Quebec City: Difference between revisions
this is OK |
Cleanup notes |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Provincial capital of Quebec, Canada}} |
|||
{{Dablink|For the Canadian province, see [[Quebec]]. For other uses, see [[Quebec (disambiguation)]].}} |
|||
{{Use Canadian English|date=March 2014}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=December 2019}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
| name = Québec<!-- DO NOT change without discussion--> |
|||
|name = Quebec City |
|||
|official_name = |
| official_name = {{native name|fr|Ville de Québec}} |
||
| settlement_type = [[List of cities in Quebec|City]] |
|||
|nickname = La Vieille Capitale'' |
|||
| image_skyline = {{multiple image |
|||
|settlement_type = City |
|||
| border = infobox |
|||
|motto = Don de Dieu ferai valoir<br />("I shall put God's gift to good use"; the ''Don de Dieu'' was Champlain's ship) |
|||
| total_width = 300 |
|||
|image_skyline = Quebec city-Vieux-Québec.jpg |
|||
| |
| image_style = |
||
| |
| perrow = 2/2/2/1 |
||
| |
| image1 = Quebec City Rue St-Louis 2010.jpg |
||
| caption1=[[Old Quebec]] |
|||
|image_shield = Armoiries de la ville de Québec.svg |
|||
| |
| image2 = Old quebec city.jpg |
||
| caption2=[[Terrasse Dufferin]] |
|||
|image_seal = |
|||
| |
| image3 = Québec - Hôtel du Parlement 3.jpg |
||
| caption3= [[Parliament Building (Quebec)|Quebec Parliament Building]] |
|||
|map_caption1 = |
|||
| image5 = Place Royale at night, Vieux-Québec, Quebec ville, Canada.jpg |
|||
|image_dot_map = |
|||
| caption5=[[Place Royale, Quebec City|Place Royale]] |
|||
|dot_map size = |
|||
| image10 = Château Frontenac city at night.jpg |
|||
|dot_map_caption = |
|||
| caption10 =[[Chateau Frontenac]] |
|||
|dot_x = |dot_y = |
|||
| image7 =Le pont de Québec et le pont Pierre-Laporte vus du boulevard Champlain.jpg |
|||
|pushpin_map = Canada Quebec<!-- the name of a location map as per http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Location_map --> |
|||
| caption7 =[[Pierre Laporte Bridge]] |
|||
|push pin_label_position =<!-- the position of the pushpin label: left, right, top, bottom, none --> |
|||
| image9 = Grand-Séminaire-Québec.jpg |
|||
|push pin_map_caption = |
|||
| caption9 = [[Laval University|Séminaire Québec]] |
|||
|push pin_map size = |
|||
}} |
|||
|subdivision_type = Country |
|||
| |
| image_caption = |
||
| image_flag = Flag of Quebec City.svg |
|||
|subdivision_type1 = Province |
|||
| |
| flag_size = 120x100px |
||
| image_seal = |
|||
|subdivision_type2 = Administrative Region |
|||
| seal_size = 1 |
|||
|subdivision_name2 = [[Capitale-Nationale]] |
|||
| image_shield = Armoiries de la ville de Québec.svg |
|||
|subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan community |
|||
| shield_size = 74x100px |
|||
|subdivision_name3 = [[Communauté métropolitaine de Québec]] |
|||
| image_blank_emblem = Quebec City.svg |
|||
|subdivision_type4 = [[Agglomeration]] |
|||
| blank_emblem_type = Logo |
|||
|subdivision_name4 = [[Agglomeration of Quebec City]] |
|||
| nickname = {{lang|fr|[[List of city nicknames in Canada#Quebec|La Vieille Capitale]]}}<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Marceau |first1=Stéphane G. |title=Ville de Québec |last2=Rémillard |first2=François |publisher=Guides de voyage Ulysse |year=2002 |isbn=2-89464-510-4 |edition=4th |location=Montreal |page=14 |language=fr}}</ref> |
|||
|government_footnotes = |
|||
| motto = {{lang|fr|Don de Dieu feray valoir}}<br />("I shall put God's gift to good use"; the ''Don de Dieu'' was Champlain's ship) |
|||
|government_type = |
|||
| |
| pushpin_map = Quebec#Canada |
||
| pushpin_map_caption = Location in Quebec##Location in Canada |
|||
|leader_name = [[Régis Labeaume]] |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|46|48|50|N|71|12|29|W|region:CA-QC|notes=<ref name=cgndb>{{Cite cgndb|EHTWR|Quebec City}}</ref>|display=inline,title}} |
|||
|leader_title1 = Majority leader |
|||
| coor_pinpoint = |
|||
|leader_name1 = [[Jean-Marie Matte]] |
|||
| coordinates_footnotes = <ref name="toponymie" /> |
|||
|leader_title2 = Federal senator |
|||
| subdivision_type = Country |
|||
|leader_name2 = [[Dennis Dawson]] |
|||
| subdivision_name = Canada |
|||
|leader_title3 = [[Members of the Canadian House of Commons|MPs]] |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = [[Provinces and territories of Canada|Province]] |
|||
|leader_name3 = {{Collapsible list |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = [[Region (Quebec)|Region]] |
|||
| subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan community |
|||
| subdivision_type4 = [[Urban agglomeration|Agglomeration]] |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Quebec]] |
|||
| subdivision_name2 = [[Capitale-Nationale]] |
|||
| subdivision_name3 = [[Communauté métropolitaine de Québec]] |
|||
| subdivision_name4 = [[Agglomeration of Quebec City]] |
|||
| subdivision_type5 = [[History of Quebec|Historic countries]] |
|||
| subdivision_name5 = [[Kingdom of France]]<br />[[Kingdom of Great Britain]] |
|||
| established_title = First settled |
|||
| established_date = 11 October 1535, <br />by [[Jacques Cartier]] |
|||
| established_title1 = Founded |
|||
| established_date1 = 3 July 1608, <br />by [[Samuel de Champlain]] |
|||
| established_title2 = Constituted |
|||
| established_date2 = 1 January 2002 |
|||
| established_title3 = Incorporated |
|||
| established_date3 = 1832<ref name="incor">{{Cite web |title=Incorporation de Québec |date=23 October 2007 |url=http://grandquebec.com/capitale-quebec/incorporation-ville/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235911/https://grandquebec.com/capitale-quebec/incorporation-ville/ |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=11 March 2018}}</ref> |
|||
| established_title4 = |
|||
| established_date4 = |
|||
| parts_type = Boroughs |
|||
| parts_style = <!-- =list (for list), coll (for collapsed list), para (for paragraph format) |
|||
Default is list if up to 5 items, coll if more than 5--> |
|||
| parts = <!-- parts text, or header for parts list --> |
|||
| p1 = [[Beauport, Quebec City|Beauport]] |
|||
| government_footnotes = <ref name="mamrot" /> |
|||
| government_type = [[Quebec City Council]] |
|||
| leader_title = Mayor |
|||
| leader_name = [[Bruno Marchand]] |
|||
| leader_title1 = [[Current members of the Canadian House of Commons|MPs]] |
|||
| leader_name1 = {{Collapsible list |
|||
|title = List of MPs |
|title = List of MPs |
||
|frame_style = border:none; padding: 0; |
|frame_style = border:none; padding: 0; |
||
|list_style = text-align:left;display:none; |
|list_style = text-align:left;display:none; |
||
|1 = [[ |
|1 = [[Gérard Deltell]] ([[Conservative Party of Canada|C]]) |
||
|2 = [[ |
|2 = [[Caroline Desbiens]] ([[Bloc Québécois|BQ]]) |
||
|3 = [[ |
|3 = [[Jean-Yves Duclos]] ([[Liberal Party of Canada|L]]) |
||
|4 = [[ |
|4 = [[Joël Godin]] ([[Conservative Party of Canada|C]]) |
||
|5 = [[ |
|5 = [[Joël Lightbound]] ([[Liberal Party of Canada|L]]) |
||
|6 = [[ |
|6 = [[Pierre Paul-Hus]] ([[Conservative Party of Canada|C]]) |
||
|7 = |
|7 = [[Julie Vignola]] ([[Bloc Québécois|BQ]]) |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| area_footnotes = <ref name="mamrot" /><ref name="auto2">{{Cite web |publisher=[[Government of Canada]], [[Statistics Canada]]|date=8 February 2017 |title=Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2016 Census |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/hlt-fst/pd-pl/Table.cfm?Lang=Eng&T=301&SR=3426&RPP=25&S=86&O=A&CMA=0&PR=0#2016A00052423027 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235847/https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/hlt-fst/pd-pl/Table.cfm?Lang=Eng&T=301&SR=3426&RPP=25&S=86&O=A&CMA=0&PR=0#2016A00052423027 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=15 February 2017}}</ref><ref name="auto">{{Cite web |publisher=Government of Canada, Statistics Canada |title=Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2021 Census |date=9 February 2022 |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2021/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&SearchText=Quebec&DGUIDlist=2021S0503421&GENDERlist=1,2,3&STATISTIClist=1,4&HEADERlist=0}}</ref> |
|||
|leader_title4 = [[National Assembly of Quebec|MNAs]] |
|||
| area_magnitude = |
|||
|leader_name4 = {{Collapsible list |
|||
| |
| area_total_km2 = 452.30 |
||
| area_land_km2 = 453.38 |
|||
|frame_style = border:none; padding: 0; |
|||
| area_urban_km2 = 442.85 |
|||
|list_style = text-align:left;display:none; |
|||
| area_water_km2 = |
|||
|1 = [[Raymond Bernier]] |
|||
| area_water_percent = |
|||
|2 = [[Yves Bolduc]] |
|||
| area_metro_km2 = 3499.46 |
|||
|3 = [[André Drolet]] |
|||
| elevation_footnotes = <ref>{{Cite web |last=Vallières |first=Marc |title=Québec City |url=http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/articles/quebec-city |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120522050125/http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/articles/quebec-city |archive-date=22 May 2012 |access-date=17 June 2012}}</ref><!--for references: use tags--> |
|||
|4 = [[Sam Hamad]] |
|||
| |
| elevation_m = 98 |
||
| |
| elevation_ft = |
||
| population_total = 549,459 ([[List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population|12th]]) |
|||
|7 = [[Agnès Maltais]] |
|||
| population_urban = 733,156 ([[List of the largest population centres in Canada|8th]]) |
|||
|8 = [[Michel Pigeon]] |
|||
| population_as_of = 2021 |
|||
|9 = [[Gérard Deltell]] |
|||
| population_footnotes = <ref name="auto2" /> |
|||
| population_density_km2 = 1214.8 |
|||
| population_density_urban_km2 = 1655.5 |
|||
| population_metro = 839,311 ([[List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada|7th]]) |
|||
| population_metro_footnotes = <ref name="auto" /> |
|||
| population_density_metro_km2 = 239.8 |
|||
| population_demonym = Québécois or Québécois de Québec (to distinguish residents of the city from those of the province) |
|||
| population_blank1_title = Pop <small>2016–2021</small> |
|||
| population_blank1 = {{increase}} 4.1% |
|||
| population_density_blank1_km2 = |
|||
| postal_code_type = [[Canadian postal code|Postal codes]] |
|||
| postal_code = [[List of postal codes of Canada: G|G1A to G2N]] |
|||
| area_codes = [[Area codes 418, 581, and 367|{{hlist|418|581|367}}]] |
|||
| blank_name_sec2 = [[GDP]] (Québec {{Abbr|CMA|Census metropolitan area}}) |
|||
| blank_info_sec2 = [[Canadian dollar|CA$]]47.94 billion (2020)<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/t1/tbl1/en/tv.action?pid=3610046801 | title=Gross domestic product (GDP) at basic prices, by census metropolitan area (CMA) | date=December 6, 2023 }}</ref> |
|||
| blank1_name_sec2 = GDP per capita (Québec {{Abbr|CMA|Census metropolitan area}}) |
|||
| blank1_info_sec2 = CA$53,477 (2016) |
|||
| website = {{Official URL}} |
|||
| footnotes = {{designation list |embed=yes |
|||
| designation1 = World Heritage Site |
|||
| designation1_offname = Historic District of Old Quebec |
|||
| designation1_date = 1985 <small>(9th [[World Heritage Committee|session]])</small> |
|||
| designation1_type = Cultural |
|||
| designation1_criteria = iv, vi |
|||
| designation1_number = [https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/300 300] |
|||
| designation1_free1name = Region |
|||
| designation1_free1value = [[List of World Heritage Sites in North America|Europe and North America]] |
|||
}} |
|||
| p2 = [[Charlesbourg, Quebec City|Charlesbourg]] |
|||
| p3 = [[La Cité-Limoilou]] |
|||
| p4 = [[La Haute-Saint-Charles, Quebec City|La Haute-Saint-Charles]] |
|||
| p5 = [[Les Rivières, Quebec City|Les Rivières]] |
|||
| p6 = [[Sainte-Foy–Sillery–Cap-Rouge]] |
|||
| leader_title2 = [[List of Quebec provincial electoral districts|MNAs]] |
|||
| leader_name2 = {{Collapsible list |
|||
|title = List |
|||
|frame_style = border:none; padding: 0; |
|||
|list_style = text-align:left;display:none; |
|||
|1 = [[Jonatan Julien]] ([[Coalition Avenir Québec|C]]) |
|||
|2 = [[Kariane Bourassa]] ([[Coalition Avenir Québec|C]]) |
|||
|3 = [[Éric Caire]] ([[Coalition Avenir Québec|C]]) |
|||
|4 = [[Sol Zanetti]] ([[Québec Solidaire|QS]]) |
|||
|5 = [[Geneviève Guilbault]] ([[Coalition Avenir Québec|C]]) |
|||
|6 = [[Mario Asselin]] ([[Coalition Avenir Québec|C]]) |
|||
|7 = [[Étienne Grandmont]] ([[Québec Solidaire|QS]]) |
|||
|8 = [[Joëlle Boutin]] ([[Coalition Avenir Québec|C]]) |
|||
|9 = [[Sylvain Lévesque]] ([[Coalition Avenir Québec|C]]) |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| area_metro_footnotes = <ref name="cp2011-CA" /> |
|||
|established_title = Founded |
|||
| |
| timezone = [[Eastern Time Zone|EST]] |
||
| utc_offset = −05:00 |
|||
|established_title2 = Constitution date |
|||
| |
| timezone_DST = EDT |
||
| utc_offset_DST = −04:00 |
|||
|established_title3 =<!-- Incorporated (city) --> |
|||
| blank_emblem_size = 100px |
|||
|established_date3 = |
|||
|area_magnitude = |
|||
|unit_pref =<!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired--> |
|||
|area_footnotes = |
|||
|area_total_km2 = 454.26 <!-- ALL fields dealing with a measurements are subject to automatic unit conversion--> |
|||
|area_land_km2 =<!--See table @ Template:Infobox Settlement for details on automatic unit conversion--> |
|||
|area_water_km2 = |
|||
|area_total_sq_mi = |
|||
|area_land_sq_mi = |
|||
|area_water_sq_mi = |
|||
|area_water_percent = |
|||
|area_urban_km2 = 670.10 |
|||
|area_urban_sq_mi = |
|||
|area_metro_km2 = 3276.53 |
|||
|area_metro_sq_mi = |
|||
|population_as_of = [[Canada 2006 Census|2006]]<ref name="StatCan1">[http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/profiles/community/Details/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423027&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchText=Quebec&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&Custom= Statistics Canada.] 2006 Community Profiles — Census Subdivision — Quebec City</ref><ref name="StatCan2">[http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/profiles/community/Details/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CMA&Code1=421__&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchText=Quebec&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&Custom= Statistics Canada.] 2006 Community Profiles — Census Metropolitan Area — Quebec City</ref> |
|||
|population_footnotes = |
|||
|population_note = |
|||
|population_total = 491,142 ([[List of the 100 largest municipalities in Canada by population|10th]]) |
|||
|population_density_km2 = 1081.2 |
|||
|population_density_sq_mi = |
|||
|population_urban = 659,545 |
|||
|population_density_urban_km2 = 984.2 |
|||
|population_density_urban_sq_mi = |
|||
|population_metro = 715,515 ([[List of the 100 largest metropolitan areas in Canada|7th]]) |
|||
|population_density_metro_km2 = 218.4 |
|||
|population_density_metro_sq_mi = |
|||
|population_blank1_title = |
|||
|population_blank1 = |
|||
|population_density_blank1_km2 = |
|||
|population_density_blank1_sq_mi= |
|||
|timezone = Eastern |
|||
|utc_offset = −5 |
|||
|timezone_DST = EDT |
|||
|utc_offset_DST = −4 |
|||
|latd=46 |latm=48 |lats=47 |latNS=N |
|||
|longd=71 |longm=13 |longs= |longEW=W |
|||
|elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use<ref></ref> tags--> |
|||
|elevation_m = |
|||
|elevation_ft = |
|||
|postal_code_type = <!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... --> |
|||
|postal_code = |
|||
|area_code = [[Area code 418/581|418/581]] |
|||
|blank_name = [[Standard Geographical Classification code (Canada)|SGC code]] |
|||
|blank_info = 24 23 027 |
|||
|blank1_name = [[National Topographic System|NTS]] Map |
|||
|blank1_info = 021L14 |
|||
|blank2_name = [[Geographical Names Board of Canada|GNBC]] Code |
|||
|blank2_info = EHTWR |
|||
|blank3_name = |
|||
|blank3_info = |
|||
|website = [http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/index.aspx Official website of Quebec City] |
|||
|footnotes = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Quebec''' ({{IPA-en|kwɨˈbɛk|}} or {{IPA|/kəˈbɛk/}}), {{lang-fr|'''Québec'''}} ({{IPA-fr|keˈbɛk||FR-Québec.ogg}}), also '''Quebec City''' or '''Québec City''' ({{lang-fr|Ville de Québec}})<ref>According to the [[Government of Canada|federal]] and [[Politics of Quebec#Government of Quebec|provincial government]]s, '''Québec''' (with the [[acute accent]]) is the city's official name in both [[Quebec French|French]] and [[Canadian English|English]]. Even though French place names in Canada typically retain their accents in English and the city's name is [http://geonames.nrcan.gc.ca/info/pan_can_e.php not among 81 locales of pan-Canadian significance with official forms in both languages], as is the case with the province of [[Quebec|Quebec/''Québec'']], '''Quebec''' is a legitimate and well-established exception in English (as is [[Montreal]]). Similarly, '''Quebec City''' is common (e.g., per the ''[[Canadian Oxford Dictionary]]'' (ISBN 0-19-541816-6, p. 1265)), and is used particularly to distinguish the city from the province. According to ''Editing Canadian English'' (ISBN 1-55199-045-8, p. 77) the form '''Québec City''' makes no sense in either English or French; nonetheless, it is used by the [http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/EN/apropos/portrait/symbole_identitaire.aspx municipal government] and other sources (e.g., [[Québec City Jean Lesage International Airport]]).</ref> is the [[Capital (political)|capital]] of the [[Canada|Canadian]] [[Provinces and territories of Canada|province]] of [[Quebec]] and is located within the [[Capitale-Nationale]] region. It is the second most populous city in Quebec – after [[Montreal]], about {{convert|233|km|0}} to the southwest. As of the [[Canada 2006 Census|2006 Canadian Census]], the city has a population of 491,142,<ref name = "StatCan1"/> and the [[Communauté métropolitaine de Québec|metropolitan area]] has a population of 715,515.<ref name = "StatCan2"/> |
|||
'''Quebec City'''{{efn|{{IPAc-en|audio=En-Quebec.ogv|k|w|ᵻ|ˈ|b|ɛ|k}} or {{IPAc-en|k|ə|ˈ|b|ɛ|k}};<ref name="oedpron">{{cite OED|Quebec}}</ref> {{langx|fr|Ville de Québec}}), officially known as '''Québec''' ({{IPA|fr|kebɛk|FR-Québec.ogg}})<ref>{{Cite web |last=Government of Canada |first=Natural Resources Canada |title=Place names – Québec |url=http://www4.rncan.gc.ca/search-place-names/unique/EHTWR |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235550/http://www4.rncan.gc.ca/search-place-names/unique/EHTWR |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=31 March 2019 |website=www4.rncan.gc.ca}}</ref>}} is the capital city of the [[Provinces and territories of Canada|Canadian province]] of [[Quebec]]. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459,<ref name="Statistics Canada Census 2021">{{Cite web |title=Québec, Ville [Census subdivision], Quebec and Québec, Territoire équivalent [Census division], Quebec |url=http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423027&Geo2=CD&Code2=2423 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235554/https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423027&Geo2=CD&Code2=2423 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=3 March 2017 |website=Census 2016 | date=8 February 2017 |publisher=Statistics Canada}}</ref> and the [[Communauté métropolitaine de Québec|metropolitan area]] had a population of 839,311.<ref>{{Cite web |publisher=Government of Canada, Statistics Canada|date=8 February 2017 |title=Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2016 Census |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/hlt-fst/pd-pl/Table.cfm?Lang=Eng&T=205&S=3&RPP=100 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180923090409/https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/hlt-fst/pd-pl/Table.cfm?Lang=Eng&T=205&S=3&RPP=100 |archive-date=23 September 2018 |access-date=15 February 2017 |website=www12.statcan.gc.ca}}</ref> It is the twelfth[[List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population|-largest city]] and the seventh[[List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada|-largest metropolitan area]] in Canada. It is also the [[List of towns in Quebec|second-largest city]] in the province, after [[Montreal]]. It has a [[humid continental climate]] with warm summers coupled with cold and snowy winters. |
|||
The narrowing of the [[Saint Lawrence River]] approximate to Quebec City and [[Lévis, Quebec|Lévis]], on the opposite bank, provided the name given to the city, ''Kébec'', an [[Algonquin]] word meaning "where the river narrows". Founded in 1608 by [[Samuel de Champlain]], Quebec City is one of the [[List of North American cities by year of foundation|oldest cities]] in [[North America]]. The [[Ramparts of Quebec City|ramparts]] surrounding [[Old Quebec]] (''Vieux-Québec'') are the only remaining fortified [[city walls]] that still exist in the [[Americas]] north of [[Mexico]], and were declared a [[World Heritage Site]] by [[United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization|UNESCO]] in 1985 as the 'Historic District of Old Québec'.<ref>"[http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/300 Historic District of Old Québec]". [[World Heritage Site|World Heritage]]; [[UNESCO]]. Retrieved January 12, 2009.</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.cbc.ca/sevenwonders/wonder_quebec_city.html |title=Old Quebec City, Seven Wonders of Canada |accessdate=February 12, 2008 |work=cbc.ca }}</ref> |
|||
Explorer [[Samuel de Champlain]] founded a French settlement here in 1608, and adopted the Algonquin name. Quebec City is one of the [[List of North American cities by year of foundation|oldest European settlements]] in North America. The [[Ramparts of Quebec City|ramparts]] surrounding [[Old Quebec]] ({{Lang|fr|Vieux-Québec}}) are the only fortified [[city walls]] remaining in the Americas north of [[Mexico]]. This area was declared a [[World Heritage Site]] by [[UNESCO]] in 1985 as the "Historic District of Old Québec".<ref>"[https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/300 Historic District of Old Québec] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110628191918/https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/300 |date=28 June 2011 }}". [[World Heritage Site|World Heritage]]; [[UNESCO]]. Retrieved 12 January 2009.</ref><ref>{{Cite news |title=Old Quebec City, Seven Wonders of Canada |work=cbc.ca |url=http://www.cbc.ca/sevenwonders/wonder_quebec_city.html |url-status=live |access-date=12 February 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080207024051/http://www.cbc.ca/sevenwonders/wonder_quebec_city.html |archive-date=7 February 2008}}</ref> |
|||
==Name and usage== |
|||
{{Further|Name of Quebec City|Quebec#Etymology}} |
|||
Common [[English language|English-language]] usage distinguishes the city from the province by referring to the former as Quebec City.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Government of Canada |first1=Public Services and Procurement Canada |title=Québec, City of Québec, Quebec City – Writing Tips Plus – Writing Tools – Resources of the Language Portal of Canada – Canada.ca |url=https://www.noslangues-ourlanguages.gc.ca/en/writing-tips-plus/quebec-city-of |website=Writing Tips Plus |access-date=20 May 2022 |date=28 February 2020}}</ref> |
|||
According to the Government of Canada, the Government of Quebec, and the Geographical Names Board of Canada, the names of Canadian cities and towns have only one official form. Thus, Québec is officially spelled with an accented é in both [[Canadian English]] and [[French language|French]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=2016 |title=Québec, City of Québec, Quebec City |url=http://www.btb.termiumplus.gc.ca/tpv2guides/guides/wrtps/index-eng.html?lang=eng&lettr=indx_catlog_q&page=9M186EWC4Ldg.html#zz9M186EWC4Ldg |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160914012658/http://www.btb.termiumplus.gc.ca/tpv2guides/guides/wrtps/index-eng.html?lang=eng&lettr=indx_catlog_q&page=9M186EWC4Ldg.html#zz9M186EWC4Ldg |archive-date=14 September 2016 |access-date=29 October 2016 |publisher=Public Works and Government Services Canada}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Names (geographical) |url=http://www.psc-cfp.gc.ca/abt-aps/stgd-gdst/index-eng.htm#toc2.15 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161121144149/http://www.psc-cfp.gc.ca/abt-aps/stgd-gdst/index-eng.htm#toc2.15 |archive-date=21 November 2016 |access-date=29 October 2016 |publisher=Public Service Commission of Canada}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Government of Canada |date=8 October 2009 |title=Geographical Names |url=http://www.btb.termiumplus.gc.ca/tcdnstyl-chap?lang=eng&lettr=chapsect15&info0=15#zz15 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161030002236/http://www.btb.termiumplus.gc.ca/tcdnstyl-chap?lang=eng&lettr=chapsect15&info0=15#zz15 |archive-date=30 October 2016 |access-date=29 October 2016 |publisher=The Canadian Style}}</ref> However, province names can have different forms in English and French. As a result, in English, the federal government style distinguishes the city and province by spelling the city with an acute accent (Québec) and the province without one (Quebec). The government of Quebec spells both names "Québec", including when writing in English.<ref>{{cite web |title=Faut-il traduire les toponymes? |url=https://toponymie.gouv.qc.ca/ct/normes-procedures/regles-ecriture/traduire-toponymes.html |website=Commission de toponymie |access-date=20 May 2022 |date=26 November 2020}}</ref> |
|||
In French, the two are distinguished in that province names including Quebec generally take [[definite article]]s, while city names do not. As a result, the city is {{lang|fr|Québec}} and the province is {{lang|fr|le Québec}}; "in Quebec City" is {{lang|fr|à Québec}} and "in the province of Quebec" is {{lang|fr|au Québec}}; and so forth.<ref>{{cite web |title=Québec en quelques mots |url=https://immigrantquebec.com/fr/reussir-votre-installation/vivre-a-quebec/connaitre-quebec/quebec-en-quelques-mots/ |website=Immigrant Québec |access-date=20 May 2022 |language=fr-CA |date=22 October 2021}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Algonquian people]] had originally named the area {{lang|alq|Kébec}}, an [[Algonquin language|Algonquin]]{{efn|The [[Algonquin language]] is a distinct language of the [[Algonquian languages|Algonquian language family]], and is not a misspelling.}} word meaning "where the river narrows", because the [[Saint Lawrence River]] narrows proximate to the [[promontory of Quebec]] and its [[Cap Diamant|Cape Diamant]]. |
|||
Quebec City is internationally known for its [[Quebec City Summer Festival|Summer Festival]], [[Quebec Winter Carnival|Winter Carnival]], and the [[Château Frontenac]], a [[hotel]] which dominates the city skyline. The [[National Assembly of Quebec]], the [[Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec]] (''National Museum of Fine Arts of Quebec''), and the [[Musée de la civilisation]] (''Museum of Civilization'') are found within or near [[Vieux-Québec]]. Among the other attractions near the city are [[Montmorency Falls]] and the [[Basilica of Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré]] in the town of [[Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré, Quebec|Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré]]. |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
{{See also|History of Quebec City|Timeline of Quebec City history |
{{See also|History of Quebec City|Timeline of Quebec City history}} |
||
=== French regime (1500s–1763) === |
|||
===Early history: from Stadacona to Seven Years War=== |
|||
Quebec City is one of the oldest European settlements in [[North America]] and the only fortified city north of [[Mexico]] whose walls still exist.<ref>{{Cite web |title=CBC.CA – Seven Wonders of Canada – Your Nominations – Old Quebec City, Quebec |url=https://www.cbc.ca/sevenwonders/wonder_quebec_city.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190401022236/https://www.cbc.ca/sevenwonders/wonder_quebec_city.html |archive-date=1 April 2019 |access-date=31 March 2019 |website=www.cbc.ca}}</ref> While many of the major cities in [[Latin America]] date from the 16th century, among cities in Canada and the United States, few were created earlier than Quebec City ([[St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador|St. John's]], [[Harbour Grace]], [[Port-Royal (Acadia)|Port Royal]], [[St. Augustine, Florida|St. Augustine]], [[Santa Fe, New Mexico|Santa Fe]], [[Jamestown, Virginia|Jamestown]], and [[Tadoussac]]). |
|||
[[File:Samuel de champlain.jpg|thumb|left|Traditional representation of [[Samuel de Champlain]]]] |
|||
[[File:Jacques Cartier rencontre les indiens de Stadacone, 1535.jpg|left|thumb|Depiction of [[Jacques Cartier]]'s meeting with the indigenous people of [[Stadacona]] in 1535]] |
|||
Quebec City is one of the oldest European settlements in North America. While many of the major cities in Mexico date from the sixteenth century, among cities in Canada and the U.S.A. only [[St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador]]; [[Port Royal, Nova Scotia]]; [[St. Augustine, Florida]]; [[Santa Fe, New Mexico]]; [[Jamestown, Virginia]]; and [[Tadoussac, Quebec]] were created earlier than Quebec City. However, Quebec City is the first to have been founded with the goal of permanent [[Settlement (migration)|settlement]], and not as a [[Commerce|commercial]] [[outpost]], and therefore is considered to be the first European-built city in non-[[Spanish colonization of the Americas|Spanish North America]]. |
|||
It is home to the earliest known French settlement in North America, [[Charlesbourg-Royal|Fort Charlesbourg-Royal]], established in 1541 by explorer [[Jacques Cartier]] with some 400 persons but abandoned less than a year later due to the harsh winter and resistance of indigenous inhabitants to colonial incursion on their land.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Fort Charlesbourg Royal National Historic Site of Canada |url=https://www.historicplaces.ca/en/rep-reg/place-lieu.aspx?id=16661 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235615/https://www.historicplaces.ca/en/rep-reg/place-lieu.aspx?id=16661 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=6 October 2018 |website=www.historicplaces.ca |publisher=Parks Canada |language=en}}</ref> The fort was at the mouth of the [[Rivière du Cap Rouge]], in the suburban former [[Cap-Rouge, Quebec City|town of Cap-Rouge]] (which merged into Quebec City in 2002). |
|||
French explorer [[Jacques Cartier]] built a fort at the site in 1535, where he stayed for the winter before going back to [[France]] in spring 1536. He came back in 1541 with the goal of building a permanent settlement. This first settlement was abandoned less than one year after its foundation, in the summer 1542, due in large part to the hostility of the natives combined with the harsh living conditions during winter. |
|||
Quebec was founded by [[Samuel de Champlain]], a French explorer and diplomat on July |
Quebec was founded by [[Samuel de Champlain]], a French explorer and diplomat, on 3 July 1608,<ref name="WDL1">{{Cite web |title=View of Quebec, Capital of Canada |url=http://www.wdl.org/en/item/224 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235552/https://www.wdl.org/en/item/224/nearest-items.json?limit=25 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=11 February 2013 |publisher=[[World Digital Library]]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Moss |first=William |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_CJBDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT334 |title=The Recent Archaeology of the Early Modern Period in Quebec City: 2009 |date=2 December 2017 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=9781351193337 |pages=334 |language=en |access-date=30 June 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235557/https://books.google.com/books?id=_CJBDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT334 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> and at the site of a long abandoned [[Laurentian language|St. Lawrence Iroquoian]] settlement called [[Stadacona]]. Champlain, who came to be called "The Father of [[New France]]", served as its administrator for the rest of his life. |
||
The [[ |
The [[name of Canada|name "Canada"]] was given to the colony that developed around the settlement at Quebec. Although the [[Acadia]]n settlement at [[Port-Royal (Acadia)|Port-Royal]] was established three years earlier, Quebec came to be known as the cradle of North America's [[French language|Francophone]] population. The location seemed favourable to the establishment of a permanent colony. |
||
[[File:Quebec nouvelle france.jpg|thumb|Quebec City in 1700]] |
|||
[[File:Château Frontenac01.jpg|thumb|alt=Château Frontenac in Quebec City|upright=1,5|[[Château Frontenac]]]] |
|||
[[File:Plaque des premiers colons de Quebec.jpg|thumb|left|Plaque honouring the first settlers of Québec City. (affixed to back of monument to {{ill|Guillaume Couillard (settler)|fr|Guillaume Couillard|lt=Guillaume Couillard}}, which accompanies those to [[Louis Hébert]] and [[Marie Rollet]]). [[Parc Montmorency]], [[Québec City]].]] |
|||
In 1665, there were 550 people in 70 houses living in the city. One-quarter of the people were religious: secular priests, Jesuits, Ursulines nuns and the order running the local hospital, Hotel-Dieu.<ref>{{cite book |last = Morison |first = Samuel Eliot |authorlink = Samuel Eliot Morison |coauthors = |title = The Oxford History of the American People |publisher = [[Mentor]] |year = 1972 |location = New York City |pages = 150|url = |doi = |id = |isbn = 0-451-62600-1 }}</ref> |
|||
The population of the settlement remained small for decades. In 1629 it was [[surrender of Quebec|captured by English privateers]], led by [[David Kirke]], during the [[Anglo-French War (1627–1629)|Anglo-French War]].<ref name="kirkbio">[http://www.biographi.ca/009004-119.01-e.php?id_nbr=368&PHPSESSID=5741tch9j1hgc3ki456h1e5uv7 "KIRKE, SIR DAVID, adventurer, trader, colonizer, leader of the expedition that captured Quebec in 1629, and later governor of Newfoundland"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200917104640/http://www.biographi.ca/en/bio.php?id_nbr=368%2F |date=17 September 2020 }}, ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online''</ref> Samuel de Champlain argued that the English seizing of French lands was illegal as the war had already ended, and worked to have them returned to France. As part of the ongoing negotiations following the end of the Anglo-French War, in 1632 the English king [[Charles I of England|Charles I]] agreed to return captured lands in exchange for [[Louis XIII of France|Louis XIII]] paying his wife's [[dowry]].<ref name=kirkbio /> These terms were signed into law with the [[Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1632)|Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye]]. The colonies of [[Canada (New France)|Canada]] and [[Acadia]] were returned to the French [[Company of One Hundred Associates]].<ref name=kirkbio /> |
|||
Quebec City was captured by the British in 1759 and held until 1763. It was the site of three battles during [[Seven Years War]] - the [[Battle of Beauport]], a French victory (July 31, 1759); the [[Battle of the Plains of Abraham]], in which British troops under General [[James Wolfe]] defeated the French General [[Louis-Joseph de Montcalm]] on September 13, 1759 and shortly thereafter took the city; and the final [[Battle of Sainte-Foy]], a French victory (April 28, 1760). France ceded [[New France]], including the city, to Britain in 1763. |
|||
In 1665, there were 550 people in 70 houses living in the city. One-quarter of the people were members of religious orders: secular priests, Jesuits, Ursulines nuns and the order running the local hospital, Hôtel-Dieu.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Morison |first=Samuel Eliot |title=The Oxford history of the American people. |publisher=Mentor |year=1972 |isbn=0-451-62600-1 |location=New York |pages=150 |oclc=7384608}}</ref> |
|||
At the end of French rule in 1763, the territory of present-day Quebec City was a world of contrasts. Forests, villages, fields and pastures surrounded the town of 8 000 inhabitants. The town distinguished itself by its monumental architecture, fortifications, muddy and filthy streets, affluent homes of masonry and shacks in the suburbs St-Jean and St-Roch. Despite its urbanity and its status as capital, Quebec City remained a small colonial city with close ties to its rural surroundings. Nearby inhabitants traded their farm surpluses and firewood for imported goods from France at the two city markets. |
|||
Quebec was the headquarters of many raids against [[New England]] during the [[French and Indian Wars]]. In 1690 the city [[battle of Quebec (1690)|was attacked by the English]], but was successfully defended. In the last of the conflicts, the [[French and Indian War]] ([[Seven Years' War]]), Quebec was captured by the British in 1759, and held until the end of the war in 1763. In that time many battles and sieges took place: the [[Battle of Beauport]], a French victory (31 July 1759); the [[Battle of the Plains of Abraham]], in which British troops under General [[James Wolfe]] defeated the French General [[Louis-Joseph de Montcalm]] on 13 September 1759, and shortly thereafter took the city after a short siege. A French counterattack saw a French victory at the [[Battle of Sainte-Foy]] (28 April 1760) but the subsequent second [[Siege of Quebec (1760)|Siege of Quebec]] the following month however saw a final British victory.[[File:PlainsOfAbraham2007.jpg|thumb|left|After a campaign of three months British forces captured Quebec City after the Battle of the Plains of Abraham.]] |
|||
===British rule=== |
|||
During the [[American Revolution]], revolutionary troops from the southern colonies assaulted the British garrison in an attempt to 'liberate' Quebec City now known as the [[Battle of Quebec (1775)|Battle of Quebec]]. The defeat of the revolutionaries from the south put an end to the hopes that the peoples of Quebec would rise and join the [[American Revolution]] so that Canada would join the [[Continental Congress]] and become part of the original [[United States of America]] along with the other British colonies of continental North America. In effect, the outcome of the battle would be the effective split of British North America into two distinct political entities. Following the battle, Major General [[Isaac Brock]] further fortified Quebec City by strengthening the walls and building an elevated [[artillery]] battery known as the [[Citadelle of Quebec]] before the [[War of 1812]]. A series of [[Martello towers]] was also built on elevated terrain beyond the city walls to provide further artillery support effectively turning the city into a [[fortress]]. In the end, the city was not attacked during the war of 1812 but continued to house a large British garrison until 1871. The Citadel is still in use by the military and three of the Martello towers are still maintained as museums and tourist attractions. |
|||
France ceded [[New France]], including the city, to Britain in 1763,<ref>{{Cite web |date=7 October 1763 |title=George R, Proclamation, 7 October 1763 (Royal Proclamation) |url=https://primarydocuments.ca/royal-proclamation-1763/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190401032305/https://primarydocuments.ca/royal-proclamation-1763/ |archive-date=1 April 2019 |access-date=31 March 2019 |website=PrimaryDocuments.ca |language=en-CA}}</ref> when the [[French and Indian War]] officially ended. |
|||
In 1840, after the Province of Canada was formed, the role of capital was shared between [[Kingston, Ontario|Kingston]], [[Montreal]], [[Toronto]], [[Ottawa]] and Quebec City (from 1852 to 1856 and from 1859 to 1866). In 1867, Ottawa (which was chosen to be the permanent capital of the Province of Canada) was chosen to be the capital of the Dominion of Canada. The [[Quebec Conference, 1864|Quebec Conference]] on [[Canadian Confederation]] was held here. |
|||
At the end of French rule, Quebec was a town of 8,000 inhabitants, surrounded by forests, villages, fields and pastures. The town was distinguished by its monumental architecture, fortifications, and affluent homes of masonry and shacks in the suburbs of Saint-Jean and Saint-Roch. Despite its urbanity and its status as capital, Quebec remained a small city with close ties to its rural surroundings. Nearby inhabitants traded their farm surpluses and firewood for imported goods from France at the two city markets. |
|||
===20th and 21st centuries=== |
|||
[[File:Quebec-wharf.jpg|thumb|left|Port of Quebec City in the early 20th century]] |
|||
[[File:Quebec City Map 1906.jpg|thumb|Quebec City map, 1906]] |
|||
Quebec City was struck by the [[1925 Charlevoix-Kamouraska earthquake]]. |
|||
=== British and Canadian rule (1763–present)=== |
|||
During [[World War II]], two conferences were held in Quebec City. The [[Quebec Conference, 1943|First Quebec Conference]] was held in 1943 with [[Franklin Delano Roosevelt]] (the United States' president at the time), [[Winston Churchill]] (the [[United Kingdom]]'s prime minister), [[William Lyon Mackenzie King]] (Canada's prime minister) and [[T.V. Soong]] ([[republic of China|China's]] minister of foreign affairs). The [[Second Quebec Conference]] was held in 1944, and was attended by Churchill and Roosevelt. They took place in the buildings of the [[Citadelle of Quebec|Citadelle]] and of nearby [[Château Frontenac]]. A large part of the [[D-Day]] Landings plans were made during those meetings. |
|||
{{more citations needed section|date=April 2016}} |
|||
[[File:Canadian militiamen and British soldiers repulse the American assault at Sault-au-Matelot.jpg|thumb|British regulars and [[Canadian militia]] engage the [[Continental Army]] in the streets of the city. The Americans' failure to take Quebec in 1775 led to the end of their [[Invasion of Quebec (1775)|campaign in Canada.]]]] |
|||
During the [[American Revolution]], revolutionary troops from the southern colonies [[Battle of Quebec (1775)|assaulted the British garrison in the city]] in the hope that the peoples of Quebec would rise and join the [[American Revolution]] so that Canada would join the [[Continental Congress]], along with the other British colonies of continental North America. The American invasion failed, however, and the war resulted in a permanent split of British North America into two entitles: the newly independent [[United States of America]], and those colonies (including Quebec) that remained under British control, which would later become the country of [[Canada]]. |
|||
===Capital=== |
|||
Throughout its over four hundred years of existence, Quebec City has served as a capital. From 1608 to 1627 and 1632 to 1763, it was capital of French [[Canada (New France)|Canada]] and all of [[New France]]; from 1763 to 1791, it was the capital of the [[Province of Quebec (1763-1791)|Province of Quebec]]; from 1791 to 1841, it was the capital of [[Lower Canada]]; from 1852 to 1856 and from 1859 to 1866, it was capital of the [[Province of Canada]]; and since 1867, it has been capital of the Province of [[Quebec]]. The administrative region in which Quebec City is situated is officially referred to as [[Capitale-Nationale]]<ref>Décret concernant la révision des limites des régions administratives du Québec, R.Q. c. D-11, r.2, made pursuant to the Territorial Division Act, R.S.Q. c. D-11</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gouv.qc.ca/portail/quebec/pgs/commun/portrait/regions/description/?lang=en#03|title=Québec Portal > Portrait of Québec > Administrative Regions > Regions|accessdate=May 13, 2009}}</ref> and the term "national capital" is used to refer to Quebec City itself at provincial level.<ref name="CanLII">{{cite web|url=http://www.canlii.org/en/qc/laws/stat/rsq-c-c-33.1/latest/rsq-c-c-33.1.html|title=An Act respecting the National capital commission, R.S.Q. c. C-33.1|date=May 4, 2009|publisher=CanLII|accessdate=May 13, 2009}}</ref> |
|||
The city itself was not attacked during the [[War of 1812]], when the United States again attempted to annex Canadian lands. Amid fears of another American attack on Quebec City, construction of the [[Citadelle of Quebec]] began in 1820. The Americans did not attack Canada after the War of 1812, but the Citadelle continued to house a large British garrison until 1871. It is still in use by the military and is also a tourist attraction. |
|||
Until the late 18th century Québec was the most populous city in present-day Canada. As of the census of 1790, Montreal surpassed it with 18,000 inhabitants, but Quebec, which had about 14,000 of population at that time, remained the administrative capital of the former New France.<ref name="Cartier">{{Cite journal |last=Cartier |first=Gwenaël |date=2009 |title=Québec 1608–2008 : 400 ans de statistiques démographiques tirées des recensements |url=https://www.erudit.org/en/journals/cqd/2008-v37-n1-cqd2900/029642ar/ |url-status=live |journal=Cahiers québécois de démographie |language=fr |volume=37 |page=143 |doi=10.7202/029642ar |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180729111705/https://www.erudit.org/en/journals/cqd/2008-v37-n1-cqd2900/029642ar/ |archive-date=29 July 2018 |access-date=29 July 2018 |doi-access=}}</ref> It was then made the capital of [[Lower Canada]] by the [[Constitutional Act of 1791]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Ville de Québec – Québec City, Fortress and Port (1756–1867) |url=https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/en/apropos/portrait/histoire/1756-1867.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235646/https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/en/apropos/portrait/histoire/1756-1867.aspx |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=31 March 2019 |website=Ville de Québec}}</ref> From 1841 to 1867, the capital of the [[Province of Canada]] rotated between [[Kingston, Ontario|Kingston]], [[Montreal]], [[Toronto]], [[Ottawa]] and Quebec City (from 1851 to 1855 and from 1859 to 1865).<ref>{{cite web |last1=Clapperton |first1=Nina |title=13 Canada Capital Cities |url=https://ninaoutandabout.ca/canada-capital-cities/ |website=Nina Out and About |date=18 November 2021 |access-date=10 April 2022}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Loading ship with square timber through the bow port Quebec City QC 1872.jpg|thumb|Square timber being loaded on a sail ship at the port of Québec in 1872]] |
|||
