Uttar Pradesh: Difference between revisions
Ugog Nizdast (talk | contribs) Reverted good faith edits by 182.74.15.26 (talk). (WT) |
Alexeyevitch (talk | contribs) fix typo |
||
| (1,000 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|State in northern India}} |
|||
{{Redirect|U.P.||UP (disambiguation)}} |
|||
{{Pp|small=yes}} |
|||
{{Good article}} |
|||
{{Use Indian English|date=May 2024}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=May 2024}} |
|||
{{Infobox Indian state or territory |
|||
| name = Uttar Pradesh |
|||
| image_skyline = {{multiple image |
|||
| border = infobox |
|||
| total_width = 300 |
|||
| image_style = |
|||
| perrow = 1/2/2/2/1 |
|||
| image1 = Taj Mahal (Edited).jpeg |
|||
| caption1 = [[Taj Mahal]] |
|||
| image2 = India-5163 - Flickr - archer10 (Dennis).jpg |
|||
| caption2 = [[Sarnath]] |
|||
| image3= Dept of Electrical Engineering IIT-BHU.jpg |
|||
| caption3 = [[IIT (BHU) Varanasi|IIT Varanasi]] |
|||
| image4 = Dudhwa National Park, Lucknow division, Uttar Pradesh, India (30783128830).jpg |
|||
| caption4 = [[Dudhwa National Park]] |
|||
| image5 = Fatehpur Sikri near Agra 2016-03 img09.jpg |
|||
| caption5 = [[Fatehpur Sikri]] |
|||
| image7 = Agra 03-2016 14 Agra Fort.jpg |
|||
| caption7 = [[Agra Fort]] |
|||
}} |
|||
| type = State |
|||
| image_seal = Seal of Uttar Pradesh.svg |
|||
| etymology = Northern Province |
|||
| motto = [[Satyameva Jayate]] (Truth alone triumphs) |
|||
| image_map = IN-UP.svg |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|26.85|80.91|region:IN-UP_type:adm1st|display=it}} |
|||
| region = North India |
|||
| before_was = [[United Provinces (1937–1950)]] |
|||
| formation_date2 = formation1 |
|||
| formation_date4 = 24 January 1950<ref name="UPDay">{{Cite news |date=2 May 2017 |title=United Province, UP was notified in Union gazette on January 24, 1950 |work=[[The New Indian Express]] |url=https://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/2017/may/02/uttar-pradesh-introduces-new-transfer-policy-1600219.html |url-status=live |access-date=4 May 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170508200722/http://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/2017/may/02/uttar-pradesh-introduces-new-transfer-policy-1600219.html |archive-date=8 May 2017}}</ref> |
|||
| capital = Lucknow |
|||
| largestcity = capital |
|||
| metro = Lucknow |
|||
| districts = [[List of districts of Uttar Pradesh|75 (18 divisions)]]<ref name="districts">{{Cite web |title=Uttar Pradesh District |url=http://up.gov.in/upmap.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170415123851/http://up.gov.in/upmap.aspx |archive-date=15 April 2017 |access-date=12 April 2017 |website=up.gov.in |publisher=Government of Uttar Pradesh}}</ref><ref name="list of district">{{Cite web |title=List of districts in Uttar Pradesh |url=http://www.archive.india.gov.in/knowindia/districts/andhra1.php?stateid=UP |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170426231823/http://www.archive.india.gov.in/knowindia/districts/andhra1.php?stateid=UP |archive-date=26 April 2017 |access-date=12 April 2017 |website=archive.india.gov.in |publisher=Government of India }}</ref> |
|||
| Governor = [[Anandiben Patel]]<ref>{{Cite news |last=PTI |date=20 July 2019 |title=Anandiben Patel made UP governor, Lal ji Tandon to replace her in Madhya Pradesh|work=India Today |url=https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/anandiben-patel-made-up-governor-lal-ji-tandon-to-replace-her-in-madhya-pradesh-1571562-2019-07-20 |url-status=live |access-date=20 July 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190720111904/https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/anandiben-patel-made-up-governor-lal-ji-tandon-to-replace-her-in-madhya-pradesh-1571562-2019-07-20 |archive-date=20 July 2019}}</ref><ref name="Governor of UP">{{Cite web |title=The Governor of Uttar Pradesh |url=http://uplegisassembly.gov.in/ENGLISH/governor_current.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170503081924/http://uplegisassembly.gov.in/ENGLISH/governor_current.htm |archive-date=3 May 2017 |access-date=12 April 2017 |website=uplegisassembly.gov.in |publisher=Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly }}</ref> |
|||
| Chief_Minister = [[Yogi Adityanath]] |
|||
| party = [[Bharatiya Janata Party|BJP]] |
|||
| Deputy_CM = [[Keshav Prasad Maurya]] ([[BJP]]) <br/> [[Brajesh Pathak]] ([[BJP]]) |
|||
| legislature_type = Bicameral |
|||
| council = [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council]] |
|||
| council_seats = 100 seats |
|||
| assembly = [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly]] |
|||
| assembly_seats = 403 seats |
|||
| rajya_sabha_seats = 31 seats |
|||
| lok_sabha_seats = 80 seats |
|||
| judiciary = [[Allahabad High Court]] |
|||
| area_total_km2 = 243286 |
|||
| area_rank = 4th |
|||
| length_km = 650 |
|||
| width_km = 240 |
|||
| elevation_footnotes = <ref>{{Cite news |title=Uttar Pradesh {{!}} History, Government, Map, & Population {{!}} Britannica|work=Encyclopedia Britannica |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Uttar-Pradesh |access-date=24 March 2023 |archive-date=1 April 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200401072447/https://www.britannica.com/place/Uttar-Pradesh |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| elevation_m = 300 |
|||
| elevation_max_m = 957 |
|||
| elevation_max_point = [[Sivalik Hills]]<ref>{{Cite web |date=29 July 2017 |title=List of Highest Mountain Peaks State-wise |url=https://wordpandit.com/list-highest-mountain-peaks-state-wise/ |access-date=24 March 2023 |website=Wordpandit|archive-date=24 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230324212911/https://wordpandit.com/list-highest-mountain-peaks-state-wise/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| elevation_min_m = 60 |
|||
| elevation_min_point = Easter side |
|||
| population_total = {{Increase}} 241,066,874 |
|||
| population_as_of = 2021 |
|||
| population_rank = 1st |
|||
| population_density = 1001 |
|||
| population_urban = 22.27% |
|||
| population_rural = 77.73% |
|||
| 0fficial_Langs = [[Hindi]]<ref name="2011lang" /> |
|||
| additional_official = [[Urdu]] |
|||
| official_script = [[Devanagari script]] |
|||
| GDP_footnotes = <ref name="UP_budjet">{{Cite web |title=Handbook of Statistics of Indian States 2021–22 |url=https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/Publications/PDFs/0HBS19112022_FLFE4F2F9158294692B030A251E00555F8.PDF |access-date=11 February 2022 |website=[[Reserve Bank of India]] |pages=37–42 |archive-date=29 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220129151430/https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/Publications/PDFs/0HSIS241121FL7A6B5C0ECBC64B0ABF0A097B1AD40C83.PDF |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| GDP_total = {{Increase}}{{INRConvert|24.39|lc|lk=r}} |
|||
| GDP_year = 2022–2023 |
|||
| GDP_rank = 2nd |
|||
| GDP_per_capita = {{Increase}}{{INRConvert|105000|lk=r}} |
|||
| GDP_per_capita_rank = 28th |
|||
| HDI = {{decrease}} 0.600 {{color|#fc0|Medium}}<ref name="snhdi-gdl">{{Cite web |title=Sub-national HDI – Area Database |url=https://hdi.globaldatalab.org/areadata/shdi/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180923120638/https://hdi.globaldatalab.org/areadata/shdi/ |archive-date=23 September 2018 |access-date=25 September 2018 |website=Global Data Lab |publisher=Institute for Management Research, Radboud University}}</ref> |
|||
| HDI_year = 2018 |
|||
| HDI_rank = 35th |
|||
| literacy = {{Increase}} 67.68%<ref name="pc-census2011">{{Cite web |title=Census 2011 (Final Data) – Demographic details, Literate Population (Total, Rural & Urban) |url=http://planningcommission.gov.in/data/datatable/data_2312/DatabookDec2014%20307.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180127163347/http://planningcommission.gov.in/data/datatable/data_2312/DatabookDec2014%20307.pdf |archive-date=27 January 2018 |access-date=3 October 2018 |website=planningcommission.gov.in |publisher=Planning Commission, Government of India}}</ref> |
|||
| literacy_year = 2011 |
|||
| literacy_rank = 29th |
|||
| sex_ratio = 1015 [[female|♀]]/1000 [[male|♂]]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Sex ratio of State and Union Territories of India as per National Health survey (2019–2021) |url=https://main.mohfw.gov.in/basicpage-14 |website=Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, India |access-date=8 January 2023 |archive-date=8 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230108164803/https://main.mohfw.gov.in/basicpage-14 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| sexratio_year = 2021 |
