Snake River: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CarlStrokes (talk | contribs) Correction as this picture was not taken very close to Jackson Hole but was taken about 30 or so miles north in the central region of Grand Teton National Park. Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Major river in the northwestern United States}} |
|||
The Snake [[River]], at 1,038 miles (1,670 km) in length, is the [[Columbia River|Columbia River's]] main tributary. |
|||
{{about|the river in the northwestern United States}} |
|||
The Lewis and Clark expedition (1803-6) was the first major U.S. exploration of the river. |
|||
{{Infobox river |
|||
Once known as the Lewis River, the Snake originates at [[Yellowstone National Park]] in NW [[Wyoming]], flows through |
|||
| name = Snake River |
|||
[[Jackson Lake]] in the [[Grand Teton National Park]], through Idaho where it cascades down several notable falls. |
|||
| native_name = {{plainlist| |
|||
After many twists and turns it finally joins the Columbia River near [[Pasco Washington]]. |
|||
*{{native name|nez|Kimooenim}} |
|||
*{{native name|shh|Yampapah}} |
|||
}} |
|||
| native_name_lang = |
|||
| name_other = |
|||
| name_etymology = |
|||
| image = Adams The Tetons and the Snake River.jpg |
|||
| image_caption = ''[[The Tetons and the Snake River]]'' (photographed by [[Ansel Adams]], 1942) shows the Snake River and the [[Grand Tetons]]. |
|||
| image_alt = A black and white photograph shows a view over a river bend in foreground, to a rugged mountain range under cloudy skies |
|||
| image_size = 280 |
|||
| map = Snake_River_watershed_map.png |
|||
| map_size = 280 |
|||
| map_caption = Map of the Snake River watershed |
|||
| pushpin_map = |
|||
| pushpin_map_size = |
|||
| pushpin_map_caption = |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = Country |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = [[United States]] |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = State |
|||
| subdivision_name2 = [[Wyoming]], [[Idaho]], [[Oregon]], [[Washington (state)|Washington]] |
|||
| subdivision_type3 = Region |
|||
| subdivision_name3 = [[Pacific Northwest]] |
|||
| subdivision_type4 = |
|||
| subdivision_name4 = |
|||
| subdivision_type5 = Cities |
|||
| subdivision_name5 = [[Jackson, Wyoming]], [[Idaho Falls, Idaho]], [[Blackfoot, Idaho]], [[American Falls, Idaho]], [[Burley, Idaho]], [[Twin Falls, Idaho]], [[Ontario, Oregon]], [[Lewiston, Idaho]], [[Clarkston, Washington]], [[Tri-Cities, Washington]] |
|||
| length = {{convert|1080|mi|km|abbr=on}}<ref name="TNM"/> |
|||
| width_min = |
|||
| width_avg = |
|||
| width_max = |
|||
| depth_min = |
|||
| depth_avg = |
|||
| depth_max = |
|||
| discharge1_location = [[Ice Harbor Dam]], [[Washington (state)|Washington]], {{convert|9+1/2|mi|km}} above the mouth, 1962–2023 average<ref name=iceharbordam>{{cite web|url=https://www.nwd-wc.usace.army.mil/dd/common/dataquery/www/?k=ice%20harbor|title=Data Query: Ice Harbor Dam and Lake Sacajawea|publisher=U.S. Army Corps of Engineers|accessdate=January 31, 2024}} Data collected at this station must be downloaded in CSV format.</ref> |
|||
| discharge1_min = {{convert|2000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}}<ref name=iceharbordam/> |
|||
| discharge1_avg = {{convert|49580|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}}<ref name=iceharbordam/> |
|||
| discharge1_max = {{convert|305000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}}<ref name=iceharbordam/> |
|||
| source1 = [[Rocky Mountains]] |
|||
| source1_location = [[Yellowstone National Park]], [[Wyoming]] |
|||
| source1_coordinates = {{coord|44|07|49|N|110|13|10|W}}<ref name="GNIS"/> |
|||
| source1_elevation = {{convert|9200|ft|abbr=on}}<ref name="USGS Badger Creek">{{Cite web |url=https://topoquest.com/map-detail.php?usgs_cell_id=2080|title=U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Badger Creek, Wyoming quad |author=U.S. Geological Survey |publisher=TopoQuest |access-date=January 27, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
| mouth = [[Columbia River]] at [[Lake Wallula]] |
|||
| mouth_location = [[Burbank, Washington|Burbank]], [[Washington (state)|Washington]], near the [[Tri-Cities, Washington|Tri-Cities]] |
|||
| mouth_coordinates = {{coord|46|11|10|N|119|1|43|W|display=inline,title}}<ref name="GNIS">{{cite gnis|id=1533479|name=Snake River|entrydate=December 31, 1981|accessdate=January 27, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
| mouth_elevation = {{convert|341|ft|abbr=on}}<ref name="GNIS"/> |
|||
| progression = |
|||
| river_system = |
|||
| basin_size = {{convert|107500|sqmi | abbr = on}}<ref name="USGS">{{cite web | title = Boundary Descriptions and Names of Regions, Subregions, Accounting Units and Cataloging Units | url = http://water.usgs.gov/GIS/huc_name.html | publisher = U.S. Geological Survey | access-date = August 22, 2010 | archive-date = April 27, 2012 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120427215107/http://water.usgs.gov/GIS/huc_name.html | url-status = live }}</ref> |
|||
| tributaries_left = [[Gros Ventre River]], [[Salt River (Wyoming)|Salt River]], [[Blackfoot River (Idaho)|Blackfoot River]], [[Portneuf River (Idaho)|Portneuf River]], [[Bruneau River]], [[Owyhee River]], [[Malheur River]], [[Burnt River (Oregon)|Burnt River]], [[Powder River (Oregon)|Powder River]], [[Imnaha River]], [[Grande Ronde River]], [[Tucannon River]]<ref name="TNM"/> |
|||
| tributaries_right = [[Henrys Fork (Snake River tributary)|Henrys Fork]], [[Malad River (Gooding County, Idaho)|Malad River]], [[Boise River]], [[Payette River]], [[Weiser River]], [[Salmon River (Idaho)|Salmon River]], [[Clearwater River (Idaho)|Clearwater River]], [[Palouse River]]<ref name="TNM"/> |
|||
| custom_label = |
|||
| custom_data = {{Designation list |
|||
| embed = yes |
|||
| designation1 = nwsr |
|||
| designation1_type = Wild {{convert|260.8|mi|km}}<br />Scenic {{convert|186.4|mi|km}}<br /> Recreational {{convert|33.8|mi|km}} |
|||
| designation1_number = P.L. 94-199; P.L. 111-11<ref>{{cite web | url = https://www.rivers.gov/|title=National Wild and Scenic Rivers System | website = rivers.gov|publisher=National Wild and Scenic Rivers System | access-date = January 5, 2023 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
| extra = {{Infobox mapframe |wikidata=yes |zoom=5 |height=250 | stroke-width=1.5 |coord {{WikidataCoord|display=i}}}} |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''Snake River''' is a major river in the interior [[Pacific Northwest]] region of the United States. About {{convert|1080|mi|km}} long, it is the largest tributary of the [[Columbia River]], which is the largest North American river that empties into the [[Pacific Ocean]]. Beginning in [[Yellowstone National Park]], western [[Wyoming]], it flows across the arid [[Snake River Plain]] of southern [[Idaho]], the rugged [[Hells Canyon]] on the borders of Idaho, [[Oregon]] and [[Washington (state)|Washington]], and finally the rolling [[Palouse Hills]] of southeast Washington. It joins the Columbia River just downstream from the [[Tri-Cities, Washington]], in the southern [[Columbia Plateau|Columbia Basin]]. |
|||
The river's [[Drainage basin|watershed]], which drains parts of six [[U.S. state]]s, is situated between the [[Rocky Mountains]] to the north and east, the [[Great Basin]] to the south, and the [[Blue Mountains (Pacific Northwest)|Blue Mountains]] and [[High Desert (Oregon)|Oregon high desert]] to the west. The region has a long history of [[volcanism]]; millions of years ago, [[Columbia River Basalt Group|Columbia River basalts]] covered vast areas of the western Snake River watershed, while the Snake River Plain was a product of the [[Yellowstone hotspot|Yellowstone volcanic hotspot]]. The river was further altered by catastrophic flooding in the most recent [[Last glacial period|Ice Age]], which created such features as the [[Snake River Canyon (Idaho)|Snake River Canyon]] and [[Shoshone Falls]]. |
|||
Tributaries of the Snake include [[Henrys Fork River]], the [[Boise River]], the [[Salmon River]], and |
|||
the [[Clearwater River]]. |
|||
The Snake River once hosted some of the largest North American runs of [[Pacific salmon|salmon]] and other [[anadromous fish]]. For thousands of years, salmon fishing has played a central role in the culture and diet of indigenous peoples. The [[Shoshone]] and [[Nez Perce]] were the largest of several tribes that lived along the river by the turn of the 19th century. In 1805, while searching for a route from the eastern US to the Pacific, [[Lewis and Clark Expedition|Lewis and Clark]] became the first non-natives to see the river. [[North American fur trade|Fur trapper]]s explored more of the watershed, and drove [[North American beaver|beaver]] to near extinction as the Americans and British vied for control of [[Oregon Territory]]. |
|||
The Snake River's many hydroelectric power plants are a major source of electricity in the region. Its watershed provides irrigation for various projects, including the Minidoka, Boise, Palisades, and Owyhee projects by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, as well as a variety of private projects such as at Twin Falls. |
|||
Although travelers on the [[Oregon Trail]] initially shunned the dry and rocky Snake River region, a flood of settlers followed gold discoveries in the 1860s, leading to decades of military conflict and the eventual expulsion of tribes to reservations. At the turn of the 20th century, some of the first large irrigation projects in the western US were developed along the Snake River. South-central Idaho earned the nickname "[[Magic Valley]]" with the rapid transformation of desert into farmland. Numerous hydroelectric dams were also constructed, and four navigation dams on its lower section created a shipping channel to [[Lewiston, Idaho]] – the furthest inland seaport on the West Coast. |
|||
The Snake runs through a number of gorges. The gorges include one of the deepest in the world, Hell's Canyon, with a maximum depth of 7,900 feet (2,410 m). |
|||
While dam construction, commercial fishing and other human activities have greatly reduced anadromous fish populations since the late 19th century, the Snake River watershed is still considered important habitat for these fish. The Snake and its tributary, the [[Salmon River (Idaho)|Salmon River]], host the longest [[sockeye salmon]] run in the world, stretching {{convert|900|mi|km}} from the Pacific to [[Redfish Lake]], Idaho. Since the 1950s, public agencies, tribal governments and private utilities have invested heavily in fishery restoration and [[Fish hatchery|hatchery]] programs, with limited success. The proposed removal of the four lower Snake River dams for fish passage is a significant ongoing policy debate in the Pacific Northwest. |
|||
==Course== |
|||
The Snake River begins on Two Oceans Plateau near the southern border of [[Yellowstone National Park]], about {{convert|9200|ft|m}} above sea level in the Rocky Mountains of [[Wyoming]].<ref name="USGS Badger Creek"/> From there, it flows west then south into [[Grand Teton National Park]], where it feeds [[Jackson Lake (Wyoming)|Jackson Lake]], a natural glacial lake enlarged by [[Jackson Lake Dam]]. It flows south through the alpine valley of [[Jackson Hole]], which is situated between the [[Teton Range]] (to the west) and the [[Gros Ventre Range]].<ref name="TNM"/> Below the town of [[Jackson, Wyoming|Jackson]] it forms the [[Snake River Canyon (Wyoming)|Snake River Canyon of Wyoming]], turns west and crosses into [[Idaho]], where the [[Palisades Dam]] forms [[Palisades Reservoir]]. From there it flows northwest through Swan Valley to join the [[Henrys Fork (Snake River tributary)|Henrys Fork]] on an [[alluvial plain]] near [[Rexburg, Idaho|Rexburg]].<ref name="TNM">{{cite web|url=https://apps.nationalmap.gov/downloader/|title=National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data from The National Map|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|accessdate=December 15, 2023}}</ref> The Henrys Fork is sometimes called the "North Fork" of the Snake River,<ref name="GNIS Henrys Fork"/> while the section of the main Snake River above their confluence is sometimes called the "South Fork".<ref name="GNIS"/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.blm.gov/visit/south-fork-snake|title=South Fork of the Snake|publisher=U.S. Bureau of Land Management|date=|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Turning southwest, the river begins its long journey across the Snake River Plain, passing through [[Idaho Falls, Idaho|Idaho Falls]] and receiving the [[Blackfoot River (Idaho)|Blackfoot River]] from the left before entering the {{convert|20|mi|km|adj=on}}-long [[American Falls Reservoir]], formed by [[American Falls Dam]].<ref name="TNM"/> From [[American Falls, Idaho|American Falls]] it turns west, flowing through [[Minidoka Dam]] and [[Milner Dam]], where large volumes of water are diverted for irrigation.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.waterdistrict1.com/media/uabos05r/wd01-procedures-manual-4-12-2023.pdf|title=Concepts, practices and procedures used to distribute water within Water District #1, Upper Snake River Basin, Idaho|author=Olenichak, Tony|date=April 14, 2023|publisher=Idaho Water District 1|accessdate=January 27, 2024}}</ref> Below Milner Dam it enters the [[Snake River Canyon (Idaho)|Snake River Canyon of Idaho]], where the river narrows, forming rapids and waterfalls. In the {{convert|70|mi|km|adj=on}} stretch between Milner Dam and the confluence with the [[Malad River (Gooding County, Idaho)|Malad River]] near [[Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument]], the Snake River descends a total of {{convert|1300|ft|m}} over a series of cataracts and rapids, chief of which include [[Caldron Linn (Idaho)|Caldron Linn]], [[Twin Falls (Idaho)|Twin]], [[Shoshone]], [[Pillar Falls|Pillar]], Auger, and [[Salmon Falls (Snake River)|Salmon Falls]].<ref name="USGS Kimberly">{{Cite web |url=https://topoquest.com/map-detail.php?usgs_cell_id=23558|title=U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Kimberly, Idaho quad |author=U.S. Geological Survey |publisher=TopoQuest |access-date=January 27, 2024}}</ref><ref name="USGS Twin Falls">{{Cite web |url=https://topoquest.com/map-detail.php?usgs_cell_id=46106|title=U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Twin Falls, Idaho quad |author=U.S. Geological Survey |publisher=TopoQuest |access-date=January 27, 2024}}</ref><ref name="USGS Jerome">{{Cite web |url=https://topoquest.com/map-detail.php?usgs_cell_id=22551|title=U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Jerome, Idaho quad |author=U.S. Geological Survey |publisher=TopoQuest |access-date=January 27, 2024}}</ref><ref name="USGS Hagerman">{{Cite web |url=https://topoquest.com/map-detail.php?usgs_cell_id=18897|title=U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Hagerman, Idaho quad |author=U.S. Geological Survey |publisher=TopoQuest |access-date=January 27, 2024}}</ref> [[Idaho Power]] operates several small hydroelectric plants along this stretch of the river.<ref name="Idaho Power hydro plants"/> The largest single drop is {{convert|212|ft|m|adj=on}} [[Shoshone Falls]], which in the spring flows with such force that 19th-century writers called it the "Niagara of the West".<ref name="Williamson 1997">{{cite book|author=Williamson, Darcy|title=River Tales of Idaho|publisher=Caxton Press|isbn=9780870045318|year=1997|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yYmbiFgrg5kC}}</ref>{{rp|89–90}} |
|||
[[Image:Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey NCA (9423934512).jpg|thumb|left|280px|The Snake River flows through canyons in the [[Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area]], south of Boise.|alt=Wide view over a river valley surrounded by cliffs and shrub land]] |
|||
The Snake River continues flowing west, through the [[C. J. Strike Reservoir]] where it is joined from the left by the [[Bruneau River]], then through the [[Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area]] before entering farmland on the western side of Idaho's [[Treasure Valley]].{{#tag:ref|The Treasure Valley was historically known as the Boise Valley or Snake River Valley, and was only given the modern name in 1959.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.ktvb.com/article/news/local/208/how-treasure-valley-got-its-name-oregon-trail/277-cc3131bd-6798-43ac-80f6-85818b911e55|title=How a Caldwell businessman in 1959 gave the Treasure Valley its name|work=KTVB 7|author=Holmes, Brian|date=October 22, 2021|accessdate=January 27, 2024}}</ref> Uses of the name "Boise Valley" in this article, in a historical context, refer to the Treasure Valley.|group=n}} Passing {{convert|30|mi|km}} west of [[Boise, Idaho|Boise]], it crosses briefly into [[Oregon]] before turning north to form the Oregon–Idaho border.<ref name="TNM"/> It is joined by several major tributaries in quick succession – the [[Boise River]] from the right, the [[Owyhee River|Owyhee]] and [[Malheur River]]s from the left, the [[Payette River|Payette]] and [[Weiser River]]s from the right near [[Ontario, Oregon]], then the [[Powder River (Oregon)|Powder]] and [[Burnt River (Oregon)|Burnt River]]s from the left.<ref name="TNM"/> Continuing north, the river enters [[Hells Canyon]], which slices between the Rocky Mountains of Idaho and the [[Blue Mountains (Pacific Northwest)|Blue Mountains]] of Oregon and Washington.<ref name="TNM"/> The Hells Canyon Hydroelectric Complex includes the [[Brownlee Dam|Brownlee]], [[Oxbow Dam|Oxbow]] and [[Hells Canyon Dam]]s in the upper reaches of the canyon.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://docs.idahopower.com/pdfs/relicensing/hellscanyon/hellspdfs/hc_licenseapp.pdf|title=Hells Canyon Complex FERC No. 1971 License Application|publisher=Idaho Power|year=|accessdate=January 27, 2024}}</ref> Since its construction in 1967, Hells Canyon Dam has been the upriver limit for migrating salmon; in the past, salmon swam as far upriver as Shoshone Falls.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://critfc.org/tribal-treaty-fishing-rights/policy-support/columbia-river-treaty/area-blocked-salmon-columbia-basin/|title=Columbia Basin Passage Barriers|publisher=Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission|date=|accessdate=January 27, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Emerging from Hells Canyon Dam, the Snake surges northward through the [[Hells Canyon Wilderness (Oregon and Idaho)|Hells Canyon Wilderness]], where the majority of the river corridor is accessible only by boat and numerous [[International scale of river difficulty|Class III-IV]] rapids<ref>{{cite book|author=Stahl, Greg|title=Paddling Idaho: A Guide to the State's Best Paddling Routes|publisher=Falcon Guides|year=2016|isbn=9781493027088}}</ref>{{rp|128–131}} historically posed a major barrier to navigation.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|url=https://www.oregonencyclopedia.org/articles/hells-canyon/|title=Hells Canyon|author=Sowards, Adam M.|publisher=Oregon Historical Society|encyclopedia=Oregon Encyclopedia|date=August 9, 2023|accessdate=February 2, 2024}}</ref> Today, the canyon and the surrounding [[Hells Canyon National Recreation Area]] are a popular location for whitewater boating, fishing, horseback riding and backpacking.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fs.usda.gov/detail/wallowa-whitman/specialplaces/?cid=stelprdb5227248|title=Wild and Scenic Snake River- Trip Planning|publisher=U.S. Forest Service|date=|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref><ref name="Snake NWSR"/> With the adjacent [[Seven Devils Mountains]] rising up to {{convert|8000|ft|m}} above the river, Hells Canyon is one of the deepest canyons in North America, almost one-third deeper than the [[Grand Canyon]].<ref name="USFS Hells Canyon">{{cite web|url=https://www.fs.usda.gov/detail/wallowa-whitman/specialplaces/?cid=stelprdb5239080|title=Hells Canyon National Recreation Area - Fast Facts |
|||
|publisher=U.S. Forest Service|date=|accessdate=January 27, 2024}}</ref> Within the canyon it is joined from the left by the [[Imnaha River]], then from the right by its longest tributary, the [[Salmon River (Idaho)|Salmon River]]. Further north, it begins to form the Idaho–[[Washington (state)|Washington]] border, and receives the [[Grande Ronde River]] from the left.<ref name="TNM"/> From the end of Hells Canyon at [[Asotin, Washington]], it flows north to [[Lewiston, Idaho]], where it is joined from the right by the [[Clearwater River (Idaho)|Clearwater River]], its largest tributary by volume. The Snake then turns sharply west to enter Washington.<ref name="TNM"/> |
|||
The final stretch of the Snake River flows through steep-sided valleys in the [[Palouse Hills]] of southeast Washington. Near [[Lyons Ferry State Park]], it is joined from the left by the [[Tucannon River]], then from the right by the [[Palouse River]], which forms [[Palouse Falls]] about {{convert|8|mi|km}} upstream of its confluence with the Snake.<ref name="TNM"/> The Lower Snake River Project consists of four dams equipped with [[Lock (water navigation)|navigation locks]] – [[Lower Granite Dam|Lower Granite]], [[Little Goose Dam|Little Goose]], [[Lower Monumental Dam|Lower Monumental]] and [[Ice Harbor]] – which have transformed the once fast-flowing lower Snake River into a series of lakes, enabling heavy barges to travel between the Columbia River and the Port of Lewiston.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://portoflewiston.com/our-rivers/columbia-snake-river-system-eis-process/|title=Columbia-Snake River System|publisher=Port of Lewiston|date=|accessdate=January 27, 2024}}</ref> About {{convert|10|mi|km}} downstream from Ice Harbor Dam, the Snake empties into the Columbia River at [[Burbank, Washington]], southeast of the [[Tri-Cities, Washington|Tri-Cities]].<ref name="TNM"/> The confluence is located on [[Lake Wallula]], the impoundment behind [[McNary Dam]] on the Columbia,<ref name="TNM"/> {{convert|341|ft|m}} above sea level.<ref name="GNIS"/> From there, the Columbia River flows another {{convert|325|mi|km}} west to empty into the Pacific Ocean.<ref name="USGS Pasco">{{Cite web |url=https://topoquest.com/map-detail.php?usgs_cell_id=34340|title=U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Pasco, Washington quad |author=U.S. Geological Survey |publisher=TopoQuest |access-date=January 27, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
===Discharge=== |
|||
[[Image:Snake River, Hell's Canyon Road, Idaho - DPLA - f093871da3a1279fc4ada15e8ecd4bcf.jpg|thumb|right|The Snake River in Hells Canyon|alt=View of a river canyon surrounded by high, broken cliff faces]] |
|||
The [[U.S. Army Corps of Engineers]] has measured the [[Discharge (hydrology)|discharge]], or flow rate, of the Snake River at Ice Harbor Dam since 1962. The mean annual discharge for the 61-year period between 1962 and 2023 was {{convert|49580|cuft/s|m3/s}}, with a maximum recorded daily mean of {{convert|305000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}} on June 19, 1974, and a minimum daily mean of {{convert|2000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}} on November 29, 1961.<ref name=iceharbordam/> A historic June 1894 flood at the Ice Harbor site reached an estimated peak of {{convert|409000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}}.<ref name="Perkins 1973">{{cite report|title=Ice Harbor Dam, Snake River, Washington: Hydraulic Model Investigations|author=Perkins, L.Z.|year=1973|publisher=U.S. Army Corps of Engineers|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8hDZC64tYf0C|page=1}}</ref> In terms of discharge, the Snake River is the twelfth largest river in the United States, and it contributes about one-fifth of the Columbia's total outflow into the Pacific.<ref name="USGSrivers">{{cite web |first = J. C. |last = Kammerer |url = http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1987/ofr87-242/ |title = Largest Rivers in the United States |publisher =U.S. Geological Survey |date = May 1990 |access-date = April 1, 2008 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170129040848/https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1987/ofr87-242/ |archive-date = January 29, 2017 |url-status = live }}</ref> |
|||
The volume of the Snake River peaks in late spring and early summer as snow melts in the Rocky Mountains, and reaches its lowest point in the fall. Despite the numerous dams regulating its flow, its discharge into the Columbia remains highly seasonal.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|607}} At Ice Harbor Dam, the mean monthly discharge is highest in May and June at over {{convert|100000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}}, and lowest in September and October at less than {{convert|25000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}}.<ref name=iceharbordam/> Mean annual discharge also fluctuates significantly, from a record high of {{convert|86240|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}} in 1965, to a low of {{convert|27890|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}} in 1997.<ref name=iceharbordam/> |
|||
In southern Idaho, Snake River flows are significantly influenced by the [[Snake River Aquifer#Eastern Snake River Plain Aquifer|Eastern Snake River Plain Aquifer]]. One of the largest groundwater reserves in the US, the aquifer is founded in porous volcanic rock underneath the plain. It absorbs and stores large volumes of water from the Snake River in the eastern Plain to re-emerge further west as springs in the Snake River Canyon.<ref name="uppersnakeprovince">{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.nwcouncil.org/media/120275/1IntroOverview.pdf |
|||
|title=Upper Snake Province Assessment |
|||
|publisher=Northwest Watershed Council |
|||
|date=May 28, 2004 |
|||
|access-date=January 6, 2024 |
|||
|archive-date=October 18, 2021 |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211018074023/https://www.nwcouncil.org/sites/default/files/1IntroOverview.pdf |
|||
|url-status=live |
|||
}}</ref> Water from the [[lost streams of Idaho]], several rivers that disappear underground in the eastern Plain, travels through the aquifer to reach the Snake River,<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.ephemeroptera-galactica.com/pubs/pub_a/pubandrewsd1979p140.pdf|title=Distribution of Benthic Invertebrates in the Lost Streams of Idaho|author=Andrews, Douglas A. |author2=Minshall, G. Wayne|journal=The American Midland Naturalist|year=1979|volume=102|number=1|pages=140–148|doi=10.2307/2425075 |jstor=2425075 |accessdate=January 17, 2024}}</ref> as does excess irrigation water absorbed into the ground.<ref name="Snake River Plain hydrogeology"/> The major spring complexes at American Falls and Thousand Springs (near [[Hagerman, Idaho]]) keep the river flowing steadily even in the driest of summers.<ref name="ISU Snake River Plain aquifer">{{cite web|url=https://www.isu.edu/digitalgeologyidaho/srp-aquifer/|title=Snake River Plain aquifer|publisher=Idaho State University|accessdate=January 17, 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://idwr.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/legal/american-falls/AF-20020118-ESPA-Surface-Water-and-Groundwater-Interaction.pdf|title=Eastern Snake River Plain Surface and Ground Water Interaction|publisher=Idaho Department of Water Resources|date=January 18, 2002|accessdate=January 17, 2024}}</ref> At [[King Hill, Idaho|King Hill]], about {{convert|50|mi|km}} northwest of Twin Falls, water levels remain about {{convert|10000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}} for most of the year, increasing about 20 percent during snowmelt and decreasing about 20 percent with late summer irrigation diversions.<ref name="Snake River Plain hydrogeology">{{cite web|url=https://digitalatlas.cose.isu.edu/hydr/snakervr/srhyge.htm|title=Eastern Snake River Plain- Hydrogeology|publisher=Idaho State University|work=Digital Atlas of Idaho|date=|accessdate=January 17, 2024}}</ref><ref name="USGS Snake River at King Hill">{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13154500.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13154500 Snake River at King Hill, ID: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 17, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Despite its great length, the Snake River accumulates most of its water in the lower one-fourth of its course. By the time it reaches [[Hells Canyon Dam]], {{convert|247|mi|km}} from the mouth, the mean annual discharge is about {{convert|19000|cuft/s|m3/s|abbr=on}} – just over a third of the discharge at the mouth.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13290450.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13213100 Snake River at Hells Canyon Dam: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> Just two downstream tributaries, the Clearwater and Salmon Rivers, contribute about half of the total flow of the Snake.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|607}} |
|||
==Watershed== |
|||
[[Image:UP EMD SD9043AC Joso Bridge, USA.jpg|thumb|right|The [[Union Pacific Railroad]] crosses the lower Snake River via the Joso Bridge near [[Starbuck, Washington]].|alt=A freight train crosses a wide river on a steel bridge]] |
|||
The {{convert|107500|mi2|km2|adj=on}}<ref name="USGS"/> Snake River watershed drains about 87 percent of the state of Idaho, 18 percent of Washington and 17 percent of Oregon, in addition to small portions of Wyoming, [[Utah]] and [[Nevada]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.deq.idaho.gov/water-quality/surface-water/total-maximum-daily-loads/snake-river-hells-canyon-subbasins/|title=Snake River – Hells Canyon Subbasins|publisher=Idaho Department of Environmental Quality|accessdate=February 2, 2024}}</ref> From the [[Lost Trail Pass]] north of [[Salmon, Idaho]] to Tri-Basin Divide south of [[Afton, Wyoming]], the eastern edge of the Snake River watershed follows the [[Continental Divide of the Americas|Continental Divide]]. As the Continental Divide also forms the Idaho–Montana border south of Lost Trail Pass, the Snake watershed touches Montana for a long distance, but does not extend into it.<ref name="TNM"/> The Snake drains by far the largest area of any Columbia River tributary, making up about 40 percent of the entire Columbia River watershed.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|602}} Compared with the Columbia above their confluence, the Snake River is about {{convert|180|mi|km}} longer{{#tag:ref|The Columbia River above the Snake has a length of approximately {{convert|900|mi|km}}.<ref name="TNM"/>|group=n}} and drains a similarly sized area,<ref name="USGS"/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://nwis.waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis/inventory/?site_no=12514000&agency_cd=USGS|title=USGS Gage #12514000 Columbia River at Pasco, WA|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|accessdate=April 28, 2024}}</ref> though the Columbia carries more than twice the volume of water.<ref name=iceharbordam/><ref name="Columbia at Priest Rapids">{{cite web |
|||
|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/12472800.2013.pdf |
|||
|title=USGS Gage #12472800 on the Columbia River below Priest Rapids Dam, WA (Water-Data Report 2013) |
|||
|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey |
|||
|work=National Water Information System |
|||
|access-date=December 15, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
The Snake River watershed is very mountainous, with the northern two-thirds of it occupied by vast mountain ranges of the Rockies, primarily the [[Salmon River Mountains]] of central Idaho and the [[Bitterroot Range]] along the Idaho–Montana border. The Blue Mountains form much of the western boundary of the Snake watershed from southeast Washington down into Oregon. To the south are numerous small isolated mountain ranges of the [[Basin and Range Province]], such as the [[Independence Mountains|Independence]] and [[Albion Mountains]].<ref name="TNM"/> To the east are more ranges of the Rockies including the Tetons and the [[Wind River Range]]; the latter includes [[Gannett Peak]], the highest point in the Snake River basin<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|604}} at {{convert|13816|ft|m}}.<ref>{{cite gnis|id=1599903|name=Gannett Peak|entrydate=December 31, 1981|accessdate=January 27, 2024}}</ref> Surface volcanic features – such as lava fields, [[Volcanic cone|cones]], and thermal springs – are replete in the southern part of the Snake watershed, from [[Craters of the Moon National Monument]] northeast of Twin Falls to the Yellowstone caldera, while ancient lava flows of the [[Columbia River Basalt Group|Columbia River basalts]] underlie the western part of the watershed. The Snake River Plain is the largest area without mountains, but it still features rugged terrain, being crisscrossed by canyons formed by the Snake River and its tributaries.<ref name="TNM"/><ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|604–606}} |
|||
Due to the [[rain shadow]] effect of the [[Cascade Range|Cascades]], precipitation as a whole is scant, averaging {{convert|14|in|mm}} across the entire watershed. Most precipitation falls at higher elevations as snow, thus, most runoff in the Snake River watershed derives from snowmelt.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|605–607}} Jackson Hole, Wyoming experiences an [[alpine climate]] with an average of {{convert|30|in|mm|abbr=on}} of rain and {{convert|252|in|mm|abbr=on}} of snow. The coldest month is January, with a mean temperature of {{convert|13|F|C}}, and the hottest is July at {{convert|57.7|F|C}}.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?wy8315 |
|||
|title=Snake River, Wyoming Period of Record General Climate Summary |
|||
|publisher=Western Regional Climate Center |
|||
|access-date=February 2, 2024 |
|||
|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20220117101618/http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?wy8315 |
|||
|archivedate=January 17, 2022 |
|||
}}</ref> Twin Falls experiences a [[semi-arid climate]], with about {{convert|9|in|mm|abbr=on}} of rain and {{convert|13|in|mm|abbr=on}} of snow. Monthly mean temperatures range from {{convert|29.4|F|C}} in January to {{convert|73.1|F|C}} in July.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?id9293 |
|||
|title=Twin Falls, Idaho Period of Record General Climate Summary |
|||
|publisher=Western Regional Climate Center |
|||
|access-date=February 24, 2016 |
|||
|archive-date=April 4, 2012 |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120404031720/http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?id9293 |
|||
|url-status=live |
|||
}}</ref> The Columbia Basin around the river's mouth also has a semi-arid climate, with about {{convert|10|in|mm|abbr=on}} of rain and {{convert|5|in|mm|abbr=on}} of snow as measured at Ice Harbor Dam. January is the coldest month with a mean temperature of {{convert|34.3|F|C}}, and July is the hottest month at {{convert|74.6|F|C}}.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=https://wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?wa3883 |
|||
|title=Ice Harbor Dam, Washington: Period of Record General Climate Summary |
|||
|publisher=Western Regional Climate Center |
|||
|access-date=February 2, 2024 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:My Public Lands Roadtrip- South Fork of the Snake River in BLM Idaho (18434847188).jpg|thumb|left|Fall colors along the Snake River upstream of the Henrys Fork, Idaho|alt=A river flows through a mountain valley lined with autumn foliage]] |
|||
[[Semi-arid climate|Semi-arid]] [[shrubland]] and [[rangeland]] covers about 50 percent of the Snake River watershed. Natural vegetation is primarily [[sagebrush]], mixed with [[wheatgrass]]es and [[bunchgrass]]es. About 30 percent of the watershed is farmland; irrigated farming of potatoes, sugar beets, onions, cereal grains and alfalfa are dominant in the Snake River Plain, while the Palouse Hills of the northwest host mainly dryland wheat and legume production.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|603–605}} About 15 percent of the watershed is forested, distributed across two [[temperate coniferous forest]] [[ecoregion]]s: [[South Central Rockies forests]], consisting primarily of [[Douglas fir]], [[Engelmann spruce]], [[subalpine fir]], and [[lodgepole pine]], and [[North Central Rockies forests]], which include [[mountain hemlock]], [[white spruce]], [[alpine fir]] and [[western larch]]. About 4 percent of the watershed is barren desert, and only about 1 percent is urbanized.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005">{{cite book|title=Rivers of North America|editor=Benke, Arthur C. |editor2=Cushing, Colbert E.|publisher=Elsevier Academic Press|year=2005|isbn=0-12-088253-1}}</ref>{{rp|604–606}} |
|||
Most of the Snake River watershed is public land, with the [[U.S. Forest Service]] managing the [[Nez Perce National Forest|Nez Perce]], [[Clearwater National Forest|Clearwater]], [[Bitterroot National Forest|Bitterroot]], [[Umatilla National Forest|Umatilla]], [[Wallowa–Whitman National Forest|Wallowa–Whitman]], [[Payette National Forest|Payette]], [[Boise National Forest|Boise]], [[Salmon–Challis National Forest|Salmon–Challis]], [[Sawtooth National Forest|Sawtooth]], [[Caribou–Targhee National Forest|Caribou–Targhee]] and [[Bridger–Teton National Forest]]s that cover much of the northern and eastern parts of the watershed.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|606}} The forests contain numerous designated wilderness areas, including the [[Sawtooth Wilderness|Sawtooth]], [[Selway–Bitterroot Wilderness|Selway–Bitterroot]], [[Frank Church-River of No Return Wilderness|Frank Church-River of No Return]], [[Gospel Hump Wilderness|Gospel Hump]], [[Hells Canyon Wilderness (Oregon and Idaho)|Hells Canyon]], [[Teton Wilderness|Teton]] and [[Gros Ventre Wilderness|Gros Ventre]].<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|606}} [[U.S. National Park Service|National Park Service]] land includes Craters of the Moon National Monument and Yellowstone and Grand Teton National Parks. Large areas of privately owned farmland are concentrated in the Snake River Plain and the Palouse, though the majority of the Snake River Plain is [[U.S. Bureau of Land Management|Bureau of Land Management]] land.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.loc.gov/resource/g4051g.ct011662/?r=0.191,0.223,0.324,0.163,0|title=Bureau of Land Management public lands and administrative jurisdictions : [western United States]. |
|||
|publisher=Library of Congress|year=2005|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
The Snake River watershed borders several other major North American watersheds. To the south it borders the [[endorheic]] [[Great Basin]], including the area draining to Utah's [[Great Salt Lake]]. To the east it borders the watersheds of the [[Green River (Colorado River tributary)|Green River]] (part of the [[Colorado River]] system which drains to the [[Sea of Cortez]]) and the [[Yellowstone River|Yellowstone]] and upper [[Missouri River]]s (part of the [[Mississippi River]] system which drains to the [[Gulf of Mexico]]). On the north it borders the watersheds of the [[Clark Fork (river)|Clark Fork]] and [[Spokane River]]s, both part of the Columbia River system. To the northwest it borders several other tributary watersheds of the Columbia River, including those of the [[John Day River|John Day]] and [[Umatilla River]]s.<ref name="watershed-map">{{cite web |title = Watersheds (map) |publisher = Commission for Environmental Cooperation |year = 2006 |url = http://www.cec.org/naatlas/img/NA-Watersheds.gif |archive-url = http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20080807145118/http://www.cec.org/naatlas/img/NA-Watersheds.gif |archive-date = August 7, 2008 |url-status = dead }}</ref> |
|||
===Major tributaries=== |
|||
{{See also|List of tributaries of the Columbia River}} |
|||
Fifty-four named tributaries of the Snake River drain more than {{convert|100|mi2|km2}}.<ref name="TNM"/> Of these, the twelve listed below drain an area greater than {{convert|2000|mi2|km2}}.<ref name="TNM"/> |
|||
{|class="wikitable sortable" border = "1" |
|||
!colspan=9|Major tributaries of the Snake River |
|||
|- |
|||
!Name |
|||
!Confluence location |
|||
!Confluence coordinates |
|||
!Confluence elevation |
|||
!Length (mainstem)<ref name="TNM"/> |
|||
!Length (to furthest source)<ref name="TNM"/>{{#tag:ref|Measured to the head of the longest tributary beyond the head of the main stem.|group=n}} |
|||
!Watershed<ref name="USGS"/> |
|||
!Discharge |
|||
!Picture |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Henrys Fork (Snake River)|Henrys Fork]] |
|||
|[[Rexburg, Idaho]] |
|||
|{{coord|43|45|10|N|111|57|28|W}}<ref name="GNIS Henrys Fork">{{cite gnis|id=383107|name=Henrys Fork|entrydate=June 21, 1979|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|4,800}} ft<br>(1,463 m)<ref name="GNIS Henrys Fork"/> |
|||
|{{nts|129.3}} mi<br>(208.1 km) |
|||
|{{nts|129.3}} mi<br>(208.1 km) |
|||
|{{nts|3,260}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(8,450 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|2,105}} cu ft/s<br>(59.7 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13056500.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13056500 Henrys Fork near Rexburg, ID: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Upper Mesa Falls - Idaho (12145650713).jpg|140px|alt=A waterfall plunges in lush coniferous forest]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Salmon Falls Creek]] |
|||
|[[Hagerman, Idaho]] |
|||
|{{coord|42|42|55|N|114|51|12|W}}<ref name="GNIS Salmon Falls Creek">{{cite gnis|id=395878|name=Salmon Falls Creek|entrydate=June 21, 1979|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|2,884}} ft<br>(879 m)<ref name="GNIS Salmon Falls Creek"/> |
|||
|{{nts|121.1}} mi<br>(195.0 km) |
|||
|{{nts|152.6}} mi<br>(245.7 km){{#tag:ref|To the head of Sun Creek.|group=n}} |
|||
|{{nts|2,120}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(5,500 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|151}} cu ft/s<br>(4.3 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13108150.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13108150 Salmon Falls Creek near Hagerman, ID: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Balance_(5).jpg|140px|alt=A gently flowing stream at the bottom of a desert canyon]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Malad River (Gooding County, Idaho)|Malad River]] |
|||
|[[Hagerman, Idaho]] |
|||
|{{coord|42|51|45|N|114|54|18|W}}<ref name="GNIS Malad River">{{cite gnis|id=376083|name=Malad River|entrydate=May 1, 1989|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|2,658}} ft<br>(810 m)<ref name="GNIS Malad River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|12.0}} mi<br>(19.3 km) |
|||
|{{nts|149.0}} mi<br>(239.9 km){{#tag:ref|To the head of [[Big Wood River]].|group=n}} |
|||
|{{nts|3,250}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(8,420 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|1,500}} cu ft/s<br>(42.5 m<sup>3</sup>/s){{#tag:ref|A significant amount of water is diverted just above the mouth of Malad River for hydropower generation and discharged into the Snake River. Malad River discharge is calculated by the sum of USGS gage # 13153500 (Malad River near Bliss)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nwis.waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis/monthly/?referred_module=sw&site_no=13153500&por_13153500_326201=1154587,00060,326201,1899-04,2022-09&start_dt=1985-07&end_dt=1999-09&format=html_table&date_format=YYYY-MM-DD&rdb_compression=file&submitted_form=parameter_selection_list|title=USGS Gage #13153500 Malad River near Bliss, ID: Monthly Statistics|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> and #13152940 (Malad River hydropower diversion)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nwis.waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis/monthly/?referred_module=sw&site_no=13152940&por_13152940_45810=1154582,00060,45810,1985-06,1999-09&format=html_table&date_format=YYYY-MM-DD&rdb_compression=file&submitted_form=parameter_selection_list|title= USGS Gage #13152940 Malad River Power Flume near Bliss, ID: Monthly Statistics|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|accessdate=January 16, 2024}}</ref>|group=n}} |
|||
|[[Image:Devils_Wash_Bowl,_Apr_17.jpg|140px|alt=A powerful waterfall and rapids cut through jumbled rocks]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Bruneau River]] |
|||
|[[Mountain Home, Idaho]] |
|||
|{{coord|42|56|57|N|115|57|43|W}}<ref name="GNIS Bruneau River">{{cite gnis|id=394740|name=Bruneau River|entrydate=June 21, 1979|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|2,457}} ft<br>(749 m)<ref name="GNIS Bruneau River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|152.9}} mi<br>(246.2 km) |
|||
|{{nts|152.9}} mi<br>(246.2 km) |
|||
|{{nts|3,290}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(8,530 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|375}} cu ft/s<br>(10.6 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13168500.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13168500 Bruneau River near Hot Spring, ID: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Bruneau Wild and Scenic River (23780771472).jpg|140px|alt=A stream calmly flows by at the bottom of light gray cliffs]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Owyhee River]] |
|||
|[[Nyssa, Oregon]] |
|||
|{{coord|43|48|46|N|117|01|32|W}}<ref name="GNIS Owyhee River">{{cite gnis|id=1147319|name=Owyhee River|entrydate=November 28, 1980|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|2,185}} ft<br>(666 m)<ref name="GNIS Owyhee River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|346.5}} mi<br>(557.9 km) |
|||
|{{nts|346.5}} mi<br>(557.9 km) |
|||
|{{nts|10,950}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(28,380 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|918}} cu ft/s<br>(26.0 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13181000.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13181000 Owyhee River near Rome, OR: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Owyhee River (9092356441).jpg|140px|alt=View over a river bend in a shrubby desert landscape framed by vertical cliffs]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Boise River]] |
|||
|[[Parma, Idaho]] |
|||
|{{coord|43|49|15|N|117|01|34|W}}<ref name="GNIS Boise River">{{cite gnis|id=378007|name=Boise River|entrydate=June 21, 1979|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|2,185}} ft<br>(666 m)<ref name="GNIS Boise River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|103.1}} mi<br>(166.0 km) |
|||
|{{nts|155.5}} mi<br>(250.4 km){{#tag:ref|To the head of [[Middle Fork Boise River]].|group=n}} |
|||
|{{nts|4,010}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(10,390 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|1,574}} cu ft/s<br>(44.6 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13213000.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13213000 Boise River near Parma, ID: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Boise River and Canal Bridge (Caldwell, Idaho) (5).jpg|140px|alt=A river flows under a steel bridge through a wooded area]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Malheur River]] |
|||
|[[Ontario, Oregon]] |
|||
|{{coord|44|03|33|N|116|58|31|W}}<ref name="GNIS Malheur River">{{cite gnis|id=1145769|name=Malheur River|entrydate=November 28, 1980|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|2,133}} ft<br>(650 m)<ref name="GNIS Malheur River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|189.8}} mi<br>(305.6 km) |
|||
|{{nts|205.7}} mi<br>(331.2 km){{#tag:ref|To the head of Lake Creek.|group=n}} |
|||
|{{nts|4,710}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(12,210 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|208}} cu ft/s<br>(5.9 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13213000.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13233300 Malheur River below Nevada Dam near Vale, OR: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Malheur_River_(Malheur_County,_Oregon_scenic_images)_(malDA0030).jpg|140px|alt=A river forms multiple channels as it flows through a desert valley]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Payette River]] |
|||
|[[Payette, Idaho]] |
|||
|{{coord|44|05|32|N|116|57|09|W}}<ref name="GNIS Payette River">{{cite gnis|id=388284|name=Payette River|entrydate=December 31, 1992|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|2,126}} ft<br>(648 m)<ref name="GNIS Payette River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|82.7}} mi<br>(133.1 km) |
|||
|{{nts|163.0}} mi<br>(262.4 km){{#tag:ref|To the head of [[South Fork Payette River]].|group=n}} |
|||
|{{nts|3,300}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(8,550 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|2,960}} cu ft/s<br>(83.8 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13251000.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13251000 Payette River near Payette, ID: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Payette_River_Scenic_Byway_-_Payette_River's_Allure_-_NARA_-_7720998.jpg|140px|alt=A river flows through grassy meadows surrounded by coniferous forest]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Salmon River (Idaho)|Salmon River]] |
|||
|[[Hells Canyon National Recreation Area|Hells Canyon NRA, Idaho]] |
|||
|{{coord|45|51|23|N|116|47|37|W}}<ref name="GNIS Salmon River">{{cite gnis|id=400069|name=Salmon River|entrydate=December 31, 1992|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|919}} ft<br>(280 m)<ref name="GNIS Salmon River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|425.3}} mi<br>(684.7 km) |
|||
|{{nts|425.3}} mi<br>(684.7 km) |
|||
|{{nts|14,000}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(36,290 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|11,090}} cu ft/s<br>(314.0 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13317000.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13317000 Salmon River at White Bird, ID: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Rafting the Salmon River ID.jpg|140px|alt=River rapids cut through a mountain landscape, with several boaters visible in the foreground]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Grande Ronde River]] |
|||
|[[Rogersburg, Washington]] |
|||
|{{coord|46|04|49|N|116|58|47|W}}<ref name="GNIS Grande Ronde River">{{cite gnis|id=1505215|name=Grande Ronde River|entrydate=September 10, 1979|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|820}} ft<br>(250 m)<ref name="GNIS Grande Ronde River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|210.4}} mi<br>(338.7 km) |
|||
|{{nts|210.4}} mi<br>(338.7 km) |
|||
|{{nts|4,130}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(10,710 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|3,027}} cu ft/s<br>(85.7 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13333000.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13333000 Grande Ronde River at Troy, OR: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Grande Ronde River, Troy Road - DPLA - 8a04ffea7c5c25492bc3815b1d6bb697.jpg|140px|alt=View over a river bend framed by high cliffs of horizontally layered rock]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Clearwater River (Idaho)|Clearwater River]] |
|||
|[[Lewiston, Idaho]] |
|||
|{{coord|46|25|30|N|117|02|14|W}}<ref name="GNIS Clearwater River">{{cite gnis|id=379406|name=Clearwater River|entrydate=June 21, 1979|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|738}} ft<br>(220 m)<ref name="GNIS Clearwater River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|74.8}} mi<br>(120.4 km) |
|||
|{{nts|198.3}} mi<br>(319.2 km){{#tag:ref|To the head of [[Selway River]].|group=n}} |
|||
|{{nts|9,420}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(24,420 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|14,860}} cu ft/s<br>(420.8 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13342500.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13342500 Clearwater River at Spalding, ID: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:Clearwater River in Ahsahka, Idaho.jpg|140px|alt=A wide river flows through coniferous forest in a mountain valley]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Palouse River]] |
|||
|[[Starbuck, Washington]] |
|||
|{{coord|46|35|24|N|118|12|55|W}}<ref name="GNIS Palouse River">{{cite gnis|id=1513182|name=Palouse River|entrydate=September 10, 1979|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|{{nts|541}} ft<br>(165 m)<ref name="GNIS Palouse River"/> |
|||
|{{nts|166.4}} mi<br>(267.9 km) |
|||
|{{nts|166.4}} mi<br>(267.9 km) |
|||
|{{nts|3,320}} mi<sup>2</sup><br>(8,610 km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
|{{nts|599}} cu ft/s<br>(17.0 m<sup>3</sup>/s)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://wdr.water.usgs.gov/wy2013/pdfs/13351000.2013.pdf|title=USGS Gage #13351000 Palouse River at Hooper, WA: Water-Data Report 2013|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|work=National Water Information System|year=2013|accessdate=January 15, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|[[Image:03-18-07, palouse river canyon - panoramio.jpg|140px|alt=View over a desert river canyon surrounded by vertical cliffs]] |
|||
|} |
|||
==Geology== |
|||
[[Image:Hells Canyon Dam, Snake River - DPLA - 8521af84128ad4ffab75e7e3814da93f.jpg|thumb|upright|Hells Canyon, the connection between the Snake River Plain and the lower Snake River drainage systems, formed about 2.5 million years ago from the overflow of Lake Idaho.|alt=View down a river entering a rocky canyon framed by high cliffs]] |
|||
{{See also|Geology of the Pacific Northwest}} |
|||
The present-day course of the Snake River was pieced together over millions of years from several formerly disconnected drainage systems. Much of what would become the Pacific Northwest lay under shallow seas until it was uplifted starting about 60 million years ago (Ma). The outlet of the ancestral Columbia River to the Pacific was established about 40 Ma.<ref>{{cite web |title = The Geologic Story of the Columbia Basin |url = https://www.bpa.gov/power/pl/columbia/4-geology.htm |publisher = Bonneville Power Administration |access-date = June 20, 2017 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170708070906/https://www.bpa.gov/Power/pl/columbia/4-geology.htm |archive-date = July 8, 2017 |url-status = live }}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Moclock, Leslie |author2=Selander, Jacob|title=Rocks, Minerals, and Geology of the Pacific Northwest|year=2021|publisher=Timber Press |isbn=9781604699159|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Eb3dDwAAQBAJ}}</ref>{{rp|288}} By about 17 Ma, the "Salmon-Clearwater River", or the modern day lower Snake River, flowed west into the Columbia and on to the Pacific. Another ancient river system drained what is now the western Snake River Plain. Some geologists propose that this flowed to the Columbia on a course south of the present-day Blue Mountains, while others propose it drained towards [[Northern California]].<ref name="Reidel"/>{{rp|208–210}}<ref>{{cite book|author=Bingham, Richard T.|title=Plants of the Seven Devils Mountains of Idaho|publisher=U.S. Department of Agriculture|year=1987|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nAFq1UCnxlcC}}</ref>{{rp|11}} The [[Columbia River Basalt Group|Columbia River basalts]], a series of massive [[flood basalt]] events that engulfed the Columbia Basin and surrounding lands, reshaped the landscape and erased most evidence of the pre-volcanic river channels starting about 17 Ma. Erupting from fissures in the southern Columbia Basin, the first basalt flows pushed the ancient Salmon-Clearwater much further north than its present course.<ref name="Reidel">{{cite book|editor=Reidel, Stephen P.|title=The Columbia River Flood Basalt Province|publisher=The Geological Society of America|isbn=9780813724973|year=2013|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xWpIDgAAQBAJ}}</ref>{{rp|201–208}} |
|||
