Australia: Difference between revisions
Daddynnoob (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Country in Oceania}} |
|||
{{about|the country}} |
|||
{{About|the country|the continent|Australia (continent)|other uses}} |
|||
{{pp-semi|small=yes}}{{pp-move-indef}} |
|||
{{Distinguish|Australasia|Austrasia|Austria}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=March 2011}} |
|||
{{Featured article}} |
|||
{{protection padlock|small=yes}} |
|||
{{Use Australian English|date=December 2024}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=December 2024}} |
|||
{{Infobox country |
{{Infobox country |
||
| conventional_long_name = Commonwealth of Australia |
|||
|native_name = |
|||
| common_name = Australia |
|||
|conventional_long_name = Commonwealth of Australia |
|||
| |
| image_flag = Flag of Australia (converted).svg |
||
| alt_flag = A blue field with the Union Flag in the upper hoist quarter, a large white seven-pointed star in the lower hoist quarter, and constellation of five white stars in the fly – one small five-pointed star and four, larger, seven-pointed stars |
|||
|image_flag = Flag of Australia.svg |
|||
|image_coat |
| image_coat = Coat of Arms of Australia.svg |
||
| alt_coat = <!--alt text for coat of arms--> |
|||
|image_map = Australia (orthographic projection).svg |
|||
| national_anthem = "[[Advance Australia Fair]]"{{Lower|0.2em|{{Refn|Australia also has a [[royal anthem]], "[[God Save the King]]", which may be played in place of or alongside the national anthem when members of the [[House of Windsor|royal family]] are present. If not played alongside the royal anthem, the national anthem is instead played at the end of an official event.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Australian National Anthem |url=https://www.pmc.gov.au/honours-and-symbols/australian-national-symbols/australian-national-anthem |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231027193111/https://www.pmc.gov.au/honours-and-symbols/australian-national-symbols/australian-national-anthem |archive-date=27 October 2023 |access-date=9 January 2024 |website=Department of Prime Minister and Cabinet|date=19 January 2022 }}</ref>|name="anthem explanation"|group="N"}}<!--end lower:-->}}<br /> <div style="display:inline-block;margin-top:0.4em;">{{Center|[[File:Advance Australia Fair.ogg]]}}</div> |
|||
|map_width = 220px |
|||
| image_map = Australia with AAT (orthographic projection).svg |
|||
|national_anthem = "[[Advance Australia Fair]]"{{#tag:ref|Australia also has a [[royal anthem]], "[[God Save the Queen|God Save the Queen (or King)]]", which is played in the presence of a member of the [[House of Windsor|Royal family]] when they are in Australia. In all other appropriate contexts, the [[national anthem]] of Australia, "[[Advance Australia Fair]]", is played.<ref>[http://www.itsanhonour.gov.au/symbols/anthem.cfm It's an Honour – Symbols – Australian National Anthem] and [http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/nat_anthem.html DFAT – "The Australian National Anthem"]; {{Cite book|title=Parliamentary Handbook of the Commonwealth of Australia|edition=29th|year=2002 (updated 2005)|chapter=National Symbols|chapterurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070611101901/http://www.aph.gov.au/library/handbook/40thparl/national+symbols.pdf|accessdate=7 June 2007}}</ref>|name="anthem explanation"|group="N"}} |
|||
| map_caption = {{Legend|#316831|Commonwealth of Australia}} |
|||
|official_languages = None{{#tag:ref|English does not have [[de jure]] status.<ref name=language/>|name="official language"|group="N"}} |
|||
{{Legend|#8DC78C|[[Australian Antarctic Territory|Australian territorial claim in Antarctica]]}} |
|||
|languages_type = [[National language]] |
|||
| alt_map = A map of the eastern hemisphere centred on Australia, using an orthographic projection |
|||
|languages = [[English language|English]] (''[[de facto]]'')<ref name="official language" group="N" /> |
|||
|capital = [[Canberra]] |
| capital = [[Canberra]] |
||
| coordinates = {{Coord|35|18|29|S|149|07|28|E|type:city_region:AU}} |
|||
|largest_city = [[Sydney]] |
|||
| largest_city = [[Sydney]] (metropolitan)<br />[[Melbourne]] (urban){{Refn|Sydney is the largest city based on Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) Greater Capital City Statistical Areas (GCCSAs). These represent labour markets and the functional area of Australian capital cities.<ref name="ABS-regional-population-2022">{{cite web |title=Regional population, 2021-22 financial year |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/regional-population/2021-22 |date=20 April 2023 |publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics |access-date=27 May 2023 |archive-date=20 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420020126/https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/regional-population/2021-22 |url-status=live }}</ref> Melbourne is larger based on ABS Significant Urban Areas (SUAs). These represent Urban Centres, or groups of contiguous Urban Centres, that contain a population of 10,000 people or more.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Turnbull |first1=Tiffanie |title=Melbourne overtakes Sydney as Australia's biggest city |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-australia-65261720 |access-date=27 May 2023 |publisher=BBC News |date=17 April 2023 |archive-date=21 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230521093900/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-australia-65261720 |url-status=live }}</ref>|group="N"}}<!-- See discussion on the talk page --> |
|||
|government_type = [[Federalism|Federal]] [[parliamentary system|parliamentary democracy]] and [[constitutional monarchy]] |
|||
| languages_type = [[Official language]] and [[national language]] |
|||
|leader_title1 = [[Monarchy of Australia|Monarch]] |
|||
| languages = [[Australian English|English]] (''[[de facto]]'')<br />None (''[[de jure]]'') |
|||
|leader_title2 = [[Governor-General of Australia|Governor-General]] |
|||
| languages2_type = |
|||
|leader_title3 = [[Prime Minister of Australia|Prime Minister]] |
|||
| languages2 = |
|||
|leader_name1 = [[Elizabeth II]] |
|||
| demonym = {{Hlist|[[Australians|Australian]]|Aussie (colloquial){{Refn|Pronounced "Ozzy"}}<ref>{{Cite web |title=Aussie |url=https://www.macquariedictionary.com.au/features/word/search/?search_word_type=Dictionary&word=aussie |url-access=subscription |access-date=8 February 2024 |website=[[Macquarie Dictionary]] |date=16 October 2023 |archive-date=10 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240610132406/https://www.macquariedictionary.com.au/?time=1718025846039 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=Collins English Dictionary |year=2009 |publisher=[[HarperCollins]] |location=Bishopbriggs, Glasgow |isbn=978-0-0078-6171-2 |page=18 |title-link=Collins English Dictionary }}</ref><!--end hlist:-->}} |
|||
|leader_name2 = [[Quentin Bryce]] |
|||
| religion = {{Ublist |
|||
|leader_name3 = [[Julia Gillard]] |
|||
| |
|title = [[Religion in Australia|Various]] |
||
| |
|43.9% [[Christianity in Australia|Christianity]] |
||
| |
|38.9% [[Irreligion in Australia|no religion]] |
||
|3.2% [[Islam in Australia|Islam]] |
|||
|area_rank = 6th |
|||
|2.7% [[Hinduism in Australia|Hinduism]] |
|||
|area_magnitude = 1 E12 |
|||
|2.4% [[Buddhism in Australia|Buddhism]] |
|||
|area_km2 = 7617930 |
|||
|1.7% [[Religion in Australia#Other religions|other]] |
|||
|percent_water = |
|||
|7.2% unanswered{{Refn|The religion question is optional in the Australian census.|group="N"}} |
|||
|population_estimate = {{formatnum:{{#expr: 22579660 + (86400 / 97) * {{Age in days|2011|4|12}} round 0}}}}<!--AUTOUPDATES DAILY at 09:30 UTC, Australia pop clock adds 1 person every 97 seconds --><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/94713ad445ff1425ca25682000192af2/1647509ef7e25faaca2568a900154b63?OpenDocument|title=Population clock|work=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] website|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia|accessdate=12 April 2011}} The population estimate shown is automatically calculated daily at 00:00 UTC and is based on data obtained from the population clock on the date shown in the citation.</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
|population_estimate_year = {{CURRENTYEAR}} |
|||
| religion_year = [[2021 Australian census|2021]] |
|||
|population_estimate_rank = 50th |
|||
| religion_ref = <ref name="Australian-Bureau-of-Statistics-2022"/> |
|||
|population_census = 19,855,288<ref>{{Census 2006 AUS|id=0|name=Australia|accessdate=14 October 2008|quick=on}}</ref> |
|||
| government_type = [[Federalism|Federal]] parliamentary [[constitutional monarchy]] |
|||
|population_census_year = 2006 |
|||
| leader_title1 = [[Monarchy of Australia|Monarch]] |
|||
|population_density_km2 = 2.833 |
|||
| leader_name1 = [[Charles III]] |
|||
|population_density_rank = 233rd |
|||
| leader_title2 = {{Nowrap|[[Governor-General of Australia|Governor-General]]}} |
|||
|sovereignty_type = Independence |
|||
| leader_name2 = [[Sam Mostyn]] |
|||
|sovereignty_note = from the [[United Kingdom]] |
|||
| |
| leader_title3 = [[Prime Minister of Australia|Prime Minister]] |
||
| leader_name3 = [[Anthony Albanese]] |
|||
|established_event2 = [[Statute of Westminster 1931|Statute of Westminster]] |
|||
| legislature = [[Parliament of Australia|Parliament]] |
|||
|established_event3 = [[Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942|Statute of Westminster Adoption Act]] |
|||
| upper_house = [[Australian Senate|Senate]] |
|||
|established_event4 = [[Australia Act 1986|Australia Act]] |
|||
| lower_house = [[Australian House of Representatives|House of Representatives]] |
|||
|established_date1 = 1 January 1901 |
|||
| sovereignty_type = [[Independence]] |
|||
|established_date2 = 11 December 1931 |
|||
| sovereignty_note = from the [[United Kingdom]] |
|||
|established_date3 = 9 October 1942 (with effect from 3 September 1939) |
|||
| established_event1 = [[Federation of Australia|Federation]] |
|||
|established_date4 = 3 March 1986 |
|||
| established_date1 = 1 January 1901 |
|||
|currency = [[Australian dollar]] |
|||
| established_event2 = [[Balfour Declaration of 1926|Balfour Declaration]] |
|||
|currency_code = AUD |
|||
| established_date2 = 15 November 1926 |
|||
|time_zone = [[Time in Australia|various]]<ref name="time" group="N">There are minor variations from these three time zones, see [[Time in Australia]].</ref> |
|||
| established_event3 = [[Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942|Statute of Westminster Adoption Act]] |
|||
|utc_offset = +8 to +10.5 |
|||
| established_date3 = 9 October 1942 |
|||
|time_zone_DST = [[Time in Australia|various]]<ref name="time" group="N" /> |
|||
| established_event4 = [[Australia Acts]] |
|||
|utc_offset_DST = +8 to +11.5 |
|||
| established_date4 = 3 March 1986 |
|||
|demonym = [[Australians|Australian]], [[Aussie]]<ref>The [[Macquarie Dictionary]]</ref><ref>{{Cite book|title=[[Collins English Dictionary]]|year=2009|publisher=[[HarperCollins]]|location=Bishopbriggs, Glasgow|isbn=978-0-00-786171-2|page=18|accessdate=19 April 2010}}</ref> |
|||
| area_km2 = 7,688,287<ref name="Geoscience-Australia-2014">{{Cite web|url=https://www.ga.gov.au/scientific-topics/national-location-information/dimensions/area-of-australia-states-and-territories|title=Area of Australia - States and Territories|date=27 June 2014|website=Geoscience Australia|access-date=18 February 2024|archive-date=18 January 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240118174336/https://www.ga.gov.au/scientific-topics/national-location-information/dimensions/area-of-australia-states-and-territories|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Factbook-Geography">{{Cite CIA World Factbook |country=Australia |section=Geography |access-date=16 August 2024}}</ref><ref name="Organisation-for-Economic-Cooperation-and-Development-OECD">{{Cite web|title=Surface water and surface water change|access-date=11 October 2020|publisher=[[Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development]] (OECD)|url=https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=SURFACE_WATER|archive-date=24 March 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210324133453/https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=SURFACE_WATER|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|drives_on = left |
|||
| area_rank = 6th |
|||
|cctld = [[.au]] |
|||
| percent_water = 1.79 (2015)<ref name="Organisation-for-Economic-Cooperation-and-Development-OECD"/> |
|||
|calling_code = [[+61]] |
|||
| population_estimate = {{IncreaseNeutral}} {{Data Australia|poptoday|formatnum}}<ref name="popclock">{{Cite web|url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/population-clock-pyramid|title=Population clock and pyramid|work=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] website|date=5 March 2024|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia|access-date=5 March 2024|archive-date=8 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240208102513/https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/population-clock-pyramid|url-status=live}} The population estimate shown is automatically calculated daily at 00:00 UTC and is based on data obtained from the population clock on the date shown in the citation.</ref> |
|||
|ISO_3166-1_alpha2 = AU |
|||
| population_census = {{IncreaseNeutral}} 25,890,773<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/national-state-and-territory-population/mar-2022|title=National, state and territory population|publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics|date=26 September 2022|access-date=26 September 2022|archive-date=21 November 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221121204624/https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/national-state-and-territory-population/mar-2022|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|ISO_3166-1_alpha3 = AUS |
|||
| population_estimate_year = {{CURRENTYEAR}} |
|||
|ISO_3166-1_numeric = 036 |
|||
| population_estimate_rank = 54th |
|||
|sport_code = AUS |
|||
| population_census_year = 2021 |
|||
|vehicle_code = AUS |
|||
| population_density_km2 = {{#expr:{{Data Australia|poptoday}} / 7692024 round 1}} |
|||
|GDP_PPP_year = 2010 |
|||
| population_density_rank = 244th |
|||
|GDP_PPP = $882.362 billion<ref name=imf2>{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2008&ey=2011&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=193&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=&pr.x=109&pr.y=5 |title=Australia|work=IMF website|publisher=International Monetary Fund|location=Washington, D.C.|accessdate=12 April 2011}}</ref> |
|||
| GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $1.898 trillion<ref name="IMFWEO.AU">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/October/weo-report?c=193,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2022&ey=2029&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Australia) |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |website=www.imf.org |date=22 October 2024 |access-date=22 October 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|GDP_PPP_rank = 17th |
|||
| GDP_PPP_year = 2024 |
|||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = $39,699<ref name=imf2/> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_rank = 19th |
|||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 9th |
|||
| |
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $69,475<ref name="IMFWEO.AU" /> |
||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 23rd |
|||
|GDP_nominal_rank = 13th |
|||
| GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $1.802 trillion<ref name="IMFWEO.AU" /> |
|||
|GDP_nominal_year = 2010 |
|||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2024 |
|||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = $55,589<ref name=imf2/> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_rank = 14th |
|||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 6th |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $65,966<ref name="IMFWEO.AU" /> |
|||
|Gini = 30.5<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2172.html|title=Distribution of family income – Gini index|work=The World Factbook|publisher=CIA|accessdate=2009-09-01}}</ref> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 12th |
|||
|Gini_category = <span style="color:#fc0;">medium</span> |
|||
| Gini = 32.4 |
|||
|Gini_year = 2006 |
|||
| Gini_year = 2020 |
|||
|HDI_year = 2010 |
|||
| Gini_change = decrease <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
|HDI = {{increase}} 0.937<ref name="HDI">{{cite web|url=http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDR_2010_EN_Tables_reprint.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2010 - tables|year=2010|publisher=United Nations|accessdate=25 April 2011}}</ref> |
|||
| Gini_ref = <ref>{{Cite web |title=Australia Gini Coefficient, 1995 – 2023 {{!}} CEIC Data |url=https://www.ceicdata.com/en/indicator/australia/gini-coefficient |access-date=4 March 2024 |website=www.ceicdata.com |archive-date=4 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240304002624/https://www.ceicdata.com/en/indicator/australia/gini-coefficient |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
|HDI_rank = 2nd |
|||
| HDI = 0.946<!--number only--> |
|||
|HDI_category = <span style="color:#090;">very high</span> |
|||
| HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> |
|||
}}<!-- PLEASE USE AUSTRALIAN ENGLISH THROUGHOUT, i.e., use centre not center, neighbour not neighbor, and maximise the use of -is- rather than -iz-. The dash style is unspaced em dash (in accord with current AGPS Style Manual), not spaced em dash or spaced en dash (see [[WP:MOS]]). Maintain consistency of style, suppressing personal preferences.--> |
|||
| HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| HDI_ref = <ref>{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2023/24|language=en|publisher=[[United Nations Development Programme]]|date=13 March 2024|access-date=13 March 2024|archive-date=13 March 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240313164319/https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
| HDI_rank = 10th |
|||
| currency = [[Australian dollar]] ($) |
|||
| currency_code = AUD |
|||
| time_zone = [[Time in Australia|AWST, ACST, AEST]]<ref name="time" group="N">There are minor variations from three basic time zones; see [[Time in Australia]].</ref> |
|||
| utc_offset = +8; +9.5; +10 |
|||
| time_zone_DST = [[Time in Australia|ACDT, AEDT]]<ref name="time" group="N"/> |
|||
| utc_offset_DST = +10.5; +11 |
|||
| DST_note = [[Daylight saving time|DST]] not observed in Qld, WA and NT |
|||
| date_format = {{Abbr|dd|day}}/{{Abbr|mm|month}}/{{Abbr|yyyy|year}}<ref>{{Cite web |last=Australian Government |date=March 2023 |title=Dates and time |url=https://www.stylemanual.gov.au/grammar-punctuation-and-conventions/numbers-and-measurements/dates-and-time |access-date=6 May 2023 |website=Style Manual |archive-date=29 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230529074659/https://www.stylemanual.gov.au/grammar-punctuation-and-conventions/numbers-and-measurements/dates-and-time |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| drives_on = left |
|||
| calling_code = [[Telephone numbers in Australia|+61]] |
|||
| cctld = [[.au]] |
|||
}} |
|||
<!-- PLEASE USE AUSTRALIAN ENGLISH THROUGHOUT, i.e. use "centre" instead of "center"; "neighbour" rather than "neighbor", etc.; and maximise the use of "-is-" and "-ys-" (as in "organise" and "analyse") rather than "-iz-" or "-yz-" ("organize", "analyze"). The dash style is unspaced em dash, write {{Mdash}}, not spaced en dash. An exception applies to proper nouns that have standardised non-Australian spellings in their name, such as the "World Trade Organization" and not "World Trade Organisation". The relevant Manual of Style guidelines for this are located at [[MOS:ENGVAR]]. --> |
|||
'''Australia''', officially the '''Commonwealth of Australia''',<ref>''[[Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act]]'' (Imp) 63 & 64 Vict, c 12, [https://www8.austlii.edu.au/cgi-bin/viewdoc/au/legis/cth/consol_act/coaca430/s3.html s 3] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240109071637/https://www8.austlii.edu.au/cgi-bin/viewdoc/au/legis/cth/consol_act/coaca430/s3.html |date=9 January 2024 }}</ref> is a country comprising [[mainland Australia|the mainland]] of the [[Australia (continent)|Australian continent]], the island of [[Tasmania]] and [[list of islands of Australia|numerous smaller islands]].{{Refn|[[Australian Antarctic Territory|41% of the Antarctic continent is also claimed by the country]], however this is only recognised by the UK, France, New Zealand and Norway.}} Australia has a total area of {{cvt|7,688,287|km2}}, making it the [[list of countries and dependencies by area|sixth-largest country in the world]] and the largest in [[Oceania]]. It is the world's oldest,<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Korsch RJ. |display-authors=et al |year=2011 |title=Australian island arcs through time: Geodynamic implications for the Archean and Proterozoic |journal=Gondwana Research|volume=19|issue=3|pages=716–734|doi=10.1016/j.gr.2010.11.018|bibcode=2011GondR..19..716K | issn=1342-937X }}</ref> flattest,<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.smh.com.au/news/National/Map-from-above-shows-Australia-is-a-very-flat-place/2005/01/21/1106110947946.html |title=Map from above shows Australia is a very flat place |date=21 January 2005 |last=Macey |first=Richard |work=[[The Sydney Morning Herald]] |access-date=5 April 2010 |issn=0312-6315 |oclc=226369741 |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010152047/http://www.smh.com.au/news/National/Map-from-above-shows-Australia-is-a-very-flat-place/2005/01/21/1106110947946.html |url-status=live }}</ref> and driest inhabited continent,<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Australian continent |url=https://www.australia.gov.au/about-australia/our-country/the-australian-continent |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200313202829/https://www.australia.gov.au/about-australia/our-country/the-australian-continent |archive-date=13 March 2020 |access-date=13 August 2018 |website=australia.gov.au |publisher=}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.ga.gov.au/scientific-topics/national-location-information/landforms/deserts |title=Deserts |work=Geoscience Australia |publisher=Australian Government |access-date=13 August 2018 |date=15 May 2014 |archive-date=5 June 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140605132206/http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/landforms/deserts.html |url-status=live }}</ref> with some of the least fertile soils.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.abc.net.au/quantum/info/q95-19-5.htm |title=A Chat with Tim Flannery on Population Control |last=Kelly |first=Karina |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |date=13 September 1995 |access-date=23 April 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100113095438/http://www.abc.net.au/quantum/info/q95-19-5.htm |archive-date=13 January 2010}} "Well, Australia has by far the world's least fertile soils".</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Damaged Dirt |work=[[The Advertiser (Adelaide)|The Advertiser]] |last=Grant |first=Cameron |url=http://www.1degree.com.au/files/AdvertiserPartworks_Part3_Page8.pdf?download=1&filename=AdvertiserPartworks_Part3_Page8.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706100423/http://www.1degree.com.au/files/AdvertiserPartworks_Part3_Page8.pdf?download=1&filename=AdvertiserPartworks_Part3_Page8.pdf |archive-date=6 July 2011 |date=August 2007 |access-date=23 April 2010 |quote=Australia has the oldest, most highly weathered soils on the planet.}}</ref> It is a [[megadiverse countries|megadiverse country]], and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates including [[deserts of Australia|deserts]] in the [[Outback|interior]] and [[forests of Australia|tropical rainforests]] along the [[Eastern states of Australia|coast]]. |
|||
'''Australia''' ({{IPAc-en|icon|ə|ˈ|s|t|r|eɪ|l|j|ə}}), officially the '''Commonwealth of Australia''', is a country in the [[Southern Hemisphere]] comprising the mainland of the [[Australia (continent)|Australian continent]], the island of [[Tasmania]] and numerous [[list of islands of Australia|smaller islands]] in the [[Indian Ocean|Indian]] and [[Pacific Ocean]]s.{{#tag:ref|Australia describes the body of water south of its mainland as the [[Southern Ocean]], rather than the Indian Ocean as defined by the [[International Hydrographic Organization]] (IHO). In 2000, a vote of IHO member nations defined the term "Southern Ocean" as applying only to the waters between Antarctica and [[60th parallel south|60 degrees south]] latitude.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://geography.about.com/od/learnabouttheearth/a/fifthocean.htm|last=Rosenberg|first=Matt|title=The New Fifth Ocean–The World's Newest Ocean – The Southern Ocean|publisher=About.com: Geography|date=20 August 2009|accessdate=5 April 2010}}</ref>|name="Southern Ocean"|group="N"}} Neighbouring countries include [[Indonesia]], [[East Timor]] and [[Papua New Guinea]] to the north, the [[Solomon Islands]], [[Vanuatu]] and [[New Caledonia]] to the northeast and [[New Zealand]] to the southeast. |
|||
The ancestors of [[Aboriginal Australians]] began arriving from [[south-east Asia]] 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the [[Last Glacial Period|last glacial period]].<ref name="ClarksonJacobs2017">{{Cite journal |last1=Clarkson |first1=Chris |last2=Jacobs |first2=Zenobia |last3=Marwick |first3=Ben |last4=Fullagar |first4=Richard |last5=Wallis |first5=Lynley |last6=Smith |first6=Mike |last7=Roberts |first7=Richard G. |last8=Hayes |first8=Elspeth |last9=Lowe |first9=Kelsey |last10=Carah |first10=Xavier |last11=Florin |first11=S. Anna |last12=McNeil |first12=Jessica |last13=Cox |first13=Delyth |last14=Arnold |first14=Lee J. |last15=Hua |first15=Quan |display-authors=1 |year=2017 |title=Human occupation of northern Australia by 65,000 years ago |journal=Nature |volume=547 |issue=7663 |pages=306–310 |bibcode=2017Natur.547..306C |doi=10.1038/nature22968 |issn=0028-0836 |pmid=28726833 |s2cid=205257212 |hdl-access=free |last16=Huntley |first16=Jillian |last17=Brand |first17=Helen E. A. |last18=Manne |first18=Tiina |last19=Fairbairn |first19=Andrew |last20=Shulmeister |first20=James |last21=Lyle |first21=Lindsey |last22=Salinas |first22=Makiah |last23=Page |first23=Mara |last24=Connell |first24=Kate |last25=Park |first25=Gayoung |last26=Norman |first26=Kasih |last27=Murphy |first27=Tessa |last28=Pardoe |first28=Colin |hdl=2440/107043}}</ref><ref name="Veth" /><ref name="Williams-2021">{{cite journal |last1=Williams |first1=Martin A. J. |last2=Spooner |first2=Nigel A. |last3=McDonnell |first3=Kathryn |last4=O'Connell |first4=James F. |date=January 2021 |title=Identifying disturbance in archaeological sites in tropical northern Australia: Implications for previously proposed 65,000-year continental occupation date |journal=Geoarchaeology |language=en |volume=36 |issue=1 |pages=92–108 |bibcode=2021Gearc..36...92W |doi=10.1002/gea.21822 |issn=0883-6353 |s2cid=225321249 |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/gea.21822 |url-access= |access-date=16 October 2023 |archive-date=4 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231004091731/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/gea.21822 |url-status=live }}</ref> By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct languages and had one of the oldest living cultures in the world.<ref name="Flood" /> [[history of Australia|Australia's written history]] commenced with [[European maritime exploration of Australia|Dutch exploration]] of most of the coastline in the 17th-century. British colonisation began in 1788 with the establishment of the penal [[colony of New South Wales]]. By the mid-19th century, most of the continent had been explored by European settlers and five additional self-governing [[Crown colony|British colonies]] were established, each gaining [[responsible government]] by 1890. The [[Federation of Australia|colonies federated]] in 1901, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. This continued a process of increasing autonomy from the United Kingdom, highlighted by the ''[[Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942]]'', and culminating in the [[Australia Acts]] of 1986.<ref name="Contiades Fotiadou 2020 p. 389">{{Cite book | last1=Contiades | first1=X. | last2=Fotiadou | first2=A. | title=Routledge Handbook of Comparative Constitutional Change | publisher=Taylor & Francis | year=2020 | isbn=978-1-3510-2097-8 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GmoPEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA389 | page=389 | access-date=17 July 2023 | archive-date=19 April 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230419202011/https://books.google.com/books?id=GmoPEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA389 | url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
For at least 40,000 years before European settlement in the late 18th century, Australia was inhabited by [[indigenous Australians]],<ref>[http://news.softpedia.com/news/Both-Aborigines-and-Europeans-Rooted-in-Africa-54225.shtml Both Australian Aborigines and Europeans Rooted in Africa – 50,000 years ago].</ref> |
|||
who belonged to one or more of roughly [[Indigenous Australian languages|250 language groups]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.NSF/2f762f95845417aeca25706c00834efa/aadb12e0bbec2820ca2570ec001117a5!OpenDocument|title=Australian Social Trends|work=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] website|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia|accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref><ref>Michael Walsh. 'Overview of indigenous languages of Australia' in Suzane Romaine (ed) ''Language in Australia'' (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1991) ISBN 0-521-33983-9</ref> After discovery by [[Dutch Republic|Dutch]] explorers in 1606, Australia's eastern half was claimed by [[Kingdom of Great Britain|Britain]] in 1770 and initially settled through [[penal transportation]] to the colony of [[New South Wales]], formally founded on 7 February 1788<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.baseline.nsw.gov.au/history.html |title=The Heritage of the Land and Property Management Authority |publisher=Baseline.nsw.gov.au |date= |accessdate=2010-10-27}}{{dead link|date=April 2011}}</ref> (although formal possession of the land had occurred on 26 January 1788). The population grew steadily in subsequent decades; the continent was explored and an additional five [[Responsible government|self-governing]] [[British Overseas Territories|Crown Colonies]] were established. |
|||
Australia is a [[federalism in Australia|federal]] [[parliamentary democracy]] and [[constitutional monarchy]] comprising [[states and territories of Australia|six states and ten territories]]. Its population of more than {{#expr:{{Data Australia|poptoday}} / 1000000 round 0}} million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard.<ref name="popclock"/><ref>{{Cite web |url= http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/Lookup/by%20Subject/1301.0~2012~Main%20Features~Geographic%20distribution%20of%20the%20population~49 |title= Geographic Distribution of the Population |access-date= 1 December 2012 |date= 24 May 2012 |archive-date= 14 April 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20210414084634/https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/Lookup/by%20Subject/1301.0~2012~Main%20Features~Geographic%20distribution%20of%20the%20population~49 |url-status= live }}</ref> [[Canberra]] is the nation's capital, while [[List of cities in Australia by population|its most populous cities]] are [[Sydney]] and [[Melbourne]], both with a population of more than 5 million.<ref name="ABS-regional-population-latest">{{Cite web |date=20 April 2023 |title=Regional population |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/regional-population/latest-release |access-date=23 April 2023 |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics |archive-date=10 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231010145251/https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/regional-population/latest-release |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Culture of Australia|Australia's culture]] is diverse,<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024 |title=Culturally and linguistically Diverse Australian |url=https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports-data/population-groups/cald-australians/overview |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240219224057/https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports-data/population-groups/cald-australians/overview |archive-date=19 February 2024 |access-date=20 February 2024 |website=Australian Government, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare}}</ref> and the country has one of the [[List of sovereign states by immigrant and emigrant population|highest foreign-born populations in the world]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=O'Donnell |first=James |date=27 November 2023 |title=Is Australia a cohesive nation? |url=https://www.abc.net.au/religion/social-cohesion-australia-diversity-inequality-threats/103133458 |access-date=21 February 2024 |website=ABC Australia |archive-date=20 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240220034741/https://www.abc.net.au/religion/social-cohesion-australia-diversity-inequality-threats/103133458 |url-status=live }}</ref> It has a highly [[developed economy]] and one of the [[List of countries by GNI (PPP) per capita|highest per capita incomes globally]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=6 September 2015 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, April 2015 |url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2015/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=39&pr.y=6&sy=2012&ey=2012&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=512,668,914,672,612,946,614,137,311,962,213,674,911,676,193,548,122,556,912,678,313,181,419,867,513,682,316,684,913,273,124,868,339,921,638,948,514,943,218,686,963,688,616,518,223,728,516,558,918,138,748,196,618,278,522,692,622,694,156,142,624,449,626,564,628,565,228,283,924,853,233,288,632,293,636,566,634,964,238,182,662,453,960,968,423,922,935,714,128,862,611,135,321,716,243,456,248,722,469,942,253,718,642,724,643,576,939,936,644,961,819,813,172,199,132,733,646,184,648,524,915,361,134,362,652,364,174,732,328,366,258,734,656,144,654,146,336,463,263,528,268,923,532,738,944,578,176,537,534,742,536,866,429,369,433,744,178,186,436,925,136,869,343,746,158,926,439,466,916,112,664,111,826,298,542,927,967,846,443,299,917,582,544,474,941,754,446,698,666&s=NGDPDPC&grp=0&a= |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150906100138/http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2015/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=39&pr.y=6&sy=2012&ey=2012&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=512,668,914,672,612,946,614,137,311,962,213,674,911,676,193,548,122,556,912,678,313,181,419,867,513,682,316,684,913,273,124,868,339,921,638,948,514,943,218,686,963,688,616,518,223,728,516,558,918,138,748,196,618,278,522,692,622,694,156,142,624,449,626,564,628,565,228,283,924,853,233,288,632,293,636,566,634,964,238,182,662,453,960,968,423,922,935,714,128,862,611,135,321,716,243,456,248,722,469,942,253,718,642,724,643,576,939,936,644,961,819,813,172,199,132,733,646,184,648,524,915,361,134,362,652,364,174,732,328,366,258,734,656,144,654,146,336,463,263,528,268,923,532,738,944,578,176,537,534,742,536,866,429,369,433,744,178,186,436,925,136,869,343,746,158,926,439,466,916,112,664,111,826,298,542,927,967,846,443,299,917,582,544,474,941,754,446,698,666&s=NGDPDPC&grp=0&a= |archive-date=6 September 2015 |access-date=1 April 2019 |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2022 |title=Human Development Report 2021-22 |url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2021-22pdf_1.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220908114232/http://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2021-22pdf_1.pdf |archive-date=8 September 2022 |access-date=9 September 2022 |website=United Nations Development Programme}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=31 October 2011 |title=Australians the world's wealthiest |url=https://www.smh.com.au/executive-style/luxury/australians-the-worlds-wealthiest-20111101-1mt2r.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140710153747/http://www.smh.com.au/executive-style/luxury/australians-the-worlds-wealthiest-20111101-1mt2r.html |archive-date=10 July 2014 |access-date=24 July 2012 |work=The Sydney Morning Herald}}</ref> Its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade relations are crucial to [[Economy of Australia|the country's economy]]. It [[International rankings of Australia|ranks highly]] for quality of life, health, education, economic freedom, civil liberties and political rights.<ref name="Global Australia 2021">{{Cite web | title=Statistics and rankings | website=Global Australia | date=18 May 2021 | url=https://www.globalaustralia.gov.au/why-australia/statistics-and-rankings | access-date=28 March 2023 | archive-date=28 March 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230328003912/https://www.globalaustralia.gov.au/why-australia/statistics-and-rankings | url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
On 1 January 1901, the six colonies [[Federation of Australia|became a federation]] and the Commonwealth of Australia was formed. Since Federation, Australia has maintained a stable [[liberal democracy|liberal democratic]] political system and is a [[Commonwealth realm]]. The population is 22 million, with approximately 60 per cent concentrated in and around the mainland state capitals of [[Sydney]], [[Melbourne]], [[Brisbane]], [[Perth, Western Australia|Perth]] and [[Adelaide]]. The nation's capital city is [[Canberra]], in the [[Australian Capital Territory]]. Approximately 56 per cent of Australia's population live in either Victoria or New South Wales, and approximately 77 per cent live on the mainland's east coast. |
|||
Australia is a [[middle power]], and has the world's [[List of countries by military expenditures|thirteenth-highest military expenditure]]. It is a member of international groups including the United Nations; the [[G20]]; the [[OECD]]; the [[World Trade Organization]]; [[Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation]]; the [[Pacific Islands Forum]]; the [[Pacific Community]]; the [[Commonwealth of Nations]]; and the defence and security organisations [[ANZUS]], [[AUKUS]], and the [[Five Eyes]]. It is also a [[major non-NATO ally]] of the United States.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Rachman |first=Gideon |date=13 March 2023 |title=Aukus, the Anglosphere and the return of great power rivalry |url=https://www.ft.com/content/e4abd866-54cb-4923-9a66-ebb5b5ed67bf |url-access=subscription |access-date=19 March 2023 |work=Financial Times |archive-date=20 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320005932/https://www.ft.com/content/e4abd866-54cb-4923-9a66-ebb5b5ed67bf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
A prosperous [[developed country]], Australia is the [[List of countries by GDP (nominal)|world's thirteenth largest economy]]. Australia ranks highly in many international comparisons of national performance such as human development, quality of life, health care, life expectancy, public education, [[economic freedom]] and the protection of civil liberties and political rights.<ref name="World Audit">{{cite web|url=http://www.worldaudit.org/countries/australia.htm|title=Australia: World Audit Democracy Profile|work=WorldAudit.org|accessdate=5 January 2008}}</ref> Australia is a member of the [[United Nations]], [[G20]], [[Commonwealth of Nations]], [[ANZUS]], [[Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development|OECD]], [[Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation|APEC]], [[Pacific Islands Forum]] and the [[World Trade Organization]]. |
|||
==Etymology== |
==Etymology== |
||
{{Main|Name of Australia}} |
|||
Pronounced {{IPA|[[Australian English phonology|[əˈstɹæɪljə, -liə]]]}} in [[Australian English]],<ref>Australian pronunciations: ''[[Macquarie Dictionary|Macquarie Dictionary, Fourth Edition]]'' (2005). Melbourne, The Macquarie Library Pty Ltd. ISBN 1-876429-14-3</ref> the name ''[[List of country name etymologies#A|Australia]]'' is derived from the [[Latin]] ''australis'', meaning "southern". The country has been referred to colloquially as ''Oz'' since the early 20th century.{{#tag:ref|The [[Oxford English Dictionary]] records a first occurrence in 1908, in the form ''Oss''. ''Oz'' is often taken as an oblique reference to the fictional Land of Oz in the film ''[[The Wizard of Oz (1939 film)|The Wizard of Oz]]'' (1939), based on [[L. Frank Baum]]'s novel ''[[The Wonderful Wizard of Oz]]'' (1900).<ref>Jacobson, H., ''In the Land of Oz'', Penguin, 1988, ISBN 0-14-010966-8.</ref> Australians' "image of Australia as a 'Land of Oz' is not new, and dedication to it runs deep".<ref>''The Americana Annual: 1988'', Americana Corporation, vol. 13, 1989, p. 66, ISBN 0-7172-0220-8.</ref> The spelling ''Oz'' is likely to have been influenced by the 1939 film, though the pronunciation was probably always with a /z/, as it is also for ''Aussie'', sometimes spelt ''Ozzie''.<ref>[[Eric Partridge|Partridge, Eric]], et al., ''The New Partridge Dictionary of Slang and Unconventional English'', Taylor & Francis, 2006, ISBN 0-415-25938-X, entries "Oz" and "Ozzie", p. 1431.</ref> The [[Baz Luhrmann]] film ''[[Australia (2008 film)#Recurring motifs|Australia]]'' (2008) makes repeated reference to ''The Wizard of Oz'', which appeared just before the wartime action of ''Australia''. Some critics have even speculated that Baum was inspired by Australia, in naming the ''Land of Oz'': "In ''Ozma of Oz'' (1907) Dorothy gets back to Oz as the result of a storm at sea while she and Uncle Henry are traveling by ship to Australia. So, like Australia, Oz is somewhere to the west of California. Like Australia, Oz is an island continent. Like Australia, Oz has inhabited regions bordering on a great desert. One might almost imagine that Baum intended Oz to be Australia, or perhaps a magical land in the center of the great Australian desert."<ref>Algeo, J., "Australia as the Land of Oz", ''American Speech'', Vol. 65, No. 1, 1990, pp. 86–89.</ref>|group="N"|name="Oss"}} ''[[Aussie]]'' is a common, colloquial term for "Australian". |
|||
The name ''Australia'' (pronounced {{IPAc-en|ə|ˈ|s|t|r|eɪ|l|i|ə}} in [[Australian English]])<ref>Australian pronunciations: ''[[Macquarie Dictionary]], Fourth Edition'' (2005) Melbourne, The Macquarie Library Pty Ltd. {{ISBN|978-1-876429-14-0}}</ref>{{page needed|date=December 2024}} is derived from the Latin {{Lang|la|[[Terra Australis]]}} ({{Gloss|southern land}}), a name used for a hypothetical continent in the Southern Hemisphere since ancient times.<ref>{{Cite web|title=australia {{pipe}} Etymology, origin and meaning of the name australia by etymonline|url=https://www.etymonline.com/word/australia|access-date=15 January 2022|website=www.etymonline.com|language=en|archive-date=29 January 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220129005011/https://www.etymonline.com/word/Australia|url-status=live}}</ref> Several 16th-century cartographers used the word Australia on maps, but not to identify modern Australia.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Clarke |first1=Jacqueline |last2=Clarke |first2=Philip |date=10 August 2014 |title=Putting 'Australia' on the map |url=http://theconversation.com/putting-australia-on-the-map-29816 |access-date=15 January 2022 |website=The Conversation |language=en |archive-date=2 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220302195128/https://theconversation.com/putting-australia-on-the-map-29816 |url-status=live }}</ref> When Europeans began visiting and mapping Australia in the 17th century, the name {{Lang|la|Terra Australis}} was applied to the new territories.{{Refn|The earliest recorded use of the word ''Australia'' in English was in 1625 in "A note of Australia del Espíritu Santo, written by Sir [[Richard Hakluyt]]", published by [[Samuel Purchas]] in ''Hakluytus Posthumus'', a corruption of the original Spanish name "Austrialia del Espíritu Santo" (Southern Land of the Holy Spirit)<ref>[http://www.sl.nsw.gov.au/discover_collections/history_nation/queiros/index.html "He named it Austrialia del Espiritu Santo and claimed it for Spain"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130817051612/http://www.sl.nsw.gov.au/discover_collections/history_nation/queiros/index.html |date=17 August 2013}} ''The Spanish quest for Terra Australis|State Library of New South Wales Page 1''</ref><ref>[http://rupertgerritsen.tripod.com/pdf/published/Austrialia_Globe_72_2013_pp23-30.pdf "A note on 'Austrialia' or 'Australia' Rupert Gerritsen – Journal of The Australian and New Zealand Map Society Inc. The Globe Number 72, 2013] {{Webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160612021158/http://rupertgerritsen.tripod.com/pdf/published/Austrialia_Globe_72_2013_pp23-30.pdf|date=12 June 2016}} ''Posesion en nombre de Su Magestad (Archivo del Museo Naval, Madrid, MS 951) p. 3''.</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article63620938|title=The Illustrated Sydney News|newspaper=Illustrated Sydney News|date=26 January 1888|access-date=29 January 2012|page=2|publisher=National Library of Australia|archive-date=11 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231011073045/https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/63620938|url-status=live}}</ref> for an island in [[Vanuatu]].<ref>Purchas, vol. iv, pp. 1422–1432, 1625</ref> The Dutch adjectival form ''australische'' was used in a Dutch book in [[History of Jakarta|Batavia]] ([[Jakarta]]) in 1638, to refer to the newly discovered lands to the south.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DDNEle_1NzkC&pg=PA299|page=299|last=Scott|first=Ernest|orig-year=1914|title=The Life of Captain Matthew Flinders|isbn=978-1-4191-6948-9|year=2004|publisher=Kessinger Publishing|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=10 June 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240610132503/https://books.google.com/books?id=DDNEle_1NzkC&pg=PA299|url-status=live}}</ref>|group="N"}} |
|||
Legends of ''[[Terra Australis|Terra Australis Incognita]]''—an "unknown land of the South"—date back to Roman times and were commonplace in medieval geography, although not based on any documented knowledge of the continent. Following European discovery, names for the Australian landmass were often references to the famed ''Terra Australis''. |
|||
Until the early 19th century, Australia was best known as ''[[New Holland (Australia)|New Holland]]'', a name first applied by the Dutch explorer [[Abel Tasman]] in 1644 (as {{Lang|nl|Nieuw-Holland}}) and subsequently anglicised. {{Lang|la|Terra Australis}} still saw occasional usage, such as in scientific texts.{{Refn|For instance, the 1814 work ''[[A Voyage to Terra Australis]]''.|group="N"}} The name ''Australia'' was popularised by the explorer [[Matthew Flinders]], who said it was "more agreeable to the ear, and an assimilation to the names of the other great portions of the Earth".<ref>{{Cite book|last=Scott|first=Ernest|title=The Life of Captain Matthew Flinders, R.N.|publisher=Angus & Robertson|place=Sydney|year=1914|page=428|chapter=The naming of Australia}}</ref> The first time that ''Australia'' appears to have been officially used was in April 1817, when Governor [[Lachlan Macquarie]] acknowledged the receipt of Flinders' charts of Australia from [[Henry Bathurst, 3rd Earl Bathurst|Lord Bathurst]].<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article58549315|title=Who Named Australia?|newspaper=The Mail (Adelaide, South Australia)|location=Adelaide|date=11 February 1928|access-date=14 February 2012|page=16|publisher=National Library of Australia|archive-date=17 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210417085724/https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/58549315|url-status=live}}</ref> In December 1817, Macquarie recommended to the [[Colonial Office]] that it be formally adopted.<ref>Weekend Australian, 30–31 December 2000, p. 16</ref> In 1824, the [[British Admiralty|Admiralty]] agreed that the continent should be known officially by that name.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Department of Immigration and Citizenship |title=Life in Australia|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia|year=2007|page=11|isbn=978-1-9214-4630-6|url=http://www.immi.gov.au/living-in-australia/values/book/english/lia_english_part1.pdf |access-date=30 March 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091017070336/http://www.immi.gov.au/living-in-australia/values/book/english/lia_english_part1.pdf |archive-date=17 October 2009}}</ref> The first official published use of the new name came with the publication in 1830 of ''The Australia Directory'' by the [[United Kingdom Hydrographic Office|Hydrographic Office]].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Coman|first=Brian J.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=P5m4zNxaaSUC&pg=PA40|title=A Loose Canon: Essays on History, Modernity and Tradition|date=2007|publisher=Connor Court Publishing Pty Ltd|isbn=978-0-9802-9362-3|language=en|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=27 March 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230327193458/https://books.google.com/books?id=P5m4zNxaaSUC&pg=PA40|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
The earliest recorded use of the word ''Australia'' in English was in 1625 in "A note of Australia del Espíritu Santo, written by Master Hakluyt" and published by [[Samuel Purchas]] in ''Hakluytus Posthumus'', a corruption of the original Spanish name ''Austrialia del Espíritu Santo'' for an island in [[Vanuatu]].<ref>Purchas, vol. iv, pp. 1422–32, 1625. This appears to be variation of the original Spanish "Austrialia" [''sic''].[http://web.archive.org/web/20060822033701/http://www.hispanicfiesta.com.au/pics/pdf_mag_2004/42.PDF] A copy at the Library of Congress can be read online [http://memory.loc.gov/service/rbc/rbdk/d0404/02951422.jpg].</ref> The Dutch adjectival form ''Australische'' was used in a Dutch book in [[History of Jakarta|Batavia]] ([[Jakarta]]) in 1638, to refer to the newly discovered lands to the south.<ref>{{Cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=DDNEle_1NzkC&pg=PA299&dq=Australische+1638+batavia#v=onepage&q=Australische%201638%20batavia&f=false|page=299|last=Scott|first=Ernest|origyear=1914|title=The Life of Captain Matthew Flinders|isbn=978-1-4191-6948-9|year=2004|publisher=Kessinger Publishing}}</ref> ''Australia'' was later used in a 1693 translation of ''Les Aventures de Jacques Sadeur dans la Découverte et le Voyage de la Terre Australe'', a 1676 French novel by [[Gabriel de Foigny]], under the pen-name Jacques Sadeur.<ref>Sidney J. Baker, ''The Australian Language'', second edition, 1966.</ref> <!-- The 1676 version is rare. Regardless, it was the first edition of this book — some details are at http://www.ilab.org/db/detail.php?booknr=293280177 --> Referring to the entire South Pacific region, [[Alexander Dalrymple]] used it in ''An Historical Collection of Voyages and Discoveries in the South Pacific Ocean'' in 1771. By the end of the 18th century, the name was being used to refer specifically to Australia, with the botanists [[George Shaw]] and [[James Edward Smith|Sir James Smith]] writing of "the vast island, or rather continent, of Australia, Australasia or [[New Holland (Australia)|New Holland]]" in their 1793 ''Zoology and Botany of New Holland'',<ref name="Ferguson">{{Cite book|last=Ferguson|first=John Alexander|title=Bibliography of Australia: 1784–1830|publisher=National Library of Australia|year=1975|edition=reprint|volume=1|page=77|isbn=0-642-99044-1|url=http://books.google.com/?id=KQzgC-xeQkIC}}</ref> and [[James Wilson]] including it on a 1799 chart.<ref name="Estensen 2002 p354">{{Cite book|first=Miriam|last=Estensen|year=2002|title=The Life of Matthew Flinders|publisher=Allen & Unwin|isbn=1-74114-152-4|page=354}}</ref> |
|||
Colloquial names for Australia include "[[Name of Australia#Oz|Oz]]", "[[Straya]]" and "[[Down Under]]".<ref>{{Cite web |title=Straya |url=http://macquariedictionary.com.au/ |url-access=subscription |access-date=12 February 2024 |website=[[Macquarie Dictionary]] |archive-date=9 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240209174709/https://www.macquariedictionary.com.au/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Other epithets include "the Great Southern Land", "the Lucky Country" (from [[the Lucky Country|the 1964 book of the same name]]), "the Sunburnt Country", and "the Wide Brown Land". The latter two both derive from [[Dorothea Mackellar]]'s 1908 poem "[[My Country]]".<ref>{{Cite web|last1=School|first1=Head of|last2=admin.hal@anu.edu.au|title=Australian National Dictionary Centre|url=https://slll.cass.anu.edu.au/centres/andc|access-date=15 January 2022|website=ANU School of Literature, Languages and Linguistics|language=en|archive-date=12 March 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110312000501/http://www.anu.edu.au/ANDC/pubs/ozwords/June_98/2._aitch.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
The name ''Australia'' was popularised by the explorer [[Matthew Flinders]], who pushed for it to be formally adopted as early as 1804. When preparing his manuscript and charts for his 1814 ''[[A Voyage to Terra Australis]]'', he was persuaded by his patron, [[Joseph Banks|Sir Joseph Banks]], to use the term ''Terra Australis'' as this was the name most familiar to the public. Flinders did so, but allowed himself the footnote: {{quote|"Had I permitted myself any innovation on the original term, it would have been to convert it to Australia; as being more agreeable to the ear, and an assimilation to the names of the other great portions of the earth."<ref>{{Cite book|first=Matthew|last=Flinders|year=1814|title=[[A Voyage to Terra Australis]]|publisher=G. and W. Nicol}}</ref>}} This is the only occurrence of the word ''Australia'' in that text; but in Appendix III, [[Robert Brown (botanist)|Robert Brown]]'s ''[[General remarks, geographical and systematical, on the botany of Terra Australis]]'', Brown makes use of the adjectival form ''Australian'' throughout,<ref name="Bennett 1868">{{Cite book|editor=Bennett, J. J.|year=1866–68|title=The Miscellaneous Botanical Works of Robert Brown, Esq., D.C.L., F.R.S.|volume=2|chapter=General remarks, geographical and systematical, on the botany of Terra Australis|pages=1–89}}</ref>—the first known use of that form.<ref name="Mabberley 1985">{{Cite book|first=David|last=Mabberley|year=1985|title=Jupiter botanicus: Robert Brown of the British Museum|publisher=British Museum (Natural History)|isbn=3-7682-1408-7}}</ref> Despite popular conception, the book was not instrumental in the adoption of the name: the name came gradually to be accepted over the following ten years.<ref name="Estensen 2002 p450">Estensen, p. 450</ref> [[Lachlan Macquarie]], a [[Governor of New South Wales]], subsequently used the word in his dispatches to England, and on 12 December 1817 recommended to the Colonial Office that it be formally adopted.<ref>Weekend Australian, 30–31 December 2000, p. 16</ref> In 1824, the Admiralty agreed that the continent should be known officially as ''Australia''.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Department of Immigration and Citizenship|title=Life in Australia|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia|year=2007|page=11|isbn=978-1-921446-30-6|url=http://www.immi.gov.au/living-in-australia/values/book/english/lia_english_part1.pdf|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
{{Main|History of Australia}} |
{{Main|History of Australia}} |
||
{{For timeline|Timeline of Australian history}} |
|||
[[File:Australia discoveries by Europeans before 1813 en.png|thumb|right|300px|alt=Map of Australia with coloured arrows showing the path of early explorers around the coast of Australia and surrounding islands|Exploration by Europeans till 1812<br> |
|||
{{legend|#000000|1606 [[Willem Janszoon]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#ff9955|1606 [[Luis Váez de Torres]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#39842c|1616 [[Dirk Hartog]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#ffd42a|1619 [[Frederick de Houtman]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#835b38|1644 [[Abel Tasman]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#516778|1696 [[Willem de Vlamingh]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#000080|1699 [[William Dampier]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#8000ff|1770 [[James Cook]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#0055d4|1797–1799 [[George Bass]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#ff0000|1801–1803 [[Matthew Flinders]]}}]] |
|||
Human habitation of Australia is estimated to have begun between 42,000 and 48,000 years ago,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Gillespie, Richard |year=2002 |url=http://www-personal.une.edu.au/~pbrown3/Gillespie02.pdf |title=Dating the First Australians (full text) |journal=Radiocarbon |volume=44 |issue=2 |format=PDF |pages=455–472 |accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref> possibly with the migration of people by [[land bridge]]s and short sea-crossings from what is now [[Southeast Asia]]. These first inhabitants may have been ancestors of modern Indigenous Australians. At the time of European settlement in the late 18th century, most Indigenous Australians were [[hunter-gatherer]]s, with a complex [[oral tradition|oral culture]] and spiritual values based on reverence for the land and a belief in the [[Dreamtime]]. The [[Torres Strait Islanders]], ethnically [[Melanesia]]n, were originally horticulturalists and hunter-gatherers.<ref>{{cite web|title=Early Aussie Tattoos Match Rock Art|last=Viegas|first=Jennifer|publisher=Discovery News|date=3 July 2008|accessdate=30 March 2010|url=http://dsc.discovery.com/news/2008/07/03/australia-tattoos-art.html}}</ref> |
|||
=== Indigenous prehistory === |
|||
Following sporadic visits by fishermen from the [[Malay Archipelago]],<ref>{{Cite book|last=MacKnight|first=CC|year=1976|title=The Voyage to Marege: Macassan Trepangers in Northern Australia|publisher=[[Melbourne University Press]]}}</ref> the first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent were attributed to the Dutch navigator [[Willem Janszoon]]. He sighted the coast of [[Cape York Peninsula]] on an unknown date in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the [[Pennefather River]] on the western shore of Cape York, near the modern town of [[Weipa, Queensland|Weipa]].<ref name=dhm233>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 233.</ref> The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines of "New Holland" during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement.<ref name=dhm233/> [[William Dampier]], an English explorer/privateer landed on the northwest coast of Australia in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, [[James Cook]] sailed along and mapped the east coast of Australia, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/australianhistory/|title=European discovery and the colonisation of Australia|work=Australian Government: Culture Portal|publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia|date=11 January 2008|accessdate=7 May 2010}}</ref> Cook's discoveries prepared the way for establishment of a new [[penal colony]]. The British [[British overseas territories|Crown Colony]] of New South Wales was formed on 26 January 1788, when Captain [[Arthur Phillip]] led the [[First Fleet]] to [[Port Jackson]].<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 157, 254.</ref> This date became Australia's national day, [[Australia Day]]. [[Van Diemen's Land]], now known as Tasmania, was settled in 1803 and became a separate colony in 1825.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 464–65, 628–29.</ref> The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Australia in 1828.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 678.</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Prehistory of Australia|Indigenous Australians}} |
|||
[[File:Bradshaw rock paintings.jpg|thumb|upright=1.0|right|[[Aboriginal rock art]] in the [[Kimberley (Western Australia)|Kimberley]] region of Western Australia]] |
|||
[[Indigenous Australians]] comprise two broad groups: |
|||
Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: [[South Australia]] in 1836, [[Victoria (Australia)|Victoria]] in 1851, and Queensland in 1859.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 464.</ref> The [[Northern Territory]] was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 470.</ref> South Australia was founded as a "free province"—it was never a penal colony.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 598.</ref> Victoria and Western Australia were also founded "free", but later accepted [[convicts in Australia|transported convicts]].<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 679.</ref><ref>[http://www.access.prov.vic.gov.au/public/PROVguides/PROVguide057/PROVguide057.jsp Convict Records] Public Record office of Victoria; [http://www.sro.wa.gov.au/collection/convict.asp State Records Office of Western Australia].</ref> A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.<ref>{{cite web|year=1988 |url=http://www.abs.gov.au/Ausstats/abs%40.nsf/0/A890E87A9AB97424CA2569DE0025C18B?Open |title=1998 Special Article – The State of New South Wales – Timeline of History |publisher=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]]}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Aboriginal Australians]], who are the various [[Indigenous peoples]] of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, including [[Aboriginal Tasmanians|Tasmania]] |
|||
* [[Torres Strait Islanders]], who are a distinct [[Melanesia]]n people of [[Torres Strait Islands]] |
|||
Human habitation of the Australian continent is estimated to have begun 50,000 to 65,000 years ago,<ref name="ClarksonJacobs2017" /><ref name="Nunn2018">{{Cite book|first=Patrick|last=Nunn|title=The Edge of Memory: Ancient Stories, Oral Tradition and the Post-Glacial World|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Z4xaDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT16|year=2018|publisher=Bloomsbury Publishing|isbn=978-1-4729-4327-9|page=16|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=3 December 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231203142811/https://books.google.com/books?id=Z4xaDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT16#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="FaganDurrani2018">{{Cite book|first1=Brian M.|last1=Fagan|first2=Nadia|last2=Durrani|title=People of the Earth: An Introduction to World Prehistory|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=W0NvDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT250|year=2018|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-1-3517-5764-5|pages=250–253|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=3 December 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231203142816/https://books.google.com/books?id=W0NvDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT250#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Veth">{{Cite book |last1=Veth |first1=Peter |url=https://archive.org/details/cambridgehistory0001unse_m8y7 |title=The Cambridge History of Australia, Volume 1, Indigenous and Colonial Australia |last2=O'Connor |first2=Sue |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-1070-1153-3 |editor-last=Bashford |editor-first=Alison |location=Cambridge |pages=19 |chapter=The past 50,000 years: an archaeological view |editor-last2=MacIntyre |editor-first2=Stuart |url-access=registration}}</ref> with the migration of people by [[land bridge]]s and short sea crossings from what is now Southeast Asia.<ref name="Oppenheimer2013">{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VQQvDwAAQBAJ&pg=PP111|title=Out of Eden: The Peopling of the World|first=Stephen|last=Oppenheimer|date=2013|publisher=Little, Brown Book Group|isbn=978-1-7803-3753-1|pages=111–|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=3 December 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231203142820/https://books.google.com/books?id=VQQvDwAAQBAJ&pg=PP111#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> It is uncertain how many waves of immigration may have contributed to these ancestors of modern Aboriginal Australians.<ref name="Malaspinas Westaway Muller Sousa 2016 pp. 207–214" /><ref>{{Cite web |last=Dorey |first=Fran |title=When did modern humans get to Australia? |url=https://australian.museum/learn/science/human-evolution/the-spread-of-people-to-australia |publisher=Australian Museum |access-date=21 August 2020 |archive-date=17 August 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200817140725/https://australian.museum/learn/science/human-evolution/the-spread-of-people-to-australia/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The [[Madjedbebe]] rock shelter in [[Arnhem Land]] is possibly the oldest site showing the presence of humans in Australia.<ref name="Gilligan2018">{{Cite book|first=Ian|last=Gilligan|title=Climate, Clothing, and Agriculture in Prehistory: Linking Evidence, Causes, and Effects|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Ux50DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA237|date=2018|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-1-1084-7008-7|page=237|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=3 December 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231203142816/https://books.google.com/books?id=Ux50DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA237#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Williams-2021" /> The oldest human remains found are the [[Lake Mungo remains]], which have been dated to around 41,000 years ago.<ref name="TunizGillespie2016">{{Cite book|first1=Claudio|last1=Tuniz|first2=Richard|last2=Gillespie|first3=Cheryl|last3=Jones|title=The Bone Readers: Science and Politics in Human Origins Research|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WrJmDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA43|year=2016|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-3154-1888-9|page=43|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=3 December 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231203142820/https://books.google.com/books?id=WrJmDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA43#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Castillo2015">{{Cite book|first=Alicia|last=Castillo|title=Archaeological Dimension of World Heritage: From Prevention to Social Implications|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jV64BAAAQBAJ&pg=PA41|date=2015|publisher=Springer Science|isbn=978-1-4939-0283-5|page=41|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=3 December 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231203142821/https://books.google.com/books?id=jV64BAAAQBAJ&pg=PA41#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Port Arthur Seeseite.jpg|thumb|left|alt=A calm body of water is in the foreground. The shoreline is about 200 metres away. To the left, close to the shore, are three tall [[gum tree]]s; behind them on an incline are ruins, including walls and watchtowers of light-coloured stone and brick, what appear to be the foundations of walls, and grassed areas. To the right lie the outer walls of a large rectangular four-storey building dotted with regularly spaced windows. Forested land rises gently to a peak several kilometres back from the shore.|[[Port Arthur, Tasmania]] was Australia's largest [[gaol]] for transported convicts.]] |
|||
Aboriginal Australian culture is one of the oldest continuous cultures on Earth.<ref name="Flood">{{cite book | last=Flood | first=J. | title=The Original Australians: The story of the Aboriginal People | publisher=Allen & Unwin | year=2019 | isbn=978-1-76087-142-0 |edition=2nd |location=Crows Nest NSW |page=161 |author-link=Josephine Flood}}</ref><ref name="Australian Geographic 2011 i652">{{cite web | title=DNA confirms Aboriginal culture one of Earth's oldest | website=Australian Geographic | date=23 September 2011 | url=https://www.australiangeographic.com.au/news/2011/09/dna-confirms-aboriginal-culture-one-of-earths-oldest/ | access-date=9 February 2024 | archive-date=20 January 2024 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240120022657/https://www.australiangeographic.com.au/news/2011/09/dna-confirms-aboriginal-culture-one-of-earths-oldest/ | url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Jozuka 2016 i592">{{cite web | last=Jozuka | first=Emiko | title=Aboriginal Australians are Earth's oldest civilization: DNA study | website=CNN | date=22 September 2016 | url=https://www.cnn.com/2016/09/22/asia/indigenous-australians-earths-oldest-civilization/index.html#:~:text=A%20new%20genomic%20study%20has,stretching%20back%20roughly%2075%2C000%20years. | access-date=9 February 2024 | archive-date=4 March 2024 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240304225419/https://www.cnn.com/2016/09/22/asia/indigenous-australians-earths-oldest-civilization/index.html#:~:text=A%20new%20genomic%20study%20has,stretching%20back%20roughly%2075%2C000%20years. | url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Malaspinas Westaway Muller Sousa 2016 pp. 207–214">{{cite journal |last1=Malaspinas |first1=Anna-Sapfo |last2=Westaway |first2=Michael C. |last3=Muller |first3=Craig |last4=Sousa |first4=Vitor C. |last5=Lao |first5=Oscar |last6=Alves |first6=Isabel |last7=Bergström |first7=Anders |last8=Athanasiadis |first8=Georgios |last9=Cheng |first9=Jade Y. |last10=Crawford |first10=Jacob E. |last11=Heupink |first11=Tim H. |last12=Macholdt |first12=Enrico |last13=Peischl |first13=Stephan |last14=Rasmussen |first14=Simon |last15=Schiffels |first15=Stephan |display-authors=1 |date=21 September 2016 |title=A genomic history of Aboriginal Australia |journal=Nature |publisher=Springer Science and Business Media LLC |volume=538 |issue=7624 |pages=207–214 |bibcode=2016Natur.538..207M |doi=10.1038/nature18299 |issn=0028-0836 |pmid=27654914 |hdl-access=free |hdl=10754/622366 |last16=Subramanian |first16=Sankar |last17=Wright |first17=Joanne L. |last18=Albrechtsen |first18=Anders |last19=Barbieri |first19=Chiara |last20=Dupanloup |first20=Isabelle |last21=Eriksson |first21=Anders |last22=Margaryan |first22=Ashot |last23=Moltke |first23=Ida |last24=Pugach |first24=Irina |last25=Korneliussen |first25=Thorfinn S. |last26=Levkivskyi |first26=Ivan P. |last27=Moreno-Mayar |first27=J. Víctor |last28=Ni |first28=Shengyu |last29=Racimo |first29=Fernando |last30=Sikora |first30=Martin|pmc=7617037 }}</ref> At the time of first European contact, Aboriginal Australians belonged to wide range of societies, with diverse economies spread across at least [[Australian Aboriginal languages|250 different language groups]].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Williams |first=Elizabeth |year=2015 |title=Complex hunter-gatherers: a view from Australia |journal=Antiquity |publisher=Cambridge University Press |volume=61 |issue=232 |pages=310–321 |doi=10.1017/S0003598X00052182 |s2cid=162146349}}</ref><ref name="SáenzEmbrick2015">{{Cite book |last1=Sáenz |first1=Rogelio |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=v_bLCQAAQBAJ&pg=PA602 |title=The International Handbook of the Demography of Race and Ethnicity |last2=Embrick |first2=David G. |last3=Rodríguez |first3=Néstor P. |date=3 June 2015 |publisher=Springer |isbn=978-9-0481-8891-8 |pages=602– |access-date=17 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240610132454/https://books.google.com/books?id=v_bLCQAAQBAJ&pg=PA602#v=onepage&q&f=false |archive-date=10 June 2024 |url-status=live}}</ref> Estimates of the Aboriginal population before British settlement range from 300,000 to 3 million.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Bradshaw |first1=Corey J. A. |last2=Williams |first2=Alan N |last3=Saltré |first3=Frédérik |last4=Norman |first4=Kasih |last5=Ulm |first5=Sean |date=30 April 2021 |title=The First Australians grew to a population of millions, much more than previous estimates |url=https://theconversation.com/the-first-australians-grew-to-a-population-of-millions-much-more-than-previous-estimates-142371 |access-date= |website=[[The Conversation (website)|The Conversation]] |language=en-AU}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=25 January 2002 |title=1301.0 - Year Book Australia, 2002: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander population |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/94713ad445ff1425ca25682000192af2/bfc28642d31c215cca256b350010b3f4!OpenDocument |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230327193612/https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/94713ad445ff1425ca25682000192af2/bfc28642d31c215cca256b350010b3f4!OpenDocument |archive-date=27 March 2023 |access-date= |website=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] |language=en}}</ref><ref>Gough, Myles (11 May 2011). [https://web.archive.org/web/20120912060604/http://www.cosmosmagazine.com/news/4305/prehistoric-aboriginal-populations-australia-were-growing "Prehistoric Australian Aboriginal populations were growing"]. ''[[Cosmos Magazine]]''. Archived from [https://cosmosmagazine.com/news/4305/prehistoric-aboriginal-populations-australia-were-growing the original] on 12 September 2012.</ref> Aboriginal Australians cultures were (and remain) deeply connected with the land and the environment, with stories of [[The Dreaming]] maintained through [[oral tradition]], [[Songline|songs]], dance and paintings.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Mawson |first=Stephanie |date=2021 |title=The Deep Past of Pre-Colonial Australia |journal=The Historical Journal |language=en |volume=64 |issue=5 |pages=1483–6 |doi=10.1017/S0018246X20000369 |issn=0018-246X |doi-access=free}}</ref> Certain groups engaged in [[fire-stick farming]],<ref>{{Cite web |last=Wyrwoll |first=Karl-Heinz |date=11 January 2012 |title=How Aboriginal burning changed Australia's climate |url=http://theconversation.com/how-aboriginal-burning-changed-australias-climate-4454 |access-date=1 November 2023 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US |archive-date=15 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230715015907/https://theconversation.com/how-aboriginal-burning-changed-australias-climate-4454 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Williams |first=Robbie |date=21 June 2023 |title=Before the colonists came, we burned small and burned often to avoid big fires. It's time to relearn cultural burning |url=http://theconversation.com/before-the-colonists-came-we-burned-small-and-burned-often-to-avoid-big-fires-its-time-to-relearn-cultural-burning-201475 |access-date=1 November 2023 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US |archive-date=8 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240308085331/https://theconversation.com/before-the-colonists-came-we-burned-small-and-burned-often-to-avoid-big-fires-its-time-to-relearn-cultural-burning-201475 |url-status=live }}</ref> [[fish farming]],<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Bates |first1=Badger |last2=Westaway |first2=Michael |last3=Jackson |first3=Sue |date=15 December 2022 |title=Aboriginal people have spent centuries building in the Darling River. Now there are plans to demolish these important structures |url=http://theconversation.com/aboriginal-people-have-spent-centuries-building-in-the-darling-river-now-there-are-plans-to-demolish-these-important-structures-195966 |access-date=1 November 2023 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US |archive-date=1 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231101042204/https://theconversation.com/aboriginal-people-have-spent-centuries-building-in-the-darling-river-now-there-are-plans-to-demolish-these-important-structures-195966 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Clark |first=Anna |date=31 August 2023 |title=Friday essay: traps, rites and kurrajong twine – the incredible ingenuity of Indigenous fishing knowledge |url=http://theconversation.com/friday-essay-traps-rites-and-kurrajong-twine-the-incredible-ingenuity-of-indigenous-fishing-knowledge-210467 |access-date=1 November 2023 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US |archive-date=11 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240211091555/https://theconversation.com/friday-essay-traps-rites-and-kurrajong-twine-the-incredible-ingenuity-of-indigenous-fishing-knowledge-210467 |url-status=live }}</ref> and built [[Indigenous architecture#Australia|semi-permanent shelters]].<ref>{{Cite news |last=Wahlquist |first=Calla |date=5 September 2016 |title=Evidence of 9,000-year-old stone houses found on Australian island |url=https://www.theguardian.com/science/2016/sep/05/evidence-of-9000-year-old-stone-houses-found-on-australian-island |access-date=1 November 2023 |work=The Guardian |language=en-GB |issn=0261-3077 |archive-date=1 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231101042138/https://www.theguardian.com/science/2016/sep/05/evidence-of-9000-year-old-stone-houses-found-on-australian-island |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Flood22">{{cite book |last=Flood |first=J. |author-link=Josephine Flood |title=The Original Australians: The story of the Aboriginal People |publisher=Allen & Unwin |year=2019 |isbn=978-1-76087-142-0 |edition=2nd |location=Crows Nest NSW |pages=239–240}}</ref> These practices have variously been characterised as "[[hunter-gatherer]]", "[[Agriculture|agricultural]]", "natural cultivation" and "intensification".<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Mawson |first=Stephanie |date=2021 |title=The Deep Past of Pre-Colonial Australia |journal=The Historical Journal |language=en |volume=64 |issue=5 |pages=1486–1491 |doi=10.1017/S0018246X20000369 |issn=0018-246X |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Bender |first=Barbara |date=1978 |title=Gatherer-hunter to farmer: A social perspective |url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00438243.1978.9979731 |journal=World Archaeology |language=en |volume=10 |issue=2 |pages=204–222 |doi=10.1080/00438243.1978.9979731 |issn=0043-8243 |url-access=subscription}}</ref><ref>Gammage, Bill (October 2011). ''The Biggest Estate on Earth: How Aborigines made Australia''. Allen & Unwin. pp. 281–304.</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Gammage |first=Bill |date=19 September 2023 |title=Colonists upended Aboriginal farming, growing grain and running sheep on rich yamfields, and cattle on arid grainlands |url=http://theconversation.com/colonists-upended-aboriginal-farming-growing-grain-and-running-sheep-on-rich-yamfields-and-cattle-on-arid-grainlands-207118 |access-date=1 November 2023 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US |archive-date=12 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240212095624/https://theconversation.com/colonists-upended-aboriginal-farming-growing-grain-and-running-sheep-on-rich-yamfields-and-cattle-on-arid-grainlands-207118 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Flood2">{{cite book |last=Flood |first=J. |author-link=Josephine Flood |title=The Original Australians: The story of the Aboriginal People |publisher=Allen & Unwin |year=2019 |isbn=978-1-76087-142-0 |edition=2nd |location=Crows Nest NSW |pages=25–27, 146}}</ref> |
|||
The indigenous population, estimated at 350,000 at the time of European settlement,<ref>{{Cite book|author=Smith, L. R. |year=1980 |title=The Aboriginal Population of Australia |publisher=Australian National University Press |location=Canberra |isbn=0-9598578-9-3}}</ref> declined steeply for 150 years following settlement, mainly due to infectious disease.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Smallpox Through History|url=http://encarta.msn.com/media_701508643/Smallpox_Through_History.html|work=Encarta|archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/query?id=1257008292443871|archivedate=31 October 2009|deadurl=yes}}</ref> The "[[Stolen Generations]]" (removal of Aboriginal children from their families), which historians such as [[Henry Reynolds (historian)|Henry Reynolds]] have argued could be considered genocide,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aiatsis.gov.au/rsrch/rsrch_dp/genocide.htm|title=Genocide in Australia|accessdate=13 September 2007|last=Tatz|first=Colin|year=1999|work=AIATSIS Research Discussion Papers No 8|publisher=[[Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies]]|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20050808002313/http://www.aiatsis.gov.au/rsrch/rsrch_dp/genocide.htm|archivedate=8 August 2005}}</ref> may have contributed to the decline in the Indigenous population.<ref>{{Cite book|author=Attwood, Bain |title=Telling the truth about Aboriginal history |year=2005 |url=http://www.questia.com/read/109251500?title=Telling%20the%20Truth%20about%20Aboriginal%20History |publisher=Allen & Unwin |isbn=1-74114-577-5 |location=Crows Nest, New South Wales}}</ref> Such interpretations of Aboriginal history are disputed by conservative commentators such as former Prime Minister [[John Howard]] as exaggerated or fabricated for political or ideological reasons.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 72–73.</ref> This debate is known within Australia as the [[History wars]].<ref>{{cite web|last=Mark|first=David|url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2009/08/27/2669177.htm|title=Rudd calls for end to 'history wars' |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]|date=27 August 2009 |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> The Federal government gained the power to make laws with respect to Aborigines following the [[Australian referendum, 1967 (Aboriginals)|1967 referendum]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/messageclub/duknow/stories/s888141.htm|publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]|title=1967 Referendum|last=Dawkins|first=Kezia|date=1 February 2004|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> Traditional ownership of land—[[Native title in Australia|aboriginal title]]—was not recognised until 1992, when the [[High Court of Australia|High Court]] case ''[[Mabo v Queensland (No 2)]]'' overturned the notion of Australia as ''[[terra nullius]]'' ("land belonging to no one") before European occupation.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 5–7, 402.</ref> |
|||
Torres Strait Islander people first settled their islands at least 2,500 years ago.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=David |first1=Bruno |last2=McNiven |first2=Ian |last3=Mitchell |first3=Rod |last4=Orr |first4=Meredith |last5=Haberle |first5=Simon |last6=Brady |first6=Liam |last7=Crouch |first7=Joe |display-authors=1 |date=July 2004 |title=Badu 15 and the Papuan-Austronesian settlement of Torres Strait |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/j.1834-4453.2004.tb00564.x |journal=Archaeology in Oceania |volume=39 |issue=2 |pages=65–78 |doi=10.1002/j.1834-4453.2004.tb00564.x}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2023 |orig-date=1998 |title=Torres Strait Islands |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Torres-Strait-Islands |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240615102021/https://www.britannica.com/place/Torres-Strait-Islands |archive-date=15 June 2024 |access-date=17 November 2024 |website=[[Encyclopædia Britannica]] |quote=Torres Strait Islands, island group in the Torres Strait, north of Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, Australia, and south of the island of New Guinea. [...] They have been inhabited for at least 2,500 years. The present-day inhabitants are primarily of Melanesian origin, with some mixture of Polynesians and Southeast Asians.}}</ref> Culturally and linguistically distinct from mainland Aboriginal peoples, they were seafarers and obtained their livelihood from seasonal horticulture and the resources of their reefs and seas.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Early Aussie Tattoos Match Rock Art |last=Viegas|first=Jennifer|publisher=Discovery News|date=3 July 2008 |access-date=30 March 2010|url=http://dsc.discovery.com/news/2008/07/03/australia-tattoos-art.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080710014604/http://dsc.discovery.com/news/2008/07/03/australia-tattoos-art.html |archive-date=10 July 2008}}</ref> Agriculture also developed on some islands and villages appeared by the 1300s.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Veth |first1=Peter |title=The Cambridge History of Australia |last2=O'Connor |first2=Sue |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-107-01153-3 |editor-last=Bashford |editor-first=Alison |volume=1: Indigenous and Colonial Australia |location=Cambridge |pages=34–35 |chapter=The Past 50,000 Years: An Archaeological View |editor-last2=MacIntyre |editor-first2=Stuart}}</ref> By the mid-18th century in northern Australia, [[Makassan contact with Australia|contact, trade and cross-cultural engagement]] had been established between local Aboriginal groups and [[Makassar people|Makassan]] [[trepanging|trepangers]], visiting from present-day Indonesia.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Macknight |first=Charles Campbell |year=2011 |title=The view from Marege': Australian knowledge of Makassar and the impact of the trepangindustry across two centuries |journal=[[Aboriginal History]] |volume=35 |pages=134 |doi=10.22459/AH.35.2011.06 |jstor=24046930 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=T. Vigilante |display-authors=etal |year=2013 |title=Biodiversity values on selected Kimberley Islands, Australia |url=http://museum.wa.gov.au/sites/default/files/WAM_Supp81_Internals%20pp145-181.pdf |access-date=2 August 2021 |publisher=[[Western Australian Museum]] |archive-date=5 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181005235850/http://museum.wa.gov.au/sites/default/files/WAM_Supp81_Internals%20pp145-181.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Russell |first=Denise |date=22 March 2004 |title=Aboriginal-Makassan interactions in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries in northern Australia and contemporary sea rights claims |url=http://lryb.aiatsis.gov.au/PDFs/aasj04.1_%20makassan.pdf |journal=Australian Aboriginal Studies |publisher=Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies |volume=2004 |issue=1 |pages=3–17 |issn=0729-4352 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190306230858/http://lryb.aiatsis.gov.au/PDFs/aasj04.1_%20makassan.pdf |archive-date=6 March 2019 |access-date=21 April 2019}}</ref> |
|||
A [[gold rush]] began in Australia in the early 1850s,<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 283–85.</ref> and the [[Eureka Rebellion]] against mining licence fees in 1854 was an early expression of [[civil disobedience]].<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp.227–29.</ref> Between 1855 and 1890, the six colonies individually gained [[responsible government]], managing most of their own affairs while remaining part of the [[British Empire]].<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 556.</ref> The Colonial Office in London retained control of some matters, notably foreign affairs,<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 138–39.</ref> defence,<ref>{{Cite news|title=Colonial Defence and Imperial Repudiation|url=http://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/cgi-bin/paperspast?a=d&d=DSC18601113.2.12&l=mi&e=-------10--1----0-all|date=13 November 1860|issue=vol XVII, issue 1349|newspaper=Daily Southern Cross|accessdate=4 April 2010}}</ref> and international shipping. |
|||
===European exploration and colonisation=== |
|||
[[File:Anzac2.jpg|thumb|left|alt=A balding man wearing a suit and playing a bugle, while standing in front of a crowd of other people and a stone monument.|The [[Last Post]] is played at an [[ANZAC Day]] ceremony in [[Port Melbourne, Victoria]]. Similar ceremonies are held in most suburbs and towns.]] |
|||
{{Main|European maritime exploration of Australia|European land exploration of Australia|History of Australia (1788–1850)}} |
|||
[[File:Landing of Lieutenant James Cook at Botany Bay, 29 April 1770 (painting by E Phillips Fox).jpg|alt=Landing of Lieutenant James Cook at Botany Bay, 29 April 1770|left|thumb|Landing of [[James Cook]] at [[Botany Bay]] on 29 April 1770 to claim Australia's east coast for [[Kingdom of Great Britain|Great Britain]]]] |
|||
[[Dutch people|The Dutch]] are the first Europeans that recorded sighting and making landfall on the Australian mainland.<ref name="BarberBarnes2013">{{Cite book|first1=Peter|last1=Barber|first2=Katherine|last2=Barnes|author3=Nigel Erskine|title=Mapping Our World: Terra Incognita To Australia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uZ_sAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA99|year=2013|publisher=National Library of Australia|isbn=978-0-6422-7809-8|page=99|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=27 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231027123323/https://books.google.com/books?id=uZ_sAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA99#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the ''[[Duyfken]]'', captained by Dutch navigator [[Willem Janszoon]].<ref name="SmithBurke2007">{{Cite book|first1=Claire|last1=Smith|first2=Heather|last2=Burke|title=Digging It Up Down Under: A Practical Guide to Doing Archaeology in Australia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0HsRb_AY9jQC&pg=PA47|date=2007|publisher=Springer Science|isbn=978-0-3873-5263-3|page=47|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=27 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231027123306/https://books.google.com/books?id=0HsRb_AY9jQC&pg=PA47#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> He sighted the coast of [[Cape York Peninsula]] in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February 1606 at the [[Pennefather River]] near the modern town of [[Weipa, Queensland|Weipa]] on Cape York.<ref name=dhm233>{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|p=233}}</ref> Later that year, Spanish explorer [[Luís Vaz de Torres]] sailed through and navigated the [[Torres Strait Islands]].<ref>Brett Hilder (1980) ''The Voyage of Torres'' University of Queensland Press, St. Lucia, Queensland {{ISBN|978-0-7022-1275-8}}</ref> The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent "[[New Holland (Australia)|New Holland]]" during the 17th century, and although no attempt at settlement was made,<ref name=dhm233/> [[Shipwrecks of Western Australia#Notable wrecks|a number of shipwrecks]] left men either stranded or, as in the case of the ''[[Batavia (1628 ship)|Batavia]]'' in 1629, marooned for mutiny and murder, thus becoming the first Europeans to permanently inhabit the continent.<ref>Davis, Russell Earls (2019) ''A Concise History of Western Australia'' Woodslane Press {{ISBN|978-1-9258-6822-7}} pp. 3–6</ref> In 1770, Captain [[James Cook]] sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named "[[New South Wales]]" and claimed for Great Britain.<ref name="GoucherWalton2013">{{Cite book|first1=Candice|last1=Goucher|first2=Linda|last2=Walton|title=World History: Journeys from Past to Present|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=O_3fCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA427|year=2013|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-1350-8829-3|pages=427–428|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=10 June 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240610132402/https://books.google.com/books?id=O_3fCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA427#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Following the loss of its [[Thirteen Colonies|American colonies]] in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the [[First Fleet]], under the command of Captain [[Arthur Phillip]], to establish a new [[Colony of New South Wales|penal colony in New South Wales]]. A camp was set up and the [[Union Flag]] raised at [[Sydney Cove]], [[Port Jackson]], on 26 January 1788,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://australia.gov.au/about-australia/australian-story/european-discovery-and-colonisation |title=European discovery and the colonisation of Australia|publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia|quote=[The British] moved north to Port Jackson on 26 January 1788, landing at Camp Cove, known as 'cadi' to the Cadigal people. Governor Phillip carried instructions to establish the first British Colony in Australia. The First Fleet was underprepared for the task, and the soil around Sydney Cove was poor.|date=11 January 2008 |access-date=7 May 2010 |archive-date=13 December 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171213231728/http://www.australia.gov.au/about-australia/australian-story/european-discovery-and-colonisation |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="Egan2003">{{Cite book|first=Ted|last=Egan|title=The Land Downunder|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ND3OqVdOwqoC&pg=PA25|year=2003|publisher=Grice Chapman Publishing|isbn=978-0-9545-7260-0|pages=25–26|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=28 March 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240328153358/https://books.google.com/books?id=ND3OqVdOwqoC&pg=PA25#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> a date which later became [[Australia Day|Australia's national day]]. |
|||
On 1 January 1901 [[Federation of Australia|federation of the colonies]] was achieved after a decade of planning, consultation, and voting.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 243–44.</ref> The Commonwealth of Australia was established and it became a [[dominion]] of the British Empire in 1907. The Federal Capital Territory (later renamed the Australian Capital Territory) was formed in 1911 as the location for the future federal capital of Canberra. Melbourne was the temporary seat of government from 1901 to 1927 while Canberra was constructed.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://uninews.unimelb.edu.au/news/4332/|title=When Melbourne was Australia’s capital city|last=Otto|first=Kristin|date=25 June – 9 July 2007|publisher=University of Melbourne|accessdate=29 March 2010|location=Melbourne, Victoria}}</ref> The Northern Territory was transferred from the control of the South Australian government to the federal parliament in 1911.<ref>{{Cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=-embDa-x6MwC|title=Official year book of the Commonwealth of Australia|publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics|year=1957|accessdate=29 March 2010}}</ref> In 1914, Australia joined Britain in fighting World War I, with support from both the outgoing Liberal Party and the incoming Labor Party.<ref>Stuart Macintyre, ''The Oxford History of Australia: vol 4'' (1986), p. 142; C. Bean Ed. (1941). [http://www.awm.gov.au/histories/ww1/1/index.asp Volume I – The Story of Anzac: the first phase], First World War Official Histories, Eleventh Edition.</ref> Australians took part in many of the major battles fought on the [[Western Front (World War I)|Western Front]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.awm.gov.au/atwar/ww1.htm|title=First World War 1914–1918|publisher=Australian War Memorial|accessdate=5 December 2006}}</ref> Of about 416,000 who served, about 60,000 were killed and another 152,000 were wounded.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Tucker|first=Spencer|title=Encyclopedia of World War I|publisher=ABC-CLIO|location=Santa Barbara, CA|year=2005|page=273|isbn=1-85109-420-2|url=http://books.google.com/?id=2YqjfHLyyj8C&pg=PA273&dq&q|accessdate=7 May 2010}}</ref> Many Australians regard the defeat of the [[Australian and New Zealand Army Corps]] (ANZACs) at [[Gallipoli Campaign|Gallipoli]] as the birth of the nation—its first major military action.<ref>Macintyre, 151–53</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Reed|first=Liz|title=Bigger than Gallipoli: war, history, and memory in Australia|year=2004|page=5|location=Crawley, WA |publisher=University of Western Australia |isbn=1-920694-19-6}}</ref> The [[Kokoda Track campaign]] is regarded by many as an analogous nation-defining event during [[World War II]].<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Nelson|first=Hank|year=1997|title=Gallipoli, Kokoda and the Making of National Identity|journal=Journal of Australian Studies|volume=53|issue=1|pages=148–60|url=http://www.api-network.com/main/pdf/scholars/jas53_nelson.pdf}}</ref> |
|||
Most early settlers were [[convicts in Australia|convicts]], [[penal transportation|transported]] for petty crimes and [[convict assignment|assigned]] as labourers or servants to "free settlers" (willing immigrants). Once [[emancipist|emancipated]], convicts tended to integrate into colonial society. Convict rebellions and uprisings were suppressed under martial law,<ref>Kercher, Bruce (2020). ''An Unruly Child: A History of Law in Australia''. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781000248470. pp. 26–27.</ref> which lasted for two years following the 1808 [[Rum Rebellion]], Australia's only successful ''[[coup d'état]]''.<ref>Matsuda, Matt K. (2012) ''Pacific Worlds: A History of Seas, Peoples, and Cultures'' Cambridge University Press {{ISBN|978-0-5218-8763-2}} pp. 165–167</ref> During the next two decades, social and economic reforms, together with the establishment of a [[New South Wales Legislative Council|Legislative Council]] and [[Supreme Court of New South Wales|Supreme Court]], saw the penal colony transition to a civil society.<ref>{{Cite book| last=Ward| first=Russel| title=Australia: a short history| year=1975| publisher=Ure Smith| edition=rev| isbn=978-0-7254-0164-1| url=https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/9442954| pages=37–38| access-date=15 January 2022| archive-date=20 November 2018| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181120221059/https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/9442954| url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book | last=Molony | first=John Neylon | title=The Penguin History of Australia | year=1987 | publisher=Penguin | location=Ringwood, Vic | isbn=978-0-1400-9739-9 | url=https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/18412463 | pages=47 | access-date=15 January 2022 | archive-date=21 November 2018 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181121021802/https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/18412463 | url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Britain's [[Statute of Westminster 1931]] formally ended most of the constitutional links between Australia and the UK. Australia [[Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942|adopted it]] in 1942,<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 609.</ref> but it was backdated to 1939 to confirm the validity of legislation passed by the Australian Parliament during World War II.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.foundingdocs.gov.au/item.asp?sdID=96|title=Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942 (Cth)|publisher=[[National Archives of Australia]]|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.comlaw.gov.au/comlaw/Legislation/ActCompilation1.nsf/0/AEA1CBA4FD61CFCFCA256F71005017A1/$file/StatuteWestminAdopt1942.pdf|title=Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942|publisher=ComLaw|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> The shock of the UK's defeat in Asia in 1942 and the [[Military history of Australia during World War II#Defence of Australia|threat of Japanese invasion]] caused Australia to turn to the [[United States]] as a new ally and protector.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 22–23.</ref> Since 1951, Australia has been a formal military ally of the US, under the [[ANZUS]] treaty.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 30.</ref> After World War II Australia encouraged immigration from Europe. Since the 1970s and following the abolition of the [[White Australia policy]], immigration from Asia and elsewhere was also promoted.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 338–39, 681–82.</ref> As a result, Australia's demography, culture, and self-image were transformed.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 442–43.</ref> The final constitutional ties between Australia and the UK were severed with the passing of the [[Australia Act 1986]], ending any British role in the government of the Australian States, and closing the option of judicial appeals to the [[Privy council|Privy Council]] in London.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/cth/consol_act/aa1986114/index.html |title=Australia Act 1986 |accessdate=17 June 2010 | publisher=[[Australasian Legal Information Institute]]}}</ref> In a [[Australian republic referendum, 1999|1999 referendum]], 55% of Australian voters and a majority in every Australian state rejected a proposal to become a [[republic]] with a president appointed by a two-thirds vote in both Houses of the Australian Parliament. Since the election of the [[Gough Whitlam|Whitlam Government]] in 1972,<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.theage.com.au/news/opinion/whitlam-turned-focus-on-to-asia/2005/11/10/1131578173705.html|title=Whitlam turned focus on to Asia|last=Woodard|first=Garry|date=11 November 2005|publisher=[[The Age]]|accessdate=30 March 2010 | location=Melbourne}}</ref> there has been an increasing focus in foreign policy on ties with other [[Pacific Rim]] nations, while maintaining close ties with Australia's traditional allies and trading partners.<ref>{{Cite book|title=The Pacific Basin since 1945: A history of the foreign relations of the Asian, Australasian, and American rim states and the Pacific islands|last=Thompson|first=Roger C.|isbn=0-582-02127-8|publisher=Longman|year=1994}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- Please take note of talk page discussion (archive 21, Colonial expansion, treaties and land rights) before editing -->The indigenous population declined for 150 years following European settlement, mainly due to infectious disease.<ref>{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Smallpox Through History |url=http://encarta.msn.com/media_701508643/Smallpox_Through_History.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040618142015/http://encarta.msn.com/media_701508643/Smallpox_Through_History.html |archive-date=18 June 2004 |work= |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="Flood 2019 p."/> British colonial authorities did not sign any treaties with [[Aboriginal Australians#Groups and sub-groups|Aboriginal groups]].<ref name="Flood 2019 p.">{{cite book | last=Flood | first=J. | title=The Original Australians: The story of the Aboriginal People | publisher=Allen & Unwin | year=2019 | isbn=978-1-76087-142-0 |edition=2nd |location=Crows Nest NSW |pages=42, 111, 147–59, 300 |author-link=Josephine Flood}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Rule of Law Education Centre |title=European Settlement and Terra Nullius |url=https://www.ruleoflaw.org.au/education/australian-colonies/terra-nullius/ |access-date=26 January 2024 |archive-date=26 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240126110348/https://www.ruleoflaw.org.au/education/australian-colonies/terra-nullius/ |url-status=live }}</ref> As settlement expanded, tens of thousands of Indigenous people and thousands of settlers were killed in [[Australian frontier wars|frontier conflicts]] while settlers dispossessed surviving Indigenous peoples of most of their land.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Reynolds |first=Henry |title=Forgotten War |publisher=NewSouth |year=2022 |isbn=9781742237596 |edition=2nd |location=Sydney |pages=103–104, 134, 241–242, 182–192}}</ref> |
|||
==Politics== |
|||
{{Main|Government of Australia|Politics of Australia|Monarchy of Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Parliament House Canberra NS.jpg|thumb|alt=A large white and cream coloured building with grass on its roof. The building is topped with a large flagpole.|[[Parliament House, Canberra]] was opened in 1988, replacing the [[Old Parliament House, Canberra|provisional Parliament House building]] opened in 1927.]] |
|||
Australia is a [[constitutional monarchy]] with a [[federalism|federal]] division of powers. It uses a [[parliamentary system]] of government with [[Elizabeth II|Queen Elizabeth II]] at its apex as the [[Queen of Australia]], a role that is distinct from her position as monarch of the other [[Commonwealth realm]]s. The Queen resides in the United Kingdom, and she is represented by her viceroys in Australia, (the [[Governor-General of Australia|Governor-General]] at the federal level and by the [[Governors of the Australian states|Governors]] at the state level), who by convention act on the advice of her ministers. Supereme executive authority is vested by the [[constitution of Australia]] in the sovereign, but the power to exercise it is conferred by the constitution specifically to the Governor-General.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 287–88.</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gg.gov.au/governorgeneral/category.php?id=2|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20080804130529/http://www.gg.gov.au/governorgeneral/category.php?id=2|archivedate=2008-08-04|title=Governor-General's Role |publisher=Governor-General of Australia|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> The most notable exercise of the Governor-General's [[reserve power]]s outside a Prime Minister's request was the dismissal of the Whitlam Government in the [[1975 Australian constitutional crisis|constitutional crisis of 1975]].<ref>{{cite web|publisher=[[Parliament of Australia]] | date=23 January 1998 |accessdate=18 June 2010 |url=http://www.aph.gov.au/library/pubs/rn/1997-98/98rn25.htm |title=The Reserve Powers of the Governor-General |author=Downing, Susan}}</ref> |
|||
===Colonial expansion=== |
|||
The federal government is [[Separation of powers in Australia|separated]] into three branches: |
|||
{{Main|History of Australia (1788–1850)|History of Australia (1851–1900)}} |
|||
* The legislature: the bicameral [[Parliament of Australia|Parliament]], comprising the Queen (represented by the Governor-General), the [[Australian Senate|Senate]], and the [[Australian House of Representatives|House of Representatives]]; |
|||
[[File:PortArthurPenitentiary.jpg|thumb|upright=1.0|right|alt=A calm body of water is in the foreground. The shoreline is about 200 metres away. To the left, close to the shore, are three tall [[Eucalyptus|gum trees]]; behind them on an incline are ruins, including walls and watchtowers of light-coloured stone and brick, what appear to be the foundations of walls, and grassed areas. To the right lie the outer walls of a large rectangular four-storey building dotted with regularly spaced windows. Forested land rises gently to a peak several kilometres back from the shore.|Tasmania's [[Port Arthur, Tasmania|Port Arthur]] penal settlement is one of eleven UNESCO World Heritage-listed [[Australian Convict Sites]].]] |
|||
* The executive: the [[Federal Executive Council]], in practice the Governor-General as advised by the Prime Minister and Ministers of State;<ref name="CIAfactbook">{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html|title=The World Factbook 2009|year=2009|publisher=Central Intelligence Agency|accessdate=29 March 2010|location=Washington D.C.}}</ref> |
|||
* The judiciary: the [[High Court of Australia]] and other [[Australian court hierarchy|federal courts]], whose judges are appointed by the Governor-General on advice of the Council. |
|||
In 1803, a settlement was established in [[Van Diemen's Land]] (present-day [[Tasmania]]),<ref name="Davison pp464-5">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|pages=464–465, 628–629}}</ref> and in 1813, [[Gregory Blaxland]], [[William Lawson (explorer)|William Lawson]] and [[William Wentworth]] [[1813 crossing of the Blue Mountains|crossed]] the [[Blue Mountains (New South Wales)|Blue Mountains]] west of Sydney, opening the interior to European settlement.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Conway |first=Jill |title=Biography – Gregory Blaxland – Australian Dictionary of Biography |publisher=National Centre of Biography, Australian National University |chapter=Blaxland, Gregory (1778–1853) |access-date=14 July 2011 |chapter-url=http://adbonline.anu.edu.au/biogs/A010109b.htm?hilite=blaxland |archive-date=8 April 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110408201858/http://adbonline.anu.edu.au/biogs/A010109b.htm?hilite=blaxland |url-status=live }}</ref> The British claim extended to the whole Australian continent in 1827 when Major [[Edmund Lockyer]] established a settlement on [[King George Sound]] (modern-day [[Albany, Western Australia|Albany]]).<ref>{{Cite book|last=Grey|first=Jeffrey |title=A Military History of Australia|url=https://archive.org/details/militaryhistorya00grey_277|url-access=limited |publisher=Cambridge University Press|location=Port Melbourne|year=2008|edition=Third|isbn=978-0-5216-9791-0|pages=[https://archive.org/details/militaryhistorya00grey_277/page/n43 28]–40}}</ref> The [[Swan River Colony]] (present-day [[Perth]]) was established in 1829, evolving into the largest Australian colony by area, [[Western Australia]].<ref name="Davison p678">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|p=678}}</ref> In accordance with population growth, separate colonies were carved from New South Wales: Tasmania in 1825, [[South Australia]] in 1836, [[New Zealand]] in 1841, [[Victoria (Australia)|Victoria]] in 1851, and [[Queensland]] in 1859.<ref name="Davison p464">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|p=464}}</ref> South Australia was founded as a free colony—it never accepted transported convicts.<ref name="Davison p598">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|p=598}}</ref> Growing [[Australasian Anti-Transportation League|opposition to the convict system]] culminated in its abolition in the eastern colonies by the 1850s. Initially a free colony, Western Australia practised penal transportation from 1850 to 1868.<ref>{{Cite web |date=25 December 2005 |title=Public Record Office Victoria online catalogue |url=http://www.access.prov.vic.gov.au/public/PROVguides/PROVguide057/PROVguide057.jsp |access-date=15 January 2022 |website= |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051225154618/http://www.access.prov.vic.gov.au/public/PROVguides/PROVguide057/PROVguide057.jsp |archive-date=25 December 2005 |url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
In the Senate (the upper house), there are 76 senators: twelve each from the states and two each from the mainland territories (the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory).<ref name=sen>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/guide/senatecomposition.htm|title=Senate Summary |publisher= [[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> The [[Australian House of Representatives|House of Representatives]] (the lower house) has 150 members elected from single-member electoral divisions, commonly known as "electorates" or "seats", allocated to states on the basis of population,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aec.gov.au/Voting/How_to_vote/Voting_HOR.htm|title=Voting HOR|publisher=[[Australian Electoral Commission]]|date=31 July 2007|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> with each original state guaranteed a minimum of five seats.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/guide/state_tas.htm|title=Election Summary: Tasmania |publisher= [[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Elections for both chambers are normally held every three years, simultaneously; senators have overlapping six-year terms except for those from the territories, whose terms are not fixed but are tied to the electoral cycle for the lower house; thus only 40 of the 76 places in the Senate are put to each election unless the cycle is interrupted by a [[double dissolution]].<ref name=sen/> |
|||
The six colonies individually gained [[responsible government]] between 1855 and 1890, thus becoming elective democracies managing most of their own affairs while remaining part of the [[British Empire]].<ref name="Davison p556">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|p=556}}</ref> The Colonial Office in London retained control of some matters, notably foreign affairs.<ref name="Davison p138-9679">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|pages=138–39}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Government House Yarralumla (2168368150).jpg|thumb|alt=A white, two-storey building photographed with trees in the foreground and a mountain topped by a tower in the background.|[[Government House, Canberra|The official residence]] of the [[Governor-General of Australia]]]] |
|||
Australia's [[Australian electoral system|electoral system]] uses [[preferential voting]] for all lower house elections with the exception of Tasmania and the ACT, which, along with the Senate and most state upper houses, combine it with [[proportional representation]] in a system known as the [[single transferable vote]]. [[Compulsory voting|Voting is compulsory]] for all enrolled citizens 18 years and over in every jurisdiction,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aec.gov.au/pdf/voting/compulsory_voting.pdf|title=Compulsory Voting in Australia|last=Evans|first=Tim|year=2006|publisher=[[Australian Electoral Commission]]|page=4|accessdate=21 June 2009}}</ref> as is enrolment (with the exception of South Australia).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://aec.gov.au/FAQs/Voting_Australia.htm#What%20happens%20if%20I%20do%20not%20vote|title=What happens if I do not vote?|work=Voting Australia – Frequently Asked Questions|publisher=[[Australian Electoral Commission]]|accessdate=8 January 2008}}</ref> Although the Prime Minister is appointed by the Governor-General, in practice the party with majority support in the House of Representatives forms government and its leader becomes Prime Minister.{{citation needed|date=December 2010}} |
|||
In the mid-19th century, explorers such as [[Burke and Wills expedition|Burke and Wills]] charted Australia's interior.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/explorers |title=Early explorers|publisher=Australia's Culture Portal |access-date=6 November 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110408183209/http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/explorers/ |archive-date=8 April 2011}}</ref> A [[Australian gold rushes|series of gold rushes]] beginning in the early 1850s led to an influx of new migrants from [[Chinese Australians|China]], North America and continental Europe,<ref name="JuppJupp2001">{{Harvnb|Jupp2|pp=35–36}}</ref> as well as outbreaks of [[bushranger|bushranging]] and civil unrest; the latter peaked in 1854 when [[Ballarat]] miners launched the [[Eureka Rebellion]] against gold licence fees.<ref name="Davison pp227-9">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998 |pages=227–29}}</ref> The 1860s saw the rise of [[blackbirding]], where [[South Sea Islanders]] were coerced or abducted into indentured labour, mainly by Queensland colonists.<ref>[https://www.slq.qld.gov.au/discover/exhibitions/australian-south-sea-islanders "Australian South Sea Islanders"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231210065156/https://www.slq.qld.gov.au/discover/exhibitions/australian-south-sea-islanders |date=10 December 2023 }}, State Library of Queensland. Retrieved 21 February 2024.</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Higginbotham |first=Will |date=17 September 2017 |title=Blackbirding: Australia's history of luring, tricking and kidnapping Pacific Islanders |url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-09-17/blackbirding-australias-history-of-kidnapping-pacific-islanders/8860754 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240126044712/https://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-09-17/blackbirding-australias-history-of-kidnapping-pacific-islanders/8860754 |archive-date=26 January 2024 |website=ABC News}}</ref> |
|||
There are two major political groups that usually form government, federally and in the states: the [[Australian Labor Party]]<!-- NOTE TO EDITORS: The name of the party is spelt ‘Labor’ (i.e., no ‘u’) even though Australian spelling for all other use of the word is ‘labour’. -->, and the [[Coalition (Australia)|Coalition]] which is a formal grouping of the [[Liberal Party of Australia|Liberal Party]] and its minor partner, the [[National Party of Australia|National Party]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/guide/glossary.htm#coalition|title=Glossary of Election Terms |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/results/sop.htm|title=State of the Parties |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Independent members and several minor parties—including the [[Australian Greens|Greens]] and the [[Australian Democrats]]—have achieved representation in Australian parliaments, mostly in upper houses. |
|||
From 1886, Australian colonial governments began [[Stolen Generations|removing many Aboriginal children]] from their families and communities, justified on the grounds of child protection and [[forced assimilation]] policies.<ref>Banivanua Mar, Tracey; Edmonds, Penelope (2013). "Indigenous and settler relations". ''The Cambridge History of Australia, Volume I''. p. 355–58, 363–64</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Marlow |first=Karina |date=1 December 2016 |title=Explainer: the Stolen Generations |url=https://www.sbs.com.au/nitv/article/explainer-the-stolen-generations/5ust2jtjy |access-date= |website=NITV |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=O'Loughlin |first=Michael |date=22 June 2020 |title=The Stolen Generation |url=https://australian.museum/learn/first-nations/stolen-generation/ |website=[[Australian Museum]]}}</ref> The [[Second Boer War]] (1899–1902) marked the largest overseas deployment of [[colonial forces of Australia|Australia's colonial forces]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=2 June 2021 |title=Australia and the Boer War, 1899–1902 |url=https://www.awm.gov.au/articles/atwar/boer |access-date= |website=Australian War Memorial |archive-date=24 March 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180324185402/https://www.awm.gov.au/articles/atwar/boer |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>Wilcox, Craig (2002). ''Australia's Boer War: The War in South Africa, 1899-1902''. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195516371.</ref> |
|||
Following a [[Australian Labor Party leadership election, 2010|partyroom leadership challenge]], [[Julia Gillard]] became the first female Prime Minister in June 2010.<ref>{{Cite news|title=Gillard ousts Rudd in bloodless coup |url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2010/06/24/2935500.htm|accessdate=24 June 2010|publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]|date=24 June 2010}}</ref> The last federal election was held [[Australian federal election, 2010|on 21 August 2010]] and resulted in the first [[hung parliament]] in over 50 years. Gillard was able to form a minority Labor government with the support of independents. |
|||
===Federation to the World Wars=== |
|||
==States and territories== |
|||
{{Main| |
{{Main|History of Australia (1901–1945)}} |
||
{{See also|Federation of Australia|Military history of Australia during World War I|Military history of Australia during World War II}} |
|||
{{Australia states imagemap}} |
|||
[[File:Opening of the first parliament.jpg|thumb|''[[The Big Picture (painting)|The Big Picture]]'', a painting by [[Tom Roberts]], depicts the opening of the first Australian Parliament in 1901.]] |
|||
Australia has six [[federated state|states]]—[[New South Wales]], [[Queensland]], [[South Australia]], [[Tasmania]], [[Victoria (Australia)|Victoria]], and [[Western Australia]]—and two major mainland territories—the [[Northern Territory]] and the [[Australian Capital Territory]] (ACT). In most respects these two territories function as states, but the Commonwealth Parliament can override any legislation of their parliaments. By contrast, federal legislation overrides state legislation only in areas that are set out in [[Section 51 of the Australian Constitution]]; state parliaments retain all residual legislative powers, including those over schools, state police, the state judiciary, roads, public transport, and local government, since these do not fall under the provisions listed in Section 51.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.australia.gov.au/about-australia/our-government/state-and-territory-government|title=State and Territory Government|publisher=Government of Australia|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> |
|||
On 1 January 1901, [[Federation of Australia|federation of the colonies]] was achieved after a decade of planning, [[Constitutional Convention (Australia)|constitutional conventions]] and [[1898–1900 Australian constitutional referendums|referendums]], resulting in the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia as a nation under the new [[Constitution of Australia|Australian Constitution]].<ref name="Davison pp243-4">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998 |pages=243–44}}</ref> |
|||
After the [[1907 Imperial Conference]], Australia and several other self-governing British [[settler colonialism|settler colonies]] were given the status of self-governing [[dominion]]s within the British Empire.<ref name="dominionstatus">{{Cite web|title=History of the Commonwealth|url=http://www.commonwealthofnations.org/commonwealth/history/|website=Commonwealth Network|publisher=Commonwealth of Nations|access-date=16 February 2015|archive-date=25 April 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200425043631/http://www.commonwealthofnations.org/commonwealth/history/|url-status=live}}</ref> Australia was one of the founding members of the [[League of Nations]] in 1920,<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Covenant of the League of Nations |url=https://www.ungeneva.org/en/about/league-of-nations/covenant |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240127003532/https://www.ungeneva.org/en/about/league-of-nations/covenant |archive-date=27 January 2024 |access-date=8 February 2024 |website=The United Nations Office at Geneva |language=en}}</ref> and the [[Member states of the United Nations|United Nations]] in 1945.<ref>{{Cite web |last= |first= |title=Growth in United Nations membership |url=https://www.un.org/en/about-us/growth-in-un-membership |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240201204200/https://www.un.org/en/about-us/growth-in-un-membership |archive-date=1 February 2024 |access-date=8 February 2024 |website=United Nations |language=en}}</ref> The ''[[Statute of Westminster 1931]]'' formally ended the ability of the UK to pass federal laws without Australia's consent. Australia [[Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942|adopted it]] in 1942, but it was backdated to 1939 to confirm the validity of legislation passed during World War II.<ref name="Davison p609">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|p=609}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://foundingdocs.gov.au/item-did-25.html |title=Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942 (Cth) |publisher=National Archives of Australia |access-date=28 July 2014 |archive-date=12 February 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140212020054/http://foundingdocs.gov.au/item-did-25.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite Legislation AU|Cth|act|sowaa1942379|Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942}}</ref> |
|||
Each state and major mainland territory has its own [[Parliaments of the Australian states and territories|parliament]]—[[unicameralism|unicameral]] in the Northern Territory, the ACT, and Queensland, and bicameral in the other states. The states are sovereign entities, although subject to certain powers of the Commonwealth as defined by the Constitution. The [[lower house]]s are known as the [[Legislative Assembly]] (the [[House of Assembly]] in South Australia and Tasmania); the [[upper house]]s are known as the [[Legislative Council]]. The [[head of government|head of the government]] in each state is the [[Premiers of the Australian states|Premier]], and in each territory the [[Chief Minister]]. The [[Monarchy of Australia|Queen]] is represented in each state by a [[Governors of the Australian states|Governor]]; and in the Northern Territory, the [[Administrator of the Northern Territory|Administrator]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nt.gov.au/administrator/administrator.shtml|publisher=Government House Northern Territory|title=Role of the Administrator|date=16 June 2008|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> In the Commonwealth, the Queen's representative is the [[Governor-General of Australia|Governor-General]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gg.gov.au/governorgeneral/category.php?id=2|publisher=Governor–General of the Commonwealth of Australia|title=Governor-General's Role|accessdate=30 March 2010| archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20080804130529/http://www.gg.gov.au/governorgeneral/category.php?id=2| archivedate = 4 August 2008}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Australian Capital Territory]] was formed in 1911 as the location for the future federal capital of [[Canberra]].<ref>{{Cite web |last= |first= |date=25 April 2020 |title=Establishing the nation's capital |url=https://www.parliament.act.gov.au/visit-and-learn/resources/factsheets/establishing-the-nations-capital |access-date=8 February 2024 |website=Legislative Assembly for the Australian Capital Territory |language=en |archive-date=8 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240208115409/https://www.parliament.act.gov.au/visit-and-learn/resources/factsheets/establishing-the-nations-capital |url-status=live }}</ref> While it was being constructed, [[Melbourne]] served as the temporary capital from 1901 to 1927.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://uninews.unimelb.edu.au/news/4332 |title=When Melbourne was Australia's capital city|last=Otto|first=Kristin|date=25 June – 9 July 2007|publisher=University of Melbourne |access-date=29 March 2010|location=Melbourne, Victoria |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100402083202/http://uninews.unimelb.edu.au/news/4332/ |archive-date=2 April 2010 |url-status=dead}}</ref> The [[Northern Territory]] was transferred from the control of South Australia to the Commonwealth in 1911.<ref name="Souter2012">{{Cite book|first=Gavin|last=Souter|title=Lion & Kangaroo: The Initiation of Australia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oQIBMD23lL0C&pg=PT141|year=2012|publisher=Xoum Publishing|isbn=978-1-9220-5700-6|page=141|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=13 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230413130303/https://books.google.com/books?id=oQIBMD23lL0C&pg=PT141|url-status=live}}</ref> Australia became the colonial ruler of the [[Territory of Papua]] (which had initially been annexed by Queensland in 1883) in 1902 and of the [[Territory of New Guinea]] (formerly [[German New Guinea]]) in 1920.<ref name="McDermott">{{Cite journal |last=McDermott |first=Peter M |date=2009 |title=Australian Citizenship and the Independence of Papua New Guinea |url=https://austlii.edu.au/cgi-bin/viewdoc/au/journals/UNSWLawJl/2009/3.html |journal=UNSW Law Journal |volume=32 |issue=1 |pages=50–2 |via=[[Austlii]] |access-date=8 February 2024 |archive-date=8 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240208072215/https://austlii.edu.au/cgi-bin/viewdoc/au/journals/UNSWLawJl/2009/3.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite Legislation AU|Cth|num_act|nga1920251920138|New Guinea Act 1920}}</ref> The two were unified as the [[Territory of Papua and New Guinea]] in 1949 and gained independence from Australia in 1975.<ref name="McDermott" /><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://unimelb.libguides.com/png |title=Papua New Guinea Legal Research Guide |publisher=University of Melbourne |access-date=2 April 2021 |archive-date=4 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230604205454/https://unimelb.libguides.com/png |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The federal parliament directly administers the following territories:<ref name="CIAfactbook" /> |
|||
* [[Jervis Bay Territory]], a naval base and sea port for the national capital in land that was formerly part of New South Wales |
|||
* [[Christmas Island]] and [[Cocos (Keeling) Islands]] |
|||
* [[Ashmore and Cartier Islands]] |
|||
* [[Coral Sea Islands]] |
|||
* [[Heard Island and McDonald Islands]] |
|||
* [[Australian Antarctic Territory]] |
|||
[[File:Darwin 42.jpg|thumb|The 1942 [[Bombing of Darwin]], the first of more than 100 [[Air raids on Australia, 1942–1943|Japanese air raids on Australia]] during [[World War II]]]] |
|||
[[Norfolk Island]] is also technically an external territory; however, under the Norfolk Island Act 1979 it has been granted more autonomy and is governed locally by its own legislative assembly. The Queen is represented by an [[List of administrative heads of Norfolk Island|Administrator]], currently [[Owen Walsh]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ag.gov.au/www/agd/agd.nsf/Page/Territories_of_AustraliaNorfolk_IslandAdministrator_of_Norfolk_Island|title= Administrator of Norfolk Island|publisher=Australian Government Attorney-General's Department|accessdate=21 July 2009}}{{dead link|date=April 2011}}</ref> |
|||
In 1914, Australia joined the [[Allies of World War I|Allies]] in fighting the First World War, and took part in many of the major battles fought on the [[Western Front (World War I)|Western Front]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=2 June 2021 |title=First World War 1914–18 |url=https://www.awm.gov.au/articles/atwar/first-world-war |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240120020555/https://www.awm.gov.au/articles/atwar/first-world-war |archive-date=20 January 2024 |access-date= |website=Australian War Memorial}}</ref> Of about 416,000 who served, about 60,000 were killed and another 152,000 were wounded.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Tucker|first=Spencer |title=Encyclopedia of World War I|publisher=ABC-CLIO|location=Santa Barbara, California|year=2005|page=273|isbn=978-1-8510-9420-2|url={{GBurl|id=2YqjfHLyyj8C|p=273}}}}</ref> Many Australians regard the defeat of the [[Australian and New Zealand Army Corps]] (ANZAC) at [[Gallipoli Campaign|Gallipoli]] in 1915 as the "baptism of fire" that forged the [[Anzac spirit|new nation's identity]].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Reed |first=Liz |title=Bigger than Gallipoli: war, history, and memory in Australia |publisher=University of Western Australia |year=2004 |isbn=978-1-9206-9419-7 |location=Crawley, Western Australia |page=5}}</ref><ref>Macintyre, Stuart (2000) ''A Concise History of Australia'' Cambridge: [[Cambridge University Press]], pp. 151–53, {{ISBN|978-0-521-62359-9}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=17 January 2024 |title=The Anzac legend |url=https://anzacportal.dva.gov.au/wars-and-missions/ww1/personnel/anzac-legend |website=Department of Veterans' Affairs |access-date=9 February 2024 |archive-date=4 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240304225421/https://anzacportal.dva.gov.au/wars-and-missions/ww1/personnel/anzac-legend |url-status=live }}</ref> The [[Landing at Anzac Cove|beginning of the campaign]] is commemorated annually on [[Anzac Day]], a date which rivals [[Australia Day]] as the nation's most important.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Dennis |first1=Peter |title=The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History |last2=Grey |first2=Jeffrey |last3=Morris |first3=Ewan |last4=Prior |first4=Robin |last5=Bou |first5=Jean |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-1955-1784-2 |edition=2nd |location=Melbourne |pages=32, 38 |author2-link=Jeffrey Grey}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Manne |first=Robert |date=25 April 2007 |title=The war myth that made us |url=https://www.theage.com.au/opinion/the-war-myth-that-made-us-20070425-ge4qmh.html |access-date=9 February 2024 |website=The Age |language=en |archive-date=4 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240304225419/https://www.theage.com.au/opinion/the-war-myth-that-made-us-20070425-ge4qmh.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
From 1939 to 1945, Australia joined the [[Allies of World War II|Allies]] in fighting the Second World War. Australia's [[Australian Defence Force|armed forces]] fought in the [[Pacific War|Pacific]], [[European Theatre of World War II|European]] and [[Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II|Mediterranean and Middle East]] [[List of theaters and campaigns of World War II|theatres]].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Beaumont |first=Joan |editor=Beaumont, Joan|author-link=Joan Beaumont |title=Australia's War, 1939–1945 |year=1996 |publisher=Allen & Unwin |location=Sydney |isbn=978-1-86448-039-9 |chapter=Australia's war: Europe and the Middle East}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Beaumont |first=Joan |editor=Beaumont, Joan |title=Australia's War, 1939–1945 |year=1996a |publisher=Allen & Unwin |location=Sydney |isbn=978-1-86448-039-9 |chapter=Australia's war: Asia and the Pacific}}</ref> The shock of Britain's [[fall of Singapore|defeat in Singapore]] in 1942, followed soon after by the [[bombing of Darwin]] and [[Air raids on Australia, 1942–43|other Japanese attacks on Australian soil]], led to a widespread belief in Australia that [[Proposed Japanese invasion of Australia during World War II|a Japanese invasion was imminent]], and a shift from the United Kingdom to the [[Australia–United States relations|United States]] as Australia's principal ally and security partner.<ref name="Davison pp22-3">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|pages=22–23}}</ref> Since 1951, Australia has been allied with the United States under the [[ANZUS]] treaty.<ref name="Davison p30">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|p=30}}</ref> |
|||
==Foreign relations and military== |
|||
{{Main|Foreign relations of Australia|Australian Defence Force}} |
|||
[[File:2RAR 070622-F-1644L-095.jpg|thumb|alt=A group of Australian soldiers with rifles moving along a path in a wooded area|[[Australian Army]] soldiers conducting a foot patrol during a joint training exercise with [[United States Armed Forces|US forces]] in [[Shoalwater Bay]] (2007).]] |
|||
Over recent decades, [[Foreign relations of Australia|Australia's foreign relations]] have been driven by a close association with the [[United States]] through the [[ANZUS|ANZUS pact]], and by a desire to develop relationships with Asia and the Pacific, particularly through [[ASEAN]] and the [[Pacific Islands Forum]]. In 2005 Australia secured an inaugural seat at the [[East Asia Summit]] following its accession to the [[Treaty of Amity and Cooperation in Southeast Asia]], and in 2011 will attend the [[Sixth East Asia Summit]] in Indonesia. Australia is a member of the [[Commonwealth of Nations]], in which the [[Commonwealth Heads of Government]] meetings provide the main forum for cooperation.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.thecommonwealth.org/subhomepage/33247/|title=Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting|year=2009|work=Commonwealth website|publisher=Commonwealth Secretariat|accessdate=16 April 2010|location=Pall Mall, London}}</ref> |
|||
===Post-war and contemporary eras=== |
|||
Australia has pursued the cause of international [[trade liberalisation]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2009/03/04/2507564.htm|title=S Korean President backs anti-protectionism moves |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]|date=4 March 2009|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/newsitems/200203/s498805.htm|title=Crean calls for Govt to 'mobilise anger' over US steel tariffs |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]|date=7 March 2002|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.trademinister.gov.au/speeches/2009/090805_sydin.html|title=The Triumph of Trade Liberalisation Over Protectionism |author=[[Simon Crean|Crean, Simon]] |publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> It led the formation of the [[Cairns Group]] and [[Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation]].<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Gallagher, P. W. |title=Setting the agenda for trade negotiations: Australia and the Cairns group |journal=Australian Journal of International Affairs |volume=42 |issue=1 April 1988 |pages= 3–8 |doi=10.1080/10357718808444955 |year=1988}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.apec2007.org/aa.htm|title=APEC and Australia|publisher=APEC 2007|date=1 June 2007|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Australia is a member of the [[Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development]] and the [[World Trade Organization]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.oecd.org/about/0,3347,en_33873108_33873229_1_1_1_1_1,00.html|title=Australia:About|publisher=[[Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/countries_e/australia_e.htm|title=Australia – Member information|publisher=[[World Trade Organization]] |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> and has pursued several major bilateral free trade agreements, most recently the [[Australia – United States Free Trade Agreement]]<ref name="AUSdfat">{{cite web|url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/trade/negotiations/us_fta/index.html|title=Australia-United States Free Trade Agreement|publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade|accessdate=30 March 2010|location=Canberra, ACT}}</ref> and [[Closer Economic Relations]] with New Zealand,<ref name="CERdfat">{{cite web|url=http://replay.web.archive.org/20091008192957/http://www.dfat.gov.au/geo/new_zealand/anz_cer/anz_cer.html|title=Closer Economic Relations|publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade|accessdate=30 March 2010|location=Canberra, ACT}}</ref> with another free trade agreement being negotiated with [[China]] - the [[Australia–China Free Trade Agreement]] - and [[Japan]]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/region/asia-paci/australia/index.html |title=Japan-Australia Relations |publisher=Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan|accessdate=19 June 2010}}</ref>, [[South Korea]] in 2011<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2011/04/25/3200038.htm |title=Gillard confident of S Korean trade deal — ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation) |publisher=Abc.net.au |date= |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://nz.news.yahoo.com/a/-/full-coverage/9256348/s-korea-australia-set-freetrade-talks-deadline/ |title=S. Korea, Australia set free-trade talks deadline|publisher=Nz.news.yahoo.com |date= |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref>, [[Australia–Chile Free Trade Agreement]], [[ASEAN – Australia – New Zealand Free Trade Area]], and the [[Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership]]. |
|||
{{Main|History of Australia (1945–present)}} |
|||
[[File:Dutch Migrant 1954 MariaScholte=50000thToAustraliaPostWW2.jpg|thumb|left|[[Post-war immigration to Australia|Postwar migrants]] from Europe arriving in Australia in 1954]] |
|||
In the decades following World War II, Australia enjoyed significant increases in living standards, leisure time and suburban development.<ref name="Susan_Something">{{Cite book|editor-first=Susan|editor-last=Hosking|display-editors=etal |title=Something Rich and Strange: Sea Changes, Beaches and the Littoral in the Antipodes|url={{GBurl|id=6mQ_-ZD5xBUC|p=6}}|year=2009|publisher=Wakefield Press|isbn=978-1-8625-4870-1|pages=6–}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|first1=Brian|last1=Hodge|first2=Allen|last2=Whitehurst|title=Nation and People: An Introduction to Australia in a Changing World|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qE0OAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA184|year=1967|publisher=Hicks, Smith|pages=184–|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=28 March 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240328153346/https://books.google.com/books?id=qE0OAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA184|url-status=live}}</ref> Governments encouraged a [[Post-war immigration to Australia|large wave of immigration from across Europe]], with such immigrants referred to as "[[New Australians]]".<ref>{{Cite web |year=2001 |title=Immigration to Australia During the 20th Century – Historical Impacts on Immigration Intake, Population Size and Population Composition – A Timeline |url=http://www.immi.gov.au/media/publications/statistics/federation/timeline1.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080801014246/http://www.immi.gov.au/media/publications/statistics/federation/timeline1.pdf |archive-date=1 August 2008 |access-date=18 July 2008 |publisher=Department of Immigration and Citizenship (Australia)}}</ref> This required a relaxation of the [[white Australia policy]], which was justified to Australians using the slogan "populate or perish".<ref>{{Cite web |title='Populate or perish': Australia's postwar migration program |url=https://www.naa.gov.au/learn/learning-resources/learning-resource-themes/society-and-culture/migration-and-multiculturalism/populate-or-perish-australias-postwar-migration-program |access-date=31 August 2024 |website=[[National Archives of Australia]] |publisher=[[Australian Government]]}}</ref> |
|||
A member of the [[Western Bloc]] during the [[Cold War]], Australia participated in the [[Australia in the Korean War|Korean War]] and the [[Military history of Australia during the Malayan Emergency|Malayan Emergency]] during the 1950s and the [[Military history of Australia during the Vietnam War|Vietnam War]] from 1962 to 1972.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Fighting Australia's Cold War |date=2021 |publisher=ANU Press |isbn=978-1-76046-482-0 |editor-last=Dean |editor-first=Peter |location=Canberra |pages=1 |chapter=Introduction |editor-last2=Moss |editor-first2=Tristan |chapter-url=https://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/n9414/pdf/introduction.pdf |access-date=9 February 2024 |archive-date=12 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240112170033/https://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/n9414/pdf/introduction.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> During this time, tensions over communist influence in society led to [[1951 Australian Communist Party ban referendum|unsuccessful attempts]] by the [[Menzies Government (1949–1966)|Menzies Government]] to ban the [[Communist Party of Australia]],<ref>Frank Crowley (1973) ''Modern Australia in Documents, 1939–1970''. pp. 222–26. Wren Publishing, Melbourne. {{ISBN|978-0-1700-5300-6}}</ref> and a [[Australian Labor Party split of 1955|bitter split]] in the [[Australian Labor Party|Labor Party]] in 1955.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Calwell|first=Arthur Augustus |title=Be just and fear not|url=https://archive.org/details/bejustfearnot0000calw|url-access=registration|publisher=Lloyd O'Neil Pty Ltd.|location=[[Hawthorn, Victoria|Hawthorn]], [[Victoria, Australia|Victoria]]|year=1972|isbn=978-0-8555-0352-9 |page=[https://archive.org/details/bejustfearnot0000calw/page/188 188]}}</ref> |
|||
Along with New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Malaysia, and Singapore, Australia is party to the [[Five Power Defence Arrangements]], a regional defence agreement. A founding member country of the United Nations, Australia is strongly committed to [[multilateralism]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://cpd.org.au/article/in-defence-multilateralism|title=In Defence of Multilateralism|author=Arvanitakis, James; Tyler, Amy|date=3 June 2008|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> and maintains an international aid program under which some 60 countries receive assistance. The 2005–06 budget provides A$2.5 billion for development assistance;<ref name="budget">Australian Government. (2005). [http://www.budget.gov.au/ Budget 2005–2006]</ref> as a percentage of GDP, this contribution is less than that recommended in the UN [[Millennium Development Goals]]. Australia ranks seventh overall in the [[Center for Global Development]]'s 2008 [[Commitment to Development Index]].<ref>Center for Global Development. [http://www.cgdev.org/section/initiatives/_active/cdi/_country/australia Commitment to Development Index: Australia], www.cgdev.org. Retrieved on 5 January 2008.</ref> |
|||
As a result of a [[Australian referendum, 1967 (Aboriginals)|1967 referendum]], the federal government gained the power to legislate with regard to Indigenous Australians, and Indigenous Australians were fully included in the [[Census in Australia|census]].<ref name="Edwards2004">{{Cite book|first=William Howell|last=Edwards|title=An Introduction to Aboriginal Societies|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kF-_Pe5WX6UC&pg=PA132|year=2004|publisher=Cengage Learning Australia|isbn=978-1-8766-3389-9|pages=25–26, 30, 132–133|access-date=17 July 2023|archive-date=12 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230412154810/https://books.google.com/books?id=kF-_Pe5WX6UC&pg=PA132|url-status=live}}</ref> [[Aboriginal title|Pre-colonial land interests]] (referred to as [[Native title in Australia|native title]] in Australia) was recognised in law for the first time when the [[High Court of Australia]] held in ''[[Mabo v Queensland (No 2)]]'' that Australia was neither ''[[terra nullius]]'' ({{Gloss|land belonging to no one}}) or "desert and uncultivated land" at the time of European settlement.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Galloway |first=Kate |date=26 April 2017 |title=Australian politics explainer: the Mabo decision and native title |url=http://theconversation.com/australian-politics-explainer-the-mabo-decision-and-native-title-74147 |access-date=25 January 2024 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US |archive-date=25 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240125000636/http://theconversation.com/australian-politics-explainer-the-mabo-decision-and-native-title-74147 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Davison pp. 5-7, 402">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|pages=5–7, 402}}</ref> |
|||
Australia's armed forces—the [[Australian Defence Force]] (ADF)—comprise the [[Royal Australian Navy]] (RAN), the [[Australian Army]], and the [[Royal Australian Air Force]] (RAAF), in total numbering 80,561 personnel (including 55,068 regulars and 25,493 reservists).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.defence.gov.au/budget/08-09/dar/vol1/append07_01.htm|title=Appendix 7: People: Defence actual staffing|work=Defence Annual Report 2008-09|publisher=[[Department of Defence (Australia)|Department of Defence]]|accessdate=28 June 2010}}</ref> The titular role of Commander-in-Chief is vested in the Governor-General, who appoints a [[Chief of the Defence Force (Australia)|Chief of the Defence Force]] from one of the armed services on the advice of the government.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Australian Defence Almanac 2004–05|last=Khosa|first=Raspal|year=2004|publisher=[[Australian Strategic Policy Institute]]|location=Canberra|page=4}}</ref> Day-to-day force operations are under the command of the Chief, while broader administration and the formulation of defence policy is undertaken by the [[Minister for Defence (Australia)|Minister]] and [[Department of Defence (Australia)|Department of Defence]]. |
|||
Following the abolition of the last vestiges of the [[White Australia policy]] in 1973,<ref>{{Cite web |url= http://www.border.gov.au/about/corporate/information/fact-sheets/08abolition |title= Fact Sheet – Abolition of the 'White Australia' Policy|location= Commonwealth of Australia|publisher= National Communications Branch, Department of Immigration and Citizenship|work= Australian Immigration |access-date= 27 March 2013 |archive-date= 19 September 2015 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20150919131355/http://www.border.gov.au/about/corporate/information/fact-sheets/08abolition |url-status= dead}}</ref> Australia's demography and culture transformed as a result of a large and ongoing wave of non-European immigration, mostly from Asia.<ref name="Davison pp338-6, 681-2">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|pages=338–39, 442–43, 681–82}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Sawer |first1=Geoffrey |title=The Australian Constitution and the Australian Aborigines |journal=Federal Law Review |date=1966 |volume=2 |issue=1 |pages=17–36 |publisher=Australian National University |location=Canberra |doi=10.1177/0067205X6600200102 |s2cid=159414135 |issn=1444-6928 |url=http://classic.austlii.edu.au/au/journals/FedLawRw/1967/2.pdf |access-date=3 August 2020 |archive-date=17 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200917034746/http://classic.austlii.edu.au/au/journals/FedLawRw/1967/2.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> The late 20th century also saw an increasing focus on foreign policy ties with other [[Pacific Rim]] nations.<ref>{{Cite book |title=The Pacific Basin since 1945: A history of the foreign relations of the Asian, Australasian, and American rim states and the Pacific islands|last=Thompson|first=Roger C. |isbn=978-0-5820-2127-3|publisher=Longman|year=1994|url=https://archive.org/details/pacificbasinsinc0000thom}}</ref> The [[Australia Acts]] severed the remaining constitutional ties between Australia and the United Kingdom while maintaining the monarch in her independent capacity as [[Queen of Australia]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.foundingdocs.gov.au/item-did-32.html|title=Australia Act 1986 (Cth)|access-date=25 July 2020|work=Documenting a Democracy|publisher=Museum of Australian Democracy at Old Parliament House|archive-date=22 April 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190422204352/https://www.foundingdocs.gov.au/item-did-32.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Twomey |first=Anne |date=January 2008 |title=The States, the Commonwealth and the Crown—the Battle for Sovereignty |url=https://www.aph.gov.au/About_Parliament/Senate/Powers_practice_n_procedures/pops/pop48/battlesovereignty |access-date= |website=Parliament of Australia |series=Papers on Parliament No. 48 |language=en-AU |quote= |archive-date=9 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220909014023/https://www.aph.gov.au/About_Parliament/Senate/Powers_practice_n_procedures/pops/pop48/battlesovereignty |url-status=live }}</ref> In a [[1999 Australian republic referendum|1999 constitutional referendum]], 55% of voters rejected [[Republicanism in Australia|abolishing the monarchy]] and becoming a republic.<ref>{{Cite web |title=1999: Republic referendum: Queen and/or Country |url=https://moadoph.gov.au/explore/democracy/1999-republic-referendum |access-date=10 February 2024 |website=Museum of Australian Democracy at Old Parliament House |archive-date=17 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240117083033/https://www.moadoph.gov.au/explore/democracy/1999-republic-referendum |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
In the 2010–11 budget, defence spending was A$25.7 billion,<ref>Australian Department of Defence (2010). [http://www.minister.defence.gov.au/Faulknertpl.cfm?CurrentId=10273 ''Budget 2010–11: Portfolio budget overview'']. Media release. Retrieved 28 June 2010.</ref> representing the [[List of countries by military expenditure|14th largest defence budget]] in the world but accounting for only 1.2% of global military spending.<ref>Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (2010). [http://www.sipri.org/media/media/pressreleases/pressreleasetranslations/storypackage_milex "SIPRI Yearbook 2010 — Military expenditure"], p.8. Retrieved 28 June 2010.</ref> Australia has been involved in UN and regional peacekeeping, disaster relief, and armed conflict; it [[Current Australian Defence Force deployments|currently has deployed]] approximately 3,330 defence force personnel in varying capacities to 12 overseas operations in areas including [[Operation Astute|East Timor]], [[Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands|Solomon Islands]] and [[Operation Slipper|Afghanistan]].<ref name="Global ops">Australian Department of Defence. [http://www.defence.gov.au/opEx/global/index.htm Global Operations]. Retrieved 9 March 2009.</ref> |
|||
Following the [[September 11 attacks]] on the United States, Australia joined the United States in fighting the [[Military history of Australia during the War in Afghanistan|Afghanistan War]] from 2001 to 2021 and the [[Australian contribution to the 2003 invasion of Iraq|Iraq War]] from 2003 to 2009.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Neville |first=Leigh |year=2019 |title=The Australian Army at War 1976–2016|edition=First |publisher=Bloomsbury |location=London |isbn=978-1-4728-2631-2}}</ref> The nation's trade relations also became increasingly oriented towards East Asia in the 21st century, with China becoming the nation's [[List of the largest trading partners of Australia|largest trading partner]] by a large margin.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.dfat.gov.au/sites/default/files/fifty-years-of-Australias-trade.pdf |title=Fifty years of Australia's trade |website=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade |access-date=11 January 2022 |archive-date=6 December 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221206235853/http://www.dfat.gov.au/sites/default/files/fifty-years-of-Australias-trade.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
==Geography and climate== |
|||
{{Main|Geography of Australia|Climate of Australia|Geology of Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Australia-climate-map MJC01.png|right|thumb|alt=Australia divided into different colours indicating its climatic zones|Climatic zones in Australia, based on the [[Köppen climate classification]].]] |
|||
Australia's landmass of {{convert|7617930|km2|sqmi|adj=off}}<ref name="Size">{{cite web|url=http://www.ga.gov.au/education/facts/dimensions/compare.htm|title=Australia's Size Compared|publisher=Geoscience Australia|accessdate=19 May 2007| archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20070324194241/http://www.ga.gov.au/education/facts/dimensions/compare.htm| archivedate = 24 March 2007}}</ref> is on the [[Indo-Australian Plate]]. Surrounded by the Indian<ref name="Southern Ocean" group="N"/> and Pacific oceans, it is separated from Asia by the [[Arafura Sea|Arafura]] and [[Timor Sea|Timor]] seas. The world's smallest continent<ref name="NatlGeo">{{cite web|url=http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/places/continents/index.html|title=Continents: What is a Continent?|publisher=[[National Geographic Society]]|accessdate=22 August 2009}} "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia, from largest to smallest—although sometimes Europe and Asia are considered a single continent, Eurasia."</ref> and [[List of countries and outlying territories by total area|sixth largest country by total area]],<ref name="Britannica">{{cite web|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/43654/Australia|title=Australia|publisher=[[Encyclopædia Britannica]]|accessdate=22 August 2009}} "Smallest continent and sixth largest country (in area) on Earth, lying between the Pacific and Indian oceans."</ref> Australia—owing to its size and isolation—is often dubbed the 'island continent'<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/landforms/islands.jsp|title=Islands|publisher=[[Geoscience Australia]]|accessdate=22 August 2009}}{{dead link|date=January 2011}} "Being surrounded by ocean, Australia often is referred to as an island continent. As a continental landmass it is significantly larger than the many thousands of fringing islands ..."</ref> and variably considered the [[List of islands by area|world's largest island]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/aib/island_continent.html|title=Australia in Brief: The island continent|publisher=[[Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade]]|accessdate=29 May 2009}} "Mainland Australia, with an area of 7.69 million square kilometres, is the Earth’s largest island but smallest continent."</ref> Australia has {{convert|34218|km|mi|0}} of coastline (excluding all offshore islands)<ref name="Coast">{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.gov.au/soe/2006/publications/drs/indicator/142/index.html|title=State of the Environment 2006|publisher=Department of the Environment and Water Resources|accessdate=19 May 2007}}</ref> and claims an extensive [[Exclusive Economic Zone]] of {{convert|8148250|km2|sqmi}}. This exclusive economic zone does not include the Australian Antarctic Territory.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/dimensions/oceans-seas.jsp|title=Oceans and Seas – Geoscience Australia|publisher=[[Geoscience Australia]]|date=9 April 2008|accessdate=23 April 2010}}{{dead link|date=January 2011}}</ref> Excluding [[Macquarie Island]], Australia lies between latitudes [[9th parallel south|9°]] and [[44th parallel south|44°S]], and longitudes [[112th meridian east|112°]] and [[154th meridian east|154°E]]. |
|||
In 2020, during the [[COVID-19 pandemic in Australia|COVID-19 pandemic]], several of Australia's largest cities were [[COVID-19 lockdowns|locked down]] for extended periods and free movement across the national and state borders was restricted in an attempt to slow the spread of the [[Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2|SARS-CoV-2 virus]].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Dawson |first=Emma |year=2020 |title=What Happens Next? Reconstructing Australia After COVID-19| publisher=Melbourne University Press |location=Melbourne |isbn=978-0-5228-7721-2}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Great Barrier Reef]], the world's largest coral reef,<ref name=UNEP>{{cite web|author=UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre|year=1980|title=Protected Areas and World Heritage – Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area|url=http://sea.unep-wcmc.org/sites/wh/gbrmp.html|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070528210526/http://sea.unep-wcmc.org/sites/wh/gbrmp.html|archivedate=2007-05-28|publisher=[[Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts|Department of the Environment and Heritage]]|accessdate=19 May 2007}}</ref> lies a short distance off the north-east coast and extends for over {{convert|2000|km|mi|-1}}. [[Mount Augustus National Park|Mount Augustus]], claimed to be the world's largest monolith,<ref name="Monolith">{{Cite news|url=http://www.smh.com.au/news/Western-Australia/Mount-Augustus/2005/02/17/1108500208314.html|title=Mount Augustus|publisher=[[The Sydney Morning Herald]]|date=17 February 2005 |accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> is located in Western Australia. At {{convert|2228|m|ft|0}}, [[Mount Kosciuszko]] on the [[Great Dividing Range]] is the highest mountain on the Australian mainland, although [[Mawson Peak]] on the remote Australian territory of [[Heard Island and McDonald Islands|Heard Island]] is taller at {{convert|2745|m|ft|0}}.<ref name=high>{{cite web|url=http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/landforms/highest-mountains.jsp|title=Highest Mountains|publisher=[[Geoscience Australia]]|date=23 December 2009|accessdate=30 March 2010}}{{dead link|date=January 2011}}</ref> |
|||
==Geography== |
|||
Australia is the flattest continent,<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.smh.com.au/news/National/Map-from-above-shows-Australia-is-a-very-flat-place/2005/01/21/1106110947946.html|title=Map from above shows Australia is a very flat place|date=21 January 2005|last=Macey|first=Richard|publisher=[[The Sydney Morning Herald]]|accessdate=5 April 2010}}</ref> with the oldest and least fertile soils;<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/quantum/info/q95-19-5.htm|title=A Chat with Tim Flannery on Population Control|last=Kelly|first=Karina|publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]|date=13 September 1995|accessdate=23 April 2010}} "Well, Australia has by far the world's least fertile soils".</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Damaged Dirt|publisher=''[[The Advertiser (Adelaide)|The Advertiser]]''|last=Grant|first= Cameron|url=http://www.1degree.com.au/files/AdvertiserPartworks_Part3_Page8.pdf?download=1&filename=AdvertiserPartworks_Part3_Page8.pdf|date=August 2007|accessdate=23 April 2010}} "Australia has the oldest, most highly weathered soils on the planet."</ref> [[Deserts of Australia|desert]] or semi-arid land commonly known as the [[outback]] makes up by far the largest portion of land. The driest inhabited continent, only its south-east and south-west corners have a [[temperate climate]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bom.gov.au/lam/climate/levelthree/ausclim/zones.htm|title=Australia – Climate of a Continent|publisher=Bureau of Meterorology|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> The [[List of countries and dependencies by population density|population density]], 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, is among the lowest in the world,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.worldatlas.com/aatlas/populations/ctydensityl.htm|title=Countries of the World (by lowest population density)|publisher=WorldAtlas|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> although a large proportion of the population lives along the temperate south-eastern coastline.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/bb8db737e2af84b8ca2571780015701e/5A717784C2562A99CA2573D20010FF17?opendocument|title=1301.0 – Year Book Australia, 2008|publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics|date=7 February 2008|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Geography of Australia|Environment of Australia}} |
|||
{{See also|Environmental issues in Australia}} |
|||
===General characteristics=== |
|||
Eastern Australia is marked by the Great Dividing Range that runs parallel to the coast of Queensland, New South Wales and much of Victoria – although the name is not strictly accurate, as in parts the range consists of low hills and the highlands are typically no more than {{convert|1600|m|ft|0}} in height.<ref name="Johnson2009p202">{{Cite book| last = Johnson | first = David | year = 2009 | title = The Geology of Australia | edition = 2 | publisher = [[Cambridge University Press]] | isbn = 978-0-521-76741-5 | page = 202 }}</ref> The [[Eastern Australian temperate forests|coastal uplands]] and a [[Brigalow Belt|belt of Brigalow grasslands]] lie between the coast and the mountains while inland of the dividing range are large areas of grassland.<ref name="Johnson2009p202" /><ref>{{Cite journal| last1 = Seabrooka | first1 = Leonie | last2 = McAlpinea | first2 = Clive | last3 = Fenshamb | first3 = Rod | year = 2006 | title = Cattle, crops and clearing: Regional drivers of landscape change in the Brigalow Belt, Queensland, Australia, 1840–2004 | journal = Landscape and Urban Planning | volume = 78 | issue = 4 | pages = 375–376 | doi = 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2005.11.00 }}</ref> These include the [[Southeast Australia temperate savanna|western plains]] of New South Wales and the [[Einasleigh Uplands]], [[Barkly Tableland]] and the [[Mulga Lands]] of inland Queensland. The northern point of the east coast is the tropical rainforested [[Cape York Peninsula]].<ref>{{cite web| last = Ford | first = Fred | year = 2001 | title = Einasleigh upland savanna (AA0705) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa0705_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| last = Ford | first = Fred | year = 2001 | title=Mitchell grass downs (AA0707) | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa0707_full.html | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| last = Wilson | first = Bruce | year = 2001 | title = Eastern Australia mulga shrublands (AA0802) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa0802_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| last = Mockrin | first = Miranda | year = 2001 | title = Southeast Australia temperate savanna (AA0803) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa0803_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Reliefmap of Australia.png|thumb|upright=1.3|right|alt=Map showing the topography of Australia, showing some elevation in the west and very high elevation in mountains in the south-east|Topographic map of Australia (dark green represents the lowest elevation and dark brown the highest)]] |
|||
Surrounded by the Indian and Pacific oceans,{{Refn|Australia describes the body of water south of its mainland as the [[Southern Ocean]], rather than the Indian Ocean as defined by the [[International Hydrographic Organization]] (IHO). In 2000, a vote of IHO member nations defined the term "Southern Ocean" as applying only to the waters between [[Antarctica]] and [[60th parallel south|60° south]] latitude.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://geography.about.com/od/learnabouttheearth/a/fifthocean.htm|last=Rosenberg|first=Matt |title=The New Fifth Ocean – The World's Newest Ocean – The Southern Ocean|publisher=About.com: Geography|date=20 August 2009 |access-date=5 April 2010 |archive-date=26 January 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120126025233/http://geography.about.com/od/learnabouttheearth/a/fifthocean.htm |url-status=dead}}</ref>|name="Southern Ocean"|group="N"}} Australia is separated from Asia by the [[Arafura Sea|Arafura]] and [[Timor Sea|Timor]] seas, with the [[Coral Sea]] lying off the Queensland coast, and the [[Tasman Sea]] lying between Australia and New Zealand. The world's smallest continent<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/places/continents/index.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080714145306/http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/places/continents/index.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=14 July 2008 |title=Continents: What is a Continent?|publisher=National Geographic Society |access-date=22 August 2009}} "Most people recognize seven continents — [[Asia]], [[Africa]], [[North America]], [[South America]], [[Antarctica]], [[Europe]], and Australia, from largest to smallest — although sometimes Europe and Asia are considered a single continent, [[Eurasia]]".</ref> and [[List of countries and outlying territories by total area|sixth-largest country by total area]],<ref name="Britannica">{{Cite web |url=https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/43654/Australia |title=Australia |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |access-date=22 August 2009 |archive-date=22 September 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090922214422/http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/43654/Australia |url-status=live }} "Smallest continent and sixth largest country (in area) on Earth, lying between the Pacific and Indian oceans".</ref> Australia—owing to its size and isolation—is often dubbed the "island continent"<ref>{{Cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100423151730/http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/landforms/islands.jsp|url=http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/landforms/islands.jsp |publisher=Geoscience Australia |title=Islands |archive-date=23 April 2010}} "Being surrounded by ocean, Australia often is referred to as an island continent. As a continental landmass it is significantly larger than the many thousands of fringing islands{{Nbsp}}..."</ref> and is sometimes considered the world's [[List of islands by area|largest island]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/aib/island_continent.html |title=Australia in Brief: The island continent|publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (Australia) |access-date=29 May 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090604082917/http://www.dfat.gov.au/aib/island_continent.html |archive-date=4 June 2009 |url-status=dead}} "Mainland Australia, with an area of 7.69 million square kilometres, is the Earth's largest island but smallest continent".</ref> Australia has {{Cvt|34218|km}} of coastline (excluding all offshore islands),<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/soe/2006/publications/drs/indicator/142/index.html |title=State of the Environment 2006|publisher=Department of the Environment and Water Resources |access-date=19 May 2007 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070710224519/http://www.environment.gov.au/soe/2006/publications/drs/indicator/142/index.html |archive-date=10 July 2007}}</ref> and claims [[Exclusive economic zone of Australia|an extensive exclusive economic zone]] of {{Convert|8148250|km2|sqmi}}. This exclusive economic zone does not include the [[Australian Antarctic Territory]].<ref>{{Cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090620022412/http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/dimensions/oceans-seas.jsp|url=http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/dimensions/oceans-seas.jsp |publisher=Geoscience Australia |title=Oceans and Seas – Geoscience Australia |archive-date=20 June 2009}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Reliefmap of Australia.png|thumb|alt=Map showing the topography of Australia, showing a some elevation in the west and very high elevation in mountains in the southeast|Topographic map of Australia]] |
|||
The landscapes of the northern part of the country, the [[Top End]] and the [[Gulf Country]] behind the [[Gulf of Carpentaria]], with their tropical climate, consist of [[woodland]], [[grassland]] and desert.<ref>{{cite web| last = Woinarski | first = John | year = 2001 | title = Arnhem Land tropical savanna (AA0701) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa0701_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| date = 27 June 2009 | title = Rangelands – Overview | work = Australian Natural Resources Atlas | publisher = Australian Government | url = http://www.anra.gov.au/topics/rangelands/overview/qld/ibra-gup.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| last = Mockrin | first = Miranda | year = 2001 | title = Cape York Peninsula tropical savanna (AA0703) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa0703_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref> At the northwest corner of the continent is the sandstone cliffs and gorges of [[Kimberley (Western Australia)|The Kimberley]] and below that the [[Pilbara]] while south and inland of these lie more areas of grassland, the [[Ord Victoria Plain]] and the [[Western Australian Mulga shrublands]].<ref>{{Cite book| last = Van Driesum | first = Rob | year = 2002 | title = Outback Australia | publisher = Lonely Planet | isbn = 1-86450-187-1 | page = 306 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| last = Woinarski | first = John | year = 2001 | title = Victoria Plains tropical savanna (AA0709) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa0709_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| last = Hopkins | first = Angas | year = 2001 | title = Western Australian Mulga shrublands (AA1310) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa1310_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref> The heart of the country is the [[Central Ranges xeric scrub|uplands of central Australia]] while prominent features of the centre and south include the inland [[Simpson Desert|Simpson]], [[Tirari-Sturt stony desert|Tirari and Sturt Stony]], [[Gibson Desert|Gibson]], [[Great Sandy-Tanami desert|Great Sandy, Tanami]] and [[Great Victoria Desert]]s with the famous [[Nullarbor Plain]] on the southern coast.<ref>{{cite web| year = 2001 | title = Central Ranges xeric scrub (AA1302) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa1302_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book| last = Banting | first = Erinn | year = 2003 | title = Australia: The land | publisher = Crabtree Publishing Company | isbn = 0-7787-9343-5 | page = 10 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| last = Hopkins | first = Angas | year = 2001 | title = Tirari-Sturt stony desert (AA1309) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa1309_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web| last = Hopkins | first = Angas | year = 2001 | title = Great Sandy-Tanami desert (AA1304) | work = Terrestrial Ecoregions | publisher = World Wildlife Fund | url = http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/aa/aa1304_full.html | accessdate = 16 June 2010 }}</ref> |
|||
Mainland Australia lies between latitudes [[9th parallel south|9°]] and [[44th parallel south|44° south]], and longitudes [[112th meridian east|112°]] and [[154th meridian east|154° east]].<ref name="Geoscience-Australia-2014"/> Australia's size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with tropical rainforests in the north-east, mountain ranges in the south-east, south-west and east, and desert in the centre.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/parks/national-landscapes/index.html |title=Parks and Reserves—Australia's National Landscapes|website=environment.gov.au|date=23 November 2011 |access-date=4 January 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120104114011/http://environment.gov.au/parks/national-landscapes/index.html |archive-date=4 January 2012}}</ref> The desert or semi-arid land commonly known as the [[outback]] makes up by far the largest portion of land.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Australia: Portrait of a continent|last1=Loffler|first1=Ernst|first2=Anneliese|last2=Loffler |author3=A. J. Rose|first4=Denis|last4=Warner|year=1983|publisher=Hutchinson Group (Australia)|location=Richmond, Victoria|isbn=978-0-0913-0460-7|pages=37–39}}</ref> Australia is the driest inhabited continent; its annual rainfall averaged over continental area is less than 500 mm.<ref name=bomclim/> The [[List of countries and dependencies by population density|population density]] is 3.4 inhabitants per square kilometre, although the large majority of the population lives along the temperate south-eastern coastline. The population density exceeds 19,500 inhabitants per square kilometre in central Melbourne.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/Previousproducts/3218.0Main%20Features702016-17?opendocument&tabname=Summary&prodno=3218.0&issue=2016-17&num=&view=|title=Population Density|publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics|date=26 March 2019|access-date=25 April 2020|archive-date=3 May 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200503083301/https://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs%40.nsf/Previousproducts/3218.0Main%20Features702016-17?opendocument&tabname=Summary&prodno=3218.0&issue=2016-17&num=&view=|url-status=live}}</ref> In 2021 Australia had 10% of the global permanent meadows and pastureland.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en?details=cc8166en |title=World Food and Agriculture: Statistical Yearbook 2023 |date=2023 |publisher=[[Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations]] |isbn=978-92-5-138262-2 |language=en |doi=10.4060/cc8166en |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231215161116/https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en?details=cc8166en |archive-date=15 December 2023 |url-status=live}}</ref> [[Forest cover]] is around 17% of Australia's total land area.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/enwiki/api/core/bitstreams/a6e225da-4a31-4e06-818d-ca3aeadfd635/content |title=Terms and Definitions FRA 2025 Forest Resources Assessment, Working Paper 194 |publisher=Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations |year=2023}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Australia |url=https://fra-data.fao.org/assessments/fra/2020/AUS/home/overview |website=Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations}}</ref> |
|||
The climate of Australia is significantly influenced by ocean currents, including the [[Indian Ocean Dipole]] and the [[El Niño-Southern Oscillation]], which is correlated with periodic [[Drought in Australia|drought]], and the seasonal tropical low pressure system that produces [[cyclone]]s in northern Australia.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.theage.com.au/news/climate-watch/no-more-drought-its-a-permanent-dry/2007/09/06/1188783415754.html|title=No more drought: it's a 'permanent dry'|last=Kleinman|first=Rachel|date=6 September 2007|accessdate=30 March 2010|work=[[The Age]] | location=Melbourne}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://news.independent.co.uk/world/australasia/article2465960.ece|title=Australia's epic drought: The situation is grim|last=Marks|first=Kathy|work=[[The Independent]]|date=20 April 2007|accessdate=30 March 2010|location=London}}</ref> These factors induce rainfall to vary markedly from year to year. Much of the northern part of the country has a tropical predominantly summer rainfall (monsoon) climate.<ref name=bomclim>{{cite web| title = Australia – Climate of Our Continent | publisher = Bureau of Meteorology | url = http://www.bom.gov.au/lam/climate/levelthree/ausclim/zones.htm | accessdate = 17 June 2010|year=2010}}</ref> Just under three quarters of Australia lies within a desert or semi-arid zone.<ref name="portrait">{{Cite book|title=Australia: Portrait of a continent |last=Loffler |first=Ernst |authorlink= |coauthors=Anneliese Loffler, A. J. Rose, Denis Warner |year=1983 |publisher=Hutchinson Group (Australia) |location=Richmond, Victoria |isbn=0-09-130460-1 |pages=37–39 }}</ref> The [[Southwest corner of Western Australia|southwest corner of the country]] has a [[Mediterranean climate]].<ref>{{cite web| title = Climate of Western Australia | publisher = Bureau of Meteorology | url = http://www.bom.gov.au/lam/climate/levelthree/ausclim/ausclimwa.htm | accessdate = 6 December 2009}}</ref> Much of the southeast (including Tasmania) is temperate.<ref name=bomclim/> |
|||
[[File:Fitzroy Island.jpg|thumb|upright=1.0|left|[[Fitzroy Island (Queensland)|Fitzroy Island]], one of the 600 islands within the main archipelago of the [[Great Barrier Reef]]]] |
|||
==Environment== |
|||
{{Main|Environment of Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Koala climbing tree.jpg|thumb|alt=A =koala holding onto a eucalyptus tree with its head turned so both eyes are visible|The [[koala]] and the ''[[eucalyptus]]'' form an iconic Australian pair]] |
|||
Although most of Australia is semi-arid or desert, it includes a diverse range of habitats from [[alpine climate|alpine]] heaths to [[tropical rainforest]]s, and is recognised as a [[megadiverse countries|megadiverse country]]. Because of the continent's great age, extremely variable weather patterns, and long-term geographic isolation, much of Australia's [[biota (ecology)|biota]] is unique and diverse. About 85% of flowering plants, 84% of mammals, more than 45% of [[List of birds of Australia|birds]], and 89% of in-shore, temperate-zone fish are [[endemism|endemic]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.deh.gov.au/biodiversity/about-biodiversity.html|title=About Biodiversity|accessdate=18 September 2007|publisher=Department of the Environment and Heritage|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070205015628/www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/about-biodiversity.html|archivedate=5 February 2007}}</ref> Australia has the greatest number of reptiles of any country, with 755 species.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Lambertini|first=Marco|title=A Naturalist’s Guide to the Tropics|year=2000|isbn=0-226-46828-3|publisher=University of Chicago Press|url=http://www.press.uchicago.edu/Misc/Chicago/468283.html|format=excerpt|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Great Barrier Reef]], the world's largest coral reef,<ref>{{Cite web|author=UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre|year=1980 |title=Protected Areas and World Heritage – Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area|url=http://sea.unep-wcmc.org/sites/wh/gbrmp.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070528210526/http://sea.unep-wcmc.org/sites/wh/gbrmp.html |archive-date=28 May 2007 |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |access-date=19 May 2007}}</ref> lies a short distance off the north-east coast and extends for more than {{Cvt|2000|km}}. [[Mount Augustus (Western Australia)|Mount Augustus]], claimed to be the world's largest monolith,<ref name="Monolith">{{Cite news|url=https://www.smh.com.au/news/Western-Australia/Mount-Augustus/2005/02/17/1108500208314.html|title=Mount Augustus|publisher=The Sydney Morning Herald|date=17 February 2005|access-date=30 March 2010|archive-date=6 February 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120206233728/http://www.smh.com.au/news/Western-Australia/Mount-Augustus/2005/02/17/1108500208314.html|url-status=live}}</ref> is located in Western Australia. At {{Cvt|2228|m}}, [[Mount Kosciuszko]] is the highest mountain on the Australian mainland. Even taller are [[Mawson Peak]], at {{Cvt|2745|m}}, on the remote Australian [[States and territories of Australia|external territory]] of [[Heard Island and McDonald Islands|Heard Island]], and, in the Australian Antarctic Territory, [[Mount McClintock]] and [[Mount Menzies]], at {{Cvt|3492|m}} and {{Cvt|3355|m}} respectively.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/landforms/highest-mountains.html|publisher=Geoscience Australia|title=Highest Mountains|access-date=2 February 2012|date=15 May 2014|archive-date=21 March 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120321184228/http://ga.gov.au/education/geoscience-basics/landforms/highest-mountains.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
[[Forests of Australia|Australian forests]] are mostly made up of evergreen species, particularly [[eucalyptus]] trees in the less arid regions, [[acacia|Wattles]] replace them in drier regions and deserts as the most dominant species.<ref name=dfat>{{cite web|url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/flora_and_fauna.html|title=About Australia: Flora and fauna|accessdate=15 May 2010|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia|date=May 2008|work=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade website}}</ref> Among well-known [[fauna of Australia|Australian fauna]] are the [[monotreme]]s (the [[platypus]] and [[echidna]]); a host of [[marsupial]]s, including the [[kangaroo]], [[koala]], and [[wombat]], and birds such as the [[emu]] and the [[kookaburra]].<ref name=dfat/> Australia is home to [[Animal attacks in Australia|many dangerous animals]] including some of the most venomous snakes in the world.<ref>"Snake Bite", ''[http://www.avru.org/compendium/biogs/A000084b.htm The Australian Venom Compendium]''.</ref> The [[dingo]] was introduced by Austronesian people who traded with Indigenous Australians around 3000 [[Common Era|BCE]].<ref name="savolainen2004">Savolainen, P. et al. 2004. A detailed picture of the origin of the Australian dingo, obtained from the study of mitochondrial DNA. ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America''. 101:12387–12390 PMID.</ref> Many plant and animal species became extinct soon after first human settlement,<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://uninews.unimelb.edu.au/view.php?articleID=170|title=Humans to blame for extinction of Australia's megafauna|publisher=The [[University of Melbourne]]|date=8 June 2001|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> including the [[Australian megafauna]]; others have disappeared since European settlement, among them the [[thylacine]].<ref name="NW">{{cite web|url=http://www.naturalworlds.org/thylacine/additional/persecution/image_6.htm|title=Additional Thylacine Topics: Persecution|publisher=The Thylacine Museum|year=2006|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.deh.gov.au/biodiversity/threatened/ts-day/index.html|title=National Threatened Species Day|publisher=Department of the Environment and Heritage, Australian Government|year=2006|accessdate=21 November 2006}}</ref> |
|||
Eastern Australia is marked by the [[Great Dividing Range]], which runs parallel to the coast of Queensland, New South Wales and much of Victoria. The name is not strictly accurate, because parts of the range consist of low hills, and the highlands are typically no more than {{Cvt|1600|m}} in height.<ref name="Johnson2009p202">{{Cite book|last=Johnson|first=David|year=2009 |
|||
Many of Australia's ecoregions, and the species within those regions, are threatened by human activities and [[Invasive species in Australia|introduced]] plant and animal species.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/invasive/index.html |title=Invasive species |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |date=2010-03-17 |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref> The federal ''Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999'' is the legal framework for the protection of threatened species.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.gov.au/epbc/about/index.html |title=About the EPBC Act |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |date= |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref> Numerous [[Protected areas of Australia|protected areas]] have been created under the [[Biodiversity Action Plan|National Strategy for the Conservation of Australia's Biological Diversity]] to protect and preserve unique ecosystems;<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/publications/strategy/index.html |title=National Strategy for the Conservation of Australia's Biological Diversity |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |
|||
|title=The Geology of Australia|edition=2|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-5217-6741-5|page=202}}</ref> The [[Eastern Australian temperate forests|coastal uplands]] and a [[Brigalow Belt|belt of Brigalow grasslands]] lie between the coast and the mountains, while inland of the dividing range are large areas of grassland and shrubland.<ref name="Johnson2009p202"/><ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Seabrooka |
|||
|date=2010-01-21 |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/publications/strategy/chap1.html |title=Conservation of biological diversity across Australia |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts|date=2009-01-19 |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref> 65 [[wetland]]s are [[List of Ramsar sites in Australia|listed]] under the [[Ramsar Convention]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ramsar.org/pdf/sitelist.pdf |title=The List of Wetlands of International Importance |publisher=[[Ramsar Convention]] |pages=6–7 |format=PDF |date=22 May 2010 |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref> and 15 natural [[World Heritage Site]]s have been established.<ref name="WHC">{{cite web|url=http://whc.unesco.org/en/statesparties/au|title=Australia|work=UNESCO World Heritage Centre|publisher=UNESCO|accessdate=5 September 2009}}</ref> Australia was ranked 51th of 163 countries in the world on the 2010 [[Environmental Performance Index]].<ref name="EPI">{{cite web|url=http://epi.yale.edu/Countries|title=2010 Environmental Performance Index|publisher=[[Yale University]]|accessdate=11 November 2010}}</ref> |
|||
|first1=Leonie|last2=McAlpinea|first2=Clive|last3=Fenshamb|first3=Rod|year=2006 |title=Cattle, crops and clearing: Regional drivers of landscape change in the Brigalow Belt, Queensland, Australia, 1840–2004 |
|||
|journal=Landscape and Urban Planning|volume=78|issue=4|pages=375–376|doi=10.1016/j.landurbplan.2005.11.007|bibcode=2006LUrbP..78..373S }}</ref> These include the [[Southeast Australia temperate savanna|western plains]] of New South Wales, and the [[Mitchell Grass Downs]] and [[Mulga Lands]] of inland Queensland.<ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Einasleigh Uplands savanna|id=aa0705|access-date =16 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Mitchell grass downs|id=aa0707 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Eastern Australia mulga shrublands|id=aa0802 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Southeast Australia temperate savanna|id=aa0803 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref> The northernmost point of the mainland is the tropical [[Cape York Peninsula]].<ref name="Geoscience-Australia-2014"/> |
|||
[[File:Uluru, helicopter view, cropped.jpg|thumb|upright=1.0|right|[[Uluru]] in the semi-arid region of Central Australia]] |
|||
[[Climate change in Australia|Climate change]] has become an increasing concern in Australia in recent years,<ref>[http://www.environment.gov.au/soe/2006/publications/commentaries/atmosphere/climate-change.html Atmosphere: Major issue: climate change], Australian State of the Environment Committee, 2006.</ref> with many Australians considering protection of the environment to be the most important issue facing the country.<ref>[http://news.anu.edu.au/?p=335 ANU poll finds ‘it’s the environment, stupid’], [[Australian National University]]. Retrieved on 8 January 2008.</ref> The [[Rudd Ministry]] has initiated several emission reduction activities;<ref>{{cite web|author=Tom Young|url=http://www.businessgreen.com/business-green/news/2232626/australia-makes-carbon |title=Australia Sets Target of 15% Carbon Reduction by 2020, Announces 2010 Carbon Market |publisher=Businessgreen.com |date= |accessdate=2010-09-12}}</ref> Rudd's first official act, on his first day in office, was to sign the instrument of ratification of the [[Kyoto Protocol]]. Nevertheless, Australia's [[List of countries by carbon dioxide emissions per capita|carbon dioxide emissions per capita]] are among the highest in the world, lower than those of only a few other industrialised nations.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.smh.com.au/news/environment/australias-greenhouse-emissions-twice-world-rate/2007/05/22/1179601374518.html|title=Australia's carbon dioxide emissions twice world rate|publisher=[[The Sydney Morning Herald]]|last=Smith|first=Deborah|date=22 May 2007|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> Rainfall in Australia has slightly increased over the past century, both nationwide and for two quadrants of the nation,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/change/rerain.shtml|title=Regional Rainfall Trends|publisher=Bureau of Meteorology|accessdate=8 July 2009}}</ref> while annual mean temperatures increased significantly over the past decades.<ref name="climate08">{{cite web|url=http://www.bom.gov.au/announcements/media_releases/climate/change/20090105.shtml|title=Annual Australian Climate Statement 2008|date=5 January 2009|publisher=Bureau of Meteorology|accessdate=5 September 2009}}</ref> [[Water restrictions in Australia|Water restrictions]] are currently in place in many regions and cities of Australia in response to chronic shortages due to urban population increases and localised [[Drought in Australia|drought]].<ref>{{Cite news| url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/7361210.stm |title=Saving Australia's water |publisher=BBC News |date=23 April 2008 |accessdate=1 June 2010}}</ref> |
|||
The landscapes of the [[Top End]] and the [[Gulf Country]]—with their tropical climate—include forest, woodland, wetland, grassland, rainforest and desert.<ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Arnhem Land tropical savanna|id=aa0701 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=27 June 2009 |title=Rangelands – Overview|work=Australian Natural Resources Atlas|publisher=Australian Government |url=http://www.anra.gov.au/topics/rangelands/overview/qld/ibra-gup.html|access-date =16 June 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100313224717/http://www.anra.gov.au/topics/rangelands/overview/qld/ibra-gup.html |archive-date=13 March 2010}}</ref><ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Cape York Peninsula tropical savanna|id=aa0703 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref> At the north-west corner of the continent are the sandstone cliffs and gorges of [[Kimberley (Western Australia)|The Kimberley]], and below that the [[Pilbara]]. The [[Victoria Plains tropical savanna]] lies south of the [[Kimberley tropical savanna|Kimberley]] and [[Arnhem Land tropical savanna|Arnhem Land]] savannas, forming a transition between the coastal savannas and the interior deserts.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Van Driesum|first=Rob|year=2002 |title=Outback Australia|publisher=Lonely Planet|isbn=978-1-8645-0187-2|page=306}}</ref><ref>{{WWF ecoregion |name=Victoria Plains tropical savanna|id=aa0709|access-date =16 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Western Australian Mulga shrublands|id=aa1310 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref> At the heart of the country are the [[Central Ranges xeric scrub|uplands of central Australia]]. Prominent features of the centre and south include [[Uluru]] (also known as Ayers Rock), the famous sandstone monolith, and the inland [[Simpson Desert|Simpson]], [[Tirari-Sturt stony desert|Tirari and Sturt Stony]], [[Gibson Desert|Gibson]], [[Great Sandy-Tanami desert|Great Sandy, Tanami]], and [[Great Victoria Desert|Great Victoria]] deserts, with the famous [[Nullarbor Plain]] on the southern coast.<ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Central Ranges xeric scrub|id=aa1302 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Banting|first=Erinn |
|||
|year=2003 |title=Australia: The land|publisher=Crabtree Publishing Company|isbn=978-0-7787-9343-4|page=[https://archive.org/details/australia00bant_2/page/10 10] |
|||
|url=https://archive.org/details/australia00bant_2/page/10}}</ref><ref name="Terrestrial-Ecoregions">{{WWF ecoregion|name=Tirari-Sturt stony desert|id=aa1309 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Great Sandy-Tanami desert|id=aa1304 |access-date=16 June 2010}}</ref> The [[Western Australian mulga shrublands]] lie between the interior deserts and Mediterranean-climate [[Southwest Australia]].<ref name="Terrestrial-Ecoregions"/><ref>{{WWF ecoregion|name=Western Australian mulga shrublands|id=aa1301 |access-date=1 June 2020}}</ref> |
|||
===Geology=== |
|||
{{Main|Geology of Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Ausgeolbasic.jpg|thumb|upright=1.2|right|Basic geological regions of Australia (by age)]] |
|||
Lying on the [[Indo-Australian Plate]], the mainland of Australia is the lowest and most primordial landmass on Earth with a relatively stable geological history.<ref>Pirajno, F., Occhipinti, S.A. and Swager, C.P., 1998. ''Geology and tectonic evolution of the Palaeoproterozoic Bryah, Padbury and Yerrida basins, Western Australia: implications for the history of the south-central Capricorn orogen'' Precambrian Research, 90: 119–40</ref><ref>Pain, C.F., Villans, B.J., Roach, I.C., Worrall, L. & Wilford, J.R. (2012) "Old, flat and red – Australia's distinctive landscape" In: ''Shaping a Nation: A Geology of Australia'' Blewitt, R.S. (Ed.) Geoscience Australia and ANU E Press, Canberra. pp. 227–75 {{ISBN|978-1-9221-0343-7}}</ref> The landmass includes virtually all known rock types and from all geological time periods spanning more than 3.8 billion years of the Earth's history. The [[Pilbara Craton]] is one of only two pristine [[Archean|Archaean]] 3.6–2.7 Ga (billion years ago) crusts identified on the Earth.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Gray|first1=DR|last2=Foster|first2=DA|year=2004 |title=Tectonic review of the Lachlan Orogen: historical review, data synthesis and modern perspectives|journal=Australian Journal of Earth Sciences|volume=51|issue=6|pages=773–817|doi=10.1111/j.1400-0952.2004.01092.x|s2cid=128901742}}</ref> |
|||
Having been part of all major [[supercontinent]]s, the [[Australia (continent)|Australian continent]] began to form after the break-up of [[Gondwana]] in the [[Permian]], with the separation of the continental landmass from the African continent and Indian subcontinent. It separated from Antarctica over a prolonged period beginning in the [[Permian]] and continuing through to the [[Cretaceous]].<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Hawkesworth|first1=CJ|display-authors=et al.|year=2010 |title=The generation and evolution of the continental crust|journal=Journal of the Geological Society|volume=167|issue=2|pages=229–248 |doi=10.1144/0016-76492009-072|bibcode=2010JGSoc.167..229H|s2cid=131052922}}</ref> When the [[last glacial period]] ended in about 10,000 BC, rising sea levels formed [[Bass Strait]], separating [[Tasmania]] from the mainland. Then between about 8,000 and 6,500 BC, the lowlands in the north were flooded by the sea, separating New Guinea, the [[Aru Islands]], and the mainland of Australia.<ref>Hillis RR & Muller RD. (eds) 2003 ''Evolution and dynamics of the Australian Plate'' Geological Society of Australia Special Publication 22: 432 p.</ref> The Australian continent is moving toward [[Eurasia]] at the rate of 6 to 7 centimetres a year.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Cawood|first1=PA|year=2005 |title=Terra Australis Orogen: ''Rodinia breakup and development of the Pacific and Iapetus margins of Gondwana during the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic''|journal=Earth-Science Reviews|volume=69|issue=3–4|pages=249–279|doi=10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.09.001|bibcode=2005ESRv...69..249C}}</ref> |
|||
The Australian mainland's [[continental crust]], excluding the thinned margins, has an average thickness of 38{{Nbsp}}km, with a range in thickness from 24 km to 59 km.<ref>McKenzie et al. (ed) 2004 Australian Soils and Landscapes: an illustrated compendium [[CSIRO]] Publishing: 395 p.</ref> Australia's geology can be divided into several main sections, showcasing that the continent grew from west to east: the Archaean [[craton]]ic shields found mostly in the west, [[Proterozoic]] [[orogeny|fold belts]] in the centre and [[Phanerozoic]] [[sedimentary basins]], metamorphic and [[igneous rocks]] in the east.<ref>Bishop P & Pillans B. (eds) 2010, Australian Landscapes Geological Society of London Special Publication 346</ref> |
|||
The Australian mainland and Tasmania are situated in the middle of the [[tectonic plate]] and have no active volcanoes,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.australiangeographic.com.au/journal/land-of-earthquakes-and-volcanoes.htm |title=Land of earthquakes and volcanoes?|first=Kevin|last=Mccue |access-date=25 April 2010|date=26 February 2010|publisher=Australian Geographic |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100306150520/http://www.australiangeographic.com.au/journal/land-of-earthquakes-and-volcanoes.htm |archive-date=6 March 2010}}</ref> but due to passing over the [[East Australia hotspot]], recent volcanism has occurred during the [[Holocene]], in the [[Newer Volcanics Province]] of western Victoria and south-eastern South Australia. Volcanism also occurs in the island of New Guinea (considered geologically as part of the Australian continent), and in the Australian external territory of [[Heard Island and McDonald Islands]].<ref>Van Ufford AQ & Cloos M. 2005 ''Cenozoic tectonics of New Guinea'' AAPG Bulletin 89: 119–140</ref> [[List of earthquakes in Australia|Seismic activity]] in the Australian mainland and Tasmania is also low, with the greatest number of fatalities having occurred in the [[1989 Newcastle earthquake]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.ga.gov.au/urban/factsheets/earthquakes_newcastle.jsp |title=Earthquake History, Regional Seismicity And The 1989 Newcastle Earthquake |publisher=Geoscience Australia|date=22 June 2004 |access-date=27 June 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040826220212/http://www.ga.gov.au/urban/factsheets/earthquakes_newcastle.jsp |archive-date=26 August 2004}}</ref> |
|||
===Climate=== |
|||
{{Main|Climate of Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Australia Köppen.svg|thumb|upright=1.2|right|[[Köppen climate classification|Köppen climate types]] of Australia<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Beck|first1=Hylke E.|last2=Zimmermann|first2=Niklaus E. |last3=McVicar|first3=Tim R.|last4=Vergopolan|first4=Noemi|last5=Berg|first5=Alexis|last6=Wood|first6=Eric F.|title=Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution |journal=Scientific Data|date=30 October 2018|volume=5|issue=1|page=180214|doi=10.1038/sdata.2018.214|pmid=30375988|pmc=6207062|bibcode=2018NatSD...580214B}}</ref>]] |
|||
The climate of Australia is significantly influenced by ocean currents, including the [[Indian Ocean Dipole]] and the [[El Niño–Southern Oscillation]], which is correlated with periodic [[Drought in Australia|drought]], and the seasonal tropical low-pressure system that produces cyclones in northern Australia.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.theage.com.au/news/climate-watch/no-more-drought-its-a-permanent-dry/2007/09/06/1188783415754.html|title=No more drought: it's a 'permanent dry'|last=Kleinman|first=Rachel|date=6 September 2007|access-date=30 March 2010|publisher=The Age|location=Melbourne|archive-date=10 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010150803/http://www.theage.com.au/news/climate-watch/no-more-drought-its-a-permanent-dry/2007/09/06/1188783415754.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://news.independent.co.uk/world/australasia/article2465960.ece |title=Australia's epic drought: The situation is grim|last=Marks|first=Kathy|newspaper=The Independent|date=20 April 2007 |access-date=30 March 2010|location=London |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070422065131/http://news.independent.co.uk/world/australasia/article2465960.ece |archive-date=22 April 2007}}</ref> These factors cause rainfall to vary markedly from year to year. Much of the northern part of the country has a tropical, predominantly summer-rainfall ([[monsoon]]).<ref name=bomclim>{{Cite web |title=Australia – Climate of Our Continent|publisher=Bureau of Meteorology|url=http://www.bom.gov.au/lam/climate/levelthree/ausclim/zones.htm |access-date=17 June 2010 |archive-url=https://webarchive.nla.gov.au/awa/20090317054300/http://pandora.nla.gov.au/pan/96122/20090317-1643/www.bom.gov.au/lam/climate/levelthree/ausclim/zones.html |archive-date=17 March 2009}}{{Cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> The south-west corner of the country has a [[Mediterranean climate]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Climate of Western Australia|publisher=Bureau of Meteorology|url=http://www.bom.gov.au/lam/climate/levelthree/ausclim/ausclimwa.htm |access-date=6 December 2009 |archive-url=https://webarchive.nla.gov.au/awa/20090317054300/http://pandora.nla.gov.au/pan/96122/20090317-1643/www.bom.gov.au/lam/climate/levelthree/ausclim/ausclimwa.html |archive-date=17 March 2009}}{{Cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> The south-east ranges from [[oceanic climate|oceanic]] (Tasmania and coastal Victoria) to [[humid subtropical]] (upper half of New South Wales), with the highlands featuring [[alpine climate|alpine]] and [[subpolar oceanic climate]]s. The interior is [[arid]] to [[semi-arid]].<ref name=bomclim/> |
|||
Driven by [[Climate change in Australia|climate change]], average temperatures have risen [[Climate change in Australia|more than 1°C since 1960]]. Associated changes in rainfall patterns and climate extremes exacerbate existing issues such as drought and [[Bushfires in Australia|bushfires]]. 2019 was Australia's warmest recorded year,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.bom.gov.au/state-of-the-climate/documents/State-of-the-Climate-2020.pdf|title=State of the Climate 2020|publisher=Bureau of Meteorology|date=November 2020|access-date=2 December 2020|archive-date=24 November 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201124014610/http://www.bom.gov.au/state-of-the-climate/documents/State-of-the-Climate-2020.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> and the [[2019–20 Australian bushfire season|2019–2020 bushfire season]] was the country's worst [[List of Australian bushfire seasons|on record]].<ref>{{Cite news|title=Australia fires: Life during and after the worst bushfires in history|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/newsround/52410744|publisher=BBC News|date=28 April 2020|access-date=18 July 2020|archive-date=15 July 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220715111438/https://www.bbc.co.uk/newsround/52410744|url-status=live}}</ref> [[Greenhouse gas emissions by Australia|Australia's greenhouse gas emissions]] per capita are among the highest in the world.<ref>{{Cite report|date=9 March 2020|title=Environment at a Glance Indicators: Climate change|url=https://www.oecd.org/environment/environment-at-a-glance/Climate-Change-Archive-February-2020.pdf|publisher=OECD|page=6|access-date=3 December 2020|archive-date=21 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201221214907/https://www.oecd.org/environment/environment-at-a-glance/Climate-Change-Archive-February-2020.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
[[Water restrictions in Australia|Water restrictions]] are frequently in place in many regions and cities of Australia in response to chronic shortages due to urban population increases and localised drought.<ref>{{Cite news|last1=Heggie|first1=Jon |title=Making Every Drop Count: How Australia is Securing its Water Future|url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2019/08/partner-content-how-australia-is-securing-its-water-future/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200718182729/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2019/08/partner-content-how-australia-is-securing-its-water-future/|url-status=dead|archive-date=18 July 2020|publisher=National Geographic|date=August 2019}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.nwc.gov.au/urban/more/national-review-of-water-restrictions-in-australia |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120227083656/http://www.nwc.gov.au/urban/more/national-review-of-water-restrictions-in-australia |archive-date=27 February 2012 |title=National review of water restrictions in Australia|publisher=Australian Government National Water Commission|date=15 January 2010 |access-date=27 September 2012}}</ref> Throughout much of the continent, [[Floods in Australia|major flooding]] regularly follows extended periods of drought, flushing out inland river systems, overflowing dams and inundating large inland flood plains, as occurred throughout Eastern Australia in the early 2010s after the [[2000s Australian drought]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://theconversation.com/yes-australia-is-a-land-of-flooding-rains-but-climate-change-could-be-making-it-worse-157586|last=Gergis|first=Joelle|title=Yes, Australia is a land of flooding rains. But climate change could be making it worse|date=23 March 2021|website=The Conversation|access-date=2 April 2021|archive-date=4 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210404091437/https://theconversation.com/yes-australia-is-a-land-of-flooding-rains-but-climate-change-could-be-making-it-worse-157586|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Biodiversity=== |
|||
{{See also|Fauna of Australia|Flora of Australia|Fungi of Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Koala climbing tree.jpg|thumb|upright=1.0|left|alt=A koala holding onto a eucalyptus tree with its head turned so both eyes are visible|The [[koala]] and the ''[[Eucalyptus]]'']] |
|||
Although most of Australia is semi-arid or desert, the continent includes a diverse range of habitats from [[alpine climate|alpine]] heaths to [[tropical rainforest]]s. Fungi typify that diversity—an estimated 250,000 species—of which only 5% have been described—occur in Australia.<ref>Pascoe, I. G.; (1991) History of systematic mycology in Australia ''History of Systematic Botany in Australasia'' Ed. by: P. Short Australian Systematic Botany Society Inc. pp. 259–264</ref> Because of the continent's great age, extremely variable weather patterns, and long-term geographic isolation, much of Australia's [[biota (ecology)|biota]] is unique. About 85% of flowering plants, 84% of mammals, more than 45% of [[List of birds of Australia|birds]], and 89% of in-shore, temperate-zone fish are [[endemism|endemic]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.deh.gov.au/biodiversity/about-biodiversity.html |title=About Biodiversity |access-date=18 September 2007|publisher=Department of the Environment and Heritage |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070205015628/http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/about-biodiversity.html |archive-date=5 February 2007}}</ref> Australia has at least 755 species of reptile, more than any other country in the world.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Lambertini|first=Marco|title=A Naturalist's Guide to the Tropics|year=2000|isbn=978-0-2264-6828-0|publisher=University of Chicago Press|url=http://www.press.uchicago.edu/Misc/Chicago/468283.html|format=excerpt|access-date=30 March 2010|archive-date=5 February 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170205010300/http://www.press.uchicago.edu/Misc/Chicago/468283.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Besides Antarctica, Australia is the only continent that developed without feline species. Feral cats may have been introduced in the 17th century by Dutch shipwrecks, and later in the 18th century by European settlers. They are now considered a major factor in the decline and extinction of many vulnerable and endangered native species.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2014-11-13/greg-hunt-feral-cat-native-animals-fact-check/5858282|title=Fact check: Are feral cats killing over 20 billion native animals a year?|date=20 November 2014|work=ABC News|access-date=22 January 2017|archive-date=8 January 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170108001903/http://www.abc.net.au/news/2014-11-13/greg-hunt-feral-cat-native-animals-fact-check/5858282|url-status=live}}</ref> Seafaring immigrants from Asia are believed to have brought the [[dingo]] to Australia sometime after the end of the last ice age{{Mdash}}perhaps 4000 years ago{{Mdash}}and Aboriginal people helped disperse them across the continent as pets, contributing to the demise of [[thylacines]] on the mainland.<ref name=jackson2015>{{cite book|last1=Jackson|first1=Stephen|last2=Groves|first2=Colin|title=Taxonomy of Australian Mammals|publisher=CSIRO Publishing, Clayton, Victoria, Australia|year=2015|pages=287–290|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RPznCQAAQBAJ&pg=PA288|isbn=978-1-4863-0013-6}}</ref> Australia is also one of 17 megadiverse countries.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Evans |first1=Megan C. |last2=Watson |first2=James E. M. |last3=Fuller |first3=Richard A. |last4=Venter |first4=Oscar |last5=Bennett |first5=Simon C. |last6=Marsack |first6=Peter R. |last7=Possingham |first7=Hugh P. |title=The Spatial Distribution of Threats to Species in Australia |journal=BioScience |date=April 2011 |volume=61 |issue=4 |page=282 |doi=10.1525/bio.2011.61.4.8 |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
[[Forests of Australia|Australian forests]] are mostly made up of evergreen species, particularly [[eucalyptus]] trees in the less arid regions; [[Acacia|wattles]] replace them as the dominant species in drier regions and deserts.<ref name=dfat>{{Cite web |url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/flora_and_fauna.html |title=About Australia: Flora and fauna |access-date=15 May 2010|date=May 2008|publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140211203954/http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/flora_and_fauna.html |archive-date=11 February 2014}}</ref> Among well-known [[fauna of Australia|Australian animals]] are the [[monotreme]]s (the [[platypus]] and [[echidna]]); a host of [[marsupial]]s, including the [[kangaroo]], [[koala]], and [[wombat]], and birds such as the [[emu]] and the [[kookaburra]].<ref name=dfat/> Australia is home to [[Animal attacks in Australia|many dangerous animals]] including some of the most venomous snakes in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |date=15 January 2015 |title=Snake bite – The Australian Venom Compendium Concept |url=http://www.avru.org/compendium/biogs/A000084b.htm |access-date=15 January 2022 |website= |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150115112947/http://www.avru.org/compendium/biogs/A000084b.htm |archive-date=15 January 2015 |url-status=dead}}</ref> The [[dingo]] was introduced by Austronesian people who traded with Indigenous Australians around 3000 [[Common Era|BCE]].<ref name="savolainen2004">{{Cite journal|last1=Savolainen|first1=P.|last2=Leitner|first2=T.|last3=Wilton|first3=A.N.|last4=Matisoo-Smith|first4=E. |
|||
|last5=Lundeberg|first5=J.|title=A detailed picture of the origin of the Australian dingo, obtained from the study of mitochondrial DNA|doi=10.1073/pnas.0401814101|journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|volume=101|issue=33|pages=12387–12390|year=2004|pmid=15299143|pmc=514485|bibcode=2004PNAS..10112387S|doi-access=free}}</ref> Many animal and plant species became extinct soon after first human settlement,<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://uninews.unimelb.edu.au/view.php?articleID=170 |title=Humans to blame for extinction of Australia's megafauna|publisher=University of Melbourne|date=8 June 2001 |access-date=30 March 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100402065113/http://uninews.unimelb.edu.au/view.php?articleID=170 |archive-date=2 April 2010 |url-status=dead}}</ref> including the [[Australian megafauna]]; others have disappeared since European settlement, among them the thylacine.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.naturalworlds.org/thylacine/index.htm |title=The Thylacine Museum – A Natural History of the Tasmanian Tiger |publisher=The Thylacine Museum |access-date=14 October 2013 |archive-date=15 March 2006 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060315214219/http://www.naturalworlds.org/thylacine/index.htm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.deh.gov.au/biodiversity/threatened/ts-day/index.html |title=National Threatened Species Day |publisher=Department of the Environment and Heritage, Australian Government|year=2006 |access-date=21 November 2006 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061209084616/http://www.deh.gov.au/biodiversity/threatened/ts-day/index.html |archive-date=9 December 2006 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Many of Australia's ecoregions, and the species within those regions, are threatened by human activities and [[Invasive species in Australia|introduced]] animal, [[chromista]]n, fungal and plant species.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/invasive/index.html |title=Invasive species|publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts|date=17 March 2010 |access-date=14 June 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100629001302/http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/invasive/index.html |archive-date=29 June 2010 |url-status=live}}</ref> All these factors have led to Australia's having the highest mammal extinction rate of any country in the world.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.australiangeographic.com.au/topics/wildlife/2012/10/australias-most-endangered-species|title=Australia's most endangered species|publisher=Australian Geographic|access-date=16 June 2014|date=2 October 2012|archive-date=7 July 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140707222631/http://www.australiangeographic.com.au/topics/wildlife/2012/10/australias-most-endangered-species|url-status=live}}</ref> The federal ''Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999'' is the legal framework for the protection of threatened species.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/epbc/about/index.html |title=About the EPBC Act|publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |access-date=14 June 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100531084042/http://www.environment.gov.au/epbc/about/index.html |archive-date=31 May 2010 |url-status=live}}</ref> Numerous [[Protected areas of Australia|protected areas]] have been created under the [[Biodiversity action plan|National Strategy for the Conservation of Australia's Biological Diversity]] to protect and preserve unique ecosystems;<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/publications/strategy/index.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110312021249/http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/publications/strategy/index.html |archive-date=12 March 2011 |title=National Strategy for the Conservation of Australia's Biological Diversity|publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts|date=21 January 2010 |access-date=14 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/publications/strategy/chap1.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110313222100/http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/publications/strategy/chap1.html |archive-date=13 March 2011 |title=Conservation of biological diversity across Australia |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts|date=19 January 2009 |access-date=14 June 2010}}</ref> 65 [[wetland]]s are [[List of Ramsar sites in Australia|listed]] under the [[Ramsar Convention]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.ramsar.org/document/the-list-of-wetlands-of-international-importance-the-ramsar-list|title=The List of Wetlands of International Importance|publisher=Ramsar Convention|pages=6–7|date=22 May 2010|access-date=14 June 2010|archive-date=15 October 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151015201559/http://www.ramsar.org/document/the-list-of-wetlands-of-international-importance-the-ramsar-list|url-status=live}}</ref> and 16 natural [[World Heritage Site]]s have been established.<ref name="WHC">{{Cite web|url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/statesparties/au|title=Australia|work=UNESCO World Heritage Centre |access-date=5 September 2009|archive-date=2 October 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091002202106/http://whc.unesco.org/en/statesparties/au|url-status=live}}</ref> Australia was ranked 21st out of 178 countries in the world on the 2018 [[Environmental Performance Index]].<ref>{{Citation |title=2018 EPI Results|url=https://epi.envirocenter.yale.edu/epi-topline|work=Environmental Performance Index|publisher=Yale Center for International Earth Science Information Network |access-date=24 September 2018 |archive-date=23 July 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190723205354/https://epi.envirocenter.yale.edu/epi-topline |url-status=dead}}</ref> There are more than 1,800 animals and plants on Australia's threatened species list, including more than 500 animals.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2019-06-24/australias-long-list-of-threatened-species/11234090|title='Haunting': What it's like watching the last of a species die|last=March|first=Stephanie|date=24 June 2019|work=ABC News|access-date=16 July 2019|archive-date=13 July 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190713234527/https://www.abc.net.au/news/2019-06-24/australias-long-list-of-threatened-species/11234090|url-status=live}}</ref> [[Paleontologists]] discovered a [[fossil]] site of a [[prehistoric]] [[rainforest]] in [[McGraths Flat]], in South Australia, that presents evidence that this now arid [[desert]] and dry [[shrubland]]/[[grassland]] was once home to an abundance of life.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Mind-Blowing New Fossil Site Found in The 'Dead' Heart of Australia |author=Michelle Starr |date=7 January 2022 |website=Science Alert |url=https://www.sciencealert.com/incredible-new-fossil-site-found-in-the-dead-heart-of-australia |access-date=7 January 2022 |archive-date=7 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220107221514/https://www.sciencealert.com/incredible-new-fossil-site-found-in-the-dead-heart-of-australia |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=See the spectacular fossils from a newly discovered prehistoric rainforest |date=7 January 2022 |author=Michael Greshko |website=National Geographic |url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/see-the-spectacular-fossils-from-a-newly-discovered-prehistoric-rainforest|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220107192025/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/see-the-spectacular-fossils-from-a-newly-discovered-prehistoric-rainforest|url-status=dead|archive-date=7 January 2022}}</ref> |
