Antoine Watteau: Difference between revisions
Removing from Category:People of the Ancien Régime using Cat-a-lot |
|||
| (426 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|French painter (1684–1721)}} |
|||
[[Image:Rosalba Carriera Portrait Antoine Watteau.jpg|thumb|Watteau in the last year of his life, by [[Rosalba Carriera]], 1721]] |
|||
{{redirect|Watteau|the fictional character|Watto|other uses|Watteau (disambiguation)}} |
|||
'''Jean-Antoine Watteau''' (October 10, 1684 – July 18, 1721) was a [[France|French]] [[Painting|painter]] whose brief career spurred the revival of interest in colour and movement (in the tradition of [[Correggio]] and [[Peter Paul Rubens|Rubens]]), and revitalized the waning [[Baroque]] idiom, which eventually became known as [[Rococo]]. He is credited with inventing the genre of ''[[fête galante|fêtes galantes]]'': scenes of bucolic and idyllic charm, suffused with an air of theatricality. Some of his best known subjects were drawn from the world of [[Italy|Italian]] [[comedy]] and [[ballet]]. |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=September 2024}} |
|||
{{Infobox artist |
|||
| name = Antoine Watteau |
|||
| image = Rosalba Carriera Portrait Antoine Watteau.jpg |
|||
| caption = [[Rosalba Carriera]], ''Portrait of Antoine Watteau'', {{circa}} 1721, showing the artist in the last year of his life. {{Interlanguage link|Musei Civici di Treviso|lt=Musei Civici|it|Musei civici di Treviso|WD=}}, [[Treviso]] |
|||
| birth_name = Jean-Antoine Watteau |
|||
| birth_date = baptised {{birth date|1684|10|10|df=y}} |
|||
| birth_place = [[Valenciennes]], [[Habsburg Netherlands]] |
|||
| death_date = {{death date and age|1721|7|18|1684|10|10|df=y}} |
|||
| death_place = [[Nogent-sur-Marne]],<ref name=Lev/> [[Kingdom of France|France]] |
|||
| nationality = [[Kingdom of France|French]] |
|||
| field = [[Painting]] and [[drawing]] |
|||
| movement = [[Rococo]] |
|||
| works = ''[[Embarkation for Cythera]]'', 1717–1718<br/> ''[[L'Enseigne de Gersaint]]'', 1720–1721 |
|||
| education = {{hlist|[[Claude Gillot]]|[[Claude Audran III]]}} |
|||
| patrons = {{hlist|[[Jean de Jullienne]]|[[Pierre Crozat]]|[[Edme-François Gersaint]]}} |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Jean-Antoine Watteau''' ({{IPAc-en|UK|ˈ|w|ɒ|t|əʊ}}, {{IPAc-en|US|w|ɒ|ˈ|t|oʊ}},<ref>{{cite LPD|3}}</ref><ref>{{cite EPD|18}}</ref> {{IPA|fr|ʒɑ̃ ɑ̃twan vato|lang}}; baptised 10 October 1684{{snd}}died 18 July 1721)<ref name="Wine">{{Cite encyclopedia|title=Watteau|date=1996|encyclopedia=[[The Dictionary of Art]]|publisher=Grove's Dictionaries|location=New York|url=https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofart0032unse/page/913/mode/1up|last1=Wine|first1=Humphrey|last2=Scottez-De Wambrechies|first2=Annie|editor-last=Turner|editor-first=Jane|isbn=1-884446-00-0|pages=913–921|via=the Internet Archive|volume=32}} Also [http://www.oxfordartonline.com/subscriber/article/grove/art/T090852pg1 available] via [[Oxford Art Online]] (subscription needed).</ref> was a French [[Painting|painter]] and [[Drawing|draughtsman]] whose brief career spurred the revival of interest in colour and movement, as seen in the tradition of [[Antonio da Correggio|Correggio]] and [[Peter Paul Rubens|Rubens]]. He revitalized the waning [[Baroque]] style, shifting it to the less severe, more naturalistic, less formally classical, [[Rococo]]. Watteau is credited with inventing the genre of ''[[fête galante|fêtes galantes]]'', scenes of bucolic and idyllic charm, suffused with a theatrical air. Some of his best known subjects were drawn from the world of [[commedia dell'arte|Italian comedy]] and [[ballet]]. |
|||
==Biography== |
|||
===Early life and training=== |
|||
[[Image:The Embarktion for Cythera.jpg|thumb|right|[[Embarkation for Cythera|''Pilgrimage on the Isle of Cythera'']], 1717, [[Louvre Museum|Louvre]]. Many commentators note that it depicts a ''departure'' from the island of [[Cythera]], the birthplace of [[Venus (mythology)|Venus]], thus symbolizing the brevity of love.]] |
|||
Watteau was born in the town of [[Valenciennes]], which had recently passed from the [[Spanish Netherlands]] to [[France]]. His father was a master tiler. Showing an early interest in [[painting]], he was apprenticed to [[Jacques-Albert Gérin]], a local painter. Having little to learn from Gérin, Watteau left for [[Paris]] in about 1702. There he found employment in a workshop at [[Pont Notre-Dame]], making copies of popular [[Genre works|genre painting]]s in the Flemish and Dutch tradition; it was in that period that he developed his characteristic sketchlike technique. |
|||
==Early life and training== |
|||
In 1703 he was employed as an assistant by the painter [[Claude Gillot]], whose work represented a reaction against the turgid official art of [[Louis XIV]]'s reign. In Gillot's studio Watteau became acquainted with the characters of the ''[[commedia dell'arte]]'' (its actors had been expelled from France several years before), a favorite subject of Gillot's that would become one of Watteau's lifelong passions. Afterward he moved to the workshop of [[Claude Audran III]], an [[interior decorator]], under whose influence he began to make drawings admired for their consummate elegance. Audran was the curator of the [[Palais du Luxembourg]], where Watteau was able to see the magnificent series of canvases painted by [[Peter Paul Rubens]] for Queen [[Marie de Medici]]. The Flemish painter would become one of his major influences, together with the [[Venice|Venetian]] masters he would later study in the collection of his patron and friend, the banker [[Pierre Crozat]]. |
|||
Jean-Antoine Watteau{{refn|group=n.|The surname Watteau is presumed to originate from the word ''gâteau'' ({{trans|cake}}), possibly alluding to the trade carried on by the painter's distant ancestors;{{sfn|Camesasca|1971|p=[https://archive.org/details/completepainting0000watt/page/83/mode/1up 83]}}<ref>{{Cite book|last1=Germain|first1=Jean|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4bYErd60g3YC|title=Dictionnaire des noms de famille en Wallonie et à Bruxelles|last2=Herbillon|first2=Jules|publisher=E. Racine|year=2007|isbn=978-2-87386-506-1|location=Bruxelles|page=[https://books.google.com/books?id=4bYErd60g3YC&pg=PA1039 1039]|language=fr|via=Google Books|oclc=159955388}}</ref> according to {{harvnb|Mollett|1883|p=[https://archive.org/details/gri_33125003298433/page/n26/mode/1up 11]}}, "In the old Walloon language the W is substituted for G, and the very name 'Wallon' is derived from 'Gallus.' 'Watteau' stands for 'Gateau,' as 'William' does for 'Guillaume,' &c." In French, the surname is usually pronounced with the [[voiced labiodental fricative]] {{IPA|fr|v|}},<ref>{{Cite book|last=Pierret|first=Jean-Marie|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mP4JUXoFLBoC|title=Phonétique historique du français et notions de phonétique générale|publisher=Peeters|year=1994|isbn=9068316087|location=Leuven|page=[https://books.google.com/books?id=mP4JUXoFLBoC&pg=PA107 107]|issn=0779-1658|via=Google Books}}</ref> though in Hainaut, the pronunciation with the [[voiced labio-velar approximant]] {{IPA|fr|w|}} is present.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Pohl|first=Jacques|date=1983|title=Quelques caractéristiques de la phonologie du français parlé en Belgique|journal=Langue française|volume=60|issue=6|pages=30–41|doi=10.3406/lfr.1983.5173}}</ref><br/>Various spelling of the surname notably include ''Wateau'', ''Watau'', ''Vuateau'', ''Vateau'', and ''Vatteau''.{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|pp=15–28|loc="Chronology"}}}} was born in October 1684{{refn|group=n.|It is generally agreed that Watteau was the Jean-Antoine Watteau baptised on 10 October 1684, in Valenciennes at the Eglise de Saint-Jacques.{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|p=16}} However, it has been suggested by Michel Vangheluwe in 1984 that the painter could be the Antoine Watteau born on 6 May 1676, eight years before the traditional date.<ref>{{cite book|last=Vangheluwe|first=Michel|chapter=Watteau à Valenciennes|pages=7–9|title=Antoine Watteau, 1684-1721: le peintre, son temps et sa légende|publisher=Champion — Slatkin|year=1987|isbn=2852030381|editor-last=Moureau|editor-first=François|editor-last2=Grasselli|editor-first2=Margaret|location=Paris, Genève}}</ref>{{sfn|Michel|2008|p=30}}}} in [[Valenciennes]],<ref name=Lev>{{cite book|author-link=Michael Levey|last=Levey|first=Michael|date=1993|title=Painting and sculpture in France 1700-1789|location=New Haven|publisher=Yale University Press|page=29|isbn=0300064942}}</ref> once an important town in the [[County of Hainaut]] which became sequently part of the [[Burgundian Netherlands|Burgundian]] and [[Habsburg Netherlands]] until its secession to France following the [[Franco-Dutch War]]. He was the second of four sons born to Jean-Philippe Watteau (1660–1720) and Michelle Lardenois (1653–1727),{{refn|group=n.|Jean-Philippe Watteau and Michelle Lardenois, married on 7 January 1681, had four sons: Jean-François ({{abbr|b.|born}} 1682), Jean-Antoine, Antoine Roch (1687–1689), and Noël Joseph (1689–1758).{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|p=17}}}} and was presumed to be of [[Walloons|Walloon descent]].{{refn|group=n.|Contemporary authors disputed if Watteau could be considered as a Frenchman, given his origin from a recently seized region. In ''The Temple of Taste'', [[Voltaire]] described Watteau as a Flemish artist;<ref>{{Cite book|last=Voltaire|url=https://archive.org/details/oeuvrescomplete31voltgoog|title=Oeuvres completes de Voltaire|language=fr|publisher=Impr. de la Société littéraire-typographique|year=1784|volume=12|location=Paris|pages=[https://archive.org/details/oeuvrescomplete31voltgoog/page/n179/mode/1up 171 n. 6]|chapter=Le Temple du Goût|oclc=83543415|quote=Vateau eft un peintre flamand qui a travaillé à Paris, où il est mort il y a quelques années. Il a réussi dans les petites figures qu'il a dessinées & qu'il a très-bien grouppées; mais il n'a jamais rien fait de grand, il en était incapable.|author-link=Voltaire|via=the Internet Archive}}</ref> similarly, [[Frederick the Great]] labeled Watteau and Nicolas Lancret as "French painters of the school of Brabant" in a letter to his sister, the [[Wilhelmine of Prussia, Margravine of Brandenburg-Bayreuth|Margravine of Brandenburg-Bayreuth]].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Frederick II of Prussia|author-link=Frederick the Great|url=https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_-M-ZhNokjVoC|title=Oeuvres de Frédéric Le Grand|publisher=R. Decker|year=1856|volume=27|location=Berlin|page=[https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_-M-ZhNokjVoC/page/n110/mode/1up 75]|language=fr|chapter=72. A La Margrave de Baireuth (Ruppin, 9 novembre 1739)|issue=1|quote=La plupart de mes tableaux sont de Watteau ou de Laucret, a tous deux peintres français de l'éeole de Brabant.