About 12–10 Ma, the Blue Mountains region began to experience uplift, raising the basalt layers to form a plateau.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.dnr.wa.gov/programs-and-services/geology/explore-popular-geology/geologic-provinces-washington/blue-mountains|title=Blue Mountains|publisher=Washington State Department of Natural Resources|date=|accessdate=January 20, 2024}}</ref> From about 11–9 Ma, crustal deformation related to the [[Yellowstone hotspot]] caused the western half of the Snake River Plain to sink, creating a [[graben]]-type valley between parallel fault zones to the northeast and southwest.<ref name="Lifton"/> The outlet of the ancient Snake River was blocked, and water accumulated to form the vast [[Lake Idaho]] starting about 10 Ma.<ref name="Lifton">{{cite web|url=https://www.usgs.gov/observatories/yvo/news/snake-river-plain-a-tale-two-basins|title=The Snake River Plain: A Tale of Two Basins|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|author=Lifton, Zach|date=November 21, 2022|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> The eastern half of the Snake River Plain formed as the [[North American Plate]] moved westward over the Yellowstone hotspot. Upwelling [[magma]] caused the continental crust to rise, forming highlands in a similar fashion to the modern Yellowstone plateau and leaving behind enormous basalt flows in its wake. As the hotspot migrated east relative to the North American Plate, the land behind it collapsed and sank, creating the geographic depression of the eastern Snake River Plain.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/35549/snake-river-plain-idaho|title=Snake River Plain, Idaho|publisher=NASA Earth Observatory|date=August 29, 2008|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://digitalgeology.aws.cose.isu.edu/Digital_Geology_Idaho/Module11/mod11.htm|title=Neogene Snake River Plain-Yellowstone Volcanic Province|publisher=Idaho State University|author=Link, Paul|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Columbia_River_Flood-Basalt_Province.jpg|thumb|right|The Columbia River Basalt Province covers a vast area of the inland Pacific Northwest.|alt=Map showing the extent of the Columbia River Basalt Province, a volcanic geologic province of the inland Pacific Northwest]] |
|||
The gradual eastward migration of this topographic high had the effect of pushing the Continental Divide to the east. Prior to the formation of the eastern Snake River Plain, the drainage area east of about [[Arco, Idaho]] – the modern headwaters and upper course of the Snake River – flowed towards the [[Atlantic Ocean]] via the [[Mississippi River]] system.<ref name="Wood and Clemens"/> The migrating Continental Divide tilted the regional slope such that drainage flowed west into Lake Idaho, whose water levels saw a significant increase about 4.5 Ma.<ref name="Lifton"/><ref name="Wood and Clemens"/> The Snake River Plain drainage system continued to expand east, towards what is now Yellowstone National Park. During this expansion, the Snake also captured the [[Bear River (Great Salt Lake)|Bear River]], which was only rerouted towards its modern outlet in the Great Salt Lake Basin about 50,000 or 60,000 years ago by lava flows in southeast Idaho.<ref name="ISU"/><ref>{{cite journal|title=The Bear River's History and Diversion: Constraints, Unsolved Problems, and Implications for the Lake Bonneville Record|journal=Developments in Earth Surface Processes|volume=20|year=2016|pages=28–59|author1=Pederson, J.L.|author2=Janecke, S.U.|author3=Reheis, M.C.|author4=Kaufman, D.S.|author5=Oaks, R.Q. Jr.|doi=10.1016/B978-0-444-63590-7.00002-0|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780444635907000020|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
In the Columbia Basin about 10.5 Ma, the Elephant Mountain basalt eruption forced the Salmon-Clearwater River into roughly its present course through southeast Washington.<ref name="Reidel"/>{{rp|221–222}}<ref>{{cite book|title=Floods, Faults, and Fire: Geological Field Trips in Washington State and Southwest British Columbia|publisher=Geological Society of America|editor=Tucker, David Samuel |editor2=Stelling, Peter L.|year=2007|isbn=978-0-8137-0009-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=F1Sx3i2CZyUC}}</ref>{{rp|237}} By 8.5 Ma the Salmon-Clearwater was established in the Columbia River's modern path through [[Wallula Gap]], although the Columbia itself still flowed somewhere to the west. The last of the Columbia basalt flows occurred around 6 Ma; by then, the present-day confluence of the Columbia River and Salmon-Clearwater had been established, with the combined flow draining through Wallula Gap.<ref name="Reidel"/>{{rp|222–223}} About 2.5 Ma, Lake Idaho reached a maximum elevation of {{convert|3600|ft|m}} above modern sea level, and overflowed northward into the Salmon-Clearwater drainage near present-day [[Huntington, Oregon]]. Over a period of about two million years, the outflow carved Hells Canyon, emptying Lake Idaho and integrating the upper Snake and Salmon-Clearwater into a single river system.<ref name="Lifton"/><ref name="Wood and Clemens">{{cite web|url=https://idwr.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/projects/north-ada-county/199807-WOODCLEM-2002.pdf|title=Geologic and Tectonic History of the Western Snake River Plain, Idaho and Oregon|author=Wood, Spencer H. |author2=Clemens, Drew M.|publisher=Idaho Department of Water Resources|year=2002|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
The Teton Range, a defining topographic feature of the modern Snake River headwaters, first began to rise about 10 Ma as the Teton Fault began to move, displacing the mountain block upward as the surrounding land dropped.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.usgs.gov/geology-and-ecology-of-national-parks/geology-grand-teton-national-park|title=Geology of Grand Teton National Park |
|||
|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> About 2 Ma, the Hoback Fault formed east of the Tetons, and a graben valley developed between the Hoback and Teton fault zones, creating Jackson Hole.<ref name="Jackson Hole geology">{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/parkhistory/online_books/grte/grte_geology/sec9.htm|title=Quaternary – Time of Ice, More Lakes, and Continued Crustal Disturbance|work=Creation of the Teton Landscape: The Geologic Story of Grand Teton National Park|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|author=Love, J.D. |author2=Reed, John C.|year=1971|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> As the valley dropped, water filled it to create Lake Teewinot, which drained east into the [[Green River (Colorado River tributary)|Green River]]–[[Colorado River]] system. About 1 Ma, the Snake River captured the Jackson Hole watershed, draining Lake Teewinot and finally connecting the modern-day Snake headwaters to the rest of the river.<ref name="ISU">{{cite web|url=https://www.isu.edu/media/libraries/college-of-science-and-engineering/geology/digital-geology-of-idaho/srptopo_development.pdf|title=Snake River Plain Topographic Development|publisher=Idaho State University|date=|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> This landscape around the Snake headwaters was sculpted by multiple Ice Age glaciations. Starting about 200,000 years ago, the Buffalo glaciation filled Jackson Hole to a depth of {{convert|2000|ft|m}}. Ice flowed down the Snake River Canyon all the way to Idaho.<ref name="Jackson Hole geology"/> The Bull Lake glaciation, about 80,000–35,000 years ago, and the Pinedale glaciation, ending about 15,000 years ago, were much smaller and did not fill the entire valley. These glaciations carved the distinctive peaks of the Tetons into their present form and scoured lake basins in the valley floor, including modern-day Jackson Lake.<ref name="Jackson Hole geology"/> |
|||
While the Snake River course beyond Jackson Hole was not directly impacted by glaciations, its landscape was dramatically changed by Ice Age flooding events. About 30,000 years ago, the climate of western North America was much wetter than today. The Great Salt Lake Basin filled with water to form the massive [[Lake Bonneville]], about the size of modern-day [[Lake Michigan]]. About 15,000 years ago the lip of [[Red Rock Pass (Idaho)|Red Rock Pass]] south of present-day [[Pocatello, Idaho]] abruptly collapsed, releasing a tremendous volume of water from Lake Bonneville into the Snake River Plain. The peak of the flood was about 500 times bigger than the largest recorded flood of the Snake at Idaho Falls in modern times.<ref name="isu bonneville">{{cite web|url=https://www.isu.edu/digitalgeologyidaho/bonneville/|title=Lake Bonneville flood|publisher=Idaho State University|work=Digital Geology of Idaho|date=|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> The flood completely altered the landscape of the Snake River Plain, creating the Snake River Canyon and its waterfalls, vast boulder fields, cliffs and [[coulee]]s.<ref name="isu bonneville"/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://digitalatlas.cose.isu.edu/hydr/lkbflood/lbf.htm|title=The Lake Bonneville Flood|publisher=Idaho State University|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> The floodwaters then emptied through Hells Canyon; however, most evidence of their effects on the lower Snake River was erased by the much larger [[Missoula Floods]] that engulfed the Columbia Basin during the same period.<ref name="isu bonneville"/> Caused by the repeated collapse of an ice dam in western Montana, dozens of floods overflowed into the lower Snake River from the north, backing water as far upstream as Lewiston. The formerly west-flowing Palouse River was rerouted to flow south into the Snake River, forming Palouse Falls, whose outsized [[plunge pool]] attests to the force of the floods.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.isu.edu/digitalgeologyidaho/palouse-lake-missoula/|title=Palouse and glacial Lake Missoula|publisher=Idaho State University|work=Digital Geology of Idaho|date=|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://parks.wa.gov/sites/default/files/2023-07/Ice%20Age%20Floods%20Brochure.pdf|title=Ice Age Floods|publisher=Washington State Parks|date=April 13, 2022|accessdate=December 18, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
==History== |
|||
===Indigenous peoples=== |
|||
[[Image:RemingtonBannockIndiansFordingSnake.jpg|thumb|right|[[Bannock people|Bannock]] hunting party fording the Snake River southwest of the Tetons, illustration by [[Frederic Remington]] c. 1895|alt=A drawing shows a group of about 10 people on horseback, fording a river]] |
|||
Starting around the end of the last glacial period, the Snake River Plain was inhabited by hunter-gatherers of the ancient [[Clovis culture|Clovis]] (10000–9000 BCE), [[Folsom culture|Folsom]] (9000–8000 BCE) and [[Plano culture|Plano]] (8600–5800 BCE) cultures.<ref name="COTM Ch2">{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/parkhistory/online_books/crmo/hcs/chap2.htm|title=Native Inhabitants of the Craters of the Moon Region|work=Historic Context Statements: Craters of the Moon National Monument, Idaho|author=Louter, David|year=1995|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> Along the lower Snake River in Washington, the [[Marmes Rockshelter]] – flooded in 1968 after the construction of [[Lower Monumental Dam]] – has yielded archeological evidence of continuous human occupation from about 9000 BCE until about 1300 CE.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://archaeology.wsu.edu/major-archaeological-sites/the-marmes-rockshelter-site-45fr50/site-interpretations/|title=The Marmes Rockshelter Site: Site Interpretations|publisher=Washington State University|date=|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> Starting about 2200 BCE, people in the western Snake River basin began to adopt a semi-sedentary lifestyle, with an increased reliance on fish (primarily salmon) and food preservation and storage.<ref name="Fremont">{{cite web |
|||
|last=Meatte |
|||
|first=Daniel S. |
|||
|url=http://imnh.isu.edu/digitalatlas/arch/Prehist/Pre_Summ/SW_Snake/SW_Snake.htm |
|||
|title=The Fremont Culture |
|||
|publisher=Digital Atlas of Idaho |
|||
|work=The Prehistory of the Western Snake River Basin |
|||
|year=1990 |
|||
|access-date=October 5, 2009 |
|||
|archive-date=June 26, 2012 |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120626212056/http://imnh.isu.edu/digitalatlas/arch/Prehist/Pre_Summ/SW_Snake/SW_Snake.htm |
|||
|url-status=live |
|||
}}</ref> [[Shoshoni language|Shoshoni]]-speaking peoples arrived in the Snake River Plain between 600 and 1500 CE.<ref name="COTM Ch2"/> |
|||
By the time of first European contact, the Snake River watershed was populated by several Native American tribes. The territory of the [[Nez Perce]] (Nimiipuu) stretched across what is now north-central Idaho, southeast Washington and northeast Oregon, including much of the lower Snake River below Hells Canyon, most of the Clearwater and Grande Ronde River, and the lower Salmon River.<ref name="Treaty Period">{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/nepe/learn/historyculture/the-treaty-era.htm|title=The Treaty Period|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|work=Nez Perce National Historic Park|date=|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> The [[Northern Shoshone]] and the [[Bannock people|Bannock]], a [[Northern Paiute]] group that became culturally associated with the Shoshone, occupied an area stretching from the Snake River Plain east to the Rocky Mountains and south towards the Great Basin, as well as valleys of the upper Salmon River.<ref name="COTM Ch2"/> A Nez Perce name for the river was ''Kimooenim'' or variations thereof,<ref name="Lewis and Clark Journal"/>{{rp|635}} meaning "the stream/place of the hemp weed".<ref>{{cite book |
|||
|title=The Trail of Lewis and Clark, 1804-1904: A Story of the Great Exploration Across the Continent in 1804-6; with a Description of the Old Trail, Based Upon Actual Travel Over It, and of the Changes Found a Century Later|author=Wheeler, Olin Dunbar|year=1904|publisher=G.P. Putnam's Sons|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lfIMAAAAIAAJ}}</ref>{{rp|128}} Another Nez Perce name for the Snake River was ''Pikúunen'', specifically referring to the stretch upstream of the Clearwater confluence. The [[Wanapum people|Wanapum]] and [[Walla Walla people]] called the lower Snake River below the Clearwater ''Naxíyam Wána''.<ref>{{cite book|title=Cáw Pawá Láakni, They Are Not Forgotten: Sahaptian Place Names Atlas of the Cayuse, Umatilla and Walla Walla|author=Hunn, Eugene S. |author2=Morning Owl, E. Thomas |author3=Cash, Phillip E Cash |author4=Engum, Karson Jennifer|publisher=University of Washington Press|isbn=978-0-295-99026-2}}</ref>{{rp|118–120}} The Shoshone called the river ''Yampapah'', after the ''[[Perideridia|yampah]]'' plant that grew profusely along its banks.<ref>{{cite book|title=Reminiscences of Early Days, A Series of Historical Sketches and Happenings in the Early Days of Snake River Valley.|author=Walgamott, C.S.|year=1927|publisher=Idaho Citizen|volume=2|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8I7sx-W1yhYC}}</ref>{{rp|44}} |
|||
Downriver of Shoshone Falls, salmon and their cousins such as [[steelhead trout]] – anadromous fish which spend their adult lives in the ocean, returning to fresh water to spawn – were a key food source for indigenous peoples, and were of great cultural importance. Rituals such as the first salmon ceremony were widely observed along the Columbia, Snake and other Northwest rivers, and so were strict catch limits, such that a healthy number of salmon would survive to reach their natal streams.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fs.usda.gov/pnw/pubs/pnw_gtr451.pdf|title=Characterization and Assessment of Economic Systems in the Interior Columbia Basin: Fisheries|publisher=U.S. Forest Service|author=Fluharty, David L.|date=April 2000|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> The Nez Perce had more than seventy permanent villages among their fishing grounds on the Snake, Clearwater and Salmon Rivers.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/stelprdb5369277.pdf|title= |
|||
The Southern Nez Perce Trail, Wise'isskit|author=Schacher, Cindy L.|publisher=U.S. Forest Service|year=2004|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> Clans gathered at communal fishing sites starting about May or June. Fishing moved from the lower rivers to higher elevation streams throughout the summer, while fall-run fish were preserved for winter use.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/nepe/learn/nature/fish.htm|title=Fish|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|work=Nez Perce National Historical Park|date=|accessdate=February 5, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Shoshones in the western part of the Snake River Plain also depended heavily on the salmon run. At Shoshone Falls and the smaller cataracts downstream, fishing platforms, temporary brush weirs, spears, baskets and fish traps were employed at large scale. Captain [[Benjamin Bonneville]] in 1832 observed that "Indians at Salmon Falls on the Snake River took several thousand salmon in one afternoon by means of spears."<ref>{{cite journal|title=The Shoshone-Bannock: An Anthropological Reassessment|journal=Northwest Anthropological Research Notes|author=Walker, Deward E. Jr.|year=1993|volume=27|number=2|pages=230–237|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pMa4DwAAQBAJ|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> To the east and upriver of the falls, many Shoshone and Bannock lived in more nomadic groups, traveling to the falls during the spring salmon run then gathering [[Camassia|camas]] bulbs and hunting bison through the summer and autumn months.<ref>{{cite report|title=Southwestern Idaho Class I Cultural Resources Overview, Boise and Shoshone Districts, Part 5: Cultural Resources Narrative|publisher=U.S. Bureau of Land Management|author=Gehr, Elliott A. |author2=Lee, Evelyn |author3=Johnson, Gretchen |author4=Merritt, J. Donald |author5=Nelson, Steven|date=December 1982|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gWH-VKscau4C|accessdate=February 2, 2024|pages=39–44}}</ref> |
|||
The Snake River at Hells Canyon formed a natural dividing line between the Nez Perce and Shoshone, who considered each other enemies. The Nez Perce allied with the [[Cayuse people|Cayuse]] against the Shoshone, Bannock and Northern Paiute, and stopped the latter from expanding their territory towards the Columbia Plateau.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Skeletal evidence of pre-contact conflict among native groups in the Columbia Plateau of the Pacific Northwest|author=Harrod, Ryan P. |author2=Tyler, Donald E.|journal=Journal of Northwest Anthropology|volume=50|number=2|pages=228–264|year=2016|isbn=978-1-5391-2889-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dcRVDwAAQBAJ|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> Both the Nez Perce and Shoshone acquired horses in the late 1600s or early 1700s, enabling far-reaching trade and hunting expeditions.<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://www.americanheritage.com/how-indian-got-horse|title=How the Indian Got The Horse|author=Haines, Francis|date=February 1964|journal=American Heritage|volume=15|issue=2|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> With horses, the Nez Perce were able to travel east of the [[Bitterroot Mountains]] to hunt bison, via the trail over [[Lolo Pass (Idaho–Montana)|Lolo Pass]], which the Lewis and Clark expedition would later follow in order to reach the Snake and Columbia Rivers.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/nepe/learn/historyculture/lolo-trail-and-pass-history.htm|title=Lolo Trail and Pass History|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|work=Nez Perce National Historical Park|date=|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
====Origin of name==== |
|||
The river's modern name comes from a misunderstanding of the Shoshone Tribal Sign in [[Plains_Indian_Sign_Language|PISL]].<ref>{{cite book | url=https://archive.org/details/shoshonissentine0000tren/page/4/mode/2up | isbn=978-0-8061-0628-1 | title=The Shoshonis : Sentinels of the Rockies | date=1969 | last1=Trenholm | first1=Virginia Cole | last2=Carley | first2=Maurine | publisher=University of Oklahoma Press }}</ref> The [[Plains Indians]] referred to the Shoshone people as "Snake People", while the Shoshone are believed to have referred to themselves as "People of the River of Many Fish". However, the Shoshone sign for "salmon" was the same or similar to the Plains Indian common sign for "snake."<ref>{{cite web | url=http://plainshumanities.unl.edu/encyclopedia/doc/egp.na.105 | title=Encyclopedia of the Great Plains | SHOSHONES }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://archive.org/details/indiansignlangua0000clar/page/8/mode/2up | title=The Indian sign language | date=1982 }}</ref> The English name for the river was likely derived from this interpretation of the hand gesture, although it is uncertain when the name was first used.<ref name="Snake NWSR">{{cite web|url=https://www.rivers.gov/river/snake|title=Snake River|publisher=National Wild and Scenic Rivers System|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=February 1964 |title=Snake River |url=https://history.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/0038.pdf |journal=Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series |volume=38 |issue= |pages=2 |access-date=December 15, 2022}}</ref> |
|||
===Exploration and fur trade=== |
|||
The first Euro-Americans to reach the Snake River watershed were the Lewis and Clark Expedition, who in August 1805 crossed the Continental Divide at [[Lemhi Pass]] and descended to the Salmon River at what is now [[Salmon, Idaho]], naming the stream "Lewis's River". Thwarted by the river's rapids, they were forced to cross the Bitterroot Mountains via the Nez Perce trail at Lolo Pass. After paddling down the ''Kooskooskee'' (Clearwater River), they reached the junction with the Snake and camped there with the Nez Perces on October 10, 1805.<ref name="Lewis and Clark Journal">{{cite book|title=History of the Expedition Under the Command of Lewis and Clark To the Sources of the Missouri River, Thence Across the Rocky Mountains and Down the Columbia River to the Pacific Ocean, Performed During the Years 1804-5-6, by Order of the Government of the United States · Volume 2|publisher=F.P. Harper|year=1893|editor=Coues, Elliott|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lOATAAAAYAAJ}}</ref>{{rp|620–622}} They correctly surmised that the river coming from the south was a continuation of "Lewis's" or Salmon River. The expedition journals note the Nez Perce called it ''Kimooenim'', although William Clark later erased mentions of the name to replace with "Lewis's".<ref name="Lewis and Clark Journal"/>{{rp|635}} Six days later they reached the confluence of the Snake and Columbia Rivers, after noting a number of dangerous rapids as well as many native fishing sites on the lower Snake.<ref name="Lewis and Clark Journal"/>{{rp|625–635}} The expedition established friendly relations with the Nez Perces, who they visited again on their return trip in 1806.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/nepe/learn/historyculture/lewis-and-clark.htm|title=Lewis and Clark and the Nez Perce|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|work=Nez Perce National Historic Park|date=|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
Other explorers quickly followed, many of them fur trappers who began scouting the upper Snake River watershed for beaver. [[John Colter]], a former member of the Lewis and Clark expedition, explored the Jackson Hole area in 1808.<ref name="explorers">{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.history.idaho.gov/sites/default/files/uploads/reference-series/0938.pdf |
|||
|title=Snake River Explorers |
|||
|publisher=Idaho State Historical Society |
|||
|work=Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series |
|||
|date=April 1992 |
|||
|access-date=June 24, 2013 |
|||
|archive-date=May 15, 2012 |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120515011912/http://www.history.idaho.gov/sites/default/files/uploads/reference-series/0938.pdf |
|||
|url-status=dead |
|||
}}</ref> In 1810, [[Andrew Henry (fur trader)|Andrew Henry]] explored and named the Henrys Fork of the Snake River. He established Fort Henry, the first American fur trading post west of the Rocky Mountains, but abandoned it after that year's harsh winter.<ref name="explorers"/> The 1811 [[Pacific Fur Company]] expedition led by [[Wilson Price Hunt]] attempted to find a route from Henrys Fork to the Columbia River. After suffering a wreck in the falls of the Snake River Canyon, they took an overland route through the Snake River Plain, through what is now the Boise Valley or Treasure Valley, then crossed the Blue Mountains to bypass Hells Canyon and reach the lower Snake River.<ref name="COTM"/> After the hazardous experience, Hunt gave it the name "Mad River".<ref>{{cite web|url=https://truewestmagazine.com/article/trailing-wilson-price-hunts-astorians-west/|title=Trailing Wilson Price Hunt's Astorians West|publisher=True West|author=Moulton, Candy|date=October 1, 2005|accessdate=February 1, 2023}}</ref> A group led by [[Robert Stuart (explorer)|Robert Stuart]], a member of the Hunt expedition, returned eastward across the plain the following year. The route they mapped would eventually become that section of the [[Oregon Trail]].<ref name="COTM">{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/parkhistory/online_books/crmo/hcs/chap3.htm|title=Close Encounters: The Fur Trade in the Craters of the Moon Region, 1820-1856|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|work=Historic Context Statements: Craters of the Moon National Monument, Idaho|author=Louter, David|year=1995|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Twin Falls Snake River Idaho, O.S.L.R.R. C.R. Savage, Salt Lake. (cropped).jpg|thumb|right|280px|The cataracts of the Snake River forced early explorers and settlers to travel overland. This is Twin Falls, upstream of Shoshone Falls, as it appeared c. 1871.|alt=Black and white photograph of two parallel waterfalls, dropping over a dark cliff face into a turbulent pool.]] |
|||
In 1818 [[Donald Mackenzie (explorer)|Donald Mackenzie]] and [[Alexander Ross (fur trader)|Alexander Ross]] established [[Fort Nez Percés]] for the [[North West Company]] near the confluence of the Snake and Columbia Rivers.<ref>{{cite book|title=The Nez Perce Indians and the Opening of the Northwest|author=Josephy, Alvin M.|publisher=Houghton Mifflin|isbn=9780395850114|year=1997|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=D1Ffhzz0UOkC}}</ref>{{rp|53–58}} The following year, Mackenzie traveled up the Snake River and reached Boise Valley by making the first recorded river ascent of Hells Canyon.<ref name="explorers"/> Mackenzie's goal was to bypass the arduous trek over the Blue Mountains. He wrote that "the passage by water is now proved to be safe and practicable for loaded boats, without one single carrying place or portage; therefore, the doubtful question is set at rest forever. Yet from the force of the current and the frequency of rapids, it may still be advisable, and perhaps preferable, to continue the land transport."<ref name="Williamson 1997"/>{{rp|19}} |
|||
Canadian fur trappers with the British [[Hudson's Bay Company]] (HBC) reached the Snake River watershed in 1819.<ref name="EOI">{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.uh.edu/engines/epi2411.htm |
|||
|title=Hudson's Bay Company |
|||
|publisher=University of Houston |
|||
|work=Engines of our Ingenuity |
|||
|last=Kaza |
|||
|first=Roger |
|||
|access-date=October 5, 2009 |
|||
|archive-date=September 28, 2012 |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120928053341/http://www.uh.edu/engines/epi2411.htm |
|||
|url-status=live |
|||
}}</ref> As American fur trappers kept coming to the region, the HBC ordered the Canadians to kill as many beavers as they could, under the rationale that "if there are no beavers, there will be no reason for the Yanks to come," and even if the Americans did ultimately gain control, the HBC would already have taken all the profit.<ref name="EOI"/> Focused primarily on the upper Snake River region, the "fur desert" policy was carried out in nine expeditions from about 1824–1831 and aimed to decrease the Americans' economic interest in the [[Oregon Country]], the vast region of the Pacific Northwest centering on modern-day British Columbia, Washington, Oregon and Idaho. By the time the Americans annexed [[Oregon Territory]] in 1848, beaver were nearly extirpated across much of the Rocky Mountains.<ref name="EOI"/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://scholarworks.umt.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2828&context=etd|title=Clearing the Country: A History of the Hudson's Bay Company's Fur Desert Policy|author=Ott, Jennifer Susan|publisher=University of Montana|year=1997|accessdate=January 6, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Starting in the 1840s, the Oregon Trail became well established, and thousands of settlers passed through the Snake River Plain on their way to the [[Willamette Valley]]. Coming from Wyoming, the Oregon Trail reached the Snake River at [[Fort Hall, Idaho]], and stayed south of the river until [[Three Island Crossing State Park|Three Island Crossing]] near modern-day [[Glenns Ferry, Idaho|Glenns Ferry]].<ref name="Idaho Parks Three Island Crossing">{{cite web|url=https://parksandrecreation.idaho.gov/parks/three-island-crossing/history/|title=History of Three Island Crossing State Park|publisher=Idaho Department of Parks and Recreation|date=|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> Here the trail diverged, with the northern route fording the river to reach the HBC trading post at [[Fort Boise]] while the southern route continued into what is now the eastern Oregon desert. While the northern route passed through more favorable country, the Snake River posed a formidable barrier; during high water, many travelers were forced to take the hot, dry southern route, or risk drowning.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/oreg/planyourvisit/three-island-crossing.htm|title=Three Island Crossing State Park|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|work=Oregon National Historic Trail|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> Travelers going via Fort Boise had to cross the river one more time to rejoin the trail heading west. A ferry existed at Fort Boise since at least 1843;<ref name="Snake River ferries">{{cite web|url=https://apps.itd.idaho.gov/apps/env/cultural/ENV_SnakeRiverFerries2017.pdf|title=Research Guide on Snake River Ferries|publisher=Idaho Transportation Department|date=Jan 2017|accessdate=January 6, 2024}}</ref> the Three Island crossing was also replaced by a ferry in 1869.<ref name="Idaho Parks Three Island Crossing"/> A new wave of travelers came in the 1860s with the [[Montana Trail]] providing access to gold strikes in Montana Territory. This crossed the Snake River by the Eagle Rock Ferry and later a bridge which the city of Idaho Falls would soon grow around.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://history.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/0033.pdf|title=Eagle Rock|publisher=Idaho State Historical Society|work=Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series|date=Jan 1993|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
===Conquest and conflict=== |
|||
[[Image:Fort Boise showing exterior walls, Snake River near the mouth of the Boise River, Idaho, 1849 (AL+CA 1475).jpg|thumb|right|The first [[Fort Boise]] (illustration by Major Osborne Cross, c. 1849) was an key supply point on the Oregon Trail.|alt=Sketch of a square walled fort on a low hill above a waterway; in the foreground are a boat and a person fishing]] |
|||
As the flow of settlers increased, the Nez Perce and their neighbors the [[Cayuse people|Cayuse]] and [[Walla Walla people|Walla Walla]] came under pressure to cede portions of their territory. Tensions flared in 1855 after tribes were coerced into relinquishing huge amounts of territory in the [[Treaty of Walla Walla]].<ref name="Treaty Period"/> In retaliation for [[Edward Steptoe|Lt. Col. Edward Steptoe]]'s defeat at the 1858 [[Battle of Pine Creek]], a force led by [[George Wright (general)|Col. George Wright]] entered the lower Snake River country in 1859 and constructed Fort Taylor at the confluence of the Tucannon River below present-day [[Starbuck, Washington]]. Over several months Wright fought the natives along the river, killing their horses and destroying stored food.<ref name="Petersen and Reed">{{cite web|url=https://damsense.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/CCC_aHistoryOf-LSRdevelopment_OCR.pdf|title=Controversy, Conflict and Compromise: A History of the Lower Snake River Development|publisher=DamSense|author=Petersen, Keith C. |author2=Reed, Mary E.|date=|accessdate=January 6, 2024}}</ref>{{rp|37}} The sternwheeler ''[[Colonel Wright (sternwheeler)|Colonel Wright]]'' was commissioned to haul supplies up the Snake River to Fort Taylor. Captained by veteran Oregon river pilot Len White, the ''Wright'' was the first steamboat to run on the Snake River and the Columbia above [[The Dalles, Oregon|The Dalles]].<ref name="Williamson 1997"/>{{rp|75–76}}<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|37}} |
|||
Two years later, [[Elias D. Pierce]] discovered gold to the east on Nez Perce treaty land.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|42–43}} As thousands of fortune seekers flocked to the area, the city of Lewiston was founded in 1861, in violation of the 1855 treaty. The US government sided with the settlers, and pressured some Nez Perce leaders into signing a second treaty which shrank their reservation by 90 percent. Many Nez Perce including [[Chief Joseph]]'s band refused to leave, calling the new treaty the "thief treaty".<ref name="Treaty Period"/> In March 1863, the [[Idaho Territory]] was split from Oregon, and Lewiston became its capital. More than 60,000 prospectors and others entered the Lewiston Valley by 1863.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|43}} Many new steamboats were pressed into service, including the ''Spray'', ''Cascadilla'', ''[[Tenino (sternwheeler)|Tenino]]'', ''Okanogan'', and ''[[Nez Perce Chief (sternwheeler)|Nez Perce Chief]]''. The river's rapids posed a major navigation hazard, and from November to April the river was generally too low for ships. Despite these challenges, the water transport of freight and passengers was greatly profitable.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|43}} |
|||
Up river, the Shoshone and other tribes were also becoming increasingly wary of settlers; in 1854 a Shoshone war party attacked a wagon train in the Boise Valley, and the U.S. Army mounted a counterattack, the [[Winnas Expedition]]. The situation became so unstable that Fort Boise was abandoned, and the Army had to escort wagon trains through the area.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.hmdb.org/m.asp?m=22328|title=The Ward Massacre|publisher=The Historical Marker Database|date=|accessdate=December 14, 2023}}</ref> While early settlers had simply passed through this area on their way to Oregon, gold strikes brought renewed interest in the 1860s. The Army rebuilt Fort Boise further east of the original site in 1863. A military detachment was stationed there to quell any further violence; however, tensions continued to increase, and more wagon trains and mining parties were attacked. Starting in 1864, the [[Snake War]] was fought across much of southern Idaho, with numerous battles between the U.S. Army and the Shoshone, Bannock and Paiute.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://history.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/0236.pdf|title=The Snake War, 1864–1868|publisher=Idaho State Historical Society|work=Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series|year=1966|accessdate=December 14, 2023}}</ref> By 1868, exhausted after years of fighting, [[Pocatello (Shoshone leader)|Chief Pocatello]] and many others surrendered and relocated to the [[Fort Hall Indian Reservation]] on the Snake River in southeast Idaho.<ref>{{cite book|author=Treuer, Anton|title=Atlas of Indian Nations|publisher=National Geographic Books|isbn=9781426211607|year=2013|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XQbaCwAAQBAJ}}</ref>{{rp|226}} |
|||
[[Image:American Falls, Idaho with view of Union Pacific Railroad, between 1910 and 1920 (AL+CA 1499).jpg|thumb|left|280px|A train crosses the Snake River at American Falls, c. 1915. Railroads first reached the Snake River Plain in the 1880s.|alt=A painted postcard shows a train crossing a bridge above a wide waterfall and turbulent river.]] |
|||
Tribal resistance would continue for years to come. In 1877 the US government attempted to force the remaining Nez Perce onto their reservation, at which point Chief Joseph's band and several others opted to seek refuge elsewhere. After a treacherous crossing of the Snake at Dug Bar, Hells Canyon on May 31,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/nepe/planyourvisit/visit-dug-bar.htm|title=Visit Dug Bar|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|work=Nez Perce National Historic Park|date=|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> the Nez Perce were pursued by the Army for over {{convert|1000|mi|km}} east, through Yellowstone before turning north through Montana, fighting several battles along the way. On October 5, 1877, Chief Joseph surrendered to US forces. thus ending the [[Nez Perce War]]. The survivors were distributed to various reservations across the western US.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.usgs.gov/index.php/observatories/yvo/news/flight-nez-perce|title=The Flight of the Nez Perce|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|date=July 18, 2022|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> In 1878, an uprising occurred in response to overcrowding and food shortages at the Fort Hall Reservation, leading to the [[Bannock War]]. The US army defeated the Bannock and their Paiute allies and proceeded to restrict travel in and out of the reservation.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.intermountainhistories.org/items/show/412|title=1878 Bannock War and Chief Buffalo Horn|publisher=Intermountain Histories|author=Richardson, Camilla|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
While Lewiston was now well connected by river, travel to Boise and other points upstream on the Snake River remained difficult due to the formidable obstacle of Hells Canyon. In 1865, Thomas Stump attempted to pilot the ''Colonel Wright'' up Hells Canyon, making it {{convert|80|mi|km}} upriver before hitting rocks in a rapid, forcing their retreat.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|45}} On the Snake River above Hells Canyon, several steamboats were built at great expense (as manufactured parts such as engines had to be hauled in overland), the first being the ''[[Shoshone (Snake River sternwheeler)|Shoshone]]'' in 1866. However, running the upper Snake proved unprofitable, due to lack of demand. The owners of ''Shoshone'' decided to move her to the lower Snake River, and in April 1870, they made the first successful river descent of Hells Canyon, a harrowing ride that skirted disaster several times.<ref name="Williamson 1997"/>{{rp|85–88}} In 1895 the steamboat ''Norma'', which had been built to haul copper ore on the Snake River above Hells Canyon, also made the run under similar circumstances.<ref name="USFS Hells Canyon"/><ref name="Williamson 1997"/>{{rp|167–172}} |
|||
In the 1870s, Boise (to which Idaho's capital was moved in 1866) expanded rapidly as growth slowed in Lewiston. Gold drew more than 25,000 prospectors to the Boise Valley, and a new city quickly grew around the U.S. Army post at Fort Boise.<ref name="Long 2021">{{cite web|url=https://www.historylink.org/file/10443|title=Salmon in the Pacific Northwest|author=Long, Priscilla|publisher=HistoryLink|date=January 7, 2021|accessdate=December 12, 2023}}</ref><ref name="Idaho irrigation"/> With Hells Canyon impractical for river navigation, interest grew in connecting the area by rail. By 1884, the [[Oregon Railroad & Navigation Company]] (later integrated into [[Union Pacific Railroad|Union Pacific]]) had connected [[Portland, Oregon]], to the Union Pacific line at [[Granger, Wyoming]], via [[Huntington, Oregon|Huntington]] and [[Pocatello, Idaho|Pocatello]]. Boise, initially bypassed due to a steep grade, was connected three years later.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://utahrails.net/pdf/UP-Idaho-Division_1871-1981.pdf|title=A Brief History of Union Pacific Railroad's Idaho Division|publisher=Utah Rails|date=|accessdate=December 12, 2023}}</ref> In addition to commerce, the railroad also opened the Snake River region – which just a few years ago had been seen as a remote, rough frontier – to recreation. The Union Pacific heavily promoted tourism in places like Shoshone Falls, [[Payette Lake]] and [[Soda Springs, Idaho]]. Countering the reputation of southern Idaho as a wasteland, a brochure described Shoshone Falls: "Shoshone differs from every other waterfall in this or the old country. It is its lonely grandeur that impresses one so deeply; all of the other historic places have the adjuncts of civilization, and one is almost overshadowed by a city while in their presence."<ref>{{cite journal|title=Tourists in Wonderland: Early Railroad Tourism in the Pacific Northwest|journal=Columbia Magazine|volume=7|number=4|year=1994|author=Schwantes, Carlos A.|url=https://www.washingtonhistory.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/tourists-in-wonderland.pdf|accessdate=December 12, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
==Reclamation and development== |
|||
===Irrigation=== |
|||
Most travelers on the Oregon Trail regarded the arid Snake River Plain as an obstacle to be crossed, not a land to be settled. This began to change with the Boise gold strikes, where the demands of the mining industry and the difficulty of importing goods set off an agricultural boom in the Boise Valley.<ref name="Long 2021"/><ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|45}} By the 1880s, settlers also came to the upper Snake River north of Idaho Falls, where fertile, sandy soils presented ideal conditions for the iconic [[russet potato]] ("Idaho potato").<ref name="Idaho Falls Power">{{cite web|url=https://www.idahofallsidaho.gov/DocumentCenter/View/495/Idaho-Falls-Power-History-PDF?bidId=|title=Idaho Falls Power – History|publisher=City of Idaho Falls|date=|accessdate=December 9, 2023}}</ref> The dry climate made irrigation necessary, and numerous private irrigation companies were formed.<ref name="Boise irrigation">{{cite web|url=https://history.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/0171.pdf|title=Early Irrigation Canals Pre-Project Ventures|publisher=Idaho State Historical Society|work=Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series|accessdate=December 9, 2023}}</ref> Private canal systems around Boise and Idaho Falls saw some success, but all the easily farmable land was soon developed, and they could not raise the capital for further expansion. In addition, low water by late summer posed a challenge to farmers, and the irrigation companies could not afford to build dams to provide water storage.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/articles/idaho-arrowrock-dam.htm|title=Idaho: Arrowrock Dam|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|date=January 13, 2017|accessdate=December 9, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:-IDAHO-A-0009-_American_Falls_Dam_(5440020069).jpg|thumb|right|280px|The first [[American Falls Dam]] (1927, rebuilt 1978) was constructed to store water for the federal [[Minidoka Project]].|alt=View across a river, with a concrete dam on the left and a bridge on the right with a town on the opposite bank.]] |
|||
With many private irrigation companies verging on insolvency, the federal government began to explore programs assisting agricultural development. The 1894 [[Carey Act]] granted large tracts of dry federal land to western states, which then sold the land to farmers and solicited private investors to organize irrigation districts. Investors would then recoup their capital by selling water rights to farmers.<ref name="Idaho irrigation"/> Irrigation plans were reviewed by engineers, who determined the economic feasibility of the projects. Although the Carey Act saw little success in most states, it greatly benefited Idaho. Some 60 percent of all lands developed under the Carey Act were in Idaho, and almost all of that utilized Snake River water.<ref name="Idaho irrigation">{{cite web|url=https://history.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/0260_Irrigation-in-Idaho-1.pdf|title=Irrigation in Idaho|publisher=Idaho State Historical Society|work=Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series|date=Jun 1971|accessdate=December 9, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
[[I. B. Perrine]], who homesteaded near Shoshone Falls in the 1880s, went on to develop one of the most successful Carey Act projects. In 1900 Perrine filed a claim for water from the Snake River, and backed by significant private capital, oversaw the construction of [[Milner Dam]] and a canal system to irrigate some {{convert|250000|acre|ha}} of the Snake River Plain.<ref name="Milner Dam"/> Completed in 1905, the project was an immediate success. The rapid transformation of the barren landscape into productive farmland led to the moniker "[[Magic Valley]]", and led to massive growth of the city of Twin Falls.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://twinfallscanal.com/milner-dam/|title=History of Milner Dam|publisher=Twin Falls Canal Company|date=|accessdate=December 10, 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.tfid.org/DocumentCenter/View/422/History-of-Twin-Falls?bidId=|title=The History of Twin Falls|publisher=City of Twin Falls|date=|accessdate=December 10, 2023}}</ref> During certain times of the year, almost all the Snake River's flow was diverted at Milner Dam, and since then, Shoshone Falls has regularly run dry in the summer.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.idahoconservation.org/blog/the-power-of-water-making-the-magic-valley-magic/|title=The power of water: Making the Magic Valley magic|publisher=Idaho Conservation League|author=Urbanek, Abby|date=March 7, 2023|accessdate=December 19, 2023}}</ref> The [[Idaho State Historical Society]] writes that "Perrine’s venture contrasted remarkably with private canal company failures that led to congressional provision for federal reclamation projects after 1902. As a rare successful example of state supervised private irrigation development provided for in [the Carey Act] of 1894, Milner Dam and its canal system have national significance in agricultural history."<ref name="Milner Dam">{{cite web|url=https://history.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/0497_Milner-Dam.pdf|title=Milner Dam|publisher=Idaho State Historical Society|work=Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series|year=1985|accessdate=December 10, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
With the creation of the Reclamation Service (now the [[Bureau of Reclamation]]) in 1902, the federal government began to play a more direct role in water resources development. The expansive [[Minidoka Project]] was the first federal reclamation project in Idaho.<ref name="NPS Minidoka">{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/articles/idaho-minidoka-dam.htm|title=Idaho: Minidoka Dam|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|date=|accessdate=December 11, 2023}}</ref> Starting with [[Minidoka Dam]] in 1906, the project would grow over the next few decades to include major reservoirs at [[Jackson Lake Dam|Jackson Lake]], [[American Falls Dam|American Falls]] and [[Island Park Dam|Island Park]], and a large network of canals and pump stations. The Minidoka Project would eventually bring water to a million acres (2,500 km<sup>2</sup>) of the Magic Valley.<ref name="NPS Minidoka"/> During World War II, many [[Minidoka National Historic Site|Japanese Americans interned at Minidoka]] were made to work on the project.<ref name="NPS Minidoka"/> The [[Boise Project]], which would ultimately water {{convert|500000|acre|ha}} in and around the Boise Valley, was another major early reclamation undertaking. At its completion, [[Arrowrock Dam]] (1915) on the Boise River was the tallest dam in the world, and its construction process was an important prototype for future federal projects such as [[Hoover Dam]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.intermountainhistories.org/items/show/114|title=Arrowrock Dam, Engineering Innovation and Building Block to Boise's Expansion|publisher=Intermountain Histories|author=Hyde, Luke|accessdate=December 19, 2023}} |
|||
</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.usbr.gov/projects/pdf.php?id=74|title=The Boise Project|author=Simonds, Joe|work=Bureau of Reclamation History Program|year=1997|publisher=U.S. Bureau of Reclamation|accessdate=December 19, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Palisades_Dam_(4306260425).jpg|thumb|left|[[Palisades Dam]] (1956) provides irrigation and flood control for the Snake River upstream of Idaho Falls.|alt=Aerial view looking upstream at an earthen dam and a reservoir stretching off into a mountain valley in the distance]] |
|||
Starting around the 1950s, farmers made heavy use of the Snake River aquifer, bringing large new areas into production.<ref name="Idaho irrigation"/> Surface water development also increased with projects such as [[Cascade Dam]] (1948) and [[Anderson Ranch Dam]] (1950), which provided additional storage for the Boise Project. [[Palisades Dam]] was built in 1956, providing flood control and irrigation for the Snake River above Idaho Falls, an area which the Bureau of Reclamation had previously overlooked.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.intermountainhistories.org/items/show/92|title=The Palisades Dam: Irrigation of the Snake River|author=Franzen, Josh|publisher=Intermountain Histories|accessdate=December 19, 2023}} |
|||
</ref> Near Rexburg, the [[Teton Dam]] was also built to provide water for this area. In 1976, the Teton Dam failed catastrophically, killing eleven people and causing at least $400 million in damage along the Henrys Fork and Snake Rivers.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://damfailures.org/case-study/teton-dam-idaho-1976/|title=Case Study: Teton Dam (Idaho), 1976|publisher=Association of State Dam Safety Officials|date=|accessdate=January 10, 2024}}</ref> The political fallout from this disaster marked the end of large new irrigation developments not only for the Snake River system, but for the Bureau of Reclamation as a whole.<ref>{{cite book|title=The Bureau of Reclamation: From Developing to Managing Water, 1945-2000|publisher=U.S. Government Printing Office|isbn=9780160913648|year=2013|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=65sl1m7QntkC}}</ref> {{rp|839–841}} |
|||
Agriculture has significantly impacted water quality in the Snake River upstream of Hells Canyon. Water removed from the river for irrigation becomes contaminated with chemical fertilizers and manure, and percolates into the Snake River Aquifer. Pollutants collect in the groundwater and eventually enter the river via spring flows.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://imnh.isu.edu/digitalatlas/hydr/concepts/gwater/gwr.htm |
|||
|title=Groundwater Resources |
|||
|work=Digital Atlas of Idaho |
|||
|publisher=Idaho Museum of Natural History |
|||
|access-date=October 11, 2009 |
|||
|archive-date=June 25, 2010 |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100625013845/http://imnh.isu.edu/digitalatlas/hydr/concepts/gwater/gwr.htm |
|||
|url-status=live |
|||
}}</ref> Excess nitrogen, phosphorus and bacterial loads occur in many locations across southern Idaho.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.idahoconservation.org/blog/pollution-science-understanding-the-building-blocks-for-restoring-idahos-snake-river/|title=Pollution Science: Understanding the building blocks for restoring Idaho's Snake River|publisher=Idaho Conservation League|author=Black, Lexi|date=January 26, 2024|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> Large [[algae bloom]]s are a recurring issue in summer.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url = http://www.cwnp.org/naturalist/snakealgae.html |
|||
|title = Pollution of the Snake River |
|||
|publisher = Central Washington Native Plants |
|||
|work = Ecology and Conservation |
|||
|access-date = October 11, 2009 |
|||
|url-status = dead |
|||
|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20091023133751/http://www.cwnp.org/naturalist/snakealgae.html |
|||
|archive-date = October 23, 2009 |
|||
}}</ref> The [[U.S. Environmental Protection Agency]] has established water quality guidelines for Snake River flows entering Hells Canyon, which cover bacteria, mercury, excess nutrients, pesticides, sediments and water temperature. Implementation of the guidelines include [[Best management practice for water pollution|best management practices]] for agriculture and forestry, and regular water quality monitoring.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://attains.epa.gov/attains-public/enwiki/api/documents/actions/IDEQ/10745/106704|title=Snake River - Hells Canyon Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL)|publisher=U.S. Environmental Protection Agency|year=2004|accessdate=January 31, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
===Hydroelectricity=== |
|||
{{See also|List of dams in the Columbia River watershed|Bonneville Power Administration}} |
|||
Power development of the Snake River began in the early 20th century as cities, farms, mines and industry grew around the river. The first small hydroelectric plant on the Snake River, [[Swan Falls Dam]], was built in 1901,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.idahopower.com/community-recreation/recreation/parks-and-campgrounds/swan-falls-park/|title=Swan Falls Park|publisher=Idaho Power|date=|accessdate=November 27, 2023}}</ref> followed by one at [[American Falls, Idaho|American Falls]] in 1902.<ref name="Idaho Power hydro plants"/> Many other projects followed, particularly around Shoshone Falls where the natural drop of the river offered great energy potential. After developing the Milner Dam irrigation scheme, I. B. Perrine built a hydroelectric plant at Shoshone Falls in 1907.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://magicvalley.com/news/local/hidden-history-the-power-plant-at-shoshone-falls/article_e03d8ccf-eb52-5ddd-a6c5-ec581a16472d.html|title=Hidden History: The Power Plant at Shoshone Falls|work=The Times-News|author=Matthews, Mychel|date=December 20, 2012|accessdate=November 27, 2023}}</ref> Small private utilities built power plants at Salmon Falls (1910) and Thousand Springs (1912). [[Idaho Power]] was incorporated in 1915, and acquired all the aforementioned plants the following year. It proceeded to build a second, larger plant at Shoshone Falls in 1921, and another plant at Twin Falls in 1935.<ref name="Idaho Power hydro plants">{{cite web|url=https://www.idahopower.com/energy-environment/energy/energy-sources/hydroelectric/hydroelectric-plants/|title=Hydroelectric Plants|publisher=Idaho Power|accessdate=November 26, 2023}}</ref> The advent of electric pumps opened up large new areas to agriculture, which had previously been limited to land where water could flow by gravity. The Minidoka Project, which included the Bureau of Reclamation's first hydroelectric plant in Idaho, was an early adopter of this system. The project generated more power than it needed, and surplus was sold to nearby towns such as [[Burley, Idaho|Burley]] and [[Rupert, Idaho|Rupert]], which created their own municipal electric systems.<ref>{{cite book|title=The Wired Northwest: The History of Electric Power, 1870s-1970s|author=Hirt, Paul W.|publisher=University Press of Kansas|year=2012|isbn=9780700618736|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1FmqEAAAQBAJ}}</ref>{{rp|89–92}} |
|||
[[Image:Hells Canyon High Dam ID-OR1.jpg|thumb|left|Rendering of the Army Corps' proposed high dam in Hells Canyon|alt=Black and white sketch of a proposed dam project in a steep river canyon]] |
|||
[[Image:Snake River, Hell's Canyon Dam - DPLA - 3388c494be113a0741a34f3e564b98ad.jpg|thumb|left|Hells Canyon Dam is the lowermost of three dams in Idaho Power's Hells Canyon hydroelectric complex.|alt=Front view of a concrete dam, with a river flowing off downstream to the left.]] |
|||
By the 1940s, following the construction of massive hydropower dams on the Columbia River such as Grand Coulee, interest turned to the considerable untapped power potential of the Snake River in Hells Canyon. In 1947, Idaho Power set its sights on the upper section of the canyon, where it proposed a series of three medium-sized dams. Two years later, the [[U.S. Army Corps of Engineers]] (Army Corps) proposed a single massive dam, over {{convert|700|ft|m}} high, to be built in lower Hells Canyon. In 1955 the Federal Power Commission authorized the Idaho Power project, but initially only one of the three dams, [[Brownlee Dam|Brownlee]] (completed 1958), was built. The other dams, located downstream, would have been in the flood zone of not only the Army Corps' high dam, but two other competing proposals.<ref name="Hells Canyon high dams"/> |