|||
==Government and politics== |
|||
{{Main|Australian Government|Politics of Australia|Monarchy of Australia}} |
|||
{{Multiple image |
|||
| caption_align = center |
|||
| total_width = 340 |
|||
| image1 = King Charles III (July 2023).jpg |
|||
| caption1 = [[Charles III]],<br />[[Monarchy of Australia|King of Australia]] |
|||
| image2 = Sam Mostyn 2024.jpg |
|||
| caption2 = [[Sam Mostyn]],<br />[[Governor-General of Australia|Governor-General]] |
|||
| image3 = Anthony Albanese portrait (cropped).jpg |
|||
| caption3 = [[Anthony Albanese]],<br />[[Prime Minister of Australia|Prime Minister]] |
|||
}} |
|||
Australia is a [[constitutional monarchy]], a [[parliamentary democracy]] and a [[federation]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=12 January 2024 |title=Australian system of government |url=https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/how-parliament-works/system-of-government/australian-system-of-government |access-date= |website=Parliamentary Education Office |language=en |archive-date=14 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240214204120/https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/how-parliament-works/system-of-government/australian-system-of-government |url-status=live }}</ref> The country has maintained its mostly unchanged [[Constitution of Australia|constitution]] alongside a stable [[Liberal democracy|liberal democratic]] political system since [[Federation of Australia|Federation]] in 1901. It is one of the world's oldest federations, in which power is divided between the federal and [[States and territories of Australia|state]] governments. The [[Politics of Australia|Australian system of government]] combines elements derived from the political systems of the United Kingdom (a [[Fusion of powers|fused executive]], constitutional monarchy and [[Party discipline|strong party discipline]]) and the United States ([[federalism]], a [[written constitution]] and [[bicameralism|strong bicameralism]] with an elected upper house), resulting in a distinct hybrid.<ref name="Thompson-1980">{{Cite journal |last=Thompson |first=Elaine |year=1980 |title=The 'Washminster' Mutation |journal=[[Australian Journal of Political Science|Politics]] |volume=15 |issue=2 |page=32 |doi=10.1080/00323268008401755}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=14 December 2023 |title=What is the Washminster system? |url=https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/your-questions-on-notice/questions/what-is-the-washminster-system |access-date= |website=Parliamentary Education Office |language=en |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215070719/https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/your-questions-on-notice/questions/what-is-the-washminster-system |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
[[Separation of powers in Australia|Federal government power is partially separated]] between three groups:<ref name="Parliamentary Education Office-2023_2">{{Cite web |title=Separation of powers: Parliament, Executive and Judiciary |url=https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/how-parliament-works/system-of-government/separation-of-powers-parliament-executive-and-judiciary/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231031132705/https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/how-parliament-works/system-of-government/separation-of-powers-parliament-executive-and-judiciary/ |archive-date=31 October 2023 |access-date=8 November 2023 |website=Parliamentary Education Office |publisher= |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
* Legislature: the bicameral [[Parliament of Australia|Parliament]], comprising the [[Monarchy of Australia|monarch]], the [[Australian Senate|Senate]], and the [[Australian House of Representatives|House of Representatives]] |
|||
* Executive: the [[Australian Government]], led by the prime minister (the leader of the party or coalition with a majority in the House of Representatives), their chosen [[Cabinet of Australia|Cabinet]] and other ministers; formally appointed by the governor-general<ref name="Factbook-Government">{{Cite CIA World Factbook |country=Australia |section=Government |access-date=16 August 2024}}</ref> |
|||
* Judiciary: the [[High Court of Australia|High Court]] and other [[Australian court hierarchy|federal courts]] |
|||
[[Charles III]] reigns as [[King of Australia]] and is represented in Australia by the [[Governor-General of Australia|governor-general]] at the federal level and by the [[Governors of the Australian states|governors]] at the state level, who by [[Chapter II of the Constitution of Australia#Section 63: Provisions referring to Governor-General|section 63]] of the Constitution and convention act on the advice of their ministers.<ref name="Davison pp287–8">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|pages=287–88}}</ref><ref name="gg">{{Cite web |url=http://www.gg.gov.au/governorgeneral/category.php?id=2 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080804130529/http://www.gg.gov.au/governorgeneral/category.php?id=2 |archive-date=4 August 2008 |title=Governor-General's Role|publisher=Governor-General of Australia |access-date=23 April 2010}}</ref> Thus, in practice the governor-general acts as a legal figurehead for the actions of the [[Prime Minister of Australia|prime minister]] and the Cabinet. The governor-general may in some situations exercise [[reserve power]]s: powers exercisable in the absence or contrary to ministerial advice. When these powers may be exercised is governed by convention and their precise scope is unclear. The most notable exercise of these powers was the dismissal of the [[Whitlam government]] in the [[1975 Australian constitutional crisis|constitutional crisis of 1975]].<ref>{{Cite web|publisher=Parliament of Australia|date=23 January 1998 |access-date=18 June 2010|url=http://www.aph.gov.au/library/pubs/rn/1997-98/98rn25.htm |title=The Reserve Powers of the Governor-General|author=Downing, Susan |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100726170040/http://www.aph.gov.au/library/pubs/rn/1997-98/98rn25.htm |archive-date=26 July 2010 |url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Canberra (AU), Parliament House -- 2019 -- 1746.jpg|alt=A large white and cream coloured building with grass on its roof. The building is topped with a large flagpole.|left|thumb|[[Parliament House, Canberra|Parliament House]], [[Canberra]]]] |
|||
In the Senate (the upper house), there are 76 senators: twelve each from the states and two each from the mainland territories (the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory).<ref name=sen>{{Cite web |url=http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/guide/senatecomposition.htm |title=Senate Summary|publisher=Australian Broadcasting Corporation |access-date=23 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100506235552/http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/guide/senatecomposition.htm |archive-date=6 May 2010 |url-status=live}}</ref> The House of Representatives (the lower house) has 151 members elected from single-member [[Divisions of the Australian House of Representatives|electoral divisions]], commonly known as "electorates" or "seats", allocated to states on the basis of population, with each of the current states guaranteed a minimum of five seats.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Muller |first=Damon |date=26 April 2023 |title=The process for, and consequences of, changing the size of the Commonwealth Parliament: a quick guide |url=https://www.aph.gov.au/About_Parliament/Parliamentary_departments/Parliamentary_Library/pubs/rp/rp2223/Quick_Guides/ChangingSizeCommonwealthParliament |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230511175801/https://www.aph.gov.au/About_Parliament/Parliamentary_departments/Parliamentary_Library/pubs/rp/rp2223/Quick_Guides/ChangingSizeCommonwealthParliament |archive-date=11 May 2023 |access-date= |website=Parliament of Australia |language=en-AU}}</ref> The lower house has a maximum term of three years, but this is not fixed and governments usually dissolve the house early for an election at some point in the 6 months before the maximum.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Joint Standing Committee on Electoral Matters |url=https://www.aph.gov.au/Parliamentary_Business/Committees/Joint/Completed_Inquiries/em/elect04/report |title=The 2004 Federal Election |date=10 October 2005 |publisher=Parliament of Australia |isbn=978-0-642-78705-7 |at=paras. 7.26–7.27 |language=en-AU |chapter=Parliamentary terms |chapter-url=https://www.aph.gov.au/Parliamentary_Business/Committees/Joint/Completed_Inquiries/em/elect04/chapter7 |access-date=25 January 2024 |archive-date=25 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240125005940/https://www.aph.gov.au/Parliamentary_Business/Committees/Joint/Completed_Inquiries/em/elect04/report |url-status=live }}</ref> Elections for both chambers are generally held simultaneously with senators having overlapping six-year terms except for those from the territories, whose terms are not fixed but are tied to the electoral cycle for the lower house. Thus only 40 of the 76 places in the Senate are put to each election unless the cycle is interrupted by a [[double dissolution]].<ref name="sen" /> |
|||
Australia's [[electoral system of Australia|electoral system]] uses [[Instant-runoff voting|preferential voting]] for the House of Representatives and all state and territory lower house elections (with the exception of Tasmania and the ACT which use the [[Hare-Clark system]]). The Senate and most state upper houses use the [[single transferable vote|proportional system]] which combines preferential voting with [[proportional representation]] for each state. [[Compulsory voting|Voting and enrolment is compulsory]] for all enrolled citizens 18 years and older in every jurisdiction.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.aec.gov.au/pdf/voting/compulsory_voting.pdf |title=Compulsory Voting in Australia|last=Evans|first=Tim|year=2006|publisher=Australian Electoral Commission|page=4 |access-date=21 June 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090611200653/http://www.aec.gov.au/pdf/voting/compulsory_voting.pdf |archive-date=11 June 2009 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://aec.gov.au/FAQs/Enrolment.htm#compulsory |title=Is it compulsory to enrol, regardless of age or disability?|work=Enrolment – Frequently Asked Questions|publisher=Australian Electoral Commission |access-date=11 September 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210524015925/https://aec.gov.au/FAQs/Enrolment.htm |archive-date=24 May 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |first=Judith |last=Brett |title=From Secret Ballot to Democracy Sausage: How Australia Got Compulsory Voting |publisher=Text Publishing Co |year=2019 |isbn=978-1-9256-0384-2}}</ref> The party with majority support in the House of Representatives forms the government and its leader becomes Prime Minister. In cases where no party has majority support, the governor-general has the constitutional power to appoint the prime minister and, if necessary, dismiss one that has lost the confidence of Parliament.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.gg.gov.au/content.php/page/id/3/title/governor-generals-role |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121014171300/http://www.gg.gov.au/content.php/page/id/3/title/governor-generals-role |archive-date=14 October 2012 |title=Governor-General's Role|publisher=Governor-General of the Commonwealth of Australia |access-date=13 January 2012}}</ref> Due to the relatively unique position of Australia operating as a [[Westminster system|Westminster]] parliamentary democracy with a powerful and elected upper house, the system has sometimes been referred to as having a "Washminster mutation",<ref name="Thompson-1980" /> or as a semi-parliamentary system.<ref name=Ganghof>{{Cite journal |last1=Ganghof |first1=S |title=A new political system model: Semi-parliamentary government |journal=European Journal of Political Research |date=May 2018 |volume=57 |issue=2 |pages=261–281 |doi=10.1111/1475-6765.12224 |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
There are two major political groups that usually form government federally: the [[Australian Labor Party]] <!-- NOTE TO EDITORS: The name of the party is spelt "Labor" (i.e., no "u") even though the usual Australian spelling is "labour". --> and the [[Coalition (Australia)|Coalition]], which is a formal grouping of the [[Liberal Party of Australia|Liberal Party]] and its minor partner, the [[National Party of Australia|National Party]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/guide/glossary.htm#coalition |title=Glossary of Election Terms |publisher=Australian Broadcasting Corporation |access-date=23 April 2010 |archive-date=6 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210306034515/http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/guide/glossary.htm#coalition |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/results/sop.htm |title=State of the Parties|publisher=Australian Broadcasting Corporation |access-date=23 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100418163914/http://www.abc.net.au/elections/federal/2007/results/sop.htm |archive-date= 18 April 2010 |url-status=live}}</ref> At the state level of government, the relationship between the Nationals and the Liberal Party differs, with the parties [[Liberal National Party of Queensland|merged in Queensland]] and the [[Country Liberal Party|Northern Territory]] (federal parliamentarians sit in either the Liberal or National partyroom however); in coalition in New South Wales, Victoria and Western Australia; and in competition with the Liberals in South Australia and Tasmania.<ref>{{Cite web |date=30 July 2008 |title=The Liberal-National Party – a new model party? |url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2008-07-30/the-liberal-national-party---a-new-model-party/457812 |access-date=8 September 2021 |website=ABC News |language=en-AU |archive-date=7 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221007033647/https://www.abc.net.au/news/2008-07-30/the-liberal-national-party---a-new-model-party/457812 |url-status=live }}</ref> Within Australian political culture, the Coalition is considered [[centre-right]] and the Labor Party is considered [[centre-left]].<ref>{{Cite book|last1=Fenna|first1=Alan|last2=Robbins|first2=Jane|last3=Summers|first3=John |title=Government Politics in Australia|publisher=Pearson Higher Education AU|location=London|year=2013|isbn=978-1-4860-0138-5|page=139}}</ref> Independent members and several minor parties have achieved representation in Australian parliaments, mostly in upper houses. The [[Australian Greens]] are the third largest party by both vote and membership and the fourth largest by parliamentary representation.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.smh.com.au/politics/federal/old-greens-wounds-reopen-as-members-vote-on-directly-electing-leader-20200422-p54m5r.html|title=Old Greens wounds reopen as members vote on directly electing leader|last=Harris|first=Rob|date=22 April 2020|newspaper=The Sydney Morning Herald|access-date=24 April 2020|archive-date=22 April 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200422080256/https://www.smh.com.au/politics/federal/old-greens-wounds-reopen-as-members-vote-on-directly-electing-leader-20200422-p54m5r.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Jackson |first1=Stewart |title=The Australian Greens : from activism to Australia's third party |date=2016 |publisher=Melbourne University Press |isbn=978-0-5228-6794-7}}</ref> The [[2022 Australian federal election|most recent federal election]] was held on 21 May 2022 and resulted in the Australian Labor Party, led by [[Anthony Albanese]], being elected to [[Government of Australia|government]].<ref>{{Cite news |date=22 May 2022 |title=Anthony Albanese sworn in as Prime Minister |language=en-AU |work=ABC News |url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2022-05-23/anthony-albanese-to-be-sworn-in-prime-minister/101089902 |access-date=22 May 2022 |archive-date=22 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220522182422/https://www.abc.net.au/news/2022-05-23/anthony-albanese-to-be-sworn-in-prime-minister/101089902 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
===States and territories=== |
|||
{{Main|States and territories of Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Australia states and territories labelled.svg|thumb|upright=1.5|right|Australia's states and territories]] |
|||
Australia has six states—[[New South Wales]] (NSW), [[Victoria (state)|Victoria]] (Vic), [[Queensland]] (Qld), [[Western Australia]] (WA), [[South Australia]] (SA) and [[Tasmania]] (Tas)—and two mainland self-governing territories—the [[Australian Capital Territory]] (ACT) and the [[Northern Territory]] (NT).<ref>{{Cite web |date=14 December 2023 |title=What's the difference between a territory and a state parliament? |url=https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/your-questions-on-notice |access-date= |website=Parliamentary Education Office |language=en |archive-date=18 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240318145108/https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/your-questions-on-notice |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The states have the general power to make laws except in the few areas where the constitution grants the Commonwealth exclusive powers.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Pyke |first=John |title=Government powers under a Federal Constitution: constitutional law in Australia |date=2020 |publisher=Lawbook Co |isbn=978-0-455-24415-0 |edition=2nd |location=Pyrmont, NSW |pages=405–6}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=19 July 2022 |title=Three levels of government: governing Australia |url=https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/how-parliament-works/three-levels-of-government/three-levels-of-government-governing-australia |access-date=25 January 2024 |website=Parliamentary Education Office |language=en |archive-date=4 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240104073724/https://peo.gov.au/understand-our-parliament/how-parliament-works/three-levels-of-government/three-levels-of-government-governing-australia |url-status=live }}</ref> The Commonwealth can only make laws on topics listed in the constitution but its laws prevail over those of the states to the extent of any inconsistency.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Pyke |first=John |title=Government powers under a Federal Constitution: constitutional law in Australia |date=2020 |publisher=Lawbook Co |isbn=978-0-455-24415-0 |edition=2nd |location=Pyrmont, NSW |pages=528–30, 577–80}}</ref><ref>{{Cite Legislation AU|Cth|act|coaca430|Australian Constitution|109}}. "When a law of a State is inconsistent with a law of the Commonwealth, the latter shall prevail, and the former shall, to the extent of the inconsistency, be invalid."</ref> Since Federation, the Commonwealth's power relative to the states [[Australian constitutional law#Growth of federal power|has significantly increased]] due to the increasingly wide interpretation given to listed Commonwealth powers{{snd}}and because of the states' [[Fiscal imbalance in Australia|heavy financial reliance]] on Commonwealth grants.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Pyke |first=John |title=Government powers under a Federal Constitution: constitutional law in Australia |date=2020 |publisher=Lawbook Co |isbn=978-0-455-24415-0 |edition=2nd |location=Pyrmont, NSW |pages=607–9}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Beck |first=Luke |title=Australian constitutional law: concepts and cases |date=2020 |publisher=Cambridge university press |isbn=978-1-108-70103-7 |location=Port Melbourne, VIC |pages=521–8}}</ref> |
|||
Each state and major mainland territory has its own [[Parliaments of the Australian states and territories|parliament]]—[[unicameralism|unicameral]] in the Northern Territory, the ACT and Queensland, and bicameral in the other states. The lower houses are known as the [[Legislative Assembly]] (the [[House of Assembly]] in South Australia and Tasmania); the upper houses are known as the [[Legislative council|Legislative Council]]. The [[head of government|head of the government]] in each state is the [[Premiers of the Australian states|Premier]] and in each territory the [[Chief Minister]]. The King is represented in each state by a [[Governors of the Australian states|governor]]. At the Commonwealth level, the King's representative is the governor-general.<ref name="gg"/> |
|||
The Commonwealth government directly administers the internal [[Jervis Bay Territory]] and the external territories: the [[Ashmore and Cartier Islands]], the [[Coral Sea Islands]], the [[Heard Island and McDonald Islands]], the [[Australian Indian Ocean Territories|Indian Ocean territories]] (Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands), [[Norfolk Island]],{{Refn|Norfolk Island previously was self-governed, however this was revoked in 2015.<ref>{{Cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080806021653/http://ag.gov.au/www/agd/agd.nsf/Page/Territories_of_AustraliaNorfolk_IslandAdministrator_of_Norfolk_Island|url=http://ag.gov.au/www/agd/agd.nsf/Page/Territories_of_AustraliaNorfolk_Island|publisher=Australian Government Attorney-General's Department |title=Administrator of Norfolk Island |archive-date=6 August 2008}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/australia-news/2015/may/12/norfolk-island-loses-its-parliament-as-canberra-takes-control|title=Norfolk Island loses its parliament as Canberra takes control|first1=Monica|last1=Tan|author2=Australian Associated Press|date=12 May 2015|newspaper=The Guardian|access-date=21 October 2015|archive-date=28 October 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151028072820/http://www.theguardian.com/australia-news/2015/may/12/norfolk-island-loses-its-parliament-as-canberra-takes-control|url-status=live}}</ref>}} and the [[Australian Antarctic Territory]].{{Refn|This [[Territorial claims in Antarctica|Antarctic claim]] is recognised by only by New Zealand, the United Kingdom, France, and Norway.}}<ref>{{Cite web |title=Australian Territories |url=https://www.infrastructure.gov.au/territories-regions-cities/australian-territories |access-date=16 February 2024 |website=Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development, Communications and the Arts |archive-date=8 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240308213252/https://www.infrastructure.gov.au/territories-regions-cities/australian-territories |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Factbook-Government"/> The remote [[Macquarie Island]] and [[Lord Howe Island]] are part of Tasmania and New South Wales respectively.<ref>{{Cite news|title=Macquarie Island research station to be closed in 2017|url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2016-09-13/macquarie-island-research-station-to-be-closed-in-2017/7839640|work=ABC News|date=13 September 2016|access-date=19 October 2019|archive-date=25 October 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191025034637/https://www.abc.net.au/news/2016-09-13/macquarie-island-research-station-to-be-closed-in-2017/7839640|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Southerden |first=Louise |date=8 November 2017 |title=Which island should you visit - Lord Howe or Norfolk? A guide to both |url=https://www.smh.com.au/traveller/inspiration/a-tale-of-two-islands-lord-howe-v-norfolk-20171107-gzg8tz.html |access-date= |website=The Sydney Morning Herald |language=en |archive-date=16 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240216030715/https://www.smh.com.au/traveller/inspiration/a-tale-of-two-islands-lord-howe-v-norfolk-20171107-gzg8tz.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
===Foreign relations=== |
|||
{{Main|Foreign relations of Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Diplomatic missions of Australia.png|thumb|left|upright=1.3|[[List of diplomatic missions of Australia|Diplomatic missions of Australia]]]] |
|||
Australia is a [[middle power]],<ref name="Lowy">{{Cite report |url=https://power.lowyinstitute.org/downloads/lowy-institute-2023-asia-power-index-key-findings-report.pdf |title=Lowy Institute Asian Power Index |date=2023 |page=29 |isbn=978-0-6480189-3-3 |access-date=4 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240220212559/https://power.lowyinstitute.org/downloads/lowy-institute-2023-asia-power-index-key-findings-report.pdf |archive-date=20 February 2024 |url-status=live}}</ref> whose foreign relations has three core bi-partisan pillars: commitment to the US alliance, engagement with the [[Indo-Pacific]] and support for international institutions, rules and co-operation.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Gyngell |first=Allan |date=31 July 2022 |title=A new Australian foreign policy agenda under Albanese |url=https://eastasiaforum.org/2022/07/31/a-new-australian-foreign-policy-agenda-under-albanese/ |access-date= |website=East Asia Forum |language=en-AU |archive-date=17 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240217023926/https://eastasiaforum.org/2022/07/31/a-new-australian-foreign-policy-agenda-under-albanese/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Australian-Government-2017">{{Cite report |url=https://www.dfat.gov.au/sites/default/files/2017-foreign-policy-white-paper.pdf |title=2017 Foreign Policy White Paper |date=2017 |publisher=Australian Government |pages=1–8 |access-date=17 February 2024 |archive-date=19 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240119034716/https://www.dfat.gov.au/sites/default/files/2017-foreign-policy-white-paper.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Firth |first=Stewart |title=Australia in international politics: an introduction to Australian foreign policy |date=2011 |publisher=Allen & Unwin |isbn=978-1-74237-263-1 |edition=3rd |location=Crows Nest, NSW |pages=332–8 |language=en-AU}}</ref> Through the [[ANZUS]] pact and its status as a [[major non-NATO ally]], Australia maintains a [[Australia–United States relations|close relationship with the US]], which encompasses strong defence, security and trade ties.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Australia and the United States |url=https://usa.embassy.gov.au/australia-and-united-states |access-date=17 February 2024 |website=Australian Embassy and Consulates |archive-date=17 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240217023926/https://usa.embassy.gov.au/australia-and-united-states |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Bureau of Political-Military Affairs |date=20 January 2021 |title=Major Non-NATO Ally Status |url=https://www.state.gov/major-non-nato-ally-status/ |access-date=25 January 2024 |website=[[United States Department of State]] |language=en-US |archive-date=27 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220227062358/https://www.state.gov/major-non-nato-ally-status/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In the Indo-Pacific, the country seeks to increase its trade ties through the open flow of trade and capital, while managing the rise of Chinese power by supporting the existing rules based order.<ref name="Australian-Government-2017" /> Regionally, the country is a member of the [[Pacific Islands Forum]], the [[Pacific Community]], the [[Association of Southeast Asian Nations#ASEAN Plus Three and ASEAN Plus Six|ASEAN+6 mechanism]] and the [[East Asia Summit]]. Internationally, the country is a member of the [[United Nations]] (of which it was a founding member), the [[Commonwealth of Nations]], the [[OECD]] and the [[G20]]. This reflects the country's generally strong commitment to [[multilateralism]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Page |first=Mercedes |date=31 May 2022 |title=Multilateralism matters again |url=https://www.lowyinstitute.org/the-interpreter/multilateralism-matters-again |access-date= |website=The Interpreter |publisher=Lowy Institute |language=en |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215011829/https://www.lowyinstitute.org/the-interpreter/multilateralism-matters-again |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Watson |first=Mark R |date=30 October 2023 |title=Australia and the Quad: A Watering Can or a Hammer? |url=https://www.nbr.org/publication/australia-and-the-quad-a-watering-can-or-a-hammer/ |access-date=15 February 2024 |website=The National Bureau of Asian Research |language=en |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215011829/https://www.nbr.org/publication/australia-and-the-quad-a-watering-can-or-a-hammer/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Australia is a member of several defence, intelligence and security groupings including the [[Five Eyes]] intelligence alliance with the United States, United Kingdom, Canada and New Zealand; the ANZUS alliance with the United States and New Zealand; the [[AUKUS]] security treaty with the United States and United Kingdom; the [[Quadrilateral Security Dialogue]] with the United States, India and Japan; the [[Five Power Defence Arrangements]] with New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Malaysia and Singapore; and the [[Reciprocal Access Agreement|Reciprocal Access]] defence and security agreement with Japan.[[File:P20220524AS-1533 (52245766080).jpg|thumb|Australian Prime Minister [[Anthony Albanese]] with American President [[Joe Biden]] in 2022]] |
|||
Australia has pursued the cause of international [[trade liberalisation]].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Capling|first=Ann |title=Australia and the Global Trade System: From Havana to Seattle|publisher=Cambridge University Press|year=2013|isbn=978-0-5217-8525-9|page=116}}</ref> It led the formation of the [[Cairns Group]] and [[Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation]],<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Gallagher, P. W.|title=Setting the agenda for trade negotiations: Australia and the Cairns group|journal=Australian Journal of International Affairs|volume=42|issue=1 April 1988|pages=3–8|doi=10.1080/10357718808444955|year=1988}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.apec2007.org/aa.htm|title=APEC and Australia|publisher=APEC 2007|date=1 June 2007|access-date=23 April 2010|archive-date=21 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210421170701/http://www.apec2007.org/aa.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> and is a member of the [[OECD|Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development]] (OECD) and the [[World Trade Organization]] (WTO).<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.oecd.org/about/0,3347,en_33873108_33873229_1_1_1_1_1,00.html |title=Australia:About|publisher=Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |access-date=23 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100420083545/http://www.oecd.org/about/0%2C3347%2Cen_33873108_33873229_1_1_1_1_1%2C00.html |archive-date=20 April 2010 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/countries_e/australia_e.htm |title=Australia – Member information|publisher=World Trade Organization |access-date=23 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100525011833/http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/countries_e/australia_e.htm |archive-date=25 May 2010 |url-status=live}}</ref> Beginning in the 2000s, Australia entered into the [[Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership]] and the [[Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership]] multilateral [[free trade agreement]]s as well as bilateral free trade agreements with the [[Australia–United States Free Trade Agreement|United States]], [[China–Australia Free Trade Agreement|China]], [[Japan–Australia Economic Partnership Agreement|Japan]], [[Australia–Korea Free Trade Agreement|South Korea]], [[Indonesia–Australia Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement|Indonesia]], the [[Australia–United Kingdom Free Trade Agreement|United Kingdom]] and [[Closer Economic Relations|New Zealand]], with the most recent deal signed in 2023 with the UK.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Australia's free trade agreements (FTAs) |url=https://www.dfat.gov.au/trade/agreements/trade-agreements |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240119034906/https://www.dfat.gov.au/trade/agreements/trade-agreements |archive-date=19 January 2024 |access-date=25 January 2024 |website=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade}}</ref> |
|||
Australia maintains a deeply integrated relationship with neighbouring New Zealand, with free mobility of citizens between the two countries under the [[Trans-Tasman Travel Arrangement]] and free trade under the [[Closer Economic Relations]] agreement.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Trans-Tasman Roadmap to 2035 |url=https://www.dfat.gov.au/geo/new-zealand/trans-tasman-roadmap-2035 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230726060824/https://www.dfat.gov.au/geo/new-zealand/trans-tasman-roadmap-2035 |archive-date=26 July 2023 |access-date=7 February 2024 |website=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade}}</ref> The most favourably viewed countries by the Australian people in 2021 include New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Japan, Germany, Taiwan, Thailand, the United States and South Korea.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://poll.lowyinstitute.org/files/lowyinsitutepoll-2021.pdf|title=2021 Lowy Institute Poll|last=Kassam|first=Natasha|date=2021|publisher=Lowy Institute|access-date=16 January 2022|archive-date=19 March 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220319051732/https://poll.lowyinstitute.org/files/lowyinsitutepoll-2021.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> It also maintains an [[International aid|international aid program]] under which some 75 countries receive assistance.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Australian Aid |url=https://www.dfat.gov.au/about-us/publications/Pages/australian-aid |website=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade |access-date=15 February 2024 |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215012143/https://www.dfat.gov.au/about-us/publications/Pages/australian-aid |url-status=live }}</ref> Australia ranked fourth in the [[Center for Global Development]]'s 2021 [[Commitment to Development Index]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cgdev.org/publication/commitment-development-index-2021|title=The Commitment to Development Index 2021|last1=Mitchell|first1=Ian|last2=Robinson|first2=Lee|last3=Cichocka|first3=Beata|last4=Ritchie|first4=Euan|date=13 September 2021|access-date=17 August 2022|publisher=[[Center for Global Development]]|location=[[Washington, D.C.]]|archive-date=5 October 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221005091011/https://www.cgdev.org/publication/commitment-development-index-2021|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
The power over foreign policy is highly concentrated in the prime minister and the [[National Security Committee (Australia)|national security committee]], with major decision such as joining the [[2003 invasion of Iraq]] made with without prior Cabinet approval.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Lee |first=David |date=31 December 2023 |title=Cabinet papers 2003: Howard government sends Australia into the Iraq war |url=http://theconversation.com/cabinet-papers-2003-howard-government-sends-australia-into-the-iraq-war-217812 |access-date=17 February 2024 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US |archive-date=17 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240217023925/http://theconversation.com/cabinet-papers-2003-howard-government-sends-australia-into-the-iraq-war-217812 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Firth |first=Stewart |title=Australia in international politics: an introduction to Australian foreign policy |date=2011 |publisher=Allen & Unwin |isbn=978-1-74237-263-1 |edition=3rd |location=Crows Nest, NSW |pages=78–84 |language=en-AU}}</ref> Similarly, the Parliament does not play a formal role in foreign policy and the power to declare war lies solely with the executive government.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Appleby |first=Gabrielle |date=2 September 2014 |title=Explainer: Australia's war powers and the role of parliament |url=http://theconversation.com/explainer-australias-war-powers-and-the-role-of-parliament-31112 |access-date=17 February 2024 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US |archive-date=6 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230906181159/https://theconversation.com/explainer-australias-war-powers-and-the-role-of-parliament-31112 |url-status=live }}</ref> The [[Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade]] supports the executive in its policy decisions.<ref>{{Cite web |date=June 2013 |title=Capability review: Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade |url=https://www.apsc.gov.au/capability-review-department-foreign-affairs-and-trade |access-date=20 December 2024 |website=Australian Public Service Commission |publisher= |page=2}}</ref> |
|||
===Military=== |
|||
{{Main|Australian Defence Force}} |
|||
[[File:HMAS Arunta and Canberra sailing in formation with other warships.jpg|thumb|upright=1.0|right|[[HMAS Canberra (L02)|HMAS ''Canberra'']], a [[Canberra-class landing helicopter dock|''Canberra''-class]] [[landing helicopter dock]], and [[HMAS Arunta (FFH 151)|HMAS ''Arunta'']], an [[Anzac-class frigate|''Anzac''-class]] [[frigate]], sailing in formation]] |
|||
The two main institutions involved in the management of Australia's armed forces are the [[Australian Defence Force]] (ADF) and the [[Department of Defence (Australia)|Department of Defence]], together known as "[[Australian Defence Organisation|Defence]]".<ref>{{Cite web |title=Organisation structure |url=https://www.defence.gov.au/about/who-we-are/organisation-structure |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231103154937/https://www.defence.gov.au/about/who-we-are/organisation-structure |archive-date=3 November 2023 |access-date=16 February 2024 |website=Australian Government: Defence}}</ref> The Australian Defence Force is the military wing, headed by the [[Chief of the Defence Force (Australia)|chief of the defence force]], and contains three branches: the [[Royal Australian Navy]], the [[Australian Army]] and the [[Royal Australian Air Force]]. In 2021, it had 84,865 currently serving personnel (including 60,286 regulars and 24,581 reservists).<ref>{{Cite web |date=29 June 2022 |title=Australian Defence Force service |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/articles/australian-defence-force-service |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231119193626/https://www.abs.gov.au/articles/australian-defence-force-service |archive-date=19 November 2023 |website=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]]}}</ref> The Department of Defence is the civilian wing and is headed by the secretary of defence. These two leaders collective manage Defence as a [[diarchy]], with shared and joint responsibilities.<ref>{{Cite report |url=https://www.defence.gov.au/sites/default/files/2023-10/Defence-Annual-Report-2022-23.pdf |title=Defence Annual Report 2022–23 |date=18 September 2023 |publisher=Australian Government: Defence |page=23 |isbn=978-1-925890-47-1 |issn=1323-5036 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231217203427/https://www.defence.gov.au/sites/default/files/2023-10/Defence-Annual-Report-2022-23.pdf |archive-date=17 December 2023 |url-status=live}}</ref> The titular role of [[Commander-in-Chief|commander-in-chief]] is held by the [[Governor-General of Australia|governor-general]]; however, actual command is vested in the chief of the Defence Force.<ref>{{Cite Legislation AU|Cth|act|da190356|Defence Act 1903|9}}</ref> The executive branch of the Commonwealth government has overall control of the military through the [[Minister for Defence (Australia)|minister of defence]], who is subject to the decisions of Cabinet and its [[National Security Committee (Australia)|National Security Committee]].<ref>{{Cite report |url=https://ad-aspi.s3.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/import/12_53_35_PM_ASPI_defence_almanac_2011_12.pdf?VersionId=vNzXEQtA5bqdxWO9r60xyDAD45g2_d1H |title=Australian Defence Almanac: 2011–2012 |last=Khosa |first=Raspal |date=July 2011 |publisher=Australian Strategic Policy Institute |pages=2, 12 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231002182101/https://ad-aspi.s3.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/import/12_53_35_PM_ASPI_defence_almanac_2011_12.pdf?VersionId=vNzXEQtA5bqdxWO9r60xyDAD45g2_d1H |archive-date=2 October 2023 |url-status=live}}</ref> Major [[Australian intelligence agencies]] include the [[Australian Secret Intelligence Service]] (foreign intelligence), the [[Australian Signals Directorate]] (signals intelligence) and the [[Australian Security Intelligence Organisation]] (domestic security). |
|||
In 2022, defence spending was 1.9% of [[GDP]], representing the world's [[List of countries by military expenditures|13th-largest defence budget]].<ref>{{cite web |date=April 2023 |title=Trends in World Military Expenditure, 2022 |url=https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/2023-04/2304_fs_milex_2022.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230423231601/https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/2023-04/2304_fs_milex_2022.pdf |archive-date=23 April 2023 |access-date=29 April 2023 |publisher=[[Stockholm International Peace Research Institute]] |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2024, the ADF had active operations in the Middle East and the Indo-Pacific (including security and aid provisions); was contributing to UN forces in relation to [[United Nations Mission in South Sudan|South Sudan]], [[United Nations Disengagement Observer Force|Syria–Israel peacekeeping]], and [[Operation Argos|North Korea]]; and domestically was [[Operation Resolute|assisting to prevent asylum-seekers enter the country]] and assisting in [[natural disaster]] relief.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Operations |url=https://www.defence.gov.au/defence-activities/operations |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240130011529/https://www.defence.gov.au/defence-activities/operations |archive-date=30 January 2024 |access-date=25 February 2024 |website=[[Australian Defence Organisation|Defence]] |publisher=[[Australian Government]]}}</ref> |
|||
===Human rights=== |
|||
{{See also|Human rights in Australia}} |
|||
Australia has generally strong protections for [[civil and political rights]], and the country has signed up to a wide range of international rights treaties.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Australia: Events of 2023 |url=https://www.hrw.org/world-report/2024/country-chapters/australia |access-date=30 August 2024 |website=World Report 2024 |publisher=[[Human Rights Watch]]}}</ref> Important documents protecting human rights include the [[Australian Constitution|Constitution]], the ''[[Racial Discrimination Act 1975]]'', the ''[[Sex Discrimination Act 1984]]'', the ''[[Disability Discrimination Act 1992]]'', and the ''[[Age Discrimination Act 2004]]''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Legal - Legislation |url=https://humanrights.gov.au/our-work/legal/legislation |access-date=3 September 2023 |website=Australian Human Rights Commission}}</ref> [[Same-sex marriage in Australia|Same-sex marriage]] has been legal in the nation since 2017.<ref>{{cite news |date=26 June 2013 |title=The 20 most and least gay-friendly countries in the world |url=https://www.pri.org/stories/2013-06-26/20-most-and-least-gay-friendly-countries-world |access-date=31 December 2017 |work=Public Radio International}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Same-Sex Marriage Around the World |url=https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/fact-sheet/gay-marriage-around-the-world/ |access-date=3 September 2023 |website=Pew Research Center}}</ref> Unlike other comparable Western democracies, Australia does not have a single federal [[charter of rights]] in the Constitution or under legislation; however, the ACT, Victoria, and Queensland have state-based ones. |
|||
International organisations such as [[Human Rights Watch]] and [[Amnesty International]] have expressed concerns in areas including [[Immigration detention in Australia|asylum-seeker policy]], [[Indigenous deaths in custody]], the lack of entrenched [[Charter of rights|rights protection]], and [[Laws governing public demonstrations in Australia|laws restricting protesting]].<ref>{{Cite web |last= |first= |date=28 March 2023 |title=Amnesty International Report 2022/23: The state of the world's human rights |url=https://www.amnesty.org.au/amnesty-international-report-2022-23-the-state-of-the-worlds-human-rights/ |access-date=25 January 2024 |website=[[Amnesty International Australia]] |language=en-AU}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=11 January 2024 |title=Australia: Setbacks, Inaction on Key Rights Issues |url=https://www.hrw.org/news/2024/01/11/australia-setbacks-inaction-key-rights-issues |access-date=25 January 2024 |website=[[Human Rights Watch]] |language=en-AU}}</ref> |
|||
==Economy== |
==Economy== |
||
{{Main|Economy of Australia}} |
{{Main|Economy of Australia}} |
||
{{ |
{{Further|Economic history of Australia|Tourism in Australia}} |
||
[[File:Sydney central business district skyline, August 2021.jpg|thumb|The [[Sydney central business district|central business district of Sydney]] is the [[financial centre]] of Australia.]] |
|||
[[File:Kalgoorlie The Big Pit DSC04498.JPG|thumb|alt=A deep opencut mine in which some roads can be seen, the dirt is a rusty colour|[[Super Pit gold mine|The Super Pit]] gold mine in [[Kalgoorlie]], Australia's largest [[Open-pit mining|open cut]] mine.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2010/04/20/2877497.htm |title=Government to help Kalgoorlie quake victims |accessdate=2 June 2010 |date=20 April 2010 |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]}}</ref>]] |
|||
Australia's [[World Bank high-income economy|high-income]] [[mixed economy|mixed-market economy]] is rich in [[Mining in Australia|natural resources]].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Russell|first=Clyde|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/uk-column-russell-commodities-australia-idUKKBN2BM0WC |title=Column: Resource-rich Australia shows vagaries of any commodity supercycle|date=30 March 2021|work=[[Reuters]] |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref> It is the world's [[List of countries by GDP (nominal)|fourteenth-largest]] by nominal terms, and the [[List of countries by GDP (PPP)|18th-largest]] by [[purchasing power parity|PPP]]. {{As of|2021}}, it has the [[List of countries by wealth per adult|second-highest amount]] of wealth per adult, after [[Luxembourg]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Wealth Databook 2021|url=https://www.credit-suisse.com/media/assets/corporate/docs/about-us/research/publications/global-wealth-databook-2021.pdf |access-date=14 August 2022|publisher=[[Credit Suisse]]}}</ref> and has the [[List of countries by financial assets per capita|thirteenth-highest]] financial assets per capita.<ref>{{Cite web|last1=Carrera|first1=Jordi Bosco|last2=Grimm|first2=Michaela|last3=Halzhausen|first3=Arne|last4=Pelaya|first4=Patricia|url=https://www.allianz.com/content/dam/onemarketing/azcom/Allianz_com/economic-research/publications/specials/en/2021/october/2021_10_07_Global-Wealth-Report.pdf |title=ALLIANZ GLOBAL WEALTH REPORT 2021|date=7 October 2021|publisher=[[Allianz]] |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref> Australia has a labour force of some 13.5 million, with an unemployment rate of 3.5% as of June 2022.<ref name="ABSLabourForce">{{Cite web|website=Australian Bureau of Statistics|url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/labour/employment-and-unemployment/labour-force-australia/latest-release |title=Labour Force, Australia|date=14 July 2022 |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref> According to the [[Australian Council of Social Service]], the [[Poverty in Australia|poverty rate of Australia]] exceeds 13.6% of the population, encompassing 3.2 million. It also estimated that there were 774,000 (17.7%) children under the age of 15 living in relative poverty.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://povertyandinequality.acoss.org.au/poverty/|title=Poverty – Poverty and Inequality}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.acoss.org.au/media_release/report-shows-three-million-people-in-poverty-in-australia-and-why-we-must-act-to-support-each-other/|title=Report shows three million people in poverty in Australia and why we must act to support each other|date=21 February 2020|website=ACOSS}}</ref> The [[Australian dollar]] is the national currency, which is also used by three island states in the Pacific: [[Kiribati]], [[Nauru]], and [[Tuvalu]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/30205/ado2013-small-island-economies.pdf |title=Small island economies|year=2013|publisher=[[Asian Development Bank]] |access-date=14 August 2022|quote=All three countries use the Australian dollar as legal tender.}}</ref> |
|||
Australia has a [[market economy]] with high GDP per capita and low rate of poverty. The [[Australian dollar]] is the currency for the nation, including Christmas Island, Cocos (Keeling) Islands, and Norfolk Island, as well as the independent [[Pacific Islands|Pacific Island states]] of [[Kiribati]], [[Nauru]], and [[Tuvalu]]. After the 2006 merger of the Australian Stock Exchange and the Sydney Futures Exchange, the [[Australian Securities Exchange]] is now the ninth largest in the world.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.asx.com.au/about/pdf/asx_speech_eric_mayne_061106.pdf|title=On the International Realignment of Exchanges and Related Trends in Self-Regulation – Australian Stock Exchange|format=PDF|accessdate=3 January 2010}}{{dead link|date=April 2011}}</ref> |
|||
[[Australian government debt]], about $963 billion in June 2022, exceeds 45.1% of the country's total GDP, and is the world's [[List of countries by government debt|eighth-highest]].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Dossor|first=Rob|url=https://www.aph.gov.au/About_Parliament/Parliamentary_Departments/Parliamentary_Library/pubs/rp/BudgetReview202122/CommonwealthDebt |title=Commonwealth debt|publisher=[[Parliament of Australia]] |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref> Australia had the [[List of countries by household debt|second-highest level]] of [[household debt]] in the world in 2020, after Switzerland.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/HH_LS@GDD/AUS/CHE |title=Household debt, loans and debt securities|publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref> [[Australian property market|Its house prices]] are among the highest in the world, especially in the large urban areas.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Neubauer|first=Ian|url=https://www.aljazeera.com/economy/2022/4/6/australians-home-ownership-dream-turns-soar-as-prices-soar |title='Ridiculous prices': Australians' home ownership dreams turn sour|work=[[Al Jazeera English|Al Jazeera]]|date=6 April 2022 |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref> The large service sector accounts for about 71.2% of total GDP, followed by the industrial sector (25.3%), while [[Agriculture in Australia|its agriculture sector]] is by far the smallest, making up only 3.6% of total GDP.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/australia |title=Australia. CIA – The World Factbook |work=[[The World Factbook]]|publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency]] |access-date=22 January 2011}}</ref> Australia is the world's [[List of countries by exports|21st-largest exporter]] and [[List of countries by imports|24th-largest importer]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.trademap.org/Country_SelProductCountry.aspx?nvpm=1%7c036%7c%7c%7c%7cTOTAL%7c%7c%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c2%7c1%7c%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c1 |title=List of importing markets for the product exported by Austral1ia in 2021|publisher=[[International Trade Centre]] |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.trademap.org/Country_SelProductCountry.aspx?nvpm=1%7c036%7c%7c%7c%7cTOTAL%7c%7c%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c1%7c1%7c%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c1 |title=List of supplying markets for the product imported by Australia in 2021|publisher=[[International Trade Centre]] |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref> China is Australia's [[List of the largest trading partners of Australia|largest trading partner]] by a wide margin, accounting for roughly 40% of the country's exports and 17.6% of its imports.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.cnbc.com/2020/12/29/trade-war-with-china-australias-economy-after-covid-19-pandemic.html |title=Australia's growth may 'never return' to its pre-virus path after trade trouble with China, says economist|last=Tan|first=Weizhen|date=29 December 2020|publisher=[[CNBC]] |access-date=10 February 2021}}</ref> Other major export markets include Japan, the United States, and South Korea.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.dfat.gov.au/publications/trade-and-investment/trade-and-investment-glance-2020 |title=Trade and investment at a glance 2020|publisher=[[Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade]] |access-date=14 August 2022}}</ref> |
|||
Ranked third in the [[Index of Economic Freedom]] (2010),<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.heritage.org/index/Country/Australia|title=Australia|publisher=2010 Index of Economic Freedom|accessdate=30 March 2010}}</ref> Australia is the [[List of countries by GDP (nominal)|world's thirteenth largest economy]] and has the [[List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita|ninth highest per capita GDP]]; higher than that of the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Canada, Japan, and the United States. The country was ranked second in the United Nations 2010 [[Human Development Index]] and first in [[Legatum#The Legatum Institute|Legatum]]'s 2008 [[Legatum Prosperity Index|Prosperity Index]].<ref name="HDI"/> All of Australia's major cities fare well in global comparative liveability surveys;<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2004/02/06/1075854028808.html|title=Melbourne 'world's top city'|date=6 February 2004|work=The Age|accessdate=31 January 2009}}</ref> Melbourne reached second place on ''The Economist'''s 2008 [[World's Most Livable Cities]] list, followed by Perth, Adelaide, and Sydney in fourth, seventh and ninth place respectively.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.economist.com/markets/rankings/displaystory.cfm?story_id=11116839 |title=Liveability ranking |date=28 April 2008 |accessdate=28 May 2010 |work=The Economist}}</ref> Total government debt in Australia is about $190 billion.<ref>{{cite web|author=Tim Hughes |url=http://www.couriermail.com.au/money/money-matters/australian-dollar-continues-astronomical-rise-to-30-year-highs-as-us-dollar-euro-tank/story-fn3hskur-1226044717380 |title=Australian dollar continues astronomical rise to 30-year highs as US dollar, euro tank |publisher=Courier Mail |date= |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref> Australia has amongst the highest house prices and some of the highest household debt levels in the world.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/thereporters/nickbryant/2011/04/australian_affordablity.html |title=Nick Bryant's Australia: Australian affordablity |publisher=BBC |date= |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref> |
|||
Australia has high levels of competitiveness and economic freedom, and was ranked tenth in the [[Human Development Index]] in 2022.<ref>{{Cite web |last=United Nations Development Programme |date=September 2022 |title=United Nations Development Programme, The 2021/2022 Human Development Report: Uncertain times, unsettled lives, Shaping our future in a transforming world (p 272) |url=https://hdr.undp.org/content/human-development-report-2021-22 |access-date=13 August 2023 |website=United Nations}}</ref> {{As of|2022}}, it is ranked twelfth in the [[Index of Economic Freedom]] and nineteenth in the [[Global Competitiveness Report]].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Country Rankings|url=https://www.heritage.org/index/ranking|publisher=[[The Heritage Foundation]]|access-date=14 August 2022|archive-date=30 April 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200430170123/https://www.heritage.org/index/ranking|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2022.pdf |title=The Global Competitiveness Report|publisher=[[World Economic Forum]]|last=Schwab|first=Klaus|author-link=Klaus Schwab|year=2022}}</ref> It attracted 9.5 million international tourists in 2019,<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://statistics.jnto.go.jp/en/graph/#graph--inbound--travelers--transition |title=Trends in the Visitor Arrivals to Japan by Year|publisher=JNTO |access-date=11 December 2020}}</ref> and was [[World Tourism rankings|ranked thirteenth]] among the countries of [[Asia-Pacific]] in 2019 for inbound tourism.<ref name="WTOB">{{Cite journal|date=August–September 2020|publisher=UNWTO |title=Statistical Annex|journal=UNWTO World Tourism Barometer|volume=18|issue=5|page=18|doi=10.18111/wtobarometereng.2020.18.1.5|doi-access=free}}</ref> The 2021 ''[[Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report]]'' ranked Australia seventh-highest in the world out of 117 countries.<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Travel & Tourism Development Index 2021 |date=May 2022|publisher=[[World Economic Forum]]|url=https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Travel_Tourism_Development_2021.pdf |access-date=31 July 2022}}</ref> Its international tourism receipts in 2019 amounted to $45.7 billion.<ref name="WTOB"/> |
|||
[[File:2006Australian exports.svg|thumb|left|300px|alt=World map showing the distribution of Australian goods|Destination and value of Australian exports in 2006<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/DetailsPage/5368.0Apr%202007?OpenDocument |title=5368.0 – International Trade in Goods and Services, Australia, Apr 2007 |publisher=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] |date=31 May 2007 |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref>]] |
|||
An emphasis on exporting commodities rather than manufactured goods has underpinned a significant increase in Australia's [[terms of trade]] since the start of the century, due to rising commodity prices. [[Australia's balance of payments|Australia has a balance of payments]] that is more than 7% of GDP negative, and has had persistently large [[current account]] deficits for more than 50 years.<ref name="downwonder">{{Cite news|url=http://www.economist.com/finance/displaystory.cfm?story_id=8931798 |title=Might Australia's economic fortunes turn? |work=The Economist |date=29 March 2007 |accessdate=28 May 2010}}</ref> Australia has grown at an average annual rate of 3.6% for over 15 years, in comparison to the OECD annual average of 2.5%.<ref name="downwonder"/> There are differing opinions based on evidence as to whether or not Australia had been one of the few OECD nations to avoid experiencing a recession during the [[Late-2000s recession|late 2000s global financial downturn]].<ref name="autogenerated1">{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8080446.stm |title=Australia able to avoid recession |publisher=BBC News |date=2009-06-03 |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|author=David Uren |url=http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/australia-faces-recession-analyst/story-e6frg73x-1111115754520 |title=Australia faces recession: analyst |publisher=The Australian |date=2008-03-10 |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref><ref name="autogenerated1"/> Six of Australia's major trading partners had been in recession which in turn affected Australia, and economic growth was hampered significantly over recent years.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/australasia/australia-slashes-immigration-as-recession-looms-1646048.html |title=Australia slashes immigration as recession looms |publisher=The Independent |date=2009-03-16 |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=Mclennan |first=David |url=http://www.canberratimes.com.au/news/national/national/general/australian-economy-growing-as-new-recession-fears-fade/2130847.aspx |title=Australian economy growing as new recession fears fade |publisher=The Canberra Times |date=2011-04-12 |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref> |
|||
===Energy=== |
|||
The [[Bob Hawke|Hawke Government]] [[Floating exchange rate|floated]] the Australian dollar in 1983 and partially deregulated the financial system.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
{{Main|Energy policy of Australia|Renewable energy in Australia}} |
|||
|url=http://www.rba.gov.au/publications/bulletin/1998/oct/pdf/bu-1098-2.pdf |
|||
In 2021–22, Australia's generation of electricity was sourced from [[Bituminous coal|black coal]] (37.2%), [[brown coal]] (12%), [[natural gas]] (18.8%), [[Hydroelectricity|hydro]] (6.5%), [[Wind power|wind]] (11.1%), [[Solar power|solar]] (13.3%), [[Bioenergy|bio-energy]] (1.2%) and others (1.7%).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Australian electricity generation - fuel mix |url=https://www.energy.gov.au/energy-data/australian-energy-statistics/data-charts/australian-electricity-generation-fuel-mix |access-date=5 February 2024 |website=energy.gov.au}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Australian electricity generation renewable sources |url=https://www.energy.gov.au/energy-data/australian-energy-statistics/data-charts/australian-electricity-generation-renewable-sources |access-date=5 February 2024 |website=energy.gov.au}}</ref> Total consumption of energy in this period was sourced from coal (28.4%), oil (37.3%), gas (27.4%) and renewables (7%).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Australian energy mix by state and territory 2021-22 |url=https://www.energy.gov.au/energy-data/australian-energy-statistics/data-charts/australian-energy-mix-state-and-territory-2021-22 |access-date=5 February 2024 |website=energy.gov.au}}</ref> From 2012 to 2022, the energy sourced from renewables has increased 5.7%, while energy sourced from coal has decreased 2.6%. The use of gas also increased by 1.5% and the use of oil stayed relatively stable with a reduction of only 0.2%.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Energy consumption |url=https://www.energy.gov.au/energy-data/australian-energy-statistics/energy-consumption |access-date=5 February 2024 |website=energy.gov.au}}</ref> |
|||
|title=Australian Monetary Policy in the Last Quarter of the Twentieth Century |
|||
|author=Macfarlane, I. J. |
|||
|publisher=''Reserve Bank of Australia Bulletin'' |
|||
|format=PDF |
|||
|date=October 1998 |
|||
|accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref> The [[Howard Government]] followed with a [[WorkChoices|partial deregulation of the labour market]] and the further [[privatisation]] of state-owned businesses, most notably in the [[telecommunications in Australia|telecommunications]] industry.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.pc.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0009/9369/mrrag.pdf |
|||
|title=Microeconomic reforms and the revival in Australia’s growth in productivity and living standards |
|||
|author=Dean Parham |
|||
|publisher=''Conference of Economists'' Adelaide |
|||
|format=PDF |
|||
|date=1 October 2002 |
|||
|accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref> The indirect tax system was substantially changed in July 2000 with the introduction of a 10% [[Goods and Services Tax (Australia)|Goods and Services Tax]] (GST).<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/journals/JATax/2000/23.html|author=Tran-Nam, Binh |title=The Implementation Costs of the GST in Australia: Concepts, Preliminary Estimates and Implications [2000] JlATax 23; (2000) 3(5) |journal=Journal of Australian Taxation 331|publisher=[[Australasian Legal Information Institute]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> In [[Taxation in Australia|Australia's tax system]], personal and company [[Income tax in Australia|income tax]] are the main sources of government revenue.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.budget.gov.au/2008-09/content/fbo/html/part_1.htm|title=Part 1: Australian Government Budget Outcome|publisher=Budget 2008–09 – Australian Government|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> |
|||
In 2020, Australia produced 27.7% of its electricity from renewable sources, exceeding the [[Renewable energy target|target]] set by the Commonwealth government in 2009 of 20% renewable energy by 2020.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Renewable Energy Target Scheme Design |url=http://www.climatechange.gov.au/renewabletarget/pubs/RET-scheme-design.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090515035607/http://www.climatechange.gov.au/renewabletarget/pubs/RET-scheme-design.pdf |archive-date=15 May 2009 |access-date=15 May 2009}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last1=Clean Energy Council Australia |title=Clean Energy Australia Report 2021 |url=https://assets.cleanenergycouncil.org.au/documents/resources/reports/clean-energy-australia/clean-energy-australia-report-2021.pdf |access-date=3 June 2021 |website=Clean Energy Australia}}</ref> A new target of 82% per cent renewable energy by 2030 was set in 2022<ref>{{Cite news |date=5 August 2023 |title=Australia will fall well short of 82 per cent renewable energy by 2030, analysts predict, as problems mount |url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2023-08-06/australia-likely-to-fall-short-of-82pc-renewable-energy-target/102689392 |access-date=5 February 2024 |work=ABC News |language=en-AU}}</ref> and a target for [[net zero emissions]] by 2050 was set in 2021.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Evans |first=Jake |date=26 October 2021 |title=What is the government's plan to get Australia to net zero? |url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2021-10-26/how-will-australia-reach-net-zero-by-2050-and-2030-targets/100565342 |access-date=11 February 2024 |work=[[ABC News (Australia)]] |language=en-AU}}</ref> |
|||
In January 2007, there were 10,033,480 people employed<!--Is this full-time equivalent? How is part-time employment included here?-->, with an unemployment rate of 5.1%.<ref>Australian Bureau of Statistics. Labour Force Australia. Cat#6202.0.</ref> Youth unemployment (15-24) rose from 8.7% to 9.7% over 2008-2009.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.oecd.org/document/21/0,3746,en_33873108_33873229_42569009_1_1_1_1,00.html |title=Australia should intervene quickly to avert a major rise in youth unemployment, says OECD |publisher=Oecd.org |date= |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref> Over the past decade<!--MOS breach—see "Vague chronological terms". "Since ?1998"-->, inflation has typically been 2–3% and the base interest rate 5–6%. The service sector of the economy, including tourism, education, and financial services, accounts for about 70% of GDP.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/as.html |title=Australia. CIA — The World Factbook |publisher=Cia.gov |date= |accessdate=2011-01-22}}</ref> Although [[Agriculture in Australia|agriculture]] and natural resources account for only 3% and 5% of GDP respectively, they contribute substantially to export performance. Australia's largest export markets are Japan, [[China]], the US, South Korea, and New Zealand.<ref name="Year Book 2005">Australian Bureau of Statistics. [http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/94713ad445ff1425ca25682000192af2/1a79e7ae231704f8ca256f720082feb9!OpenDocument Year Book Australia 2005].</ref> Australia is the world's fourth largest exporter of wine, in an industry contributing $5.5 billion per annum to the nation's economy.<ref name="wineaustralia1">{{cite news |publisher=wineaustralia |url=http://www.wineaustralia.com/australia/ |title= Wine Australia |accessdate=2010-10-22}}</ref> |
|||
===Science and technology=== |
|||
==Demography== |
|||
In 2019, Australia spent $35.6 billion on [[research and development]], allocating about 1.79% of GDP.<ref>{{Cite web |date=9 March 2021 |title=Research and Experimental Development, Businesses, Australia, 2019–20 financial year |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/industry/technology-and-innovation/research-and-experimental-development-businesses-australia/latest-release |access-date=20 May 2022 |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics}}</ref> A recent study by [[Accenture]] for the Tech Council shows that the Australian tech sector combined contributes $167 billion a year to the economy and employs 861,000 people.<ref>{{Cite web |date=12 April 2022 |title=Australia wants a place in ranks of global tech nations |url=https://www.afr.com/technology/australia-wants-a-place-in-ranks-of-global-tech-nations-20220328-p5a8kh |access-date=20 May 2022 |website=Australian Financial Review |language=en}}</ref> In addition, recent [[startup ecosystem]]s in Sydney and Melbourne are already valued at $34 billion combined.<ref>{{Cite web |date=23 September 2021 |title=Sydney's startup ecosystem is worth $24 billion, Melbourne's $10.5bn |url=https://www.startupdaily.net/2021/09/sydneys-startup-ecosystem-is-worth-24-billion-melbournes-10-5bn |access-date=20 May 2022 |website=Startup Daily |language=en-US}}</ref> Australia ranked 23rd in the [[Global Innovation Index]] 2024.<ref>{{Cite book |year=2024 |title=Global Innovation Index 2024: Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship |url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/ |access-date=6 October 2024 |page=18 |publisher=[[World Intellectual Property Organization]] |language=en |doi=10.34667/tind.50062 |isbn=978-92-805-3681-2 |author1=World Intellectual Property Organization. |last2=Dutta |first2=Soumitra. |last3=Lanvin |first3=Bruno. |last4=Rivera León |first4=Lorena. |last5=Wunsch-Vincent |first5=Sacha. }}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Demographics of Australia|Immigration to Australia}} |
|||
With only 0.3% of the world's population, Australia contributed 4.1% of the world's published research in 2020, making it one of the top 10 research contributors in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Research Output {{!}} Australian Innovation System Monitor |url=https://publications.industry.gov.au/publications/australianinnovationsystemmonitor/science-and-research/research-output/index.html |access-date=24 July 2022 |website=publications.industry.gov.au}}</ref><ref name="Berthold-2021">{{Cite web |last=Berthold |first=Emma |date=17 May 2021 |title=Science in Australia |url=https://www.science.org.au/curious/policy-features/science-australia |access-date=24 July 2022 |website=Curious |language=en}}</ref> [[CSIRO]], Australia's national science agency, contributes 10% of all research in the country, while the rest is carried out by universities.<ref name="Berthold-2021"/> Its most notable contributions include the invention of [[atomic absorption spectroscopy]],<ref>{{Cite web |last=Hannaford |first=Peter |title=Alan Walsh 1916–1998 |url=http://www.science.org.au/academy/memoirs/walsh2.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070224214248/http://www.science.org.au/academy/memoirs/walsh2.htm |archive-date=24 February 2007 |access-date=5 December 2022 |website=AAS Biographical Memoirs |publisher=[[Australian Academy of Science]]}}</ref> the essential components of [[Wi-Fi]] technology,<ref>{{Cite web |title= Wi-fi |url=https://www.nma.gov.au/defining-moments/resources/wi-fi |access-date=6 December 2022 |website=National Museum of Australia |publisher= |language=en}}</ref> and the development of the first commercially successful [[polymer banknote]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=25 November 2014 |title=Proceeds of crime: how polymer banknotes were invented |url=https://blog.csiro.au/proceeds-of-crime-how-polymer-banknotes-were-invented |access-date=6 December 2022 |website=CSIROscope |language=en-AU}}</ref> {{As of|2024}}, 13 Australian scientists have been awarded the [[Nobel Prize]] in physics, chemistry or medicine,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Nobel Australians |url=https://www.science.org.au/education/history-australian-science/nobel-australians |access-date=21 December 2024 |website=[[Australian Academy of Science]] |language=}}</ref> and two have been awarded the [[Fields Medal]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Watson |first=Laura |date=1 August 2018 |title=AMSI Congratulates Australia's Second Ever Fields Medallist |url=https://amsi.org.au/2018/08/02/amsi-congratulates-australias-second-ever-fields-medallist/ |access-date=21 December 2024 |website=[[Australian Mathematical Sciences Institute]] |language=}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="float:right; margin-left:0.8em; margin-bottom:0.4em;" |
|||
! colspan="3"|'''Historic population'''<ref>{{cite web|url=http://populstat.info/Oceania/australc.htm|title=<!-- Do not remove the following capitalisation. This is the actual title of the page. See the citation for clarification! -->Australia: population growth of the whole country|publisher=populstat.info|accessdate=22 July 2008}} 19th century figures do not include the indigenous population.</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
! Year || Indigenous population || |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| pre 1788 || style="text-align:right;"| 350,000 approximate |
|||
|- |
|||
! Year || Non Indigenous population || Increase |
|||
|- style="text-align:center;" |
|||
|| 1788 || style="text-align:right;"| 900 || style="text-align:center;"| — |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1800 || style="text-align:right;"| 5,200 || style="text-align:right;"| 477.8% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1850 || style="text-align:right;"| 405,400 || style="text-align:right;"| 7,696.2% |
|||
|- |
|||
! Year || Total population || Increase |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1900 || style="text-align:right;"| 3,765,300 || style="text-align:right;"| — |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1910 || style="text-align:right;"| 4,525,100 || style="text-align:right;"| 20.2% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1920 || style="text-align:right;"| 5,411,000 || style="text-align:right;"| 19.6% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1930 || style="text-align:right;"| 6,501,000 || style="text-align:right;"| 20.1% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1940 || style="text-align:right;"| 7,078,000 || style="text-align:right;"| 8.9% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1950 || style="text-align:right;"| 8,307,000 || style="text-align:right;"| 17.4% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1960 || style="text-align:right;"| 10,392,000 || style="text-align:right;"| 25.1% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1970 || style="text-align:right;"| 12,663,000 || style="text-align:right;"| 21.9% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1980 || style="text-align:right;"| 14,726,000 || style="text-align:right;"| 16.3% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 1990 || style="text-align:right;"| 17,169,000 || style="text-align:right;"| 16.6% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 2000 || style="text-align:right;"| 19,169,100 || style="text-align:right;"| 11.6% |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="text-align:center;"| 2009 || style="text-align:right;"| 21,828,704<!-- 21,828,704 is the estimated population, taken from the population clock, as of 29 June 2009. For consistency with ABS projections that are typically made on 30 June, current year estimated population should be as estimated on, or as near to 30 June as possible. -->|| style="text-align:right;"| 13.6% |
|||
|} |
|||
Australia is a key player in supporting [[space exploration]]. Facilities such as the [[Square Kilometre Array]] and [[Australia Telescope Compact Array]] radio telescopes, telescopes such as the [[Siding Spring Observatory]], and ground stations such as the [[Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex]] are of great assistance in [[deep space exploration]] missions, primarily by [[NASA]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Williams |first=Dave |title=Australia's part in 50 years of space exploration with NASA |url=http://theconversation.com/australias-part-in-50-years-of-space-exploration-with-nasa-24530 |access-date=13 December 2022 |website=The Conversation |date=19 March 2014 |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
Most of the estimated 22 million Australians are descended from colonial-era settlers and post-Federation immigrants from Europe, with almost 90% of the population being of European descent.{{citation needed|date=April 2011}} For generations, the vast majority of immigrants came from the British Isles, and the people of Australia are still mainly of British or Irish ethnic origin.{{citation needed|date=April 2011}} In the 2006 Australian census, the most commonly nominated ancestry was Australian (37.13%),<ref>The Australian Bureau of Statistics has stated that most who list "Australian" as their ancestry are part of the [[Anglo-Celtic Australian|Anglo-Celtic]] group. [http://www.abs.gov.au/Ausstats/abs@.nsf/94713ad445ff1425ca25682000192af2/49f609c83cf34d69ca2569de0025c182!OpenDocument]</ref> followed by [[English Australian|English]] (32%), [[Irish Australian|Irish]] (9%), [[Scottish Australian|Scottish]] (8%), [[Italian Australian|Italian]] (4%), [[German Australian|German]] (4%), [[Chineses Australian|Chinese]] (3%), and [[Greek Australian|Greek]] (2%).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.censusdata.abs.gov.au/ABSNavigation/prenav/ViewData?action=404&documentproductno=0&documenttype=Details&order=1&tabname=Details&areacode=0&issue=2006&producttype=Census%20Tables&javascript=true&textversion=false&navmapdisplayed=true&breadcrumb=LPTD&&collection=Census&period=2006&productlabel=Ancestry%20by%20Country%20of%20Birth%20of%20Parents%20-%20Time%20Series%20Statistics%20(2001,%202006%20Census%20Years)&producttype=Census%20Tables&method=Place%20of%20Usual%20Residence&topic=Ancestry&|title=20680-Ancestry by Country of Birth of Parents – Time Series Statistics (2001, 2006 Census Years) – Australia|publisher=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]]|date=27 June 2007|accessdate=30 December 2008}}</ref> |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
Australia's population has quadrupled since the end of World War I,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/DetailsPage/3105.0.65.0012006?OpenDocument|title=3105.0.65.001—Australian Historical Population Statistics, 2006|accessdate=18 September 2007|date=23 May 2006|format=[[Microsoft Excel|XLS]]|publisher=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]]|quote=Australian population: (1919) 5,080,912; (2006) 20,209,993}}</ref> spurred by an ambitious [[Immigration to Australia|immigration program]]. Following World War II and through to 2000, almost 5.9 million of the total population settled in the country as new immigrants, meaning that nearly two out of every seven Australians were born overseas.<ref name="Immigration">{{cite web|url=http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/2698.htm|title=Background note: Australia|publisher=US Department of State|accessdate=19 May 2007}}</ref> Most immigrants are skilled,<ref name="immig">{{cite web|url=http://www.immi.gov.au/media/fact-sheets/20planning.htm |title=Fact Sheet 20 – Migration Program Planning Levels |accessdate=17 June 2010 |date=11 August 2009 |publisher=Department of Immigration and Citizenship}}</ref> but the immigration quota includes categories for family members and [[refugee]]s.<ref name="immig"/> The Federal Government estimates that cutting immigration from 280,000 to its target of 180,000 will result in a population of 36 million by 2050.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dailytelegraph.com.au/news/well-be-a-nation-of-new-migrants/story-e6freuy9-1225854962993 |title=We'll be a nation of new migrants |work=[[The Daily Telegraph (Australia)|The Sunday Telegraph]] |date=18 April 2010 |accessdate=17 June 2010|author=Gardner, Nick}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Demographics of Australia}} |
|||
Australia has a [[population density]] of 3.4 persons per square kilometre of total land area, which makes it one of the [[List of countries by population density|most sparsely populated countries in the world]]. The population is heavily concentrated on the east coast, and in particular in the south-eastern region between [[South East Queensland]] to the north-east and [[Adelaide]] to the south-west.<ref name="ABS-regional-population-latest" /> |
|||
Australia is also highly urbanised, with 67% of the population living in the Greater Capital City Statistical Areas (metropolitan areas of the state and mainland territorial capital cities) in 2018.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/mf/3218.0 |title=Main Features – Main Features |publisher=Commonwealth of Australia |agency=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] |date=27 March 2019|work=3218.0 – Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2017–18}}</ref> Metropolitan areas with more than one million inhabitants are [[Sydney]], [[Melbourne]], [[Brisbane]], [[Perth]] and [[Adelaide]].<ref name="ABS-regional-population-latest" /> |
|||
In 2001, 23.1% of Australians were born overseas; the five largest immigrant groups were those from the [[Anglo-Celtic Australian|United Kingdom]], New Zealand, Italy, [[Vietnamese Australian|Vietnam]], and China.<ref name="Year Book 2005" /><ref>{{Cite journal|url=http://elecpress.monash.edu.au/pnp/free/pnpv7n4/v7n4_3price.pdf |author=Price, Charles|title=Australian Population: Ethnic Origins |pages=12–16 |journal=People and Place |volume=7 |issue=4}}</ref> Following the abolition of the [[White Australia policy]] in 1973, numerous government initiatives have been established to encourage and promote racial harmony based on a policy of [[multiculturalism]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.immi.gov.au/facts/06evolution.htm|title=The Evolution of Australia's Multicultural Policy|accessdate=18 September 2007|year=2005|publisher=Department of Immigration and Multicultural and Indigenous Affairs|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20060219130703/http://www.immi.gov.au/facts/06evolution.htm|archivedate=19 February 2006}}</ref> In 2005–06, more than 131,000 people emigrated to Australia, mainly from Asia and [[Oceania]].<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.minister.immi.gov.au/media/media-releases/2006/v06297.htm |
|||
|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070609123847/http://www.minister.immi.gov.au/media/media-releases/2006/v06297.htm |
|||
|archivedate=2007-06-09 |
|||
|title=Settler numbers on the rise |
|||
|publisher=Minister for Immigration and Citizenship |
|||
|date=27 December 2006 |
|||
|accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref> The migration target for 2006–07 was 144,000.<ref name=immig/><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.migrationinformation.org/datahub/countrydata/country.cfm |title=Country and Comparative Data |accessdate=17 June 2010 |publisher=Migration Policy Institute}}</ref> The total immigration quota for 2008–09 is around 300,000—its highest level since the Immigration Department was created after World War II.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/lateline/content/2007/s2272014.htm|title=Immigration intake to rise to 300,000|author=Iggulden, Tom|date=11 June 2008|work=[[Lateline]]|publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]|accessdate=23 June 2010}}</ref> |
|||
In common with many other developed countries, Australia is experiencing a demographic shift towards an older population, with more retirees and fewer people of working age. In 2021, the [[median age|average age]] of the population was 39 years.<ref>{{Cite web |date=28 June 2022 |title=Population: Census |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/population-census/latest-release |publisher=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]]}}</ref> In 2015, 2.15% of the Australian population [[Australian diaspora|lived overseas]], one of the [[List of sovereign states and dependent territories by immigrant population#UN 2015 report: emigrant population|lowest proportions]] worldwide.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/data/estimates2/estimates15.shtml |title=United Nations Population Division – Department of Economic and Social Affairs |access-date=13 May 2016}}</ref> |
|||
The Indigenous population—mainland [[Indigenous Australians|Aborigines]] and [[Torres Strait Islands|Torres Strait Islanders]]—was counted at 410,003 (2.2% of the total population) in 2001, a significant increase from 115,953 in the 1976 census.<ref name="Year Book 2004">{{cite web|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/Previousproducts/1301.0Feature%20Article52004?opendocument&tabname=Summary&prodno=1301.0&issue=2004&num=&view=|title=1301.0 – Year Book Australia, 2004 |
|||
|date=27 February 2004|accessdate=24 April 2009|publisher=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]]}}</ref> A large number of Indigenous people are not identified in the Census due to undercount and cases where their Indigenous status is not recorded on the form; after adjusting for these factors, the ABS estimated the true figure for 2001 to be around 460,140 (2.4% of the total population).<ref name="Indigenous ERP 2001">{{cite web |url=http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/ProductsbyReleaseDate/2315409AD11513DFCA2573370013F824?OpenDocument |title=4705.0 – Population Distribution, Indigenous Australians, 2001 |publisher=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] |date=26 June 2002 |accessdate=24 April 2009}}</ref> |
|||
===Cities=== |
|||
Indigenous Australians experience higher than average rates of imprisonment and unemployment, lower levels of education, and life expectancies for males and females that are 11–17 years lower than those of non-indigenous Australians.<ref name="Year Book 2005"/><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/nation/life-gap-figures-not-black-and-white/story-e6frg6nf-1111118141529 |title=Life gap figures not black and white |author=Lunn, Stephen |work=[[The Australian]] |publisher=News Limited |date=26 November 2008 |accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.smh.com.au/national/indigenous-health-gap-closes-by-five-years-20090409-a27x.html |title=Indigenous health gap closes by five years |author=Gibson, Joel |work= [[The Sydney Morning Herald]] |publisher=[[Fairfax Media|Fairfax]] |date=10 April 2009 |accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref><!-- The Australian and SMH refs should be replaced with the finalised ABS estimate when this becomes available. --> Some remote Indigenous communities have been described as having "[[failed state]]"-like conditions.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.theage.com.au/news/national/australia-hides-a-failed-state/2006/12/07/1165081088385.html |title=Australia hides a 'failed state' |author=[[Michelle Grattan|Grattan, Michelle]] |publisher=[[The Age]] |location=Melbourne |date=8 December 2006 |accessdate=17 October 2008}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=[[Robert Manne|Manne, Robert]] |url=http://www.safecom.org.au/dear-mr-rudd.htm |title=Extract: Dear Mr Rudd |publisher=Safecom |accessdate=17 October 2008}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.theage.com.au/news/opinion/russell-skelton/2008/03/16/1205602190300.html |title=Poor fellow, failed state |publisher=[[The Age]] |date=17 March 2008 |accessdate=26 May 2010 |author=Skelton, Russell |location=Melbourne}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2008/09/15/2364336.htm |title=Remote Australia a 'failed state' |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |date=15 September 2008 |accessdate=26 May 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2008/09/04/2354860.htm |title=Remote Australia a failed state: Indigenous policy makers |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |date=4 September 2008 |accessdate=26 May 2010}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|List of cities in Australia by population|List of cities in Australia}} |
|||
Australia has five cities (including their suburbs) that have populations larger than one million people. The majority of Australia's population lives near coastlines.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/beach/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100226144234/http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/beach/ |archive-date=26 February 2010 |title=The Beach |work=Australian Government: Culture Portal |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia |date=17 March 2008 }}</ref> |
|||
{{Largest cities of Australia}} |
|||
=== Ancestry and immigration === |
|||
In common with many other developed countries, Australia is experiencing a demographic shift towards an older population, with more retirees and fewer people of working age. In 2004, the [[Population pyramid|average age]] of the civilian population was 38.8 years.<ref>Parliament of Australia, Parliamentary Library (2005). [http://www.aph.gov.au/Library/pubs/rn/2004-05/05rn35.pdf Australia’s aging workforce].</ref> A large number of Australians (759,849 for the period 2002–03)<ref>Parliament of Australia, Senate (2005). [http://www.aph.gov.au/Senate/committee/legcon_ctte/expats03/ Inquiry into Australian Expatriates].</ref> live outside their home country. |
|||
{{Main|Immigration to Australia}} |
|||
[[File:Australian Residents by Country of Birth 2021 Census.svg|thumb|upright=1.2| Australian residents by country of birth (2021 census)]] |
|||
Between 1788 and the [[Second World War]], the vast majority of [[settlers]] and [[immigrants]] came from the [[Anglo-Celtic Australians|British Isles]] (principally [[English Australians|England]], [[Irish Australians|Ireland]] and [[Scottish Australians|Scotland]]), although there was significant immigration from [[Chinese Australians|China]] and [[German Australians|Germany]] during the 19th century. Following Federation in 1901, the [[white Australia policy]] was strengthened, restricting further migration from these areas. However, this policy was relaxed following WW2 and in the decades following, Australia received a [[Post-war immigration to Australia|large wave of immigration]] from across [[European Australians|Europe]], with many more immigrants arriving from [[Southern Europe|Southern]] and [[Eastern Europe]] than in previous decades. All overt racial discrimination ended in 1973, with [[Multiculturalism in Australia|multiculturalism]] becoming official policy.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.immi.gov.au/facts/06evolution.htm |title=The Evolution of Australia's Multicultural Policy |access-date=18 September 2007|year=2005|publisher=Department of Immigration and Multicultural and Indigenous Affairs |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060219130703/http://www.immi.gov.au/facts/06evolution.htm |archive-date=19 February 2006}}</ref> Subsequently, there has been a large and continuing wave of immigration from across the world, with [[Asian Australians|Asia]] being the largest source of immigrants in the 21st century.<ref name="Australian-Government-Department-of-Home-Affairs-2019">{{Cite web |url=https://www.homeaffairs.gov.au/research-and-stats/files/report-migration-program-2018-19.pdf |title=2018–19 Migration Program Report|website=Australian Government Department of Home Affairs|date=30 June 2019}}</ref> |
|||
Today, Australia has the world's [[List of sovereign states and dependent territories by immigrant population|eighth-largest]] immigrant population, with immigrants accounting for 30% of the population, the [[List of sovereign states and dependent territories by immigrant population|highest proportion]] among major [[Western world|Western]] nations.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/migration-australia/2019-20#australia-s-population-by-country-of-birth |title=Main Features – Australia's Population by Country of Birth|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia |agency=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] |date=23 April 2021 |work=3412.0 – Migration, Australia, 2019–20}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=International migrant stock 2017: maps |website=United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division|url=https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/data/estimates2/estimatesmaps.shtml?1t1 |access-date=15 January 2022 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181209122006/https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/data/estimates2/estimatesmaps.shtml?1t1 |archive-date= 9 December 2018 }}</ref> In 2022–23, 212,789 permanent migrants were admitted to Australia, with a net migration population gain of 518,000 people inclusive of non-permanent residents.<ref>{{Cite web |date=15 December 2023 |title=Overseas Migration |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/overseas-migration/latest-release |access-date=7 February 2024 |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics |language=en-AU}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2023 |title=Australia's Migration Trends 2022–23 |url=https://www.homeaffairs.gov.au/research-and-stats/files/migration-trends-2022-23.PDF |publisher=Department of Home Affairs}}</ref> Most entered on skilled visas,<ref name="Australian-Government-Department-of-Home-Affairs-2019"/> however the immigration program also offers visas for family members and [[refugee]]s.<ref name="immig">{{Cite web |title=Net Overseas Migration |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/Latestproducts/3412.0Main%20Features52018-19?opendocument&tabname=Summary&prodno=3412.0&issue=2018-19&num=&view= |access-date=4 May 2020 |publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics}}</ref> |
|||
{{Largest cities of Australia}} |
|||
The [[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] asks each Australian resident to nominate up to two [[ancestry|ancestries]] each [[Census in Australia|census]] and the responses are classified into broad ancestry groups.<ref>{{Cite web |date=28 June 2022 |title=Understanding and using Ancestry data |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/detailed-methodology-information/information-papers/understanding-and-using-ancestry-data |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240209190954/https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/detailed-methodology-information/information-papers/understanding-and-using-ancestry-data |archive-date=9 February 2024 |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics}}</ref><ref name="abs">{{Cite web | url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/classifications/australian-standard-classification-cultural-and-ethnic-groups-ascceg/latest-release | title=Australian Standard Classification of Cultural and Ethnic Groups (ASCCEG), 2019 |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics | date=18 December 2019 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20231121023512/https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/classifications/australian-standard-classification-cultural-and-ethnic-groups-ascceg/latest-release |archive-date= 21 November 2023 }}</ref> At the 2021 census, the most commonly nominated ancestry groups as a proportion of the total population were:<ref name="abs.gov.au">[https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/people-and-communities/cultural-diversity-census/2021/Cultural%20diversity%20data%20summary.xlsx Cultural diversity data summary]. 2021. Australian Bureau of Statistics.</ref> 57.2% [[European Australians|European]] (including 46% [[Northwestern Europe#Ethnographic definitions|North-West European]] and 11.2% [[Southern Europe|Southern]] and [[Eastern Europe]]an), 33.8% [[Demographics of Oceania|Oceanian]],{{Refn|group="N"|Includes those who nominate "Australian" as their ancestry.<ref name="Australian-Bureau-of-Statistics-2022"/> The Australian Bureau of Statistics has stated that most who nominate "Australian" as their ancestry have at least partial [[Anglo-Celtic Australian|Anglo-Celtic]] [[European Australian|European]] ancestry.<ref name="13010-Year-Book-Australia-1995">{{Cite news|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/Ausstats/abs@.nsf/94713ad445ff1425ca25682000192af2/49f609c83cf34d69ca2569de0025c182!OpenDocument |title=Feature Article – Ethnic and Cultural Diversity in Australia (Feature Article) |publisher=Commonwealth of Australia |agency=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] |work=1301.0 – Year Book Australia, 1995}}</ref>}} 17.4% [[Asian Australians|Asian]] (including 6.5% [[South Asia|Southern]] and [[Central Asia#Demographics|Central Asian]], 6.4% [[East Asia|North-East Asian]], and 4.5% [[Southeast Asia|South-East Asian]]), 3.2% [[Demographics of the Middle East and North Africa|North African and Middle Eastern]], 1.4% [[Americas#Demography|Peoples of the Americas]], and 1.3% [[Sub-Saharan Africa#Demographics|Sub-Saharan African]]. At the 2021 census, the most commonly nominated individual ancestries as a proportion of the total population were:{{Refn|group="N"|Each person may nominate more than one ancestry, so the total may exceed 100%.<ref>{{cite web | title=Understanding and using Ancestry data | website=Australian Bureau of Statistics | date=28 June 2022 | url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/detailed-methodology-information/information-papers/understanding-and-using-ancestry-data | access-date=30 May 2024}}</ref>}}<ref name="Australian-Bureau-of-Statistics-2022"/> <!-- Only ancestries with >1% are listed. --> |
|||
{{Columns-list|colwidth=12em| |
|||
* [[English Australian|English]] (33%) |
|||
* [[Australians|Australian]] (29.9%){{Refn|group="N"|The Australian Bureau of Statistics has stated that most who nominate "Australian" as their ancestry have at least partial [[Anglo-Celtic Australian|Anglo-Celtic]] [[European Australian|European]] ancestry.<ref name="13010-Year-Book-Australia-1995"/>}} |
|||
* [[Irish Australian|Irish]] (9.5%) |
|||
* [[Scottish Australian|Scottish]] (8.6%) |
|||
* [[Chinese Australian|Chinese]] (5.5%) |
|||
* [[Italian Australian|Italian]] (4.4%) |
|||
* [[German Australian|German]] (4%) |
|||
* [[Indian Australian|Indian]] (3.1%) |
|||
* [[Aboriginal Australians|Aboriginal]] (2.9%){{Refn|group="N"|Those who nominated their ancestry as "Australian Aboriginal". Does not include [[Torres Strait Islanders]]. This relates to nomination of ancestry and is distinct from persons who identify as Indigenous (Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander) which is a separate question.}} |
|||
* [[Greek Australian|Greek]] (1.7%) |
|||
* [[Filipino Australian|Filipino]] (1.6%) |
|||
* [[Dutch Australian|Dutch]] (1.5%) |
|||
* [[Vietnamese Australian|Vietnamese]] (1.3%) |
|||
* [[Lebanese Australian|Lebanese]] (1%) |
|||
}} |
|||
At the 2021 census, 3.8% of the Australian population identified as being [[Indigenous Australians|Indigenous]]—[[Aboriginal Australians]] and [[Torres Strait Islanders]].{{Refn|group="N"|Indigenous identification is separate to the ancestry question on the Australian Census and persons identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander may identify any ancestry.}}<ref name="abs"/> |
|||
===Language=== |
===Language=== |
||
{{Main| |
{{Main|Languages of Australia}} |
||
Although English is not the official language of Australia in law, it is the ''[[de facto]]'' official and national language.<ref name="language2">{{Cite web |title=Pluralist Nations: Pluralist Language Policies? |url=http://www.immi.gov.au/media/publications/multicultural/confer/04/speech18b.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081220020910/http://www.immi.gov.au/media/publications/multicultural/confer/04/speech18b.htm |archive-date=20 December 2008 |access-date=11 January 2009 |work=1995 Global Cultural Diversity Conference Proceedings, Sydney |publisher=[[Department of Immigration and Citizenship]]}} "English has no de jure status but it is so entrenched as the common language that it is de facto the official language as well as the national language."</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Ward |first=Rowena |date=2019 |title='National' and 'Official' Languages Across the Independent Asia-Pacific |journal=Journal of Multidisciplinary International Studies |volume=16 |issue=1/2 |pages=83–4 |doi=10.5130/pjmis.v16i1-2.6510 | doi-access=free |quote=The use of English in Australia is one example of both a de facto national and official language: it is widely used and is the language of government and the courts, but has never been legally designated as the country's official language.}}</ref> [[Australian English]] is a major variety of the language with a distinctive accent and lexicon,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Moore |first=Bruce |title=The Vocabulary Of Australian English |url=http://www.nma.gov.au/libraries/attachments/exhibitions/vocabulary_of_australian_english/files/5471/Vocabulary%20of%20Australian%20English.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110320004658/http://www.nma.gov.au/libraries/attachments/exhibitions/vocabulary_of_australian_english/files/5471/Vocabulary%20of%20Australian%20English.pdf |archive-date=20 March 2011 |access-date=5 April 2010 |publisher=National Museum of Australia}}</ref> and differs slightly from other varieties of English in grammar and spelling.<ref>"The Macquarie Dictionary", Fourth Edition. The Macquarie Library Pty Ltd, 2005.</ref> [[General Australian]] serves as the standard dialect.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Lalande |first=Line |date=4 May 2020 |title=Australian English in a nutshell |url=https://www.noslangues-ourlanguages.gc.ca/en/blogue-blog/australian-english-eng |publisher=Government of Canada}}</ref> The Australian [[sign language]] known as [[Auslan]] was used at home by 16,242 people at the time of the 2021 census.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Census of Population and Housing: Cultural diversity data summary, 2021, TABLE 5. LANGUAGE USED AT HOME BY STATE AND TERRITORY |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/people-and-communities/cultural-diversity-census/2021#data-downloads |access-date=7 May 2021 |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Surfers Paradise Beach Queensland.jpg|thumb|alt=A beach sloping down from a grassy area on the left to the sea on the right, a city can be seen in the horizon|Nearly three quarters of Australians live in metropolitan cities and coastal areas. The beach is an integral part of the Australian identity.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/beach/|title=The Beach|work=Australian Government: Culture Portal|publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia|date=17 March 2008|accessdate=7 May 2010}}</ref>]] |
|||
[[File:Barossa Valley South Australia.jpg|right|thumb|alt=Ariel view of farming fields interspersed with roads, a small forest near the front of the photo|The [[Barossa Valley (wine)|Barossa Valley]] is a [[Australian wine|wine-producing]] region in [[South Australian wine|South Australia]]. Fewer than 15% of Australians live in rural areas.]] |
|||
Although Australia has no official language, English is so entrenched that it has become the de facto national language.<ref name=language>{{cite web|url=http://www.immi.gov.au/media/publications/multicultural/confer/04/speech18b.htm|title=Pluralist Nations: Pluralist Language Policies?|work=1995 Global Cultural Diversity Conference Proceedings, Sydney|publisher=[[Department of Immigration and Citizenship]]|accessdate=11 January 2009}} "English has no de jure status but it is so entrenched as the common language that it is de facto the official language as well as the national language."</ref> [[Australian English]] is a major variety of the language with a distinctive accent and lexicon. Grammar and spelling are similar to that of [[British English]] with some notable exceptions.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nma.gov.au/libraries/attachments/exhibitions/vocabulary_of_australian_english/files/5471/Vocabulary%20of%20Australian%20English.pdf|title=The Vocabulary Of Australian English|last=Moore|first=Bruce|publisher=National Museum of Australia|accessdate=5 April 2010}}</ref> According to the 2006 census, English is the only language spoken in the home for close to 79% of the population. The next most common languages spoken at home are Italian (1.6%), Greek (1.3%) and Cantonese (1.2%);<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/Ausstats/abs@.nsf/7d12b0f6763c78caca257061001cc588/5a47791aa683b719ca257306000d536c!OpenDocument|title=Australians overall claim more than 250 ancestries, speak 400 languages at home: Census|last=Australian Bureau of Statistics|date=27 June 2007|work=Media Fact Sheet|publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics|accessdate=29 March 2010|location=Canberra}}</ref> a considerable proportion of first- and second-generation migrants are bilingual. A 2010-2011 study by the Australia Early Development Index found that the most common language spoken by children after English was Arabic, followed by Vietnamese, Greek, Chinese, and Hindi.<ref>[[Agence France-Presse]]/[[Jiji Press]], "Arabic Australia's second language", ''[[Japan Times]]'', 16 April 2011, p. 4.</ref> |
|||
At the 2021 census, English was the only language spoken in the home for 72% of the population. The next most common languages spoken at home were [[Mandarin Chinese|Mandarin]] (2.7%), [[Arabic language|Arabic]] (1.4%), [[Vietnamese language|Vietnamese]] (1.3%), [[Cantonese]] (1.2%) and [[Punjabi language|Punjabi]] (0.9%).<ref>{{Cite web |title=2021 Australia, Census All persons QuickStats |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/census/find-census-data/quickstats/2021/AUS |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240315155123/https://www.abs.gov.au/census/find-census-data/quickstats/2021/AUS |archive-date= 15 March 2024 }}</ref> |
|||
Between 200 and 300 [[Indigenous Australian languages]] are thought to have existed at the time of first European contact, of which only about 70 have survived. Many of these are exclusively spoken by older people; only 18 Indigenous languages are still spoken by all age groups.<ref name=nilsr>{{cite web |url=http://www.arts.gov.au/indigenous/national_indigenous_languages_survey_report_2005 |title=National Indigenous Languages Survey Report 2005 |publisher=Department of Communications, Information Technology and the Arts |accessdate=5 September 2009}}</ref> At the time of the 2006 Census, 52,000 Indigenous Australians, representing 12% of the Indigenous population, reported that they spoke an Indigenous language at home.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/mf/4713.0 |title=4713.0 – Population Characteristics, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians, 2006 |last=Australian Bureau of Statistics |date=04/05/2010 |publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics |language=Canberra |accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref> Australia has a [[sign language]] known as [[Auslan]], which is the main language of about 5,500 deaf people.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.censusdata.abs.gov.au/ABSNavigation/prenav/ViewData?action=404&documentproductno=0&documenttype=Details&order=1&tabname=Details&areacode=0&issue=2006&producttype=Census%20Tables&javascript=true&textversion=false&navmapdisplayed=true&breadcrumb=POTLD&&collection=Census&period=2006&productlabel=Language%20Spoken%20at%20Home%20(full%20classification%20list)%20by%20Sex&producttype=Census%20Tables&method=Place%20of%20Usual%20Residence&topic=Language& |title=20680-Language Spoken at Home (full classification list) by Sex – Australia |last=Australian Bureau of Statistics |date=27 June 2007 |work=2006 Census Tables : Australia |location=Canberra |publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics |accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref> |
|||
More than 250 [[Australian Aboriginal languages]] are thought to have existed at the time of first European contact.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://www.arts.gov.au/what-we-do/indigenous-arts-and-languages/indigenous-languages-and-arts-program/national-indigenous-languages-report |title=National Indigenous Languages Report |publisher=Commonwealth of Australia |year=2020 |location=Canberra |pages=13}}</ref> The National Indigenous Languages Survey (NILS) for 2018–19 found that more than 120 Indigenous language varieties were in use or being revived, although 70 of those in use were endangered.<ref>National Indigenous Language Report (2020). pp. 42, 65</ref> The 2021 census found that 167 Indigenous languages were spoken at home by 76,978 Indigenous Australians — Yumplatok ([[Torres Strait Creole]]), [[Djambarrpuyngu]] (a [[Yolŋu languages|Yolŋu language]]) and [[Pitjantjatjara dialect|Pitjantjatjara]] (a [[Western Desert language]]) were among the most widely spoken.<ref>{{Cite web |date=28 June 2022 |title=Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people: Census |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/aboriginal-and-torres-strait-islander-peoples/aboriginal-and-torres-strait-islander-people-census/2021 |access-date=7 May 2023 |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics}}</ref> NILS and the Australian Bureau of Statistics use different classifications for Indigenous Australian languages.<ref>National Indigenous Languages Report (2020). p. 46</ref> |
|||
===Religion=== |
===Religion=== |
||
{{Main|Religion in Australia}} |
{{Main|Religion in Australia}} |
||
[[File:St Mary's Cathedral as viewed from Hyde Park, Sydney b.jpg|thumb|[[St Mary's Cathedral, Sydney|St Mary's Cathedral]] in Sydney belongs to the [[Catholic Church|Roman Catholic Church]], Australia's largest religious denomination.]] |
|||
Australia has no [[state religion]]. In the 2006 census, 64% of Australians listed themselves as [[Christian]], including 26% as [[Roman Catholicism in Australia|Roman Catholic]] and 19% as [[Anglican Communion|Anglican]]. About 19% of the population cited "[[Irreligion in Australia|No religion]]" (which includes [[secular humanism|humanism]], [[atheism]], [[agnosticism]], and [[rationalism]]), which was the fastest-growing group from 2001 to 2006, and a further 12% did not answer (the question is optional) or did not give a response adequate for interpretation. The largest non-Christian religion in Australia is [[Buddhism]] (2.1%), followed by [[Islam]] (1.7%), [[Hinduism]] (0.8%), and [[Judaism]] (0.5%). Overall, fewer than 6% of Australians identify with non-Christian religions.<ref name=religion>{{cite web |url=http://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/bb8db737e2af84b8ca2571780015701e/636F496B2B943F12CA2573D200109DA9?opendocument |title=Cultural Diversity |work=1301.0 – Year Book Australia, 2008 |publisher=[[Australian Bureau of Statistics]] |date=7 February 2008 |accessdate=23 January 2009}} (See subsection titled "Religion").</ref> Weekly attendance at church services in 2004 was about 1.5 million: about 7.5% of the population.<ref>[http://www.ncls.org.au/default.aspx?docid=2250&track=82083 NCLS releases latest estimates of church attendance], National Church Life Survey, Media release, 28 February 2004.</ref> |
|||
Australia has no [[state religion]]; section 116 of the [[Australian Constitution]] prohibits federal legislation |
|||
that would establish any religion, impose any religious observance, or prohibit the free exercise of any religion.<ref>{{Cite web |title=About Australia: Religious Freedom |url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/religion.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110806061716/http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/religion.html |archive-date=6 August 2011 |access-date=31 December 2011 |publisher=Dfat.gov.au}}</ref> However, the states still retain the power to pass religiously discriminatory laws.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Puls |first=Joshua |date=1998 |title=The Wall of Separation: Section 116, the First Amendment and Constitutional Religious Guarantees |url=https://www.austlii.edu.au/au/journals/FedLRev/1998/6.pdf |journal=Federal Law Review |page=160 |via=Austlii}}</ref> |
|||
At the 2021 census, 38.9% of the population identified as having [[Irreligion in Australia|no religion]],<ref name="Australian-Bureau-of-Statistics-2022">{{Cite web |date=2022 |title=General Community Profile |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/census/find-census-data/community-profiles/2021/AUS/download/GCP_AUS.xlsx |series=2021 Census of Population and Housing |publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics |type=[[Excel]] file}}</ref> up from 15.5% in 2001.<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://www.abs.gov.au/census/find-census-data/quickstats/2001/0 | title=2001 Australia, Census All persons QuickStats |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240308064233/https://www.abs.gov.au/census/find-census-data/quickstats/2001/0 |archive-date= 8 March 2024 }}</ref> The largest religion is [[Christianity]] (43.9% of the population).<ref name="Australian-Bureau-of-Statistics-2022"/> The largest Christian denominations are the [[Catholic Church in Australia|Roman Catholic Church]] (20% of the population) and the [[Anglican Church of Australia]] (9.8%). Non-British immigration since the [[Second World War]] has led to the growth of non-Christian religions, the largest of which are [[Islam]] (3.2%), [[Hinduism]] (2.7%), [[Buddhism]] (2.4%), [[Sikhism]] (0.8%), and [[Judaism]] (0.4%).<ref>{{Cite web |date=7 April 2022 |title=Religious affiliation in Australia |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/articles/religious-affiliation-australia |access-date= |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics |language=en}}</ref><ref name="Australian-Bureau-of-Statistics-2022"/> |
|||
Religion does not play a central role in the lives of much of the population.<ref>{{cite web |author=Stephanie Painter, Vivienne Ryan and Bethany Hiatt |url=http://au.news.yahoo.com/thewest/a/-/newshome/7399215/australians-losing-the-faith/ |title=Australians losing the faith |date=15 June 2010 |work=[[The West Australian]] |accessdate= 23 June 2010}}</ref> |
|||
In 2021, just under 8,000 people declared an affiliation with traditional Aboriginal religions.<ref name="Australian-Bureau-of-Statistics-2022"/> In [[Australian Aboriginal mythology]] and the [[animist]] framework developed in Aboriginal Australia, the [[Dreaming (spirituality)|Dreaming]] is a [[sacred]] era in which ancestral [[totem]]ic spirit beings formed [[Creation myth|The Creation]]. The Dreaming established the laws and structures of society and the ceremonies performed to ensure continuity of life and land.<ref>Flood, Josephine (2019). pp. 163–69</ref> |
|||
===Health=== |
|||
{{See also|Health care in Australia}} |
|||
Australia's life expectancy of 83 years (81 years for males and 85 years for females)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.LE00.IN?locations=AU |title=Life expectancy at birth, total (years) – Australia|publisher=[[World Bank]] |access-date=17 August 2022}}</ref> is the [[List of countries by life expectancy|fifth-highest in the world]]. It has the highest rate of skin cancer in the world,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.health.gov.au/internet/skincancer/publishing.nsf/Content/fact-2 |title=Skin cancer – key statistics|year=2008|publisher=[[Department of Health and Ageing]] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140208171642/http://www.health.gov.au/internet/skincancer/publishing.nsf/Content/fact-2 |archive-date=8 February 2014}}</ref> while [[Tobacco smoking|cigarette smoking]] is the largest preventable cause of death and disease, responsible for 7.8% of the total mortality and disease. Ranked second in preventable causes is [[hypertension]] at 7.6%, with obesity third at 7.5%.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.aihw.gov.au/publications/hwe/bodaiia03/bodaiia03-c05.pdf |title=Risks to health in Australia|website=Australian Institute of Health and Welfare|date=26 February 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110226105813/http://www.aihw.gov.au/publications/hwe/bodaiia03/bodaiia03-c05.pdf |archive-date=26 February 2011}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=19 February 2011 |title=quitnow – Smoking – A Leading Cause of Death |url=http://quitnow.info.au/internet/quitnow/publishing.nsf/Content/warnings-graph |access-date=15 January 2022 |website= |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110219073743/http://quitnow.info.au/internet/quitnow/publishing.nsf/Content/warnings-graph |archive-date=19 February 2011 |url-status=dead}}</ref> Australia ranked 35th in the world in 2012 for its proportion of obese women<ref>{{Cite web |title= Global prevalence of adult obesity | date=January 2012 |url=http://www.iaso.org/site_media/uploads/Global_prevalence_of_adult_obesity_Ranking_by_country_2012.pdf |access-date=15 January 2022 |website= |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120829014750/http://www.iaso.org/site_media/uploads/Global_prevalence_of_adult_obesity_Ranking_by_country_2012.pdf |archive-date=29 August 2012 |url-status=dead}}</ref> and near the top of [[Developed country|developed nations]] for its proportion of [[Obesity in Australia|obese]] adults;<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/Publishing.nsf/Content/health-pubhlth-strateg-hlthwt-obesity.htm |title=About Overweight and Obesity|publisher=Department of Health and Ageing |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100507033011/http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/health-pubhlth-strateg-hlthwt-obesity.htm |archive-date=7 May 2010 |url-status=dead |access-date=11 May 2010}}</ref> 63% of its adult population is either overweight or obese.<ref name="aihw">{{Cite web |url=http://www.aihw.gov.au/overweight-and-obesity |title=Overweight and obesity|date=25 February 2021 |publisher=Australian Institute of Health and Welfare}}</ref> |
|||
Australia spent around 9.91% of its total GDP to health care in 2021.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.XPD.CHEX.GD.ZS?locations=AU |title=Current healthcare expenditure (% of GDP) – Australia|publisher=[[World Bank]] |access-date=17 August 2022}}</ref> It introduced a [[National health insurance|national insurance scheme]] in 1975.<ref name="Biggs-2004">{{Cite web |url=http://www.aph.gov.au/library/intguide/SP/medicare.htm |title=Medicare – Background Brief|last=Biggs|first=Amanda|date=29 October 2004|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia|location=Canberra, ACT|work=Parliament of Australia: Parliamentary Library |access-date=16 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100414012007/http://www.aph.gov.au/library/intguide/SP/medicare.htm |archive-date=14 April 2010 |url-status=dead}}</ref> Following a period in which access to the scheme was restricted, the scheme became [[Universal health care|universal]] once more in 1981 under the name of [[Medicare (Australia)|Medicare]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=5 June 2020 |title=International Health Care System Profiles: Australia |url=https://www.commonwealthfund.org/international-health-policy-center/countries/australia |access-date=7 February 2024 |website=The Commonwealth Fund |language=en}}</ref> The program is nominally funded by an income tax surcharge known as the [[Medicare levy]], currently at 2%.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.ato.gov.au/Individuals/Medicare-levy |title=Medicare levy|publisher=Australian Taxation Office|date=18 October 2017 |access-date=9 April 2018 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130629085049/http://www.ato.gov.au/Individuals/Medicare-levy/ |archive-date=29 June 2013}}</ref> The states manage hospitals and attached outpatient services, while the Commonwealth funds the [[Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme]] (subsidising the costs of medicines) and [[general practice]].<ref name="Biggs-2004"/> |
|||
===Education=== |
===Education=== |
||
{{Main|Education in Australia}} |
{{Main|Education in Australia}} |
||
[[File:Parkville - University of Melbourne (Ormond College).jpg|thumb|upright|Australia has the highest ratio of international students per capita in the world, with Melbourne ranking fifth among the 2023 ''[[QS World University Rankings#QS Best Student Cities|QS Best Student Cities]]'' ([[University of Melbourne]] pictured).]] |
|||
{{Main|Tertiary education fees in Australia}} |
|||
School attendance, or registration for [[Homeschooling in Australia|home schooling]],<ref>{{Cite news|last1=Townsend|first1=Ian |title=Thousands of parents illegally home schooling|url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/2012-01-28/thousands-of-parents-illegally-home-schooling/3798008 |access-date=2 December 2015|work=ABC News|date=30 January 2012}}</ref> is compulsory throughout Australia. Education is primarily the responsibility of the individual states and territories; however, the Commonwealth has significant influence through funding agreements.<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Australian Education System |url=https://www.dfat.gov.au/sites/default/files/australian-education-system-foundation.pdf |access-date=6 February 2024 |publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade |pages=7–9}}</ref> Since 2014, a [[Australian Curriculum|national curriculum]] developed by the Commonwealth has been implemented by the states and territories.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Ross |first=Emily |date=18 November 2021 |title=Why do Australian states need a national curriculum, and do teachers even use it? |url=http://theconversation.com/why-do-australian-states-need-a-national-curriculum-and-do-teachers-even-use-it-171745 |access-date=6 February 2024 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US}}</ref> Attendance rules vary between states, but in general children are required to attend school from the age of about 5 until about 16.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.immi.gov.au/living-in-australia/settle-in-australia/everyday-life/education |title=Education|publisher=Department of Immigration and Citizenship |access-date=14 January 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140218220904/http://www.immi.gov.au/living-in-australia/settle-in-australia/everyday-life/education |archive-date=18 February 2014}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/education_in_australia.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110514101140/http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/education_in_australia.html |archive-date=14 May 2011 |title=Our system of education|publisher=Australian Government: Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade |access-date=13 January 2012}}</ref> In some states (Western Australia, Northern Territory and New South Wales), children aged 16–17 are required to either attend school or participate in vocational training, such as an [[apprenticeship]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://det.wa.edu.au/schoolsandyou/detcms/navigation/parents-and-community/schooling/?oid=Category-id-3869597 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120321204923/http://det.wa.edu.au/schoolsandyou/detcms/navigation/parents-and-community/schooling/?oid=Category-id-3869597 |archive-date=21 March 2012 |title=The Department of Education – Schools and You – Schooling|website=det.wa.edu.au |access-date=31 December 2011}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Education Act (NT) – Section 20 |url=http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/nt/consol_act/ea104/s20.html|website=austlii.edu.au}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Education Act 1990 (NSW) – Section 21 |url=http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/nsw/consol_act/ea1990104/s21b.html|work=austlii.edu.au}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Minimum school leaving age jumps to 17|url=http://news.theage.com.au/breaking-news-national/minimum-school-leaving-age-jumps-to-17-20090128-7r4d.html|publisher=The Age |access-date=30 May 2013|date=28 January 2009}}</ref> According to the 2022 [[PISA]] evaluations, Australian 15-year-olds ranked ninth in the OECD for reading and science and tenth for maths. However, less than 60% of Australian students achieved the National Proficiency Standard – 51% in maths, 58% in science and 57% in reading.<ref>{{Cite web |date=4 December 2023 |title=PISA 2022 Results (Volume I and II) - Country Notes: Australia |url=https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/2023/11/pisa-2022-results-volume-i-and-ii-country-notes_2fca04b9/australia_aa76963a.html |access-date=31 July 2024 |website= |publisher=OECD |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Long |first=Claudia |date=6 December 2023 |title=Australia is now in the world's top 10 academic performers – but the data paints a complex picture |url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2023-12-05/pisa-international-school-rankings-in-maths-science-reading/103185468 |access-date=31 July 2024 |work=ABC News Australia}}</ref> |
|||
School attendance is compulsory throughout Australia. All children receive 11 years of compulsory education from the age of 6 to 16 (Year 1 to 10),<ref name="aei">{{cite web |url=http://www.aei.gov.au/AEI/CEP/Australia/EducationSystem/Overview/default.htm |publisher=Australia Education International – Australian Government |title=Overview of education system, Australia |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> before they can undertake two more years (Years 11 and 12), contributing to an adult literacy rate that is assumed to be 99%. A [[kindergarten|preparatory year]] prior to Year 1, although not compulsory, is almost universally undertaken.<ref name="aei"/> In the [[Programme for International Student Assessment]], Australia regularly scores among the top five of thirty major developed countries (member countries of the [[Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development]]). Government grants have supported the establishment of Australia's 38 universities; all but one is public.{{cn|date=April 2011}} [[OECD]] places Australia as among the most expensive nations to attend university.<ref>http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/44/35/37376068.pdf</ref> There is a state-based system of vocational training, known as [[Technical and Further Education|TAFE Institutes]], and many trades conduct apprenticeships for training new tradespeople.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://replay.web.archive.org/20091111234035/http://www.australianapprenticeships.gov.au/about/default.asp |title=About Australian Apprenticeships |publisher=Australian Government |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Approximately 58% of Australians aged from 25 to 64 have vocational or tertiary qualifications,<ref name="Year Book 2005"/> and the tertiary graduation rate of 49% is the highest among OECD countries. The ratio of international to local students in tertiary education in Australia is the highest in the OECD countries.<ref>[http://www.ecs.org/html/offsite.asp?document=http%3A%2F%2Fwww%2Eoecd%2Eorg%2Fdataoecd%2F20%2F25%2F35345692%2Epdf Education at Glance 2005] by OECD: Percentage of foreign students in tertiary education.</ref> |
|||
Australia has an adult literacy rate that was estimated to be 99% in 2003.<ref name=cialittab>{{Cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2103.html#136 |title=Literacy|work=CIA World Factbook |access-date=10 October 2013 |archive-date=24 November 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161124171442/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2103.html#136 |url-status=dead}}</ref> However, a 2011–2012 report for the Australian Bureau of Statistics found that 44% of the population does not have high literary and numeracy competence levels, interpreted by others as suggesting that they do not have the "skills needed for everyday life".<ref>{{Cite web |date=9 October 2013 |title=Programme for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies, Australia |url=https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/education/programme-international-assessment-adult-competencies-australia/latest-release |website=Australian Bureau of Statistics}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.abc.net.au/radionational/programs/backgroundbriefing/2013-09-22/4962902 |title=A literacy deficit|website=abc.net.au|date=22 September 2013 |access-date=10 October 2013}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=12 April 2021 |title=Australia's adult literacy crisis |url=https://ala.asn.au/stories/australias-adult-literacy-crisis/ |access-date=26 January 2024 |website=Adult Learning Australia |language=en-US}}</ref> |
|||
===Health=== |
|||
{{Main|Health care in Australia}} |
|||
Life expectancy in Australia is relatively high, with figures of 78.7 years for males and 83.5 years for females born in 2006.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.aihw.gov.au/mortality/life_expectancy/index.cfm |title=Life expectancy |publisher=Australian Institute of Health and Welfare |accessdate=11 May 2010}}</ref> Australia has the highest rates of skin cancer in the world,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.health.gov.au/internet/skincancer/publishing.nsf/Content/fact-2 |title=Skin cancer – key statistics |year=2008 |publisher=[[Department of Health and Ageing]] |accessdate=11 May 2010}}</ref> while [[cigarette smoking]] is the largest preventable cause of death and disease.<ref>[http://www.quitnow.info.au/internet/quitnow/publishing.nsf/content/warnings-graph Smoking – A Leading Cause of Death] The National Tobacco Campaign. Retrieved 17 October 2007.</ref> Australia has one of the [[Obesity in Australia|highest proportions]] of overweight citizens amongst [[Developed country|developed nations]];<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/Publishing.nsf/Content/health-pubhlth-strateg-hlthwt-obesity.htm |title=About Overweight and Obesity |publisher=Department of Health and Ageing|accessdate=11 May 2010}}</ref> it has also been one of the most successful in managing the spread of [[HIV/AIDS in Australia|HIV/AIDS]].<ref>{{cite book |last=Bowtell |first=William |title=Australia’s Response to HIV/AIDS 1982–2005 |publisher=Lowy Institute for International Policy |year=2005}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Plummer |first=D. |coauthors=Irwin, L. |title=Grassroots activities, national initiatives and HIV prevention: clues to explain Australia's dramatic early success in controlling the HIV epidemic |journal=International Journal of STD & AIDS |volume=17 |issue=12 |year=2006 |pages=787–793 |doi=10.1258/095646206779307612 |pmid=17212850}}</ref> |
|||
Australia has 37 government-funded universities and three private universities, as well as a number of other specialist institutions that provide approved courses at the higher education level.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.ausitaleem.com.pk/australian-education-system.shtml |title=Australian Education {{pipe}} Australian Education System {{pipe}} Education {{pipe}} Study in Australia|publisher=Ausitaleem.com.pk |access-date=31 December 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120119063252/http://www.ausitaleem.com.pk/australian-education-system.shtml |archive-date=19 January 2012}}</ref> The OECD places Australia among the most expensive nations to attend university.<ref>[http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/44/35/37376068.pdf Education at a Glance 2006] {{Webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102101942/http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/44/35/37376068.pdf|date=2 January 2016}} Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development</ref> There is a state-based system of vocational training, known as [[Technical and further education|TAFE]], and many trades conduct apprenticeships for training new tradespeople.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.australianapprenticeships.gov.au/about/default.asp |title=About Australian Apprenticeships|publisher=Australian Government |access-date=23 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091111234035/http://www.australianapprenticeships.gov.au/about/default.asp |archive-date=11 November 2009}}</ref> About 58% of Australians aged from 25 to 64 have vocational or tertiary qualifications<ref>{{Cite web|website=Australian Bureau of Statistics|url=http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/94713ad445ff1425ca25682000192af2/1a79e7ae231704f8ca256f720082feb9!OpenDocument |title=Year Book Australia 2005 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160409132916/http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs%40.nsf/94713ad445ff1425ca25682000192af2/1a79e7ae231704f8ca256f720082feb9%21OpenDocument |archive-date=9 April 2016 |date=21 January 2005 }}</ref> and the tertiary graduation rate of 49% is the highest among OECD countries. 30.9% of Australia's population has attained a higher education qualification, which is among the highest percentages in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://finance.yahoo.com/news/the-most-educated-countries-in-the-world.html;_ylt=AlaWy8IcyeBaviKi7_.WJyhE6odG;_ylu=X3oDMTJrY2d2NGZyBG1pdANDeFMgRmluYW5jaWFsbHkgRml0IEFydGljbGUgQXJ0aWNsZSBCb2R5IFByb2QEcG9zAzMEc2VjA01lZGlhQXJ0aWNsZUJvZHlBc3NlbWJseQ--;_ylg=X3oDMTNjdGVoaXJqBGludGwDdXMEbGFuZwNlbi11cwRwc3RhaWQDY2IyOTRhMGEtYmY2OS0zYTdlLThlYTUtZWFlNTU3YWI1ZTc3BHBzdGNhdANleGNsdXNpdmVzfGZpbmFuY2lhbGx5Zml0BHB0A3N0b3J5cGFnZQ--;_ylv=3?page=1 |title=The Most Educated Countries in the World – Yahoo Finance|last=Sauter|first=Michael B.|publisher=Finance.yahoo.com|date=24 September 2012 |access-date=14 November 2015 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160204213400/http://finance.yahoo.com/news/the-most-educated-countries-in-the-world.html%3B_ylt%3DAlaWy8IcyeBaviKi7_.WJyhE6odG%3B_ylu%3DX3oDMTJrY2d2NGZyBG1pdANDeFMgRmluYW5jaWFsbHkgRml0IEFydGljbGUgQXJ0aWNsZSBCb2R5IFByb2QEcG9zAzMEc2VjA01lZGlhQXJ0aWNsZUJvZHlBc3NlbWJseQ--%3B_ylg%3DX3oDMTNjdGVoaXJqBGludGwDdXMEbGFuZwNlbi11cwRwc3RhaWQDY2IyOTRhMGEtYmY2OS0zYTdlLThlYTUtZWFlNTU3YWI1ZTc3BHBzdGNhdANleGNsdXNpdmVzfGZpbmFuY2lhbGx5Zml0BHB0A3N0b3J5cGFnZQ--%3B_ylv%3D3?page=1 |archive-date=4 February 2016}}</ref><ref>{{Cite magazine|url=https://newsfeed.time.com/2012/09/27/and-the-worlds-most-educated-country-is/ |title=And the World's Most Educated Country Is ...|magazine=Time|first=Samantha |last=Grossman|date=27 September 2012 |access-date=14 November 2015}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.censusdata.abs.gov.au/census_services/getproduct/census/2016/quickstat/036 |title=2016 Census QuickStats: Australia |website=censusdata.abs.gov.au |access-date=14 February 2018 |archive-date=20 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180620052901/http://www.censusdata.abs.gov.au/census_services/getproduct/census/2016/quickstat/036 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
Australia introduced [[universal health care]], known as Medibank, in 1975.<ref name="medicbrief">{{cite web |url=http://www.aph.gov.au/library/intguide/SP/medicare.htm |title=Medicare – Background Brief |last=Biggs |first=Amanda |date=29 October 2004 |work=Parliament of Australia: Parliamentary Library |publisher=Commonwealth of Australia |accessdate=16 April 2010 |location=Canberra, ACT}}</ref> Reworked by successive governments, its current incarnation, [[Medicare (Australia)|Medicare]] came into existence in 1984. It is now nominally funded by an income tax surcharge known as the ''Medicare levy'', currently set at 1.5%.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ato.gov.au/individuals/content.asp?doc=/content/17482.htm&pc=001/002/030/003/001&mnu=&mfp=&st=&cy=1 |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20080610171946/http://www.ato.gov.au/individuals/content.asp?doc=/content/17482.htm&pc=001/002/030/003/001&mnu=&mfp=&st=&cy=1 |archivedate=2008-06-10 |title=What is the Medicare levy? |accessdate=17 April 2010 |author=Australian Taxation Office |work=Australian Taxation Office website |publisher=Australian Government |date=19 June 2007}}</ref> Traditionally, the management of public health has been split between the state and federal governments. The states manage hospitals and attached outpatient services, while the commonwealth funds the [[Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme]] (reducing the costs of medicines) and general practice.<ref name="medicbrief"/> Under the Rudd government, a health reform plan has emerged which will allow the federal government to take "full responsibility for primary health care", essentially taking control of hospitals and outpatient services from the states.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.news.com.au/national/kevin-rudd-outlines-radical-health-care-reform/story-e6frfkvr-1225836517546 |author=Staff writers and wires |publisher=news.com.au |date=3 March 2010 |accessdate=18 April 2010 |title=Kevin Rudd to take control of primary health care under reform plan}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Kevin Rudd to take control of primary health care under reform plan |date=12 April 2010 |publisher=Australian Associated Press |url=http://www.news.com.au/breaking-news/kevin-rudd-to-take-control-of-primary-health-care-under-reform-plan/story-e6frfku0-1225852712033 |accessdate=18 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=PM eyes last-ditch deal: possible sweeteners for states |url=http://www.smh.com.au/national/pm-eyes-lastditch-deal-possible-sweeteners-for-states-20100417-slh9.html |last=Peatling |first=Stephanie |date=18 April 2010 |accessdate=18 April 2010 |work=[[The Sydney Morning Herald]]}}</ref> Total expenditure on health (including private sector spending) is around 9.8 per cent of GDP.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/healthcare.html |title=Health care in Australia |year=2008 |work=About Australia |publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade |accessdate=11 May 2010}}</ref> |
|||
Australia has the highest ratio of [[International students in Australia|international students]] per head of population in the world by a large margin, with 812,000 international students enrolled in the nation's universities and vocational institutions in 2019.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.theaustralian.com.au/subscribe/news/1/?sourceCode=TAWEB_WRE170_a&dest=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.theaustralian.com.au%2Fbusiness%2Fproperty%2Fbooming-student-market-a-valuable-property%2Fnews-story%2F6bb3823260aa3443f0c26909406d089b&memtype=anonymous&mode=premium&nk=5cfb870de12779cf853780286e352a51-1587312248 |title=Subscribe to The Australian {{pipe}} Newspaper home delivery, website, iPad, iPhone & Android apps|website=theaustralian.com.au}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.macrobusiness.com.au/2019/11/australian-universities-double-down-on-international-students |title=Australian universities double down on international students|first1=Leith van OnselenLeith van Onselen is Chief Economist at the MB|last1=Fund|first2=MB Super Leith has previously worked at the Australian|last2=Treasury|first3=Victorian |last3=Treasury|first4=Goldman|last4=Sachs|date=31 October 2019|website=MacroBusiness}}</ref> Accordingly, in 2019, international students represented on average 26.7% of the student bodies of Australian universities. International education therefore represents one of the country's largest exports and has a pronounced influence on the country's demographics, with a significant proportion of international students remaining in Australia after graduation on various skill and employment visas.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2018-07-27/temporary-graduate-visa-485-boom/10035390 |title=Record number of international students sticking around on work visas|first=political reporter Jackson|last=Gothe-Snape|date=27 July 2018|newspaper=ABC News}}</ref> Education is Australia's third-largest export, after iron ore and coal, and contributed more than $28 billion to the economy in the 2016–17 financial year.<ref group="N">That is, 1 July 2016 to 30 June 2017.</ref><ref name="Berthold-2021"/> |
|||
==Culture== |
==Culture== |
||
{{Main|Culture of Australia}} |
{{Main|Culture of Australia}} |
||
[[File:Sydney Opera House, botanic gardens 1.jpg|thumb|The [[Sydney Opera House]] was completed in 1973 and declared a UNESCO [[World Heritage Site]] in 2007, making it the youngest building to have received the designation.<ref>''[[Architect Magazine]]'' (August 2007), '''96''' (11), p. 14</ref>]] |
|||
[[File:Royal exhibition building tulips straight.jpg|thumb|left|alt=Ornate white building with an elevated dome in the middle, fronted by a golden fountain and orange flowers|The [[Royal Exhibition Building]] in Melbourne was the first building in Australia to be listed as a UNESCO [[World Heritage Site]] in 2004<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.dfat.gov.au/facts/world_heritage.html |title=About Australia: World Heritage properties|publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade |date= |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref>]] |
|||
Contemporary Australian culture reflects the [[Australian Aboriginal culture|country's Indigenous traditions]], [[Culture of the United Kingdom|Anglo-Celtic heritage]], and post-1945 history of [[multiculturalism in Australia|multicultural immigration]].<ref>{{Harvnb|Jupp1|pp=796–802}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Teo|White|2003|pp=118–20}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Jupp1|pp=808–12, 74–77}}</ref> The [[culture of the United States]] has also been influential.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=White |first1=Richard |date=1 January 1983 |title=A Backwater Awash: The Australian Experience of Americanisation |journal=Theory, Culture and Society |volume=1 |issue=3 |pages=108–122 |doi=10.1177/026327648300100309 |s2cid=144339300}}</ref> The evolution of Australian culture since British colonisation has given rise to distinctive cultural traits.<ref name="Davison pp98–92">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|pages=98–99}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Teo|White|2003|pp=125–27}}</ref> |
|||
Since 1788, the basis of Australian culture has been strongly influenced by [[Anglo-Celtic]] [[Western culture]].<ref>Jupp, pp. 796–802.</ref><ref>Teo and White, pp. 118–20.</ref> Distinctive cultural features have also arisen from Australia's natural environment and Indigenous cultures.<ref name=bush>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 98–99.</ref><ref>Teo and White, pp. 125–27.</ref> Since the mid-20th century, [[Culture of the United States|American popular culture]] has strongly influenced Australia, particularly through television and cinema.<ref name=tw>Teo and White, pp. 121–23.</ref> Other cultural influences come from neighbouring Asian countries, and through large-scale immigration from non-English-speaking nations.<ref name=tw/><ref>Jupp, pp. 808–12, 74–77.</ref> |
|||
Many Australians identify [[egalitarianism]], [[mateship]], irreverence and a lack of formality as part of their [[national identity]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Cultural life |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Australia/Cultural-life |access-date=5 February 2024 |website=www.britannica.com |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2016 |title=Australian Culture: Core Concepts |url=https://culturalatlas.sbs.com.au/australian-culture/australian-culture-core-concepts |access-date=5 February 2024 |website=Cultural Atlas |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Australian Citizenship: Our Common Bond |url=https://immi.homeaffairs.gov.au/citizenship-subsite/files/our-common-bond-testable.pdf |publisher=Australian Government |page=36}}</ref> These find expression in [[Australian slang]], as well as [[Australian comedy|Australian humour]], which is often characterised as dry, irreverent and ironic.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Luu |first=Chi |date=7 February 2018 |title=Small Poppy Syndrome: Why are Australians so Obsessed With Nicknaming Things? |url=https://daily.jstor.org/australians-obsessed-nicknaming/ |access-date=12 February 2024 |website=JSTOR Daily |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Kidd |first1=Evan |last2=Kemp |first2=Nenagh |author-link2=Nenagh Kemp |last3=Kashima |first3=Emiko S. |last4=Quinn |first4=Sara |date=June 2016 |title=Language, Culture, and Group Membership: An Investigation Into the Social Effects of Colloquial Australian English |url=http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0022022116638175 |journal=Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology |language=en |volume=47 |issue=5 |pages=713–733 |doi=10.1177/0022022116638175 |issn=0022-0221 |s2cid=147360478 |url-access=subscription |hdl-access=free |hdl=11858/00-001M-0000-002E-24A7-F}}</ref> New citizens and visa holders are required to commit to "Australian values", which are identified by the [[Department of Home Affairs (Australia)|Department of Home Affairs]] as including: a respect for the freedom of the individual; recognition of the rule of law; opposition to racial, gender and religious discrimination; and an understanding of the "[[:wikt:fair go|fair go]]", which is said to encompass the equality of opportunity for all and compassion for those in need.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Meeting our requirements: Australian values |url=https://immi.homeaffairs.gov.au/help-support/meeting-our-requirements/australian-values |access-date=6 February 2024 |publisher=Department of Home Affairs}}</ref> What these values mean, and whether or not Australians uphold them, has been debated since before Federation.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Snow |first=Deborah |date=18 January 2019 |title=Australian values: what the bloody hell are they? |url=https://www.smh.com.au/national/australian-values-what-the-bloody-hell-are-they-20190118-p50s76.html |access-date=6 February 2024 |website=The Sydney Morning Herald |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Dyrenfurth |first=Nick |date=June 2007 |title=John Howard's Hegemony of Values: The Politics of 'Mateship' in the Howard Decade |url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10361140701319994 |journal=Australian Journal of Political Science |language=en |volume=42 |issue=2 |pages=211–230 |doi=10.1080/10361140701319994 |s2cid=154041199 |issn=1036-1146 |url-access=subscription}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Crowe |first=Shaun |date=14 January 2015 |title=Book review: Mateship – A Very Australian History |url=http://theconversation.com/book-review-mateship-a-very-australian-history-35858 |access-date=6 February 2024 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Zhuang |first=Yan |date=19 November 2021 |title=What Does Mateship Mean to You? |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2021/11/19/world/asia/what-does-mateship-mean-to-you.html |work=New York Times}}</ref> |
|||
===Arts=== |
===Arts=== |
||
{{Main| |
{{Main|Australian art|Australian literature|Theatre of Australia|Dance in Australia|Music of Australia}} |
||
[[File:Sidney Nolan Snake.jpg|thumb|Held at the [[Museum of Old and New Art]] in Hobart, Tasmania, [[Sidney Nolan]]'s ''[[Snake (Nolan)|Snake]]'' mural (1970) is inspired by the Aboriginal creation myth of the [[Rainbow Serpent]], as well as desert flowers in bloom after a drought.<ref>"Sidney Nolan's Rainbow Serpent is larger than life" (16 June 2012), ''The Australasian''.</ref>]] |
|||
[[File:Sunlight Sweet Coogee Arthur Streeton.jpg|thumb|upright|alt=Painting of a woman in and orange coat with a broad brimmed yellow hat standing on a cliff above a beach, with the bush visible in the background|''Sunlight Sweet'' by Australian [[landscape]] artist [[Arthur Streeton]].]] |
|||
Australia has more than 100,000 [[Indigenous Australian art#Stone art|Aboriginal rock art]] sites,<ref>Tacon, Paul S. C.; Ouzman, Sven (2004). "Worlds within stone: the inner and outer rock-art landscapes of northern Australia and southern Africa". In Nash, George; Chippindale, Christopher (ed.). ''The Figured Landscapes of Rock-Art: Looking at Pictures in Place''. Cambridge University Press. pp. 39–68. 9780521524247.</ref> and traditional designs, patterns and stories infuse [[contemporary Indigenous Australian art]], "the last great art movement of the 20th century" according to critic [[Robert Hughes (critic)|Robert Hughes]];<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2005/11/06/arts/06iht-aborigine.html |title=Powerful growth of Aboriginal art |last=Henly |first=Susan Gough |date=6 November 2005 |work=The New York Times}}</ref> its exponents include [[Emily Kame Kngwarreye]].<ref>Smith, Terry (1996). "Kngwarreye Woman, Abstract Painter", p. 24 in ''Emily Kngwarreye – Paintings'', North Ryde NSW: Craftsman House / G + B Arts International. {{ISBN|978-90-5703-681-1}}.</ref> Early colonial artists showed a fascination with the unfamiliar land.<ref name="wwwartgallerynswgovau"/> The [[impressionism|impressionistic]] works of [[Arthur Streeton]], [[Tom Roberts]] and other members of the 19th-century [[Heidelberg School]]—the first "distinctively Australian" movement in Western art—gave expression to nationalist sentiments in the lead-up to Federation.<ref name="wwwartgallerynswgovau">{{Cite web |title=Collection {{pipe}} Art Gallery of NSW|url=https://www.artgallery.nsw.gov.au/collection/ |access-date=15 January 2022|website=www.artgallery.nsw.gov.au}}</ref> While the school remained influential into the 1900s, [[modern art|modernists]] such as [[Margaret Preston]] and [[Clarice Beckett]], and, later, [[Sidney Nolan]], explored new artistic trends.<ref name="wwwartgallerynswgovau"/> The landscape remained central to the work of Aboriginal watercolourist [[Albert Namatjira]],<ref>Sayers, Andrew (2001). ''Australian Art''. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. pp. 78–88. {{ISBN|978-0-19-284214-5}}.</ref> as well as [[Fred Williams (artist)|Fred Williams]], [[Brett Whiteley]] and other post-war artists whose works, eclectic in style yet uniquely Australian, moved between the [[figurative art|figurative]] and the [[abstract art|abstract]].<ref name="wwwartgallerynswgovau"/><ref>{{Cite web |title=Brett Whiteley: nature :: Art Gallery NSW|url=https://www.artgallery.nsw.gov.au/exhibitions/brett-whiteley-nature/ |access-date=15 January 2022|website=www.artgallery.nsw.gov.au}}</ref> |
|||
[[Visual arts of Australia|Australian visual arts]] are thought to have begun with the [[cave painting|cave]] and [[bark painting]]s of its Indigenous peoples. The traditions of Indigenous Australians are largely transmitted orally, through ceremony and the telling of [[Dreamtime]] stories.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://journal.oraltradition.org/files/articles/1ii/3_ross.pdf |title=Australian Aboriginal Oral Traditions |last=Ross |first=Margaret Clunies |year=1986 |publisher=Center for Study in Oral Tradition |accessdate=4 April 2010}}</ref> From the time of European settlement, a theme in [[Visual arts of Australia|Australian art]] has been the natural landscape,<ref name=bush/> seen for example in the works of [[Albert Namatjira]],<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 452.</ref> [[Arthur Streeton]] and others associated with the [[Heidelberg School]],<ref name=bush/> and [[Arthur Boyd]].<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 85.</ref> |
|||
[[Australian literature]] grew slowly in the decades following European settlement though Indigenous [[oral tradition]]s, many of which have since been recorded in writing, are much older.<ref>Sarwal, Amit; Sarwal, Reema (2009). ''Reading Down Under: Australian Literary Studies Reader''. SSS Publications. p. xii. {{ISBN|978-8-1902-2821-3}}.</ref> In the 19th century, [[Henry Lawson]] and [[Banjo Paterson]] captured the experience of [[Australian bush|the bush]] using a distinctive Australian vocabulary.<ref>Mulligan, Martin; Hill, Stuart (2001). ''Ecological Pioneers: A Social History of Australian Ecological Thought and Action''. Cambridge University Press. {{ISBN|978-0-5210-0956-0}}, p. 72.</ref> Their works are still popular; Paterson's [[bush poetry|bush poem]] "[[Waltzing Matilda]]" (1895) is regarded as Australia's unofficial national anthem.<ref>O'Keeffe, Dennis (2012). ''Waltzing Matilda: The Secret History of Australia's Favourite Song''. [[Allen & Unwin]]. p. back cover. {{ISBN|978-1-7423-7706-3}}.</ref> [[Miles Franklin]] is the namesake of Australia's [[Miles Franklin Award|most prestigious literary prize]], awarded annually to the best novel about Australian life.<ref>{{Cite web |date=27 February 2012 |title=The Miles Franklin Literary Award – australia.gov.au |url=http://australia.gov.au/about-australia/australian-story/miles-franklin-literary-award |access-date=15 January 2022 |website= |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120227135804/http://australia.gov.au/about-australia/australian-story/miles-franklin-literary-award |archive-date=27 February 2012 |url-status=dead}}</ref> Its first recipient, [[Patrick White]], went on to win the [[Nobel Prize in Literature]] in 1973.<ref>[http://www.australia.gov.au/about-australia/australian-story/australias-nobel-laureates Australia's Nobel Laureates and the Nobel Prize] {{Webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160819205739/http://www.australia.gov.au/about-australia/australian-story/australias-nobel-laureates |date=19 August 2016 }}, australia.gov.au. Retrieved 17 April 2015.</ref> Australian [[Booker Prize]] winners include [[Peter Carey (novelist)|Peter Carey]], [[Thomas Keneally]] and [[Richard Flanagan]].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Hughes-d'Aeth|first=Tony |title=Australia's Booker prize record suggests others will come in Flanagan's wake|url=http://theconversation.com/australias-booker-prize-record-suggests-others-will-come-in-flanagans-wake-33025 |access-date=15 January 2022|website=The Conversation |date=15 October 2014 |language=en}}</ref> Australian public intellectuals have also written seminal works in their respective fields, including feminist [[Germaine Greer]] and philosopher [[Peter Singer]].<ref>Williams, Robyn (12 November 2016). [https://www.abc.net.au/news/2016-11-12/three-books-australian-authors-changed-20th-century/8008380 "Three Australian books that changed history"], ABC Radio National. Retrieved 12 November 2016.</ref> |
|||
The country's landscape remains a source of inspiration for Australian modernist artists; it has been depicted in acclaimed works by the likes of [[Sidney Nolan]],<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 469–70.</ref> [[Fred Williams]],<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 686–87.</ref> [[Sydney Long]],<ref>Smith and Smith, pp. 97–103.</ref> and [[Clifton Pugh]].<ref>Smith and Smith, pp. 323–28, 407–08.</ref> Australian artists influenced by modern American and European art include [[cubist]] [[Grace Crowley]],<ref>Smith and Smith, pp. 208–12.</ref> [[surrealist]] [[James Gleeson]],<ref>Smith and Smith, pp. 226–233.</ref> and [[pop art]]ist [[Martin Sharp]].<ref>Smith and Smith, pp. 397–403.</ref> [[Contemporary Indigenous Australian art]] is the only art movement of international significance to emerge from Australia<ref name="Bell08">{{Cite journal |last=Bell |first=Richard |year=2008 |title=We're not allowed to own anything |journal=Art and Australia |volume=46 |issue=2 |pages=228–229}}</ref><ref>Michael Pickering, 'Sand, seed, hair and paint', in Johnson 2007, p. 1.</ref> and "the last great art movement of the 20th century";<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2005/11/06/arts/06iht-aborigine.html |title=Powerful growth of Aboriginal art |last=Henly |first=Susan Gough |date=6 November 2005 |work=The New York Times |accessdate=11 May 2010}}</ref> its exponents have included [[Emily Kngwarreye]].<ref>McCulloch ''et al.'', p. 88.</ref><ref>Terry Smith, 'Kngwarreye Woman, Abstract Painter', in ''Emily Kngwarreye – Paintings'', p. 24.</ref> Art critic [[Robert Hughes (critic)|Robert Hughes]] has written several influential books about Australian history and art, and was described as the "world's most famous art critic" by ''[[The New York Times]]''.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.abc.net.au/rn/arts/sunmorn/stories/s1509883.htm |title=The Critics part 5 – Robert Hughes |last=Copeland |first=Julie |date=20 November 2005 |work=Sunday Morning |publisher=Australian Broadcasting Corporation |accessdate=11 May 2010}}</ref> The [[National Gallery of Australia]] and state galleries maintain Australian and overseas collections.<ref>Germaine, pp. 756–58, 796–97, 809–10, 814–15, 819–20, 826–27, 829–30.</ref> |
|||
[[File:ACDC-Hughes-long ago.jpg|thumb|upright|Arising from the [[Pub rock (Australia)|Australian pub rock]] scene, [[AC/DC]] ranks among the world's [[List of best-selling music artists|best-selling music acts]].]] |
|||
{{Main|Theatre of Australia|Dance in Australia}} |
|||
Many of Australia's performing arts companies receive funding through the |
In the performing arts, Aboriginal peoples have traditions of religious and secular song, dance and rhythmic music often performed in [[corroboree]]s.<ref>Flood (2019). pp. 62, 64-5</ref> At the beginning of the 20th century, [[Nellie Melba]] was one of the world's leading opera singers,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.themonthly.com.au/encounters-shane-maloney-nellie-melba-enrico-caruso--160 |title=Nellie Melba & Enrico Caruso |work=[[The Monthly]]|author=Maloney, Shane |date= January 2006 |access-date=23 April 2010}}</ref> and later popular music acts such as the [[Bee Gees]], [[AC/DC]], [[INXS]] and [[Kylie Minogue]] achieved international recognition.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Compagnoni |first=Tom |date=4 September 2022 |title=The 43-year-old invention behind 2022's biggest music sensation |url=https://www.smh.com.au/culture/music/the-sydney-invention-that-transformed-the-sound-of-music-20220904-p5bf93.html |website=The Sydney Morning Herald}}</ref> Many of Australia's performing arts companies receive funding through the Australian government's [[Australia Council for the Arts|Australia Council]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.australiacouncil.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/13753/Australia_Council_for_the_Arts_-_Funding_Guide_2010.pdf |year=2010 |title=Arts funding guide 2010 |publisher=[[Australia Council]] |access-date=14 June 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100705002654/http://www.australiacouncil.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/13753/Australia_Council_for_the_Arts_-_Funding_Guide_2010.pdf |archive-date=5 July 2010 |url-status=dead}}</ref> There is a symphony orchestra in each state,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.australiacouncil.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0011/50231/LECG_Orchestras_Review_evaluation_summary.pdf |title=Evaluation of the Orchestras Review 2005 funding package implementation |access-date=23 April 2010 |publisher=Australia Council |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110314080534/http://www.australiacouncil.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0011/50231/LECG_Orchestras_Review_evaluation_summary.pdf |archive-date=14 March 2011 }}</ref> and a national opera company, [[Opera Australia]],<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.australiacouncil.gov.au/the_arts/artists_and_orgs/artists/opera_australia |title=Opera Australia |publisher=Australia Council |access-date=23 April 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080723135113/http://www.australiacouncil.gov.au/the_arts/artists_and_orgs/artists/opera_australia |archive-date=23 July 2008 }}</ref> well known for its famous [[soprano]] [[Joan Sutherland]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/music/opera |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110406111552/http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/music/opera |archive-date=6 April 2011 |title=Opera in Australia |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |date=5 March 2007}}</ref> Ballet and dance are represented by [[The Australian Ballet]] and various state companies. Each state has a publicly funded theatre company.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.minister.dbcde.gov.au/brandis/media/media_releases/2007/35_per_cent_increase_in_funding_for_australias_major_performing_arts_companies |title=35 per cent increase in funding for Australia's major performing arts companies |author=Brandis, George |publisher=Department of Communications, Information Technology and the Arts |date=8 May 2007 |access-date=23 April 2010 |author-link=George Brandis |archive-url=https://webarchive.nla.gov.au/awa/20071112025600/http://pandora.nla.gov.au/pan/36698/20071112-1356/www.minister.dcita.gov.au/brandis/media/media_releases/2007/35_per_cent_increase_in_funding_for_australias_major_performing_arts_companies.html |archive-date=12 November 2007}}{{Cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> |
||
[[File:Aboriginal song and dance.jpg|thumb|alt=Aboriginal man performing on the Digeridoo indoors with 4 people watching, aboriginal paintings can be seen on the wall behind him|Performance of Aboriginal song and dance in the [[Australian National Maritime Museum]] in Sydney]] |
|||
===Media=== |
===Media=== |
||
{{Main |
{{Main|Cinema of Australia|Television in Australia|Media of Australia}} |
||
[[File:The Story of the Kelly Gang 1906.jpg|thumb|left|Actor playing the [[bushranger]] and outlaw [[Ned Kelly]] in ''[[The Story of the Kelly Gang]]'' (1906), the world's first feature-length narrative film]] |
|||
The [[Cinema of Australia|Australian cinema industry]] began with the 1906 release of ''[[The Story of the Kelly Gang]]'', which is regarded as being the world's first [[feature length|feature-length]] film,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://portal.unesco.org/en/ev.php-URL_ID=37899&URL_DO=DO_TOPIC&URL_SECTION=201.html |title=Return of the Kelly Gang |work=[[UNESCO Courier]] |author=Chichester, Jo |publisher=[[UNESCO]] |year=2007 |accessdate=1 February 2009}}</ref> but both Australian feature film production and the distribution of British-made features declined dramatically after World War I as American studios and distributors monopolised the industry<ref>{{cite web |url=http://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:a0bny9r0rpkJ:www.afc.gov.au/downloads/policies/early%2520history_final1.pdf+australian+film+production+%2B+hollywood+%2B+1920s&hl=en&gl=au&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEESgSRefiOTOyLQEmeKt6CgCdo2vNSCscav9DLNNt0yc9iUfLnuc0S02qForlyo3T0wLCj_8Hnw2kRlN8jZxyZer_9QXlngel05Rr8NDnAsZWP-8UqmzB0kWW9T4yVDlWQYmhsm7-&sig=AHIEtbRziGrWdip9B8rYLyNLrH02b8IYuQ |title=The first wave of Australian feature film production |publisher=Docs.google.com |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> and by the 1930s around 95% of the feature films screened in Australia were produced in [[Hollywood]]. By the late 1950s feature film production in Australia had effectively ceased and there were no all-Australian feature films made in the decade between 1959 and 1969.<ref>{{cite web |work=Australian Government: Culture Portal |url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/film/ |title=Culture.gov.au – "Film in Australia" |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia |date=22 November 2007 |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> |
|||
''[[The Story of the Kelly Gang]]'' (1906), the world's first [[feature film|feature-length]] narrative film, spurred a boom in [[cinema of Australia|Australian cinema]] during the [[silent film]] era.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://portal.unesco.org/en/ev.php-URL_ID=37899&URL_DO=DO_TOPIC&URL_SECTION=201.html |title=Return of the Kelly Gang |work=[[UNESCO Courier]] |author=Chichester, Jo |publisher=[[UNESCO]] |year=2007 |access-date=1 February 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100204220758/http://portal.unesco.org/en/ev.php-URL_ID%3D37899%26URL_DO%3DDO_TOPIC%26URL_SECTION%3D201.html |archive-date= 4 February 2010 |url-status=dead}}</ref> After World War I, [[Hollywood (film industry)|Hollywood]] monopolised the industry,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.afc.gov.au/downloads/policies/early%20history_final1.pdf |title=The first wave of Australian feature film production |access-date=23 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090706104843/http://www.afc.gov.au/downloads/policies/early%20history_final1.pdf |archive-date=6 July 2009}}</ref> and by the 1960s Australian film production had effectively ceased.<ref>{{Cite web |work=Australian Government: Culture Portal |url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/film |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110327002350/http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/film |archive-date=27 March 2011 |title=Culture.gov.au – "Film in Australia" |publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia |date=22 November 2007}}</ref> With the benefit of government support, the [[Australian New Wave]] of the 1970s brought provocative and successful films, many exploring themes of national identity, such as ''[[Picnic at Hanging Rock (film)|Picnic at Hanging Rock]]'', ''[[Wake in Fright]]'' and ''[[Gallipoli (1981 film)|Gallipoli]]'',<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Krausz |first=Peter |date=2002 |title=Australian Identity: A Cinematic Roll Call |url=http://students.adelaidehs.sa.edu.au/Subjects/Issues/australianidentity.pdf |journal=Australian Screen Education Online |issue=29 |pages=24–29 |issn=1443-1629 |access-date=22 January 2016 |archive-date=3 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303200657/http://students.adelaidehs.sa.edu.au/Subjects/Issues/australianidentity.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> while ''[[Crocodile Dundee]]'' and the [[Ozploitation]] movement's ''[[Mad Max (franchise)|Mad Max]]'' series became international blockbusters.<ref>Moran, Albert; Vieth, Errol (2009). ''The A to Z of Australian and New Zealand Cinema''. Scarecrow Press. {{ISBN|978-0-8108-6347-7}}, p. 35.</ref> In a film market flooded with foreign content, Australian films delivered a 7.7% share of the local box office in 2015.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Quinn|first=Karl|date=4 December 2015 |title=Australian film has had its biggest year at the box office ever. Why? |url=https://www.smh.com.au/entertainment/movies/australian-film-has-had-its-biggest-year-at-the-box-office-ever-why-20151204-glfut3.html |access-date=15 January 2022|website=The Sydney Morning Herald |language=en}}</ref> The [[AACTA Awards|AACTAs]] are Australia's premier film and television awards, and notable [[List of Australian Academy Award winners and nominees|Academy Award winners from Australia]] include [[Geoffrey Rush]], [[Nicole Kidman]], [[Cate Blanchett]] and [[Heath Ledger]].<ref>[http://www.news.com.au/entertainment/awards/ten-great-australian-moments-at-the-oscars/story-e6frfpli-1226841441307 "Ten Great Australian Moments at the Oscars"] {{Webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140308090335/http://www.news.com.au/entertainment/awards/ten-great-australian-moments-at-the-oscars/story-e6frfpli-1226841441307 |date=8 March 2014 }} (26 February 2014), news.com.au. Retrieved 7 February 2016.</ref> |
|||
Thanks to initiatives by the [[John Gorton|Gorton]] and [[Gough Whitlam|Whitlam]] federal governments, the [[Australian New Wave|New Wave of Australian cinema]] of the 1970s brought provocative and successful films, some exploring the nation's colonial past, such as ''[[Picnic at Hanging Rock]]'' and ''[[Breaker Morant (film)|Breaker Morant]]'',<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 252–53.</ref> while the so-called "[[Ocker]]" genre produced several highly successful urban-based comedy features including ''[[The Adventures of Barry McKenzie]]'' and ''[[Alvin Purple]]''.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://afcarchive.screenaustralia.gov.au/newsandevents/afcnews/feature/tim_burstall/newspage_113.aspx |title=Screen Australia – Former AFC – News Archive – Tim Burstall |publisher=[[Australian Film Commission]] |date=7 April 2010 |accessdate=2010-12-07}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://aso.gov.au/titles/features/alvin-purple/notes/ |title=Alvin Purple |publisher=[[National Film and Sound Archive]] |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.theage.com.au/news/culture/the-fall-guy/2008/07/25/1216492692315.html?page=fullpage#contentSwap2|title=The fall guy |author= Pecujac, Yvonne|work=[[The Age]]|date=25 July 2008|accessdate=23 April 2010 | location=Melbourne}}</ref> Later hits included ''[[Mad Max]]'' and ''[[Gallipoli (1981 film)|Gallipoli]]''.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://aso.gov.au/titles/features/mad-max/notes/|title=Mad Max |publisher=[[National Film and Sound Archive]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://aso.gov.au/titles/features/gallipoli/notes/|title=Gallipoli |publisher=[[National Film and Sound Archive]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> More recent successes included ''[[Shine (film)|Shine]]'' and ''[[Rabbit-Proof Fence (film)|Rabbit-Proof Fence]]''.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://aso.gov.au/titles/features/shine/notes/|title=Shine|publisher=[[National Film and Sound Archive]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://aso.gov.au/titles/features/rabbit-proof-fence/notes/|title=Rabbit-Proof Fence |publisher=[[National Film and Sound Archive]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Notable Australian actors include [[Judith Anderson]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/dimensions/dimensions_in_time/Transcripts/s796896.htm|title=Dame Judith Anderson|publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]]|date=3 March 2003 |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> [[Errol Flynn]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://adbonline.anu.edu.au/biogs/A080725b.htm|title=Flynn, Errol Leslie (1909–1959) |work=[[Australian Dictionary of Biography]] |publisher=[[Australian National University]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> [[Nicole Kidman]], [[Hugh Jackman]], [[Heath Ledger]], [[Geoffrey Rush]] and current joint director of the [[Sydney Theatre Company]], [[Cate Blanchett]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/2698.htm|title=Australia (11/09)|publisher=State.gov|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2010/01/01/2784026.htm|title=Blanchett extends stay at theatre company|publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |date=1 January 2010|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> |
|||
[[Australian literature]] has also been influenced by the landscape; the works of writers such as [[Banjo Paterson]], [[Henry Lawson]], and [[Dorothea Mackellar]] captured the experience of the Australian [[The Bush|bush]].<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 381–82, 393–94, 404, 496–497.</ref> The character of the nation's colonial past, as represented in early literature, is popular with modern Australians.<ref name=bush /> In 1973, [[Patrick White]] was awarded the [[Nobel Prize in Literature]],<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 683.</ref> the first Australian to have achieved this.<ref>{{cite web|title=Patrick White – Existential Explorer|url=http://nobelprize.virtual.museum/nobel_prizes/literature/articles/hansson/index.html|date=29 August 2001|accessdate=10 June 2010 |last=Hansson|first=Karin|publisher=The Nobel Foundation| archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20071213052008/http://nobelprize.virtual.museum/nobel_prizes/literature/articles/hansson/index.html| archivedate = 13 December 2007}}</ref> Australian winners of the [[Man Booker Prize]] have included [[Peter Carey (novelist)|Peter Carey]] and [[Thomas Keneally]];<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.themanbookerprize.com/downloads/Whos_who_2009-0.pdf|title=Who’s who in the Man Booker Prize|year=2009|publisher=The Booker Prize Foundation|accessdate=11 May 2010}}</ref> [[David Williamson]], and [[David Malouf]] are also renowned writers,<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, p. 394.</ref> and [[Les Murray (poet)|Les Murray]] is regarded as "one of the leading poets of his generation".<ref name="JT77">{{cite web|url=http://johntranter.com/reviewer/1977-murray.shtml |title=Tranter, John (1977) A warrior poet living still at Anzac Cove: Review of ''The Vernacular Republic: Selected Poems'' |publisher=Johntranter.com |date=1977-01-29 |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref> |
|||
Australia has two public broadcasters (the [[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] and the multicultural [[Special Broadcasting Service]]), three commercial television networks, several pay-TV services,<ref name= |
Australia has two public broadcasters (the [[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] and the multicultural [[Special Broadcasting Service]]), three commercial television networks, several pay-TV services,<ref name="BBC-News-2009">{{Cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/1250188.stm|publisher=BBC News |title=Country profile: Australia|date=13 October 2009 |access-date=7 April 2010}}</ref> and numerous public, non-profit television and radio stations. Each major city has at least one daily newspaper,<ref name="BBC-News-2009"/> and there are two national daily newspapers, ''[[The Australian]]'' and ''[[The Australian Financial Review]]''.<ref name="BBC-News-2009"/> In 2024, [[Reporters Without Borders]] placed Australia 39th on a list of 180 countries ranked by [[freedom of the press|press freedom]], behind New Zealand (19th) and the United Kingdom (23rd), but ahead of the United States (55th).<ref>{{Cite web |year=2024 |title=Press Freedom Index 2024 |url=https://rsf.org/en/index |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160424043201/https://rsf.org/en/ranking_table |archive-date=24 April 2016 |access-date=30 November 2024 |publisher=[[Reporters Without Borders]]}}</ref> This relatively low ranking is primarily because of the limited diversity of commercial media ownership in Australia;<ref>{{Cite web |title=Media Ownership In Australia – 1999 {{pipe}} AustralianPolitics.com|url=https://australianpolitics.com/1999/12/01/media-ownership-in-australia.html |access-date=15 January 2022|website=australianpolitics.com}}</ref> most print media are under the control of [[News Corp Australia]] (59%) and [[Nine Entertainment]] (23%).<ref>{{Cite web |last=Minter |first=Elizabeth |date=12 April 2021 |title=Media concentration by Murdoch, Nine and Stokes, and ABC cuts, a danger to democracy – report |url=https://michaelwest.com.au/media-concentration-by-murdoch-nine-and-stokes-and-abc-cuts-a-danger-to-democracy-report/ |access-date=7 February 2024 |website=Michael West |language=en}}</ref> |
||
===Cuisine=== |
===Cuisine=== |
||
{{Main|Australian cuisine}} |
{{Main|Australian cuisine}} |
||
[[File:Shiraz Wein.jpg|thumb|[[South Australian wine]]s]] |
|||
The food of [[Indigenous Australians]] was largely influenced by the area in which they lived. Most tribal groups subsisted on a simple [[hunter-gatherer diet]], hunting native game and fish and collecting native plants and fruit. The general term for native [[Australian flora]] and [[Australian fauna|fauna]] used as a source of food is [[bush tucker]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.teachers.ash.org.au/bushtucker/ |title=Bush Tucker Plants, or Bush Food |publisher=Teachers.ash.org.au |date= |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.theepicentre.com/Australia/aufood2.html |title=Bush Tucker |publisher=Theepicentre.com |date= |accessdate=2011-04-26}}</ref> The [[First Fleet|first settlers]] introduced [[British cuisine|British food]] to the continent<ref name=food/> which much of what is now considered typical Australian food is based on the [[Sunday roast]] has become an enduring tradition for many Australians.<ref name=f2/> Since the beginning of the 20th century, food in Australia has increasingly been influenced by immigrants to the nation, particularly from [[Southern European]] and [[Culture of Asia|Asian cultures]].<ref name=food>{{cite web|url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/foodanddrink/|title=Australian food and drink|publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |date=23 September 2008|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref name=f2>{{cite web|url=http://www.sbs.com.au/food/cuisineindex/RecipeByCuisineMain/383|title=Modern Australian recipes and Modern Australian cuisine|publisher=[[Special Broadcasting Service]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> [[Australian wine]] is produced in 60 distinct production areas totaling approximately 160,000 hectares, mainly in the southern, cooler parts of the country. The wine regions in each of these states produce different wine varieties and styles that take advantage of local climates and soil types. The predominant varieties are [[Syrah|Shiraz]], [[Cabernet Sauvignon]], [[Chardonnay]], [[Merlot]], [[Sémillon]], [[Pinot noir]], [[Riesling]], and [[Sauvignon blanc]].<ref>{{cite news |publisher=Winebiz – Wine Industry Statistics |url=http://www.winebiz.com.au/statistics/domestic.asp |title=Australian Wine Industry Statistics |accessdate=2010-10-22}}</ref><ref name="Wine for Dummies">{{cite book |title= Wine For Dummies |last= Ed |first= McCarthy |coauthors= Mary Ewing-Mulligan |year= 2006 |publisher= For Dummies |isbn= 0-470-04579-5 |url= http://au.dummies.com/how-to/content/the-wine-regions-of-australia.html}}</ref><ref name="Sotheby">T. Stevenson ''"The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia"'' Dorling Kindersley 2005 ISBN 0-7566-1324-8</ref><ref name="wineaustralia1"/><ref>{{cite book |title= The World Atlas of Wine |publisher= Mitchell Beazley; 6th Revised edition edition year=2007 |isbn=978-1-84533-414-7 |author=Hugh Johnson & Jancis Robinson}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Oz Clarke's New Wine Atlas: Wines and Wine Regions of the World |publisher=Harcourt; 6th Revised edition edition |year= 2002 |isbn=978-0-15-100913-8 |author=Oz Clarke}}</ref> In 1995, an Australian red wine, [[Penfolds Grange]], won the [[Wine Spectator]] award for Wine of the Year, the first time a wine from outside France or California achieved this distinction.<ref>{{cite book|title=Spinning the bottle: case studies in wine public relations|first=Harvey|last= Posert|coauthors=Paul Franson|publisher=HPPR Press|year=2004|isbn=9780974756608|page=182}}</ref> |
|||
Most Indigenous Australian groups subsisted on a diet of native fauna and flora, otherwise called [[bush tucker]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.teachers.ash.org.au/bushtucker |title=Bush Tucker Plants, or Bush Food |publisher=Teachers.ash.org.au |access-date=26 April 2011| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511094258/http://www.teachers.ash.org.au/bushtucker/| archive-date= 11 May 2011 | url-status=live}}</ref> It has increased in popularity among non-Indigenous Australians since the 1970s, with examples such as [[Backhousia citriodora|lemon myrtle]], the [[Macadamia|macadamia nut]] and [[kangaroo meat]] now widely available.<ref>Lockhart, Jessica Wynne (4 August 2023). [https://www.smithsonianmag.com/travel/the-next-superfoods-may-come-from-australia-180982660/ "The Next Superfoods May Come From Australia"], ''[[Smithsonian (magazine)|Smithsonian]]''. Retrieved 5 February 2024.</ref><ref>McCubbing, Gus (4 November 2022). [https://www.afr.com/companies/agriculture/bush-food-industry-worth-80m-but-could-double-by-2025-study-20221104-p5bvn3#:~:text=The%20bush%20food%20industry%2C%20according,potential%20to%20double%20by%202025. "Bush food industry worth $80m but could double by 2025: study"], ''[[Australian Financial Review]]''. Retrieved 5 February 2024.</ref> |
|||
The first colonists introduced [[British cuisine|British]] and [[Irish cuisine]] to the continent.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/foodanddrink/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100326134155/http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/foodanddrink/ |archive-date=26 March 2010 |title=Australian food and drink|publisher=Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts |date=23 September 2008}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.sbs.com.au/food/cuisineindex/RecipeByCuisineMain/383 |title=Modern Australian recipes and Modern Australian cuisine|publisher=[[Special Broadcasting Service]] |access-date=23 April 2010| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100503111747/http://www.sbs.com.au/food/cuisineindex/RecipeByCuisineMain/383| archive-date= 3 May 2010 | url-status=live}}</ref> This influence is seen in dishes such as [[fish and chips]], and in the [[Meat pie (Australia and New Zealand)|Australian meat pie]], which is related to the British [[steak pie]]. Also during the colonial period, Chinese migrants paved the way for a distinctive [[Australian Chinese cuisine]].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Jonsen|first=Helen |title=Kangaroo's Comments and Wallaby's Words: The Aussie Word Book|publisher=Hippocrene Books|year=1999|isbn=978-0-7818-0737-1|page=23}}</ref> |
|||
===Sport=== |
|||
Post-war migrants transformed Australian cuisine, bringing with them their culinary traditions and contributing to new [[fusion cuisine|fusion]] dishes.<ref>Newton, John (2018). ''The Getting of Garlic: Australian Food from Bland to Brilliant, with Recipes Old and New''. NewSouth Publishing. ISBN 9781742244365, pp. 32, 230–231.</ref> Italians introduced espresso coffee and, along with Greeks, helped develop Australia's café culture, of which the [[flat white]] and [[avocado toast]] are now considered Australian staples.<ref>Waters, Cara (15 June 2015). [https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/australia-food-blog/2015/jun/15/smashed-avo-anyone-five-australian-creations-taking-the-world-by-storm "Smashed avo, anyone? Five Australian creations taking the world by storm"], ''The Guardian''. Retrieved 6 February 2024.</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.independent.co.uk/life-style/flat-white-coffee-culture-antipodean-mcdonalds-advert-starbucks-latte-a8246111.html |title=How the flat white conquered the coffee scene|work=[[The Independent]]|date=9 April 2018 |access-date=4 October 2018}}</ref> [[pavlova (food)|Pavlovas]], [[lamington]]s, [[Vegemite]] and [[Anzac biscuits]] are also often called iconic Australian foods.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Santich|first=Barbara |title=Bold Palates: Australia's Gastronomic Heritage|publisher=Wakefield Press|year=2012|isbn=978-1-7430-5094-1|page=290}}</ref> |
|||
Australia is a leading exporter and consumer of [[wine]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.wineaustralia.com/report-downloads/08d4027a-e89e-469d-bf9a-a5b548237ea4 |title=Australian wine: Production, sales and inventory report, 2018–19|date=12 February 2020|website=wineaustralia.com|publisher=Wine Australia |access-date=11 April 2020 |archive-date=11 April 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200411112731/https://www.wineaustralia.com/report-downloads/08d4027a-e89e-469d-bf9a-a5b548237ea4 |url-status=dead}}</ref> [[Australian wine]] is produced mainly in the southern, cooler parts of the country.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cellarmasters.com.au/discover/wine-regions/australia|publisher=Cellarmasters|title=Wine Regions of Australia|access-date=2 April 2021|archive-date=14 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210414225154/https://www.cellarmasters.com.au/discover/wine-regions/australia|url-status=dead}}</ref> The nation also ranks highly in [[List of countries by beer consumption per capita|beer consumption]],<ref name="Kirin">[http://www.kirinholdings.co.jp/english/ir/news_release051215_4.html Per Capita Beer Consumption by Country (2004)] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080623213209/http://www.kirinholdings.co.jp/english/ir/news_release051215_4.html |date=23 June 2008 }}, Table 3, Kirin Research Institute of Drinking and Lifestyle – Report Vol. 29–15 December 2005, Kirin Holdings Company.</ref> with each state and territory hosting numerous breweries. |
|||
===Sport and recreation=== |
|||
{{Main|Sport in Australia}} |
{{Main|Sport in Australia}} |
||
[[File:2017 AFL Grand Final panorama during national anthem.jpg|thumb|The [[Melbourne Cricket Ground]] is strongly associated with the history and development of [[cricket]] and [[Australian rules football]], Australia's two most popular spectator sports.<ref>{{Cite web |date=14 September 2009 |title=National Sports Museum – Heritage Listing |url=http://www.nsm.org.au/The%2520MCG/Heritage%2520Listing.aspx?p=1 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090914092919/http://www.nsm.org.au/The%20MCG/Heritage%20Listing.aspx?p=1 |url-status=dead |archive-date=14 September 2009 |access-date=15 January 2022 |website= }}</ref>]] |
|||
[[File:4th Test Woodfull.jpg|thumb|alt=Black and white photo of a cricket pitch|[[Cricket]] has been an important part of Australia's sporting culture since the 19th century.<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 162–163.</ref>]] |
|||
The most popular sports in Australia by adult participation are: swimming, athletics, cycling, soccer, golf, tennis, basketball, surfing, netball and cricket.<ref>{{Cite web |date=October 2023 |title=Clearinghouse for sport: Ausplay National Sport and Activity Physical Participation Report 2022-23, p 9 |url=https://www.clearinghouseforsport.gov.au/research/ausplay/results#latest |access-date=11 May 2024 |website=Australian Sports Commission}}</ref> |
|||
Around 24% Australians over the age of 15 regularly participate in organised sporting activities in Australia.<ref name="Year Book 2005" /> Australia has strong international teams in [[cricket]], [[field hockey]], [[netball]], [[rugby league]] and [[rugby union]], having been Olympic or world champions at least twice in each sport in the last 25 years for both men and women where applicable.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cricinfo.com/wc2007/content/story/264535.html|title=A brief history|publisher=[[Cricinfo]]|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/sport2/hi/cricket/womens_cricket/4237521.stm|title=Women's World Cup history|publisher=BBC News|date=15 March 2005|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/sport2/hi/cricket/womens_cricket/4421651.stm|title=Australia lift Women's World Cup|publisher=BBC News|date=10 April 2005|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fihockey.org/vsite/vnavsite/page/directory/0,10853,1181-193815-211038-nav-list,00.html|title=Results Archive|publisher=International Hockey Federation|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.wnc2011.com/home/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=160&Itemid=213|publisher=World Netball Championships 2011 |title=History|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.rlwc08.com/about/history.aspx|title=History|publisher=Rugby League World Cup 2008 |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/cbbcnews/hi/find_out/guides/sport/rugby_world_cup_history/newsid_3171000/3171524.stm|title=Rugby World Cup History | 1999|publisher=BBC News|accessdate=23 April 2010 | date=7 October 2003}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/cbbcnews/hi/find_out/guides/sport/rugby_world_cup_history/newsid_3171000/3171520.stm|title=Rugby World Cup History | 1991|publisher=BBC News|accessdate=23 April 2010 | date=7 October 2003}}</ref> Australia is also powerful in track cycling, rowing, and swimming, having consistently been in the top-five medal-winners at Olympic or World Championship level since 2000.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://80.83.47.230/n_results.fwx |title=Video2000 Sa |publisher=80.83.47.230 |date= |accessdate=2010-06-14}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://cyclingworld.dk/cph2010/index.php?p=nyheder/profil.php&id=157|title=Track World Championships 2010 – Bane VM 2010|publisher=Cyclingworld.dk|date=28 March 2010|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://track-pruszkow2009.com/news/2009_pruszkow_wch_are_a_history_now-s648.html|title=2009 Pruszkow WCH are a history now!|publisher=track-pruszkow2009.com|date=29 March 2009|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Swimming is the strongest of these sports; Australia is the second-most prolific medal winner in the sport in Olympic history.<ref>{{Cite news|title=Swimming's big splash |
|||
|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/sport2/hi/olympics_2004/swimming/history/3477381.stm|publisher=BBC Sports|date=5 July 2004|accessdate=8 November 2006}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|title=Phelps causes biggest splash |
|||
|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/sport2/hi/olympics_2004/swimming/3587554.stm|publisher=BBC Sports|date=21 August 2004|accessdate=19 November 2006 | first=Phil | last=Gordos}}</ref><ref name="aoc50">{{cite web|url=http://corporate.olympics.com.au/index.cfm?p=25|title=100 of our Finest|accessdate=31 January 2009|publisher=[[Australian Olympic Committee]]}}</ref> |
|||
Australia is one of five nations to have participated in every [[Summer Olympics]] of the modern era,<ref>{{Cite book |last=Oxlade |first=Chris |author-link=Chris Oxlade (writer) |url=https://archive.org/details/olympics0000oxla/page/61 |title=Olympics |author2=Ballheimer, David |publisher=DK |year=2005 |isbn=978-0-7566-1083-8 |series=DK Eyewitness |page=[https://archive.org/details/olympics0000oxla/page/61 61]}}</ref> and has hosted the Games twice: [[1956 Summer Olympics|1956]] in Melbourne and [[2000 Summer Olympics|2000]] in Sydney.<ref name="Davison pp479-80">{{Harvnb|Davison|Hirst|Macintyre|1998|pages=479–80}}</ref> It is also set to host the [[2032 Summer Olympics|2032 Games]] in [[Brisbane]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=21 July 2021 |title=Brisbane announced as 2032 Olympic Games host city at IOC meeting in Tokyo |url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2021-07-21/brisbane-queensland-announced-as-2032-olympic-games-host-city/100311320 |access-date=22 July 2021 |work=[[ABC News (Australia)]]}}</ref> Australia has also participated in every [[Commonwealth Games]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Flag Bearers |url=http://www.commonwealthgames.org.au/page/65/by-games |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140726210627/http://www.commonwealthgames.org.au/page/65/by-games |archive-date=26 July 2014 |access-date=23 April 2010 |publisher=Australian Commonwealth Games Association}}</ref> hosting the event in [[1938 British Empire Games|1938]], [[1962 British Empire and Commonwealth Games|1962]], [[1982 Commonwealth Games|1982]], [[2006 Commonwealth Games|2006]] and [[2018 Commonwealth Games|2018]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Past Commonwealth Games |url=http://www.thecgf.com/games/games_index.asp?linkresults=1 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100315102922/http://www.thecgf.com/games/games_index.asp?linkresults=1 |archive-date=15 March 2010 |access-date=23 April 2010 |publisher=Commonwealth Games Federation}}</ref> |
|||
Some of Australia's most internationally well-known and successful sportspeople are swimmers [[Dawn Fraser]], [[Murray Rose]], [[Shane Gould]] and [[Ian Thorpe]]; sprinters [[Shirley Strickland]], [[Betty Cuthbert]] and [[Cathy Freeman]];<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.abc.net.au/olympics/2008/top10/|title=Australia's Greatest Olympian |publisher=[[Australian Broadcasting Corporation]] |accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> tennis players [[Rod Laver]], [[Roy Emerson]], [[Ken Rosewall]], [[Evonne Goolagong]], and [[Margaret Court]]; cricketers [[Donald Bradman]] and [[Shane Warne]]; three-time [[Formula One]] world champion [[Jack Brabham]]; five-time motorcycle grand prix world champion [[Mick Doohan]]; golfers [[Greg Norman]] and [[Karrie Webb]];<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.lpga.com/player_results.aspx?id=200|title=Player: Karrie Webb|work=LPGA.com|publisher=Ladies Professional Golf Association|accessdate=6 July 2010}}</ref> cyclist [[Hubert Opperman]]; and prodigious billiards player [[Walter Lindrum]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sahof.org.au/hallOfFame/legends/index.php|title= Recognising Australia's greatest athletes and providing scholarships to Australia's youth|publisher=Sport Australia Hall of Fame|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Nationally, other popular sports include [[Australian rules football]], horse racing, squash, surfing, soccer, and motor racing. |
|||
The [[Australia national cricket team|Australian national cricket team]] competed against [[England cricket team|England]] in the first [[Test cricket|Test]] match (1877) and the first [[One Day International]] (1971), and against [[New Zealand cricket team|New Zealand]] in the first [[Twenty20 International]] (2004), winning all three games.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Harte |first1=Chris |title=The Penguin History of Australian Cricket |last2=Whimpress |first2=Bernard |publisher=Viking |year=2008 |isbn=9780670072880 |edition=3rd |location=Camberwell, Vic |pp=92-94, 528, 722}}</ref> It has also won the men's [[Cricket World Cup]] a record six times.<ref>{{Cite news |date=20 November 2023 |title=Australia stuns India to claim record-extending sixth Cricket World Cup crown in Ahmedabad |url=https://www.abc.net.au/news/2023-11-19/live-updates-cricket-world-cup-final-india-vs-australia/103124084 |access-date=20 November 2023 |publisher=Australian Broadcasting Corporation}}</ref> |
|||
Australia has participated in every summer Olympics of the modern era,<ref>{{Cite book|last=Oxlade|first=Chris|coauthors=Ballheimer, David|title=Olympics|publisher=DK|series=DK Eyewitness|page=61|isbn=0-7566-1083-4}}</ref> and every [[Commonwealth Games]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.commonwealthgames.org.au/Templates/Games_FlagBearers.htm|publisher=Australian Commonwealth Games Association |title=Flag Bearers|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Australia hosted the [[1956 Summer Olympics]] in Melbourne and the [[2000 Summer Olympics]] in Sydney,<ref>Davison, Hirst and Macintyre, pp. 479–480.</ref> and has ranked among the top six medal-takers since 2000.<ref>{{cite web| |
|||
url=http://www.abs.gov.au/Ausstats/abs@.nsf/57a31759b55dc970ca2568a1002477b6/be9f47591541e29eca256ef40004f25a!OpenDocument |title=ABS medal tally: Australia finishes third |publisher=Australian Bureau of Statistics |date=30 August 2004 |accessdate=25 January 2008}}</ref> Australia has also hosted the [[1938 British Empire Games|1938]], [[1962 British Empire and Commonwealth Games|1962]], [[1982 Commonwealth Games|1982]], and [[2006 Commonwealth Games]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.thecgf.com/games/games_index.asp?linkresults=1|publisher=Commonwealth Games Federation |title=Past Commonwealth Games|accessdate=23 April 2010}}</ref> Other major international events held in Australia include the [[Australian Open]] tennis [[Grand Slam (tennis)|grand slam]] tournament, international cricket matches, and the [[Australian Grand Prix|Australian Formula One Grand Prix]]. The highest-rating television programs include sports telecasts such as the summer Olympics, FIFA World Cup, [[Rugby League State of Origin|State of Origin]], and the [[grand final]]s of the [[National Rugby League]] and [[Australian Football League]].<ref>"Australian Film Commission. What are Australians Watching?" [http://www.afc.gov.au/gtp/freetv.html Free-to-Air, 1999–2004 TV]{{dead link|date=April 2011}}.</ref> |
|||
Australia has professional leagues for [[football in Australia|four football codes]], whose relative popularity is [[Barassi Line|divided geographically]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Fujak |first=Hunter |date=15 July 2022 |title=The Barassi Line: a globally unique divider splitting Australia's footy fans |url=http://theconversation.com/the-barassi-line-a-globally-unique-divider-splitting-australias-footy-fans-185132 |access-date=4 February 2024 |website=The Conversation |language=en-US}}</ref> Originating in Melbourne in the 1850s, [[Australian rules football]] attracts the most television viewers in all states except New South Wales and Queensland, where [[rugby league]] holds sway, followed by [[rugby union]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273772263|date=21 December 2013 |title=The 'Barassi Line': Quantifying Australia's Great Sporting Divide |access-date=16 August 2018}}</ref> [[Association football|Soccer]], while ranked fourth in television viewers and resources, has the highest overall participation rates.<ref>{{Cite book|last1 = Skinner |first1 = James |last2 = Zakus H. |first2 = Dwight | last3 = Edwards |first3 = Allan | editor-first= Brown|editor-last = Adam|title = Football and Community in the Global Context: Studies in Theory and Practice|publisher = Routledge|year = 2013|pages = 92–93|chapter = Coming in from the Margins: Ethnicity, Community Support and the Rebranding of Australian Soccer |isbn = 978-1-317-96905-1}}</ref> |
|||
The [[surf lifesaving]] movement originated in Australia in the early 20th century, following the relaxation of laws prohibiting daylight bathing on Australian beaches. The volunteer lifesaver is one of the country's icons.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Booth|first=Douglas|author-link=Doug Booth |title=Australian Beach Cultures: The History of Sun, Sand and Surf|publisher=Routledge|year=2012|isbn=978-0-7146-8178-8|page=39}}</ref><ref name=Aust_SLSC>[http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/surflifesaving/ "Surf Life Saving - Stories from Australia's Culture and Recreation Portal"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060511163956/http://www.cultureandrecreation.gov.au/articles/surflifesaving/ |date=11 May 2006 }}. [Online], Commonwealth Government of Australia, 2006.</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{Portal|Australia}} |
{{Portal|Australia|Oceania}} |
||
* [[Outline of Australia]] |
|||
* [[Index of Australia-related articles]] |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
==Notes== |
==Notes== |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist|group="N"}} |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist |
{{Reflist}} |
||
* {{Free-content attribution |
|||
| title = World Food and Agriculture – Statistical Yearbook 2023 |
|||
| author = FAO |
|||
| publisher = FAO |
|||
| documentURL = https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en?details=cc8166en |
|||
| licence statement URL = https://commons.wikimedia.org/whttps://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:World_Food_and_Agriculture_-_Statistical_Yearbook_2023.pdf |
|||
| license = CC BY-SA IGO 3.0 |
|||
}} |
|||
==Bibliography== |
==Bibliography== |
||
{{Refbegin |
{{Refbegin}} |
||
* {{Cite book |title=The Oxford Companion to Australian History|publisher=Oxford University Press|location=Melbourne|year=1998|isbn=978-0-1955-3597-6|last1=Davison|first1=Graeme|last2=Hirst|first2=John|author-link2=John Hirst (historian)|last3=Macintyre|first3=Stuart|author-link3=Stuart Macintyre}} |
|||
* Denoon, Donald, et al. (2000). ''A History of Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific''. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-17962-3. |
|||
* |
* Flood, Josephine (2019). The Original Australians: The Story of the Aboriginal People (2nd ed.). Crows Nest, NSW: Allen and Unwin. ISBN 9781760527075. |
||
* {{Cite book|title=The |
* {{Cite book|first=James|last=Jupp|year=2001 |title=The Australian people: an encyclopedia of the nation, its people, and their origins|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-5218-0789-0|ref=CITEREFJupp1}} |
||
* {{Cite book|first1=James|last1=Jupp|author2=Director Centre for Immigration and Multicultural Studies James Jupp |title=The Australian People: An Encyclopedia of the Nation, Its People and Their Origins|url={{GBurl|id=wgoFxfSTfYAC|p=35}}|year=2001|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-5218-0789-0|ref=CITEREFJupp2}} |
|||
* ''Emily Kngwarreye – Paintings'' (no editor given) (1996). North Ryde NSW: Craftsman House / G + B Arts International. ISBN 90-5703-681-9. |
|||
* {{Cite book|title= |
* {{Cite book |title=Australian painting 1788–1990|publisher=Oxford University Press|location=Melbourne|year=1991|isbn=978-0-1955-4901-0|author1=Smith, Bernard|author2=Smith, Terry|ref=Smith|url=https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/6028116/}} |
||
* {{Cite book| |
* {{Cite book|last1=Teo|first1=Hsu-Ming |last2=White|first2=Richard|year=2003 |title=Cultural history in Australia|publisher=University of New South Wales Press|isbn=978-0-8684-0589-6}} |
||
{{Refend}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|first=James|last=Jupp|year=2001|title=The Australian people: an encyclopedia of the nation, its people, and their origins|publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]]|isbn=0-521-80789-1}} |
|||
* Macintyre, Stuart (2000). ''A Concise History of Australia''. Cambridge, U.K.: [[Cambridge University Press]]. ISBN 0-521-62359-6. |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
* McCulloch, Alan; Susan McCulloch, Emily McCulloch Childs (2006). ''The new McCulloch's encyclopedia of Australian art''. Fitzroy, VIC: Aus Art Editions in association with The Miegunyah Press. ISBN 0-522-85317-X. |
|||
{{Further|Bibliography of Australian history}} |
|||
* Powell JM (1988). ''An Historical Geography of Modern Australia: The Restive Fringe''. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-25619-4. |
|||
{{Refbegin}} |
|||
* Robinson GM, Loughran RJ, and Tranter PJ (2000) ''Australia and New Zealand: economy, society and environment''. London: Arnold; NY: OUP; 0340720336 paper 0-340720328 hard. |
|||
* Blainey, Geoffrey (2015). The Story of Australia's People, Volume 1: The Rise and Fall of Ancient Australia, Penguin Books Australia Ltd., Vic. {{ISBN|978-0-6700-7871-4}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|title=Australian painting 1788–1990|publisher=Oxford University Press|location=Melbourne, Vic.|year=1991|isbn=0-19-554901-5|author=Smith, Bernard; Smith, Terry}} |
|||
* Denoon, Donald, et al. (2000). ''A History of Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific''. Oxford: Blackwell. {{ISBN|978-0-631-17962-7}}. |
|||
* {{Cite book|author=Teo, Hsu-Ming; White, Richard|year=2003|title=Cultural history in Australia|publisher=[[University of New South Wales Press]]|isbn=0-86840-589-2}} |
|||
* Goad, Philip and Julie Willis (eds.) (2011). ''The Encyclopedia of Australian Architecture''. Port Melbourne, Victoria: Cambridge University Press. {{ISBN|978-0-5218-8857-8}}. |
|||
* Hughes, Robert (1986). ''The Fatal Shore: The Epic of Australia's Founding''. Knopf. {{ISBN|978-0-394-50668-5}}. |
|||
* [[John Milne|Milne, John (1886)]]. [https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/69580 Colonial facts and fictions: Humorous sketches]. United Kingdom: Chatto and Windus. |
|||
* {{Cite book |last=Kemp |first=David |title=The Land of Dreams: How Australians Won Their Freedom, 1788–1860 |url={{GBurl|id=LUVvDwAAQBAJ}} |year=2018 |publisher=Melbourne University Publishing |isbn=978-0-5228-7334-4 |oclc=1088319758}} |
|||
* Powell, J.M. (1988). ''An Historical Geography of Modern Australia: The Restive Fringe''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. {{ISBN|978-0-521-25619-3}} |
|||
* Robinson, G.M., Loughran, R.J., and Tranter, P.J. (2000). ''Australia and New Zealand: Economy, Society and Environment''. London: Arnold; New York: Oxford University Press. {{ISBN|978-0-340-72033-2}} paperback, {{ISBN|978-0-340-72032-5}} hardback. |
|||
{{Refend}} |
{{Refend}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Spoken Wikipedia|date=17 January 2006|AustraliaPart1.ogg|AustraliaPart2.ogg}} |
|||
{{Sister project links}} |
|||
{{Sister project links|voy=Australia|d=Q408|collapsible=collapsed}} |
|||
{{Spoken Wikipedia-2|2006-01-17|AustraliaPart1.ogg|AustraliaPart2.ogg|}} |
|||
* [https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/australia/ Australia profile] on ''[[The World Factbook]]'' |
|||
{{Wikiatlas|Australia}} |
|||
* [https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-15674351 Australia profile] from [[BBC News]] |
|||
* [http://www.dfat.gov.au/geo/australia/ About Australia] from the [[Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade]] website |
|||
* [ |
* [https://www.oecd.org/australia/ Australia profile] from the [[Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development|OECD]] |
||
* {{Wikiatlas|Australia}} |
|||
* [http://www.australia.gov.au/ Australian Government website] |
|||
* {{Osmrelation-inline|80500}} |
|||
* [http://www.aph.gov.au/whoswho/index.htm Parliament of Australia: Who's Who (includes head of state)] |
|||
* [http://www.abs.gov.au/ Australian Bureau of Statistics] |
|||
'''Government''' |
|||
* [http://www.community.gov.au/ Community organisations portal] |
|||
* [ |
* [https://www.aph.gov.au/ Parliament of Australia] |
||
* [https://www.dfat.gov.au/ Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade] |
|||
* {{Wikitravel|Australia}} |
|||
* |
* [https://www.naa.gov.au/ National Archives of Australia] |
||
* [https://www.abs.gov.au/ Australian Bureau of Statistics] |
|||
* [http://ucblibraries.colorado.edu/govpubs/for/australia.htm Australia] at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' |
|||
* {{dmoz|Regional/Oceania/Australia}} |
|||
'''Travel''' |
|||
<!--===========================({{NoMoreLinks}}) ===============================--> |
|||
* {{official website|https://www.australia.com/}} of Tourism Australia |
|||
<!--| DO ''not'' ADD MORE LINKS TO THIS ARTICLE. WIKIPEDIA IS ''not'' A COLLECTION OF |--> |
|||
{{Prone to spam|date=May 2021}} |
|||
<!--| LINKS. If you think that your link might be useful, do not add it here, |--> |
|||
<!-- {{No more links}} |
|||
<!--| but put it on this article's discussion page first or submit your link |--> |
|||
<!--| to the appropriate category at the Open Directory Project (www.dmoz.org)|--> |
|||
Please be cautious adding more external links. |
|||
<!--| and link back to that category using the {{dmoz}} template. |--> |
|||
<!--| |--> |
|||
Wikipedia is not a collection of links and should not be used for advertising. |
|||
<!--| Links that have not been verified WILL BE DELETED. |--> |
|||
<!--| See [[Wikipedia:External links]] and [[Wikipedia:Spam]] for details |--> |
|||
Excessive or inappropriate links will be removed. |
|||
<!--===========================({{NoMoreLinks}}) ===============================--> |
|||
{{Template group |
|||
See [[Wikipedia:External links]] and [[Wikipedia:Spam]] for details. |
|||
|title = Articles Related to Australia |
|||
|list = |
|||
If there are already suitable links, propose additions or replacements on |
|||
the article's talk page. |
|||
--> |
|||
{{Australia topics}} |
{{Australia topics}} |
||
{{Navboxes |
|||
{{Template group |
|||
|title= Articles related to Australia |
|||
|title = [[File:Gnome-globe.svg|25px]]{{nbsp}}Geographic locale |
|||
|list = |
|list = |
||
'''[[Geographic coordinate system|Lat. <small>and</small> Long.]] {{Coord|35|18|S|149|8|E|display=inline}} <span style="color:darkblue;">(Canberra)</span>''' |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Countries and territories of Oceania}} |
{{Countries and territories of Oceania}} |
||
{{Commonwealth realms}} |
|||
{{The Commonwealth}} |
|||
{{English official language clickable map}} |
{{English official language clickable map}} |
||
{{Pacific Islands Forum (PIF)}} |
|||
{{Commonwealth Realms}} |
|||
{{Monarchies}} |
|||
{{Commonwealth of Nations}} |
|||
{{National personifications}} |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{ |
{{Authority control}} |
||
{{Coord|25|S|133|E|type:country_region:AU_scale:20000000|display=title}} |
|||
[[Category:Australia| ]] |
[[Category:Australia| ]] |
||
[[Category:Constitutional monarchies]] |
|||
[[Category:English-speaking countries and territories]] |
[[Category:English-speaking countries and territories]] |
||
[[Category:Federal countries]] |
|||
[[Category:Former British colonies]] |
|||
[[Category:G20 nations]] |
|||
[[Category:Liberal democracies]] |
|||
[[Category:Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations]] |
|||
[[Category:Oceanian countries]] |
|||
[[Category:Countries of the Indian Ocean]] |
|||
[[Category:Countries bordering the Pacific Ocean]] |
|||
[[Category:States and territories established in 1901]] |
[[Category:States and territories established in 1901]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:G20 members]] |
||
[[Category:Member states of the United Nations]] |
|||
[[Category:Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations]] |
|||
{{Link GA|es}} |
|||
[[Category:Countries in Oceania]] |
|||
{{Link GA|is}} |
|||
[[Category:Countries in Australasia]] |
|||
{{Link GA|sv}} |
|||
[[Category:Geographical articles missing image alternative text]] |
|||
{{Link GA|zh}} |
|||
[[Category:OECD members]] |
|||
{{Link FA|af}} |
|||
{{Link FA|de}} |
|||
{{Link FA|ka}} |
|||
{{Link FA|pt}} |
|||
{{Link FA|sr}} |
|||
{{Link FA|tt}} |
|||
[[ace:Australia]] |
|||
[[af:Australië]] |
|||
[[als:Australien]] |
|||
[[am:አውስትራልያ]] |
|||
[[ang:Australia]] |
|||
[[ar:أستراليا]] |
|||
[[an:Australia]] |
|||
[[arc:ܐܘܣܛܪܠܝܐ (ܐܬܪܐ)]] |
|||
[[roa-rup:Australia]] |
|||
[[frp:Ôstralie]] |
|||
[[ast:Australia]] |
|||
[[az:Avstraliya]] |
|||
[[bm:Ostralia]] |
|||
[[bn:অস্ট্রেলিয়া]] |
|||
[[bjn:Australia]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Australia]] |
|||
[[ba:Австралия]] |
|||
[[be:Аўстралія]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Аўстралія]] |
|||
[[bcl:Australya]] |
|||
[[bi:Ostrelia]] |
|||
[[bar:Australien]] |
|||
[[bo:ཨོ་སེ་ཐེ་ལི་ཡ།]] |
|||
[[bs:Australija]] |
|||
[[br:Aostralia]] |
|||
[[bg:Австралия]] |
|||
[[ca:Austràlia]] |
|||
[[cv:Австрали]] |
|||
[[ceb:Awstralya]] |
|||
[[cs:Austrálie]] |
|||
[[co:Australia]] |
|||
[[cy:Awstralia]] |
|||
[[da:Australien]] |
|||
[[pdc:Australie]] |
|||
[[de:Australien]] |
|||
[[dv:އޮސްޓަރުލިޔާ]] |
|||
[[nv:Nahatʼeʼiitsoh Bikéyah]] |
|||
[[dsb:Awstralska]] |
|||
[[dz:ཨས་ཊེཡེ་ལི་ཡ]] |
|||
[[et:Austraalia]] |
|||
[[el:Αυστραλία]] |
|||
[[es:Australia]] |
|||
[[eo:Aŭstralio]] |
|||
[[ext:Austrália]] |
|||
[[eu:Australia]] |
|||
[[ee:Australia]] |
|||
[[fa:استرالیا]] |
|||
[[hif:Australia]] |
|||
[[fo:Avstralia]] |
|||
[[fr:Australie]] |
|||
[[fy:Austraalje (lân)]] |
|||
[[fur:Australie]] |
|||
[[ga:An Astráil]] |
|||
[[gv:Yn Austrail]] |
|||
[[gag:Avstraliya]] |
|||
[[gd:Astràilia]] |
|||
[[gl:Australia]] |
|||
[[gan:澳大利亞]] |
|||
[[gu:ઑસ્ટ્રેલિયા]] |
|||
[[hak:Àu-thai-li-â]] |
|||
[[xal:Австралмудин Ниицән]] |
|||
[[ko:오스트레일리아]] |
|||
[[ha:Asturaliya]] |
|||
[[haw:‘Aukekulelia]] |
|||
[[hy:Ավստրալիա]] |
|||
[[hi:ऑस्ट्रेलिया]] |
|||
[[hsb:Awstralska]] |
|||
[[hr:Australija]] |
|||
[[io:Australia]] |
|||
[[ig:Ostraliya]] |
|||
[[bpy:অস্ট্রেলিয়া]] |
|||
[[id:Australia]] |
|||
[[ia:Australia]] |
|||
[[ie:Australia]] |
|||
[[iu:ᐊᔅᑦᕌᓕᐊ/astraalia]] |
|||
[[os:Австрали]] |
|||
[[zu:I-Ostreliya]] |
|||
[[is:Ástralía]] |
|||
[[it:Australia]] |
|||
[[he:אוסטרליה]] |
|||
[[jv:Australia]] |
|||
[[kl:Australia]] |
|||
[[kn:ಆಸ್ಟ್ರೇಲಿಯ]] |
|||
[[pam:Australia]] |
|||
[[kbd:Аустралиэ]] |
|||
[[krc:Австралия]] |
|||
[[ka:ავსტრალია]] |
|||
[[kk:Австралия Одағы]] |
|||
[[kw:Ostrali]] |
|||
[[rw:Ositaraliya]] |
|||
[[ky:Австралия]] |
|||
[[rn:Australiya]] |
|||
[[sw:Australia]] |
|||
[[kv:Австралия]] |
|||
[[kg:Australia]] |
|||
[[ht:Ostrali]] |
|||
[[ku:Awistralya]] |
|||
[[lo:ປະເທດອົດສະຕາລີ]] |
|||
[[la:Australia]] |
|||
[[lv:Austrālija]] |
|||
[[lb:Australien]] |
|||
[[lt:Australija]] |
|||
[[lij:Australia]] |
|||
[[li:Australië]] |
|||
[[jbo:sralygu'e]] |
|||
[[lmo:Aüstralia]] |
|||
[[hu:Ausztrália (ország)]] |
|||
[[mk:Австралија]] |
|||
[[mg:Aostralia]] |
|||
[[ml:ഓസ്ട്രേലിയ]] |
|||
[[mt:Awstralja]] |
|||
[[mi:Ahitereiria]] |
|||
[[mr:ऑस्ट्रेलिया]] |
|||
[[arz:اوستراليا]] |
|||
[[ms:Australia]] |
|||
[[cdo:Ó̤-ciŭ]] |
|||
[[mwl:Oustrália]] |
|||
[[mdf:Австралие]] |
|||
[[mn:Австрали]] |
|||
[[my:ဩစတြေးလျနိုင်ငံ]] |
|||
[[nah:Australia]] |
|||
[[na:Otereiriya]] |
|||
[[nl:Australië (land)]] |
|||
[[ne:अष्ट्रेलिया]] |
|||
[[ja:オーストラリア]] |
|||
[[ce:Австрали]] |
|||
[[pih:Ostrielya]] |
|||
[[no:Australia]] |
|||
[[nn:Australia]] |
|||
[[nrm:Australie]] |
|||
[[nov:Australia]] |
|||
[[oc:Austràlia]] |
|||
[[mhr:Австралий]] |
|||
[[om:Australia]] |
|||
[[uz:Avstraliya Hamjamiyati]] |
|||
[[pa:ਆਸਟ੍ਰੇਲੀਆ]] |
|||
[[pnb:آسٹریلیا]] |
|||
[[pap:Australia]] |
|||
[[ps:آسټراليا]] |
|||
[[km:អូស្ត្រាលី]] |
|||
[[pms:Australia]] |
|||
[[tpi:Ostrelia]] |
|||
[[nds:Australien]] |
|||
[[pl:Australia]] |
|||
[[pnt:Αυστραλία]] |
|||
[[pt:Austrália]] |
|||
[[crh:Avstraliya]] |
|||
[[ty:Autereraria]] |
|||
[[ro:Australia]] |
|||
[[rm:Australia]] |
|||
[[qu:Awstralya]] |
|||
[[rue:Австральскій Союз]] |
|||
[[ru:Австралия]] |
|||
[[sah:Аустралиа]] |
|||
[[se:Austrália]] |
|||
[[sm:Ausetalia]] |
|||
[[sa:आस्ट्रेलिया]] |
|||
[[sg:Ostralïi]] |
|||
[[sco:Australie]] |
|||
[[stq:Australien (Lound)]] |
|||
[[sq:Australia]] |
|||
[[scn:Australia]] |
|||
[[si:ඕස්ට්රේලියාව]] |
|||
[[simple:Australia]] |
|||
[[sk:Austrália (štát)]] |
|||
[[cu:Аѵстралі́ꙗ]] |
|||
[[sl:Avstralija]] |
|||
[[szl:Australijo]] |
|||
[[so:Australia]] |
|||
[[ckb:ئۆسترالیا]] |
|||
[[sr:Аустралија]] |
|||
[[sh:Australija]] |
|||
[[su:Australia]] |
|||
[[fi:Australia]] |
|||
[[sv:Australien]] |
|||
[[tl:Australya]] |
|||
[[ta:ஆஸ்திரேலியா]] |
|||
[[tt:Австралия]] |
|||
[[te:ఆస్ట్రేలియా]] |
|||
[[tet:Austrália]] |
|||
[[th:ประเทศออสเตรเลีย]] |
|||
[[ti:ኣውስትራሊያ]] |
|||
[[tg:Австралия]] |
|||
[[chr:ᏒᎳᏗᏝ]] |
|||
[[tr:Avustralya]] |
|||
[[tk:Awstraliýa]] |
|||
[[uk:Австралійський Союз]] |
|||
[[ur:آسٹریلیا]] |
|||
[[ug:ئاۋستىرالىيە]] |
|||
[[za:Audaihleihya]] |
|||
[[vec:Austrałia]] |
|||
[[vi:Úc]] |
|||
[[vo:Laustralän]] |
|||
[[fiu-vro:Austraalia]] |
|||
[[zh-classical:澳大利亞]] |
|||
[[vls:Australië (land)]] |
|||
[[war:Australya]] |
|||
[[wo:Óstraali]] |
|||
[[yi:אויסטראליע]] |
|||
[[yo:Austrálíà]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:澳洲]] |
|||
[[diq:Awıstralya]] |
|||
[[zea:Australië]] |
|||
[[bat-smg:Australėjė]] |
|||
[[zh:澳大利亚]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 05:29, 11 January 2025
Commonwealth of Australia | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "Advance Australia Fair"[N 1] | |
 Commonwealth of Australia
| |
| Capital | Canberra 35°18′29″S 149°07′28″E / 35.30806°S 149.12444°E |
| Largest city | Sydney (metropolitan) Melbourne (urban)[N 2] |
| Official language and national language | English (de facto) None (de jure) |
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Charles III |
| Sam Mostyn | |
| Anthony Albanese | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 1 January 1901 | |
| 15 November 1926 | |
| 9 October 1942 | |
| 3 March 1986 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 7,688,287[8][9][10] km2 (2,968,464 sq mi) (6th) |
• Water (%) | 1.79 (2015)[10] |
| Population | |
• 2025 estimate | |
• 2021 census | |
• Density | 3.6/km2 (9.3/sq mi) (244th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2020) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | very high (10th) |
| Currency | Australian dollar ($) (AUD) |
| Time zone | UTC+8; +9.5; +10 (AWST, ACST, AEST[N 4]) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+10.5; +11 (ACDT, AEDT[N 4]) |
| DST not observed in Qld, WA and NT | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy[16] |
| Drives on | Left |
| Calling code | +61 |
| ISO 3166 code | AU |
| Internet TLD | .au |
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia,[17] is a country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands.[18] Australia has a total area of 7,688,287 km2 (2,968,464 sq mi), making it the sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. It is the world's oldest,[19] flattest,[20] and driest inhabited continent,[21][22] with some of the least fertile soils.[23][24] It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates including deserts in the interior and tropical rainforests along the coast.
The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the last glacial period.[25][26][27] By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct languages and had one of the oldest living cultures in the world.[28] Australia's written history commenced with Dutch exploration of most of the coastline in the 17th-century. British colonisation began in 1788 with the establishment of the penal colony of New South Wales. By the mid-19th century, most of the continent had been explored by European settlers and five additional self-governing British colonies were established, each gaining responsible government by 1890. The colonies federated in 1901, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. This continued a process of increasing autonomy from the United Kingdom, highlighted by the Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942, and culminating in the Australia Acts of 1986.[29]
Australia is a federal parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories. Its population of more than 28 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard.[11][30] Canberra is the nation's capital, while its most populous cities are Sydney and Melbourne, both with a population of more than 5 million.[31] Australia's culture is diverse,[32] and the country has one of the highest foreign-born populations in the world.[33] It has a highly developed economy and one of the highest per capita incomes globally.[34][35][36] Its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade relations are crucial to the country's economy. It ranks highly for quality of life, health, education, economic freedom, civil liberties and political rights.[37]
Australia is a middle power, and has the world's thirteenth-highest military expenditure. It is a member of international groups including the United Nations; the G20; the OECD; the World Trade Organization; Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation; the Pacific Islands Forum; the Pacific Community; the Commonwealth of Nations; and the defence and security organisations ANZUS, AUKUS, and the Five Eyes. It is also a major non-NATO ally of the United States.[38]
Etymology
The name Australia (pronounced /əˈstreɪliə/ in Australian English)[39][page needed] is derived from the Latin Terra Australis ('southern land'), a name used for a hypothetical continent in the Southern Hemisphere since ancient times.[40] Several 16th-century cartographers used the word Australia on maps, but not to identify modern Australia.[41] When Europeans began visiting and mapping Australia in the 17th century, the name Terra Australis was applied to the new territories.[N 5]
Until the early 19th century, Australia was best known as New Holland, a name first applied by the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman in 1644 (as Nieuw-Holland) and subsequently anglicised. Terra Australis still saw occasional usage, such as in scientific texts.[N 6] The name Australia was popularised by the explorer Matthew Flinders, who said it was "more agreeable to the ear, and an assimilation to the names of the other great portions of the Earth".[47] The first time that Australia appears to have been officially used was in April 1817, when Governor Lachlan Macquarie acknowledged the receipt of Flinders' charts of Australia from Lord Bathurst.[48] In December 1817, Macquarie recommended to the Colonial Office that it be formally adopted.[49] In 1824, the Admiralty agreed that the continent should be known officially by that name.[50] The first official published use of the new name came with the publication in 1830 of The Australia Directory by the Hydrographic Office.[51]
Colloquial names for Australia include "Oz", "Straya" and "Down Under".[52] Other epithets include "the Great Southern Land", "the Lucky Country" (from the 1964 book of the same name), "the Sunburnt Country", and "the Wide Brown Land". The latter two both derive from Dorothea Mackellar's 1908 poem "My Country".[53]
History
Indigenous prehistory