|via=the Internet Archive}}</ref>{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|pp=505, 548}} Nonetheless, later authors, such as [[Karl Woermann]]<ref>{{Cite book|last=Woermann|first=Karl|url=https://archive.org/details/geschichtederkun05woer_0|title=Die Kunst der mittleren Neuzeit von 1550 bis 1750 (Barock und Rokoko)|language=de|publisher=Bibliographisches Institut|year=1920|series=Geschichte der Kunst aller Zeiten und Völker|volume=5|location=Leipzig, Wien|pages=[https://archive.org/details/geschichtederkun05woer_0/page/196/mode/1up 196]|oclc=1045561032|quote=In Valenciennes geboren, das Flandern damals erft vor kerzem an Frankreich verloren hatte, war Watteau von Haus aus Wallone.|author-link=Karl Woermann|via=the Internet Archive}}</ref> and [[René Huyghe]],<ref>{{Cite book|last=Huyghe|first=René|url=https://archive.org/details/artspiritofman0000huyg|title=Art and the Spirit of Man|publisher=H. N. Abrams|year=1962|location=New York|page=[https://archive.org/details/artspiritofman0000huyg/page/413/mode/1up 413]|chapter=Watteau: Song of the Soul|oclc=1147729820|others=Translated from the French by Norbert Guterman|quote=Watteau was a Frenchman, but a Frenchman of recent vintage, for it was only in 1678, six years before he was born, that Valenciennes became French under the Treaty of Nijmegen. He was thoroughly French, for the province of Hainaut had always been French-speaking and culturally oriented to France. Watteau was not a Fleming, as his contemporaries liked to call him; he was a Walloon.|author-link=René Huyghe|chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/artspiritofman0000huyg/page/409/mode/1up|url-access=registration|via=the Internet Archive}}</ref> define Watteau as a Walloon.}} The Watteaus were a quite well-to-do family, although Jean-Philippe, a roofer in second generation, was said to be given to brawling.{{refn|group=n.|At least one case of such behavior was documented; in 1690, Jean-Philippe Watteau was charged of having broken the leg to Abraham Lesne, burgher.{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|p=17}}}} Showing an early interest in [[painting]], Jean-Antoine may have been apprenticed to [[Jacques-Albert Gérin]],<ref>For further reading on Jacques-Albert Gérin, see the following:{{bulleted list|{{Cite encyclopedia|title=Gérin, Jacques-Albert|url=https://archive.org/details/allgemeineslexik13thie/page/462/mode/1up|encyclopedia=[[Thieme-Becker|Allgemeines Lexikon der bildenden Künstler]]|publisher=E. A. Seemann|location=Leipzig|date=1920|editor-last=Thieme|editor-first=Ulrich|editor-link=Ulrich Thieme|volume=13|page=439|language=de|oclc=1039498097|via=the Internet Archive}}|{{cite encyclopedia|last=Zimmermann|first=Michael F.|editor-last=Roman d'Amat|editor-first=Jean-Charles|editor-last2=Prevost|editor-first2=Michel|editor-last3=Tribout de Morembert|editor-first3=Henri|name-list-style=amp|date=1989|title=Gérin (Jacques-Albert)|encyclopedia=Dictionnaire de biographie française|volume=15|location=Paris|publisher=Letouzey et Ané|at=col. 1295}}|{{Cite book|last=Bénézit|first=Emmanuel|author-link=Emmanuel Bénézit|title=[[Benezit Dictionary of Artists]]|publisher=Gründ|year=2006|isbn=2-7000-3076-1|volume=6|location=Paris|pages=[https://archive.org/details/benezitdictionar06bene/page/67/mode/1up 67]|orig-date=first published in French in 1911–1923|via=the [[Internet Archive]]}}|{{cite encyclopedia|last=Poinsignon|first=Jean-Claude|editor-last=Kasten|editor-first=Eberhard|display-editors=etal|date=2006|title=Gérin, Jacques-Albert|encyclopedia=[[Allgemeines Künstlerlexikon]]|language=de|volume=52|location=München, Leipzig|publisher=Saur|pages=141–142|isbn=3-598-22792-2}}}}</ref> a local painter, and his first artistic subjects were charlatans selling quack remedies on the streets of Valenciennes.<ref name=Lev/> Watteau left for Paris in 1702.{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|p=19}} After a period spent as a scene-painter, and in poor health, he found employment in a workshop at [[Pont Notre-Dame]], making copies of popular [[Genre works|genre painting]]s in the Flemish and Dutch tradition;{{refn|group=n.|For further discussion of Watteau's early years in Paris, see {{Cite journal|last=Glorieux|first=Guillaume|date=2002|title=Les débuts de Watteau à Paris: le pont Notre-Dame en 1702|journal=[[Gazette des Beaux-Arts]]|volume=139|pages=251–262|oclc=887046528}}}} it was in that period that he developed his characteristic sketchlike technique.{{sfn|Konody|1911|p=417}} |
|||
His drawings attracted the attention of the painter [[Claude Gillot]], and by 1705 he was employed as an assistant to Gillot, whose work, influenced by those of [[Francesco Primaticcio]] and the [[school of Fontainebleau]], represented a reaction against the turgid official art of [[Louis XIV]]'s reign.{{sfn|Huyghe|1970|p=[https://archive.org/details/watteau0000huyg/page/13/mode/1up 13]|postscript=: "The standards Gillot used for his figures had nothing in common with those of the Royal French Academy. His were fine, slight, and mannered: much closer, in fact, to these of Francesco Primaticcio and the School of Fontainbleau."}}<ref name=newencyclopaedia12ency>{{Cite encyclopedia|title=Watteau, (Jean-)Antoine|date=1986|encyclopedia=[[New Encyclopaedia Britannica]]|last=Macchia|first=Giovanni|edition=15th|volume=12|publisher=Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc.|location=Chicago et al.|pages=529–530|isbn=9780852294345|url=https://archive.org/details/newencyclopaedia12ency/page/529/mode/1up|via=the Internet Archive}} Also [https://www.britannica.com/biography/Antoine-Watteau available] via [[Britannica.com]].</ref><ref>{{Cite encyclopedia|title=Gillot, Claude|date=1996|encyclopedia=The Dictionary of Art|publisher=Grove's Dictionaries|location=New York|url=https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofart0012unse/|last=Roland Michel|first=Marianne|editor-last=Turner|editor-first=Jane|volume=12|pages=[https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofart0012unse/page/637/mode/1up 637]–[https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofart0012unse/page/638/mode/1up 638]|isbn=1-884446-00-0|via=the Internet Archive}} Also [https://www.oxfordartonline.com/groveart/view/10.1093/gao/9781884446054.001.0001/oao-9781884446054-e-7000032279?rskey=IRAby5 available] via Oxford Art Online.</ref> In Gillot's studio, Watteau became acquainted with the characters of the ''[[commedia dell'arte]]'' (which moved onto the ''[[théâtre de la foire]]'' following the [[Comédie-Italienne]]'s departure in 1697), a favorite subject of Gillot's that would become one of Watteau's lifelong passions.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Eidelberg|first=Martin|title=Antoine Watteau, 1684-1721: le peintre, son temps et sa légende|publisher=Champion — Slatkin|year=1987|isbn=2852030381|editor-last=Moureau|editor-first=François|location=Paris, Genève|pages=45–57|chapter=Watteau in the Atelier of Gillot|oclc=468860156|editor-last2=Grasselli|editor-first2=Margaret}}</ref><ref name="Wine"/> |
|||
===Career=== |
|||
[[Image:Antoine Watteau 035.jpg|left|thumb|''Pilgrimage to Cythera'' is an embellished repetition of his painting of 1717, and exemplifies the frivolity and sensuousness of [[Rococo]] painting. (1721, [[Berlin]])]] |
|||
In 1709 Watteau tried to obtain the [[Prix de Rome]] and was rejected by the [[Académie de peinture et de sculpture|Academy]]. In 1712 he tried again and was considered so good that, rather than receiving the one-year stay in [[Rome]] for which he had applied, he was accepted as a full member of the Academy. He took five years to deliver the required "[[reception piece]]," but it was one of his masterpieces: the ''Pilgrimage to Cythera'', also called the ''[[Embarkation for Cythera]]''. |
|||
After a quarrel with Gillot, Watteau moved to the workshop of [[Claude Audran III]], an [[interior decorator]], under whose influence he began to make drawings admired for their consummate elegance. Audran was the curator of the [[Palais du Luxembourg]], and from him Watteau acquired his knowledge of decorative art and ornamental design.{{sfn|Konody|1911|p=417}} At the palace, Watteau was able to see the [[Marie de' Medici cycle|magnificent series of canvases]] painted by [[Peter Paul Rubens]] for Queen [[Marie de Medici]]. The Flemish painter would become one of his major influences, together with the [[Venetian painting|Venetian masters]] that he would later study in the collection of his patron and friend, the banker [[Pierre Crozat]].<ref name="Wine"/> |
|||
Interestingly, while Watteau's paintings seem to epitomize the aristocratic elegance of the ''[[Régence]]'' (though he actually lived most of his short life under the oppressive climate of [[Louis XIV of France|Louis XIV]]'s later reign), he never had aristocratic [[patron]]s. His buyers were [[bourgeoisie|bourgeois]] such as bankers and dealers. |
|||
During this period Watteau painted ''The Departing Regiment'', the first picture in his second and more personal manner, showing influence of Rubens, and the first of a long series of camp pictures. He showed the painting to Audran, who made light of it, and advised him not to waste his time and gifts on such subjects. Watteau determined to leave him, advancing as excuse his desire to return to Valenciennes. He found a purchaser, at the modest price of 60 [[French livre|livres]], in a man called Sirois, the father-in-law of his later friend and patron [[Edme-François Gersaint]], and was thus enabled to return to the home of his childhood. In Valenciennes he painted a number of the small camp-pieces, notably the ''Camp-Fire'', which was again bought by Sirois, the price this time being raised to 200 livres.{{sfn|Konody|1911|p=417}} |
|||
Although his mature paintings seem to be so many depictions of frivolous ''[[fête galante|fêtes galantes]]'', they in fact display a sober melancholy, a sense of the ultimate futility of life, that makes him, among 18th century painters, one of the closest to modern sensibilities. His many imitators, such as [[Nicolas Lancret]] and [[Jean-Baptiste Pater]], borrowed his themes but could not capture his spirit. |
|||
==Later career== |
|||
Among his most famous paintings, beside the two versions of the ''Pilgrimage to Cythera'' (one in the [[Louvre]], the other in the [[Schloss Charlottenburg]], [[Berlin]]), are ''Pierrot'' (long identified as ''"Gilles"''), ''Fêtes venitiennes'', ''Love in the Italian Theater'', ''Love in the French Theater'', ''"Voulez-vous triompher des belles?"'' and ''Mezzetin.'' The subject of his hallmark painting, Pierrot or Gilles, with his slowly fading smile, seems a confused actor who appears to have forgotten his lines; he has materialized into the fearful reality of existence, sporting as his only armor the pathetic clown costume. The painting may be read as Watteau's wry comment on his mortal illness. [[Image:Gersaint.jpg|thumb|350px|''L'Enseigne de Gersaint'' (1720): In one of Watteau's last paintings, the portrait of [[Louis XIV]] and his own artworks are being packed away. The painter had no reason to expect that his name would be remembered long.]] |