|||
| sexratio_rank = 19th |
|||
| iso_code = IN-UP |
|||
| registration_plate = UP |
|||
| website = up.gov.in |
|||
| foundation_day = Uttar Pradesh Day |
|||
| mammal = [[Barasingha]] |
|||
| bird = [[Sarus crane]] |
|||
| flower = [[Butea monosperma|Palash]] |
|||
| tree = [[Saraca asoca|Ashoka]] |
|||
| image_highway = SH IN-UP.png |
|||
| SH_numbers = [[List of state highways in Uttar Pradesh|UP SH1 – UP SH99]] |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Uttar Pradesh''' ({{IPAc-en|ˌ|ʊ|t|ər|_|p|r|ə|ˈ|d|ɛ|ʃ}} {{respell|UUT|ər|_|prə|DESH}};<ref>{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Uttar Pradesh |encyclopedia=[[Lexico]] UK English Dictionary |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |url=http://www.lexico.com/definition/Uttar_Pradesh |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220426121106/https://www.lexico.com/definition/uttar_pradesh |archive-date=26 April 2022 |url-status=dead}}</ref> {{IPA|hi|ˈʊtːəɾ pɾəˈdeːʃ|lang}}; {{small|abbr.}} '''UP''') is a [[States and union territories of India|state]] in [[North India|northern India]]. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the [[List of states and union territories of India by population|most populated state]] in India as well as the [[List of first-level administrative divisions by population|most populous country subdivision]] in the world – more populous than [[List of countries and dependencies by population|all but four other countries]] outside of [[India]] ([[China]], [[US]], [[Indonesia]], and [[Pakistan]])<ref>{{Cite news |last1=Kopf |first1=Dan |last2=Varathan |first2=Preeti |date=11 October 2017 |title=If Uttar Pradesh were a country|work=Quartz India |url=https://qz.com/india/1094942/if-uttar-pradesh-were-a-country-where-would-it-rank-by-size-wealth-and-other-measures/ |url-status=live |access-date=20 May 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190622011953/https://qz.com/india/1094942/if-uttar-pradesh-were-a-country-where-would-it-rank-by-size-wealth-and-other-measures/ |archive-date=22 June 2019}}</ref> – and accounting for 16.5 percent of the population of India or around 3 percent of the total world population. The state is bordered by [[Rajasthan]] to the west, [[Haryana]], [[Himachal Pradesh]] and [[Delhi]] to the northwest, [[Uttarakhand]] and [[Nepal]] to the north, [[Bihar]] to the east, [[Madhya Pradesh]], [[Chhattisgarh]] and [[Jharkhand]] to the south. It is the [[List of states of India by area|fourth-largest Indian state by area]] covering {{convert|243286|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}}, accounting for 7.3 percent of the total area of India. [[Lucknow]] serves as the [[state capital]], with [[Prayagraj]] being the [[Allahabad High Court|judicial capital]]. It is divided into 18 [[Administrative divisions of Uttar Pradesh|divisions]] and 75 [[List of districts of Uttar Pradesh|districts]]. |
|||
{{EngvarB|date=January 2014}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=January 2014}} |
|||
Uttar Pradesh was established in 1950 after India had become a republic. It is a successor to the [[United Provinces (1937–1950)|United Provinces]], established in 1935 by renaming the [[United Provinces of Agra and Oudh]], in turn established in 1902 from the [[North-Western Provinces]] and the [[List of Chief Commissioners of Oudh|Oudh Province]]. Though long known for sugar production, the state's economy is now dominated by the services industry. The service sector comprises travel and [[tourism]], [[hotel industry]], [[real estate]], [[insurance]] and financial consultancies. The [[economy of Uttar Pradesh]] is the [[List of Indian states and union territories by GDP|third-largest state economy]] in India, with {{INRConvert|18.63|lc|lk=on}} in [[gross domestic product]] and a per capita GSDP of {{INRConvert|68810}}.<ref name="UP_budjet" /> The [[Allahabad High Court|High Court]] of the state is located in [[Prayagraj]]. The state contributes 80 seats to the lower house [[Lok Sabha]] and 31 seats and the upper house [[Rajya Sabha]]. |
|||
{{Good article}} |
|||
On 9 November 2000, a new state, Uttaranchal (now [[Uttarakhand]]), was created from Uttar Pradesh's western Himalayan hill region. The two major rivers of the state, the [[Ganges]] and its tributary [[Yamuna]], meet at the [[Triveni Sangam]] in Prayagraj, a Hindu pilgrimage site. Other notable rivers are [[Gomti River|Gomti]] and [[Sarayu River (Ayodhya)|Saryu]]. The forest cover in the state is 6.1 percent of the state's geographical area. The cultivable area is 82 percent of the total geographical area, and the net area sown is 68.5 percent of the cultivable area.<ref name="Cultivation">{{Cite web |title=Agriculture |url=https://niti.gov.in/planningcommission.gov.in/docs/plans/stateplan/upsdr/vol-2/Chap_b1.pdf |access-date=19 October 2021 |website=niti.gov.in |publisher=[[NITI Aayog]] |archive-date=7 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211007073805/https://niti.gov.in/planningcommission.gov.in/docs/plans/stateplan/upsdr/vol-2/Chap_b1.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
|||
| name = Uttar Pradesh |
|||
|native_name = उत्तर प्रदेश<br>اتر پردیش |
|||
| type = [[States and union territories of India|State of India]] |
|||
Inhabitants of the state are called [[Awadhi people|Awadhi]], [[Braj]]wasi, or [[Bundelkhand|Bundeli]], depending upon their region of origin. [[Hinduism]] is practised by more than three-fourths of the population, followed by [[Islam]]. [[Hindi]] is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state, along with [[Urdu]]. Uttar Pradesh was home to most of the mainstream political entities that existed in [[Ancient India|ancient]] and [[medieval India]] including the [[Maurya Empire]], [[Harsha Empire]], [[Gupta Empire]], [[Pala Empire]], [[Delhi Sultanate]] and [[Mughal Empire]] as well as many other empires. At the time of the [[Indian independence movement]] in the early 20th century, there were three major [[princely states]] in Uttar Pradesh – Ramgadi, [[Rampur State|Rampur]] and [[Benares State|Benares]] and served as a focal point for the [[Indian Rebellion of 1857|1857 rebellion]] against British rule. The state houses several holy Hindu temples and pilgrimage centres. Along with several historical, natural and religious tourist destinations, including [[Agra]], [[Aligarh]], [[Ayodhya]], [[Bareilly]], [[Gorakhpur]], [[Kanpur]], [[Kushinagar]], [[Lucknow]], [[Mathura]], [[Meerut]], [[Prayagraj]], [[Varanasi]], and [[Vrindavan]], Uttar Pradesh is also home to three [[List of World Heritage Sites in India|World Heritage sites]]. |
|||
| background_color = #FFA500 |
|||
| text_color = #FFFFFF |
|||
| image_shield = Seal of Uttar Pradesh.png |
|||
| shield_caption = Seal of Uttar Pradesh |
|||
| image_skyline = Taj Mahal 2012.jpg |
|||
| image_alt = |
|||
| image_caption = Southern view of the [[Taj Mahal]] |
|||
| image_seal = |
|||
| seal_alt = |
|||
| image_map = India Uttar Pradesh locator map.svg |
|||
| map_alt = |
|||
| map_caption = Location of Uttar Pradesh (marked in red) in [[India]] |
|||
| image_map1 = Uttar Pradesh locator map.svg |
|||
| map_caption1 = Map of Uttar Pradesh |
|||
| latd = 26.85 |
|||
| longd = 80.91 |
|||
| coor_pinpoint = |
|||
| coordinates_type = region:IN-UP_type:adm1st |
|||
| coordinates_display = inline,title |
|||
| coordinates_footnotes = |
|||
| coordinates_region = IN-UP |
|||
| subdivision_type = [[List of sovereign states|Country]] |
|||
| subdivision_name = {{IND}} |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = Region |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Awadh]], [[Baghelkhand]], [[Braj]], [[Bundelkhand]], [[Doab]], [[Purvanchal]], [[Rohilkhand]] |
|||
| established_title = Established |
|||
| established_date = Modern: 1805 (as [[Ceded and Conquered Provinces]]) |
|||
| established_title1 = History |
|||
| established_date1 = |
|||
{{hidden begin|title=Summary}} |
|||
* 1805 : [[Ceded and Conquered Provinces]] |
|||
* 14 Nov 1834 : [[Presidency of Agra]] |
|||
* 1 Jan 1836 : [[North-Western Provinces]] |
|||
* 3 Apr 1858 : [[Oudh]] taken under British control, [[Delhi]] taken away from [[North-Western Provinces|NWP]] and merged into [[Punjab (British India)|Punjab]] |
|||
* 1 Apr 1871 : [[Ajmer]], [[Mewar|Merwara]] & [[Kekri]] made separate commissionership |
|||
* 15 Feb 1877 : Oudh added to [[North-Western Provinces]] |
|||
* 22 Mar 1902 : Renamed [[United Provinces of Agra and Oudh]] |
|||
* 3 Jan 1921 : Renamed [[United Provinces of British India]] |
|||
* 1 Apr 1937 : Renamed [[United Provinces]] |
|||
