Lesser Sunda Islands: Difference between revisions
Burmesedays (talk | contribs) |
Baqotun0023 (talk | contribs) fixed |
||
| (265 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Group of islands in Indonesian Archipelago}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=April 2024}} |
|||
{{Infobox Islands |
{{Infobox Islands |
||
|name = Lesser Sunda Islands |
| name = Lesser Sunda Islands |
||
| map_image = Lesser Sunda Islands en.png |
|||
|image name = |
|||
| native_name = {{ubl|{{nativename|id|Kepulauan Sunda Kecil}}|{{nativename |tet|Illá Sunda ki'ik sirá}}|{{nativename |ban|ᬓᬧᬸᬮᭀᬯᬦ᭄ᬲᬸᬦ᭄ᬤᬘᬾᬦᬶᬓ᭄}}}} |
|||
|image caption = |
|||
| location = [[Southeast Asia]] |
|||
|locator map = NusaTenggara.png |
|||
| coordinates= {{coord|9|00|S|120|00|E|region:ID_type:isle}} |
|||
|native name = |
|||
| archipelago = [[Sunda Islands]] |
|||
|native name link = |
|||
| total_islands = 975 |
|||
|location = [[South East Asia]] |
|||
| major_islands = [[Bali]], [[Lombok]], [[Sumbawa]], [[Sumba]], [[Flores]], [[Timor]] |
|||
|coordinates= {{coord|9|00|S|120|00|E|region:ID_type:isle}} |
|||
| |
| highest_mount = [[Mount Rinjani]] |
||
| elevation_m = 3,726 |
|||
|total islands = |
|||
| ethnic_groups = [[Balinese people|Balinese]], [[Sasak people|Sasak]], [[Sumbawa people|Sumbawan]], [[Bimanese people|Bimanese]], [[Atoni]], [[Manggarai people|Manggaraian]], [[Sumba people|Sumbese]], [[Lamaholot people|Lamaholot]], Tetum, [[Mambai people (Timor)|Mambai]], [[Kemak people|Kemak]], [[Moluccans]], [[Alfur people|Alfur]], [[Javanese people|Javanese]], [[Bugis]], [[Bali Aga]]. |
|||
|major islands = |
|||
|area = |
|||
|highest mount = |
|||
|elevation = |
|||
|country = Indonesia |
|||
|country admin divisions title = Provinces |
|||
|country admin divisions = [[Bali]],<br>[[West Nusa Tenggara]],<br>[[East Nusa Tenggara]] |
|||
|country 1 = East Timor |
|||
|population = |
|||
|population as of = |
|||
|density = |
|||
|ethnic groups = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Contains special characters|Balinese|compact=yes}} |
|||
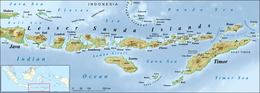
[[Image:Lesser Sunda Islands.png|thumb|upright|right|Map of Lesser Sunda Islands]] |
|||
[[Image:SundaIslands.A2003242.0225.500m.jpg|thumb|Satellite picture of the Lesser Sunda Islands]] |
|||
[[File:Lesser Sunda Islands.png|thumb|Map of Lesser Sunda Islands, east of Java]] |
|||
The '''Nusa Tenggara''' (lit. Southeast Islands), or '''Lesser Sunda Islands''', are a group of [[island]]s in the middle-south part of [[Maritime Southeast Asia]]. Together with the [[Greater Sunda Islands]] to the west they make up the [[Sunda Islands]]. The islands are part of a [[volcanic arc]], the [[Sunda Arc]], formed by [[subduction]] along the [[Java Trench]]. |
|||
[[File:SundaIslands.A2003242.0225.500m.jpg|thumb|Satellite picture of the Lesser Sunda Islands]] |
|||
The '''Lesser Sunda Islands''' ({{langx|id|Kepulauan Sunda Kecil}}, {{langx|tet|Illá Sunda ki'ik sirá}}, {{langx|ban|ᬓᬧᬸᬮᭀᬯᬦ᭄ᬲᬸᬦ᭄ᬤᬘᬾᬦᬶᬓ᭄|Kapuloan Sunda cénik}}), now known as '''Nusa Tenggara Islands''' ({{langx|id|Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara}}, or "Southeast Islands"),<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.sundamedia.com/2015/07/badak-sunda-dan-harimau-sunda.html |title=Badak Sunda dan Harimau Sunda. |publisher="[...] Mr. M. Yamin yang pada 1950-an ketika menjadi Menteri P.P. dan K. mengganti istilah Kepulauan Sunda Kecil menjadi Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara. Sebab, istilah Kepulauan Sunda Kecil diganti dengan Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, maka istilah Kepulauan Sunda Besar juga tidak lagi digunakan dalam ilmu bumi dan perpetaan nasional Indonesia – meskipun dalam perpetaan Internasional istilah Greater Sunda Islands dan Lesser Sunda Islands masih tetap digunakan." – [[Ajip Rosidi]]: Penulis, budayawan. [[Pikiran Rakyat]], 21 August 2010 |access-date=7 July 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150708065327/http://www.sundamedia.com/2015/07/badak-sunda-dan-harimau-sunda.html |archive-date=8 July 2015 |url-status=dead }}</ref> are an [[archipelago]] in [[Indonesian archipelago]]. Most of the Lesser Sunda Islands are located within the [[Wallacea]] region, except for the [[Bali]] province which is west of the [[Wallace Line]] and is within the [[Sunda Shelf]]. Together with the [[Greater Sunda Islands]] to the west, they make up the [[Sunda Islands]]. The islands are part of a [[volcanic arc]], the [[Sunda Arc]], formed by [[subduction]] along the [[Sunda Trench]] in the [[Java Sea]]. In 1930 the population was 3,460,059;<ref>{{cite book |last1= Nitisastro |first1= Widjojo |year= 2006 |chapter= |editor-last= |editor-first= |title= Population Trends in Indonesia |type= 1st publication 1970, Cornell University Press |publisher= Equinox Publishing |pages= 75 |isbn= 978-979-3780-43-6 |oclc= 86608 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=RQbd3-G6riUC&dq=Nusa+Tenggara+population+1930&pg=PA71 }}</ref> today slightly over 15.5 million people live on the islands. Etymologically, Nusa Tenggara means "Southeast Islands" from the words of ''nusa'' which means 'island' from [[Old Javanese language]] and ''tenggara'' means 'southeast'. |