|||
[[File:Antoine Watteau - Pleasures of Love - Google Art Project.jpg|thumb|350px|''Pleasures of Love'' (1718–1719)]] |
|||
[[File:Antoine Watteau - The Feast of Love - Google Art Project.jpg|thumb|350px|''The Feast (or Festival) of Love'' (1718–1719)]] |
|||
[[Image:L'Embarquement pour Cythère, by Antoine Watteau, from C2RMF retouched.jpg|thumb|350px|''[[The Embarkation for Cythera]]'', 1717, [[Louvre Museum|Louvre]]. Many commentators note that it depicts a ''departure'' from the island of [[Cythera (island)|Cythera]], the birthplace of [[Venus (mythology)|Venus]], thus symbolizing the brevity of love.]] |
|||
Watteau's final masterpiece, the ''Shop-sign of Gersaint''[http://www.wga.hu/html/enwiki/w/watteau/antoine/2/21enseig.html], exits the pastoral forest locale for a mundane urban set of encounters. Painted at Watteau's own insistence, "to take the chill off his fingers", this sign for an art shop in Paris is effectively the final curtain of Watteau's theatre. It has been described as Watteau's ''[[Las Meninas]]'', in that the theme appears to be the promotion of art. The scene is an art gallery where the façade has magically vanished. The gallery and street in the canvas are fused into one contiguous drama. |
|||
In 1709, Watteau tried to obtain a one-year stay in [[Rome]] by winning the [[Prix de Rome]] from the [[Académie de peinture et de sculpture|Academy]], but managed only to get awarded with the second prize.{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|p=20}} In 1712 he tried again and was persuaded by [[Charles de La Fosse]] that he had nothing to learn from going to Rome; thanks to Fosse he was accepted as an associate member of the Academy in 1712 and a full member in 1717.{{sfn|Konody|1911|p=417}}{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|p=21}} He took those five years to deliver the required "[[reception piece]]", one of his masterpieces: the ''Pilgrimage to Cythera'', also called the ''[[Embarkation for Cythera]]''.{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|p=396}} |
|||
[[Image:WatteauPierrot.jpg|thumb|left|Watteau's ''[[commedia dell'arte]]'' player of [[Pierrot]], ''ca'' 1718-19, traditionally identified as "Gilles" ([[Louvre Museum|Louvre]])]] |
|||
Watteau alarmed his friends by a carelessness about his future and financial security, as if foreseeing he would not live for long. In fact he had been sickly and physically fragile since childhood. In 1720, he travelled to London, England to consult Dr [[Richard Mead]], one of the most fashionable physicians of his time and an admirer of Watteau's work. However London's damp and smoky air offset any benefits of Dr. Mead's wholesome food and medicines. Watteau returned to France and spent his last few months on the estate of his patron, Abbé Haranger, where he died in 1721 perhaps from [[Tuberculosis|tuberculous]] laryngitis at the age of 36. The Abbé said Watteau was semi conscious and mute during his final days, clutching a paint brush and painting imaginary paintings in the air.<ref>Dormandy, Thomas. "The white death: the history of tuberculosis". New York University Press, 2000. p.11.</ref> |
|||
Watteau then went to live with the collector [[Pierre Crozat]], who eventually on his death in 1740 left around 400 paintings and 19,000 drawings by the masters. Thus Watteau was able to spend even more time becoming familiar with the works of Rubens and the Venetian masters.{{sfn|Konody|1911|p=418}} |
|||
[[Image:Antoine Watteau 030.jpg|thumb|''La Boudeuse'' from the [[Hermitage Museum]]: "Flirting coquettishly yet innocently, the artist's imaginary heroes – the deliberately indifferent lady and her insistently attentive cavalier – are shown with gentle irony. Their fragile, elegant world is dominated by a lyrical mood with just a touch of elegiac melancholy."[http://hermitagemuseum.org].]] |
|||
He lacked aristocratic [[patron]]s; his buyers were [[bourgeoisie|bourgeois]] such as bankers and dealers. Among his most famous paintings, beside the two versions of the ''[[The Embarkation for Cythera|Pilgrimage to Cythera]]'', one in the [[Louvre]], the other in the [[Schloss Charlottenburg]], [[Berlin]], are ''[[Pierrot (painting)|Pierrot]]'' (long identified as ''"Gilles"''), ''[[Fêtes venitiennes]]'', ''Love in the Italian Theater'', ''Love in the French Theater'', ''"Voulez-vous triompher des belles?"'' and ''Mezzetin''. The subject of his hallmark painting, ''Pierrot'' (''Gilles''), is an actor in a white satin costume who stands isolated from his four companions, staring ahead with an enigmatic expression on his face.{{sfn|Grasselli|Rosenberg|Parmantier|1984|pp= 429–434}} |
|||
Watteau's final masterpiece, the [[L'Enseigne de Gersaint|''Shop-sign of Gersaint'']], exits the pastoral forest locale for a mundane urban set of encounters. Painted at Watteau's own insistence, "in eight days, working only in the mornings ... in order to warm up his fingers",<ref name="Watteau_2009">{{Cite book|title=Watteau, Music, and Theater|publisher=The Metropolitan Museum of Art|others=Rosenberg, Pierre (an introduction by); Cowart, Georgia J. (an essay by)|year=2009|isbn=978-1-58839-335-7|editor-last=Baetjer|editor-first=Katharine|location=New York|page=6}}.</ref> this sign for the shop in Paris of the paintings dealer [[Edme François Gersaint]] is effectively the final curtain of Watteau's theatre. It has been compared with ''[[Las Meninas]]'' as a meditation on art and illusion.<ref name="Watteau_2009"/> The scene is an art gallery where the façade has magically vanished, and the gallery and street in the canvas are fused into one contiguous drama.<ref>{{cite book|last=Schwartz|first=Sanford|date=1990|title=Artists and Writers|url=https://archive.org/details/artistswriters00schw|url-access=registration|location=New York|publisher=Yarrow Press|pages=[https://archive.org/details/artistswriters00schw/page/140 140–141]|isbn=1-878274-01-5}}</ref> |
|||
Watteau alarmed his friends by a carelessness about his future and financial security, as if foreseeing he would not live for long. In fact he had been sickly and physically fragile since childhood. In 1720, he travelled to London, England, to consult Dr. [[Richard Mead]], one of the most fashionable physicians of his time and an admirer of Watteau's work. However, London's damp and smoky air offset any benefits of Dr. Mead's wholesome food and medicines. Watteau returned to France, spending six months with Gersaint,{{sfn|Konody|1911|p=418}} and then spent his last few months on the estate of his patron, Abbé Haranger, where he died in 1721, perhaps from [[Tuberculosis|tuberculous]] laryngitis, at the age of 36. The Abbé said Watteau was semi-conscious and mute during his final days, clutching a paint brush and painting imaginary paintings in the air.{{sfn|Dormandy|2000|p=11}} |
|||
His nephew, [[Louis Joseph Watteau]], son of Antoine's brother Noël Joseph Watteau (1689–1756), and grand nephew, [[François-Louis-Joseph Watteau]], son of Louis, followed Antoine into painting. |
|||
[[File:Antoine Watteau - Seated Woman.jpg|thumb|''Seated Woman'' (1716/1717), drawing by Watteau]] |
|||
==Critical assessment and legacy== |
==Critical assessment and legacy== |
||
{{See also|:fr:Liste de peintures d'Antoine Watteau|l1=List of paintings by Antoine Watteau}} |
|||
Little known during his lifetime beyond a small circle of his devotees, Watteau "was mentioned but seldom in contemporary art criticism and then usually reprovingly".<ref>Arnold Hauser. ''Rococo, Classicism and Romanticism''. Routledge (UK), 1999. P. 21.</ref> Sir [[Michael Levey]] once noted that Watteau "created, unwittingly, the concept of the individualistic artist loyal to himself, and himself alone". If his immediate followers (Lancret and Pater) would depict the unabashed frillery of aristocratic romantic pursuits, Watteau in a few masterpieces anticipates an art about art, the world of art as seen through the eyes of an artist. In contrast to the Rococo whimsicality and licentiousness cultivated by [[François Boucher|Boucher]] and [[Jean-Honoré Fragonard|Fragonard]] in the later part of [[Louis XV]]'s reign, Watteau's theatrical panache is usually tinged with a note of sympathy, wistfulness, and sadness at the transience of love and other earthly delights. |
|||
Little known during his lifetime beyond a small circle of his devotees, Watteau "was mentioned but seldom in contemporary art criticism and then usually reprovingly".<ref>{{cite book|first=Arnold|last=Hauser|author-link=Arnold Hauser (art historian)|url=https://archive.org/details/socialhistoryofa0000unse_m4n2|title=Rococo, Classicism and Romanticism|series=Social History of Art|volume=3|publisher=Vintage Books|location=New York|date=1958|page=[https://archive.org/details/socialhistoryofa0000unse_m4n2/page/24/mode/2up 24–25]|isbn=9780203981245 |url-access=registration|via=the Internet Archive|oclc=61403934}}</ref> Sir [[Michael Levey]] once noted that Watteau "created, unwittingly, the concept of the individualistic artist loyal to himself, and himself alone".{{sfn|Levey|1966}} If his immediate followers, Lancret and Pater, would depict the unabashed frillery of aristocratic romantic pursuits, Watteau in a few masterpieces anticipates an art ''about'' art, the world of art as seen through the eyes of an artist. In contrast to the Rococo whimsicality and licentiousness cultivated by [[François Boucher|Boucher]] and [[Jean-Honoré Fragonard|Fragonard]] in the later part of [[Louis XV]]'s reign, Watteau's theatrical panache is usually tinged with a note of sympathy, wistfulness, and sadness at the transience of love and other earthly delights.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Cunningham|first1=Lawrence|name-list-style=amp|first2=John J.|last2=Reich|date=2010|title=Culture and Values: A Survey of the Western Humanities|location=Boston, MA|publisher=Wadsworth Cengage Learning|page=399|isbn=9780495568773}}</ref> Famously, the [[Victorian era|Victorian]] essayist [[Walter Pater]] wrote of Watteau: "He was always a seeker after something in the world, that is there in no satisfying measure, or not at all."<ref>{{Cite magazine|last=Pater|first=Walter|date=October 1885|title=A Prince of Court Painters|url=https://archive.org/details/macmillansmagazi52macmuoft/page/400|magazine=Macmillan's Magazine|volume=52|issue=312|pages=401–414|via=the Internet Archive}}</ref>{{rp|414}} |
|||
