Giza: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Undid revision 1263587950 by Magnolia677 (talk) |
||
| (828 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|City in Greater Cairo, Egypt}} |
|||
: ''"Gizeh" redirects here. For the name of a German brand of cigarette rolling papers, see [[Mascotte (rolling papers)]].'' |
|||
{{distinguish|Gaza City}} |
|||
: ''"Jizah" redirects here. For the [[Wu-Tang Clan]] member and rapper, see [[GZA]].'' |
|||
{{About|the city in Egypt|other uses}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=August 2022}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
<!--See the Table at Infobox Settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage--> |
<!--See the Table at Infobox Settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage--> |
||
<!-- Basic info ----------------> |
<!-- Basic info ---------------->| name = Giza |
||
| |
| native_name = {{lang|ar|الجيزة}} |
||
|other_name |
| other_name = |
||
| settlement_type = [[City]] |
|||
|native_name = الجيزة |
|||
| image_skyline = {{Photomontage |
|||
|nickname = |
|||
| photo1a = Giza-Nile.JPG |
|||
|settlement_type = |
|||
| photo2a = Giza-pyramids.JPG |
|||
|motto = |
|||
| photo2b = All Gizah Pyramids.jpg |
|||
<!-- images and maps -----------> |
|||
| photo3a = Great Sphinx of Giza May 2015.JPG |
|||
|image_skyline = Giza Landmark.png |
|||
| photo3b = CairoUniv.jpg |
|||
|imagesize = 300px |
|||
| size = 281 |
|||
|image_caption = |
|||
| spacing = 2 |
|||
|image_flag = |
|||
| color = transparent |
|||
|flag_size = |
|||
| border = 0 |
|||
|image_seal = |
|||
}} |
|||
|seal_size = |
|||
| image_caption = '''Clockwise from top:''' <br /> Giza panorama, [[Pyramids of Giza]], [[Cairo University]], [[Great Sphinx of Giza]], aerial view of Pyramids |
|||
|image_shield = |
|||
| |
| image_flag = Flag of Giza Governorate.png |
||
| flag_size = |
|||
|pushpin_map=Egypt |
|||
| image_seal = Coat_of_arms_of_Giza_Governorate.png |
|||
|pushpin_mapsize=300 |
|||
| seal_size = 100px |
|||
<!-- Location ------------------> |
|||
| |
| image_shield = |
||
| |
| shield_size = |
||
| motto = <!-- images and maps -----------> |
|||
|subdivision_name = {{flag|Egypt}} |
|||
| |
| pushpin_map = Egypt#Africa |
||
| pushpin_label_position = left |
|||
|subdivision_name1 = [[Giza Governorate|Giza]] |
|||
| pushpin_relief = yes |
|||
|subdivision_type2 = |
|||
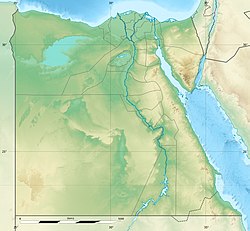
| pushpin_map_caption = Location of Giza within Egypt |
|||
|subdivision_name2 = |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|29.9870|31.2118|region:EG|display=inline,title}} |
|||
|subdivision_type3 = |
|||
| subdivision_type = Country |
|||
|subdivision_name3 = |
|||
| subdivision_name = {{flag|Egypt}} |
|||
|<!-- Politics -----------------> |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = [[Governorates of Egypt|Governorate]] |
|||
|government_footnotes = |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = |
|||
|government_type = |
|||
| subdivision_type3 = |
|||
|leader_title = |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Giza Governorate|Giza]] |
|||
|leader_name = |
|||
| subdivision_name2 = |
|||
|leader_title1 = <!-- for places with, say, both a mayor and a city manager --> |
|||
| subdivision_name3 = |
|||
|leader_name1 = |
|||
|established_title |
| established_title = Founded |
||
|established_date |
| established_date = 642 AD |
||
<!-- Area ---------------------> |
<!-- Area --------------------->| government_footnotes = |
||
| government_type = |
|||
|area_magnitude = |
|||
| leader_title = Governor |
|||
|unit_pref =Imperial <!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired--> |
|||
| leader_name = Ahmed Rashed<ref>{{citation|url=https://www.masrawy.com/news/news_egypt/details/2022/8/30/2283325/%D9%85%D8%AD%D8%A7%D9%81%D8%B8-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%8A%D8%B2%D8%A9-%D9%8A%D8%AA%D8%B1%D8%A3%D8%B3-%D8%A7%D8%AC%D8%AA%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%B9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%86%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AA%D9%86%D9%81%D9%8A%D8%B0%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D9%84%D9%84%D9%85%D8%A8%D8%A7%D8%AF%D8%B1%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%88%D8%B7%D9%86%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D9%84%D9%84%D9%85%D8%B4%D8%B1%D9%88%D8%B9%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AE%D8%B6%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%A1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B0%D9%83%D9%8A%D8%A9|title=محافظ الجيزة يترأس اجتماع اللجنة التنفيذية للمبادرة الوطنية للمشروعات الخضراء الذكية|website=Masrawy|access-date=2 September 2022|archive-date=2 September 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220902035440/https://www.masrawy.com/news/news_egypt/details/2022/8/30/2283325/%D9%85%D8%AD%D8%A7%D9%81%D8%B8-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%8A%D8%B2%D8%A9-%D9%8A%D8%AA%D8%B1%D8%A3%D8%B3-%D8%A7%D8%AC%D8%AA%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%B9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%86%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AA%D9%86%D9%81%D9%8A%D8%B0%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D9%84%D9%84%D9%85%D8%A8%D8%A7%D8%AF%D8%B1%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%88%D8%B7%D9%86%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D9%84%D9%84%D9%85%D8%B4%D8%B1%D9%88%D8%B9%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AE%D8%B6%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%A1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B0%D9%83%D9%8A%D8%A9|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|area_footnotes = |
|||
| |
| leader_title1 = <!-- for places with, say, both a mayor and a city manager --> |
||
| leader_name1 = |
|||
|area_land_km2 = <!--See table @ Template:Infobox Settlement for details on automatic unit conversion--> |
|||
| unit_pref = Metric <!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired--> |
|||
<!-- Population -----------------------> |
|||
| area_footnotes = <ref name="citypopulation">{{cite web |title=Egypt: Governorates, Major Cities & Towns - Population Statistics, Maps, Charts, Weather and Web Information |url=https://citypopulation.de/en/egypt/cities/?cityid=566 |website=citypopulation.de |access-date=17 March 2023 |archive-date=17 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230317020114/https://citypopulation.de/en/egypt/cities/?cityid=566 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
|population_as_of = |
|||
| area_magnitude = |
|||
|population_footnotes = |
|||
| area_total_km2 = 98.4 |
|||
|population_note = |
|||
| area_land_km2 = <!--See table @ Template:Infobox Settlement for details on automatic unit conversion--> |
|||
|population_total = 2,681,863 |
|||
<!-- Population ----------------------->| elevation_footnotes = <ref name="citypopulation" /> |
|||
|population_density_km2 = |
|||
| |
| elevation_m = 30 |
||
<!-- Area/postal codes & others -------->| population_total = 4,458,135 |
|||
|population_metro = |
|||
| population_urban = |
|||
|population_density_metro_km2 = |
|||
| population_as_of = 2023 |
|||
|population_density_metro_sq_mi = |
|||
| population_footnotes = <ref name="citypopulation" /> |
|||
|population_blank1_title =Ethnicities |
|||
| population_density_km2 = auto |
|||
|population_blank1 = |
|||
| population_blank1_title = [[Demonym]] |
|||
|population_density_blank1_km2 = |
|||
| population_blank1 = Gizan (m), Gizanne (f) |
|||
|population_density_blank1_sq_mi = |
|||
<!-- General information ---------------> |
<!-- General information --------------->| population_note = |
||
| postal_code_type = Postal code |
|||
|timezone =[[Egypt Standard Time|EST]] |
|||
| |
| postal_code = 5-Digit |
||
| |
| area_code = (+20) 2 |
||
| website = [http://www.giza.gov.eg/English/default.aspx Giza.gov.eg] |
|||
|utc_offset_DST = |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
|latd=30|latm=01|lats=|latNS=N |
|||
| timezone = [[Egypt Standard Time|EST]] |
|||
|longd=31|longm=13|longs=|longEW=E |
|||
| utc_offset = +2 |
|||
|elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use <ref> </ref> tags--> |
|||
| |
| timezone_DST = |
||
| utc_offset_DST = |
|||
|elevation_ft = |
|||
| official_name = |
|||
<!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> |
|||
}} |
|||
|postal_code_type = <!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... --> |
|||
|postal_code = |
|||
|area_code = |
|||
|blank_name = |
|||
|blank_info = |
|||
|blank1_name = |
|||
|blank1_info = |
|||
|website = |
|||
|footnotes = }} |
|||