|||
The Pacific Northwest Power Company, a consortium of four private utilities, proposed the "High Mountain Sheep Dam" on the Snake River just upstream of the Salmon River. The even bigger "Nez Perce Dam", proposed by the Washington Public Power Supply System, would be located downstream of the Salmon River. While that location offered greater power potential, the fishery supported by the Salmon River was considered too economically valuable to wipe out, and in 1964 the Commission chose to authorize the High Mountain Sheep project.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://collaboration.idfg.idaho.gov/FisheriesTechnicalReports/Mgt-Smith1957%20Mountain%20Sheep-Pleasant%20Valley%20Hydroelectric%20Project%20on%20the%20Middle%20Snake%20River%20in%20Idaho%20and%20Oregon%20by%20PacNWPow.pdf|title=Mountain Sheep-Pleasant Valley Hydroelectric Project on the Middle Snake River in Idaho and Oregon|publisher=Idaho Department of Fish and Game|accessdate=November 26, 2023}}</ref><ref name="Hells Canyon high dams">{{cite web|url=https://www.nwcouncil.org/reports/columbia-river-history/hellscanyon/|title=Hells Canyon|publisher=Northwest Power and Conservation Council|date=|accessdate=November 26, 2023}}</ref> By then, significant public opposition had formed against the high dam, as it would still block salmon migration to the upper Snake, and adversely affect wildlife and recreational values in Hells Canyon. It was also challenged by Washington Public Power, which argued that the commission should give priority to public utilities over private ones.<ref name="Public History PDX"/> |
|||
The case reached the [[U.S. Supreme Court|Supreme Court]], which in the landmark 1967 ruling of ''Udall v. Federal Power Commission'' issued an injunction temporarily halting the project.<ref name="Hells Canyon high dams"/> Justice [[William O. Douglas]] wrote that in licensing projects, the Commission must consider "future power demand and supply, alternate sources of power, the public interest in preserving reaches of wild rivers and wilderness areas, the preservation of anadromous fish for commercial and recreational purposes, and the protection of wildlife."<ref name="Hells Canyon high dams"/><ref name="Public History PDX">{{cite web|url=https://publichistorypdx.org/2017/06/04/us-supreme-court-halts-construction-high-mountain-sheep-dam/|title=U.S. Supreme Court Halts the Construction of the High Mountain Sheep Dam|publisher=Portland State University|work=Public History PDX|date=June 4, 2017|accessdate=December 10, 2023}}</ref> This was the first time the court cited environmental protection as a consideration for whether to approve a dam project.<ref name="Public History PDX"/> |
|||
In 1975, President [[Gerald R. Ford]] signed the Hells Canyon Wilderness into law, ending the high dam project for good.<ref name="Hells Canyon high dams"/> |
|||
Meanwhile, Idaho Power moved forward with the [[Oxbow Dam|Oxbow]] and [[Hells Canyon Dam]]s, though the question of fish passage still remained. From 1956 to 1964, returning adult salmon had been trapped at the base of Brownlee Dam (whose height made a fish ladder impractical) and released upstream. Downstream passage of juvenile salmon posed a much bigger problem; many were killed passing through the hydroelectric turbines, and efforts to trap and release them downstream met with failure.<ref name="Hells Canyon high dams"/> In 1960, Idaho Power proposed abandoning fish passage altogether and compensating for the loss by building [[fish hatchery|fish hatcheries]]. By 1966 it reached an agreement with the Federal Power Commission to move forward with the hatchery plan, and by 1967 both Oxbow and Hells Canyon dams had been completed, neither with provision for fish passage. Idaho Power was tasked with building and operating the Oxbow, Rapid River, Niagara Springs and Pahsimeroi fish hatcheries at its own expense.<ref name="Hells Canyon high dams"/><ref name="Columbia River fish passage"/> |
|||
As of 2007, the Hells Canyon Hydroelectric Complex was responsible for 40 percent of Idaho Power's total power generation.<ref name="HCHP relicensing"/> The three dams have a capacity of 1,167 [[megawatt]]s combined<ref>{{cite web|url=https://oemr.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/Idaho-Energy-Landscape-2021.pdf|title=Idaho Energy Landscape|year=2021|publisher=Idaho Governor's Office of Energy and Mineral Resources|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> and produce about 6,053 gigawatt hours per year.<ref name="HCHP relicensing">{{cite web|url=https://docs.idahopower.com/pdfs/relicensing/hellscanyon/hellspdfs/hcc_feis_2007.pdf|title=Final Environmental Impact Statement for Hydropower License, Hells Canyon Hydroelectric Project|publisher=Idaho Power|date=August 2007|accessdate=December 10, 2023}}</ref> Idaho Power's hatcheries produce almost seven million salmon and steelhead smolt to release in the Snake River system each year.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.idahopower.com/energy-environment/environmental-stewardship/fish-aquatic-life/our-hatchery-program/|title=Our Hatchery Program|publisher=Idaho Power|date=|accessdate=December 10, 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://hydroleadermagazine.com/jim-chandler-on-idaho-powers-plans-to-improve-fisheries-and-water-quality-in-the-snake-river/|title=Jim Chandler on Idaho Power's Plans to Improve Fisheries and Water Quality in the Snake River|publisher=Hydro Leader|date=9 May 2022|accessdate=December 10, 2023}}</ref> Since the completion of the Hells Canyon complex, with the exception of the lower Snake River dams, only one major hydroelectric dam has been built in the Snake River system – the Army Corps' [[Dworshak Dam]] (1973), in the Clearwater River basin. Like the Hells Canyon dams, Dworshak also generated controversy over its impact on fisheries, and also made no provision for fish passage; rather, a hatchery was built at the base of the dam.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://news.yahoo.com/dworshak-dam-last-kind-reaches-035900576.html|title=Dworshak Dam: The 'last of its kind' reaches milestone|publisher=Yahoo News|work=Moscow-Pullman Daily News|author=Hedberg, Kathy|date=October 1, 2023|accessdate=December 10, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
===Navigation=== |
|||
[[Image:08395-Lewiston, Idaho-1906-Loading Wheat on the Snake River-Brück & Sohn Kunstverlag.jpg|thumb|right|Bags of grain are loaded on the sternwheeler ''Spokane'' at Lewiston, c. 1906.|alt=A steamboat waits at a pier on a river bank while sacks of cargo are loaded.]] |
|||
As gold mining declined in the late 19th century, the wheat industry boomed in the Palouse of southeast Washington. By the 1870s, the [[Oregon Steam Navigation Company]] was operating seven steamboats transporting grain from the Snake River to lower Columbia River ports. These were the ''[[Harvest Queen (sternwheeler)|Harvest Queen]]'', ''John Gates'', ''Spokane'', ''[[Annie Faxon (sternwheeler)|Annie Faxon]]'', ''Mountain Queen'', ''[[R.R. Thompson (sternwheeler)|R.R. Thompson]]'', and ''[[Wide West]]''.<ref name="Gulick">{{cite book |
|||
|last=Gulick |
|||
|first=Bill |
|||
|title=Steamboats on Northwest Rivers |
|||
|publisher=Caxton Press |
|||
|year=2004 |
|||
|isbn=0-87004-438-9}}</ref>{{rp|122}} In the 1890s, a huge copper deposit was discovered at Eureka Bar in Hells Canyon. Several ships transported ore from there to Lewiston, including ''[[Imnaha (sternwheeler)|Imnaha]]'', ''[[Mountain Gem (sternwheeler)|Mountain Gem]]'', and ''Norma''.<ref name="Gulick"/>{{rp|162}} In 1893 the ''Annie Faxon'' suffered a boiler explosion and sank on the Snake below Lewiston, killing five people.<ref name="hlsteamboats">{{cite web |
|||
|last=Dougherty |
|||
|first=Phil |
|||
|url=http://www.historylink.org/index.cfm?DisplayPage=output.cfm&File_Id=7722 |
|||
|title=Steamers on the Lower Snake |
|||
|publisher=HistoryLink |
|||
|date=April 9, 2006 |
|||
|access-date=October 5, 2009 |
|||
|archive-date=August 18, 2009 |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090818191314/http://www.historylink.org/index.cfm?displaypage=output.cfm&file_id=7722 |
|||
|url-status=live |
|||
}}</ref><ref name="Williamson 1997"/>{{rp|160}} Starting in the 1880s, the Army Corps began dredging the Snake River below Lewiston to maintain a {{convert|5|ft|m|adj=on}} deep navigation channel.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|67}} |
|||
River traffic declined rapidly once railroads arrived. By 1899, the Union Pacific line along the south bank of the Snake River had reached [[Riparia, Washington]]. It then joined forces with the [[Northern Pacific Railroad]], which was building a line along the north bank, to build the shared Camas Prairie Railroad the rest of the way to Lewiston, which it reached in 1908.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|56, 80–81}} The Open River Transportation Company, which operated steamboats between Lewiston and [[Celilo Falls]] on the Columbia, went bankrupt in 1912. The 1915 completion of the [[Celilo Canal]] made it much easier for boats from the upper Columbia and Snake to reach Portland, and the Columbia River Transportation Company began operating a water route between Lewiston and Portland. Still, steamboats were unable to compete with railroads on speed and efficiency. The last steamboat on the lower Snake ran in 1920.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|67}} |
|||
Once the railroads monopolized grain shipments, they raised shipping rates, to farmers' consternation. In 1934, political activist Herbert G. West organized the Inland Empire Waterways Association (IEWA), to promote an "open river" – a deep-water shipping channel on the Snake and Columbia Rivers that could compete with rail.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nwcouncil.org/reports/columbia-river-history/visionaries/|title=Visionaries|publisher=Northwest Power and Conservation Council|date=|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> The IEWA initially pushed for improvements such as bigger locks at [[Bonneville Dam]] in 1938 and the construction of [[McNary Dam]] on the Columbia, which would improve navigation to the mouth of the Snake.<ref name="Columbia River fish passage"/> In 1941 a bill was first introduced in Congress authorizing the Army Corps to develop the lower Snake River. The 1941 bill failed, but after several years of debate, Congress finally authorized the Snake River development in 1945.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|83–85}} Early plans included anywhere from six to ten low dams for the lower Snake. Eventually this was reduced to four bigger dams, which would lower costs, but would require what at the time were the tallest navigation locks in the world, at over {{convert|100|ft|m}}.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|83–85}} |
|||
Tribes, state wildlife agencies and the fishing industry opposed the dams, arguing that they would kill too many salmon.<ref name="Columbia River fish passage"/> In 1947, the [[U.S. Department of the Interior]] proposed a ten-year moratorium on dam construction while the fishery problem was studied. With the onset of the [[Cold War]], rising electricity demand in the Pacific Northwest – particularly at the nearby [[Hanford Site|Hanford nuclear site]] – turned the project's focus towards hydropower. By 1948, the Army Corps estimated that over 80 percent of the economic benefits would come from power, and only 15 percent from navigation.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|97–101}} Dam opponents countered that if the primary objective was now power, other dam sites existed in the Northwest that would have less impact on fish. These objections proved futile, as the lower Snake River dams were already authorized, and the federal government had little interest in studying alternatives.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|100–103}} While opponents continued to stall the project for a few more years, Washington Senator [[Warren G. Magnuson]] pushed through a budget amendment in 1955 to start construction on the first dam, [[Ice Harbor Dam|Ice Harbor]].<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|104}} |
|||
[[Image:IcHrbrDam2.jpg|thumb|left|[[Ice Harbor Dam]] (1962) was the first of four Army Corps dams constructed along the lower Snake River, and the final dam on the river before it joins the Columbia.|alt=Aerial view of a concrete dam on a river surrounded by rolling hills and farmland]] |
|||
Once construction began in 1956, Congress quickly approved more money to finish the project. Ice Harbor Dam was completed in 1962, and [[Lower Monumental Dam|Lower Monumental]] and [[Little Goose Dam]]s were completed in 1969 and 1970.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.spokesman.com/stories/2016/oct/24/lower-snake-river-dams-have-a-long-history-of-cont/|title=Lower Snake River dams have a long history of controversy|author=Kramer, Becky|work=The Spokesman-Review|date=October 24, 2016|accessdate=January 16, 2024}}</ref> The Lower Monumental project generated controversy as it threatened to flood the [[Marmes Rockshelter]] archeological site. Although the Army Corps agreed to build a dike around the site, it began to leak as the reservoir filled and the site was inundated.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.seattletimes.com/pacific-nw-magazine/site-unseen-floodwaters-buried-a-treasure-trove-at-marmes-rockshelter/|title=Site unseen: Floodwaters buried a treasure trove at Marmes Rockshelter|author=Judd, Ron|work=Pacific NW Magazine/The Seattle Times|date=November 22, 2017|accessdate=January 17, 2024}}</ref> By the 1970s, the environmental movement in the US had become significantly larger, and groups such as the [[Association of Northwest Steelheaders]] lobbied to stop the construction of the fourth dam, [[Lower Granite Dam|Lower Granite]]. These efforts were unsuccessful, and the dam was completed in 1975. The first upriver barge reached Lewiston on April 10 of that year.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|141}} The Army Corps had planned one more dam at [[Asotin, Washington|Asotin]], which would have extended navigation to mines upstream of Lewiston.<ref name="Petersen and Reed"/>{{rp|127–134}} Faced with public opposition, Congress deauthorized the project in 1975.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.rivers.gov/sites/rivers/files/2022-10/Public%20Law%2094-199.pdf|title=Public Law 94-199, 94th Congress: An act to establish the Hells Canyon National Recreation Area in the States of Oregon and Idaho, and for other purposes|publisher=U.S. National Wild and Scenic Rivers System|date=December 31, 1975|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Once the dams were completed, barges up to 12,000 tonnes and drawing {{convert|14|ft|m}} of water were able to reach Lewiston.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1975/04/13/archives/idaho-gets-a-seaport-capping-a-costly-10year-effort.html|title=Idaho Gets a Seaport, Capping a Costly 10-Year Effort|work=The New York Times|author=Blumenthal, Ralph|date=April 13, 1975|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> Today, multiple barge terminals operate along the lower Snake, including Lewiston, Clarkston, [[Port of Whitman County|Wilma]], Central Ferry and [[Almota, Washington#History of Almota|Almota]].<ref name="LSRD Benefit Replacement Report"/> Grain accounts for the majority of barge traffic on the river; other shipments include forestry products, fuel, chemicals and fertilizers. In 2020, a total of {{convert|4.2|e6ST|t}} of cargo were barged on the Snake River.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.pnwa.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Snake-River-dredging.pdf|title=Snake River Dredging|publisher=Pacific Northwest Waterways Association|year=2023|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref><ref name="LSRD Benefit Replacement Report">{{cite web|url=https://governor.wa.gov/sites/default/files/2022-11/LSRD%20Benefit%20Replacement%20Final%20Report_August%202022.pdf|title=Lower Snake River Dams: Benefit Replacement Report|date=August 2022|publisher=Office of the Governor, State of Washington|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> Since 2000, the tonnage of commercial shipping on the Snake River has declined, due mostly to the loss of petroleum products after a pipeline was constructed. After the general decline of the [[Great Recession]], other sectors have been slow to recover.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://portoflewiston.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/port-of-lewiston-dredging-analysis-Fruits-2014.pdf|title=Review of Comments Regarding the Economics of Lower Snake River Dredging|author=Fruits, Eric|publisher=Port of Lewiston|date=October 2014|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> As of 2015, grain tonnage had fallen about a third from 2000 levels, while forestry products had fallen by nearly three-quarters, with many shipments switching back to rail.<ref name="Jones 2015">{{cite web|url=https://www.wildsalmon.org/images/PDFs/Fact_Sheets/LSD.Navigation.Study.2015.Final.pdf|title=Lower Snake River Dam Navigation Study|publisher=Save Our Wild Salmon|author=Jones, Anthony|date=September 30, 2015|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> [[Container shipping]] at the Port of Lewiston ceased in 2015,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://damsense.org/port-of-lewiston-loses-100-percent-of-its-container-traffic/|title=Port of Lewiston loses 100 percent of its container traffic|publisher=DamSense|date=April 8, 2015|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> due to its primary source, the [[Port of Portland (Oregon)|Port of Portland]], no longer receiving containers.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.idahorivers.org/news/2018/1/4/2017-lower-snake-river-freight-transportation-review|title=Lower Snake River commerce hits all-time low|publisher=Idaho Rivers United|author=Laughy, Linwood|date=January 4, 2017|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> From 2015 to 2023, grain exports from the Port of Lewiston have remained relatively steady while [[breakbulk cargo]] has increased.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://portoflewiston.com/our-rivers/shipping-reports/|title=Shipping Reports|publisher=Port of Lewiston|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
As dam opponents had feared, Snake River salmon returns declined greatly after the dams were built. Since 2000, there have been renewed calls for [[Snake River#Dam removal|removing the lower Snake River dams]], which have become a significant political issue for the Pacific Northwest.<ref name="NRDC 2018">{{cite web|url=https://www.nrdc.org/stories/columbia-snake-river-basin-salmon-are-losing-their-way|title=In the Columbia–Snake River Basin, Salmon Are Losing Their Way|author=Helmer, Jodie|date=July 18, 2018|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
==Ecology and environmental issues== |
|||
===Aquatic habitats=== |
|||
[[Image:Shoshone_Falls,_March_2011.jpg|thumb|right|Shoshone Falls forms a complete barrier to upstream movement of fish in the Snake River, and was the historical upper limit of Snake River salmon and steelhead.|alt=A wide, multi-stage waterfall, backed by dark cliffs, cascades into a rocky canyon]] |
|||
The [[World Wide Fund for Nature]] (WWF) divides the Snake River into two [[freshwater ecoregion]]s – the Upper Snake and Columbia Unglaciated – with Shoshone Falls marking the boundary between the two. Shoshone Falls has presented a total barrier to the upstream movement of fish at least since the Bonneville flood 15,000 years ago. The [[Big Wood River]] (the main tributary of the [[Malad River (Gooding County, Idaho)|Malad River]]) is also included in the Upper Snake ecoregion, due to the presence of a separate natural waterfall barrier. As a result, only 35 percent of the fish fauna above Shoshone falls, and 40 percent of the Big Wood River's fish fauna, are shared with the lower Snake River.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.feow.org/ecoregion_details.php?eco=121 |
|||
|title=Columbia Unglaciated |
|||
|publisher=Freshwater Ecoregions of the World |
|||
|work=World Wide Fund for Nature and the Nature Conservancy |
|||
|access-date=April 14, 2010 |
|||
|url-status=dead |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110726052618/http://www.feow.org/ecoregion_details.php?eco=121 |
|||
|archive-date=July 26, 2011 |
|||
}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.feow.org/ecoregion_details.php?eco=122 |
|||
|title=Upper Snake |
|||
|publisher=Freshwater Ecoregions of the World |
|||
|work=World Wide Fund for Nature and the Nature Conservancy |
|||
|access-date=April 14, 2010 |
|||
|url-status=dead |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110726052702/http://www.feow.org/ecoregion_details.php?eco=122 |
|||
|archive-date=July 26, 2011 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
Compared to the lower Snake River and the rest of the Columbia River system, the Upper Snake ecoregion has a high level of [[endemism]], especially among [[freshwater mollusc]]s such as [[Gastropoda|snails]] and [[Bivalvia|clams]]. At least 21 snail and clam species are of special concern, including 15 that appear to exist only in single clusters.<ref name=abell/>{{rp|167–169}} There are 14 fish species found in the Upper Snake region that do not occur elsewhere in the Columbia's watershed, but which do occur in some western Utah watersheds and the [[Yellowstone River]]. These include healthy populations of [[Yellowstone cutthroat trout]] and [[Snake River fine-spotted cutthroat trout]].<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|608}} The [[Wood River sculpin]] is endemic to the Wood River. The [[Shoshone sculpin]] is endemic to the small portion of the Snake River between Shoshone Falls and the Wood River.<ref name=abell>{{cite book |last= Abell |first= Robin A. |author2= David M. Olsen |author3= Eric Dinerstein |author4= Patrick T. Hurley |title= Freshwater Ecoregions of North America: A Conservation Assessment |year= 2000 |publisher= [[Island Press]] |isbn= 1-55963-734-X |display-authors= etal |url= https://archive.org/details/freshwaterecoreg0000unse/page/167 }}</ref>{{rp|167–169}} |
|||
The Snake River below Shoshone Falls is home to about 35 native fish species, of which 12 are also found in the Columbia River and four of which are endemic to the Snake or nearby watersheds: the [[Percopsis transmontana|sand roller]], [[shorthead sculpin]], [[margined sculpin]] and the [[Oregon chub]], which also occurs in a few other Oregon streams.<ref name=abell/> [[Bull trout]] migrate from the main stem of the Snake to spawn in several tributary basins, including the Bruneau,<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|608}} Imnaha and Grande Ronde Rivers.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fws.gov/project/bull-trout-redd-monitoring-wallowa-mountains|title=Bull Trout Redd Monitoring in the Wallowa Mountains|publisher=U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service|date=March 31, 2021|accessdate=January 8, 2024}}</ref> Large [[white sturgeon]], introduced to the Snake River in the 19th century, were once widespread in the Snake River below Shoshone Falls; due to dam construction, only a few fragmented populations remain.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|608–609}} The [[Idaho Department of Fish and Game]] has occasionally recorded sturgeon more than {{convert|10|ft|m}} long in Hells Canyon.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://idfg.idaho.gov/blog/2021/12/when-big-ones-were-biting|title=Hells Canyon sturgeon are so big that anglers don't need to lie about how big they are|publisher=Idaho Department of Fish and Game|date=December 27, 2021|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> Other common introduced species include [[Mountain whitefish|whitefish]], [[pikeminnow]], [[smallmouth bass]], and [[rainbow trout|rainbow]], [[brown trout|brown]], [[brook trout|brook]] and [[lake trout]].<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|608}} |
|||
====Anadromous fish==== |
|||
[[Anadromous]] [[salmonid]]s (''[[Oncorhynchus]]''), including chinook, coho, and sockeye salmon, and [[Columbia River redband trout|redband]] and steelhead trout, were historically the most abundant fish and a [[keystone species]] of the Snake River system.<ref name="American Rivers"/> Benke and Cushing's ''Rivers of North America'' describes the Snake as a "wild salmon factory;"<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|608}} prior to the 19th century, between two and six million adult salmon and steelhead returned each year from the Pacific to spawn in the Snake River watershed.<ref name="American Rivers">{{cite web|url=https://www.americanrivers.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/SnakeRiver_MER2022_Report_Final_03302022.pdf|title=America's Most Endangered Rivers: Snake River|publisher=American Rivers|year=2022|accessdate=January 8, 2024}}</ref> Salmon die after spawning, and their carcasses represent a crucial influx of organic matter to mountain rivers that have few natural nutrient sources.<ref name="Long 2021"/> Tributaries below Hells Canyon, particularly the Salmon River, held the richest spawning grounds, although substantial numbers also made it above Hells Canyon as far as Shoshone Falls.<ref name="Nemeth">{{cite web|url=https://collaboration.idfg.idaho.gov/FisheriesTechnicalReports/Snake%20River%20Spring%20and%20Summer%20Chinook%20Salmon%20-%20The%20Choice%20for%20Recovery.pdf|title=Snake River Spring and Summer Chinook Salmon - The Choice for Recovery|author=Nemeth, Douglas J. |author2=Kiefer, Russell B.|publisher=Idaho Department of Fish and Game|date=October 1999|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> The Snake River produced about 40 percent of all chinook salmon and 50 percent of all steelhead in the Columbia River watershed.<ref name="American Rivers"/> |
|||
[[Image:Lower Monumental Dam - a fish ladder (11955632415).jpg|thumb|left|Adult salmon and steelhead returning to the Snake River must surmount fish ladders at several dams, including this one at Lower Monumental Dam.|alt=Detail view of a portion of a concrete dam, showing a fish ladder in between a spillway to the left and a navigation lock to the right.]] |
|||
Populations of anadromous fish began to decline in the late 1800s due to the impact of commercial fishing, logging, mining and agriculture,<ref name="Long 2021"/> but even in the 1930s, returning fall chinook alone numbered 500,000.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://critfc.org/2012/11/09/snake-river-fall-chinook/|title=Snake River Fall Chinook Recovery|publisher=Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission|date=November 9, 2012|accessdate=January 8, 2024}}</ref> Populations further collapsed once dams were built on the lower Snake and Columbia Rivers, and Hells Canyon Dam blocked access to the upper Snake. Wild Snake River spring and summer chinook returns declined from 130,000 in the 1950s to less than 5,000 in the 1990s. Wild steelhead returns followed a similar pattern, falling from 110,000 in the 1960s to less than 10,000 in the 1990s. Spring, summer and fall-run chinook were all listed as threatened in 1992.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/west-coast/endangered-species-conservation/snake-river-spring-summer-run-chinook-salmon|title=Snake River Spring/Summer-run Chinook Salmon|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|date=November 8, 2023|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/west-coast/endangered-species-conservation/snake-river-fall-run-chinook-salmon|title=Snake River Fall-run Chinook Salmon|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|date=January 22, 2024|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref> Snake River steelhead were also listed as threatened in 1997.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/west-coast/endangered-species-conservation/snake-river-basin-steelhead|title=Snake River Basin Steelhead|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|date=August 17, 2023|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Wild chinook salmon and steelhead continued to decline into the 1990s, but have begun an unsteady recovery since 2000, with both chinook and steelhead returns up to 20,000–30,000 in some years.<ref name="Snake River salmon graph"/> Coho salmon had disappeared from the Snake River by the 1980s, they were reintroduced to the watershed in 1995.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://critfc.org/press-releases/nez-perce-tribal-program-resurrects-snake-river-basin-coho-salmon/|title=Nez Perce Tribal Program Resurrects Snake River Basin Coho Salmon|publisher=Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission|accessdate=January 22, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Snake River sockeye once numbered to up 150,000 adults.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book |last=National Marine Fisheries Service West Coast Region |title=Status of the Species. Snake River Sockeye Salmon |year=2003 |pages=1–2}}</ref> Between 24,000 and 30,000 sockeye returned to Wallowa Lake in the Grande Ronde River watershed, but the run was eliminated by 1905 due to overharvest and unscreened irrigation diversions.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Cramer |last2=Witty |first1=Steven |first2=Kenneth |title=Feasibility for Reintroducing Sockeye and Coho Salmon in the Grande Ronde Basin |publisher=BPA |id=Report DOE/BP 30423 1 |year=1998}}</ref> The [[Payette Lake]] population once numbering up to 100,000 was blocked by the Black Canyon Dam in 1924.<ref name=":0" /> Sockeye in the Yellowbelly, Stanley, and Pettit Lakes of the Sawtooth basin were eradicated by management actions of the Idaho Department of Fish and Game in the 1950s, and irrigation diversions lead to the extirpation of the Pettit Lake population.<ref name=":0" /> Snake River sockeye returns declined to 4,500 in the 1950s and only a few dozen by the late 1960s.<ref name="Snake River salmon graph">{{cite web|url=http://www.wildsalmon.org/images/factsheets-and-reports/2017.Graphs.Snake.River.Adult.Returns.pdf|title=Snake River Adult Returns for wild Spring/Summer Chinook Salmon, Sockeye Salmon and Steelhead: 1950s to Present|publisher=Save Our Wild Salmon|accessdate=January 8, 2024}}</ref> Snake River sockeye were listed as endangered in 1991.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/west-coast/endangered-species-conservation/snake-river-sockeye-salmon|title=Snake River Sockeye Salmon|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|date=February 22, 2023|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Numerous hatcheries are operated by agencies such as the Army Corps, Idaho Power, the [[Bonneville Power Administration]], the [[U.S. Bureau of Indian Affairs]] and the [[U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service]], to supplement wild fish populations.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/west-coast/endangered-species-conservation/snake-river-basin-hatchery-programs|title=Snake River Basin Hatchery Programs|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|date=2 October 2019|accessdate=February 4, 2024}}</ref> Hatcheries release about 33 million salmon and steelhead smolt into the Snake River watershed each year.<ref name="McMillan 2021"/> However, the survival rate for hatchery fish is poor. Just 0.4 percent of hatchery chinook and 1.5 percent of hatchery steelhead returned as adults, as measured at Lower Granite Dam between 2007 and 2016.<ref name="McMillan 2021">{{cite web|url=https://www.tu.org/magazine/conservation/barriers/hatcheries-cant-save-snake-river-salmon-and-steelhead/|title=Hatcheries can't save Snake River salmon and steelhead|author=McMillan, John|publisher=Trout Unlimited|date=July 1, 2021|accessdate=January 22, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Upstream of the four lower dams, the Snake River watershed contains some of the best remaining spawning habitat in the Columbia River system, particularly along the Clearwater and Salmon Rivers; the latter is one of the longest undammed rivers in the continental US.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|609}} A much depleted sockeye salmon run continues to spawn in Redfish Lake near [[Stanley, Idaho]], more than {{convert|900|mi|km}} inland from the Pacific Ocean. This represents the southernmost, highest elevation and longest sockeye run in the world.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Putting the Red Back in Redfish Lake, 20 Years of Progress Toward Saving the Pacific Northwest's Most Endangered Salmon Population|author=Kline, Paul A. |author2=Flagg, Thomas A.|year=2014|journal=Fisheries|volume=39|number=11|pages=488–500|doi=10.1080/03632415.2014.966087|bibcode=2014Fish...39..488K |url=https://fisheries.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Putting-the-Red-Back-in-Redfish-Lake-20-Years-of-Progress-Toward-Saving-the-Pacific-Northwests-Most-Endangered-Salmon-Population.pdf|accessdate=January 22, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
===Terrestrial and wetland habitats=== |
|||
[[Image:Snake River Area of Critical Environmental Concern, Idaho (15665553301).jpg|thumb|right|Riparian forest and floodplain habitat lines the Snake River in Swan Valley, east of Rexburg, Idaho.|alt=A river forms multiple channels as it winds through a forested floodplain in a wide valley]] |
|||
{{See also|Snake River Plain (ecoregion)}} |
|||
The Snake River provides important wildlife habitat along much of its course, particularly in the arid Snake River Plain where it is the only source of water for many miles. The upper reaches of the Snake River, including in Jackson Hole and the floodplain north of Idaho Falls where it joins the Henrys Fork, have extensive [[Riparian zone|riparian]] [[gallery forest]]s dominated by [[Populus trichocarpa|black cottonwood]] and [[Populus angustifolia|narrowleaf cottonwood]].<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|607}} The [[Northwest Power and Conservation Council]] describes these as "some of the most important cottonwood gallery forests in the Intermountain West".<ref name="uppersnakeprovince"/> Seasonal floods scour and change the shoreline, clearing areas of older trees and making way for new growth. [[Spiranthes diluvialis|Ute lady's tresses]], a rare orchid, are found in riparian wetlands along with willows, rushes, sedges and horsetails.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|607}} |
|||
The Fort Hall Bottoms in the southern Snake River Plain are an important wetland along the river, and create a major wintering and nesting site for waterfowl, shorebirds and raptors, including bald eagles and trumpeter swans.<ref name="Fort Hall Bottoms">{{cite web|url=https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc935064/m2/1/high_res_d/964647.pdf|title=Habitat Restoration/Enhancement, Fort Hall Reservation: 2008 Annual Report|author=Osborne, Hunter|publisher=University of North Texas|accessdate=January 20, 2024}}</ref> Part of these wetlands were flooded with the construction of American Falls Dam, and large portions of the remainder have been degraded by cattle grazing.<ref name="Fort Hall Bottoms"/> Ponds and wetlands in the Hagerman Valley, near the [[Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument]], are also heavily used by both migratory and resident birds.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/thingstodo/hafo_birding.htm|title=Birding in the Hagerman Valley|publisher=U.S National Park Service|accessdate=January 20, 2024}}</ref> On the Snake River south of Boise is the nearly {{convert|500000|acre|ha|adj=on}} [[Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area]], which hosts the densest concentration of nesting raptors in the US.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.blm.gov/programs/national-conservation-lands/idaho/morley-nelson-snake-river-birds-of-prey|title=Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey|publisher=U.S. Bureau of Land Management|date=|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
The Snake River headwaters are part of the [[Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem]], which the National Park Service describes as "one of the largest nearly intact temperate-zone ecosystems on Earth." The region is home to some of the largest wild elk and bison populations in the US, and provides habitat for grizzly bear, wolverine and lynx.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nps.gov/yell/learn/nature/greater-yellowstone-ecosystem.htm|title=Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem|publisher=U.S. National Park Service|date=August 21, 2020|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref> The other major wild area in the Snake River watershed centers on Idaho's extremely rugged [[Frank Church–River of No Return Wilderness]], the largest federally designated wilderness in the contiguous US.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fs.usda.gov/detail/scnf/specialplaces/?cid=stelprdb5360033|title=Frank Church River of No Return Wilderness|publisher=U.S. Forest Service|date=|accessdate=February 2, 2024}}</ref><ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|609}} Although the Snake River watershed remains lightly populated, most of its landscape has seen significant human impact since the 19th century. Heavy logging has historically occurred in the Boise area<ref>{{cite web|url=https://history.idaho.gov/wp-content/uploads/0173.pdf|title=Lumber in the Boise Region|publisher=Idaho State Historical Society|work=Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> and on the Clearwater River, which hosted the last whitewater [[log driving|log drive]] in the US in 1971.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://foresthistory.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/mccollister_the-clearwater-river-log-drives.pdf|title=The Clearwater River Log Drives|author=McCollister, Charles |author2=McCollister, Sarah|publisher=Forest History Society|work=Forest History Today|year=2000|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> Logging is still a major industry in the region, though since the 1990s, logging south of the Clearwater has decreased.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GOVPUB-A13-PURL-gpo53246/pdf/GOVPUB-A13-PURL-gpo53246.pdf|title=Logging Utilization in Idaho: Current and Past Trends|author=Simmons, Eric A. |author2=Morgan, Todd A. |author3=Berg, Erik C. |author4=Zarnoch, Stanley J. |author5=Hayes, Steven W. |author6=Thompson, Mike T.|publisher=U.S. Government Publishing Office|date=March 2014|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> Large areas of native sagebrush-steppe ecosystems, mostly in the Snake River Plain and Palouse, have been developed for agriculture. About two-thirds of the Snake River Plain remains grassland or shrubland; however, much of this acreage is impacted by livestock grazing, and fire regimes have become more severe with the proliferation of invasive species like [[cheatgrass]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/1794/a/chapters/pp1794a_chapter24.pdf|title=Snake River Basin Ecoregion|author=Sleeter, Benjamin M.|work=U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1794–A, Status and Trends of Land Change in the Western United States, 1973 to 2000|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|year=2012|accessdate=February 2, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
===Proposed dam removal=== |
|||
[[Image:Un-Cruise Adventures - Legacy of Discovery (itinerary map).jpg|thumb|right|280px|Map showing locations of dams on the lower Snake and Columbia rivers|alt=A map showing the lower Snake and Columbia rivers, with locations of dams, cities and significant landmarks indicated]] |
|||
The lower Snake River dams have remained controversial since their construction, and in the 21st century there has been increased debate over potentially removing the dams. Although the dams were built with fish ladders, the warm, slow-moving water in reservoirs disoriented migrating fish,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.idahorivers.org/lsrd|title=The Lower Snake River Dams|publisher=Idaho Rivers United|date=|accessdate=February 2, 2024}}</ref> and juvenile fish experienced significant mortality passing through the dams.<ref name="Columbia River fish passage"/> In 1980 Congress passed the Northwest Power Act, which requires federal agencies in the Northwest to mitigate the impact of their dams on fish and wildlife. While installation of fish screens and bypasses have improved survival rates for juvenile fish,<ref name="Columbia River fish passage">{{cite web|url=https://www.nwcouncil.org/reports/columbia-river-history/fishpassage/|title=Fish passage at dams|publisher=Northwest Power and Conservation Council|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref> efforts to capture fish and transport them around the dams have seen little success.<ref name="Benke and Cushing 2005"/>{{rp|609–610}} Although wild salmonid returns have seen a positive trend since their nadir in the 1990s, they remain well below pre-dam levels.<ref name="Snake River salmon graph"/> |
|||
Supporters of dam removal, which include tribal organizations such as the [[Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission]] and environmental advocacy groups such as the [[Natural Resources Defense Council]] and the [[Sierra Club]], argue that the most economical way to restore the fishery is to remove the dams, rather than continuing recovery efforts at great expense. As of 2023, over $17 billion had been spent on Snake River salmon recovery and hatchery operations.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nwf.org/Northern-Rockies-and-Pacific-Region/Conservation/Snake-River-Salmon|title=Recovering Snake River Salmon|publisher=National Wildlife Federation|accessdate=February 2, 2024}}</ref> There are other economic arguments for dam removal, particularly that the annual cost of maintaining the barge channel exceeds the economic benefits provided by shipping, and the freight can be moved by rail instead.<ref name="Jones 2015"/><ref name="Revenue Stream">{{cite web|url=https://www.webpages.uidaho.edu/fish510/PDF/revenuestream8.pdf|title=Revenue Stream: An Economic Analysis of the Costs and Benefits of Removing the Four Dams on the Lower Snake River|publisher=University of Idaho|date=|accessdate=January 21, 2024}}</ref> Furthermore, the dams only account for a small percentage of the total hydropower in the Northwest.<ref name="Revenue Stream"/> A [[University of Idaho]] analysis estimated that over a 20-year period, removing the dams would be less expensive than the cost of continuing fish recovery efforts with the dams in place.<ref name="Revenue Stream"/> Representative [[Mike Simpson]] (R-ID) has been a major supporter of dam removal, and in 2021 put forth an ambitious proposal to remove the dams,<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.hcn.org/issues/55.1/indigenous-affairs-dams-can-dam-removal-save-the-snake-river|title=Can dam removal save the Snake River?|work=High Country News|author=Austin, Hayley |author2=Smith, Anna V.|date=January 1, 2023|accessdate=January 24, 2024}}</ref> though Simpson's plan has come under scrutiny as among other actions, it would also impose "a 35-year moratorium on litigation related to anadromous fish" at federal Columbia River Basin dams.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.uidaho.edu/-/media/UIdaho-Responsive/Files/cnr/research/PAG/Issue/pag-ib24.pdf|title=Northwest In Transition: The Simpson Plan|publisher=University of Idaho|author=Wilson, Patrick|date=Aug 2021|accessdate=January 5, 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://wildfishconservancy.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Simpson-Concept-Environmental-Justice-FINAL-4-12-2021-3.pdf|title=Rep. Simpson's Concept for the Lower Snake River Dams and Environmental Justice|publisher=Wild Fish Conservancy|year=2022|accessdate=January 5, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Opponents of dam removal include farmers, local governments such as the city of Lewiston,<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.bigcountrynewsconnection.com/idaho/lewiston-city-council-votes-to-support-keeping-snake-river-dams/article_1c3dd8b2-64ef-11ed-ab10-2b84daf92a3f.html|title=Lewiston City Council Votes to Support Keeping Snake River Dams|work=Big Country News|date=November 15, 2022|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> congressional representatives in eastern Washington<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.tri-cityherald.com/news/local/article284650755.html|title=GOP reps ramp up fight on 'hypocritical assault' on Snake River dams in Eastern WA|work=Tri-City Herald|author=Cary, Annette|date=January 24, 2024}}</ref> and the Bonneville Power Administration, which manages federal hydroelectric dams in the Northwest.<ref name="NRDC 2018"/> In the context of shipping, while river traffic has declined in recent years, it remains important to the area's economy, and moving cargo by barge is cheaper and twice as fuel-efficient as diesel trains.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.uswheat.org/wheatletter/legislation-supports-barge-transportation-and-lower-snake-river-dams/|title=Legislation Supports Barge Transportation and Lower Snake River Dams|publisher=U.S. Wheat Associates|date=December 9, 2022|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> While the dams do not generate much [[baseload power]], they are crucial to managing peak demand on a daily basis, as hydropower can be ramped up and down quickly. As more wind and solar energy is added to the Northwest grid, more load balancing will be needed to compensate for the intermittent nature of those sources.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nwriverpartners.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/2019-12-09-PPC-NRU-LSRD-fact-sheet_FINAL.pdf|title=Lower Snake River Dams Fact Sheet|publisher=Northwest River Partners|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.seattletimes.com/seattle-news/environment/for-first-time-in-20-years-feds-take-deep-look-at-hydrodam-removal-on-lower-snake-river/|title=For first time in 20 years, feds take deep look at hydroelectric dam removal on Lower Snake River|author=Mapes, Lynda V.|work=The Seattle Times|date=February 27, 2020|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> Although Washington governor [[Jay Inslee]] and Washington Senator [[Patty Murray]] have tentatively endorsed dam removal, they stressed that hydropower must be replaced by other renewable sources, and economic impacts such as the loss of the ship channel should be "mitigated or replaced."<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.hatchmag.com/articles/inslee-and-murray-would-support-snake-river-dam-removal/7715550|title=Inslee and Murray would support Snake River dam removal|work=Hatch|author=Hunt, Chris|date=August 30, 2022|accessdate=February 3, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
In December 2023, the [[Presidency of Joe Biden|Biden administration]] expressed its support for the Columbia Basin Restoration Initiative, which would develop a strategy to replace the power and navigation benefits provided by the Snake River dams, and explore options for post-dam river restoration. The initiative is an agreement between the federal government, four tribal nations, the states of Washington and Oregon, and several conservation groups. It would not authorize the removal of the dams, which would require a separate act of Congress.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.hcn.org/articles/dams-lower-snake-river-dams-closer-to-coming-down-with-new-agreement|title=Lower Snake River dams closer to coming down with new agreement|work=High Country News|author=Smith, Anna V.|date=December 15, 2023|accessdate=January 31, 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://earthjustice.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/snake-river-litigation-cbri.pdf|title=Columbia Basin Restoration Initiative|publisher=EarthJustice|date=December 14, 2023|accessdate=January 31, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{portal|Idaho|Rivers|Geography}} |
|||
*[[List of crossings of the Snake River]] |
|||
*[[List of tributaries of the Columbia River]] |
|||
*[[List of rivers of Idaho]] |
|||
*[[List of rivers of Oregon]] |
|||
*[[List of rivers of Washington (state)]] |
|||
*[[List of rivers of Wyoming]] |
|||
*[[List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem)]] |
|||
*[[List of longest streams of Idaho]] |
|||
*[[List of longest streams of Oregon]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
===Notes=== |
|||
{{reflist|group=n}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{commons category|Snake River}} |
|||
* [https://snoflo.org/river-levels/snake-river Snake River flow conditions] at SnoFlo |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080530002513/http://www.idahopower.com/riversrec/ Idaho Power] |
|||
* [https://www.rivers.gov/rivers/river/snake Wild and Scenic Snake River] - National Wild and Scenic Rivers System |
|||
{{Columbia River}} |
|||
{{Idaho}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{good article}} |
|||
[[Category:Snake River| ]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Oregon]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Washington (state)]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Wyoming]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Yellowstone National Park]] |
|||
[[Category:Tributaries of the Columbia River]] |
|||
[[Category:Physiographic sections]] |
|||
[[Category:Wild and Scenic Rivers of the United States]] |
|||
[[Category:Borders of Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Borders of Oregon]] |
|||
[[Category:Borders of Washington (state)]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Wallowa County, Oregon]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Baker County, Oregon]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Malheur County, Oregon]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Bonneville County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Madison County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Power County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Twin Falls County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Ada County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Owyhee County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Nez Perce County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Bingham County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Fremont County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Elmore County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Payette County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Gooding County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Canyon County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Washington County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Adams County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Idaho County, Idaho]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Jerome County, Idaho]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 04:39, 20 December 2024
The Snake River is a major river in the interior Pacific Northwest region of the United States. About 1,080 miles (1,740 km) long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, which is the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. Beginning in Yellowstone National Park, western Wyoming, it flows across the arid Snake River Plain of southern Idaho, the rugged Hells Canyon on the borders of Idaho, Oregon and Washington, and finally the rolling Palouse Hills of southeast Washington. It joins the Columbia River just downstream from the Tri-Cities, Washington, in the southern Columbia Basin.
The river's watershed, which drains parts of six U.S. states, is situated between the Rocky Mountains to the north and east, the Great Basin to the south, and the Blue Mountains and Oregon high desert to the west. The region has a long history of volcanism; millions of years ago, Columbia River basalts covered vast areas of the western Snake River watershed, while the Snake River Plain was a product of the Yellowstone volcanic hotspot. The river was further altered by catastrophic flooding in the most recent Ice Age, which created such features as the Snake River Canyon and Shoshone Falls.
The Snake River once hosted some of the largest North American runs of salmon and other anadromous fish. For thousands of years, salmon fishing has played a central role in the culture and diet of indigenous peoples. The Shoshone and Nez Perce were the largest of several tribes that lived along the river by the turn of the 19th century. In 1805, while searching for a route from the eastern US to the Pacific, Lewis and Clark became the first non-natives to see the river. Fur trappers explored more of the watershed, and drove beaver to near extinction as the Americans and British vied for control of Oregon Territory.
Although travelers on the Oregon Trail initially shunned the dry and rocky Snake River region, a flood of settlers followed gold discoveries in the 1860s, leading to decades of military conflict and the eventual expulsion of tribes to reservations. At the turn of the 20th century, some of the first large irrigation projects in the western US were developed along the Snake River. South-central Idaho earned the nickname "Magic Valley" with the rapid transformation of desert into farmland. Numerous hydroelectric dams were also constructed, and four navigation dams on its lower section created a shipping channel to Lewiston, Idaho – the furthest inland seaport on the West Coast.
While dam construction, commercial fishing and other human activities have greatly reduced anadromous fish populations since the late 19th century, the Snake River watershed is still considered important habitat for these fish. The Snake and its tributary, the Salmon River, host the longest sockeye salmon run in the world, stretching 900 miles (1,400 km) from the Pacific to Redfish Lake, Idaho. Since the 1950s, public agencies, tribal governments and private utilities have invested heavily in fishery restoration and hatchery programs, with limited success. The proposed removal of the four lower Snake River dams for fish passage is a significant ongoing policy debate in the Pacific Northwest.
Course
[edit]The Snake River begins on Two Oceans Plateau near the southern border of Yellowstone National Park, about 9,200 feet (2,800 m) above sea level in the Rocky Mountains of Wyoming.[2] From there, it flows west then south into Grand Teton National Park, where it feeds Jackson Lake, a natural glacial lake enlarged by Jackson Lake Dam. It flows south through the alpine valley of Jackson Hole, which is situated between the Teton Range (to the west) and the Gros Ventre Range.[3] Below the town of Jackson it forms the Snake River Canyon of Wyoming, turns west and crosses into Idaho, where the Palisades Dam forms Palisades Reservoir. From there it flows northwest through Swan Valley to join the Henrys Fork on an alluvial plain near Rexburg.[3] The Henrys Fork is sometimes called the "North Fork" of the Snake River,[7] while the section of the main Snake River above their confluence is sometimes called the "South Fork".[1][8]
Turning southwest, the river begins its long journey across the Snake River Plain, passing through Idaho Falls and receiving the Blackfoot River from the left before entering the 20-mile (32 km)-long American Falls Reservoir, formed by American Falls Dam.[3] From American Falls it turns west, flowing through Minidoka Dam and Milner Dam, where large volumes of water are diverted for irrigation.[9] Below Milner Dam it enters the Snake River Canyon of Idaho, where the river narrows, forming rapids and waterfalls. In the 70-mile (110 km) stretch between Milner Dam and the confluence with the Malad River near Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument, the Snake River descends a total of 1,300 feet (400 m) over a series of cataracts and rapids, chief of which include Caldron Linn, Twin, Shoshone, Pillar, Auger, and Salmon Falls.[10][11][12][13] Idaho Power operates several small hydroelectric plants along this stretch of the river.[14] The largest single drop is 212-foot (65 m) Shoshone Falls, which in the spring flows with such force that 19th-century writers called it the "Niagara of the West".[15]: 89–90