Watteau's influence on the arts (not only painting, but the [[decorative art]]s, [[costume]], [[film]], [[poetry]], [[music]]) was more extensive than that of almost any other 18th-century artist. According to the [[1911 Britannica]], "in his treatment of the landscape background and of the atmospheric surroundings of the figures can be found the germs of [[Impressionism]]". The ''[[1700-1750 in fashion#Gowns|Watteau dress]]'', a long, sacklike dress with loose pleats hanging from the shoulder at the back, similar to those worn by many of the women in his paintings, is named after him. A revived vogue for Watteau began in Europe during the [[Victorian era]] and was later encapsulated by the [[Goncourt brothers]] and the ''[[Mir iskusstva|World of Art]]''. In 1984 Watteau societies were created in Paris and [[London]]. Since 2000 a Watteau centre has been established at Valenciennes. |
|||
Watteau was a prolific draftsman. His drawings, typically executed in ''[[trois crayons]]'' technique, were collected and admired even by those, such as [[Anne Claude de Caylus|count de Caylus]] or Gersaint, who found fault with his paintings.<ref name="Wine"/> In 1726 and 1728, [[Jean de Jullienne]] published suites of etchings after Watteau's drawings, and in 1735 he published a series of engravings after his paintings, ''The Recueil Jullienne''.<ref name="Wine"/> The quality of the reproductions, using a mixture of engraving and etching following the practice of the Rubens engravers, varied according to the skill of the people employed by Jullienne, but was often very high. Such a comprehensive record was hitherto unparalleled.<ref name="Wine"/> This helped disseminate his influence round Europe and into the decorative arts. |
|||
===Lost painting found in country house=== |
|||
''La Surprise'', painted around 1718, was known only through a copy in the [[Royal Collection]] before the original was found during a routine insurance valuation in 2007. The oil painting shows an actor playing a guitar on a stone bench looking across at a couple locked in an amorous embrace. The action is watched by a small dog in the corner. The painting was sold at auction on July 8, 2008 for 15 million Euros; this set a world record price for a painting by Watteau. |
|||
Watteau's influence on the arts (not only painting, but the [[decorative art]]s, [[costume]], [[film]], [[poetry]], [[music]]) was more extensive than that of almost any other 18th-century artist. The ''[[1700–1750 in fashion#Gowns and dresses|Watteau dress]]'', a long, sacklike dress with loose [[pleat]]s hanging from the shoulder at the back, similar to those worn by many of the women in his paintings, is named after him. According to Konody's critical assessment in the [[Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition|''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Eleventh Edition]], in part, "in his treatment of the landscape background and of the atmospheric surroundings of the figures can be found the germs of [[Impressionism]]".{{sfn|Konody|1911|p=418}} His influence on later generations of painters may have been less apparent in France than in England, where [[J. M. W. Turner]] was among his admirers.<ref>Gowing, Lawrence, and [[Michel Laclotte]]. 1987. ''Paintings in the Louvre''. New York: Stewart, Tabori & Chang. p. 506. {{ISBN|1556700075}}.</ref> A revived vogue for Watteau began in England during the [[British Regency]], and was later encapsulated by the [[Goncourt brothers]] in France ([[Edmond de Goncourt]] having published a {{lang|fr|[[catalogue raisonné]]}} in 1875) and the ''[[Mir iskusstva|World of Art]]'' union in Russia. |
|||
==Family== |
|||
The son ([[Louis Joseph Watteau]]) and grandson ([[François-Louis-Joseph Watteau]]) of Antoine's brother Noël Joseph Watteau (1689-1756) both also became painters. LOLZ |
|||
In 1984 Watteau societies were created in Paris, by [[Jean Ferré]], and London, by Dr. Selby Whittingham. A major exhibition in Paris, Washington and Berlin commemorated the 1984 tercentenary of his birth. Since 2000 a Watteau centre has been established at Valenciennes by Professor Chris Rauseo. A catalogue raisonné of Watteau's drawings has been compiled by [[Pierre Rosenberg]] and Louis-Antoine Prat, replacing the one by Sir [[Karl Parker]] and Jacques Mathey;<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Roland Michel|first=Marianne|date=November 1998|title=The Rosenberg-Prat Catalogue of Watteau's Drawings|journal=[[The Burlington Magazine]]|volume=140|issue=1148|pages=749–754|jstor=888091}}</ref> similar projects on his paintings are undertaken by Alan Wintermute<ref>{{Cite news|last=Melikian|first=Souren|date=10 July 2008|title=A Watteau sets record at £12.36 million in an uneven Old Masters sale|work=[[The New York Times]]|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2008/07/10/arts/10iht-melik10.1.14356658.html|access-date=29 October 2020|quote=Alan Wintermute, a Christie's specialist based in New York who is currently writing the catalogue raisonné of Watteau's paintings, was able to retrace its history from the beginning down to the middle of the 19th century.}}</ref> and [[Martin Eidelberg]],<ref>{{Cite web|last=Osborne|first=Ruth|date=5 December 2014|title=A Weight of Evidence: An Interview with Dr. Martin Eidelberg on the Watteau Abecedario|url=https://www.artwatchinternational.org/watteau-abecedario/|access-date=29 October 2020|website=ArtWatch International}}</ref> respectively.{{citation needed|date=April 2016}} |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
== |
==Gallery== |
||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> |
|||
* Dormandy, Thomas. ''"The White Death: the History of Tuberculosis".'' [[New York University Press]], 2000. |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau - Pierrot Content - WGA25440.jpg|''Pierrot Content'', c. 1711–1712, [[Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum]], Madrid.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Pierrot Content|url=https://www.museothyssen.org/en/collection/artists/watteau-jean-antoine/pierrot-content|access-date=July 21, 2020|website=Museo Nacional Thyssen-Bornemisza|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
* Levey, Michael, ''Rococo to Revolution''. [[Thames and Hudson]], 1966. |
|||
File:Capitulaciones de boda y baile campestre (Watteau).jpg|''[[Marriage Contract and Country Dancing]]'', c. 1711, [[Museo del Prado|Prado Museum]], Madrid.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Marriage Contract and Country Dance - The Collection - Museo Nacional del Prado|url=https://www.museodelprado.es/en/the-collection/art-work/marriage-contract-and-country-dance/011a63d7-d68a-4806-86a9-c9431e13a5fa|access-date=July 21, 2020|website=www.museodelprado.es}}</ref> |
|||
* Roland Michel, Marianne, ''Watteau''. [[Flammarion]], 1984. |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau - La Perspective (View through the Trees in the Park of Pierre Crozat) - WGA25444.jpg|''La Perspective (View through the Trees in the Park of Pierre Crozat)'', c. 1715, [[Museum of Fine Arts, Boston]] |
|||
* Schneider, Pierre, ''The World of Watteau''. [[Time-Life Books]], 1967. |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau, Le Savoyard et la marmotte (1716).jpg|''[[Savoyard with a Marmot]]'', c. 1716, [[Hermitage Museum]], [[St. Petersburg]] |
|||
* <http://www.news.com.au/heraldsun/story/0,21985,23433317-5005961,00.html> |
|||
File:Jean-Antoine Watteau - Mezzetin.JPG|''[[Mezzetino (painting)|Mezzetino]]'', c. 1717–1720, [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]], New York |
|||
File:Jean-Antoine Watteau - Pierrot, dit autrefois Gilles.jpg|''[[Pierrot (painting)|Pierrot]]'', c. 1718–1719, [[Louvre]], Paris |
|||
File:Watteau, Antoine - Quellnymphe - 1708.jpg|''Quellnymphe'', c. 1718, private collection |
|||
File:Jean-Antoine Watteau - The Love Song.JPG|''The Love Song'', c. 1717, [[National Gallery]], London |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau 012.jpg|''[[The Robber of the Sparrow's Nest]]'', c. 1712, [[National Galleries of Scotland]], [[Edinburgh]] |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau - The Dance - WGA25477.jpg|''The Dance'', c. 1716–1718, [[Gemäldegalerie, Berlin|Gemäldegalerie]], Berlin |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau 062.jpg|''[[Actors of the Comédie-Française]]'', between 1711–1718, [[Hermitage Museum]], Saint Petersburg |
|||
File:WatteauLes Fetesvenitiennes.jpg|''[[Fêtes Vénitiennes]]'', c. 1718–1719, National Galleries of Scotland, Edinburgh |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau - The Love Lesson - Google Art Project.jpg|''The Love Lesson'', c. 1716–1717, [[Nationalmuseum]], Stockholm |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau 001.jpg|''Les Plaisirs du Bal'', c. 1717, [[Dulwich Picture Gallery]], London |
|||
File:Jean-Antoine Watteau La Surprise, oil on panel.jpg|''[[The Surprise (Watteau)|La Surprise]]'', c. 1718, [[Getty Center]], Los Angeles |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau 030.jpg|''[[La Boudeuse (painting)|La Boudeuse]]'', c. 1715–1718, Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg<ref>{{cite web|url=http://hermitagemuseum.org/wps/portal/hermitage/digital-collection/01.+paintings/37767|work=Hermitagemuseum.org|title=La Boudeuse (The Capricious Girl)|publisher=State Hermitage Museum|location=Saint Petersburg|df=mdy-all|access-date=2017-09-27}}</ref> |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau - L'imbarco per Citera.jpg|''Pilgrimage to Cythera'', c. 1718–1719, [[Charlottenburg Palace]], Berlin |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau - The Italian Comedians - Google Art Project.jpg|''The Italian Comedians'', c. 1719–1721, [[National Gallery of Art]], [[Washington, D.C.]] |
|||
File:Gersaint.jpg|''[[L'Enseigne de Gersaint]]'', c. 1720–1721, Charlottenburg Palace, Berlin |
|||
File:Antoine Watteau, Ceres (Summer), c. 1717-1718, NGA 46149.jpg|''Ceres (Summer)'', c. 1717–1718, National Gallery of Art, Washington, D. C. <!--File:Watteau Polish woman.jpg|''Polish Woman Standing'', [[National Museum, Warsaw]]--> <!--File:Watteau, Jean-Antoine - Fete Champetre - Google Art Project.jpg|''Fete Champetre'', 1722--> |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
== External links == |
|||
{{reflist|30em|group=n.}} |
|||
{{commonscat|Antoine Watteau}} |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
==Bibliography== |
|||
<!--{{Further information|Bibliography of works on Jean-Antoine Watteau}}--> |
|||
{{refbegin|2|indent=yes}} |
|||
