Flag: Difference between revisions
→Flagpoles: the highest flagpole is in Azerbaijan Tag: references removed |
Removing link(s) to "Through and through": Deleted PROD. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Piece of fabric with a distinctive design and colours}} |
|||
{{Other uses}} |
|||
{{other uses}} |
|||
{{pp-vandalism|small=yes}} |
|||
{{EngvarB|date=December 2018}} |
|||
[[File:United Nations Flags - cropped.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.25|[[United Nations]] members' [[national flag]]s]] |
|||
[[File:Lenini mäetipp (J. Künnap).jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.25|Setting up a flag could also possess the meaning of conquering something. [[Jaan Künnap]] with the [[flag of Estonia]] at the top of [[Lenin Peak]] ({{convert|7134|m|abbr=in|disp=sqbr}}) in 1989.]] |
|||
A '''flag''' is a piece of [[textile|fabric]] (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a [[symbol]], a [[signalling]] device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the [[graphic design]] employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the [[Maritime flag|maritime environment]], where [[Flag semaphore|semaphore]] is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called [[flag families]].<ref name=":0">{{Cite book |last=Znamierowski |first=Alfred |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OwueMQEACAAJ |title=The World Encyclopedia of Flags: The Definitive Guide to International Flags, Banners, Standards and Ensigns, with Over 1400 Illustration |date=2013 |publisher=Lorenz Books |isbn=978-0-7548-2629-3 |pages=100–129 |language=en}}</ref> The study of flags is known as "[[vexillology]]" from the [[Latin]] {{Lang|la|vexillum}}, meaning "flag" or "[[banner]]". |
|||
[[File:Flag-map of the world.svg|thumb|450px|A world map showing most national flags.]] |
|||
[[National flag]]s are [[patriotic]] symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong [[military]] associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in [[messaging]], [[advertising]], or for [[decorative]] purposes. |
|||
A '''flag''' is a piece of fabric with a distinctive design that is usually rectangular and used as a (nation's) symbol), as a signaling device, or decoration<ref>http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/flag?show=1&t=1300195800</ref>. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the [[graphic design]] employed by a flag, or to its depiction in another medium. |
|||
Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: {{Lang|ar|لواء|italic=no}}) is equivalent to a [[brigade]] in Arab countries. In Spain, a ''flag'' (Spanish: ''{{Lang|es|bandera}}'') is a [[battalion]]-equivalent in the [[Spanish Legion]].{{cn|date=December 2023}} |
|||
The first flags were used to assist military coordination on battlefields, and flags have since evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is similarly challenging (such as the maritime environment where [[Flag semaphore|semaphore]] is used). National flags are potent patriotic symbols with varied wide-ranging interpretations, often including strong military associations due to their original and ongoing military uses. Flags are also used in messaging, [[advertising]], or for other decorative purposes. The study of flags is known as [[vexillology]], from the [[Latin]] ''vexillum'' meaning flag or [[banner]]. |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
{{Main|History of flags}} |
|||
{{see|Vexilloid|Heraldic flag|Royal Standard}} |
|||
[[File:Bronze flag, Shadad Kerman, Iran.JPG|upright|thumb|right|Bronze flag Derafsh Shahdad found in [[Shahdad]], Iran, third millennium BC]] |
|||
The usage of flags spread from [[India]] and [[China]], where they were almost certainly invented,<ref name="EB1">flag. (2008). Encyclopædia Britannica. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica.</ref> to neighboring [[Burma]], [[Thailand|Siam]], and [[southeastern Asia]].<ref name="EB1" /> |
|||
The origin of the flag is unknown<ref>Inglefield, p. 39.</ref> and it remains unclear when the first flag was raised.<ref name="archive.org">{{Cite book |last=Smith |first=Whitney |url=http://archive.org/details/flagsthroughages00smit |title=Flags through the ages and across the world |date=1975 |publisher=New York |others=Internet Archive |isbn=978-0-07-059093-9 |pages=33}}</ref> |
|||
In antiquity, [[field sign]]s or standards were used in warfare that can be categorized as [[vexilloid]] or "flag-like". Examples include the [[Achaemenid]] battle standard [[Derafsh Kaviani]], and the standards of the [[Roman legion]]s such as the [[aquila (Roman)|eagle]] of [[Augustus Caesar]]'s [[Legio X Fretensis|Xth legion]], or the [[Draconarius|dragon standard]] of the [[Sarmatians]]; the latter was let fly freely in the wind, carried by a horseman, but judging from depictions it was more similar to an elongated [[dragon kite]] than to a simple flag. |
|||
Ships with vexilloids were represented on predynastic Egyptian pottery {{circa|3500 BC}}.<ref name="archive.org"/> In antiquity, [[field sign]]s that can be categorised as [[vexilloid]] or "flag-like" were used in warfare, originating in [[ancient Egypt]] or [[Assyria]].<ref name="Britannica">[https://www.britannica.com/topic/flag-heraldry Flag | heraldry]. ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Retrieved February 15, 2019.</ref> Examples include the [[Sassanid]] battle standard [[Derafsh Kaviani]], and the standards of the [[Roman legion]]s such as the [[aquila (Roman)|eagle]] of [[Augustus Caesar]]'s [[Legio X Fretensis|Xth legion]] and the [[Draconarius|dragon standard]] of the [[Sarmatians]]; the latter was allowed to fly freely in the wind, carried by a horseman, but depictions suggest that it bore more similarity to an elongated [[dragon kite]] than to a simple flag. |
|||
While the origin of the flag remains a mystery, the oldest flag discovered is made of bronze: a [[Derafsh]] or 'flag-like' Shahdad, which was found in [[Shahdad]], Iran, and dates back to {{Circa|2400 BC}}. It features a seated man and a kneeling woman facing each other, with a star in between. This iconography was found in other Iranian Bronze Age pieces of art.<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qsmtxmD5kWcC&q=shahdad+standard&pg=PA19|title=Susa and Elam. Archaeological, Philological, Historical and Geographical Perspectives.: Proceedings of the International Congress Held at Ghent University, December 14–17, 2009.|first1=Katrien De|last1=Graef|first2=Jan|last2=Tavernier|date=7 December 2012|publisher=BRILL|isbn=978-9004207400|via=Google Books}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Qbnyh2YH2KQC&q=shahdad+standard&pg=PA24|title=Art of the Bronze Age: Southeastern Iran, Western Central Asia, and the Indus Valley|first1=Holly|last1=Pittman|first2=Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York|last2=N.Y.)|date=12 December 1984|publisher=Metropolitan Museum of Art|isbn=9780870993657|via=Google Books}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6lDgYxV0DN8C&q=shahdad+standard&pg=PA227|title=Leaving No Stones Unturned: Essays on the Ancient Near East and Egypt in Honor of Donald P. Hansen|first1=Donald P.|last1=Hansen|first2=Erica|last2=Ehrenberg|date=12 December 2017|publisher=Eisenbrauns|isbn=9781575060552|via=Google Books}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=M2QMAQAAMAAJ&q=shahdad+standard|title=Shahdad: archaeological excavations of a bronze age center in Iran|first1=Ali|last1=Hakemi|first2=Istituto italiano per il Medio ed Estremo Oriente Centro Scavi e Ricerche|last2=Archeologiche|date=12 December 1997|publisher=IsMEO|isbn=9788120410176|via=Google Books}}</ref> |
|||
During the [[High Middle Ages]] flags came to be used primarily as a [[heraldic flag|heraldic device]] in battle, allowing more easily to identify a knight than only from the heraldic device painted on the shield. |
|||
Already during the high medieval period, and increasingly during the [[Late Middle Ages]], [[city state]]s and [[medieval commune|communes]] such as those of the [[Old Swiss Confederacy]] also began to use flags as field signs. |
|||
Regimental flags for individual units became commonplace during the [[Early Modern period]]. |
|||
Flags made of cloth were almost certainly<ref name="Britannica"/> the invention of the ancient peoples of the [[Indian subcontinent]] or the [[Zhou dynasty]] of [[Ancient China]]. Chinese flags had iconography such as a red bird, a white tiger, or a blue dragon, and royal flags were to be treated with a level of respect similar to that given to the ruler. Indian flags were often triangular and decorated with attachments such as a [[yak]]'s tail and the state umbrella.{{Explain|reason=The term ''state umbrella'' needs explanation.|date=July 2023}} Silk flags either spread to the Near East from China or it was just the [[silk]] itself, later fashioned by people who had independently conceptualized a rectangular cloth attached to a pole.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Smith |first=Whitney |url=http://archive.org/details/flagsthroughages00smit |title=Flags through the ages and across the world |date=1975 |publisher=New York |others=Internet Archive |isbn=978-0-07-059093-9 |pages=41}}</ref> Flags were probably transmitted to Europe via the [[Muslim world]], where plainly coloured flags were used due to [[Aniconism in Islam|Islamic proscriptions]]. They are often mentioned in the early history of Islam and may have been copied from India.<ref name="Britannica"/> |
|||
During the peak of the [[age of sail]], beginning in the early 17th century, it has been customary (and later a legal requirement) for ships to carry flags designating their nationality;<ref>Articles 90–94 of the [[UN Convention on the Law of the Sea]]</ref> these flags eventually evolved into the national flags and [[maritime flags]] of today. Flags also became the preferred means of [[communication]]s at sea, resulting in various systems of flag signals; ''see, [[International maritime signal flags]]''. |
|||
In Europe, during the [[High Middle Ages]], flags came to be used primarily as a [[heraldic flag|heraldic device]] in battle, allowing easier identification of a knight over only the heraldic icon painted on the shield. Already during the high medieval period, and increasingly during the [[Late Middle Ages]], [[city state]]s and [[medieval commune|communes]] such as those of the [[Old Swiss Confederacy]] also began to use flags as field signs. Regimental flags for individual units became commonplace during the [[Early Modern period]]. |
|||
Use of flags outside of military or naval context begins only with the rise of [[nationalism|nationalist]] sentiment by the end of the 18th century; the earliest [[national flag]]s date to that period, and during the 19th century it became common for every sovereign state to introduce a national flag. |
|||
[[File:Sujagi (1871).jpg|upright|left|thumb|''[[Sujagi]]'' of [[Eo Jae-yeon]], captured in 1871]] |
|||
During the peak of the [[age of sail|sailing age]], beginning in the early 17th century, it was customary (and later a legal requirement) for ships to fly flags designating their nationality;<ref>Articles 90–94 of the [[UN Convention on the Law of the Sea]]</ref> these flags eventually evolved into the national flags and [[maritime flags]] of today. Flags also became the preferred means of [[communication]]s at sea, resulting in various systems of flag signals; ''see, [[International maritime signal flags]]''. |
|||
Use of flags beyond a military or naval context began with the rise of [[nationalism]] by the end of the 18th century, although some flags date back earlier. The flags of countries such as Austria, Denmark or Turkey have legendary origins while many others, including those of Poland and Switzerland, grew out of the heraldic emblems of the Middle Ages. The 17th century saw the birth of several [[national flag]]s through revolutionary struggle. One of these was the flag of the Netherlands, which appeared during the [[Eighty Years' War|80-year Dutch rebellion]] which began in 1568 against Spanish domination.<ref>Inglefield, p. 48.</ref> |
|||
Political change and social reform, allied with a growing sense of nationhood among ordinary people, led to the creation of new nations and flags all over the world in the 19th and 20th centuries.<ref>Inglefield, p. 50.</ref> |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
==National flags== |
==National flags== |
||
{{Main|National flag}} |
{{Main|National flag}} |
||
[[File:Flags at half-staff outside Central Plaza.jpg|thumb|Flags at [[half-mast]] outside [[Central Plaza, Hong Kong]], after the [[2008 Sichuan earthquake]]. The [[Flag of Saudi Arabia]] is exempted.]] |
|||
[[File:Dutch-flag-in-sky.jpg|thumb|200 px|The [[Flag of the Kingdom of the Netherlands|Dutch flag]] is the oldest tricolor.]] |
|||
[[File: |
[[File:Meeting Place Monument.JPG|thumb|Tribal flags at Meeting Place Monument/Flag Plaza at the Oklahoma State Capitol]] |
||
[[File:Flags at half-staff outside Central Plaza.jpg|thumb|200 px|Flags at half-staff outside [[Central Plaza, Hong Kong]], after the Sichuan Earthquake. The [[Flag of Saudi Arabia]] is exempted.]] |
|||
One of the most popular uses of a flag is to |
One of the most popular uses of a flag is to symbolise a [[nation]] or [[country]]. Some [[national flag]]s have been particularly inspirational to other nations, countries, or subnational entities in the design of their own flags. Some prominent examples include: |
||
* The [[flag of Denmark]] is the oldest [[state flag]] still in use (dates back to the 13th century). This flag, called the [[Flag of Denmark|Dannebrog]], inspired the [[Nordic Cross Flag|cross design]] of the other [[Nordic countries]]: [[Flag of Norway|Norway]], [[Flag of Sweden|Sweden]], [[Flag of Finland|Finland]], [[Flag of Iceland|Iceland]], and regional Scandinavian flags for the [[Flag of the Faroe Islands|Faroe Islands]], [[Flag of Åland|Åland]], [[Flag of Skåneland|Scania]] and [[Flag of Bornholm|Bornholm]], as well as flags for the non-Scandinavian [[Flag of Shetland|Shetland]] and [[Flag of Orkney|Orkney]]. |
|||
[[File:Dannebrog isamsø.jpg|thumb|upright|right|The Danish national flag (Dannebrog) waving in [[Samsø]] ]] |
|||
* The [[Flag of the Netherlands|Tricolour]] of the [[Netherlands]] is the oldest [[tricolour|tricolor]], first appearing in 1572 as the [[Prince's Flag]] in [[Orange (colour)|orange]]–[[white]]–[[blue]]. Soon the more famous [[red]]–white–blue began appearing—it is however unknown why, though many stories are known. After 1630 the red–white–blue was the most commonly seen flag. The [[Flag of the Kingdom of the Netherlands|Dutch Tricolor]] has inspired{{Citation needed |date=October 2007}} many flags but most notably those of [[Russia]], [[New York City]], and [[South Africa]] (the 1928–94 flag). |
|||
* The national flag of [[France]], the [[Tricolour|Tricolore]] was designed in 1794. As a forerunner of revolution, France's [[tricolour]] flag style has been adopted by other nations. ''Examples'': [[Flag of Italy|Italy]], [[flag of Costa Rica|Costa Rica]], [[flag of Dominican Republic|Dominican Republic]], [[Flag of Ireland|Ireland]], [[flag of Haiti|Haiti]], [[Flag of Romania|Romania]], [[Flag of Mexico|Mexico]], etc. |
|||
* The [[flag of Denmark]], the ''Dannebrog'', is attested in 1478, and is the oldest national flag still in use.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/oldest-continuously-used-national-flag/ | title=Oldest continuously used national flag | work=Guinness World Records | access-date=2023-11-10}}</ref> It inspired the [[Nordic Cross Flag|cross design]] of the other [[Nordic countries]]: [[Flag of Norway|Norway]], [[Flag of Sweden|Sweden]], [[Flag of Iceland|Iceland]], [[Flag of Finland|Finland]], and regional Scandinavian flags for the [[Flag of the Faroe Islands|Faroe Islands]], [[Flag of Åland|Åland]], [[Flag of Skåneland|Scania]] and [[Flag of Bornholm|Bornholm]], as well as flags for the non-Scandinavian [[Flag of Shetland|Shetland]] and [[Flag of Orkney|Orkney]].<ref>[http://denmark.dk/en/quick-facts/national-flag/ National Flag -The official website of Denmark] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180203070136/http://denmark.dk/en/quick-facts/national-flag/ |date=2018-02-03 }}. Earlier use of the white cross on red is attested by an armorial (Netherlands) of 1370-1386. In later monastic tradition, the Dannebrog made its first, miraculous appearance at the Battle of Lindanise on 15 June 1219.</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Khag6tbsIn4C&pg=PA88|author=Jeroen Temperman|title=State Religion Relationships and Human Rights Law: Towards a Right to Religiously Neutral Governance|year=2010|page=88|publisher=[[Martinus Nijhoff Publishers]]|isbn=978-9004181489|quote=Many predominantly Christian states show a cross, symbolising Christianity, on their national flag. The so-called Scandinavian crosses or Nordic crosses on the flags of the Nordic countries–Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden–also represent Christianity.|access-date=31 December 2007|archive-date=23 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230423140657/https://books.google.com/books?id=Khag6tbsIn4C&pg=PA88|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
* The [[flag of Russia]], the source for the [[Pan-Slavic colors]] red, white and blue, adopted by many [[Slavic peoples|Slavic]] states and peoples as their symbols. ''Examples'': [[Flag of Slovakia|Slovakia]], [[Flag of Serbia|Serbia]], [[Flag of Croatia|Croatia]], and [[Flag of Slovenia|Slovenia]]. |
|||
* The [[flag of the Netherlands]] is the oldest [[tricolour (flag)|tricolour]]. Its three colours of red, white and blue go back to [[Charlemagne]]'s time, the ninth century. The coastal region of what today is the Netherlands was then known for its cloth in these colours. Maps from the early 16th century already put flags in these colours next to this region, like Texeira's map of 1520. A century before that, during the 15th century, the three colours were mentioned as the coastal signals for this area, with the three bands straight or diagonal, single or doubled. As [[state flag]] it first appeared around 1572 as the [[Prince's Flag]] in orange–white–blue. Soon the more famous red–white–blue began appearing, becoming the prevalent version from around 1630. Orange made a comeback during the civil war of the late 18th century, signifying the orangist or pro-[[stadtholder]] party. During World War II the pro-Nazi [[National Socialist Movement in the Netherlands|NSB]] used it. Any symbolism has been added later to the three colours, although the orange comes from the [[House of Orange-Nassau]]. This use of orange comes from Nassau, which today uses orange-blue, not from Orange, which today uses red-blue. However, the usual way to show the link with the House of Orange-Nassau is the orange pennant above the red-white-blue. It is said that the Dutch Tricolour has inspired<ref>{{Cite web |last=Smith |first=Whitney |title=flag of France {{!}} History & Meaning |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/flag-of-France |access-date=2019-02-24 |website=Encyclopedia Britannica |language=en}}</ref>{{Citation needed |date=October 2007}} many flags but most notably those of Russia, [[Flags of New York City|New York City]], and [[Flag of South Africa|South Africa]] (the [[Flag of South Africa (1928–1994)|1928–94 flag]] as well the current flag). As the probable inspiration for the [[Russian flag]], it is the source too for the [[pan-Slavic colours]] red, white and blue, adopted by many [[Slavic peoples|Slavic]] states and peoples as their symbols; examples are [[Flag of Slovakia|Slovakia]], [[Flag of Serbia|Serbia]], and [[Flag of Slovenia|Slovenia]].<ref name="Shelley">{{cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5qlXatHRJtMC&q=Pan-Slavic+flag&pg=PR16 | title=Nation Shapes: The Story behind the World's Borders | publisher=ABC-CLIO | author=Shelley, Fred M. | year=2013 | pages=xvi | isbn=9781610691062}}</ref> |
|||
* The [[Union Flag]] (Union Jack) of the [[United Kingdom]] is the most commonly used. British colonies typically flew a flag based on one of the ensigns based on this flag, and many former colonies have retained the design to acknowledge their cultural history. ''Examples'': [[Flag of Australia|Australia]], [[Flag of Fiji|Fiji]], [[Flag of New Zealand|New Zealand]], [[Flag of Tuvalu|Tuvalu]], and also the Canadian provinces of [[Flag of Manitoba|Manitoba]], [[Flag of Ontario|Ontario]] and [[Flag of British Columbia|British Columbia]], and the American state of [[Flag of Hawaii|Hawaii]]; ''see [[commons:Flags based on British ensigns]]''. |
|||
* The [[flag of |
* The national [[flag of France]] was designed in 1794. As a forerunner of revolution, France's tricolour flag style has been adopted by other nations. Examples: [[Flag of Italy|Italy]], [[Flag of Belgium|Belgium]], [[Flag of Ireland|Ireland]], [[Flag of Romania|Romania]] and [[Flag of Mexico|Mexico]].{{citation needed|date=December 2016}} |
||
* The [[Union Flag]] (Union Jack) of the United Kingdom is the most commonly used. British colonies typically flew a flag based on one of the ensigns based on this flag, and many former colonies have retained the design to acknowledge their cultural history. Examples: [[Flag of Australia|Australia]], [[Flag of Fiji|Fiji]], [[Flag of New Zealand|New Zealand]], [[Flag of Tuvalu|Tuvalu]], and also the Canadian provinces of [[Flag of Manitoba|Manitoba]], [[Flag of Ontario|Ontario]] and [[Flag of British Columbia|British Columbia]], and the American state of [[Flag of Hawaii|Hawaii]]; ''see [[commons:Flags based on British ensigns]]''. |
|||
* The original tricolor [[Flag of Iran]], the source for the [[Pan-Iranian colors]] ''Green'', ''White'' and ''Red'' adopted by many [[Indo-Iranians|Indo-Iranian]] or [[Aryan]] states and peoples as their symbols. ''Examples'': [[Flag of Tajikistan|Tajikistan]], [[Flag of Kurdistan|Kurdistan]], [[Republic of Ararat]], [[Talysh-Mughan Autonomous Republic|Talysh-Mughan]]. |
|||
* The [[flag of the United States]] is nicknamed ''The Stars and Stripes'' or ''Old Glory''.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Smith |first=Whitney |title=Flag of the United States of America |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/flag-of-the-United-States-of-America |access-date=2019-05-24 |website=Encyclopedia Britannica |language=en}}</ref> Some nations imitated this flag to symbolise their similarity to the United States or the [[American Revolution]]. Examples: [[Flag of Liberia|Liberia]],<ref>{{Cite web |last=Smith |first=Whitney |title=Flag of Liberia |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/flag-of-Liberia |access-date=2019-05-24 |website=Encyclopedia Britannica |language=en}}</ref> [[Flag of Chile|Chile]], [[Flag of the Republic of China|Taiwan (ROC)]], and the French region of [[Flag of Brittany|Brittany]]. |
|||
* [[Ethiopia]] was seen as a model by emerging [[Africa]]n states of the 1950s and 1960s, as it was one of the oldest independent states in Africa. Accordingly, its [[Flag of Ethiopia|flag]] became the source of the [[Pan-African colours|Pan-African colors]], or "Rasta colors". ''Examples'': [[Flag of Togo|Togo]], [[Flag of Senegal|Senegal]], [[Flag of Ghana|Ghana]], [[Flag of Mali|Mali]]. |
|||
[[File:Flag of Ethiopia (1975–1987).svg|thumb|The [[Flag of Ethiopia]]'s colours inspired the colours of many African national flags.]] |
|||