Indigenous Australians comprise two broad groups:
- Aboriginal Australians, who are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, including Tasmania
- Torres Strait Islanders, who are a distinct Melanesian people of Torres Strait Islands
Human habitation of the Australian continent is estimated to have begun 50,000 to 65,000 years ago,[25][54][55][26] with the migration of people by land bridges and short sea crossings from what is now Southeast Asia.[56] It is uncertain how many waves of immigration may have contributed to these ancestors of modern Aboriginal Australians.[57][58] The Madjedbebe rock shelter in Arnhem Land is possibly the oldest site showing the presence of humans in Australia.[59][27] The oldest human remains found are the Lake Mungo remains, which have been dated to around 41,000 years ago.[60][61]
Aboriginal Australian culture is one of the oldest continuous cultures on Earth.[28][62][63][57] At the time of first European contact, Aboriginal Australians belonged to wide range of societies, with diverse economies spread across at least 250 different language groups.[64][65] Estimates of the Aboriginal population before British settlement range from 300,000 to 3 million.[66][67][68] Aboriginal Australians cultures were (and remain) deeply connected with the land and the environment, with stories of The Dreaming maintained through oral tradition, songs, dance and paintings.[69] Certain groups engaged in fire-stick farming,[70][71] fish farming,[72][73] and built semi-permanent shelters.[74][75] These practices have variously been characterised as "hunter-gatherer", "agricultural", "natural cultivation" and "intensification".[76][77][78][79][80]
Torres Strait Islander people first settled their islands at least 2,500 years ago.[81][82] Culturally and linguistically distinct from mainland Aboriginal peoples, they were seafarers and obtained their livelihood from seasonal horticulture and the resources of their reefs and seas.[83] Agriculture also developed on some islands and villages appeared by the 1300s.[84] By the mid-18th century in northern Australia, contact, trade and cross-cultural engagement had been established between local Aboriginal groups and Makassan trepangers, visiting from present-day Indonesia.[85][86][87]
European exploration and colonisation