* {{cite book|first=Ettore|last=Camesasca|author-link=:pt:Ettore Camesasca|url=https://archive.org/details/completepainting0000watt|url-access=registration|title=The Complete Paintings of Watteau|series=Classics of the World's Great Art|year=1971|orig-date=first published in Italian in 1968|location=New York|publisher=Harry N. Abrams|others=Introduction by John Sunderland|isbn=0810955253|oclc=143069|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|title=Painters and Public Life in Eighteenth-Century Paris|url=https://archive.org/details/painterspublicli0000crow/mode/2up|url-access=registration|last=Crow|first=Thomas E.|publisher=Yale University Press|year=1985|isbn=0-300-03764-3|location=New Haven; London|oclc=1200566051|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* [[:fr:Émile Dacier|Dacier, Émile]]; Vuaflart, Albert; Herold, Jacques (1921–1929). ''Jean de Julienne et les graveurs de Watteau au XVIII-e siècle'' (in French). Paris: M. Rousseau. Volumes [https://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/dacier1929bd1 1], [https://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/dacier1922bd2 2], [http://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/dacier1922bd3 3], and [https://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/dacier1921bd4 4] available via the [[Heidelberg University Library]] repository |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Dormandy|first=Thomas|title=The White Death: the History of Tuberculosis|url=https://archive.org/details/whitedeathhistor0000dorm|url-access=registration|publisher=[[New York University Press]]|year=2000}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Goncourt|first=Edmond et Jules de|author-link=Goncourt brothers|title=L'art du XVIIIme siècle|language=fr|trans-title=The Art of the Eighteenth Century|location=Paris|publisher=G. Charpentier|oclc=1048224230|via=the Internet Archive|url=https://archive.org/details/lartduxviiimesi01gonc|volume=1|year=1881}} |
|||
* {{cite book|editor-last=Grasselli|editor-first=Margaret Morgan|editor-last2=Rosenberg|editor-first2=Pierre|editor2-link=Pierre Rosenberg|editor-last3=Parmantier|editor-first3=Nicole|name-list-style=amp|title=Watteau, 1684-1721|type=exhibition catalogue|year=1984|publisher=National Gallery of Art |via=the National Gallery of Art archive|url=https://www.nga.gov/content/dam/ngaweb/research/publications/pdfs/watteau-1684-1721.pdf|isbn=0-89468-074-9|oclc=557740787|url-access=registration}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Hind|first=Charles Lewis|author-link=C. Lewis Hind|title=Watteau|url=https://archive.org/details/watteau00hind|publisher=T.C. & E.C. Jack|location=London|year=1910|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Huyghe|first=René|author-link=René Huyghe|url=https://archive.org/details/watteau0000huyg|url-access=registration|title=Watteau: The Artist and His Drawings|others=Translated by Barbara Bray|location=New York|publisher=Braziller|year=1970|isbn=9780269027093 |orig-date=1950|via=the Internet Archive|oclc=556662493}} |
|||
* {{Cite EB1911|wstitle=Watteau, Antoine|volume=28|pages=417–418|first=Paul George|last=Konody|author-link=Paul George Konody}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Levey|first=Michael|author-link=Michael Levey|title=Rococo to Revolution: Major Trends in Eighteenth-Century Painting|url=https://archive.org/details/rococotorevoluti0000unse|url-access=registration|via=the Internet Archive|oclc=1036855531|location=London|publisher=[[Thames and Hudson]]|year=1966}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Mauclair|first=Camille|author-link=Camille Mauclair|url=https://archive.org/details/antoinewatteau1600mauc|title=Antoine Watteau (1684-1721)|publisher=Duckworth & Co|year=1906|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|last=Michel|first=Christian|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nm3WpbfjmlgC|title=Le "célèbre Watteau"|language=fr|publisher=Droz|year=2008|isbn=978-2-600-01176-1|location=Genève|oclc=1158803919}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Mollett|first=John William|title=Watteau|series=Illustrated Biographies of the Great Artists|url=https://archive.org/details/gri_33125003298433|publisher=S. Low, Marston, Searle & Rivington|location=London|year=1883|via=the Internet Archive|oclc=557720162}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Perl|first=Jed|author-link=Jed Perl|title=Antoine's Alphabet: Watteau and His World|url=https://archive.org/details/antoinesalphabet0000perl|year=2009|publisher=Vintage Books|location=New York|isbn=978-0-307-38594-9}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Phillips|first=Claude|author-link=Claude Phillips|title=Antoine Watteau|url=https://archive.org/details/antoinewatteau00phil|year=1895|publisher=Seeley and co. Limited|oclc=729123867|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Plax|first=Julie Anne|title=Watteau and the Cultural Politics of Eighteenth-Century France|year=2000|location=Cambridge etc.|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=0-521-64268-X|oclc=803847893}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|last1=Plomp|first1=Michiel|title=Watteau: Der Zeichner|last2=Sonnabend|first2=Martin|publisher=Hirmer|year=2016|isbn=978-3-941399-66-2|location=München|language=de|type=exhibition catalogue}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Posner|first=Donald|title=Antoine Watteau|url=https://archive.org/details/antoinewatteau0000posn|url-access=registration|year=1984|location=London|publisher=Weidenfeld & Nicolson|isbn=0-8014-1571-3|oclc=10736607|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Roland Michel|first=Marianne|url=https://archive.org/details/watteauartistofe0000rola/|url-access=registration|title=Watteau: an Artist of the Eighteenth Century|publisher=Trefoil|location=London|year=1984|isbn=0-86294-049-4|oclc=1302554747|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|title=Vies anciennes de Watteau|publisher=Hermann|year=1984|isbn=2-7056-5985-4|editor-last=Roseberg|editor-first=Pierre|location=Paris}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last1=Rosenberg|first1=Pierre|name-list-style=amp|last2=Prat|first2=Louis-Antoine|date=1996|title=Antoine Watteau: catalogue raisonné des dessins|location=Paris|publisher=Gallimard-Electa|isbn=2-07-015043-7|oclc=463981169|language=fr}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|last1=Rosenberg|first1=Pierre|last2=Prat|first2=Louis-Antoine|last3=Eidelberg|first3=Martin|name-list-style=amp|title=Watteau: The Drawings|publisher=Royal Academy of Arts|year=2011|isbn=9781905711703|location=London|type=exhibition catalogue|oclc=740683643}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Schneider|first=Pierre|title=The World of Watteau|url=https://archive.org/details/worldofwatteau1600schn|url-access=registration|location=New York|publisher=[[Time-Life Books]]|year=1967|oclc=680174683|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* {{cite book|editor-last=Sheriff|editor-first=Mary D.|title=Antoine Watteau: Perspectives on the Artist and the Culture of His Time|location=Newark|publisher=University of Delaware|year=2006|isbn=978-0-87413-934-1|oclc=185456942}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|url=https://archive.org/details/gri_33125001770060|title=Watteau and His School|last=Staley|first=Edgcumbe|publisher=George Bell and Sons|year=1902|location=London|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* {{cite web|last=Stein|first=Perrin|url=http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/watt/hd_watt.htm|title=Antoine Watteau (1684–1721)|format=essay|work=Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History|location=New York|publisher=Metropolitan Museum of Art|date=October 2003|access-date=18 September 2020}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|title=Watteau's Painted Conversations: Art, Literature, and Talk in Seventeenth- and Eighteenth-Century France|last=Vidal|first=Mary|publisher=Yale University Press|year=1992|isbn=0-300-05480-7|oclc=260176725|location=New Haven, London}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|last=Walsh|first=Linda|url=https://archive.org/details/changingstatusof0000unse/|title=The Changing Status of the Artist|publisher=Yale University Press|year=1999|isbn=0-300-07740-8|editor-last=Barker|editor-first=Emma|series=Art and Its Histories|volume=2|location=New Haven, London|pages=220–248|chapter=Subjects, Society, Style: Changing Evaluations of Watteau and His Art|oclc=1148191287|editor-last2=Webb|editor-first2=Nick|editor-last3=Woods|editor-first3=Kim|chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/changingstatusof0000unse/page/220/mode/2up|url-access=registration|via=the Internet Archive}} |
|||
* The Watteau Society Bulletin, London. |
|||
* Martin Eidelberg, watteauandhiscircle.org |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{Commons-inline}} |
|||
*{{Art UK bio}} |
|||
*[http://watteau-abecedario.org/Acceptedpaintings.htm Alphabetical list of accepted paintings and copies at A Watteau Abecedario] |
|||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20101105214950/http://www.nga.gov/collection/gallery/gg54/gg54-main1.html The Rococo and Watteau] |
|||
*[http://www.jean-antoine-watteau.org www.Jean-Antoine-Watteau.org] 89 works by Antoine Watteau |
*[http://www.jean-antoine-watteau.org www.Jean-Antoine-Watteau.org] 89 works by Antoine Watteau |
||
*[http://www. |
*[http://www.wga.hu/frames-e.html?/html/enwiki/w/watteau/antoine/1/index.html Watteau paintings at the Web Gallery of Art] |
||
* |
* {{cite magazine|url=http://www.nybooks.com/articles/archives/2009/feb/12/the-pleasure-of-watteau/|title=The Pleasure of Watteau|author-link=Julian Bell|last=Bell|first=Julian|magazine=[[The New York Review of Books]]|date=12 February 2009|access-date=3 May 2020|url-access=subscription}} |
||
*[http://collection.cooperhewitt.org/people/18042561/ Works by Watteau in the collection of the] [[Cooper-Hewitt, National Design Museum]] |
|||
{{Watteau}} |
|||
*The Watteau Abecedario http://watteau-abecedario.org/default.htm |
|||
{{Antoine Watteau}} |
|||
{{Authority control (arts)}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Watteau, Antoine}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Watteau, Antoine}} |
||
[[Category:1684 births]] |
[[Category:1684 births]] |
||
[[Category:1721 deaths]] |
[[Category:1721 deaths]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Artists from Valenciennes]] |
||
[[Category:French painters]] |
|||
[[Category:Rococo painters]] |
[[Category:Rococo painters]] |
||
[[Category:Prix de Rome for painting]] |
[[Category:Prix de Rome for painting]] |
||
[[Category:18th-century French painters]] |
|||
[[Category:French male painters]] |
|||
[[ar:أنطوان واتو]] |
|||
[[Category:People of the Regency of Philippe d'Orléans]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Антуан Вато]] |
|||
[[Category:Mythological painters]] |
|||
[[bg:Жан-Антоан Вато]] |
|||
[[Category:18th-century deaths from tuberculosis]] |
|||