'''Giza''' ({{lang-ar|الجيزة}} {{transl|ar|''Al J(Ǧ)īza''}}), sometimes spelt ''G(J)izah'', is the third largest city in [[Egypt]]. It is located on the west bank of the [[Nile]] River, some {{convert|20|km|2|abbr=on|lk=out}} southwest of central [[Cairo]]. Along with [[Shubra El-Kheima]], [[Cairo]] and [[Helwan]], the four cities form the Province of [[Greater Cairo]] metropolis. The city of Giza is the capital of the [[Giza Governorate]], and is located near the northeast border of this governorate in coordinates. It is located right on the banks of the [[River Nile]]. The city's population was 2,681,863 in the 2006 national census, while the governorate had 6,272,571 at the same census. Its large population makes it the second largest suburb in the world, tied with [[Incheon]], South Korea and [[Quezon City]], Philippines, second only to [[Yokohama]], Japan. |
|||
'''Giza''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|g|iː|z|ə}}; sometimes spelled ''Gizah, Gizeh, Geeza, Jiza''; {{langx|ar|الجيزة|al-Jīzah}}, {{IPA|ar|ald͡ʒiːzah|pron}}, {{langx|arz|الجيزة}} ''{{transliteration|arz|el-Gīza}}'' {{IPA|arz|elˈgiːzæ|}})<ref>{{Citation|url=https://discoverdiscomfort.com/egyptian-arabic-place-names-monuments/|title=Egyptian Arabic Place Names and Monument Names|date=11 February 2019 |access-date=30 June 2023}}</ref> is the [[list of cities and towns in Egypt|third-largest city]] in [[Egypt]] by area after [[Cairo]] and [[Alexandria]]; and [[List of cities in Africa by population|fourth-largest city]] in Africa by population after [[Kinshasa]], [[Lagos]], and Cairo. It is the capital of [[Giza Governorate]] with a total population of 4,872,448 in the 2017 census.<ref name=":0" /> It is located on the west bank of the [[Nile]] opposite central Cairo, and is a part of the [[Greater Cairo]] metropolis. Giza lies less than {{convert|30|km|2|abbr=on}} north of [[Memphis, Egypt|Memphis]] (''Men-nefer,'' today the village of Mit Rahina), which was the capital city of the unified Egyptian state during the reign of pharaoh [[Narmer]], roughly 3100 BC. |
|||
Giza is most famous as the location of the [[Giza Plateau]]: the site of some of the most impressive ancient monuments in the world, including a complex of [[ancient Egypt]]ian royal mortuary and sacred structures, including the [[Great Sphinx]], the [[Great Pyramid of Giza]], and a number of other large [[pyramid]]s and [[temple]]s. The plateau and its monuments have been recorded in the Giza Plateau Mapping Project run by [[Ancient Egypt Research Associates]], directed by Dr. [[Mark Lehner]].<ref>''"The Giza Plateau Mapping Project"'', Lehner, Mark; Hunt, Brian V. [http://www.aeraweb.org/gpmp_home.asp link]</ref> AERA's 2009 field season was recorded in a blog.<ref>''"An archaeology blog from the Giza Pyramids in Egypt"'', 2009 Hunt, Brian V. [http://aerablog.wordpress.com/ link]</ref> |
|||
Giza is most famous as the location of the [[Giza Plateau]], the site of some of the most impressive ancient monuments in the world, including a complex of [[ancient Egypt]]ian royal mortuary and [[sacred]] structures, among which are the [[Great Sphinx]], the [[Great Pyramid of Giza]], and a number of other large [[pyramid]]s and temples. Giza has always been a focal point in Egypt's history due to its location close to Memphis, the ancient pharaonic capital of the [[Old Kingdom of Egypt|Old Kingdom]]. |
|||
The Great Pyramid of Giza at one time was advocated (1884) as the location for the [[Prime Meridian]], a reference point used for determining a base longitude.<ref>''"The Canary Islands and the Question of the Prime Meridian: The Search for Precision in the Measurement of the Earth"'', Wilcomb E. Washburn. [http://muweb.millersville.edu/~columbus/data/geo/WASHBR04.GEO link]</ref> |
|||
== Districts and population == |
|||
== History == |
|||
The city of Giza is the capital of the [[Giza Governorate]], and is located near the northeast border of this governorate. |
|||
"[[Memphis, Egypt|Mn Nefer]]" (Memphis, in [[Greek language|Greek]]) - which means "the beautiful wall" in the [[ancient Egyptian language]] -, the capital city of the first unified Egyptian state since the days of Pharaoh King [[Narmer]], lies nearly {{convert|20|km|2|abbr=on|lk=out}} south of Giza. Giza's most famous archaeological site, the [[Giza Plateau]], holds some of the most astonishing [[monuments]] in [[History of Egypt|Egyptian history]]. Once thriving with the [[Nile]] that flowed right into the Giza Plateau, the [[Giza Necropolis|pyramids of Giza]] were built overlooking the [[ancient Egyptian]] capital city of [[Memphis, Egypt|Memphis]], which was near modern day [[Cairo]]. |
|||
===2017 population and administrative divisions=== |
|||
[[File:All Gizah Pyramids.jpg|thumb|right|300px|[[Giza Pyramids]]]] |
|||
Giza city is a municipal division and capital of Giza governorate with an appointed city head.<ref>{{Cite web |last= |first= |date=2020-02-11 |title="أبو النجا" يتفقد المراحل النهائية لتطوير نفق مشاه بميدان الجيزة |url=https://m.akhbarelyom.com/news/newdetails/2997491/1/-%D8%A3%D8%A8%D9%88-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%86%D8%AC%D8%A7-%D9%8A%D8%AA%D9%81%D9%82%D8%AF-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%AD%D9%84-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%86%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%A6%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D9%84%D8%AA%D8%B7%D9%88%D9%8A%D8%B1 |access-date=2023-01-08 |website=بوابة اخبار اليوم |archive-date=5 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230405210849/https://m.akhbarelyom.com/news/newdetails/2997491/1/-%D8%A3%D8%A8%D9%88-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%86%D8%AC%D8%A7-%D9%8A%D8%AA%D9%81%D9%82%D8%AF-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%AD%D9%84-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%86%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%A6%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D9%84%D8%AA%D8%B7%D9%88%D9%8A%D8%B1 |url-status=live }}</ref> It comprises nine [[district]]s (''ahya''<nowiki/>', singl. ''hayy'') and five [[Planned community|new towns]] ''(mudun jadidah)'' administered by the [[New Urban Communities Authority]] (NUCA). |
|||
The [[Giza Plateau]] is also home to many other [[ancient Egyptian]] monuments, including the tomb of Pharaoh [[Djet]] of the [[First dynasty of Egypt|First Dynasty]], as well as that of Pharaoh [[Ninetjer]] of the [[Second dynasty of Egypt|Second Dynasty]]. |
|||
The districts/qisms fully subsume to the city head and according to the 2017 census had 4,872,448 residents:<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |last=Central Agency for Public Mobilisation and Statistics (CAPMAS) |date=2017 |title=2017 Census for Population and Housing Conditions |url=https://www.cedejcapmas.org/adws/app/4d5b52dc-669d-11e9-b6a6-975656a88994/index.html |access-date=2023-02-21 |website=CEDEJ-CAPMAS |archive-date=10 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230410043544/https://www.cedejcapmas.org/adws/app/4d5b52dc-669d-11e9-b6a6-975656a88994/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=الصفحة الرئيسية - الأحياء |url=http://www.giza.gov.eg/areas/default.aspx |access-date=2023-01-08 |website=www.giza.gov.eg |archive-date=8 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230108203912/http://www.giza.gov.eg/areas/default.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
== Infrastructure == |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
Giza has seen many changes over time. Changes in [[infrastructure]] during the different occupations of [[Egypt]] by various rulers, including the [[Great Britain|British]] in the 18th and early 20th century, focused on the construction of [[roads]], [[street]]s, and [[buildings]] in the area. Giza is a thriving centre of [[Culture of Egypt|Egyptian culture]] and is quite heavily populated, with many facilities and buildings in the current area. Giza saw much attention in particular to its vast amount of [[ancient Egypt]]ian [[monuments]] found on the [[Giza Plateau]], and has astonished thousands of visitors and tourists over the years. Giza's infrastructure saw much attention from both the British government prior to the 1952 [[coup d'etat]], as well as the current [[Egypt]]ian government due to the city's importance in [[tourism]]. |
|||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |District/qism |
|||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Code 2017 |
|||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Population |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Imbaba|Shamal (North)/ Imbâba]] |
|||
|210100 |
|||
|632,599 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Agouza|Agouza, al-]] |
|||
|210200 |
|||
|278,479 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Dokki|Duqqî, al-]] |
|||
|210300 |
|||
|70,926 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Janoub (South)/ Jîza, al- |
|||
|210400 |
|||
|285,723 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Bûlâq al-Dakrûr |
|||
|210500 |
|||
|960,031 |
|||
|- |
|||
|`Umrâniyya, al- |
|||
|210600 |
|||
|366,066 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Ṭâlbiyya, al- |
|||
|210700 |
|||
|457,667 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Ahrâm, al- |
|||
|210800 |
|||
|659,305 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[El Warraq|Warrâq, al-]] |
|||
|211700 |
|||
