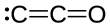Dicarbon monoxide: Difference between revisions
correct pages from doi citation |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Chembox |
{{Chembox |
||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
| verifiedrevid = 443636285 |
| verifiedrevid = 443636285 |
||
| |
| ImageFileL1 = Dicarbon-monoxide-2D.svg |
||
| |
| ImageNameL1 = Stick model of dicarbon monoxide |
||
| |
| ImageFileR1 = Dicarbon-monoxide-3D-vdW.png |
||
| |
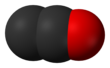
| ImageNameR1 = Spacefill model of dicarbon monoxide |
||
| |
| ImageFile2 = Dicarbon-monoxide-3D-balls.png |
||
| |
| ImageName2 = Ball and stick model of dicarbon monoxide |
||
| |
| IUPACName = 2-Oxoethenylidene |
||
| |
| OtherNames = Ketenylidene |
||
| |
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers |
||
| |
| InChI1 = 1/C2O/c1-2-3 |
||
| InChIKey1 = VILAVOFMIJHSJA-UHFFFAOYAI |
| InChIKey1 = VILAVOFMIJHSJA-UHFFFAOYAI |
||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} |
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} |
||
| CASNo = 119754-08-4 |
| CASNo = 119754-08-4 |
||
| |
| PubChem = 189691 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| PubChem_Ref = {{Pubchemcite}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C2O/c1-2-3 |
| StdInChI = 1S/C2O/c1-2-3 |
||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| StdInChIKey = VILAVOFMIJHSJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| StdInChIKey = VILAVOFMIJHSJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
||
| SMILES = [C]=C=O |
| SMILES = [C]=C=O |
||
| |
| InChI = 1S/C2O/c1-2-3 |
||
| |
| InChIKey = VILAVOFMIJHSJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N}} |
||
| |
|Section2={{Chembox Properties |
||
| |
| C=2 | O=1 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| MolarMass = 40.02 g mol<sup>−1</sup> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Dicarbon monoxide''' ({{chem2|C2O}}) is a [[molecule]] that contains two [[carbon]] [[atom]]s and one [[oxygen]] atom. It is a [[linear molecule]] that, because of its simplicity, is of interest in a variety of areas. It is, however, so extremely [[Reactivity (chemistry)|reactive]] that it is not encountered in everyday life. It is classified as a [[carbene]], [[cumulene]] and an [[oxocarbon]].<ref>Frenking, Gernot; Tonner, Ralf "Divalent carbon(0) compounds" Pure and Applied Chemistry 2009, vol. 81, pp. 597-614. {{doi|10.1351/PAC-CON-08-11-03}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Occurrence== |
|||
| ⚫ | Dicarbon monoxide is a product of the [[Photodissociation|photolysis]] of [[carbon suboxide]]:<ref>{{ cite journal | author= Bayes, K. | title = Photolysis of Carbon Suboxide | journal = [[Journal of the American Chemical Society]] | volume = 83 | year = 1961 | issue = 17 | pages = 3712–3713 | doi = 10.1021/ja01478a033 }}</ref><ref>{{ cite journal |author1=Anderson, D. J. |author2=Rosenfeld, R. N. | title = Photodissociation of Carbon Suboxide | journal = [[Journal of Chemical Physics]] | volume = 94 | year = 1991 | issue = 12 | pages = 7857–7867 | doi = 10.1063/1.460121 }}</ref> |
||
:C<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub> → CO + C<sub>2</sub>O |
:C<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub> → CO + C<sub>2</sub>O |
||
It is stable enough to observe reactions with [[nitric oxide|NO]] and [[nitrogen dioxide|NO<sub>2</sub>]].<ref>{{ cite journal | |
It is stable enough to observe reactions with [[nitric oxide|NO]] and [[nitrogen dioxide|NO<sub>2</sub>]].<ref>{{ cite journal |author1=Thweatt, W. D. |author2=Erickson, M. A. |author3=Hershberger, J. F. | title = Kinetics of the CCO + NO and CCO + NO<sub>2</sub> reactions | journal = [[Journal of Physical Chemistry A]] | year = 2004 | volume = 108 | issue = 1 | pages = 74–79 | doi = 10.1021/jp0304125 |bibcode=2004JPCA..108...74T }}</ref> |