[[ca:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[Category:Members of the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture]] |
|||
[[cs:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[Category:Tuberculosis deaths in France]] |
|||
[[da:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[Category:18th-century French male artists]] |
|||
[[de:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[el:Αντουάν Βαττώ]] |
|||
[[es:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[fr:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[gl:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[ko:앙투안 바토]] |
|||
[[hy:Անտուան Վատտո]] |
|||
[[hr:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[it:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[he:אנטואן ואטו]] |
|||
[[lb:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[hu:Jean-Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[nl:Jean Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[ja:アントワーヌ・ヴァトー]] |
|||
[[no:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[pl:Jean Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[pt:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[ro:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[ru:Ватто, Антуан]] |
|||
[[simple:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[sk:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[sr:Антоан Вато]] |
|||
[[sh:Jean Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[fi:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[sv:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[th:ฌอง อองตวน วัตโตว์]] |
|||
[[tr:Antoine Watteau]] |
|||
[[uk:Антуан Ватто]] |
|||
[[zh:让-安东尼·华托]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 8 December 2024
Antoine Watteau | |
|---|---|
 Rosalba Carriera, Portrait of Antoine Watteau, c. 1721, showing the artist in the last year of his life. Musei Civici, Treviso | |
| Born | Jean-Antoine Watteau baptised 10 October 1684 |
| Died | 18 July 1721 (aged 36) |
| Nationality | French |
| Education | |
| Known for | Painting and drawing |
| Notable work | Embarkation for Cythera, 1717–1718 L'Enseigne de Gersaint, 1720–1721 |
| Movement | Rococo |
| Patron(s) | |
Jean-Antoine Watteau (UK: /ˈwɒtoʊ/, US: /wɒˈtoʊ/,[2][3] French: [ʒɑ̃ ɑ̃twan vato]; baptised 10 October 1684 – died 18 July 1721)[4] was a French painter and draughtsman whose brief career spurred the revival of interest in colour and movement, as seen in the tradition of Correggio and Rubens. He revitalized the waning Baroque style, shifting it to the less severe, more naturalistic, less formally classical, Rococo. Watteau is credited with inventing the genre of fêtes galantes, scenes of bucolic and idyllic charm, suffused with a theatrical air. Some of his best known subjects were drawn from the world of Italian comedy and ballet.
Early life and training
[edit]Jean-Antoine Watteau[n. 1] was born in October 1684[n. 2] in Valenciennes,[1] once an important town in the County of Hainaut which became sequently part of the Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands until its secession to France following the Franco-Dutch War. He was the second of four sons born to Jean-Philippe Watteau (1660–1720) and Michelle Lardenois (1653–1727),[n. 3] and was presumed to be of Walloon descent.[n. 4] The Watteaus were a quite well-to-do family, although Jean-Philippe, a roofer in second generation, was said to be given to brawling.[n. 5] Showing an early interest in painting, Jean-Antoine may have been apprenticed to Jacques-Albert Gérin,[19] a local painter, and his first artistic subjects were charlatans selling quack remedies on the streets of Valenciennes.[1] Watteau left for Paris in 1702.[20] After a period spent as a scene-painter, and in poor health, he found employment in a workshop at Pont Notre-Dame, making copies of popular genre paintings in the Flemish and Dutch tradition;[n. 6] it was in that period that he developed his characteristic sketchlike technique.[21]
His drawings attracted the attention of the painter Claude Gillot, and by 1705 he was employed as an assistant to Gillot, whose work, influenced by those of Francesco Primaticcio and the school of Fontainebleau, represented a reaction against the turgid official art of Louis XIV's reign.[22][23][24] In Gillot's studio, Watteau became acquainted with the characters of the commedia dell'arte (which moved onto the théâtre de la foire following the Comédie-Italienne's departure in 1697), a favorite subject of Gillot's that would become one of Watteau's lifelong passions.[25][4]
After a quarrel with Gillot, Watteau moved to the workshop of Claude Audran III, an interior decorator, under whose influence he began to make drawings admired for their consummate elegance. Audran was the curator of the Palais du Luxembourg, and from him Watteau acquired his knowledge of decorative art and ornamental design.[21] At the palace, Watteau was able to see the magnificent series of canvases painted by Peter Paul Rubens for Queen Marie de Medici. The Flemish painter would become one of his major influences, together with the Venetian masters that he would later study in the collection of his patron and friend, the banker Pierre Crozat.[4]
During this period Watteau painted The Departing Regiment, the first picture in his second and more personal manner, showing influence of Rubens, and the first of a long series of camp pictures. He showed the painting to Audran, who made light of it, and advised him not to waste his time and gifts on such subjects. Watteau determined to leave him, advancing as excuse his desire to return to Valenciennes. He found a purchaser, at the modest price of 60 livres, in a man called Sirois, the father-in-law of his later friend and patron Edme-François Gersaint, and was thus enabled to return to the home of his childhood. In Valenciennes he painted a number of the small camp-pieces, notably the Camp-Fire, which was again bought by Sirois, the price this time being raised to 200 livres.[21]
Later career
[edit]


In 1709, Watteau tried to obtain a one-year stay in Rome by winning the Prix de Rome from the Academy, but managed only to get awarded with the second prize.[26] In 1712 he tried again and was persuaded by Charles de La Fosse that he had nothing to learn from going to Rome; thanks to Fosse he was accepted as an associate member of the Academy in 1712 and a full member in 1717.[21][27] He took those five years to deliver the required "reception piece", one of his masterpieces: the Pilgrimage to Cythera, also called the Embarkation for Cythera.[28]
Watteau then went to live with the collector Pierre Crozat, who eventually on his death in 1740 left around 400 paintings and 19,000 drawings by the masters. Thus Watteau was able to spend even more time becoming familiar with the works of Rubens and the Venetian masters.[29] He lacked aristocratic patrons; his buyers were bourgeois such as bankers and dealers. Among his most famous paintings, beside the two versions of the Pilgrimage to Cythera, one in the Louvre, the other in the Schloss Charlottenburg, Berlin, are Pierrot (long identified as "Gilles"), Fêtes venitiennes, Love in the Italian Theater, Love in the French Theater, "Voulez-vous triompher des belles?" and Mezzetin. The subject of his hallmark painting, Pierrot (Gilles), is an actor in a white satin costume who stands isolated from his four companions, staring ahead with an enigmatic expression on his face.[30]
Watteau's final masterpiece, the Shop-sign of Gersaint, exits the pastoral forest locale for a mundane urban set of encounters. Painted at Watteau's own insistence, "in eight days, working only in the mornings ... in order to warm up his fingers",[31] this sign for the shop in Paris of the paintings dealer Edme François Gersaint is effectively the final curtain of Watteau's theatre. It has been compared with Las Meninas as a meditation on art and illusion.[31] The scene is an art gallery where the façade has magically vanished, and the gallery and street in the canvas are fused into one contiguous drama.[32]
Watteau alarmed his friends by a carelessness about his future and financial security, as if foreseeing he would not live for long. In fact he had been sickly and physically fragile since childhood. In 1720, he travelled to London, England, to consult Dr. Richard Mead, one of the most fashionable physicians of his time and an admirer of Watteau's work. However, London's damp and smoky air offset any benefits of Dr. Mead's wholesome food and medicines. Watteau returned to France, spending six months with Gersaint,[29] and then spent his last few months on the estate of his patron, Abbé Haranger, where he died in 1721, perhaps from tuberculous laryngitis, at the age of 36. The Abbé said Watteau was semi-conscious and mute during his final days, clutching a paint brush and painting imaginary paintings in the air.[33]
His nephew, Louis Joseph Watteau, son of Antoine's brother Noël Joseph Watteau (1689–1756), and grand nephew, François-Louis-Joseph Watteau, son of Louis, followed Antoine into painting.

Critical assessment and legacy
[edit]Little known during his lifetime beyond a small circle of his devotees, Watteau "was mentioned but seldom in contemporary art criticism and then usually reprovingly".[34] Sir Michael Levey once noted that Watteau "created, unwittingly, the concept of the individualistic artist loyal to himself, and himself alone".[35] If his immediate followers, Lancret and Pater, would depict the unabashed frillery of aristocratic romantic pursuits, Watteau in a few masterpieces anticipates an art about art, the world of art as seen through the eyes of an artist. In contrast to the Rococo whimsicality and licentiousness cultivated by Boucher and Fragonard in the later part of Louis XV's reign, Watteau's theatrical panache is usually tinged with a note of sympathy, wistfulness, and sadness at the transience of love and other earthly delights.[36] Famously, the Victorian essayist Walter Pater wrote of Watteau: "He was always a seeker after something in the world, that is there in no satisfying measure, or not at all."[37]: 414
Watteau was a prolific draftsman. His drawings, typically executed in trois crayons technique, were collected and admired even by those, such as count de Caylus or Gersaint, who found fault with his paintings.[4] In 1726 and 1728, Jean de Jullienne published suites of etchings after Watteau's drawings, and in 1735 he published a series of engravings after his paintings, The Recueil Jullienne.[4] The quality of the reproductions, using a mixture of engraving and etching following the practice of the Rubens engravers, varied according to the skill of the people employed by Jullienne, but was often very high. Such a comprehensive record was hitherto unparalleled.[4] This helped disseminate his influence round Europe and into the decorative arts.