|722,083 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Sheikh Zayed City|Shaykh Zâyid]], al (new city)<ref>{{Cite web |title=الصفحة الرئيسية - الشيخ زايد |url=http://www.newcities.gov.eg/know_cities/Sheikh_Zayed/(1).aspx |access-date=2023-01-08 |website=www.newcities.gov.eg |archive-date=19 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170719202051/http://www.newcities.gov.eg/know_cities/Sheikh_Zayed/(1).aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
|211900 |
|||
|90,699 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[6th of October (city)|6 October]] 1 (new city)<ref>{{Cite web |title=الهيكل الإداري |url=http://www.6october.gov.eg/pages/%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%87%D9%8A%D9%83%D9%84%20%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A5%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%D9%89%20%D9%84%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%B2/%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%87%D9%8A%D9%83%D9%84%20%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A5%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%D9%89%20%D9%84%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%B2.aspx |access-date=2023-01-08 |website=www.6october.gov.eg |archive-date=8 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230108203910/http://www.6october.gov.eg/pages/%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%87%D9%8A%D9%83%D9%84%20%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A5%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%D9%89%20%D9%84%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%B2/%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%87%D9%8A%D9%83%D9%84%20%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A5%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%D9%89%20%D9%84%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%B2.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
|212000 |
|||
|93,012 |
|||
|- |
|||
|6 October 2 (new city) |
|||
|212100 |
|||
|196,373 |
|||
|- |
|||
|6 October 3 (new city) |
|||
|212300 |
|||
|59,485 |
|||
|} |
|||
The new towns are mostly administered by the national level [[New Urban Communities Authority]] (NUCA), with some public services under the jurisdiction of Giza. They are confusingly named ''madina'' (city), however they are not administratively incorporated as such where many are formed of a single district or qism. Ones not in the 2017 census as they were not yet incorporated, or inhabited at that time are: |
|||
*New 6th of October<ref>{{Cite web |title=الصفحة الرئيسية - مدينة 6 أكتوبر الجديدة |url=http://www.newcities.gov.eg/know_cities/NewOctober/default.aspx |access-date=2023-01-08 |website=www.newcities.gov.eg |archive-date=29 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201129193335/http://www.newcities.gov.eg/know_cities/NewOctober/default.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The city hosts the first zoo on the entire African continent and one of the oldest in the [[Mediterranean]] region, the [[Giza Zoo]]. In addition, there are several parks, the most famous among them is [[Orman Park]] which means "Forest Park" in the [[Turkish language]]. |
|||
*October Gardens<ref>{{Cite web |title=الصفحة الرئيسية - حدائق اكتوبر |url=http://www.newcities.gov.eg/know_cities/October_Gardens/default.aspx |access-date=2023-01-08 |website=www.newcities.gov.eg |archive-date=8 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230108203910/http://www.newcities.gov.eg/know_cities/October_Gardens/default.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
*New Sphinx<ref>{{Cite web |title=الصفحة الرئيسية - مدينة سفنكس الجديدة |url=http://www.newcities.gov.eg/know_cities/New_Sphinx/default.aspx |access-date=2023-01-08 |website=www.newcities.gov.eg |archive-date=22 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220522130912/http://www.newcities.gov.eg/know_cities/New_Sphinx/default.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Permanently inhabited Nile islands: |
|||
=== Health === |
|||
Giza has advanced level of medical care just like its elder twin Cairo. |
|||
* [[Qorsaya Island]] (Janoub/Giza district) |
|||
A list of famous hospitals in Giza: |
|||
* |
* [[Dahab Island]] (Janoub/Giza district) |
||
* [[El Warraq|Al-Warraq Island]] (Al-Warraq district) |
|||
* Al Salam in [[Mohandessin]] neighbourhood. |
|||
* Badran in [[Dokki]] district. |
|||
* El Safa. |
|||
* Haram Hospital in Haram. |
|||
* El Shoruk Hospital. |
|||
* Cairo Medical Lab |
|||
In addition to hospitals there are numerous medical facilities, private clinics, medical check laboratories, etc. |
|||
=== |
=== 2006 population === |
||
The city's population was reported as 2,681,863 in the 2006 national census,<ref name="Appiah(Jr.)20102">{{cite book |author1=Anthony Appiah |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=A0XNvklcqbwC |title=Encyclopedia of Africa |author2=Henry Louis Gates (Jr.) |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-19-533770-9 |page=403 |access-date=8 August 2019 |archive-date=11 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230111210158/https://books.google.com/books?id=A0XNvklcqbwC |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Giza, Egypt |url=https://www.goneagaintravel.com/location/giza |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190221224106/https://www.goneagaintravel.com/location/giza |archive-date=21 February 2019 |access-date=21 February 2019}}</ref> while the governorate had 6,272,571 at the same census, without specifying what the city is. The former figure corresponds to the sum of nine districts/qisms. |
|||
Transportation in Giza comprises an extensive road network, rail system, subway system, and maritime services. Road transport is facilitated by personal vehicles, taxi cabs, privately owned public buses, and microbuses. |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
|||
Giza shares with Cairo the subway system, officially called the "Metro (مترو)", a fast and efficient way of getting around. An extensive road network connects Giza with [[6th of October City]], Cairo and other cities. There are flyovers and bridges such as the 15th of May bridge. |
|||
! rowspan="2" |Region |
|||
Giza traffic is known to be overwhelming and overcrowded. |
|||
!(Population) |
|||
! rowspan="2" |Area<br />km<sup>2</sup> |
|||
|- |
|||
! 2006 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Giza, 9 kisms (contiguous) || 2,681,863 || 98.4 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Giza, 10 kisms (not contiguous) || 2,822,271 || 115.7 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Giza, 10 kisms + Giza markaz (contiguous) || 3,063,777 || 187 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Giza, 10 kisms + Giza, [[Kerdasa]], Ossim markaz (contiguous) || – || 338.9 |
|||
|} |
|||
== Geography and Climate== |
|||
* [[Cairo Taxi]] |
|||
Giza's most famous landform and archaeological site, the [[Giza Plateau]], holds some major monuments of [[History of Egypt|Egyptian history]], and is home to the [[Great Sphinx]]. Once thriving with the [[Nile]] that flowed right into the Giza Plateau, the [[Giza Necropolis|pyramids of Giza]] were built overlooking the [[ancient Egyptian]] capital city of [[Memphis, Egypt|Memphis]], across the river from modern day Cairo. The Great Pyramid of Giza at one time was advocated (1884) as the location for the [[Prime Meridian]], a reference point used for determining a base longitude.<ref>''"The Canary Islands and the Question of the Prime Meridian: The Search for Precision in the Measurement of the Earth"'', Wilcomb E. Washburn. [http://muweb.millersville.edu/~columbus/data/geo/WASHBR04.GEO link] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070529031631/http://muweb.millersville.edu/~columbus/data/geo/WASHBR04.GEO |date=29 May 2007 }}</ref> |
|||
* [[Cairo Metro]] |
|||
* [[Cairo Yellow Cab]] |
|||
* [[Cairo Nile Ferry]] |
|||
===Climate=== |
|||
== Districts and Neighbourhoods of Giza == |
|||
Giza experiences a [[hot desert climate|hot desert]] like [[arid climate]] ([[Köppen climate classification system|Köppen]]: BWh). Its climate is similar to Cairo, owing to its proximity. Windstorms can be frequent across [[climate of Egypt|Egypt]] in spring, bringing [[mineral dust|Saharan dust]] into the city during the months of March and April. High temperatures in winter range from {{convert|16|to|20|°C|0|abbr=on}}, while nighttime lows drop to below {{convert|7|°C|0|abbr=on}}. In summer, the highs are {{convert|40|°C|0|abbr=on}}, and the lows can drop to about {{convert|20|°C|0|abbr=on}}. Rain is infrequent in Giza; snow is extremely rare. |
|||
*[[Dokki]] District: 93,660 93,025 |
|||
*[[Agouza]] District: 174,460 162,851 |
|||
*[[Giza District]]: 180,568 246,325, Kism Al Jizah 238,567 248,897 |
|||
*[[Bulaq ad Dakrur]]: 453,884 564,791 |
|||
*[[Imbabah]]: 287,357 389,049, Kism Imbabah 523,265 597,160 |
|||
*[[Haram District]]200,076 295,704 |
|||
*[[Omrania]] |
|||
*[[Monib]] |
|||
*[[Kafr Tuhurmus]] |
|||
The centre of the city is [[Giza Square]]. |
|||