The city experienced an economic golden age in the 1800s, due to its favorable location on the Saint Lawrence River which gave rise to industries of wooden [[Sailing ship|sailing]] ships manufacture, export of squared [[Lumber|timber logs]]. to Europe, as wall as associated enterprises such as [[sawmill]]s. However, by the 1870s, Québec City entered a period of economic decline. Contributing factors included the rise of steel-hulled [[Steamship|steamships]], the expansion of railroads at the expense of waterways for continental commerce; the depletion of forest resources near major rivers upstream of Québec City and in the west of the province, which were transported to [[Port of Quebec|Québec's port]] by [[log driving]]; the construction of [[St. Lawrence Seaway|locks on the Saint Lawrence Seaway]], opening up trade routes to the U.S. from Montreal; and the city's inability to retain immigrant populations.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Langlois |first=Simon |date=2007 |title=Sociologie de la ville de Québec |url=https://www.erudit.org/fr/revues/cdd/2007-n61-cdd3633/039157ar/ |journal=Les Cahiers des dix |language=fr |issue= 61|page=196 |doi=10.7202/039157ar |issn=0575-089X}}</ref> This unfavourable context, coupled with the departure of the British army from the city's Citadel in 1871, contributed to the exodus of English speaking populations, such as local bourgeoisie of Scottish origin or workers of Irish background, to Montreal in the second half of the 19th century. Anglophones made up approximately 40% of the city's population in 1861, but 16% in 1901.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Langlois |first=Simon |date=2007 |title=Sociologie de la ville de Québec |url=https://www.erudit.org/fr/revues/cdd/2007-n61-cdd3633/039157ar/ |journal=Les Cahiers des dix |language=fr |issue= 61|page=197 |doi=10.7202/039157ar |issn=0575-089X}}</ref> |
|||
Before the [[Royal Military College of Canada]] was established in 1876, the only French-speaking officer training school was the Quebec City School of Military Instruction, founded in 1864.<ref>{{Cite web |date=June 2017 |title=Canadian Military Heritage Volume 2 (1755–1871). Canadian Militia Unpopular with Francophones |url=http://cmhg-phmc.forces.gc.ca/cmh-pmc/page-501-eng.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181012181855/http://cmhg-phmc.forces.gc.ca/cmh-pmc/page-501-eng.aspx |archive-date=12 October 2018 |access-date=6 October 2018 |website=Canadian Military History Gateway |publisher=Department of National Defence |language=en}}</ref> The school was retained at Confederation, in 1867. In 1868, The School of Artillery was formed in Montreal.<ref>Richard Preston 'Canada's RMC: A History of the Royal Military College of Canada' published by the RMC Club by U of Toronto Press.</ref> |
|||
[[File:The Quebec Conference, Canada, August 1943 TR1347.jpg|thumb|left|[[William Lyon Mackenzie King|Mackenzie King]], [[Franklin Delano Roosevelt|Franklin D. Roosevelt]], [[Winston Churchill]], and the [[Alexander Cambridge, 1st Earl of Athlone|Earl of Athlone]] (left to right) at the [[First Quebec Conference]], a secret military conference held in [[World War II]]]] |
|||
The [[Quebec Conference, 1864|Quebec Conference]] on [[Canadian Confederation]] was held in the city in 1864. In 1867, [[Queen Victoria]] chose Ottawa as the definite capital of the Dominion of Canada, while Quebec City was confirmed as the capital of the newly created province of Quebec. |
|||
During World War II, two conferences were held in Quebec City. The [[Quebec Conference, 1943|First Quebec Conference]] was held in 1943 with [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] (President of the United States), [[Winston Churchill]] (Prime Minister of the United Kingdom), [[William Lyon Mackenzie King]] (Prime Minister of Canada) and [[T. V. Soong]] (minister of foreign affairs of [[Republic of China (1912–1949)|China]]). The [[Second Quebec Conference]] was held in 1944 and was attended by Churchill and Roosevelt. They took place in the buildings of the Citadelle and at the nearby [[Château Frontenac]]. A large part of the [[D-Day]] landing plans were made during those meetings. |
|||
Until 2002, Quebec was a mostly urbanized city and its territory coterminous with today's borough of [[La Cité-Limoilou]]. The Government of Quebec then mandated a [[2000–06 municipal reorganization in Quebec|municipal reorganization in the province]], and many [[suburbs]] of the north shore of the Saint-Lawrence were merged into Quebec City, taking the form of [[Borough#Canada|boroughs]], thus constituting the boundary of present-day Québec City. In 2008 the city celebrated its [[400th anniversary of Quebec City|400th anniversary]] and was gifted funds for festivities and construction projects by provincial and federal governments, as well as [[public artwork]] by various entities, including foreign countries. |
|||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
[[File:Québec City – Boulevard Champlain - Le Fleuve Saint-Lorent - panoramio (1).jpg|thumb|The Promontory of Quebec at the narrowing of the Saint Lawrence River and surrounded by the [[Laurentian Mountains]]]] |
|||
[[File:Quebec city-satellite image.jpg|thumb|left|Quebec City on the north bank of the Saint Lawrence river, [[Lévis]] on the south bank, Laurentians mountains lies on the north of the city and the western point of the [[Île d'Orléans]] can be seen at right]] |
|||
[[File:Quebec city observatory view.JPG|thumb|[[Saint Lawrence River]] and the Château Frontenac during winter]] |
|||
Quebec City was built on the north bank of the [[Saint Lawrence River]], where it narrows and meets the mouth of the [[Saint-Charles River (Quebec City)|Saint-Charles River]]. [[Old Quebec]] is located on top and at the foot of [[Cap Diamant|Cap-Diamant]], which is on the eastern edge of a [[plateau]] called the [[promontory of Quebec]] (Quebec hill). Because of this topographic feature, the oldest and most urbanized borough of [[La Cité-Limoilou]] can be divided into upper and lower town.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Geological Survey of Canada |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=T0N_uGojlOoC&pg=PA63 |title=The 1988 Saguenay Earthquake – a Site Visit Report |date=1999 |page=63}}</ref> North of the hill, the [[Saint Lawrence Lowlands]] is flat and has rich, arable soil. Past this valley, the [[Laurentian Mountains]] lie to the north of the city but its [[foothills]] are within the municipal limits. |
|||
Quebec City is located in the [[Saint Lawrence River]] valley, on the north bank of the Saint Lawrence River near its meeting with the St. Charles River. The region is low-lying and flat. The river valley has rich, arable soil, which makes this region the most fertile in the province. The [[Laurentian Mountains]] lie to the north of the city. |
|||
The [[Plains of Abraham]] are located on the southeastern extremity of the plateau, where [[Fortifications of Quebec|high stone walls]] were integrated during colonial days. On the northern foot of the promontory, the lower town neighbourhoods of [[Saint-Roch, Quebec City|Saint-Roch]] and [[Saint-Sauveur, Quebec City|Saint-Sauveur]], traditionally working class,<ref>{{Cite book |last=Stelter |first=Gilbert |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bZRE9gaBnvAC&pg=PA163 |title=Shaping the Urban Landscape: Aspects of the Canadian City-Building Process |date=1982 |publisher=McGill Queen University Press |isbn=9780773584860 |access-date=6 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235552/https://books.google.com/books?id=bZRE9gaBnvAC&pg=PA163 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> are separated from uptown's [[Saint-Jean-Baptiste, Quebec City|Saint-Jean-Baptiste]] and {{ill|Saint-Sacrement|fr|Saint-Sacrement (quartier)}} by a woody area attested as {{ill|Coteau Sainte-Geneviève|fr|Coteau Sainte-Geneviève}}. |
|||
The area was affected by the [[1925 Charlevoix–Kamouraska earthquake]]. |
|||
The [[List of regions of Quebec#Administrative Regions|administrative region]] in which it is situated is officially referred to as [[Capitale-Nationale]],<ref>Décret concernant la révision des limites des régions administratives du Québec, R.Q. c. D-11, r.2, made pursuant to the Territorial Division Act, R.S.Q. c. D-11</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Québec Portal > Portrait of Québec > Administrative Regions > Regions |url=http://www.gouv.qc.ca/portail/quebec/pgs/commun/portrait/regions/description/?lang=en#03 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090201034242/http://gouv.qc.ca/portail/quebec/pgs/commun/portrait/regions/description/?lang=en#03 |archive-date=1 February 2009 |access-date=13 May 2009}}</ref> and the term "national capital" is used to refer to Quebec City itself at the provincial level.<ref name="CanLII">{{Cite web |date=4 May 2009 |title=An Act respecting the National capital commission, R.S.Q. c. C-33.1 |url=http://www.canlii.org/en/qc/laws/stat/rsq-c-c-33.1/latest/rsq-c-c-33.1.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100506073634/http://www.canlii.org/en/qc/laws/stat/rsq-c-c-33.1/latest/rsq-c-c-33.1.html |archive-date=6 May 2010 |access-date=13 May 2009 |publisher=CanLII}}</ref> |
|||
Upper Town lies on the top of Cap-Diamant (Cape Diamond) promontory. A high stone wall surrounds this portion of the city. The [[Plains of Abraham]] are located near the edge of the promontory. Lower Town is located at shore level, below Cap-Diamant. |
|||
===Climate=== |
===Climate=== |
||
{{Main article|Climate of Quebec City}} |
|||
Quebec City lies at the confluence of several climatic regions. Usually, the [[climate]] is classified as [[humid continental climate|humid continental]] or [[hemiboreal]] ([[Köppen climate classification]] ''Dfb'').<ref>{{cite web |
|||
[[File:Château Frontenac after a freezing rain day in Quebec city.jpg|thumb|left|Winter scene at the [[Château Frontenac]]]] |
|||
| url = http://www.climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca/climate_normals/results_e.html?Province=ALL&StationName=montreal&SearchType=BeginsWith&LocateBy=Province&Proximity=25&ProximityFrom=City&StationNumber=&IDType=MSC&CityName=&ParkName=&LatitudeDegrees=&LatitudeMinutes=&LongitudeDegrees=&LongitudeMinutes=&NormalsClass=A&SelNormals=&StnId=5415& |
|||
| title = Canadian Climate Normals 1971-2000 |
|||
| publisher = |accessdate =2006-12-18 |dateformat=dmy}}</ref> |
|||
Quebec City is classified as a [[hemiboreal]] [[humid continental climate]] ([[Köppen climate classification]] ''Dfb'', [[Trewartha climate classification|Trewartha]] ''Dcbc'').<ref name="Peel">{{Cite journal |last1=Peel, M. C. |last2=Finlayson, B. L. |last3=McMahon, T. A. |year=2007 |title=Updated world map of the Köppen–Geiger climate classification |url=http://www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/11/1633/2007/hess-11-1633-2007.pdf |url-status=live |journal=Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. |volume=11 |issue=5 |pages=1633–1644 |bibcode=2007HESS...11.1633P |doi=10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007 |issn=1027-5606 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120203170339/http://www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/11/1633/2007/hess-11-1633-2007.pdf |archive-date=3 February 2012 |access-date=10 February 2013 |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
Quebec City's summer are warm, and at humid with average high temperatures of 22–25°C (72–77°F) and lows of 11–13°C (51–56°F), but sometimes heat index with warmer than actual temperature. Winter brings very cold, often windy and snowy weather, with average high temperature of -5 to -8°C (18–23°F) and lows of -13 to -18°C (0–8°F). Because of wind chill, it sometimes feels much colder than actual temperature. Spring and fall are short, although mild. Late heat waves as well as "[[Indian summer]]s" are a common occurrence. |
|||
Quebec City experiences four distinct seasons. Summers are warm and occasionally hot, with periods of hotter temperatures which compounded with the high humidity, create a high heat index that belies the average high of {{convert|22|-|25|C}} and lows of {{Convert|11|-|13|C}}. Winters are cold, windy and snowy with average high temperatures {{Convert|-5|to|-8|C}} and lows {{convert|-13|to|-18|C}}. Spring and fall, although short, bring chilly to warm temperatures. Late heat waves as well as "[[Indian summer]]s" are a common occurrence.{{citation needed|reason=more common than elsewhere?|date=March 2011}} |
|||
Annual precipitation is around {{convert|123|cm|in|abbr=on}}, including {{convert|316|cm|in|abbr=on}} of snowfall, which is among the snowiest cities in Canada, and could occur from late fall to early spring.{{Citation needed|date=March 2010}} The city experiences around 1950 hours of sunshine annually, with summer being the sunniest, but also slightly the wettest season.{{Citation needed|date=March 2010}} Quebec City has more winter sunshine than other large cities in Europe, such as [[London]] and [[Paris]].{{Citation needed|extravagant, and maybe irrelevant, claim must be documented with a real, and [[WP:RELY]] footnote|date=March 2010}} |
|||
On average, Quebec City receives {{convert|1190|mm|2}} of precipitation, of which {{convert|899|mm|2}} is rain and {{convert|303|mm|2}} is the melt from {{convert|316|cm|1}} of snowfall per annum.{{efn|Although snow is measured in cm the melted snow (water equivalent) is measured in mm and added to the rainfall to obtain the total precipitation. An approximation of the water equivalent can be made by dividing the snow depth by ten. Thus {{convert|1|cm|1|abbr=on}} of snow is equivalent to approximately {{convert|1|mm|2|abbr=on}} of water. See [[snow gauge]], <ref>[http://www.climate.weatheroffice.gc.ca/prods_servs/normals_documentation_e.html#ND2 Rainfall, Snowfall, and Precipitation] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121228044057/http://www.climate.weatheroffice.gc.ca/prods_servs/normals_documentation_e.html |date=28 December 2012 }}</ref> and <ref>[http://www.ec.gc.ca/Publications/A192EDCE-8394-4662-BE0F-AAD3E32F23E9%5CMANOBS7A17_e.pdf MANOBS 7th Edition Amendment 17]{{dead link|date=September 2018|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref>}} The city experiences around 1,916 hours of bright sunshine annually or 41.5% of possible sunshine, with summer being the sunniest, but also slightly the wettest season. During winter, snow generally stays on the ground from the end of November till mid-April. |
|||
<!--Infobox begins-->{{Infobox Weather<!-- Important: remove all unused fields--> |
|||
|collapsed=<!--Any entry in this line will make the template initially collapsed. Leave blank or remove line for uncollapsed.--> |
|||
|metric_first=yes<!--Any entry in this line will display metric first. Leave blank or remove line for imperial.--> |
|||
|single_line=yes<!--Any entry in this line will display metric and imperial units on same line. Leave blank or remove line for separate lines--> |
|||
|location = Quebec |
|||
|Jan_REC_Hi_°C =10 |
|||
|Feb_REC_Hi_°C =11.7 |
|||
|Mar_REC_Hi_°C =17.8 |
|||
|Apr_REC_Hi_°C =29.9 |
|||
|May_REC_Hi_°C =33 |
|||
|Jun_REC_Hi_°C =33.9 |
|||
|Jul_REC_Hi_°C =35.6 |
|||
|Aug_REC_Hi_°C =34.4 |
|||
|Sep_REC_Hi_°C =33.9 |
|||
|Oct_REC_Hi_°C =28.3 |
|||
|Nov_REC_Hi_°C =20 |
|||
|Dec_REC_Hi_°C =13.9 |
|||
|Year_REC_Hi_°C =35.6 |
|||
|Jan_Hi_°C =-7.9 |
|||
|Feb_Hi_°C =-6.1 |
|||
|Mar_Hi_°C =0.1 |
|||
|Apr_Hi_°C =7.8 |
|||
|May_Hi_°C =17.1 |
|||
|Jun_Hi_°C =22.2 |
|||
|Jul_Hi_°C =25 |
|||
|Aug_Hi_°C =23.4 |
|||
|Sep_Hi_°C =17.7 |
|||
|Oct_Hi_°C =10.7 |
|||
|Nov_Hi_°C =2.9 |
|||
|Dec_Hi_°C =-4.8 |
|||
|Year_Hi_°C =9.0 |
|||
|Jan_MEAN_°C = -12.8 |
|||
|Feb_MEAN_°C = -11.1 |
|||
|Mar_MEAN_°C = -4.6 |
|||
|Apr_MEAN_°C = 3.3 |
|||
|May_MEAN_°C = 11.2 |
|||
|Jun_MEAN_°C = 16.5 |
|||
|Jul_MEAN_°C = 19.2 |
|||
|Aug_MEAN_°C = 17.9 |
|||
|Sep_MEAN_°C = 12.5 |
|||
|Oct_MEAN_°C = 6.2 |
|||
|Nov_MEAN_°C = -0.7 |
|||
|Dec_MEAN_°C = -9.1 |
|||
|Year_MEAN_°C = 4.0 |
|||
|Jan_Lo_°C =-17.6 |
|||
|Feb_Lo_°C =-16 |
|||
|Mar_Lo_°C =-9.4 |
|||
|Apr_Lo_°C =-1.3 |
|||
|May_Lo_°C =5.3 |
|||
|Jun_Lo_°C =10.6 |
|||
|Jul_Lo_°C =13.4 |
|||
|Aug_Lo_°C =12.4 |
|||
|Sep_Lo_°C =7.2 |
|||
|Oct_Lo_°C =1.7 |
|||
|Nov_Lo_°C =-4.3 |
|||
|Dec_Lo_°C =-13.4 |
|||
|Year_Lo_°C =-1.0 |
|||
|Jan_REC_Lo_°C =-35.4 |
|||
|Feb_REC_Lo_°C =-36.1 |
|||
|Mar_REC_Lo_°C =-30 |
|||
|Apr_REC_Lo_°C =-18.9 |
|||
|May_REC_Lo_°C =-7.8 |
|||
|Jun_REC_Lo_°C =-0.6 |
|||
|Jul_REC_Lo_°C =3.9 |
|||
|Aug_REC_Lo_°C =2.2 |
|||
|Sep_REC_Lo_°C =-4.8 |
|||
|Oct_REC_Lo_°C =-10 |
|||
|Nov_REC_Lo_°C =-24 |
|||
|Dec_REC_Lo_°C =-32.3 |
|||
|Year_REC_Lo_°C =-36.1 |
|||
|Jan_Snow_cm =72.9 |
|||
|Feb_Snow_cm =63.9 |
|||
|Mar_Snow_cm =49 |
|||
|Apr_Snow_cm =17.6 |
|||
|May_Snow_cm =0.4 |
|||
|Jun_Snow_cm =0 |
|||
|Jul_Snow_cm =0 |
|||
|Aug_Snow_cm =0 |
|||
|Sep_Snow_cm =0 |
|||
|Oct_Snow_cm =1.9 |
|||
|Nov_Snow_cm =33.2 |
|||
|Dec_Snow_cm =77.7 |
|||
|Year_Snow_cm =316.6 |
|||
|Jan_Rain_mm =26.1 |
|||
|Feb_Rain_mm =12.6 |
|||
|Mar_Rain_mm =39 |
|||
|Apr_Rain_mm =59.5 |
|||
|May_Rain_mm =105.5 |
|||
|Jun_Rain_mm =114.2 |
|||
|Jul_Rain_mm =127.8 |
|||
|Aug_Rain_mm =116.7 |
|||
|Sep_Rain_mm =125.5 |
|||
|Oct_Rain_mm =99.5 |
|||
|Nov_Rain_mm =67.9 |
|||
|Dec_Rain_mm =29.5 |
|||
|Year_Rain_mm =923.8 |
|||
|Jan_Precip_mm =89.8 |
|||
|Feb_Precip_mm =70.6 |
|||
|Mar_Precip_mm =90.3 |
|||
|Apr_Precip_mm =81.2 |
|||
|May_Precip_mm =106.1 |
|||
|Jun_Precip_mm =114.2 |
|||
|Jul_Precip_mm =127.8 |
|||
|Aug_Precip_mm =116.7 |
|||
|Sep_Precip_mm =125.5 |
|||
|Oct_Precip_mm =101.7 |
|||
|Nov_Precip_mm =102 |
|||
|Dec_Precip_mm =104.4 |
|||
|Year_Precip_mm =1230.2 |
|||
|Jan_Sun= 100.3 |
|||
|Feb_Sun= 123.6 |
|||
|Mar_Sun= 149.4 |
|||
|Apr_Sun= 168.6 |
|||
|May_Sun= 215.9 |
|||
|Jun_Sun= 232 |
|||
|Jul_Sun= 251.7 |
|||
|Aug_Sun= 225.2 |
|||
|Sep_Sun= 155.5 |
|||
|Oct_Sun= 119.8 |
|||
|Nov_Sun= 81.6 |
|||
|Dec_Sun= 81.1 |
|||
|Year_Sun= 1904.7 |
|||
|source = [[Environment Canada]]<ref name= "climate">[[Environment Canada]] |
|||
[http://www.climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca/climate_normals/results_e.html?Province=ALL&StationName=Quebec&SearchType=BeginsWith&LocateBy=Province&Proximity=25&ProximityFrom=City&StationNumber=&IDType=MSC&CityName=&ParkName=&LatitudeDegrees=&LatitudeMinutes=&LongitudeDegrees=&LongitudeMinutes=&NormalsClass=A&SelNormals=&StnId=5251&&autofwd=1 Canadian Climate Normals 1971–2000], accessed July 23, 2009</ref> |
|||
|accessdate = July 23, 2009 |
|||
}}<!--Infobox ends--> |
|||
The highest temperature ever recorded in Quebec City was {{convert|36.1|C}} on 17 July 1953.<ref name="July 1953">{{Cite web |date=31 October 2011 |title=Daily Data Report for July 1953 |url=http://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/daily_data_e.html?hlyRange=%7C&dlyRange=1872-06-01%7C1959-02-28&mlyRange=1872-01-01%7C1959-12-01&StationID=5249&Prov=QC&urlExtension=_e.html&searchType=stnName&optLimit=yearRange&StartYear=1840&EndYear=1930&selRowPerPage=25&Line=0&searchMethod=contains&Month=7&Day=8&txtStationName=quebec&timeframe=2&Year=1953 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160816185758/http://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/daily_data_e.html?hlyRange=%7C&dlyRange=1872-06-01%7C1959-02-28&mlyRange=1872-01-01%7C1959-12-01&StationID=5249&Prov=QC&urlExtension=_e.html&searchType=stnName&optLimit=yearRange&StartYear=1840&EndYear=1930&selRowPerPage=25&Line=0&searchMethod=contains&Month=7&Day=8&txtStationName=quebec&timeframe=2&Year=1953 |archive-date=16 August 2016 |access-date=8 July 2016 |website=Canadian Climate Data |publisher=[[Environment Canada]]}}</ref> The coldest temperature ever recorded was {{convert|-36.7|C}} on 10 January 1890 and 14 January 2015.<ref name="January 1890">{{Cite web |date=31 October 2011 |title=Daily Data Report for January 1890 |url=http://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/daily_data_e.html?hlyRange=%7C&dlyRange=1872-06-01%7C1959-02-28&mlyRange=1872-01-01%7C1959-12-01&StationID=5249&Prov=QC&urlExtension=_e.html&searchType=stnName&optLimit=yearRange&StartYear=1840&EndYear=1930&selRowPerPage=25&Line=0&searchMethod=contains&Month=1&Day=8&txtStationName=quebec&timeframe=2&Year=1890 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160816163141/http://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/daily_data_e.html?hlyRange=%7C&dlyRange=1872-06-01%7C1959-02-28&mlyRange=1872-01-01%7C1959-12-01&StationID=5249&Prov=QC&urlExtension=_e.html&searchType=stnName&optLimit=yearRange&StartYear=1840&EndYear=1930&selRowPerPage=25&Line=0&searchMethod=contains&Month=1&Day=8&txtStationName=quebec&timeframe=2&Year=1890 |archive-date=16 August 2016 |access-date=8 July 2016 |website=Canadian Climate Data |publisher=[[Environment Canada]]}}</ref><ref name="January 2015">{{Cite web |date=31 October 2011 |title=Daily Data Report for January 2015 |url=http://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/daily_data_e.html?hlyRange=2005-03-24%7C2016-07-07&dlyRange=1992-12-04%7C2016-07-06&mlyRange=1998-01-01%7C2016-03-01&StationID=26892&Prov=QC&urlExtension=_e.html&searchType=stnName&optLimit=yearRange&StartYear=1840&EndYear=2016&selRowPerPage=25&Line=4&searchMethod=contains&Month=1&Day=1&txtStationName=quebec&timeframe=2&Year=2015 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160816171831/http://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/daily_data_e.html?hlyRange=2005-03-24%7C2016-07-07&dlyRange=1992-12-04%7C2016-07-06&mlyRange=1998-01-01%7C2016-03-01&StationID=26892&Prov=QC&urlExtension=_e.html&searchType=stnName&optLimit=yearRange&StartYear=1840&EndYear=2016&selRowPerPage=25&Line=4&searchMethod=contains&Month=1&Day=1&txtStationName=quebec&timeframe=2&Year=2015 |archive-date=16 August 2016 |access-date=8 July 2016 |website=Canadian Climate Data |publisher=[[Environment Canada]]}}</ref> |
|||
===Districts=== |
|||
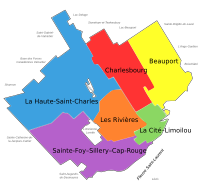
[[File:Quebec Arrondissements.svg|right|thumb|Quebec City's six boroughs]] |
|||
On January 1, 2002, the former towns of [[Sainte-Foy, Quebec|Sainte-Foy]], [[Beauport, Quebec|Beauport]], [[Charlesbourg, Quebec|Charlesbourg]], [[Sillery, Quebec|Sillery]], [[Loretteville, Quebec|Loretteville]], [[Val-Bélair, Quebec|Val-Bélair]], [[Cap-Rouge, Quebec|Cap-Rouge]], [[Saint-Émile, Quebec|Saint-Émile]], [[Vanier, Quebec|Vanier]], [[L'Ancienne-Lorette, Quebec|L'Ancienne-Lorette]], [[Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures, Quebec|Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures]] and [[Lac-Saint-Charles, Quebec|Lac-Saint-Charles]] were annexed by Quebec City. This was one of several [[municipal reorganization in Quebec|municipal mergers]] which took place across Quebec on that date. Following a demerger referendum, L'Ancienne-Lorette and Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures were reconstituted as separate municipalities on January 1, 2006, but the other former municipalities remain part of Quebec City. On November 1, 2009, the Quebec City re-organized its boroughs, reducing the number from 8 to 6. |
|||
{{Quebec City weatherbox}} |
|||
Quebec City has thirty-four [[district]]s in six [[borough]]s. |
|||
===Boroughs and neighbourhoods=== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" style="margin:auto;" |
|||
{{more citations needed section|date=April 2016}} |
|||
[[File:Quebec Arrondissements.svg|thumb|Map of the six boroughs that make up Quebec City]] |
|||
On 1 January 2002, the 12 former towns of [[Sainte-Foy, Quebec City|Sainte-Foy]], [[Beauport, Quebec City|Beauport]], [[Charlesbourg, Quebec City|Charlesbourg]], [[Sillery, Quebec City|Sillery]], [[Loretteville, Quebec City|Loretteville]], [[Val-Bélair, Quebec City|Val-Bélair]], [[Cap-Rouge, Quebec City|Cap-Rouge]], [[Saint-Émile, Quebec City|Saint-Émile]], [[Vanier, Quebec City|Vanier]], [[L'Ancienne-Lorette, Quebec|L'Ancienne-Lorette]], [[Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures]] and [[Lac-Saint-Charles, Quebec City|Lac-Saint-Charles]] were annexed by Quebec City. This was one of several [[municipal reorganization in Quebec|municipal mergers]] which took place across Quebec on that date. Following a demerger referendum, L'Ancienne-Lorette and Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures were reconstituted as separate municipalities on 1 January 2006, but the other former municipalities remain part of Quebec City. On 1 November 2009, Quebec City re-organized its boroughs, reducing the number from 8 to 6.<ref name="nouveauDécoupage">{{Cite web |title=Nouveau découpage des arrondissements - Modifications territoriales |url=http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/temp/modifications_arrondissements/index.aspx |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090925182848/http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/temp/modifications_arrondissements/index.aspx |archive-date=25 September 2009 |website=www.ville.quebec.qc.ca |publisher=Ville de Québec |language=fr}}</ref><!-- Definitely correct, but I unfortunately couldn't find a better reference for this. The announcement seems to be gone from the city's website. Chealer 20121208 --> |
|||
Quebec City's six [[borough]]s ({{langx|fr|arrondissements}}) are further divided into 35 neighbourhoods ({{langx|fr|quartiers}}).<ref name="carte10jan2011">{{Cite map |url=http://clubdimension.org/docs/KINOMADA/Ville_quartiers_arrondissements.pdf |title=Les arrondissements et leurs quartiers |trans-title=The boroughs and their quarters |last1=Rainville |first1=Candide |author2=Service de l'ingénierie. Division de l'arpentage et de la cartographie. Ville de Québec |date=10 January 2011 |website=clubdimension.org |language=fr |format=PDF |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191105091049/http://clubdimension.org/docs/KINOMADA/Ville_quartiers_arrondissements.pdf |archive-date=5 November 2019 |access-date=5 November 2019}}</ref> In most cases, the name of the latter remained the same as the historical [[List of towns in Quebec|town]] ({{langx|fr|ville}}) or [[Types of municipalities in Quebec#Local municipalities|parish municipality]] it replaced. Neighbourhoods each elect their own council, whose powers rest in [[public consultation]]s. |
|||
Compared to many other cities in North America, there is less variation between average household incomes between the neighbourhoods. However, some disparities exist. The southwest former cities of [[Sillery, Quebec City|Sillery]], [[Cap-Rouge, Quebec City|Cap-Rouge]] and [[Sainte-Foy, Quebec City|Sainte-Foy]] are considered to be the wealthiest, along with some parts of Montcalm and Old Quebec.{{Citation needed|date=October 2018}} |
|||
The city's traditional working-class areas are found in the lower town below Old Quebec (Saint-Sauveur and Saint-Roch) and directly across the [[Saint-Charles River (Quebec City)|Saint-Charles River]] to the north (Vanier and Limoilou). However, parts of Limoilou, Saint-Sauveur and particularly Saint-Roch have seen [[gentrification]] in the last 20 years, attracting young professionals and the construction of new offices and condos.<ref name="cbd" /> |
|||
[[File:Québec City - Saint Louis - panoramio (cropped).jpg|North-east aerial view from the Quebec Bridge area. The foreground shows the Sainte-Foy neighbourhood of Saint-Louis and the modern buildings of boulevard Laurier.|thumb]] |
|||
Northern sections (Loretteville, Val-Bélair) and eastern sections (Beauport, Charlesbourg) are mostly a mix of middle-class residential suburbs with industrial pockets. |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto;" |
|||
|- style="background:#ccc;" |
|- style="background:#ccc;" |
||
|'' |
|''Boroughs'' || style="text-align:center;"| ''Neighbourhoods'' |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[La |
| 1 [[La Cité-Limoilou]] |
||
| [[ |
|''La Cité'': 1-1 [[Vieux-Québec–Cap-Blanc–colline Parlementaire]] · 1-2 [[Saint-Roch, Quebec City|Saint-Roch]] · 1-3 [[Saint-Jean-Baptiste, Quebec City|Saint-Jean-Baptiste]] · 1-4 [[Montcalm, Quebec City|Montcalm]] · 1-5 [[Saint-Sauveur, Quebec City|Saint-Sauveur]] · 1-6 [[Saint-Sacrement, Quebec City|Saint-Sacrement]] · ''Limoilou'': 6-1 [[Vieux-Limoilou]] · 6-2 [[Lairet]] · 6-3 [[Maizerets]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Les Rivières (Quebec City)|Les Rivières]] |
| 2 [[Les Rivières (Quebec City)|Les Rivières]] |
||
|[[ |
|2-1 [[Neufchâtel-Est–Lebourgneuf]] · 2-2 [[Duberger-Les Saules]] · 2-3 [[Vanier, Quebec City|Vanier]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Sainte-Foy–Sillery–Cap-Rouge]] |
| 3 [[Sainte-Foy–Sillery–Cap-Rouge]] |
||
| Cité universitaire |
|3-1 [[Sillery, Quebec City|Sillery]] · 3-2 [[Cité universitaire, Quebec City|Cité universitaire]] · 3-3 [[Saint-Louis, Quebec City|Saint-Louis]] · 3-4 [[Plateau, Quebec City|Plateau]] · 3-5 [[Pointe-de-Ste-Foy, Quebec|Pointe-de-Ste-Foy]] 8-2 · [[L'Aéroport, Quebec City|L'Aéroport]] · 8-3 [[Cap-Rouge, Quebec City|Cap-Rouge]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Charlesbourg, Quebec|Charlesbourg]] |
| 4 [[Charlesbourg, Quebec City|Charlesbourg]] |
||
|4-1 [[Notre-Dame-des-Laurentides]] · 4-2 Quartier 4-2 · 4-3 Quartier 4-3 · 4-4 [[Jésuites, Quebec City]] · 4-5 Quartier 4-5 · 4-6 Quartier 4–6 |
|||
| Saint-Rodrigue '''·''' Des Sentiers '''·''' Des Monts |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Beauport, Quebec|Beauport]] |
| 5 [[Beauport, Quebec City|Beauport]] |
||
| 5-1 Quartier 5-1 · 5-2 Quartier 5-2 · 5-3 [[Chutes-Montmorency, Quebec City|Chutes-Montmorency]] · 5-4 Quartier 5-4 · 5-5 [[Vieux-Moulin, Quebec City|Vieux-Moulin]] |
|||
| Vieux-Moulin '''·''' Sainte-Thérèse-de-Lisieux '''·''' Villeneuve '''·''' Courville |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[La Haute-Saint-Charles]] |
| 7 [[La Haute-Saint-Charles]] |
||
| [[Lac-Saint-Charles, Quebec|Lac-Saint-Charles]] |
|7-1 [[Lac-Saint-Charles, Quebec City|Lac-Saint-Charles]] · 7-2 [[Saint-Émile, Quebec City|Saint-Émile]] · 7-3 [[Loretteville, Quebec City|Loretteville]] · 7-4 [[Des Châtels, Quebec City|Des Châtels]] · 8-1 [[Val-Bélair, Quebec City|Val-Bélair]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
== Demographics == |
|||
{{wide image|79_-_Québec_-_Juin_2009.jpg|1000px|<center>Panorama of Quebec City's skyline</center>}} |
|||
{{more citations needed section|date=April 2016}} |
|||
{{Historical populations |
|||
|title = Quebec City<ref name="scpast">Statistics Canada: [[Canada 1871 Census|1871]], 1881, 1891, 1901, [[Canada 1911 Census|1911]], [[Canada 1921 Census|1921]], [[Canada 1931 Census|1931]], [[Canada 1941 Census|1941]], [[Canada 1951 Census|1951]], 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, [[Canada 1991 Census|1991]], [[Canada 1996 Census|1996]], [[Canada 2001 Census|2001]], [[Canada 2006 Census|2006]], [[Canada 2011 Census|2011]], [[Canada 2016 Census|2016]], [[Canada 2021 Census|2021]] census</ref> |
|||
|type = Canada |
|||
|align = right |
|||
|width = |
|||
|state = |
|||
|shading = |
|||
|percentages = |
|||
|1665|547 |
|||
|1667|444 |
|||
|1681|1345 |
|||
|1685|1205 |
|||
|1688|1407 |
|||
|1692|1570 |
|||
|1695|1549 |
|||
|1698|1988 |
|||
|1706|1771 |
|||
|1739|4603 |
|||
|1754|8001 |
|||
|1765|8967 |
|||
|1790|14000 |
|||
|1825|22101 |
|||
|1851|42052 |
|||
|1861|51109 |
|||
|1871|59699 |
|||
|1881|62446 |
|||
|1891<sup>a</sup>|63090 |
|||
|1901|68940 |
|||
|[[Canada 1911 Census|1911]]<sup>b</sup>|78118 |
|||
|1921<sup>c</sup>|95193 |
|||
|1931|130594 |
|||
|1941|150757 |
|||
|1951|164016 |
|||
|1956|170703 |
|||
|1961|171979 |
|||
|1966|166984 |
|||
|1971<sup>d</sup>|186088 |
|||
|1976<sup>e</sup>|177082 |
|||
|1981|165968 |
|||
|1986|164580 |
|||
|1991|167517 |
|||
|1996|167264 |
|||
|2001|169076 |
|||
|2006<sup>f</sup>|491142 |
|||
|2011|516622 |
|||
|2016|531902 |
|||
|2021|549459 |
|||
| footnote = {{center|'''<sup>a</sup> Quebec City annexed the Village of Saint-Sauveur-de-Québec<br /><sup>b</sup>Quebec City annexed the Town of Limoilou and the Village of Saint-Malo<br /><sup>c</sup>Quebec City annexed the Town of Montcalm<br /><sup>d</sup>Quebec City annexed the Town of Duberger and the Town of Les Saules<br /><sup>e</sup>Quebec City annexed the Town of Neufchâtel and the Municipality of Charlesbourg-Ouest<br /><sup>f</sup>Quebec City annexed the cities of Beauport, Cap-Rouge, Charlesbourg, Lac-Saint-Charles, Loretteville, Saint-Émile, Sainte-Foy, Sillery, Val-Bélair and Vanier'''}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Historical populations |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
|title = Quebec City (in its present city boundaries)<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.stat.gouv.qc.ca/donstat/societe/demographie/dons_regnl/regional/Tableau_top_10.htm |title=Évolution démographique des 10 principales villes du Québec (Sur la base de 2006) selon leur limites territoriales actuelles1, Recensements du Canada de 1871 à 2006 |website=www.stat.gouv.qc.ca |access-date=19 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131006173408/http://www.stat.gouv.qc.ca/donstat/societe/demographie/dons_regnl/regional/Tableau_top_10.htm |archive-date=6 October 2013 |url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:GarePalaisQuebec.JPG|thumb|left|Quebec City's main train station, [[Gare du Palais]]]] |
|||
|type = Canada |
|||
According to the 2006 census, there were 491,142 people residing in Quebec City proper, and 715,515 people in the city's [[census metropolitan area]]. Of the former total, 48.2% were male and 51.8% were female. Children under five accounted for approximately 4.7% of the resident population of Quebec City. This compares with 5.2% in the province of Quebec, and 5.6% for Canada overall. |
|||
|align = right |
|||
|width = |
|||
|state = |
|||
|shading = |
|||
|percentages = |
|||
|1871|76593 |
|||
|1881|80249 |
|||
|1891|80546 |
|||
|1901|88615 |
|||
|[[Canada 1911 Census|1911]]|102214 |
|||
|1921|122698 |
|||
|1931|168249 |
|||
|1941|199588 |
|||
|1951|245742 |
|||
|1956|279521 |
|||
|1961|321917 |
|||
|1966|372373 |
|||
|1971|408440 |
|||
|1976|429757 |
|||
|1981|434980 |
|||
|1986|440598 |
|||
|1991|461894 |
|||
|1996|473569 |
|||
|2001|476330 |
|||
|2006|491142 |
|||
|2011|516622 |
|||
|2016|531902 |
|||
|2021|549459 |
|||
}} |
|||
In the [[2021 Canadian census|2021 Census of Population]] conducted by [[Statistics Canada]], Québec had a population of {{val|549459|fmt=commas}} living in {{val|265711|fmt=commas}} of its {{val|283219|fmt=commas}} total private dwellings, a change of {{percentage|{{#expr:549459-531902}}|531902|1}} from its 2016 population of {{val|531902|fmt=commas}}. With a land area of {{convert|452.3|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}}, it had a population density of {{Pop density|549459|452.3|km2|sqmi|prec=1}} in 2021.<ref name=2021census>{{cite web |url=https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/t1/tbl1/en/tv.action?pid=9810000202&geocode=A000224 |title=Population and dwelling counts: Canada, provinces and territories, and census subdivisions (municipalities), Quebec |publisher=[[Statistics Canada]] |date=February 9, 2022 |accessdate=August 29, 2022}}</ref> |
|||
While Montreal is considered by many to have a bilingual population, in which many of its residents have a working knowledge of both French and English, Quebec City and its surrounding region are largely [[Francophone]]. The vast majority of city residents are native [[French language|French]]-speakers. The English-speaking community peaked in relative terms during the 1860s, when 40% of Quebec City's residents were [[English language|Anglophone]].<ref>{{cite web | author= Morrin Centre|publisher= Literary and Historical Society of Quebec|title= Anglos in Québec|accessdate=March 15, 2007 |url=http://www.morrin.org/pages/anglos.php}}</ref> Today, Anglophones make up only 1.5% of the population of both the city and its metropolitan area.<ref>{{cite web | publisher= Voice of English-speaking Québec|title= Voice of English-speaking Québec: A Portrait of the English-speaking Community in Quebec| year=2007|accessdate=March 15, 2007 |url=http://www.veq.qc.ca/enter/pages/portrait.htm}}</ref> However, the annual [[Quebec Winter Carnival]] attracts both Francophone and Anglophone tourists alike, so the Anglophone population increases considerably during the duration of the event. |
|||
According to Statistics Canada, there were 839,311 people residing in the Quebec City census metropolitan area.<ref>{{Cite web |publisher=Government of Canada, Statistics Canada|date=8 February 2017 |title=Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2016 Census |url=http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/hlt-fst/pd-pl/Table.cfm? |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170210214952/http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/hlt-fst/pd-pl/Table.cfm |archive-date=10 February 2017 |access-date=9 February 2017 |website=www12.statcan.gc.ca}}</ref> |
|||
In 2001, 13.0% of the resident population in Quebec City was of retirement age (65 and over for males and females) compared with 13.2% in Canada. The average age is 39.5 years of age compared to 37.6 years of age for Canada as a whole. |
|||
In 2016, 20.6% of the resident population in Quebec City was of retirement age (65 and over for males and females) compared with 16.9% in Canada. The median age is 43.3 years of age compared to 41.2 years of age for Canada as a whole. In the five years between 2011 and 2016, the population of Quebec City grew by 3%.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Government of Canada |first=Statistics Canada |date=8 February 2017 |title=Census Profile, 2016 Census – Québec, Ville [Census subdivision], Quebec and Canada [Country] |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423027&Geo2=PR&Code2=01&SearchText=Canada&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&TABID=1&type=1 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235556/https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423027&Geo2=PR&Code2=01&SearchText=Canada&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&TABID=1&type=1 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=16 July 2019 |website=www12.statcan.gc.ca}}</ref> |
|||
In the five years between 1996 and 2001, the population of Quebec City grew by 1.6%, compared with an increase of 1.4% for the province of Quebec as a whole. The population density of Quebec City averaged 216.4 people per square kilometre, compared with an average of 5.3 for the province as a whole. |
|||
=== Ethnicity === |
|||
At the time of the 2001 census, the population of the Quebec City authority was 682,757, but was 710,700 when encompassing the Greater Quebec City Area, compared with a resident population in the province of Quebec of 7,237,479 people. |
|||
In 2021,<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=Census Profile, 2021 - Québec, Ville |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2021/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&GENDERlist=1,2,3&STATISTIClist=1&HEADERlist=0&DGUIDlist=2021A00052423027&SearchText=quebec |website=Statistics Canada| date=9 February 2022 }}</ref> 9.4% of Quebec City residents reported [[visible minority]] status, a relatively low figure for a large Canadian city; the national average was 26.5%.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Census Profile, 2021 - Canada [Country] |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2021/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&DGUIDList=2021A000011124&GENDERList=1,2,3&STATISTICList=1&HEADERList=0&SearchText=Canada |website=Statistics Canada| date=9 February 2022 }}</ref> The largest visible minority group were [[Black Canadians]], who formed 4.1% of the population. Quebec City also had a lower percentage of Indigenous Canadians (1.8%) than the national average of 5.0%.<ref name="2021censusB"/> |
|||
{| class="wikitable collapsible sortable" |
|||
According to the 2001 census, over 90% of the population was [[Roman Catholic]]. The city also contains small [[Protestant]] and [[Jewish]] communities. |
|||
|+ [[Panethnicity|Panethnic]] groups in Quebec City (2001−2021) |
|||
! rowspan="2" |[[Panethnicity|Panethnic]]<br>group |
|||
<center> |
|||
! colspan="2" |2021<ref name="2021censusB"/> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" |
|||
! colspan="2" |2016<ref name="2016census">{{Cite web |last=Government of Canada |first=Statistics Canada |date=2021-10-27 |title= Census Profile, 2016 Census |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423027&Geo2=CD&Code2=2423&SearchText=Quebec&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&TABID=1&type=0 |access-date=2023-01-12 |website=www12.statcan.gc.ca}}</ref> |
|||
! colspan="2" |2011<ref name="2011census">{{Cite web |last=Government of Canada |first=Statistics Canada |date=2015-11-27 |title= NHS Profile |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/nhs-enm/2011/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423027&Data=Count&SearchText=Quebec&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&A1=All&B1=All&Custom=&TABID=1 |access-date=2023-01-12 |website=www12.statcan.gc.ca}}</ref> |
|||
! colspan="2" |2006<ref name="2006census">{{Cite web |last=Government of Canada |first=Statistics Canada |date=2019-08-20 |title= 2006 Community Profiles |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2006/dp-pd/prof/92-591/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423027&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchText=Quebec&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&Custom= |access-date=2023-01-12 |website=www12.statcan.gc.ca}}</ref> |
|||
! colspan="2" |2001<ref name="2001census">{{Cite web |last=Government of Canada |first=Statistics Canada |date=2019-07-02 |title= 2001 Community Profiles |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/english/Profil01/CP01/Details/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2423025&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchText=Qu%C3%A9bec&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&Custom= |access-date=2023-01-12 |website=www12.statcan.gc.ca}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
![[Population|{{abbr|Pop.|Population}}]] |
|||
|+Quebec City Metropolitan population by year |
|||
!{{Abbr|%|percentage}} |
|||
!{{abbr|Pop.|Population}} |
|||
!{{Abbr|%|percentage}} |
|||
!{{abbr|Pop.|Population}} |
|||
!{{Abbr|%|percentage}} |
|||
!{{abbr|Pop.|Population}} |
|||
!{{Abbr|%|percentage}} |
|||
!{{abbr|Pop.|Population}} |
|||
!{{Abbr|%|percentage}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[European Canadians|European]]<ref group="note">Statistic includes all persons that did not make up part of a visible minority or an indigenous identity.</ref> |
|||
! scope="col" | 1931 |
|||
| 473,770 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 473770 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 475,720 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 475720 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 477,715 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 477715 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 465,115 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 465115 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 160,940 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 160940 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[African-Canadian|Black]] |
|||
| 21,955 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 21955 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 12,430 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 12430 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 5,760 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 5760 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 4,550 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 4550 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 1,335 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1335 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Middle Eastern Canadians|Middle Eastern]]<ref group="note">Statistic includes total responses of "West Asian" and "Arab" under visible minority section on census.</ref> |
|||
| 10,510 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 10510 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 6,850 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 6850 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 4,045 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 4045 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 2,980 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 2980 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 370 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 370 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Indigenous peoples in Canada|Indigenous]] |
|||
| 9,395 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 9395 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 7,290 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 7290 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 4,635 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 4635 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 3,140 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 3140 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 1,055 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1055 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Latin American Canadians|Latin American]] |
|||
| 8,585 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 8585 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 6,675 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 6675 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 5,085 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 5085 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 2,725 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 2725 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 1,095 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1095 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Southeast Asia]]n<ref group="note">Statistic includes total responses of "Filipino" and "Southeast Asian" under visible minority section on census.</ref> |
|||
| 3,275 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 3275 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 2,590 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 2590 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 1,855 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1855 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 1,470 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1470 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 820 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 820 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[East Asian Canadians|East Asian]]<ref group="note">Statistic includes total responses of "Chinese", "Korean", and "Japanese" under visible minority section on census.</ref> |
|||
| 2,970 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 2970 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 2,565 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 2565 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 2,080 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 2080 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 1,730 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1730 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 420 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 420 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[South Asian Canadians|South Asian]] |
|||