|||
The main Lesser Sunda Islands are, from west to east: [[Bali]], [[Lombok]], [[Sumbawa]], [[Flores]], [[Sumba]], [[Savu]], [[Rote Island|Rote]], [[Timor]], [[Atauro]], [[Alor archipelago]], [[Barat Daya Islands]], and [[Tanimbar Islands]]. Apart from the eastern half of [[Timor]] island and [[Atauro]] island which constitute the nation of [[Timor Leste]], all the other islands are part of [[Indonesia]]. |
|||
== Partial list == |
|||
{{columns |col1 = |
|||
* [[Adonara]] |
|||
* [[Alor Island|Alor]] |
|||
* [[Bali]] |
|||
* [[Flores]] |
|||
* [[Komodo (island)|Komodo]] |
|||
* [[Lombok]] |
|||
* [[Nusa Ceningan]] |
|||
* [[Nusa Lembongan]] |
|||
* [[Nusa Penida]] |
|||
|col2 = |
|||
* [[Palu'e]] |
|||
* [[Pantar]] |
|||
* [[Rote (island)|Rote]] |
|||
* [[Solor]] |
|||
* [[Sangeang]] |
|||
* [[Savu]] |
|||
* [[Sumba]] |
|||
* [[Sumbawa]] |
|||
* [[Timor]] |
|||
}} |
|||
== |
== Geology == |
||
The Lesser Sunda Islands consist of two geologically distinct archipelagos.<ref name="Audley-Charles">{{cite book |last1= Audley-Charles |first1= Michael Geoffrey |year= 1987 |chapter= Dispersal of Gondwanaland: relevance to evolution of the Angiosperms |editor-last= Whitmore |editor-first= T.C. |title= Biogeographical Evolution of the Malay Archipelago |type= International Congress of Systematic and Evolutionary Biology |series= Oxford Monographs on Biogeography 4 |location= Oxford and New York |publisher= Oxford University Press, Clarendon Press |pages= 5–25 |isbn= 0-19-854185-6 |oclc= 14692633 }}</ref> The northern archipelago, which includes [[Bali]], [[Lombok]], [[Sumbawa]], [[Flores]] and [[Wetar]], is volcanic in origin. A number of these [[volcano]]es, like [[Mount Rinjani]] on Lombok, are still active while others, such as Ilikedeka on Flores, are extinct. The northern archipelago began to be formed during the [[Pliocene]], about 15 million years ago, as a result of the collision between the [[Indo-Australian Plate|Australian]] and the [[Eurasian Plate|Asian plates]].<ref name="Audley-Charles"/> The islands of the southern archipelago, including [[Sumba]], [[Timor]] and [[Babar Islands|Babar]], are non-volcanic and appear to belong to the [[Indo-Australian Plate|Australian plate]].<ref>{{cite journal |last1= Veevers |first1= J.J. |author-link1= John Veevers |date= 1991 |title= Phanerozoic Australia in the changing configuration of ProtoPangea through Gondwanaland and Pangea to the present dispersed continents |journal= Australian Systematic Botany |volume= 4 |issue= 1 |pages= 1–11 |doi= 10.1071/SB9910001 }}</ref> The geology and ecology of the northern archipelago share similar history, characteristics, and processes with the southern [[Maluku Islands]], which continue the same island arc to the east. |
|||
There is a long history of geological study of these regions since [[Dutch East Indies|Indonesian colonial times]]; however, the geological formation and progression is not fully understood, and theories of the geological evolution of the islands changed extensively during the last decades of the 20th century.{{sfn|Monk|Fretes|Reksodiharjo-Lilley|1996|p=9}} |
|||
They are split into the independent state of [[East Timor]] (Timor-Leste) and the [[Indonesia]]n [[Provinces of Indonesia|provinces]] of [[Bali]], [[West Nusa Tenggara]] (Nusa Tenggara Barat) and [[East Nusa Tenggara]] (Nusa Tenggara Timur). |
|||
Lying at the collision of two [[Plate tectonics|tectonic plates]], the Lesser Sunda Islands comprise some of the most geologically complex and active regions in the world. The province of [[Bali]] is the only part of Nusa Tenggara located on the [[Sunda Shelf]] and that is not within the [[Wallacea]] region and that is west of the [[Wallace Line]].{{sfn|Monk|Fretes|Reksodiharjo-Lilley|1996|p=9}} |
|||
==Geology and ecology== |
|||