Up to August 2013, the highest recorded temperature was {{convert|46|C}} on 13 June 1965, while the lowest recorded temperature was {{convert|2|C}} on 8 January 1966.<ref name="Voodoo Skies">{{cite web|title=El-Giza, Egypt|url=http://voodooskies.com/weather/egypt/el-giza|publisher=Voodoo Skies|access-date=16 August 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131029183711/http://voodooskies.com/weather/egypt/el-giza|archive-date=29 October 2013}}</ref> |
|||
== Climate == |
|||
Giza experiences an [[arid climate]] (Koeppen ''BWh''), but often with high humidity due to the [[Nile]] River Valley's effects. Wind storms can be frequent, bringing [[Mineral dust|Saharan dust]] into the city during the months of March and April. High temperatures in winter range from {{convert|12|°C|0|abbr=on}} to {{convert|17|°C|0|abbr=on}}, while nighttime lows drop to below {{convert|7|°C|0|abbr=on}}, often to 5°C; the lowest recorded temperature was {{convert|0.8|°C|0|abbr=on}}. In summer, the highs rarely surpass {{convert|40|°C|0|abbr=on}}, and the lows drop to about {{convert|20|°C|0|abbr=on}}. Rainfall is sparse, but sudden showers do cause harsh flooding. Hail and sleet might take place. |
|||
{{Weather box |
|||
|width = auto |
|||
|location = Giza |
|||
|single line = Yes |
|||
|metric first = Yes |
|||
|Jan record high C=28 |
|||
|Feb record high C=30 |
|||
|Mar record high C=36 |
|||
|Apr record high C=41 |
|||
|May record high C=43 |
|||
|Jun record high C=46 |
|||
|Jul record high C=41 |
|||
|Aug record high C=43 |
|||
|Sep record high C=39 |
|||
|Oct record high C=40 |
|||
|Nov record high C=36 |
|||
|Dec record high C=30 |
|||
|Jan high C=19.3 |
|||
|Feb high C=20.9 |
|||
|Mar high C=24.2 |
|||
|Apr high C=28.4 |
|||
|May high C=32.0 |
|||
|Jun high C=34.9 |
|||
|Jul high C=34.5 |
|||
|Aug high C=34.4 |
|||
|Sep high C=32.4 |
|||
|Oct high C=30.2 |
|||
|Nov high C=25.4 |
|||
|Dec high C=21.1 |
|||
|Jan mean C=13.0 |
|||
|Feb mean C=14.0 |
|||
|Mar mean C=17.2 |
|||
|Apr mean C=20.5 |
|||
|May mean C=24.0 |
|||
|Jun mean C=27.1 |
|||
|Jul mean C=27.5 |
|||
|Aug mean C=27.5 |
|||
|Sep mean C=25.6 |
|||
|Oct mean C=23.5 |
|||
|Nov mean C=19.2 |
|||
|Dec mean C=15.0 |
|||
|Jan low C=6.8 |
|||
|Feb low C=7.2 |
|||
|Mar low C=10.3 |
|||
|Apr low C=12.7 |
|||
|May low C=16.1 |
|||
|Jun low C=19.3 |
|||
|Jul low C=20.6 |
|||
|Aug low C=20.7 |
|||
|Sep low C=18.9 |
|||
|Oct low C=16.8 |
|||
|Nov low C=13.0 |
|||
|Dec low C=8.9 |
|||
|Jan record low C=2 |
|||
|Feb record low C=4 |
|||
|Mar record low C=5 |
|||
|Apr record low C=8 |
|||
|May record low C=11 |
|||
|Jun record low C=16 |
|||
|Jul record low C=17 |
|||
|Aug record low C=17 |
|||
|Sep record low C=16 |
|||
|Oct record low C=11 |
|||
|Nov record low C=4 |
|||
|Dec record low C=4 |
|||
|precipitation colour=green |
|||
|Jan precipitation mm=4 |
|||
|Feb precipitation mm=3 |
|||
|Mar precipitation mm=2 |
|||
|Apr precipitation mm=1 |
|||
|May precipitation mm=0 |
|||
|Jun precipitation mm=0 |
|||
|Jul precipitation mm=0 |
|||
|Aug precipitation mm=0 |
|||
|Sep precipitation mm=0 |
|||
|Oct precipitation mm=0 |
|||
|Nov precipitation mm=3 |
|||
|Dec precipitation mm=4 |
|||
|source 1 = ''Climate-Data.org''<ref>{{cite web|title=Climate: Giza – Climate graph, Temperature graph, Climate table|url=http://en.climate-data.org/location/551/|publisher=Climate-Data.org|access-date=16 August 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130914095803/http://en.climate-data.org/location/551/|archive-date=14 September 2013|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|source 2 = ''Voodoo Skies''<ref name="Voodoo Skies"/> for record temperatures |
|||
}} |
|||
==History== |
|||
[[File:Giza-pyramids.JPG|thumb|The [[Giza pyramid complex]]]] |
|||
===Ancient era=== |
|||
The area in what is now Giza served as the necropolis of several [[pharaohs]] who ruled [[ancient Egypt]], during the second millennium BC. Three of these tombs, in the form of giant pyramids, are what is now the famed [[Giza pyramid complex]], featuring the [[Great Pyramid of Giza]]. |
|||
===Classical to medieval era=== |
|||
[[File:Description de l'Egypte - Etat Moderne - Pl 16.jpg|thumb|Giza and the bridge from [[Roda Island]] in {{circa|1800}} ''[[Description de l'Égypte]]'']] |
|||
As ancient Egypt passed under several conquests under the Persians, Greeks, Romans and Byzantines, so did the area in what is now Giza. A Byzantine village named ''Phylake'' ({{Langx|el|Φυλακή}}) or ''Terso'' ({{Langx|cop|ϯⲣⲥⲱ}}, meaning "the fortress", now ''Tersa'') was located south of Giza and should not be confused with it.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.trismegistos.org/place/10908|title=TM Places|website=www.trismegistos.org|access-date=18 April 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190418092737/https://www.trismegistos.org/place/10908|archive-date=18 April 2019|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>موسوعة " القاموس الجغرافى للبلاد المصرية " – محمد رمزى بك (قسم ثانى ج3 – ص4): مركز وثائق وتاريخ مصر المعاصر الهيئة المصرية العامةللكتاب ط 1994 |
|||
</ref><ref>جغرافية مصر في العصر القبطى – الفرنسى أميلينو : الهيئة المصرية العامة للكتاب2013 ترجمة ميخائيل مكسى إسكندر – استدراكات العلامة محمد رمزى على الكتاب في الجزء الثالث من ص 274: نشر المعهد العلمى الفرنسى |
|||
</ref> |
|||
[[Egyptians]] called the area '''Tipersis''' (Bohairic {{Langx|cop|ϯⲡⲉⲣⲥⲓⲥ}}{{efn|Other forms are {{langx|cop|ⲧⲡⲉⲣⲥⲓⲥ}}, {{langx|cop|ϯⲡⲉⲣⲥⲓⲟⲓ}}, {{langx|cop|ϯⲡⲉⲣⲥⲓⲟⲥ}}, {{langx|cop|ϯⲡⲉⲣⲥⲓⲱϯ}} and {{langx|cop|ⲡⲣⲥⲱⲓ}}}} and Sahidic {{Langx|cop|ⲧⲡⲉⲣⲥⲓⲥ ⲛ̀ⲃⲁⲃⲩⲗⲱⲛ|lit=the Persian (fortress) of [[Babylon fortress|Babylon]]}}).<ref>{{Cite book|title=La géographie de l'Egypte à l'époque copte|url=https://archive.org/details/lagographiedele00amgoog|last=Amélineau|first=Emile|publisher=Imprimerie nationale|year=1893|location=Paris|pages=[https://archive.org/details/lagographiedele00amgoog/page/n241 190]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.trismegistos.org/place/50123|title=Trismegistos|website=www.trismegistos.org|access-date=22 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171201034757/http://www.trismegistos.org/place/50123|archive-date=1 December 2017|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Stefan |first=Timm |title=Das christlich-koptische Agypten in arabischer Zeit |year=1988 |pages=1055}}</ref> [[Eutychius of Alexandria|Eutychius]] gives a legend about the city's name and its foundation by [[Artaxerxes III|Artaxerxes Ochus]] or Hūš ({{Langx|ar|خوش}}),<ref>{{Cite book |last=Evetts |first=B. T. A. |title=The Churches and Monasteries of Egypt and Some Neighbouring Countries |pages=177}}</ref> and Abu Salih says it was found by him at the same time as [[Babylon Fortress|Qasr ash-Sham]],<ref>{{Cite book|title=Das christlich-koptische Agypten in arabischer Zeit (Teil 3 G-L)|last=Timm|first=Stefan|year=1985|location=Wiesbaden|pages=1058}}</ref> but in view of the fact that older evidence is missing, it is perhaps most likely to have been founded during the [[Sasanian conquest of Egypt]] in the early [[7th century]].<ref name=":02">{{Cite web |last=Peust |first=Carsten |title=Die Toponyme vorarabischen Ursprungs im modernen Ägypten |url=http://www.peust.de/ortsnamen_original.pdf |page=44 |access-date=13 May 2020 |archive-date=9 October 2022 |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.peust.de/ortsnamen_original.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
As [[Muslims]] of the fledgling [[Islamic]] [[Rashidun Caliphate|caliphate]] went on with their conquest of Egypt from the Byzantine Empire beginning in 639 AD, three years after their victory at the [[battle of Yarmouk]] in 636 AD, they conquered all of the land by the time they [[Siege of Alexandria 641|captured]] the city of [[Alexandria]] in 641 AD. A year later in 642 AD ([[Hijri year|year]] 21 in Islamic calendar), they founded the city of Giza. The exact etymology of its name is unknown. [[Al-Maqrizi]] suggested an irregular Arameo-Arabic root meaning "edge, side" to be the source. Everett-Heath suggested {{Langx|egy|r-gs-ḥr}} "on the side of the height (pyramid)". Peust also suggests a Persian etymology of the word from {{Langx|pal|𐭣𐭦|lit=fortress, castle|translit=diz}}, which Persians could have given to the pyramids or a fortress they found in the area.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Die Toponyme vorarabischen Ursprungs im modernen Ägypten|url=http://www.peust.de/ortsnamen_original.pdf|last=Peust|first=Carsten|access-date=13 May 2020|archive-date=9 October 2022|archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.peust.de/ortsnamen_original.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
==Infrastructure== |
|||
[[File:Giza-sunset.JPG|200px|thumb|Sunset in Giza]] |
|||
