||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center;"| ''мажи'''ве'''''/''жени'''ве''''' |
|||
{{legend|#B7E62B|Štip / Strumica}} |
|||
| ''деца'''ва''''' |
|||
{{legend|#D9F486|Maleševo / Pirin}} |
|||
|- |
|||
;Southeastern |
|||
!Distal |
|||
{{legend|#AE9E62|Korča}} |
|||
| ''маж'''он''''' |
|||
{{legend|#DBC985|Kostur}} |
|||
| ''жена'''на''''' |
|||
{{legend|#EDED90|Nestram}} |
|||
| ''дете'''нo''''' |
|||
{{legend|#F8DA63|Solun / Voden}} |
|||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center;"| ''мажи'''не'''''/''жени'''не''''' |
|||
{{legend|#D8CB64|Ser / Drama}} |
|||
| ''деца'''на''''' |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
A characteristic feature of the nominal system is the indication of [[definiteness]]. As with other Slavic languages, there is no [[indefinite article]] in Macedonian. The [[definite article]] in Macedonian is postpositive, i.e. it is added as a suffix to nouns. An individual feature of the Macedonian language is the use of three definite articles, inflected for gender and related to the position of the object, which can be unspecified, proximate or distal. |
|||
Based on a large group of features, Macedonian dialects can be divided into Eastern and Western groups (the boundary runs approximately from [[Skopje]] and [[Skopska Crna Gora]] along the rivers [[Vardar]] and Crna). In addition, a more detailed classification can be based on the modern reflexes of the [[Proto-Slavic]] reduced vowels ([[yer]]s), vocalic sonorants, and the back nasal *{{Unicode|ǫ}}. That classification distinguishes between the following 5 groups:<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Comrie|Corbett|2002|p=247}}</ref> |
|||
*Definite articles ''-ов, -ва, -во, -ве'' are used for objects located close to the speaker (''човек'''ов''''': - this person here) |
|||
*Definite articles ''-он, -на, -но, -не'' are used for objects located further away from the speaker that can still be perceived (''жена'''на''''': - that woman there) |
|||
*Definite articles ''-от, -та, -то, -те'' are most commonly used as general indicators of definiteness regardless of the referred object's position (''дете'''то''''': the child). Additionally, these suffixes can be used to indicate objects referred to by the speaker that are in the proximity of the listener, e.g. ''дај ми ја книгата што е до тебе'' - give me the book next to you.{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|p={{pn|date=August 2021}}}} |
|||
[[Proper nouns]] are per definition definite and are not usually used together with an article, although exceptions exist in the spoken and literary language such as ''Совче'''то''''', ''Маре'''то''''', ''Наде'''то''''' to demonstrate feelings of [[endearment]] to a person. |
|||
Western Dialects: |
|||
===Adjectives=== |
|||
*'''Ohrid-Prespa Group''' |
|||
Adjectives accompany nouns and serve to provide additional information about their referents. Macedonian adjectives [[Agreement (linguistics)|agree]] in form with the noun they modify and are thus inflected for gender, number and definiteness and ''убав'' changes to ''убава'' (''убава жена'', a beautiful woman) when used to describe a feminine noun, ''убаво'' when used to describe a neuter noun (''убаво дете'', a beautiful child) and ''убави'' when used to form the plural (''убави мажи, убави жени, убави деца'').{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
**[[Ohrid dialect]] |
|||
**[[Struga dialect]] |
|||
**[[Vevčani-Radοžda dialect]] |
|||
**[[Upper Prespa dialect]] |
|||
**[[Lower Prespa dialect]]. |
|||
*'''Debar Group''' |
|||
**[[Debar dialect]] |
|||
**[[Reka Dialect]] |
|||
**[[Drimkol-Golo Brdo dialect]] |
|||
**[[Galičnik dialect]] |
|||
**[[Skopska Crna Gora dialect]] |
|||
**[[Našinski|Gora dialect]] |
|||
*'''Polog Group''' |
|||
**[[Upper Polog Dialect]] |
|||
**[[Lower Polog Dialect]] |
|||
**[[Prilep-Bitola dialect]] |
|||
**[[Kičevo-Poreče dialect]] |
|||
**[[Skopje-Veles dialect]] |
|||
*'''Kostur-Korča Group''' |
|||
**[[Korča dialect]] |
|||
**[[Kostur dialect]] |
|||
**[[Nestram-Kostenar dialect]] |
|||
Adjectives can be analytically inflected for degree of [[Comparison (grammar)|comparison]] with the prefix ''по-'' marking the [[comparative]] and the prefix ''нај-'' marking the [[superlative]]. Both prefixes cannot be written separately from the adjective: ''Марија е паметна девојка'' (Marija is a smart girl), ''Марија е попаметна од Сара'' (Marija is smarter than Sara), ''Марија е најпаметната девојка во нејзиниот клас'' (Marija is the smartest girl in her class). The only adjective with an irregular comparative and superlative form is ''многу'' which becomes ''повеќе'' in the comparative and ''најмногу'' in the superlative form.{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=27}} Another modification of adjectives is the use of the prefixes ''при-'' and ''пре-'' which can also be used as a form of comparison: ''престар човек'' (a very old man) or ''пристар човек'' (a somewhat old man).{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|p={{pn|date=August 2021}}}} |
|||
Eastern Dialects: |
|||
===Pronouns=== |
|||
*'''Northern Group''' |
|||
Three types of pronouns can be distinguished in Macedonian: [[personal pronouns|personal]] (''лични''), [[relative pronouns|relative]] (''лично-предметни'') and [[demonstrative pronouns|demonstrative]] (''показни''). Case relations are marked in pronouns. Personal pronouns in Macedonian appear in three genders and both in singular and plural. They can also appear either as [[accusative|direct]] or [[dative|indirect object]] in long or short forms. Depending on whether a definite direct or indirect object is used, a [[clitic pronoun]] will refer to the object with the verb: ''Јас не му ја дадов книгата на момчето'' ("I did not give the book to the boy").{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=437}} The direct object is a remnant of the accusative case and the indirect of the dative. Reflexive pronouns also have forms for both direct and indirect objects: ''себе се'', ''себе си''. Examples of personal pronouns are shown below: |
|||
**[[Kumanovo dialect]] |
|||
*Personal pronoun: '''''Јас''' читам книга''. ("I am reading a book") |
|||
**[[Kratovo dialect]] |
|||
*Direct object pronoun: ''Таа '''мене ме''' виде во киното''. ("She saw me at the cinema") |
|||
**[[Kriva Palanka dialect]] |
|||
*Indirect object pronoun: ''Тој '''мене ми''' рече да дојдам''. ("He told me to come") |
|||
**[[Ovče Pole dialect]] |
|||
*'''Eastern Group''' |
|||
**[[Štip - Kočani dialect]] |
|||
**[[Strumica dialect]] |
|||
**[[Tikveš-Mariovo dialect]] |
|||
**[[Maleševo-Pirin dialect]] |
|||
**[[Solun-Voden dialect]] |
|||
**[[Ser-Drama-Lagadin-Nevrokop dialect]]. |
|||
Relative pronouns can refer to a person (''кој, која, кое'' - who), objects (''што'' - which) or serve as indicators of possession (''чиј, чија, чие'' - whose) in the function of a question or a relative word. These pronouns are inflected for gender and number and other word forms can be derived from them (''никој'' - nobody, ''нешто'' - something, ''сечиј'' - everybody's). There are three groups of demonstrative pronouns that can indicate proximate (''овој'' - this one (mas.)), distal (''онаа'' - the one there (fem.)) and unspecific (''тоа'' - that one (neut.)) objects. These pronouns have served as a basis for the definite article.{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|p={{pn|date=August 2021}}}}{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
The [[Ser-Drama-Lagadin-Nevrokop dialect]] and [[Maleševo-Pirin dialect]] are considered to also be [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]] dialects<ref>{{cite book |title=Българска диалектология (Bulgarian dialectology)|last=Стойков (Stoykov)|first=Стойко |authorlink=Stoyko Stoykov |origyear=1962 |year=2002 |location=София |publisher=Акад. изд. "Проф. Марин Дринов" |language=Bulgarian |url=http://www.promacedonia.org/jchorb/st/index.htm |isbn=9544308466 |oclc=53429452 }}</ref> or transitional dialects between Macedonian and Bulgarian.{{Fact|date=September 2008}} |
|||
{|class="wikitable" |
|||
==Phonology== |
|||
|+Macedonian personal pronouns |
|||
|- |
|||
{{IPA notice}} |
|||
!Person |
|||
!Singular |
|||
!Direct object |
|||
!Indirect object |
|||
!Plural |
|||
!Direct object |
|||
!Indirect object |
|||
|- |
|||
!1. |
|||
| ''јас'' |
|||
| ''мене ме'' |
|||
| ''мене ми'' |
|||
| ''ние'' |
|||
| ''нас нѐ'' |
|||
| ''нам ни'' |
|||
|- |
|||
!2. |
|||
| ''ти''<br/>''вие'' (formal) |
|||
| ''тебе те''<br/>''вас ве'' (formal) |
|||
| ''тебе ти''<br/>''вас ви'' (formal) |
|||
| ''вие'' |
|||
| ''вас ве'' |
|||
| ''вас ви'' |
|||
|- |
|||
!3. |
|||
| ''тој'' (masculine)<br/>''таа'' (feminine)<br/>''тоа'' (neuter) |
|||
| ''него го'' (masc./neut.)<br/>''неа ја'' (fem.) |
|||
| ''нему му'' (masc./neut.)<br/>''нејзе ѝ'' (fem.) |
|||
| ''тие'' |
|||
| ''нив ги'' |
|||
| ''ним им'' |
|||
|} |
|||
===Verbs=== |
|||
[[File:LinguisticdivideinMacedonian1.png|thumb|250px|right|Map of the use of the intervocalic phenome ''kj'' in the Macedonian language]] |
|||
{{Main|Macedonian conjugation}} |
|||
[[File:LinguisticdivideinMacedonian2.png|thumb|right|250px|Map of the use of the intervocalic phenome ''gj'' in the Macedonian language]] |
|||
Macedonian verbs agree with the subject in [[grammatical person|person]] (first, second or third) and number (singular or plural). Some dependent verb constructions (''нелични глаголски форми'') such as verbal adjectives (''глаголска придавка'': ''плетен/плетена''), verbal l-form (''глаголска л-форма'': ''играл/играла'') and [[verbal noun]] (''глаголска именка'': ''плетење'') also demonstrate gender. There are several other grammatical categories typical of Macedonian verbs, namely type, transitiveness, mood, superordinate aspect (imperfective/perfective [[grammatical aspect|aspect]]).{{sfn|Friedman|2001|page=33}} Verb forms can also be classified as simple, with eight possible verb constructions or complex with ten possible constructions.{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
Macedonian has developed a grammatical category which specifies the opposition of witnessed and reported actions (also known as renarration). Per this grammatical category, one can distinguish between ''минато определено'' i.e. definite past, denoting events that the speaker witnessed at a given definite time point, and ''минато неопределено'' i.e. indefinite past denoting events that did not occur at a definite time point or events reported to the speaker, excluding the time component in the latter case. Examples: ''Но, потоа се случија работи за кои не знаев'' ("But then things happened that I did not know about") vs. ''Ми кажаа дека потоа се случиле работи за кои не знаев'' ("They told me that after, things happened that I did not know about").{{sfn|Friedman|2001|page=43}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+[[Vowel]]s of Macedonian<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Lunt|1952|p=1}}</ref> |
|||
====Tense==== |
|||
! |
|||
{|class="wikitable floatleft" |
|||
![[Front vowel|Front]] |
|||
|+Conjugation of ''сум'' in present, aorist, present perfect and future tense |
|||
![[Central vowel|Central]] |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Back vowel|Back]] |
|||
!Person |
|||
|-align=center |
|||
!Singular |
|||
![[Close vowel|Close]] |
|||
!Plural |
|||
|и {{IPA|/i/}} |
|||
| |
|- |
||
!1. |
|||
|у {{IPA|/u/}} |
|||
| ''сум'', ''бев'', ''сум бил'', ''ќе бидам'' |
|||
|-align=center |
|||
| ''сме'', ''бевме'', ''сме биле'', ''ќе бидеме'' |
|||
![[Mid vowel|Mid]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|е {{IPA|/ɛ/}} |
|||
!2. |
|||
| |
|||
| ''си'', ''беше'', ''си бил'', ''ќе бидеш'' |
|||
|о {{IPA|/ɔ/}} |
|||
| ''сте'', ''бевте'', ''сте биле'', ''ќе бидете'' |
|||
|-align=center |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Open vowel|Open]] |
|||
!3. |
|||
| |
|||
| ''е'', ''беше'', ''бил'', ''ќе биде'' |
|||
|а {{IPA|/a/}} |
|||
| ''се'', ''беа'', ''биле'', ''ќе бидат'' |
|||
| |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
The present tense in Macedonian is formed by adding a suffix to the verb stem which is inflected per person, form and number of the subject. Macedonian verbs are conventionally divided into three main conjugations according to the [[thematic vowel]] used in the [[citation form]] (i.e. {{Smallcaps|{{lc:[[Grammatical person|3p]]-[[Present tense|pres]]-[[Grammatical number|sg]]}}}}).{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|p={{pn|date=August 2021}}}} These groups are: ''a''-group, ''e''-group and ''и''-group. Furthermore, the ''и''-subgroup is divided into three more subgroups: ''а-'', ''е-'' and ''и-''subgroups. The verb ''сум'' (to be) is the only exception to the rule as it ends with a consonant and is conjugated as an irregular verb. |
|||
The perfect tense can be formed using both to be (''сум'') and to have (''има'') as [[auxiliary verbs]]. The first form inflects the verb for person and uses a past active participle: ''сум видел многу работи'' ("I have seen a lot of things"). The latter form makes use of a clitic that agrees in number and gender with the object of the sentence and the passive participle of the verb in its uninflected form (''го имам гледано филмот'', "I have seen that movie").{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=106}}{{sfn|Friedman|2001|page=33}} Another past form, the aorist is used to describe actions that have finished at a given moment in the past: ''одев'' ("I walked"), ''скокаа'' ("they jumped").{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
In addition, the [[schwa]] {{IPA|[ə]}} may appear in certain dialects or [[loanword]]s. |
|||
Future forms of verbs are conjugated using the particle ''ќе'' followed by the verb conjugated in present tense, ''ќе одам'' (I will go). The construction used to express negation in the future can be formed by either adding the negation particle at the beginning ''не ќе одам'' (I will not go) or using the construction ''нема да'' (''нема да одам''). There is no difference in meaning, although the latter form is more commonly used in spoken language. Another future tense is future in the past which is formed using the clitic ''ќе'' and the past tense of the verb inflected for person, ''таа ќе заминеше'' ("she would have left").{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|- align="center" |
|||
|+[[Consonant]]s of Macedonian<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Lunt|1952|p=1}}</ref> |
|||
! |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Bilabial]] |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Labiodental|Labio]]-<br>[[Labiodental|Dental]] |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Dental consonant|Dental]] |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Alveolar consonant|Alveolar]] |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Postalveolar consonant|Post]]-<br>[[Postalveolar consonant|Alveolar]] |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Palatal consonant|Palatal]] |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Velar consonant|Velar]] |
|||
|- align="center" |
|||
! [[Nasal consonant|Nasal]] |
|||
| colspan="2" | {{IPA|m}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | {{IPA|n}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | {{IPA|ɲ}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
|- align="center" |
|||
! [[Plosive consonant|Plosive]] |
|||
| {{IPA|p}} |
|||
| {{IPA|b}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| {{IPA|t}} |
|||
| {{IPA|d}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| {{IPA|c}} |
|||
| {{IPA|ɟ}} |
|||
| {{IPA|k}} |
|||
| {{IPA|ɡ}} |
|||
|- align="center" |
|||
! [[Affricate consonant|Affricate]] |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| {{IPA|ts}} |
|||
| {{IPA|dz}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| {{IPA|tʃ}} |
|||
| {{IPA|dʒ}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
|- align="center" |
|||
! [[Fricative consonant|Fricative]] |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| {{IPA|f}} |
|||
| {{IPA|v}} |
|||
| {{IPA|s}} |
|||
| {{IPA|z}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| {{IPA|ʃ}} |
|||
| {{IPA|ʒ}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | {{IPA|x}} |
|||
|- align="center" |
|||
! [[Approximant consonant|Approximant]] |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" |{{IPA|j}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
|- align="center" |
|||
! [[Trill consonant|Trill]] |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | {{IPA|r}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
|- align="center" |
|||
! [[Lateral consonant|Lateral]] |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" |{{IPA|ɫ}} |
|||
| colspan="2" |{{IPA|l}} |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
| colspan="2" | |
|||
|} |
|||
====Aspect, voice and mood==== |
|||
Macedonian exhibits final obstruent devoicing and syllabic {{IPA|/r/}} |
|||
Similar to other Slavic languages, Macedonian verbs have a grammatical aspect (''глаголски вид'') that is a [[Grammatical aspect in Slavic languages|typical feature of Slavic languages]]. Verbs can be divided into [[imperfective aspect|imperfective]] (''несвршени'') and [[perfective aspect|perfective]] (''свршени'') indicating actions whose time duration is unknown or occur repetitively or those that show an action that is finished in one moment. The former group of verbs can be subdivided into verbs which take place without interruption (e.g. ''Тој спие цел ден'', "He sleeps all day long) or those that signify repeated actions (e.g. ''Ја бараше книгата но не можеше да ја најде'', "He was looking for the book but he could not find it"). Perfective verbs are usually formed by adding prefixes to the stem of the verb, depending on which, they can express actions that took place in one moment (''чукна'', "knocked"), actions that have just begun (''запеа'', "start to sing"), actions that have ended (''прочита'', "read") or partial actions that last for short periods of time (''поработи'', "worked").{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
The contrast between transitive and intransitive verbs can be expressed analytically or syntactically and virtually all verbs denoting actions performed by living beings can become transitive if a short personal pronoun is added: ''Тоj легна'' ("He laid down") vs. ''Тоj го легна детето'' ("He laid the child down"). Additionally, verbs which are expressed with the reflexive pronoun ''се'' can become transitive by using any of the contracted pronoun forms for the direct object: ''Тој '''се''' смее'' - He is laughing, vs. ''Тој '''ме''' смее'' - "He is making me laugh"). Some verbs such as sleep or die do not traditionally have the property of being transitive.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=117}} |
|||
Other than recent loanwords, [[word stress]] in Macedonian is [[wiktionary:antepenultimate|antepenultimate]], meaning it falls on the third from last [[syllable]] in words with three or more syllables, and on the first or only syllable in other words. By comparison, in standard Bulgarian, the stress can fall anywhere within a word. |
|||
Macedonian verbs have three [[grammatical moods]] (''глаголски начин''): [[indicative]], [[imperative mood|imperative]] and [[conditional mood|conditional]]. The imperative mood can express both a wish or an order to finish a certain action. The imperative only has forms for the second person and is formed using the suffixes ''-ј'' (''пеј''; sing) or ''-и'' (''оди'', walk) for singular and ''-јте'' (''пејте'', sing) or ''-ете'' for plural (''одете'', walk). The first and third subject forms in singular and plural express indirect orders and are conjugated using ''да'' or ''нека'' and the verb in present tense (''да живееме долго'', may we live long). In addition to its primary functions, the imperative is used to indicate actions in the past, eternal truths as is the case in sayings and a condition. The Macedonian conditional is conjugated in the same way for all three persons using the particle ''би'' and the verbal l-form, ''би читал'' (I/you/he would read).{{sfn|Bogdanoska|2008}} |