* 1 Apr 1946 : Self rule granted |
|||
* 15 Aug 1947 : Part of independent India |
|||
* 26 Jan 1950 : Renamed Uttar Pradesh |
|||
* 9 Nov 2000 : Uttaranchal state, now known as [[Uttarakhand]], created from part of Uttar Pradesh{{hidden end}} |
|||
| parts_type = [[List of districts of Uttar Pradesh|Districts]] |
|||
| parts_style = para |
|||
| p1 = [[List of districts of Uttar Pradesh|75]]<ref name="GOI_2011" /> |
|||
| seat_type = Capital |
|||
| seat = [[Lucknow]] |
|||
| government_footnotes = |
|||
| governing_body = [[Government of Uttar Pradesh]] |
|||
| leader_title = [[Governors of Uttar Pradesh|Governor]] |
|||
| leader_name = [[Ram Naik]]<ref>{{cite news|title=Centre in a hurry, but Governors won’t quit|url=http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/centre-in-a-hurry-but-governors-wont-quit/article6123902.ece?homepage=true|accessdate=17 June 2014|agency=The Hindu|publisher=Hindu}}</ref> |
|||
| leader_title1 = [[Chief Ministers of Uttar Pradesh|Chief Minister]] |
|||
| leader_name1 = [[Akhilesh Yadav]] ([[Samajwadi Party|SP]]) |
|||
| leader_title2 = [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly|Legislature]] |
|||
| leader_name2 = [[Bicameral]] <br> [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council|Legislative Council]] 108 <br> [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly|Legislative Assembly]] 404 |
|||
| leader_title3 = [[Parliament of India|Parliamentary constituency]] |
|||
| leader_name3 = [[Rajya Sabha]] 31 <br> [[Lok Sabha]] 80 |
|||
| leader_title4 = [[High Courts of India|High Court]] |
|||
| leader_name4 = [[Allahabad High Court]] |
|||
<!-- |
|||
| leader_title5 = [[Chief Secretary]] |
|||
| leader_name5 = Suraj Mishra |
|||
--> |
|||
| unit_pref = Metric<!-- or US or UK --> |
|||
| area_footnotes = |
|||
| area_total_km2 = 243286 |
|||
| area_note = |
|||
| area_rank = 4th |
|||
| elevation_footnotes = |
|||
| elevation_m = |
|||
| population_footnotes = <ref name="GOI_2011">{{cite web|title = Statistics of Uttar Pradesh |url=http://upgov.nic.in/upstateglance.aspx |work=Census of India 2011|publisher=UP Government|date =1 March 2011|accessdate =31 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| population_total = 199,581,477 |
|||
| population_as_of = 2011 |
|||
| population_rank = [[List of states and union territories of India by population|1st]] |
|||
| population_density_km2 = auto |
|||
| population_note = |
|||
| population_demonym = Uttarpradeshi |
|||
|GDPYear = 2011 |
|||
|GDP = 6,76,083<br />US$125.86 billion |
|||
|GDPRank = 3rd |
|||
|GDPperCapita = 30,051 |
|||
|GDPperCapitaRank = 31st |
|||
== History == |
|||
| sex_ratio = 908/1000 |
|||
{{main|History of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
| timezone1 = [[Indian Standard Time|IST]] |
|||
| utc_offset1 = +05:30 |
|||
| ISO = [[ISO 3166-2:IN|IN-UP]] |
|||
| blank_name_sec1 = [[Human Development Index|HDI]] |
|||
| blank_info_sec1 = {{increase}} 0.490 (<span style="color:#f00;">low</span>) |
|||
| blank1_name_sec1 = HDI rank |
|||
| blank1_info_sec1 = 32nd (2005) |
|||
| blank_name_sec2 = [[Literacy in India|Literacy]] |
|||
| blank_info_sec2 = 67.68% <br />77.28% (male)<br />57.18% (female) |
|||
| blank1_name_sec2 = Official language |
|||
| blank1_info_sec2 = [[Hindi]] [[Urdu]] [[Bhojpuri]] |
|||
| area_code_type = [[UN/LOCODE]] |
|||
| area_code = [[ISO 3166-2:IN|IN-UP]] |
|||
| registration_plate = UP 01—XX |
|||
| website = [http://www.up.gov.in/ UP.gov.in] |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
}} |
|||
=== Prehistory === |
|||
'''Uttar Pradesh''' ({{IPAc-en|'|U|t|@r|_|p|r|@|'|d|E|sh}}, <small>lit.</small> "Northern Province"), <small>abbr.</small> '''UP''', is a [[States and union territories of India|state]] located in northern [[India]]. It was created on 1 April 1937 as the '''United Provinces''', and was renamed ''Uttar Pradesh'' in 1950. [[Lucknow]] is the administrative capital of Uttar Pradesh. [[Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh|Ghaziabad]], [[Kanpur]], [[Moradabad]], [[Aligarh]], and [[Varanasi]] are known for their industrial importance in the state as well as in India. On 9 November 2000, a new state, [[Uttarakhand]], was carved out from the Himalayan hill region of Uttar Pradesh. |
|||
[[Early modern human|Modern human]] hunter-gatherers have been in Uttar Pradesh<ref>{{Cite book |last=Virendra N. Misra, Peter Bellwood |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gMoJj-0Z94UC&pg=PA69 |title=Recent Advances in Indo-Pacific Prehistory: proceedings of the international symposium held at Poona |year=1985 |isbn=9004075127 |page=69 | publisher=BRILL |access-date=23 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180303134041/https://books.google.com/books?id=gMoJj-0Z94UC&pg=PA69 |archive-date=3 March 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Bridget Allchin, Frank Raymond Allchin |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=r4s-YsP6vcIC&pg=PA58 |title=The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1982 |isbn=052128550X |page=58 |access-date=23 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170325035117/https://books.google.com/books?id=r4s-YsP6vcIC&pg=PA58 |archive-date=25 March 2017 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Hasmukhlal Dhirajlal Sankalia |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=35DP1Z-2dnYC&pg=PA96 |title=Studies in Indian Archaeology: Professor H.D. Sankalia Felicitation Volume |last2=Shantaram Bhalchandra Deo |last3=Madhukar Keshav Dhavalikar |date=1985 |publisher=Popular Prakashan |isbn=978-0861320882 |page=96 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170324205017/https://books.google.com/books?id=35DP1Z-2dnYC&pg=PA96 |archive-date=24 March 2017 |url-status=live}}</ref> since between around<ref>Confidence limits for the age are 85 (±11) and 72 (±8) thousand years ago.</ref> 85,000 and 72,000 years ago. There have also been prehistorical finds in the state from the [[Middle Paleolithic|Middle]] and [[Upper Paleolithic]] dated to 21,000–31,000 years old<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Gibling |first1=Sinha |last2=Sinha |first2=Roy |last3=Roy |first3=Tandon |last4=Tandon |first4=Jain |last5=Jain |first5=M |year=2008 |title=Quaternary fluvial and eolian deposits on the Belan river, India: paleoclimatic setting of Paleolithic to Neolithic archeological sites over the past 85,000 years |journal=Quaternary Science Reviews |volume=27 |issue=3–4 |page=391 |bibcode=2008QSRv...27..391G |doi=10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.11.001 |s2cid=129392697|issn=0277-3791}}</ref> and [[Mesolithic]]/[[Microlithic]] [[hunter-gatherer]] settlement, near [[Pratapgarh, Uttar Pradesh|Pratapgarh]], from around 10550–9550 BCE. Villages with domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats and evidence of agriculture began as early as 6000 BCE, and gradually developed between c. 4000 and 1500 BCE beginning with the [[Indus Valley Civilisation]] and [[Culture of Harappa|Harappa culture]] to the [[Vedic period]] and extending into the [[Iron Age]].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Kenneth A. R. Kennedy |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=W6zQHNavWlsC&pg=PA263 |title=God-apes and Fossil Men |publisher=University of Michigan Press |year=2000 |isbn=0472110136 |page=263 |access-date=23 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170324214237/https://books.google.com/books?id=W6zQHNavWlsC&pg=PA263 |archive-date=24 March 2017 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Bridget Allchin, Frank Raymond Allchin |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=r4s-YsP6vcIC&pg=PA119 |title=The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1982 |isbn=052128550X |page=119 |access-date=23 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180303134041/https://books.google.com/books?id=r4s-YsP6vcIC&pg=PA119 |archive-date=3 March 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Misra |first=V N |date=November 2001 |title=Prehistoric human colonization of India |url=http://www.ias.ac.in/describe/article/jbsc/026/04/0491-0531 |url-status=live |journal=Journal of Biosciences |publisher=[[Indian Academy of Sciences]] |volume=26 |pages=491–531 |doi=10.1007/bf02704749 |pmid=11779962 |s2cid=26248907 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171007171203/http://www.ias.ac.in/describe/article/jbsc/026/04/0491-0531 |archive-date=7 October 2017 |access-date=19 September 2017 |number=4 Supp}}</ref> |
|||
=== Ancient and classical period === |
|||