Giza has seen many changes over time. Changes in infrastructure during the different occupations of [[Egypt]] by various rulers, including the British in the 18th and early 20th century, focused on the construction of [[roads]], streets, and [[buildings]] in the area. Giza is a thriving centre of [[Culture of Egypt|Egyptian culture]] and is quite heavily populated, with many facilities and buildings in the current area. Giza saw much attention in particular to its vast amount of [[ancient Egypt]]ian monuments found on the [[Giza Plateau]], and has astonished thousands of visitors and tourists over the years. Giza's infrastructure saw much attention from both the British government prior to the 1952 coup d'état, as well as the current Egyptian government due to the city's importance in tourism. Giza's St. George Cathedral is the [[episcopal see]] of the [[Coptic Catholic Eparchy of Giza]]. |
|||
The city hosts the first zoo on the entire African continent and one of the oldest in the [[Mediterranean]] region, the [[Giza Zoo]]. In addition, there are several parks, the most famous among them is Orman Park, which means "Forest Park" in the [[Turkish language]]. |
|||
== Giza Zoo == |
|||
The [[Giza Zoo]] ({{lang|ar|حديقة حيوان الجيزة}}, ''Ḥadīqat Ḥaywān Al-Gīzah''), established on March 1, 1891, holds the distinction of being Africa's first zoo and the world's third oldest zoological garden<ref>{{cite web |title=Giza Zoo: the third oldest within the world and the first in Africa |url=https://egyptiangeographic.com/en/news/show/645 |website=Egyptian Geographic |access-date=2024-01-16}}</ref>. Located on approximately 80 acres (32 hectares), the zoo was originally designed as a botanical garden and features several historical architectural elements<ref>{{cite web |title=Egypt's Giza Zoo: A Chequered History and a Promising Future |url=https://egyptianstreets.com/2023/09/14/egypts-giza-zoo-a-chequered-history-and-promising-future/ |website=Egyptian Streets |date=2023-09-14 |access-date=2024-01-16}}</ref>. |
|||
=== Historical Features === |
|||
The zoo contains several notable architectural and cultural landmarks: |
|||
* A suspension bridge designed by Gustave Eiffel (1875-1879), considered the world's first elevated zoo viewing platform<ref>{{cite web |title=Giza Zoo Cairo Egypt tours, prices, booking, reviews |url=https://www.etltravel.com/cairo/giza-zoo-egypt/ |website=ETL Travel |access-date=2024-01-16}}</ref> |
|||
* The Japanese Kiosk, constructed in 1924 during King Fuad's reign |
|||
* Original gates from the Khedive's Palace and Haramlik Palace |
|||
* Roads paved with black stone imported from Trieste |
|||
* Mosaic-decorated footpaths |
|||
* A marble island known as Tea Island |
|||
=== Animal Collection === |
|||
The zoo houses approximately 4,000 animals representing over 175 species<ref>{{cite web |title=Giza Zoo, Egypt: A Guide to Egypt's Oldest and Largest Zoo |url=https://arabmls.org/giza-zoo-egypt/ |website=Arab MLS |access-date=2024-01-16}}</ref>, including: |
|||
* Large mammals: Lions, tigers, giraffes, rhinoceros, hippopotamuses |
|||
* Primates: Various monkey and ape species |
|||
* Birds: Native and exotic species including flamingos and rare birds |
|||
* Reptiles: Including Egyptian cobras and Nile crocodiles |
|||
=== Recent Developments === |
|||
In 2023, the Egyptian government announced plans to expand the number of animal species from 71 to 186<ref>{{cite web |title=Egypt's PM reviews final designs for Giza Zoo development project |url=https://www.egypttoday.com/Article/1/121493/Egypt-s-PM-reviews-final-designs-for-Giza-Zoo-development |website=Egypt Today |access-date=2024-01-16}}</ref>. The renovation project includes: |
|||
* Creation of specialized zones: Asia, Africa, America, Family Zone, Safari Trips |
|||
* Establishment of educational centers |
|||
* Preservation of historical landmarks |
|||
* Improvement of animal enclosures |
|||
=== Operating Hours === |
|||
* Summer (April-September): 8:30 AM - 5:00 PM |
|||
* Winter (October-March): 8:30 AM - 4:00 PM |
|||
The zoo serves multiple functions as a recreational facility, research institute, and cultural landmark<ref>{{cite web |title=Egyptians fear for historic Giza Zoo as UAE investor steps in |url=https://www.middleeasteye.net/news/egypt-uae-giza-zoo-historic-fear-investor-steps-in |website=Middle East Eye |access-date=2024-01-16}}</ref>. |
|||
===Transportation=== |
|||
[[File:Metro-1-l.jpg|thumb|right|The Cairo Metro (line 2)]] |
|||
Transportation in Giza comprises an extensive road network, rail system, subway system, and maritime services. Road transport is facilitated by personal vehicles, taxi cabs, privately owned public buses and microbuses. |
|||
Giza shares with Cairo [[Cairo Metro|a subway system]], officially called the "Metro (مترو)", a fast and efficient way of getting around. An extensive road network connects Giza with [[6th of October City]], Cairo and other cities. There are flyovers and bridges such as the 15th. Traffic in Giza is known to be overwhelming and overcrowded. |
|||
Other means of transport include: |
|||
* Cairo Taxi |
|||
* [[Uber]] (available in Cairo and Giza since 2015)<ref>{{cite web| url=https://www.uber.com/en-EG/blog/ya-om-el-donia-your-uber-has-just-arrived-cairo/| title=Ya Om El Donia. Your Uber Has Just Arrived, Cairo! – Uber Blog| date=20 November 2014| work=[[Uber]]| access-date=9 September 2017| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180721120657/https://www.uber.com/en-EG/blog/ya-om-el-donia-your-uber-has-just-arrived-cairo| archive-date=21 July 2018| url-status=live| df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Careem]] (available in Cairo and Giza since 2015)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.careem.com/cairo|title=Ride or Drive with Careem in Cairo, Egypt – Careem|website=Careem.com|access-date=16 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161212120700/http://www.careem.com/cairo|archive-date=12 December 2016|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Swvl]] (available in Cairo and Giza since 2017) |
|||
* [[Water taxi]]s (motorized [[felucca]]s) available for transport to nearby places along the Nile River |
|||
==Economy== |
==Economy== |
||
[[File:A grass farm near the Nile River in Egypt.jpg|thumb|Grass farm near the Nile.]] |
|||
Industries here include movies, chemicals, machinery and cigarettes. In addition, Giza has many luxury apartment buildings along the Nile, making it a popular place to live. |
|||
{{unreferenced section|date=August 2022}} |
|||
Industries here include movies, [[chemicals]], Giza cotton, machinery and cigarettes. In addition, Giza has many luxury apartment buildings along the [[Nile]], making it a popular place to live. |
|||
=== |
===International access=== |
||
Access to the city of Giza, which has its own [[governorate]] adjacent to the |
Access to the city of Giza, which has its own [[governorate]] adjacent to the Governorate of Cairo, is dependent on the [[Cairo International Airport]]. Another local airport is found in Giza, called the [[Embaba Airport|Imbaba Airport]], but recently the Egyptian government has decided to shut down the area and turn it into a cultural or an athletic area. |
||
[[Sphinx International Airport]] was opened in 2018 as an alternative to the already congested Cairo International Airport, but also to improve accessibility to the Giza necropolis as well as to the [[Grand Egyptian Museum]]. |
|||
==Education== |
==Education== |
||
[[File:Cairo University-3.JPG|thumb|[[Cairo University]]]] |
|||
Giza's learning institutions include the [[University of Cairo]] which was moved to Giza in [[1924]]. The city is a hub of education and educational services not only for Egypt but also for the entire [[Mediterranean Region]]. Giza has numerous schools, kindergartens, and institutes of higher learning. |
|||
Giza's learning institutions include [[Cairo University]], which was moved to Giza in 1924. The city is a hub of education and educational services not only for Egypt but also for the entire [[Mediterranean Region]]. Giza has numerous schools, kindergartens, and institutes of higher learning. |
|||
The [[Cairo Japanese School]], a Japanese international school, is in Giza.<ref>[http://www.cjseg.com/index.html Home] ([https://archive.today/20140102134859/http://www.cjseg.com/index.html Archive]). [[Cairo Japanese School]]. Retrieved on 2 January 2014. "NAZLET EL BATRAN EL AHRAM GIZA, A.R.EGYPT"</ref> The [[Deutsche Evangelische Oberschule]], a German international school, is located in [[Dokki]] in Giza.<ref>"[http://www.deokairo.com/kontakt.html Kontakt] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150118114317/http://www.deokairo.com/kontakt.html |date=18 January 2015 }}." [[Deutsche Evangelische Oberschule]]. Retrieved on 18 January 2015. "6, El Dokki St. Dokki / Giza"</ref> Previously the Pakistan International School of Cairo had its campus in Giza.<ref>"[https://web.archive.org/web/20150813091618/http://www.pakistanschool.edu.eg/Contact.htm Contact Us]." [[Pakistan International School Cairo]]. Retrieved on 21 April 2015. "12 Midan Tehran, Dokki, Cairo."</ref> |
|||
== Sports == |
|||
The city hosts the second most successful club in [[Egypt]] and [[Africa]], [[El Zamalek]], which is located in the [[Mit Oqba]] neighbourhood near the [[Mohandesin]] neighbourhood. Beside El Zamalek there are other clubs like El [[Tersana]] and [[Seid Shooting Club]] which is one of the elite clubs in Egypt. |
|||
== |
==Sports== |
||