The Snake River continues flowing west, through the C. J. Strike Reservoir where it is joined from the left by the Bruneau River, then through the Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area before entering farmland on the western side of Idaho's Treasure Valley.[n 1] Passing 30 miles (48 km) west of Boise, it crosses briefly into Oregon before turning north to form the Oregon–Idaho border.[3] It is joined by several major tributaries in quick succession – the Boise River from the right, the Owyhee and Malheur Rivers from the left, the Payette and Weiser Rivers from the right near Ontario, Oregon, then the Powder and Burnt Rivers from the left.[3] Continuing north, the river enters Hells Canyon, which slices between the Rocky Mountains of Idaho and the Blue Mountains of Oregon and Washington.[3] The Hells Canyon Hydroelectric Complex includes the Brownlee, Oxbow and Hells Canyon Dams in the upper reaches of the canyon.[17] Since its construction in 1967, Hells Canyon Dam has been the upriver limit for migrating salmon; in the past, salmon swam as far upriver as Shoshone Falls.[18]
Emerging from Hells Canyon Dam, the Snake surges northward through the Hells Canyon Wilderness, where the majority of the river corridor is accessible only by boat and numerous Class III-IV rapids[19]: 128–131 historically posed a major barrier to navigation.[20] Today, the canyon and the surrounding Hells Canyon National Recreation Area are a popular location for whitewater boating, fishing, horseback riding and backpacking.[21][22] With the adjacent Seven Devils Mountains rising up to 8,000 feet (2,400 m) above the river, Hells Canyon is one of the deepest canyons in North America, almost one-third deeper than the Grand Canyon.[23] Within the canyon it is joined from the left by the Imnaha River, then from the right by its longest tributary, the Salmon River. Further north, it begins to form the Idaho–Washington border, and receives the Grande Ronde River from the left.[3] From the end of Hells Canyon at Asotin, Washington, it flows north to Lewiston, Idaho, where it is joined from the right by the Clearwater River, its largest tributary by volume. The Snake then turns sharply west to enter Washington.[3]
The final stretch of the Snake River flows through steep-sided valleys in the Palouse Hills of southeast Washington. Near Lyons Ferry State Park, it is joined from the left by the Tucannon River, then from the right by the Palouse River, which forms Palouse Falls about 8 miles (13 km) upstream of its confluence with the Snake.[3] The Lower Snake River Project consists of four dams equipped with navigation locks – Lower Granite, Little Goose, Lower Monumental and Ice Harbor – which have transformed the once fast-flowing lower Snake River into a series of lakes, enabling heavy barges to travel between the Columbia River and the Port of Lewiston.[24] About 10 miles (16 km) downstream from Ice Harbor Dam, the Snake empties into the Columbia River at Burbank, Washington, southeast of the Tri-Cities.[3] The confluence is located on Lake Wallula, the impoundment behind McNary Dam on the Columbia,[3] 341 feet (104 m) above sea level.[1] From there, the Columbia River flows another 325 miles (523 km) west to empty into the Pacific Ocean.[25]
Discharge
[edit]
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers has measured the discharge, or flow rate, of the Snake River at Ice Harbor Dam since 1962. The mean annual discharge for the 61-year period between 1962 and 2023 was 49,580 cubic feet per second (1,404 m3/s), with a maximum recorded daily mean of 305,000 cu ft/s (8,600 m3/s) on June 19, 1974, and a minimum daily mean of 2,000 cu ft/s (57 m3/s) on November 29, 1961.[5] A historic June 1894 flood at the Ice Harbor site reached an estimated peak of 409,000 cu ft/s (11,600 m3/s).[26] In terms of discharge, the Snake River is the twelfth largest river in the United States, and it contributes about one-fifth of the Columbia's total outflow into the Pacific.[27]
The volume of the Snake River peaks in late spring and early summer as snow melts in the Rocky Mountains, and reaches its lowest point in the fall. Despite the numerous dams regulating its flow, its discharge into the Columbia remains highly seasonal.[28]: 607 At Ice Harbor Dam, the mean monthly discharge is highest in May and June at over 100,000 cu ft/s (2,800 m3/s), and lowest in September and October at less than 25,000 cu ft/s (710 m3/s).[5] Mean annual discharge also fluctuates significantly, from a record high of 86,240 cu ft/s (2,442 m3/s) in 1965, to a low of 27,890 cu ft/s (790 m3/s) in 1997.[5]
In southern Idaho, Snake River flows are significantly influenced by the Eastern Snake River Plain Aquifer. One of the largest groundwater reserves in the US, the aquifer is founded in porous volcanic rock underneath the plain. It absorbs and stores large volumes of water from the Snake River in the eastern Plain to re-emerge further west as springs in the Snake River Canyon.[29] Water from the lost streams of Idaho, several rivers that disappear underground in the eastern Plain, travels through the aquifer to reach the Snake River,[30] as does excess irrigation water absorbed into the ground.[31] The major spring complexes at American Falls and Thousand Springs (near Hagerman, Idaho) keep the river flowing steadily even in the driest of summers.[32][33] At King Hill, about 50 miles (80 km) northwest of Twin Falls, water levels remain about 10,000 cu ft/s (280 m3/s) for most of the year, increasing about 20 percent during snowmelt and decreasing about 20 percent with late summer irrigation diversions.[31][34]
Despite its great length, the Snake River accumulates most of its water in the lower one-fourth of its course. By the time it reaches Hells Canyon Dam, 247 miles (398 km) from the mouth, the mean annual discharge is about 19,000 cu ft/s (540 m3/s) – just over a third of the discharge at the mouth.[35] Just two downstream tributaries, the Clearwater and Salmon Rivers, contribute about half of the total flow of the Snake.[28]: 607
Watershed
[edit]
The 107,500-square-mile (278,000 km2)[4] Snake River watershed drains about 87 percent of the state of Idaho, 18 percent of Washington and 17 percent of Oregon, in addition to small portions of Wyoming, Utah and Nevada.[36] From the Lost Trail Pass north of Salmon, Idaho to Tri-Basin Divide south of Afton, Wyoming, the eastern edge of the Snake River watershed follows the Continental Divide. As the Continental Divide also forms the Idaho–Montana border south of Lost Trail Pass, the Snake watershed touches Montana for a long distance, but does not extend into it.[3] The Snake drains by far the largest area of any Columbia River tributary, making up about 40 percent of the entire Columbia River watershed.[28]: 602 Compared with the Columbia above their confluence, the Snake River is about 180 miles (290 km) longer[n 2] and drains a similarly sized area,[4][37] though the Columbia carries more than twice the volume of water.[5][38]
The Snake River watershed is very mountainous, with the northern two-thirds of it occupied by vast mountain ranges of the Rockies, primarily the Salmon River Mountains of central Idaho and the Bitterroot Range along the Idaho–Montana border. The Blue Mountains form much of the western boundary of the Snake watershed from southeast Washington down into Oregon. To the south are numerous small isolated mountain ranges of the Basin and Range Province, such as the Independence and Albion Mountains.[3] To the east are more ranges of the Rockies including the Tetons and the Wind River Range; the latter includes Gannett Peak, the highest point in the Snake River basin[28]: 604 at 13,816 feet (4,211 m).[39] Surface volcanic features – such as lava fields, cones, and thermal springs – are replete in the southern part of the Snake watershed, from Craters of the Moon National Monument northeast of Twin Falls to the Yellowstone caldera, while ancient lava flows of the Columbia River basalts underlie the western part of the watershed. The Snake River Plain is the largest area without mountains, but it still features rugged terrain, being crisscrossed by canyons formed by the Snake River and its tributaries.[3][28]: 604–606
Due to the rain shadow effect of the Cascades, precipitation as a whole is scant, averaging 14 inches (360 mm) across the entire watershed. Most precipitation falls at higher elevations as snow, thus, most runoff in the Snake River watershed derives from snowmelt.[28]: 605–607 Jackson Hole, Wyoming experiences an alpine climate with an average of 30 in (760 mm) of rain and 252 in (6,400 mm) of snow. The coldest month is January, with a mean temperature of 13 °F (−11 °C), and the hottest is July at 57.7 °F (14.3 °C).[40] Twin Falls experiences a semi-arid climate, with about 9 in (230 mm) of rain and 13 in (330 mm) of snow. Monthly mean temperatures range from 29.4 °F (−1.4 °C) in January to 73.1 °F (22.8 °C) in July.[41] The Columbia Basin around the river's mouth also has a semi-arid climate, with about 10 in (250 mm) of rain and 5 in (130 mm) of snow as measured at Ice Harbor Dam. January is the coldest month with a mean temperature of 34.3 °F (1.3 °C), and July is the hottest month at 74.6 °F (23.7 °C).[42]