| 1,610 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1610 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 1,390 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1390 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 855 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 855 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 425 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 425 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 120 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 120 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
| Other/[[Multiracial people|Multiracial]]<ref group="note">Statistic includes total responses of "Visible minority, {{abbr|n.i.e.|not included elsewhere}}" and "Multiple visible minorities" under visible minority section on census.</ref> |
|||
| 1,465 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 1465 | 533540 | 2 }} |
|||
| 730 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 730 | 516250 | 2 }} |
|||
| 570 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 570 | 502595 | 2 }} |
|||
| 405 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 405 | 482545 | 2 }} |
|||
| 110 |
|||
| {{Percentage | 110 | 166255 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
! Total responses |
|||
! 533,540 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 533540 | 549459 | 2 }} |
|||
! 516,250 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 516250 | 531902 | 2 }} |
|||
! 502,595 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 502595 | 516622 | 2 }} |
|||
! 482,545 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 482545 | 491142 | 2 }} |
|||
! 166,255 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 166255 | 169076 | 2 }} |
|||
|- |
|||
! Total population |
|||
! 549,459 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 549459 | 549459 | 2 }} |
|||
! 531,902 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 531902 | 531902 | 2 }} |
|||
! 516,622 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 516622 | 516622 | 2 }} |
|||
! 491,142 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 491142 | 491142 | 2 }} |
|||
! 169,076 |
|||
! {{Percentage | 169076 | 169076 | 2 }} |
|||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|||
| colspan="15" | {{small|Note: Totals greater than 100% due to multiple origin responses}} |
|||
{{noteFoot}} |
|||
|} |
|||
=== Immigration === |
|||
The [[2021 Canadian census|2021 census]] reported that [[Immigration to Canada|immigrants]] (individuals born outside Canada) comprise 45,230 persons or 8.5% of the total population of Quebec City. Of the total immigrant population, the top countries of origin were France (7,360 persons or 16.3%), Colombia (2,865 persons or 6.3%), Morocco (2,715 persons or 6.0%), Ivory Coast (2,500 persons or 5.5%), Cameroon (2,225 persons or 4.9%), Algeria (1,920 persons or 4.2%), Tunisia (1,795 persons or 4.0%), Democratic Republic of the Congo (1,315 persons or 1,315%), Haiti (1,120 persons or 2.5%), and Brazil (1,115 persons or 2.5%).<ref name="2021censusB"/> |
|||
=== Language === |
|||
The great majority of city residents are native French speakers. The English-speaking community peaked in relative terms during the 1860s, when 40% of Quebec City's residents were [[English language|Anglophone]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Morrin Centre |title=Anglos in Québec |url=http://www.morrin.org/pages/anglos.php |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120306032111/http://www.morrin.org/pages/anglos.php |archive-date=6 March 2012 |access-date=15 March 2007 |publisher=Literary and Historical Society of Quebec}}</ref><ref>Blair, Louisa. The Anglos: The Hidden Face of Quebec City. Volume 1: 1608–1850; Volume 2: Since 1850. Québec: Commission de la capitale nationale du Québec & Éditions Sylvain Harvey, 2005.</ref> Today, native Anglophones make up only about 1.5% of the population of both the city and its metropolitan area.<ref>{{Cite web |year=2007 |title=Voice of English-speaking Québec: A Portrait of the English-speaking Community in Quebec |url=http://www.veq.qc.ca/enter/pages/portrait.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070929131149/http://www.veq.qc.ca/enter/pages/portrait.htm |archive-date=29 September 2007 |access-date=15 March 2007 |publisher=Voice of English-speaking Québec}}</ref> However, the summer tourist season and the [[Quebec Winter Carnival]] attract significant numbers of Anglophone (as well as [[Francophone]]) visitors, and English can often be heard in areas frequented by tourists. |
|||
In 2021, according to Statistics Canada, 90.6% of Quebec City's population spoke French as their sole mother tongue. More than a third of city residents reported being capable of speaking both French and English. |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
! scope="col" | 1941 |
|||
|+Canada Census Mother Tongue – Quebec City, Quebec<ref name="scpast"/> |
|||
! scope="col" | 1951 |
|||
! scope="col" | 1961 |
|||
! scope="col" | 1971 |
|||
! scope="col" | 1981 |
|||
! scope="col" | 1991 |
|||
! scope="col" | 2001 |
|||
! scope="col" | 2006 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! rowspan="2"|Census<br />Year |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 131 000 |
|||
| |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 151 000 |
|||
! rowspan="2"|Total<br />Responses |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 289 000 |
|||
|colspan="1"| |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 379 000 |
|||
!colspan="3"|{{center|French}} |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 481 000 |
|||
|colspan="1"| |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 576 000 |
|||
!colspan="3"|{{center|English}} |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 645,550<ref name="StatCan1996">[http://www12.statcan.ca/english/Profil/Details/details1.cfm?SEARCH=BEGINS&ID=223&PSGC=24&SGC=42100&DataType=1&LANG=E&Province=All&PlaceName=Quebec&CMA=421&CSDNAME=Qu%C3%A9bec&A=&TypeNameE=Census%20Metropolitan%20Area Statistics Canada.] Community Profile — Quebec City -1996</ref> |
|||
|colspan="1"| |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 686 569<ref name = "StatCan2"/> |
|||
!colspan="3"|{{center|French & English}} |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 715 515<ref name="StatCan2"/> |
|||
|colspan="1"| |
|||
!colspan="3"|{{center|Other}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
! Count |
|||
! Trend |
|||
! Pop. % |
|||
| |
|||
! Count |
|||
! Trend |
|||
! Pop. % |
|||
| |
|||
! Count |
|||
! Trend |
|||
! Pop. % |
|||
| |
|||
! Count |
|||
! Trend |
|||
! Pop. % |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{center|2021}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{center|542,435}} |
|||
| |
|||
| 491,515 |
|||
| {{increase}} 1.6% |
|||
| 90.6% |
|||
| |
|||
| 7,685 |
|||
| {{increase}} 3.9% |
|||
| 1.4% |
|||
| |
|||
| 4,530 |
|||
| {{increase}} 73.2% |
|||
| 0.8% |
|||
| |
|||
| 33,255 |
|||
| {{increase}} 26.1% |
|||
| 6.1% |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{center|2016}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{center|523,560}} |
|||
| |
|||
| 483,790 |
|||
| {{increase}} 1.1% |
|||
| 92.4% |
|||
| |
|||
| 7,395 |
|||
| {{increase}} 0.0% |
|||
| 1.4% |
|||
| |
|||
| 2,615 |
|||
| {{increase}} 13.0% |
|||
| 0.5% |
|||
| |
|||
| 26,370 |
|||
| {{increase}} 33.3% |
|||
| 5.0% |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{center|2011}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{center|516,622}} |
|||
| |
|||
| 478,395 |
|||
| {{increase}} 4.6% |
|||
| 92.6% |
|||
| |
|||
| 7,370 |
|||
| {{increase}} 4.6% |
|||
| 1.4% |
|||
| |
|||
| 2,315 |
|||
| {{increase}} 36.9% |
|||
| 0.5% |
|||
| |
|||
| 19,790 |
|||
| {{increase}} 9.9% |
|||
| 3.8% |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{center|2006}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{center|491,142}} |
|||
| |
|||
| 456,225 |
|||
| {{increase}} 1.8% |
|||
| 92.9% |
|||
| |
|||
| 7,030 |
|||
| {{increase}} 2.8% |
|||
| 1.4% |
|||
| |
|||
| 1,460 |
|||
| {{decrease}} 38.4% |
|||
| 0.3% |
|||
| |
|||
| 17,825 |
|||
| {{increase}} 35.3% |
|||
| 3.6% |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{center|2001}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{center|471,962}} |
|||
| |
|||
| 447,840 |
|||
| {{increase}} 0.4% |
|||
| 94.9% |
|||
| |
|||
| 6,830 |
|||
| {{decrease}} 21.6% |
|||
| 1.5% |
|||
| |
|||
| 2,020 |
|||
| {{increase}} 3.2% |
|||
| 0.4% |
|||
| |
|||
| 11,535 |
|||
| {{increase}} 14.8% |
|||
| 2.4% |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{center|1996}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{center|467,455}} |
|||
| |
|||
| 446,194 |
|||
| n/a |
|||
| 95.5% |
|||
| |
|||
| 8,309 |
|||
| n/a |
|||
| 1.8% |
|||
| |
|||
| 1,955 |
|||
| n/a |
|||
| 0.4% |
|||
| |
|||
| 9,830 |
|||
| n/a |
|||
| 2.1% |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
</center> |
|||
=== Religion === |
|||
According to the [[2021 Canadian census|2021 census]], religious groups in Quebec City included:<ref name="2021censusB">{{Cite web |last=Government of Canada |first=Statistics Canada |date=2022-10-26 |title=Census Profile, 2021 Census of Population |url=https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2021/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&GENDERlist=1,2,3&STATISTIClist=1&HEADERlist=0&DGUIDlist=2021A00052423027&SearchText=quebec |access-date=2022-11-09 |website=www12.statcan.gc.ca}}</ref> |
|||
*[[Christianity in Canada|Christianity]] (349,320 residents, or 65.5%) |
|||
*[[Irreligion in Canada|Irreligion]] (162,900; 30.5%) |
|||
*[[Islam in Canada|Islam]] (17,490; 3.3%) |
|||
*[[Buddhism in Canada|Buddhism]] (1,565; 0.3%) |
|||
*[[Hinduism in Canada|Hinduism]] (515; 0.1%) |
|||
*[[Judaism in Canada|Judaism]] (305; 0.1%) |
|||
*[[Mythologies of the indigenous peoples of the Americas|Indigenous Spirituality]] (75; <0.1%) |
|||
*[[Sikhism in Canada|Sikhism]] (20; <0.1%) |
|||
*Other (1,355; 0.3%) |
|||
==Economy== |
==Economy== |
||
[[File:Hôtel-Dieu de Québec.jpg|thumb|[[Hôtel-Dieu de Québec]] is one of three hospitals operated by [[Centre hospitalier universitaire de Québec|CHUQ]], the largest employer in Quebec City.]] |
|||
Most jobs in Quebec City are concentrated in public administration, defence, services, commerce, and transport. As the provincial capital, the city benefits from being a regional administrative and services centre: apropos, the provincial government is the largest employer in the city, employing 27,900 people as of 2007.<ref>"[http://www.lib.uwo.ca/programs/companyinformationcanada/canadaslargestemployersbycity2007.html#quebec Canada's largest employers by city, 2007: Quebec City]." London: [[University of Western Ontario]]. Retrieved 12 January 2009.</ref> [[Centre hospitalier universitaire de Québec|CHUQ (the local hospital network)]] is the city's largest institutional employer, with more than 10,000 employees in 2007. In 2008, the unemployment rate in Quebec City was 4.5%,<ref>"[http://www40.statcan.gc.ca/l01/cst01/labor35-eng.htm Labour: Labour force characteristics, population 15 years and older, by census metropolitan area]." [[Statistics Canada]]. Retrieved 12 January 2009.</ref> well below provincial and national averages (7.3% and 6.6%, respectively).<ref>"[http://www.statcan.gc.ca/subjects-sujets/labour-travail/lfs-epa/lfs-epa-eng.htm Latest release from the Labour Force Survey]." [[Statistics Canada]]. Retrieved 12 January 2009.</ref> |
|||
Most jobs in Quebec City are concentrated in public administration, defence, services, commerce, transport and tourism. As the provincial capital, the city benefits from being a regional administrative and services centre: apropos, the provincial government is the largest employer in the city, employing 27,900 people as of 2007.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Canada's largest employers by city, 2007: Quebec City |url=http://www.lib.uwo.ca/programs/companyinformationcanada/canadaslargestemployersbycity2007.html#quebec |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100418062010/http://www.lib.uwo.ca/programs/companyinformationcanada/canadaslargestemployersbycity2007.html |archive-date=18 April 2010 |publisher=[[University of Western Ontario]]}}</ref> [[Centre hospitalier universitaire de Québec|CHUQ (the local hospital network)]] is the city's largest institutional employer, with more than 10,000 employees in 2007. The unemployment rate in June 2018 was 3.8%, below the national average (6.0%) and the second-lowest of Canada's 34 largest cities, behind [[Peterborough, Ontario|Peterborough]] (2.7%).<ref>{{Cite news |date=6 July 2018 |title=Here's a quick glance at unemployment rates for June, by Canadian city |url=https://business.financialpost.com/pmn/business-pmn/heres-a-quick-glance-at-unemployment-rates-for-june-by-canadian-city-2 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181009211313/https://business.financialpost.com/pmn/business-pmn/heres-a-quick-glance-at-unemployment-rates-for-june-by-canadian-city-2 |archive-date=9 October 2018 |access-date=9 October 2018 |website=Financial Post}}</ref> |
|||
Around 10% of jobs are in manufacturing.<ref>"[http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/index.cfm?PgNm=TCE&Params=A1SEC906233 Québec City: Economy, transportation, and labour force]." ''[[The Canadian Encyclopedia]].'' Historical Foundation of Canada, 2008. Retrieved 12 January 2009.</ref> Principal products include pulp and paper, processed food, metal/wood items, chemicals, electronics and electrical equipment, and printed materials.Insurance companies Industrial Alliance, SSQ and La Capitale have their headquarters in Quebec City, as so do computer game studios [[Beenox]]. |
|||
Around 10% of jobs are in manufacturing.<ref>[https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/quebec-city "Québec City: Economy, transportation, and labour force"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170925083644/http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/en/article/quebec-city/#h3_jump_4 |date=25 September 2017 }}. ''The Canadian Encyclopedia''. Historical Foundation of Canada, 2008. Retrieved 12 January 2009.</ref> Principal products include pulp and paper, processed food, metal/wood items, chemicals, electronics and electrical equipment, and printed materials. The city hosts the headquarters of a variety of prominent companies, including: fashion retailer [[La Maison Simons]], engineering firms [[BPR (Quebec firm)|BPR]] and [[Norda Stelo]]; [[Cominar]] real estate investment trust; [[Beneva]], [[Industrial Alliance]], Promutuel, and Union Canadienne in the insurance sector; [[Beenox]], [[Gearbox Software]], [[Frima Studio]], [[Sarbakan]] and [[Ubisoft]] in the computer games industry; AeternaZentaris and DiagnoCure in pharmaceuticals; Amalgame, Cossette and Vision 7 in marketing and advertising; [[Institut National d'Optique (INO)]], EXFO, OptoSecurity in technology. It is also the domicile of the sole manufactory of the cigarette maker [[Rothmans, Benson & Hedges]]. |
|||
==Architecture== |
|||
{{Main|Architecture of Quebec City}} |
|||
[[File:quebec city lower town 2010.JPG|thumb|A street in the Lower Town]] |
|||
Much of the city's most notable architecture is located east of the fortification walls in [[Vieux-Québec]] (Old Quebec) and [[Old Quebec|Place Royale]]. This area has a distinct European feel with its stone buildings and winding streets lined with shops and restaurants. Porte St-Louis and Porte St-Jean are the main gates through the walls from the modern section of downtown. West of the walls are the Parliament Hill district and the [[Plains of Abraham]]. |
|||
=== Business districts === |
|||
The Up Town is linked by the ''Escalier «casse-cou»'' (literally "neck-breaking" steps) and the [[Old Quebec Funicular]] to the Lower Town, which includes such sites as the ancient [[Notre Dame des Victoires]] church, the historic Petit Champlain district, the port, and the [[Musée de la Civilisation]] (Museum of Civilization). The Lower Town is filled with original architecture and street designs, dating back to the city's beginnings. Murals and statues are also featured. The Lower Town is also noted for its wide variety of [[boutiques]], many featuring hand-crafted goods. |
|||
[[File:Coin St-Valier et Dorchester vu de l'escalier du Faubourg.jpg|thumb|right|[[Saint-Roch, Quebec City|Saint-Roch]]'s garden, lower town]] |
|||
While the traditional [[central business district]]s and their large office buildings are found on [[Parliament Hill (Quebec City)|Parliament Hill]] (especially for provincial administration) and just below in [[Saint-Roch, Quebec City|Saint-Roch]] (nowadays notable for [[Information technology|IT]] and the video game industry), a newer one has emerged in the {{ill|Boulevard Laurier|fr|boulevard Laurier}} area of [[Sainte-Foy, Quebec City|Sainte-Foy]], where a number of accounting and [[law firm]]s have moved since the 2000s. Other suburban places identified by the city for their potential are the Lebourgneuf area for private offices, as well as Estimauville Street where the [[Government of Canada]] already has many civil servants and where several city officials are expected to move in the 2020s.<ref name="cbd">{{Cite web |date=7 October 2018 |title=Où sera le centre-ville de Québec dans le futur? |url=https://ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/1128103/centre-ville-futur-quebec-urbanisme |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181009212737/https://ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/1128103/centre-ville-futur-quebec-urbanisme |archive-date=9 October 2018 |access-date=9 October 2018 |website=Radio-Canada.ca |language=fr-ca}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:QuebecCitySum04.jpg|left|thumb|[[Notre Dame des Victoires, Quebec City|Notre Dame des Victoires]] Church, Basse-Ville (Down Town)]] |
|||
Quebec city's downtown is on the lower part of the town. Its epicentre is adjacent to the old town, spanning from the Saint-Roch district, throughout the Saint Sauveur, Saint-Sacrement and Limoilou quarters. Some interpretations consider Quebec's Down town to be the central southern portion of the town ranging from the old city and Saint Roch, all the way west to the Quebec city Bridge. |
|||
==Arts and culture== |
|||
Quebec City's skyline is dominated by the massive [[Château Frontenac]] Hotel, perched on top of Cap-Diamant. It was designed by architect [[Bruce Price]], as one of a series of [[Canada's railway hotels|"château" style hotels]] built for the [[Canadian Pacific Railway]] company. The railway company sought to encourage luxury tourism and bring wealthy travelers to its trains. The hotel is beside the Terrasse Dufferin (Dufferin Terrace), a walkway along the edge of the cliff, offering beautiful views of the Saint Lawrence River. |
|||
[[File:Defile du Pere Noel Montreal 2011 - 040.jpg|thumb|Quebec City's [[Quebec Winter Carnival|Winter Carnival]] is the world's largest winter festival.]] |
|||
{{See also|List of events in Quebec City|Media in Quebec City}} |
|||
[[File:Quebec city rue st jean 2010.JPG|thumb|Rue St-Louis]] |
|||
The Terrasse Dufferin leads toward the nearby [[Plains of Abraham]], site of the battle in which the British took Quebec from France, and the [[Citadelle of Quebec]], a [[Canadian Forces]] installation and the [[Governor General of Canada|federal vice-regal secondary residence]]. The [[Parliament Building (Quebec)|Parliament Building]], the meeting place of the [[Parliament of Quebec]], is also near the [[Citadelle]]. |
|||
Quebec City is known for its [[Quebec Winter Carnival|Winter Carnival]], its [[Festival d'été de Québec|summer music festival]] and its [[Fete nationale du Québec|Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day]] celebrations. |
|||
Near the Château Frontenac is [[Notre-Dame de Québec Cathedral]], mother church of the [[Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Quebec]]. It is the first church in the [[New World]] to be raised to a [[basilica]] and is the [[primate (religion)|primatial]] church of Canada. |
|||
The [[Jardin zoologique du Québec]], now closed, reopened in 2002 after extensive repairs before ultimately shutting permanently in 2006. It featured 750 specimens of 300 different species of animals. The zoo specialized in winged fauna and garden themes but also featured several species of mammals. While it emphasized Quebec's indigenous fauna, one of its main attractions was the Indo-Australian greenhouse, which initially cost $14 million to build.<ref>{{cite news |title=Abandoned zoo greenhouse faces demolition |url=https://qcna.qc.ca/news/abandoned-zoo-greenhouse-faces-demolition |access-date=28 September 2022 |work=QCNA EN |date=23 November 2021 |language=en}}</ref> It featured fauna and flora from regions surrounding the [[Indian Ocean]].<ref>{{cite web |title=2022 - The greenhouse of the former Quebec zoo will indeed be demolished, confirms the City - Actual News Magazine |url=https://actualnewsmagazine.com/english/the-greenhouse-of-the-former-quebec-zoo-will-indeed-be-demolished-confirms-the-city/ |access-date=28 September 2022 |language=tr |date=9 December 2021}}</ref> |
|||
[[Parc Aquarium du Québec]], which reopened in 2002 on a site overlooking the [[Saint Lawrence River]], features more than 10,000 specimens of mammals, reptiles, fish and other aquatic [[Wildlife of Canada|fauna of North America]] and the [[Arctic]]. [[Polar bear]]s and various species of [[Pinniped|seal]]s of the Arctic sector and the "Large Ocean", a large basin offering visitors a view from underneath, make up part of the aquarium's main attractions. |
|||
==Culture== |
|||
{{See also|List of events in Quebec City|Media in Quebec City}} |
|||
Québec City has a number of historic sites, art galleries and museums, including [[Citadelle of Quebec]], [[Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec]], [[Ursulines of Quebec]], and [[Musée de la civilisation]]. |
|||
[[File:Parc de la Chute-Montmorency en juin.JPG|thumb|left|[[Montmorency Falls]] is a major waterfall in the city's east end.]] |
|||
Other tourist attractions include [[Montmorency Falls]], and, just outside the city limits, the [[Basilica of Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré]], the [[Mont-Sainte-Anne]] ski resort, and the [[Ice Hotel (Québec)|Ice Hotel]]. |
|||
==Attractions== |
|||
Given the mass of [[Cap Diamant]] and the presence of [[Citadelle of Quebec|la Citadelle]] atop it, overlooking the waters of the St. Lawrence River, [[Charles Dickens]] described Quebec City as the "[[Gibraltar]] of [[North America]]".<ref>{{citation| url=https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/quebec-city-in-the-war-of-1812| last=Marsh| first=James A.| title=Quebec City in the War of 1812| date=30 October 2014| encyclopedia=The Canadian Encyclopedia| publisher=Historica Canada| accessdate=26 March 2023}}</ref> |
|||
===Architecture=== |
|||
{{Main|Architecture of Quebec City}} |
|||
[[File:Rue St Jean.jpg|alt=|left|thumb|The [[Ramparts of Quebec City|St. Jean (St. John) Gate]]]] |
|||
Much of the city's notable traditional architecture is located in [[Vieux-Québec]] (Old Quebec), within and below the [[Ramparts of Quebec City|fortifications]]. This area has a distinct European feel with its stone buildings and winding streets lined with shops and restaurants. Porte Saint-Louis and Porte Saint-Jean are the main gates through the walls from the modern section of downtown; the Kent Gate was a gift to the province from [[Queen Victoria]] and the foundation stone was laid by the Queen's daughter, [[Princess Louise, Duchess of Argyll|Princess Louise, Marchioness of Lorne]], on 11 June 1879.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hubbard |first=R.H. |url=https://archive.org/details/rideauhallillust00hubb/page/49 |title=Rideau Hall |publisher=McGill-Queen's University Press |year=1977 |isbn=978-0-7735-0310-6 |page=[https://archive.org/details/rideauhallillust00hubb/page/49 49] |url-access=registration}}</ref> West of the walls are the [[Parliament Hill (Quebec City)|Parliament Hill]] area, and to the south the [[Plains of Abraham]]. |
|||
The upper and lower town are linked by numerous stairs such as the ''Escalier « casse-cou »'' ("breakneck stairway") or the [[Old Quebec Funicular]] on the historic [[Rue du Petit-Champlain]], where many small boutiques are found. A small town square nearby, the Place Royale, now surrounded by picturesque stone buildings, is the site of [[Champlain]]'s founding of the city in 1608. On it is the [[Notre-Dame-des-Victoires, Quebec City|Notre-Dame-des-Victoires]] church. The [[Musée de la Civilisation]] is located nearby by the river. |
|||
[[File:Chateau Frontenac in Quebec City (3875826553).jpg|alt=|thumb|Chateau Frontenac in Quebec City]] |
|||
[[File:Quartier Petit Champlain 001.jpg|thumb|The [[Petit Champlain]], containing the pictured [[Rue du Petit-Champlain]], is claimed to be the oldest commercial district in North America.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Simard |first1=Luc |title=Du cap au rivage : promenades dans les rues de Québec |last2=Émond |first2=Chantale |date=1994 |publisher=Ville de Québec |others=Québec (Québec) |isbn=978-2-92-086077-3 |location=Québec |language=fr |oclc=31779784}}</ref>]] |
|||
[[File:Le Diamant Theatre.jpg|thumb|[[Le Diamant Theatre]] in Quebec City's Saint-Roch neighborhood]] |
|||
[[File:Vieew of Québec from Lévis city, Québec 11.jpg|thumb|Québec, photographed from Lévis]] |
|||
Along with concrete high-rises such as [[Édifice Marie-Guyart]] and [[Hôtel Le Concorde|Le Concorde]] on parliament hill (see [[List of tallest buildings in Quebec City]]), the city's skyline is dominated by the massive [[Château Frontenac]] hotel, perched on top of Cap-Diamant. It was designed by architect [[Bruce Price]], as one of a series of [[Canada's railway hotels|"château" style hotels]] built for the [[Canadian Pacific Railway]] company. The railway company sought to encourage luxury tourism and bring wealthy travellers to its trains. |
|||
Alongside the Château Frontenac is the [[Terrasse Dufferin]], a walkway along the edge of the cliff, offering views of the Saint Lawrence River. The terrace leads toward the nearby [[Plains of Abraham]], site of the battle in which the British took Quebec from France, and the [[Citadelle of Quebec]], a [[Canadian Forces]] installation and the [[Governor General of Canada|federal vice-regal secondary residence]]. The [[Parliament Building (Quebec)|Parliament Building]], the meeting place of the [[Parliament of Quebec]], is also near the [[Citadelle of Quebec|Citadelle]]. |
|||
Near the Château Frontenac is [[Notre-Dame de Québec Cathedral]], mother church of the [[Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Quebec]]. It is the first church in the [[New World]] to be raised to a [[basilica]] and is the [[primate (bishop)|primatial]] church of Canada. There are 37 [[List of National Historic Sites of Canada in Quebec City|National Historic Sites of Canada]] in Quebec City and its enclaves.<ref>The 37 sites in Quebec City are listed in the [https://archive.today/20120906071404/http://www.pc.gc.ca/apps/dfhd/search-recherche_eng.aspx Directory of Federal Heritage Designations] as being located in Québec and the following boroughs/enclaves: Beauport, Cap-Rouge, Notre-Dame-des-Anges, Sainte-Foy and Wendake.</ref> |
|||
===Parks=== |
|||
[[File:Carnival 1.jpg|thumb|left|A picture of an ice castle during the [[Quebec Winter Carnival|carnival]]]] |
|||
One of the most notable is [[The Battlefields Park]], which is home to 50 historical artillery pieces and the [[Plains of Abraham]]. The park offers views of the St. Lawrence River and has multiple historical structures and statues like the ''[[Joan of Arc]] on Horseback'' and a couple of [[Martello Towers]].<ref name="ville.quebec.qc.ca">{{Cite web |title=Ville de Québec – Parks and Gardens |url=http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/EN/touristes/voir/attraits/parcs_jardins.aspx#tabs |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161114083801/http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/EN/touristes/voir/attraits/parcs_jardins.aspx#tabs |archive-date=14 November 2016 |access-date=14 November 2016 |website=www.ville.quebec.qc.ca}}</ref> Historically this was the site of the [[Battle of the Plains of Abraham]] (1759), a decisive British victory in the [[Seven Years' War]] which ended French rule in what would become Canada, and the later [[Battle of Quebec (1775)]] during the [[American Revolutionary War]], where the British were able to hold onto its last stronghold in the Northern extent of its North American territory. |
|||
Other large and centrally located parks are [[Parc Victoria, Quebec|Parc Victoria]], Parc [[Maizerets]] and [[Cartier-Brébeuf National Historic Site]]. |
|||
Quebec City is known for its [[Quebec Winter Carnival|Winter Carnival]] and for its [[Fete nationale du Québec|Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day]] celebrations. |
|||
Quebec City's largest park is the {{ill|Parc Chauveau|fr|Parc Chauveau}}, which is crossed by the suburban section of the city-wide [[Saint-Charles River (Quebec City)|Saint-Charles River]] and is thus also part of the {{convert|31|km|abbr=on}} long Saint-Charles River's [[linear park]]. At Chauveau, activities such as [[canoeing]], fishing and [[cross-country skiing]] are offered depending on the season, in addition to an interior soccer stadium.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Le Parc Chauveau: la nature à ma portée! |url=https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/docs/publications/277_publication_2_530.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304115853/http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/docs/publications/277_publication_2_530.pdf |archive-date=4 March 2016 |access-date=6 October 2018 |publisher=Ville de Québec |language=fr}}</ref> Among others, there is also the beach of Beauport Bay, as well as the Marais du Nord (north-end [[marsh]] land). |
|||
Quebec is the only large city in Canada along with [[Halifax, Nova Scotia|Halifax]] lacking a public [[greenhouse]]. Nonetheless, outside areas known for their public [[gardens]] or [[landscaping]] include:<ref>{{Cite web |last=Hogdson |first=Larry |date=8 September 2018 |title=Québec, toujours un désert botanique? |url=https://www.lesoleil.com/maison/horticulture/quebec-toujours-un-desert-botanique-902ac285ddcced46037a826d41aa4b23 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181006234927/https://www.lesoleil.com/maison/horticulture/quebec-toujours-un-desert-botanique-902ac285ddcced46037a826d41aa4b23 |archive-date=6 October 2018 |access-date=6 October 2018 |website=Le Soleil |language=fr-CA}}</ref> |
|||
Tourist attractions located near Quebec City include [[Montmorency Falls]], the [[Basilica of Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré]], the [[Mont-Sainte-Anne]] [[ski resort]], and the [[Ice Hotel (Québec)|Ice Hotel]]. |
|||
* The linear park named {{ill|Promenade Samuel-De Champlain|fr|Promenade Samuel-De Champlain}} that stretches {{convert|4.6|km|abbr=on}} alongside the Saint Lawrence River, from [[Pierre Laporte Bridge]] to Sillery's east-end. Its bicycle and pedestrian paths then continues to Old Quebec and then along the Saint-Charles River.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Québec |first=Office du tourisme de |title=Promenade Samuel-De Champlain |url=https://www.quebecregion.com/en/businesses/sports-outdoor-activities-wellbeing/hiking/promenade-samuel-de-champlain/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181006235526/https://www.quebecregion.com/en/businesses/sports-outdoor-activities-wellbeing/hiking/promenade-samuel-de-champlain/ |archive-date=6 October 2018 |access-date=6 October 2018 |website=Official Web Site – Québec City Tourism |language=en}}</ref> Just like the beach at Beauport Bay, the construction of the ''Promenade'' was funded by provincial and federal governments to celebrate the [[400th anniversary of Quebec City]] in 2008. |
|||
* [[Government House (Quebec)]], slightly west of the Plains of Abraham in [[Sillery, Quebec City|Sillery]], and known for its [[natural landscaping]] as well as traditional gardens, such as those surrounding the historical {{ill|Villa Bagatelle|fr|Villa Bagatelle}}. The historical significance of the park also lies in the former presence of the viceregal [[Government House (Quebec)|Government House of Quebec]] (1845–1966). |
|||
* The [[Maizerets#Domaine de Maizerets|Domaine de Maizerets]], where are found an [[arboretum]] and an [[observation tower]], not far from the Saint Lawrence River and Beauport Bay. |
|||
* {{ill|Domaine Cataraqui|fr|Domaine Cataraqui}} in Sillery. |
|||
* The {{ill|Roger-Van den Hende Botanical Garden|fr|Jardin universitaire Roger-Van den Hende}} of {{Lang|fr|[[Université Laval]]|italic=no}}. |
|||
==Sports== |
|||
Jardin zoologique du Québec, reopened in 2002 after two years of restorations but closed in 2006 after a political decision. It featured 750 specimens of 300 different species of animals. The zoo specialized in winged fauna and garden themes, but also presented several species of mammals. While it emphasizes the indigenous fauna of Quebec, one of its principal attractions was the Indo-Australian greenhouse, featuring fauna and flora from these areas. |
|||
Quebec City has hosted a number of recent sporting events, as well as being shortlisted for the [[Bids for the 2002 Winter Olympics|2002 Winter Olympics city selection]]. The [[Special Olympics Canada|Special Olympics Canada National Winter Games]] was held in the city from 26 February to 1 March 2008.<ref>{{Cite web |date=29 January 2007 |title=History of Major Special Olympics Canada (SOC) Events |url=http://www.specialolympics.ca/en/images/pdfs/sports_gameshistory.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706203531/http://www.specialolympics.ca/en/images/pdfs/sports_gameshistory.pdf |archive-date=6 July 2011 |access-date=14 July 2011 |publisher=Special Olympics Canada}}</ref> Quebec City co-hosted with [[Halifax Regional Municipality|Halifax]], Nova Scotia, the [[2008 IIHF World Championship]]. Regular sporting events held in the city include the [[Tournoi de Québec|Coupe Banque Nationale]], a [[Women's Tennis Association]] tournament; [[Crashed Ice]], an extreme downhill skating race; [[Quebec International Pee-Wee Hockey Tournament]], a [[minor hockey]] tournament; and the Tour de Québec International cycling stage race.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Here comes the 4th Tour de Québec! |url=http://www.tourdequebec.com/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120309024254/http://www.tourdequebec.com/ |archive-date=9 March 2012 |access-date=14 July 2011 |publisher=tourdequebec.com}}</ref> In December 2011, Quebec City hosted the [[ISU Grand Prix of Figure Skating Final]] at the Pavillon de la Jeunesse at ExpoCité. |
|||
[[File:Stade Municipal.JPG|thumb|upright=1.5|The [[Québec Capitales]] play their home games at [[Stade Canac]], a stadium primarily used for baseball.]] |
|||
[[Parc Aquarium du Québec]], reopened in 2002 on a site overlooking the [[Saint Lawrence River]], presents more than 10,000 specimens of mammals, reptiles, fish and other aquatic fauna of North America and the [[Arctic]]. [[Polar bear]]s and various species of [[Pinniped|seal]]s of the Arctic sector and the "Large Ocean", a large basin offering visitors a view from underneath, form part of the principal attractions. |
|||
The city currently has one professional team, the baseball team [[Quebec Capitales|Capitales de Québec]], which plays in the [[Frontier League]] in downtown's [[Stade Canac]]. The team was established in 1999 and originally played in the [[Northern League (baseball, 1993–2010)|Northern League]]. It has nine league titles, won in 2006, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2017, 2022 and 2023. A professional basketball team, the [[Quebec Kebs]], played in [[National Basketball League of Canada]] in 2011 but folded before the 2012 season, and a semi-professional [[association football|soccer]] team, the [[Dynamo de Québec]], played in the [[Première ligue de soccer du Québec]], until 2019. |
|||
There are a number of historic sites, art galleries and museums in Quebec City, such as [[Citadelle of Quebec]], [[Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec]], [[Ursulines of Quebec]], and [[Musée de la civilisation]] |
|||
The city had a professional ice hockey team, the [[Quebec Nordiques]], which played in the [[World Hockey Association]] (WHA) from 1972 to 1979 and the [[National Hockey League]] (NHL) from 1979 to 1995, maintaining a strong rivalry with the [[Montreal Canadiens]]. Due to a disadvantageous exchange rate with respect to the US dollar, the team moved to [[Denver, Colorado]], in 1995, becoming the [[Colorado Avalanche]]. A lower-tier team, the [[Atlanta Knights#Quebec Rafales|Quebec Rafales]], played in the professional [[International Hockey League (1945–2001)|International Hockey League]] from 1996 to 1998. |
|||
==Sport== |
|||
As well as having a number of local sports teams, Quebec City has hosted a number of sporting events. The [[Special Olympics Canada|Special Olympics Canada National Winter Games]] was held in the city from February 26 to March 1, 2008.<ref>[http://www.specialolympics.ca/en/images/pdfs/sports_gameshistory.pdf HISTORY OF MAJOR SPECIAL OLYMPICS CANADA]</ref> Quebec City co-hosted with [[Halifax Regional Municipality|Halifax]], [[Nova Scotia]], the [[2008 IIHF World Championship]]. Regular sporting events held in the city, include the [[Bell Challenge|Challenge Bell]], a [[Women's Tennis Association]] tournament; [[Crashed Ice]], an extreme downhill skating race; Quebec City International Pee-Wee Tournament, a [[minor hockey]] tournament; and the Tour de Québec International cycling stage race.<ref>[http://www.tourdequebec.com/ tourdequebec.com]</ref> |
|||
[[File:CentreVideotron-StephaneGroleau-0800.jpg|thumb|left|[[Videotron Centre]] is an indoor [[arena]] and is presently used as the home arena for the [[QMJHL|major junior hockey]] [[Quebec Remparts]].]] |
|||
The city has a professional baseball team, the [[Quebec Capitales|Capitales de Québec]] which currently play in the [[Canadian American Association of Professional Baseball]]. The team was established in 1999, and originally played in the [[Northern League (baseball)|Northern League]]. The team has two league titles, won in 2006 and 2009. The team's stadium is the [[Stade Municipal (Quebec City)|Stade Municipal]]. |
|||
The [[Videotron Centre]] was built with the hope of getting an [[National Hockey League|NHL]] franchise (relocation or expansion) in Quebec City.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Karine Gagnon, Qmi Agency |date=1 March 2011 |title=Quebecor joins arena plan, eyes NHL team | Hockey | Sports |newspaper=Toronto Sun |url=http://www.torontosun.com/sports/hockey/2011/03/01/17451741.html |url-status=live |access-date=2 January 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121001195519/http://www.torontosun.com/sports/hockey/2011/03/01/17451741.html |archive-date=1 October 2012}}</ref> The project was funded regardless of whether an NHL team arrives.<ref>{{Cite news |last=McParland |first=Kelly |date=2 March 2011 |title=The Quebec gravy train chugs off without Ottawa on board for once |url=https://nationalpost.com/full-comment/the-quebec-gravy-chain-chugs-off-without-ottawa-on-board-for-once |url-status=live |archive-url=http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20110311212859/http%3A//fullcomment.nationalpost.com/2011/03/02/the%2Dquebec%2Dgravy%2Dchain%2Dchugs%2Doff%2Dwithout%2Dottawa%2Don%2Dboard%2Dfor%2Donce/ |archive-date=11 March 2011 |newspaper=National Post}}</ref> It is also hoped that the arena can help Quebec City win a future [[Winter Olympics]] games bid.<ref>{{Cite web |date=16 October 2009 |title=Quebec City plans $400 million arena to attract NHL team, Winter Olympics — ESPN |url=https://www.espn.com/nhl/news/story?id=4564924 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110629035635/http://sports.espn.go.com/nhl/news/story?id=4564924 |archive-date=29 June 2011 |access-date=2 January 2012 |website=[[ESPN]]}}</ref> It has now replaced the [[Colisée de Québec]] as the main multifunctional arena in Quebec City. |
|||
Other teams include the local football team, the [[Laval Rouge-et-Or|Rouge & Or]] of the [[Université Laval]]; the basketball team, [[Quebec Kebs]] of the [[Premier Basketball League]]; the junior hockey team, [[Quebec Remparts]] of the [[Quebec Major Junior Hockey League]]; the football teams, [[Quebec City Monarks]] and [[Quebec City Rebelles]] of the [[Ligue de football majeur du Québec]]; the soccer team, [[FC Quebec]] of the [[Canadian Soccer League (current)|Canadian Soccer League]]; the women's hockey team [[Quebec Phoenix]] of the [[Canadian Women's Hockey League]]; and [[Quebec City Amiral|Quebec Arsenal]] of the [[W-League]]. |
|||
Other teams include the [[Quebec Remparts]] in major junior hockey ([[QMJHL]]), Université Laval varsity team [[Laval Rouge-et-Or|Rouge & Or]], the [[Quebec City Monarks]], and [[Quebec City Rebelles]] of La Ligue de Football de Québec; the Alouettes de Charlesbourg of the [[Ligue de Baseball Junior Élite du Québec]]; the women's hockey team Quebec Phoenix of the [[Canadian Women's Hockey League]]; and soccer club [[Quebec City Amiral|Quebec Arsenal]] of the [[USL W-League (1995–2015)|W-League]]. |
|||
The city had a hockey team, the [[Quebec Nordiques]], who played in the [[World Hockey Association]] (WHA) from 1972 to 1979 and then in the [[National Hockey League]] (NHL) from 1979 to 1995, maintaining a strong rivalry with the [[Montreal Canadiens]]. Due to financial problems, the team moved to [[Denver, Colorado]] in 1995, becoming [[Colorado Avalanche]]. There has been discussion of bringing a team back to the city, but former mayor [[Andrée Boucher]] had not supported the project. It is generally expected that Quebec City will need to build a new arena to get a new team, replacing the [[Colisée Pepsi]], as well as organizing an ownership group. There have also been discussions around getting a [[Canadian Football League]] team. Quebec City is expected to be in competition with [[Moncton]] and [[Halifax Regional Municipality|Halifax]] for the franchise, though a new stadium would likely be needed as well. |
|||
Quebec City holds the Coop [[FIS Cross-Country World Cup]]. This is a [[ski]] event that welcomes the best of that sport.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Quebec city FIS Cross-Country World Cup 2019 |url=https://worldcupccquebec.com/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200806191917/https://worldcupccquebec.com/ |archive-date=6 August 2020 |access-date=30 March 2020 |website=Quebec City FIS Cross-Country World Cup |language=en-US}}</ref> |
|||
{{wide image|Stade Municipal.JPG|1000px|<center>The [[Quebec Capitales]], which play in the [[Stade Municipal (Quebec City)|Stade Municipal]] are the province of [[Quebec]]'s only professional baseball team, playing in the [[Canadian American Association of Professional Baseball|Can-Am League]]</center>}} |
|||
==Government== |
==Government== |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Monument Honore-Mercier 07.jpg|thumb|The provincial [[Parliament Building (Quebec)|Parliament Building]] is located in the city.]] |
||
[[File:Quebec national assembly.jpg|thumb|left|[[Parliament Building (Quebec)|Parliament Building]], Quebec City]] |
|||
The current [[mayor]] of Quebec City is [[Régis Labeaume]], who was elected in a special election on 2 December 2007, following the death in office of [[Andrée Boucher|Andrée P. Boucher]], an independent, on 24 August. [[Jacques Joli-Coeur]] of the [[Renouveau municipal de Québec]] party served as interim mayor between Boucher's death and the by-election. |
|||
Since the 1960s, [[Centre-right politics|centre-right]] parties such as [[Union Nationale (Quebec)|Union Nationale]], [[Ralliement créditiste|Crédit social]], [[Conservative Party of Canada]] (CPC), [[Action démocratique du Québec]] and [[Coalition Avenir Québec]] (CAQ) have been more popular in the Quebec City region than elsewhere in the province.<ref name="duval">{{Cite web |last=Duval |first=Alexandre |title=Politique : un chercheur perce une partie du " mystère Québec " |url=https://ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/1049716/mystere-region-quebec-politique-vote-droite-etude |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181009211158/https://ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/1049716/mystere-region-quebec-politique-vote-droite-etude |archive-date=9 October 2018 |access-date=8 October 2018 |website=Radio-Canada.ca |date=11 August 2017 |language=fr-ca}}</ref> After the [[2006 Canadian federal election|federal election of 2006]], six of the ten conservative ridings of the province were found in its metropolitan area (where the CPC garnered 39% of the vote, against 25% at the provincial scale)<ref>{{Cite web |last=Daoust |first=Jean-François |date=15 August 2017 |title=Le mystère de Québec: les moins bien nantis rejettent la gauche |url=https://www.ledevoir.com/opinion/idees/505698/le-mystere-de-quebec-les-citoyens-moins-bien-nantis-rejettent-la-gauche |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181009211813/https://www.ledevoir.com/opinion/idees/505698/le-mystere-de-quebec-les-citoyens-moins-bien-nantis-rejettent-la-gauche |archive-date=9 October 2018 |access-date=8 October 2018 |website=Le Devoir |language=fr}}</ref> and in the city proper, the CPC won three of the four seats that existed at that time (the [[Québec (electoral district)|riding of Quebec]] went to the [[Bloc Québécois|Bloc]]).<ref>{{Cite web |last=Himelfarb |first=Jordan |date=10 October 2018 |title=The Bloc's Quebec City fortress |url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/the-blocs-quebec-city-fortress/article20388363/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235556/https://mb.moatads.com/yi/v2?ol=0&qn=%604%7BZEYwoqI%24%5BK%2BdLLU)%2CMm~tB%23a.%5BMhS%3A15.sn_003etW6~P6Jn)s)wC%24GL3jX%7BQqDOJ%3Eoy)G3p%2FhFjrR8whh%2B%7D%407%25w_2C%3FP%3ElK%3DbH%2FH%40%26%2Bc%5B5IUOG(%2CWV%7BGrV~1HmDkP8D4rUDtmxT%3Bwv%40V374BKm55%3D%261fp%5BoU5tWhX%3C%3Ce%24%26~1%3Axkr%5BUe31k5X%5BG%5E%5B)%2C2iVSX%3C_Y%7B!7IQ3HbmUZzCFm%5Du!x2l.uBlTVU%2F.%3Dh%3FtDJq%409BG&tf=1_nMzjG---CSa7H-nHVQZC-bW7qhB-LRwqH-nMzjG-&vi=111111&rc=1%2C1%2C0%2C3%2C3326192205%2C1%2C4%2C0%2Cprobably%2Cprobably&rb=1-8BRYrdgGjXhDLOlS9taa18sl5UMbMAFrHQZRAnlp9pAdeA91T5s1LwZtUqv15LnesVBD&rs=1-%2BvQzXjcST%2BDrDg%3D%3D&sc=1&os=1-gQ%3D%3D&qp=10000&is=BBBBB2BBEYBvGl2BBCBBtUTBBRmsqbKW8BsrBu0rCFE48CRBeeBS2hWTMBBQeQBBn2soYggyUig0CBlWZ0uBBCCCCCCOgRBBiOfnE6Bkg7OxBb8MxOtJYHCBdm5kBhBBC9Y8oBXckXBR76iUUsJBCBBBBBBBBBWBSqj3BBBZeGV2BBBCMciUBBBjgEBBBBBB94UMgTdJMtEcpMBBBQBBBniOccBBBBBB47kNwxBbBBBBBBBBBhcjG6BBJM2L4Bk8BwCBQmIoRBBCzBz1BBCTClBBrbGBC4ehueB57NG9aJeRzBqEKiuwBBBB&iv=8&qt=0&gz=0&hh=0&hn=0&tw=%7D%3Bra%40QlRww1%3Co%40~RfrE%3D%25.%7CRwJO!BQwi!GM%3D%3Dkue8!Jw%5B%40Km_wAbe%2CHT%7BQ5%3DgE&qc=10&qd=10&qf=1100&qe=784&qh=1100&qg=900&qm=0&qa=1600&qb=1000&qi=1600&qj=1000&to=000&po=1-0020002000002120&vy=ot%24b%5Bh%40%22oD%7BMx5%3C1%3B(8.%7CLK2_v%5Eq%2BGs1%7B%2CyB%3AU!%2FoD%7BMx5%3C1%3B(Oy%2CUy%3CD&qr=0&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.theglobeandmail.com%2Fnews%2Fpolitics%2Fthe-blocs-quebec-city-fortress%2Farticle20388363%2F&pcode=globeandmailheader638913312107&callback=MoatNadoAllJsonpRequest_91959890 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=8 October 2018 |website=The Globe and Mail}}</ref> Along with the city's lesser support for [[Quebec sovereignty]], this led political pundits to speculate about a "Quebec City mystery".<ref>{{Cite web |last=Peritz |first=Ingrid |date=31 August 2012 |title=Seeking clues to Quebec City's ballot box mystery |url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/seeking-clues-to-quebec-citys-ballot-box-mystery/article4511569/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120901005509/http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/seeking-clues-to-quebec-citys-ballot-box-mystery/article4511569/ |archive-date=1 September 2012 |access-date=8 October 2018 |website=The Globe and Mail}}</ref> |
