Meckenheim, Rhineland-Palatinate: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Alter: title. Removed parameters. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by BrownHairedGirl | #UCB_webform 2140/3838 |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 26 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox German location |
{{Infobox German location |
||
| |
|name = Meckenheim |
||
| |
|image_coa = DEU Meckenheim (Pfalz) COA.svg |
||
|coordinates = {{coord|49|24|13|N|8|14|24|E|format=dms|display=inline,title}} |
|||
|lat_deg = 49 |lat_min = 24 |lat_sec = 13 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|lon_deg = 8 |lon_min = 14 |lon_sec = 24 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
|district = Bad Dürkheim |
||
|Landkreis = Bad Dürkheim |
|||
|Verbandsgemeinde = Deidesheim |
|Verbandsgemeinde = Deidesheim |
||
| |
|elevation = 111 |
||
| |
|area = 15.06 |
||
| |
|postal_code = 67149 |
||
| |
|area_code = 06326 |
||
| |
|licence = DÜW |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
|Kfz = DÜW |
|||
|mayor = Julia Kren<ref>[https://www.wahlen.rlp.de/de/kw/wahlen/kd/gebiete/3320000000000.html Direktwahlen 2019, Landkreis Bad Dürkheim], Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 3 August 2021.</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|leader_term = 2019–24 |
|||
|Adresse-Verband = Am Bahnhof 5<br />67146 Deidesheim |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
|Bürgermeister = Heiner Dopp |
|||
|Partei = FWG |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Meckenheim''' is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a [[Municipalities of Germany|municipality]] belonging to a ''[[Verbandsgemeinde]]'', a kind of collective municipality – in the [[Bad Dürkheim (district)|Bad Dürkheim]] district in [[Rhineland-Palatinate]], [[Germany]]. |
'''Meckenheim''' is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a [[Municipalities of Germany|municipality]] belonging to a ''[[Verbandsgemeinde]]'', a kind of collective municipality – in the [[Bad Dürkheim (district)|Bad Dürkheim]] district in [[Rhineland-Palatinate]], [[Germany]]. |
||
== Geography == |
== Geography == |
||
=== Location === |
=== Location === |
||
The municipality lies at the edge of the Weinstraße region (as distinct from the ''Deutsche Weinstraße'' – or [[German Wine Route]] – itself) and is part of the [[Rhine-Neckar]] urban agglomeration. Meckenheim belongs to the [[Deidesheim (Verbandsgemeinde)|''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Deidesheim]], whose seat is in the [[Deidesheim|like-named town]]. |
The municipality lies at the edge of the Weinstraße region (as distinct from the ''Deutsche Weinstraße'' – or [[German Wine Route]] – itself) and is part of the [[Rhine-Neckar]] urban agglomeration. Meckenheim belongs to the [[Deidesheim (Verbandsgemeinde)|''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Deidesheim]], whose seat is in the [[Deidesheim|like-named town]]. |
||
| Line 32: | Line 30: | ||
The [[Franks|Frankish]] village of Meckenheim is believed to have arisen in the 5th century AD. In 768, a first donation from Meckenheim to [[Lorsch Abbey]] was documented; further donations to other monasteries followed. In 991, some Meckenheim holdings passed to Duke Otto of Weißenburg (now [[Wissembourg]] in nearby [[Alsace]], [[France]]). In the 12th century, [[Saint Giles]]’s Church (''Ägidiuskirche'') was built. |
The [[Franks|Frankish]] village of Meckenheim is believed to have arisen in the 5th century AD. In 768, a first donation from Meckenheim to [[Lorsch Abbey]] was documented; further donations to other monasteries followed. In 991, some Meckenheim holdings passed to Duke Otto of Weißenburg (now [[Wissembourg]] in nearby [[Alsace]], [[France]]). In the 12th century, [[Saint Giles]]’s Church (''Ägidiuskirche'') was built. |
||
