UUM-125 Sea Lance: Difference between revisions
Corrected Lead title to match article title; clean-up/corrections |
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
||
| (47 intermediate revisions by 31 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Refimprove|article|date=February 2010}} |
||
{{Infobox |
{{Infobox weapon |
||
|is_missile=yes |
| is_missile = yes |
||
|name=UUM-125 Sea Lance |
| name = UUM-125 Sea Lance |
||
|image= |
| image = Uum-125a.jpg |
||
| image_size = 250 |
|||
|caption= Artist concept |
| caption = Artist concept |
||
|origin=United States |
| origin = United States |
||
|type=Standoff Anti-Submarine |
| type = Standoff Anti-Submarine |
||
|used_by=[[United States Navy]] |
| used_by = [[United States Navy]] |
||
|manufacturer=[[Boeing]] |
| manufacturer = [[Boeing]] |
||
|unit_cost= |
| unit_cost = |
||
|production_date=Cancelled |
| production_date = Cancelled, 1990 |
||
|service= |
|||
| service = |
|||
|engine=Hercules EX 116 MOD 0 solid-fuel rocket |
| engine = Hercules EX 116 MOD 0 [[solid-fuel rocket]] |
||
|weight=1,400 kg (3,086 [[pound (mass)|pounds]]) |
| weight = 1,400 kg (3,086 [[pound (mass)|pounds]]) |
||
|length=6.25 m (20 feet, 6 inches) |
|||
| length = {{convert|6.25|m|ftin|abbr=on}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| height = |
|||
|diameter=53.3 |
| diameter = {{convert|53.3|cm|in|abbr=on}} (capsule diameter) |
||
|wingspan= |
| wingspan = |
||
|speed=[[mach number|Mach]] 1.5 |
| speed = [[mach number|Mach]] 1.5 |
||
|vehicle_range='''UUM-125A'''<br />185 |
| vehicle_range = '''UUM-125A'''<br />{{convert|185|km|nmi|abbr=off}}<br />'''UUM-125B'''<br />{{convert|65|km|nmi|abbr=off}} |
||
|ceiling= |
|||
| ceiling = |
|||
|altitude= |
| altitude = |
||
|filling= |
|||
| filling = |
|||
|guidance=Mk 117 digital fire-control system |
| guidance = Mk 117 digital fire-control system |
||
|detonation='''UUM-125A'''<br />W-89 thermonuclear<br />'''UUM-125B'''<br />Mark 50 homing torpedo |
|||
|launch_platform='''Submarines'''<br />[[Los Angeles |
| detonation = '''RUM/UUM-125A'''<br />[[W89]] [[Thermonuclear weapon|thermonuclear]]<br />'''RUM/UUM-125B'''<br />[[Mark 50 torpedo|Mark 50]] [[Torpedo#Homing|homing torpedo]] |
||
| launch_platform = '''Submarines'''<br />[[Los Angeles-class submarine|• ''Los Angeles'' class]]<br />• [[Seawolf-class submarine|''Seawolf'' class]]<br />'''Surface Warships'''<br />• [[Ticonderoga-class cruiser|''Ticonderoga'' class]]<br />• [[Spruance-class destroyer|''Spruance'' class]]<br />• [[Arleigh Burke-class destroyer|''Arleigh Burke'' class]] |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File:Capsule for UUM-125 Sea Lance.jpg|thumb|right|Sea Lance in-service capsule]] |
[[File:Capsule for UUM-125 Sea Lance.jpg|thumb|right|Sea Lance in-service capsule]] |
||
The '''UUM-125 Sea Lance''' |
The '''UUM-125 Sea Lance''', known early in development as the ''Common ASW Standoff Weapon'', was to be an American [[Standoff missile|standoff]] [[anti-submarine missile]], initially intended to carry a [[W89]] [[Thermonuclear weapon|thermonuclear warhead]]. It was conceived in 1980 as a successor to both the [[UUM-44 SUBROC]] and [[RUR-5 ASROC]] anti-submarine missiles. The Sea Lance was to be available in two versions, known as UUM-125A and RUM-125A. The former would be a [[Submarine-launched missile|submarine-launched]] version, the latter surface-launched. It was cancelled in 1990 as its importance was obviated by the [[Dissolution of the Soviet Union|collapse of the Soviet Union]]. |
||
==Design and development== |
==Design and development== |
||
In 1982, [[Boeing]] was awarded the main contract to develop the system, named the Sea Lance. By the following year, it had become apparent that developing two different versions of the missile was too ambitious, and further development of the RUM-125 was suspended. The RUM-139, a vertical-launch model of the ASROC, was developed as a stopgap weapon in this role. |
In 1982, [[Boeing]] was awarded the main contract to develop the system, named the Sea Lance. By the following year, it had become apparent that developing two different versions of the missile was too ambitious, and further development of the RUM-125 was suspended. The RUM-139, a vertical-launch model of the ASROC, was developed as a stopgap weapon in this role. |
||