Watteau's influence on the arts (not only painting, but the decorative arts, costume, film, poetry, music) was more extensive than that of almost any other 18th-century artist. The Watteau dress, a long, sacklike dress with loose pleats hanging from the shoulder at the back, similar to those worn by many of the women in his paintings, is named after him. According to Konody's critical assessment in the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, in part, "in his treatment of the landscape background and of the atmospheric surroundings of the figures can be found the germs of Impressionism".[29] His influence on later generations of painters may have been less apparent in France than in England, where J. M. W. Turner was among his admirers.[38] A revived vogue for Watteau began in England during the British Regency, and was later encapsulated by the Goncourt brothers in France (Edmond de Goncourt having published a catalogue raisonné in 1875) and the World of Art union in Russia.
In 1984 Watteau societies were created in Paris, by Jean Ferré, and London, by Dr. Selby Whittingham. A major exhibition in Paris, Washington and Berlin commemorated the 1984 tercentenary of his birth. Since 2000 a Watteau centre has been established at Valenciennes by Professor Chris Rauseo. A catalogue raisonné of Watteau's drawings has been compiled by Pierre Rosenberg and Louis-Antoine Prat, replacing the one by Sir Karl Parker and Jacques Mathey;[39] similar projects on his paintings are undertaken by Alan Wintermute[40] and Martin Eidelberg,[41] respectively.[citation needed]
Gallery
[edit]-
Pierrot Content, c. 1711–1712, Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum, Madrid.[42]
-
La Perspective (View through the Trees in the Park of Pierre Crozat), c. 1715, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston
-
Mezzetino, c. 1717–1720, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
-
Quellnymphe, c. 1718, private collection
-
The Love Song, c. 1717, National Gallery, London
-
The Dance, c. 1716–1718, Gemäldegalerie, Berlin
-
Actors of the Comédie-Française, between 1711–1718, Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg
-
Fêtes Vénitiennes, c. 1718–1719, National Galleries of Scotland, Edinburgh
-
The Love Lesson, c. 1716–1717, Nationalmuseum, Stockholm
-
Les Plaisirs du Bal, c. 1717, Dulwich Picture Gallery, London
-
La Surprise, c. 1718, Getty Center, Los Angeles
-
La Boudeuse, c. 1715–1718, Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg[44]
-
Pilgrimage to Cythera, c. 1718–1719, Charlottenburg Palace, Berlin
-
The Italian Comedians, c. 1719–1721, National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C.
-
L'Enseigne de Gersaint, c. 1720–1721, Charlottenburg Palace, Berlin
-
Ceres (Summer), c. 1717–1718, National Gallery of Art, Washington, D. C.
Notes
[edit]- ^ The surname Watteau is presumed to originate from the word gâteau (transl. cake), possibly alluding to the trade carried on by the painter's distant ancestors;[5][6] according to Mollett 1883, p. 11, "In the old Walloon language the W is substituted for G, and the very name 'Wallon' is derived from 'Gallus.' 'Watteau' stands for 'Gateau,' as 'William' does for 'Guillaume,' &c." In French, the surname is usually pronounced with the voiced labiodental fricative [v],[7] though in Hainaut, the pronunciation with the voiced labio-velar approximant [w] is present.[8]
Various spelling of the surname notably include Wateau, Watau, Vuateau, Vateau, and Vatteau.[9] - ^ It is generally agreed that Watteau was the Jean-Antoine Watteau baptised on 10 October 1684, in Valenciennes at the Eglise de Saint-Jacques.[10] However, it has been suggested by Michel Vangheluwe in 1984 that the painter could be the Antoine Watteau born on 6 May 1676, eight years before the traditional date.[11][12]
- ^ Jean-Philippe Watteau and Michelle Lardenois, married on 7 January 1681, had four sons: Jean-François (b. 1682), Jean-Antoine, Antoine Roch (1687–1689), and Noël Joseph (1689–1758).[13]
- ^ Contemporary authors disputed if Watteau could be considered as a Frenchman, given his origin from a recently seized region. In The Temple of Taste, Voltaire described Watteau as a Flemish artist;[14] similarly, Frederick the Great labeled Watteau and Nicolas Lancret as "French painters of the school of Brabant" in a letter to his sister, the Margravine of Brandenburg-Bayreuth.[15][16] Nonetheless, later authors, such as Karl Woermann[17] and René Huyghe,[18] define Watteau as a Walloon.
- ^ At least one case of such behavior was documented; in 1690, Jean-Philippe Watteau was charged of having broken the leg to Abraham Lesne, burgher.[13]
- ^ For further discussion of Watteau's early years in Paris, see Glorieux, Guillaume (2002). "Les débuts de Watteau à Paris: le pont Notre-Dame en 1702". Gazette des Beaux-Arts. 139: 251–262. OCLC 887046528.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Levey, Michael (1993). Painting and sculpture in France 1700-1789. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 29. ISBN 0300064942.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ Jones, Daniel (2011). Roach, Peter; Setter, Jane; Esling, John (eds.). Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary (18th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-15255-6.
- ^ a b c d e f Wine, Humphrey; Scottez-De Wambrechies, Annie (1996). "Watteau". In Turner, Jane (ed.). The Dictionary of Art. Vol. 32. New York: Grove's Dictionaries. pp. 913–921. ISBN 1-884446-00-0 – via the Internet Archive. Also available via Oxford Art Online (subscription needed).
- ^ Camesasca 1971, p. 83.
- ^ Germain, Jean; Herbillon, Jules (2007). Dictionnaire des noms de famille en Wallonie et à Bruxelles (in French). Bruxelles: E. Racine. p. 1039. ISBN 978-2-87386-506-1. OCLC 159955388 – via Google Books.
- ^ Pierret, Jean-Marie (1994). Phonétique historique du français et notions de phonétique générale. Leuven: Peeters. p. 107. ISBN 9068316087. ISSN 0779-1658 – via Google Books.
- ^ Pohl, Jacques (1983). "Quelques caractéristiques de la phonologie du français parlé en Belgique". Langue française. 60 (6): 30–41. doi:10.3406/lfr.1983.5173.
- ^ Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, pp. 15–28, "Chronology".
- ^ Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, p. 16.
- ^ Vangheluwe, Michel (1987). "Watteau à Valenciennes". In Moureau, François; Grasselli, Margaret (eds.). Antoine Watteau, 1684-1721: le peintre, son temps et sa légende. Paris, Genève: Champion — Slatkin. pp. 7–9. ISBN 2852030381.
- ^ Michel 2008, p. 30.
- ^ a b Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, p. 17.
- ^ Voltaire (1784). "Le Temple du Goût". Oeuvres completes de Voltaire (in French). Vol. 12. Paris: Impr. de la Société littéraire-typographique. pp. 171 n. 6. OCLC 83543415 – via the Internet Archive.
Vateau eft un peintre flamand qui a travaillé à Paris, où il est mort il y a quelques années. Il a réussi dans les petites figures qu'il a dessinées & qu'il a très-bien grouppées; mais il n'a jamais rien fait de grand, il en était incapable.
- ^ Frederick II of Prussia (1856). "72. A La Margrave de Baireuth (Ruppin, 9 novembre 1739)". Oeuvres de Frédéric Le Grand (in French). Vol. 27. Berlin: R. Decker. p. 75 – via the Internet Archive.
La plupart de mes tableaux sont de Watteau ou de Laucret, a tous deux peintres français de l'éeole de Brabant.
- ^ Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, pp. 505, 548.
- ^ Woermann, Karl (1920). Die Kunst der mittleren Neuzeit von 1550 bis 1750 (Barock und Rokoko). Geschichte der Kunst aller Zeiten und Völker (in German). Vol. 5. Leipzig, Wien: Bibliographisches Institut. pp. 196. OCLC 1045561032 – via the Internet Archive.
In Valenciennes geboren, das Flandern damals erft vor kerzem an Frankreich verloren hatte, war Watteau von Haus aus Wallone.
- ^ Huyghe, René (1962). "Watteau: Song of the Soul". Art and the Spirit of Man. Translated from the French by Norbert Guterman. New York: H. N. Abrams. p. 413. OCLC 1147729820 – via the Internet Archive.
Watteau was a Frenchman, but a Frenchman of recent vintage, for it was only in 1678, six years before he was born, that Valenciennes became French under the Treaty of Nijmegen. He was thoroughly French, for the province of Hainaut had always been French-speaking and culturally oriented to France. Watteau was not a Fleming, as his contemporaries liked to call him; he was a Walloon.
- ^ For further reading on Jacques-Albert Gérin, see the following:
- Thieme, Ulrich, ed. (1920). "Gérin, Jacques-Albert". Allgemeines Lexikon der bildenden Künstler (in German). Vol. 13. Leipzig: E. A. Seemann. p. 439. OCLC 1039498097 – via the Internet Archive.
- Zimmermann, Michael F. (1989). "Gérin (Jacques-Albert)". In Roman d'Amat, Jean-Charles; Prevost, Michel & Tribout de Morembert, Henri (eds.). Dictionnaire de biographie française. Vol. 15. Paris: Letouzey et Ané. col. 1295.
- Bénézit, Emmanuel (2006) [first published in French in 1911–1923]. Benezit Dictionary of Artists. Vol. 6. Paris: Gründ. pp. 67. ISBN 2-7000-3076-1 – via the Internet Archive.
- Poinsignon, Jean-Claude (2006). "Gérin, Jacques-Albert". In Kasten, Eberhard; et al. (eds.). Allgemeines Künstlerlexikon (in German). Vol. 52. München, Leipzig: Saur. pp. 141–142. ISBN 3-598-22792-2.
- ^ Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, p. 19.
- ^ a b c d Konody 1911, p. 417.
- ^ Huyghe 1970, p. 13: "The standards Gillot used for his figures had nothing in common with those of the Royal French Academy. His were fine, slight, and mannered: much closer, in fact, to these of Francesco Primaticcio and the School of Fontainbleau."