In 1287, Meckenheim was bought by Count Palatine Louis II, and thus it thereafter belonged to the [[Electorate of the Palatinate]]. In 1459 or 1460, Meckenheim was burnt down by the [[House of Leiningen|Counts of Leiningen]] (Emich VII). With the introduction of the [[Protestant Reformation|Reformation]] into the |
In 1287, Meckenheim was bought by Count Palatine Louis II, and thus it thereafter belonged to the [[Electorate of the Palatinate]]. In 1459 or 1460, Meckenheim was burnt down by the [[House of Leiningen|Counts of Leiningen]] (Emich VII). With the introduction of the [[Protestant Reformation|Reformation]] into the Electorate of the Palatinate, Meckenheim became [[Protestantism|Protestant]]. In 1585, Saint Giles’s Church was newly built. |
||
After widespread destruction in the [[Thirty Years' War]], Meckenheim’s inhabitants forsook it in 1641. The Meckenheim church passed to the [[Roman Catholicism|Catholics]] in 1707; in 1747 and 1748, the Protestant church was built. During the [[French Revolutionary Wars]] in the late 18th century, Meckenheim sustained great damage. As a result of decisions made at the [[Congress of Vienna]], Meckenheim passed in 1816, together with the rest of the [[Palatinate (region)|Palatinate]] to the [[Kingdom of Bavaria]]. |
After widespread destruction in the [[Thirty Years' War]], Meckenheim’s inhabitants forsook it in 1641. The Meckenheim church passed to the [[Roman Catholicism|Catholics]] in 1707; in 1747 and 1748, the Protestant church was built. During the [[French Revolutionary Wars]] in the late 18th century, Meckenheim sustained great damage. As a result of decisions made at the [[Congress of Vienna]], Meckenheim passed in 1816, together with the rest of the [[Palatinate (region)|Palatinate]] to the [[Kingdom of Bavaria]]. |
||
| Line 43: | Line 41: | ||
=== Religion === |
=== Religion === |
||
In 2007, 54.4% of the inhabitants were [[Evangelical Church in Germany|Evangelical]] and 29.4% [[Roman Catholicism|Catholic]]. The rest belonged to other faiths or adhered to none<ref>[http://www.kommwis.de/uploads/media/Online-Gemeindestatistik_02.htm KommWis, Stand: 31.12.2007]</ref> |
In 2007, 54.4% of the inhabitants were [[Evangelical Church in Germany|Evangelical]] and 29.4% [[Roman Catholicism|Catholic]]. The rest belonged to other faiths or adhered to none.<ref>[http://www.kommwis.de/uploads/media/Online-Gemeindestatistik_02.htm KommWis, Stand: 31.12.2007] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070929133331/http://www.kommwis.de/uploads/media/Online-Gemeindestatistik_02.htm |date=2007-09-29 }}</ref> |
||
== Politics == |
== Politics == |
||
[[File:Meckenheim Hauptstrasse.JPG|thumb|Hauptstraße]] |
[[File:Meckenheim Hauptstrasse.JPG|thumb|Hauptstraße]] |
||
=== Municipal council === |
=== Municipal council === |
||
The municipal election held on 7 June 2009 yielded the following results: |
The municipal election held on 7 June 2009 yielded the following results: |
||
{| class=" |
{| class="wikitable right" |
||
|- class="hintergrundfarbe5" |
|- class="hintergrundfarbe5" |
||
! Party||Result in %<ref>[http://www.wahlen.rlp.de/kw/wahlen/2009/vgratswahlen/ergebnisse/3320100000.html Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz], zugegriffen am 11. Juni 2009</ref>||No. of seats |
! Party||Result in %<ref>[http://www.wahlen.rlp.de/kw/wahlen/2009/vgratswahlen/ergebnisse/3320100000.html Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz], zugegriffen am 11. Juni 2009</ref>||No. of seats |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[ |
|[[Christian Democratic Union of Germany|CDU]]||align="center"|23.6 (+0.9)||align="center"|4 (=) |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Free Voters|FWG]]||align="center"|52,6 (+3,5)||align="center"|11 (+1) |
|[[Free Voters|FWG]]||align="center"|52,6 (+3,5)||align="center"|11 (+1) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 60: | ||
=== Coat of arms === |
=== Coat of arms === |
||
The German blazon reads: ''In geviertem Schild oben rechts und unten links in Schwarz ein rotbewehrter, -bezungter und -bekrönter goldener Löwe, oben links und unten rechts von Silber und Blau gerautet, in der Mitte belegt mit einem schwarzumrandeten goldenen Kreis, darin ein schwarzes M.'' |