The state is bordered by [[Rajasthan]] to the west, [[Haryana]] and [[Delhi]] to the northwest, [[Uttarakhand]] and the country of [[Nepal]] to the north, [[Bihar]] to the east, [[Jharkhand]] to the southeast, [[Chhattisgarh]] to the south and [[Madhya Pradesh]] to the southwest. It covers {{convert|93933|sqmi|km2}}, equal to 6.88% of the total area of India, and is the [[List of states of India by area|fourth largest Indian state by area]]. With over 200 million inhabitants in 2011, it is the [[List of states and union territories of India by population|most populous state]] in the country as well as the [[List of country subdivisions by population|most populous country subdivision in the world]]. [[Hindi]] is the official and most widely spoken language in its 75 districts. Uttar Pradesh is the [[List of Indian states by GDP|fourth largest Indian state by economy]], with a GDP of {{INRConvert|7080|b}}. Agriculture and service industries are the largest parts of the state's economy. The service sector comprises travel and tourism, [[hotel industry]], real estate, insurance and financial consultancies. |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| perrow = 2 |
|||
| total_width = 250 |
|||
| caption_align = center |
|||
| align = left |
|||
| image1 = |
|||
| caption1 = Kausambi fort walls from Period I with burnt brick revetment, 1025–700 BCE, PGW culture. Weeping holes at the base can be clearly observed. |
|||
| image2 = Dhamek Stupta and the Ancient Buddhist Site at Sarnath.jpg |
|||
| background colour = #FDF5E6 |
|||
| caption2 = The [[Dhamekh Stupa]] in Sarnath is where [[Gautama Buddha]] first taught the [[Dharma]], and where the Buddhist [[Sangha (Buddhism)|Sangha]] came into existence through the [[Enlightenment in Buddhism|enlightenment]] of [[Kondanna Buddha|Kondanna]]. |
|||
| direction = |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
}} |
|||
Out of the sixteen ''[[mahajanapadas]]'' (lit. 'great realms') or [[Oligarchy|oligarchic]] [[republic]]s that existed in ancient India, seven fell entirely within the present-day boundaries of the state.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Uttar Pradesh – History |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Uttar-Pradesh |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200401072447/https://www.britannica.com/place/Uttar-Pradesh |archive-date=1 April 2020 |access-date=12 January 2020 |website=Encyclopædia Britannica|quote=A systematic history of India and the area of Uttar Pradesh dates to the end of the 7th century BCE, when 16 mahajanapadas (great states) in northern India were contending for supremacy. Of those, seven fell entirely within the present-day boundaries of Uttar Pradesh.}}</ref> The kingdom of [[Kosala]], in the [[Mahajanapada]] era, was also located within the regional boundaries of modern-day Uttar Pradesh.<ref name="Sen1999">{{Cite book |last=Sailendra Nath Sen |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Wk4_ICH_g1EC&pg=PA105 |title=Ancient Indian History And Civilization |publisher=New Age International |year=1999 |isbn=978-8122411980 |pages=105–106 |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528155843/http://books.google.com/books?id=Wk4_ICH_g1EC&pg=PA105 |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> According to Hinduism, the divine King [[Rama]] of the [[Ramayana]] epic reigned in [[Ayodhya]], the capital of Kosala.<ref name="Buck2000">{{Cite book |last=William Buck |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vvuIp2kqIkMC |title=Ramayana |date=2000 |publisher=Motilal Banarsidass |isbn=978-8120817203 |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130604213755/http://books.google.com/books?id=vvuIp2kqIkMC |archive-date=4 June 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> [[Krishna]], another divine king of Hindu legend, who plays a key role in the [[Mahabharata]] epic and is revered as the eighth reincarnation ([[Avatar]]) of the Hindu god [[Vishnu]], is said to have been born in the city of [[Mathura]].<ref name="Sen1999" /> The aftermath of the [[Kurukshetra War]] is believed to have taken place in the area between the [[Doab#Upper Doab|Upper Doab]] and [[Delhi]], (in what was [[Kuru Kingdom|Kuru]] Mahajanapada), during the reign of the [[Pandava]] King [[Yudhishthira]]. The kingdom of the Kurus corresponds to the [[Black and Red Ware]] and [[Painted Gray Ware]] culture and the beginning of the Iron Age in northwest India, around 1000 BCE.<ref name="Sen1999" /> |
|||
Uttar Pradesh was home to powerful empires of ancient and medieval India, including [[Haryanka dynasty|Magadha]], [[Nanda Empire|Nanda]], [[Maurya Empire|Mauryan]], [[Sunga Empire|Sunga]], [[Kushan Empire|Kushan]], [[Gupta Empire|Gupta]], [[Gurjara-Pratihara|Gurjara]], [[Rashtrakuta Empire|Rashtrakuta]], [[Pala Empire|Pala]] and [[Mughal Empire|Mughal]] which many say was improved by the [[Nawabs of Awadh]]. The two major rivers of the state, the [[Ganges|Ganga]] and [[Yamuna]], join at [[Allahabad]] and then flow as the Ganga further east. The state has several historical, natural, and religious tourist destinations, such as the [[Taj Mahal]], [[Varanasi]], [[Piprahwa]], [[Kaushambi]], [[Kanpur]], [[Ballia]], [[Shravasti District|Shravasti]], [[Kushinagar]], [[Lucknow]], [[Chitrakoot district|Chitrakoot]], [[Jhansi]], [[Allahabad]], [[Budaun]], [[Meerut]] and [[Mathura]]. |
|||
Control over Gangetic plains region was of vital importance to the power and stability of all of India's major empires, including the [[Maurya Empire|Maurya]] (320–200 BCE), [[Kushan Empire|Kushan]] (100–250 CE), [[Gupta Empire|Gupta]] (350–600), and [[Gurjara-Pratihara]] (650–1036) empires.<ref name="White2010">{{Cite book |last=Richard White |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fHLfiOZVzmMC |title=The Middle Ground: Indians, Empires, and Republics in the Great Lakes Region, 1650–1815 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2010 |isbn=978-1107005624 |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528145049/http://books.google.com/books?id=fHLfiOZVzmMC |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> Following the [[Huns]]' invasions that broke the Gupta empire, the [[Doab#The Doab|Ganges-Yamuna Doab]] saw the rise of [[Kannauj]].<ref name="Corporation2007">{{Cite book |last=Marshall Cavendish Corporation |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=V1pQkwIXTG0C&pg=PA331 |title=World and Its Peoples: Eastern and Southern Asia |date=2007 |publisher=Marshall Cavendish |isbn=978-0761476313 |pages=331–335 |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130605122741/http://books.google.com/books?id=V1pQkwIXTG0C&pg=PA331 |archive-date=5 June 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> During the reign of [[Harshavardhana]] (590–647), the Kannauj empire reached its zenith.<ref name="Corporation2007" /> It spanned from [[Punjab]] in the north and [[Gujarat]] in the west to [[Bengal]] in the east and [[Odisha]] in the south.<ref name="Sen1999" /> It included parts of central India, north of the [[Narmada River]] and it encompassed the entire [[Indo-Gangetic Plain]].<ref name="Chopra2003" /> Many communities in various parts of India claim descent from the migrants of Kannauj.<ref name="Bowman2000" /> Soon after Harshavardhana's death, his empire disintegrated into many kingdoms, which were invaded and ruled by the Gurjara-Pratihara empire, which challenged Bengal's [[Pala Empire]] for control of the region.<ref name="Chopra2003">{{Cite book |last=Pran Nath Chopra |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gE7udqBkACwC&pg=PA196 |title=A Comprehensive History of Ancient India |date=2003 |publisher=Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd |isbn=978-8120725034 |page=196 |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528140148/http://books.google.com/books?id=gE7udqBkACwC&pg=PA196 |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> Kannauj was several times invaded by the South Indian [[Rashtrakuta dynasty]], from the 8th century to the 10th century.<ref>The History of India by Kenneth Pletcher p. 102</ref><ref>The City in South Asia by James Heitzman p. 37</ref> After the fall of the Pala empire, the [[Chero dynasty]] ruled from the 12th century to the 18th century.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Singh |first=Pradyuman |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=399UDwAAQBAJ&q=chero+dynasty&pg=PT71 |title=Bihar General Knowledge Digest |date=19 January 2021 |publisher=Prabhat Prakashan |isbn=978-9352667697}}</ref> |
|||
==History== |
|||
{{Main|History of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
=== |
==== Delhi Sultanate ==== |
||