|||
The current leader of the Renouveau municipal de Québec party, and leader of the majority group on [[Quebec City Council]], is [[Jean-Marie Matte]]. |
|||
Various lines of thought were offered, including the popularity of the [[talk radio]] stations [[CHOI-FM|CHOI]] and [[CJMF-FM|FM93]] expressing [[Fiscal conservatism|fiscally conservative]] and non-[[Political correctness|politically correct]] opinions.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Castonguay |first=Alec |title=Le faux mystère de Québec |url=https://lactualite.com/politique/2012/08/31/le-faux-mystere-de-quebec/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181010011113/https://lactualite.com/politique/2012/08/31/le-faux-mystere-de-quebec/ |archive-date=10 October 2018 |access-date=8 October 2018 |website=L’actualité |date=31 August 2012 |language=fr-CA}}</ref> Over the years, this genre has been qualified by its detractors as {{lang|fr|radio poubelle}} ({{langx|en|[[trash radio]]}}) and hosts like [[Jeff Fillion]] and [[André Arthur]] likened to [[shock jock]]s.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Bilefsky |first=Dan |date=18 August 2018 |title=Quebec's 'Trash Radio' Host Fires Up Outrage, and Big Ratings |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2018/08/18/world/canada/quebec-trash-radio-jeff-fillion.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181009211552/https://www.nytimes.com/2018/08/18/world/canada/quebec-trash-radio-jeff-fillion.html |archive-date=9 October 2018 |access-date=8 October 2018 |website=The New York Times}}</ref> Also, compared to the rest of the province, people of the area may favour harsher criminal sentences, and lower-class households may share political views more in line with those earning more. The reasons for this remain unclear.<ref name="duval" /> Another researcher put forward the historical factors that led to Montreal surpassing Quebec as the metropolis of [[British North America]] in the early 19th century. According to this theory, its permanent status of "second city" (albeit the capital) engendered feelings of "repressed jealousy".<ref>{{Cite web |last=Lachance |first=Nicolas |date=20 December 2015 |title=Il perce (enfin) le mystère Québec |url=https://www.journaldequebec.com/2015/12/20/il-perce-enfin-le-mystere-quebec |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181010011006/https://www.journaldequebec.com/2015/12/20/il-perce-enfin-le-mystere-quebec |archive-date=10 October 2018 |access-date=8 October 2018 |website=Le Journal de Québec |language=fr-CA}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" |
|||
The "mystery" was relativized following the [[2011 Canadian federal election|2011 federal election]]. All five ridings within the city were won by the leftist [[New Democratic Party]], in the so-called "orange wave" that temporarily swept the province. Nonetheless, five of the six seats won by the Conservatives in the province were found in the greater Quebec City area.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Séguin |first=Rheal |date=2 May 2011 |title=Quebec City gives NDP control over the region |url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/quebec-city-gives-ndp-control-over-the-region/article578479/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235554/https://www.theglobeandmail.com/pf/dist/components/output-types/default.css?d=95 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=8 October 2018 |website=The Globe and Mail}}</ref> At the [[2018 Quebec general election|2018 provincial election]], the leftist party [[Québec solidaire]] managed to win two districts, [[Taschereau (electoral district)|Taschereau]] and [[Jean-Lesage]], the most densely populated in town, but the centre-right CAQ, as it swept the province, won six of the nine districts encompassing the city, and 15 of the 18 in the administrative regions of [[Capitale-Nationale]] and [[Chaudière-Appalaches]] (south shore of the city). |
|||
{{stack begin}} |
|||
{|class="wikitable" style="float:right; width:400; font-size:90%; margin-left:1em;" |
|||
|+'''Quebec City federal election results'''<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.elections.ca/content.aspx?section=res&dir=rep/off/44gedata&document=bypro&lang=e |title=Official Voting Results Raw Data (poll by poll results in Quebec City)|date=7 April 2022 |publisher=Elections Canada |access-date=February 28, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | Year |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[Liberal Party of Canada|Liberal]] |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[Conservative Party of Canada|Conservative]] |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[Bloc Québécois]] |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[New Democratic Party|New Democratic]] |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[Green Party of Canada|Green]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="2" style="width: 0.25em; background-color: {{Canadian party colour|CA|Conservative}}| |
|||
! scope="col" | Party |
|||
! [[2021 Canadian federal election|2021]] |
|||
! scope="col" | Initial |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|Liberal|background}} | 27% |
|||
! scope="col" | Chief |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#EA6D6A;"| ''76,734'' |
|||
! scope="col" | Governorship |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|Conservative|background}} | '''34%''' |
|||
! scope="col" | Opposition |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#6495ED;"| ''96,875'' |
|||
! scope="col" | Seats |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|BQ|background}} | 27% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#87CEFA;"| ''75,949'' |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|NDP|background}} | 8% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#F4A460;"| ''23,129'' |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|Green|background}} | 2% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#99C955;"| ''5,715'' |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! [[2019 Canadian federal election|2019]] |
|||
| style="background: white;" | [[Renouveau municipal de Québec]] |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|Liberal|background}} | 28% |
|||
| style="background: white;" | R.M.Q. |
|||
| style=" |
| style="text-align:right; background:#EA6D6A;"| ''82,742'' |
||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|Conservative|background}} | '''29%''' |
|||
| style="background: white;" | 1989–2005 |
|||
| style=" |
| style="text-align:right; background:#6495ED;"| ''84,656'' |
||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|BQ|background}} | 28% |
|||
| style="background: white;" | '''23''' |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#87CEFA;"| ''82,950'' |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|NDP|background}} | 9% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#F4A460;"| ''25,969'' |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|CA|Green|background}} | 4% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#99C955;"| ''11,789'' |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|} |
|||
| style="background: white;" | [[Action civique de Québec]] |
|||
| style="background: white;" | A.C.Q. |
|||
{|class="wikitable" style="float:right; width:400; font-size:90%; margin-left:1em;" |
|||
| style="background: white;" | Claude Larose |
|||
|+'''Quebec City provincial election results'''<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.electionsquebec.qc.ca/en/results-and-statistics/general-election-results/2018-10-01/ |title=Official Voting Results by polling station (poll by poll results in Quebec City)|date=3 December 2021 |publisher=Elections Québec |access-date=February 28, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
| style="background: white;" | N/A |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | Year |
|||
| style="background: white;" | N/A |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[Coalition Avenir Québec|CAQ]] |
|||
| style="background: white;" | '''5''' |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[Quebec Liberal Party|Liberal]] |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[Québec solidaire|QC solidaire]] |
|||
! colspan="2" scope="col" | [[Parti Québécois]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| style="width: 0.25em; background-color: {{Canadian party colour|QC|CAQ}}| |
|||
| style="background: white;" | Parti Vision Québec |
|||
! [[2018 Quebec general election|2018]] |
|||
| style="background: white;" | V.Q. |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|QC|CAQ|background}} | '''41%''' |
|||
| style="background: white;" | [[Marc Bellemare]] |
|||
| style=" |
| style="text-align:right; background:#1E90FF;"| ''118,468'' |
||
| {{Canadian party colour|QC|Liberal|background}} | 22% |
|||
| style="background: white;" | N/A |
|||
| style="background: |
| style="text-align:right; background:#EA6D6A;"| ''65,462'' |
||
| {{Canadian party colour|QC|QS|background}} | 19% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#FF8040;"| ''55,126'' |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|QC|PQ|background}} | 12% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#87CEFA;"| ''34,079'' |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| style="width: 0.25em; background-color: {{Canadian party colour|QC|Liberal}}| |
|||
| style="background: white;" | Option Capitale |
|||
! [[Quebec general election, 2014|2014]] |
|||
| style="background: white;" | O.C. |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|QC|CAQ|background}} | 32% |
|||
| style="background: white;" | Pierre Coté |
|||
| style=" |
| style="text-align:right; background:#1E90FF;"| ''95,770'' |
||
| {{Canadian party colour|QC|Liberal|background}} | '''39%''' |
|||
| style="background: white;" | N/A |
|||
| style="background: |
| style="text-align:right; background:#EA6D6A;"| ''118,564'' |
||
| {{Canadian party colour|QC|QS|background}} | 7% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#FF8040;"| ''21,123'' |
|||
| {{Canadian party colour|QC|PQ|background}} | 19% |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#87CEFA;"| ''57,481'' |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| style="background: white;" | Independent |
|||
| style="background: white;" | Ind. |
|||
| style="background: white;" | X |
|||
| style="background: white;" | X |
|||
| style="background: white;" | X |
|||
| style="background: white;" | '''9''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="background: white;" | Vacant |
|||
| style="background: white;" | X |
|||
| style="background: white;" | X |
|||
| style="background: white;" | X |
|||
| style="background: white;" | X |
|||
| style="background: white;" | '''0''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''Total''' |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| '''37''' |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
{{stack end}} |
|||
==Education== |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
[[Université Laval]] is located in the eastern end of the city, in the borough of [[Sainte-Foy, Quebec|Sainte-Foy]]. However, the school of architecture of Université Laval is located in Old Quebec. The central campus of the [[Université du Québec]], originally in Sainte-Foy, is also, since the amalgamation, located in Quebec City, as are the Université du Québec's [[École nationale d'administration publique]] and [[Institut national de la recherche scientifique]], as well as [[Télé-université]], the distance learning component of the [[Université du Québec à Montréal]]. |
|||
{{Further|List of presidents of districts of Quebec City}} |
|||
===Municipal government=== |
|||
[[File:City Hall in Quebec City.jpg|thumb|[[City Hall of Quebec City|Quebec City Hall]] serves as the seat for the [[Quebec City Council]].]] |
|||
Quebec City is governed by a [[mayor–council government]], which includes the 21 [[single-member district]]s of the legislative [[Quebec City Council]] and the separately elected [[List of mayors of Quebec City|mayor]]. The [[councilors]] are elected by [[first-past-the-post voting]] while the mayor is elected by the city [[at-large]]. Both usually belong to [[political parties]] and are elected at the same time every 4 years. The mayor is an [[ex officio member]] of the council but is not its president and has no vote. The current one is [[Bruno Marchand]], elected in [[2021 Quebec City municipal election|2021]]. |
|||
Each of the city's six boroughs has a council composed of 3 to 5 of the aforementioned councillors, depending on the size of its population. It has jurisdiction with matters such as local road maintenance, leisure, [[waste collection]], and small grants for community projects and others, but cannot tax or borrow money.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Conseils d'arrondissement |url=https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/apropos/gouvernance/conseils-arrondissement/index.aspx |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141006105250/http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/apropos/vie_democratique/elus/conseils_arrondissement/index.aspx |archive-date=6 October 2014 |website=Ville de Québec}}</ref> The boroughs are further divided into [[#Boroughs and neighbourhoods|35 neighbourhoods]], which also have councils devoted to [[public consultation]]s, each led by 11 citizens. Their geographical limits may be distinct from those of the city's 21 electoral districts, and councillors also sit at their neighbourhood councils as non-voting ex officio members.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Conseils de quartier |url=https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/citoyens/participation-citoyenne/conseils_quartier/role-et-composition.aspx |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170308044912/http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/apropos/vie_democratique/participation_citoyenne/conseils_quartier/index.aspx |archive-date=8 March 2017 |website=Ville de Québec}}</ref> |
|||
====Public safety==== |
|||
The city is protected by [[Service de police de la Ville de Québec]] and [[Service de protection contre les incendies de Québec]] (fire dept.) The [[Census geographic units of Canada#Census metropolitan areas|census metropolitan area]] (CMA) of Quebec City has one of the lowest crime rates in Canada, with 3,193 per 100,000 persons in 2017, only behind [[Greater Toronto Area#Census metropolitan area|Toronto's CMA]] (3,115).<ref>{{Cite web |title=2017 Police-reported Crime Severity Index and crime rate, by census metropolitan area |url=https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/daily-quotidien/180723/t003b-eng.htm |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181021164003/https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/daily-quotidien/180723/t003b-eng.htm |archive-date=21 October 2018 |access-date=9 October 2018 |website=Statistics Canada |date=23 July 2018 |language=en}}</ref> Exceptionally, no [[Culpable homicide#Canada|homicide]] (defined as a criminal death, deliberate or not) was reported in 2007.<ref>{{Cite news |last=White |first=Marianne |date=28 December 2007 |title=Quebec City closing in on a year without murder |work=Nationalpost.com |url=https://nationalpost.com/news/canada/story.html?id=203698 |access-date=14 July 2011}}</ref> Still, eight homicides occurred the following year.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Neron |first=Jean-François |date=2010 |title=Bas taux d'homicide: fiche impressionnante pour Québec |url=https://www.lesoleil.com/archives/bas-taux-dhomicide-fiche-impressionnante-pour-quebec-0e29dab9039864f5d92c0a8bb6fe6dd6 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180729081454/https://www.lesoleil.com/archives/bas-taux-dhomicide-fiche-impressionnante-pour-quebec-0e29dab9039864f5d92c0a8bb6fe6dd6 |archive-date=29 July 2018 |access-date=29 July 2018 |publisher=Le Soleil |language=fr}}</ref> |
|||
On 29 January 2017, a university student [[Quebec City mosque shooting|shot and killed six people]] with another 17 injured in a mass shooting at the [[Islamic Cultural Centre of Quebec City|Quebec Islamic Cultural Centre]].<ref>{{Cite news |date=30 January 2017 |title=Suspect in Quebec mosque terror attack was of Moroccan origin, reports show |language=en-US |work=Fox News |url=https://www.foxnews.com/world/suspect-charged-with-murder-in-quebec-mosque-terror-attack |url-status=live |access-date=30 January 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170130164553/http://www.foxnews.com/world/2017/01/30/at-least-five-killed-in-shooting-at-quebec-city-mosque.html |archive-date=30 January 2017}}</ref> Even after accounting for this event, the CMA of Quebec had the second lowest Crime Severity Index in the country in 2017, at 48.5, after that of [[Barrie]] (45.3).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Police-reported crime statistics in Canada, 2017 |url=https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/85-002-x/2018001/article/54974-eng.htm#a2 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181021102135/https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/85-002-x/2018001/article/54974-eng.htm#a2 |archive-date=21 October 2018 |access-date=9 October 2018 |website=Statistics Canada|date=23 July 2018 }}</ref> For the year 2017, the number of reported incidents investigated as [[hate crimes]] by the city police increased from 57 to 71, and for those specifically targeting Muslims from 21 to 42.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Hate crimes targeting Muslims doubled in 2017, says Quebec City police chief |language=en |work=CBC News |url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/quebec-city-hate-crimes-1.4434028 |url-status=live |access-date=3 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181021040349/https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/quebec-city-hate-crimes-1.4434028 |archive-date=21 October 2018}}</ref> The overall rate of reported hate crimes was thus 7.1 per 100,000 population — higher than the national average (3.9) and in Montreal (4.7) but lower than rates in [[Hamilton, Ontario|Hamilton]], [[Ottawa]] and [[Thunder Bay]].<ref>{{Cite news |date=29 November 2018 |title=Reported hate crimes jumped in Quebec City in year prior to mosque shooting |language=en |work=CBC News |url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/quebec-city-hate-crimes-1.4423245 |url-status=live |access-date=3 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181216124655/https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/quebec-city-hate-crimes-1.4423245 |archive-date=16 December 2018}}</ref> |
|||
There were two [[Murder (Canadian law)#Murder|first-degree murders]] in 2018, seven in 2017 (six of which were due to the mosque shooting), one in 2016, two in 2015 and three in 2014.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Rapport annuel 2018 |url=https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/publications/docs_ville/rapport_annuel_police_2018.pdf#page=16 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211028235554/https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/publications/docs_ville/rapport_annuel_police_2018.pdf#page=16 |archive-date=28 October 2021 |access-date=22 June 2019 |website=Service de Police de la Ville de Québec |page=14 |language=fr}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Rapport annuel 2017 |url=https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/publications/docs_ville/rapport_annuel_police_2017.pdf#page=14 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181221230422/https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/publications/docs_ville/rapport_annuel_police_2017.pdf#page=14 |archive-date=21 December 2018 |access-date=8 December 2018 |website=Service de Police de la Ville de Québec |page=12 |language=fr}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Rapport annuel 2016 |url=https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/citoyens/police/nouvelles/FichierNouvelle.ashx?fichier=183-Rapport%20annuel%202016.pdf#page=20 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180213022229/https://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/citoyens/police/nouvelles/FichierNouvelle.ashx?fichier=183-Rapport%20annuel%202016.pdf#page=20 |archive-date=13 February 2018 |access-date=8 December 2018 |website=Service de Police de la Ville de Québec |page=20 |language=fr}}</ref> |
|||
Numerous [[CEGEP]]s are located in Quebec city, including Cégep François-Xavier-Garneau, Cégep O'Sullivan, [[Cégep Limoilou]], [[Cégep de Sainte-Foy]] and [[Champlain-St. Lawrence College]], as well as private institutions such as Collège Notre-Dame-de-Foy, Collège Mérici, Collège Bart, [[CDI College|Collège CDI]] and Collège Multihexa. |
|||
On 1 November 2020, the Quebec City police [[2020 Quebec City stabbing|arrested a man]] dressed in medieval costume and armed with a Japanese sword. Carl Girouard, the arrestee, reportedly killed 2 people and hospitalized 5 others.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Halloween Stabbing Attack in Quebec City Leaves 2 Dead |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/01/world/canada/quebec-city-stabbing-deaths-halloween-medieval-costume.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210104225853/https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/01/world/canada/quebec-city-stabbing-deaths-halloween-medieval-costume.html |archive-date=4 January 2021 |access-date=1 November 2020 |website=The New York Times |date=November 2020 |last1=Bilefsky |first1=Dan}}</ref> |
|||
Quebec City has the oldest educational institution for women in North America, the [[Ursulines of Quebec]] monastery, located at 12 Rue Donnacona. |
|||
==Infrastructure== |
==Infrastructure== |
||
{{more citations needed section|date=April 2016}} |
|||
===Transport=== |
|||
[[File:Quebec and Pierre-Laporte Bridges.jpg|thumb|The [[Quebec Bridge]] (left) and the [[Pierre Laporte Bridge]] (right)]] |
|||
;Roads |
|||
Three bridges, the [[Quebec Bridge]] and [[Pierre Laporte Bridge]] connect the city with the south shore of the [[Saint Lawrence River]], as does a [[ferry]] service to [[Lévis]], and [[Île d'Orléans Bridge|Orleans Island Bridge]] connects Quebec City with [[Île d'Orléans|the Orleans Island]]. The city is a major hub in the Quebec provincial road network, fanning out from both sides of the river with an extensive [[autoroute]] system. |
|||
===Roads=== |
|||
Several important motorways of the Quebec road network pass by Quebec City, of which [[Quebec Autoroute 40|Autoroute 40]] connects it towards the west to Montreal and [[Quebec Route 175|Route 175]] connects it towards the north to [[Chicoutimi]]. |
|||
Two bridges (the [[Quebec Bridge]] and [[Pierre Laporte Bridge]]) and a ferry service connect the city with [[Lévis]] and its suburbs along the south shore of the [[Saint Lawrence River]]. The [[Île d'Orléans Bridge|Orleans Island Bridge]] links Quebec City with pastoral [[Île d'Orléans|Orleans Island]]. |
|||
[[File:Le pont de Québec et le pont Pierre-Laporte vus du boulevard Champlain.jpg|left|thumb|The [[Pierre Laporte Bridge|Pierre-Laporte]] [[Quebec Bridge]]s connect the city with neighbouring [[Lévis]].]] |
|||
Three principal expressways cross the agglomeration from the north to the south (starting from the west): [[Quebec Autoroute 573|Autoroute Henri-IV]], [[Quebec Autoroute 740|Autoroute Robert-Bourassa]], and [[Quebec Autoroute 73|Autoroute Laurentienne]]. Three other motorways cross the western part of town (from north to south): [[Quebec Autoroute 40|Autoroute Félix Leclerc]] (known by the inhabitants as "Autoroute de la Capitale"), [[Quebec Autoroute 440 (Quebec City)|Autoroute Charest]], as well as Champlain Boulevard, which goes along the river to the Downtown area, then another Autoroute called [[Quebec Autoroute 440 (Quebec City)|Dufferin-Montmorency]] allows easier access to the extreme east of the city. |
|||
{{clr}} |
|||
Quebec City is an important hub in the province's [[Autoroutes of Quebec|autoroute]] system, as well as boasting one of the highest "expressway lane kilometres per 1000 persons" in the country (1.10 km), behind [[Calgary]] (1.74), [[Hamilton, Ontario|Hamilton]] (1.61) and [[Edmonton]] (1.24).<ref>{{Cite web |date=2004 |title=Projet de prolongement de l'axe du Vallon |url=http://www.bape.gouv.qc.ca/sections/mandats/du_vallon/documents/DQ5-1.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180329002416/http://www.bape.gouv.qc.ca/sections/mandats/du_vallon/documents/DQ5-1.pdf |archive-date=29 March 2018 |access-date=21 March 2017 |website=BAPE |page=2 |language=fr}}</ref> [[Quebec Autoroute 40|Autoroute 40]] connects the region with [[Montreal]] and [[Ottawa]] to the west and [[Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré, Quebec|Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré]] and the [[Charlevoix]] region to the east. [[Quebec Autoroute 20|Autoroute 20]] parallels the south shore of the St. Lawrence River, linking Quebec City with Montreal and [[Toronto]] to the west and [[Rivière-du-Loup]], [[Rimouski]], and the [[Maritime Provinces]] to the east. [[Quebec Autoroute 73|Autoroute 73]] provides a north–south link through the metropolitan area, linking it with [[Saint-Georges, Quebec|Saint-Georges]], the [[Beauce, Quebec|Beauce]] region, and Maine to the south and [[Saguenay, Quebec|Saguenay]] and the [[Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean|Lac-Saint-Jean]] region to the north. |
|||
;Public transit |
|||
Within the metropolitan region, Autoroutes 40, 73, and several spur routes link the city centre with its suburbs. |
|||
The [[Réseau de transport de la Capitale]] is responsible for public transit in the region. The RTC operates a fleet of buses and will eventually implement articulated buses. The RTC is studying the return of a [[tram]] system to help ease overcrowding on its busiest lines as well as attract new users to public transit. The $900-million revitalization project needs approval from higher levels of government since the city does not have the financial resources to fund such an ambitious project on its own. |
|||
[[Quebec Autoroute 573|Autoroute 573 (Autoroute Henri-IV)]] connects the city with [[CFB Valcartier]]. [[Quebec Autoroute 740|Autoroute 740 (Autoroute Robert-Bourassa)]] serves as a north–south inner belt. [[Quebec Autoroute 440 (Quebec City)|Autoroute 440]] comprises two separate autoroutes to the west and east of the urban core. Originally meant to be connected by a tunnel under the city centre, the two sections are separated by a {{Convert|6|km|abbr=on}} gap. There are no current plans to connect them. The western section (Autoroute Charest) connects Autoroutes 40 and 73 with Boulevard Charest (a main east–west avenue) while the eastern section (Autoroute Dufferin-Montmorency) links the city centre with [[Beauport, Quebec City|Beauport]] and [[Montmorency Falls]]. |
|||
Rail transport is operated by [[VIA Rail]] at the ([[Gare du Palais]]). The station is the eastern terminus of the railway's main [[Quebec City-Windsor Corridor]]. |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
An inter-city bus station, with connections to the provincial long-distance bus network, is adjacent to the train station. |
|||
===Public transport=== |
|||
;Air and sea |
|||
[[File:RTC Métrobus Québec City 14786209214.jpg|thumb|RTC's ''Métrobus'' is a six lines, higher frequency and capacity bus service.]] |
|||
Quebec City is served by [[Québec City Jean Lesage International Airport|Jean Lesage International Airport]], located in the West of the city. The city also has a large major [[Seaport|port]] on the St-Lawrence in the first, fifth and sixth boroughs.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.portquebec.ca/index.php?lang=en_GR |title=Port of Quebec |accessdate=June 24, 2009}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Tram on Maple Avenue, Quebec City, QC, 1898.jpg|thumb|A tram in Quebec City in 1898]] |
|||
The [[Réseau de transport de la Capitale]] (RTC) is responsible for public transport in the region. The RTC operates a fleet of buses and has recently implemented articulated buses. The RTC is studying the return of a [[Quebec City Tramway|tramway]] system to help ease overcrowding on its busiest lines as well as attract new users to public transit. The two billion dollar revitalization project needs approval from higher levels of government since the city does not have the financial resources to fund such an ambitious project on its own. As of 2022, the project named Quebec City Tramway is under development.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/tramway-quebec-city-approved-1.6410943 |title=Quebec City tramway finally gets green light as province gives unconditional approval |publisher=CBC |date=6 April 2022}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.transportaction.ca/topics/urban-transit/quebec-city-tramway-wins-provincial-backing/|title=We represent the interests of rail and bus passengers and advocate for public transport services in Canada.|date=April 28, 2021}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.railforthevalley.com/latest-news/zweisystem/quebec-city-tram-will-be-a-reality/|title=Quebec city Tram Will Be A Reality : Rail for the Valley|date=6 April 2022 }}</ref> |
|||
===Public safety=== |
|||
Quebec City is protected by [[Service de police de la Ville de Québec]] and [[Service de protection contre les incendies de Québec]]. Quebec City has one of the lowest crime rates in Canada. The city reported no murders in 2007, a streak that stretched back to October 31, 2006.<ref>[http://www.nationalpost.com/news/canada/story.html?id=203698 Quebec City closing in on a year without murder<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> |
|||
Rail transport is operated by [[Via Rail]] at the [[Gare du Palais]] ('Palace Station'). The station is the eastern terminus of the railway's main [[Quebec City-Windsor Corridor]]. An inter-city bus station, with connections to the provincial long-distance bus network, is adjacent to the train station, and is used by operators such as [[Orleans Express]] and [[Intercar]]. |
|||
==Partner cities== |
|||
{{Refimprovesect|date=February 2008}} |
|||
<!--Source: http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/fr/exploration/partenariats.shtml--> |
|||
*{{flagicon|United States}} '''[[Albany, New York|Albany,NY]]''', United States |
|||
*{{flagicon|Lebanon}} '''[[Beirut]]''', [[Lebanon]]<ref name="twins">{{cite web| url=http://www.beirut.gov.lb/MCMSTest/Menu-Pages/SisterCitiesEN.aspx?NRMODE=Published&NRORIGINALURL=%2fwww%2ebeirut%2egov%2elb%2fMCMSEN%2fTwinning%2bthe%2bCities%2f&NRNODEGUID=%7b18839037-0140-436E-A1AF-7F8F3693C3E6%7d&NRCACHEHINT=NoModifyGuest#| title=Twinning the Cities| publisher=City of Beirut| accessdate=January 13, 2008}}</ref> |
|||
*{{flagicon|France}} '''[[Bordeaux]]''', [[Aquitaine]], France ''(since 1962)''<ref name="sisters">[http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/apropos/portrait/ville_internationale/partenariats.aspx Ville de Quebec - Partenariats]</ref> |
|||
*{{flagicon|Canada}} '''[[Calgary]]''', [[Alberta]], Canada ''(since 1956)''<ref name="sisters"/> |
|||
*{{flagicon|France}} '''[[Cannes]]''', France |
|||
*{{flagicon|China}} '''[[Changchun]]''', China |
|||
*{{flagicon|Romania}} '''[[Iaşi]]''', [[Romania]] |
|||
*{{flagicon|Mexico}} '''[[Guanajuato, Guanajuato]]''', Mexico ''(since 2002)'' |
|||
*{{flagicon|Vietnam}} '''[[Huế]]''', [[Vietnam]] ''(since 2005)'' |
|||
*{{flagicon|Belgium}} '''[[Liège]]''', Belgium ''(since 2002)'' |
|||
*{{flagicon|Norway}} '''[[Bergen]]''', Norway |
|||
*{{flagicon|Uruguay}} '''[[Montevideo]]''', [[Uruguay]] ''(since 2000)'' |
|||
*{{flagicon|Belgium}} '''[[Namur (city)|Namur]]''', Belgium ''(since 1999)''<ref name="sisters"/> |
|||
*{{flagicon|Burkina Faso}} '''[[Ouagadougou]]''', [[Burkina Faso]] ''(since 2000)''<ref name="sisters"/> |
|||
*{{flagicon|France}} '''[[Paris]]''', France ''(since 2003)''<ref name="sisters"/> |
|||
*{{flagicon|Tunisia}} '''[[Sousse]]''', [[Tunisia]] ''(since 2004)'' |
|||
*{{flagicon|Russia}} '''[[St. Petersburg]]''', Russia ''(since 2002)''<ref name="sisters"/> |
|||
*{{flagicon|China}} '''[[Xi'an]]''', China ''(since 2001)''<ref name="sisters"/> |
|||
== |
===Air and sea=== |
||
Quebec City is served by [[Québec City Jean Lesage International Airport|Jean Lesage International Airport]], located {{convert|13|km|abbr=on}} west of the city centre. |
|||
{{reflist|2}} |
|||
{{Sisterlinks|Quebec City}} |
|||
{{portal|New France|Pavillon LouisXIV.svg}} |
|||
{{portal|Quebec}} |
|||
{{portal|Canada}} |
|||
The [[Port of Quebec]] is a seaport on the St. Lawrence with facilities in the first, fifth and sixth boroughs.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Port of Quebec |url=http://www.portquebec.ca/index.php?lang=en_GR |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120203072407/http://www.portquebec.ca/index.php?lang=en_GR |archive-date=3 February 2012 |access-date=24 June 2009}}</ref> |
|||
==External links== |
|||
<!-- NOTE: External links sections on Wikipedia are not meant to serve as detailed or exhaustive web directories of every website remotely related to the topic; only primary and official pages about Quebec City itself should be listed here. --> |
|||
* [http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/EN/index.aspx Official website of ''Ville de Québec''] ([http://www.ville.quebec.qc.ca/ French]) |
|||
* [http://www.quebecregion.com/e/index.asp Official website of Québec City Tourism] ([http://www.quebecregion.com/f/ French]) |
|||
* [http://www.quebec400.gc.ca/bienvenue-welcome-eng.cfm Québec City's 400th Anniversary - 2008] ([http://www.quebec400.gc.ca/bienvenue-welcome-fra.cfm French]) |
|||
== |
==Education== |
||
[[File:Promenade Les Cent-Associes UL 08.jpg|thumb|An alley of {{Lang|fr|[[Université Laval]]|italic=no}} campus]] |
|||
* [http://archives.cbc.ca/lifestyle/travel/clips/15099/ CBC Television Archives] on Preserving Quebec City (1976) |
|||
* [http://archives.cbc.ca/society/celebrations/topics/3512/ CBC Digital Archives - Quebec City: 400 Years of History] |
|||
The {{Lang|fr|[[Université Laval]]|italic=no}} (Laval University) is in the southwestern part of the city, in the borough of [[Sainte-Foy, Quebec|Sainte-Foy]], except for its school of architecture, which is at the "[[Séminaire de Québec|Vieux-Séminaire]]" building in Old Quebec. |
|||
The [[Université du Québec|Université du Québec system]] administrative headquarters and some of its specialized schools ({{Lang|fr|[[École nationale d'administration publique]]|italic=no}}, [[Institut national de la recherche scientifique]] and [[Télé-université]]) are in the [[Saint-Roch, Quebec City|Saint-Roch neighbourhood]]. |
|||
[[CEGEP]]s of Quebec city are [[Collège François-Xavier-Garneau]], [[Cégep Limoilou]], [[Cégep de Sainte-Foy]] and [[Champlain College St. Lawrence]], as well as private and specialized post-secondary institutions such as Campus Notre-Dame-de-Foy, [[Collège Mérici]], [[Collège Bart]], [[CDI College|Collège CDI]], Collège O'Sullivan and Collège Multihexa. |
|||
Three [[school boards]], including [[Commission scolaire de la Capitale]], operate secular francophone schools, and [[Central Quebec School Board]] operates the few existing anglophone ones. Until 1998 [[Commission des écoles catholiques de Québec]] operated public Catholic schools of all languages. |
|||
Quebec City has the oldest educational institution for women in North America, led by the [[Ursulines of Quebec]], which is now a private elementary school. |
|||
==Sister cities== |
|||
Quebec City is [[Twin towns and sister cities|twinned]] with: |
|||
* [[Bordeaux]], [[France]] |
|||
* [[Calgary]], [[Alberta]]. |
|||
It has formal agreements with other cities although they are not active as of 2012. These include [[Saint Petersburg]] in [[Russia]], [[Guanajuato City]] in [[Mexico]], [[Huế]] in [[Vietnam]], [[Paris]], [[Xi'an]] in [[China]], and [[Liège]] and [[Namur]] in [[Wallonia|francophone Belgium]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=7 September 2012 |title=Québec fait le ménage dans ses jumelages |url=http://www.lapresse.ca/le-soleil/actualites/la-capitale/201209/06/01-4571850-quebec-fait-le-menage-dans-ses-jumelages.php |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160921034654/http://www.lapresse.ca/le-soleil/actualites/la-capitale/201209/06/01-4571850-quebec-fait-le-menage-dans-ses-jumelages.php |archive-date=21 September 2016 |website=Le Soleil |language=fr}}</ref> |
|||
== Notable people == |
|||
{{Main category|People from Quebec City}} |
|||
{{Main list|List of people from Quebec City}} |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{Portal|Canada}} |
|||
* [[List of regional county municipalities and equivalent territories in Quebec]] |
|||
== References == |
|||
'''Informational notes''' |
|||
{{notelist}} |
|||
'''Citations''' |
|||
{{Reflist |
|||
|refs = |
|||
<ref name="cp2011-CA">{{SCref |unit=cma |code=421 }}</ref> |
|||
<ref name="mamrot">{{mamrot |type=municipalite |23027 }}</ref> |
|||
<ref name="toponymie">{{toponymie|51718}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
== External links == |
|||
{{Sister project links|Quebec City|voy=Quebec City}} |
|||
<!-- NOTE: External links sections on Wikipedia are not meant to serve as detailed or exhaustive web directories of every website remotely related to the topic; only primary and official pages about Quebec City itself should be listed here. --> |
|||
* {{Official website}} |
|||
* [https://www.quebec-cite.com/en/ Official website of Québec City Tourism] |
|||
* [https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/as-sa/fogs-spg/Facts-csd-eng.cfm?LANG=eng&GK=CSD&GC=2423027&TOPIC=1 ''Focus on Geography Series, 2016 Census''] — Census subdivision of Québec City from [[Statistics Canada]] |
|||
* [https://www.cbc.ca/archives/entry/preserving-old-quebec-city CBC Digital Archives] — CBC Television Special: Preserving Quebec City (1976) |
|||
* [https://www.cbc.ca/archives/topic/quebec-city-400-years-of-history CBC Digital Archives] — Quebec City: 400 Years of History |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
<!--Templates--> |
|||
{{Quebec City}} |
|||
{{Navboxes |
|||
{{Administrative divisions of Quebec region|Capitale-Nationale}} |
|||
|list = |
|||
{{Greater Quebec}} |
{{Greater Quebec}} |
||
{{Subdivisions of Quebec|regions=yes|cities=yes}} |
|||
{{Canada capitals}} |
{{Canada capitals}} |
||
{{Subdivisions of Quebec City}} |
|||
{{World Heritage Sites in Canada}} |
|||
{{New France}} |
{{New France}} |
||
{{Chemin du Roy}} |
{{Chemin du Roy}} |
||
}} |
|||
{{Commons category|Postcards of Quebec City}} |
|||
{{use mdy dates}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Quebec City| ]] |
[[Category:Quebec City| ]] |
||
[[Category:Cities and towns in Quebec]] |
|||
[[Category:World Heritage Sites in Canada]] |
[[Category:World Heritage Sites in Canada]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Quebec populated places on the Saint Lawrence River]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Populated places established in 1608]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:1608 establishments in New France]] |
||
[[Category:Former colonial capitals in Canada]] |
|||
[[Category:Hudson's Bay Company trading posts]] |
[[Category:Hudson's Bay Company trading posts]] |
||
[[Category:Port settlements in Quebec]] |
[[Category:Port settlements in Quebec]] |
||
[[Category:1608 in North America]] |
|||
[[Category:1600s in Canada]] |
|||
<!--Other languages--> |
|||
[[Category:1608 in New France]] |
|||
[[af:Quebecstad]] |
|||
[[ar:مدينة كيبك]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Québec-chhī]] |
|||
[[bg:Квебек (град)]] |
|||
[[ca:Ciutat de Quebec]] |
|||
[[cs:Québec]] |
|||
[[cy:Québec (dinas)]] |
|||
[[da:Québec (by)]] |
|||
[[de:Québec (Stadt)]] |
|||
[[el:Κεμπέκ (πόλη)]] |
|||
[[es:Ciudad de Quebec]] |
|||
[[eo:Kebeko (Kebekio)]] |
|||
[[eu:Quebec Hiria]] |
|||
[[fa:کبک (شهر)]] |
|||
[[fr:Québec (ville)]] |
|||
[[fy:Kebek (stêd)]] |
|||
[[gd:Quebec (baile)]] |
|||
[[gl:Quebec (cidade)]] |
|||
[[ko:퀘벡 (도시)]] |
|||
[[hr:Québec (grad)]] |
|||
[[id:Kota Quebec]] |
|||
[[os:Квебек (сахар)]] |
|||
[[is:Québecborg]] |
|||
[[it:Québec (città)]] |
|||
[[he:קוויבק סיטי]] |
|||
[[ka:კვებეკი (ქალაქი)]] |
|||
[[sw:Jiji la Quebec]] |
|||
[[la:Urbs Quebeci]] |
|||
[[lt:Kvebekas (miestas)]] |
|||
[[lmo:Québec (cità)]] |
|||
[[hu:Québec (település)]] |
|||
[[mg:Québec (tanàna)]] |
|||
[[mr:क्वेबेक सिटी]] |
|||
[[nl:Québec (stad)]] |
|||
[[ja:ケベック (ケベック州)]] |
|||
[[no:Québec (by)]] |
|||
[[nn:Québec]] |
|||
[[oc:Vila de Quebèc]] |
|||
[[pap:Quebec City]] |
|||
[[pl:Québec (miasto)]] |
|||
[[pt:Quebec (cidade)]] |
|||
[[ro:Québec (oraş)]] |
|||
[[ru:Квебек (город)]] |
|||
[[sah:Куэбэк (куорат)]] |
|||
[[simple:Quebec City]] |
|||
[[sk:Quebec (mesto)]] |
|||
[[sl:Quebec City]] |
|||
[[sr:Квебек (град)]] |
|||
[[fi:Québec (kaupunki)]] |
|||
[[sv:Québec (stad)]] |
|||
[[tl:Lungsod ng Québec]] |
|||
[[ta:கியூபெக் நகரம்]] |
|||
[[th:ควิเบก (เมือง)]] |
|||
[[tr:Québec (şehir)]] |
|||
[[uk:Квебек (місто)]] |
|||
[[ur:کیوبک شہر]] |
|||
[[ug:Kwébék Shehiri]] |
|||
[[vi:Thành phố Québec]] |
|||
[[vo:Québec (zif)]] |
|||
[[war:Quebec (syudad)]] |
|||
[[zh:魁北克市]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 02:13, 12 December 2024
Québec | |
|---|---|
| Ville de Québec (French) | |
|
| |
| Nicknames: | |
| Motto(s): Don de Dieu feray valoir ("I shall put God's gift to good use"; the Don de Dieu was Champlain's ship) | |
| Coordinates: 46°48′50″N 71°12′29″W / 46.81389°N 71.20806°W[2][3] | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | Quebec |
| Region | Capitale-Nationale |
| Metropolitan community | Communauté métropolitaine de Québec |
| Agglomeration | Agglomeration of Quebec City |
| Historic countries | Kingdom of France Kingdom of Great Britain |
| First settled | 11 October 1535, by Jacques Cartier |
| Founded | 3 July 1608, by Samuel de Champlain |
| Constituted | 1 January 2002 |
| Incorporated | 1832[4] |
| Boroughs | |
| Government | |
| • Type | Quebec City Council |
| • Mayor | Bruno Marchand |
| • MPs | List of MPs |
| • MNAs | List |
| Area | |
• City | 452.30 km2 (174.63 sq mi) |
| • Land | 453.38 km2 (175.05 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 442.85 km2 (170.99 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 3,499.46 km2 (1,351.15 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 98 m (322 ft) |
| Population (2021)[6] | |
• City | 549,459 (12th) |
| • Density | 1,214.8/km2 (3,146/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 733,156 (8th) |
| • Urban density | 1,655.5/km2 (4,288/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 839,311 (7th) |
| • Metro density | 239.8/km2 (621/sq mi) |
| • Pop 2016–2021 | |
| Demonym | Québécois or Québécois de Québec (to distinguish residents of the city from those of the province) |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (EDT) |
| Postal codes | |
| Area codes |
|
| GDP (Québec CMA) | CA$47.94 billion (2020)[10] |
| GDP per capita (Québec CMA) | CA$53,477 (2016) |
| Website | www |
| Official name | Historic District of Old Quebec |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | iv, vi |
| Designated | 1985 (9th session) |
| Reference no. | 300 |
| Region | Europe and North America |
Quebec City[a] is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459,[13] and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311.[14] It is the twelfth-largest city and the seventh-largest metropolitan area in Canada. It is also the second-largest city in the province, after Montreal. It has a humid continental climate with warm summers coupled with cold and snowy winters.
Explorer Samuel de Champlain founded a French settlement here in 1608, and adopted the Algonquin name. Quebec City is one of the oldest European settlements in North America. The ramparts surrounding Old Quebec (Vieux-Québec) are the only fortified city walls remaining in the Americas north of Mexico. This area was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1985 as the "Historic District of Old Québec".[15][16]
Name and usage
[edit]Common English-language usage distinguishes the city from the province by referring to the former as Quebec City.[17]
According to the Government of Canada, the Government of Quebec, and the Geographical Names Board of Canada, the names of Canadian cities and towns have only one official form. Thus, Québec is officially spelled with an accented é in both Canadian English and French.[18][19][20] However, province names can have different forms in English and French. As a result, in English, the federal government style distinguishes the city and province by spelling the city with an acute accent (Québec) and the province without one (Quebec). The government of Quebec spells both names "Québec", including when writing in English.[21]
In French, the two are distinguished in that province names including Quebec generally take definite articles, while city names do not. As a result, the city is Québec and the province is le Québec; "in Quebec City" is à Québec and "in the province of Quebec" is au Québec; and so forth.[22]
The Algonquian people had originally named the area Kébec, an Algonquin[b] word meaning "where the river narrows", because the Saint Lawrence River narrows proximate to the promontory of Quebec and its Cape Diamant.
History
[edit]French regime (1500s–1763)
[edit]Quebec City is one of the oldest European settlements in North America and the only fortified city north of Mexico whose walls still exist.[23] While many of the major cities in Latin America date from the 16th century, among cities in Canada and the United States, few were created earlier than Quebec City (St. John's, Harbour Grace, Port Royal, St. Augustine, Santa Fe, Jamestown, and Tadoussac).