|||
==Grammar== |
|||
===Syntax=== |
|||
{{Ethnic Macedonians}} |
|||
Macedonian syntax has a [[subject-verb-object]] (SVO) [[word order]] which is nevertheless flexible and can be [[topicalization|topicalized]].{{sfn|Friedman|2001}} For instance, the sentence ''Марија го сака Иван'' (Marija loves Ivan) can become of the [[object–verb–subject]] (OVS) form as well, ''Иван го сака Марија''.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=116}} Topicalization can also be achieved using a combination of word order and intonation; as an example all of the following sentences give a different point of emphasis: |
|||
{{main|Macedonian grammar}} |
|||
*''Мачката ја каса кучето.'' – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on the object) |
|||
*''Кучето мачката ја каса.'' – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on the object) |
|||
*''Мачката кучето ја каса.'' – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on the subject) |
|||
*''Ја каса кучето мачката.'' – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on both the subject and the verb) |
|||
*''Ја каса мачката кучето.'' – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on the verb and the object){{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=50}} |
|||
Macedonian is a [[null-subject language]] which means that the subject pronoun can be omitted, for instance ''Што сакаш (ти)?'' (what do you want?), ''(јас) читам книга'' (I am reading a book), ''(ние) го видовме'' (we saw him).{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=116}} Macedonian [[passive voice|passive]] construction is formed using the short reflexive pronoun ''се'' (''девојчето се уплаши'', the girl got scared) or a combination of the verb "to be" with verbal adjectives (''Тој е миен'', he is washed). In the former case, the active-passive distinction is not very clear.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=117}} Subordinate clauses in Macedonian are introduced using [[relativizer]]s, which can be wh-question words or relative pronouns.{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=58}} A [[Interlinear gloss|glossed]] example of this is: |
|||
Macedonian grammar is markedly [[Analytic language|analytic]] in comparison with other Slavic languages, having lost the common Slavic case system. The Macedonian language shows some special and, in some cases, unique characteristics due to its central position in the Balkans. |
|||
{{interlinear|abbreviations=ITR:intransitive; IM:imperfect|indent=3 |
|||
Literary Macedonian is the only South Slavic literary language that has three forms of the definite article, based on the degree of proximity to the speaker, and a past tense formed by means of an [[auxiliary verb]] "to have", followed by a [[past tense|past]] [[grammatical voice|passive]] [[participle]] in the [[neuter]]. |
|||
|човек-от со кого(што) се шета-ше вчера |
|||
|person-DEF with whom(that) ITR stroll-3SG.IM yesterday |
|||
|the person with whom he walked yesterday{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=58}}}} |
|||
Due to the absence of a case system, Macedonian makes wide use of [[prepositions]] (''предлози'') to express relationships between words in a sentence. The most important Macedonian preposition is ''на'' which can have local ('on') or motional meanings ('to').{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=49}} As a replacement for the [[dative case]], the preposition ''на'' is used in combination with a short indirect object form to denote an action that is related to the indirect object of a sentence, ''Му давам книга на Иван'' (I am giving a book to Ivan), ''Им велам нешто на децата'' (I am saying something to the children).{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=116}} Additionally, ''на'' can serve to replace the [[genitive case]] and express possession, ''таткото на другар ми'' (my friend's father).{{sfn|Friedman|2001|p=49}} |
|||
Both [[clitic doubling|double object]] and mediative (sometimes referred to as ''[[renarrative mood|renarrative]]'' or ''admirative'') [[mood (linguistics)|mood]] are also found in the Bulgarian language, although the use of double object is much more restricted in the Bulgarian standard (see also [[Bulgarian language#syntax|Bulgarian syntax]]). |
|||
==Vocabulary== |
==Vocabulary== |
||
{{See also|Balkan sprachbund#Vocabulary}} |
|||
As a result of the close relatedness with [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]] and [[Serbian language|Serbian]], Macedonian shares a considerable amount of its [[lexicon]] with these languages. Other languages which have been in positions of power, such as [[Ottoman Turkish language|Ottoman Turkish]] and increasingly [[English language|English]] also provide a significant proportion of the [[loan word]]s. Prestige languages, such as [[Old Church Slavonic]], which occupies a relationship to modern Macedonian comparable to the relationship of [[medieval Latin]] to modern [[Romance languages]], and [[Russian language|Russian]] also provided a source for lexical borrowings. |
|||
[[File:Police car of Macedonia 04.JPG|thumb|Macedonian police car, with the Macedonian word ''Полиција'' (Policija), for "police".]] |
|||
Macedonian exhibits lexical similarities with all other Slavic languages, and numerous nouns are cognates, including those related to familial relations and numbers.{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|page=43}} Additionally, as a result of the close relationship with Bulgarian and Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian shares a considerable amount of its [[lexicon]] with these languages. Other languages that have been in positions of power, such as [[Ottoman Turkish language|Ottoman Turkish]] and, increasingly, [[English language|English]] have also provided a significant proportion of the loanwords. Prestige languages, such as Old Church Slavonic—which occupies a relationship to modern Macedonian comparable to the relationship of [[medieval Latin]] to modern [[Romance languages]]—and Russian also provided a source for lexical items. Other loanwords and vocabulary also came from Greek and Albanian as well as [[Prestige (sociolinguistics)|prestige languages]] such as [[French language|French]] and [[German language|German]].{{sfn|Friedman|1998|p=36}}{{sfn|Usikova|2005|p=136}} |
|||
During the [[Codification (linguistics)|standardization process]], there was deliberate care taken to try |
During the [[Codification (linguistics)|standardization process]], there was deliberate care taken to try to [[Linguistic purism|purify]] the lexicon of the language. Words that were associated with the Serbian or Bulgarian standard languages, which had become common due to the influence of these languages in the region, were rejected in favor of words from native dialects and [[archaism]]s. This is not to say that there are no words associated with the Serbian, Bulgarian, or even Russian standard languages in the language, but rather that they were discouraged on a principle of "seeking native material first".{{sfn|Friedman|1998|p={{pn|date=August 2021}}}} |
||
The language of the writers at the turn of 19th century abounded with Russian and, more specifically, Old Church Slavonic lexical and morphological elements |
The language of the writers at the turn of the 19th century abounded with Russian and, more specifically, Old Church Slavonic lexical and morphological elements that in the contemporary norm have been replaced by native words or [[calque]]d using [[Productivity (linguistics)|productive]] [[morpheme]]s.<ref name="Dimitrovski">Т. Димитровски. ''Литературната лексика на македонскиот писмен јазик во XIX в. и нашиот однос кон неа'': Реферати на македонските слависти за VI Меѓународен славистички конгрес во Прага, Скопје, 1968 (T. Dimitrovski. ''The literary vocabulary of the Macedonian written language in the 19th century and our attitude to it''. Abstracts of Macedonian Slavists for the 6th International Slavic Studies Congress in Prague. Skopje, 1968)</ref> New words were [[Neologism|coined]] according to internal logic and others calqued from related languages (especially Serbo-Croatian) to replace those taken from Russian, which include ''известие'' (Russ. ''известие'') → ''извештај'' 'report', ''количество'' (Russ. ''количество'') → ''количина'' 'amount, quantity', ''согласие'' (Russ. ''согласие'') → ''слога'' 'concord, agreement', etc.<ref name="Dimitrovski" /> This change was aimed at bringing written Macedonian closer to the spoken language, effectively distancing it from the more Russified Bulgarian language, representing a successful puristic attempt to abolish a lexicogenic tradition once common in written [[literature]].<ref name="Dimitrovski" /> The use of Ottoman Turkish loanwords is discouraged in the [[Register (sociolinguistics)|formal register]] when a native equivalent exists (e.g. ''комшија'' (← Turk. ''komşu'') vs. ''сосед'' (← [[Proto-Slavic language|PSl.]] *sǫsědъ) 'neighbor'), and these words are typically restricted to the archaic, colloquial, and ironic registers.{{sfn|Friedman|1998|p=8}} |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto; text-align:center;" |
|||
Many words and expressions were borrowed from the [[Serbian language]] to replace those taken from Old Church Slavonic, but also present in the Bulgarian language, which include ''известие'' → ''извештај'', ''количество'' → ''количина'', ''согласие'' → ''слога'', etc.<ref name="Dimitrovski" /> This change was aimed at bringing written Macedonian closer to spoken language and distancing it from the Bulgarian language which has kept its numerous [[Russian language|Russian]] loans, and represents a successful [[Linguistic purism|puristic]] attempt at abolishing a lexicogenic tradition once common in written [[literature]].<ref name="Dimitrovski" /> |
|||
|+ Lexical comparison of 5 words among 11 Slavic languages{{sfn|Bojkovska|Minova-Gjurkova|Pandev|Cvetanovski|2008|page=44}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! English !! Macedonian !! Bulgarian !! Serbian !! [[Croatian language|Croatian]] !! Slovenian !! Russian !! [[Belarusian language|Belarusian]] !! [[Ukrainian language|Ukrainian]] !! [[Polish language|Polish]] !! [[Czech language|Czech]] !! [[Slovak language|Slovak]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| dream || {{lang|mk|сон}}<br>{{lang|mk-Latn|son}} || {{lang|bg|сън}}<br>{{lang|bg-Latn|sŭn}} || {{lang|sr|сан}}<br>{{lang|sr-Latn|san}} || {{lang|hr|san}} || {{lang|sl|sen}} || {{lang|ru|сон}}<br>{{lang|ru-Latn|son}} || {{lang|be|сон}}<br>{{lang|be-Latn|son}} || {{lang|uk|сон}}<br>{{lang|uk-Latn|son}} || {{lang|pl|sen}} || {{lang|cs|sen}} || {{lang|sk|sen}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| day|| {{lang|mk|ден}}<br>{{lang|mk-Latn|den}} || {{lang|bg|ден}}<br>{{lang|bg-Latn|den}} || {{lang|sr|дан}}<br>{{lang|sr-Latn|dan}} || {{lang|hr|dan}} || {{lang|sl|dan}} || {{lang|ru|день}}<br>{{lang|ru-Latn|den'}} || {{lang|be|дзень}}<br>{{lang|be-Latn|dzień}} || {{lang|uk|день}}<br>{{lang|uk-Latn|den}} || {{lang|pl|dzień}} || {{lang|cs|den}} || {{lang|sk|den}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| arm|| {{lang|mk|рака}}<br>{{lang|mk-Latn|raka}} || {{lang|bg|ръка}}<br>{{lang|bg-Latn|rŭka}} || {{lang|sr|рука}}<br>{{lang|sr-Latn|ruka}} || {{lang|hr|ruka}} || {{lang|sl|roka}} || {{lang|ru|рука}}<br>{{lang|ru-Latn|ruka}} || {{lang|be|рука}}<br>{{lang|be-Latn|ruka}} || {{lang|uk|рука}}<br>{{lang|uk-Latn|ruka}} || {{lang|pl|ręka}} || {{lang|cs|ruka}} || {{lang|sk|ruka}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| flower|| {{lang|mk|цвет}}<br>{{lang|mk-Latn|cvet}} || {{lang|bg|цвят}}<br>{{lang|bg-Latn|tsvyat}} || {{lang|sr|цвет}}<br>{{lang|sr-Latn|cvet}} || {{lang|hr|cvijet}} || {{lang|sl|cvet}} || {{lang|ru|цветок}}<br>{{lang|ru-Latn|tsvetok}} || {{lang|be|кветка}}<br>{{lang|be-Latn|kvietka}} || {{lang|uk|квітка}}<br>{{lang|uk-Latn|kvitka}} || {{lang|pl|kwiat}} || {{lang|cs|květ/květina}}|| {{lang|sk|kvet/kvetina}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| night|| {{lang|mk|ноќ}}<br>{{lang|mk-Latn|nokj}} || {{lang|bg|нощ}}<br>{{lang|bg-Latn|nosht}} || {{lang|sr|ноћ}}<br>{{lang|sr-Latn|noć}} || {{lang|hr|noć}} || {{lang|sl|noč}} || {{lang|ru|ночь}}<br>{{lang|ru-Latn|noch'}} || {{lang|be|ноч}}<br>{{lang|be-Latn|noč}} || {{lang|uk|нiч}}<br>{{lang|uk-Latn|nich}} || {{lang|pl|noc}} || {{lang|cs|noc}} || {{lang|sk|noc}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
==Writing system== |
==Writing system== |
||
===Alphabet=== |
===Alphabet=== |
||
{{ |
{{Main|Macedonian alphabet|Macedonian braille}} |
||
The official Macedonian alphabet was codified on 5 May 1945 by the Presidium of the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (abbreviated as ASNOM in Macedonian) headed by [[Blaže Koneski]].<ref name="javno">{{cite web|url=http://javno.mk/reshenie-na-asnom-72-godini-od-usvojuvaneto-na-makedonskata-azbuka/|title=Со решение на АСНОМ: 72 години од усвојувањето на македонската азбука|trans-title=With the declaration of ASNOM: 72 years of the adoption of the Macedonian alphabet|work=Javno|date=5 May 2017|language=mk|access-date=15 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200320001638/http://javno.mk/reshenie-na-asnom-72-godini-od-usvojuvaneto-na-makedonskata-azbuka/|archive-date=20 March 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> There are several letters that are specific for the Macedonian Cyrillic script, namely [[ѓ]], [[ќ]], [[ѕ]], [[џ]], [[љ]] and [[њ]],{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=105–106}} with the last three letters being borrowed from the Serbo-Croatian phonetic alphabet adapted by Serbian linguist [[Vuk Stefanović Karadžić]], while the grapheme ѕ has an equivalent in the Church Slavonic alphabet.{{sfn|Friedman|1993|p=251}} Letters љ and њ were previously used by Macedonian writer Krste Petkov Misirkov written as л' and н'.<ref name="javno" /> The Macedonian alphabet also uses the apostrophe sign (') as a sound. It is used to mark the syllable forming /''р˳''/ , at the beginning of the word ({{lang|mk|'рж}} - rye, {{lang|mk|'рбет}} - spine) and to represent the phoneme schwa in some literary words or Turkish loanwords ({{lang|mk|'к'смет}} - fortune). А [[grave accent]] (`) [[diacritic]] is used over three vowels in orthography: {{lang|mk|ѝ}} - her, different from {{lang|mk|и}} - and, {{lang|mk|нè}} - us, different from {{lang|mk|не}} - no and {{lang|mk|сѐ}} - everything different from {{lang|mk|сe}} - short reflexive pronoun accompanying reflexive verbs.{{sfn|Usikova|2005|page=105–106}} The standard Macedonian alphabet contains 31 letters. The following table provides the upper and lower case forms of the Macedonian alphabet, along with the [[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA]] value for each letter: |
|||
The modern Macedonian alphabet was developed by linguists in the period after the [[World War II|Second World War]], who based their alphabet on the phonetic alphabet of [[Vuk Stefanović Karadžić]], though a similar writing system was used by [[Krste Misirkov]] in the late 19th century. The Macedonian language had previously been written using the [[Early Cyrillic alphabet]], or later using the [[Cyrillic alphabet]] with local adaptations from either the [[Serbian Cyrillic alphabet|Serbian]] or [[Bulgarian alphabet|Bulgarian]] alphabets. |
|||
{| cellpadding="10" style="margin:auto; text-align:center;" |
|||
The following table provides the upper and lower case forms of the Macedonian alphabet, along with the [[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA]] value for each letter: |
|||
{| align=center cellpadding=10 style="text-align:center;" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="left"|''Cyrillic''<br />''[[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA]]''||[[A (Cyrillic)|А а]]<br />{{IPA|/a/}}||[[Be (Cyrillic)|Б б]]<br />{{IPA|/b/}}||[[Ve (Cyrillic)|В в]]<br />{{IPA|/v/}}||[[Ge (Cyrillic)|Г г]]<br />{{IPA|/ɡ/}}||[[De (Cyrillic)|Д д]]<br />{{IPA|/d/}}||[[Gje|Ѓ ѓ]]<br />{{IPA|/ɟ/}}||[[Ye (Cyrillic)|Е е]]<br />{{IPA|/ɛ/}}||[[Zhe (Cyrillic)|Ж ж]]<br />{{IPA|/ʒ/}}||[[Ze (Cyrillic)|З з]]<br />{{IPA|/z/}}||[[Dze|Ѕ ѕ]]<br />{{IPA|/ |
|align="left"|''Cyrillic''<br />''[[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA]]''||[[A (Cyrillic)|А а]]<br />{{IPA|/a/}}||[[Be (Cyrillic)|Б б]]<br />{{IPA|/b/}}||[[Ve (Cyrillic)|В в]]<br />{{IPA|/v/}}||[[Ge (Cyrillic)|Г г]]<br />{{IPA|/ɡ/}}||[[De (Cyrillic)|Д д]]<br />{{IPA|/d/}}||[[Gje|Ѓ ѓ]]<br />{{IPA|/ɟ/}}||[[Ye (Cyrillic)|Е е]]<br />{{IPA|/ɛ/}}||[[Zhe (Cyrillic)|Ж ж]]<br />{{IPA|/ʒ/}}||[[Ze (Cyrillic)|З з]]<br />{{IPA|/z/}}||[[Dze|Ѕ ѕ]]<br />{{IPA|/d͡z/}}||[[I (Cyrillic)|И и]]<br />{{IPA|/i/}} |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="left"|''Cyrillic''<br />''[[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA]]''||[[Je (Cyrillic)|Ј ј]]<br />{{IPA|/j/}}||[[Ka (Cyrillic)|К к]]<br />{{IPA|/k/}}||[[El (Cyrillic)|Л л]]<br />{{IPA|/l/}}||[[Lje|Љ љ]]<br />{{IPA|/ |
|align="left"|''Cyrillic''<br />''[[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA]]''||[[Je (Cyrillic)|Ј ј]]<br />{{IPA|/j/}}||[[Ka (Cyrillic)|К к]]<br />{{IPA|/k/}}||[[El (Cyrillic)|Л л]]<br />{{IPA|/ɫ, l/}}<ref name="l">{{angbr|л}} is pronounced {{IPA|/l/}} before {{IPA|/e, i, j/}}, and {{IPA|/ɫ/}} otherwise. {{angbr|љ}} is always pronounced {{IPA|/l/}} but is not used before {{IPA|/e, i, j/}}. Cf. how the final љ in биљби'''''љ''''' {{nowrap|{{IPA|/ˈbilbil/}}}} "nightingale" is changed to a л in the plural form биљби'''''л'''''и {{nowrap|{{IPA|/ˈbilbili/}}}}.</ref>||[[Lje|Љ љ]]<br />{{IPA|/l/}}<ref name="l"/>||[[Em (Cyrillic)|М м]]<br />{{IPA|/m/}}||[[En (Cyrillic)|Н н]]<br />{{IPA|/n/}}||[[Nje|Њ њ]]<br />{{IPA|/ɲ/}}||[[O (Cyrillic)|О о]]<br />{{IPA|/ɔ/}}||[[Pe (Cyrillic)|П п]]<br />{{IPA|/p/}}||[[Er (Cyrillic)|Р р]]<br />{{IPA|/r/}}||[[Es (Cyrillic)|С с]]<br />{{IPA|/s/}} |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="left"|''Cyrillic''<br />''[[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA]]''||[[Te (Cyrillic)|Т т]]<br />{{IPA|/t/}}||[[Kje|Ќ ќ]]<br />{{IPA|/c/}}||[[U (Cyrillic)|У у]]<br />{{IPA|/u/}}||[[Ef (Cyrillic)|Ф ф]]<br />{{IPA|/f/}}||[[Kha (Cyrillic)|Х х]]<br />{{IPA|/x/}}||[[Tse (Cyrillic)|Ц ц]]<br />{{IPA|/ |
|align="left"|''Cyrillic''<br />''[[International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA]]''||[[Te (Cyrillic)|Т т]]<br />{{IPA|/t/}}||[[Kje|Ќ ќ]]<br />{{IPA|/c/}}||[[U (Cyrillic)|У у]]<br />{{IPA|/u/}}||[[Ef (Cyrillic)|Ф ф]]<br />{{IPA|/f/}}||[[Kha (Cyrillic)|Х х]]<br />{{IPA|/x/}}||[[Tse (Cyrillic)|Ц ц]]<br />{{IPA|/t͡s/}}||[[Che (Cyrillic)|Ч ч]]<br />{{IPA|/t͡ʃ/}}||[[Dzhe|Џ џ]]<br />{{IPA|/d͡ʒ/}}||[[Sha (Cyrillic)|Ш ш]]<br />{{IPA|/ʃ/}} |
||
|} |
|} |
||
===Orthography=== |
===Orthography=== |
||
Similar to the Macedonian alphabet, Macedonian orthography was officially codified on 7 June 1945 at an ASNOM meeting.<ref name="javno" /> Rules about the orthography and [[orthoepy]] (correct pronunciation of words) were first collected and outlined in the book ''Правопис на македонскиот литературен јазик'' (''Orthography of the Macedonian standard language'') published in 1945. Updated versions have subsequently appeared with the most recent one published in 2016.<ref>{{cite web|title=Правописот на македонски јазик од денес бесплатно на интернет|trans-title=The orthography of the Macedonian language for free on the Internet from today|date=7 December 2017|work=sdk.mk |url=https://sdk.mk/index.php/kultura/pravopisot-na-makedonski-jazik-od-denes-besplatno-na-internet/|access-date=18 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200318184353/https://sdk.mk/index.php/kultura/pravopisot-na-makedonski-jazik-od-denes-besplatno-na-internet/|archive-date=18 March 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> Macedonian orthography is consistent and phonemic in practice, an approximation of the principle of one [[grapheme]] per [[phoneme]]. This one-to-one correspondence is often simply described by the principle, "write as you speak and read as it is written".{{sfn|Friedman|2001}} There is only one exception to this rule with the letter /''л''/ which is pronounced as /l/ before front vowels (e.g. ''лист'' (leaf); pronounced as [list]) and /j/ (e.g. ''полјанка'' (meadow); pronounced as [poljanka]) but [[velar]] /ł/ elsewhere (e.g. ''бела'' (white) pronounced as [beła]). Another sound that is not represented in the written form but is pronounced in words is the [[schwa]].{{sfn|Friedman|2001}} |