The Lesser Sunda Islands consist of two geologically distinct archipelagos.<ref name="Audley-Charles">Audley-Charles, M.G. (1987) "Dispersal of Gondwanaland: relevance to evolution of the Angiosperms" ''In'': Whitmore, T.C. (ed.) (1987) ''Biogeographical Evolution of the Malay Archipelago'' Oxford Monographs on Biogeography 4, Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp. 5–25, ISBN 0-19-854185-6</ref> The northern archipelago, which includies [[Bali]], [[Lombok]], [[Sumbawa]], [[Flores]] and [[Wetar]], is volcanic in origin. It began to be formed during the [[Pliocene]], about 15 million years ago, as a result of the collision between the [[Indo-Australian Plate|Australian]] and the [[Eurasian Plate|Asian plates]].<ref name="Audley-Charles"/> The islands of the southern archipelago, including [[Sumba]], [[Timor]] and [[Babar Islands|Babar]], are non-volcanic and appear to belong to the [[Indo-Australian Plate|Australian plate]].<ref>Veevers, J.J. (1991) "Phanerozoic Australia in the changing configuration of ProtoPangea through Gondwanaland and Pangea to the present dispersed continents" ''Australian Systematic Botany'' 4: pp. 1–11</ref> The geology and ecology of the northern archipelago share a similar history, characteristics and processes with the southern [[Maluku Islands]], which continue the same island arc to the east. |
|||
There are a number of volcanoes located on the Lesser Sunda Islands.<ref>{{cite web |title= Indonesia Volcanoes |website= volcano.si.edu |publisher= Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History |agency= Global Volcanism Program |url= https://volcano.si.edu/volcanolist_countries.cfm?country=Indonesia |access-date= 7 June 2024 }};<br>{{cite web |title= Holocene Volcano List |website= volcano.si.edu |url= https://volcano.si.edu/volcanolist_holocene.cfm |access-date= 7 June 2024 }}</ref> |
|||
There is a long history of geological study of these regions since [[Dutch East Indies|Indonesian colonial times]]; however, the geological formation and progression is not fully understood, and theories of the geological evolution of the islands changed extensively during the last decades of the 20th century.<ref name="Monk 1996, page 9">{{cite book |last=Monk, |first=K.A. |coauthors=Fretes, Y., Reksodiharjo-Lilley, G. |title=The Ecology of Nusa Tenggara and Maluku |publisher=Periplus Editions Ltd. |year=1996 |page=9|location=Hong Kong |isbn=962-593-076-0}}</ref> |
|||
== Ecology == |
|||
Lying at the collision of two [[Plate tectonics|tectonic plates]], the Lesser Sunda Islands comprise some of the most geologically complex and active regions in the world.<ref name="Monk 1996, page 9"/> Biodiversity and distribution is affected by various tectonic activities. The islands of the northern archipelago are geologically young being from 1 to 15 million years old, and have never been attached to a larger land mass. |
|||
The Lesser Sunda Islands differ from the large islands of [[Java]] or [[Sumatra]] in consisting of many small islands, sometimes divided by deep [[oceanic trench]]es. Movement of flora and fauna between islands is limited, leading to the evolution of a high rate of localized species, most famously the [[Komodo dragon]].{{sfn|Monk|Fretes|Reksodiharjo-Lilley|1996|p=9}} As described by [[Alfred Wallace]] in ''[[The Malay Archipelago]]'', the [[Wallace Line]] passes between Bali and Lombok, along the deep waters of the [[Lombok Strait]] which formed a water barrier even when lower sea levels linked the now-separated islands and landmasses on either side. The islands east of the Lombok Strait are part of [[Wallacea]], and are thus characterised by a blend of wildlife of [[Asia]]n and [[Australasia]]n origin in this region.{{sfn|Monk|Fretes|Reksodiharjo-Lilley|1996|p=4}} Asian species predominate in the Lesser Sundas: [[Max Carl Wilhelm Weber|Weber's Line]], which marks the boundary between the parts of Wallacea with mainly Asian and Australasian species respectively, runs to the east of the group. These islands have the driest climate in Indonesia, and [[tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests|tropical dry broadleaf forests]] are predominant, in contrast to the [[tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests|tropical moist forests]] that prevail in most of Indonesia. |
|||
=== Ecoregions === |
|||
The Lesser Sunda Islands differ from the large islands of [[Java]] or [[Sumatra]] containing many small islands as well as deep [[oceanic trench]]es. Flora and fauna immigration between islands is restricted, leading to the evolution of a high rate of localized species.<ref name="Monk 1996, page 9"/> The [[Wallace Line]] passes through the islands between Bali and Lombok, along the deep waters of the [[Lombok Strait]] which formed a water barrier even when lower sea levels linked the now-separated islands and landmasses on either side. [[Alfred Wallace]]'s famous book, ''[[The Malay Archipelago]]'' was the first significant recording of this natural history, and remains one of the most important sources on Indonesian natural history.<ref>Monk (1996), page 4</ref> |
|||
The Lesser Sunda Islands are divided among six ecoregions:<ref>{{cite book |last1= Wikramanayake |first1= Eric |last2= Dinerstein |first2= Eric |last3= Loucks |first3= Colby J. |last4= Olson |first4= David M. |last5= Morrison |first5= John |last6= Lamoreaux |first6= John |last7= McKnight |first7= Meghan |year= 2002 |title= Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a Conservation Assessment |type= |location= Washington, DC |publisher= Island Press |pages= |isbn= 9781559639231 |oclc= 48435361 }}</ref> |