* The [[flag of Turkey|flag]] of [[Turkey]], which is very similar to last flag of the old [[Ottoman Empire]], has been an inspiration for the flag designs of many other Muslim nations. During the time of the Ottomans the [[crescent]] began to be associated with [[Islam]] and this is reflected on the flags of [[Flag of Algeria|Algeria]], [[Flag of Azerbaijan|Azerbaijan]], [[Flag of Comoros|Comoros]], [[Flag of Malaysia|Malaysia]], [[Flag of Mauritania|Mauritania]], [[Flag of Pakistan|Pakistan]] and of [[Flag of Tunisia|Tunisia]]. |
|||
* |
* [[Ethiopia]] was seen as a model by emerging African states of the 1950s and 1960s, as it was one of the oldest independent states in Africa. Accordingly, its [[Flag of Ethiopia|flag]] became the source of the [[Pan-African colours]], or 'Rasta colours'. Examples: [[Flag of Benin|Benin]], [[Flag of Togo|Togo]], [[Flag of Senegal|Senegal]], [[Flag of Ghana|Ghana]], [[Flag of Mali|Mali]], [[Flag of Guinea|Guinea]]. |
||
* The [[ |
* The [[flag of Turkey]], which is very similar to the last flag of the old [[Ottoman Empire]], has been an inspiration for the flag designs of many other Muslim nations. During the time of the Ottomans the [[crescent]] began to be associated with [[Islam]] and this is reflected on the flags of [[Flag of Algeria|Algeria]], [[Flag of Azerbaijan|Azerbaijan]], [[Flag of the Comoros|Comoros]], [[Flag of Libya|Libya]], [[Flag of Mauritania|Mauritania]], [[Flag of Pakistan|Pakistan]], [[Flag of Tunisia|Tunisia]] and [[Flag of Maldives|Maldives]].<ref>Cyril Glassé , ''The New Encyclopedia of Islam'' (revised ed. 2001), s.v. "Moon" (p. 314).</ref> |
||
* The [[Pan-Arab colours]], green, white, red and black, are derived from the flag of the [[Arab Revolt|Great Arab Revolt]] as seen on the flags of [[Flag of Jordan|Jordan]], [[Flag of Libya|Libya]], [[Flag of Kuwait|Kuwait]], [[Flag of Sudan|Sudan]], [[Flag of Syria|Syria]], the [[Flag of the United Arab Emirates|United Arab Emirates]], [[Flag of the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic|Western Sahara]], [[Flag of Egypt|Egypt]], [[Flag of Iraq|Iraq]], [[Flag of Yemen|Yemen]] and [[Palestinian flag|Palestine]]. |
|||
* The [[Flag of Venezuela|flag]] of [[Venezuela]], created by [[Francisco de Miranda]] to represent the independence movement in Venezuela that later gave birth to the [[Republic of Gran Colombia|"Gran Colombia"]], inspired the flags of [[Flag of Colombia|Colombia]] and [[Flag of Ecuador|Ecuador]], both sharing three bands of [[yellow]], [[blue]] and [[red]] with the flag of Venezuela. |
|||
* The [[Flag of |
* The [[Flag of the Soviet Union|Soviet flag]], with its golden symbols of the [[hammer and sickle]] on a red field, was an inspiration to flags of other [[communism|communist]] states, such as [[Flag of East Germany|East Germany]], the [[Flag of the People's Republic of China|People's Republic of China]], [[Flag of Vietnam|Vietnam]], [[Flag of Angola|Angola]], [[Flag of Afghanistan|Afghanistan (1978–1980)]] and [[Flag of Mozambique|Mozambique]]. |
||
* The [[flag of Venezuela]], created by [[Francisco de Miranda]] to represent the independence movement in Venezuela that later gave birth to the [[Republic of Gran Colombia|Gran Colombia]], inspired the flags of [[Flag of Colombia|Colombia]], [[Flag of Ecuador|Ecuador]], and the [[Flag of the Federal Territory (Malaysia)|Federal Territories in Malaysia]], all sharing three bands of yellow, blue and red with the flag of Venezuela. |
|||
* The [[flag of Argentina]], created by [[Manuel Belgrano]] during the war of independence, was the inspiration for the [[United Provinces of Central America]]'s flag, which in turn was the origin for the flags of [[Flag of Guatemala|Guatemala]], [[Flag of Honduras|Honduras]], [[Flag of El Salvador|El Salvador]], and [[Flag of Nicaragua|Nicaragua]]. |
|||
National flag designs are often used to signify nationality in other forms, such as [[flag patch]]es. |
National flag designs are often used to signify nationality in other forms, such as [[flag patch]]es. |
||
| Line 45: | Line 60: | ||
===Civil flags=== |
===Civil flags=== |
||
{{Main|Civil flag}} |
{{Main|Civil flag}} |
||
{{multiple image |
|||
A ''civil'' flag is a version of the national flag that is flown by civilians on non-government installations or craft. The use of civil flags was more common in the past, in order to denote buildings or ships that were not manned by the military. In some countries the civil flag is the same as the [[war flag]] or [[state flag]], but without the coat of arms, such as in the case of [[Flag of Spain|Spain]], and in others it's an alteration of the war flag. |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| width = 160 |
|||
| image_gap = 10 |
|||
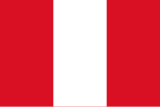
| image1 = Flag of Peru.svg |
|||
| alt1 = Civil flag of Peru |
|||
| caption1 = |
|||
| image2 = Flag of Peru (state).svg |
|||
| alt2 = State flag of Peru |
|||
| caption2 = |
|||
| footer = The civil and state flags of [[Peru]] share the same red and white bands, but only the state flag (right) is [[Defacement (flag)|defaced]] with the national ensign. |
|||
}} |
|||
A ''civil'' flag is a version of the national flag that is flown by civilians on non-government installations or craft. The use of civil flags was more common in the past, in order to denote buildings or ships that were not crewed by the military. In some countries the civil flag is the same as the [[war flag]] or [[state flag]], but without the coat of arms, such as in the case of [[Flag of Spain|Spain]], and in others it is an alteration of the war flag. |
|||
===War flags=== |
===War flags=== |
||
{{Main|War flag}} |
{{Main|War flag|Colours, standards and guidons}} |
||
[[File:Ensign of the Royal Air Force.svg|thumb|Standard for the [[UK]]'s [[Royal Air Force]], the [[Royal Air Force Ensign|Ensign of the RAF]] displays the RAF [[roundel]] that is also displayed on the fuselage and wings of British warplanes.]] |
|||
Several countries |
Several countries, including the [[Royal Air Force]], [[British Army]] and the [[Royal Navy]] ([[White Ensign]]) of the [[United Kingdom]] and the [[Soviet Union]] have had [[Union Jack|unique flags]] flown by their [[armed forces]] separately, rather than the [[national flag]]. |
||
Other countries' armed forces (such as those of the |
Other countries' armed forces (such as those of the United States or Switzerland) use their standard [[Flag of the United States|national flag]]; in addition, the U.S. has alongside flags and seals designed from long tradition for each of its six uniformed military services/military sub-departments in the [[United States Department of Defense|Department of Defense]] and the [[United States Department of Homeland Security|Department of Homeland Security]]. The Philippines' armed forces may use their [[Flag of the Philippines|standard national flag]], but during times of war the flag is turned upside down. [[Flag of Bulgaria|Bulgaria's flag]] is also turned upside down during times of war. These are also considered war flags, though the terminology only applies to the flag's military usage. |
||
Large versions of the war flag flown on the [[warship]]s of countries' [[navy|navies]] are known as [[battle ensign]]s. In war waving a white flag is a banner of truce. |
Large versions of the war flag flown on the [[warship]]s of countries' [[navy|navies]] are known as [[battle ensign]]s. In addition, besides flying the national standard or a military services' emblem flag at a military fort, base, station or post and at sea at the stern (rear) or main top mast of a warship, a [[Jack (flag)|Naval Jack flag]] and other [[maritime flag]]s, [[Pennant (commissioning)|pennants]] and emblems are flown at the bow (front). In times of war waving a white flag is a banner of truce, talks/negotiations or surrender. |
||
Four distinctive African flags currently in the collection of the [[National Maritime Museum]] in Britain were flown in action by [[Itsekiri]] ships under the control of [[Nana Olomu]] during conflict in the late 19th century. One is the flag generally known as the [[Flag of the Benin Empire|Benin flag]] and one is referred to as |
Four distinctive African flags currently in the collection of the [[National Maritime Museum]] in [[United Kingdom|Britain]] were flown in action by [[Itsekiri]] ships under the control of [[Nana Olomu]] during the conflict in the late 19th century. One is the flag generally known as the [[Flag of the Benin Empire|Benin Empire flag]] and one is referred to as Nana Olomu's flag.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.rog.nmm.ac.uk/upload/amaxus_pdf/amaxus_conWebDoc_229.pdf|title=Welcome to the Royal Museums Greenwich Blogs - Royal Museums Greenwich Blogs|access-date=2010-05-24|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110928144651/http://www.rog.nmm.ac.uk/upload/amaxus_pdf/amaxus_conWebDoc_229.pdf|archive-date=2011-09-28|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
||
===International flags=== |
===International flags=== |
||
[[File:Flag of the United Nations.svg|thumb|The [[Flag of the United Nations]], sky blue field with north polar view looking down on a world map in white with two olive branches wreaths curved around. First version presented April–June 1945 to the [[United Nations|United Nations Organization]] (UNO) at the [[United Nations Conference on International Organization|San Francisco Conference]], second version adopted by the U.N., December 1946]] |
|||
Among international flags are the [[Flag of the United Nations]], the [[Olympic symbols#Flag|Olympic flag]], the [[Paralympic symbols#Flag|Paralympic flag]], The [[EU flag]] and the [[World Flag]]. |
|||
Among international flags are the [[Flag of the United Nations|United Nations]], [[Flag of Europe|Europe]], [[Olympic symbols#Flag|Olympic]], [[flag of NATO|NATO]] and [[Paralympic symbols#Flag|Paralympic flags]]. |
|||
===Similar flags=== |
|||
Please see [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Gallery_of_flags_by_design Gallery of flags by design] |
|||
== |
==Maritime flags== |
||
{{Main|Maritime flag}} |
{{Main|Maritime flag}} |
||
[[File:Arndt Flag Tallinn 31 July 2014.JPG|thumb|left|[[Ensign (flag)|Ensign]]s are flown on boats to indicate the country of registration of the boat.]] |
|||
{{flag image|Image = ICS Delta.svg|Caption = The international maritime signal flag ''Delta'' (letter ''D'')}} |
|||
Flags are particularly important at sea, where they can mean the difference between life and death, and consequently where the rules and regulations for the flying of flags are strictly enforced. A national flag flown at sea is known as an [[ensign]]. A courteous, peaceable [[merchant navy|merchant ship]] or [[yacht]] customarily flies its ensign (in the usual ensign position), together with the flag of whatever nation it is currently visiting at the mast (known as a [[courtesy flag]]). To fly one's ensign alone in foreign waters, a foreign port or in the face of a foreign warship traditionally indicates a willingness to fight, with [[cannon]], for the right to do so. As of 2009, this custom is still taken seriously by many naval and port authorities and is readily enforced in many parts of the world by boarding, confiscation and other civil penalties. |
|||
Flags are particularly important at sea, where they can mean the difference between life and death, and consequently where the rules and regulations for the flying of flags are strictly enforced. A national flag flown at sea is known as an [[Ensign (flag)|ensign]]. A courteous, peaceable [[merchant navy|merchant ship]] or [[yacht]] customarily flies its ensign (in the usual ensign position), together with the flag of whatever nation it is currently visiting at the mast (known as a [[courtesy flag]]). To fly one's ensign alone in foreign waters, a foreign port or in the face of a foreign warship traditionally indicates a willingness to fight, with [[cannon]], for the right to do so. {{As of|2009}}, this custom is still taken seriously by many naval and port authorities and is readily enforced in many parts of the world by boarding, confiscation and other civil penalties. In some countries [[yacht ensign]]s are different from merchant ensigns in order to signal that the yacht is not carrying [[cargo]] that requires a [[customs]] declaration. Carrying commercial cargo on a boat with a yacht ensign is deemed to be [[smuggling]] in many jurisdictions. Traditionally, a vessel flying under the courtesy flag of a specific nation, regardless of the vessel's country of registry, is considered to be operating under the law of her 'host' nation. |
|||
In some countries yacht ensigns are different from merchant ensigns in order to signal that the yacht is not carrying [[cargo]] that requires a [[customs]] declaration. Carrying commercial cargo on a boat with a yacht ensign is deemed to be [[smuggling]] in many jurisdictions. |
|||
[[File:ICS Kilo.svg|thumb|The international maritime signal flag ''Kilo'' (letter ''K'')]] |
|||
There is a system of [[international maritime signal flags]] for numerals and letters of the alphabet. Each flag or pennant has a specific meaning when flown individually. |
|||
As well, [[Flag semaphore|semaphore flags]] can be used to communicate on an ''ad hoc'' basis from ship to ship over short distances. |
There is a system of [[international maritime signal flags]] for numerals and letters of the alphabet. Each flag or pennant has a specific meaning when flown individually. As well, [[Flag semaphore|semaphore flags]] can be used to communicate on an ''ad hoc'' basis from ship to ship over short distances. |
||
Another category of maritime flag flown by some [[United States Government|United States government]] ships is the [[distinctive mark]]. Although the [[United States Coast Guard]] has its own service ensign, all other U.S. government ships fly the national ensign as their service ensign, following [[United States Navy]] practice. To distinguish themselves from ships of the Navy, such ships historically have flown their parent organisation's flag from a forward mast as a distinctive mark. Today, for example, commissioned ships of the [[National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration]] (NOAA) fly the [[National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration#Flag|NOAA flag]] as a distinctive mark. |
|||
==Shapes and designs== |
==Shapes and designs== |
||
[[File:Flag of Nepal.svg|thumb|The [[flag of Nepal]], a non-rectangular flag that is a [[Pennon|double-pennon]]]] |
|||
[[File:Flag of Ohio.svg|thumb|The Ohio flag, a [[pennon]]]] |
|||
Flags are usually rectangular in shape (often in the ratio 2:3, 1:2, or 3:5), but may be of any shape or size that is practical for flying, including square, triangular, or swallow tailed. A more unusual flag shape is that of the [[flag of Nepal]], which is in the shape of two stacked triangles. Other unusual flag shapes include the [[flag of Ohio]] and the [[flag of Tampa, Florida|flag of Tampa]]. |
|||
[[File:Flag of Mauritania.svg|thumb|The [[flag of Mauritania]], a yellow crescent and star on a green field between two red stripes.]] |
|||
Flags are usually rectangular in shape (often in the ratio 2:3, 1:2, or 3:5), but may be of any shape or size that is practical for flying, including square, triangular, or swallow tailed. A more unusual flag shape is that of the [[flag of Nepal]], which is in the shape of two stacked triangles. Other unusually shaped flags include the civil flags of [[Flag of Ohio|Ohio]] (a [[Swallowtail (flag)|swallowtail]]); [[Flag of Tampa, Florida|Tampa, Florida]]; and [[Pike County, Ohio]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Pike|work=County Flags|publisher=[[Ohio Statehouse]] Museum|location=Columbus, Ohio|access-date=July 20, 2019|url=http://www.ohiostatehouse.org/museum/county-flags/pike}}</ref> |
|||
Many flags are dyed [[through and through]] to be inexpensive to manufacture, such that the reverse side is the [[mirror image]] of the [[obverse]] (front) side, generally the side displayed when the flag is flying flying from the observer's point of view from left, the side of the pole, to right. This presents two possibilities: |
|||
#If the design is [[symmetric]]al in an axis parallel to the flag pole, obverse and reverse will be identical despite the mirror-reversal, such as the [[flag of India|Indian Flag]] or [[Flag of Canada|Canadian Flag]] |
|||
#If not, the obverse and reverse will present two variants of the same design, one with the [[Flag terminology#Description of standard flag parts and terms|hoist]] on the left (usually considered the obverse side, see [[Flag terminology#Illustrations|flag illustrations]]), the other with the hoist on the right (usually considered the reverse side of the flag). This is very common and usually not disturbing if there is no text in the design. See also [[Flag of the United States#Reverse side flag|US reverse side flag]]. |
|||
{{flag image|Image = Flag of Kiribati.svg|Caption = The [[flag of Kiribati]], a [[banner of arms]]}} |
|||
Some complex flag designs are not intended for through and through implementation, requiring separate obverse and reverse sides if made correctly. In these cases there is a design element (usually text) which is not symmetric and should be read in the same direction, regardless of whether the hoist is to the viewer's left or right. These cases can be divided into two types: |
|||
#The same (asymmetric) design may be duplicated on both sides. Such flags can be manufactured by creating two identical through and through flags and then sewing them back to back, though this can affect the resulting combination's responsiveness to the wind. Depictions of such flags may be marked with the symbol [[File:IFIS Equal.svg]], indicating the reverse is congruent to (rather than a mirror image of) the obverse. |
|||
#Rarely, the reverse design may differ, in whole or in part, from that of the obverse. Examples are the [[flag of Paraguay]], the [[flag of Oregon]], and the historical [[flag of the Soviet Union]]. Depictions of such flags may be marked with the symbol [[File:IFIS Two-sided.svg]]. |
|||
{{See also|Flags whose reverse differs from the obverse}} |
|||
Many flags are dyed through and through to be inexpensive to manufacture, such that the reverse side is the [[mirror image]] of the [[obverse]] (front) side, generally the side displayed when, from the observer's point of view, the flag flies from pole-side left to right. This presents two possibilities: |
|||
<!--removed pending Guinness verification of the may 2010 Moroccan flag |
|||
# If the design is [[symmetric]]al in an axis parallel to the flag pole, obverse and reverse will be identical despite the mirror-reversal, such as the [[flag of India|Indian Flag]] or [[Flag of Canada|Canadian Flag]] |
|||
# If not, the obverse and reverse will present two variants of the same design, one with the [[Flag terminology#Description of standard flag parts and terms|hoist]] on the left (usually considered the obverse side), the other with the hoist on the right (usually considered the reverse side of the flag). This is very common and usually not disturbing if there is no text in the design. |
|||
Some complex flag designs are not intended to be shown on both sides, requiring separate obverse and reverse sides if made correctly. In these cases there is a design element (usually text) which is not symmetric and should be read in the same direction, regardless of whether the hoist is to the viewer's left or right. These cases can be divided into two types: |
|||
# The same (asymmetric) design may be duplicated on both sides. Such flags can be manufactured by creating two identical through and through flags and then sewing them back to back, though this can affect the resulting combination's responsiveness to the wind. Depictions of such flags may be marked with the symbol [[File:IFIS Equal.svg]], indicating the reverse is congruent to (rather than a mirror image of) the obverse. |
|||
# Rarely, the reverse design may differ, in whole or in part, from that of the obverse. Examples of [[flags whose reverse differs from the obverse]] include the [[flag of Paraguay]], the [[flag of Oregon]], and the historical [[flag of the Soviet Union]]. Depictions of such flags may be marked with the symbol [[File:IFIS Two-sided.svg]]. |
|||
<!--removed pending Guinness verification of the May 2010 Moroccan flag |
|||
{{flag image|Image = Israelisuperflag.jpg|Caption = The largest flag in the world, a [[flag of Israel]]}} |
{{flag image|Image = Israelisuperflag.jpg|Caption = The largest flag in the world, a [[flag of Israel]]}} |
||
/--> |
/--> |
||
[[File:Flag of Kiribati.svg|thumb|The [[flag of Kiribati]], a [[banner of arms]] ]] |
|||
Common designs on flags include crosses, stripes, and divisions of the surface, or ''field'', into bands or quarters—patterns and principles mainly derived from [[heraldry]]. A heraldic coat of arms may also be flown as a [[Banner#Heraldic banners|banner of arms]], as is done on both the state [[flag of Maryland]] and the [[flag of Kiribati]]. |
Common designs on flags include crosses, stripes, and divisions of the surface, or ''field'', into bands or quarters—patterns and principles mainly derived from [[heraldry]]. A heraldic coat of arms may also be flown as a [[Banner#Heraldic banners|banner of arms]], as is done on both the state [[flag of Maryland]] and the [[flag of Kiribati]]. |
||
The [[flag of Libya]], which |
The ''de jure'' [[flag of Libya]] under [[Muammar Gaddafi]], which consisted of a rectangular field of green, was for a long period the only national flag using a single colour and no design or insignia. However, other historical states have also used flags without designs or insignia, such as the short-lived [[Hungarian Soviet Republic|Soviet Republic of Hungary]] and the more recent [[Muscat and Oman|Sultanate of Muscat and Oman]], whose flags were both a plain field of red. |
||
Colours are normally described with common names, such as "red", but may be further specified using [[colorimetry|colourimetry]]. |
|||
The largest flag flown from a flagpole worldwide, according to Guinness World Records, is the [[flag of the United Arab Emirates]] flown in [[Sharjah]]. This flag was {{convert|2448.56|m2|abbr=on}}.<ref>{{cite web | title=Largest flag flown |date=28 March 2022 |url=http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/3000/largest-flag-flown}}</ref> The largest flag ever made was the [[flag of Qatar]]; the flag, which measures at {{convert|101,978|m2|abbr=on}}, was completed in December 2013 in [[Doha]].<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-middle-east-25414490|publisher=BBC|title=Qatar breaks record for world's largest flag|date=December 17, 2013|access-date=December 17, 2013}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Nanobayrak.jpg|thumb|left|The smallest flag of the world made by [[Nanophysics]] technology]] |
|||
===Parts of a flag=== |
|||
The smallest flag is believed to be a [[flag of Turkey]], being 700 nm wide (in comparison, a human hair is typically 50,000 nm in diameter). It was produced at the [[Bilkent University]] [[Nanophysics]] Department.<ref>{{cite news |title=Nano-Scale Turkish Flag Presented to Prime Minister Erdoğan |author= |newspaper=Bilkent News |date=May 2, 2006 |url=http://www.bilkent.edu.tr/~Bilnews/issue_12_27/index.html}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Glossary of vexillology}} |
|||
The general parts of a flag are: canton (the upper inner section of the flag), field or ground (the entire flag except the canton), the hoist (the edge used to attach the flag to the hoist), and the fly (the furthest edge from the hoist end).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.netstate.com/states/symb/flags/flag_terminology.htm|website=Flag Terminology|title=The Parts of a Flag|publisher=NSTATE|access-date=2019-08-02}}</ref> |