{{unreferenced section|date=August 2022}} |
|||
*{{flagicon|USA}} [[Los Angeles]], [[United States]] |
|||
The city hosts the second most successful sports club in Egypt and Africa, [[El Zamalek]], which is located in the [[Meet Okba]] neighbourhood near the [[Mohandesin]] neighbourhood. Beside El Zamalek there are other clubs like El [[Tersana]] and Seid Shooting Club which is one of the elite clubs in Egypt. |
|||
*{{flagicon|Sweden}} [[Rinkeby]], [[Stockholm]], [[Sweden]] |
|||
*{{flagicon|Brunei}} [[Bandar Seri Begawan]], [[Brunei Darussalam]],(Start since 02 August 2011) |
|||
== |
== Twin towns and sister cities == |
||
{{See also|List of twin towns and sister cities in Egypt}} |
|||
*[[Giza Governorate]] |
|||
*[[Pyramids of Giza]] |
|||
*[[Great Sphinx]] |
|||
*[[List of Egyptian pyramids]] |
|||
*[[List of megalithic sites]] |
|||
Giza is [[sister city|twinned]] with: |
|||
==Giza Images gallery== |
|||
<center> |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 11.jpg|[[Giza District]] facing [[Nile]] --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 12.jpg|[[Giza Pyramids]] appear from a hotel [[Haram District]] --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 18.jpg|Haram Street and the Giza pyramids --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 2.jpg|[[Mohandessin]] Neighbourhood --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 22.jpg|The city of Giza as seen from [[Cairo Tower]] --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 23.jpg|Giza City as seen from its elder twin [[Cairo]] --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 27.jpg|One of Giza Hotels --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 48.jpg|Giza Pyramids looking at the modern city --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 51.jpg|Giza Zoo, [[Nahdet Masr Statue]] and the boulevard which leads to Cairo University. --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza 56.jpg|Cairo University Headquarter Campus in Giza --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza, Mena palace 1.jpg| --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Mohandesin, Mostafa Mahmoud Square 2.jpg|[[Mostafa Mahmoud]] Square one of the most famous squares in [[Giza Governorate]] --> |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: File:Giza_67.jpg|Gamet Dewal Boulevard, Giza --> |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
</center> |
|||
* {{flagicon|BRU}} [[Bandar Seri Begawan]], [[Brunei Darussalam]] |
|||
==Notes & references== |
|||
* {{flagicon|NOR}} [[Bergen]], [[Norway]] |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
* {{flagicon|USA}} [[Los Angeles]], United States |
|||
* {{flagicon|SWE}} [[Rinkeby]], [[Stockholm]], Sweden |
|||
==Notable people== |
|||
== External links == |
|||
<!---♦♦♦ Only add a person to this list if they already have their own article on the English Wikipedia ♦♦♦---> |
|||
{{commons|Giza|Giza}} |
|||
<!---♦♦♦ Please keep the list in alphabetical order by LAST NAME ♦♦♦---> |
|||
* [http://www.gizapyramids.org/ Giza Archives Project] |
|||
*[[Amr Abou El Seoud]] (born 1968), bank CEO |
|||
* [[wikitravel:Cairo/Giza|Giza]] on [[wikitravel:Main Page|Wikitravel]] |
|||
*[[Maher El-Kady]] (born 1983), scientist, known for his work in nanotechnology, particularly in graphene-based materials, energy storage, and advanced materials. |
|||
* [http://www.sas.upenn.edu/aamw/resources/fieldwork/#Giza%20%28Egypt%29 University of Pennsylvania Museum excavations at Giza] |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{coord|30|01|N| 31|13|E|type:city|display=title}} |
|||
{{portal|Egypt}} |
|||
* [[Giza church fire]] |
|||
* [[List of cities and towns in Egypt]] |
|||
* [[List of ancient Egyptian sites]] |
|||
* [[List of megalithic sites]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{EgyptLargestCities}} |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
{{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
*Der Manuelian, Peter. 2017. ''Digital Giza: Visualizing the Pyramids.'' Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. |
|||
*Hawass, Zahi A. 2010. ''Wonders of the Pyramids: The Sound and Light of Giza.'' Cairo: Misr Company for Sound, Light, & Cinema. |
|||
*--. 2011. ''Newly-Discovered Statues From Giza, 1990–2009.'' Cairo: Ministry of State for Antiquities. |
|||
*Magli, G. 2016. "The Giza 'written' landscape and the double project of King Khufu." ''Time & Mind-the Journal of Archaeology Consciousness and Culture'' 9, no.1: 57–74. |
|||
*Khattab, Hind A. S., Nabil Younis, and Huda Zurayk. 1999. ''Women, Reproduction, and Health In Rural Egypt: The Giza Study.'' Cairo, Egypt: American University in Cairo Press. |
|||
*Kormysheva, Ė. E., Svetlana Malykh, and Sergey Vetokhov. 2010. ''Giza, Eastern Necropolis: Russian Archaeological Mission In Giza.'' Moscow: Institute of Oriental Studies, Russian Academy of Sciences. |
|||
*Lawton, Ian, and Chris Ogilvie-Herald. 2000. ''Giza: The Truth: the People, Politics and History Behind the World's Most Famous Archaeological Site.'' Rev. ed. London: Virgin. |
|||
*Lehner, Mark, and Zahi A. Hawass. 2017. ''Giza and the Pyramids: The Definitive History.'' Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. |
|||
{{Giza}} |
|||
{{Cities of Egypt|}} |
|||
{{Egyptian cities}} |
|||
{{Governorates capital of Egypt}} |
{{Governorates capital of Egypt}} |
||
{{Ancient Egypt topics}} |
{{Ancient Egypt topics}} |
||
{{Portal bar|Egypt}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Giza| ]] |
[[Category:Giza| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:642 establishments]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Cities in Egypt]] |
||
[[Category:Giza Plateau]] |
[[Category:Giza Plateau]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Governorate capitals in Egypt]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Greater Cairo]] |
||
[[Category:Populated places established in the 7th century]] |
|||
[[Category:Populated places in Giza Governorate]] |
|||
[[af:Gizeh]] |
|||
[[ar:مدينة الجيزة]] |
|||
[[be:Горад Гіза]] |
|||
[[bs:Giza]] |
|||
[[br:Gizah]] |
|||
[[bg:Гиза]] |
|||
[[ca:Gizeh]] |
|||
[[cv:Гиза]] |
|||
[[cs:Gíza]] |
|||
[[cy:Giza]] |
|||
[[da:Giza]] |
|||
[[de:Gizeh]] |
|||
[[et:Giza]] |
|||
[[es:Guiza]] |
|||
[[eo:Gizo]] |
|||
[[eu:Giza (Egipto)]] |
|||
[[fa:جیزه]] |
|||
[[fr:Gizeh]] |
|||
[[fy:Gizeh]] |
|||
[[ga:Giza]] |
|||
[[gl:Giza - الجيزة]] |
|||
[[ko:기자 (이집트)]] |
|||
[[hy:Գիզա]] |
|||
[[hi:गीज़ा]] |
|||
[[hr:Giza]] |
|||
[[id:Giza]] |
|||
[[it:Giza]] |
|||
[[he:גיזה]] |
|||
[[ka:გიზა]] |
|||
[[la:Giza]] |
|||
[[lv:Giza]] |
|||
[[lt:Giza]] |
|||
[[ms:Giza]] |
|||
[[nl:Gizeh]] |
|||
[[nds-nl:Piramides van Giza]] |
|||
[[ja:ギーザ]] |
|||
[[no:Giza]] |
|||
[[pnb:غیزہ]] |
|||
[[pl:Giza]] |
|||
[[pt:Guizé]] |
|||
[[ro:Giza]] |
|||
[[ru:Гиза]] |
|||
[[sco:Giza]] |
|||
[[simple:Giza]] |
|||
[[sk:Al-Džíza (mesto)]] |
|||
[[sl:Giza]] |
|||
[[sr:Гиза]] |
|||
[[sh:Giza]] |
|||
[[fi:Giza]] |
|||
[[sv:Giza]] |
|||
[[th:กีซา]] |
|||
[[tr:Gize]] |
|||
[[uk:Гіза]] |
|||
[[vi:Giza]] |
|||
[[war:Giza]] |
|||
[[zh:吉萨]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 10:54, 23 December 2024
Giza
الجيزة | |
|---|---|
Clockwise from top: Giza panorama, Pyramids of Giza, Cairo University, Great Sphinx of Giza, aerial view of Pyramids | |
| Coordinates: 29°59′13″N 31°12′42″E / 29.9870°N 31.2118°E | |
| Country | |
| Governorate | Giza |
| Founded | 642 AD |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Ahmed Rashed[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 98.4 km2 (38.0 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 30 m (100 ft) |
| Population (2023)[2] | |
• Total | 4,458,135 |
| • Density | 45,000/km2 (120,000/sq mi) |
| • Demonym | Gizan (m) Gizanne (f) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EST) |
| Postal code | 5-Digit |
| Area code | (+20) 2 |
| Website | Giza.gov.eg |
Giza (/ˈɡiːzə/; sometimes spelled Gizah, Gizeh, Geeza, Jiza; Arabic: الجيزة, romanized: al-Jīzah, pronounced [ald͡ʒiːzah], Egyptian Arabic: الجيزة el-Gīza [elˈgiːzæ])[3] is the third-largest city in Egypt by area after Cairo and Alexandria; and fourth-largest city in Africa by population after Kinshasa, Lagos, and Cairo. It is the capital of Giza Governorate with a total population of 4,872,448 in the 2017 census.[4] It is located on the west bank of the Nile opposite central Cairo, and is a part of the Greater Cairo metropolis. Giza lies less than 30 km (18.64 mi) north of Memphis (Men-nefer, today the village of Mit Rahina), which was the capital city of the unified Egyptian state during the reign of pharaoh Narmer, roughly 3100 BC.
Giza is most famous as the location of the Giza Plateau, the site of some of the most impressive ancient monuments in the world, including a complex of ancient Egyptian royal mortuary and sacred structures, among which are the Great Sphinx, the Great Pyramid of Giza, and a number of other large pyramids and temples. Giza has always been a focal point in Egypt's history due to its location close to Memphis, the ancient pharaonic capital of the Old Kingdom.