Semi-arid shrubland and rangeland covers about 50 percent of the Snake River watershed. Natural vegetation is primarily sagebrush, mixed with wheatgrasses and bunchgrasses. About 30 percent of the watershed is farmland; irrigated farming of potatoes, sugar beets, onions, cereal grains and alfalfa are dominant in the Snake River Plain, while the Palouse Hills of the northwest host mainly dryland wheat and legume production.[28]: 603–605 About 15 percent of the watershed is forested, distributed across two temperate coniferous forest ecoregions: South Central Rockies forests, consisting primarily of Douglas fir, Engelmann spruce, subalpine fir, and lodgepole pine, and North Central Rockies forests, which include mountain hemlock, white spruce, alpine fir and western larch. About 4 percent of the watershed is barren desert, and only about 1 percent is urbanized.[28]: 604–606
Most of the Snake River watershed is public land, with the U.S. Forest Service managing the Nez Perce, Clearwater, Bitterroot, Umatilla, Wallowa–Whitman, Payette, Boise, Salmon–Challis, Sawtooth, Caribou–Targhee and Bridger–Teton National Forests that cover much of the northern and eastern parts of the watershed.[28]: 606 The forests contain numerous designated wilderness areas, including the Sawtooth, Selway–Bitterroot, Frank Church-River of No Return, Gospel Hump, Hells Canyon, Teton and Gros Ventre.[28]: 606 National Park Service land includes Craters of the Moon National Monument and Yellowstone and Grand Teton National Parks. Large areas of privately owned farmland are concentrated in the Snake River Plain and the Palouse, though the majority of the Snake River Plain is Bureau of Land Management land.[43]
The Snake River watershed borders several other major North American watersheds. To the south it borders the endorheic Great Basin, including the area draining to Utah's Great Salt Lake. To the east it borders the watersheds of the Green River (part of the Colorado River system which drains to the Sea of Cortez) and the Yellowstone and upper Missouri Rivers (part of the Mississippi River system which drains to the Gulf of Mexico). On the north it borders the watersheds of the Clark Fork and Spokane Rivers, both part of the Columbia River system. To the northwest it borders several other tributary watersheds of the Columbia River, including those of the John Day and Umatilla Rivers.[44]
Major tributaries
[edit]Fifty-four named tributaries of the Snake River drain more than 100 square miles (260 km2).[3] Of these, the twelve listed below drain an area greater than 2,000 square miles (5,200 km2).[3]
| Major tributaries of the Snake River | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Confluence location | Confluence coordinates | Confluence elevation | Length (mainstem)[3] | Length (to furthest source)[3][n 3] | Watershed[4] | Discharge | Picture |
| Henrys Fork | Rexburg, Idaho | 43°45′10″N 111°57′28″W / 43.75278°N 111.95778°W[7] | 4,800 ft (1,463 m)[7] |
129.3 mi (208.1 km) |
129.3 mi (208.1 km) |
3,260 mi2 (8,450 km2) |
2,105 cu ft/s (59.7 m3/s)[45] |