The German blazon reads: ''{{lang|de|In geviertem Schild oben rechts und unten links in Schwarz ein rotbewehrter, -bezungter und -bekrönter goldener Löwe, oben links und unten rechts von Silber und Blau gerautet, in der Mitte belegt mit einem schwarzumrandeten goldenen Kreis, darin ein schwarzes M.}}'' |
||
The municipality’s [[Coat of arms|arms]] might in English [[Heraldry|heraldic]] language be described thus: Quarterly, first and fourth sable a lion rampant Or armed, langued and crowned gules, second and third bendy lozengy argent and azure, surmounting the whole at the fess point a roundel of the first, itself surmounted by a bezant charged with the letter M of the first. |
The municipality’s [[Coat of arms|arms]] might in English [[Heraldry|heraldic]] language be described thus: Quarterly, first and fourth sable a lion rampant Or armed, langued and crowned gules, second and third bendy lozengy argent and azure, surmounting the whole at the fess point a roundel of the first, itself surmounted by a bezant charged with the letter M of the first. |
||
The arms were approved in 1926 by the Bavarian State Ministry of the Interior and go back to a court seal from 1473. It is similar to arms borne by |
The arms were approved in 1926 by the Bavarian State Ministry of the Interior and go back to a court seal from 1473. It is similar to arms borne by [[Electoral Palatinate]]. The first and fourth quarters show the Palatine Lion, and the second and third show the Bavarian “bendy lozengy” pattern (that is, diamond shapes formed by two sets of bends set at different angles overlapping). The M in the middle is an old municipal symbol used for marking the municipal area.<ref>Karl Heinz Debus: ''Das große Wappenbuch der Pfalz''. Neustadt an der Weinstraße 1988, {{ISBN|3-9801574-2-3}}</ref> |
||
=== Town partnerships === |
=== Town partnerships === |
||
| Line 72: | Line 71: | ||
== Economy and infrastructure == |
== Economy and infrastructure == |
||
=== Winegrowing === |
=== Winegrowing === |
||
[[File:Meckenheim Dorfplatz.JPG|thumb|Village square]] |
[[File:Meckenheim Dorfplatz.JPG|thumb|Village square]] |
||
Meckenheim’s vineyards belong to the [[Palatinate (wine region)|Palatinate wine region]] and also more locally to the ''Mittelhaardt-Deutsche Weinstraße'' growing area. Belonging to Meckenheim are two local appellations, namely ''Neuberg'' and ''Spielberg'', themselves both within the greater appellation of ''Hofstück''. |
Meckenheim’s vineyards belong to the [[Palatinate (wine region)|Palatinate wine region]] and also more locally to the ''Mittelhaardt-Deutsche Weinstraße'' growing area. Belonging to Meckenheim are two local appellations, namely ''Neuberg'' and ''Spielberg'', themselves both within the greater appellation of ''Hofstück''. |
||
In Meckenheim there are 51 [[winegrowing]] businesses with planted vineyard areas of 0.3 ha or more; the average area for each business is 4.8 ha. All together, vineyards cover 258 ha within Meckenheim’s municipal area. [[White wine]]s produced by Meckenheim winegrowing businesses account for 57% of the production, while the other 43% is [[red wine]]s (as at 2003)<ref>http://www.statistik.rlp.de/index.html</ref> |
In Meckenheim there are 51 [[winegrowing]] businesses with planted vineyard areas of 0.3 ha or more; the average area for each business is 4.8 ha. All together, vineyards cover 258 ha within Meckenheim’s municipal area. [[White wine]]s produced by Meckenheim winegrowing businesses account for 57% of the production, while the other 43% is [[red wine]]s (as at 2003).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.statistik.rlp.de/index.html |title=StLA RLP - Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz |accessdate=2010-01-08 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20100210062832/http://www.statistik.rlp.de/index.html |archivedate=2010-02-10 }}</ref> |