|||
===Vertical flags=== |
|||
Vertical flags are sometimes used in lieu of the standard horizontal flag in central and eastern Europe, particularly in the German-speaking countries. This practice came about because the relatively brisk wind needed to display horizontal flags is not common in these countries.<ref name=DGF>{{cite web|publisher=German Vexillological Society (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Flaggenkunde e. V., DGF)|url=http://www.flaggenkunde.de/deutscheflaggen/d-typ.htm|title=Flaggentypen|access-date=20 February 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Flag Types.svg|frameless|center|upright=1.25]] |
|||
The standard '''horizontal flag''' (no. 1 in the preceding illustration) is nonetheless the form most often used even in these countries.<ref>[[Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany)|German Federal Ministry of the Interior]]: ''[http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Hissflagge/hissflagge_node.html Hissflagge] {{Webarchive|url=https://archive.today/20120908125818/http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Hissflagge/hissflagge_node.html |date=2012-09-08 }}'', accessed 20 February 2012</ref> |
|||
[[File:NTB-Buchs-Campus with national and international flags.jpg|thumb|Vertical flags seen in Switzerland]] |
|||
The '''vertical flag''' (German: ''Hochformatflagge'' or ''Knatterflagge''; no. 2) is a vertical form of the standard flag. The flag's design may remain unchanged (No. 2a) or it may change, e.g. by changing horizontal stripes to vertical ones (no. 2b). If the flag carries an emblem, it may remain centred or may be shifted slightly upwards.<ref name=DGF /><ref>[[Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany)|German Federal Ministry of the Interior]]: ''[http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Hochformatflagge/hochformatflagge_node.html Hochformatflagge] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120803075053/http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Hochformatflagge/hochformatflagge_node.html |date=2012-08-03 }}'', accessed 20 February 2012</ref> |
|||
The '''vertical flag for hoisting from a beam''' (German: ''Auslegerflagge'' or ''Galgenflagge''; no. 3) is additionally attached to a horizontal beam, ensuring that it is fully displayed even if there is no wind.<ref name=DGF /><ref>[[Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany)|German Federal Ministry of the Interior]]: ''[http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Auslegerflagge/auslegerflagge_node.html Auslegerflagge] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120803085923/http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Auslegerflagge/auslegerflagge_node.html |date=2012-08-03 }}'', accessed 20 February 2012</ref> |
|||
The '''vertical flag for hoisting from a horizontal pole''' (German: ''Hängeflagge''; no. 4) is hoisted from a horizontal pole, normally attached to a building. The topmost stripe on the horizontal version of the flag faces away from the building.<ref name=DGF /><ref>[[Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany)|German Federal Ministry of the Interior]]: ''[http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Haengeflagge/haengeflagge_node.html Hängeflagge] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120803082212/http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Haengeflagge/haengeflagge_node.html |date=2012-08-03 }}'', accessed 20 February 2012</ref> |
|||
The '''vertical flag for hoisting from a crossbar''' or [[banner]] (German: ''Bannerflagge''; no. 5) is firmly attached to a horizontal crossbar from which it is hoisted, either by a vertical pole (no. 5a) or a horizontal one (no. 5b). The topmost stripe on the horizontal version of the flag normally faces to the left.<ref name=DGF /><ref>[[Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany)|German Federal Ministry of the Interior]]: ''[http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Haengeflagge/haengeflagge_node.html Hängeflagge] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120803082212/http://www.protokoll-inland.de/PI/DE/Beflaggung/Allgemeines/Haengeflagge/haengeflagge_node.html |date=2012-08-03 }}'', accessed 20 February 2012</ref> |
|||
==Religious flags== |
==Religious flags== |
||
{{See also|Religion in national symbols}} |
{{See also|Religion in national symbols}} |
||
{{flag image|Image = In-jain.svg|Caption = [[Jain flag|Jain – Five-Colored Flag]]}} |
|||
{{flag image|Image = Buddhist flag.svg|Caption = [[Buddhist flag|Buddhist Flag]]}} |
|||
Flags can play many different roles in religion. In [[Buddhism]], [[prayer flags]] are used, usually in sets of five differently colored flags. Many [[religion in national flags|national flags]] and other flags include religious symbols such as the cross, the crescent, or a reference to a patron saint. Flags are also adopted by religious groups and flags such as the [[Jain flag]] and the [[Christian flag]] are used to represent a whole religion. |
|||
Flags can play many different roles in religion. In [[Buddhism]], [[prayer flags]] are used, usually in sets of five differently coloured flags. Several flags and banners including the [[Black Standard]] are [[Islamic flags|associated with Islam]].<ref>{{cite book|title=Studies in Muslim Apocalyptic|url=https://archive.org/details/studiesmuslimapo00cook|url-access=limited|author=David Cook |year=2002|publisher=Darwin Press|page=[https://archive.org/details/studiesmuslimapo00cook/page/n105 197]|isbn=9780878501427}} from Majlisi,</ref> Many [[religion in national flags|national flags]] and other flags include religious symbols such as the [[List of flags with Christian symbolism|cross]], the [[Star and crescent|crescent]], or a reference to a patron saint.<ref>{{Cite web | url=http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2014/11/25/64-countries-have-religious-symbols-on-their-national-flags/ | title=64 countries have religious symbols on their national flags| date=25 November 2014}}</ref> Flags are also adopted by religious groups and flags such as the [[Jain flag]], [[Nishan Sahib]] ([[Sikhism]]),<ref>{{cite book |last1=Mayled |first1=Jon |title=Sikhism |date=2002 |publisher=Heinemann |isbn=978-0-435-33627-1 |page=24 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=H9jKt0dLz1IC |access-date=29 July 2024 |language=en}}</ref> the [[Bhagwa Dhwaj|Saffron flag]] ([[Hindu]])<ref>{{Cite web |date=28 October 2023 |title=The Bhagwa Dhwaj (Saffron Flag) |url=https://hssuk.org/the-bhagwa-dhwaj-saffron-flag/ |access-date=28 October 2023 |website=Hindu Swayamsevak Sangh (UK) |archive-date=3 December 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221203065338/https://hssuk.org/the-bhagwa-dhwaj-saffron-flag/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and the [[Christian flag]] are used to represent a whole religion.<ref>{{cite journal|year=1942|title=Resolution|journal=Federal Council Bulletin|publisher=Religious Publicity Service of the Federal Council of the Churches of Christ in America|volume=25-27}}</ref> |
|||
==Linguistic flags== |
|||
{{flag image|Image = Flag of La Francophonie.svg|Caption = Flag of La [[Francophonie]]}} |
|||
{{flag image|Image = Flag of the Hispanicity.svg|Caption = Flag of [[Hispanidad|Hispanicity]]}} |
|||
{{flag image|Image = Flag of Esperanto.svg|Caption = Flag of [[Esperanto]]}} |
|||
As languages rarely have a flag designed to represent them,<ref>[http://www.cs.tut.fi/~jkorpela/flags.html Why you should not use a flag as a symbol of language<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> it is a common but unofficial practice to use national flags to identify them. Examples of this use include: |
|||
* representing language skills of an individual, like a staff member of a company |
|||
* displaying available languages on a multilingual website or software. |
|||
Though this can be done in an uncontroversial manner in some cases, this can easily lead to some problems for certain languages: |
|||
* languages generating [[language dispute]], such as [[Romanian language|Romanian]] and [[Moldovan language|Moldavian]] which some consider two different languages; and |
|||
* languages spoken in [[World language|more than one country]], such as English, Arabic, French, German, Mandarin, Portuguese, Russian or Spanish. |
|||
In this second case, common solutions include symbolising these languages by: |
|||
* the flag of the country where the language originated |
|||
* the flag of the country having the largest number of native speakers |
|||
* a mixed flag of the both (when this is not the same) |
|||
* the flag of the country most identified with that language in a specific region (e.g. Portuguese Language: Flag of Portugal in Europe and Flag of Brazil in South America) |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
Thus, on the Internet, it is most common to see the English language associated to the [[flag of the United Kingdom]], but sometimes to the [[flag of England]], the [[flag of the United States]] or a US-UK mixed flag, usually divided diagonally. |
|||
File:Pro2.2.jpg|Poland (Gorzów Wlkp.). Religious flags |
|||
File:Christian flag.svg|[[Christian Flag|Christian flag]] adopted by several [[Protestantism|Protestant]] denominations |
|||
File:In-jain.svg|[[Jain flag]] (on occasion, the bottom black bar is replaced with a dark blue one) |
|||
File:Flag of Buddhism.svg|[[Buddhist flag]] |
|||
File:Nishan Sahib.svg|[[Nishan Sahib]] (the [[Sikhism|Sikh]] flag) |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
{{anchor|sport}} |
|||
==In sports== |
==In sports== |
||
[[File:Auto Racing Chequered.svg|thumb|150px|Flags flown at a car race]] |
|||
Because of their ease of signalling and identification, flags are often used in [[sport]]s. |
Because of their ease of signalling and identification, flags are often used in [[sport]]s. |
||
* In [[association football]], [[assistant referee (association football)|linesmen]] carry small flags along the touch lines. They use the flags to indicate to the [[Referee (Football)|referee]] potential infringements of the laws, or who is entitled to possession of the ball that has gone out of the field of play, or, most famously, raising the flag to indicate an [[offside law (football)|offside]] offence. Officials called ''touch judges'' use flags for similar purposes in both codes of [[Rugby football|rugby]]. |
|||
* In [[association football]], [[assistant referee (association football)|linesmen]] carry small flags along the touch lines. They use the flags to indicate to the [[Referee (Football)|referee]] potential infringements of the laws, or who is entitled to possession of the ball that has gone out of the field of play, or, most famously, raising the flag to indicate an [[offside (association football)|offside]] offence. Officials called ''touch judges'' use flags for similar purposes in both codes of [[Rugby football|rugby]]. |
|||
* In [[American Football|American]] and [[Canadian football]], [[referee]]s use [[penalty flag]]s to indicate that a foul has been committed in game play. The phrase used for such an indication is ''flag on the play''. The flag itself is a small, weighted handkerchief, tossed on the field at the approximate point of the infraction; the intent is usually to sort out the details after the current play from scrimmage has concluded. In American football, the flag is usually yellow; in Canadian football, it is usually orange. |
|||
* In [[American football|American]] and [[Canadian football]], [[referee]]s use [[penalty flag]]s to indicate that a foul has been committed in game play. The phrase used for such an indication is ''flag on the play''. The flag itself is a small, weighted handkerchief, tossed on the field at the approximate point of the infraction; the intent is usually to sort out the details after the current play from scrimmage has concluded. In American football, the flag is yellow; in Canadian football the flag is orange, but at the professional level the flag is yellow. In both the [[Canadian Football League]] and [[National Football League]], coaches also use red challenge flags to indicate that they wish to contest a ruling on the field. |
|||
* In [[yacht racing]], flags are used to communicate information from the race committee boat to the racers. Different flags hoisted from the committee boat may communicate a false start, changes in the course, a cancelled race, or other important information. Racing boats themselves may also use flags to symbolize a protest or distress. The flags are often part of the nautical alphabetic system of [[International maritime signal flags]], in which 26 different flags designate the 26 letters of the Latin alphabet. |
|||
* In [[yacht racing]], flags are used to communicate information from the race committee boat to the racers. Different flags hoisted from the committee boat may communicate a false start, changes in the course, a cancelled race, or other important information. Racing boats themselves may also use flags to symbolise a protest or distress. The flags are often part of the nautical alphabetic system of [[International maritime signal flags]], in which 26 different flags designate the 26 letters of the Latin alphabet. |
|||
[[File:Auto Racing Chequered.svg|thumb|Flag flown at a [[auto racing|car race]] ]] |
|||
* In [[auto racing|auto]] and [[Motorcycle sport|motorcycle racing]], [[racing flags]] are used to communicate with drivers. Most famously, a checkered flag of black and white squares indicates the end of the race, and victory for the leader. A yellow flag is used to indicate caution requiring slow speed and a red flag requires racers to stop immediately. A black flag is used to indicate penalties. |
* In [[auto racing|auto]] and [[Motorcycle sport|motorcycle racing]], [[racing flags]] are used to communicate with drivers. Most famously, a checkered flag of black and white squares indicates the end of the race, and victory for the leader. A yellow flag is used to indicate caution requiring slow speed and a red flag requires racers to stop immediately. A black flag is used to indicate penalties. |
||
| Line 137: | Line 183: | ||
* In addition, fans of almost all sports wave flags in the stands to indicate their support for the participants. Many sports teams have their own flags, and, in individual sports, fans will indicate their support for a player by waving the flag of his or her home country. |
* In addition, fans of almost all sports wave flags in the stands to indicate their support for the participants. Many sports teams have their own flags, and, in individual sports, fans will indicate their support for a player by waving the flag of his or her home country. |
||
* [[Capture the flag]] is a popular children's sport. |
* [[Capture the flag]] is a popular children's sport. |
||
* In [[Gaelic football]] and [[Hurling]] a green flag is |
* In [[Gaelic football]] and [[Hurling]] a green flag is used to indicate a goal while a white flag is used to indicate a point |
||
* In [[Australian rules football]], the [[Umpire (Australian rules football)|goal umpire]] will wave two flags to indicate a goal (worth six points) and a single flag to indicate a behind (worth one point). |
* In [[Australian rules football]], the [[Umpire (Australian rules football)|goal umpire]] will wave two flags to indicate a goal (worth six points) and a single flag to indicate a behind (worth one point). |
||
* For safety, [[ |
* For safety, [[diver down flag|dive flags]] indicate the locations of underwater [[SCUBA diving|scuba divers]] or that diving operations are being conducted in the vicinity. |
||
* In water sports such as |
* In water sports such as wakeboarding and Water-Skiing, an orange flag is held in between runs to indicate someone is in the water. |
||
* In [[golf]], the hole is almost always marked with a flag. The flagpole is designed to fit centered within the base of the hole and is removable. Many courses will use colour-coded flags to determine a hole location at the front, middle or rear of the green. However, colour-coded flags are not used in the professional tours. (A rare example of a golf course that does not use flags to mark the hole is the East Course of [[Merion Golf Club]], which instead uses flagpoles topped by [[Merion Golf Club#Wicker baskets|wicker baskets]].) |
|||
* Flag poles with flags of all shapes and sizes are used by marching bands, drum corps, and winter guard teams use flags as a method of visual enhancement in performances. |
* Flag poles with flags of all shapes and sizes are used by marching bands, drum corps, and winter guard teams use flags as a method of visual enhancement in performances. |
||
==Diplomatic and political flags== |
|||
==In politics== |
|||
{{Main|Diplomatic flag}} |
|||
{{flag image|Image = Gay flag.svg|Caption = The [[Rainbow flag]] of the [[LGBT]] social movement. A similar flag is used in Europe to support pacifism.}} |
|||
Social and political movements have adopted flags, to increase their visibility and as a unifying symbol. |
|||
Some countries use diplomatic flags, such as the United Kingdom <!--([[List of British flags#Diplomatic flags]])-->(see [[:File:British Ambassador Ensign.svg|image of the Embassy flag]]) and the Kingdom of [[Thailand]] <!--([[List of Thai flags#Diplomatic flags]])-->(see [[:File:Embassador Flag of Thailand.svg|image of the Embassy flag]]). |
|||
The [[Socialism|socialist]] movement uses [[red flag]]s to represent their cause. The [[Anarchism|anarchist]] movement has a variety of different flags, but the primary flag associated with them is the [[Anarchist symbolism#Black flag|black flag]]. In the 1970s, the [[Rainbow flag (gay movement)|rainbow flag]] was adopted as a symbol of the [[LGBT social movements]]. [[Bisexual pride flag|Bisexual]] and [[transgender pride flag]]s were later designed, in an attempt to emulate the rainbow flag's success. |
|||
The [[Socialism|socialist]] movement uses [[Red flag (politics)|red flag]]s to represent their cause. The [[Anarchism|anarchist]] movement has a variety of different flags, but the primary flag associated with them is the [[Anarchist symbolism#Black flag|black flag]]. In the [[Spanish Civil War]], the anarchists used the red-and-black bisected flag. In the 20th century, the [[Rainbow flag (gay movement)|rainbow flag]] was adopted as a symbol of the [[LGBT social movements]]. Its derivatives include the [[Bisexual pride flag|Bisexual pride]] and [[Transgender pride flag]]s. |
|||
Some of these political flags have become national flags, such as the red flag of the [[Soviet Union]] and national socialist banners for [[Nazi Germany]]. The present [[Flag of Portugal]] is based on what had been the political flag of the Portuguese Republican Party previous to the [[5 October 1910 revolution]] which brought this party to power. |
|||
Some of these political flags have become national flags, such as the red flag of the [[Soviet Union]] and national socialist banners for [[Nazi Germany]]. The present [[Flag of Portugal]] is based on what had been the political flag of the [[Portuguese Republican Party]] previous to the [[5 October 1910 revolution]] which brought this party to power. |
|||
==Personal flags== |
|||
[[File:Personal flag of Queen Elizabeth II.svg|thumb|Personal flag of Queen [[Elizabeth II]] ]] |
|||
Throughout history, [[monarchy|monarchs]] have often had personal flags (including [[royal standard]]s), representing the royal person, including in [[personal union]] of national monarchies. |
|||
==Vehicle flags== |
==Vehicle flags== |
||
Flags are often representative of an individual's affinity or allegiance to a country, team or business and can be presented in various ways. A popular trend that has surfaced revolves around the idea of the 'mobile' flag in which an individual displays their particular flag of choice on their vehicle. These items are commonly referred to as car flags and are usually manufactured from high strength polyester material and are attached to a vehicle via a polypropylene pole and clip window attachment. |
|||
==Swimming flags== |
==Swimming flags== |
||
[[File:Flags - swim between the.png|thumb|Open swimming area]] |
[[File:Flags - swim between the.png|thumb|Open swimming area]] |
||
[[File:Flags crossed - do not swim.png|thumb|Closed swimming area]] |
[[File:Flags crossed - do not swim.png|thumb|Closed swimming area]] |
||
[[File:Red flag at beach.jpg|thumb|upright|Red flag at a beach in Ireland, indicating that the water is not safe for swimming]] |
|||
In [[Australia]], [[Canada]], [[New Zealand]], [[Philippines]], and the [[United Kingdom]] a pair of red/yellow flags is used to mark the limits of the bathing area on a beach, usually guarded by [[surf lifesaving|surf lifesavers]]. If the beach is closed, the poles of the flags are crossed. The flags are colored with a red triangle and a yellow triangle making a rectangular flag, or a red rectangle over a yellow rectangle. On many Australian beaches there is a slight variation with beach condition signaling. A red flag signifies a closed beach (or, in the UK, some other danger), yellow signifies strong current or difficult swimming conditions, and green represents a beach safe for general swimming. In [[Ireland]], a red and yellow flag indicates that it is safe to swim; a red flag that it is unsafe; and no flag indicates that there are no lifeguards on duty. Blue flags may also be used away from the yellow-red lifesaver area to designate a zone for surfboarding and other small, non-motorised watercraft. |
|||
In Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the Philippines, Ireland and the United Kingdom, a pair of red-yellow flags is used to mark the limits of the bathing area on a beach, usually guarded by [[surf lifesaving|surf lifesavers]]. If the beach is closed, the poles of the flags are crossed. The flags are coloured with a red triangle and a yellow triangle making a rectangular flag, or a red rectangle over a yellow rectangle. On many Australian beaches there is a slight variation with beach condition signalling. A red flag signifies a closed beach (in the UK also other dangers), yellow signifies strong current or difficult swimming conditions, and green represents a beach safe for general swimming. In Ireland, a red and yellow flag indicates that it is safe to swim; a red flag that it is unsafe; and no flag indicates that there are no lifeguards on duty. Blue flags may also be used away from the yellow-red lifesaver area to designate a zone for surfboarding and other small, non-motorised watercraft. |
|||
Reasons for closing the beach include: |
Reasons for closing the beach include: |
||
* [[dangerous rip]] |
* [[dangerous rip]] |
||
* [[hurricane]] warning |
* [[hurricane]] warning |
||
| Line 171: | Line 227: | ||
[[International maritime signal flags|Signal flag]] "India" (a black circle on a yellow square) is frequently used to denote a "blackball" zone where surfboards cannot be used but other water activities are permitted. |
[[International maritime signal flags|Signal flag]] "India" (a black circle on a yellow square) is frequently used to denote a "blackball" zone where surfboards cannot be used but other water activities are permitted. |
||
The United States uses beach warning flags created by the [[International Life Saving Federation]] and endorsed and conditionally approved by the [[United States Lifesaving Association]].<ref>{{cite web|title=USLA Approved Beach Warning Flags|url=https://www.usla.org/page/beach-warning-flags|website=United States Lifesaving Association|access-date=August 31, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