|
| Salmon Falls Creek | Hagerman, Idaho | 42°42′55″N 114°51′12″W / 42.71528°N 114.85333°W[46] | 2,884 ft (879 m)[46] |
121.1 mi (195.0 km) |
152.6 mi (245.7 km)[n 4] |
2,120 mi2 (5,500 km2) |
151 cu ft/s (4.3 m3/s)[47] |

|
| Malad River | Hagerman, Idaho | 42°51′45″N 114°54′18″W / 42.86250°N 114.90500°W[48] | 2,658 ft (810 m)[48] |
12.0 mi (19.3 km) |
149.0 mi (239.9 km)[n 5] |
3,250 mi2 (8,420 km2) |
1,500 cu ft/s (42.5 m3/s)[n 6] |

|
| Bruneau River | Mountain Home, Idaho | 42°56′57″N 115°57′43″W / 42.94917°N 115.96194°W[51] | 2,457 ft (749 m)[51] |
152.9 mi (246.2 km) |
152.9 mi (246.2 km) |
3,290 mi2 (8,530 km2) |
375 cu ft/s (10.6 m3/s)[52] |

|
| Owyhee River | Nyssa, Oregon | 43°48′46″N 117°01′32″W / 43.81278°N 117.02556°W[53] | 2,185 ft (666 m)[53] |
346.5 mi (557.9 km) |
346.5 mi (557.9 km) |
10,950 mi2 (28,380 km2) |
918 cu ft/s (26.0 m3/s)[54] |

|
| Boise River | Parma, Idaho | 43°49′15″N 117°01′34″W / 43.82083°N 117.02611°W[55] | 2,185 ft (666 m)[55] |
103.1 mi (166.0 km) |
155.5 mi (250.4 km)[n 7] |
4,010 mi2 (10,390 km2) |
1,574 cu ft/s (44.6 m3/s)[56] |

|
| Malheur River | Ontario, Oregon | 44°03′33″N 116°58′31″W / 44.05917°N 116.97528°W[57] | 2,133 ft (650 m)[57] |
189.8 mi (305.6 km) |
205.7 mi (331.2 km)[n 8] |
4,710 mi2 (12,210 km2) |
208 cu ft/s (5.9 m3/s)[58] |

|
| Payette River | Payette, Idaho | 44°05′32″N 116°57′09″W / 44.09222°N 116.95250°W[59] | 2,126 ft (648 m)[59] |
82.7 mi (133.1 km) |
163.0 mi (262.4 km)[n 9] |
3,300 mi2 (8,550 km2) |
2,960 cu ft/s (83.8 m3/s)[60] |

|
| Salmon River | Hells Canyon NRA, Idaho | 45°51′23″N 116°47′37″W / 45.85639°N 116.79361°W[61] | 919 ft (280 m)[61] |
425.3 mi (684.7 km) |
425.3 mi (684.7 km) |
14,000 mi2 (36,290 km2) |
11,090 cu ft/s (314.0 m3/s)[62] |

|
| Grande Ronde River | Rogersburg, Washington | 46°04′49″N 116°58′47″W / 46.08028°N 116.97972°W[63] | 820 ft (250 m)[63] |
210.4 mi (338.7 km) |
210.4 mi (338.7 km) |
4,130 mi2 (10,710 km2) |
3,027 cu ft/s (85.7 m3/s)[64] |

|
| Clearwater River | Lewiston, Idaho | 46°25′30″N 117°02′14″W / 46.42500°N 117.03722°W[65] | 738 ft (220 m)[65] |
74.8 mi (120.4 km) |
198.3 mi (319.2 km)[n 10] |
9,420 mi2 (24,420 km2) |
14,860 cu ft/s (420.8 m3/s)[66] |

|
| Palouse River | Starbuck, Washington | 46°35′24″N 118°12′55″W / 46.59000°N 118.21528°W[67] | 541 ft (165 m)[67] |
166.4 mi (267.9 km) |
166.4 mi (267.9 km) |
3,320 mi2 (8,610 km2) |
599 cu ft/s (17.0 m3/s)[68] |

|
Geology
[edit]
The present-day course of the Snake River was pieced together over millions of years from several formerly disconnected drainage systems. Much of what would become the Pacific Northwest lay under shallow seas until it was uplifted starting about 60 million years ago (Ma). The outlet of the ancestral Columbia River to the Pacific was established about 40 Ma.[69][70]: 288 By about 17 Ma, the "Salmon-Clearwater River", or the modern day lower Snake River, flowed west into the Columbia and on to the Pacific. Another ancient river system drained what is now the western Snake River Plain. Some geologists propose that this flowed to the Columbia on a course south of the present-day Blue Mountains, while others propose it drained towards Northern California.[71]: 208–210 [72]: 11 The Columbia River basalts, a series of massive flood basalt events that engulfed the Columbia Basin and surrounding lands, reshaped the landscape and erased most evidence of the pre-volcanic river channels starting about 17 Ma. Erupting from fissures in the southern Columbia Basin, the first basalt flows pushed the ancient Salmon-Clearwater much further north than its present course.[71]: 201–208
About 12–10 Ma, the Blue Mountains region began to experience uplift, raising the basalt layers to form a plateau.[73] From about 11–9 Ma, crustal deformation related to the Yellowstone hotspot caused the western half of the Snake River Plain to sink, creating a graben-type valley between parallel fault zones to the northeast and southwest.[74] The outlet of the ancient Snake River was blocked, and water accumulated to form the vast Lake Idaho starting about 10 Ma.[74] The eastern half of the Snake River Plain formed as the North American Plate moved westward over the Yellowstone hotspot. Upwelling magma caused the continental crust to rise, forming highlands in a similar fashion to the modern Yellowstone plateau and leaving behind enormous basalt flows in its wake. As the hotspot migrated east relative to the North American Plate, the land behind it collapsed and sank, creating the geographic depression of the eastern Snake River Plain.[75][76]
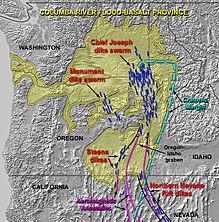
The gradual eastward migration of this topographic high had the effect of pushing the Continental Divide to the east. Prior to the formation of the eastern Snake River Plain, the drainage area east of about Arco, Idaho – the modern headwaters and upper course of the Snake River – flowed towards the Atlantic Ocean via the Mississippi River system.[77] The migrating Continental Divide tilted the regional slope such that drainage flowed west into Lake Idaho, whose water levels saw a significant increase about 4.5 Ma.[74][77] The Snake River Plain drainage system continued to expand east, towards what is now Yellowstone National Park. During this expansion, the Snake also captured the Bear River, which was only rerouted towards its modern outlet in the Great Salt Lake Basin about 50,000 or 60,000 years ago by lava flows in southeast Idaho.[78][79]
In the Columbia Basin about 10.5 Ma, the Elephant Mountain basalt eruption forced the Salmon-Clearwater River into roughly its present course through southeast Washington.[71]: 221–222 [80]: 237 By 8.5 Ma the Salmon-Clearwater was established in the Columbia River's modern path through Wallula Gap, although the Columbia itself still flowed somewhere to the west. The last of the Columbia basalt flows occurred around 6 Ma; by then, the present-day confluence of the Columbia River and Salmon-Clearwater had been established, with the combined flow draining through Wallula Gap.[71]: 222–223 About 2.5 Ma, Lake Idaho reached a maximum elevation of 3,600 feet (1,100 m) above modern sea level, and overflowed northward into the Salmon-Clearwater drainage near present-day Huntington, Oregon. Over a period of about two million years, the outflow carved Hells Canyon, emptying Lake Idaho and integrating the upper Snake and Salmon-Clearwater into a single river system.[74][77]
The Teton Range, a defining topographic feature of the modern Snake River headwaters, first began to rise about 10 Ma as the Teton Fault began to move, displacing the mountain block upward as the surrounding land dropped.[81] About 2 Ma, the Hoback Fault formed east of the Tetons, and a graben valley developed between the Hoback and Teton fault zones, creating Jackson Hole.[82] As the valley dropped, water filled it to create Lake Teewinot, which drained east into the Green River–Colorado River system. About 1 Ma, the Snake River captured the Jackson Hole watershed, draining Lake Teewinot and finally connecting the modern-day Snake headwaters to the rest of the river.[78] This landscape around the Snake headwaters was sculpted by multiple Ice Age glaciations. Starting about 200,000 years ago, the Buffalo glaciation filled Jackson Hole to a depth of 2,000 feet (610 m). Ice flowed down the Snake River Canyon all the way to Idaho.[82] The Bull Lake glaciation, about 80,000–35,000 years ago, and the Pinedale glaciation, ending about 15,000 years ago, were much smaller and did not fill the entire valley. These glaciations carved the distinctive peaks of the Tetons into their present form and scoured lake basins in the valley floor, including modern-day Jackson Lake.[82]
While the Snake River course beyond Jackson Hole was not directly impacted by glaciations, its landscape was dramatically changed by Ice Age flooding events. About 30,000 years ago, the climate of western North America was much wetter than today. The Great Salt Lake Basin filled with water to form the massive Lake Bonneville, about the size of modern-day Lake Michigan. About 15,000 years ago the lip of Red Rock Pass south of present-day Pocatello, Idaho abruptly collapsed, releasing a tremendous volume of water from Lake Bonneville into the Snake River Plain. The peak of the flood was about 500 times bigger than the largest recorded flood of the Snake at Idaho Falls in modern times.[83] The flood completely altered the landscape of the Snake River Plain, creating the Snake River Canyon and its waterfalls, vast boulder fields, cliffs and coulees.[83][84] The floodwaters then emptied through Hells Canyon; however, most evidence of their effects on the lower Snake River was erased by the much larger Missoula Floods that engulfed the Columbia Basin during the same period.[83] Caused by the repeated collapse of an ice dam in western Montana, dozens of floods overflowed into the lower Snake River from the north, backing water as far upstream as Lewiston. The formerly west-flowing Palouse River was rerouted to flow south into the Snake River, forming Palouse Falls, whose outsized plunge pool attests to the force of the floods.[85][86]
History
[edit]Indigenous peoples
[edit]
Starting around the end of the last glacial period, the Snake River Plain was inhabited by hunter-gatherers of the ancient Clovis (10000–9000 BCE), Folsom (9000–8000 BCE) and Plano (8600–5800 BCE) cultures.[87] Along the lower Snake River in Washington, the Marmes Rockshelter – flooded in 1968 after the construction of Lower Monumental Dam – has yielded archeological evidence of continuous human occupation from about 9000 BCE until about 1300 CE.[88] Starting about 2200 BCE, people in the western Snake River basin began to adopt a semi-sedentary lifestyle, with an increased reliance on fish (primarily salmon) and food preservation and storage.[89] Shoshoni-speaking peoples arrived in the Snake River Plain between 600 and 1500 CE.[87]
By the time of first European contact, the Snake River watershed was populated by several Native American tribes. The territory of the Nez Perce (Nimiipuu) stretched across what is now north-central Idaho, southeast Washington and northeast Oregon, including much of the lower Snake River below Hells Canyon, most of the Clearwater and Grande Ronde River, and the lower Salmon River.[90] The Northern Shoshone and the Bannock, a Northern Paiute group that became culturally associated with the Shoshone, occupied an area stretching from the Snake River Plain east to the Rocky Mountains and south towards the Great Basin, as well as valleys of the upper Salmon River.[87] A Nez Perce name for the river was Kimooenim or variations thereof,[91]: 635 meaning "the stream/place of the hemp weed".[92]: 128 Another Nez Perce name for the Snake River was Pikúunen, specifically referring to the stretch upstream of the Clearwater confluence. The Wanapum and Walla Walla people called the lower Snake River below the Clearwater Naxíyam Wána.[93]: 118–120 The Shoshone called the river Yampapah, after the yampah plant that grew profusely along its banks.[94]: 44
Downriver of Shoshone Falls, salmon and their cousins such as steelhead trout – anadromous fish which spend their adult lives in the ocean, returning to fresh water to spawn – were a key food source for indigenous peoples, and were of great cultural importance. Rituals such as the first salmon ceremony were widely observed along the Columbia, Snake and other Northwest rivers, and so were strict catch limits, such that a healthy number of salmon would survive to reach their natal streams.[95] The Nez Perce had more than seventy permanent villages among their fishing grounds on the Snake, Clearwater and Salmon Rivers.[96] Clans gathered at communal fishing sites starting about May or June. Fishing moved from the lower rivers to higher elevation streams throughout the summer, while fall-run fish were preserved for winter use.[97]
Shoshones in the western part of the Snake River Plain also depended heavily on the salmon run. At Shoshone Falls and the smaller cataracts downstream, fishing platforms, temporary brush weirs, spears, baskets and fish traps were employed at large scale. Captain Benjamin Bonneville in 1832 observed that "Indians at Salmon Falls on the Snake River took several thousand salmon in one afternoon by means of spears."[98] To the east and upriver of the falls, many Shoshone and Bannock lived in more nomadic groups, traveling to the falls during the spring salmon run then gathering camas bulbs and hunting bison through the summer and autumn months.[99]
The Snake River at Hells Canyon formed a natural dividing line between the Nez Perce and Shoshone, who considered each other enemies. The Nez Perce allied with the Cayuse against the Shoshone, Bannock and Northern Paiute, and stopped the latter from expanding their territory towards the Columbia Plateau.[100] Both the Nez Perce and Shoshone acquired horses in the late 1600s or early 1700s, enabling far-reaching trade and hunting expeditions.[101] With horses, the Nez Perce were able to travel east of the Bitterroot Mountains to hunt bison, via the trail over Lolo Pass, which the Lewis and Clark expedition would later follow in order to reach the Snake and Columbia Rivers.[102]
Origin of name
[edit]The river's modern name comes from a misunderstanding of the Shoshone Tribal Sign in PISL.[103] The Plains Indians referred to the Shoshone people as "Snake People", while the Shoshone are believed to have referred to themselves as "People of the River of Many Fish". However, the Shoshone sign for "salmon" was the same or similar to the Plains Indian common sign for "snake."[104][105] The English name for the river was likely derived from this interpretation of the hand gesture, although it is uncertain when the name was first used.[22][106]
Exploration and fur trade
[edit]The first Euro-Americans to reach the Snake River watershed were the Lewis and Clark Expedition, who in August 1805 crossed the Continental Divide at Lemhi Pass and descended to the Salmon River at what is now Salmon, Idaho, naming the stream "Lewis's River". Thwarted by the river's rapids, they were forced to cross the Bitterroot Mountains via the Nez Perce trail at Lolo Pass. After paddling down the Kooskooskee (Clearwater River), they reached the junction with the Snake and camped there with the Nez Perces on October 10, 1805.[91]: 620–622 They correctly surmised that the river coming from the south was a continuation of "Lewis's" or Salmon River. The expedition journals note the Nez Perce called it Kimooenim, although William Clark later erased mentions of the name to replace with "Lewis's".[91]: 635 Six days later they reached the confluence of the Snake and Columbia Rivers, after noting a number of dangerous rapids as well as many native fishing sites on the lower Snake.[91]: 625–635 The expedition established friendly relations with the Nez Perces, who they visited again on their return trip in 1806.[107]
Other explorers quickly followed, many of them fur trappers who began scouting the upper Snake River watershed for beaver. John Colter, a former member of the Lewis and Clark expedition, explored the Jackson Hole area in 1808.[108] In 1810, Andrew Henry explored and named the Henrys Fork of the Snake River. He established Fort Henry, the first American fur trading post west of the Rocky Mountains, but abandoned it after that year's harsh winter.[108] The 1811 Pacific Fur Company expedition led by Wilson Price Hunt attempted to find a route from Henrys Fork to the Columbia River. After suffering a wreck in the falls of the Snake River Canyon, they took an overland route through the Snake River Plain, through what is now the Boise Valley or Treasure Valley, then crossed the Blue Mountains to bypass Hells Canyon and reach the lower Snake River.[109] After the hazardous experience, Hunt gave it the name "Mad River".[110] A group led by Robert Stuart, a member of the Hunt expedition, returned eastward across the plain the following year. The route they mapped would eventually become that section of the Oregon Trail.[109]