||
== Famous people == |
== Famous people == |
||
=== Sons and daughters of the town === |
=== Sons and daughters of the town === |
||
* Norbert Meder, (1947– ), educator |
* Norbert Meder, (1947– ), educator |
||
* Ludwig Scharf, (1864-1938), lyricist and translator |
* [[Ludwig Scharf]], (1864-1938), lyricist and translator |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
| Line 87: | Line 88: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{commons category|Meckenheim (Pfalz)|Meckenheim}} |
|||
* [http://www.meckenheim-pfalz.de/ Municipality’s official webpage] {{ |
* [http://www.meckenheim-pfalz.de/ Municipality’s official webpage] {{in lang|de}} |
||
{{de}} |
|||
{{BadDürkheim-geo-stub}} |
|||
{{Cities and towns in Bad Dürkheim (district)}} |
{{Cities and towns in Bad Dürkheim (district)}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[de:Meckenheim (Pfalz)]] |
|||
[[ |
[[Category:Bad Dürkheim (district)]] |
||
[[Category:Palatinate (region)]] |
|||
[[fr:Meckenheim (Rhénanie-Palatinat)]] |
|||
[[it:Meckenheim (Renania-Palatinato)]] |
|||
[[kk:Меккенхайм (Пфальц)]] |
|||
[[nl:Meckenheim (Palts)]] |
|||
[[uz:Meckenheim (Pfalz)]] |
|||
[[pfl:Meckrem]] |
|||
[[pl:Meckenheim (Nadrenia-Palatynat)]] |
|||
[[pt:Meckenheim (Renânia-Palatinado)]] |
|||
[[ro:Meckenheim (Pfalz)]] |
|||
[[ru:Меккенхайм (Пфальц)]] |
|||
[[sr:Мекенхајм (Палатинат)]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[war:Meckenheim, Rhineland-Palatinate]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 06:04, 22 August 2022
Meckenheim | |
|---|---|
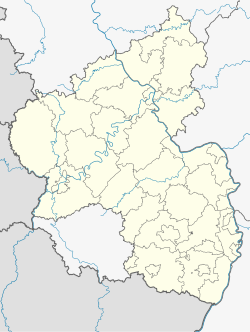
Location of Meckenheim within Bad Dürkheim district  | |
| Coordinates: 49°24′13″N 8°14′24″E / 49.40361°N 8.24000°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| District | Bad Dürkheim |
| Municipal assoc. | Deidesheim |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2019–24) | Julia Kren[1] (FW) |
| Area | |
• Total | 15.06 km2 (5.81 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 111 m (364 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
• Total | 3,450 |
| • Density | 230/km2 (590/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 67149 |
| Dialling codes | 06326 |
| Vehicle registration | DÜW |
| Website | www.meckenheim-pfalz.de |
Meckenheim is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Bad Dürkheim district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Geography
[edit]Location
[edit]The municipality lies at the edge of the Weinstraße region (as distinct from the Deutsche Weinstraße – or German Wine Route – itself) and is part of the Rhine-Neckar urban agglomeration. Meckenheim belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Deidesheim, whose seat is in the like-named town.
History
[edit]

The Frankish village of Meckenheim is believed to have arisen in the 5th century AD. In 768, a first donation from Meckenheim to Lorsch Abbey was documented; further donations to other monasteries followed. In 991, some Meckenheim holdings passed to Duke Otto of Weißenburg (now Wissembourg in nearby Alsace, France). In the 12th century, Saint Giles’s Church (Ägidiuskirche) was built.
In 1287, Meckenheim was bought by Count Palatine Louis II, and thus it thereafter belonged to the Electorate of the Palatinate. In 1459 or 1460, Meckenheim was burnt down by the Counts of Leiningen (Emich VII). With the introduction of the Reformation into the Electorate of the Palatinate, Meckenheim became Protestant. In 1585, Saint Giles’s Church was newly built.
After widespread destruction in the Thirty Years' War, Meckenheim’s inhabitants forsook it in 1641. The Meckenheim church passed to the Catholics in 1707; in 1747 and 1748, the Protestant church was built. During the French Revolutionary Wars in the late 18th century, Meckenheim sustained great damage. As a result of decisions made at the Congress of Vienna, Meckenheim passed in 1816, together with the rest of the Palatinate to the Kingdom of Bavaria.