|||
* The [[Eastern Java-Bali rain forests]] and [[Eastern Java-Bali montane rain forests]] cover [[Bali]], which is the only of the Lesser Sunda Islands in the [[Indomalayan realm]], and not part of Wallacea. Bali was once attached to the Asian continent (see [[Sundaland]]), and home to large Asiatic mammals like [[Asian elephant]]s and the extinct [[Bali tiger]]. |
|||
* The [[Lesser Sundas deciduous forests]] include the northern chain of islands, from Lombok and Sumbawa east to Flores and Alor. The higher slopes of the islands contain forests of tall ''[[Podocarpus]]'' conifers and [[Engelhardia]]s with an undergrowth of [[liana]]s, [[epiphyte]]s, and orchids such as ''[[Corybas (plant)|Corybas]]'', ''[[Corymborkis]]'', and ''[[Malaxis]]'' (adder's mouth), while the coastal plains were originally [[savanna]] grasses such as the savanna with [[Borassus flabellifer]] palm trees on the coasts of Komodo, Rincah and Flores. Although most of the vegetation on these islands is dry forest there are patches of rainforest on these islands too, especially in lowland areas and riverbanks on Komodo, and there is a particular area of dry thorny forest on the southeast coast of Lombok. Thorn trees used to be more common in coastal areas of the islands but have largely been cleared. These islands are home to unique species including seventeen endemic birds (of the 273 birds found on the islands). The endemic mammals are the endangered Flores shrew ''([[Suncus mertensi]])'', the vulnerable Komodo rat ''([[Komodomys rintjanus]])'', and Lombok flying fox ''([[Pteropus lombocensis]])'', Sunda long-eared bat ''([[Nyctophilus heran]])'' while the carnivorous Komodo dragon, which at three metres long and ninety kilograms in weight is the world's largest lizard, is found on Komodo, Rincah, Gili Motang, and the coast of northwestern Flores. |
|||
* The [[Sumba deciduous forests]] ecoregion includes [[Sumba]]. |
|||
* The [[Timor and Wetar deciduous forests]] ecoregion includes Timor, [[Wetar]] (actually in [[Maluku (province)|Maluku]] Province), [[Rote Island|Rote]], and [[Savu]]. |
|||
* The more humid [[Banda Sea Islands moist deciduous forests]] ecoregion includes the Barat Daya Islands (except for Wetar), the [[Tanimbar Islands]], and the [[Kai Islands]]. |
|||
=== Threats and preservation === |
|||
While many ecological problems affect both small islands and large landmasses, small islands suffer their particular problems and are highly exposed to external forces. Development pressures on small islands are increasing, although their effects are not always anticipated. Although Indonesia is richly endowed with natural resources, the resources of the small islands of Nusa Tenggara are limited and specialised; furthermore human resources in particular are limited.<ref name="Monk 1996, page 1">Monk (1996), page 1</ref> |
|||
More than half of the original vegetation of the islands has been cleared for planting of rice and other crops, for settlement and by consequent forest fires. Only Sumbawa now contains a large area of intact natural forest, while Komodo, Rincah and Padar are now protected as [[Komodo National Park]]. |
|||
While many ecological problems affect both small islands and large landmasses, small islands suffer their particular problems and are highly exposed to external forces. Development pressures on small islands are increasing, although their effects are not always anticipated. Although Indonesia is richly endowed with natural resources, the resources of the small islands of Nusa Tenggara are limited and specialised; furthermore human resources in particular are limited.{{sfn|Monk|Fretes|Reksodiharjo-Lilley|1996|p=1}} |
|||
General observations<ref>Beller, W., P. d'Ayala, and P. Hein. 1990. ''Sustainable development and environmental management of small islands.'' Paris and New Jersey: United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation and Parthenon Publishing Group Inc.; Hess, A, 1990. Overview: sustainable development and environmental management of small islands. In ''Sustainable development and environmental management of small islands.'' eds W. Beller, P. d'Ayala, and P. Hein, Paris and New Jersey: United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation and Parthenon Publishing Group Inc. (both cited in Monk)</ref> about small islands that can be applied to Nusa Tenggara include:<ref name="Monk 1996, page 1"/> |
|||
* a higher proportion of the landmass will be affected by [[List of volcanoes in Indonesia|volcanic activity]], earthquakes, landslips, and cyclone damage; |