Uttar Pradesh was partially or entirely ruled by the [[Delhi Sultanate]] for 320 years (1206–1526). Five dynasties ruled over the Delhi Sultanate sequentially: the [[Mamluk dynasty (Delhi)|Mamluk dynasty]] (1206–90), the [[Khalji dynasty]] (1290–1320), the [[Tughlaq dynasty]] (1320–1414), the [[Sayyid dynasty]] (1414–51), and the [[Lodi dynasty]] (1451–1526).<ref>* {{Cite book |last=Srivastava |first=Ashirvadi Lal |url=https://archive.org/stream/sultanateofdelhi001929mbp#page/n5/mode/2up |title=The Sultanate of Delhi 711–1526 A D |publisher=Shiva Lal Agarwala & Company |year=1929 |author-link=Ashirbadi Lal Srivastava |access-date=29 April 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160408110410/https://archive.org/stream/sultanateofdelhi001929mbp#page/n5/mode/2up |archive-date=8 April 2016 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Unesco1998">{{Cite book |last1=Islam |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=18eABeokpjEC&pg=PA269 |title=History of Civilizations of Central Asia |last2=Bosworth |publisher=UNESCO |year=1998 |isbn=978-9231034671 |pages=269–291 |access-date=21 May 2020 |archive-date=28 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240328162944/https://books.google.com/books?id=18eABeokpjEC&pg=PA269#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Archeological finds have indicated the presence of [[Stone Age]] ''[[Homo sapiens]]'' hunter-gatherers in Uttar Pradesh<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=gMoJj-0Z94UC&pg=PA69|page=69|title=Recent Advances in Indo-Pacific Prehistory: proceedings of the international symposium held at Poona |author=Virendra N. Misra, Peter Bellwood|isbn=90-04-07512-7|accessdate=23 July 2012|year=1985}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=r4s-YsP6vcIC&pg=PA58|page=58|title=The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan|author=Bridget Allchin, Frank Raymond Allchin|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=0-521-28550-X|accessdate=23 July 2012|date=29 July 1982}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=35DP1Z-2dnYC&pg=PA96|page=96|title= Studies in Indian Archaeology|author=Hasmukhlal Dhirajlal Sankalia, Shantaram Bhalchandra Deo, Madhukar Keshav Dhavalikar|publisher=Popular Prakashan|isbn=0-86132-088-3|accessdate=23 July 2012|year=1985}}</ref> between around<ref>Confidence limits for the age are 85 (±11) and 72 (±8) thousand years ago.</ref> 85 and 73 thousand years old. Other pre-historical finds have included Middle and Upper Paleolithic artifacts dated to 21–31 thousand years old<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Gibling|first1=Sinha|last2=Sinha|first2=Roy|last3=Roy|first3=Tandon|last4=Tandon|first4=Jain|last5=Jain|first5=M|title=Quaternary fluvial and eolian deposits on the Belan river, India: paleoclimatic setting of Paleolithic to Neolithic archeological sites over the past 85,000 years|journal=Quaternary Science Reviews|volume=27|page=391|year=2008|doi=10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.11.001|issue=3–4|ref=harv}}</ref> and [[Mesolithic]]/[[Microlithic]] [[hunter-gatherer]]'s settlement, near [[Pratapgarh, Uttar Pradesh|Pratapgarh]], from around 10550–9550 BC. Villages with domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats and evidence of agriculture began as early as 6000 BC, and gradually developed between c. 4000 and 1500 BC beginning with the [[Indus Valley Civilization]] and [[Culture of Harappa|Harappa Culture]] to the [[Vedic period]]; extending into the [[Iron Age]].<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=W6zQHNavWlsC&pg=PA263|publisher=University of Michigan Press|year= 2000|isbn=0-472-11013-6|page=263|title=God-apes and Fossil Men|author=Kenneth A. R. Kennedy|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=r4s-YsP6vcIC&pg=PA119|page=119|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=0-521-28550-X|year=1982|title=The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan|author=Bridget Allchin, Frank Raymond Allchin|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ias.ac.in/jbiosci/nov2001/491.pdf |title=Prehistoric human colonization of India |format=PDF |accessdate=5 April 2012}}</ref> |
|||
The first Sultan of Delhi, [[Qutb ud-Din Aibak]], conquered some parts of Uttar Pradesh, including [[Meerut]], [[Aligarh]], and [[Etawah]]. His successor, [[Iltutmish]], expanded the Sultanate's rule over Uttar Pradesh by defeating the King of [[Kannauj]]. During the reign of Sultan [[Balban]], the Mamluk dynasty faced numerous rebellions in the state, but he was able to suppress them and establish his authority. [[Alauddin Khilji]], extended his conquests to various regions in the state, including [[Varanasi]] and [[Prayagraj]]. Apart from the rulers, the Delhi Sultanate era also saw the growth of [[Sufism]] in Uttar Pradesh. Sufi saints, such as [[Nizamuddin Auliya]] and [[Qutbuddin Bakhtiar Kaki]], lived during this period and their teachings had a significant impact on the people of the region. Sultanat era in the state also witnessed the construction of mosques and tombs, including the [[Atala Masjid]] in [[Jaunpur, Uttar Pradesh|Jaunpur]], the [[Jama Masjid]] in [[Fatehpur Sikri]], and the [[Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq's Tomb]] in [[Tughlaqabad]].<ref name="Atala">{{cite web | title=Atala Masjid | website=District Jaunpur, Government of Uttar Pradesh | date=20 June 2017 | url=https://jaunpur.nic.in/tourist-place/atala-masjid/ | access-date=6 May 2024}}</ref><ref name="Tughluq Tomb">{{cite web | last=Datta | first=Rangan | title=The tomb of Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq | website=Telegraph India | date=22 July 2022 | url=https://www.telegraphindia.com/my-kolkata/places/exploring-the-tomb-of-ghiyasuddin-tughlaq-near-tughlaqabad-fort-in-south-delhi/cid/1875958 | access-date=6 May 2024}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Rama in forest.jpg|thumb|upright|left|alt=Painting of goddess Rama alongside Sita and Laxman|Rama portrayed as exile in the forest, accompanied by his wife Sita and brother Lakshmana]] |
|||
The kingdom of [[Kosala]], in the [[Mahajanapada]] era, was located within the regional boundaries of modern day Uttar Pradesh.<ref name="Sen1999">{{cite book|author=Sailendra Nath Sen|title=Ancient Indian History And Civilization|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Wk4_ICH_g1EC&pg=PA105|accessdate=1 October 2012|date=1 January 1999|publisher=New Age International|isbn=978-81-224-1198-0|pages=105–106}}</ref> According to Hindu legend, the divine king [[Rama]] of the [[Ramayana]] epic reigned in [[Ayodhya]], the capital of Kosala.<ref name="Buck2000">{{cite book|author=William Buck|title=Ramayana|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=vvuIp2kqIkMC|accessdate=1 October 2012|date=1 January 2000|publisher=Motilal Banarsidass Publ.|isbn=978-81-208-1720-3}}</ref> [[Krishna]], another divine king of Hindu legend, who plays a key role in the [[Mahabharata]] epic and is revered as the eighth reincarnation ([[Avatar]]) of the Hindu god [[Vishnu]], is said to have been born in the city of [[Mathura]], in Uttar Pradesh.<ref name="Sen1999"/> The aftermath of the [[Mahabharata yuddh]] is believed to have taken place in the area between the Upper [[Doab]] and [[Delhi]], (in what was [[Kuru Kingdom|Kuru]] Mahajanapada), during the reign of the [[Pandava]] king [[Yudhisthira]]. The kingdom of the [[Kuru (India)|Kurus]] corresponds to the [[Black and Red Ware]] and [[Painted Gray Ware]] culture and the beginning of the Iron Age in North-west India, around 1000 BC.<ref name="Sen1999"/> |
|||
=== Medieval and early modern period === |
|||