|||
==Political views on the language== |
|||
{{Main|Political views on the Macedonian language|Macedonian language naming dispute}} |
|||
Politicians and scholars from North Macedonia, Bulgaria and Greece have opposing views about the existence and distinctiveness of the Macedonian language. Through history Macedonian has been referred mainly to as a variant of Bulgarian,<ref name="bg">{{cite book |author=Institute of Bulgarian Language |title=Единството на българския език в миналото и днес |trans-title=The unity of the Bulgarian language in the past and today |publisher=[[Bulgarian Academy of Sciences]] |year=1978 |page=4 |language=bg |location=[[Sofia]] |oclc=6430481}}</ref> but especially during the first half of the 20th century also as Serbian,{{sfn|Comrie|Corbett|2002|p=251}} and as a distinct language of its own.{{sfn|Adler|1980|p=215}}{{sfn|Seriot|1997|pp=270–271}} Historically, after its codification, the use of the language has been a subject of different views and internal policies in Serbia, Bulgaria and Greece.{{sfn|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001|page=436}}{{sfn|Kramer|1999|pp=237–245}} Some international scholars also maintain Macedo-Bulgarian was a single pluricentric language until the 20th century and argue that the idea of linguistic separatism emerged in the late 19th century with the advent of [[Macedonian nationalism]] and the need for a separate Macedonian standard language subsequently appeared in the early 20th century.{{sfn|Fishman|1993|page=161–162}} Different linguists have argued that during its codification, the Macedonian standard language was [[Serbianization|Serbianized]] with regards to its orthography{{sfn|Friedman|1998|p=38}}<ref>{{cite journal|first=Tchavdar |last=Marinov |journal=Sociétés Politiques Comparées |title=Historiographical Revisionism and Re-Articulation of Memory in the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia|page=7|date=25 May 2010|volume=25|s2cid=174770777 |url=https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/a3e1/ea1d51204ae39b35916870d2f149aeb83856.pdf|access-date=3 April 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200215022342/https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/a3e1/ea1d51204ae39b35916870d2f149aeb83856.pdf|archive-date=15 February 2020|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>Voss C., The Macedonian Standard Language: Tito—Yugoslav Experiment or Symbol of 'Great Macedonian' Ethnic Inclusion? in C. Mar-Molinero, P. Stevenson as ed. Language Ideologies, Policies and Practices: Language and the Future of Europe, Springer, 2016, {{ISBN|0230523889}}, p. 126.</ref><ref>De Gruyter as contributor. The Slavic Languages. Volume 32 of Handbooks of Linguistics and Communication Science (HSK), Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG, 2014, p. 1472. {{ISBN|3110215470}}.</ref><ref>Lerner W. Goetingen, Formation of the standard language - Macedonian in the Slavic languages, Volume 32, Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, 2014, {{ISBN|3110393689}}, chapter 109.</ref> and vocabulary.{{sfn|Voß|2018|p=9}} |
|||
[[Government of Bulgaria|The government of Bulgaria]], Bulgarian academics, the [[Bulgarian Academy of Sciences]] and the general public have and continue to widely consider Macedonian part of the [[Bulgarian dialects|Bulgarian dialect area]].{{ref|Mahon1}}<ref>{{cite web|url=https://bnr.bg/en/post/101203235/bulgarian-academy-of-sciences-is-firm-that-macedonian-language-is-bulgarian-dialect|title=Bulgarian Academy of Sciences is firm that "Macedonian language" is Bulgarian dialect|publisher=Bulgarian National Radio|date=12 November 2019|access-date=20 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200404041259/https://www.bnr.bg/en/post/101203235/bulgarian-academy-of-sciences-is-firm-that-macedonian-language-is-bulgarian-dialect|archive-date=4 April 2020|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://balkaninsight.com/2019/10/10/bulgaria-sets-tough-terms-for-north-macedonias-eu-progress/ |title=Bulgaria Sets Tough Terms for North Macedonia's EU Progress|first=Sinisa|last=Jakov Marusic|date=10 October 2019|access-date=18 March 2020|work=[[Balkan Insight]]|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191211184245/https://balkaninsight.com/2019/10/10/bulgaria-sets-tough-terms-for-north-macedonias-eu-progress/|archive-date=11 December 2019|url-status=live}}</ref> During the Communist era, Macedonian was recognized as a minority language in Bulgaria and utilized in education from 1946 to 1948. Subsequently, it was described as a dialect of Bulgarian.<ref>Ranko Bugarski, Celia Hawkesworth as editors, Language in the Former Yugoslav Lands, Slavica Publishers, 2004, {{ISBN|0893572985}}, p. 201.</ref> In 1956 the Bulgarian government signed an agreement on mutual legal defense with Yugoslavia, where the Macedonian language is named as one of the languages to be used for legal purposes, together with Bulgarian, Serbo-Croatian and Slovenian.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ciela.net/svobodna-zona-darjaven-vestnik/document/2135462838/issue/4107/dogovor-mezhdu-narodna-republika-balgariya-i-federativna-narodna-republika-yugoslaviya-za-vzaimna-pravna-pomosht--------|title=Agreement between Bulgaria and Yugoslavia for mutual legal defense |publisher=Държавен вестник No 16 |date=22 February 1957 | accessdate=13 January 2020}}</ref> The same year Bulgaria revoked its recognition of Macedonian nationhood and language and implicitly resumed its prewar position of their non-existence.<ref>Raymond Detrez, (2010) The A to Z of Bulgaria, Issue 223 of A to Z Guides, Edition 2, Scarecrow Press, 2010, {{ISBN|0810872021}}.</ref> In 1999 the government in [[Sofia]] signed a [[s:en:Joint Declaration of 22 February 1999|Joint Declaration]] in the official languages of the two countries, marking the first time it agreed to sign a bilateral agreement written in Macedonian.{{sfn|Kramer|1999}} Dialect experts of the Bulgarian language refer to the Macedonian language as ''македонска езикова норма'' (Macedonian linguistic norm) of the Bulgarian language.{{sfn|Reimann|2014|page=41}} As of 2019, disputes regarding the language and its origins are ongoing in academic and political circles in the two countries. |
|||
The Greek scientific and local community opposed using the denomination Macedonian to refer to the language in light of the [[Macedonia naming dispute|Greek-Macedonian naming dispute]]. Instead, the language is often called "Slavic", "Slavomacedonian" (translated to "Macedonian Slavic" in English), ''makedonski'', ''makedoniski'' ("Macedonian"),{{sfn|Whitman|1994|page=37}} ''slaviká'' (Greek: "Slavic"), ''dópia'' or ''entópia'' (Greek: "local/indigenous [language]"),<ref>{{cite web |publisher=Greek Helsinki Monitor |title=Report about Compliance with the Principles of the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities |url=http://dev.eurac.edu:8085/mugs2/do/blob.html?type=html&serial=1044526702223 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030523145306/http://dev.eurac.edu:8085/mugs2/do/blob.html?type=html&serial=1044526702223 |archive-date=23 May 2003 |url-status=dead |access-date=12 January 2009}}</ref> ''balgàrtzki'' (Bulgarian) or "Macedonian" in some parts of the region of [[Kastoria]],{{sfn|Danforth|1995|page=62}} ''bògartski'' ("Bulgarian") in some parts of Dolna Prespa<ref>{{cite book |last1=Shklifov|first1=Blagoy|first2=Ekaterina|last2=Shklifova|title=Български деалектни текстове от Егейска Македония|location=Sofia|year=2003|pages=28–36|language=bg|trans-title=Bulgarian dialect texts from Aegean Macedonia}}</ref> along with ''naši'' ("our own") and ''stariski'' ("old").{{sfn|Whitman|1994|page=37}} However, with the [[Prespa agreement]] signed in June 2018 and ratified by the [[Greek Parliament]] on 25 January 2019, Greece officially recognized the name "Macedonian" for the language.<ref>{{cite web |title=Republic of North Macedonia with Macedonian language and identity, says Greek media |url=https://meta.mk/en/republic-of-north-macedonia-with-macedonian-language-and-identity-says-greek-media/ |website=Meta.mk |publisher=Meta |access-date=12 June 2018 |date=12 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180613015138/http://meta.mk/en/republic-of-north-macedonia-with-macedonian-language-and-identity-says-greek-media/ |archive-date=13 June 2018 |url-status=live }}</ref> Additionally, on 27 July 2022,<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.slobodenpecat.mk/en/sudska-pobeda-na-makedonskiot-jazik-vo-grcija-sudot-vo-lerin-gi-odbi-tuzhbite-za-zabrana-na-centarot-za-makedonski-jazik-vo-grcija/|title=Judicial victory for the Macedonian language in Greece: The court in Lerin rejected the lawsuits to ban the Macedonian Language Center in Greece|newspaper=[[Sloboden Pečat]]|date=19 March 2023}}</ref> in a landmark ruling, the [[Centre for the Macedonian Language in Greece]] was officially registered as a non-governmental organization. This is the first time that a cultural organization promoting the Macedonian language has been legally approved in Greece and the first legal recognition of the Macedonian language in Greece since at least 1928.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.dw.com/mk/grcija-go-registrirase-centarot-za-makedonski-jazik/a-63925047|title=Грција го регистрираше центарот за македонски јазик|trans-title=Greece Registered the Macedonian-language Center|publisher=Deutsche Welle|date=29 November 2022|language=Macedonian}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.slobodenpecat.mk/centarot-na-makedonskiot-jazik-vo-grcija-oficijalno-registriran-od-sudskite-vlasti/|title="Центарот на македонскиот јазик во Грција" официјално регистриран од судските власти|trans-title="The Center of Macedonian language in Greece" officially registered by court laws|publisher=Sloboden Pecat|date=29 November 2022|language=Macedonian}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ethnos.gr/greece/article/234940/egkrithhkekentromakedonikhsglossassthnflorinaeyxaristieszaefsetsipramhtsotakh|title=Εγκρίθηκε «Κέντρο Μακεδονικής Γλώσσας» στην Φλώρινα: Ευχαριστίες Ζάεφ σε Τσίπρα - Μητσοτάκη|trans-title="Centre for Macedonian Language" was approved in Florina: Zaev thanks Tsipras - Mitsotakis|publisher=Ethnos|date=29 November 2022|access-date=29 November 2022|language=Greek}}</ref><ref name="George">Mavrogordatos, George. ''Stillborn Republic: Social Coalitions and Party Strategies in Greece, 1922–1936''. University of California Press, 1983. {{ISBN|9780520043589}}, p. 227, 247</ref> |
|||
Macedonian orthography is consistent and phonemic in practice, an approximation of the principle of one [[grapheme]] per [[phoneme]]. A principle represented by [[Adelung]]'s saying, "write as you speak and read as it is written" („пишувај како што зборуваш и читај како што е напишано“). Though as with most, if not all, living languages it has its share of inconsistencies and exceptions. |
|||
== |
==Sample text== |
||
The following is the [[Lord's Prayer]] in standard Macedonian. |
|||
{{ |
{{col-begin|width=auto}} |
||
{{col-break}} |
|||
:'''Оче наш''' |
|||
:'''Оче наш''' (Cyrillic alphabet) |
|||
:Оче наш, кој си на |
:Оче наш, кој си на небесата, |
||
:да се свети името Твое, |
:да се свети името Твое, |
||
:да |
:да дојде царството Твое, |
||
:да биде волјата Твоја, |
:да биде волјата Твоја, |
||
:како на небото, така и на |
:како на небото, така и на земјата; |
||
: |
:лебот наш насушен дај ни го денес |
||
:и прости |
:и прости ни ги долговите наши |
||
:како што им ги проштеваме |
:како и ние што им ги проштеваме на нашите должници; |
||
:и не нѐ воведувај во искушение, |
|||
:на нашите должници. |
|||
:но избави нѐ од лукавиот |
|||
:И не воведи нè во искушение, |
|||
:Зашто Твое е Царството и Силата и Славата, во вечни векови. |
|||
:но избави нè од лукавиот. |
|||
:Амин! |
:Амин! |
||
{{col-break|gap=2em}} |
|||
{{ColBreak}} |
|||
:'''Oče naš''' |
:'''Oče naš''' ([[Romanization of Macedonian|Romanized version]]) |
||
:''Oče naš, koj si na |
:''Oče naš, koj si na nebesata'' |
||
:''da se sveti imeto Tvoe,'' |
:''da se sveti imeto Tvoe,'' |
||
:''da |
:''da dojde carstvoto Tvoe,'' |
||
:''da bide voljata Tvoja,'' |
:''da bide voljata Tvoja,'' |
||
:''kako na neboto, taka i na |
:''kako na neboto, taka i na zemjata;'' |
||
:'' |
:''lebot naš nasušen daj ni go denes'' |
||
:''i prosti |
:''i prosti ni gi dolgovite naši'' |
||
:''kako što im gi proštevame |
:''kako i nie što im gi proštevame na našite dolžnici'' |
||
:''I ne nè voveduvaj vo iskušenie,'' |
|||
:''na našite dolžnici.'' |
|||
:''I ne vovedi nè vo iskušenie,'' |
|||
:''no izbavi nè od lukaviot.'' |
:''no izbavi nè od lukaviot.'' |
||
:''Zašto Tvoe e Carstvoto i Silata i Slavata, vo večni vekovi.'' |
|||
:''Amin!'' |
:''Amin!'' |
||
{{ |
{{col-end}} |
||
==History== |
|||
{{South Slavic languages sidebar}} |
|||
{{main|History of the Macedonian language}} |
|||
The region of [[Macedonia (region)|Macedonia]] and the [[Republic of Macedonia]] are located on the [[Balkan peninsula]]. The [[Slavs]] first came to the Balkan Peninsula in the sixth and seventh centuries AD. In the ninth century, the [[Byzantine Greeks|Byzantine Greek]] monks [[Saints Cyril and Methodius]] developed the first writing system for the Slavonic languages. At this time, the Slavic dialects were so close as to make it practical to develop the written language on the dialect of a single region. There is dispute as to the precise region, but it is likely that they were developed in the region around [[Thessalonika]]. The [[Ohrid Literary School]] was established in Ohrid in 886 by [[Saint Clement of Ohrid]] on orders of [[Boris I of Bulgaria]]. In the fourteenth century, the Ottoman Turks invaded and conquered most of the Balkans, incorporating Macedonia into the [[Ottoman Empire]]. While the written language, now called [[Old Church Slavonic]], remained static as a result of Turkish domination, the spoken dialects moved further apart. During the increase of national consciousness in the Balkans, standards for the languages of [[Slovenian language|Slovenian]], [[Serbo-Croatian]] and [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]] were created. As Turkish influence in Macedonia waned, schools were opened up that taught the Bulgarian standard language in areas with significant Bulgarian population. However the label "''Bulgarian language''" for various [[Macedonian dialects]] can be seen from early vernacular texts such as the four-language dictionary of [[Daniel Mоscopolites]], the early works of [[Kiril Peichinovich]] and [[Yoakim Karchovski]] and some vernacular gospels written in the Greek alphabet. These written works influenced by or completely written in the local Slavic [[vernacular]] appeared in Macedonia in the 18th and beginning of the 19th century and their authors referred to their language as Bulgarian.<ref> F. A. K. Yasamee "NATIONALITY IN THE BALKANS: THE CASE OF THE MACEDONIANS" in Balkans: A Mirror of the New World Order, Istanbul: EREN, 1995; pp. 121-132.</ref> |
|||
In 1845 the [[Russia]]n scholar [[Viktor Grigorovich]] travelled in the Balkans in order to study the south Slavic dialects of Macedonia. His work articulated for the first time a distinct pair of two groups of [[Bulgarian dialects]]: Eastern and Western. According to his findings, the Western Bulgarian variety, spoken in Macedonia, was characterized by traces of Old Slavic nasal vowels.<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Seriot|1997|p=177}}</ref> It wasn't until the works of [[Krste Misirkov]] that parts of what had been regarded as West Bulgarian dialects were defined as a separate 'Macedonian' language. Misirkov was born in a village near [[Pella]] in [[Macedonia (Greece)|Greek Macedonia]]. Although literature had been written in the Slavic dialects of Macedonia before, arguably the most important book published in relation to the Macedonian language was Misirkov's ''On Macedonian Matters'', published in 1903. In that book, he argued for the creation of a standard literary Macedonian language from the central dialects of Macedonia which would use a [[phonemic orthography]]. |
|||
After the first two Balkan wars, the region of Macedonia was split among Greece, Bulgaria, and the [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]]. Yugoslavia occupied the area that is currently the Republic of Macedonia incorporating it into the Kingdom as "Southern Serbia." During this time, Yugoslav Macedonia became known as [[Vardar Banovina]] (Vardar province) and the language of public life, education and the church was Serbo-Croatian. In the other two parts of Macedonia, the respective national languages, Greek and Bulgarian, were made official. In Bulgarian (Pirin) Macedonia, the local dialects were described as dialects of Bulgarian. |
|||
During the [[second World War]], a part of Yugoslav Macedonia was occupied by the Bulgarian army, who were allied with the Axis. The Bulgarian language was reintroduced in schools and [[liturgies]]. The Bulgarians were initially welcomed as liberators from Serbian domination until connections were made between the imposition of the Bulgarian language and unpopular Serbian [[Cultural assimilation|assimilation]] policies; the Bulgarians were quickly seen as conquerors by communist movement. |
|||
There were a number of groups fighting the Bulgarian occupying force, some advocating independence and others union with Bulgaria. The eventual outcome was that almost all of [[Vardar Banovina]] (i.e. the areas which geographically became known as [[Vardar Macedonia]]) was incorporated into the [[Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]] as a constituent [[Socialist Republic]] with the Macedonian language holding official status within both the Federation and Republic. The Macedonian language was proclaimed the official language of the Republic of Macedonia at the First Session of the Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia, held on [[August 2]], [[1944]]. The first official Macedonian grammar was developed by Krume Kepeski. One of the most important contributors in the standardisation of the Macedonian literary language was [[Blaže Koneski]]. The first document written in the literary standard Macedonian language is the first issue of the ''[[Nova Makedonija]]'' newspaper in 1944. ''Makedonska Iskra'' (Macedonian Spark) was the first Macedonian newspaper to be published in Australia, from 1946 to 1957. A monthly with national distribution, it commenced in Perth and later moved to Melbourne and Sydney. |
|||
==Political views on the language== |
|||
{{main|Political views on the Macedonian language|Macedonian language naming dispute}} |
|||
As with the issue of [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonian ethnicity]], the politicians, linguists and common people from Macedonia and neighbouring countries have opposing views about the existence and distinctiveness of the Macedonian language. |
|||
In the ninth century AD, saints [[St. Cyril|Cyril]] and [[St. Methodius|Methodius]] introduced [[Old Church Slavonic]], the first Slavic language of literacy. Written with their newly invented [[Glagolitic]] script, this language was based largely on the dialect of Slavs spoken in [[Thessaloniki]]; this dialect is closest to present day [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]] and Macedonian.<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Dostál|1965|p=69}}</ref> |
|||
Although described as being dialects of Bulgarian prior to the establishment of the standard{{Fact|date=May 2009}}, the current academic consensus (outside the Balkans) is that Macedonian is an [[autonomous language]] within the South Slavic dialect continuum<ref>{{Harvcoltxt|Trudgill|1992|p=?}}</ref>.{{Verify source|date=September 2008}} |
|||
===Bulgaria view=== |
|||