The Dutch are the first Europeans that recorded sighting and making landfall on the Australian mainland.[88] The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken, captained by Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon.[89] He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February 1606 at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York.[90] Later that year, Spanish explorer Luís Vaz de Torres sailed through and navigated the Torres Strait Islands.[91] The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent "New Holland" during the 17th century, and although no attempt at settlement was made,[90] a number of shipwrecks left men either stranded or, as in the case of the Batavia in 1629, marooned for mutiny and murder, thus becoming the first Europeans to permanently inhabit the continent.[92] In 1770, Captain James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named "New South Wales" and claimed for Great Britain.[93]
Following the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the Union Flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788,[94][95] a date which later became Australia's national day.
Most early settlers were convicts, transported for petty crimes and assigned as labourers or servants to "free settlers" (willing immigrants). Once emancipated, convicts tended to integrate into colonial society. Convict rebellions and uprisings were suppressed under martial law,[96] which lasted for two years following the 1808 Rum Rebellion, Australia's only successful coup d'état.[97] During the next two decades, social and economic reforms, together with the establishment of a Legislative Council and Supreme Court, saw the penal colony transition to a civil society.[98][99]
The indigenous population declined for 150 years following European settlement, mainly due to infectious disease.[100][101] British colonial authorities did not sign any treaties with Aboriginal groups.[101][102] As settlement expanded, tens of thousands of Indigenous people and thousands of settlers were killed in frontier conflicts while settlers dispossessed surviving Indigenous peoples of most of their land.[103]
Colonial expansion