In 1818 Donald Mackenzie and Alexander Ross established Fort Nez Percés for the North West Company near the confluence of the Snake and Columbia Rivers.[111]: 53–58 The following year, Mackenzie traveled up the Snake River and reached Boise Valley by making the first recorded river ascent of Hells Canyon.[108] Mackenzie's goal was to bypass the arduous trek over the Blue Mountains. He wrote that "the passage by water is now proved to be safe and practicable for loaded boats, without one single carrying place or portage; therefore, the doubtful question is set at rest forever. Yet from the force of the current and the frequency of rapids, it may still be advisable, and perhaps preferable, to continue the land transport."[15]: 19
Canadian fur trappers with the British Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) reached the Snake River watershed in 1819.[112] As American fur trappers kept coming to the region, the HBC ordered the Canadians to kill as many beavers as they could, under the rationale that "if there are no beavers, there will be no reason for the Yanks to come," and even if the Americans did ultimately gain control, the HBC would already have taken all the profit.[112] Focused primarily on the upper Snake River region, the "fur desert" policy was carried out in nine expeditions from about 1824–1831 and aimed to decrease the Americans' economic interest in the Oregon Country, the vast region of the Pacific Northwest centering on modern-day British Columbia, Washington, Oregon and Idaho. By the time the Americans annexed Oregon Territory in 1848, beaver were nearly extirpated across much of the Rocky Mountains.[112][113]
Starting in the 1840s, the Oregon Trail became well established, and thousands of settlers passed through the Snake River Plain on their way to the Willamette Valley. Coming from Wyoming, the Oregon Trail reached the Snake River at Fort Hall, Idaho, and stayed south of the river until Three Island Crossing near modern-day Glenns Ferry.[114] Here the trail diverged, with the northern route fording the river to reach the HBC trading post at Fort Boise while the southern route continued into what is now the eastern Oregon desert. While the northern route passed through more favorable country, the Snake River posed a formidable barrier; during high water, many travelers were forced to take the hot, dry southern route, or risk drowning.[115] Travelers going via Fort Boise had to cross the river one more time to rejoin the trail heading west. A ferry existed at Fort Boise since at least 1843;[116] the Three Island crossing was also replaced by a ferry in 1869.[114] A new wave of travelers came in the 1860s with the Montana Trail providing access to gold strikes in Montana Territory. This crossed the Snake River by the Eagle Rock Ferry and later a bridge which the city of Idaho Falls would soon grow around.[117]
Conquest and conflict
[edit]
As the flow of settlers increased, the Nez Perce and their neighbors the Cayuse and Walla Walla came under pressure to cede portions of their territory. Tensions flared in 1855 after tribes were coerced into relinquishing huge amounts of territory in the Treaty of Walla Walla.[90] In retaliation for Lt. Col. Edward Steptoe's defeat at the 1858 Battle of Pine Creek, a force led by Col. George Wright entered the lower Snake River country in 1859 and constructed Fort Taylor at the confluence of the Tucannon River below present-day Starbuck, Washington. Over several months Wright fought the natives along the river, killing their horses and destroying stored food.[118]: 37 The sternwheeler Colonel Wright was commissioned to haul supplies up the Snake River to Fort Taylor. Captained by veteran Oregon river pilot Len White, the Wright was the first steamboat to run on the Snake River and the Columbia above The Dalles.[15]: 75–76 [118]: 37
Two years later, Elias D. Pierce discovered gold to the east on Nez Perce treaty land.[118]: 42–43 As thousands of fortune seekers flocked to the area, the city of Lewiston was founded in 1861, in violation of the 1855 treaty. The US government sided with the settlers, and pressured some Nez Perce leaders into signing a second treaty which shrank their reservation by 90 percent. Many Nez Perce including Chief Joseph's band refused to leave, calling the new treaty the "thief treaty".[90] In March 1863, the Idaho Territory was split from Oregon, and Lewiston became its capital. More than 60,000 prospectors and others entered the Lewiston Valley by 1863.[118]: 43 Many new steamboats were pressed into service, including the Spray, Cascadilla, Tenino, Okanogan, and Nez Perce Chief. The river's rapids posed a major navigation hazard, and from November to April the river was generally too low for ships. Despite these challenges, the water transport of freight and passengers was greatly profitable.[118]: 43
Up river, the Shoshone and other tribes were also becoming increasingly wary of settlers; in 1854 a Shoshone war party attacked a wagon train in the Boise Valley, and the U.S. Army mounted a counterattack, the Winnas Expedition. The situation became so unstable that Fort Boise was abandoned, and the Army had to escort wagon trains through the area.[119] While early settlers had simply passed through this area on their way to Oregon, gold strikes brought renewed interest in the 1860s. The Army rebuilt Fort Boise further east of the original site in 1863. A military detachment was stationed there to quell any further violence; however, tensions continued to increase, and more wagon trains and mining parties were attacked. Starting in 1864, the Snake War was fought across much of southern Idaho, with numerous battles between the U.S. Army and the Shoshone, Bannock and Paiute.[120] By 1868, exhausted after years of fighting, Chief Pocatello and many others surrendered and relocated to the Fort Hall Indian Reservation on the Snake River in southeast Idaho.[121]: 226

Tribal resistance would continue for years to come. In 1877 the US government attempted to force the remaining Nez Perce onto their reservation, at which point Chief Joseph's band and several others opted to seek refuge elsewhere. After a treacherous crossing of the Snake at Dug Bar, Hells Canyon on May 31,[122] the Nez Perce were pursued by the Army for over 1,000 miles (1,600 km) east, through Yellowstone before turning north through Montana, fighting several battles along the way. On October 5, 1877, Chief Joseph surrendered to US forces. thus ending the Nez Perce War. The survivors were distributed to various reservations across the western US.[123] In 1878, an uprising occurred in response to overcrowding and food shortages at the Fort Hall Reservation, leading to the Bannock War. The US army defeated the Bannock and their Paiute allies and proceeded to restrict travel in and out of the reservation.[124]
While Lewiston was now well connected by river, travel to Boise and other points upstream on the Snake River remained difficult due to the formidable obstacle of Hells Canyon. In 1865, Thomas Stump attempted to pilot the Colonel Wright up Hells Canyon, making it 80 miles (130 km) upriver before hitting rocks in a rapid, forcing their retreat.[118]: 45 On the Snake River above Hells Canyon, several steamboats were built at great expense (as manufactured parts such as engines had to be hauled in overland), the first being the Shoshone in 1866. However, running the upper Snake proved unprofitable, due to lack of demand. The owners of Shoshone decided to move her to the lower Snake River, and in April 1870, they made the first successful river descent of Hells Canyon, a harrowing ride that skirted disaster several times.[15]: 85–88 In 1895 the steamboat Norma, which had been built to haul copper ore on the Snake River above Hells Canyon, also made the run under similar circumstances.[23][15]: 167–172
In the 1870s, Boise (to which Idaho's capital was moved in 1866) expanded rapidly as growth slowed in Lewiston. Gold drew more than 25,000 prospectors to the Boise Valley, and a new city quickly grew around the U.S. Army post at Fort Boise.[125][126] With Hells Canyon impractical for river navigation, interest grew in connecting the area by rail. By 1884, the Oregon Railroad & Navigation Company (later integrated into Union Pacific) had connected Portland, Oregon, to the Union Pacific line at Granger, Wyoming, via Huntington and Pocatello. Boise, initially bypassed due to a steep grade, was connected three years later.[127] In addition to commerce, the railroad also opened the Snake River region – which just a few years ago had been seen as a remote, rough frontier – to recreation. The Union Pacific heavily promoted tourism in places like Shoshone Falls, Payette Lake and Soda Springs, Idaho. Countering the reputation of southern Idaho as a wasteland, a brochure described Shoshone Falls: "Shoshone differs from every other waterfall in this or the old country. It is its lonely grandeur that impresses one so deeply; all of the other historic places have the adjuncts of civilization, and one is almost overshadowed by a city while in their presence."[128]
Reclamation and development
[edit]Irrigation
[edit]Most travelers on the Oregon Trail regarded the arid Snake River Plain as an obstacle to be crossed, not a land to be settled. This began to change with the Boise gold strikes, where the demands of the mining industry and the difficulty of importing goods set off an agricultural boom in the Boise Valley.[125][118]: 45 By the 1880s, settlers also came to the upper Snake River north of Idaho Falls, where fertile, sandy soils presented ideal conditions for the iconic russet potato ("Idaho potato").[129] The dry climate made irrigation necessary, and numerous private irrigation companies were formed.[130] Private canal systems around Boise and Idaho Falls saw some success, but all the easily farmable land was soon developed, and they could not raise the capital for further expansion. In addition, low water by late summer posed a challenge to farmers, and the irrigation companies could not afford to build dams to provide water storage.[131]

With many private irrigation companies verging on insolvency, the federal government began to explore programs assisting agricultural development. The 1894 Carey Act granted large tracts of dry federal land to western states, which then sold the land to farmers and solicited private investors to organize irrigation districts. Investors would then recoup their capital by selling water rights to farmers.[126] Irrigation plans were reviewed by engineers, who determined the economic feasibility of the projects. Although the Carey Act saw little success in most states, it greatly benefited Idaho. Some 60 percent of all lands developed under the Carey Act were in Idaho, and almost all of that utilized Snake River water.[126]
I. B. Perrine, who homesteaded near Shoshone Falls in the 1880s, went on to develop one of the most successful Carey Act projects. In 1900 Perrine filed a claim for water from the Snake River, and backed by significant private capital, oversaw the construction of Milner Dam and a canal system to irrigate some 250,000 acres (100,000 ha) of the Snake River Plain.[132] Completed in 1905, the project was an immediate success. The rapid transformation of the barren landscape into productive farmland led to the moniker "Magic Valley", and led to massive growth of the city of Twin Falls.[133][134] During certain times of the year, almost all the Snake River's flow was diverted at Milner Dam, and since then, Shoshone Falls has regularly run dry in the summer.[135] The Idaho State Historical Society writes that "Perrine’s venture contrasted remarkably with private canal company failures that led to congressional provision for federal reclamation projects after 1902. As a rare successful example of state supervised private irrigation development provided for in [the Carey Act] of 1894, Milner Dam and its canal system have national significance in agricultural history."[132]
With the creation of the Reclamation Service (now the Bureau of Reclamation) in 1902, the federal government began to play a more direct role in water resources development. The expansive Minidoka Project was the first federal reclamation project in Idaho.[136] Starting with Minidoka Dam in 1906, the project would grow over the next few decades to include major reservoirs at Jackson Lake, American Falls and Island Park, and a large network of canals and pump stations. The Minidoka Project would eventually bring water to a million acres (2,500 km2) of the Magic Valley.[136] During World War II, many Japanese Americans interned at Minidoka were made to work on the project.[136] The Boise Project, which would ultimately water 500,000 acres (200,000 ha) in and around the Boise Valley, was another major early reclamation undertaking. At its completion, Arrowrock Dam (1915) on the Boise River was the tallest dam in the world, and its construction process was an important prototype for future federal projects such as Hoover Dam.[137][138]

Starting around the 1950s, farmers made heavy use of the Snake River aquifer, bringing large new areas into production.[126] Surface water development also increased with projects such as Cascade Dam (1948) and Anderson Ranch Dam (1950), which provided additional storage for the Boise Project. Palisades Dam was built in 1956, providing flood control and irrigation for the Snake River above Idaho Falls, an area which the Bureau of Reclamation had previously overlooked.[139] Near Rexburg, the Teton Dam was also built to provide water for this area. In 1976, the Teton Dam failed catastrophically, killing eleven people and causing at least $400 million in damage along the Henrys Fork and Snake Rivers.[140] The political fallout from this disaster marked the end of large new irrigation developments not only for the Snake River system, but for the Bureau of Reclamation as a whole.[141] : 839–841
Agriculture has significantly impacted water quality in the Snake River upstream of Hells Canyon. Water removed from the river for irrigation becomes contaminated with chemical fertilizers and manure, and percolates into the Snake River Aquifer. Pollutants collect in the groundwater and eventually enter the river via spring flows.[142] Excess nitrogen, phosphorus and bacterial loads occur in many locations across southern Idaho.[143] Large algae blooms are a recurring issue in summer.[144] The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has established water quality guidelines for Snake River flows entering Hells Canyon, which cover bacteria, mercury, excess nutrients, pesticides, sediments and water temperature. Implementation of the guidelines include best management practices for agriculture and forestry, and regular water quality monitoring.[145]
Hydroelectricity
[edit]Power development of the Snake River began in the early 20th century as cities, farms, mines and industry grew around the river. The first small hydroelectric plant on the Snake River, Swan Falls Dam, was built in 1901,[146] followed by one at American Falls in 1902.[14] Many other projects followed, particularly around Shoshone Falls where the natural drop of the river offered great energy potential. After developing the Milner Dam irrigation scheme, I. B. Perrine built a hydroelectric plant at Shoshone Falls in 1907.[147] Small private utilities built power plants at Salmon Falls (1910) and Thousand Springs (1912). Idaho Power was incorporated in 1915, and acquired all the aforementioned plants the following year. It proceeded to build a second, larger plant at Shoshone Falls in 1921, and another plant at Twin Falls in 1935.[14] The advent of electric pumps opened up large new areas to agriculture, which had previously been limited to land where water could flow by gravity. The Minidoka Project, which included the Bureau of Reclamation's first hydroelectric plant in Idaho, was an early adopter of this system. The project generated more power than it needed, and surplus was sold to nearby towns such as Burley and Rupert, which created their own municipal electric systems.[148]: 89–92


By the 1940s, following the construction of massive hydropower dams on the Columbia River such as Grand Coulee, interest turned to the considerable untapped power potential of the Snake River in Hells Canyon. In 1947, Idaho Power set its sights on the upper section of the canyon, where it proposed a series of three medium-sized dams. Two years later, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (Army Corps) proposed a single massive dam, over 700 feet (210 m) high, to be built in lower Hells Canyon. In 1955 the Federal Power Commission authorized the Idaho Power project, but initially only one of the three dams, Brownlee (completed 1958), was built. The other dams, located downstream, would have been in the flood zone of not only the Army Corps' high dam, but two other competing proposals.[149]
The Pacific Northwest Power Company, a consortium of four private utilities, proposed the "High Mountain Sheep Dam" on the Snake River just upstream of the Salmon River. The even bigger "Nez Perce Dam", proposed by the Washington Public Power Supply System, would be located downstream of the Salmon River. While that location offered greater power potential, the fishery supported by the Salmon River was considered too economically valuable to wipe out, and in 1964 the Commission chose to authorize the High Mountain Sheep project.[150][149] By then, significant public opposition had formed against the high dam, as it would still block salmon migration to the upper Snake, and adversely affect wildlife and recreational values in Hells Canyon. It was also challenged by Washington Public Power, which argued that the commission should give priority to public utilities over private ones.[151]
The case reached the Supreme Court, which in the landmark 1967 ruling of Udall v. Federal Power Commission issued an injunction temporarily halting the project.[149] Justice William O. Douglas wrote that in licensing projects, the Commission must consider "future power demand and supply, alternate sources of power, the public interest in preserving reaches of wild rivers and wilderness areas, the preservation of anadromous fish for commercial and recreational purposes, and the protection of wildlife."[149][151] This was the first time the court cited environmental protection as a consideration for whether to approve a dam project.[151] In 1975, President Gerald R. Ford signed the Hells Canyon Wilderness into law, ending the high dam project for good.[149]
Meanwhile, Idaho Power moved forward with the Oxbow and Hells Canyon Dams, though the question of fish passage still remained. From 1956 to 1964, returning adult salmon had been trapped at the base of Brownlee Dam (whose height made a fish ladder impractical) and released upstream. Downstream passage of juvenile salmon posed a much bigger problem; many were killed passing through the hydroelectric turbines, and efforts to trap and release them downstream met with failure.[149] In 1960, Idaho Power proposed abandoning fish passage altogether and compensating for the loss by building fish hatcheries. By 1966 it reached an agreement with the Federal Power Commission to move forward with the hatchery plan, and by 1967 both Oxbow and Hells Canyon dams had been completed, neither with provision for fish passage. Idaho Power was tasked with building and operating the Oxbow, Rapid River, Niagara Springs and Pahsimeroi fish hatcheries at its own expense.[149][152]
As of 2007, the Hells Canyon Hydroelectric Complex was responsible for 40 percent of Idaho Power's total power generation.[153] The three dams have a capacity of 1,167 megawatts combined[154] and produce about 6,053 gigawatt hours per year.[153] Idaho Power's hatcheries produce almost seven million salmon and steelhead smolt to release in the Snake River system each year.[155][156] Since the completion of the Hells Canyon complex, with the exception of the lower Snake River dams, only one major hydroelectric dam has been built in the Snake River system – the Army Corps' Dworshak Dam (1973), in the Clearwater River basin. Like the Hells Canyon dams, Dworshak also generated controversy over its impact on fisheries, and also made no provision for fish passage; rather, a hatchery was built at the base of the dam.[157]
Navigation
[edit]
As gold mining declined in the late 19th century, the wheat industry boomed in the Palouse of southeast Washington. By the 1870s, the Oregon Steam Navigation Company was operating seven steamboats transporting grain from the Snake River to lower Columbia River ports. These were the Harvest Queen, John Gates, Spokane, Annie Faxon, Mountain Queen, R.R. Thompson, and Wide West.[158]: 122 In the 1890s, a huge copper deposit was discovered at Eureka Bar in Hells Canyon. Several ships transported ore from there to Lewiston, including Imnaha, Mountain Gem, and Norma.[158]: 162 In 1893 the Annie Faxon suffered a boiler explosion and sank on the Snake below Lewiston, killing five people.[159][15]: 160 Starting in the 1880s, the Army Corps began dredging the Snake River below Lewiston to maintain a 5-foot (1.5 m) deep navigation channel.[118]: 67
River traffic declined rapidly once railroads arrived. By 1899, the Union Pacific line along the south bank of the Snake River had reached Riparia, Washington. It then joined forces with the Northern Pacific Railroad, which was building a line along the north bank, to build the shared Camas Prairie Railroad the rest of the way to Lewiston, which it reached in 1908.[118]: 56, 80–81 The Open River Transportation Company, which operated steamboats between Lewiston and Celilo Falls on the Columbia, went bankrupt in 1912. The 1915 completion of the Celilo Canal made it much easier for boats from the upper Columbia and Snake to reach Portland, and the Columbia River Transportation Company began operating a water route between Lewiston and Portland. Still, steamboats were unable to compete with railroads on speed and efficiency. The last steamboat on the lower Snake ran in 1920.[118]: 67
Once the railroads monopolized grain shipments, they raised shipping rates, to farmers' consternation. In 1934, political activist Herbert G. West organized the Inland Empire Waterways Association (IEWA), to promote an "open river" – a deep-water shipping channel on the Snake and Columbia Rivers that could compete with rail.[160] The IEWA initially pushed for improvements such as bigger locks at Bonneville Dam in 1938 and the construction of McNary Dam on the Columbia, which would improve navigation to the mouth of the Snake.[152] In 1941 a bill was first introduced in Congress authorizing the Army Corps to develop the lower Snake River. The 1941 bill failed, but after several years of debate, Congress finally authorized the Snake River development in 1945.[118]: 83–85 Early plans included anywhere from six to ten low dams for the lower Snake. Eventually this was reduced to four bigger dams, which would lower costs, but would require what at the time were the tallest navigation locks in the world, at over 100 feet (30 m).[118]: 83–85
Tribes, state wildlife agencies and the fishing industry opposed the dams, arguing that they would kill too many salmon.[152] In 1947, the U.S. Department of the Interior proposed a ten-year moratorium on dam construction while the fishery problem was studied. With the onset of the Cold War, rising electricity demand in the Pacific Northwest – particularly at the nearby Hanford nuclear site – turned the project's focus towards hydropower. By 1948, the Army Corps estimated that over 80 percent of the economic benefits would come from power, and only 15 percent from navigation.[118]: 97–101 Dam opponents countered that if the primary objective was now power, other dam sites existed in the Northwest that would have less impact on fish. These objections proved futile, as the lower Snake River dams were already authorized, and the federal government had little interest in studying alternatives.[118]: 100–103 While opponents continued to stall the project for a few more years, Washington Senator Warren G. Magnuson pushed through a budget amendment in 1955 to start construction on the first dam, Ice Harbor.[118]: 104

Once construction began in 1956, Congress quickly approved more money to finish the project. Ice Harbor Dam was completed in 1962, and Lower Monumental and Little Goose Dams were completed in 1969 and 1970.[161] The Lower Monumental project generated controversy as it threatened to flood the Marmes Rockshelter archeological site. Although the Army Corps agreed to build a dike around the site, it began to leak as the reservoir filled and the site was inundated.[162] By the 1970s, the environmental movement in the US had become significantly larger, and groups such as the Association of Northwest Steelheaders lobbied to stop the construction of the fourth dam, Lower Granite. These efforts were unsuccessful, and the dam was completed in 1975. The first upriver barge reached Lewiston on April 10 of that year.[118]: 141 The Army Corps had planned one more dam at Asotin, which would have extended navigation to mines upstream of Lewiston.[118]: 127–134 Faced with public opposition, Congress deauthorized the project in 1975.[163]
Once the dams were completed, barges up to 12,000 tonnes and drawing 14 feet (4.3 m) of water were able to reach Lewiston.[164] Today, multiple barge terminals operate along the lower Snake, including Lewiston, Clarkston, Wilma, Central Ferry and Almota.[165] Grain accounts for the majority of barge traffic on the river; other shipments include forestry products, fuel, chemicals and fertilizers. In 2020, a total of 4.2 million short tons (3,800,000 t) of cargo were barged on the Snake River.[166][165] Since 2000, the tonnage of commercial shipping on the Snake River has declined, due mostly to the loss of petroleum products after a pipeline was constructed. After the general decline of the Great Recession, other sectors have been slow to recover.[167] As of 2015, grain tonnage had fallen about a third from 2000 levels, while forestry products had fallen by nearly three-quarters, with many shipments switching back to rail.[168] Container shipping at the Port of Lewiston ceased in 2015,[169] due to its primary source, the Port of Portland, no longer receiving containers.[170] From 2015 to 2023, grain exports from the Port of Lewiston have remained relatively steady while breakbulk cargo has increased.[171]
As dam opponents had feared, Snake River salmon returns declined greatly after the dams were built. Since 2000, there have been renewed calls for removing the lower Snake River dams, which have become a significant political issue for the Pacific Northwest.[172]
Ecology and environmental issues
[edit]Aquatic habitats
[edit]
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) divides the Snake River into two freshwater ecoregions – the Upper Snake and Columbia Unglaciated – with Shoshone Falls marking the boundary between the two. Shoshone Falls has presented a total barrier to the upstream movement of fish at least since the Bonneville flood 15,000 years ago. The Big Wood River (the main tributary of the Malad River) is also included in the Upper Snake ecoregion, due to the presence of a separate natural waterfall barrier. As a result, only 35 percent of the fish fauna above Shoshone falls, and 40 percent of the Big Wood River's fish fauna, are shared with the lower Snake River.[173][174]
Compared to the lower Snake River and the rest of the Columbia River system, the Upper Snake ecoregion has a high level of endemism, especially among freshwater molluscs such as snails and clams. At least 21 snail and clam species are of special concern, including 15 that appear to exist only in single clusters.[175]: 167–169 There are 14 fish species found in the Upper Snake region that do not occur elsewhere in the Columbia's watershed, but which do occur in some western Utah watersheds and the Yellowstone River. These include healthy populations of Yellowstone cutthroat trout and Snake River fine-spotted cutthroat trout.[28]: 608 The Wood River sculpin is endemic to the Wood River. The Shoshone sculpin is endemic to the small portion of the Snake River between Shoshone Falls and the Wood River.[175]: 167–169
The Snake River below Shoshone Falls is home to about 35 native fish species, of which 12 are also found in the Columbia River and four of which are endemic to the Snake or nearby watersheds: the sand roller, shorthead sculpin, margined sculpin and the Oregon chub, which also occurs in a few other Oregon streams.[175] Bull trout migrate from the main stem of the Snake to spawn in several tributary basins, including the Bruneau,[28]: 608 Imnaha and Grande Ronde Rivers.[176] Large white sturgeon, introduced to the Snake River in the 19th century, were once widespread in the Snake River below Shoshone Falls; due to dam construction, only a few fragmented populations remain.[28]: 608–609 The Idaho Department of Fish and Game has occasionally recorded sturgeon more than 10 feet (3.0 m) long in Hells Canyon.[177] Other common introduced species include whitefish, pikeminnow, smallmouth bass, and rainbow, brown, brook and lake trout.[28]: 608
Anadromous fish
[edit]Anadromous salmonids (Oncorhynchus), including chinook, coho, and sockeye salmon, and redband and steelhead trout, were historically the most abundant fish and a keystone species of the Snake River system.[178] Benke and Cushing's Rivers of North America describes the Snake as a "wild salmon factory;"[28]: 608 prior to the 19th century, between two and six million adult salmon and steelhead returned each year from the Pacific to spawn in the Snake River watershed.[178] Salmon die after spawning, and their carcasses represent a crucial influx of organic matter to mountain rivers that have few natural nutrient sources.[125] Tributaries below Hells Canyon, particularly the Salmon River, held the richest spawning grounds, although substantial numbers also made it above Hells Canyon as far as Shoshone Falls.[179] The Snake River produced about 40 percent of all chinook salmon and 50 percent of all steelhead in the Columbia River watershed.[178]