In most sources in and out of Bulgaria before the Second World War, the [[South Slavic dialect continuum|southern Slavonic dialect continuum]] covering the area of today's [[Republic of Macedonia]] and [[Northern Greece]] was referred to as group of Bulgarian dialects. The local variants of the name of the language were also ''balgàrtzki'', ''bùgarski'' or ''bugàrski''; i.e. ''Bulgarian''.<ref>Шклифов, Благой and Екатерина Шклифова, Български деалектни текстове от Егейска Македония, София 2003, с. 28-33 (Shklifov, Blagoy and Ekaterina Shklifova. Bulgarian dialect texts from Aegean Macedonia Sofia 2003, p. 28-36)</ref> Although Bulgaria was the first country to recognize the independence of the Republic of Macedonia, most of its academics, as well as the general public, regard the language spoken there as a form of Bulgarian.{{ref|Mahon1}} However after years of diplomatic impasse caused by an academic dispute, in 1999 the government in Sofia solved the problem with the [[Macedonian Language]] under the [[euphemistic]] formula: "''the official language of the country (Republic of Macedonia) in accordance with its constitution''".<ref>[http://www.aimpress.ch/dyn/trae/archive/data/199902/90222-005-trae-sof.htm 1999/02/22 23:50 Bulgaria Recognises Macedonian Language]</ref> |
|||
===Greece view=== |
|||
{{also|Macedonia naming dispute}} |
|||
The use of the name ''Macedonian'' for the language is considered offensive by Greeks, who use "Macedonian" to refer to the dialect of modern Greek spoken in northern Greece{{Fact|date=May 2009}}. Furthermore Greece asserts that the [[ancient Macedonian language]] is the only "Macedonian language" and it considers it a dialect of [[ancient Greek language|ancient Greek]]. Greeks object to the use of the "Macedonian" name in reference to the modern Slavic language, calling it "[[Slavomacedonian language|Slavomacedonian]]" (Macedonian: славомакедонски јазик, {{lang-el|σλαβομακεδονική γλώσσα}}), a term coined by some members of the Slavic-speaking community of northern Greece itself.<ref name="offensivegr">Although acceptable in the past, current use of this name in reference to both the ethnic group and the language can be considered [[pejorative]] and offensive by ethnic Macedonians. In the past, the Macedonian Slavs in Greece seemed relieved to be acknowledged as "Slavomacedonians". Pavlos Koufis, a native of Greek Macedonia, pioneer of ethnic Macedonian schools in the region and local historian, says in ''Laografika Florinas kai Kastorias'' (Folklore of Florina and Kastoria), Athens 1996: |
|||
<blockquote>"[During its Panhellenic Meeting in September 1942, the KKE mentioned that it recognises the equality of the ethnic minorities in Greece] the KKE recognised that the Slavophone population was ethnic minority of Slavomacedonians]. This was a term, which the inhabitants of the region accepted with relief. [Because] Slavomacedonians = Slavs+Macedonians. The first section of the term determined their origin and classified them in the great family of the Slav peoples."</blockquote> |
|||
The [[Greek Helsinki Monitor]] reports: |
|||
<blockquote>"... the term Slavomacedonian was introduced and was accepted by the community itself, which at the time had a much more widespread non-Greek Macedonian ethnic consciousness. Unfortunately, according to members of the community, this term was later used by the Greek authorities in a pejorative, discriminatory way; hence the reluctance if not hostility of modern-day Macedonians of Greece (i.e. people with a Macedonian national identity) to accept it."</blockquote></ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{InterWiki|code=mk}} |
|||
{{wikibooks|Macedonian}} |
|||
* [[Ausbausprache - Abstandsprache - Dachsprache]] |
|||
* [[Balkan linguistic union]] |
|||
* [[Macedonian alphabet]] |
|||
* [[Macedonian language naming dispute]] |
|||
* [[Political views on the Macedonian language]] |
|||
* [[Romanisation of Macedonian]] |
* [[Romanisation of Macedonian]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Abstand and ausbau languages]] |
||
* [[Sociolinguistics]] |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
* [[Torlakian dialect]] |
|||
{{reflist|colwidth=30em}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
;Books |
|||
{{reflist|2}} |
|||
{{refbegin|indent=yes|30em}} |
|||
* {{citation|first=Max K.|last=Adler|title=Marxist Linguistic Theory and Communist Practice: A Sociolinguistic Study|isbn=3871184195|publisher=Buske Verlag|year=1980}} |
|||
* {{citation|url={{Google books |plainurl=yes |id=1jSg3lxgSy8C |page=134 }} |title=Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia Historical Dictionaries of Europe|first= Dimitar|last= Bechev|publisher= Scarecrow Press |isbn=978-0-8108-6295-1|date=13 April 2009}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Bogdanoska|first=Biljana|year=2008|title=За матуранти македонски јазик и литература|trans-title=Macedonian language and literature for matura students|language=mk|publisher=Bomat Grafiks|location=[[Skopje]]}} |
|||
* {{citation|last1=Bojkovska|first1=Stojka|last2=Minova-Gjurkova|first2=Liljana|last3=Pandev|first3=Dimitar |last4=Cvetanovski|first4=Živko|year=2008|title=Општа граматика на македонскиот јазик|trans-title=Grammar of the Macedonian language|location=Skopje|language=mk|publisher=Prosvetno Delo|isbn=9789989006623}} |
|||
* {{citation| last=Campbell | first=George L. | title=Compendium of the World's Languages | publisher=Routledge |year = 2000 |isbn=0415202965| place=London}} |
|||
* {{citation|last1=Comrie|first1=Bernard|last2=Corbett|first2=Greville|year=2002|chapter=The Macedonian language|title=The Slavonic Languages|place=New York|publisher=Routledge Publications}} |
|||
* {{citation|title=South Slavic Discourse Particles|year=2010|first1=Mirjana N.|last1=Dedaić|first2=Mirjana |last2=Mišković-Luković|series=Pragmatics & Beyond New Series|volume=197|place=Amsterdam|publisher=Benjamins |doi=10.1075/pbns.197|isbn=978-90-272-5601-0}} |
|||
* {{citation|title=The Macedonian conflict: ethnic nationalism in a transnational world|first=Loring M. |last=Danforth|isbn=0-691-04356-6|publisher=Princeton University Press|date=1995}} |
|||
* {{citation|title=The Earliest Stage of Language Planning: The "First Congress" Phenomenon|first=Joshua A. |last=Fishman|isbn=3-11-013530-2|publisher=Mouton De Gruyter|date=1993 |url={{Google books |plainurl=yes |id=T-gHxC8J4PwC |page=161}}}} |
|||
* {{citation|first=Benjamin W.|last=Fortson |title=Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction Blackwell textbooks in linguistics |publisher=John Wiley and Sons |isbn=978-1-4051-8896-8|date=31 August 2009 |url={{Google books |plainurl=yes |id=_kn5c5dJmNUC |page=431}}}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Friedman|first=Victor|author-link=Victor Friedman|year=1993|title=The Slavonic Languages |chapter=Macedonian|editor=Comrie B.|editor2=Corbett G.|location=London, New York|publisher=Routledge |pages=249–305 |isbn=0-415-04755-2}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Friedman|first=Victor|year=2001|title=Macedonian|publisher=Slavic and Eurasian Language Resource Center (SEELRC), [[Duke University]] |url=http://www.seelrc.org:8080/grammar/mainframe.jsp?nLanguageID=3|access-date=3 February 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140728194528/http://www.seelrc.org:8080/grammar/mainframe.jsp?nLanguageID=3|archive-date=28 July 2014|url-status=live}} |
|||
*{{citation|ref={{sfnref|Friedman|Garry|Rubino|2001}}|last=Friedman|first=Victor|author-link=Victor Friedman|editor-last=Garry|editor-first=Jane|editor2-last=Rubino|editor2-first=Carl|year=2001 |title=Macedonian: Facts about the World's Languages: An Encyclopedia of the Worlds Major Languages, Past and Present |url=http://humstatic.uchicago.edu/mahimahi/media/faculty/vfriedm/164Friedman01.pdf|place=New York|publisher=Holt|pages=435–439|access-date=18 March 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190710210850/http://humstatic.uchicago.edu/mahimahi/media/faculty/vfriedm/164Friedman01.pdf|archive-date=10 July 2019|url-status=live}} |
|||
* {{citation|url={{Google books |plainurl=yes |id=vi_VCm51kpkC |page=515 }}|title=Languages and Linguistics of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide|last1=Kortmann|first1=Bernd|last2=van der Auwera|first2=Johan|date=27 July 2011 |publisher=De Gruyter Mouton|location=Berlin/Boston|isbn=978-3-11-022025-4}} |
|||
* {{citation|last1=Levinson|first1=David|last2=O'Leary|first2=Timothy|title=Encyclopedia of World Cultures |publisher=G.K. Hall|year=1992|isbn=0-8161-1808-6 |url=https://archive.org/details/encyclopediaofwo0000unse_q6n9/page/239}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Lunt|first=Horace G.|year=1952|title=A Grammar of the Macedonian Literary Language|publisher=Državno knigoizdatelstvo|place=Skopje}} |
|||
* {{citation|first=Horace Gray|last=Lunt|title=Old Church Slavonic Grammar|publisher=Walter de Gruyter|year=2001|isbn=3110162849}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Poulton|first=Hugh|title=Who Are the Macedonians?|year=2000|publisher=C. Hurst & Co. |place=United Kingdom|isbn=0-253-34598-7|url-access=registration|url=https://archive.org/details/whoaremacedonian00poul}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Reimann|first=Daniel|title=Kontrastive Linguistik und Fremdsprachendidaktik Iberoromanisch|year=2014|language=de|publisher=Gunter Narr Verlag|isbn=978-3823368250}} |
|||
* {{citation|last1=Thornburg|first1=Linda L.|last2=Fuller|first2=Janet M. |title=Studies in contact linguistics: Essays in Honor of Glenn G. Gilbert|publisher=Peter Lung Publishing Inc.|location=New York|isbn=978-0-8204-7934-7 |year=2006 |url={{Google books |id=60aFAS1crFEC |page=213 |plainurl=yes}}}} |
|||
* {{citation|title=Polski-macedoński, gramatyka konfrontatywna: Zarys problematyki|trans-title=Polish-Macedonian, confrontational grammar|first1=Zuzanna|last1=Topolińska|year=1984|language=pl|publisher=[[Ossolineum|Zakład Narodowy im. Ossolińskich]]|isbn=978-8304016682}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Usikova|first=Rina Pavlovna|title=О языковой ситуации в Республике Македонии|trans-title = About the language situation in the Republic of Macedonia|language=ru|location=Moscow|publisher=[[Nauka (publisher)|Nauka]] |year=1994|pages=221–231|isbn=5-02-011187-2}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Usikova|first=Rina Pavlovna|title= Языки мира. Славянские языки: Македонский язык|trans-title = Languages of the world. Slavic languages: Macedonian language|language=ru|location=Moscow|publisher=[[Academia (Soviet publishing house)|Academia]]|year=2005|pages=102–139|isbn=5-87444-216-2}} |
|||
* {{citation|last=Vidoeski|first=Bozhidar|year=1999|title=Дијалектите на македонскиот јазик: том 1 |trans-title=The dialects of the Macedonian language: Book 1|publisher=MANU|language=mk|isbn=9989649634}} |
|||
* {{citation|first=Lois|last=Whitman|year=1994|title=Denying ethnic identity: The Macedonians of Greece|location=New York|isbn=1564321320|publisher=Helsinki Human Rights Watch}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
;Journal articles |
|||
==Bibliography== |
|||
{{refbegin|indent=yes|30em}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
*{{citation|last=Hill|first=P.|year=1999|title=Macedonians in Greece and Albania: A comparative study of recent developments|journal=Nationalities Papers|volume=27|issue=1|doi=10.1080/009059999109163|page=17|s2cid=154201780 }} |
|||
|last=Comrie |
|||
*{{citation|last=Friedman|first=Victor|year=1998|title=The implementation of standard Macedonian: problems and results|journal=[[International Journal of the Sociology of Language]]|issue=131|pages=31–57|doi=10.1515/ijsl.1998.131.31|s2cid=143891784}} |
|||
|first=Bernard |
|||
*{{citation|title=Official Language, Minority Language, No Language at All: The History of Macedonian in Primary Education in the Balkans|journal=[[Language Problems and Language Planning]]|first=Christina|last=Kramer|author-link=Christina Kramer|year=1999|volume=23|issue=3|pages=233–250|doi=10.1075/lplp.23.3.03kra}} |
|||
|last2=Corbett |
|||
* {{citation|title=Language, Cultural Identity and Politics in the Cases of Macedonian and Scots|journal=Slavonica|first=Atina|last=Nihtinen|date=1999|pages=46–58|volume=5|issue=1|doi=10.1179/sla.1999.5.1.46}} |
|||
|first2=Greville |
|||
* {{citation|title=Histoire de la langue macédonienne|trans-title=History of the Macedonian language|language=fr|first=Frosa|last=Pejoska-Bouchereau|work=[[Revue des études slaves]]|year=2008|pages=145–161}} |
|||
|year=2002 |
|||
* {{citation|last=Seriot|first=Patrick|editor-last=Tabouret-Keller|editor-first=Andrée|year=1997|chapter=Faut-il que les langues aient un nom? Le cas du macédonien|trans-chapter=Do languages have to have a name? The case of Macedonian|chapter-url=http://www2.unil.ch/slav/ling/recherche/biblio/97macedTK.html|title=Le nom des langues. L'enjeu de la nomination des langues|language=fr|volume=1|place=Louvain|publisher=Peeters|pages=167–190|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20010905201539/http://www.unil.ch/slav/ling/recherche/biblio/97macedTK.html|archive-date=5 September 2001}} |
|||
|chapter=The Macedonian language |
|||
* {{citation|last=Topolinjska|first=Z.|year=1998|title=In place of a foreword: facts about the Republic of Macedonia and the Macedonian language|journal=International Journal of the Sociology of Language|issue=131|pages=1–11|doi=10.1515/ijsl.1998.131.1|s2cid=143257269}} |
|||
|title=The Slavonic Languages |
|||
* {{citation|last=Trudgill|first=Peter|year=1992|title=Ausbau sociolinguistics and the perception of language status in contemporary Europe|journal=[[International Journal of Applied Linguistics]]|volume=2|issue=2|pages=167–177|doi=10.1111/j.1473-4192.1992.tb00031.x}} |
|||
|place=New York |
|||
* {{citation|last=Voß|first=C|year=2018|title=Linguistic emancipation within the Serbian mental map: The implementation of the Montenegrin and Macedonian standard languages|journal=Aegean Working Papers in Ethnographic Linguistics|volume=2|issue=1|pages=1–16|doi=10.12681/awpel.20021|doi-access=free}} |
|||
|publisher=Routledge Publications |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Dostál |
|||
|first=Antonín |
|||
|year=1965 |
|||
|title=The Origins of the Slavonic Liturgy |
|||
|journal=Dumbarton Oaks Papers |
|||
|volume=19 |
|||
|pages=67–87 |
|||
|doi=10.2307/1291226 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Hill |
|||
|first=P. |
|||
|year=1999 |
|||
|title="Macedonians in Greece and Albania: A comparative study of recent developments" |
|||
|journal=Nationalities Papers |
|||
|volume=27 |
|||
|issue=1 |
|||
|doi=10.1080/009059999109163 |
|||
|pages=17 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Friedman |
|||
|first=Victor |
|||
|editor-last=Garry |
|||
|editor-first=Jane |
|||
|editor2-last=Rubino |
|||
|editor2-first=Carl |
|||
|year=2001 |
|||
|chapter=Macedonian |
|||
|title=Facts about the World's Languages: An Encyclopedia of the Worlds Major Languages, Past and Present |
|||
|place=New York |
|||
|publisher=Holt |
|||
|pages=435–439 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Friedman |
|||
|first=Victor |
|||
|year=1998 |
|||
|title=The implementation of standard Macedonian: problems and results |
|||
|journal=International Journal of the Sociology of Language |
|||
|issue=131 |
|||
|pages=31–57 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Hoxha |
|||
|first=Artan |
|||
|last2=Gurraj |
|||
|first2=Alma |
|||
|year=2001 |
|||
|chapter=Local self-government and decentralization: case of Albania. History, reformes [sic] and challenges. |
|||
|url=http://www.fes.hr/E-books/pdf/Local%20Self%20Government/09.pdf |
|||
|format=PDF|title=Local Self Government and Decentralization in South-East Europe:Proceedings of the Workshop held in Zagreb, 6th April 2001 |
|||
|pages=194–224 |
|||
}} |
|||
{{citation |
|||
|last=Levinson |
|||
|first=David |
|||
|last2=O'Leary |
|||
|first2=Timothy |
|||
|title=Encyclopedia of World Cultures |
|||
|publisher=G.K. Hall |
|||
|year =1992 |
|||
|pages=p.239 |
|||
|isbn=0816118086 }} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Lunt |
|||
|first=Horace G. |
|||
|year=1952 |
|||
|title=Grammar of the Macedonian Literary Language |
|||
|place=Skopje |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Mahon |
|||
|first=Milena |
|||
|year=1998 |
|||
|title=The Macedonian question in Bulgaria |
|||
|journal=[[Nations and Nationalism]] |
|||
|volume=4 |
|||
|issue=3 |
|||
|pages=389–407 |
|||
|doi=10.1111/j.1354-5078.1998.00389.x |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Poulton |
|||
|first=Hugh |
|||
|title=Who Are the Macedonians? |
|||
|year=2000 |
|||
|publisher=C. Hurst & Co. Ltd. |
|||
|place= United Kingdom |
|||
|isbn=0253345987 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Seriot |
|||
|first=Patrick |
|||
|editor-last=Tabouret-Keller |
|||
|editor-first=Andrée |
|||
|year=1997 |
|||
|chapter=Faut-il que les langues aient un nom? Le cas du macédonien |
|||
|url=http://www2.unil.ch/slav/ling/recherche/biblio/97macedTK.html |
|||
|title=Le nom des langues. L'enjeu de la nomination des langues |
|||
|volume=1 |
|||
|place=Louvain |
|||
|publisher=Peeters |
|||
|pages=167–190 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Topolinjska |
|||
|first=Z. |
|||
|year=1998 |
|||
|title=In place of a foreword: facts about the Republic of Macedonia and the Macedonian language |
|||
|journal=International Journal of the Sociology of Language |
|||
|issue=131 |
|||
|pages=1–11 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{citation |
|||
|last=Trudgill |
|||
|first=Peter |
|||
|year=1992 |
|||
|title=Ausbau sociolinguistics and the perception of language status in contemporary Europe |
|||
|journal=International Journal of Applied Linguistics |
|||
|volume=2 |
|||
|issue=2 |
|||
|pages=167–177 |
|||
|doi=10.1111/j.1473-4192.1992.tb00031.x |
|||
}} |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
*{{cite book |
|||
|last=Kramer |
|||
|first=Christina |
|||
|authorlink=Christina Kramer |
|||
|year=2003 |
|||
|title=Macedonian: A Course for Beginning and Intermediate Students. |
|||
|edition=2nd |
|||
|publisher=University of Wisconsin Press |
|||
|isbn=9780299188047 |
|||
}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{InterWiki|code=mk}} |
|||
===Documents=== |
|||
{{Commons category|Macedonian language}} |
|||
*[http://www.seelrc.org:8080/grammar/mainframe.jsp?nLanguageID=3 A grammar of Macedonian by Victor Friedman] |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0001Pulevski%20Trijazichnik.pdf Dictionary of three languages, Gjorgjija Pulevski] - 1875 |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0002Macedonischen%20Slaven.pdf Zur Sprachlichen Beurtellung der Macedonischen slaven,Leonhard Masing] - 1890, on German |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0003Macedoslavischen%20Dialekte.pdf Zur Laut und Akzentlehre der Macedonischen dialekte,Leonhard Masing] - 1891, on German |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0004Vatroslav%20Oblak.pdf MACEDONISCHEN STUDIEN, Vatroslav Oblak] - 1896, on German |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0005%20Za%20makedonckite%20raboti.pdf For the Macedonian matters, Krste Petkov Misirkov] - 1903 |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0006ABECEDAR%201925.pdf Abecedar] - 1925, Greece |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0007Dwie%20Gwary%20Macedonskie%201.pdf Dwie gwary macedońskie(Suhe i Wysoka w Soluńskiem) – Teksty , Mieczysław Małecki] - 1934, on Polish |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0008Dwie%20Gwary%20Macedonskie%202.pdf Dwie gwary macedońskie(Suhe i Wysoka w Soluńskiem) – Teksty, Mieczysław Małecki] - 1936, on Polish |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0009%20Andre%20Mazon.pdf Documents, Contes et Chansons Slaves de l'Albanie du Sud, Andre Mazon] - 1936, on French |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0010%20Kulakia.pdf L'Evangeliaire de Kulakia Un parler Slave du Bas-Vardar, Andre Mazon et Andre Vaillant] - 1938, on French |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0011%20Makedonska%20gramatika-krume.pdf Macedonian grammar, Krume Kepeski] - 1946, on Macedonian |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0012%20Makedonski%20pravopis.pdf Macedonian orthography and dictionary, Blaže Koneski and Krum Tošev] - 1950, on Macedonian |