|||
General observations<ref>{{cite book |last1= Beller |first1= William S. |last2= D'Ayala |first2= Pier Giovanni |last3= Hein |first3= Philippe |year= 1990 |title= Sustainable development and environmental management of small islands |type= Papers from the Interoceanic Workshop on Sustainable Development and Environmental Management of Small Islands, Puerto Rico, Nov. 3-7, 1986 |location= Paris, Carnforth (England) and Park Ridge (N.J.) |publisher= [[United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation|UNESCO]] and Parthenon Publishing Group Inc. |series= Man and the biosphere (5) |pages= |oclc= 21044238 |url= }}; including Hess, Allison L., 1990. "Overview: Sustainable Development and Environmental Management of Small Islands". (both cited in {{harvnb|Monk|Fretes|Reksodiharjo-Lilley|1996|p=}})</ref> about small islands that can be applied to Nusa Tenggara include:{{sfn|Monk|Fretes|Reksodiharjo-Lilley|1996|p=1}} |
|||
* A higher proportion of the landmass will be affected by [[List of volcanoes in Indonesia|volcanic activity]], earthquakes, landslips, and cyclone damage; |
|||
* Climates are more likely to be [[maritime climate|maritime]] influenced; |
* Climates are more likely to be [[maritime climate|maritime]] influenced; |
||
* [[Catchment area]]s are smaller and degree of [[erosion]] higher; |
* [[drainage basin|Catchment area]]s are smaller and degree of [[erosion]] higher; |
||
* A higher proportion of the landmass is made up of coastal areas; |
* A higher proportion of the landmass is made up of coastal areas; |
||
* A higher degree of environmental specialisation, including a higher proportion of [[Endemism|endemic]] species in an overall [[depauperate]] community; |
* A higher degree of environmental specialisation, including a higher proportion of [[Endemism|endemic]] species in an overall [[depauperate]] community; |
||
* Societies may retain a strong sense of culture |
* Societies having developed in relative isolation may retain a strong sense of culture; |
||
* Small island populations are more likely to be affected by economic migration. |
* Small island populations are more likely to be affected by economic migration. |
||
<gallery mode="packed"> |
|||
==References== |
|||
File:Palau Banta Nusa Tenggara Barat Indonesia.jpg|Banta Island of Lesser Sunda Islands |
|||
* {{cite book |last=Monk |first=K.A. |coauthors=Fretes, Y., Reksodiharjo-Lilley, G. |title=The Ecology of Nusa Tenggara and Maluku |publisher=Periplus Editions Ltd. |year=1996 |location=Hong Kong |isbn=962-593-076-0}} |
|||
File:Rinca Island.jpg|[[Rinca]] island |
|||
File:Komodo dragon at Komodo National Park.jpg|[[Komodo dragon]] at Komodo National Park |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== Administration == |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
The Lesser Sundas comprise many islands stretching east of [[Java]], most of which are part of [[Indonesia]] and from 1945 were administered (apart from the easternmost islands which have been always administered as part of [[Maluku (province)|Maluku]] Province) as the Lesser Sunda Islands (''Sunda Kecil'') Province of Indonesia, later called Nusa Tenggara. In 1958 this was split into three new provinces, as the [[provinces of Indonesia|provinces]] of [[Bali]], [[West Nusa Tenggara]] and [[East Nusa Tenggara]]. |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
The eastern half of [[Timor]] Island is the separate nation of [[East Timor]] (officially Timor Leste}. |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
===Religion=== |
|||
{{Pie chart |
|||
|thumb = right |
|||
|caption = Religion in Lesser Sunda Islands (December 2023)<ref name="RELIGION">{{cite web|url=https://satudata.kemenag.go.id/dataset/detail/jumlah-penduduk-menurut-agama|title=Jumlah Penduduk Menurut Agama|publisher=[[Ministry of Religious Affairs (Indonesia)|Ministry of Religious Affairs]]|date=31 August 2022|access-date=29 October 2023|language=id|quote=Muslim 241 Million (87), Christianity 29.1 Million (10.5), Hindu 4.69 million (1.7), Buddhist 2.02 million (0.7), Folk, Confucianism, and others 192.311 (0.1), Total 277.749.673 Million}}</ref> |
|||
|label1 = [[Islam]] |
|||
|value1 = 41.20 |
|||
|color1 = DarkGreen |
|||
|label2 = [[Hinduism]] |
|||
|value2 = 25.05 |
|||
|color2 = DarkOrange |
|||
|label3 = [[Roman Catholicism]] |
|||
|value3 = 19.65 |
|||
|color3 = DarkBlue |
|||
|label4 = [[Protestantism]] |
|||
|value4 = 13.59 |
|||
|color4 = SkyBlue |
|||
|label5 = [[Buddhism]] |
|||
|value5 = 0.30 |
|||
|color5 = Yellow |
|||
|label6 = [[Folk religion]] |
|||
|value6 = 0.20 |
|||
|color6 = Black |
|||
|label7 = [[Confucianism]] |
|||
|value7 = 0.004 |
|||
|color7 = Red |
|||
}} |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
{{portal|Indonesia}} |
|||