Districts and population
[edit]The city of Giza is the capital of the Giza Governorate, and is located near the northeast border of this governorate.
2017 population and administrative divisions
[edit]Giza city is a municipal division and capital of Giza governorate with an appointed city head.[5] It comprises nine districts (ahya', singl. hayy) and five new towns (mudun jadidah) administered by the New Urban Communities Authority (NUCA).
The districts/qisms fully subsume to the city head and according to the 2017 census had 4,872,448 residents:[4][6]
| District/qism | Code 2017 | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Shamal (North)/ Imbâba | 210100 | 632,599 |
| Agouza, al- | 210200 | 278,479 |
| Duqqî, al- | 210300 | 70,926 |
| Janoub (South)/ Jîza, al- | 210400 | 285,723 |
| Bûlâq al-Dakrûr | 210500 | 960,031 |
| `Umrâniyya, al- | 210600 | 366,066 |
| Ṭâlbiyya, al- | 210700 | 457,667 |
| Ahrâm, al- | 210800 | 659,305 |
| Warrâq, al- | 211700 | 722,083 |
| Shaykh Zâyid, al (new city)[7] | 211900 | 90,699 |
| 6 October 1 (new city)[8] | 212000 | 93,012 |
| 6 October 2 (new city) | 212100 | 196,373 |
| 6 October 3 (new city) | 212300 | 59,485 |
The new towns are mostly administered by the national level New Urban Communities Authority (NUCA), with some public services under the jurisdiction of Giza. They are confusingly named madina (city), however they are not administratively incorporated as such where many are formed of a single district or qism. Ones not in the 2017 census as they were not yet incorporated, or inhabited at that time are:
Permanently inhabited Nile islands:
- Qorsaya Island (Janoub/Giza district)
- Dahab Island (Janoub/Giza district)
- Al-Warraq Island (Al-Warraq district)
2006 population
[edit]The city's population was reported as 2,681,863 in the 2006 national census,[12][13] while the governorate had 6,272,571 at the same census, without specifying what the city is. The former figure corresponds to the sum of nine districts/qisms.
| Region | (Population) | Area km2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2006 | ||
| Giza, 9 kisms (contiguous) | 2,681,863 | 98.4 |
| Giza, 10 kisms (not contiguous) | 2,822,271 | 115.7 |
| Giza, 10 kisms + Giza markaz (contiguous) | 3,063,777 | 187 |
| Giza, 10 kisms + Giza, Kerdasa, Ossim markaz (contiguous) | – | 338.9 |
Geography and Climate
[edit]Giza's most famous landform and archaeological site, the Giza Plateau, holds some major monuments of Egyptian history, and is home to the Great Sphinx. Once thriving with the Nile that flowed right into the Giza Plateau, the pyramids of Giza were built overlooking the ancient Egyptian capital city of Memphis, across the river from modern day Cairo. The Great Pyramid of Giza at one time was advocated (1884) as the location for the Prime Meridian, a reference point used for determining a base longitude.[14]
Climate
[edit]Giza experiences a hot desert like arid climate (Köppen: BWh). Its climate is similar to Cairo, owing to its proximity. Windstorms can be frequent across Egypt in spring, bringing Saharan dust into the city during the months of March and April. High temperatures in winter range from 16 to 20 °C (61 to 68 °F), while nighttime lows drop to below 7 °C (45 °F). In summer, the highs are 40 °C (104 °F), and the lows can drop to about 20 °C (68 °F). Rain is infrequent in Giza; snow is extremely rare.
Up to August 2013, the highest recorded temperature was 46 °C (115 °F) on 13 June 1965, while the lowest recorded temperature was 2 °C (36 °F) on 8 January 1966.[15]
| Climate data for Giza | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
30 (86) |
36 (97) |
41 (106) |
43 (109) |
46 (115) |
41 (106) |
43 (109) |
39 (102) |
40 (104) |
36 (97) |
30 (86) |
46 (115) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 19.3 (66.7) |
20.9 (69.6) |
24.2 (75.6) |
28.4 (83.1) |
32.0 (89.6) |
34.9 (94.8) |
34.5 (94.1) |
34.4 (93.9) |
32.4 (90.3) |
30.2 (86.4) |
25.4 (77.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
28.1 (82.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.0 (55.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
17.2 (63.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.5 (81.5) |
25.6 (78.1) |
23.5 (74.3) |
19.2 (66.6) |
15.0 (59.0) |
21.2 (70.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
7.2 (45.0) |
10.3 (50.5) |
12.7 (54.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
19.3 (66.7) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.7 (69.3) |
18.9 (66.0) |
16.8 (62.2) |
13.0 (55.4) |
8.9 (48.0) |
14.3 (57.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 2 (36) |
4 (39) |
5 (41) |
8 (46) |
11 (52) |
16 (61) |
17 (63) |
17 (63) |
16 (61) |
11 (52) |
4 (39) |
4 (39) |
2 (36) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 4 (0.2) |
3 (0.1) |
2 (0.1) |
1 (0.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
3 (0.1) |
4 (0.2) |
17 (0.7) |
| Source 1: Climate-Data.org[16] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Voodoo Skies[15] for record temperatures | |||||||||||||
History
[edit]
Ancient era
[edit]The area in what is now Giza served as the necropolis of several pharaohs who ruled ancient Egypt, during the second millennium BC. Three of these tombs, in the form of giant pyramids, are what is now the famed Giza pyramid complex, featuring the Great Pyramid of Giza.
Classical to medieval era
[edit]
As ancient Egypt passed under several conquests under the Persians, Greeks, Romans and Byzantines, so did the area in what is now Giza. A Byzantine village named Phylake (Greek: Φυλακή) or Terso (Coptic: ϯⲣⲥⲱ, meaning "the fortress", now Tersa) was located south of Giza and should not be confused with it.[17][18][19]
Egyptians called the area Tipersis (Bohairic Coptic: ϯⲡⲉⲣⲥⲓⲥ[a] and Sahidic Coptic: ⲧⲡⲉⲣⲥⲓⲥ ⲛ̀ⲃⲁⲃⲩⲗⲱⲛ, lit. 'the Persian (fortress) of Babylon').[20][21][22] Eutychius gives a legend about the city's name and its foundation by Artaxerxes Ochus or Hūš (Arabic: خوش),[23] and Abu Salih says it was found by him at the same time as Qasr ash-Sham,[24] but in view of the fact that older evidence is missing, it is perhaps most likely to have been founded during the Sasanian conquest of Egypt in the early 7th century.[25]
As Muslims of the fledgling Islamic caliphate went on with their conquest of Egypt from the Byzantine Empire beginning in 639 AD, three years after their victory at the battle of Yarmouk in 636 AD, they conquered all of the land by the time they captured the city of Alexandria in 641 AD. A year later in 642 AD (year 21 in Islamic calendar), they founded the city of Giza. The exact etymology of its name is unknown. Al-Maqrizi suggested an irregular Arameo-Arabic root meaning "edge, side" to be the source. Everett-Heath suggested Ancient Egyptian: r-gs-ḥr "on the side of the height (pyramid)". Peust also suggests a Persian etymology of the word from Middle Persian: 𐭣𐭦, romanized: diz, lit. 'fortress, castle', which Persians could have given to the pyramids or a fortress they found in the area.[26]
Infrastructure
[edit]
Giza has seen many changes over time. Changes in infrastructure during the different occupations of Egypt by various rulers, including the British in the 18th and early 20th century, focused on the construction of roads, streets, and buildings in the area. Giza is a thriving centre of Egyptian culture and is quite heavily populated, with many facilities and buildings in the current area. Giza saw much attention in particular to its vast amount of ancient Egyptian monuments found on the Giza Plateau, and has astonished thousands of visitors and tourists over the years. Giza's infrastructure saw much attention from both the British government prior to the 1952 coup d'état, as well as the current Egyptian government due to the city's importance in tourism. Giza's St. George Cathedral is the episcopal see of the Coptic Catholic Eparchy of Giza.
The city hosts the first zoo on the entire African continent and one of the oldest in the Mediterranean region, the Giza Zoo. In addition, there are several parks, the most famous among them is Orman Park, which means "Forest Park" in the Turkish language.
Giza Zoo
[edit]The Giza Zoo (حديقة حيوان الجيزة, Ḥadīqat Ḥaywān Al-Gīzah), established on March 1, 1891, holds the distinction of being Africa's first zoo and the world's third oldest zoological garden[27]. Located on approximately 80 acres (32 hectares), the zoo was originally designed as a botanical garden and features several historical architectural elements[28].
Historical Features
[edit]The zoo contains several notable architectural and cultural landmarks:
- A suspension bridge designed by Gustave Eiffel (1875-1879), considered the world's first elevated zoo viewing platform[29]
- The Japanese Kiosk, constructed in 1924 during King Fuad's reign
- Original gates from the Khedive's Palace and Haramlik Palace
- Roads paved with black stone imported from Trieste
- Mosaic-decorated footpaths
- A marble island known as Tea Island
Animal Collection
[edit]The zoo houses approximately 4,000 animals representing over 175 species[30], including:
- Large mammals: Lions, tigers, giraffes, rhinoceros, hippopotamuses
- Primates: Various monkey and ape species
- Birds: Native and exotic species including flamingos and rare birds
- Reptiles: Including Egyptian cobras and Nile crocodiles
Recent Developments
[edit]In 2023, the Egyptian government announced plans to expand the number of animal species from 71 to 186[31]. The renovation project includes:
- Creation of specialized zones: Asia, Africa, America, Family Zone, Safari Trips
- Establishment of educational centers
- Preservation of historical landmarks
- Improvement of animal enclosures
Operating Hours
[edit]- Summer (April-September): 8:30 AM - 5:00 PM
- Winter (October-March): 8:30 AM - 4:00 PM
The zoo serves multiple functions as a recreational facility, research institute, and cultural landmark[32].