Most of the invaders of south India passed through the Gangetic plains of what is today Uttar Pradesh. Control over this region was of vital importance to the power and stability of all of India's major empires, including the [[Maurya Empire|Maurya]] (320–200 BC), [[Kushan Empire|Kushan]] (100–250 CE), [[Gupta Empire|Gupta]] (350–600 CE), and [[Gurjara-Pratihara]] (650–1036 CE) empires.<ref name="White2010">{{cite book|author=Richard White|title=The Middle Ground: Indians, Empires, and Republics in the Great Lakes Region, 1650-1815|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=fHLfiOZVzmMC|accessdate=1 October 2012|date=8 November 2010|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-1-107-00562-4}}</ref> Following the [[Huns]] invasions that broke the Gupta empire, the Ganges-Yamuna Doab saw the rise of [[Kannauj]].<ref name="Corporation2007">{{cite book|author=Marshall Cavendish Corporation|title=World and Its Peoples: Eastern and Southern Asia|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=V1pQkwIXTG0C&pg=PA331|accessdate=1 October 2012|date=September 2007|publisher=Marshall Cavendish|isbn=978-0-7614-7631-3|pages=331–335}}</ref> During the reign of [[Harshavardhana]] (590–647 CE), the Kannauj empire reached its zenith.<ref name="Corporation2007"/> It spanned from [[Punjab region|Punjab]] in the north and [[Gujarat]] in the west to [[Bengal]] in the east and [[Odisha]] in the south.<ref name="Sen1999"/> It included parts of central India, north of the [[Narmada River]] and it encompassed the entire [[Indo-Gangetic plain]].<ref name="Chopra2003"/> Many communities in various parts of India claim descent from the migrants of Kannauj.<ref name="Bowman2000"/> Soon after Harshavardhana's death, his empire disintegrated into many kingdoms, which were invaded and ruled by the Gurjara-Pratihara empire, which challenged Bengal's [[Pala Empire]] for control of the region.<ref name="Chopra2003">{{cite book|author=Pran Nath Chopra|title=A Comprehensive History of Ancient India|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=gE7udqBkACwC&pg=PA196|accessdate=1 October 2012|date=1 December 2003|publisher=Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd|isbn=978-81-207-2503-4|page=196}}</ref> [[Kannauj]] was several times invaded by the south Indian [[Rashtrakuta Dynasty]] from the 8th century to the 10th century.<ref>The History of India by Kenneth Pletcher p.102</ref><ref>The City in South Asia by James Heitzman p.37</ref> |
|||
In the 16th century, [[Babur]], a [[Timurid dynasty|Timurid]] descendant of [[Timur]] and [[Descent from Genghis Khan|Genghis Khan]] from [[Fergana Valley]] (modern-day [[Uzbekistan]]), swept across the [[Khyber Pass]] and founded the [[Mughal Empire]], covering [[India]], along with modern-day [[Afghanistan]], Pakistan and [[Bangladesh]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Islamic World to 1600: Rise of the Great Islamic Empires (The Mughal Empire) |url=https://www.ucalgary.ca/applied_history/tutor/islam/empires/mughals/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110927121217/http://www.ucalgary.ca/applied_history/tutor/islam/empires/mughals/ |archive-date=27 September 2011}}</ref> The Mughals were descended from Persianised Central Asian [[Turkic people|Turks]] (with significant [[Mongol]] admixture). In the [[Mughal Empire|Mughal]] era, Uttar Pradesh became the heartland of the empire.<ref name="Bowman2000">{{Cite book |last=John Stewart Bowman |url=https://archive.org/details/columbiachronolo00john |title=Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture |publisher=Columbia University Press |year=2000 |isbn=978-0231110044 |page=[https://archive.org/details/columbiachronolo00john/page/273 273] |access-date=2 August 2012 |url-access=registration}}</ref> Mughal emperors Babur and Humayun ruled from Delhi.<ref name="Schimmel2004">{{Cite book |last=Annemarie Schimmel |url=https://archive.org/details/empireofgreatmug00anne |title=The Empire of the Great Mughals: History, Art and Culture |date=2004 |publisher=Reaktion Books |isbn=978-1861891853 |access-date=1 October 2012 |url-access=registration}}</ref><ref name="HindustanHiro2006">{{Cite book |last1=Babur (Emperor of Hindustan) |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VW2HJL689wgC |title=Babur Nama: Journal of Emperor Babur |last2=Dilip Hiro |date=2006 |publisher=Penguin Books India |isbn=978-0144001491 |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528160214/http://books.google.com/books?id=VW2HJL689wgC |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> In 1540 an Afghan, [[Sher Shah Suri]], took over the reins of Uttar Pradesh after defeating the Mughal King Humanyun.<ref name="Ramirez-Faria2007">{{Cite book |last=Carlos Ramirez-Faria |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gGKsS-9h4BYC&pg=PA171 |title=Concise Encyclopedia of World History |publisher=Atlantic Publishers & Dist |year=2007 |isbn=978-8126907755 |page=171 |access-date=2 August 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528155918/http://books.google.com/books?id=gGKsS-9h4BYC&pg=PA171 |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> Sher Shah and his son Islam Shah ruled Uttar Pradesh from their capital at [[Gwalior]].<ref name="Hindustan">{{Cite book |last=Stronge |first=Susan |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PVrSYgEACAAJ&q=hindustan+by+mughal |title=Mughal Hindustan is renowned for its opulence |publisher=The Arts of the Sikh Kingdoms |year=2012 |isbn=9788174366962 |location=London |page=255 |access-date=23 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170216115741/https://books.google.com/books?id=PVrSYgEACAAJ&dq=hindustan+by+mughal |archive-date=16 February 2017 |url-status=live}}</ref> After the death of [[Islam Shah Suri]], his prime minister [[Hemu]] became the ''de facto'' ruler of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and the western parts of Bengal. He was bestowed the title of ''[[Hemu|Hemchandra Vikramaditya]]'' (title of [[Vikramāditya]] adopted from [[Vedic period]]) at his formal coronation took place at [[Purana Qila]] in Delhi on 7 October 1556. A month later, Hemu died in the [[Second Battle of Panipat]], and Uttar Pradesh came under Emperor [[Akbar]]'s rule.<ref name="Agrawal1983">{{Cite book |last=Ashvini Agrawal |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AZdCrUxFAHEC&pg=PA30 |title=Studies in Mughal History |date=1983 |publisher=Motilal Banarsidass |isbn=978-8120823266 |pages=30–46 |access-date=27 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528153902/http://books.google.com/books?id=AZdCrUxFAHEC&pg=PA30 |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> Akbar ruled from [[Agra]] and [[Fatehpur Sikri]].<ref>Fergus Nicoll, ''Shah Jahan: The Rise and Fall of the Mughal Emperor'' (2009)</ref> |
|||
In the 18th century, after the fall of Mughal authority, the power vacuum was filled by the [[Maratha Empire]], in the mid-18th century, the Maratha army invaded the Uttar Pradesh region, which resulted in [[Rohilla]]s losing control of [[Rohilkhand]] to the Maratha forces led by [[Raghunath Rao]] and [[Malhar Rao Holkar|Malha Rao Holkar]]. The conflict between Rohillas and Marathas came to an end on 18 December 1788 with the arrest of [[Ghulam Kadir|Ghulam Qadir]], the grandson of Najeeb-ud-Daula, who was defeated by the Maratha general [[Mahadji Scindia|Mahadaji Scindia]]. In 1803–04, following the [[Second Anglo-Maratha War]], when the [[British East India Company]] defeated the Maratha Empire, much of the region came under British suzerainty.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Mayaram |first=Shail |title=Against history, against state: counterperspectives from the margins Cultures of history |publisher=Columbia University Press |year=2003 |isbn=978-0231127318}}</ref> |
|||
In the 16th century, [[Babur]], a [[Timurid Dynasty|Timurid]] descendant of [[Timur]] and [[Descent from Genghis Khan|Genghis Khan]] from [[Fergana Valley]] (modern-day [[Uzbekistan]]), swept across the [[Khyber Pass]] and founded the [[Mughal Empire]], covering [[India]], along with modern-day [[Afghanistan]], Pakistan and [[Bangladesh]]<ref>[http://www.ucalgary.ca/applied_history/tutor/islam/empires/mughals/ The Islamic World to 1600: Rise of the Great Islamic Empires (The Mughal Empire)]</ref> The Mughals were descended from Persianised Central Asian [[Turkic people|Turks]] (with significant [[Mongol]] admixture). In the [[Mughal Empire|Mughal]] era, Uttar Pradesh became the heartland of the empire.<ref name="Bowman2000">{{cite book|author=John Stewart Bowman|title=Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=cYoHOqC7Yx4C&pg=PA273|accessdate=2 August 2012|year=2000|publisher=Columbia University Press|isbn=978-0-231-11004-4|page=273}}</ref> Mughal emperors Babur and Humayun ruled from Delhi.<ref name="Schimmel2004">{{cite book|author=Annemarie Schimmel|title=The Empire of the Great Mughals: History, Art and Culture|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=N7sewQQzOHUC|accessdate=1 October 2012|date=5 February 2004|publisher=Reaktion Books|isbn=978-1-86189-185-3}}</ref><ref name="Hindustan)Hiro2006">{{cite book|author1=Babur (Emperor of Hindustan)|author2=Dilip Hiro|title=Babur Nama: Journal of Emperor Babur|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=VW2HJL689wgC|accessdate=1 October 2012|date=1 March 2006|publisher=Penguin Books India|isbn=978-0-14-400149-1}}</ref> In 1540 an Afghan, [[Sher Shah Suri]], took over the reins of Uttar Pradesh after defeating the Mughal king Humanyun.