The Sea Lance was to be housed inside a watertight capsule which could be launched from an ordinary 21 |
The Sea Lance was to be housed inside a watertight capsule which could be launched from an ordinary 21 inch [[torpedo]] tube. The Mk 117 digital [[fire-control system]] provided targeting information to the missile prior to launch. After being fired, the capsule would float to the surface where the rocket would ignite and its fins would deploy. An [[Inertial navigation system|inertial guidance]] system would direct the missile to the general location of the target. Initial plans were to have the surface-launched version operate in a similar manner: launched from the [[Mark 41 Vertical Launching System|Mk 41]] [[vertical launching system]]. When the missile reached the intended area, the payload would separate from the missile, then deploy a parachute to decelerate the warhead or torpedo. Both missiles were initially planned to carry a [[depth charge]] with a 200 [[TNT equivalent|kiloton]] [[W89]] [[Thermonuclear weapon|thermonuclear]] [[warhead]]. Such a yield would have given the missile a lethal radius against submarines of around {{Convert|10|km|mi|abbr=out}}. This massive warhead, combined with the fact that the target would be unable to detect the missile until the payload hit the water, made it virtually impossible for a target to escape. |
||
In the mid-1980s, a conventional variant of this missile was proposed which would carry the new [[Mark 50 torpedo]] submarine-seeking weapon. This version was dubbed the UUM-125B. |
In the mid-1980s, a conventional variant of this missile was proposed which would carry the new [[Mark 50 torpedo]] submarine-seeking weapon. This version was dubbed the UUM-125B. |
||
A contract for the full-scale development of the Sea Lance was awarded in 1986. In 1988, it was decided to proceed again with the surface-launched RUM-125 version. The nuclear warhead was canceled in favor of a purely conventional missile |
A contract for the full-scale development of the Sea Lance was awarded in 1986. In 1988, it was decided to proceed again with the surface-launched RUM-125 version. The nuclear warhead was canceled in favor of a purely conventional missile. |
||
| ⚫ | In 1990, the entire program was canceled as a result of the collapse of the Soviet Union. Today the [[United States Navy|U.S. Navy]] [[attack submarine]]s do not have any long-range supersonic stand-off anti-submarine weapon, while U.S. Navy surface warships do have the new, vertical-launch version of the ASROC. |
||
==Gallery== |
|||
| ⚫ | In 1990, the entire program was canceled |
||
{{Gallery |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| align = |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| style = |
|||
| state = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| width = |
|||
| captionstyle = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| Sea Lance in-service capsule |
|||
| alt1= |
|||
| File:W89 NDB.png |
|||
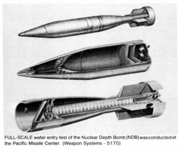
| Depth bomb shell. The W89 warhead would be fitted to this device. |
|||
| alt2= |
|||
| File: |
|||
| Write a caption here |
|||
| alt3= |
|||
| File: |
|||
| Write a caption here |
|||
| alt4= |
|||
| File: |
|||
| Write a caption here |
|||
| alt5= |
|||
}} |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
* |
* {{lwc|RUM-139 VL-ASROC}} |
||
* |
* {{lwc|RUR-5 ASROC}} |
||
* |
* {{lwc|UGM-89 Perseus}} |
||
* |
* {{lwc|UUM-44 SUBROC}} |
||
* {{lwc|RPK-2 Vyuga}} |
|||
* {{lwc|Ikara (missile)}} |
|||
==Suggested Reading== |
==Suggested Reading== |
||
* {{cite book| last = Polmar| first = Norman |
* {{cite book| last = Polmar| first = Norman| title = The Naval Institute Guide to the Ships and Aircraft of the U.S. Fleet | edition = 15th | year = 1993| publisher = [[Naval Institute|Naval Institute Press]]| location = [[Annapolis, Maryland | Annapolis, MD]] |isbn= 1-55750675-2}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
| Line 58: | Line 87: | ||
{{US missiles}} |
{{US missiles}} |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Cold War anti-submarine weapons of the United States]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Anti-submarine missiles of the United States]] |
||
[[Category:Ballistic missiles of the United States]] |
|||