In 1824, the schoolhouse-municipal house (Hauptstraße 98) was built, and in 1872 the building that now serves as town hall (Hauptstraße 58). In 1894, the agricultural coöperative society and the Raiffeisen credit coöperative, which were merged in 1938, were founded.
In 1911, the Lokalbahn – or local railway – between Ludwigshafen and Dannstadt, which had opened in 1890, was extended to Meckenheim. Service continued until 1955, when it was replaced by buslines. In 1913, Meckenheim was connected to a public electrical grid, and in 1928 to a public water supply system. In 1922, the Meckenheim Winemakers’ Association was founded. In 1936, the fruit market hall was built.
After the Second World War, Meckenheim passed in 1946 together with the rest of the Palatinate to the newly founded state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Between 1952 and 1955, the sporting ground with the clubhouse was laid out. In 1956, Meckenheim was connected to a public gas supply system. In 1961, a new folk high school opened and in 1964, it was connected to a public sewer system.
Religion
[edit]In 2007, 54.4% of the inhabitants were Evangelical and 29.4% Catholic. The rest belonged to other faiths or adhered to none.[3]
Politics
[edit]
Municipal council
[edit]The municipal election held on 7 June 2009 yielded the following results:
| Party | Result in %[4] | No. of seats |
|---|---|---|
| CDU | 23.6 (+0.9) | 4 (=) |
| FWG | 52,6 (+3,5) | 11 (+1) |
| SPD | 23.7 (−4.5) | 5 (−1) |
Coat of arms
[edit]The German blazon reads: In geviertem Schild oben rechts und unten links in Schwarz ein rotbewehrter, -bezungter und -bekrönter goldener Löwe, oben links und unten rechts von Silber und Blau gerautet, in der Mitte belegt mit einem schwarzumrandeten goldenen Kreis, darin ein schwarzes M.
The municipality’s arms might in English heraldic language be described thus: Quarterly, first and fourth sable a lion rampant Or armed, langued and crowned gules, second and third bendy lozengy argent and azure, surmounting the whole at the fess point a roundel of the first, itself surmounted by a bezant charged with the letter M of the first.
The arms were approved in 1926 by the Bavarian State Ministry of the Interior and go back to a court seal from 1473. It is similar to arms borne by Electoral Palatinate. The first and fourth quarters show the Palatine Lion, and the second and third show the Bavarian “bendy lozengy” pattern (that is, diamond shapes formed by two sets of bends set at different angles overlapping). The M in the middle is an old municipal symbol used for marking the municipal area.[5]
Town partnerships
[edit]Meckenheim fosters partnerships with the following places:
 Lugny, Saône-et-Loire, France since 1980
Lugny, Saône-et-Loire, France since 1980
Economy and infrastructure
[edit]Winegrowing
[edit]
Meckenheim’s vineyards belong to the Palatinate wine region and also more locally to the Mittelhaardt-Deutsche Weinstraße growing area. Belonging to Meckenheim are two local appellations, namely Neuberg and Spielberg, themselves both within the greater appellation of Hofstück.
In Meckenheim there are 51 winegrowing businesses with planted vineyard areas of 0.3 ha or more; the average area for each business is 4.8 ha. All together, vineyards cover 258 ha within Meckenheim’s municipal area. White wines produced by Meckenheim winegrowing businesses account for 57% of the production, while the other 43% is red wines (as at 2003).[6]
Famous people
[edit]Sons and daughters of the town
[edit]- Norbert Meder, (1947– ), educator
- Ludwig Scharf, (1864-1938), lyricist and translator
References
[edit]- ^ Direktwahlen 2019, Landkreis Bad Dürkheim, Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 3 August 2021.
- ^ "Bevölkerungsstand 2022, Kreise, Gemeinden, Verbandsgemeinden" (PDF) (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz. 2023.
- ^ KommWis, Stand: 31.12.2007 Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz, zugegriffen am 11. Juni 2009
- ^ Karl Heinz Debus: Das große Wappenbuch der Pfalz. Neustadt an der Weinstraße 1988, ISBN 3-9801574-2-3
- ^ "StLA RLP - Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz". Archived from the original on 2010-02-10. Retrieved 2010-01-08.
External links
[edit]- Municipality’s official webpage (in German)