<ref name="Ramirez-Faria2007">{{cite book|author=Carlos Ramirez-Faria|title=Concise Encyclopeida Of World History|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=gGKsS-9h4BYC&pg=PA171|accessdate=2 August 2012|date=1 January 2007|publisher=Atlantic Publishers & Dist|isbn=978-81-269-0775-5|page=171}}</ref> Sher Shah and his son Islam Shah ruled Uttar Pradesh from their capital at [[Gwalior]].<ref name=hindustan>{{cite book|last=Stronge|first=Susan|title=Mughal Hindustan is renowned for its opulence|date=16 October 2012|publisher=The Arts of the Sikh Kingdoms (V&A 1999)|location=London|page=255|url=http://books.google.com/?id=PVrSYgEACAAJ&dq=hindustan+by+mughal|accessdate=23 July 2012|isbn=9788174366962}}</ref> After the death of [[Islam Shah Suri]], his prime minister [[Hemu]] became the ''de facto'' ruler of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and the western parts of Bengal. He was bestowed the title of ''[[Vikramaditya]]'' at his coronation or ''Rajyabhishake'' at [[Purana Quila]] in Delhi and was titled as ''[[Samrat Hem Chandra Vikramaditya]]''. Hemu died in the [[Second Battle of Panipat]], and Uttar Pradesh came under Emperor [[Akbar]]'s rule.<ref name="Agrawal1983">{{cite book|author=Ashvini Agrawal|title=Studies In Mughal History|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=AZdCrUxFAHEC&pg=PA30|accessdate=27 July 2012|date=1 January 1983|publisher=Motilal Banarsidass Publ.|isbn=978-81-208-2326-6|pages=30–46}}</ref> Akbar ruled from [[Agra]] and [[Fatehpur Sikri]].<ref>Fergus Nicoll, ''Shah Jahan: The Rise and Fall of the Mughal Emperor'' (2009)</ref> In the 18th century, after the fall of Mughal authority, the power vacuum was filled by the [[Maratha Empire]], in mid 18th century, the Maratha army invaded the Uttar Pradesh region, which resulted in Rohillas losing control of Rohillkhand to the Maratha rulers [[Raghunathrao|Raghunath Rao]] and [[Malharao Holkar]]. The conflict between Rohillas and Marathas came to an end on 18{{nbsp}}December 1788 with the arrest of Ghulam Qadir, the grandson of Najeeb-ud-Daula, who was defeated by the Maratha general [[Mahadji Scindia|Mahadaji Scindia]]. In 1803, following the [[Second Anglo-Maratha War]], when the [[British East India Company]] defeated the Maratha Empire, much of the region came under British suzerainty.<ref>{{cite book |
|||
|last = Mayaram |
|||
|first = Shail |
|||
|title = Against history, against state: counterperspectives from the margins Cultures of history |
|||
|publisher = Columbia University Press, 2003 |
|||
|isbn = 978-0-231-12731-8}}</ref> |
|||
===British |
==== British India era ==== |
||
{{Infobox |
|||
Starting from [[Bengal]] in the second half of the 18th century, a series of battles for north Indian lands finally gave the [[British East India Company]] accession over the state's territories.<ref name="Kudaisya2006">{{cite book|author=Gyanesh Kudaisya|title=Region, nation, "heartland": Uttar Pradesh in India's body-politiqEPgvENHg2MC&pg=PA126|accessdate=26 July 2012|year=1994|publisher=LIT Verlag Münster|isbn=978-3-8258-2097-8|pages=126–376}}</ref> [[Ajmer]] and [[Jaipur]] kingdoms were also included in this northern territory, which was named the "[[North-Western Provinces]]" (of Agra). Although UP later became the fifth largest state of India, NWPA was one of the smallest states of the British Indian empire.<ref name="Sivaramakrishnan1999">{{cite book|author=K. Sivaramakrishnan|title=Modern Forests: Statemaking and Environmental Change in Colonial Eastern India|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=TM7oYBG4M04C&pg=PA240|accessdate=26 July 2012|date=3 December 1999|publisher=Stanford University Press|isbn=978-0-8047-4556-7|pages=240–276}}</ref> Its capital shifted twice between Agra and Allahabad.<ref name="Markovits2002">{{cite book|author=Claude Markovits|title=A History of Modern India, 1480-1950|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=uzOmy2y0Zh4C&pg=PA586|accessdate=26 July 2012|year=2002|publisher=Anthem Press|isbn=978-1-84331-004-4|pages=586–593}}</ref> |
|||
| above = Timeline of reorganisation and name changes of UP<ref>{{Cite web |date=3 May 2017 |title=Uttar Pradesh Day: How the state was born 67 years back |url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/lucknow/uttar-pradesh-day-how-the-state-was-born-67-years-back/story-Y2JhCTBIo2UuQYvQSTBNgN.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170503114407/http://www.hindustantimes.com/lucknow/uttar-pradesh-day-how-the-state-was-born-67-years-back/story-Y2JhCTBIo2UuQYvQSTBNgN.html |archive-date=3 May 2017 |access-date=3 May 2017}}</ref> |
|||
| label2 = 1807 |
|||
| data2 = [[Ceded and Conquered Provinces]] |
|||
| label3 = 14 November 1834 |
|||
| data3 = [[Presidency of Agra]] |
|||
| label4 = 1 January 1836 |
|||
| data4 = [[North-Western Provinces]] |
|||
| label5 = 3 April 1858 |
|||
| data5 = [[Oudh]] taken under British control, [[Delhi]] taken away from [[North-Western Provinces|NWP]] and merged into [[Punjab (British India)|Punjab]] |
|||
| label6 = 1 April 1871 |
|||
| data6 = [[Ajmer]], [[Mewar|Merwara]] & [[Kekri, Rajasthan|Kekri]] made separate commissioner-ship |
|||
| label7 = 15 February 1877 |
|||
| data7 = Oudh added to [[North-Western Provinces]] |
|||
| label8 = 22 March 1902 |
|||
| data8 = Renamed [[United Provinces of Agra and Oudh]] |
|||
| label9 = 3 January 1921 |
|||
| data9 = Renamed [[United Provinces of British India]] |
|||
| label10 = 1 April 1937 |
|||
| data10 = Renamed [[United Provinces (1937–1950)|United Provinces]] |
|||
| label11 = 1 April 1946 |
|||
| data11 = Self rule granted |
|||
| label12 = 15 August 1947 |
|||
| data12 = Part of independent India |
|||
| label13 = 24 January 1950 |
|||
| data13 = Renamed Uttar Pradesh |
|||
| label14 = 9 November 2000 |
|||
| data14 = Uttaranchal state, now known as [[Uttarakhand]], created from part of Uttar Pradesh |
|||
}} |
|||
Starting from [[Bengal]] in the second half of the 18th century, a series of battles for north Indian lands finally gave the [[British East India Company]] accession over the state's territories.<ref name="Kudaisya2006">{{Cite book |last=Gyanesh Kudaisya |title=Region, nation, "heartland": Uttar Pradesh in India's body-politic |publisher=LIT Verlag Münster |year=1994 |isbn=978-3825820978 |pages=126–376}}</ref> [[Ajmer]] and [[Jaipur]] kingdoms were also included in this northern territory, which was named the "[[North-Western Provinces]]" (of Agra). Although UP later became the fifth-largest state of India, NWPA was one of the smallest states of the British Indian empire.<ref name="Sivaramakrishnan1999">{{Cite book |last=K. Sivaramakrishnan |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TM7oYBG4M04C&pg=PA240 |title=Modern Forests: Statemaking and Environmental Change in Colonial Eastern India |publisher=Stanford University Press |year=1999 |isbn=978-0804745567 |pages=240–276 |access-date=26 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528135332/http://books.google.com/books?id=TM7oYBG4M04C&pg=PA240 |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> Its capital shifted twice between Agra and Allahabad.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Ashutosh Joshi |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UFaGME0XDBkC&q=Naini&pg=PA151 |title=Town Planning Regeneration of Cities |publisher=New India Publishing |year=2008 |isbn=978-8189422820 |page=237 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180303134041/https://books.google.com/books?id=UFaGME0XDBkC&pg=PA151&dq=Naini&hl=en&sa=X&ei=CN7OUsznI8yTrgeDwYDgCw&ved=0CDEQ6AEwATgU#v=onepage&q=Allahabad%20capital&f=false |archive-date=3 March 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Due to dissatisfaction with British rule, a serious rebellion erupted in various parts of North India; [[Bengal]] [[regiment]]'s sepoy stationed at [[Meerut]] [[cantonment]], [[Mangal Pandey]], is widely credited as its starting point.<ref name="Mukherjee2005">{{cite book|author=Rudrangshu Mukherjee|title=Mangal Pandey: brave martyr or accidental hero?|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=-SluAAAAMAAJ|accessdate=1 October 2012|date=1 June 2005|publisher=Penguin Books|isbn=978-0-14-303256-4}}</ref> It came to be known as the [[Indian Rebellion of 1857]]. After the revolt failed, the British attempted to divide the most rebellious regions by reorganising the administrative boundaries of the region, splitting the Delhi region from 'NWFP of Agra' and merging it with [[Punjab (British India)|Punjab]], while the [[Ajmer]]- [[Marwar]] region was merged with [[Rajputana]] and Oudh was incorporated into the state. The new state was called the 'North Western Provinces of Agra and Oudh', which in 1902 was renamed as the [[United Provinces of Agra and Oudh]].<ref name="(India)Drake-Brockman1934">{{cite book|author1=United Provinces of Agra and Oudh (India)|author2=D.L. Drake-Brockman|title=District Gazetteers of the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh: supp.D.Pilibhit District|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=VUNuAAAAMAAJ|accessdate=1 October 2012|year=1934|publisher=Supdt., Government Press, United Provinces}}</ref> It was commonly referred to as the United Provinces or its acronym UP.<ref name="Chakrabarti1997">{{cite book|author=Dilip K. Chakrabarti|title=Colonial Indology: sociopolitics of the ancient Indian past|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=ADZuAAAAMAAJ|accessdate=26 July 2012|date=1 June 1997|publisher=Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers Pvt. Ltd.|location=Michigan|isbn=978-81-215-0750-9|page=257}}</ref><ref name="Cohn1996">{{cite book|author=Bernard S. Cohn|title=Colonialism and Its Forms of Knowledge: The British in India|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=uIalYaenrTkC|accessdate=26 July 2012|date=19 August 1996|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-00043-5|page=189}}</ref> |