* [[Apostolic Vicariate of Lesser Sunda Islands]] (originally an Apostolic Prefecture) |
|||
* [[Banda Arc]] |
|||
* [[Greater Sunda Islands]] |
* [[Greater Sunda Islands]] |
||
* [[List of islands of Indonesia]] |
|||
* [[Malay Archipelago]] |
|||
* [[List of rivers of Lesser Sunda Islands]] |
|||
* [[Oceanic trench]] |
|||
* [[Plate tectonics]] |
|||
* [[Sunda Arc]] |
|||
* [[Sundaland]] |
|||
* [[Sunda Shelf]] |
|||
* [[Sunda Trench]] |
|||
{{clr}} |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
== Bibliography == |
|||
==External links== |
|||
* {{cite book |last1= Monk |first1= Kathryn A. |last2= Fretes |first2= Yance De |last3= Reksodiharjo-Lilley |first3= Gayatri |year= 1996 |title= The Ecology of Nusa Tenggara and Maluku |location= Hong Kong |publisher= Periplus Editions Ltd. |page= |isbn= 962-593-076-0 |oclc= 835572307 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=sQ7RAgAAQBAJ }} |
|||
* {{wikitravel}} |
|||
== External links == |
|||
{{portal|Indonesia}} |
|||
* {{Wikivoyage inline}} |
|||
*[https://lexirumah.model-ling.eu/lexirumah/ LexiRumah] (part of the [http://www.model-ling.eu/ Lesser Sunda linguistic databases]) |
|||
*[https://vici.marianklamer.org/ Reconstructing the past through languages of the present: the Lesser Sunda Islands] |
|||
{{Provinces of Indonesia}} |
|||
[[Category:Lesser Sunda Islands| ]] |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[bs:Mala Sundska ostrva]] |
|||
[[bg:Малки Зондски острови]] |
|||
[[Category:Lesser Sunda Islands| ]] |
|||
[[cs:Malé Sundy]] |
|||
[[Category:Archipelagoes of Indonesia]] |
|||
[[cy:Ynysoedd Swnda Lleiaf]] |
|||
[[Category:Archipelagoes of Southeast Asia]] |
|||
[[de:Kleine Sunda-Inseln]] |
|||
[[Category:International archipelagoes]]<!--East Timor & Indonesia--> |
|||
[[et:Väikesed Sunda saared]] |
|||
[[Category:Maritime Southeast Asia]] |
|||
[[es:Islas menores de la Sonda]] |
|||
[[Category:Tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests]] |
|||
[[eu:Sondako uharte txikiak]] |
|||
[[Category:Volcanic arc islands]] |
|||
[[fa:جزایر سوندای کوچک]] |
|||
[[Category:Wallacea]] |
|||
[[fr:Petites îles de la Sonde]] |
|||
[[gl:Illas menores da Sonda]] |
|||
[[ko:소순다 열도]] |
|||
[[hr:Mali sundski otoci]] |
|||
[[id:Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara]] |
|||
[[it:Piccole Isole della Sonda]] |
|||
[[pam:Lesser Sunda Islands]] |
|||
[[lt:Mažosios Sundos salos]] |
|||
[[lmo:Nusa Tenggara]] |
|||
[[ms:Kepulauan Sunda Kecil]] |
|||
[[mn:Бага Зондын арлууд]] |
|||
[[nl:Kleine Soenda-eilanden]] |
|||
[[ja:小スンダ列島]] |
|||
[[pms:Cite Ìsole dla Sonda]] |
|||
[[pl:Małe Wyspy Sundajskie]] |
|||
[[pt:Pequenas Ilhas da Sonda]] |
|||
[[ru:Малые Зондские острова]] |
|||
[[sk:Malé Sundy]] |
|||
[[su:Kapuloan Sunda Alit]] |
|||
[[fi:Pienet Sundasaaret]] |
|||
[[sv:Små Sundaöarna]] |
|||
[[vi:Quần đảo Nusa Tenggara]] |
|||
[[zh:小巽他群岛]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 04:30, 19 December 2024
Native name:
| |
|---|---|
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 9°00′S 120°00′E / 9.000°S 120.000°E |
| Archipelago | Sunda Islands |
| Total islands | 975 |
| Major islands | Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, Timor |
| Highest elevation | 3,726 m (12224 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Rinjani |
| Demographics | |
| Ethnic groups | Balinese, Sasak, Sumbawan, Bimanese, Atoni, Manggaraian, Sumbese, Lamaholot, Tetum, Mambai, Kemak, Moluccans, Alfur, Javanese, Bugis, Bali Aga. |

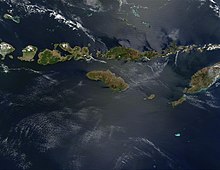
The Lesser Sunda Islands (Indonesian: Kepulauan Sunda Kecil, Tetum: Illá Sunda ki'ik sirá, Balinese: ᬓᬧᬸᬮᭀᬯᬦ᭄ᬲᬸᬦ᭄ᬤᬘᬾᬦᬶᬓ᭄, romanized: Kapuloan Sunda cénik), now known as Nusa Tenggara Islands (Indonesian: Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, or "Southeast Islands"),[1] are an archipelago in Indonesian archipelago. Most of the Lesser Sunda Islands are located within the Wallacea region, except for the Bali province which is west of the Wallace Line and is within the Sunda Shelf. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west, they make up the Sunda Islands. The islands are part of a volcanic arc, the Sunda Arc, formed by subduction along the Sunda Trench in the Java Sea. In 1930 the population was 3,460,059;[2] today slightly over 15.5 million people live on the islands. Etymologically, Nusa Tenggara means "Southeast Islands" from the words of nusa which means 'island' from Old Javanese language and tenggara means 'southeast'.
The main Lesser Sunda Islands are, from west to east: Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, Savu, Rote, Timor, Atauro, Alor archipelago, Barat Daya Islands, and Tanimbar Islands. Apart from the eastern half of Timor island and Atauro island which constitute the nation of Timor Leste, all the other islands are part of Indonesia.