==Railway flags== |
==Railway flags== |
||
Railways use a number of |
Railways use a number of coloured flags. When used as wayside signals they usually use the following meanings (exact meanings are set by the individual railroad company): |
||
* red = stop |
* red = stop |
||
* yellow = proceed with |
* yellow = proceed with caution |
||
* green or white = proceed. |
* green or white = proceed. |
||
* a flag of any |
* a flag of any colour waved vigorously means stop |
||
* a blue flag on the side of a locomotive means that it should not be moved because someone is working on it (or on the train attached to it). A blue flag on a track means that nothing on that track should be moved. The flag can only be removed by the person or group that placed it. |
* a blue flag on the side of a locomotive means that it should not be moved because someone is working on it (or on the train attached to it). A blue flag on a track means that nothing on that track should be moved. The flag can only be removed by the person or group that placed it. In the railway dominated steel industry this principle of "blue flag and tag" was extended to all operations at Bethlehem Steel, [[Lackawanna, New York]]. If a man went inside a large machine or worked on an electrical circuit for example, his blue flag and tag was sacrosanct.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.oshrc.gov/decisions/html_1990/79-2597.html|title=Docket No. 79-2597|access-date=2010-06-27|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100527155228/http://www.oshrc.gov/decisions/html_1990/79-2597.html|archive-date=2010-05-27|url-status=dead}}</ref> The "[[Lockout-tagout|Lock Out/Tag Out]]" practice is similar and now used in other industries to comply with safety regulations. |
||
* In the railway dominated steel industry this principle of "blue flag and tag" was extended to all operations at Bethlehem Steel, Lackawanna, NY. If a man went inside a large machine or worked on an electrical circuit for example, his blue flag and tag was sacrosanct. see: http://www.oshrc.gov/decisions/html_1990/79-2597.html |
|||
At night, the flags are replaced with lanterns showing the same |
At night, the flags are replaced with lanterns showing the same colours. |
||
Flags displayed on the front of a moving locomotive are an acceptable replacement for classification lights and usually have the following meanings (exact meanings are set by the individual railroad company): |
Flags displayed on the front of a moving locomotive are an acceptable replacement for classification lights and usually have the following meanings (exact meanings are set by the individual railroad company): |
||
* white = extra (not on the timetable) |
* white = extra (not on the timetable) |
||
* green = another section following |
* green = another section following |
||
* red = last section |
* red = last section |
||
Additionally, a railroad brakeman will typically carry a red flag to make his or her hand signals more visible to the engineer. [[Railway signal]]s are a development of railway flags.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://mysite.du.edu/~etuttle/rail/sigs.htm |title=Early Railway Signals | |
Additionally, a railroad brakeman will typically carry a red flag to make his or her hand signals more visible to the engineer. [[Railway signal]]s are a development of railway flags.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://mysite.du.edu/~etuttle/rail/sigs.htm |title=Early Railway Signals |access-date=7 October 2007 |last=Calvert |first=J.B. |date=25 July 2004 |publisher=University of Denver }}</ref> |
||
==Flagpoles== |
==Flagpoles== |
||
{{ |
{{main|Flagpole}} |
||
[[File:SienaFlagpole1.jpg|thumbnail|One of the two 60-foot-tall flagpoles in the [[Siena Cathedral]]. During the [[battle of Montaperti]] (1260), Bocca degli Abati, a Sienese spy, brought Florence's flag down, causing panic among the Florentine soldiers and ultimately their defeat.]] |
|||
[[File:BayraqMeydani.jpg|thumb|The world's tallest [[flagpole]] flying a [[Flag of Azerbaijan]]. ]] |
|||
A flagpole, flagstaff, or staff can be a simple support made of wood or metal. If it is taller than can be easily reached to raise the flag, a cord is used, looping around a pulley at the top of the pole with the ends tied at the bottom. The flag is fixed to one lower end of the cord, and is then raised by pulling on the other end. The cord is then tightened and tied to the pole at the bottom. The pole is usually topped by a flat plate or ball called a "truck" (originally meant to keep a wooden pole from splitting) or a [[finial]] in a more complex shape. |
|||
A flagpole, flagmast, flagstaff, or staff can be a simple support made of wood or metal. If it is taller than can be easily reached to raise the flag, a cord is used, looping around a pulley at the top of the pole with the ends tied at the bottom. The flag is fixed to one lower end of the cord, and is then raised by pulling on the other end. The cord is then tightened and tied to the pole at the bottom. The pole is usually topped by a flat plate or ball called a "[[Truck (rigging)|truck]]" (originally meant to keep a wooden pole from splitting) or a [[finial]] in a more complex shape. Very high flagpoles may require more complex support structures than a simple pole, such as a [[guyed mast]]. |
|||
[[Dwajasthambam]] are flagpoles commonly found at the entrances of [[South India]]n [[Hindu temple]]s.<ref>[[Alf Hiltebeitel|Hiltebeitel, Alf]] (1991). ''[https://books.google.com/books?id=diPh4qYtjPUC The Cult of Draupadi, Volume 2: On Hindu Ritual and the Goddess]''. University of Chicago Press. {{ISBN|0226340473}}. pp. 91–92.</ref> |
|||
===Record heights=== |
|||
[[File:Flagpole, Kew Gardens - geograph.org.uk - 227188.jpg|thumb|upright|left|The former flagpole in Kew Gardens, taken shortly before its removal in 2007]] |
|||
Since 26 December 2021, the [[List of flagpoles by height|tallest free-standing flagpole]] in the world is the Cairo Flagpole, located in the [[New Administrative Capital]] under construction in [[Egypt]] at a height of {{convert|201.952|m|ft|abbr=on}}, exceeding the former record holders, the [[Jeddah Flagpole]] in [[Saudi Arabia]] (height: {{convert|171|m|ft|abbr=on|disp=semicolon}}), the [[Dushanbe Flagpole]] in [[Tajikistan]]<ref name="Jeddah Flagpole">{{cite web|url=http://www.arabnews.com/saudi-arabia/news/634401 |title= Jeddah Flagpole inaugurated|publisher=arabnews.com |access-date=2014-09-23}}</ref><ref>Former record: {{cite web |title=Wer baut den hoechsten Fahnenmast |date=September 9, 2008 |url=http://news.tj/ru/news/v-dushanbe-na-samom-vysokom-flagshtoke-v-mire-podnyat-flag-foto |publisher=Asia Plus |access-date=May 24, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190404114645/https://news.tj/ru/news/v-dushanbe-na-samom-vysokom-flagshtoke-v-mire-podnyat-flag-foto |archive-date=April 4, 2019 |url-status=dead }}</ref> (height: {{convert|165|m|ft|abbr=on|disp=semicolon}}) and the [[National Flag Square|National Flagpole]] in [[Azerbaijan]] (height: {{convert|162|m|ft|abbr=on|disp=semicolon}}).<ref>{{cite web |title=Flag of Azerbaijan |date=July 3, 2008 |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/tajikistan/8157189/Tajikistan-takes-flag-pole-war-to-new-heights.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220111/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/tajikistan/8157189/Tajikistan-takes-flag-pole-war-to-new-heights.html |archive-date=2022-01-11 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |publisher=Telegraph.co.uk}}{{cbignore}}</ref> The flagpole in North Korea is the fourth tallest flagpole in the world, however, it is not free-standing. It is a radio tower supported flagpole. Many of these were built by American company Trident Support: the Dushanbe Flagpole, the National Flagpole in Azerbaijan, the [[Ashgabat Flagpole|Ashgabat flagpole]] in Turkmenistan at {{convert|133|m|ft|abbr=on}}; the [[Aqaba Flagpole]] in Jordan at {{convert|130|m|ft|abbr=on}}; the [[Raghadan Flagpole]] in Jordan at {{convert|126.8|m|ft|abbr=on}}; and the Abu Dhabi Flagpole in the United Arab Emirates at {{convert|122|m|ft|abbr=on}}.<ref>{{cite web|date=2017-09-05|title=Looking for Afghanistan? Turn Left at the Enormous Flagpole|url=https://www.nationalgeographic.org/projects/out-of-eden-walk/articles/2017-09-looking-afghanistan-turn-left-enormous-flagpole/?sf111671937=1#!|website=National Geographic}}</ref> |
|||
Very high flagpoles may require more complex support structures than a simple pole, such as guy wires, or need be built as a mast. |
|||
The current tallest flagpole in India (and the tallest flying the tricolour) is the {{convert|110|m|ft|adj=on}} flagpole in [[Belgaum]], Karnataka which was first hoisted on 12 March 2018.<ref>{{cite web |title=Karnataka's Belgaum is now home to India's tallest flag |url=https://www.timesnownews.com/the-buzz/article/tallest-flag-in-india-attari-border-indian-national-flag-belgaum-ramesh-jarkiholi-largest-biggest-flagpole-flag-hoisting-rules-and-regulation/206890 |website=Times Now News |date=13 March 2018 |access-date=6 July 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=Mar 12, 2018|title=Tallest flag in India: Country's tallest tricolour to be hoisted in Belagavi |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/hubballi/countrys-tallest-tricolour-to-be-hoisted-in-belagavi/articleshow/63249848.cms |website=The Times of India |access-date=6 July 2019 |language=en}}</ref> The tallest flagpole in the United Kingdom from 1959 until 2013 stood in [[Kew Gardens]]. It was made from a Canadian Douglas-fir tree and was {{convert|68.5|m|ft|abbr=on}} in height.<ref>{{cite web| title=Timber! Steeplejacks to dismantle Kew Flagpole|url=http://www.kew.org/press/flagpole.html| publisher=Kew.org| url-status=dead| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160817234628/http://www.kew.org/press/flagpole.html| archive-date=2016-08-17}}</ref> |
|||
Since 2010 with 162 m (532 ft) the tallest free-standing flagpole in the world is the [[National Flag Square|National Flagpole]] in [[Azerbaijan]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Wer baut den hoechsten Fahnenmast |date=September 9, 2008 |url=http://www.spiegel.de/fotostrecke/fotostrecke-35119.html |publisher=Der Spiegel}}</ref>, beating the formerly record holding [[Ashgabat Flagpole]] in [[Turkmenistan]] (size: 133 m; 436 ft).<ref>{{cite web |title=Flag of Turkmenistan |date=July 3, 2008 |url=http://turkmenistan.gov.tm/_eng/2008/07/03/flag_of_turkmenistan_at_the_tallest_flagpole_in_the_world.html |publisher=Official Homepage of the Republic of Turkmenistan}}</ref> The [[Aqaba Flagpole]]in [[Jordan]] (size: 132 m; 433 ft) is currently the third and the [[Raghadan Flagpole]] in [[Amman]] is the fourth tallest free-standing flagpole in the world. The latter reaches a height of 126 m (410 ft); it is illuminated at night and can be seen from 25 km (16 miles) away. |
|||
The current tallest flagpole in the United States (and the tallest flying an American flag) is the {{convert|400|ft|m|adj=on}} pole completed before [[Memorial Day]] 2014 and custom-made with an {{convert|11|ft|m|adj=on}} base in concrete by [[wind turbine]] manufacturer Broadwind Energy. It is situated on the north side of the [[Acuity Insurance]] headquarters campus along [[Interstate 43]] in [[Sheboygan, Wisconsin]], and is visible from [[Cedar Grove, Wisconsin|Cedar Grove]]. The pole can fly a 220-pound flag in light wind conditions and a heavier 350-pound flag in higher wind conditions.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.sheboyganpress.com/article/20140525/SHE0101/305250197/High-flying-Up-time-Memorial-Day-Acuity-flag-world-s-tallest|title=High-flying: Up in time for Memorial Day, Acuity flag is world's tallest|last=Weyandt|first=Janet|date=25 May 2014|work=[[The Sheboygan Press]]|access-date=26 May 2014|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150403170745/http://www.sheboyganpress.com/article/20140525/SHE0101/305250197/High-flying-Up-time-Memorial-Day-Acuity-flag-world-s-tallest|archive-date=3 April 2015}}</ref> |
|||
The largest flag regularly hoisted in the world is the Brazilian national flag flown in the [[Praça dos Três Poderes|Square of the Three Powers]] in [[Brasilia]], Brazilian capital. This flag is about 3380 square meters (8740 square feet){{cn|date=January 2011}} and has never come down since opening in the mid 1960s. |
|||
===Design=== |
===Design=== |
||
Flagpoles can be designed in one piece with a taper (typically a steel taper or a [[entasis|Greek entasis]] taper),<ref>{{cite web | |
Flagpoles can be designed in one piece with a taper (typically a steel taper or a [[entasis|Greek entasis]] taper),<ref>{{cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050228014231/http://lingoinc.com/tapers.htm |archive-date=2005-02-28 |url=http://lingoinc.com/tapers.htm |title=Cone Tapered vs. Venetian Entasis Tapered |publisher=Lingo Flagpoles Inc}}</ref> or be made from multiple pieces to make them able to expand. In the United States, [[ANSI|ANSI/NAAMM]] guide specification FP-1001-97 covers the engineering design of metal flagpoles to ensure safety. |
||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> |
|||
==Flags and communication== |
|||
File:Bickleigh , Bickleigh Maize Maze - Flagpole - geograph.org.uk - 1223767.jpg|Flagpole of modest size, with simple [[Truck (rigging)|truck]] |
|||
[[Flag semaphore|Semaphore]] is a form of communication that utilizes flags. The signalling is performed by an individual using two flags (or lighted wands), the positions of the flags indicating a symbol. The person who holds the flags is known as the signalman. This form of communication is primarily used by [[navy|naval]] signallers. This technique of signalling was adopted in the early 19th century and is still used in various forms today. |
|||
File:New Zealand flag at Auckland Airport.jpg|Large flagpole, showing structured [[Truck (rigging)|truck]] (New Zealand) |
|||
File:Two official flags of New Caledonia on same flagpole.png|[[New Caledonia]] has two flags, flown here in [[Nouméa]], the capital city, on a single flagpole with a crossbar |
|||
File:Thanjavur periya kovil-tamil nadu.JPG|[[Dwajasthambam]] (flagpole) at [[Brihadeeswarar Temple]] in [[Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu]], India |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
==Hoisting the flag== |
|||
The colors of the flags can also be used to communicate. For example; a white flag means, among other things, surrender or peace, a red flag can be used as a warning signal, and a black flag can mean war, or determined to defeat enemies. |
|||
[[File:Australia Day Citizenship Ceremony 2011 (5475200349).jpg|thumb|[[Flag of Australia]] at a flag-hoisting ceremony on [[Australian Citizenship Day]] 2011]] |
|||
Hoisting the flag is the act of raising the flag on the flagpole. Raising or lowering flags, especially national flags, usually involves ceremonies and certain sets of rules, depending on the country, and usually involve the performance of a [[national anthem]]. |
|||
Orientation of a flag is also used for communication, though the practice is rarely used given modern communication systems. Raising a flag upside-down was indicative that the raising force controlled that particular area, but that it was in severe distress. |
|||
A flag-raising squad is a group of people, usually troops, cadets, or students, that march in and bring the flags for the flag-hoisting ceremony. Flag-hoisting ceremonies involving flag-raising squads can be simple or elaborate, involving large numbers of squads. Elaborate flag-hoisting ceremonies are usually performed on national holidays. |
|||
The cord or rope that ties a flag to its pole is called a halyard. Flags may have a strip of fabric along the hoist side called a ''heading'' for the halyard to pass through, or a pair of [[grommet]]s for the halyard to be threaded through. Flags may also be held in position using [[Inglefield clip]]s.<ref>Inglefield, p. 12.</ref> |
|||
==Flags in communication== |
|||
[[File:Semaphore Signals A-Z.jpg|thumb|right|Semaphore signals for the letters of the English alphabet]] |
|||
[[Flag semaphore|Semaphore]] is a form of communication that utilises flags. The signalling is performed by an individual using two flags (or lighted wands), the positions of the flags indicating a symbol. The person who holds the flags is known as the signalman. This form of communication is primarily used by [[navy|naval]] signallers. This technique of signalling was adopted in the early 19th century and is still used in various forms today.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.anbg.gov.au/flags/semaphore.html|title=Semaphore Flag Signalling System|publisher=ANBG.gov.au|access-date=31 March 2017}}</ref> |
|||
The colours of the flags can also be used to communicate. For example; a white flag means, among other things, surrender or peace, a red flag can be used as a warning signal, and a black flag can mean war, or determination to defeat enemies. |
|||
Orientation of a flag is also used for communication, though the practice is rarely used given modern communication systems. Raising a flag upside-down was indicative that the raising force controlled that particular area, but that it was in severe distress.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.military.com/flag-day/flag-ettiquette-dos-and-donts.html|title=Flag Etiquette Do's and Don'ts|last=Scanlon|first=Caitlin|work=Military.com|access-date=2017-10-05|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 215: | Line 298: | ||
* [[Gallery of sovereign state flags]] |
* [[Gallery of sovereign state flags]] |
||
* [[List of flag names]] |
* [[List of flag names]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Lists of flags]] |
||
* [[List of flags by country]] |
|||
* [[Timeline of national flags]] |
* [[Timeline of national flags]] |
||
* [[Unofficial flags]] |
|||
;Notable flag-related topics |
;Notable flag-related topics |
||
* [[Flag families]] |
|||
* [[False flag]] |
* [[False flag]] |
||
* [[Flag Day]] |
* [[Flag Day]] |
||
* [[Flag desecration]] |
* [[Flag desecration]] |
||
* [[Flag |
* [[Flag protocol]] |
||
* [[Flag |
* [[Flag patch]] |
||
* [[Flag semaphore]] |
* [[Flag semaphore]] |
||
* [[Flag terminology]] |
|||
* [[Flag throwing]] |
* [[Flag throwing]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Glossary of vexillology]] |
||
* [[Pledge of Allegiance (United States)]] |
|||
* [[Standard-bearer]] (also enumerates various types of standards, both flag types and immobile ensigns) |
* [[Standard-bearer]] (also enumerates various types of standards, both flag types and immobile ensigns) |
||
* [[Vexillology]] |
* [[Vexillology]] |
||
* [[Flags of the World (website)|Flags of the World]], an Internet-based vexillological association and resource |
|||
* [[Windsock]] |
|||
== Citations == |
|||
;Miscellaneous |
|||
* [[Petrosomatoglyph]] Symbols and prehistory |
|||
* [[Jolly Roger]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
== General and cited references == |
|||
* [http://www.anbg.gov.au/flags/semaphore.html Australian Botany pages] |
|||
*Inglefield, Eric (1979 edition). ''Flags''. Ward Lock, London. {{ISBN|0706356527}} |
|||
* William G. Crampton; ''The World of Flags''; Rand McNally; ISBN 0-528-83720-6 (hardcover, 1994). |
|||
* [http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1E1-Morse-Sa.html Samuel Finley Breese Morse] |
|||
* ''Ultimate Pocket Flags of the World''; [[Dorling Kindersley]]; ISBN 0-7894-2085-6; (1st American edition, hardcover, 1996). |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{ |
{{Wikidata property| P163}} |
||
{{commons category|Flags}} |
|||
* [http://www.cyber-flag.net Cyberflag] |
|||
{{Wikiquote}} |
|||
* [http://flags.redpixart.com Flag icons and images] |
|||
* [http://www.anbg.gov.au/flags/signal-flags.html International Marine Signal Flags] |
|||
* [http://www.flagid.org Flag Identifier], tool for identifying a given flag |
|||
* [http://flagman.org.uk/news/ Flag news and views] |
|||
* [http://flagsforum.skalman.nu Flags Forum], discussion forum |
|||
* [http://flagpedia.net Flags of all countries] |
|||
* [http://flagsbylouis.blogspot.com Flags of the world], Flag images |
|||
* [http://www.fotw.net Fotw.net], [[Flags of the World]], an outstanding source of vexillological information, contributed to by a group of international volunteers. |
|||
* [http://www.usflagandbanner.com/flag-glossary.php Glossary of Flag Terms and Phrases] |
|||
* [http://www.rbvex.it/indice.html Historical World Flags all countries Database] |
|||
* [http://flags.otago.ac.nz Interactive Flag Design], interactive flag design page using evolutionary algorithms |
|||
* [http://holidayyear.com/flags.php List of all Country Flags] |
|||
* [http://www.flags.net World Flag Database] |
|||
* [http://flagslist.com World Flags List & World map] |
|||
* [http://www.flagsinformation.com World Flags Information & Database of Demographic Information for 240+ Countries] |
|||
{{Vexillology}} |
|||
{{ |
{{Authority control}} |
||
[[Category:Flags| ]] |
[[Category:Flags| ]] |
||
[[Category:Articles containing video clips]] |
|||
[[Category:National symbols]] |
[[Category:National symbols]] |
||
[[Category:Vexillology]] |
|||
[[af:Vlag]] |
|||
[[als:Flagge]] |
|||
[[am:ሰንደቅ ዓላማ]] |
|||
[[ar:علم (راية)]] |
|||
[[arc:ܐܬܐ]] |
|||
[[az:Bayraq]] |
|||
[[bn:পতাকা]] |
|||
[[be:Сцяг]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Сьцяг]] |
|||
[[bar:Flaggn]] |
|||
[[bs:Zastava]] |
|||
[[br:Banniel]] |
|||
[[bg:Знаме]] |
|||
[[ca:Bandera]] |
|||
[[cv:Ялав]] |
|||
[[cs:Vlajka]] |
|||
[[cbk-zam:Bandera]] |
|||
[[cy:Baner]] |
|||
[[da:Flag]] |
|||
[[pdc:Faahne]] |
|||
[[de:Flagge]] |
|||
[[et:Lipp]] |
|||
[[el:Σημαία]] |
|||
[[es:Bandera]] |
|||
[[eo:Flago]] |
|||
[[eu:Bandera]] |
|||
[[fa:پرچم]] |
|||
[[hif:Jhanda]] |
|||
[[fr:Drapeau]] |
|||
[[fy:Flagge]] |
|||
[[gv:Brattagh]] |
|||
[[gl:Bandeira]] |
|||
[[ko:깃발]] |
|||
[[haw:Hae]] |
|||
[[hy:Դրոշ]] |
|||
[[hi:ध्वज]] |
|||
[[hr:Zastava]] |
|||
[[io:Flago]] |
|||
[[bpy:বানডেইরা]] |
|||
[[id:Bendera]] |
|||
[[iu:ᓴᐃᒻᒪᑎ/saimmati]] |
|||
[[os:Тырыса]] |
|||
[[is:Fáni]] |
|||
[[it:Bandiera]] |
|||
[[he:דגל]] |
|||
[[kl:Erfalasoq]] |
|||
[[pam:Bandera]] |
|||
[[krc:Байракъ]] |
|||
[[ka:დროშა]] |
|||
[[rw:Ibendera]] |
|||
[[sw:Bendera]] |
|||
[[kv:Дӧрапас]] |
|||
[[ht:Drapo]] |
|||
[[lbe:Ттугъ]] |
|||
[[la:Vexillum]] |
|||
[[lv:Karogs]] |
|||
[[lt:Vėliava]] |
|||
[[ln:Bɛndɛ́lɛ]] |
|||
[[hu:Zászló]] |
|||
[[ml:പതാക]] |
|||
[[mr:झेंडा]] |
|||
[[arz:علم]] |
|||
[[ms:Bendera]] |
|||
[[mwl:Bandeira]] |
|||
[[nah:Pāmitl]] |
|||
[[nl:Vlag]] |
|||
[[nds-nl:Vlagge]] |
|||
[[new:ध्वांय्]] |
|||
[[ja:旗]] |
|||
[[no:Flagg]] |
|||
[[nn:Flagg]] |
|||
[[nrm:Couleu]] |
|||
[[oc:Bandièra]] |
|||
[[mhr:Тисте]] |
|||
[[uz:Bayroq]] |
|||
[[pl:Flaga]] |
|||
[[pt:Bandeira]] |
|||
[[ro:Drapel]] |
|||
[[qu:Unancha]] |
|||
[[ru:Флаг]] |
|||
[[sq:Flamuri]] |
|||
[[scn:Bannera]] |
|||
[[simple:Flag]] |
|||
[[sk:Zástava]] |
|||
[[cu:Ꙁна́мѧ]] |
|||
[[sl:Zastava]] |
|||
[[szl:Fana]] |
|||
[[so:Calan]] |
|||
[[sr:Застава]] |
|||
[[sh:Zastava]] |
|||
[[fi:Lippu]] |
|||
[[sv:Flagga]] |
|||
[[tl:Watawat]] |
|||
[[ta:கொடி (சின்னம்)]] |
|||
[[th:ธง]] |
|||
[[chr:ᎦᏓᏘ]] |
|||
[[tr:Bayrak]] |
|||
[[uk:Прапор]] |
|||
[[ur:جھنڈا]] |
|||
[[vec:Bandiera]] |
|||
[[vi:Cột cờ]] |
|||
[[vo:Stän]] |
|||
[[fiu-vro:Lipuq]] |
|||
[[wa:Drapea]] |
|||
[[yi:פאן]] |
|||
[[yo:Àsìá]] |
|||
[[zh:旗幟]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 17:24, 18 December 2024