In 1803, a settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land (present-day Tasmania),[104] and in 1813, Gregory Blaxland, William Lawson and William Wentworth crossed the Blue Mountains west of Sydney, opening the interior to European settlement.[105] The British claim extended to the whole Australian continent in 1827 when Major Edmund Lockyer established a settlement on King George Sound (modern-day Albany).[106] The Swan River Colony (present-day Perth) was established in 1829, evolving into the largest Australian colony by area, Western Australia.[107] In accordance with population growth, separate colonies were carved from New South Wales: Tasmania in 1825, South Australia in 1836, New Zealand in 1841, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859.[108] South Australia was founded as a free colony—it never accepted transported convicts.[109] Growing opposition to the convict system culminated in its abolition in the eastern colonies by the 1850s. Initially a free colony, Western Australia practised penal transportation from 1850 to 1868.[110]
The six colonies individually gained responsible government between 1855 and 1890, thus becoming elective democracies managing most of their own affairs while remaining part of the British Empire.[111] The Colonial Office in London retained control of some matters, notably foreign affairs.[112]
In the mid-19th century, explorers such as Burke and Wills charted Australia's interior.[113] A series of gold rushes beginning in the early 1850s led to an influx of new migrants from China, North America and continental Europe,[114] as well as outbreaks of bushranging and civil unrest; the latter peaked in 1854 when Ballarat miners launched the Eureka Rebellion against gold licence fees.[115] The 1860s saw the rise of blackbirding, where South Sea Islanders were coerced or abducted into indentured labour, mainly by Queensland colonists.[116][117]
From 1886, Australian colonial governments began removing many Aboriginal children from their families and communities, justified on the grounds of child protection and forced assimilation policies.[118][119][120] The Second Boer War (1899–1902) marked the largest overseas deployment of Australia's colonial forces.[121][122]
Federation to the World Wars