Geology
[edit]The Lesser Sunda Islands consist of two geologically distinct archipelagos.[3] The northern archipelago, which includes Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores and Wetar, is volcanic in origin. A number of these volcanoes, like Mount Rinjani on Lombok, are still active while others, such as Ilikedeka on Flores, are extinct. The northern archipelago began to be formed during the Pliocene, about 15 million years ago, as a result of the collision between the Australian and the Asian plates.[3] The islands of the southern archipelago, including Sumba, Timor and Babar, are non-volcanic and appear to belong to the Australian plate.[4] The geology and ecology of the northern archipelago share similar history, characteristics, and processes with the southern Maluku Islands, which continue the same island arc to the east.
There is a long history of geological study of these regions since Indonesian colonial times; however, the geological formation and progression is not fully understood, and theories of the geological evolution of the islands changed extensively during the last decades of the 20th century.[5]
Lying at the collision of two tectonic plates, the Lesser Sunda Islands comprise some of the most geologically complex and active regions in the world. The province of Bali is the only part of Nusa Tenggara located on the Sunda Shelf and that is not within the Wallacea region and that is west of the Wallace Line.[5]
There are a number of volcanoes located on the Lesser Sunda Islands.[6]
Ecology
[edit]The Lesser Sunda Islands differ from the large islands of Java or Sumatra in consisting of many small islands, sometimes divided by deep oceanic trenches. Movement of flora and fauna between islands is limited, leading to the evolution of a high rate of localized species, most famously the Komodo dragon.[5] As described by Alfred Wallace in The Malay Archipelago, the Wallace Line passes between Bali and Lombok, along the deep waters of the Lombok Strait which formed a water barrier even when lower sea levels linked the now-separated islands and landmasses on either side. The islands east of the Lombok Strait are part of Wallacea, and are thus characterised by a blend of wildlife of Asian and Australasian origin in this region.[7] Asian species predominate in the Lesser Sundas: Weber's Line, which marks the boundary between the parts of Wallacea with mainly Asian and Australasian species respectively, runs to the east of the group. These islands have the driest climate in Indonesia, and tropical dry broadleaf forests are predominant, in contrast to the tropical moist forests that prevail in most of Indonesia.
Ecoregions
[edit]The Lesser Sunda Islands are divided among six ecoregions:[8]
- The Eastern Java-Bali rain forests and Eastern Java-Bali montane rain forests cover Bali, which is the only of the Lesser Sunda Islands in the Indomalayan realm, and not part of Wallacea. Bali was once attached to the Asian continent (see Sundaland), and home to large Asiatic mammals like Asian elephants and the extinct Bali tiger.
- The Lesser Sundas deciduous forests include the northern chain of islands, from Lombok and Sumbawa east to Flores and Alor. The higher slopes of the islands contain forests of tall Podocarpus conifers and Engelhardias with an undergrowth of lianas, epiphytes, and orchids such as Corybas, Corymborkis, and Malaxis (adder's mouth), while the coastal plains were originally savanna grasses such as the savanna with Borassus flabellifer palm trees on the coasts of Komodo, Rincah and Flores. Although most of the vegetation on these islands is dry forest there are patches of rainforest on these islands too, especially in lowland areas and riverbanks on Komodo, and there is a particular area of dry thorny forest on the southeast coast of Lombok. Thorn trees used to be more common in coastal areas of the islands but have largely been cleared. These islands are home to unique species including seventeen endemic birds (of the 273 birds found on the islands). The endemic mammals are the endangered Flores shrew (Suncus mertensi), the vulnerable Komodo rat (Komodomys rintjanus), and Lombok flying fox (Pteropus lombocensis), Sunda long-eared bat (Nyctophilus heran) while the carnivorous Komodo dragon, which at three metres long and ninety kilograms in weight is the world's largest lizard, is found on Komodo, Rincah, Gili Motang, and the coast of northwestern Flores.
- The Sumba deciduous forests ecoregion includes Sumba.
- The Timor and Wetar deciduous forests ecoregion includes Timor, Wetar (actually in Maluku Province), Rote, and Savu.
- The more humid Banda Sea Islands moist deciduous forests ecoregion includes the Barat Daya Islands (except for Wetar), the Tanimbar Islands, and the Kai Islands.
Threats and preservation
[edit]More than half of the original vegetation of the islands has been cleared for planting of rice and other crops, for settlement and by consequent forest fires. Only Sumbawa now contains a large area of intact natural forest, while Komodo, Rincah and Padar are now protected as Komodo National Park.
While many ecological problems affect both small islands and large landmasses, small islands suffer their particular problems and are highly exposed to external forces. Development pressures on small islands are increasing, although their effects are not always anticipated. Although Indonesia is richly endowed with natural resources, the resources of the small islands of Nusa Tenggara are limited and specialised; furthermore human resources in particular are limited.[9]
General observations[10] about small islands that can be applied to Nusa Tenggara include:[9]
- A higher proportion of the landmass will be affected by volcanic activity, earthquakes, landslips, and cyclone damage;
- Climates are more likely to be maritime influenced;
- Catchment areas are smaller and degree of erosion higher;
- A higher proportion of the landmass is made up of coastal areas;
- A higher degree of environmental specialisation, including a higher proportion of endemic species in an overall depauperate community;
- Societies having developed in relative isolation may retain a strong sense of culture;
- Small island populations are more likely to be affected by economic migration.