|||
*[http://damj.manu.edu.mk/pdf/0013%20Horace%20Lunt_Macedonian%20grammar%201952.pdf Grammar of the Macedonian Literary Language, Horace Lunt] - 1952 |
|||
* [http://imj.ukim.edu.mk/ Институт за македонски јазик, "Крсте Петков Мисирков"] – [[Institute for Macedonian language "Krste Misirkov"]], the main regulatory body of the Macedonian language (in Macedonian) |
|||
===Macedonian language=== |
|||
* [http://www.makedonski.info/ Дигитален речник на македонскиот јазик] – Online dictionary of the Macedonian language |
|||
{{External links|date=May 2009}} |
|||
* {{citation|url=https://pravopis.mk/sites/default/files/Pravopis-2017.PDF|title=Правопис на македонскиот јазик|trans-title=Orthography of the Macedonian language|edition=2|publisher=Kultura AD|author=Institute for Macedonian language "Krste Misirkov"|location=Skopje|year=2017}} |
|||
*{{ethnologue|code=mkd}} |
|||
* {{Citation|last1=Kramer|first1=Christina|first2=Liljana|last2=Mitkovska|author-link=Christina Kramer|year=2003|title=Macedonian: A Course for Beginning and Intermediate Students.|edition=2nd|publisher=University of Wisconsin Press|isbn=978-0-299-18804-7}} |
|||
*[http://www.bbc.co.uk/languages/european_languages/countries/macedonia.shtml BBC Education - Languages: ''Macedonian, Makedonski''] |
|||
*{{Wikivoyage-inline|Macedonian phrasebook|Macedonian|a phrasebook}} |
|||
*[http://www.websters-online-dictionary.org/definition/Macedonian-english/ Macedonian - English Dictionary] |
|||
*{{wiktionary-inline|Category:Macedoninan language|Macedonian language}} |
|||
*[http://www.promacedonia.org/en/kronsteiner/ik_3_eng.html Otto Kronsteiner. The Collapse of Yugoslavia and the Future Prospects of the Macedonian Literary Language] |
|||
*{{Wikibooks-inline|Macedonian}} |
|||
*[http://www.lmp.ucla.edu/ UCLA Language materials project: ][http://www.lmp.ucla.edu/Profile.aspx?LangID=42&menu=004 Macedonian profile] |
|||
*[http://knigite.abv.bg/en/pavel/nature_of_mac_lang.html Nature of Standard Macedonian language by Mladen Srbinovski] |
|||
*[http://www.gate.net/~mango/DeBelle.htm The Macedonian nationality] |
|||
*[http://usa.ipums.org/usa/voliii/inst1920.shtml 1920 US Census, Instructions to Enumerators, where Macedonian is listed as a principal foreign language] |
|||
*[http://www.makedonski.info Digital Dictionary of the Macedonian Language] |
|||
*[http://www.idividi.com.mk/recnik/ Macedonian - English, Greek, Albanian, German, French, Italian translator] |
|||
*[http://www.makedonija.info/language.html The Macedonian Language] |
|||
{{Macedonian language|state=expanded}} |
|||
{{Macedonian dialects}} |
{{Macedonian dialects}} |
||
{{North Macedonia topics}} |
|||
{{Languages of Macedonia}} |
|||
{{Languages of Albania}} |
|||
{{Slavic languages}} |
{{Slavic languages}} |
||
{{Portal bar | North Macedonia | Language}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Macedonian Language}} |
|||
[[Category:Macedonian language| ]] |
[[Category:Macedonian language| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Analytic languages]] |
||
[[Category:Languages of |
[[Category:Languages of Albania]] |
||
[[Category:Languages of Bulgaria]] |
|||
[[Category:Languages of Greece]] |
[[Category:Languages of Greece]] |
||
[[Category:Languages of Bulgaria]] |
|||
[[Category:Languages of Serbia]] |
[[Category:Languages of Serbia]] |
||
[[Category:Languages of Vojvodina]] |
[[Category:Languages of Vojvodina]] |
||
[[Category:Languages of |
[[Category:Languages of North Macedonia]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Eastern South Slavic]] |
||
[[Category:Languages written in Cyrillic script]] |
|||
{{Link FA|mk}} |
|||
[[af:Macedonies]] |
|||
[[ar:لغة مقدونية]] |
|||
[[an:Idioma mazedonio]] |
|||
[[ast:Macedoniu]] |
|||
[[az:Makedon dili]] |
|||
[[be:Македонская мова]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Македонская мова]] |
|||
[[bs:Makedonski jezik]] |
|||
[[bg:Македонски език]] |
|||
[[ca:Macedònic]] |
|||
[[cs:Makedonština]] |
|||
[[da:Makedonsk (sprog)]] |
|||
[[de:Mazedonische Sprache]] |
|||
[[dsb:Makedońska rěc]] |
|||
[[et:Makedoonia keel]] |
|||
[[el:Σλαβομακεδονική γλώσσα]] |
|||
[[es:Idioma macedonio]] |
|||
[[eo:Makedona lingvo]] |
|||
[[eu:Mazedoniera]] |
|||
[[fr:Macédonien]] |
|||
[[gl:Lingua macedonia]] |
|||
[[ko:마케도니아어]] |
|||
[[hi:मेसिडोनियन भाषा]] |
|||
[[hsb:Makedonšćina]] |
|||
[[hr:Makedonski jezik]] |
|||
[[id:Bahasa Makedonia]] |
|||
[[is:Makedónska]] |
|||
[[it:Lingua macedone]] |
|||
[[he:מקדונית]] |
|||
[[ka:მაკედონური ენა]] |
|||
[[kw:Makedonek]] |
|||
[[la:Lingua Macedonica praesentis]] |
|||
[[lv:Maķedoniešu valoda]] |
|||
[[lt:Makedonų kalba]] |
|||
[[lij:Lengua maçedone]] |
|||
[[li:Macedonisch]] |
|||
[[hu:Macedón nyelv]] |
|||
[[mk:Македонски јазик]] |
|||
[[ms:Bahasa Macedonia]] |
|||
[[nl:Macedonisch (Slavisch)]] |
|||
[[ja:マケドニア語]] |
|||
[[no:Makedonsk]] |
|||
[[oc:Macedonian (eslau)]] |
|||
[[pl:Język macedoński]] |
|||
[[pt:Língua macedônia]] |
|||
[[ro:Limba macedoneană]] |
|||
[[qu:Makidunya simi]] |
|||
[[ru:Македонский язык]] |
|||
[[se:Makedoniagiella]] |
|||
[[sq:Gjuha sllavo-maqedone]] |
|||
[[scn:Lingua macèdoni]] |
|||
[[simple:Macedonian language]] |
|||
[[sk:Macedónčina]] |
|||
[[cu:Макєдо́ньскъ ѩꙁꙑ́къ]] |
|||
[[sl:Makedonščina]] |
|||
[[szl:Macedůńsko godka]] |
|||
[[sr:Македонски језик]] |
|||
[[sh:Makedonski jezik]] |
|||
[[fi:Makedonian kieli]] |
|||
[[sv:Makedonska]] |
|||
[[th:ภาษามาซิโดเนีย]] |
|||
[[tg:Забони мақдунӣ]] |
|||
[[tr:Makedonca]] |
|||
[[uk:Македонська мова]] |
|||
[[ug:ماكېدون تىلى]] |
|||
[[zh:马其顿语]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 14:21, 9 December 2024
| Macedonian | |
|---|---|
| македонски makedonski | |
| Pronunciation | [maˈkɛdɔnski] |
| Native to | North Macedonia, Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Romania, Serbia |
| Region | Balkans |
| Ethnicity | Macedonians |
Native speakers | 1.6 million (2022)[1] |
| Dialects | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Macedonian Language Institute "Krste Misirkov" at the Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | mk |
| ISO 639-2 | mac (B) mkd (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | mkd |
| Glottolog | mace1250 |
| Linguasphere | (part of 53-AAA-h) 53-AAA-ha (part of 53-AAA-h) |
The Macedonian-speaking world:[image reference needed] regions where Macedonian is the language of the majority regions where Macedonian is the language of a minority | |
Macedonian (/ˌmæsɪˈdoʊniən/ MASS-ih-DOH-nee-ən; македонски јазик, translit. makedonski jazik, pronounced [maˈkɛdɔnski ˈjazik] ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken as a first language by around 1.6 million people, it serves as the official language of North Macedonia.[1] Most speakers can be found in the country and its diaspora, with a smaller number of speakers throughout the transnational region of Macedonia. Macedonian is also a recognized minority language in parts of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania, and Serbia and it is spoken by expatriate communities predominantly in Australia, Canada, and the United States.
Macedonian developed out of the western dialects of the Eastern South Slavic dialect continuum, whose earliest recorded form is Old Church Slavonic. During much of its history, this dialect continuum was called "Bulgarian",[5][additional citation(s) needed] although in the late 19th century, its western dialects came to be known separately as "Macedonian".[citation needed] Standard Macedonian was codified in 1945 and has developed modern literature since.[6] As it is part of a dialect continuum with other South Slavic languages, Macedonian has a high degree of mutual intelligibility with Bulgarian and varieties of Serbo-Croatian.
Linguists distinguish 29 dialects of Macedonian, with linguistic differences separating Western and Eastern groups of dialects. Some features of Macedonian grammar are the use of a dynamic stress that falls on the ante-penultimate syllable, three suffixed deictic articles that indicate noun position in reference to the speaker and the use of simple and complex verb tenses. Macedonian orthography is phonemic with a correspondence of one grapheme per phoneme. It is written using an adapted 31-letter version of the Cyrillic script with six original letters. Macedonian syntax is the same as of all other modern Slavic languages, i.e. of the subject-verb-object (SVO) type and has flexible word order.[7][8]
Macedonian vocabulary has been historically influenced by Turkish and Russian. Somewhat less prominent vocabulary influences also came from neighboring and prestige languages. The international consensus outside of Bulgaria is that Macedonian is an autonomous language within the Eastern South Slavic dialect continuum, although since Macedonian and Bulgarian are mutually intelligible and are socio-historically related, a small minority of linguists are divided in their views of the two as separate languages or as a single pluricentric language.[9][10][11]
5 May, the day when the government of Yugoslav Macedonia adopted the Macedonian alphabet as the official script of the republic, is marked as Macedonian Language Day.[12] This is a working holiday, declared as such by the government of North Macedonia in 2019.[13]
Classification and related languages
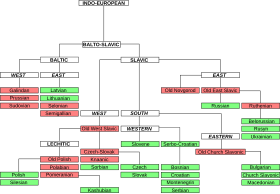
Macedonian belongs to the eastern group of the South Slavic branch of Slavic languages in the Indo-European language family, together with Bulgarian and the extinct Old Church Slavonic. Some authors also classify the Torlakian dialects in this group. Macedonian's closest relative is Bulgarian followed by Serbo-Croatian and Slovene, although the last is more distantly related.[14][15] Together, South Slavic languages form a dialect continuum.[16][17]
Macedonian, like the other Eastern South Slavic idioms has characteristics that make it part of the Balkan sprachbund, a group of languages that share typological, grammatical and lexical features based on areal convergence, rather than genetic proximity.[18] In that sense, Macedonian has experienced convergent evolution with other languages that belong to this group such as Greek, Aromanian, Albanian and Romani due to cultural and linguistic exchanges that occurred primarily through oral communication.[18]
Macedonian and Bulgarian are divergent from the remaining South Slavic languages in that they do not use noun cases (except for the vocative, and apart from some traces of once productive inflections still found scattered throughout these two) and have lost the infinitive.[19] They are also the only Slavic languages with any definite articles (unlike standard Bulgarian, which uses only one article, standard Macedonian as well as some south-eastern Bulgarian dialects[20] have a set of three deictic articles: unspecified, proximal and distal definite article). Macedonian, Bulgarian and Albanian are the only Indo-European languages that make use of the narrative mood.[21]
According to Chambers and Trudgill, the question whether Bulgarian and Macedonian are distinct languages or dialects of a single language cannot be resolved on a purely linguistic basis, but should rather take into account sociolinguistic criteria, i.e., ethnic and linguistic identity.[22] This view is supported by Jouko Lindstedt, who has suggested the reflex of the back yer as a potential boundary if the application of purely linguistic criteria were possible.[23][24]
As for the Slavic dialects of Greece, Trudgill classifies the dialects in the east Greek Macedonia as part of the Bulgarian language area and the rest as Macedonian dialects.[25] According to Riki van Boeschoten,[26] dialects in eastern Greek Macedonia (around Serres and Drama) are closest to Bulgarian, those in western Greek Macedonia (around Florina and Kastoria) are closest to Macedonian, while those in the centre (Edessa and Salonica) are intermediate between the two.[27][28]
History

The Slavic people who settled in the Balkans during the 6th century CE, spoke their own dialects and used different dialects or languages to communicate with other people.[29] The "canonical" Old Church Slavonic period of the development of Macedonian started during the 9th century and lasted until the first half of the 11th century. It saw translation of Greek religious texts.[30][31][32] The Macedonian recension of Old Church Slavonic also appeared around that period in the Bulgarian Empire and was referred to as such due to works of the Ohrid Literary School.[33] Towards the end of the 13th century, the influence of Serbian increased as Serbia expanded its borders southward.[34] During the five centuries of Ottoman rule, from the 15th to the 20th century, the vernacular spoken in the territory of current-day North Macedonia witnessed grammatical and linguistic changes that came to characterize Macedonian as a member of the Balkan sprachbund.[35][36] This period saw the introduction of many Turkish loanwords into the language.[37]

The latter half of the 18th century saw the rise of modern literary Macedonian through the written use of Macedonian dialects referred to as "Bulgarian" by writers.[35] The first half of the 19th century saw the rise of nationalism among the South Slavic people in the Ottoman Empire.[38] This period saw proponents of creating a common church for Bulgarian and Macedonian Slavs which would use a common modern Macedo-Bulgarian literary standard.[39][40]
The period between 1840 and 1870, saw a struggle to define the dialectal base of the common language called simply "Bulgarian", with two opposing views emerging.[37][39] One ideology was to create a Bulgarian literary language based on Macedonian dialects, but such proposals were rejected by the Bulgarian codifiers.[35][39] That period saw poetry written in the Struga dialect with elements from Russian.[41] Textbooks also used either spoken dialectal forms of the language or a mixed Macedo-Bulgarian language.[42] Subsequently, proponents of the idea of using a separate Macedonian language emerged.[43]
Krste Petkov Misirkov's book Za makedonckite raboti (On Macedonian Matters) published in 1903, was the first attempt to formalize a separate literary language.[44] With the book, the author proposed a Macedonian grammar and expressed the goal of codifying the language and using it in schools. The author postulated the principle that the Prilep-Bitola dialect be used as a dialectal basis for the formation of the Macedonian standard language; his idea however was not adopted until the 1940s.[35][41] On 2 August 1944 at the first Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (ASNOM) meeting, Macedonian was declared an official language.[35][45] With this, it became the last of the major Slavic languages to achieve a standard literary form.[32] As such, Macedonian served as one of the three official languages of Yugoslavia from 1945 to 1991.[46]
Geographical distribution
Although the precise number of native and second language speakers of Macedonian is unknown due to the policies of neighboring countries and emigration of the population, estimates ranging between 1.4 million and 3.5 million have been reported.[47][14] According to the 2002 census, the total population of North Macedonia was 2,022,547, with 1,344,815 citizens declaring Macedonian their native language.[48] Macedonian is also studied and spoken to various degrees as a second language by all ethnic minorities in the country.[14][49]
Outside North Macedonia, there are small ethnic Macedonian minorities that speak Macedonian in neighboring countries including 4.697 in Albania (1989 census),[50] 1,609 in Bulgaria (2011 census)[51] and 12,706 in Serbia (2011 census).[52] The exact number of speakers of Macedonian in Greece is difficult to ascertain due to the country's policies. Estimates of Slavophones ranging anywhere between 50,000 and 300,000 in the last decade of the 20th century have been reported.[53][54] Approximately 580,000 Macedonians live outside North Macedonia per 1964 estimates with Australia, Canada, and the United States being home to the largest emigrant communities. Consequently, the number of speakers of Macedonian in these countries include 66,020 (2016 census),[55] 15,605 (2016 census)[56] and 22,885 (2010 census), respectively.[57] Macedonian also has more than 50,000 native speakers in countries of Western Europe, predominantly in Germany, Switzerland and Italy.[58]
The Macedonian language has the status of an official language only in North Macedonia, and is a recognized minority and official language in parts of Albania (Pustec),[59][60] Romania, Serbia (Jabuka and Plandište)[4] and Bosnia and Herzegovina.[2] There are provisions to learn Macedonian in Romania as Macedonians are an officially recognized minority group.[3] Macedonian is studied and taught at various universities across the world and research centers focusing on the language are found at universities across Europe (France, Germany, Austria, Italy, Russia) as well as Australia, Canada and the United States (Chicago and North Carolina).[61]
Dialects
During the standardization process of the Macedonian language, the dialectal base selected was primarily based on the West-Central dialects, which spans the triangle of the communities Makedonski Brod, Kičevo, Demir Hisar, Bitola, Prilep, and Veles. These were considered the most widespread and most likely to be adopted by speakers from other regions.[62] The initial idea to select this region as a base was first proposed in Krste Petkov Misirkov's works as he believed the Macedonian language should abstract on those dialects that are distinct from neighboring Slavic languages, such as Bulgarian and Serbian.[63]

| |
| Dialect divisions of Macedonian per Macedonian dialectology.[24][64] | |
Lower Polog / Tetovo Crna Gora Kumanovo / Kratovo (Torlakian dialects)
Central Drimkol / Golo Brdo Reka Debar Small Reka / Galičnik Upper Polog / Gostivar Vevčani / Radοžda Upper Prespa / Ohrid
|
Mariovo / Tikveš Štip / Strumica Maleševo / Pirin
Solun / Voden Ser / Drama
Lower Prespa Korča Kostur Nestram
|
Based on a large group of features, Macedonian dialects can be divided into Eastern, Western and Northern groups. The boundary between them geographically runs approximately from Skopje and Skopska Crna Gora along the rivers Vardar and Crna.[29] There are numerous isoglosses between these dialectal variations, with structural differences in phonetics, prosody (accentuation), morphology and syntax.[29] The Western group of dialects can be subdivided into smaller dialectal territories, the largest group of which includes the central dialects.[65] The linguistic territory where Macedonian dialects were spoken also span outside the country and within the region of Macedonia, including Pirin Macedonia into Bulgaria and Aegean Macedonia into Greece.[18]
Variations in consonant pronunciation occur between the two groups, with most Western regions losing the /x/ and the /v/ in intervocalic position (глава (head): /ɡlava/ = /ɡla/: глави (heads): /ɡlavi/ = /ɡlaj/) while Eastern dialects preserve it. Stress in the Western dialects is generally fixed and falls on the antepenultimate syllable while Eastern dialects have non-fixed stress systems that can fall on any syllable of the word,[66] that is also reminiscent of Bulgarian dialects. Additionally, Eastern dialects are distinguishable by their fast tonality, elision of sounds and the suffixes for definiteness. The Northern dialectal group is close to South Serbian and Torlakian dialects and is characterized by 46–47 phonetic and grammatical isoglosses.[67]
In addition, a more detailed classification can be based on the modern reflexes of the Proto-Slavic reduced vowels (yers), vocalic sonorants, and the back nasal *ǫ. That classification distinguishes between the following 6 groups:[68]
- Macedonian
- Western dialects
- Ohrid-Prespa Group: Ohrid dialect, Struga dialect, Vevčani-Radožda dialect, Upper Prespa dialect and Lower Prespa dialect.