A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term flag is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families.[1] The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin vexillum, meaning "flag" or "banner".
National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes.
Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A flag (Arabic: لواء) is equivalent to a brigade in Arab countries. In Spain, a flag (Spanish: bandera) is a battalion-equivalent in the Spanish Legion.[citation needed]
History

The origin of the flag is unknown[2] and it remains unclear when the first flag was raised.[3] Ships with vexilloids were represented on predynastic Egyptian pottery c. 3500 BC.[3] In antiquity, field signs that can be categorised as vexilloid or "flag-like" were used in warfare, originating in ancient Egypt or Assyria.[4] Examples include the Sassanid battle standard Derafsh Kaviani, and the standards of the Roman legions such as the eagle of Augustus Caesar's Xth legion and the dragon standard of the Sarmatians; the latter was allowed to fly freely in the wind, carried by a horseman, but depictions suggest that it bore more similarity to an elongated dragon kite than to a simple flag.
While the origin of the flag remains a mystery, the oldest flag discovered is made of bronze: a Derafsh or 'flag-like' Shahdad, which was found in Shahdad, Iran, and dates back to c. 2400 BC. It features a seated man and a kneeling woman facing each other, with a star in between. This iconography was found in other Iranian Bronze Age pieces of art.[5][6][7][8]
Flags made of cloth were almost certainly[4] the invention of the ancient peoples of the Indian subcontinent or the Zhou dynasty of Ancient China. Chinese flags had iconography such as a red bird, a white tiger, or a blue dragon, and royal flags were to be treated with a level of respect similar to that given to the ruler. Indian flags were often triangular and decorated with attachments such as a yak's tail and the state umbrella.[further explanation needed] Silk flags either spread to the Near East from China or it was just the silk itself, later fashioned by people who had independently conceptualized a rectangular cloth attached to a pole.[9] Flags were probably transmitted to Europe via the Muslim world, where plainly coloured flags were used due to Islamic proscriptions. They are often mentioned in the early history of Islam and may have been copied from India.[4]
In Europe, during the High Middle Ages, flags came to be used primarily as a heraldic device in battle, allowing easier identification of a knight over only the heraldic icon painted on the shield. Already during the high medieval period, and increasingly during the Late Middle Ages, city states and communes such as those of the Old Swiss Confederacy also began to use flags as field signs. Regimental flags for individual units became commonplace during the Early Modern period.