[[Category:Abandoned military rocket and missile projects of the United States]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[ja:シーランス (ミサイル)]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 13:13, 28 September 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2010) |
| UUM-125 Sea Lance | |
|---|---|
 Artist concept | |
| Type | Standoff Anti-Submarine |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Service history | |
| Used by | United States Navy |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Boeing |
| Produced | Cancelled, 1990 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 1,400 kg (3,086 pounds) |
| Length | 6.25 m (20 ft 6 in) |
| Diameter | 53.3 cm (21.0 in) (capsule diameter) |
Detonation mechanism | RUM/UUM-125A W89 thermonuclear RUM/UUM-125B Mark 50 homing torpedo |
| Engine | Hercules EX 116 MOD 0 solid-fuel rocket |
Operational range | UUM-125A 185 kilometres (100 nautical miles) UUM-125B 65 kilometres (35 nautical miles) |
| Maximum speed | Mach 1.5 |
Guidance system | Mk 117 digital fire-control system |
Launch platform | Submarines • Los Angeles class • Seawolf class Surface Warships • Ticonderoga class • Spruance class • Arleigh Burke class |

The UUM-125 Sea Lance, known early in development as the Common ASW Standoff Weapon, was to be an American standoff anti-submarine missile, initially intended to carry a W89 thermonuclear warhead. It was conceived in 1980 as a successor to both the UUM-44 SUBROC and RUR-5 ASROC anti-submarine missiles. The Sea Lance was to be available in two versions, known as UUM-125A and RUM-125A. The former would be a submarine-launched version, the latter surface-launched. It was cancelled in 1990 as its importance was obviated by the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Design and development
[edit]In 1982, Boeing was awarded the main contract to develop the system, named the Sea Lance. By the following year, it had become apparent that developing two different versions of the missile was too ambitious, and further development of the RUM-125 was suspended. The RUM-139, a vertical-launch model of the ASROC, was developed as a stopgap weapon in this role.
The Sea Lance was to be housed inside a watertight capsule which could be launched from an ordinary 21 inch torpedo tube. The Mk 117 digital fire-control system provided targeting information to the missile prior to launch. After being fired, the capsule would float to the surface where the rocket would ignite and its fins would deploy. An inertial guidance system would direct the missile to the general location of the target. Initial plans were to have the surface-launched version operate in a similar manner: launched from the Mk 41 vertical launching system. When the missile reached the intended area, the payload would separate from the missile, then deploy a parachute to decelerate the warhead or torpedo. Both missiles were initially planned to carry a depth charge with a 200 kiloton W89 thermonuclear warhead. Such a yield would have given the missile a lethal radius against submarines of around 10 kilometres (6.2 mi). This massive warhead, combined with the fact that the target would be unable to detect the missile until the payload hit the water, made it virtually impossible for a target to escape.
In the mid-1980s, a conventional variant of this missile was proposed which would carry the new Mark 50 torpedo submarine-seeking weapon. This version was dubbed the UUM-125B.
A contract for the full-scale development of the Sea Lance was awarded in 1986. In 1988, it was decided to proceed again with the surface-launched RUM-125 version. The nuclear warhead was canceled in favor of a purely conventional missile. In 1990, the entire program was canceled as a result of the collapse of the Soviet Union. Today the U.S. Navy attack submarines do not have any long-range supersonic stand-off anti-submarine weapon, while U.S. Navy surface warships do have the new, vertical-launch version of the ASROC.
Gallery
[edit]See also
[edit]- RUM-139 VL-ASROC – (United States)
- RUR-5 ASROC – (United States)
- UGM-89 Perseus – (United States)
- UUM-44 SUBROC – (United States)
- RPK-2 Vyuga – (Soviet Union)
- Ikara (missile) – (Australia)
Suggested Reading
[edit]- Polmar, Norman (1993). The Naval Institute Guide to the Ships and Aircraft of the U.S. Fleet (15th ed.). Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-55750675-2.