- Debar Group: Debar dialect, Reka dialect, Drimkol-Golo Brdo dialect, Small Reka dialect (Galičnik dialect), Skopska Crna Gora dialect and Gora dialect
- Polog Group: Upper Polog dialect (Gostivar dialect), Lower Polog dialect (Tetovo dialect), Prilep-Bitola dialect, Kičevo-Poreče dialect and Skopje-Veles dialect
- Kostur-Korča Group: Korča dialect, Kostur dialect and Nestram-Kostenar dialect
- Eastern dialects
- Northern Group: Kumanovo dialect, Kratovo dialect, Kriva Palanka dialect and Ovče Pole dialect
- Eastern Group: Štip - Kočani dialect, Strumica dialect, Tikveš-Mariovo dialect, Maleševo-Pirin dialect, Solun-Voden dialect and Ser-Drama-Lagadin-Nevrokop dialect.
- Western dialects
Phonology
The phonological system of Standard Macedonian is based on the Prilep-Bitola dialect. Macedonian possesses five vowels, one semivowel, three liquid consonants, three nasal stops, three pairs of fricatives, two pairs of affricates, a non-paired voiceless fricative, nine pairs of voiced and unvoiced consonants and four pairs of stops. Out of all the Slavic languages, Macedonian has the most frequent occurrence of vowels relative to consonants with a typical Macedonian sentence having on average 1.18 consonants for every one vowel.[69]
Vowels
The Macedonian language contains 5 vowels which are /a/, /ɛ/, /ɪ/, /o/, and /u/. For the pronunciation of the middle vowels /е/ and /о/ by native Macedonian speakers, various vowel sounds can be produced ranging from [ɛ] to [ẹ] and from [o] to [ọ]. Unstressed vowels are not reduced, although they are pronounced more weakly and shortly than stressed ones, especially if they are found in a stressed syllable.[70][71] The five vowels and the letter р (/r/) which acts as a vowel when found between two consonants (e.g. црква, "church"), can be syllable-forming.[66]
The schwa is phonemic in many dialects (varying in closeness to [ʌ] or [ɨ]) but its use in the standard language is marginal.[72] When writing a dialectal word and keeping the schwa for aesthetic effect, an apostrophe is used; for example, ⟨к’смет⟩, ⟨с’нце⟩, etc. When spelling words letter-by-letters, each consonant is followed by the schwa sound. The individual letters of acronyms are pronounced with the schwa in the same way: ⟨МПЦ⟩ ([mə.pə.t͡sə]). The lexicalized acronyms ⟨СССР⟩ ([ɛs.ɛs.ɛs.ɛr]) and ⟨МТ⟩ ([ɛm.tɛ]) (a brand of cigarettes), are among the few exceptions. Vowel length is not phonemic. Vowels in stressed open syllables in disyllabic words with stress on the penultimate can be realized as long, e.g. ⟨Велес⟩ [ˈvɛːlɛs] 'Veles'. The sequence /aa/ is often realized phonetically as [aː]; e.g. ⟨саат⟩ /saat/ [saːt] 'colloq. hour', ⟨змии⟩ - snakes. In other words, two vowels appearing next to each other can also be pronounced twice separately (e.g. пооди - to walk).[66]
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | ɛ | (ə) | ɔ |
| Open | a |
Consonants
The consonant inventory of the Macedonian language consists of 26 letters and distinguishes three groups of consonants (согласки): voiced (звучни), voiceless (безвучни) and sonorant consonants (сонорни).[71] Typical features and rules that apply to consonants in the Macedonian language include assimilation of voiced and voiceless consonants when next to each other, devoicing of vocal consonants when at the end of a word, double consonants and elision.[71][74] At morpheme boundaries (represented in spelling) and at the end of a word (not represented in spelling), voicing opposition is neutralized.[71]
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n̪1 | ɲ | |||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t̪ | c3 | k | |
| voiced | b | d̪ | ɟ3 | ɡ | ||
| Affricate | voiceless | t̪͡s̪ | t͡ʃ | |||
| voiced | d̪͡z̪ | d͡ʒ | ||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | s̪ | ʃ | x2 | |
| voiced | v | z̪ | ʒ | |||
| Approximant | ɫ̪1 | l | j | |||
| Trill | r1 | |||||
^1 The alveolar trill (/r/) is syllabic between two consonants; for example, ⟨прст⟩ [ˈpr̩st] 'finger'. The dental nasal (/n/) and dental lateral (/ɫ/) are also syllabic in certain foreign words; e.g. ⟨њутн⟩ [ˈɲutn̩] 'newton', ⟨Попокатепетл⟩ [pɔpɔkaˈtɛpɛtɫ̩] 'Popocatépetl', etc. The labiodental nasal [ɱ] occurs as an allophone of /m/ before /f/ and /v/ (e.g. ⟨трамвај⟩ [ˈtraɱvaj] 'tram').[citation needed] The velar nasal [ŋ] similarly occurs as an allophone of /n/ before /k/ and /ɡ/ (e.g. ⟨англиски⟩ [ˈaŋɡliski] 'English').[75] The latter realization is avoided by some speakers who strive for a clear, formal pronunciation.[citation needed]
^2 Inherited Slavic /x/ was lost in the Western dialects of Macedonian on which the standard is based, having become zero initially and mostly /v/ otherwise. /x/ became part of the standard language through the introduction of new foreign words (e.g. хотел, hotel), toponyms (Пехчево, Pehčevo), words originating from Old Church Slavonic (дух, ghost), newly formed words (доход, income) and as a means to disambiguate between two words (храна, food vs. рана, wound). This explains the rarity of Х in the Macedonian language.[75]
^3 They exhibit different pronunciations depending on dialect. They are dorso-palatal stops in the standard language and are pronounced as such by some native speakers.[75]
Stress
The word stress in Macedonian is antepenultimate and dynamic (expiratory). This means that it falls on the third from last syllable in words with three or more syllables, and on the first or only syllable in other words. This is sometimes disregarded when the word has entered the language more recently or from a foreign source.[77] To note which syllable of the word should be accented, Macedonian uses an apostrophe over its vowels. Disyllabic words are stressed on the second-to-last syllable: дéте ([ˈdɛtɛ]: child), мáјка ([ˈmajka]: mother) and тáтко ([ˈtatkɔ]: father). Trisyllabic and polysyllabic words are stressed on the third-to-last syllable: плáнина ([ˈpɫanina]: mountain) планѝната ([pɫaˈninata]: the mountain) планинáрите ([pɫaniˈnaritɛ]: the mountaineers).[77] There are several exceptions to the rule and they include: verbal adverbs (i.e. words suffixed with -ќи): e.g. викáјќи ([viˈkajci]: shouting), одéјќи ([ɔˈdɛjci]: walking); adverbs of time: годинáва ([godiˈnava]: this year), летóво ([leˈtovo]: this summer); foreign loanwords: e.g. клишé ([kliˈʃɛ:] cliché), генéза ([ɡɛˈnɛza] genesis), литератýра ([litɛraˈtura]: literature), Алексáндар ([alɛkˈsandar], Alexander).[78]
Linking occurs when two or more words are pronounced with the same stress. Linking is a common feature of the Macedonian language. This linguistic phenomenon is called акцентска целост and is denoted with a spacing tie (‿) sign. Several words are taken as a single unit and thus follow the rules of the stress falling on the antepenultimate syllable. The rule applies when using clitics (either enclitics or proclitics) such as the negating particle не with verbs (тој нé‿дојде, he did not come) and with short pronoun forms. The future particle ќе can also be used in-between and falls under the same rules (не‿му‿јá‿даде, did not give it to him; не‿ќé‿дојде, he will not come).[79] Other uses include the imperative form accompanied by short pronoun forms (дáј‿ми: give me), the expression of possessives (мáјка‿ми), prepositions followed by a noun (зáд‿врата), question words followed by verbs (когá‿дојде) and some compound nouns (сувó‿грозје - raisins, киселó‿млеко - yoghurt) among others.[79]
Grammar
Macedonian grammar is markedly analytic in comparison with other Slavic languages, having lost the common Slavic case system. The Macedonian language shows some special and, in some cases, unique characteristics due to its central position in the Balkans. Literary Macedonian is the only South Slavic literary language that has three forms of the definite article, based on the degree of proximity to the speaker, and a perfect tense formed by means of an auxiliary verb "to have", followed by a past participle in the neuter, also known as the verbal adjective. Other features that are only found in Macedonian and not in other Slavic languages include the antepenultimate accent and the use of the same vocal ending for all verbs in first person, present simple (глед-a-м, јад-а-м, скок-а-м).[80] Macedonian distinguishes at least 12 major word classes, five of which are modifiable and include nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numbers and verbs and seven of which are invariant and include adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, particles and modal words.[74]
Nouns
Macedonian nouns (именки) belong to one of three genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter) and are inflected for number (singular and plural), and marginally for case. The gender opposition is not distinctively marked in the plural.[81] Masculine nouns usually end in a consonant or a vowel (-a, -o or -e) and neuter nouns end in a vowel (-o or -e). Virtually all feminine nouns end in the same vowel, -a.[79]
The vocative of nouns is the only remaining case in the Macedonian language and is used to address a person directly. The vocative case always ends with a vowel, which can be either an -у (јунаку: hero vocative) or an -e (човече: man vocative) to the root of masculine nouns. For feminine nouns, the most common final vowel ending in the vocative is -o (душо, sweetheart vocative; жено, wife vocative). The final suffix -e can be used in the following cases: three or polysyllabic words with the ending -ица (мајчице, mother vocative), female given names that end with -ка: Ратка becomes Ратке and -ја: Марија becomes Марије or Маријо. There is no vocative case in neuter nouns. The role of the vocative is only facultative and there is a general tendency of vocative loss in the language since its use is considered impolite and dialectal.[82] The vocative can also be expressed by changing the tone.[79][83]
There are three different types of plural: regular, counted and collective. The first plural type is most common and used to indicate regular plurality of nouns: маж - мажи (a man - men), маса - маси (a table - table), село - села (a village - villages). There are various suffixes that are used and they differ per gender; a linguistic feature not found in other Slavic languages is the use of the suffix -иња to form plural of neuter nouns ending in -е: пиле - пилиња (a chick - chicks).[80] Counted plural is used when a number or a quantifier precedes the noun; suffixes to express this type of plurality do not correspond with the regular plurality suffixes: два молива (two pencils), три листа (three leaves), неколку часа (several hours). The collective plural is used for nouns that can be viewed as a single unit: лисје (a pile of leaves), ридје (a unit of hills). Irregular plural forms also exist in the language: дете - деца (child - children).[79]
Definiteness
| Singular | Plural | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masculine | Feminine | Neuter | Masculine | Feminine | Neuter | |
| Unspecified | мажот | жената | детето | мажите/жените | децата | |
| Proximate | мажов | женава | детевo | маживе/жениве | децава | |
| Distal | мажон | женана | детенo | мажине/женине | децана | |
A characteristic feature of the nominal system is the indication of definiteness. As with other Slavic languages, there is no indefinite article in Macedonian. The definite article in Macedonian is postpositive, i.e. it is added as a suffix to nouns. An individual feature of the Macedonian language is the use of three definite articles, inflected for gender and related to the position of the object, which can be unspecified, proximate or distal.
- Definite articles -ов, -ва, -во, -ве are used for objects located close to the speaker (човеков: - this person here)
- Definite articles -он, -на, -но, -не are used for objects located further away from the speaker that can still be perceived (женана: - that woman there)
- Definite articles -от, -та, -то, -те are most commonly used as general indicators of definiteness regardless of the referred object's position (детето: the child). Additionally, these suffixes can be used to indicate objects referred to by the speaker that are in the proximity of the listener, e.g. дај ми ја книгата што е до тебе - give me the book next to you.[74]
Proper nouns are per definition definite and are not usually used together with an article, although exceptions exist in the spoken and literary language such as Совчето, Марето, Надето to demonstrate feelings of endearment to a person.
Adjectives
Adjectives accompany nouns and serve to provide additional information about their referents. Macedonian adjectives agree in form with the noun they modify and are thus inflected for gender, number and definiteness and убав changes to убава (убава жена, a beautiful woman) when used to describe a feminine noun, убаво when used to describe a neuter noun (убаво дете, a beautiful child) and убави when used to form the plural (убави мажи, убави жени, убави деца).[79]
Adjectives can be analytically inflected for degree of comparison with the prefix по- marking the comparative and the prefix нај- marking the superlative. Both prefixes cannot be written separately from the adjective: Марија е паметна девојка (Marija is a smart girl), Марија е попаметна од Сара (Marija is smarter than Sara), Марија е најпаметната девојка во нејзиниот клас (Marija is the smartest girl in her class). The only adjective with an irregular comparative and superlative form is многу which becomes повеќе in the comparative and најмногу in the superlative form.[84] Another modification of adjectives is the use of the prefixes при- and пре- which can also be used as a form of comparison: престар човек (a very old man) or пристар човек (a somewhat old man).[74]
Pronouns
Three types of pronouns can be distinguished in Macedonian: personal (лични), relative (лично-предметни) and demonstrative (показни). Case relations are marked in pronouns. Personal pronouns in Macedonian appear in three genders and both in singular and plural. They can also appear either as direct or indirect object in long or short forms. Depending on whether a definite direct or indirect object is used, a clitic pronoun will refer to the object with the verb: Јас не му ја дадов книгата на момчето ("I did not give the book to the boy").[85] The direct object is a remnant of the accusative case and the indirect of the dative. Reflexive pronouns also have forms for both direct and indirect objects: себе се, себе си. Examples of personal pronouns are shown below:
- Personal pronoun: Јас читам книга. ("I am reading a book")
- Direct object pronoun: Таа мене ме виде во киното. ("She saw me at the cinema")
- Indirect object pronoun: Тој мене ми рече да дојдам. ("He told me to come")
Relative pronouns can refer to a person (кој, која, кое - who), objects (што - which) or serve as indicators of possession (чиј, чија, чие - whose) in the function of a question or a relative word. These pronouns are inflected for gender and number and other word forms can be derived from them (никој - nobody, нешто - something, сечиј - everybody's). There are three groups of demonstrative pronouns that can indicate proximate (овој - this one (mas.)), distal (онаа - the one there (fem.)) and unspecific (тоа - that one (neut.)) objects. These pronouns have served as a basis for the definite article.[74][79]
| Person | Singular | Direct object | Indirect object | Plural | Direct object | Indirect object |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | јас | мене ме | мене ми | ние | нас нѐ | нам ни |
| 2. | ти вие (formal) |
тебе те вас ве (formal) |
тебе ти вас ви (formal) |
вие | вас ве | вас ви |
| 3. | тој (masculine) таа (feminine) тоа (neuter) |
него го (masc./neut.) неа ја (fem.) |
нему му (masc./neut.) нејзе ѝ (fem.) |
тие | нив ги | ним им |
Verbs
Macedonian verbs agree with the subject in person (first, second or third) and number (singular or plural). Some dependent verb constructions (нелични глаголски форми) such as verbal adjectives (глаголска придавка: плетен/плетена), verbal l-form (глаголска л-форма: играл/играла) and verbal noun (глаголска именка: плетење) also demonstrate gender. There are several other grammatical categories typical of Macedonian verbs, namely type, transitiveness, mood, superordinate aspect (imperfective/perfective aspect).[86] Verb forms can also be classified as simple, with eight possible verb constructions or complex with ten possible constructions.[79]
Macedonian has developed a grammatical category which specifies the opposition of witnessed and reported actions (also known as renarration). Per this grammatical category, one can distinguish between минато определено i.e. definite past, denoting events that the speaker witnessed at a given definite time point, and минато неопределено i.e. indefinite past denoting events that did not occur at a definite time point or events reported to the speaker, excluding the time component in the latter case. Examples: Но, потоа се случија работи за кои не знаев ("But then things happened that I did not know about") vs. Ми кажаа дека потоа се случиле работи за кои не знаев ("They told me that after, things happened that I did not know about").[87]
Tense
| Person | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | сум, бев, сум бил, ќе бидам | сме, бевме, сме биле, ќе бидеме |
| 2. | си, беше, си бил, ќе бидеш | сте, бевте, сте биле, ќе бидете |
| 3. | е, беше, бил, ќе биде | се, беа, биле, ќе бидат |
The present tense in Macedonian is formed by adding a suffix to the verb stem which is inflected per person, form and number of the subject. Macedonian verbs are conventionally divided into three main conjugations according to the thematic vowel used in the citation form (i.e. 3p-pres-sg).[74] These groups are: a-group, e-group and и-group. Furthermore, the и-subgroup is divided into three more subgroups: а-, е- and и-subgroups. The verb сум (to be) is the only exception to the rule as it ends with a consonant and is conjugated as an irregular verb.