-
Banta Island of Lesser Sunda Islands
-
Rinca island
-
Komodo dragon at Komodo National Park
Administration
[edit]The Lesser Sundas comprise many islands stretching east of Java, most of which are part of Indonesia and from 1945 were administered (apart from the easternmost islands which have been always administered as part of Maluku Province) as the Lesser Sunda Islands (Sunda Kecil) Province of Indonesia, later called Nusa Tenggara. In 1958 this was split into three new provinces, as the provinces of Bali, West Nusa Tenggara and East Nusa Tenggara.
The eastern half of Timor Island is the separate nation of East Timor (officially Timor Leste}.
Demographics
[edit]Religion
[edit]Religion in Lesser Sunda Islands (December 2023)[11]
See also
[edit]- Apostolic Vicariate of Lesser Sunda Islands (originally an Apostolic Prefecture)
- Banda Arc
- Greater Sunda Islands
- List of islands of Indonesia
- List of rivers of Lesser Sunda Islands
- Oceanic trench
- Plate tectonics
- Sunda Arc
- Sundaland
- Sunda Shelf
- Sunda Trench
References
[edit]- ^ "Badak Sunda dan Harimau Sunda". "[...] Mr. M. Yamin yang pada 1950-an ketika menjadi Menteri P.P. dan K. mengganti istilah Kepulauan Sunda Kecil menjadi Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara. Sebab, istilah Kepulauan Sunda Kecil diganti dengan Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, maka istilah Kepulauan Sunda Besar juga tidak lagi digunakan dalam ilmu bumi dan perpetaan nasional Indonesia – meskipun dalam perpetaan Internasional istilah Greater Sunda Islands dan Lesser Sunda Islands masih tetap digunakan." – Ajip Rosidi: Penulis, budayawan. Pikiran Rakyat, 21 August 2010. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ^ Nitisastro, Widjojo (2006). Population Trends in Indonesia (1st publication 1970, Cornell University Press). Equinox Publishing. p. 75. ISBN 978-979-3780-43-6. OCLC 86608.
- ^ a b Audley-Charles, Michael Geoffrey (1987). "Dispersal of Gondwanaland: relevance to evolution of the Angiosperms". In Whitmore, T.C. (ed.). Biogeographical Evolution of the Malay Archipelago (International Congress of Systematic and Evolutionary Biology). Oxford Monographs on Biogeography 4. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, Clarendon Press. pp. 5–25. ISBN 0-19-854185-6. OCLC 14692633.
- ^ Veevers, J.J. (1991). "Phanerozoic Australia in the changing configuration of ProtoPangea through Gondwanaland and Pangea to the present dispersed continents". Australian Systematic Botany. 4 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1071/SB9910001.
- ^ a b c Monk, Fretes & Reksodiharjo-Lilley 1996, p. 9.
- ^ "Indonesia Volcanoes". volcano.si.edu. Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. Global Volcanism Program. Retrieved 7 June 2024.;
"Holocene Volcano List". volcano.si.edu. Retrieved 7 June 2024. - ^ Monk, Fretes & Reksodiharjo-Lilley 1996, p. 4.
- ^ Wikramanayake, Eric; Dinerstein, Eric; Loucks, Colby J.; Olson, David M.; Morrison, John; Lamoreaux, John; McKnight, Meghan (2002). Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a Conservation Assessment. Washington, DC: Island Press. ISBN 9781559639231. OCLC 48435361.
- ^ a b Monk, Fretes & Reksodiharjo-Lilley 1996, p. 1.
- ^ Beller, William S.; D'Ayala, Pier Giovanni; Hein, Philippe (1990). Sustainable development and environmental management of small islands (Papers from the Interoceanic Workshop on Sustainable Development and Environmental Management of Small Islands, Puerto Rico, Nov. 3-7, 1986). Man and the biosphere (5). Paris, Carnforth (England) and Park Ridge (N.J.): UNESCO and Parthenon Publishing Group Inc. OCLC 21044238.; including Hess, Allison L., 1990. "Overview: Sustainable Development and Environmental Management of Small Islands". (both cited in Monk, Fretes & Reksodiharjo-Lilley 1996)
- ^ "Jumlah Penduduk Menurut Agama" (in Indonesian). Ministry of Religious Affairs. 31 August 2022. Retrieved 29 October 2023.
Muslim 241 Million (87), Christianity 29.1 Million (10.5), Hindu 4.69 million (1.7), Buddhist 2.02 million (0.7), Folk, Confucianism, and others 192.311 (0.1), Total 277.749.673 Million
Bibliography
[edit]- Monk, Kathryn A.; Fretes, Yance De; Reksodiharjo-Lilley, Gayatri (1996). The Ecology of Nusa Tenggara and Maluku. Hong Kong: Periplus Editions Ltd. ISBN 962-593-076-0. OCLC 835572307.
External links
[edit] Lesser Sunda Islands travel guide from Wikivoyage
Lesser Sunda Islands travel guide from Wikivoyage- LexiRumah (part of the Lesser Sunda linguistic databases)
- Reconstructing the past through languages of the present: the Lesser Sunda Islands