It is home to the earliest known French settlement in North America, Fort Charlesbourg-Royal, established in 1541 by explorer Jacques Cartier with some 400 persons but abandoned less than a year later due to the harsh winter and resistance of indigenous inhabitants to colonial incursion on their land.[24] The fort was at the mouth of the Rivière du Cap Rouge, in the suburban former town of Cap-Rouge (which merged into Quebec City in 2002).
Quebec was founded by Samuel de Champlain, a French explorer and diplomat, on 3 July 1608,[25][26] and at the site of a long abandoned St. Lawrence Iroquoian settlement called Stadacona. Champlain, who came to be called "The Father of New France", served as its administrator for the rest of his life.
The name "Canada" was given to the colony that developed around the settlement at Quebec. Although the Acadian settlement at Port-Royal was established three years earlier, Quebec came to be known as the cradle of North America's Francophone population. The location seemed favourable to the establishment of a permanent colony.

The population of the settlement remained small for decades. In 1629 it was captured by English privateers, led by David Kirke, during the Anglo-French War.[27] Samuel de Champlain argued that the English seizing of French lands was illegal as the war had already ended, and worked to have them returned to France. As part of the ongoing negotiations following the end of the Anglo-French War, in 1632 the English king Charles I agreed to return captured lands in exchange for Louis XIII paying his wife's dowry.[27] These terms were signed into law with the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye. The colonies of Canada and Acadia were returned to the French Company of One Hundred Associates.[27]
In 1665, there were 550 people in 70 houses living in the city. One-quarter of the people were members of religious orders: secular priests, Jesuits, Ursulines nuns and the order running the local hospital, Hôtel-Dieu.[28]
Quebec was the headquarters of many raids against New England during the French and Indian Wars. In 1690 the city was attacked by the English, but was successfully defended. In the last of the conflicts, the French and Indian War (Seven Years' War), Quebec was captured by the British in 1759, and held until the end of the war in 1763. In that time many battles and sieges took place: the Battle of Beauport, a French victory (31 July 1759); the Battle of the Plains of Abraham, in which British troops under General James Wolfe defeated the French General Louis-Joseph de Montcalm on 13 September 1759, and shortly thereafter took the city after a short siege. A French counterattack saw a French victory at the Battle of Sainte-Foy (28 April 1760) but the subsequent second Siege of Quebec the following month however saw a final British victory.