During the peak of the sailing age, beginning in the early 17th century, it was customary (and later a legal requirement) for ships to fly flags designating their nationality;[10] these flags eventually evolved into the national flags and maritime flags of today. Flags also became the preferred means of communications at sea, resulting in various systems of flag signals; see, International maritime signal flags.
Use of flags beyond a military or naval context began with the rise of nationalism by the end of the 18th century, although some flags date back earlier. The flags of countries such as Austria, Denmark or Turkey have legendary origins while many others, including those of Poland and Switzerland, grew out of the heraldic emblems of the Middle Ages. The 17th century saw the birth of several national flags through revolutionary struggle. One of these was the flag of the Netherlands, which appeared during the 80-year Dutch rebellion which began in 1568 against Spanish domination.[11]
Political change and social reform, allied with a growing sense of nationhood among ordinary people, led to the creation of new nations and flags all over the world in the 19th and 20th centuries.[12]
National flags


One of the most popular uses of a flag is to symbolise a nation or country. Some national flags have been particularly inspirational to other nations, countries, or subnational entities in the design of their own flags. Some prominent examples include:

- The flag of Denmark, the Dannebrog, is attested in 1478, and is the oldest national flag still in use.[13] It inspired the cross design of the other Nordic countries: Norway, Sweden, Iceland, Finland, and regional Scandinavian flags for the Faroe Islands, Åland, Scania and Bornholm, as well as flags for the non-Scandinavian Shetland and Orkney.[14][15]
- The flag of the Netherlands is the oldest tricolour. Its three colours of red, white and blue go back to Charlemagne's time, the ninth century. The coastal region of what today is the Netherlands was then known for its cloth in these colours. Maps from the early 16th century already put flags in these colours next to this region, like Texeira's map of 1520. A century before that, during the 15th century, the three colours were mentioned as the coastal signals for this area, with the three bands straight or diagonal, single or doubled. As state flag it first appeared around 1572 as the Prince's Flag in orange–white–blue. Soon the more famous red–white–blue began appearing, becoming the prevalent version from around 1630. Orange made a comeback during the civil war of the late 18th century, signifying the orangist or pro-stadtholder party. During World War II the pro-Nazi NSB used it. Any symbolism has been added later to the three colours, although the orange comes from the House of Orange-Nassau. This use of orange comes from Nassau, which today uses orange-blue, not from Orange, which today uses red-blue. However, the usual way to show the link with the House of Orange-Nassau is the orange pennant above the red-white-blue. It is said that the Dutch Tricolour has inspired[16][citation needed] many flags but most notably those of Russia, New York City, and South Africa (the 1928–94 flag as well the current flag). As the probable inspiration for the Russian flag, it is the source too for the pan-Slavic colours red, white and blue, adopted by many Slavic states and peoples as their symbols; examples are Slovakia, Serbia, and Slovenia.[17]
- The national flag of France was designed in 1794. As a forerunner of revolution, France's tricolour flag style has been adopted by other nations. Examples: Italy, Belgium, Ireland, Romania and Mexico.[citation needed]
- The Union Flag (Union Jack) of the United Kingdom is the most commonly used. British colonies typically flew a flag based on one of the ensigns based on this flag, and many former colonies have retained the design to acknowledge their cultural history. Examples: Australia, Fiji, New Zealand, Tuvalu, and also the Canadian provinces of Manitoba, Ontario and British Columbia, and the American state of Hawaii; see commons:Flags based on British ensigns.
- The flag of the United States is nicknamed The Stars and Stripes or Old Glory.[18] Some nations imitated this flag to symbolise their similarity to the United States or the American Revolution. Examples: Liberia,[19] Chile, Taiwan (ROC), and the French region of Brittany.