The perfect tense can be formed using both to be (сум) and to have (има) as auxiliary verbs. The first form inflects the verb for person and uses a past active participle: сум видел многу работи ("I have seen a lot of things"). The latter form makes use of a clitic that agrees in number and gender with the object of the sentence and the passive participle of the verb in its uninflected form (го имам гледано филмот, "I have seen that movie").[41][86] Another past form, the aorist is used to describe actions that have finished at a given moment in the past: одев ("I walked"), скокаа ("they jumped").[79]
Future forms of verbs are conjugated using the particle ќе followed by the verb conjugated in present tense, ќе одам (I will go). The construction used to express negation in the future can be formed by either adding the negation particle at the beginning не ќе одам (I will not go) or using the construction нема да (нема да одам). There is no difference in meaning, although the latter form is more commonly used in spoken language. Another future tense is future in the past which is formed using the clitic ќе and the past tense of the verb inflected for person, таа ќе заминеше ("she would have left").[79]
Aspect, voice and mood
Similar to other Slavic languages, Macedonian verbs have a grammatical aspect (глаголски вид) that is a typical feature of Slavic languages. Verbs can be divided into imperfective (несвршени) and perfective (свршени) indicating actions whose time duration is unknown or occur repetitively or those that show an action that is finished in one moment. The former group of verbs can be subdivided into verbs which take place without interruption (e.g. Тој спие цел ден, "He sleeps all day long) or those that signify repeated actions (e.g. Ја бараше книгата но не можеше да ја најде, "He was looking for the book but he could not find it"). Perfective verbs are usually formed by adding prefixes to the stem of the verb, depending on which, they can express actions that took place in one moment (чукна, "knocked"), actions that have just begun (запеа, "start to sing"), actions that have ended (прочита, "read") or partial actions that last for short periods of time (поработи, "worked").[79]
The contrast between transitive and intransitive verbs can be expressed analytically or syntactically and virtually all verbs denoting actions performed by living beings can become transitive if a short personal pronoun is added: Тоj легна ("He laid down") vs. Тоj го легна детето ("He laid the child down"). Additionally, verbs which are expressed with the reflexive pronoun се can become transitive by using any of the contracted pronoun forms for the direct object: Тој се смее - He is laughing, vs. Тој ме смее - "He is making me laugh"). Some verbs such as sleep or die do not traditionally have the property of being transitive.[88]
Macedonian verbs have three grammatical moods (глаголски начин): indicative, imperative and conditional. The imperative mood can express both a wish or an order to finish a certain action. The imperative only has forms for the second person and is formed using the suffixes -ј (пеј; sing) or -и (оди, walk) for singular and -јте (пејте, sing) or -ете for plural (одете, walk). The first and third subject forms in singular and plural express indirect orders and are conjugated using да or нека and the verb in present tense (да живееме долго, may we live long). In addition to its primary functions, the imperative is used to indicate actions in the past, eternal truths as is the case in sayings and a condition. The Macedonian conditional is conjugated in the same way for all three persons using the particle би and the verbal l-form, би читал (I/you/he would read).[79]
Syntax
Macedonian syntax has a subject-verb-object (SVO) word order which is nevertheless flexible and can be topicalized.[71] For instance, the sentence Марија го сака Иван (Marija loves Ivan) can become of the object–verb–subject (OVS) form as well, Иван го сака Марија.[89] Topicalization can also be achieved using a combination of word order and intonation; as an example all of the following sentences give a different point of emphasis:
- Мачката ја каса кучето. – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on the object)
- Кучето мачката ја каса. – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on the object)
- Мачката кучето ја каса. – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on the subject)
- Ја каса кучето мачката. – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on both the subject and the verb)
- Ја каса мачката кучето. – The dog bites the cat (the focus is on the verb and the object)[90]
Macedonian is a null-subject language which means that the subject pronoun can be omitted, for instance Што сакаш (ти)? (what do you want?), (јас) читам книга (I am reading a book), (ние) го видовме (we saw him).[89] Macedonian passive construction is formed using the short reflexive pronoun се (девојчето се уплаши, the girl got scared) or a combination of the verb "to be" with verbal adjectives (Тој е миен, he is washed). In the former case, the active-passive distinction is not very clear.[88] Subordinate clauses in Macedonian are introduced using relativizers, which can be wh-question words or relative pronouns.[91] A glossed example of this is:
човек-от
person-DEF
со
with
кого(што)
whom(that)
се
ITR
шета-ше
stroll-3SG.IM
вчера
yesterday
the person with whom he walked yesterday[91]
Due to the absence of a case system, Macedonian makes wide use of prepositions (предлози) to express relationships between words in a sentence. The most important Macedonian preposition is на which can have local ('on') or motional meanings ('to').[92] As a replacement for the dative case, the preposition на is used in combination with a short indirect object form to denote an action that is related to the indirect object of a sentence, Му давам книга на Иван (I am giving a book to Ivan), Им велам нешто на децата (I am saying something to the children).[89] Additionally, на can serve to replace the genitive case and express possession, таткото на другар ми (my friend's father).[92]
Vocabulary

Macedonian exhibits lexical similarities with all other Slavic languages, and numerous nouns are cognates, including those related to familial relations and numbers.[80] Additionally, as a result of the close relationship with Bulgarian and Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian shares a considerable amount of its lexicon with these languages. Other languages that have been in positions of power, such as Ottoman Turkish and, increasingly, English have also provided a significant proportion of the loanwords. Prestige languages, such as Old Church Slavonic—which occupies a relationship to modern Macedonian comparable to the relationship of medieval Latin to modern Romance languages—and Russian also provided a source for lexical items. Other loanwords and vocabulary also came from Greek and Albanian as well as prestige languages such as French and German.[93][94]
During the standardization process, there was deliberate care taken to try to purify the lexicon of the language. Words that were associated with the Serbian or Bulgarian standard languages, which had become common due to the influence of these languages in the region, were rejected in favor of words from native dialects and archaisms. This is not to say that there are no words associated with the Serbian, Bulgarian, or even Russian standard languages in the language, but rather that they were discouraged on a principle of "seeking native material first".[95]
The language of the writers at the turn of the 19th century abounded with Russian and, more specifically, Old Church Slavonic lexical and morphological elements that in the contemporary norm have been replaced by native words or calqued using productive morphemes.[96] New words were coined according to internal logic and others calqued from related languages (especially Serbo-Croatian) to replace those taken from Russian, which include известие (Russ. известие) → извештај 'report', количество (Russ. количество) → количина 'amount, quantity', согласие (Russ. согласие) → слога 'concord, agreement', etc.[96] This change was aimed at bringing written Macedonian closer to the spoken language, effectively distancing it from the more Russified Bulgarian language, representing a successful puristic attempt to abolish a lexicogenic tradition once common in written literature.[96] The use of Ottoman Turkish loanwords is discouraged in the formal register when a native equivalent exists (e.g. комшија (← Turk. komşu) vs. сосед (← PSl. *sǫsědъ) 'neighbor'), and these words are typically restricted to the archaic, colloquial, and ironic registers.[97]
| English | Macedonian | Bulgarian | Serbian | Croatian | Slovenian | Russian | Belarusian | Ukrainian | Polish | Czech | Slovak |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dream | сон son |
сън sŭn |
сан san |
san | sen | сон son |
сон son |
сон son |
sen | sen | sen |
| day | ден den |
ден den |
дан dan |
dan | dan | день den' |
дзень dzień |
день den |
dzień | den | den |
| arm | рака raka |
ръка rŭka |
рука ruka |
ruka | roka | рука ruka |
рука ruka |
рука ruka |
ręka | ruka | ruka |
| flower | цвет cvet |
цвят tsvyat |
цвет cvet |
cvijet | cvet | цветок tsvetok |
кветка kvietka |
квітка kvitka |
kwiat | květ/květina | kvet/kvetina |
| night | ноќ nokj |
нощ nosht |
ноћ noć |
noć | noč | ночь noch' |
ноч noč |
нiч nich |
noc | noc | noc |
Writing system
Alphabet
The official Macedonian alphabet was codified on 5 May 1945 by the Presidium of the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (abbreviated as ASNOM in Macedonian) headed by Blaže Koneski.[99] There are several letters that are specific for the Macedonian Cyrillic script, namely ѓ, ќ, ѕ, џ, љ and њ,[61] with the last three letters being borrowed from the Serbo-Croatian phonetic alphabet adapted by Serbian linguist Vuk Stefanović Karadžić, while the grapheme ѕ has an equivalent in the Church Slavonic alphabet.[100] Letters љ and њ were previously used by Macedonian writer Krste Petkov Misirkov written as л' and н'.[99] The Macedonian alphabet also uses the apostrophe sign (') as a sound. It is used to mark the syllable forming /р˳/ , at the beginning of the word ('рж - rye, 'рбет - spine) and to represent the phoneme schwa in some literary words or Turkish loanwords ('к'смет - fortune). А grave accent (`) diacritic is used over three vowels in orthography: ѝ - her, different from и - and, нè - us, different from не - no and сѐ - everything different from сe - short reflexive pronoun accompanying reflexive verbs.[61] The standard Macedonian alphabet contains 31 letters. The following table provides the upper and lower case forms of the Macedonian alphabet, along with the IPA value for each letter:
| Cyrillic IPA |
А а /a/ |
Б б /b/ |
В в /v/ |
Г г /ɡ/ |
Д д /d/ |
Ѓ ѓ /ɟ/ |
Е е /ɛ/ |
Ж ж /ʒ/ |
З з /z/ |
Ѕ ѕ /d͡z/ |
И и /i/ |
| Cyrillic IPA |
Ј ј /j/ |
К к /k/ |
Л л /ɫ, l/[101] |
Љ љ /l/[101] |
М м /m/ |
Н н /n/ |
Њ њ /ɲ/ |
О о /ɔ/ |
П п /p/ |
Р р /r/ |
С с /s/ |
| Cyrillic IPA |
Т т /t/ |
Ќ ќ /c/ |
У у /u/ |
Ф ф /f/ |
Х х /x/ |
Ц ц /t͡s/ |
Ч ч /t͡ʃ/ |
Џ џ /d͡ʒ/ |
Ш ш /ʃ/ |
Orthography
Similar to the Macedonian alphabet, Macedonian orthography was officially codified on 7 June 1945 at an ASNOM meeting.[99] Rules about the orthography and orthoepy (correct pronunciation of words) were first collected and outlined in the book Правопис на македонскиот литературен јазик (Orthography of the Macedonian standard language) published in 1945. Updated versions have subsequently appeared with the most recent one published in 2016.[102] Macedonian orthography is consistent and phonemic in practice, an approximation of the principle of one grapheme per phoneme. This one-to-one correspondence is often simply described by the principle, "write as you speak and read as it is written".[71] There is only one exception to this rule with the letter /л/ which is pronounced as /l/ before front vowels (e.g. лист (leaf); pronounced as [list]) and /j/ (e.g. полјанка (meadow); pronounced as [poljanka]) but velar /ł/ elsewhere (e.g. бела (white) pronounced as [beła]). Another sound that is not represented in the written form but is pronounced in words is the schwa.[71]
Political views on the language
Politicians and scholars from North Macedonia, Bulgaria and Greece have opposing views about the existence and distinctiveness of the Macedonian language. Through history Macedonian has been referred mainly to as a variant of Bulgarian,[103] but especially during the first half of the 20th century also as Serbian,[104] and as a distinct language of its own.[105][106] Historically, after its codification, the use of the language has been a subject of different views and internal policies in Serbia, Bulgaria and Greece.[35][107] Some international scholars also maintain Macedo-Bulgarian was a single pluricentric language until the 20th century and argue that the idea of linguistic separatism emerged in the late 19th century with the advent of Macedonian nationalism and the need for a separate Macedonian standard language subsequently appeared in the early 20th century.[108] Different linguists have argued that during its codification, the Macedonian standard language was Serbianized with regards to its orthography[109][110][111][112][113] and vocabulary.[114]
The government of Bulgaria, Bulgarian academics, the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences and the general public have and continue to widely consider Macedonian part of the Bulgarian dialect area.[1][115][116] During the Communist era, Macedonian was recognized as a minority language in Bulgaria and utilized in education from 1946 to 1948. Subsequently, it was described as a dialect of Bulgarian.[117] In 1956 the Bulgarian government signed an agreement on mutual legal defense with Yugoslavia, where the Macedonian language is named as one of the languages to be used for legal purposes, together with Bulgarian, Serbo-Croatian and Slovenian.[118] The same year Bulgaria revoked its recognition of Macedonian nationhood and language and implicitly resumed its prewar position of their non-existence.[119] In 1999 the government in Sofia signed a Joint Declaration in the official languages of the two countries, marking the first time it agreed to sign a bilateral agreement written in Macedonian.[120] Dialect experts of the Bulgarian language refer to the Macedonian language as македонска езикова норма (Macedonian linguistic norm) of the Bulgarian language.[9] As of 2019, disputes regarding the language and its origins are ongoing in academic and political circles in the two countries.
The Greek scientific and local community opposed using the denomination Macedonian to refer to the language in light of the Greek-Macedonian naming dispute. Instead, the language is often called "Slavic", "Slavomacedonian" (translated to "Macedonian Slavic" in English), makedonski, makedoniski ("Macedonian"),[121] slaviká (Greek: "Slavic"), dópia or entópia (Greek: "local/indigenous [language]"),[122] balgàrtzki (Bulgarian) or "Macedonian" in some parts of the region of Kastoria,[123] bògartski ("Bulgarian") in some parts of Dolna Prespa[124] along with naši ("our own") and stariski ("old").[121] However, with the Prespa agreement signed in June 2018 and ratified by the Greek Parliament on 25 January 2019, Greece officially recognized the name "Macedonian" for the language.[125] Additionally, on 27 July 2022,[126] in a landmark ruling, the Centre for the Macedonian Language in Greece was officially registered as a non-governmental organization. This is the first time that a cultural organization promoting the Macedonian language has been legally approved in Greece and the first legal recognition of the Macedonian language in Greece since at least 1928.[127][128][129][130]
Sample text
The following is the Lord's Prayer in standard Macedonian.
|
|
See also
Notes
- ^ a b Macedonian at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

- ^ a b "Reservations and Declarations for Treaty No.148 – European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages". Council of Europe. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- ^ a b "European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages". Council of Europe. Archived from the original on 18 October 2015. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- ^ a b Nikolovski, Valentin (30 October 2016). "Македонците во Србија ги уживаат сите малцински права, како и србите во Македонија" [Macedonians in Serbia have all the minority rights just as Serbians in Macedonia] (in Macedonian). Sitel. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ Hupchick, Dennis P. (1995). Conflict and Chaos in Eastern Europe. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 143. ISBN 0312121164.
The obviously plagiarized historical argument of the Macedonian nationalists for a separate Macedonian ethnicity could be supported only by linguistic reality, and that worked against them until the 1940s. Until a modern Macedonian literary language was mandated by the communist-led partisan movement from Macedonia in 1944, most outside observers and linguists agreed with the Bulgarians in considering the vernacular spoken by the Macedonian Slavs as a western dialect of Bulgarian
- ^ Thornburg & Fuller 2006, p. 213.
- ^ https://www.britannica.com/topic/Slavic-languages/Grammatical-characteristics
- ^ Siewierska, Anna, and Ludmila Uhlirova. "An overview of word order in Slavic languages." Empirical approaches to language typology 20 (1998): 105-150.
- ^ a b Reimann 2014, p. 41.
- ^ Trudgill 1992.
- ^ Raúl Sánchez Prieto, Politics shaping linguistic standards: the case of Dutch in Flanders and Bulgaro-Macedonian in the Republic of Macedonia, in: Exploring linguistic standards in non-dominant varieties of pluricentric languages, ISBN 3631625839, pp.227-244; Peter Lang, with Carla Amoros Negre et al. as eds.
- ^ "5 мај – Ден на македонскиот јазик". Филолошки факултет "Блаже Конески" – Скопје (in Macedonian). Retrieved 7 January 2024.
- ^ "Од 130-тата седница на Владата на РСМ: 5 Мај прогласен за Ден на македонскиот јазик". Влада на Република Северна Македонија (in Macedonian). 16 April 2019. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ a b c Friedman, Garry & Rubino 2001, p. 435.
- ^ Levinson & O'Leary 1992, p. 239.
- ^ Dedaić & Mišković-Luković 2010, p. [page needed].
- ^ Kortmann & van der Auwera 2011, p. 420.
- ^ a b c Topolinjska 1998, p. 6.
- ^ Fortson 2009, p. 431.
- ^ Comrie & Corbett 2002, p. 245.
- ^ Campbell 2000, pp. 274, 1031.
- ^ Chambers, J.K.; Trudgill, Peter (1998), Dialectology (2nd ed., Cambridge Textbooks in Linguistics), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 169–170, doi:10.1017/CBO9780511805103, ISBN 9780521593786
- ^ Tomasz Kamusella, Motoki Nomachi, Catherine Gibson as ed., The Palgrave Handbook of Slavic Languages, Identities and Borders, Springer, 2016; ISBN 1137348399, p. 436.
- ^ a b Lindstedt, Jouko (2016). "Conflicting Nationalist Discourses in the Balkan Slavic Language Area". The Palgrave Handbook of Slavic Languages, Identities and Borders. pp. 429–447. doi:10.1007/978-1-137-34839-5_21. ISBN 978-1-349-57703-3.
Macedonian dialectology... considers the dialects of south-western Bulgaria to be Macedonian, despite the lack of any widespread Macedonian national consciousness in that area. The standard map is provided by Vidoeski.(1998: 32) It would be futile to tell an ordinary citizen of the Macedonian capital, Skopje, that they do not realise that they are actually speaking Bulgarian. It would be equally pointless to tell citizens of the southwestern Bulgarian town of Blagoevgrad that they (or at least their compatriots in the surrounding countryside) do not 'really' speak Bulgarian, but Macedonian. In other words, regardless of the structural and linguistic arguments put forth by a majority of Bulgarian dialectologists, as well as by their Macedonian counterparts, they are ignoring one, essential fact – that the present linguistic identities of the speakers themselves in various regions do not always correspond to the prevailing nationalist discourses.
- ^ Trudgill P., 2000, "Greece and European Turkey: From Religious to Linguistic Identity". In: Stephen Barbour and Cathie Carmichael (eds.), Language and Nationalism in Europe, Oxford : Oxford University Press, p.259.
- ^ Riki van Boeschoten is a retired professor of the University of Thessaly and director of the Laboratory of Social Anthropology and the Oral History Archive dialects in eastern Greek Macedonia. Riki van Boeschoten - My CV. , Her work (2013)
- ^ Boeschoten, Riki van (1993): Minority Languages in Northern Greece. Study Visit to Florina, Aridea, (Report to the European Commission, Brussels) "The Western dialect is used in Florina and Kastoria and is closest to the language used north of the border, the Eastern dialect is used in the areas of Serres and Drama and is closest to Bulgarian, the Central dialect is used in the area between Edessa and Salonica and forms an intermediate dialect"
- ^ Ioannidou, Alexandra (1999). Questions on the Slavic Dialects of Greek Macedonia. Athens: Peterlang. pp. 59, 63. ISBN 9783631350652.