On 1 January 1901, federation of the colonies was achieved after a decade of planning, constitutional conventions and referendums, resulting in the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia as a nation under the new Australian Constitution.[123]
After the 1907 Imperial Conference, Australia and several other self-governing British settler colonies were given the status of self-governing dominions within the British Empire.[124] Australia was one of the founding members of the League of Nations in 1920,[125] and the United Nations in 1945.[126] The Statute of Westminster 1931 formally ended the ability of the UK to pass federal laws without Australia's consent. Australia adopted it in 1942, but it was backdated to 1939 to confirm the validity of legislation passed during World War II.[127][128][129]
The Australian Capital Territory was formed in 1911 as the location for the future federal capital of Canberra.[130] While it was being constructed, Melbourne served as the temporary capital from 1901 to 1927.[131] The Northern Territory was transferred from the control of South Australia to the Commonwealth in 1911.[132] Australia became the colonial ruler of the Territory of Papua (which had initially been annexed by Queensland in 1883) in 1902 and of the Territory of New Guinea (formerly German New Guinea) in 1920.[133][134] The two were unified as the Territory of Papua and New Guinea in 1949 and gained independence from Australia in 1975.[133][135]

In 1914, Australia joined the Allies in fighting the First World War, and took part in many of the major battles fought on the Western Front.[136] Of about 416,000 who served, about 60,000 were killed and another 152,000 were wounded.[137] Many Australians regard the defeat of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) at Gallipoli in 1915 as the "baptism of fire" that forged the new nation's identity.[138][139][140] The beginning of the campaign is commemorated annually on Anzac Day, a date which rivals Australia Day as the nation's most important.[141][142]
From 1939 to 1945, Australia joined the Allies in fighting the Second World War. Australia's armed forces fought in the Pacific, European and Mediterranean and Middle East theatres.[143][144] The shock of Britain's defeat in Singapore in 1942, followed soon after by the bombing of Darwin and other Japanese attacks on Australian soil, led to a widespread belief in Australia that a Japanese invasion was imminent, and a shift from the United Kingdom to the United States as Australia's principal ally and security partner.[145] Since 1951, Australia has been allied with the United States under the ANZUS treaty.[146]
Post-war and contemporary eras