- Ethiopia was seen as a model by emerging African states of the 1950s and 1960s, as it was one of the oldest independent states in Africa. Accordingly, its flag became the source of the Pan-African colours, or 'Rasta colours'. Examples: Benin, Togo, Senegal, Ghana, Mali, Guinea.
- The flag of Turkey, which is very similar to the last flag of the old Ottoman Empire, has been an inspiration for the flag designs of many other Muslim nations. During the time of the Ottomans the crescent began to be associated with Islam and this is reflected on the flags of Algeria, Azerbaijan, Comoros, Libya, Mauritania, Pakistan, Tunisia and Maldives.[20]
- The Pan-Arab colours, green, white, red and black, are derived from the flag of the Great Arab Revolt as seen on the flags of Jordan, Libya, Kuwait, Sudan, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, Western Sahara, Egypt, Iraq, Yemen and Palestine.
- The Soviet flag, with its golden symbols of the hammer and sickle on a red field, was an inspiration to flags of other communist states, such as East Germany, the People's Republic of China, Vietnam, Angola, Afghanistan (1978–1980) and Mozambique.
- The flag of Venezuela, created by Francisco de Miranda to represent the independence movement in Venezuela that later gave birth to the Gran Colombia, inspired the flags of Colombia, Ecuador, and the Federal Territories in Malaysia, all sharing three bands of yellow, blue and red with the flag of Venezuela.
- The flag of Argentina, created by Manuel Belgrano during the war of independence, was the inspiration for the United Provinces of Central America's flag, which in turn was the origin for the flags of Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, and Nicaragua.
National flag designs are often used to signify nationality in other forms, such as flag patches.
Civil flags
A civil flag is a version of the national flag that is flown by civilians on non-government installations or craft. The use of civil flags was more common in the past, in order to denote buildings or ships that were not crewed by the military. In some countries the civil flag is the same as the war flag or state flag, but without the coat of arms, such as in the case of Spain, and in others it is an alteration of the war flag.
War flags

Several countries, including the Royal Air Force, British Army and the Royal Navy (White Ensign) of the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union have had unique flags flown by their armed forces separately, rather than the national flag.
Other countries' armed forces (such as those of the United States or Switzerland) use their standard national flag; in addition, the U.S. has alongside flags and seals designed from long tradition for each of its six uniformed military services/military sub-departments in the Department of Defense and the Department of Homeland Security. The Philippines' armed forces may use their standard national flag, but during times of war the flag is turned upside down. Bulgaria's flag is also turned upside down during times of war. These are also considered war flags, though the terminology only applies to the flag's military usage.
Large versions of the war flag flown on the warships of countries' navies are known as battle ensigns. In addition, besides flying the national standard or a military services' emblem flag at a military fort, base, station or post and at sea at the stern (rear) or main top mast of a warship, a Naval Jack flag and other maritime flags, pennants and emblems are flown at the bow (front). In times of war waving a white flag is a banner of truce, talks/negotiations or surrender.
Four distinctive African flags currently in the collection of the National Maritime Museum in Britain were flown in action by Itsekiri ships under the control of Nana Olomu during the conflict in the late 19th century. One is the flag generally known as the Benin Empire flag and one is referred to as Nana Olomu's flag.[21]
International flags

Among international flags are the United Nations, Europe, Olympic, NATO and Paralympic flags.
Maritime flags

Flags are particularly important at sea, where they can mean the difference between life and death, and consequently where the rules and regulations for the flying of flags are strictly enforced. A national flag flown at sea is known as an ensign. A courteous, peaceable merchant ship or yacht customarily flies its ensign (in the usual ensign position), together with the flag of whatever nation it is currently visiting at the mast (known as a courtesy flag). To fly one's ensign alone in foreign waters, a foreign port or in the face of a foreign warship traditionally indicates a willingness to fight, with cannon, for the right to do so. As of 2009[update], this custom is still taken seriously by many naval and port authorities and is readily enforced in many parts of the world by boarding, confiscation and other civil penalties. In some countries yacht ensigns are different from merchant ensigns in order to signal that the yacht is not carrying cargo that requires a customs declaration. Carrying commercial cargo on a boat with a yacht ensign is deemed to be smuggling in many jurisdictions. Traditionally, a vessel flying under the courtesy flag of a specific nation, regardless of the vessel's country of registry, is considered to be operating under the law of her 'host' nation.

There is a system of international maritime signal flags for numerals and letters of the alphabet. Each flag or pennant has a specific meaning when flown individually. As well, semaphore flags can be used to communicate on an ad hoc basis from ship to ship over short distances.
Another category of maritime flag flown by some United States government ships is the distinctive mark. Although the United States Coast Guard has its own service ensign, all other U.S. government ships fly the national ensign as their service ensign, following United States Navy practice. To distinguish themselves from ships of the Navy, such ships historically have flown their parent organisation's flag from a forward mast as a distinctive mark. Today, for example, commissioned ships of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) fly the NOAA flag as a distinctive mark.
Shapes and designs



Flags are usually rectangular in shape (often in the ratio 2:3, 1:2, or 3:5), but may be of any shape or size that is practical for flying, including square, triangular, or swallow tailed. A more unusual flag shape is that of the flag of Nepal, which is in the shape of two stacked triangles. Other unusually shaped flags include the civil flags of Ohio (a swallowtail); Tampa, Florida; and Pike County, Ohio.[22]
Many flags are dyed through and through to be inexpensive to manufacture, such that the reverse side is the mirror image of the obverse (front) side, generally the side displayed when, from the observer's point of view, the flag flies from pole-side left to right. This presents two possibilities:
- If the design is symmetrical in an axis parallel to the flag pole, obverse and reverse will be identical despite the mirror-reversal, such as the Indian Flag or Canadian Flag
- If not, the obverse and reverse will present two variants of the same design, one with the hoist on the left (usually considered the obverse side), the other with the hoist on the right (usually considered the reverse side of the flag). This is very common and usually not disturbing if there is no text in the design.
Some complex flag designs are not intended to be shown on both sides, requiring separate obverse and reverse sides if made correctly. In these cases there is a design element (usually text) which is not symmetric and should be read in the same direction, regardless of whether the hoist is to the viewer's left or right. These cases can be divided into two types:
- The same (asymmetric) design may be duplicated on both sides. Such flags can be manufactured by creating two identical through and through flags and then sewing them back to back, though this can affect the resulting combination's responsiveness to the wind. Depictions of such flags may be marked with the symbol
 , indicating the reverse is congruent to (rather than a mirror image of) the obverse.
, indicating the reverse is congruent to (rather than a mirror image of) the obverse. - Rarely, the reverse design may differ, in whole or in part, from that of the obverse. Examples of flags whose reverse differs from the obverse include the flag of Paraguay, the flag of Oregon, and the historical flag of the Soviet Union. Depictions of such flags may be marked with the symbol
 .
.

Common designs on flags include crosses, stripes, and divisions of the surface, or field, into bands or quarters—patterns and principles mainly derived from heraldry. A heraldic coat of arms may also be flown as a banner of arms, as is done on both the state flag of Maryland and the flag of Kiribati.
The de jure flag of Libya under Muammar Gaddafi, which consisted of a rectangular field of green, was for a long period the only national flag using a single colour and no design or insignia. However, other historical states have also used flags without designs or insignia, such as the short-lived Soviet Republic of Hungary and the more recent Sultanate of Muscat and Oman, whose flags were both a plain field of red.
Colours are normally described with common names, such as "red", but may be further specified using colourimetry.
The largest flag flown from a flagpole worldwide, according to Guinness World Records, is the flag of the United Arab Emirates flown in Sharjah. This flag was 2,448.56 m2 (26,356.1 sq ft).[23] The largest flag ever made was the flag of Qatar; the flag, which measures at 101,978 m2 (1,097,680 sq ft), was completed in December 2013 in Doha.[24]
Parts of a flag
The general parts of a flag are: canton (the upper inner section of the flag), field or ground (the entire flag except the canton), the hoist (the edge used to attach the flag to the hoist), and the fly (the furthest edge from the hoist end).[25]
Vertical flags
Vertical flags are sometimes used in lieu of the standard horizontal flag in central and eastern Europe, particularly in the German-speaking countries. This practice came about because the relatively brisk wind needed to display horizontal flags is not common in these countries.[26]

The standard horizontal flag (no. 1 in the preceding illustration) is nonetheless the form most often used even in these countries.[27]

The vertical flag (German: Hochformatflagge or Knatterflagge; no. 2) is a vertical form of the standard flag. The flag's design may remain unchanged (No. 2a) or it may change, e.g. by changing horizontal stripes to vertical ones (no. 2b). If the flag carries an emblem, it may remain centred or may be shifted slightly upwards.[26][28]
The vertical flag for hoisting from a beam (German: Auslegerflagge or Galgenflagge; no. 3) is additionally attached to a horizontal beam, ensuring that it is fully displayed even if there is no wind.[26][29]
The vertical flag for hoisting from a horizontal pole (German: Hängeflagge; no. 4) is hoisted from a horizontal pole, normally attached to a building. The topmost stripe on the horizontal version of the flag faces away from the building.[26][30]
The vertical flag for hoisting from a crossbar or banner (German: Bannerflagge; no. 5) is firmly attached to a horizontal crossbar from which it is hoisted, either by a vertical pole (no. 5a) or a horizontal one (no. 5b). The topmost stripe on the horizontal version of the flag normally faces to the left.[26][31]
Religious flags
Flags can play many different roles in religion. In Buddhism, prayer flags are used, usually in sets of five differently coloured flags. Several flags and banners including the Black Standard are associated with Islam.[32] Many national flags and other flags include religious symbols such as the cross, the crescent, or a reference to a patron saint.[33] Flags are also adopted by religious groups and flags such as the Jain flag, Nishan Sahib (Sikhism),[34] the Saffron flag (Hindu)[35] and the Christian flag are used to represent a whole religion.[36]
-
Poland (Gorzów Wlkp.). Religious flags
-
Christian flag adopted by several Protestant denominations
-
Jain flag (on occasion, the bottom black bar is replaced with a dark blue one)
-
Nishan Sahib (the Sikh flag)
In sports
Because of their ease of signalling and identification, flags are often used in sports.
- In association football, linesmen carry small flags along the touch lines. They use the flags to indicate to the referee potential infringements of the laws, or who is entitled to possession of the ball that has gone out of the field of play, or, most famously, raising the flag to indicate an offside offence. Officials called touch judges use flags for similar purposes in both codes of rugby.
- In American and Canadian football, referees use penalty flags to indicate that a foul has been committed in game play. The phrase used for such an indication is flag on the play. The flag itself is a small, weighted handkerchief, tossed on the field at the approximate point of the infraction; the intent is usually to sort out the details after the current play from scrimmage has concluded. In American football, the flag is yellow; in Canadian football the flag is orange, but at the professional level the flag is yellow. In both the Canadian Football League and National Football League, coaches also use red challenge flags to indicate that they wish to contest a ruling on the field.
- In yacht racing, flags are used to communicate information from the race committee boat to the racers. Different flags hoisted from the committee boat may communicate a false start, changes in the course, a cancelled race, or other important information. Racing boats themselves may also use flags to symbolise a protest or distress. The flags are often part of the nautical alphabetic system of International maritime signal flags, in which 26 different flags designate the 26 letters of the Latin alphabet.