||
Called '''ketenylidene''' in [[organometallic chemistry]], it is a [[ligand]] observed in [[metal carbonyl cluster]]s, e.g. [OC<sub>2</sub>Co<sub>3</sub>(CO)<sub>9</sub>]<sup>+</sup>. Ketenylidenes are proposed as intermediates in the chain growth mechanism of the [[Fischer-Tropsch Process]], which converts [[carbon monoxide]] and [[hydrogen]] to hydrocarbon fuels.<ref>Jensen, Michael P.; Shriver, Duward F. "Carbon-carbon and carbonyl transformations in ketenylidene cluster compounds" Journal of Molecular Catalysis 1992, vol. 74, pp. 73-84. {{doi|10.1016/0304-5102(92)80225-6}}</ref> |
|||
The [[organophosphorus compound]] (C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>)<sub>3</sub>PCCO (CAS# 15596-07-3) contains the C<sub>2</sub>O functionality. Sometimes called Bestmann's Ylide, it is a yellow solid.<ref>H. J. Bestmann, R. Zimmermann, M. Riou "Ketenylidenetriphenylphosphorane" e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001. {{doi| 10.1002/047084289X.rk005.pub2}}</ref> |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
{{Oxides of carbon}} |
{{Oxides of carbon}} |
||
{{Oxides}} |
|||
{{Molecules detected in outer space}} |
|||
[[Category:Carbenes]] |
|||
[[Category:Oxocarbons]] |
[[Category:Oxocarbons]] |
||
{{Inorganic-compound-stub}} |
{{Inorganic-compound-stub}} |
||
[[es:Monóxido de dicarbono]] |
|||
[[fa:دی کربن منوکسید]] |
|||
[[fr:Monoxyde de dicarbone]] |
|||
[[id:Dikarbon monoksida]] |
|||
[[ja:一酸化二炭素]] |
|||
[[fi:Dihiilimonoksidi]] |
|||
[[zh:一氧化二碳]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 00:53, 27 August 2023
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Oxoethenylidene
| |||
| Other names
Ketenylidene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2O | |||
| Molar mass | 40.021 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Dicarbon monoxide (C2O) is a molecule that contains two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It is a linear molecule that, because of its simplicity, is of interest in a variety of areas. It is, however, so extremely reactive that it is not encountered in everyday life. It is classified as a carbene, cumulene and an oxocarbon.[1]
Occurrence
[edit]Dicarbon monoxide is a product of the photolysis of carbon suboxide:[2][3]
- C3O2 → CO + C2O
It is stable enough to observe reactions with NO and NO2.[4]
Called ketenylidene in organometallic chemistry, it is a ligand observed in metal carbonyl clusters, e.g. [OC2Co3(CO)9]+. Ketenylidenes are proposed as intermediates in the chain growth mechanism of the Fischer-Tropsch Process, which converts carbon monoxide and hydrogen to hydrocarbon fuels.[5]
The organophosphorus compound (C6H5)3PCCO (CAS# 15596-07-3) contains the C2O functionality. Sometimes called Bestmann's Ylide, it is a yellow solid.[6]
References
[edit]- ^ Frenking, Gernot; Tonner, Ralf "Divalent carbon(0) compounds" Pure and Applied Chemistry 2009, vol. 81, pp. 597-614. doi:10.1351/PAC-CON-08-11-03
- ^ Bayes, K. (1961). "Photolysis of Carbon Suboxide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 83 (17): 3712–3713. doi:10.1021/ja01478a033.
- ^ Anderson, D. J.; Rosenfeld, R. N. (1991). "Photodissociation of Carbon Suboxide". Journal of Chemical Physics. 94 (12): 7857–7867. doi:10.1063/1.460121.
- ^ Thweatt, W. D.; Erickson, M. A.; Hershberger, J. F. (2004). "Kinetics of the CCO + NO and CCO + NO2 reactions". Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 108 (1): 74–79. Bibcode:2004JPCA..108...74T. doi:10.1021/jp0304125.
- ^ Jensen, Michael P.; Shriver, Duward F. "Carbon-carbon and carbonyl transformations in ketenylidene cluster compounds" Journal of Molecular Catalysis 1992, vol. 74, pp. 73-84. doi:10.1016/0304-5102(92)80225-6
- ^ H. J. Bestmann, R. Zimmermann, M. Riou "Ketenylidenetriphenylphosphorane" e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rk005.pub2