In the decades following World War II, Australia enjoyed significant increases in living standards, leisure time and suburban development.[147][148] Governments encouraged a large wave of immigration from across Europe, with such immigrants referred to as "New Australians".[149] This required a relaxation of the white Australia policy, which was justified to Australians using the slogan "populate or perish".[150]
A member of the Western Bloc during the Cold War, Australia participated in the Korean War and the Malayan Emergency during the 1950s and the Vietnam War from 1962 to 1972.[151] During this time, tensions over communist influence in society led to unsuccessful attempts by the Menzies Government to ban the Communist Party of Australia,[152] and a bitter split in the Labor Party in 1955.[153]
As a result of a 1967 referendum, the federal government gained the power to legislate with regard to Indigenous Australians, and Indigenous Australians were fully included in the census.[154] Pre-colonial land interests (referred to as native title in Australia) was recognised in law for the first time when the High Court of Australia held in Mabo v Queensland (No 2) that Australia was neither terra nullius ('land belonging to no one') or "desert and uncultivated land" at the time of European settlement.[155][156]
Following the abolition of the last vestiges of the White Australia policy in 1973,[157] Australia's demography and culture transformed as a result of a large and ongoing wave of non-European immigration, mostly from Asia.[158][159] The late 20th century also saw an increasing focus on foreign policy ties with other Pacific Rim nations.[160] The Australia Acts severed the remaining constitutional ties between Australia and the United Kingdom while maintaining the monarch in her independent capacity as Queen of Australia.[161][162] In a 1999 constitutional referendum, 55% of voters rejected abolishing the monarchy and becoming a republic.[163]
Following the September 11 attacks on the United States, Australia joined the United States in fighting the Afghanistan War from 2001 to 2021 and the Iraq War from 2003 to 2009.[164] The nation's trade relations also became increasingly oriented towards East Asia in the 21st century, with China becoming the nation's largest trading partner by a large margin.[165]
In 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, several of Australia's largest cities were locked down for extended periods and free movement across the national and state borders was restricted in an attempt to slow the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.[166]
Geography
General characteristics
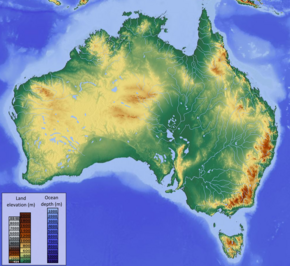
Surrounded by the Indian and Pacific oceans,[N 7] Australia is separated from Asia by the Arafura and Timor seas, with the Coral Sea lying off the Queensland coast, and the Tasman Sea lying between Australia and New Zealand. The world's smallest continent[168] and sixth-largest country by total area,[169] Australia—owing to its size and isolation—is often dubbed the "island continent"[170] and is sometimes considered the world's largest island.[171] Australia has 34,218 km (21,262 mi) of coastline (excluding all offshore islands),[172] and claims an extensive exclusive economic zone of 8,148,250 square kilometres (3,146,060 sq mi). This exclusive economic zone does not include the Australian Antarctic Territory.[173]
Mainland Australia lies between latitudes 9° and 44° south, and longitudes 112° and 154° east.[8] Australia's size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with tropical rainforests in the north-east, mountain ranges in the south-east, south-west and east, and desert in the centre.[174] The desert or semi-arid land commonly known as the outback makes up by far the largest portion of land.[175] Australia is the driest inhabited continent; its annual rainfall averaged over continental area is less than 500 mm.[176] The population density is 3.4 inhabitants per square kilometre, although the large majority of the population lives along the temperate south-eastern coastline. The population density exceeds 19,500 inhabitants per square kilometre in central Melbourne.[177] In 2021 Australia had 10% of the global permanent meadows and pastureland.[178] Forest cover is around 17% of Australia's total land area.[179][180]

The Great Barrier Reef, the world's largest coral reef,[181] lies a short distance off the north-east coast and extends for more than 2,000 km (1,200 mi). Mount Augustus, claimed to be the world's largest monolith,[182] is located in Western Australia. At 2,228 m (7,310 ft), Mount Kosciuszko is the highest mountain on the Australian mainland. Even taller are Mawson Peak, at 2,745 m (9,006 ft), on the remote Australian external territory of Heard Island, and, in the Australian Antarctic Territory, Mount McClintock and Mount Menzies, at 3,492 m (11,457 ft) and 3,355 m (11,007 ft) respectively.[183]
Eastern Australia is marked by the Great Dividing Range, which runs parallel to the coast of Queensland, New South Wales and much of Victoria. The name is not strictly accurate, because parts of the range consist of low hills, and the highlands are typically no more than 1,600 m (5,200 ft) in height.[184] The coastal uplands and a belt of Brigalow grasslands lie between the coast and the mountains, while inland of the dividing range are large areas of grassland and shrubland.[184][185] These include the western plains of New South Wales, and the Mitchell Grass Downs and Mulga Lands of inland Queensland.[186][187][188][189] The northernmost point of the mainland is the tropical Cape York Peninsula.[8]

The landscapes of the Top End and the Gulf Country—with their tropical climate—include forest, woodland, wetland, grassland, rainforest and desert.[190][191][192] At the north-west corner of the continent are the sandstone cliffs and gorges of The Kimberley, and below that the Pilbara. The Victoria Plains tropical savanna lies south of the Kimberley and Arnhem Land savannas, forming a transition between the coastal savannas and the interior deserts.[193][194][195] At the heart of the country are the uplands of central Australia. Prominent features of the centre and south include Uluru (also known as Ayers Rock), the famous sandstone monolith, and the inland Simpson, Tirari and Sturt Stony, Gibson, Great Sandy, Tanami, and Great Victoria deserts, with the famous Nullarbor Plain on the southern coast.[196][197][198][199] The Western Australian mulga shrublands lie between the interior deserts and Mediterranean-climate Southwest Australia.[198][200]
Geology

Lying on the Indo-Australian Plate, the mainland of Australia is the lowest and most primordial landmass on Earth with a relatively stable geological history.[201][202] The landmass includes virtually all known rock types and from all geological time periods spanning more than 3.8 billion years of the Earth's history. The Pilbara Craton is one of only two pristine Archaean 3.6–2.7 Ga (billion years ago) crusts identified on the Earth.[203]
Having been part of all major supercontinents, the Australian continent began to form after the break-up of Gondwana in the Permian, with the separation of the continental landmass from the African continent and Indian subcontinent. It separated from Antarctica over a prolonged period beginning in the Permian and continuing through to the Cretaceous.[204] When the last glacial period ended in about 10,000 BC, rising sea levels formed Bass Strait, separating Tasmania from the mainland. Then between about 8,000 and 6,500 BC, the lowlands in the north were flooded by the sea, separating New Guinea, the Aru Islands, and the mainland of Australia.[205] The Australian continent is moving toward Eurasia at the rate of 6 to 7 centimetres a year.[206]
The Australian mainland's continental crust, excluding the thinned margins, has an average thickness of 38 km, with a range in thickness from 24 km to 59 km.[207] Australia's geology can be divided into several main sections, showcasing that the continent grew from west to east: the Archaean cratonic shields found mostly in the west, Proterozoic fold belts in the centre and Phanerozoic sedimentary basins, metamorphic and igneous rocks in the east.[208]
The Australian mainland and Tasmania are situated in the middle of the tectonic plate and have no active volcanoes,[209] but due to passing over the East Australia hotspot, recent volcanism has occurred during the Holocene, in the Newer Volcanics Province of western Victoria and south-eastern South Australia. Volcanism also occurs in the island of New Guinea (considered geologically as part of the Australian continent), and in the Australian external territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands.[210] Seismic activity in the Australian mainland and Tasmania is also low, with the greatest number of fatalities having occurred in the 1989 Newcastle earthquake.[211]
Climate

The climate of Australia is significantly influenced by ocean currents, including the Indian Ocean Dipole and the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, which is correlated with periodic drought, and the seasonal tropical low-pressure system that produces cyclones in northern Australia.[213][214] These factors cause rainfall to vary markedly from year to year. Much of the northern part of the country has a tropical, predominantly summer-rainfall (monsoon).[176] The south-west corner of the country has a Mediterranean climate.[215] The south-east ranges from oceanic (Tasmania and coastal Victoria) to humid subtropical (upper half of New South Wales), with the highlands featuring alpine and subpolar oceanic climates. The interior is arid to semi-arid.[176]
Driven by climate change, average temperatures have risen more than 1°C since 1960. Associated changes in rainfall patterns and climate extremes exacerbate existing issues such as drought and bushfires. 2019 was Australia's warmest recorded year,[216] and the 2019–2020 bushfire season was the country's worst on record.[217] Australia's greenhouse gas emissions per capita are among the highest in the world.[218]
Water restrictions are frequently in place in many regions and cities of Australia in response to chronic shortages due to urban population increases and localised drought.[219][220] Throughout much of the continent, major flooding regularly follows extended periods of drought, flushing out inland river systems, overflowing dams and inundating large inland flood plains, as occurred throughout Eastern Australia in the early 2010s after the 2000s Australian drought.[221]
Biodiversity

Although most of Australia is semi-arid or desert, the continent includes a diverse range of habitats from alpine heaths to tropical rainforests. Fungi typify that diversity—an estimated 250,000 species—of which only 5% have been described—occur in Australia.[222] Because of the continent's great age, extremely variable weather patterns, and long-term geographic isolation, much of Australia's biota is unique. About 85% of flowering plants, 84% of mammals, more than 45% of birds, and 89% of in-shore, temperate-zone fish are endemic.[223] Australia has at least 755 species of reptile, more than any other country in the world.[224] Besides Antarctica, Australia is the only continent that developed without feline species. Feral cats may have been introduced in the 17th century by Dutch shipwrecks, and later in the 18th century by European settlers. They are now considered a major factor in the decline and extinction of many vulnerable and endangered native species.[225] Seafaring immigrants from Asia are believed to have brought the dingo to Australia sometime after the end of the last ice age—perhaps 4000 years ago—and Aboriginal people helped disperse them across the continent as pets, contributing to the demise of thylacines on the mainland.[226] Australia is also one of 17 megadiverse countries.[227]
Australian forests are mostly made up of evergreen species, particularly eucalyptus trees in the less arid regions; wattles replace them as the dominant species in drier regions and deserts.[228] Among well-known Australian animals are the monotremes (the platypus and echidna); a host of marsupials, including the kangaroo, koala, and wombat, and birds such as the emu and the kookaburra.[228] Australia is home to many dangerous animals including some of the most venomous snakes in the world.[229] The dingo was introduced by Austronesian people who traded with Indigenous Australians around 3000 BCE.[230] Many animal and plant species became extinct soon after first human settlement,[231] including the Australian megafauna; others have disappeared since European settlement, among them the thylacine.[232][233]
Many of Australia's ecoregions, and the species within those regions, are threatened by human activities and introduced animal, chromistan, fungal and plant species.[234] All these factors have led to Australia's having the highest mammal extinction rate of any country in the world.[235] The federal Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 is the legal framework for the protection of threatened species.[236] Numerous protected areas have been created under the National Strategy for the Conservation of Australia's Biological Diversity to protect and preserve unique ecosystems;[237][238] 65 wetlands are listed under the Ramsar Convention,[239] and 16 natural World Heritage Sites have been established.[240] Australia was ranked 21st out of 178 countries in the world on the 2018 Environmental Performance Index.[241] There are more than 1,800 animals and plants on Australia's threatened species list, including more than 500 animals.[242] Paleontologists discovered a fossil site of a prehistoric rainforest in McGraths Flat, in South Australia, that presents evidence that this now arid desert and dry shrubland/grassland was once home to an abundance of life.[243][244]
Government and politics
Australia is a constitutional monarchy, a parliamentary democracy and a federation.[245] The country has maintained its mostly unchanged constitution alongside a stable liberal democratic political system since Federation in 1901. It is one of the world's oldest federations, in which power is divided between the federal and state governments. The Australian system of government combines elements derived from the political systems of the United Kingdom (a fused executive, constitutional monarchy and strong party discipline) and the United States (federalism, a written constitution and strong bicameralism with an elected upper house), resulting in a distinct hybrid.[246][247]
Federal government power is partially separated between three groups:[248]
- Legislature: the bicameral Parliament, comprising the monarch, the Senate, and the House of Representatives
- Executive: the Australian Government, led by the prime minister (the leader of the party or coalition with a majority in the House of Representatives), their chosen Cabinet and other ministers; formally appointed by the governor-general[249]
- Judiciary: the High Court and other federal courts
Charles III reigns as King of Australia and is represented in Australia by the governor-general at the federal level and by the governors at the state level, who by section 63 of the Constitution and convention act on the advice of their ministers.[250][251] Thus, in practice the governor-general acts as a legal figurehead for the actions of the prime minister and the Cabinet. The governor-general may in some situations exercise reserve powers: powers exercisable in the absence or contrary to ministerial advice. When these powers may be exercised is governed by convention and their precise scope is unclear. The most notable exercise of these powers was the dismissal of the Whitlam government in the constitutional crisis of 1975.[252]

In the Senate (the upper house), there are 76 senators: twelve each from the states and two each from the mainland territories (the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory).[253] The House of Representatives (the lower house) has 151 members elected from single-member electoral divisions, commonly known as "electorates" or "seats", allocated to states on the basis of population, with each of the current states guaranteed a minimum of five seats.[254] The lower house has a maximum term of three years, but this is not fixed and governments usually dissolve the house early for an election at some point in the 6 months before the maximum.[255] Elections for both chambers are generally held simultaneously with senators having overlapping six-year terms except for those from the territories, whose terms are not fixed but are tied to the electoral cycle for the lower house. Thus only 40 of the 76 places in the Senate are put to each election unless the cycle is interrupted by a double dissolution.[253]
Australia's electoral system uses preferential voting for the House of Representatives and all state and territory lower house elections (with the exception of Tasmania and the ACT which use the Hare-Clark system). The Senate and most state upper houses use the proportional system which combines preferential voting with proportional representation for each state. Voting and enrolment is compulsory for all enrolled citizens 18 years and older in every jurisdiction.[256][257][258] The party with majority support in the House of Representatives forms the government and its leader becomes Prime Minister. In cases where no party has majority support, the governor-general has the constitutional power to appoint the prime minister and, if necessary, dismiss one that has lost the confidence of Parliament.[259] Due to the relatively unique position of Australia operating as a Westminster parliamentary democracy with a powerful and elected upper house, the system has sometimes been referred to as having a "Washminster mutation",[246] or as a semi-parliamentary system.[260]
There are two major political groups that usually form government federally: the Australian Labor Party and the Coalition, which is a formal grouping of the Liberal Party and its minor partner, the National Party.[261][262] At the state level of government, the relationship between the Nationals and the Liberal Party differs, with the parties merged in Queensland and the Northern Territory (federal parliamentarians sit in either the Liberal or National partyroom however); in coalition in New South Wales, Victoria and Western Australia; and in competition with the Liberals in South Australia and Tasmania.[263] Within Australian political culture, the Coalition is considered centre-right and the Labor Party is considered centre-left.[264] Independent members and several minor parties have achieved representation in Australian parliaments, mostly in upper houses. The Australian Greens are the third largest party by both vote and membership and the fourth largest by parliamentary representation.[265][266] The most recent federal election was held on 21 May 2022 and resulted in the Australian Labor Party, led by Anthony Albanese, being elected to government.[267]
States and territories

Australia has six states—New South Wales (NSW), Victoria (Vic), Queensland (Qld), Western Australia (WA), South Australia (SA) and Tasmania (Tas)—and two mainland self-governing territories—the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) and the Northern Territory (NT).[268]
The states have the general power to make laws except in the few areas where the constitution grants the Commonwealth exclusive powers.[269][270] The Commonwealth can only make laws on topics listed in the constitution but its laws prevail over those of the states to the extent of any inconsistency.[271][272] Since Federation, the Commonwealth's power relative to the states has significantly increased due to the increasingly wide interpretation given to listed Commonwealth powers – and because of the states' heavy financial reliance on Commonwealth grants.[273][274]
Each state and major mainland territory has its own parliament—unicameral in the Northern Territory, the ACT and Queensland, and bicameral in the other states. The lower houses are known as the Legislative Assembly (the House of Assembly in South Australia and Tasmania); the upper houses are known as the Legislative Council. The head of the government in each state is the Premier and in each territory the Chief Minister. The King is represented in each state by a governor. At the Commonwealth level, the King's representative is the governor-general.[251]
The Commonwealth government directly administers the internal Jervis Bay Territory and the external territories: the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, the Coral Sea Islands, the Heard Island and McDonald Islands, the Indian Ocean territories (Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands), Norfolk Island,[277] and the Australian Antarctic Territory.[278][279][249] The remote Macquarie Island and Lord Howe Island are part of Tasmania and New South Wales respectively.[280][281]
Foreign relations
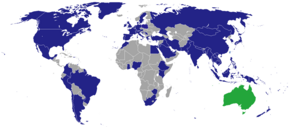
Australia is a middle power,[282] whose foreign relations has three core bi-partisan pillars: commitment to the US alliance, engagement with the Indo-Pacific and support for international institutions, rules and co-operation.[283][284][285] Through the ANZUS pact and its status as a major non-NATO ally, Australia maintains a close relationship with the US, which encompasses strong defence, security and trade ties.[286][287] In the Indo-Pacific, the country seeks to increase its trade ties through the open flow of trade and capital, while managing the rise of Chinese power by supporting the existing rules based order.[284] Regionally, the country is a member of the Pacific Islands Forum, the Pacific Community, the ASEAN+6 mechanism and the East Asia Summit. Internationally, the country is a member of the United Nations (of which it was a founding member), the Commonwealth of Nations, the OECD and the G20. This reflects the country's generally strong commitment to multilateralism.[288][289]
Australia is a member of several defence, intelligence and security groupings including the Five Eyes intelligence alliance with the United States, United Kingdom, Canada and New Zealand; the ANZUS alliance with the United States and New Zealand; the AUKUS security treaty with the United States and United Kingdom; the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue with the United States, India and Japan; the Five Power Defence Arrangements with New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Malaysia and Singapore; and the Reciprocal Access defence and security agreement with Japan.

Australia has pursued the cause of international trade liberalisation.[290] It led the formation of the Cairns Group and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,[291][292] and is a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the World Trade Organization (WTO).[293][294] Beginning in the 2000s, Australia entered into the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership multilateral free trade agreements as well as bilateral free trade agreements with the United States, China, Japan, South Korea, Indonesia, the United Kingdom and New Zealand, with the most recent deal signed in 2023 with the UK.[295]
Australia maintains a deeply integrated relationship with neighbouring New Zealand, with free mobility of citizens between the two countries under the Trans-Tasman Travel Arrangement and free trade under the Closer Economic Relations agreement.[296] The most favourably viewed countries by the Australian people in 2021 include New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Japan, Germany, Taiwan, Thailand, the United States and South Korea.[297] It also maintains an international aid program under which some 75 countries receive assistance.[298] Australia ranked fourth in the Center for Global Development's 2021 Commitment to Development Index.[299]
The power over foreign policy is highly concentrated in the prime minister and the national security committee, with major decision such as joining the 2003 invasion of Iraq made with without prior Cabinet approval.[300][301] Similarly, the Parliament does not play a formal role in foreign policy and the power to declare war lies solely with the executive government.[302] The Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade supports the executive in its policy decisions.[303]
Military

The two main institutions involved in the management of Australia's armed forces are the Australian Defence Force (ADF) and the Department of Defence, together known as "Defence".[304] The Australian Defence Force is the military wing, headed by the chief of the defence force, and contains three branches: the Royal Australian Navy, the Australian Army and the Royal Australian Air Force. In 2021, it had 84,865 currently serving personnel (including 60,286 regulars and 24,581 reservists).[305] The Department of Defence is the civilian wing and is headed by the secretary of defence. These two leaders collective manage Defence as a diarchy, with shared and joint responsibilities.[306] The titular role of commander-in-chief is held by the governor-general; however, actual command is vested in the chief of the Defence Force.[307] The executive branch of the Commonwealth government has overall control of the military through the minister of defence, who is subject to the decisions of Cabinet and its National Security Committee.[308] Major Australian intelligence agencies include the Australian Secret Intelligence Service (foreign intelligence), the Australian Signals Directorate (signals intelligence) and the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (domestic security).
In 2022, defence spending was 1.9% of GDP, representing the world's 13th-largest defence budget.[309] In 2024, the ADF had active operations in the Middle East and the Indo-Pacific (including security and aid provisions); was contributing to UN forces in relation to South Sudan, Syria–Israel peacekeeping, and North Korea; and domestically was assisting to prevent asylum-seekers enter the country and assisting in natural disaster relief.[310]
Human rights
Australia has generally strong protections for civil and political rights, and the country has signed up to a wide range of international rights treaties.[311] Important documents protecting human rights include the Constitution, the Racial Discrimination Act 1975, the Sex Discrimination Act 1984, the Disability Discrimination Act 1992, and the Age Discrimination Act 2004.[312] Same-sex marriage has been legal in the nation since 2017.[313][314] Unlike other comparable Western democracies, Australia does not have a single federal charter of rights in the Constitution or under legislation; however, the ACT, Victoria, and Queensland have state-based ones.
International organisations such as Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International have expressed concerns in areas including asylum-seeker policy, Indigenous deaths in custody, the lack of entrenched rights protection, and laws restricting protesting.[315][316]
Economy

Australia's high-income mixed-market economy is rich in natural resources.[317] It is the world's fourteenth-largest by nominal terms, and the 18th-largest by PPP. As of 2021[update], it has the second-highest amount of wealth per adult, after Luxembourg,[318] and has the thirteenth-highest financial assets per capita.[319] Australia has a labour force of some 13.5 million, with an unemployment rate of 3.5% as of June 2022.[320] According to the Australian Council of Social Service, the poverty rate of Australia exceeds 13.6% of the population, encompassing 3.2 million. It also estimated that there were 774,000 (17.7%) children under the age of 15 living in relative poverty.[321][322] The Australian dollar is the national currency, which is also used by three island states in the Pacific: Kiribati, Nauru, and Tuvalu.[323]
Australian government debt, about $963 billion in June 2022, exceeds 45.1% of the country's total GDP, and is the world's eighth-highest.[324] Australia had the second-highest level of household debt in the world in 2020, after Switzerland.[325] Its house prices are among the highest in the world, especially in the large urban areas.[326] The large service sector accounts for about 71.2% of total GDP, followed by the industrial sector (25.3%), while its agriculture sector is by far the smallest, making up only 3.6% of total GDP.[327] Australia is the world's 21st-largest exporter and 24th-largest importer.[328][329] China is Australia's largest trading partner by a wide margin, accounting for roughly 40% of the country's exports and 17.6% of its imports.[330] Other major export markets include Japan, the United States, and South Korea.[331]
Australia has high levels of competitiveness and economic freedom, and was ranked tenth in the Human Development Index in 2022.[332] As of 2022[update], it is ranked twelfth in the Index of Economic Freedom and nineteenth in the Global Competitiveness Report.[333][334] It attracted 9.5 million international tourists in 2019,[335] and was ranked thirteenth among the countries of Asia-Pacific in 2019 for inbound tourism.[336] The 2021 Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report ranked Australia seventh-highest in the world out of 117 countries.[337] Its international tourism receipts in 2019 amounted to $45.7 billion.[336]
Energy
In 2021–22, Australia's generation of electricity was sourced from black coal (37.2%), brown coal (12%), natural gas (18.8%), hydro (6.5%), wind (11.1%), solar (13.3%), bio-energy (1.2%) and others (1.7%).[338][339] Total consumption of energy in this period was sourced from coal (28.4%), oil (37.3%), gas (27.4%) and renewables (7%).[340] From 2012 to 2022, the energy sourced from renewables has increased 5.7%, while energy sourced from coal has decreased 2.6%. The use of gas also increased by 1.5% and the use of oil stayed relatively stable with a reduction of only 0.2%.[341]
In 2020, Australia produced 27.7% of its electricity from renewable sources, exceeding the target set by the Commonwealth government in 2009 of 20% renewable energy by 2020.[342][343] A new target of 82% per cent renewable energy by 2030 was set in 2022[344] and a target for net zero emissions by 2050 was set in 2021.[345]
Science and technology
In 2019, Australia spent $35.6 billion on research and development, allocating about 1.79% of GDP.[346] A recent study by Accenture for the Tech Council shows that the Australian tech sector combined contributes $167 billion a year to the economy and employs 861,000 people.[347] In addition, recent startup ecosystems in Sydney and Melbourne are already valued at $34 billion combined.[348] Australia ranked 23rd in the Global Innovation Index 2024.[349]
With only 0.3% of the world's population, Australia contributed 4.1% of the world's published research in 2020, making it one of the top 10 research contributors in the world.[350][351] CSIRO, Australia's national science agency, contributes 10% of all research in the country, while the rest is carried out by universities.[351] Its most notable contributions include the invention of atomic absorption spectroscopy,[352] the essential components of Wi-Fi technology,[353] and the development of the first commercially successful polymer banknote.[354] As of 2024[update], 13 Australian scientists have been awarded the Nobel Prize in physics, chemistry or medicine,[355] and two have been awarded the Fields Medal.[356]
Australia is a key player in supporting space exploration. Facilities such as the Square Kilometre Array and Australia Telescope Compact Array radio telescopes, telescopes such as the Siding Spring Observatory, and ground stations such as the Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex are of great assistance in deep space exploration missions, primarily by NASA.[357]
Demographics
Australia has a population density of 3.4 persons per square kilometre of total land area, which makes it one of the most sparsely populated countries in the world. The population is heavily concentrated on the east coast, and in particular in the south-eastern region between South East Queensland to the north-east and Adelaide to the south-west.[31]
Australia is also highly urbanised, with 67% of the population living in the Greater Capital City Statistical Areas (metropolitan areas of the state and mainland territorial capital cities) in 2018.[358] Metropolitan areas with more than one million inhabitants are Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.[31]
In common with many other developed countries, Australia is experiencing a demographic shift towards an older population, with more retirees and fewer people of working age. In 2021, the average age of the population was 39 years.[359] In 2015, 2.15% of the Australian population lived overseas, one of the lowest proportions worldwide.[360]
Cities
Australia has five cities (including their suburbs) that have populations larger than one million people. The majority of Australia's population lives near coastlines.[361]
| Rank | Name | State | Pop. | Rank | Name | State | Pop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sydney | NSW | 5,259,764 | 11 | Geelong | Vic | 289,400 | ||
| 2 | Melbourne | Vic | 4,976,157 | 12 | Hobart | Tas | 251,047 | ||
| 3 | Brisbane | Qld | 2,568,927 | 13 | Townsville | Qld | 181,665 | ||
| 4 | Perth | WA | 2,192,229 | 14 | Cairns | Qld | 155,638 | ||
| 5 | Adelaide | SA | 1,402,393 | 15 | Darwin | NT | 148,801 | ||
| 6 | Gold Coast–Tweed Heads | Qld/NSW | 706,673 | 16 | Toowoomba | Qld | 143,994 | ||
| 7 | Newcastle–Maitland | NSW | 509,894 | 17 | Ballarat | Vic | 111,702 | ||
| 8 | Canberra–Queanbeyan | ACT/NSW | 482,250 | 18 | Bendigo | Vic | 102,899 | ||
| 9 | Sunshine Coast | Qld | 355,631 | 19 | Albury-Wodonga | NSW/Vic | 97,676 | ||
| 10 | Wollongong | NSW | 305,880 | 20 | Launceston | Tas | 93,332 | ||
Ancestry and immigration

Between 1788 and the Second World War, the vast majority of settlers and immigrants came from the British Isles (principally England, Ireland and Scotland), although there was significant immigration from China and Germany during the 19th century. Following Federation in 1901, the white Australia policy was strengthened, restricting further migration from these areas. However, this policy was relaxed following WW2 and in the decades following, Australia received a large wave of immigration from across Europe, with many more immigrants arriving from Southern and Eastern Europe than in previous decades. All overt racial discrimination ended in 1973, with multiculturalism becoming official policy.[363] Subsequently, there has been a large and continuing wave of immigration from across the world, with Asia being the largest source of immigrants in the 21st century.[364]
Today, Australia has the world's eighth-largest immigrant population, with immigrants accounting for 30% of the population, the highest proportion among major Western nations.[365][366] In 2022–23, 212,789 permanent migrants were admitted to Australia, with a net migration population gain of 518,000 people inclusive of non-permanent residents.[367][368] Most entered on skilled visas,[364] however the immigration program also offers visas for family members and refugees.[369]
The Australian Bureau of Statistics asks each Australian resident to nominate up to two ancestries each census and the responses are classified into broad ancestry groups.[370][371] At the 2021 census, the most commonly nominated ancestry groups as a proportion of the total population were:[372] 57.2% European (including 46% North-West European and 11.2% Southern and Eastern European), 33.8% Oceanian,[N 8] 17.4% Asian (including 6.5% Southern and Central Asian, 6.4% North-East Asian, and 4.5% South-East Asian), 3.2% North African and Middle Eastern, 1.4% Peoples of the Americas, and 1.3% Sub-Saharan African. At the 2021 census, the most commonly nominated individual ancestries as a proportion of the total population were:[N 9][4]
At the 2021 census, 3.8% of the Australian population identified as being Indigenous—Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders.[N 12][371]
Language
Although English is not the official language of Australia in law, it is the de facto official and national language.[375][376] Australian English is a major variety of the language with a distinctive accent and lexicon,[377] and differs slightly from other varieties of English in grammar and spelling.[378] General Australian serves as the standard dialect.[379] The Australian sign language known as Auslan was used at home by 16,242 people at the time of the 2021 census.[380]
At the 2021 census, English was the only language spoken in the home for 72% of the population. The next most common languages spoken at home were Mandarin (2.7%), Arabic (1.4%), Vietnamese (1.3%), Cantonese (1.2%) and Punjabi (0.9%).[381]
More than 250 Australian Aboriginal languages are thought to have existed at the time of first European contact.[382] The National Indigenous Languages Survey (NILS) for 2018–19 found that more than 120 Indigenous language varieties were in use or being revived, although 70 of those in use were endangered.[383] The 2021 census found that 167 Indigenous languages were spoken at home by 76,978 Indigenous Australians — Yumplatok (Torres Strait Creole), Djambarrpuyngu (a Yolŋu language) and Pitjantjatjara (a Western Desert language) were among the most widely spoken.[384] NILS and the Australian Bureau of Statistics use different classifications for Indigenous Australian languages.[385]
Religion

Australia has no state religion; section 116 of the Australian Constitution prohibits federal legislation that would establish any religion, impose any religious observance, or prohibit the free exercise of any religion.[386] However, the states still retain the power to pass religiously discriminatory laws.[387]
At the 2021 census, 38.9% of the population identified as having no religion,[4] up from 15.5% in 2001.[388] The largest religion is Christianity (43.9% of the population).[4] The largest Christian denominations are the Roman Catholic Church (20% of the population) and the Anglican Church of Australia (9.8%). Non-British immigration since the Second World War has led to the growth of non-Christian religions, the largest of which are Islam (3.2%), Hinduism (2.7%), Buddhism (2.4%), Sikhism (0.8%), and Judaism (0.4%).[389][4]
In 2021, just under 8,000 people declared an affiliation with traditional Aboriginal religions.[4] In Australian Aboriginal mythology and the animist framework developed in Aboriginal Australia, the Dreaming is a sacred era in which ancestral totemic spirit beings formed The Creation. The Dreaming established the laws and structures of society and the ceremonies performed to ensure continuity of life and land.[390]
Health
Australia's life expectancy of 83 years (81 years for males and 85 years for females)[391] is the fifth-highest in the world. It has the highest rate of skin cancer in the world,[392] while cigarette smoking is the largest preventable cause of death and disease, responsible for 7.8% of the total mortality and disease. Ranked second in preventable causes is hypertension at 7.6%, with obesity third at 7.5%.[393][394] Australia ranked 35th in the world in 2012 for its proportion of obese women[395] and near the top of developed nations for its proportion of obese adults;[396] 63% of its adult population is either overweight or obese.[397]
Australia spent around 9.91% of its total GDP to health care in 2021.[398] It introduced a national insurance scheme in 1975.[399] Following a period in which access to the scheme was restricted, the scheme became universal once more in 1981 under the name of Medicare.[400] The program is nominally funded by an income tax surcharge known as the Medicare levy, currently at 2%.[401] The states manage hospitals and attached outpatient services, while the Commonwealth funds the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (subsidising the costs of medicines) and general practice.[399]
Education

School attendance, or registration for home schooling,[402] is compulsory throughout Australia. Education is primarily the responsibility of the individual states and territories; however, the Commonwealth has significant influence through funding agreements.[403] Since 2014, a national curriculum developed by the Commonwealth has been implemented by the states and territories.[404] Attendance rules vary between states, but in general children are required to attend school from the age of about 5 until about 16.[405][406] In some states (Western Australia, Northern Territory and New South Wales), children aged 16–17 are required to either attend school or participate in vocational training, such as an apprenticeship.[407][408][409][410] According to the 2022 PISA evaluations, Australian 15-year-olds ranked ninth in the OECD for reading and science and tenth for maths. However, less than 60% of Australian students achieved the National Proficiency Standard – 51% in maths, 58% in science and 57% in reading.[411][412]
Australia has an adult literacy rate that was estimated to be 99% in 2003.[413] However, a 2011–2012 report for the Australian Bureau of Statistics found that 44% of the population does not have high literary and numeracy competence levels, interpreted by others as suggesting that they do not have the "skills needed for everyday life".[414][415][416]
Australia has 37 government-funded universities and three private universities, as well as a number of other specialist institutions that provide approved courses at the higher education level.[417] The OECD places Australia among the most expensive nations to attend university.[418] There is a state-based system of vocational training, known as TAFE, and many trades conduct apprenticeships for training new tradespeople.[419] About 58% of Australians aged from 25 to 64 have vocational or tertiary qualifications[420] and the tertiary graduation rate of 49% is the highest among OECD countries. 30.9% of Australia's population has attained a higher education qualification, which is among the highest percentages in the world.[421][422][423]
Australia has the highest ratio of international students per head of population in the world by a large margin, with 812,000 international students enrolled in the nation's universities and vocational institutions in 2019.[424][425] Accordingly, in 2019, international students represented on average 26.7% of the student bodies of Australian universities. International education therefore represents one of the country's largest exports and has a pronounced influence on the country's demographics, with a significant proportion of international students remaining in Australia after graduation on various skill and employment visas.[426] Education is Australia's third-largest export, after iron ore and coal, and contributed more than $28 billion to the economy in the 2016–17 financial year.[N 13][351]
Culture

Contemporary Australian culture reflects the country's Indigenous traditions, Anglo-Celtic heritage, and post-1945 history of multicultural immigration.[428][429][430] The culture of the United States has also been influential.[431] The evolution of Australian culture since British colonisation has given rise to distinctive cultural traits.[432][433]
Many Australians identify egalitarianism, mateship, irreverence and a lack of formality as part of their national identity.[434][435][436] These find expression in Australian slang, as well as Australian humour, which is often characterised as dry, irreverent and ironic.[437][438] New citizens and visa holders are required to commit to "Australian values", which are identified by the Department of Home Affairs as including: a respect for the freedom of the individual; recognition of the rule of law; opposition to racial, gender and religious discrimination; and an understanding of the "fair go", which is said to encompass the equality of opportunity for all and compassion for those in need.[439] What these values mean, and whether or not Australians uphold them, has been debated since before Federation.[440][441][442][443]
Arts

Australia has more than 100,000 Aboriginal rock art sites,[445] and traditional designs, patterns and stories infuse contemporary Indigenous Australian art, "the last great art movement of the 20th century" according to critic Robert Hughes;[446] its exponents include Emily Kame Kngwarreye.[447] Early colonial artists showed a fascination with the unfamiliar land.[448] The impressionistic works of Arthur Streeton, Tom Roberts and other members of the 19th-century Heidelberg School—the first "distinctively Australian" movement in Western art—gave expression to nationalist sentiments in the lead-up to Federation.[448] While the school remained influential into the 1900s, modernists such as Margaret Preston and Clarice Beckett, and, later, Sidney Nolan, explored new artistic trends.[448] The landscape remained central to the work of Aboriginal watercolourist Albert Namatjira,[449] as well as Fred Williams, Brett Whiteley and other post-war artists whose works, eclectic in style yet uniquely Australian, moved between the figurative and the abstract.[448][450]
Australian literature grew slowly in the decades following European settlement though Indigenous oral traditions, many of which have since been recorded in writing, are much older.[451] In the 19th century, Henry Lawson and Banjo Paterson captured the experience of the bush using a distinctive Australian vocabulary.[452] Their works are still popular; Paterson's bush poem "Waltzing Matilda" (1895) is regarded as Australia's unofficial national anthem.[453] Miles Franklin is the namesake of Australia's most prestigious literary prize, awarded annually to the best novel about Australian life.[454] Its first recipient, Patrick White, went on to win the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1973.[455] Australian Booker Prize winners include Peter Carey, Thomas Keneally and Richard Flanagan.[456] Australian public intellectuals have also written seminal works in their respective fields, including feminist Germaine Greer and philosopher Peter Singer.[457]

In the performing arts, Aboriginal peoples have traditions of religious and secular song, dance and rhythmic music often performed in corroborees.[458] At the beginning of the 20th century, Nellie Melba was one of the world's leading opera singers,[459] and later popular music acts such as the Bee Gees, AC/DC, INXS and Kylie Minogue achieved international recognition.[460] Many of Australia's performing arts companies receive funding through the Australian government's Australia Council.[461] There is a symphony orchestra in each state,[462] and a national opera company, Opera Australia,[463] well known for its famous soprano Joan Sutherland.[464] Ballet and dance are represented by The Australian Ballet and various state companies. Each state has a publicly funded theatre company.[465]
Media

The Story of the Kelly Gang (1906), the world's first feature-length narrative film, spurred a boom in Australian cinema during the silent film era.[466] After World War I, Hollywood monopolised the industry,[467] and by the 1960s Australian film production had effectively ceased.[468] With the benefit of government support, the Australian New Wave of the 1970s brought provocative and successful films, many exploring themes of national identity, such as Picnic at Hanging Rock, Wake in Fright and Gallipoli,[469] while Crocodile Dundee and the Ozploitation movement's Mad Max series became international blockbusters.[470] In a film market flooded with foreign content, Australian films delivered a 7.7% share of the local box office in 2015.[471] The AACTAs are Australia's premier film and television awards, and notable Academy Award winners from Australia include Geoffrey Rush, Nicole Kidman, Cate Blanchett and Heath Ledger.[472]
Australia has two public broadcasters (the Australian Broadcasting Corporation and the multicultural Special Broadcasting Service), three commercial television networks, several pay-TV services,[473] and numerous public, non-profit television and radio stations. Each major city has at least one daily newspaper,[473] and there are two national daily newspapers, The Australian and The Australian Financial Review.[473] In 2024, Reporters Without Borders placed Australia 39th on a list of 180 countries ranked by press freedom, behind New Zealand (19th) and the United Kingdom (23rd), but ahead of the United States (55th).[474] This relatively low ranking is primarily because of the limited diversity of commercial media ownership in Australia;[475] most print media are under the control of News Corp Australia (59%) and Nine Entertainment (23%).[476]
Cuisine

Most Indigenous Australian groups subsisted on a diet of native fauna and flora, otherwise called bush tucker.[477] It has increased in popularity among non-Indigenous Australians since the 1970s, with examples such as lemon myrtle, the macadamia nut and kangaroo meat now widely available.[478][479]
The first colonists introduced British and Irish cuisine to the continent.[480][481] This influence is seen in dishes such as fish and chips, and in the Australian meat pie, which is related to the British steak pie. Also during the colonial period, Chinese migrants paved the way for a distinctive Australian Chinese cuisine.[482]
Post-war migrants transformed Australian cuisine, bringing with them their culinary traditions and contributing to new fusion dishes.[483] Italians introduced espresso coffee and, along with Greeks, helped develop Australia's café culture, of which the flat white and avocado toast are now considered Australian staples.[484][485] Pavlovas, lamingtons, Vegemite and Anzac biscuits are also often called iconic Australian foods.[486]
Australia is a leading exporter and consumer of wine.[487] Australian wine is produced mainly in the southern, cooler parts of the country.[488] The nation also ranks highly in beer consumption,[489] with each state and territory hosting numerous breweries.
Sport and recreation