- ^ Macchia, Giovanni (1986). "Watteau, (Jean-)Antoine". New Encyclopaedia Britannica. Vol. 12 (15th ed.). Chicago et al.: Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. pp. 529–530. ISBN 9780852294345 – via the Internet Archive. Also available via Britannica.com.
- ^ Roland Michel, Marianne (1996). "Gillot, Claude". In Turner, Jane (ed.). The Dictionary of Art. Vol. 12. New York: Grove's Dictionaries. pp. 637–638. ISBN 1-884446-00-0 – via the Internet Archive. Also available via Oxford Art Online.
- ^ Eidelberg, Martin (1987). "Watteau in the Atelier of Gillot". In Moureau, François; Grasselli, Margaret (eds.). Antoine Watteau, 1684-1721: le peintre, son temps et sa légende. Paris, Genève: Champion — Slatkin. pp. 45–57. ISBN 2852030381. OCLC 468860156.
- ^ Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, p. 20.
- ^ Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, p. 21.
- ^ Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, p. 396.
- ^ a b c Konody 1911, p. 418.
- ^ Grasselli, Rosenberg & Parmantier 1984, pp. 429–434.
- ^ a b Baetjer, Katharine, ed. (2009). Watteau, Music, and Theater. Rosenberg, Pierre (an introduction by); Cowart, Georgia J. (an essay by). New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art. p. 6. ISBN 978-1-58839-335-7..
- ^ Schwartz, Sanford (1990). Artists and Writers. New York: Yarrow Press. pp. 140–141. ISBN 1-878274-01-5.
- ^ Dormandy 2000, p. 11.
- ^ Hauser, Arnold (1958). Rococo, Classicism and Romanticism. Social History of Art. Vol. 3. New York: Vintage Books. p. 24–25. ISBN 9780203981245. OCLC 61403934 – via the Internet Archive.
- ^ Levey 1966.
- ^ Cunningham, Lawrence & Reich, John J. (2010). Culture and Values: A Survey of the Western Humanities. Boston, MA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning. p. 399. ISBN 9780495568773.
- ^ Pater, Walter (October 1885). "A Prince of Court Painters". Macmillan's Magazine. Vol. 52, no. 312. pp. 401–414 – via the Internet Archive.
- ^ Gowing, Lawrence, and Michel Laclotte. 1987. Paintings in the Louvre. New York: Stewart, Tabori & Chang. p. 506. ISBN 1556700075.
- ^ Roland Michel, Marianne (November 1998). "The Rosenberg-Prat Catalogue of Watteau's Drawings". The Burlington Magazine. 140 (1148): 749–754. JSTOR 888091.
- ^ Melikian, Souren (10 July 2008). "A Watteau sets record at £12.36 million in an uneven Old Masters sale". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
Alan Wintermute, a Christie's specialist based in New York who is currently writing the catalogue raisonné of Watteau's paintings, was able to retrace its history from the beginning down to the middle of the 19th century.
- ^ Osborne, Ruth (5 December 2014). "A Weight of Evidence: An Interview with Dr. Martin Eidelberg on the Watteau Abecedario". ArtWatch International. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- ^ "Pierrot Content". Museo Nacional Thyssen-Bornemisza. Retrieved 21 July 2020.
- ^ "Marriage Contract and Country Dance - The Collection - Museo Nacional del Prado". www.museodelprado.es. Retrieved 21 July 2020.
- ^ "La Boudeuse (The Capricious Girl)". Hermitagemuseum.org. Saint Petersburg: State Hermitage Museum. Retrieved September 27, 2017.
Bibliography
[edit]- Camesasca, Ettore [in Portuguese] (1971) [first published in Italian in 1968]. The Complete Paintings of Watteau. Classics of the World's Great Art. Introduction by John Sunderland. New York: Harry N. Abrams. ISBN 0810955253. OCLC 143069 – via the Internet Archive.
- Crow, Thomas E. (1985). Painters and Public Life in Eighteenth-Century Paris. New Haven; London: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-03764-3. OCLC 1200566051 – via the Internet Archive.
- Dacier, Émile; Vuaflart, Albert; Herold, Jacques (1921–1929). Jean de Julienne et les graveurs de Watteau au XVIII-e siècle (in French). Paris: M. Rousseau. Volumes 1, 2, 3, and 4 available via the Heidelberg University Library repository
- Dormandy, Thomas (2000). The White Death: the History of Tuberculosis. New York University Press.
- Goncourt, Edmond et Jules de (1881). L'art du XVIIIme siècle [The Art of the Eighteenth Century] (in French). Vol. 1. Paris: G. Charpentier. OCLC 1048224230 – via the Internet Archive.
- Grasselli, Margaret Morgan; Rosenberg, Pierre & Parmantier, Nicole, eds. (1984). Watteau, 1684-1721 (PDF) (exhibition catalogue). National Gallery of Art. ISBN 0-89468-074-9. OCLC 557740787 – via the National Gallery of Art archive.
- Hind, Charles Lewis (1910). Watteau. London: T.C. & E.C. Jack – via the Internet Archive.
- Huyghe, René (1970) [1950]. Watteau: The Artist and His Drawings. Translated by Barbara Bray. New York: Braziller. ISBN 9780269027093. OCLC 556662493 – via the Internet Archive.
- Konody, Paul George (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 417–418.
- Levey, Michael (1966). Rococo to Revolution: Major Trends in Eighteenth-Century Painting. London: Thames and Hudson. OCLC 1036855531 – via the Internet Archive.
- Mauclair, Camille (1906). Antoine Watteau (1684-1721). Duckworth & Co – via the Internet Archive.
- Michel, Christian (2008). Le "célèbre Watteau" (in French). Genève: Droz. ISBN 978-2-600-01176-1. OCLC 1158803919.
- Mollett, John William (1883). Watteau. Illustrated Biographies of the Great Artists. London: S. Low, Marston, Searle & Rivington. OCLC 557720162 – via the Internet Archive.
- Perl, Jed (2009). Antoine's Alphabet: Watteau and His World. New York: Vintage Books. ISBN 978-0-307-38594-9.
- Phillips, Claude (1895). Antoine Watteau. Seeley and co. Limited. OCLC 729123867 – via the Internet Archive.
- Plax, Julie Anne (2000). Watteau and the Cultural Politics of Eighteenth-Century France. Cambridge etc.: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-64268-X. OCLC 803847893.
- Plomp, Michiel; Sonnabend, Martin (2016). Watteau: Der Zeichner (exhibition catalogue) (in German). München: Hirmer. ISBN 978-3-941399-66-2.
- Posner, Donald (1984). Antoine Watteau. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-8014-1571-3. OCLC 10736607 – via the Internet Archive.
- Roland Michel, Marianne (1984). Watteau: an Artist of the Eighteenth Century. London: Trefoil. ISBN 0-86294-049-4. OCLC 1302554747 – via the Internet Archive.
- Roseberg, Pierre, ed. (1984). Vies anciennes de Watteau. Paris: Hermann. ISBN 2-7056-5985-4.
- Rosenberg, Pierre & Prat, Louis-Antoine (1996). Antoine Watteau: catalogue raisonné des dessins (in French). Paris: Gallimard-Electa. ISBN 2-07-015043-7. OCLC 463981169.
- Rosenberg, Pierre; Prat, Louis-Antoine & Eidelberg, Martin (2011). Watteau: The Drawings (exhibition catalogue). London: Royal Academy of Arts. ISBN 9781905711703. OCLC 740683643.
- Schneider, Pierre (1967). The World of Watteau. New York: Time-Life Books. OCLC 680174683 – via the Internet Archive.
- Sheriff, Mary D., ed. (2006). Antoine Watteau: Perspectives on the Artist and the Culture of His Time. Newark: University of Delaware. ISBN 978-0-87413-934-1. OCLC 185456942.
- Staley, Edgcumbe (1902). Watteau and His School. London: George Bell and Sons – via the Internet Archive.
- Stein, Perrin (October 2003). "Antoine Watteau (1684–1721)" (essay). Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art. Retrieved 18 September 2020.
- Vidal, Mary (1992). Watteau's Painted Conversations: Art, Literature, and Talk in Seventeenth- and Eighteenth-Century France. New Haven, London: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-05480-7. OCLC 260176725.
- Walsh, Linda (1999). "Subjects, Society, Style: Changing Evaluations of Watteau and His Art". In Barker, Emma; Webb, Nick; Woods, Kim (eds.). The Changing Status of the Artist. Art and Its Histories. Vol. 2. New Haven, London: Yale University Press. pp. 220–248. ISBN 0-300-07740-8. OCLC 1148191287 – via the Internet Archive.
- The Watteau Society Bulletin, London.
- Martin Eidelberg, watteauandhiscircle.org
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Antoine Watteau at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Antoine Watteau at Wikimedia Commons
- 40 artworks by or after Antoine Watteau at the Art UK site
- Alphabetical list of accepted paintings and copies at A Watteau Abecedario
- The Rococo and Watteau
- www.Jean-Antoine-Watteau.org 89 works by Antoine Watteau
- Watteau paintings at the Web Gallery of Art
- Bell, Julian (12 February 2009). "The Pleasure of Watteau". The New York Review of Books. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- Works by Watteau in the collection of the Cooper-Hewitt, National Design Museum
- The Watteau Abecedario http://watteau-abecedario.org/default.htm
- 1684 births
- 1721 deaths
- Artists from Valenciennes
- Rococo painters
- Prix de Rome for painting
- 18th-century French painters
- French male painters
- People of the Regency of Philippe d'Orléans
- Mythological painters
- 18th-century deaths from tuberculosis
- Members of the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture
- Tuberculosis deaths in France
- 18th-century French male artists

![Pierrot Content, c. 1711–1712, Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum, Madrid.[42]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1f/Antoine_Watteau_-_Pierrot_Content_-_WGA25440.jpg/177px-Antoine_Watteau_-_Pierrot_Content_-_WGA25440.jpg)
![Marriage Contract and Country Dancing, c. 1711, Prado Museum, Madrid.[43]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5b/Capitulaciones_de_boda_y_baile_campestre_%28Watteau%29.jpg/200px-Capitulaciones_de_boda_y_baile_campestre_%28Watteau%29.jpg)









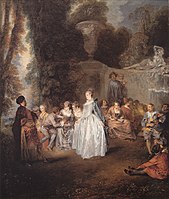



![La Boudeuse, c. 1715–1718, Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg[44]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/70/Antoine_Watteau_030.jpg/160px-Antoine_Watteau_030.jpg)