France ceded New France, including the city, to Britain in 1763,[29] when the French and Indian War officially ended.
At the end of French rule, Quebec was a town of 8,000 inhabitants, surrounded by forests, villages, fields and pastures. The town was distinguished by its monumental architecture, fortifications, and affluent homes of masonry and shacks in the suburbs of Saint-Jean and Saint-Roch. Despite its urbanity and its status as capital, Quebec remained a small city with close ties to its rural surroundings. Nearby inhabitants traded their farm surpluses and firewood for imported goods from France at the two city markets.
British and Canadian rule (1763–present)
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2016) |

During the American Revolution, revolutionary troops from the southern colonies assaulted the British garrison in the city in the hope that the peoples of Quebec would rise and join the American Revolution so that Canada would join the Continental Congress, along with the other British colonies of continental North America. The American invasion failed, however, and the war resulted in a permanent split of British North America into two entitles: the newly independent United States of America, and those colonies (including Quebec) that remained under British control, which would later become the country of Canada.
The city itself was not attacked during the War of 1812, when the United States again attempted to annex Canadian lands. Amid fears of another American attack on Quebec City, construction of the Citadelle of Quebec began in 1820. The Americans did not attack Canada after the War of 1812, but the Citadelle continued to house a large British garrison until 1871. It is still in use by the military and is also a tourist attraction.
Until the late 18th century Québec was the most populous city in present-day Canada. As of the census of 1790, Montreal surpassed it with 18,000 inhabitants, but Quebec, which had about 14,000 of population at that time, remained the administrative capital of the former New France.[30] It was then made the capital of Lower Canada by the Constitutional Act of 1791.[31] From 1841 to 1867, the capital of the Province of Canada rotated between Kingston, Montreal, Toronto, Ottawa and Quebec City (from 1851 to 1855 and from 1859 to 1865).[32]