Populations of anadromous fish began to decline in the late 1800s due to the impact of commercial fishing, logging, mining and agriculture,[125] but even in the 1930s, returning fall chinook alone numbered 500,000.[180] Populations further collapsed once dams were built on the lower Snake and Columbia Rivers, and Hells Canyon Dam blocked access to the upper Snake. Wild Snake River spring and summer chinook returns declined from 130,000 in the 1950s to less than 5,000 in the 1990s. Wild steelhead returns followed a similar pattern, falling from 110,000 in the 1960s to less than 10,000 in the 1990s. Spring, summer and fall-run chinook were all listed as threatened in 1992.[181][182] Snake River steelhead were also listed as threatened in 1997.[183]
Wild chinook salmon and steelhead continued to decline into the 1990s, but have begun an unsteady recovery since 2000, with both chinook and steelhead returns up to 20,000–30,000 in some years.[184] Coho salmon had disappeared from the Snake River by the 1980s, they were reintroduced to the watershed in 1995.[185]
Snake River sockeye once numbered to up 150,000 adults.[186] Between 24,000 and 30,000 sockeye returned to Wallowa Lake in the Grande Ronde River watershed, but the run was eliminated by 1905 due to overharvest and unscreened irrigation diversions.[187] The Payette Lake population once numbering up to 100,000 was blocked by the Black Canyon Dam in 1924.[186] Sockeye in the Yellowbelly, Stanley, and Pettit Lakes of the Sawtooth basin were eradicated by management actions of the Idaho Department of Fish and Game in the 1950s, and irrigation diversions lead to the extirpation of the Pettit Lake population.[186] Snake River sockeye returns declined to 4,500 in the 1950s and only a few dozen by the late 1960s.[184] Snake River sockeye were listed as endangered in 1991.[188]
Numerous hatcheries are operated by agencies such as the Army Corps, Idaho Power, the Bonneville Power Administration, the U.S. Bureau of Indian Affairs and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, to supplement wild fish populations.[189] Hatcheries release about 33 million salmon and steelhead smolt into the Snake River watershed each year.[190] However, the survival rate for hatchery fish is poor. Just 0.4 percent of hatchery chinook and 1.5 percent of hatchery steelhead returned as adults, as measured at Lower Granite Dam between 2007 and 2016.[190]
Upstream of the four lower dams, the Snake River watershed contains some of the best remaining spawning habitat in the Columbia River system, particularly along the Clearwater and Salmon Rivers; the latter is one of the longest undammed rivers in the continental US.[28]: 609 A much depleted sockeye salmon run continues to spawn in Redfish Lake near Stanley, Idaho, more than 900 miles (1,400 km) inland from the Pacific Ocean. This represents the southernmost, highest elevation and longest sockeye run in the world.[191]
Terrestrial and wetland habitats
[edit]
The Snake River provides important wildlife habitat along much of its course, particularly in the arid Snake River Plain where it is the only source of water for many miles. The upper reaches of the Snake River, including in Jackson Hole and the floodplain north of Idaho Falls where it joins the Henrys Fork, have extensive riparian gallery forests dominated by black cottonwood and narrowleaf cottonwood.[28]: 607 The Northwest Power and Conservation Council describes these as "some of the most important cottonwood gallery forests in the Intermountain West".[29] Seasonal floods scour and change the shoreline, clearing areas of older trees and making way for new growth. Ute lady's tresses, a rare orchid, are found in riparian wetlands along with willows, rushes, sedges and horsetails.[28]: 607
The Fort Hall Bottoms in the southern Snake River Plain are an important wetland along the river, and create a major wintering and nesting site for waterfowl, shorebirds and raptors, including bald eagles and trumpeter swans.[192] Part of these wetlands were flooded with the construction of American Falls Dam, and large portions of the remainder have been degraded by cattle grazing.[192] Ponds and wetlands in the Hagerman Valley, near the Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument, are also heavily used by both migratory and resident birds.[193] On the Snake River south of Boise is the nearly 500,000-acre (200,000 ha) Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area, which hosts the densest concentration of nesting raptors in the US.[194]
The Snake River headwaters are part of the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, which the National Park Service describes as "one of the largest nearly intact temperate-zone ecosystems on Earth." The region is home to some of the largest wild elk and bison populations in the US, and provides habitat for grizzly bear, wolverine and lynx.[195] The other major wild area in the Snake River watershed centers on Idaho's extremely rugged Frank Church–River of No Return Wilderness, the largest federally designated wilderness in the contiguous US.[196][28]: 609 Although the Snake River watershed remains lightly populated, most of its landscape has seen significant human impact since the 19th century. Heavy logging has historically occurred in the Boise area[197] and on the Clearwater River, which hosted the last whitewater log drive in the US in 1971.[198] Logging is still a major industry in the region, though since the 1990s, logging south of the Clearwater has decreased.[199] Large areas of native sagebrush-steppe ecosystems, mostly in the Snake River Plain and Palouse, have been developed for agriculture. About two-thirds of the Snake River Plain remains grassland or shrubland; however, much of this acreage is impacted by livestock grazing, and fire regimes have become more severe with the proliferation of invasive species like cheatgrass.[200]
Proposed dam removal
[edit]
The lower Snake River dams have remained controversial since their construction, and in the 21st century there has been increased debate over potentially removing the dams. Although the dams were built with fish ladders, the warm, slow-moving water in reservoirs disoriented migrating fish,[201] and juvenile fish experienced significant mortality passing through the dams.[152] In 1980 Congress passed the Northwest Power Act, which requires federal agencies in the Northwest to mitigate the impact of their dams on fish and wildlife. While installation of fish screens and bypasses have improved survival rates for juvenile fish,[152] efforts to capture fish and transport them around the dams have seen little success.[28]: 609–610 Although wild salmonid returns have seen a positive trend since their nadir in the 1990s, they remain well below pre-dam levels.[184]
Supporters of dam removal, which include tribal organizations such as the Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission and environmental advocacy groups such as the Natural Resources Defense Council and the Sierra Club, argue that the most economical way to restore the fishery is to remove the dams, rather than continuing recovery efforts at great expense. As of 2023, over $17 billion had been spent on Snake River salmon recovery and hatchery operations.[202] There are other economic arguments for dam removal, particularly that the annual cost of maintaining the barge channel exceeds the economic benefits provided by shipping, and the freight can be moved by rail instead.[168][203] Furthermore, the dams only account for a small percentage of the total hydropower in the Northwest.[203] A University of Idaho analysis estimated that over a 20-year period, removing the dams would be less expensive than the cost of continuing fish recovery efforts with the dams in place.[203] Representative Mike Simpson (R-ID) has been a major supporter of dam removal, and in 2021 put forth an ambitious proposal to remove the dams,[204] though Simpson's plan has come under scrutiny as among other actions, it would also impose "a 35-year moratorium on litigation related to anadromous fish" at federal Columbia River Basin dams.[205][206]
Opponents of dam removal include farmers, local governments such as the city of Lewiston,[207] congressional representatives in eastern Washington[208] and the Bonneville Power Administration, which manages federal hydroelectric dams in the Northwest.[172] In the context of shipping, while river traffic has declined in recent years, it remains important to the area's economy, and moving cargo by barge is cheaper and twice as fuel-efficient as diesel trains.[209] While the dams do not generate much baseload power, they are crucial to managing peak demand on a daily basis, as hydropower can be ramped up and down quickly. As more wind and solar energy is added to the Northwest grid, more load balancing will be needed to compensate for the intermittent nature of those sources.[210][211] Although Washington governor Jay Inslee and Washington Senator Patty Murray have tentatively endorsed dam removal, they stressed that hydropower must be replaced by other renewable sources, and economic impacts such as the loss of the ship channel should be "mitigated or replaced."[212]
In December 2023, the Biden administration expressed its support for the Columbia Basin Restoration Initiative, which would develop a strategy to replace the power and navigation benefits provided by the Snake River dams, and explore options for post-dam river restoration. The initiative is an agreement between the federal government, four tribal nations, the states of Washington and Oregon, and several conservation groups. It would not authorize the removal of the dams, which would require a separate act of Congress.[213][214]
See also
[edit]- List of crossings of the Snake River
- List of tributaries of the Columbia River
- List of rivers of Idaho
- List of rivers of Oregon
- List of rivers of Washington (state)
- List of rivers of Wyoming
- List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem)
- List of longest streams of Idaho
- List of longest streams of Oregon
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e "Snake River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. December 31, 1981. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ a b U.S. Geological Survey. "U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Badger Creek, Wyoming quad". TopoQuest. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v "National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data from The National Map". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved December 15, 2023.
- ^ a b c d "Boundary Descriptions and Names of Regions, Subregions, Accounting Units and Cataloging Units". U.S. Geological Survey. Archived from the original on April 27, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Data Query: Ice Harbor Dam and Lake Sacajawea". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Retrieved January 31, 2024. Data collected at this station must be downloaded in CSV format.
- ^ "National Wild and Scenic Rivers System". rivers.gov. National Wild and Scenic Rivers System. Retrieved January 5, 2023.
- ^ a b c "Henrys Fork". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. June 21, 1979. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "South Fork of the Snake". U.S. Bureau of Land Management. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ Olenichak, Tony (April 14, 2023). "Concepts, practices and procedures used to distribute water within Water District #1, Upper Snake River Basin, Idaho" (PDF). Idaho Water District 1. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey. "U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Kimberly, Idaho quad". TopoQuest. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey. "U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Twin Falls, Idaho quad". TopoQuest. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey. "U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Jerome, Idaho quad". TopoQuest. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey. "U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Hagerman, Idaho quad". TopoQuest. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ a b c "Hydroelectric Plants". Idaho Power. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f Williamson, Darcy (1997). River Tales of Idaho. Caxton Press. ISBN 9780870045318.
- ^ Holmes, Brian (October 22, 2021). "How a Caldwell businessman in 1959 gave the Treasure Valley its name". KTVB 7. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ "Hells Canyon Complex FERC No. 1971 License Application" (PDF). Idaho Power. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ "Columbia Basin Passage Barriers". Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ Stahl, Greg (2016). Paddling Idaho: A Guide to the State's Best Paddling Routes. Falcon Guides. ISBN 9781493027088.
- ^ Sowards, Adam M. (August 9, 2023). "Hells Canyon". Oregon Encyclopedia. Oregon Historical Society. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ "Wild and Scenic Snake River- Trip Planning". U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Snake River". National Wild and Scenic Rivers System. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ a b "Hells Canyon National Recreation Area - Fast Facts". U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ "Columbia-Snake River System". Port of Lewiston. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey. "U.S. Geological Survey Topographic Map: Pasco, Washington quad". TopoQuest. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ Perkins, L.Z. (1973). Ice Harbor Dam, Snake River, Washington: Hydraulic Model Investigations (Report). U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. p. 1.
- ^ Kammerer, J. C. (May 1990). "Largest Rivers in the United States". U.S. Geological Survey. Archived from the original on January 29, 2017. Retrieved April 1, 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Benke, Arthur C.; Cushing, Colbert E., eds. (2005). Rivers of North America. Elsevier Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-088253-1.
- ^ a b "Upper Snake Province Assessment" (PDF). Northwest Watershed Council. May 28, 2004. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 18, 2021. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ Andrews, Douglas A.; Minshall, G. Wayne (1979). "Distribution of Benthic Invertebrates in the Lost Streams of Idaho" (PDF). The American Midland Naturalist. 102 (1): 140–148. doi:10.2307/2425075. JSTOR 2425075. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ a b "Eastern Snake River Plain- Hydrogeology". Digital Atlas of Idaho. Idaho State University. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River Plain aquifer". Idaho State University. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ "Eastern Snake River Plain Surface and Ground Water Interaction" (PDF). Idaho Department of Water Resources. January 18, 2002. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13154500 Snake River at King Hill, ID: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13213100 Snake River at Hells Canyon Dam: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River – Hells Canyon Subbasins". Idaho Department of Environmental Quality. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #12514000 Columbia River at Pasco, WA". National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #12472800 on the Columbia River below Priest Rapids Dam, WA (Water-Data Report 2013)" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved December 15, 2023.
- ^ "Gannett Peak". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. December 31, 1981. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River, Wyoming Period of Record General Climate Summary". Western Regional Climate Center. Archived from the original on January 17, 2022. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ "Twin Falls, Idaho Period of Record General Climate Summary". Western Regional Climate Center. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved February 24, 2016.
- ^ "Ice Harbor Dam, Washington: Period of Record General Climate Summary". Western Regional Climate Center. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ "Bureau of Land Management public lands and administrative jurisdictions : [western United States]". Library of Congress. 2005. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ "Watersheds (map)". Commission for Environmental Cooperation. 2006. Archived from the original on August 7, 2008.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13056500 Henrys Fork near Rexburg, ID: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Salmon Falls Creek". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. June 21, 1979. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13108150 Salmon Falls Creek near Hagerman, ID: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Malad River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. May 1, 1989. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13153500 Malad River near Bliss, ID: Monthly Statistics". National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13152940 Malad River Power Flume near Bliss, ID: Monthly Statistics". National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ^ a b "Bruneau River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. June 21, 1979. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13168500 Bruneau River near Hot Spring, ID: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Owyhee River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. November 28, 1980. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13181000 Owyhee River near Rome, OR: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Boise River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. June 21, 1979. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13213000 Boise River near Parma, ID: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Malheur River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. November 28, 1980. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13233300 Malheur River below Nevada Dam near Vale, OR: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Payette River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. December 31, 1992. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13251000 Payette River near Payette, ID: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Salmon River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. December 31, 1992. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13317000 Salmon River at White Bird, ID: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Grande Ronde River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. September 10, 1979. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13333000 Grande Ronde River at Troy, OR: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Clearwater River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. June 21, 1979. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13342500 Clearwater River at Spalding, ID: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ a b "Palouse River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. September 10, 1979. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "USGS Gage #13351000 Palouse River at Hooper, WA: Water-Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 2013. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ^ "The Geologic Story of the Columbia Basin". Bonneville Power Administration. Archived from the original on July 8, 2017. Retrieved June 20, 2017.
- ^ Moclock, Leslie; Selander, Jacob (2021). Rocks, Minerals, and Geology of the Pacific Northwest. Timber Press. ISBN 9781604699159.
- ^ a b c d Reidel, Stephen P., ed. (2013). The Columbia River Flood Basalt Province. The Geological Society of America. ISBN 9780813724973.
- ^ Bingham, Richard T. (1987). Plants of the Seven Devils Mountains of Idaho. U.S. Department of Agriculture.
- ^ "Blue Mountains". Washington State Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved January 20, 2024.
- ^ a b c d Lifton, Zach (November 21, 2022). "The Snake River Plain: A Tale of Two Basins". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ "Snake River Plain, Idaho". NASA Earth Observatory. August 29, 2008. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Link, Paul. "Neogene Snake River Plain-Yellowstone Volcanic Province". Idaho State University. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ a b c Wood, Spencer H.; Clemens, Drew M. (2002). "Geologic and Tectonic History of the Western Snake River Plain, Idaho and Oregon" (PDF). Idaho Department of Water Resources. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ a b "Snake River Plain Topographic Development" (PDF). Idaho State University. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Pederson, J.L.; Janecke, S.U.; Reheis, M.C.; Kaufman, D.S.; Oaks, R.Q. Jr. (2016). "The Bear River's History and Diversion: Constraints, Unsolved Problems, and Implications for the Lake Bonneville Record". Developments in Earth Surface Processes. 20: 28–59. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-63590-7.00002-0. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Tucker, David Samuel; Stelling, Peter L., eds. (2007). Floods, Faults, and Fire: Geological Field Trips in Washington State and Southwest British Columbia. Geological Society of America. ISBN 978-0-8137-0009-0.
- ^ "Geology of Grand Teton National Park". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ a b c Love, J.D.; Reed, John C. (1971). "Quaternary – Time of Ice, More Lakes, and Continued Crustal Disturbance". Creation of the Teton Landscape: The Geologic Story of Grand Teton National Park. U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ a b c "Lake Bonneville flood". Digital Geology of Idaho. Idaho State University. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ "The Lake Bonneville Flood". Idaho State University. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ "Palouse and glacial Lake Missoula". Digital Geology of Idaho. Idaho State University. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ "Ice Age Floods" (PDF). Washington State Parks. April 13, 2022. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ a b c Louter, David (1995). "Native Inhabitants of the Craters of the Moon Region". Historic Context Statements: Craters of the Moon National Monument, Idaho. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ "The Marmes Rockshelter Site: Site Interpretations". Washington State University. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ Meatte, Daniel S. (1990). "The Fremont Culture". The Prehistory of the Western Snake River Basin. Digital Atlas of Idaho. Archived from the original on June 26, 2012. Retrieved October 5, 2009.
- ^ a b c "The Treaty Period". Nez Perce National Historic Park. U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ a b c d Coues, Elliott, ed. (1893). History of the Expedition Under the Command of Lewis and Clark To the Sources of the Missouri River, Thence Across the Rocky Mountains and Down the Columbia River to the Pacific Ocean, Performed During the Years 1804-5-6, by Order of the Government of the United States · Volume 2. F.P. Harper.
- ^ Wheeler, Olin Dunbar (1904). The Trail of Lewis and Clark, 1804-1904: A Story of the Great Exploration Across the Continent in 1804-6; with a Description of the Old Trail, Based Upon Actual Travel Over It, and of the Changes Found a Century Later. G.P. Putnam's Sons.
- ^ Hunn, Eugene S.; Morning Owl, E. Thomas; Cash, Phillip E Cash; Engum, Karson Jennifer. Cáw Pawá Láakni, They Are Not Forgotten: Sahaptian Place Names Atlas of the Cayuse, Umatilla and Walla Walla. University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0-295-99026-2.
- ^ Walgamott, C.S. (1927). Reminiscences of Early Days, A Series of Historical Sketches and Happenings in the Early Days of Snake River Valley. Vol. 2. Idaho Citizen.
- ^ Fluharty, David L. (April 2000). "Characterization and Assessment of Economic Systems in the Interior Columbia Basin: Fisheries" (PDF). U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Schacher, Cindy L. (2004). "The Southern Nez Perce Trail, Wise'isskit" (PDF). U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ "Fish". Nez Perce National Historical Park. U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved February 5, 2024.
- ^ Walker, Deward E. Jr. (1993). "The Shoshone-Bannock: An Anthropological Reassessment". Northwest Anthropological Research Notes. 27 (2): 230–237. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ Gehr, Elliott A.; Lee, Evelyn; Johnson, Gretchen; Merritt, J. Donald; Nelson, Steven (December 1982). Southwestern Idaho Class I Cultural Resources Overview, Boise and Shoshone Districts, Part 5: Cultural Resources Narrative (Report). U.S. Bureau of Land Management. pp. 39–44. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ Harrod, Ryan P.; Tyler, Donald E. (2016). "Skeletal evidence of pre-contact conflict among native groups in the Columbia Plateau of the Pacific Northwest". Journal of Northwest Anthropology. 50 (2): 228–264. ISBN 978-1-5391-2889-2. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ Haines, Francis (February 1964). "How the Indian Got The Horse". American Heritage. 15 (2). Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ "Lolo Trail and Pass History". Nez Perce National Historical Park. U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ Trenholm, Virginia Cole; Carley, Maurine (1969). The Shoshonis : Sentinels of the Rockies. University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-0628-1.
- ^ "Encyclopedia of the Great Plains | SHOSHONES".
- ^ "The Indian sign language". 1982.
- ^ "Snake River" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series. 38: 2. February 1964. Retrieved December 15, 2022.
- ^ "Lewis and Clark and the Nez Perce". Nez Perce National Historic Park. U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ a b c "Snake River Explorers" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series. Idaho State Historical Society. April 1992. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 15, 2012. Retrieved June 24, 2013.
- ^ a b Louter, David (1995). "Close Encounters: The Fur Trade in the Craters of the Moon Region, 1820-1856". Historic Context Statements: Craters of the Moon National Monument, Idaho. U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ Moulton, Candy (October 1, 2005). "Trailing Wilson Price Hunt's Astorians West". True West. Retrieved February 1, 2023.
- ^ Josephy, Alvin M. (1997). The Nez Perce Indians and the Opening of the Northwest. Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 9780395850114.
- ^ a b c Kaza, Roger. "Hudson's Bay Company". Engines of our Ingenuity. University of Houston. Archived from the original on September 28, 2012. Retrieved October 5, 2009.
- ^ Ott, Jennifer Susan (1997). "Clearing the Country: A History of the Hudson's Bay Company's Fur Desert Policy". University of Montana. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ a b "History of Three Island Crossing State Park". Idaho Department of Parks and Recreation. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ "Three Island Crossing State Park". Oregon National Historic Trail. U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ "Research Guide on Snake River Ferries" (PDF). Idaho Transportation Department. Jan 2017. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ "Eagle Rock" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series. Idaho State Historical Society. Jan 1993. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Petersen, Keith C.; Reed, Mary E. "Controversy, Conflict and Compromise: A History of the Lower Snake River Development" (PDF). DamSense. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ "The Ward Massacre". The Historical Marker Database. Retrieved December 14, 2023.
- ^ "The Snake War, 1864–1868" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series. Idaho State Historical Society. 1966. Retrieved December 14, 2023.
- ^ Treuer, Anton (2013). Atlas of Indian Nations. National Geographic Books. ISBN 9781426211607.
- ^ "Visit Dug Bar". Nez Perce National Historic Park. U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ "The Flight of the Nez Perce". U.S. Geological Survey. July 18, 2022. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ Richardson, Camilla. "1878 Bannock War and Chief Buffalo Horn". Intermountain Histories. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ a b c d Long, Priscilla (January 7, 2021). "Salmon in the Pacific Northwest". HistoryLink. Retrieved December 12, 2023.
- ^ a b c d "Irrigation in Idaho" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series. Idaho State Historical Society. Jun 1971. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ "A Brief History of Union Pacific Railroad's Idaho Division" (PDF). Utah Rails. Retrieved December 12, 2023.
- ^ Schwantes, Carlos A. (1994). "Tourists in Wonderland: Early Railroad Tourism in the Pacific Northwest" (PDF). Columbia Magazine. 7 (4). Retrieved December 12, 2023.
- ^ "Idaho Falls Power – History". City of Idaho Falls. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ "Early Irrigation Canals Pre-Project Ventures" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series. Idaho State Historical Society. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ "Idaho: Arrowrock Dam". U.S. National Park Service. January 13, 2017. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ a b "Milner Dam" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series. Idaho State Historical Society. 1985. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ "History of Milner Dam". Twin Falls Canal Company. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ "The History of Twin Falls". City of Twin Falls. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ Urbanek, Abby (March 7, 2023). "The power of water: Making the Magic Valley magic". Idaho Conservation League. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- ^ a b c "Idaho: Minidoka Dam". U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ Hyde, Luke. "Arrowrock Dam, Engineering Innovation and Building Block to Boise's Expansion". Intermountain Histories. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- ^ Simonds, Joe (1997). "The Boise Project". Bureau of Reclamation History Program. U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- ^ Franzen, Josh. "The Palisades Dam: Irrigation of the Snake River". Intermountain Histories. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- ^ "Case Study: Teton Dam (Idaho), 1976". Association of State Dam Safety Officials. Retrieved January 10, 2024.
- ^ The Bureau of Reclamation: From Developing to Managing Water, 1945-2000. U.S. Government Printing Office. 2013. ISBN 9780160913648.
- ^ "Groundwater Resources". Digital Atlas of Idaho. Idaho Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on June 25, 2010. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ Black, Lexi (January 26, 2024). "Pollution Science: Understanding the building blocks for restoring Idaho's Snake River". Idaho Conservation League. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ "Pollution of the Snake River". Ecology and Conservation. Central Washington Native Plants. Archived from the original on October 23, 2009. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ "Snake River - Hells Canyon Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL)". U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2004. Retrieved January 31, 2024.
- ^ "Swan Falls Park". Idaho Power. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ^ Matthews, Mychel (December 20, 2012). "Hidden History: The Power Plant at Shoshone Falls". The Times-News. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ^ Hirt, Paul W. (2012). The Wired Northwest: The History of Electric Power, 1870s-1970s. University Press of Kansas. ISBN 9780700618736.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Hells Canyon". Northwest Power and Conservation Council. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ^ "Mountain Sheep-Pleasant Valley Hydroelectric Project on the Middle Snake River in Idaho and Oregon" (PDF). Idaho Department of Fish and Game. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ^ a b c "U.S. Supreme Court Halts the Construction of the High Mountain Sheep Dam". Public History PDX. Portland State University. June 4, 2017. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e "Fish passage at dams". Northwest Power and Conservation Council. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ a b "Final Environmental Impact Statement for Hydropower License, Hells Canyon Hydroelectric Project" (PDF). Idaho Power. August 2007. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ "Idaho Energy Landscape" (PDF). Idaho Governor's Office of Energy and Mineral Resources. 2021. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ "Our Hatchery Program". Idaho Power. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ "Jim Chandler on Idaho Power's Plans to Improve Fisheries and Water Quality in the Snake River". Hydro Leader. 9 May 2022. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ Hedberg, Kathy (October 1, 2023). "Dworshak Dam: The 'last of its kind' reaches milestone". Moscow-Pullman Daily News. Yahoo News. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ a b Gulick, Bill (2004). Steamboats on Northwest Rivers. Caxton Press. ISBN 0-87004-438-9.
- ^ Dougherty, Phil (April 9, 2006). "Steamers on the Lower Snake". HistoryLink. Archived from the original on August 18, 2009. Retrieved October 5, 2009.
- ^ "Visionaries". Northwest Power and Conservation Council. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ Kramer, Becky (October 24, 2016). "Lower Snake River dams have a long history of controversy". The Spokesman-Review. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ^ Judd, Ron (November 22, 2017). "Site unseen: Floodwaters buried a treasure trove at Marmes Rockshelter". Pacific NW Magazine/The Seattle Times. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ "Public Law 94-199, 94th Congress: An act to establish the Hells Canyon National Recreation Area in the States of Oregon and Idaho, and for other purposes" (PDF). U.S. National Wild and Scenic Rivers System. December 31, 1975. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ Blumenthal, Ralph (April 13, 1975). "Idaho Gets a Seaport, Capping a Costly 10-Year Effort". The New York Times. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ a b "Lower Snake River Dams: Benefit Replacement Report" (PDF). Office of the Governor, State of Washington. August 2022. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River Dredging" (PDF). Pacific Northwest Waterways Association. 2023. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ Fruits, Eric (October 2014). "Review of Comments Regarding the Economics of Lower Snake River Dredging" (PDF). Port of Lewiston. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ a b Jones, Anthony (September 30, 2015). "Lower Snake River Dam Navigation Study" (PDF). Save Our Wild Salmon. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ "Port of Lewiston loses 100 percent of its container traffic". DamSense. April 8, 2015. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ Laughy, Linwood (January 4, 2017). "Lower Snake River commerce hits all-time low". Idaho Rivers United. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ "Shipping Reports". Port of Lewiston. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ a b Helmer, Jodie (July 18, 2018). "In the Columbia–Snake River Basin, Salmon Are Losing Their Way". Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ "Columbia Unglaciated". World Wide Fund for Nature and the Nature Conservancy. Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved April 14, 2010.
- ^ "Upper Snake". World Wide Fund for Nature and the Nature Conservancy. Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved April 14, 2010.
- ^ a b c Abell, Robin A.; David M. Olsen; Eric Dinerstein; Patrick T. Hurley; et al. (2000). Freshwater Ecoregions of North America: A Conservation Assessment. Island Press. ISBN 1-55963-734-X.
- ^ "Bull Trout Redd Monitoring in the Wallowa Mountains". U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. March 31, 2021. Retrieved January 8, 2024.
- ^ "Hells Canyon sturgeon are so big that anglers don't need to lie about how big they are". Idaho Department of Fish and Game. December 27, 2021. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ a b c "America's Most Endangered Rivers: Snake River" (PDF). American Rivers. 2022. Retrieved January 8, 2024.
- ^ Nemeth, Douglas J.; Kiefer, Russell B. (October 1999). "Snake River Spring and Summer Chinook Salmon - The Choice for Recovery" (PDF). Idaho Department of Fish and Game. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River Fall Chinook Recovery". Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission. November 9, 2012. Retrieved January 8, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River Spring/Summer-run Chinook Salmon". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. November 8, 2023. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River Fall-run Chinook Salmon". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. January 22, 2024. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River Basin Steelhead". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. August 17, 2023. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ a b c "Snake River Adult Returns for wild Spring/Summer Chinook Salmon, Sockeye Salmon and Steelhead: 1950s to Present" (PDF). Save Our Wild Salmon. Retrieved January 8, 2024.
- ^ "Nez Perce Tribal Program Resurrects Snake River Basin Coho Salmon". Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission. Retrieved January 22, 2024.
- ^ a b c National Marine Fisheries Service West Coast Region (2003). Status of the Species. Snake River Sockeye Salmon. pp. 1–2.
- ^ Cramer, Steven; Witty, Kenneth (1998). Feasibility for Reintroducing Sockeye and Coho Salmon in the Grande Ronde Basin. BPA. Report DOE/BP 30423 1.
- ^ "Snake River Sockeye Salmon". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. February 22, 2023. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ "Snake River Basin Hatchery Programs". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2 October 2019. Retrieved February 4, 2024.
- ^ a b McMillan, John (July 1, 2021). "Hatcheries can't save Snake River salmon and steelhead". Trout Unlimited. Retrieved January 22, 2024.
- ^ Kline, Paul A.; Flagg, Thomas A. (2014). "Putting the Red Back in Redfish Lake, 20 Years of Progress Toward Saving the Pacific Northwest's Most Endangered Salmon Population" (PDF). Fisheries. 39 (11): 488–500. Bibcode:2014Fish...39..488K. doi:10.1080/03632415.2014.966087. Retrieved January 22, 2024.
- ^ a b Osborne, Hunter. "Habitat Restoration/Enhancement, Fort Hall Reservation: 2008 Annual Report" (PDF). University of North Texas. Retrieved January 20, 2024.
- ^ "Birding in the Hagerman Valley". U.S National Park Service. Retrieved January 20, 2024.
- ^ "Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey". U.S. Bureau of Land Management. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ "Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem". U.S. National Park Service. August 21, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ "Frank Church River of No Return Wilderness". U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ "Lumber in the Boise Region" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Reference Series. Idaho State Historical Society. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ McCollister, Charles; McCollister, Sarah (2000). "The Clearwater River Log Drives" (PDF). Forest History Today. Forest History Society. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Simmons, Eric A.; Morgan, Todd A.; Berg, Erik C.; Zarnoch, Stanley J.; Hayes, Steven W.; Thompson, Mike T. (March 2014). "Logging Utilization in Idaho: Current and Past Trends" (PDF). U.S. Government Publishing Office. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Sleeter, Benjamin M. (2012). "Snake River Basin Ecoregion" (PDF). U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1794–A, Status and Trends of Land Change in the Western United States, 1973 to 2000. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ "The Lower Snake River Dams". Idaho Rivers United. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ "Recovering Snake River Salmon". National Wildlife Federation. Retrieved February 2, 2024.
- ^ a b c "Revenue Stream: An Economic Analysis of the Costs and Benefits of Removing the Four Dams on the Lower Snake River" (PDF). University of Idaho. Retrieved January 21, 2024.
- ^ Austin, Hayley; Smith, Anna V. (January 1, 2023). "Can dam removal save the Snake River?". High Country News. Retrieved January 24, 2024.
- ^ Wilson, Patrick (Aug 2021). "Northwest In Transition: The Simpson Plan" (PDF). University of Idaho. Retrieved January 5, 2024.
- ^ "Rep. Simpson's Concept for the Lower Snake River Dams and Environmental Justice" (PDF). Wild Fish Conservancy. 2022. Retrieved January 5, 2024.
- ^ "Lewiston City Council Votes to Support Keeping Snake River Dams". Big Country News. November 15, 2022. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Cary, Annette (January 24, 2024). "GOP reps ramp up fight on 'hypocritical assault' on Snake River dams in Eastern WA". Tri-City Herald.
- ^ "Legislation Supports Barge Transportation and Lower Snake River Dams". U.S. Wheat Associates. December 9, 2022. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ "Lower Snake River Dams Fact Sheet" (PDF). Northwest River Partners. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Mapes, Lynda V. (February 27, 2020). "For first time in 20 years, feds take deep look at hydroelectric dam removal on Lower Snake River". The Seattle Times. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Hunt, Chris (August 30, 2022). "Inslee and Murray would support Snake River dam removal". Hatch. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Smith, Anna V. (December 15, 2023). "Lower Snake River dams closer to coming down with new agreement". High Country News. Retrieved January 31, 2024.
- ^ "Columbia Basin Restoration Initiative" (PDF). EarthJustice. December 14, 2023. Retrieved January 31, 2024.
Notes
[edit]- ^ The Treasure Valley was historically known as the Boise Valley or Snake River Valley, and was only given the modern name in 1959.[16] Uses of the name "Boise Valley" in this article, in a historical context, refer to the Treasure Valley.
- ^ The Columbia River above the Snake has a length of approximately 900 miles (1,400 km).[3]
- ^ Measured to the head of the longest tributary beyond the head of the main stem.
- ^ To the head of Sun Creek.
- ^ To the head of Big Wood River.
- ^ A significant amount of water is diverted just above the mouth of Malad River for hydropower generation and discharged into the Snake River. Malad River discharge is calculated by the sum of USGS gage # 13153500 (Malad River near Bliss)[49] and #13152940 (Malad River hydropower diversion)[50]
- ^ To the head of Middle Fork Boise River.
- ^ To the head of Lake Creek.
- ^ To the head of South Fork Payette River.
- ^ To the head of Selway River.
External links
[edit]- Snake River flow conditions at SnoFlo
- Idaho Power
- Wild and Scenic Snake River - National Wild and Scenic Rivers System
- Snake River
- Rivers of Idaho
- Rivers of Oregon
- Rivers of Washington (state)
- Rivers of Wyoming
- Rivers of Yellowstone National Park
- Tributaries of the Columbia River
- Physiographic sections
- Wild and Scenic Rivers of the United States
- Borders of Idaho
- Borders of Oregon
- Borders of Washington (state)
- Rivers of Wallowa County, Oregon
- Rivers of Baker County, Oregon
- Rivers of Malheur County, Oregon
- Rivers of Bonneville County, Idaho
- Rivers of Madison County, Idaho
- Rivers of Power County, Idaho
- Rivers of Twin Falls County, Idaho
- Rivers of Ada County, Idaho
- Rivers of Owyhee County, Idaho
- Rivers of Nez Perce County, Idaho
- Rivers of Bingham County, Idaho
- Rivers of Fremont County, Idaho
- Rivers of Elmore County, Idaho
- Rivers of Payette County, Idaho
- Rivers of Gooding County, Idaho
- Rivers of Canyon County, Idaho
- Rivers of Washington County, Idaho
- Rivers of Adams County, Idaho
- Rivers of Idaho County, Idaho
- Rivers of Jerome County, Idaho