In September 1993 ... the European Commission financed and published an interesting report by Riki van Boeschoten on the "Minority Languages in Northern Greece", in which the existence of a "Macedonian language" in Greece is mentioned. The description of this language is simplistic and by no means reflective of any kind of linguistic reality; instead it reflects the wish to divide up the dialects comprehensibly into geographical (i.e. political) areas. According to this report, Greek Slavophones speak the "Macedonian" language, which belongs to the "Bulgaro-Macedonian" group and is divided into three main dialects (Western, Central and Eastern) - a theory which lacks a factual basis.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Usikova 2005, p. 103.
- ^ Spasov, Ljudmil (2007). "Периодизација на историјата на македонскиот писмен јазик и неговата стандардизација во дваесеттиот век" [Periodization of the history of the Macedonian literary language and its standardization in the twentieth century]. Filološki Studii (in Macedonian). 5 (1). Skopje: St. Cyril and Methodius University: 229–235. ISSN 1857-6060.
- ^ Koneski, Blazhe (1967). Историја на македонскиот јазик [History of the Macedonian Language] (in Macedonian). Skopje: Kultura.
- ^ a b Browne, Wayles; Vsevolodovich Ivanov, Vyacheslav. "Slavic languages". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Archived from the original on 7 June 2020. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ Lunt 2001, p. 4.
- ^ Vidoeski 1999, p. 12.
- ^ a b c d e f Friedman, Garry & Rubino 2001, p. 436.
- ^ Usikova 2005, pp. 103, 106.
- ^ a b Friedman, Garry & Rubino 2001, p. 438.
- ^ Kramer 1999, p. 234.
- ^ a b c Kramer 1999, p. 235.
- ^ Bechev 2009, p. 134.
- ^ a b c Usikova 2005, p. 106.
- ^ Nihtinen 1999, p. 51.
- ^ Nihtinen 1999, p. 47.
- ^ Kramer 1999, p. 236.
- ^ Pejoska-Bouchereau 2008, p. 146.
- ^ "Повелба за македонскиот јазик" [Charter for the Macedonian language] (PDF) (in Macedonian). Skopje: Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts. 3 December 2019. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ "Ethnologue report for Macedonian". Ethnologue. 19 February 1999. Archived from the original on 1 September 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2014.
- ^ "Попис на населението, домаќинствата и становите во Република Македонија, 2002" [Census of the population, households and dwellings in the Republic of Macedonia, 2002] (PDF). Book X (in Macedonian and English). Skopje: Republic of Macedonia State Statistical Office. May 2005. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ Crvenkovska, Emilija; Petroska, Elena. "Македонскиот јазик како втор и странски: терминолошки прашања" [Macedonian as a foreign and second language: terminological questions] (PDF) (in Macedonian). Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 June 2012. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ Artan Hoxha; Alma Gurraj (2001). "Local Self-Government and Decentralization: Case of Albania. History, Reforms and Challenges". Local Self Government and Decentralization in South - East Europe (PDF). Proceedings of the workshop held in Zagreb, Croatia. 6 April 2001. Zagreb: Friedrich Ebert Stiftung. p. 219. Retrieved 7 August 2021.
- ^ "Население по етническа група и майчин език" [Population per ethnic group and mother tongue] (in Bulgarian). Bulgarian Census Bureau. 2011. Archived from the original on 19 December 2015. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ "2011 Census – Mother tongue". Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Archived from the original on 23 October 2014. Retrieved 20 January 2015.
- ^ Hill 1999, p. 19.
- ^ Poulton 2000, p. 167.
- ^ "Language spoken at home - Ranked by size". Profile ID. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ "Data tables, 2016 Census". Statistics Canada. 2 August 2017. Archived from the original on 20 February 2020. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ "Detailed Languages Spoken at Home and Ability to Speak English for the Population 5 Years and Over: 2009-2013". United States Census. Archived from the original on 12 April 2020. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ "Броj на македонски иселеници во светот" [Number of Macedonian immigrants in the world] (in Macedonian). Ministry of Foreign Affairs (North Macedonia). Archived from the original on 30 May 2008. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ^ Naumovski, Jaklina (25 January 2014). "Minorités en Albanie : les Macédoniens craignent la réorganisation territoriale du pays" (in French). Balkan Courriers. Archived from the original on 17 May 2014. Retrieved 16 May 2014.
- ^ "On the Status of the Minorities in the Republic of Albania" (PDF). Sofia: Albanian Helsinki Committee. 2000. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ^ a b c Usikova 2005, p. 105–106.
- ^ Friedman 1998, p. 33.
- ^ Dedaić & Mišković-Luković 2010, p. 13.
- ^ After Z. Topolińska and B. Vidoeski (1984), Polski-macedonski gramatyka konfrontatiwna, z.1, PAN.
- ^ Topolinjska 1998, p. 7.
- ^ a b c Usikova 2005, p. 111.
- ^ Usikova 2005, p. 104.
- ^ Comrie & Corbett 2002, p. 247.
- ^ Kolomiec, V.T.; Linik, T.G.; Lukinova, T.V.; Meljnichuk, А.S.; Pivtorak, G.P.; Sklyarenko, V.G.; Tkachenko, V.A.; Tkachenko, O.B (1986). Историческая типология славянских языков. Фонетика, слообразование, лексика и фразеология [Historical typology of Slavic languages] (in Ukrainian). Kiev: National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine.
- ^ Friedman 1998, p. 252.
- ^ a b c d e f g Friedman 2001.
- ^ a b Friedman 2001, p. 10.
- ^ Lunt 1952, pp. 10–11.
- ^ a b c d e f Bojkovska et al. 2008, p. [page needed].
- ^ a b c d Friedman 2001, p. 11.
- ^ Lunt 1952, pp. 11–12.
- ^ a b Usikova 2005, p. 109–110.
- ^ Friedman 2001, p. 13.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Bogdanoska 2008.
- ^ a b c Bojkovska et al. 2008, p. 43.
- ^ Friedman 2001, p. 40.
- ^ Friedman 2001, p. 23.
- ^ Minova Gjurkova, Liljana (1994). Синтакса на македонскиот стандарден јазик [Syntax of the standard Macedonian language] (in Macedonian).
- ^ Friedman 2001, p. 27.
- ^ Friedman, Garry & Rubino 2001, p. 437.
- ^ a b Friedman 2001, p. 33.
- ^ Friedman 2001, p. 43.
- ^ a b Usikova 2005, p. 117.
- ^ a b c Usikova 2005, p. 116.
- ^ Friedman 2001, p. 50.
- ^ a b Friedman 2001, p. 58.
- ^ a b Friedman 2001, p. 49.
- ^ Friedman 1998, p. 36.
- ^ Usikova 2005, p. 136.
- ^ Friedman 1998, p. [page needed].
- ^ a b c Т. Димитровски. Литературната лексика на македонскиот писмен јазик во XIX в. и нашиот однос кон неа: Реферати на македонските слависти за VI Меѓународен славистички конгрес во Прага, Скопје, 1968 (T. Dimitrovski. The literary vocabulary of the Macedonian written language in the 19th century and our attitude to it. Abstracts of Macedonian Slavists for the 6th International Slavic Studies Congress in Prague. Skopje, 1968)
- ^ Friedman 1998, p. 8.
- ^ Bojkovska et al. 2008, p. 44.
- ^ a b c "Со решение на АСНОМ: 72 години од усвојувањето на македонската азбука" [With the declaration of ASNOM: 72 years of the adoption of the Macedonian alphabet]. Javno (in Macedonian). 5 May 2017. Archived from the original on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Friedman 1993, p. 251.
- ^ a b ⟨л⟩ is pronounced /l/ before /e, i, j/, and /ɫ/ otherwise. ⟨љ⟩ is always pronounced /l/ but is not used before /e, i, j/. Cf. how the final љ in биљбиљ /ˈbilbil/ "nightingale" is changed to a л in the plural form биљбили /ˈbilbili/.
- ^ "Правописот на македонски јазик од денес бесплатно на интернет" [The orthography of the Macedonian language for free on the Internet from today]. sdk.mk. 7 December 2017. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ Institute of Bulgarian Language (1978). Единството на българския език в миналото и днес [The unity of the Bulgarian language in the past and today] (in Bulgarian). Sofia: Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. p. 4. OCLC 6430481.
- ^ Comrie & Corbett 2002, p. 251.
- ^ Adler 1980, p. 215.
- ^ Seriot 1997, pp. 270–271.
- ^ Kramer 1999, pp. 237–245.
- ^ Fishman 1993, p. 161–162.
- ^ Friedman 1998, p. 38.
- ^ Marinov, Tchavdar (25 May 2010). "Historiographical Revisionism and Re-Articulation of Memory in the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (PDF). Sociétés Politiques Comparées. 25: 7. S2CID 174770777. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 February 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^ Voss C., The Macedonian Standard Language: Tito—Yugoslav Experiment or Symbol of 'Great Macedonian' Ethnic Inclusion? in C. Mar-Molinero, P. Stevenson as ed. Language Ideologies, Policies and Practices: Language and the Future of Europe, Springer, 2016, ISBN 0230523889, p. 126.
- ^ De Gruyter as contributor. The Slavic Languages. Volume 32 of Handbooks of Linguistics and Communication Science (HSK), Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG, 2014, p. 1472. ISBN 3110215470.
- ^ Lerner W. Goetingen, Formation of the standard language - Macedonian in the Slavic languages, Volume 32, Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, 2014, ISBN 3110393689, chapter 109.
- ^ Voß 2018, p. 9.
- ^ "Bulgarian Academy of Sciences is firm that "Macedonian language" is Bulgarian dialect". Bulgarian National Radio. 12 November 2019. Archived from the original on 4 April 2020. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ^ Jakov Marusic, Sinisa (10 October 2019). "Bulgaria Sets Tough Terms for North Macedonia's EU Progress". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 11 December 2019. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ Ranko Bugarski, Celia Hawkesworth as editors, Language in the Former Yugoslav Lands, Slavica Publishers, 2004, ISBN 0893572985, p. 201.
- ^ "Agreement between Bulgaria and Yugoslavia for mutual legal defense". Държавен вестник No 16. 22 February 1957. Retrieved 13 January 2020.
- ^ Raymond Detrez, (2010) The A to Z of Bulgaria, Issue 223 of A to Z Guides, Edition 2, Scarecrow Press, 2010, ISBN 0810872021.
- ^ Kramer 1999.
- ^ a b Whitman 1994, p. 37.
- ^ "Report about Compliance with the Principles of the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities". Greek Helsinki Monitor. Archived from the original on 23 May 2003. Retrieved 12 January 2009.
- ^ Danforth 1995, p. 62.
- ^ Shklifov, Blagoy; Shklifova, Ekaterina (2003). Български деалектни текстове от Егейска Македония [Bulgarian dialect texts from Aegean Macedonia] (in Bulgarian). Sofia. pp. 28–36.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Republic of North Macedonia with Macedonian language and identity, says Greek media". Meta.mk. Meta. 12 June 2018. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- ^ "Judicial victory for the Macedonian language in Greece: The court in Lerin rejected the lawsuits to ban the Macedonian Language Center in Greece". Sloboden Pečat. 19 March 2023.
- ^ "Грција го регистрираше центарот за македонски јазик" [Greece Registered the Macedonian-language Center] (in Macedonian). Deutsche Welle. 29 November 2022.
- ^ ""Центарот на македонскиот јазик во Грција" официјално регистриран од судските власти" ["The Center of Macedonian language in Greece" officially registered by court laws] (in Macedonian). Sloboden Pecat. 29 November 2022.
- ^ "Εγκρίθηκε «Κέντρο Μακεδονικής Γλώσσας» στην Φλώρινα: Ευχαριστίες Ζάεφ σε Τσίπρα - Μητσοτάκη" ["Centre for Macedonian Language" was approved in Florina: Zaev thanks Tsipras - Mitsotakis] (in Greek). Ethnos. 29 November 2022. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ Mavrogordatos, George. Stillborn Republic: Social Coalitions and Party Strategies in Greece, 1922–1936. University of California Press, 1983. ISBN 9780520043589, p. 227, 247
References
- Books
- Adler, Max K. (1980), Marxist Linguistic Theory and Communist Practice: A Sociolinguistic Study, Buske Verlag, ISBN 3871184195
- Bechev, Dimitar (13 April 2009), Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia Historical Dictionaries of Europe, Scarecrow Press, ISBN 978-0-8108-6295-1
- Bogdanoska, Biljana (2008), За матуранти македонски јазик и литература [Macedonian language and literature for matura students] (in Macedonian), Skopje: Bomat Grafiks
- Bojkovska, Stojka; Minova-Gjurkova, Liljana; Pandev, Dimitar; Cvetanovski, Živko (2008), Општа граматика на македонскиот јазик [Grammar of the Macedonian language] (in Macedonian), Skopje: Prosvetno Delo, ISBN 9789989006623
- Campbell, George L. (2000), Compendium of the World's Languages, London: Routledge, ISBN 0415202965
- Comrie, Bernard; Corbett, Greville (2002), "The Macedonian language", The Slavonic Languages, New York: Routledge Publications
- Dedaić, Mirjana N.; Mišković-Luković, Mirjana (2010), South Slavic Discourse Particles, Pragmatics & Beyond New Series, vol. 197, Amsterdam: Benjamins, doi:10.1075/pbns.197, ISBN 978-90-272-5601-0
- Danforth, Loring M. (1995), The Macedonian conflict: ethnic nationalism in a transnational world, Princeton University Press, ISBN 0-691-04356-6
- Fishman, Joshua A. (1993), The Earliest Stage of Language Planning: The "First Congress" Phenomenon, Mouton De Gruyter, ISBN 3-11-013530-2
- Fortson, Benjamin W. (31 August 2009), Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction Blackwell textbooks in linguistics, John Wiley and Sons, ISBN 978-1-4051-8896-8
- Friedman, Victor (1993), "Macedonian", in Comrie B.; Corbett G. (eds.), The Slavonic Languages, London, New York: Routledge, pp. 249–305, ISBN 0-415-04755-2
- Friedman, Victor (2001), Macedonian, Slavic and Eurasian Language Resource Center (SEELRC), Duke University, archived from the original on 28 July 2014, retrieved 3 February 2006
- Friedman, Victor (2001), Garry, Jane; Rubino, Carl (eds.), Macedonian: Facts about the World's Languages: An Encyclopedia of the Worlds Major Languages, Past and Present (PDF), New York: Holt, pp. 435–439, archived (PDF) from the original on 10 July 2019, retrieved 18 March 2020
- Kortmann, Bernd; van der Auwera, Johan (27 July 2011), Languages and Linguistics of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide, Berlin/Boston: De Gruyter Mouton, ISBN 978-3-11-022025-4
- Levinson, David; O'Leary, Timothy (1992), Encyclopedia of World Cultures, G.K. Hall, ISBN 0-8161-1808-6
- Lunt, Horace G. (1952), A Grammar of the Macedonian Literary Language, Skopje: Državno knigoizdatelstvo
- Lunt, Horace Gray (2001), Old Church Slavonic Grammar, Walter de Gruyter, ISBN 3110162849
- Poulton, Hugh (2000), Who Are the Macedonians?, United Kingdom: C. Hurst & Co., ISBN 0-253-34598-7
- Reimann, Daniel (2014), Kontrastive Linguistik und Fremdsprachendidaktik Iberoromanisch (in German), Gunter Narr Verlag, ISBN 978-3823368250
- Thornburg, Linda L.; Fuller, Janet M. (2006), Studies in contact linguistics: Essays in Honor of Glenn G. Gilbert, New York: Peter Lung Publishing Inc., ISBN 978-0-8204-7934-7
- Topolińska, Zuzanna (1984), Polski-macedoński, gramatyka konfrontatywna: Zarys problematyki [Polish-Macedonian, confrontational grammar] (in Polish), Zakład Narodowy im. Ossolińskich, ISBN 978-8304016682
- Usikova, Rina Pavlovna (1994), О языковой ситуации в Республике Македонии [About the language situation in the Republic of Macedonia] (in Russian), Moscow: Nauka, pp. 221–231, ISBN 5-02-011187-2
- Usikova, Rina Pavlovna (2005), Языки мира. Славянские языки: Македонский язык [Languages of the world. Slavic languages: Macedonian language] (in Russian), Moscow: Academia, pp. 102–139, ISBN 5-87444-216-2
- Vidoeski, Bozhidar (1999), Дијалектите на македонскиот јазик: том 1 [The dialects of the Macedonian language: Book 1] (in Macedonian), MANU, ISBN 9989649634
- Whitman, Lois (1994), Denying ethnic identity: The Macedonians of Greece, New York: Helsinki Human Rights Watch, ISBN 1564321320
- Journal articles
- Hill, P. (1999), "Macedonians in Greece and Albania: A comparative study of recent developments", Nationalities Papers, 27 (1): 17, doi:10.1080/009059999109163, S2CID 154201780
- Friedman, Victor (1998), "The implementation of standard Macedonian: problems and results", International Journal of the Sociology of Language (131): 31–57, doi:10.1515/ijsl.1998.131.31, S2CID 143891784
- Kramer, Christina (1999), "Official Language, Minority Language, No Language at All: The History of Macedonian in Primary Education in the Balkans", Language Problems and Language Planning, 23 (3): 233–250, doi:10.1075/lplp.23.3.03kra
- Nihtinen, Atina (1999), "Language, Cultural Identity and Politics in the Cases of Macedonian and Scots", Slavonica, 5 (1): 46–58, doi:10.1179/sla.1999.5.1.46
- Pejoska-Bouchereau, Frosa (2008), "Histoire de la langue macédonienne" [History of the Macedonian language], Revue des études slaves (in French), pp. 145–161
- Seriot, Patrick (1997), "Faut-il que les langues aient un nom? Le cas du macédonien" [Do languages have to have a name? The case of Macedonian], in Tabouret-Keller, Andrée (ed.), Le nom des langues. L'enjeu de la nomination des langues (in French), vol. 1, Louvain: Peeters, pp. 167–190, archived from the original on 5 September 2001
- Topolinjska, Z. (1998), "In place of a foreword: facts about the Republic of Macedonia and the Macedonian language", International Journal of the Sociology of Language (131): 1–11, doi:10.1515/ijsl.1998.131.1, S2CID 143257269
- Trudgill, Peter (1992), "Ausbau sociolinguistics and the perception of language status in contemporary Europe", International Journal of Applied Linguistics, 2 (2): 167–177, doi:10.1111/j.1473-4192.1992.tb00031.x
- Voß, C (2018), "Linguistic emancipation within the Serbian mental map: The implementation of the Montenegrin and Macedonian standard languages", Aegean Working Papers in Ethnographic Linguistics, 2 (1): 1–16, doi:10.12681/awpel.20021
External links
- Институт за македонски јазик, "Крсте Петков Мисирков" – Institute for Macedonian language "Krste Misirkov", the main regulatory body of the Macedonian language (in Macedonian)
- Дигитален речник на македонскиот јазик – Online dictionary of the Macedonian language
- Institute for Macedonian language "Krste Misirkov" (2017), Правопис на македонскиот јазик [Orthography of the Macedonian language] (PDF) (2 ed.), Skopje: Kultura AD
- Kramer, Christina; Mitkovska, Liljana (2003), Macedonian: A Course for Beginning and Intermediate Students. (2nd ed.), University of Wisconsin Press, ISBN 978-0-299-18804-7
 Macedonian travel guide from Wikivoyage
Macedonian travel guide from Wikivoyage The dictionary definition of Macedonian language at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Macedonian language at Wiktionary Macedonian at Wikibooks
Macedonian at Wikibooks