The city experienced an economic golden age in the 1800s, due to its favorable location on the Saint Lawrence River which gave rise to industries of wooden sailing ships manufacture, export of squared timber logs. to Europe, as wall as associated enterprises such as sawmills. However, by the 1870s, Québec City entered a period of economic decline. Contributing factors included the rise of steel-hulled steamships, the expansion of railroads at the expense of waterways for continental commerce; the depletion of forest resources near major rivers upstream of Québec City and in the west of the province, which were transported to Québec's port by log driving; the construction of locks on the Saint Lawrence Seaway, opening up trade routes to the U.S. from Montreal; and the city's inability to retain immigrant populations.[33] This unfavourable context, coupled with the departure of the British army from the city's Citadel in 1871, contributed to the exodus of English speaking populations, such as local bourgeoisie of Scottish origin or workers of Irish background, to Montreal in the second half of the 19th century. Anglophones made up approximately 40% of the city's population in 1861, but 16% in 1901.[34]
Before the Royal Military College of Canada was established in 1876, the only French-speaking officer training school was the Quebec City School of Military Instruction, founded in 1864.[35] The school was retained at Confederation, in 1867. In 1868, The School of Artillery was formed in Montreal.[36]

The Quebec Conference on Canadian Confederation was held in the city in 1864. In 1867, Queen Victoria chose Ottawa as the definite capital of the Dominion of Canada, while Quebec City was confirmed as the capital of the newly created province of Quebec.
During World War II, two conferences were held in Quebec City. The First Quebec Conference was held in 1943 with Franklin D. Roosevelt (President of the United States), Winston Churchill (Prime Minister of the United Kingdom), William Lyon Mackenzie King (Prime Minister of Canada) and T. V. Soong (minister of foreign affairs of China). The Second Quebec Conference was held in 1944 and was attended by Churchill and Roosevelt. They took place in the buildings of the Citadelle and at the nearby Château Frontenac. A large part of the D-Day landing plans were made during those meetings.
Until 2002, Quebec was a mostly urbanized city and its territory coterminous with today's borough of La Cité-Limoilou. The Government of Quebec then mandated a municipal reorganization in the province, and many suburbs of the north shore of the Saint-Lawrence were merged into Quebec City, taking the form of boroughs, thus constituting the boundary of present-day Québec City. In 2008 the city celebrated its 400th anniversary and was gifted funds for festivities and construction projects by provincial and federal governments, as well as public artwork by various entities, including foreign countries.
Geography
[edit]
Quebec City was built on the north bank of the Saint Lawrence River, where it narrows and meets the mouth of the Saint-Charles River. Old Quebec is located on top and at the foot of Cap-Diamant, which is on the eastern edge of a plateau called the promontory of Quebec (Quebec hill). Because of this topographic feature, the oldest and most urbanized borough of La Cité-Limoilou can be divided into upper and lower town.[37] North of the hill, the Saint Lawrence Lowlands is flat and has rich, arable soil. Past this valley, the Laurentian Mountains lie to the north of the city but its foothills are within the municipal limits.
The Plains of Abraham are located on the southeastern extremity of the plateau, where high stone walls were integrated during colonial days. On the northern foot of the promontory, the lower town neighbourhoods of Saint-Roch and Saint-Sauveur, traditionally working class,[38] are separated from uptown's Saint-Jean-Baptiste and Saint-Sacrement by a woody area attested as Coteau Sainte-Geneviève.
The area was affected by the 1925 Charlevoix–Kamouraska earthquake.
The administrative region in which it is situated is officially referred to as Capitale-Nationale,[39][40] and the term "national capital" is used to refer to Quebec City itself at the provincial level.[41]
Climate
[edit]
Quebec City is classified as a hemiboreal humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfb, Trewartha Dcbc).[42]
Quebec City experiences four distinct seasons. Summers are warm and occasionally hot, with periods of hotter temperatures which compounded with the high humidity, create a high heat index that belies the average high of 22–25 °C (72–77 °F) and lows of 11–13 °C (52–55 °F). Winters are cold, windy and snowy with average high temperatures −5 to −8 °C (23 to 18 °F) and lows −13 to −18 °C (9 to 0 °F). Spring and fall, although short, bring chilly to warm temperatures. Late heat waves as well as "Indian summers" are a common occurrence.[citation needed]
On average, Quebec City receives 1,190 millimetres (46.85 in) of precipitation, of which 899 millimetres (35.39 in) is rain and 303 millimetres (11.93 in) is the melt from 316 centimetres (124.4 in) of snowfall per annum.[c] The city experiences around 1,916 hours of bright sunshine annually or 41.5% of possible sunshine, with summer being the sunniest, but also slightly the wettest season. During winter, snow generally stays on the ground from the end of November till mid-April.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Quebec City was 36.1 °C (97.0 °F) on 17 July 1953.[45] The coldest temperature ever recorded was −36.7 °C (−34.1 °F) on 10 January 1890 and 14 January 2015.[46][47]
| Climate data for Sainte-Foy, Quebec City (Québec City Jean Lesage International Airport) WMO ID: 71708; coordinates 46°48′N 71°23′W / 46.800°N 71.383°W; elevation: 74.4 m (244 ft); 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1875–present[d] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high humidex | 10.6 | 11.7 | 19.9 | 32.9 | 40.3 | 44.1 | 49.2 | 49.3 | 40.1 | 30.9 | 24.9 | 14.6 | 49.3 |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.7 (63.9) |
12.0 (53.6) |
18.3 (64.9) |
29.9 (85.8) |
33.1 (91.6) |
34.2 (93.6) |
35.6 (96.1) |
34.4 (93.9) |
33.9 (93.0) |
28.3 (82.9) |
22.9 (73.2) |
13.9 (57.0) |
35.6 (96.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −7.1 (19.2) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
0.4 (32.7) |
8.3 (46.9) |
17.5 (63.5) |
22.5 (72.5) |
25.0 (77.0) |
24.0 (75.2) |
19.1 (66.4) |
11.3 (52.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
9.7 (49.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −11.9 (10.6) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
3.5 (38.3) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.7 (62.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
18.4 (65.1) |
13.7 (56.7) |
6.8 (44.2) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−7.3 (18.9) |
4.7 (40.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −16.7 (1.9) |
−15.7 (3.7) |
−9.3 (15.3) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
5.6 (42.1) |
10.8 (51.4) |
13.9 (57.0) |
12.8 (55.0) |
8.3 (46.9) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−11.4 (11.5) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −36.7 (−34.1) |
−36.1 (−33.0) |
−32.6 (−26.7) |
−19.3 (−2.7) |
−7.8 (18.0) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
3.9 (39.0) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−10.0 (14.0) |
−24.0 (−11.2) |
−33.4 (−28.1) |
−36.7 (−34.1) |
| Record low wind chill | −51.1 | −52.4 | −41.0 | −29.0 | −13.6 | −1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | −7.8 | −17.3 | −30.8 | −48.4 | −52.4 |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 86.7 (3.41) |
65.7 (2.59) |
77.7 (3.06) |
94.4 (3.72) |
91.8 (3.61) |
114.7 (4.52) |
118.7 (4.67) |
108.7 (4.28) |
111.3 (4.38) |
115.8 (4.56) |
90.9 (3.58) |
96.2 (3.79) |
1,172.6 (46.17) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 24.6 (0.97) |
13.8 (0.54) |
30.2 (1.19) |
71.3 (2.81) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 61.7 (2.43) |
33.7 (1.33) |
— |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 69.1 (27.2) |
64.3 (25.3) |
50.3 (19.8) |
13.1 (5.2) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 25.6 (10.1) |
75.7 (29.8) |
— |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 18.2 | 14.7 | 14.0 | 13.7 | 13.6 | 13.5 | 14.7 | 13.0 | 12.3 | 14.9 | 14.9 | 18.5 | 175.9 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 3.3 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 10.3 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 9.5 | 4.4 | — |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 15.4 | 13.2 | 10.2 | 4 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 7.0 | 16.5 | — |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 1500 LST) | 70.0 | 65.5 | 61.1 | 56.5 | 52.2 | 56.9 | 59.3 | 60.1 | 62.7 | 65.4 | 70.6 | 75.1 | 63.0 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 98.9 | 121.2 | 152.0 | 170.6 | 211.1 | 234.7 | 252.3 | 232.0 | 163.0 | 122.0 | 76.6 | 81.9 | 1,916.3 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 35.5 | 41.8 | 41.3 | 41.9 | 45.3 | 49.6 | 52.7 | 52.7 | 43.1 | 36.0 | 27.1 | 30.7 | 41.5 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Source: Environment and Climate Change Canada[48] (sun 1981–2010)[49] (extremes 1875–1959}[50] and Weather Atlas (UV index)[51] | |||||||||||||
Boroughs and neighbourhoods
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2016) |

On 1 January 2002, the 12 former towns of Sainte-Foy, Beauport, Charlesbourg, Sillery, Loretteville, Val-Bélair, Cap-Rouge, Saint-Émile, Vanier, L'Ancienne-Lorette, Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures and Lac-Saint-Charles were annexed by Quebec City. This was one of several municipal mergers which took place across Quebec on that date. Following a demerger referendum, L'Ancienne-Lorette and Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures were reconstituted as separate municipalities on 1 January 2006, but the other former municipalities remain part of Quebec City. On 1 November 2009, Quebec City re-organized its boroughs, reducing the number from 8 to 6.[52]
Quebec City's six boroughs (French: arrondissements) are further divided into 35 neighbourhoods (French: quartiers).[53] In most cases, the name of the latter remained the same as the historical town (French: ville) or parish municipality it replaced. Neighbourhoods each elect their own council, whose powers rest in public consultations.
Compared to many other cities in North America, there is less variation between average household incomes between the neighbourhoods. However, some disparities exist. The southwest former cities of Sillery, Cap-Rouge and Sainte-Foy are considered to be the wealthiest, along with some parts of Montcalm and Old Quebec.[citation needed]
The city's traditional working-class areas are found in the lower town below Old Quebec (Saint-Sauveur and Saint-Roch) and directly across the Saint-Charles River to the north (Vanier and Limoilou). However, parts of Limoilou, Saint-Sauveur and particularly Saint-Roch have seen gentrification in the last 20 years, attracting young professionals and the construction of new offices and condos.[54]

Northern sections (Loretteville, Val-Bélair) and eastern sections (Beauport, Charlesbourg) are mostly a mix of middle-class residential suburbs with industrial pockets.
| Boroughs | Neighbourhoods |
| 1 La Cité-Limoilou | La Cité: 1-1 Vieux-Québec–Cap-Blanc–colline Parlementaire · 1-2 Saint-Roch · 1-3 Saint-Jean-Baptiste · 1-4 Montcalm · 1-5 Saint-Sauveur · 1-6 Saint-Sacrement · Limoilou: 6-1 Vieux-Limoilou · 6-2 Lairet · 6-3 Maizerets |
| 2 Les Rivières | 2-1 Neufchâtel-Est–Lebourgneuf · 2-2 Duberger-Les Saules · 2-3 Vanier |
| 3 Sainte-Foy–Sillery–Cap-Rouge | 3-1 Sillery · 3-2 Cité universitaire · 3-3 Saint-Louis · 3-4 Plateau · 3-5 Pointe-de-Ste-Foy 8-2 · L'Aéroport · 8-3 Cap-Rouge |
| 4 Charlesbourg | 4-1 Notre-Dame-des-Laurentides · 4-2 Quartier 4-2 · 4-3 Quartier 4-3 · 4-4 Jésuites, Quebec City · 4-5 Quartier 4-5 · 4-6 Quartier 4–6 |
| 5 Beauport | 5-1 Quartier 5-1 · 5-2 Quartier 5-2 · 5-3 Chutes-Montmorency · 5-4 Quartier 5-4 · 5-5 Vieux-Moulin |
| 7 La Haute-Saint-Charles | 7-1 Lac-Saint-Charles · 7-2 Saint-Émile · 7-3 Loretteville · 7-4 Des Châtels · 8-1 Val-Bélair |
Demographics
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2016) |
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1665 | 547 | — |
| 1667 | 444 | −18.8% |
| 1681 | 1,345 | +202.9% |
| 1685 | 1,205 | −10.4% |
| 1688 | 1,407 | +16.8% |
| 1692 | 1,570 | +11.6% |
| 1695 | 1,549 | −1.3% |
| 1698 | 1,988 | +28.3% |
| 1706 | 1,771 | −10.9% |
| 1739 | 4,603 | +159.9% |
| 1754 | 8,001 | +73.8% |
| 1765 | 8,967 | +12.1% |
| 1790 | 14,000 | +56.1% |
| 1825 | 22,101 | +57.9% |
| 1851 | 42,052 | +90.3% |
| 1861 | 51,109 | +21.5% |
| 1871 | 59,699 | +16.8% |
| 1881 | 62,446 | +4.6% |
| 1891a | 63,090 | +1.0% |
| 1901 | 68,940 | +9.3% |
| 1911b | 78,118 | +13.3% |
| 1921c | 95,193 | +21.9% |
| 1931 | 130,594 | +37.2% |
| 1941 | 150,757 | +15.4% |
| 1951 | 164,016 | +8.8% |
| 1956 | 170,703 | +4.1% |
| 1961 | 171,979 | +0.7% |
| 1966 | 166,984 | −2.9% |
| 1971d | 186,088 | +11.4% |
| 1976e | 177,082 | −4.8% |
| 1981 | 165,968 | −6.3% |
| 1986 | 164,580 | −0.8% |
| 1991 | 167,517 | +1.8% |
| 1996 | 167,264 | −0.2% |
| 2001 | 169,076 | +1.1% |
| 2006f | 491,142 | +190.5% |
| 2011 | 516,622 | +5.2% |
| 2016 | 531,902 | +3.0% |
| 2021 | 549,459 | +3.3% |
a Quebec City annexed the Village of Saint-Sauveur-de-Québec bQuebec City annexed the Town of Limoilou and the Village of Saint-Malo cQuebec City annexed the Town of Montcalm dQuebec City annexed the Town of Duberger and the Town of Les Saules eQuebec City annexed the Town of Neufchâtel and the Municipality of Charlesbourg-Ouest fQuebec City annexed the cities of Beauport, Cap-Rouge, Charlesbourg, Lac-Saint-Charles, Loretteville, Saint-Émile, Sainte-Foy, Sillery, Val-Bélair and Vanier | ||
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1871 | 76,593 | — |
| 1881 | 80,249 | +4.8% |
| 1891 | 80,546 | +0.4% |
| 1901 | 88,615 | +10.0% |
| 1911 | 102,214 | +15.3% |
| 1921 | 122,698 | +20.0% |
| 1931 | 168,249 | +37.1% |
| 1941 | 199,588 | +18.6% |
| 1951 | 245,742 | +23.1% |
| 1956 | 279,521 | +13.7% |
| 1961 | 321,917 | +15.2% |
| 1966 | 372,373 | +15.7% |
| 1971 | 408,440 | +9.7% |
| 1976 | 429,757 | +5.2% |
| 1981 | 434,980 | +1.2% |
| 1986 | 440,598 | +1.3% |
| 1991 | 461,894 | +4.8% |
| 1996 | 473,569 | +2.5% |
| 2001 | 476,330 | +0.6% |
| 2006 | 491,142 | +3.1% |
| 2011 | 516,622 | +5.2% |
| 2016 | 531,902 | +3.0% |
| 2021 | 549,459 | +3.3% |
In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Québec had a population of 549,459 living in 265,711 of its 283,219 total private dwellings, a change of 3.3% from its 2016 population of 531,902. With a land area of 452.3 km2 (174.6 sq mi), it had a population density of 1,214.8/km2 (3,146.3/sq mi) in 2021.[57]
According to Statistics Canada, there were 839,311 people residing in the Quebec City census metropolitan area.[58]
In 2016, 20.6% of the resident population in Quebec City was of retirement age (65 and over for males and females) compared with 16.9% in Canada. The median age is 43.3 years of age compared to 41.2 years of age for Canada as a whole. In the five years between 2011 and 2016, the population of Quebec City grew by 3%.[59]
Ethnicity
[edit]In 2021,[60] 9.4% of Quebec City residents reported visible minority status, a relatively low figure for a large Canadian city; the national average was 26.5%.[61] The largest visible minority group were Black Canadians, who formed 4.1% of the population. Quebec City also had a lower percentage of Indigenous Canadians (1.8%) than the national average of 5.0%.[62]
| Panethnic group |
2021[62] | 2016[63] | 2011[64] | 2006[65] | 2001[66] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | |||||
| European[note 1] | 473,770 | 88.8% | 475,720 | 92.15% | 477,715 | 95.05% | 465,115 | 96.39% | 160,940 | 96.8% | ||||
| Black | 21,955 | 4.11% | 12,430 | 2.41% | 5,760 | 1.15% | 4,550 | 0.94% | 1,335 | 0.8% | ||||
| Middle Eastern[note 2] | 10,510 | 1.97% | 6,850 | 1.33% | 4,045 | 0.8% | 2,980 | 0.62% | 370 | 0.22% | ||||
| Indigenous | 9,395 | 1.76% | 7,290 | 1.41% | 4,635 | 0.92% | 3,140 | 0.65% | 1,055 | 0.63% | ||||
| Latin American | 8,585 | 1.61% | 6,675 | 1.29% | 5,085 | 1.01% | 2,725 | 0.56% | 1,095 | 0.66% | ||||
| Southeast Asian[note 3] | 3,275 | 0.61% | 2,590 | 0.5% | 1,855 | 0.37% | 1,470 | 0.3% | 820 | 0.49% | ||||
| East Asian[note 4] | 2,970 | 0.56% | 2,565 | 0.5% | 2,080 | 0.41% | 1,730 | 0.36% | 420 | 0.25% | ||||
| South Asian | 1,610 | 0.3% | 1,390 | 0.27% | 855 | 0.17% | 425 | 0.09% | 120 | 0.07% | ||||
| Other/Multiracial[note 5] | 1,465 | 0.27% | 730 | 0.14% | 570 | 0.11% | 405 | 0.08% | 110 | 0.07% | ||||
| Total responses | 533,540 | 97.1% | 516,250 | 97.06% | 502,595 | 97.28% | 482,545 | 98.25% | 166,255 | 98.33% | ||||
| Total population | 549,459 | 100% | 531,902 | 100% | 516,622 | 100% | 491,142 | 100% | 169,076 | 100% | ||||
Note: Totals greater than 100% due to multiple origin responses
| ||||||||||||||
Immigration
[edit]The 2021 census reported that immigrants (individuals born outside Canada) comprise 45,230 persons or 8.5% of the total population of Quebec City. Of the total immigrant population, the top countries of origin were France (7,360 persons or 16.3%), Colombia (2,865 persons or 6.3%), Morocco (2,715 persons or 6.0%), Ivory Coast (2,500 persons or 5.5%), Cameroon (2,225 persons or 4.9%), Algeria (1,920 persons or 4.2%), Tunisia (1,795 persons or 4.0%), Democratic Republic of the Congo (1,315 persons or 1,315%), Haiti (1,120 persons or 2.5%), and Brazil (1,115 persons or 2.5%).[62]
Language
[edit]The great majority of city residents are native French speakers. The English-speaking community peaked in relative terms during the 1860s, when 40% of Quebec City's residents were Anglophone.[67][68] Today, native Anglophones make up only about 1.5% of the population of both the city and its metropolitan area.[69] However, the summer tourist season and the Quebec Winter Carnival attract significant numbers of Anglophone (as well as Francophone) visitors, and English can often be heard in areas frequented by tourists.
In 2021, according to Statistics Canada, 90.6% of Quebec City's population spoke French as their sole mother tongue. More than a third of city residents reported being capable of speaking both French and English.
| Census Year |
Total Responses |
French
|
English
|
French & English
|
Other
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Trend | Pop. % | Count | Trend | Pop. % | Count | Trend | Pop. % | Count | Trend | Pop. % | |||||||
2021
|
542,435
|
491,515 | 90.6% | 7,685 | 1.4% | 4,530 | 0.8% | 33,255 | 6.1% | |||||||||
2016
|
523,560
|
483,790 | 92.4% | 7,395 | 1.4% | 2,615 | 0.5% | 26,370 | 5.0% | |||||||||
2011
|
516,622
|
478,395 | 92.6% | 7,370 | 1.4% | 2,315 | 0.5% | 19,790 | 3.8% | |||||||||
2006
|
491,142
|
456,225 | 92.9% | 7,030 | 1.4% | 1,460 | 0.3% | 17,825 | 3.6% | |||||||||
2001
|
471,962
|
447,840 | 94.9% | 6,830 | 1.5% | 2,020 | 0.4% | 11,535 | 2.4% | |||||||||
1996
|
467,455
|
446,194 | n/a | 95.5% | 8,309 | n/a | 1.8% | 1,955 | n/a | 0.4% | 9,830 | n/a | 2.1% | |||||
Religion
[edit]According to the 2021 census, religious groups in Quebec City included:[62]
- Christianity (349,320 residents, or 65.5%)
- Irreligion (162,900; 30.5%)
- Islam (17,490; 3.3%)
- Buddhism (1,565; 0.3%)
- Hinduism (515; 0.1%)
- Judaism (305; 0.1%)
- Indigenous Spirituality (75; <0.1%)
- Sikhism (20; <0.1%)
- Other (1,355; 0.3%)
Economy
[edit]
Most jobs in Quebec City are concentrated in public administration, defence, services, commerce, transport and tourism. As the provincial capital, the city benefits from being a regional administrative and services centre: apropos, the provincial government is the largest employer in the city, employing 27,900 people as of 2007.[70] CHUQ (the local hospital network) is the city's largest institutional employer, with more than 10,000 employees in 2007. The unemployment rate in June 2018 was 3.8%, below the national average (6.0%) and the second-lowest of Canada's 34 largest cities, behind Peterborough (2.7%).[71]
Around 10% of jobs are in manufacturing.[72] Principal products include pulp and paper, processed food, metal/wood items, chemicals, electronics and electrical equipment, and printed materials. The city hosts the headquarters of a variety of prominent companies, including: fashion retailer La Maison Simons, engineering firms BPR and Norda Stelo; Cominar real estate investment trust; Beneva, Industrial Alliance, Promutuel, and Union Canadienne in the insurance sector; Beenox, Gearbox Software, Frima Studio, Sarbakan and Ubisoft in the computer games industry; AeternaZentaris and DiagnoCure in pharmaceuticals; Amalgame, Cossette and Vision 7 in marketing and advertising; Institut National d'Optique (INO), EXFO, OptoSecurity in technology. It is also the domicile of the sole manufactory of the cigarette maker Rothmans, Benson & Hedges.
Business districts
[edit]
While the traditional central business districts and their large office buildings are found on Parliament Hill (especially for provincial administration) and just below in Saint-Roch (nowadays notable for IT and the video game industry), a newer one has emerged in the Boulevard Laurier area of Sainte-Foy, where a number of accounting and law firms have moved since the 2000s. Other suburban places identified by the city for their potential are the Lebourgneuf area for private offices, as well as Estimauville Street where the Government of Canada already has many civil servants and where several city officials are expected to move in the 2020s.[54]
Arts and culture
[edit]
Quebec City is known for its Winter Carnival, its summer music festival and its Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day celebrations. The Jardin zoologique du Québec, now closed, reopened in 2002 after extensive repairs before ultimately shutting permanently in 2006. It featured 750 specimens of 300 different species of animals. The zoo specialized in winged fauna and garden themes but also featured several species of mammals. While it emphasized Quebec's indigenous fauna, one of its main attractions was the Indo-Australian greenhouse, which initially cost $14 million to build.[73] It featured fauna and flora from regions surrounding the Indian Ocean.[74]
Parc Aquarium du Québec, which reopened in 2002 on a site overlooking the Saint Lawrence River, features more than 10,000 specimens of mammals, reptiles, fish and other aquatic fauna of North America and the Arctic. Polar bears and various species of seals of the Arctic sector and the "Large Ocean", a large basin offering visitors a view from underneath, make up part of the aquarium's main attractions.
Québec City has a number of historic sites, art galleries and museums, including Citadelle of Quebec, Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec, Ursulines of Quebec, and Musée de la civilisation.

Other tourist attractions include Montmorency Falls, and, just outside the city limits, the Basilica of Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré, the Mont-Sainte-Anne ski resort, and the Ice Hotel.
Attractions
[edit]Given the mass of Cap Diamant and the presence of la Citadelle atop it, overlooking the waters of the St. Lawrence River, Charles Dickens described Quebec City as the "Gibraltar of North America".[75]
Architecture
[edit]
Much of the city's notable traditional architecture is located in Vieux-Québec (Old Quebec), within and below the fortifications. This area has a distinct European feel with its stone buildings and winding streets lined with shops and restaurants. Porte Saint-Louis and Porte Saint-Jean are the main gates through the walls from the modern section of downtown; the Kent Gate was a gift to the province from Queen Victoria and the foundation stone was laid by the Queen's daughter, Princess Louise, Marchioness of Lorne, on 11 June 1879.[76] West of the walls are the Parliament Hill area, and to the south the Plains of Abraham.
The upper and lower town are linked by numerous stairs such as the Escalier « casse-cou » ("breakneck stairway") or the Old Quebec Funicular on the historic Rue du Petit-Champlain, where many small boutiques are found. A small town square nearby, the Place Royale, now surrounded by picturesque stone buildings, is the site of Champlain's founding of the city in 1608. On it is the Notre-Dame-des-Victoires church. The Musée de la Civilisation is located nearby by the river.