The most popular sports in Australia by adult participation are: swimming, athletics, cycling, soccer, golf, tennis, basketball, surfing, netball and cricket.[491]
Australia is one of five nations to have participated in every Summer Olympics of the modern era,[492] and has hosted the Games twice: 1956 in Melbourne and 2000 in Sydney.[493] It is also set to host the 2032 Games in Brisbane.[494] Australia has also participated in every Commonwealth Games,[495] hosting the event in 1938, 1962, 1982, 2006 and 2018.[496]
The Australian national cricket team competed against England in the first Test match (1877) and the first One Day International (1971), and against New Zealand in the first Twenty20 International (2004), winning all three games.[497] It has also won the men's Cricket World Cup a record six times.[498]
Australia has professional leagues for four football codes, whose relative popularity is divided geographically.[499] Originating in Melbourne in the 1850s, Australian rules football attracts the most television viewers in all states except New South Wales and Queensland, where rugby league holds sway, followed by rugby union.[500] Soccer, while ranked fourth in television viewers and resources, has the highest overall participation rates.[501]
The surf lifesaving movement originated in Australia in the early 20th century, following the relaxation of laws prohibiting daylight bathing on Australian beaches. The volunteer lifesaver is one of the country's icons.[502][503]
See also
Notes
- ^ Australia also has a royal anthem, "God Save the King", which may be played in place of or alongside the national anthem when members of the royal family are present. If not played alongside the royal anthem, the national anthem is instead played at the end of an official event.[1]
- ^ Sydney is the largest city based on Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) Greater Capital City Statistical Areas (GCCSAs). These represent labour markets and the functional area of Australian capital cities.[2] Melbourne is larger based on ABS Significant Urban Areas (SUAs). These represent Urban Centres, or groups of contiguous Urban Centres, that contain a population of 10,000 people or more.[3]
- ^ The religion question is optional in the Australian census.
- ^ a b There are minor variations from three basic time zones; see Time in Australia.
- ^ The earliest recorded use of the word Australia in English was in 1625 in "A note of Australia del Espíritu Santo, written by Sir Richard Hakluyt", published by Samuel Purchas in Hakluytus Posthumus, a corruption of the original Spanish name "Austrialia del Espíritu Santo" (Southern Land of the Holy Spirit)[42][43][44] for an island in Vanuatu.[45] The Dutch adjectival form australische was used in a Dutch book in Batavia (Jakarta) in 1638, to refer to the newly discovered lands to the south.[46]
- ^ For instance, the 1814 work A Voyage to Terra Australis.
- ^ Australia describes the body of water south of its mainland as the Southern Ocean, rather than the Indian Ocean as defined by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO). In 2000, a vote of IHO member nations defined the term "Southern Ocean" as applying only to the waters between Antarctica and 60° south latitude.[167]
- ^ Includes those who nominate "Australian" as their ancestry.[4] The Australian Bureau of Statistics has stated that most who nominate "Australian" as their ancestry have at least partial Anglo-Celtic European ancestry.[373]
- ^ Each person may nominate more than one ancestry, so the total may exceed 100%.[374]
- ^ The Australian Bureau of Statistics has stated that most who nominate "Australian" as their ancestry have at least partial Anglo-Celtic European ancestry.[373]
- ^ Those who nominated their ancestry as "Australian Aboriginal". Does not include Torres Strait Islanders. This relates to nomination of ancestry and is distinct from persons who identify as Indigenous (Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander) which is a separate question.
- ^ Indigenous identification is separate to the ancestry question on the Australian Census and persons identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander may identify any ancestry.
- ^ That is, 1 July 2016 to 30 June 2017.
References
- ^ "Australian National Anthem". Department of Prime Minister and Cabinet. 19 January 2022. Archived from the original on 27 October 2023. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ^ "Regional population, 2021-22 financial year". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 20 April 2023. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 27 May 2023.
- ^ Turnbull, Tiffanie (17 April 2023). "Melbourne overtakes Sydney as Australia's biggest city". BBC News. Archived from the original on 21 May 2023. Retrieved 27 May 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g "General Community Profile" (Excel file). 2021 Census of Population and Housing. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2022.
- ^ Pronounced "Ozzy"
- ^ "Aussie". Macquarie Dictionary. 16 October 2023. Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ^ Collins English Dictionary. Bishopbriggs, Glasgow: HarperCollins. 2009. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-0078-6171-2.
- ^ a b c "Area of Australia - States and Territories". Geoscience Australia. 27 June 2014. Archived from the original on 18 January 2024. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Australia § Geography". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 16 August 2024.
- ^ a b "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Archived from the original on 24 March 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- ^ a b "Population clock and pyramid". Australian Bureau of Statistics website. Commonwealth of Australia. 5 March 2024. Archived from the original on 8 February 2024. Retrieved 5 March 2024. The population estimate shown is automatically calculated daily at 00:00 UTC and is based on data obtained from the population clock on the date shown in the citation.
- ^ "National, state and territory population". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 26 September 2022. Archived from the original on 21 November 2022. Retrieved 26 September 2022.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Australia)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. 22 October 2024. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ "Australia Gini Coefficient, 1995 – 2023 | CEIC Data". www.ceicdata.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2024. Retrieved 4 March 2024.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ Australian Government (March 2023). "Dates and time". Style Manual. Archived from the original on 29 May 2023. Retrieved 6 May 2023.
- ^ Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act (Imp) 63 & 64 Vict, c 12, s 3 Archived 9 January 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ 41% of the Antarctic continent is also claimed by the country, however this is only recognised by the UK, France, New Zealand and Norway.
- ^ Korsch RJ.; et al. (2011). "Australian island arcs through time: Geodynamic implications for the Archean and Proterozoic". Gondwana Research. 19 (3): 716–734. Bibcode:2011GondR..19..716K. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2010.11.018. ISSN 1342-937X.
- ^ Macey, Richard (21 January 2005). "Map from above shows Australia is a very flat place". The Sydney Morning Herald. ISSN 0312-6315. OCLC 226369741. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 5 April 2010.
- ^ "The Australian continent". australia.gov.au. Archived from the original on 13 March 2020. Retrieved 13 August 2018.
- ^ "Deserts". Geoscience Australia. Australian Government. 15 May 2014. Archived from the original on 5 June 2014. Retrieved 13 August 2018.
- ^ Kelly, Karina (13 September 1995). "A Chat with Tim Flannery on Population Control". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 13 January 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010. "Well, Australia has by far the world's least fertile soils".
- ^ Grant, Cameron (August 2007). "Damaged Dirt" (PDF). The Advertiser. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
Australia has the oldest, most highly weathered soils on the planet.
- ^ a b Clarkson, Chris; et al. (2017). "Human occupation of northern Australia by 65,000 years ago". Nature. 547 (7663): 306–310. Bibcode:2017Natur.547..306C. doi:10.1038/nature22968. hdl:2440/107043. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 28726833. S2CID 205257212.
- ^ a b Veth, Peter; O'Connor, Sue (2013). "The past 50,000 years: an archaeological view". In Bashford, Alison; MacIntyre, Stuart (eds.). The Cambridge History of Australia, Volume 1, Indigenous and Colonial Australia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-1070-1153-3.
- ^ a b Williams, Martin A. J.; Spooner, Nigel A.; McDonnell, Kathryn; O'Connell, James F. (January 2021). "Identifying disturbance in archaeological sites in tropical northern Australia: Implications for previously proposed 65,000-year continental occupation date". Geoarchaeology. 36 (1): 92–108. Bibcode:2021Gearc..36...92W. doi:10.1002/gea.21822. ISSN 0883-6353. S2CID 225321249. Archived from the original on 4 October 2023. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ a b Flood, J. (2019). The Original Australians: The story of the Aboriginal People (2nd ed.). Crows Nest NSW: Allen & Unwin. p. 161. ISBN 978-1-76087-142-0.
- ^ Contiades, X.; Fotiadou, A. (2020). Routledge Handbook of Comparative Constitutional Change. Taylor & Francis. p. 389. ISBN 978-1-3510-2097-8. Archived from the original on 19 April 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ "Geographic Distribution of the Population". 24 May 2012. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2012.
- ^ a b c "Regional population". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 20 April 2023. Archived from the original on 10 October 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- ^ "Culturally and linguistically Diverse Australian". Australian Government, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. 2024. Archived from the original on 19 February 2024. Retrieved 20 February 2024.
- ^ O'Donnell, James (27 November 2023). "Is Australia a cohesive nation?". ABC Australia. Archived from the original on 20 February 2024. Retrieved 21 February 2024.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2015". International Monetary Fund. 6 September 2015. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2019.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2021-22" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 September 2022. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- ^ "Australians the world's wealthiest". The Sydney Morning Herald. 31 October 2011. Archived from the original on 10 July 2014. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
- ^ "Statistics and rankings". Global Australia. 18 May 2021. Archived from the original on 28 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023.
- ^ Rachman, Gideon (13 March 2023). "Aukus, the Anglosphere and the return of great power rivalry". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 20 March 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ Australian pronunciations: Macquarie Dictionary, Fourth Edition (2005) Melbourne, The Macquarie Library Pty Ltd. ISBN 978-1-876429-14-0
- ^ "australia | Etymology, origin and meaning of the name australia by etymonline". www.etymonline.com. Archived from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Clarke, Jacqueline; Clarke, Philip (10 August 2014). "Putting 'Australia' on the map". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 2 March 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ "He named it Austrialia del Espiritu Santo and claimed it for Spain" Archived 17 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine The Spanish quest for Terra Australis|State Library of New South Wales Page 1
- ^ "A note on 'Austrialia' or 'Australia' Rupert Gerritsen – Journal of The Australian and New Zealand Map Society Inc. The Globe Number 72, 2013 Archived 12 June 2016 at the Wayback Machine Posesion en nombre de Su Magestad (Archivo del Museo Naval, Madrid, MS 951) p. 3.
- ^ "The Illustrated Sydney News". Illustrated Sydney News. National Library of Australia. 26 January 1888. p. 2. Archived from the original on 11 October 2023. Retrieved 29 January 2012.
- ^ Purchas, vol. iv, pp. 1422–1432, 1625
- ^ Scott, Ernest (2004) [1914]. The Life of Captain Matthew Flinders. Kessinger Publishing. p. 299. ISBN 978-1-4191-6948-9. Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Scott, Ernest (1914). "The naming of Australia". The Life of Captain Matthew Flinders, R.N. Sydney: Angus & Robertson. p. 428.
- ^ "Who Named Australia?". The Mail (Adelaide, South Australia). Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 11 February 1928. p. 16. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2012.
- ^ Weekend Australian, 30–31 December 2000, p. 16
- ^ Department of Immigration and Citizenship (2007). Life in Australia (PDF). Commonwealth of Australia. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-9214-4630-6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 October 2009. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ Coman, Brian J. (2007). A Loose Canon: Essays on History, Modernity and Tradition. Connor Court Publishing Pty Ltd. ISBN 978-0-9802-9362-3. Archived from the original on 27 March 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ "Straya". Macquarie Dictionary. Archived from the original on 9 February 2024. Retrieved 12 February 2024.
- ^ School, Head of; admin.hal@anu.edu.au. "Australian National Dictionary Centre". ANU School of Literature, Languages and Linguistics. Archived from the original on 12 March 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Nunn, Patrick (2018). The Edge of Memory: Ancient Stories, Oral Tradition and the Post-Glacial World. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 16. ISBN 978-1-4729-4327-9. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Fagan, Brian M.; Durrani, Nadia (2018). People of the Earth: An Introduction to World Prehistory. Taylor & Francis. pp. 250–253. ISBN 978-1-3517-5764-5. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Oppenheimer, Stephen (2013). Out of Eden: The Peopling of the World. Little, Brown Book Group. pp. 111–. ISBN 978-1-7803-3753-1. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ a b Malaspinas, Anna-Sapfo; et al. (21 September 2016). "A genomic history of Aboriginal Australia". Nature. 538 (7624). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 207–214. Bibcode:2016Natur.538..207M. doi:10.1038/nature18299. hdl:10754/622366. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 7617037. PMID 27654914.
- ^ Dorey, Fran. "When did modern humans get to Australia?". Australian Museum. Archived from the original on 17 August 2020. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ Gilligan, Ian (2018). Climate, Clothing, and Agriculture in Prehistory: Linking Evidence, Causes, and Effects. Cambridge University Press. p. 237. ISBN 978-1-1084-7008-7. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Tuniz, Claudio; Gillespie, Richard; Jones, Cheryl (2016). The Bone Readers: Science and Politics in Human Origins Research. Routledge. p. 43. ISBN 978-1-3154-1888-9. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Castillo, Alicia (2015). Archaeological Dimension of World Heritage: From Prevention to Social Implications. Springer Science. p. 41. ISBN 978-1-4939-0283-5. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ "DNA confirms Aboriginal culture one of Earth's oldest". Australian Geographic. 23 September 2011. Archived from the original on 20 January 2024. Retrieved 9 February 2024.
- ^ Jozuka, Emiko (22 September 2016). "Aboriginal Australians are Earth's oldest civilization: DNA study". CNN. Archived from the original on 4 March 2024. Retrieved 9 February 2024.
- ^ Williams, Elizabeth (2015). "Complex hunter-gatherers: a view from Australia". Antiquity. 61 (232). Cambridge University Press: 310–321. doi:10.1017/S0003598X00052182. S2CID 162146349.
- ^ Sáenz, Rogelio; Embrick, David G.; Rodríguez, Néstor P. (3 June 2015). The International Handbook of the Demography of Race and Ethnicity. Springer. pp. 602–. ISBN 978-9-0481-8891-8. Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Bradshaw, Corey J. A.; Williams, Alan N; Saltré, Frédérik; Norman, Kasih; Ulm, Sean (30 April 2021). "The First Australians grew to a population of millions, much more than previous estimates". The Conversation.
- ^ "1301.0 - Year Book Australia, 2002: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander population". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 25 January 2002. Archived from the original on 27 March 2023.
- ^ Gough, Myles (11 May 2011). "Prehistoric Australian Aboriginal populations were growing". Cosmos Magazine. Archived from the original on 12 September 2012.
- ^ Mawson, Stephanie (2021). "The Deep Past of Pre-Colonial Australia". The Historical Journal. 64 (5): 1483–6. doi:10.1017/S0018246X20000369. ISSN 0018-246X.
- ^ Wyrwoll, Karl-Heinz (11 January 2012). "How Aboriginal burning changed Australia's climate". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 15 July 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Williams, Robbie (21 June 2023). "Before the colonists came, we burned small and burned often to avoid big fires. It's time to relearn cultural burning". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 8 March 2024. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Bates, Badger; Westaway, Michael; Jackson, Sue (15 December 2022). "Aboriginal people have spent centuries building in the Darling River. Now there are plans to demolish these important structures". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 1 November 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Clark, Anna (31 August 2023). "Friday essay: traps, rites and kurrajong twine – the incredible ingenuity of Indigenous fishing knowledge". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 11 February 2024. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Wahlquist, Calla (5 September 2016). "Evidence of 9,000-year-old stone houses found on Australian island". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 1 November 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Flood, J. (2019). The Original Australians: The story of the Aboriginal People (2nd ed.). Crows Nest NSW: Allen & Unwin. pp. 239–240. ISBN 978-1-76087-142-0.
- ^ Mawson, Stephanie (2021). "The Deep Past of Pre-Colonial Australia". The Historical Journal. 64 (5): 1486–1491. doi:10.1017/S0018246X20000369. ISSN 0018-246X.
- ^ Bender, Barbara (1978). "Gatherer-hunter to farmer: A social perspective". World Archaeology. 10 (2): 204–222. doi:10.1080/00438243.1978.9979731. ISSN 0043-8243.
- ^ Gammage, Bill (October 2011). The Biggest Estate on Earth: How Aborigines made Australia. Allen & Unwin. pp. 281–304.
- ^ Gammage, Bill (19 September 2023). "Colonists upended Aboriginal farming, growing grain and running sheep on rich yamfields, and cattle on arid grainlands". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 12 February 2024. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Flood, J. (2019). The Original Australians: The story of the Aboriginal People (2nd ed.). Crows Nest NSW: Allen & Unwin. pp. 25–27, 146. ISBN 978-1-76087-142-0.
- ^ David, Bruno; et al. (July 2004). "Badu 15 and the Papuan-Austronesian settlement of Torres Strait". Archaeology in Oceania. 39 (2): 65–78. doi:10.1002/j.1834-4453.2004.tb00564.x.
- ^ "Torres Strait Islands". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2023 [1998]. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 17 November 2024.
Torres Strait Islands, island group in the Torres Strait, north of Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, Australia, and south of the island of New Guinea. [...] They have been inhabited for at least 2,500 years. The present-day inhabitants are primarily of Melanesian origin, with some mixture of Polynesians and Southeast Asians.
- ^ Viegas, Jennifer (3 July 2008). "Early Aussie Tattoos Match Rock Art". Discovery News. Archived from the original on 10 July 2008. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ Veth, Peter; O'Connor, Sue (2013). "The Past 50,000 Years: An Archaeological View". In Bashford, Alison; MacIntyre, Stuart (eds.). The Cambridge History of Australia. Vol. 1: Indigenous and Colonial Australia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 34–35. ISBN 978-1-107-01153-3.
- ^ Macknight, Charles Campbell (2011). "The view from Marege': Australian knowledge of Makassar and the impact of the trepangindustry across two centuries". Aboriginal History. 35: 134. doi:10.22459/AH.35.2011.06. JSTOR 24046930.
- ^ T. Vigilante; et al. (2013). "Biodiversity values on selected Kimberley Islands, Australia" (PDF). Western Australian Museum. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 October 2018. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ Russell, Denise (22 March 2004). "Aboriginal-Makassan interactions in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries in northern Australia and contemporary sea rights claims" (PDF). Australian Aboriginal Studies. 2004 (1). Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies: 3–17. ISSN 0729-4352. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 21 April 2019.
- ^ Barber, Peter; Barnes, Katherine; Nigel Erskine (2013). Mapping Our World: Terra Incognita To Australia. National Library of Australia. p. 99. ISBN 978-0-6422-7809-8. Archived from the original on 27 October 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Smith, Claire; Burke, Heather (2007). Digging It Up Down Under: A Practical Guide to Doing Archaeology in Australia. Springer Science. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-3873-5263-3. Archived from the original on 27 October 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ a b Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, p. 233
- ^ Brett Hilder (1980) The Voyage of Torres University of Queensland Press, St. Lucia, Queensland ISBN 978-0-7022-1275-8
- ^ Davis, Russell Earls (2019) A Concise History of Western Australia Woodslane Press ISBN 978-1-9258-6822-7 pp. 3–6
- ^ Goucher, Candice; Walton, Linda (2013). World History: Journeys from Past to Present. Routledge. pp. 427–428. ISBN 978-1-1350-8829-3. Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ "European discovery and the colonisation of Australia". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia. 11 January 2008. Archived from the original on 13 December 2017. Retrieved 7 May 2010.
[The British] moved north to Port Jackson on 26 January 1788, landing at Camp Cove, known as 'cadi' to the Cadigal people. Governor Phillip carried instructions to establish the first British Colony in Australia. The First Fleet was underprepared for the task, and the soil around Sydney Cove was poor.
- ^ Egan, Ted (2003). The Land Downunder. Grice Chapman Publishing. pp. 25–26. ISBN 978-0-9545-7260-0. Archived from the original on 28 March 2024. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Kercher, Bruce (2020). An Unruly Child: A History of Law in Australia. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781000248470. pp. 26–27.
- ^ Matsuda, Matt K. (2012) Pacific Worlds: A History of Seas, Peoples, and Cultures Cambridge University Press ISBN 978-0-5218-8763-2 pp. 165–167
- ^ Ward, Russel (1975). Australia: a short history (rev ed.). Ure Smith. pp. 37–38. ISBN 978-0-7254-0164-1. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Molony, John Neylon (1987). The Penguin History of Australia. Ringwood, Vic: Penguin. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-1400-9739-9. Archived from the original on 21 November 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Smallpox Through History. Archived from the original on 18 June 2004.
- ^ a b Flood, J. (2019). The Original Australians: The story of the Aboriginal People (2nd ed.). Crows Nest NSW: Allen & Unwin. pp. 42, 111, 147–59, 300. ISBN 978-1-76087-142-0.
- ^ Rule of Law Education Centre. "European Settlement and Terra Nullius". Archived from the original on 26 January 2024. Retrieved 26 January 2024.
- ^ Reynolds, Henry (2022). Forgotten War (2nd ed.). Sydney: NewSouth. pp. 103–104, 134, 241–242, 182–192. ISBN 9781742237596.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 464–465, 628–629
- ^ Conway, Jill. "Blaxland, Gregory (1778–1853)". Biography – Gregory Blaxland – Australian Dictionary of Biography. National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ^ Grey, Jeffrey (2008). A Military History of Australia (Third ed.). Port Melbourne: Cambridge University Press. pp. 28–40. ISBN 978-0-5216-9791-0.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, p. 678
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, p. 464
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, p. 598
- ^ "Public Record Office Victoria online catalogue". 25 December 2005. Archived from the original on 25 December 2005. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, p. 556
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 138–39
- ^ "Early explorers". Australia's Culture Portal. Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ Jupp2, pp. 35–36
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 227–29
- ^ "Australian South Sea Islanders" Archived 10 December 2023 at the Wayback Machine, State Library of Queensland. Retrieved 21 February 2024.
- ^ Higginbotham, Will (17 September 2017). "Blackbirding: Australia's history of luring, tricking and kidnapping Pacific Islanders". ABC News. Archived from the original on 26 January 2024.
- ^ Banivanua Mar, Tracey; Edmonds, Penelope (2013). "Indigenous and settler relations". The Cambridge History of Australia, Volume I. p. 355–58, 363–64
- ^ Marlow, Karina (1 December 2016). "Explainer: the Stolen Generations". NITV.
- ^ O'Loughlin, Michael (22 June 2020). "The Stolen Generation". Australian Museum.
- ^ "Australia and the Boer War, 1899–1902". Australian War Memorial. 2 June 2021. Archived from the original on 24 March 2018.
- ^ Wilcox, Craig (2002). Australia's Boer War: The War in South Africa, 1899-1902. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195516371.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 243–44
- ^ "History of the Commonwealth". Commonwealth Network. Commonwealth of Nations. Archived from the original on 25 April 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2015.
- ^ "The Covenant of the League of Nations". The United Nations Office at Geneva. Archived from the original on 27 January 2024. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ^ "Growth in United Nations membership". United Nations. Archived from the original on 1 February 2024. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, p. 609
- ^ "Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942 (Cth)". National Archives of Australia. Archived from the original on 12 February 2014. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- ^ Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942 (Cth)
- ^ "Establishing the nation's capital". Legislative Assembly for the Australian Capital Territory. 25 April 2020. Archived from the original on 8 February 2024. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ^ Otto, Kristin (25 June – 9 July 2007). "When Melbourne was Australia's capital city". Melbourne, Victoria: University of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 2 April 2010. Retrieved 29 March 2010.
- ^ Souter, Gavin (2012). Lion & Kangaroo: The Initiation of Australia. Xoum Publishing. p. 141. ISBN 978-1-9220-5700-6. Archived from the original on 13 April 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ a b McDermott, Peter M (2009). "Australian Citizenship and the Independence of Papua New Guinea". UNSW Law Journal. 32 (1): 50–2. Archived from the original on 8 February 2024. Retrieved 8 February 2024 – via Austlii.
- ^ New Guinea Act 1920 (Cth)
- ^ "Papua New Guinea Legal Research Guide". University of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 4 June 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2021.
- ^ "First World War 1914–18". Australian War Memorial. 2 June 2021. Archived from the original on 20 January 2024.
- ^ Tucker, Spencer (2005). Encyclopedia of World War I. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 273. ISBN 978-1-8510-9420-2.
- ^ Reed, Liz (2004). Bigger than Gallipoli: war, history, and memory in Australia. Crawley, Western Australia: University of Western Australia. p. 5. ISBN 978-1-9206-9419-7.
- ^ Macintyre, Stuart (2000) A Concise History of Australia Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 151–53, ISBN 978-0-521-62359-9
- ^ "The Anzac legend". Department of Veterans' Affairs. 17 January 2024. Archived from the original on 4 March 2024. Retrieved 9 February 2024.
- ^ Dennis, Peter; Grey, Jeffrey; Morris, Ewan; Prior, Robin; Bou, Jean (2008). The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History (2nd ed.). Melbourne: Oxford University Press. pp. 32, 38. ISBN 978-0-1955-1784-2.
- ^ Manne, Robert (25 April 2007). "The war myth that made us". The Age. Archived from the original on 4 March 2024. Retrieved 9 February 2024.
- ^ Beaumont, Joan (1996). "Australia's war: Europe and the Middle East". In Beaumont, Joan (ed.). Australia's War, 1939–1945. Sydney: Allen & Unwin. ISBN 978-1-86448-039-9.
- ^ Beaumont, Joan (1996a). "Australia's war: Asia and the Pacific". In Beaumont, Joan (ed.). Australia's War, 1939–1945. Sydney: Allen & Unwin. ISBN 978-1-86448-039-9.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 22–23
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, p. 30
- ^ Hosking, Susan; et al., eds. (2009). Something Rich and Strange: Sea Changes, Beaches and the Littoral in the Antipodes. Wakefield Press. pp. 6–. ISBN 978-1-8625-4870-1.
- ^ Hodge, Brian; Whitehurst, Allen (1967). Nation and People: An Introduction to Australia in a Changing World. Hicks, Smith. pp. 184–. Archived from the original on 28 March 2024. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ "Immigration to Australia During the 20th Century – Historical Impacts on Immigration Intake, Population Size and Population Composition – A Timeline" (PDF). Department of Immigration and Citizenship (Australia). 2001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 August 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "'Populate or perish': Australia's postwar migration program". National Archives of Australia. Australian Government. Retrieved 31 August 2024.
- ^ Dean, Peter; Moss, Tristan, eds. (2021). "Introduction" (PDF). Fighting Australia's Cold War. Canberra: ANU Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-76046-482-0. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 January 2024. Retrieved 9 February 2024.
- ^ Frank Crowley (1973) Modern Australia in Documents, 1939–1970. pp. 222–26. Wren Publishing, Melbourne. ISBN 978-0-1700-5300-6
- ^ Calwell, Arthur Augustus (1972). Be just and fear not. Hawthorn, Victoria: Lloyd O'Neil Pty Ltd. p. 188. ISBN 978-0-8555-0352-9.
- ^ Edwards, William Howell (2004). An Introduction to Aboriginal Societies. Cengage Learning Australia. pp. 25–26, 30, 132–133. ISBN 978-1-8766-3389-9. Archived from the original on 12 April 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ Galloway, Kate (26 April 2017). "Australian politics explainer: the Mabo decision and native title". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 25 January 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 5–7, 402
- ^ "Fact Sheet – Abolition of the 'White Australia' Policy". Australian Immigration. Commonwealth of Australia: National Communications Branch, Department of Immigration and Citizenship. Archived from the original on 19 September 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 338–39, 442–43, 681–82
- ^ Sawer, Geoffrey (1966). "The Australian Constitution and the Australian Aborigines" (PDF). Federal Law Review. 2 (1). Canberra: Australian National University: 17–36. doi:10.1177/0067205X6600200102. ISSN 1444-6928. S2CID 159414135. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 September 2020. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ Thompson, Roger C. (1994). The Pacific Basin since 1945: A history of the foreign relations of the Asian, Australasian, and American rim states and the Pacific islands. Longman. ISBN 978-0-5820-2127-3.
- ^ "Australia Act 1986 (Cth)". Documenting a Democracy. Museum of Australian Democracy at Old Parliament House. Archived from the original on 22 April 2019. Retrieved 25 July 2020.
- ^ Twomey, Anne (January 2008). "The States, the Commonwealth and the Crown—the Battle for Sovereignty". Parliament of Australia. Papers on Parliament No. 48. Archived from the original on 9 September 2022.
- ^ "1999: Republic referendum: Queen and/or Country". Museum of Australian Democracy at Old Parliament House. Archived from the original on 17 January 2024. Retrieved 10 February 2024.
- ^ Neville, Leigh (2019). The Australian Army at War 1976–2016 (First ed.). London: Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-1-4728-2631-2.
- ^ "Fifty years of Australia's trade" (PDF). Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 December 2022. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ^ Dawson, Emma (2020). What Happens Next? Reconstructing Australia After COVID-19. Melbourne: Melbourne University Press. ISBN 978-0-5228-7721-2.
- ^ Rosenberg, Matt (20 August 2009). "The New Fifth Ocean – The World's Newest Ocean – The Southern Ocean". About.com: Geography. Archived from the original on 26 January 2012. Retrieved 5 April 2010.
- ^ "Continents: What is a Continent?". National Geographic Society. Archived from the original on 14 July 2008. Retrieved 22 August 2009. "Most people recognize seven continents — Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia, from largest to smallest — although sometimes Europe and Asia are considered a single continent, Eurasia".
- ^ "Australia". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 22 September 2009. Retrieved 22 August 2009. "Smallest continent and sixth largest country (in area) on Earth, lying between the Pacific and Indian oceans".
- ^ "Islands". Geoscience Australia. Archived from the original on 23 April 2010. "Being surrounded by ocean, Australia often is referred to as an island continent. As a continental landmass it is significantly larger than the many thousands of fringing islands ..."
- ^ "Australia in Brief: The island continent". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (Australia). Archived from the original on 4 June 2009. Retrieved 29 May 2009. "Mainland Australia, with an area of 7.69 million square kilometres, is the Earth's largest island but smallest continent".
- ^ "State of the Environment 2006". Department of the Environment and Water Resources. Archived from the original on 10 July 2007. Retrieved 19 May 2007.
- ^ "Oceans and Seas – Geoscience Australia". Geoscience Australia. Archived from the original on 20 June 2009.
- ^ "Parks and Reserves—Australia's National Landscapes". environment.gov.au. 23 November 2011. Archived from the original on 4 January 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ Loffler, Ernst; Loffler, Anneliese; A. J. Rose; Warner, Denis (1983). Australia: Portrait of a continent. Richmond, Victoria: Hutchinson Group (Australia). pp. 37–39. ISBN 978-0-0913-0460-7.
- ^ a b c "Australia – Climate of Our Continent". Bureau of Meteorology. Archived from the original on 17 March 2009. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ^ "Population Density". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 26 March 2019. Archived from the original on 3 May 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ^ World Food and Agriculture: Statistical Yearbook 2023. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023. doi:10.4060/cc8166en. ISBN 978-92-5-138262-2. Archived from the original on 15 December 2023.
- ^ Terms and Definitions FRA 2025 Forest Resources Assessment, Working Paper 194. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023.
- ^ "Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Australia". Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- ^ UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1980). "Protected Areas and World Heritage – Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. Archived from the original on 28 May 2007. Retrieved 19 May 2007.
- ^ "Mount Augustus". The Sydney Morning Herald. 17 February 2005. Archived from the original on 6 February 2012. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "Highest Mountains". Geoscience Australia. 15 May 2014. Archived from the original on 21 March 2012. Retrieved 2 February 2012.
- ^ a b Johnson, David (2009). The Geology of Australia (2 ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 202. ISBN 978-0-5217-6741-5.
- ^ Seabrooka, Leonie; McAlpinea, Clive; Fenshamb, Rod (2006). "Cattle, crops and clearing: Regional drivers of landscape change in the Brigalow Belt, Queensland, Australia, 1840–2004". Landscape and Urban Planning. 78 (4): 375–376. Bibcode:2006LUrbP..78..373S. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2005.11.007.
- ^ "Einasleigh Uplands savanna". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Mitchell grass downs". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Eastern Australia mulga shrublands". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Southeast Australia temperate savanna". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Arnhem Land tropical savanna". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Rangelands – Overview". Australian Natural Resources Atlas. Australian Government. 27 June 2009. Archived from the original on 13 March 2010. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Cape York Peninsula tropical savanna". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ Van Driesum, Rob (2002). Outback Australia. Lonely Planet. p. 306. ISBN 978-1-8645-0187-2.
- ^ "Victoria Plains tropical savanna". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Western Australian Mulga shrublands". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Central Ranges xeric scrub". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ Banting, Erinn (2003). Australia: The land. Crabtree Publishing Company. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-7787-9343-4.
- ^ a b "Tirari-Sturt stony desert". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Great Sandy-Tanami desert". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ^ "Western Australian mulga shrublands". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 1 June 2020.
- ^ Pirajno, F., Occhipinti, S.A. and Swager, C.P., 1998. Geology and tectonic evolution of the Palaeoproterozoic Bryah, Padbury and Yerrida basins, Western Australia: implications for the history of the south-central Capricorn orogen Precambrian Research, 90: 119–40
- ^ Pain, C.F., Villans, B.J., Roach, I.C., Worrall, L. & Wilford, J.R. (2012) "Old, flat and red – Australia's distinctive landscape" In: Shaping a Nation: A Geology of Australia Blewitt, R.S. (Ed.) Geoscience Australia and ANU E Press, Canberra. pp. 227–75 ISBN 978-1-9221-0343-7
- ^ Gray, DR; Foster, DA (2004). "Tectonic review of the Lachlan Orogen: historical review, data synthesis and modern perspectives". Australian Journal of Earth Sciences. 51 (6): 773–817. doi:10.1111/j.1400-0952.2004.01092.x. S2CID 128901742.
- ^ Hawkesworth, CJ; et al. (2010). "The generation and evolution of the continental crust". Journal of the Geological Society. 167 (2): 229–248. Bibcode:2010JGSoc.167..229H. doi:10.1144/0016-76492009-072. S2CID 131052922.
- ^ Hillis RR & Muller RD. (eds) 2003 Evolution and dynamics of the Australian Plate Geological Society of Australia Special Publication 22: 432 p.
- ^ Cawood, PA (2005). "Terra Australis Orogen: Rodinia breakup and development of the Pacific and Iapetus margins of Gondwana during the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic". Earth-Science Reviews. 69 (3–4): 249–279. Bibcode:2005ESRv...69..249C. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.09.001.
- ^ McKenzie et al. (ed) 2004 Australian Soils and Landscapes: an illustrated compendium CSIRO Publishing: 395 p.
- ^ Bishop P & Pillans B. (eds) 2010, Australian Landscapes Geological Society of London Special Publication 346
- ^ Mccue, Kevin (26 February 2010). "Land of earthquakes and volcanoes?". Australian Geographic. Archived from the original on 6 March 2010. Retrieved 25 April 2010.
- ^ Van Ufford AQ & Cloos M. 2005 Cenozoic tectonics of New Guinea AAPG Bulletin 89: 119–140
- ^ "Earthquake History, Regional Seismicity And The 1989 Newcastle Earthquake". Geoscience Australia. 22 June 2004. Archived from the original on 26 August 2004. Retrieved 27 June 2007.
- ^ Beck, Hylke E.; Zimmermann, Niklaus E.; McVicar, Tim R.; Vergopolan, Noemi; Berg, Alexis; Wood, Eric F. (30 October 2018). "Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution". Scientific Data. 5 (1): 180214. Bibcode:2018NatSD...580214B. doi:10.1038/sdata.2018.214. PMC 6207062. PMID 30375988.
- ^ Kleinman, Rachel (6 September 2007). "No more drought: it's a 'permanent dry'". Melbourne: The Age. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ Marks, Kathy (20 April 2007). "Australia's epic drought: The situation is grim". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 22 April 2007. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "Climate of Western Australia". Bureau of Meteorology. Archived from the original on 17 March 2009. Retrieved 6 December 2009.
- ^ "State of the Climate 2020" (PDF). Bureau of Meteorology. November 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 November 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ "Australia fires: Life during and after the worst bushfires in history". BBC News. 28 April 2020. Archived from the original on 15 July 2022. Retrieved 18 July 2020.
- ^ Environment at a Glance Indicators: Climate change (PDF) (Report). OECD. 9 March 2020. p. 6. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 December 2020. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ^ Heggie, Jon (August 2019). "Making Every Drop Count: How Australia is Securing its Water Future". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 18 July 2020.
- ^ "National review of water restrictions in Australia". Australian Government National Water Commission. 15 January 2010. Archived from the original on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- ^ Gergis, Joelle (23 March 2021). "Yes, Australia is a land of flooding rains. But climate change could be making it worse". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 4 April 2021. Retrieved 2 April 2021.
- ^ Pascoe, I. G.; (1991) History of systematic mycology in Australia History of Systematic Botany in Australasia Ed. by: P. Short Australian Systematic Botany Society Inc. pp. 259–264
- ^ "About Biodiversity". Department of the Environment and Heritage. Archived from the original on 5 February 2007. Retrieved 18 September 2007.
- ^ Lambertini, Marco (2000). A Naturalist's Guide to the Tropics (excerpt). University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-2264-6828-0. Archived from the original on 5 February 2017. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "Fact check: Are feral cats killing over 20 billion native animals a year?". ABC News. 20 November 2014. Archived from the original on 8 January 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ Jackson, Stephen; Groves, Colin (2015). Taxonomy of Australian Mammals. CSIRO Publishing, Clayton, Victoria, Australia. pp. 287–290. ISBN 978-1-4863-0013-6.
- ^ Evans, Megan C.; Watson, James E. M.; Fuller, Richard A.; Venter, Oscar; Bennett, Simon C.; Marsack, Peter R.; Possingham, Hugh P. (April 2011). "The Spatial Distribution of Threats to Species in Australia". BioScience. 61 (4): 282. doi:10.1525/bio.2011.61.4.8.
- ^ a b "About Australia: Flora and fauna". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. May 2008. Archived from the original on 11 February 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2010.
- ^ "Snake bite – The Australian Venom Compendium Concept". 15 January 2015. Archived from the original on 15 January 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Savolainen, P.; Leitner, T.; Wilton, A.N.; Matisoo-Smith, E.; Lundeberg, J. (2004). "A detailed picture of the origin of the Australian dingo, obtained from the study of mitochondrial DNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 101 (33): 12387–12390. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112387S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401814101. PMC 514485. PMID 15299143.
- ^ "Humans to blame for extinction of Australia's megafauna". University of Melbourne. 8 June 2001. Archived from the original on 2 April 2010. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "The Thylacine Museum – A Natural History of the Tasmanian Tiger". The Thylacine Museum. Archived from the original on 15 March 2006. Retrieved 14 October 2013.
- ^ "National Threatened Species Day". Department of the Environment and Heritage, Australian Government. 2006. Archived from the original on 9 December 2006. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- ^ "Invasive species". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. 17 March 2010. Archived from the original on 29 June 2010. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "Australia's most endangered species". Australian Geographic. 2 October 2012. Archived from the original on 7 July 2014. Retrieved 16 June 2014.
- ^ "About the EPBC Act". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. Archived from the original on 31 May 2010. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "National Strategy for the Conservation of Australia's Biological Diversity". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. 21 January 2010. Archived from the original on 12 March 2011. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "Conservation of biological diversity across Australia". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. 19 January 2009. Archived from the original on 13 March 2011. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "The List of Wetlands of International Importance". Ramsar Convention. 22 May 2010. pp. 6–7. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "Australia". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 2 October 2009. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
- ^ "2018 EPI Results", Environmental Performance Index, Yale Center for International Earth Science Information Network, archived from the original on 23 July 2019, retrieved 24 September 2018
- ^ March, Stephanie (24 June 2019). "'Haunting': What it's like watching the last of a species die". ABC News. Archived from the original on 13 July 2019. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ Michelle Starr (7 January 2022). "Mind-Blowing New Fossil Site Found in The 'Dead' Heart of Australia". Science Alert. Archived from the original on 7 January 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ Michael Greshko (7 January 2022). "See the spectacular fossils from a newly discovered prehistoric rainforest". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 7 January 2022.
- ^ "Australian system of government". Parliamentary Education Office. 12 January 2024. Archived from the original on 14 February 2024.
- ^ a b Thompson, Elaine (1980). "The 'Washminster' Mutation". Politics. 15 (2): 32. doi:10.1080/00323268008401755.
- ^ "What is the Washminster system?". Parliamentary Education Office. 14 December 2023. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024.
- ^ "Separation of powers: Parliament, Executive and Judiciary". Parliamentary Education Office. Archived from the original on 31 October 2023. Retrieved 8 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Australia § Government". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 16 August 2024.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 287–88
- ^ a b "Governor-General's Role". Governor-General of Australia. Archived from the original on 4 August 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ Downing, Susan (23 January 1998). "The Reserve Powers of the Governor-General". Parliament of Australia. Archived from the original on 26 July 2010. Retrieved 18 June 2010.
- ^ a b "Senate Summary". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 6 May 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ Muller, Damon (26 April 2023). "The process for, and consequences of, changing the size of the Commonwealth Parliament: a quick guide". Parliament of Australia. Archived from the original on 11 May 2023.
- ^ Joint Standing Committee on Electoral Matters (10 October 2005). "Parliamentary terms". The 2004 Federal Election. Parliament of Australia. paras. 7.26–7.27. ISBN 978-0-642-78705-7. Archived from the original on 25 January 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ Evans, Tim (2006). "Compulsory Voting in Australia" (PDF). Australian Electoral Commission. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 June 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ^ "Is it compulsory to enrol, regardless of age or disability?". Enrolment – Frequently Asked Questions. Australian Electoral Commission. Archived from the original on 24 May 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- ^ Brett, Judith (2019). From Secret Ballot to Democracy Sausage: How Australia Got Compulsory Voting. Text Publishing Co. ISBN 978-1-9256-0384-2.
- ^ "Governor-General's Role". Governor-General of the Commonwealth of Australia. Archived from the original on 14 October 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ Ganghof, S (May 2018). "A new political system model: Semi-parliamentary government". European Journal of Political Research. 57 (2): 261–281. doi:10.1111/1475-6765.12224.
- ^ "Glossary of Election Terms". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 6 March 2021. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "State of the Parties". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 18 April 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "The Liberal-National Party – a new model party?". ABC News. 30 July 2008. Archived from the original on 7 October 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2021.
- ^ Fenna, Alan; Robbins, Jane; Summers, John (2013). Government Politics in Australia. London: Pearson Higher Education AU. p. 139. ISBN 978-1-4860-0138-5.
- ^ Harris, Rob (22 April 2020). "Old Greens wounds reopen as members vote on directly electing leader". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 22 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Jackson, Stewart (2016). The Australian Greens : from activism to Australia's third party. Melbourne University Press. ISBN 978-0-5228-6794-7.
- ^ "Anthony Albanese sworn in as Prime Minister". ABC News. 22 May 2022. Archived from the original on 22 May 2022. Retrieved 22 May 2022.
- ^ "What's the difference between a territory and a state parliament?". Parliamentary Education Office. 14 December 2023. Archived from the original on 18 March 2024.
- ^ Pyke, John (2020). Government powers under a Federal Constitution: constitutional law in Australia (2nd ed.). Pyrmont, NSW: Lawbook Co. pp. 405–6. ISBN 978-0-455-24415-0.
- ^ "Three levels of government: governing Australia". Parliamentary Education Office. 19 July 2022. Archived from the original on 4 January 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ Pyke, John (2020). Government powers under a Federal Constitution: constitutional law in Australia (2nd ed.). Pyrmont, NSW: Lawbook Co. pp. 528–30, 577–80. ISBN 978-0-455-24415-0.
- ^ Australian Constitution (Cth) s 109. "When a law of a State is inconsistent with a law of the Commonwealth, the latter shall prevail, and the former shall, to the extent of the inconsistency, be invalid."
- ^ Pyke, John (2020). Government powers under a Federal Constitution: constitutional law in Australia (2nd ed.). Pyrmont, NSW: Lawbook Co. pp. 607–9. ISBN 978-0-455-24415-0.
- ^ Beck, Luke (2020). Australian constitutional law: concepts and cases. Port Melbourne, VIC: Cambridge university press. pp. 521–8. ISBN 978-1-108-70103-7.
- ^ "Administrator of Norfolk Island". Australian Government Attorney-General's Department. Archived from the original on 6 August 2008.
- ^ Tan, Monica; Australian Associated Press (12 May 2015). "Norfolk Island loses its parliament as Canberra takes control". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 28 October 2015. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ Norfolk Island previously was self-governed, however this was revoked in 2015.[275][276]
- ^ This Antarctic claim is recognised by only by New Zealand, the United Kingdom, France, and Norway.
- ^ "Australian Territories". Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development, Communications and the Arts. Archived from the original on 8 March 2024. Retrieved 16 February 2024.
- ^ "Macquarie Island research station to be closed in 2017". ABC News. 13 September 2016. Archived from the original on 25 October 2019. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ^ Southerden, Louise (8 November 2017). "Which island should you visit - Lord Howe or Norfolk? A guide to both". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 16 February 2024.
- ^ Lowy Institute Asian Power Index (PDF) (Report). 2023. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-6480189-3-3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 February 2024. Retrieved 4 February 2024.
- ^ Gyngell, Allan (31 July 2022). "A new Australian foreign policy agenda under Albanese". East Asia Forum. Archived from the original on 17 February 2024.
- ^ a b 2017 Foreign Policy White Paper (PDF) (Report). Australian Government. 2017. pp. 1–8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ^ Firth, Stewart (2011). Australia in international politics: an introduction to Australian foreign policy (3rd ed.). Crows Nest, NSW: Allen & Unwin. pp. 332–8. ISBN 978-1-74237-263-1.
- ^ "Australia and the United States". Australian Embassy and Consulates. Archived from the original on 17 February 2024. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ^ Bureau of Political-Military Affairs (20 January 2021). "Major Non-NATO Ally Status". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 27 February 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ Page, Mercedes (31 May 2022). "Multilateralism matters again". The Interpreter. Lowy Institute. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024.
- ^ Watson, Mark R (30 October 2023). "Australia and the Quad: A Watering Can or a Hammer?". The National Bureau of Asian Research. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ Capling, Ann (2013). Australia and the Global Trade System: From Havana to Seattle. Cambridge University Press. p. 116. ISBN 978-0-5217-8525-9.
- ^ Gallagher, P. W. (1988). "Setting the agenda for trade negotiations: Australia and the Cairns group". Australian Journal of International Affairs. 42 (1 April 1988): 3–8. doi:10.1080/10357718808444955.
- ^ "APEC and Australia". APEC 2007. 1 June 2007. Archived from the original on 21 April 2021. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Australia:About". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Archived from the original on 20 April 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Australia – Member information". World Trade Organization. Archived from the original on 25 May 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Australia's free trade agreements (FTAs)". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ "Trans-Tasman Roadmap to 2035". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 26 July 2023. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ Kassam, Natasha (2021). "2021 Lowy Institute Poll" (PDF). Lowy Institute. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 March 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ "Australian Aid". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ Mitchell, Ian; Robinson, Lee; Cichocka, Beata; Ritchie, Euan (13 September 2021). "The Commitment to Development Index 2021". Washington, D.C.: Center for Global Development. Archived from the original on 5 October 2022. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ Lee, David (31 December 2023). "Cabinet papers 2003: Howard government sends Australia into the Iraq war". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 17 February 2024. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ^ Firth, Stewart (2011). Australia in international politics: an introduction to Australian foreign policy (3rd ed.). Crows Nest, NSW: Allen & Unwin. pp. 78–84. ISBN 978-1-74237-263-1.
- ^ Appleby, Gabrielle (2 September 2014). "Explainer: Australia's war powers and the role of parliament". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 6 September 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ^ "Capability review: Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade". Australian Public Service Commission. June 2013. p. 2. Retrieved 20 December 2024.
- ^ "Organisation structure". Australian Government: Defence. Archived from the original on 3 November 2023. Retrieved 16 February 2024.
- ^ "Australian Defence Force service". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 29 June 2022. Archived from the original on 19 November 2023.
- ^ Defence Annual Report 2022–23 (PDF) (Report). Australian Government: Defence. 18 September 2023. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-925890-47-1. ISSN 1323-5036. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 December 2023.
- ^ Defence Act 1903 (Cth) s 9
- ^ Khosa, Raspal (July 2011). Australian Defence Almanac: 2011–2012 (PDF) (Report). Australian Strategic Policy Institute. pp. 2, 12. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 October 2023.
- ^ "Trends in World Military Expenditure, 2022" (PDF). Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. April 2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ^ "Operations". Defence. Australian Government. Archived from the original on 30 January 2024. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ "Australia: Events of 2023". World Report 2024. Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Legal - Legislation". Australian Human Rights Commission. Retrieved 3 September 2023.
- ^ "The 20 most and least gay-friendly countries in the world". Public Radio International. 26 June 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2017.
- ^ "Same-Sex Marriage Around the World". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 3 September 2023.
- ^ "Amnesty International Report 2022/23: The state of the world's human rights". Amnesty International Australia. 28 March 2023. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ "Australia: Setbacks, Inaction on Key Rights Issues". Human Rights Watch. 11 January 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ Russell, Clyde (30 March 2021). "Column: Resource-rich Australia shows vagaries of any commodity supercycle". Reuters. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ "Global Wealth Databook 2021" (PDF). Credit Suisse. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ Carrera, Jordi Bosco; Grimm, Michaela; Halzhausen, Arne; Pelaya, Patricia (7 October 2021). "ALLIANZ GLOBAL WEALTH REPORT 2021" (PDF). Allianz. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ "Labour Force, Australia". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 14 July 2022. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ "Poverty – Poverty and Inequality".
- ^ "Report shows three million people in poverty in Australia and why we must act to support each other". ACOSS. 21 February 2020.
- ^ "Small island economies" (PDF). Asian Development Bank. 2013. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
All three countries use the Australian dollar as legal tender.
- ^ Dossor, Rob. "Commonwealth debt". Parliament of Australia. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ "Household debt, loans and debt securities". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ Neubauer, Ian (6 April 2022). "'Ridiculous prices': Australians' home ownership dreams turn sour". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ "Australia. CIA – The World Factbook". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 22 January 2011.
- ^ "List of importing markets for the product exported by Austral1ia in 2021". International Trade Centre. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ "List of supplying markets for the product imported by Australia in 2021". International Trade Centre. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ Tan, Weizhen (29 December 2020). "Australia's growth may 'never return' to its pre-virus path after trade trouble with China, says economist". CNBC. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "Trade and investment at a glance 2020". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ United Nations Development Programme (September 2022). "United Nations Development Programme, The 2021/2022 Human Development Report: Uncertain times, unsettled lives, Shaping our future in a transforming world (p 272)". United Nations. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- ^ "Country Rankings". The Heritage Foundation. Archived from the original on 30 April 2020. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ Schwab, Klaus (2022). "The Global Competitiveness Report" (PDF). World Economic Forum.
- ^ "Trends in the Visitor Arrivals to Japan by Year". JNTO. Retrieved 11 December 2020.
- ^ a b "Statistical Annex". UNWTO World Tourism Barometer. 18 (5). UNWTO: 18. August–September 2020. doi:10.18111/wtobarometereng.2020.18.1.5.
- ^ "The Travel & Tourism Development Index 2021" (PDF). World Economic Forum. May 2022. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ "Australian electricity generation - fuel mix". energy.gov.au. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "Australian electricity generation renewable sources". energy.gov.au. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "Australian energy mix by state and territory 2021-22". energy.gov.au. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "Energy consumption". energy.gov.au. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "Renewable Energy Target Scheme Design" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 May 2009. Retrieved 15 May 2009.
- ^ Clean Energy Council Australia. "Clean Energy Australia Report 2021" (PDF). Clean Energy Australia. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
- ^ "Australia will fall well short of 82 per cent renewable energy by 2030, analysts predict, as problems mount". ABC News. 5 August 2023. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ Evans, Jake (26 October 2021). "What is the government's plan to get Australia to net zero?". ABC News (Australia). Retrieved 11 February 2024.
- ^ "Research and Experimental Development, Businesses, Australia, 2019–20 financial year". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 9 March 2021. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ "Australia wants a place in ranks of global tech nations". Australian Financial Review. 12 April 2022. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ "Sydney's startup ecosystem is worth $24 billion, Melbourne's $10.5bn". Startup Daily. 23 September 2021. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ World Intellectual Property Organization.; Dutta, Soumitra.; Lanvin, Bruno.; Rivera León, Lorena.; Wunsch-Vincent, Sacha. (2024). Global Innovation Index 2024: Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship. World Intellectual Property Organization. p. 18. doi:10.34667/tind.50062. ISBN 978-92-805-3681-2. Retrieved 6 October 2024.
- ^ "Research Output | Australian Innovation System Monitor". publications.industry.gov.au. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ^ a b c Berthold, Emma (17 May 2021). "Science in Australia". Curious. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ^ Hannaford, Peter. "Alan Walsh 1916–1998". AAS Biographical Memoirs. Australian Academy of Science. Archived from the original on 24 February 2007. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ "Wi-fi". National Museum of Australia. Retrieved 6 December 2022.
- ^ "Proceeds of crime: how polymer banknotes were invented". CSIROscope. 25 November 2014. Retrieved 6 December 2022.
- ^ "Nobel Australians". Australian Academy of Science. Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- ^ Watson, Laura (1 August 2018). "AMSI Congratulates Australia's Second Ever Fields Medallist". Australian Mathematical Sciences Institute. Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- ^ Williams, Dave (19 March 2014). "Australia's part in 50 years of space exploration with NASA". The Conversation. Retrieved 13 December 2022.
- ^ "Main Features – Main Features". 3218.0 – Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2017–18. Commonwealth of Australia. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 27 March 2019.
- ^ "Population: Census". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 28 June 2022.
- ^ "United Nations Population Division – Department of Economic and Social Affairs". Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- ^ "The Beach". Australian Government: Culture Portal. Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia. 17 March 2008. Archived from the original on 26 February 2010.
- ^ "Regional Population, 2021". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 11 February 2022.
- ^ "The Evolution of Australia's Multicultural Policy". Department of Immigration and Multicultural and Indigenous Affairs. 2005. Archived from the original on 19 February 2006. Retrieved 18 September 2007.
- ^ a b "2018–19 Migration Program Report" (PDF). Australian Government Department of Home Affairs. 30 June 2019.
- ^ "Main Features – Australia's Population by Country of Birth". 3412.0 – Migration, Australia, 2019–20. Commonwealth of Australia. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 23 April 2021.
- ^ "International migrant stock 2017: maps". United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Archived from the original on 9 December 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ "Overseas Migration". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 15 December 2023. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ "Australia's Migration Trends 2022–23" (PDF). Department of Home Affairs. 2023.
- ^ "Net Overseas Migration". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ "Understanding and using Ancestry data". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 28 June 2022. Archived from the original on 9 February 2024.
- ^ a b "Australian Standard Classification of Cultural and Ethnic Groups (ASCCEG), 2019". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 18 December 2019. Archived from the original on 21 November 2023.
- ^ Cultural diversity data summary. 2021. Australian Bureau of Statistics.
- ^ a b "Feature Article – Ethnic and Cultural Diversity in Australia (Feature Article)". 1301.0 – Year Book Australia, 1995. Commonwealth of Australia. Australian Bureau of Statistics.
- ^ "Understanding and using Ancestry data". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 28 June 2022. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ "Pluralist Nations: Pluralist Language Policies?". 1995 Global Cultural Diversity Conference Proceedings, Sydney. Department of Immigration and Citizenship. Archived from the original on 20 December 2008. Retrieved 11 January 2009. "English has no de jure status but it is so entrenched as the common language that it is de facto the official language as well as the national language."
- ^ Ward, Rowena (2019). "'National' and 'Official' Languages Across the Independent Asia-Pacific". Journal of Multidisciplinary International Studies. 16 (1/2): 83–4. doi:10.5130/pjmis.v16i1-2.6510.
The use of English in Australia is one example of both a de facto national and official language: it is widely used and is the language of government and the courts, but has never been legally designated as the country's official language.
- ^ Moore, Bruce. "The Vocabulary Of Australian English" (PDF). National Museum of Australia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2011. Retrieved 5 April 2010.
- ^ "The Macquarie Dictionary", Fourth Edition. The Macquarie Library Pty Ltd, 2005.
- ^ Lalande, Line (4 May 2020). "Australian English in a nutshell". Government of Canada.
- ^ "Census of Population and Housing: Cultural diversity data summary, 2021, TABLE 5. LANGUAGE USED AT HOME BY STATE AND TERRITORY". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ "2021 Australia, Census All persons QuickStats". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 15 March 2024.
- ^ National Indigenous Languages Report. Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia. 2020. p. 13.
- ^ National Indigenous Language Report (2020). pp. 42, 65
- ^ "Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people: Census". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 28 June 2022. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- ^ National Indigenous Languages Report (2020). p. 46
- ^ "About Australia: Religious Freedom". Dfat.gov.au. Archived from the original on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ^ Puls, Joshua (1998). "The Wall of Separation: Section 116, the First Amendment and Constitutional Religious Guarantees" (PDF). Federal Law Review: 160 – via Austlii.
- ^ "2001 Australia, Census All persons QuickStats". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 8 March 2024.
- ^ "Religious affiliation in Australia". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 7 April 2022.
- ^ Flood, Josephine (2019). pp. 163–69
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth, total (years) – Australia". World Bank. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ "Skin cancer – key statistics". Department of Health and Ageing. 2008. Archived from the original on 8 February 2014.
- ^ "Risks to health in Australia" (PDF). Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. 26 February 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2011.
- ^ "quitnow – Smoking – A Leading Cause of Death". 19 February 2011. Archived from the original on 19 February 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ "Global prevalence of adult obesity" (PDF). January 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 August 2012. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ "About Overweight and Obesity". Department of Health and Ageing. Archived from the original on 7 May 2010. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- ^ "Overweight and obesity". Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. 25 February 2021.
- ^ "Current healthcare expenditure (% of GDP) – Australia". World Bank. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ a b Biggs, Amanda (29 October 2004). "Medicare – Background Brief". Parliament of Australia: Parliamentary Library. Canberra, ACT: Commonwealth of Australia. Archived from the original on 14 April 2010. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ "International Health Care System Profiles: Australia". The Commonwealth Fund. 5 June 2020. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ "Medicare levy". Australian Taxation Office. 18 October 2017. Archived from the original on 29 June 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- ^ Townsend, Ian (30 January 2012). "Thousands of parents illegally home schooling". ABC News. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- ^ "The Australian Education System" (PDF). Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. pp. 7–9. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ Ross, Emily (18 November 2021). "Why do Australian states need a national curriculum, and do teachers even use it?". The Conversation. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ "Education". Department of Immigration and Citizenship. Archived from the original on 18 February 2014. Retrieved 14 January 2012.
- ^ "Our system of education". Australian Government: Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ "The Department of Education – Schools and You – Schooling". det.wa.edu.au. Archived from the original on 21 March 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ^ "Education Act (NT) – Section 20". austlii.edu.au.
- ^ "Education Act 1990 (NSW) – Section 21". austlii.edu.au.
- ^ "Minimum school leaving age jumps to 17". The Age. 28 January 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ "PISA 2022 Results (Volume I and II) - Country Notes: Australia". OECD. 4 December 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2024.
- ^ Long, Claudia (6 December 2023). "Australia is now in the world's top 10 academic performers – but the data paints a complex picture". ABC News Australia. Retrieved 31 July 2024.
- ^ "Literacy". CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 24 November 2016. Retrieved 10 October 2013.
- ^ "Programme for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies, Australia". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 9 October 2013.
- ^ "A literacy deficit". abc.net.au. 22 September 2013. Retrieved 10 October 2013.
- ^ "Australia's adult literacy crisis". Adult Learning Australia. 12 April 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2024.
- ^ "Australian Education | Australian Education System | Education | Study in Australia". Ausitaleem.com.pk. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ^ Education at a Glance 2006 Archived 2 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
- ^ "About Australian Apprenticeships". Australian Government. Archived from the original on 11 November 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Year Book Australia 2005". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 21 January 2005. Archived from the original on 9 April 2016.
- ^ Sauter, Michael B. (24 September 2012). "The Most Educated Countries in the World – Yahoo Finance". Finance.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on 4 February 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- ^ Grossman, Samantha (27 September 2012). "And the World's Most Educated Country Is ..." Time. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- ^ "2016 Census QuickStats: Australia". censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 20 June 2018. Retrieved 14 February 2018.
- ^ "Subscribe to The Australian | Newspaper home delivery, website, iPad, iPhone & Android apps". theaustralian.com.au.
- ^ Fund, Leith van OnselenLeith van Onselen is Chief Economist at the MB; Treasury, MB Super Leith has previously worked at the Australian; Treasury, Victorian; Sachs, Goldman (31 October 2019). "Australian universities double down on international students". MacroBusiness.
- ^ Gothe-Snape, political reporter Jackson (27 July 2018). "Record number of international students sticking around on work visas". ABC News.
- ^ Architect Magazine (August 2007), 96 (11), p. 14
- ^ Jupp1, pp. 796–802
- ^ Teo & White 2003, pp. 118–20
- ^ Jupp1, pp. 808–12, 74–77
- ^ White, Richard (1 January 1983). "A Backwater Awash: The Australian Experience of Americanisation". Theory, Culture and Society. 1 (3): 108–122. doi:10.1177/026327648300100309. S2CID 144339300.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 98–99
- ^ Teo & White 2003, pp. 125–27
- ^ "Cultural life". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "Australian Culture: Core Concepts". Cultural Atlas. 2016. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "Australian Citizenship: Our Common Bond" (PDF). Australian Government. p. 36.
- ^ Luu, Chi (7 February 2018). "Small Poppy Syndrome: Why are Australians so Obsessed With Nicknaming Things?". JSTOR Daily. Retrieved 12 February 2024.
- ^ Kidd, Evan; Kemp, Nenagh; Kashima, Emiko S.; Quinn, Sara (June 2016). "Language, Culture, and Group Membership: An Investigation Into the Social Effects of Colloquial Australian English". Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology. 47 (5): 713–733. doi:10.1177/0022022116638175. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-002E-24A7-F. ISSN 0022-0221. S2CID 147360478.
- ^ "Meeting our requirements: Australian values". Department of Home Affairs. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ Snow, Deborah (18 January 2019). "Australian values: what the bloody hell are they?". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ Dyrenfurth, Nick (June 2007). "John Howard's Hegemony of Values: The Politics of 'Mateship' in the Howard Decade". Australian Journal of Political Science. 42 (2): 211–230. doi:10.1080/10361140701319994. ISSN 1036-1146. S2CID 154041199.
- ^ Crowe, Shaun (14 January 2015). "Book review: Mateship – A Very Australian History". The Conversation. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ Zhuang, Yan (19 November 2021). "What Does Mateship Mean to You?". New York Times.
- ^ "Sidney Nolan's Rainbow Serpent is larger than life" (16 June 2012), The Australasian.
- ^ Tacon, Paul S. C.; Ouzman, Sven (2004). "Worlds within stone: the inner and outer rock-art landscapes of northern Australia and southern Africa". In Nash, George; Chippindale, Christopher (ed.). The Figured Landscapes of Rock-Art: Looking at Pictures in Place. Cambridge University Press. pp. 39–68. 9780521524247.
- ^ Henly, Susan Gough (6 November 2005). "Powerful growth of Aboriginal art". The New York Times.
- ^ Smith, Terry (1996). "Kngwarreye Woman, Abstract Painter", p. 24 in Emily Kngwarreye – Paintings, North Ryde NSW: Craftsman House / G + B Arts International. ISBN 978-90-5703-681-1.
- ^ a b c d "Collection | Art Gallery of NSW". www.artgallery.nsw.gov.au. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Sayers, Andrew (2001). Australian Art. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. pp. 78–88. ISBN 978-0-19-284214-5.
- ^ "Brett Whiteley: nature :: Art Gallery NSW". www.artgallery.nsw.gov.au. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Sarwal, Amit; Sarwal, Reema (2009). Reading Down Under: Australian Literary Studies Reader. SSS Publications. p. xii. ISBN 978-8-1902-2821-3.
- ^ Mulligan, Martin; Hill, Stuart (2001). Ecological Pioneers: A Social History of Australian Ecological Thought and Action. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5210-0956-0, p. 72.
- ^ O'Keeffe, Dennis (2012). Waltzing Matilda: The Secret History of Australia's Favourite Song. Allen & Unwin. p. back cover. ISBN 978-1-7423-7706-3.
- ^ "The Miles Franklin Literary Award – australia.gov.au". 27 February 2012. Archived from the original on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Australia's Nobel Laureates and the Nobel Prize Archived 19 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine, australia.gov.au. Retrieved 17 April 2015.
- ^ Hughes-d'Aeth, Tony (15 October 2014). "Australia's Booker prize record suggests others will come in Flanagan's wake". The Conversation. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Williams, Robyn (12 November 2016). "Three Australian books that changed history", ABC Radio National. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ Flood (2019). pp. 62, 64-5
- ^ Maloney, Shane (January 2006). "Nellie Melba & Enrico Caruso". The Monthly. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ Compagnoni, Tom (4 September 2022). "The 43-year-old invention behind 2022's biggest music sensation". The Sydney Morning Herald.
- ^ "Arts funding guide 2010" (PDF). Australia Council. 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2010. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "Evaluation of the Orchestras Review 2005 funding package implementation" (PDF). Australia Council. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 March 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Opera Australia". Australia Council. Archived from the original on 23 July 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Opera in Australia". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. 5 March 2007. Archived from the original on 6 April 2011.
- ^ Brandis, George (8 May 2007). "35 per cent increase in funding for Australia's major performing arts companies". Department of Communications, Information Technology and the Arts. Archived from the original on 12 November 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ Chichester, Jo (2007). "Return of the Kelly Gang". UNESCO Courier. UNESCO. Archived from the original on 4 February 2010. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
- ^ "The first wave of Australian feature film production" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Culture.gov.au – "Film in Australia"". Australian Government: Culture Portal. Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Commonwealth of Australia. 22 November 2007. Archived from the original on 27 March 2011.
- ^ Krausz, Peter (2002). "Australian Identity: A Cinematic Roll Call" (PDF). Australian Screen Education Online (29): 24–29. ISSN 1443-1629. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- ^ Moran, Albert; Vieth, Errol (2009). The A to Z of Australian and New Zealand Cinema. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-6347-7, p. 35.
- ^ Quinn, Karl (4 December 2015). "Australian film has had its biggest year at the box office ever. Why?". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ "Ten Great Australian Moments at the Oscars" Archived 8 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine (26 February 2014), news.com.au. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- ^ a b c "Country profile: Australia". BBC News. 13 October 2009. Retrieved 7 April 2010.
- ^ "Press Freedom Index 2024". Reporters Without Borders. 2024. Archived from the original on 24 April 2016. Retrieved 30 November 2024.
- ^ "Media Ownership In Australia – 1999 | AustralianPolitics.com". australianpolitics.com. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Minter, Elizabeth (12 April 2021). "Media concentration by Murdoch, Nine and Stokes, and ABC cuts, a danger to democracy – report". Michael West. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ "Bush Tucker Plants, or Bush Food". Teachers.ash.org.au. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ Lockhart, Jessica Wynne (4 August 2023). "The Next Superfoods May Come From Australia", Smithsonian. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ McCubbing, Gus (4 November 2022). "Bush food industry worth $80m but could double by 2025: study", Australian Financial Review. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "Australian food and drink". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. 23 September 2008. Archived from the original on 26 March 2010.
- ^ "Modern Australian recipes and Modern Australian cuisine". Special Broadcasting Service. Archived from the original on 3 May 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ Jonsen, Helen (1999). Kangaroo's Comments and Wallaby's Words: The Aussie Word Book. Hippocrene Books. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-7818-0737-1.
- ^ Newton, John (2018). The Getting of Garlic: Australian Food from Bland to Brilliant, with Recipes Old and New. NewSouth Publishing. ISBN 9781742244365, pp. 32, 230–231.
- ^ Waters, Cara (15 June 2015). "Smashed avo, anyone? Five Australian creations taking the world by storm", The Guardian. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ "How the flat white conquered the coffee scene". The Independent. 9 April 2018. Retrieved 4 October 2018.
- ^ Santich, Barbara (2012). Bold Palates: Australia's Gastronomic Heritage. Wakefield Press. p. 290. ISBN 978-1-7430-5094-1.
- ^ "Australian wine: Production, sales and inventory report, 2018–19". wineaustralia.com. Wine Australia. 12 February 2020. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ "Wine Regions of Australia". Cellarmasters. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 2 April 2021.
- ^ Per Capita Beer Consumption by Country (2004) Archived 23 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Table 3, Kirin Research Institute of Drinking and Lifestyle – Report Vol. 29–15 December 2005, Kirin Holdings Company.
- ^ "National Sports Museum – Heritage Listing". 14 September 2009. Archived from the original on 14 September 2009. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ "Clearinghouse for sport: Ausplay National Sport and Activity Physical Participation Report 2022-23, p 9". Australian Sports Commission. October 2023. Retrieved 11 May 2024.
- ^ Oxlade, Chris; Ballheimer, David (2005). Olympics. DK Eyewitness. DK. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-7566-1083-8.
- ^ Davison, Hirst & Macintyre 1998, pp. 479–80
- ^ "Brisbane announced as 2032 Olympic Games host city at IOC meeting in Tokyo". ABC News (Australia). 21 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- ^ "Flag Bearers". Australian Commonwealth Games Association. Archived from the original on 26 July 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Past Commonwealth Games". Commonwealth Games Federation. Archived from the original on 15 March 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ Harte, Chris; Whimpress, Bernard (2008). The Penguin History of Australian Cricket (3rd ed.). Camberwell, Vic: Viking. pp. 92–94, 528, 722. ISBN 9780670072880.
- ^ "Australia stuns India to claim record-extending sixth Cricket World Cup crown in Ahmedabad". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 20 November 2023. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ Fujak, Hunter (15 July 2022). "The Barassi Line: a globally unique divider splitting Australia's footy fans". The Conversation. Retrieved 4 February 2024.
- ^ "The 'Barassi Line': Quantifying Australia's Great Sporting Divide". 21 December 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2018.
- ^ Skinner, James; Zakus H., Dwight; Edwards, Allan (2013). "Coming in from the Margins: Ethnicity, Community Support and the Rebranding of Australian Soccer". In Adam, Brown (ed.). Football and Community in the Global Context: Studies in Theory and Practice. Routledge. pp. 92–93. ISBN 978-1-317-96905-1.
- ^ Booth, Douglas (2012). Australian Beach Cultures: The History of Sun, Sand and Surf. Routledge. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-7146-8178-8.
- ^ "Surf Life Saving - Stories from Australia's Culture and Recreation Portal" Archived 11 May 2006 at the Wayback Machine. [Online], Commonwealth Government of Australia, 2006.
 This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0. Text taken from World Food and Agriculture – Statistical Yearbook 2023, FAO, FAO.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0. Text taken from World Food and Agriculture – Statistical Yearbook 2023, FAO, FAO.
Bibliography
- Davison, Graeme; Hirst, John; Macintyre, Stuart (1998). The Oxford Companion to Australian History. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1955-3597-6.
- Flood, Josephine (2019). The Original Australians: The Story of the Aboriginal People (2nd ed.). Crows Nest, NSW: Allen and Unwin. ISBN 9781760527075.
- Jupp, James (2001). The Australian people: an encyclopedia of the nation, its people, and their origins. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5218-0789-0.
- Jupp, James; Director Centre for Immigration and Multicultural Studies James Jupp (2001). The Australian People: An Encyclopedia of the Nation, Its People and Their Origins. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5218-0789-0.
- Smith, Bernard; Smith, Terry (1991). Australian painting 1788–1990. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1955-4901-0.
- Teo, Hsu-Ming; White, Richard (2003). Cultural history in Australia. University of New South Wales Press. ISBN 978-0-8684-0589-6.
Further reading
- Blainey, Geoffrey (2015). The Story of Australia's People, Volume 1: The Rise and Fall of Ancient Australia, Penguin Books Australia Ltd., Vic. ISBN 978-0-6700-7871-4
- Denoon, Donald, et al. (2000). A History of Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-17962-7.
- Goad, Philip and Julie Willis (eds.) (2011). The Encyclopedia of Australian Architecture. Port Melbourne, Victoria: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5218-8857-8.
- Hughes, Robert (1986). The Fatal Shore: The Epic of Australia's Founding. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-394-50668-5.
- Milne, John (1886). Colonial facts and fictions: Humorous sketches. United Kingdom: Chatto and Windus.
- Kemp, David (2018). The Land of Dreams: How Australians Won Their Freedom, 1788–1860. Melbourne University Publishing. ISBN 978-0-5228-7334-4. OCLC 1088319758.
- Powell, J.M. (1988). An Historical Geography of Modern Australia: The Restive Fringe. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-25619-3
- Robinson, G.M., Loughran, R.J., and Tranter, P.J. (2000). Australia and New Zealand: Economy, Society and Environment. London: Arnold; New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-340-72033-2 paperback, ISBN 978-0-340-72032-5 hardback.
External links
- Australia profile on The World Factbook
- Australia profile from BBC News
- Australia profile from the OECD
 Wikimedia Atlas of Australia
Wikimedia Atlas of Australia Geographic data related to Australia at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Australia at OpenStreetMap
Government
- Parliament of Australia
- Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade
- National Archives of Australia
- Australian Bureau of Statistics
Travel
- Official website of Tourism Australia