- In auto and motorcycle racing, racing flags are used to communicate with drivers. Most famously, a checkered flag of black and white squares indicates the end of the race, and victory for the leader. A yellow flag is used to indicate caution requiring slow speed and a red flag requires racers to stop immediately. A black flag is used to indicate penalties.
- In addition, fans of almost all sports wave flags in the stands to indicate their support for the participants. Many sports teams have their own flags, and, in individual sports, fans will indicate their support for a player by waving the flag of his or her home country.
- Capture the flag is a popular children's sport.
- In Gaelic football and Hurling a green flag is used to indicate a goal while a white flag is used to indicate a point
- In Australian rules football, the goal umpire will wave two flags to indicate a goal (worth six points) and a single flag to indicate a behind (worth one point).
- For safety, dive flags indicate the locations of underwater scuba divers or that diving operations are being conducted in the vicinity.
- In water sports such as wakeboarding and Water-Skiing, an orange flag is held in between runs to indicate someone is in the water.
- In golf, the hole is almost always marked with a flag. The flagpole is designed to fit centered within the base of the hole and is removable. Many courses will use colour-coded flags to determine a hole location at the front, middle or rear of the green. However, colour-coded flags are not used in the professional tours. (A rare example of a golf course that does not use flags to mark the hole is the East Course of Merion Golf Club, which instead uses flagpoles topped by wicker baskets.)
- Flag poles with flags of all shapes and sizes are used by marching bands, drum corps, and winter guard teams use flags as a method of visual enhancement in performances.
Diplomatic and political flags
Some countries use diplomatic flags, such as the United Kingdom (see image of the Embassy flag) and the Kingdom of Thailand (see image of the Embassy flag).
The socialist movement uses red flags to represent their cause. The anarchist movement has a variety of different flags, but the primary flag associated with them is the black flag. In the Spanish Civil War, the anarchists used the red-and-black bisected flag. In the 20th century, the rainbow flag was adopted as a symbol of the LGBT social movements. Its derivatives include the Bisexual pride and Transgender pride flags.
Some of these political flags have become national flags, such as the red flag of the Soviet Union and national socialist banners for Nazi Germany. The present Flag of Portugal is based on what had been the political flag of the Portuguese Republican Party previous to the 5 October 1910 revolution which brought this party to power.
Personal flags

Throughout history, monarchs have often had personal flags (including royal standards), representing the royal person, including in personal union of national monarchies.
Vehicle flags
Flags are often representative of an individual's affinity or allegiance to a country, team or business and can be presented in various ways. A popular trend that has surfaced revolves around the idea of the 'mobile' flag in which an individual displays their particular flag of choice on their vehicle. These items are commonly referred to as car flags and are usually manufactured from high strength polyester material and are attached to a vehicle via a polypropylene pole and clip window attachment.
Swimming flags



In Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the Philippines, Ireland and the United Kingdom, a pair of red-yellow flags is used to mark the limits of the bathing area on a beach, usually guarded by surf lifesavers. If the beach is closed, the poles of the flags are crossed. The flags are coloured with a red triangle and a yellow triangle making a rectangular flag, or a red rectangle over a yellow rectangle. On many Australian beaches there is a slight variation with beach condition signalling. A red flag signifies a closed beach (in the UK also other dangers), yellow signifies strong current or difficult swimming conditions, and green represents a beach safe for general swimming. In Ireland, a red and yellow flag indicates that it is safe to swim; a red flag that it is unsafe; and no flag indicates that there are no lifeguards on duty. Blue flags may also be used away from the yellow-red lifesaver area to designate a zone for surfboarding and other small, non-motorised watercraft.
Reasons for closing the beach include:
- dangerous rip
- hurricane warning
- no lifeguards in attendance
- overpolluted water
- sharks
- tsunami
- waves too strong
A surf flag exists, divided into four quadrants. The top left and bottom right quadrants are black, and the remaining area is white.
Signal flag "India" (a black circle on a yellow square) is frequently used to denote a "blackball" zone where surfboards cannot be used but other water activities are permitted.
The United States uses beach warning flags created by the International Life Saving Federation and endorsed and conditionally approved by the United States Lifesaving Association.[37]
Railway flags
Railways use a number of coloured flags. When used as wayside signals they usually use the following meanings (exact meanings are set by the individual railroad company):
- red = stop
- yellow = proceed with caution
- green or white = proceed.
- a flag of any colour waved vigorously means stop
- a blue flag on the side of a locomotive means that it should not be moved because someone is working on it (or on the train attached to it). A blue flag on a track means that nothing on that track should be moved. The flag can only be removed by the person or group that placed it. In the railway dominated steel industry this principle of "blue flag and tag" was extended to all operations at Bethlehem Steel, Lackawanna, New York. If a man went inside a large machine or worked on an electrical circuit for example, his blue flag and tag was sacrosanct.[38] The "Lock Out/Tag Out" practice is similar and now used in other industries to comply with safety regulations.
At night, the flags are replaced with lanterns showing the same colours.
Flags displayed on the front of a moving locomotive are an acceptable replacement for classification lights and usually have the following meanings (exact meanings are set by the individual railroad company):
- white = extra (not on the timetable)
- green = another section following
- red = last section
Additionally, a railroad brakeman will typically carry a red flag to make his or her hand signals more visible to the engineer. Railway signals are a development of railway flags.[39]
Flagpoles

A flagpole, flagmast, flagstaff, or staff can be a simple support made of wood or metal. If it is taller than can be easily reached to raise the flag, a cord is used, looping around a pulley at the top of the pole with the ends tied at the bottom. The flag is fixed to one lower end of the cord, and is then raised by pulling on the other end. The cord is then tightened and tied to the pole at the bottom. The pole is usually topped by a flat plate or ball called a "truck" (originally meant to keep a wooden pole from splitting) or a finial in a more complex shape. Very high flagpoles may require more complex support structures than a simple pole, such as a guyed mast.
Dwajasthambam are flagpoles commonly found at the entrances of South Indian Hindu temples.[40]
Record heights

Since 26 December 2021, the tallest free-standing flagpole in the world is the Cairo Flagpole, located in the New Administrative Capital under construction in Egypt at a height of 201.952 m (662.57 ft), exceeding the former record holders, the Jeddah Flagpole in Saudi Arabia (height: 171 m; 561 ft), the Dushanbe Flagpole in Tajikistan[41][42] (height: 165 m; 541 ft) and the National Flagpole in Azerbaijan (height: 162 m; 531 ft).[43] The flagpole in North Korea is the fourth tallest flagpole in the world, however, it is not free-standing. It is a radio tower supported flagpole. Many of these were built by American company Trident Support: the Dushanbe Flagpole, the National Flagpole in Azerbaijan, the Ashgabat flagpole in Turkmenistan at 133 m (436 ft); the Aqaba Flagpole in Jordan at 130 m (430 ft); the Raghadan Flagpole in Jordan at 126.8 m (416 ft); and the Abu Dhabi Flagpole in the United Arab Emirates at 122 m (400 ft).[44]
The current tallest flagpole in India (and the tallest flying the tricolour) is the 110-metre (360 ft) flagpole in Belgaum, Karnataka which was first hoisted on 12 March 2018.[45][46] The tallest flagpole in the United Kingdom from 1959 until 2013 stood in Kew Gardens. It was made from a Canadian Douglas-fir tree and was 68.5 m (225 ft) in height.[47]
The current tallest flagpole in the United States (and the tallest flying an American flag) is the 400-foot (120 m) pole completed before Memorial Day 2014 and custom-made with an 11-foot (3.4 m) base in concrete by wind turbine manufacturer Broadwind Energy. It is situated on the north side of the Acuity Insurance headquarters campus along Interstate 43 in Sheboygan, Wisconsin, and is visible from Cedar Grove. The pole can fly a 220-pound flag in light wind conditions and a heavier 350-pound flag in higher wind conditions.[48]
Design
Flagpoles can be designed in one piece with a taper (typically a steel taper or a Greek entasis taper),[49] or be made from multiple pieces to make them able to expand. In the United States, ANSI/NAAMM guide specification FP-1001-97 covers the engineering design of metal flagpoles to ensure safety.
-
Flagpole of modest size, with simple truck
-
Large flagpole, showing structured truck (New Zealand)
-
New Caledonia has two flags, flown here in Nouméa, the capital city, on a single flagpole with a crossbar
Hoisting the flag

Hoisting the flag is the act of raising the flag on the flagpole. Raising or lowering flags, especially national flags, usually involves ceremonies and certain sets of rules, depending on the country, and usually involve the performance of a national anthem.
A flag-raising squad is a group of people, usually troops, cadets, or students, that march in and bring the flags for the flag-hoisting ceremony. Flag-hoisting ceremonies involving flag-raising squads can be simple or elaborate, involving large numbers of squads. Elaborate flag-hoisting ceremonies are usually performed on national holidays.
The cord or rope that ties a flag to its pole is called a halyard. Flags may have a strip of fabric along the hoist side called a heading for the halyard to pass through, or a pair of grommets for the halyard to be threaded through. Flags may also be held in position using Inglefield clips.[50]
Flags in communication

Semaphore is a form of communication that utilises flags. The signalling is performed by an individual using two flags (or lighted wands), the positions of the flags indicating a symbol. The person who holds the flags is known as the signalman. This form of communication is primarily used by naval signallers. This technique of signalling was adopted in the early 19th century and is still used in various forms today.[51]
The colours of the flags can also be used to communicate. For example; a white flag means, among other things, surrender or peace, a red flag can be used as a warning signal, and a black flag can mean war, or determination to defeat enemies.
Orientation of a flag is also used for communication, though the practice is rarely used given modern communication systems. Raising a flag upside-down was indicative that the raising force controlled that particular area, but that it was in severe distress.[52]
See also
- Lists and galleries of flags
- Notable flag-related topics
- Flag families
- False flag
- Flag Day
- Flag desecration
- Flag protocol
- Flag patch
- Flag semaphore
- Flag throwing
- Glossary of vexillology
- Pledge of Allegiance (United States)
- Standard-bearer (also enumerates various types of standards, both flag types and immobile ensigns)
- Vexillology
- Flags of the World, an Internet-based vexillological association and resource
- Windsock
Citations
- ^ Znamierowski, Alfred (2013). The World Encyclopedia of Flags: The Definitive Guide to International Flags, Banners, Standards and Ensigns, with Over 1400 Illustration. Lorenz Books. pp. 100–129. ISBN 978-0-7548-2629-3.
- ^ Inglefield, p. 39.
- ^ a b Smith, Whitney (1975). Flags through the ages and across the world. Internet Archive. New York. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-07-059093-9.
- ^ a b c Flag | heraldry. Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved February 15, 2019.
- ^ Graef, Katrien De; Tavernier, Jan (7 December 2012). Susa and Elam. Archaeological, Philological, Historical and Geographical Perspectives.: Proceedings of the International Congress Held at Ghent University, December 14–17, 2009. BRILL. ISBN 978-9004207400 – via Google Books.
- ^ Pittman, Holly; N.Y.), Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York (12 December 1984). Art of the Bronze Age: Southeastern Iran, Western Central Asia, and the Indus Valley. Metropolitan Museum of Art. ISBN 9780870993657 – via Google Books.
- ^ Hansen, Donald P.; Ehrenberg, Erica (12 December 2017). Leaving No Stones Unturned: Essays on the Ancient Near East and Egypt in Honor of Donald P. Hansen. Eisenbrauns. ISBN 9781575060552 – via Google Books.
- ^ Hakemi, Ali; Archeologiche, Istituto italiano per il Medio ed Estremo Oriente Centro Scavi e Ricerche (12 December 1997). Shahdad: archaeological excavations of a bronze age center in Iran. IsMEO. ISBN 9788120410176 – via Google Books.
- ^ Smith, Whitney (1975). Flags through the ages and across the world. Internet Archive. New York. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-07-059093-9.
- ^ Articles 90–94 of the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea
- ^ Inglefield, p. 48.
- ^ Inglefield, p. 50.
- ^ "Oldest continuously used national flag". Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2023-11-10.
- ^ National Flag -The official website of Denmark Archived 2018-02-03 at the Wayback Machine. Earlier use of the white cross on red is attested by an armorial (Netherlands) of 1370-1386. In later monastic tradition, the Dannebrog made its first, miraculous appearance at the Battle of Lindanise on 15 June 1219.
- ^ Jeroen Temperman (2010). State Religion Relationships and Human Rights Law: Towards a Right to Religiously Neutral Governance. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. p. 88. ISBN 978-9004181489. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 31 December 2007.
Many predominantly Christian states show a cross, symbolising Christianity, on their national flag. The so-called Scandinavian crosses or Nordic crosses on the flags of the Nordic countries–Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden–also represent Christianity.
- ^ Smith, Whitney. "flag of France | History & Meaning". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2019-02-24.
- ^ Shelley, Fred M. (2013). Nation Shapes: The Story behind the World's Borders. ABC-CLIO. pp. xvi. ISBN 9781610691062.
- ^ Smith, Whitney. "Flag of the United States of America". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2019-05-24.
- ^ Smith, Whitney. "Flag of Liberia". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2019-05-24.
- ^ Cyril Glassé , The New Encyclopedia of Islam (revised ed. 2001), s.v. "Moon" (p. 314).
- ^ "Welcome to the Royal Museums Greenwich Blogs - Royal Museums Greenwich Blogs" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-28. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
- ^ "Pike". County Flags. Columbus, Ohio: Ohio Statehouse Museum. Retrieved July 20, 2019.
- ^ "Largest flag flown". 28 March 2022.
- ^ "Qatar breaks record for world's largest flag". BBC. December 17, 2013. Retrieved December 17, 2013.
- ^ "The Parts of a Flag". Flag Terminology. NSTATE. Retrieved 2019-08-02.
- ^ a b c d e "Flaggentypen". German Vexillological Society (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Flaggenkunde e. V., DGF). Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- ^ German Federal Ministry of the Interior: Hissflagge Archived 2012-09-08 at archive.today, accessed 20 February 2012
- ^ German Federal Ministry of the Interior: Hochformatflagge Archived 2012-08-03 at the Wayback Machine, accessed 20 February 2012
- ^ German Federal Ministry of the Interior: Auslegerflagge Archived 2012-08-03 at the Wayback Machine, accessed 20 February 2012
- ^ German Federal Ministry of the Interior: Hängeflagge Archived 2012-08-03 at the Wayback Machine, accessed 20 February 2012
- ^ German Federal Ministry of the Interior: Hängeflagge Archived 2012-08-03 at the Wayback Machine, accessed 20 February 2012
- ^ David Cook (2002). Studies in Muslim Apocalyptic. Darwin Press. p. 197. ISBN 9780878501427. from Majlisi,
- ^ "64 countries have religious symbols on their national flags". 25 November 2014.
- ^ Mayled, Jon (2002). Sikhism. Heinemann. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-435-33627-1. Retrieved 29 July 2024.
- ^ "The Bhagwa Dhwaj (Saffron Flag)". Hindu Swayamsevak Sangh (UK). 28 October 2023. Archived from the original on 3 December 2022. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ "Resolution". Federal Council Bulletin. 25–27. Religious Publicity Service of the Federal Council of the Churches of Christ in America. 1942.
- ^ "USLA Approved Beach Warning Flags". United States Lifesaving Association. Retrieved August 31, 2024.
- ^ "Docket No. 79-2597". Archived from the original on 2010-05-27. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ^ Calvert, J.B. (25 July 2004). "Early Railway Signals". University of Denver. Retrieved 7 October 2007.
- ^ Hiltebeitel, Alf (1991). The Cult of Draupadi, Volume 2: On Hindu Ritual and the Goddess. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0226340473. pp. 91–92.
- ^ "Jeddah Flagpole inaugurated". arabnews.com. Retrieved 2014-09-23.
- ^ Former record: "Wer baut den hoechsten Fahnenmast". Asia Plus. September 9, 2008. Archived from the original on April 4, 2019. Retrieved May 24, 2011.
- ^ "Flag of Azerbaijan". Telegraph.co.uk. July 3, 2008. Archived from the original on 2022-01-11.
- ^ "Looking for Afghanistan? Turn Left at the Enormous Flagpole". National Geographic. 2017-09-05.
- ^ "Karnataka's Belgaum is now home to India's tallest flag". Times Now News. 13 March 2018. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ^ "Tallest flag in India: Country's tallest tricolour to be hoisted in Belagavi". The Times of India. Mar 12, 2018. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ^ "Timber! Steeplejacks to dismantle Kew Flagpole". Kew.org. Archived from the original on 2016-08-17.
- ^ Weyandt, Janet (25 May 2014). "High-flying: Up in time for Memorial Day, Acuity flag is world's tallest". The Sheboygan Press. Archived from the original on 3 April 2015. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
- ^ "Cone Tapered vs. Venetian Entasis Tapered". Lingo Flagpoles Inc. Archived from the original on 2005-02-28.
- ^ Inglefield, p. 12.
- ^ "Semaphore Flag Signalling System". ANBG.gov.au. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- ^ Scanlon, Caitlin. "Flag Etiquette Do's and Don'ts". Military.com. Retrieved 2017-10-05.
General and cited references
- Inglefield, Eric (1979 edition). Flags. Ward Lock, London. ISBN 0706356527
External links
 flag (P163) (see uses)
flag (P163) (see uses)