Along with concrete high-rises such as Édifice Marie-Guyart and Le Concorde on parliament hill (see List of tallest buildings in Quebec City), the city's skyline is dominated by the massive Château Frontenac hotel, perched on top of Cap-Diamant. It was designed by architect Bruce Price, as one of a series of "château" style hotels built for the Canadian Pacific Railway company. The railway company sought to encourage luxury tourism and bring wealthy travellers to its trains. Alongside the Château Frontenac is the Terrasse Dufferin, a walkway along the edge of the cliff, offering views of the Saint Lawrence River. The terrace leads toward the nearby Plains of Abraham, site of the battle in which the British took Quebec from France, and the Citadelle of Quebec, a Canadian Forces installation and the federal vice-regal secondary residence. The Parliament Building, the meeting place of the Parliament of Quebec, is also near the Citadelle.
Near the Château Frontenac is Notre-Dame de Québec Cathedral, mother church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Quebec. It is the first church in the New World to be raised to a basilica and is the primatial church of Canada. There are 37 National Historic Sites of Canada in Quebec City and its enclaves.[78]
Parks
[edit]One of the most notable is The Battlefields Park, which is home to 50 historical artillery pieces and the Plains of Abraham. The park offers views of the St. Lawrence River and has multiple historical structures and statues like the Joan of Arc on Horseback and a couple of Martello Towers.[79] Historically this was the site of the Battle of the Plains of Abraham (1759), a decisive British victory in the Seven Years' War which ended French rule in what would become Canada, and the later Battle of Quebec (1775) during the American Revolutionary War, where the British were able to hold onto its last stronghold in the Northern extent of its North American territory.
Other large and centrally located parks are Parc Victoria, Parc Maizerets and Cartier-Brébeuf National Historic Site. Quebec City's largest park is the Parc Chauveau, which is crossed by the suburban section of the city-wide Saint-Charles River and is thus also part of the 31 km (19 mi) long Saint-Charles River's linear park. At Chauveau, activities such as canoeing, fishing and cross-country skiing are offered depending on the season, in addition to an interior soccer stadium.[80] Among others, there is also the beach of Beauport Bay, as well as the Marais du Nord (north-end marsh land).
Quebec is the only large city in Canada along with Halifax lacking a public greenhouse. Nonetheless, outside areas known for their public gardens or landscaping include:[81]
- The linear park named Promenade Samuel-De Champlain that stretches 4.6 km (2.9 mi) alongside the Saint Lawrence River, from Pierre Laporte Bridge to Sillery's east-end. Its bicycle and pedestrian paths then continues to Old Quebec and then along the Saint-Charles River.[82] Just like the beach at Beauport Bay, the construction of the Promenade was funded by provincial and federal governments to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Quebec City in 2008.
- Government House (Quebec), slightly west of the Plains of Abraham in Sillery, and known for its natural landscaping as well as traditional gardens, such as those surrounding the historical Villa Bagatelle. The historical significance of the park also lies in the former presence of the viceregal Government House of Quebec (1845–1966).
- The Domaine de Maizerets, where are found an arboretum and an observation tower, not far from the Saint Lawrence River and Beauport Bay.
- Domaine Cataraqui in Sillery.
- The Roger-Van den Hende Botanical Garden of Université Laval.
Sports
[edit]Quebec City has hosted a number of recent sporting events, as well as being shortlisted for the 2002 Winter Olympics city selection. The Special Olympics Canada National Winter Games was held in the city from 26 February to 1 March 2008.[83] Quebec City co-hosted with Halifax, Nova Scotia, the 2008 IIHF World Championship. Regular sporting events held in the city include the Coupe Banque Nationale, a Women's Tennis Association tournament; Crashed Ice, an extreme downhill skating race; Quebec International Pee-Wee Hockey Tournament, a minor hockey tournament; and the Tour de Québec International cycling stage race.[84] In December 2011, Quebec City hosted the ISU Grand Prix of Figure Skating Final at the Pavillon de la Jeunesse at ExpoCité.

The city currently has one professional team, the baseball team Capitales de Québec, which plays in the Frontier League in downtown's Stade Canac. The team was established in 1999 and originally played in the Northern League. It has nine league titles, won in 2006, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2017, 2022 and 2023. A professional basketball team, the Quebec Kebs, played in National Basketball League of Canada in 2011 but folded before the 2012 season, and a semi-professional soccer team, the Dynamo de Québec, played in the Première ligue de soccer du Québec, until 2019.
The city had a professional ice hockey team, the Quebec Nordiques, which played in the World Hockey Association (WHA) from 1972 to 1979 and the National Hockey League (NHL) from 1979 to 1995, maintaining a strong rivalry with the Montreal Canadiens. Due to a disadvantageous exchange rate with respect to the US dollar, the team moved to Denver, Colorado, in 1995, becoming the Colorado Avalanche. A lower-tier team, the Quebec Rafales, played in the professional International Hockey League from 1996 to 1998.

The Videotron Centre was built with the hope of getting an NHL franchise (relocation or expansion) in Quebec City.[85] The project was funded regardless of whether an NHL team arrives.[86] It is also hoped that the arena can help Quebec City win a future Winter Olympics games bid.[87] It has now replaced the Colisée de Québec as the main multifunctional arena in Quebec City.
Other teams include the Quebec Remparts in major junior hockey (QMJHL), Université Laval varsity team Rouge & Or, the Quebec City Monarks, and Quebec City Rebelles of La Ligue de Football de Québec; the Alouettes de Charlesbourg of the Ligue de Baseball Junior Élite du Québec; the women's hockey team Quebec Phoenix of the Canadian Women's Hockey League; and soccer club Quebec Arsenal of the W-League.
Quebec City holds the Coop FIS Cross-Country World Cup. This is a ski event that welcomes the best of that sport.[88]
Government
[edit]
Since the 1960s, centre-right parties such as Union Nationale, Crédit social, Conservative Party of Canada (CPC), Action démocratique du Québec and Coalition Avenir Québec (CAQ) have been more popular in the Quebec City region than elsewhere in the province.[89] After the federal election of 2006, six of the ten conservative ridings of the province were found in its metropolitan area (where the CPC garnered 39% of the vote, against 25% at the provincial scale)[90] and in the city proper, the CPC won three of the four seats that existed at that time (the riding of Quebec went to the Bloc).[91] Along with the city's lesser support for Quebec sovereignty, this led political pundits to speculate about a "Quebec City mystery".[92]
Various lines of thought were offered, including the popularity of the talk radio stations CHOI and FM93 expressing fiscally conservative and non-politically correct opinions.[93] Over the years, this genre has been qualified by its detractors as radio poubelle (English: trash radio) and hosts like Jeff Fillion and André Arthur likened to shock jocks.[94] Also, compared to the rest of the province, people of the area may favour harsher criminal sentences, and lower-class households may share political views more in line with those earning more. The reasons for this remain unclear.[89] Another researcher put forward the historical factors that led to Montreal surpassing Quebec as the metropolis of British North America in the early 19th century. According to this theory, its permanent status of "second city" (albeit the capital) engendered feelings of "repressed jealousy".[95]
The "mystery" was relativized following the 2011 federal election. All five ridings within the city were won by the leftist New Democratic Party, in the so-called "orange wave" that temporarily swept the province. Nonetheless, five of the six seats won by the Conservatives in the province were found in the greater Quebec City area.[96] At the 2018 provincial election, the leftist party Québec solidaire managed to win two districts, Taschereau and Jean-Lesage, the most densely populated in town, but the centre-right CAQ, as it swept the province, won six of the nine districts encompassing the city, and 15 of the 18 in the administrative regions of Capitale-Nationale and Chaudière-Appalaches (south shore of the city).
| Year | Liberal | Conservative | Bloc Québécois | New Democratic | Green | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 27% | 76,734 | 34% | 96,875 | 27% | 75,949 | 8% | 23,129 | 2% | 5,715 | |
| 2019 | 28% | 82,742 | 29% | 84,656 | 28% | 82,950 | 9% | 25,969 | 4% | 11,789 | |
| Year | CAQ | Liberal | QC solidaire | Parti Québécois | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 41% | 118,468 | 22% | 65,462 | 19% | 55,126 | 12% | 34,079 | |
| 2014 | 32% | 95,770 | 39% | 118,564 | 7% | 21,123 | 19% | 57,481 | |
Municipal government
[edit]
Quebec City is governed by a mayor–council government, which includes the 21 single-member districts of the legislative Quebec City Council and the separately elected mayor. The councilors are elected by first-past-the-post voting while the mayor is elected by the city at-large. Both usually belong to political parties and are elected at the same time every 4 years. The mayor is an ex officio member of the council but is not its president and has no vote. The current one is Bruno Marchand, elected in 2021.
Each of the city's six boroughs has a council composed of 3 to 5 of the aforementioned councillors, depending on the size of its population. It has jurisdiction with matters such as local road maintenance, leisure, waste collection, and small grants for community projects and others, but cannot tax or borrow money.[99] The boroughs are further divided into 35 neighbourhoods, which also have councils devoted to public consultations, each led by 11 citizens. Their geographical limits may be distinct from those of the city's 21 electoral districts, and councillors also sit at their neighbourhood councils as non-voting ex officio members.[100]
Public safety
[edit]The city is protected by Service de police de la Ville de Québec and Service de protection contre les incendies de Québec (fire dept.) The census metropolitan area (CMA) of Quebec City has one of the lowest crime rates in Canada, with 3,193 per 100,000 persons in 2017, only behind Toronto's CMA (3,115).[101] Exceptionally, no homicide (defined as a criminal death, deliberate or not) was reported in 2007.[102] Still, eight homicides occurred the following year.[103]
On 29 January 2017, a university student shot and killed six people with another 17 injured in a mass shooting at the Quebec Islamic Cultural Centre.[104] Even after accounting for this event, the CMA of Quebec had the second lowest Crime Severity Index in the country in 2017, at 48.5, after that of Barrie (45.3).[105] For the year 2017, the number of reported incidents investigated as hate crimes by the city police increased from 57 to 71, and for those specifically targeting Muslims from 21 to 42.[106] The overall rate of reported hate crimes was thus 7.1 per 100,000 population — higher than the national average (3.9) and in Montreal (4.7) but lower than rates in Hamilton, Ottawa and Thunder Bay.[107]
There were two first-degree murders in 2018, seven in 2017 (six of which were due to the mosque shooting), one in 2016, two in 2015 and three in 2014.[108][109][110]
On 1 November 2020, the Quebec City police arrested a man dressed in medieval costume and armed with a Japanese sword. Carl Girouard, the arrestee, reportedly killed 2 people and hospitalized 5 others.[111]
Infrastructure
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2016) |
Roads
[edit]Two bridges (the Quebec Bridge and Pierre Laporte Bridge) and a ferry service connect the city with Lévis and its suburbs along the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River. The Orleans Island Bridge links Quebec City with pastoral Orleans Island.

Quebec City is an important hub in the province's autoroute system, as well as boasting one of the highest "expressway lane kilometres per 1000 persons" in the country (1.10 km), behind Calgary (1.74), Hamilton (1.61) and Edmonton (1.24).[112] Autoroute 40 connects the region with Montreal and Ottawa to the west and Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré and the Charlevoix region to the east. Autoroute 20 parallels the south shore of the St. Lawrence River, linking Quebec City with Montreal and Toronto to the west and Rivière-du-Loup, Rimouski, and the Maritime Provinces to the east. Autoroute 73 provides a north–south link through the metropolitan area, linking it with Saint-Georges, the Beauce region, and Maine to the south and Saguenay and the Lac-Saint-Jean region to the north.
Within the metropolitan region, Autoroutes 40, 73, and several spur routes link the city centre with its suburbs.
Autoroute 573 (Autoroute Henri-IV) connects the city with CFB Valcartier. Autoroute 740 (Autoroute Robert-Bourassa) serves as a north–south inner belt. Autoroute 440 comprises two separate autoroutes to the west and east of the urban core. Originally meant to be connected by a tunnel under the city centre, the two sections are separated by a 6 km (3.7 mi) gap. There are no current plans to connect them. The western section (Autoroute Charest) connects Autoroutes 40 and 73 with Boulevard Charest (a main east–west avenue) while the eastern section (Autoroute Dufferin-Montmorency) links the city centre with Beauport and Montmorency Falls.
Public transport
[edit]

The Réseau de transport de la Capitale (RTC) is responsible for public transport in the region. The RTC operates a fleet of buses and has recently implemented articulated buses. The RTC is studying the return of a tramway system to help ease overcrowding on its busiest lines as well as attract new users to public transit. The two billion dollar revitalization project needs approval from higher levels of government since the city does not have the financial resources to fund such an ambitious project on its own. As of 2022, the project named Quebec City Tramway is under development.[113][114][115]
Rail transport is operated by Via Rail at the Gare du Palais ('Palace Station'). The station is the eastern terminus of the railway's main Quebec City-Windsor Corridor. An inter-city bus station, with connections to the provincial long-distance bus network, is adjacent to the train station, and is used by operators such as Orleans Express and Intercar.
Air and sea
[edit]Quebec City is served by Jean Lesage International Airport, located 13 km (8.1 mi) west of the city centre.
The Port of Quebec is a seaport on the St. Lawrence with facilities in the first, fifth and sixth boroughs.[116]
Education
[edit]
The Université Laval (Laval University) is in the southwestern part of the city, in the borough of Sainte-Foy, except for its school of architecture, which is at the "Vieux-Séminaire" building in Old Quebec.
The Université du Québec system administrative headquarters and some of its specialized schools (École nationale d'administration publique, Institut national de la recherche scientifique and Télé-université) are in the Saint-Roch neighbourhood.
CEGEPs of Quebec city are Collège François-Xavier-Garneau, Cégep Limoilou, Cégep de Sainte-Foy and Champlain College St. Lawrence, as well as private and specialized post-secondary institutions such as Campus Notre-Dame-de-Foy, Collège Mérici, Collège Bart, Collège CDI, Collège O'Sullivan and Collège Multihexa.
Three school boards, including Commission scolaire de la Capitale, operate secular francophone schools, and Central Quebec School Board operates the few existing anglophone ones. Until 1998 Commission des écoles catholiques de Québec operated public Catholic schools of all languages.
Quebec City has the oldest educational institution for women in North America, led by the Ursulines of Quebec, which is now a private elementary school.
Sister cities
[edit]Quebec City is twinned with:
It has formal agreements with other cities although they are not active as of 2012. These include Saint Petersburg in Russia, Guanajuato City in Mexico, Huế in Vietnam, Paris, Xi'an in China, and Liège and Namur in francophone Belgium.[117]
Notable people
[edit]See also
[edit]References
[edit]Informational notes
- ^ /kwɪˈbɛk/ or /kəˈbɛk/;[11] French: Ville de Québec), officially known as Québec (French pronunciation: [kebɛk])[12]
- ^ The Algonquin language is a distinct language of the Algonquian language family, and is not a misspelling.
- ^ Although snow is measured in cm the melted snow (water equivalent) is measured in mm and added to the rainfall to obtain the total precipitation. An approximation of the water equivalent can be made by dividing the snow depth by ten. Thus 1 cm (0.4 in) of snow is equivalent to approximately 1 mm (0.04 in) of water. See snow gauge, [43] and [44]
- ^ Based on station coordinates provided by Environment and Climate Change Canada, climate data was recorded in the area of Old Quebec from August 1875 to February 1959, and at Québec City Jean Lesage International Airport from March 1943 to present.
Citations
- ^ Marceau, Stéphane G.; Rémillard, François (2002). Ville de Québec (in French) (4th ed.). Montreal: Guides de voyage Ulysse. p. 14. ISBN 2-89464-510-4.
- ^ "Quebec City". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.
- ^ "Banque de noms de lieux du Québec: Reference number 51718". toponymie.gouv.qc.ca (in French). Commission de toponymie du Québec.
- ^ "Incorporation de Québec". 23 October 2007. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- ^ a b "Répertoire des municipalités: Geographic code 23027". www.mamh.gouv.qc.ca (in French). Ministère des Affaires municipales et de l'Habitation.
- ^ a b "Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2016 Census". Government of Canada, Statistics Canada. 8 February 2017. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- ^ a b "Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2021 Census". Government of Canada, Statistics Canada. 9 February 2022.
- ^ "Quebec City (Code 421) Census Profile". 2011 census. Government of Canada - Statistics Canada.
- ^ Vallières, Marc. "Québec City". Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ "Gross domestic product (GDP) at basic prices, by census metropolitan area (CMA)". 6 December 2023.
- ^ "Quebec". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ Government of Canada, Natural Resources Canada. "Place names – Québec". www4.rncan.gc.ca. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- ^ "Québec, Ville [Census subdivision], Quebec and Québec, Territoire équivalent [Census division], Quebec". Census 2016. Statistics Canada. 8 February 2017. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2016 Census". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Government of Canada, Statistics Canada. 8 February 2017. Archived from the original on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- ^ "Historic District of Old Québec Archived 28 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine". World Heritage; UNESCO. Retrieved 12 January 2009.
- ^ "Old Quebec City, Seven Wonders of Canada". cbc.ca. Archived from the original on 7 February 2008. Retrieved 12 February 2008.
- ^ Government of Canada, Public Services and Procurement Canada (28 February 2020). "Québec, City of Québec, Quebec City – Writing Tips Plus – Writing Tools – Resources of the Language Portal of Canada – Canada.ca". Writing Tips Plus. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ "Québec, City of Québec, Quebec City". Public Works and Government Services Canada. 2016. Archived from the original on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- ^ "Names (geographical)". Public Service Commission of Canada. Archived from the original on 21 November 2016. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- ^ Government of Canada (8 October 2009). "Geographical Names". The Canadian Style. Archived from the original on 30 October 2016. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- ^ "Faut-il traduire les toponymes?". Commission de toponymie. 26 November 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ "Québec en quelques mots". Immigrant Québec (in Canadian French). 22 October 2021. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ "CBC.CA – Seven Wonders of Canada – Your Nominations – Old Quebec City, Quebec". www.cbc.ca. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- ^ "Fort Charlesbourg Royal National Historic Site of Canada". www.historicplaces.ca. Parks Canada. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "View of Quebec, Capital of Canada". World Digital Library. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- ^ Moss, William (2 December 2017). The Recent Archaeology of the Early Modern Period in Quebec City: 2009. Routledge. p. 334. ISBN 9781351193337. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2019.
- ^ a b c "KIRKE, SIR DAVID, adventurer, trader, colonizer, leader of the expedition that captured Quebec in 1629, and later governor of Newfoundland" Archived 17 September 2020 at the Wayback Machine, Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online
- ^ Morison, Samuel Eliot (1972). The Oxford history of the American people. New York: Mentor. p. 150. ISBN 0-451-62600-1. OCLC 7384608.
- ^ "George R, Proclamation, 7 October 1763 (Royal Proclamation)". PrimaryDocuments.ca. 7 October 1763. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- ^ Cartier, Gwenaël (2009). "Québec 1608–2008 : 400 ans de statistiques démographiques tirées des recensements". Cahiers québécois de démographie (in French). 37: 143. doi:10.7202/029642ar. Archived from the original on 29 July 2018. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ^ "Ville de Québec – Québec City, Fortress and Port (1756–1867)". Ville de Québec. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- ^ Clapperton, Nina (18 November 2021). "13 Canada Capital Cities". Nina Out and About. Retrieved 10 April 2022.
- ^ Langlois, Simon (2007). "Sociologie de la ville de Québec". Les Cahiers des dix (in French) (61): 196. doi:10.7202/039157ar. ISSN 0575-089X.
- ^ Langlois, Simon (2007). "Sociologie de la ville de Québec". Les Cahiers des dix (in French) (61): 197. doi:10.7202/039157ar. ISSN 0575-089X.
- ^ "Canadian Military Heritage Volume 2 (1755–1871). Canadian Militia Unpopular with Francophones". Canadian Military History Gateway. Department of National Defence. June 2017. Archived from the original on 12 October 2018. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Richard Preston 'Canada's RMC: A History of the Royal Military College of Canada' published by the RMC Club by U of Toronto Press.
- ^ Geological Survey of Canada (1999). The 1988 Saguenay Earthquake – a Site Visit Report. p. 63.
- ^ Stelter, Gilbert (1982). Shaping the Urban Landscape: Aspects of the Canadian City-Building Process. McGill Queen University Press. ISBN 9780773584860. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Décret concernant la révision des limites des régions administratives du Québec, R.Q. c. D-11, r.2, made pursuant to the Territorial Division Act, R.S.Q. c. D-11
- ^ "Québec Portal > Portrait of Québec > Administrative Regions > Regions". Archived from the original on 1 February 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2009.
- ^ "An Act respecting the National capital commission, R.S.Q. c. C-33.1". CanLII. 4 May 2009. Archived from the original on 6 May 2010. Retrieved 13 May 2009.
- ^ Peel, M. C.; Finlayson, B. L.; McMahon, T. A. (2007). "Updated world map of the Köppen–Geiger climate classification" (PDF). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 11 (5): 1633–1644. Bibcode:2007HESS...11.1633P. doi:10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007. ISSN 1027-5606. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 February 2012. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- ^ Rainfall, Snowfall, and Precipitation Archived 28 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ MANOBS 7th Edition Amendment 17[dead link]
- ^ "Daily Data Report for July 1953". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- ^ "Daily Data Report for January 1890". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- ^ "Daily Data Report for January 2015". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. 31 October 2011. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- ^ "Quebec Jean Lesage Airport". Canadian Climate Normals 1991–2020. Environment and Climate Change Canada. 1 October 2024. Retrieved 18 November 2024.
- ^ "Quebec/Jean Lesage INT'L A, Quebec". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment and Climate Change Canada. 1 October 2024. Archived from the original on 9 May 2014. Retrieved 18 November 2024.
- ^ "Quebec". Canadian Climate Data. Environment and Climate Change Canada. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ^ Yu Media Group d.o.o. "Quebec city, Canada – Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast". Weather Atlas. Archived from the original on 6 July 2019. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ^ "Nouveau découpage des arrondissements - Modifications territoriales". www.ville.quebec.qc.ca (in French). Ville de Québec. Archived from the original on 25 September 2009.
- ^ Rainville, Candide; Service de l'ingénierie. Division de l'arpentage et de la cartographie. Ville de Québec (10 January 2011). "Les arrondissements et leurs quartiers" [The boroughs and their quarters] (PDF) (Map). clubdimension.org (in French). Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 November 2019. Retrieved 5 November 2019.
- ^ a b "Où sera le centre-ville de Québec dans le futur?". Radio-Canada.ca (in Canadian French). 7 October 2018. Archived from the original on 9 October 2018. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ^ a b Statistics Canada: 1871, 1881, 1891, 1901, 1911, 1921, 1931, 1941, 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001, 2006, 2011, 2016, 2021 census
- ^ "Évolution démographique des 10 principales villes du Québec (Sur la base de 2006) selon leur limites territoriales actuelles1, Recensements du Canada de 1871 à 2006". www.stat.gouv.qc.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2013. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ "Population and dwelling counts: Canada, provinces and territories, and census subdivisions (municipalities), Quebec". Statistics Canada. 9 February 2022. Retrieved 29 August 2022.
- ^ "Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2016 Census". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Government of Canada, Statistics Canada. 8 February 2017. Archived from the original on 10 February 2017. Retrieved 9 February 2017.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (8 February 2017). "Census Profile, 2016 Census – Québec, Ville [Census subdivision], Quebec and Canada [Country]". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ "Census Profile, 2021 - Québec, Ville". Statistics Canada. 9 February 2022.
- ^ "Census Profile, 2021 - Canada [Country]". Statistics Canada. 9 February 2022.
- ^ a b c d Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (26 October 2022). "Census Profile, 2021 Census of Population". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 9 November 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (27 October 2021). "Census Profile, 2016 Census". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (27 November 2015). "NHS Profile". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (20 August 2019). "2006 Community Profiles". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (2 July 2019). "2001 Community Profiles". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ Morrin Centre. "Anglos in Québec". Literary and Historical Society of Quebec. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 15 March 2007.
- ^ Blair, Louisa. The Anglos: The Hidden Face of Quebec City. Volume 1: 1608–1850; Volume 2: Since 1850. Québec: Commission de la capitale nationale du Québec & Éditions Sylvain Harvey, 2005.
- ^ "Voice of English-speaking Québec: A Portrait of the English-speaking Community in Quebec". Voice of English-speaking Québec. 2007. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 15 March 2007.
- ^ "Canada's largest employers by city, 2007: Quebec City". University of Western Ontario. Archived from the original on 18 April 2010.
- ^ "Here's a quick glance at unemployment rates for June, by Canadian city". Financial Post. 6 July 2018. Archived from the original on 9 October 2018. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ^ "Québec City: Economy, transportation, and labour force" Archived 25 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine. The Canadian Encyclopedia. Historical Foundation of Canada, 2008. Retrieved 12 January 2009.
- ^ "Abandoned zoo greenhouse faces demolition". QCNA EN. 23 November 2021. Retrieved 28 September 2022.
- ^ "2022 - The greenhouse of the former Quebec zoo will indeed be demolished, confirms the City - Actual News Magazine" (in Turkish). 9 December 2021. Retrieved 28 September 2022.
- ^ Marsh, James A. (30 October 2014), "Quebec City in the War of 1812", The Canadian Encyclopedia, Historica Canada, retrieved 26 March 2023
- ^ Hubbard, R.H. (1977). Rideau Hall. McGill-Queen's University Press. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-7735-0310-6.
- ^ Simard, Luc; Émond, Chantale (1994). Du cap au rivage : promenades dans les rues de Québec (in French). Québec (Québec). Québec: Ville de Québec. ISBN 978-2-92-086077-3. OCLC 31779784.
- ^ The 37 sites in Quebec City are listed in the Directory of Federal Heritage Designations as being located in Québec and the following boroughs/enclaves: Beauport, Cap-Rouge, Notre-Dame-des-Anges, Sainte-Foy and Wendake.
- ^ "Ville de Québec – Parks and Gardens". www.ville.quebec.qc.ca. Archived from the original on 14 November 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ^ "Le Parc Chauveau: la nature à ma portée!" (PDF) (in French). Ville de Québec. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Hogdson, Larry (8 September 2018). "Québec, toujours un désert botanique?". Le Soleil (in Canadian French). Archived from the original on 6 October 2018. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Québec, Office du tourisme de. "Promenade Samuel-De Champlain". Official Web Site – Québec City Tourism. Archived from the original on 6 October 2018. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "History of Major Special Olympics Canada (SOC) Events" (PDF). Special Olympics Canada. 29 January 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ^ "Here comes the 4th Tour de Québec!". tourdequebec.com. Archived from the original on 9 March 2012. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ^ Karine Gagnon, Qmi Agency (1 March 2011). "Quebecor joins arena plan, eyes NHL team | Hockey | Sports". Toronto Sun. Archived from the original on 1 October 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2012.
- ^ McParland, Kelly (2 March 2011). "The Quebec gravy train chugs off without Ottawa on board for once". National Post. Archived from the original on 11 March 2011.
- ^ "Quebec City plans $400 million arena to attract NHL team, Winter Olympics — ESPN". ESPN. 16 October 2009. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011. Retrieved 2 January 2012.
- ^ "Quebec city FIS Cross-Country World Cup 2019". Quebec City FIS Cross-Country World Cup. Archived from the original on 6 August 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ^ a b Duval, Alexandre (11 August 2017). "Politique : un chercheur perce une partie du " mystère Québec "". Radio-Canada.ca (in Canadian French). Archived from the original on 9 October 2018. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ Daoust, Jean-François (15 August 2017). "Le mystère de Québec: les moins bien nantis rejettent la gauche". Le Devoir (in French). Archived from the original on 9 October 2018. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ Himelfarb, Jordan (10 October 2018). "The Bloc's Quebec City fortress". The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ Peritz, Ingrid (31 August 2012). "Seeking clues to Quebec City's ballot box mystery". The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on 1 September 2012. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ Castonguay, Alec (31 August 2012). "Le faux mystère de Québec". L’actualité (in Canadian French). Archived from the original on 10 October 2018. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ Bilefsky, Dan (18 August 2018). "Quebec's 'Trash Radio' Host Fires Up Outrage, and Big Ratings". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 9 October 2018. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ Lachance, Nicolas (20 December 2015). "Il perce (enfin) le mystère Québec". Le Journal de Québec (in Canadian French). Archived from the original on 10 October 2018. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ Séguin, Rheal (2 May 2011). "Quebec City gives NDP control over the region". The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ "Official Voting Results Raw Data (poll by poll results in Quebec City)". Elections Canada. 7 April 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ "Official Voting Results by polling station (poll by poll results in Quebec City)". Elections Québec. 3 December 2021. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ "Conseils d'arrondissement". Ville de Québec. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014.
- ^ "Conseils de quartier". Ville de Québec. Archived from the original on 8 March 2017.
- ^ "2017 Police-reported Crime Severity Index and crime rate, by census metropolitan area". Statistics Canada. 23 July 2018. Archived from the original on 21 October 2018. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ^ White, Marianne (28 December 2007). "Quebec City closing in on a year without murder". Nationalpost.com. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ^ Neron, Jean-François (2010). "Bas taux d'homicide: fiche impressionnante pour Québec" (in French). Le Soleil. Archived from the original on 29 July 2018. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ^ "Suspect in Quebec mosque terror attack was of Moroccan origin, reports show". Fox News. 30 January 2017. Archived from the original on 30 January 2017. Retrieved 30 January 2017.
- ^ "Police-reported crime statistics in Canada, 2017". Statistics Canada. 23 July 2018. Archived from the original on 21 October 2018. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ^ "Hate crimes targeting Muslims doubled in 2017, says Quebec City police chief". CBC News. Archived from the original on 21 October 2018. Retrieved 3 September 2018.
- ^ "Reported hate crimes jumped in Quebec City in year prior to mosque shooting". CBC News. 29 November 2018. Archived from the original on 16 December 2018. Retrieved 3 September 2018.
- ^ "Rapport annuel 2018" (PDF). Service de Police de la Ville de Québec (in French). p. 14. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 22 June 2019.
- ^ "Rapport annuel 2017" (PDF). Service de Police de la Ville de Québec (in French). p. 12. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 December 2018. Retrieved 8 December 2018.
- ^ "Rapport annuel 2016" (PDF). Service de Police de la Ville de Québec (in French). p. 20. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 February 2018. Retrieved 8 December 2018.
- ^ Bilefsky, Dan (November 2020). "Halloween Stabbing Attack in Quebec City Leaves 2 Dead". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 4 January 2021. Retrieved 1 November 2020.
- ^ "Projet de prolongement de l'axe du Vallon" (PDF). BAPE (in French). 2004. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 March 2018. Retrieved 21 March 2017.
- ^ "Quebec City tramway finally gets green light as province gives unconditional approval". CBC. 6 April 2022.
- ^ "We represent the interests of rail and bus passengers and advocate for public transport services in Canada". 28 April 2021.
- ^ "Quebec city Tram Will Be A Reality : Rail for the Valley". 6 April 2022.
- ^ "Port of Quebec". Archived from the original on 3 February 2012. Retrieved 24 June 2009.
- ^ "Québec fait le ménage dans ses jumelages". Le Soleil (in French). 7 September 2012. Archived from the original on 21 September 2016.
External links
[edit]- Official website

- Official website of Québec City Tourism
- Focus on Geography Series, 2016 Census — Census subdivision of Québec City from Statistics Canada
- CBC Digital Archives — CBC Television Special: Preserving Quebec City (1976)
- CBC Digital Archives — Quebec City: 400 Years of History
- Quebec City
- Cities and towns in Quebec
- World Heritage Sites in Canada
- Quebec populated places on the Saint Lawrence River
- Populated places established in 1608
- 1608 establishments in New France
- Former colonial capitals in Canada
- Hudson's Bay Company trading posts
- Port settlements in Quebec
- 1608 in North America
- 1600s in Canada
- 1608 in New France