Transportation
[edit]
Transportation in Giza comprises an extensive road network, rail system, subway system, and maritime services. Road transport is facilitated by personal vehicles, taxi cabs, privately owned public buses and microbuses.
Giza shares with Cairo a subway system, officially called the "Metro (مترو)", a fast and efficient way of getting around. An extensive road network connects Giza with 6th of October City, Cairo and other cities. There are flyovers and bridges such as the 15th. Traffic in Giza is known to be overwhelming and overcrowded.
Other means of transport include:
- Cairo Taxi
- Uber (available in Cairo and Giza since 2015)[33]
- Careem (available in Cairo and Giza since 2015)[34]
- Swvl (available in Cairo and Giza since 2017)
- Water taxis (motorized feluccas) available for transport to nearby places along the Nile River
Economy
[edit]
Industries here include movies, chemicals, Giza cotton, machinery and cigarettes. In addition, Giza has many luxury apartment buildings along the Nile, making it a popular place to live.
International access
[edit]Access to the city of Giza, which has its own governorate adjacent to the Governorate of Cairo, is dependent on the Cairo International Airport. Another local airport is found in Giza, called the Imbaba Airport, but recently the Egyptian government has decided to shut down the area and turn it into a cultural or an athletic area.
Sphinx International Airport was opened in 2018 as an alternative to the already congested Cairo International Airport, but also to improve accessibility to the Giza necropolis as well as to the Grand Egyptian Museum.
Education
[edit]
Giza's learning institutions include Cairo University, which was moved to Giza in 1924. The city is a hub of education and educational services not only for Egypt but also for the entire Mediterranean Region. Giza has numerous schools, kindergartens, and institutes of higher learning.
The Cairo Japanese School, a Japanese international school, is in Giza.[35] The Deutsche Evangelische Oberschule, a German international school, is located in Dokki in Giza.[36] Previously the Pakistan International School of Cairo had its campus in Giza.[37]
Sports
[edit]The city hosts the second most successful sports club in Egypt and Africa, El Zamalek, which is located in the Meet Okba neighbourhood near the Mohandesin neighbourhood. Beside El Zamalek there are other clubs like El Tersana and Seid Shooting Club which is one of the elite clubs in Egypt.
Twin towns and sister cities
[edit]Giza is twinned with:
 Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam
Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Bergen, Norway
Bergen, Norway Los Angeles, United States
Los Angeles, United States Rinkeby, Stockholm, Sweden
Rinkeby, Stockholm, Sweden
Notable people
[edit]- Amr Abou El Seoud (born 1968), bank CEO
- Maher El-Kady (born 1983), scientist, known for his work in nanotechnology, particularly in graphene-based materials, energy storage, and advanced materials.
See also
[edit]- Giza church fire
- List of cities and towns in Egypt
- List of ancient Egyptian sites
- List of megalithic sites
References
[edit]- ^ "محافظ الجيزة يترأس اجتماع اللجنة التنفيذية للمبادرة الوطنية للمشروعات الخضراء الذكية", Masrawy, archived from the original on 2 September 2022, retrieved 2 September 2022
- ^ a b c "Egypt: Governorates, Major Cities & Towns - Population Statistics, Maps, Charts, Weather and Web Information". citypopulation.de. Archived from the original on 17 March 2023. Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ^ Egyptian Arabic Place Names and Monument Names, 11 February 2019, retrieved 30 June 2023
- ^ a b Central Agency for Public Mobilisation and Statistics (CAPMAS) (2017). "2017 Census for Population and Housing Conditions". CEDEJ-CAPMAS. Archived from the original on 10 April 2023. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ ""أبو النجا" يتفقد المراحل النهائية لتطوير نفق مشاه بميدان الجيزة". بوابة اخبار اليوم. 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 5 April 2023. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ "الصفحة الرئيسية - الأحياء". www.giza.gov.eg. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ "الصفحة الرئيسية - الشيخ زايد". www.newcities.gov.eg. Archived from the original on 19 July 2017. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ "الهيكل الإداري". www.6october.gov.eg. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ "الصفحة الرئيسية - مدينة 6 أكتوبر الجديدة". www.newcities.gov.eg. Archived from the original on 29 November 2020. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ "الصفحة الرئيسية - حدائق اكتوبر". www.newcities.gov.eg. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ "الصفحة الرئيسية - مدينة سفنكس الجديدة". www.newcities.gov.eg. Archived from the original on 22 May 2022. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ Anthony Appiah; Henry Louis Gates (Jr.) (2010). Encyclopedia of Africa. Oxford University Press. p. 403. ISBN 978-0-19-533770-9. Archived from the original on 11 January 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2019.
- ^ "Giza, Egypt". Archived from the original on 21 February 2019. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ "The Canary Islands and the Question of the Prime Meridian: The Search for Precision in the Measurement of the Earth", Wilcomb E. Washburn. link Archived 29 May 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b "El-Giza, Egypt". Voodoo Skies. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ "Climate: Giza – Climate graph, Temperature graph, Climate table". Climate-Data.org. Archived from the original on 14 September 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ "TM Places". www.trismegistos.org. Archived from the original on 18 April 2019. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ^ موسوعة " القاموس الجغرافى للبلاد المصرية " – محمد رمزى بك (قسم ثانى ج3 – ص4): مركز وثائق وتاريخ مصر المعاصر الهيئة المصرية العامةللكتاب ط 1994
- ^ جغرافية مصر في العصر القبطى – الفرنسى أميلينو : الهيئة المصرية العامة للكتاب2013 ترجمة ميخائيل مكسى إسكندر – استدراكات العلامة محمد رمزى على الكتاب في الجزء الثالث من ص 274: نشر المعهد العلمى الفرنسى
- ^ Amélineau, Emile (1893). La géographie de l'Egypte à l'époque copte. Paris: Imprimerie nationale. pp. 190.
- ^ "Trismegistos". www.trismegistos.org. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- ^ Stefan, Timm (1988). Das christlich-koptische Agypten in arabischer Zeit. p. 1055.
- ^ Evetts, B. T. A. The Churches and Monasteries of Egypt and Some Neighbouring Countries. p. 177.
- ^ Timm, Stefan (1985). Das christlich-koptische Agypten in arabischer Zeit (Teil 3 G-L). Wiesbaden. p. 1058.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Peust, Carsten. "Die Toponyme vorarabischen Ursprungs im modernen Ägypten" (PDF). p. 44. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ Peust, Carsten. "Die Toponyme vorarabischen Ursprungs im modernen Ägypten" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ "Giza Zoo: the third oldest within the world and the first in Africa". Egyptian Geographic. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ "Egypt's Giza Zoo: A Chequered History and a Promising Future". Egyptian Streets. 14 September 2023. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ "Giza Zoo Cairo Egypt tours, prices, booking, reviews". ETL Travel. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ "Giza Zoo, Egypt: A Guide to Egypt's Oldest and Largest Zoo". Arab MLS. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ "Egypt's PM reviews final designs for Giza Zoo development project". Egypt Today. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ "Egyptians fear for historic Giza Zoo as UAE investor steps in". Middle East Eye. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ "Ya Om El Donia. Your Uber Has Just Arrived, Cairo! – Uber Blog". Uber. 20 November 2014. Archived from the original on 21 July 2018. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ^ "Ride or Drive with Careem in Cairo, Egypt – Careem". Careem.com. Archived from the original on 12 December 2016. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- ^ Home (Archive). Cairo Japanese School. Retrieved on 2 January 2014. "NAZLET EL BATRAN EL AHRAM GIZA, A.R.EGYPT"
- ^ "Kontakt Archived 18 January 2015 at the Wayback Machine." Deutsche Evangelische Oberschule. Retrieved on 18 January 2015. "6, El Dokki St. Dokki / Giza"
- ^ "Contact Us." Pakistan International School Cairo. Retrieved on 21 April 2015. "12 Midan Tehran, Dokki, Cairo."
Further reading
[edit]- Der Manuelian, Peter. 2017. Digital Giza: Visualizing the Pyramids. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
- Hawass, Zahi A. 2010. Wonders of the Pyramids: The Sound and Light of Giza. Cairo: Misr Company for Sound, Light, & Cinema.
- --. 2011. Newly-Discovered Statues From Giza, 1990–2009. Cairo: Ministry of State for Antiquities.
- Magli, G. 2016. "The Giza 'written' landscape and the double project of King Khufu." Time & Mind-the Journal of Archaeology Consciousness and Culture 9, no.1: 57–74.
- Khattab, Hind A. S., Nabil Younis, and Huda Zurayk. 1999. Women, Reproduction, and Health In Rural Egypt: The Giza Study. Cairo, Egypt: American University in Cairo Press.
- Kormysheva, Ė. E., Svetlana Malykh, and Sergey Vetokhov. 2010. Giza, Eastern Necropolis: Russian Archaeological Mission In Giza. Moscow: Institute of Oriental Studies, Russian Academy of Sciences.
- Lawton, Ian, and Chris Ogilvie-Herald. 2000. Giza: The Truth: the People, Politics and History Behind the World's Most Famous Archaeological Site. Rev. ed. London: Virgin.
- Lehner, Mark, and Zahi A. Hawass. 2017. Giza and the Pyramids: The Definitive History. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.