|||
Due to dissatisfaction with British rule, a serious rebellion erupted in various parts of North India, which became known as the [[Indian Rebellion of 1857]]; [[Bengal]] [[regiment]]'s sepoy stationed at [[Meerut]] [[cantonment]], [[Mangal Pandey]], is widely considered as its starting point.<ref name="Mukherjee2005">{{Cite book |last=Rudrangshu Mukherjee |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-SluAAAAMAAJ |title=Mangal Pandey: brave martyr or accidental hero? |publisher=Penguin Books |year=2005 |isbn=978-0143032564 |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130605164801/http://books.google.com/books?id=-SluAAAAMAAJ |archive-date=5 June 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> After the revolt failed, the British divided the most rebellious regions by reorganising their administrative boundaries, splitting the Delhi region from 'NWFP of Agra' and merging it with [[Punjab Province (British India)|Punjab Province]], while the [[Ajmer]]–[[Marwar]] region was merged with [[Rajputana]] and [[Oudh State|Oudh]] was incorporated into the state. The new state was called the North Western Provinces of Agra and Oudh, which in 1902 was renamed as the [[United Provinces of Agra and Oudh]].<ref name="(India)Drake-Brockman1934">{{Cite book |last1=United Provinces of Agra and Oudh (India) |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VUNuAAAAMAAJ |title=District Gazetteers of the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh: supp.D.Pilibhit District |last2=D.L. Drake-Brockman |publisher=Supdt., Government Press, United Provinces |year=1934 |access-date=1 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528131217/http://books.google.com/books?id=VUNuAAAAMAAJ |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> It was commonly referred to as the United Provinces or its acronym UP.<ref name="Chakrabarti1997">{{Cite book |last=Dilip K. Chakrabarti |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ADZuAAAAMAAJ |title=Colonial Indology: sociopolitics of the ancient Indian past |publisher=Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers Pvt. Ltd. |year=1997 |isbn=978-8121507509 |location=Michigan |page=257 |access-date=26 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528140749/http://books.google.com/books?id=ADZuAAAAMAAJ |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Cohn1996">{{Cite book |last=Bernard S. Cohn |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uIalYaenrTkC |title=Colonialism and Its Forms of Knowledge: The British in India |publisher=Princeton University Press |year=1996 |isbn=978-0691000435 |page=189 |access-date=26 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528150524/http://books.google.com/books?id=uIalYaenrTkC |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
In 1920, the capital of the province was shifted from Allahabad to [[Lucknow]]. The high court continued to be at Allahabad, but a bench was established at Lucknow. Allahabad continues to be an important administrative base of today's Uttar Pradesh and has several administrative headquarters.<ref name="Nair2004">{{cite book|author=K. Balasankaran Nair|title=Law Of Contempt Of Court In India|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=gujNYPcNETMC|accessdate=26 July 2012|date=1 January 2004|publisher=Atlantic Publishers & Dist|isbn=978-81-269-0359-7|page=320}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh continued to be central to Indian politics and was especially important in modern Indian history as a hotbed of the [[Indian independence movement]]. Uttar Pradesh hosted modern educational institutions such as the [[Benaras Hindu University]], [[Aligarh Muslim University]] and the [[Darul Uloom Deoband]]. Nationally known figures such as [[Chandra Shekhar Azad]] were among the leaders of the movement in Uttar Pradesh, and [[Motilal Nehru]], [[Jawaharlal Nehru]], [[Madan Mohan Malaviya]] and [[Gobind Ballabh Pant]] were important national leaders of the [[Indian National Congress]]. The [[All India Kisan Sabha]] (AIKS) was formed at the Lucknow session of the Congress on 11 April 1936, with the famous nationalist [[Swami Sahajanand Saraswati]] elected as its first President,<ref>{{cite book |
|||
| first = Bandyopādhyāya |
|||
| last = Śekhara |
|||
| title = From Plassey to Partition: A History of Modern India |
|||
| publisher = [[Orient Longman]] |
|||
| year = 2004 |
|||
| isbn = 978-81-250-2596-2 |
|||
| page = 407 |
|||
}}</ref> in order to address the longstanding grievances of the peasantry and mobilise them against the [[zamindari]] landlords attacks on their occupancy rights, thus sparking the Farmers movements in India.<ref>{{cite book |
|||
| first = Śekhara |
|||
| last = Bandyopādhyāya |
|||
| title = From Plassey to Partition: A History of Modern India |
|||
| publisher = [[Orient Longman]] |
|||
| year = 2004 |
|||
| isbn = 978-81-250-2596-2 |
|||
| page = 406 |
|||
}}</ref> During the [[Quit India Movement]] of 1942, [[Ballia]] district overthrew the colonial authority and installed an independent administration under [[Chittu Pandey]]. Ballia became known as "Baghi Ballia" (Rebel Ballia) for this significant role in India's independence movement.<ref name="Chatterji2006">{{cite book|author=Bankim Chandra Chatterji|title=Anandamath|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=7Gmjn63ogDUC|accessdate=26 July 2012|date=15 January 2006|publisher=Orient Paperbacks|isbn=978-81-222-0130-7|page=168}}</ref> |
|||
In 1920, the capital of the province was shifted from Allahabad to [[Lucknow]].<ref name="Wilkinson-Weber1999">{{Cite book |last=Clare M. Wilkinson-Weber |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ChwRC6hQttoC&pg=PA18 |title=Embroidering Lives: Women's Work and Skill in the Lucknow Embroidery Industry |publisher=SUNY Press |year=1999 |isbn=978-0791440872 |page=18 |access-date=24 May 2020 |archive-date=28 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240328164501/https://books.google.com/books?id=ChwRC6hQttoC&pg=PA18#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> The high court continued to be at Allahabad, but a bench was established at Lucknow.<ref name="Lucknow Bench">{{Cite web |last=Mathur |first=Prakash Narain |title=A History of the Lucknow Bench Of The Allahabad High Court |url=http://www.allahabadhighcourt.in/event/AHistoryLucknowBenchPNMathur.pdf |access-date=24 May 2020 |publisher=Allahabad High Court |archive-date=24 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210224172749/http://www.allahabadhighcourt.in/event/AHistoryLucknowBenchPNMathur.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Allahabad continues to be an important administrative base of today's Uttar Pradesh and has several administrative headquarters.<ref name="Nair2004">{{Cite book |last=K. Balasankaran Nair |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gujNYPcNETMC |title=Law of Contempt of Court in India |publisher=Atlantic Publishers & Dist |year=2004 |isbn=978-8126903597 |page=320 |access-date=26 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528143730/http://books.google.com/books?id=gujNYPcNETMC |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh continued to be central to Indian politics and was especially important in modern Indian history as a hotbed of the [[Indian independence movement]]. The state hosted modern educational institutions such as the [[Aligarh Muslim University]], [[Banaras Hindu University]] and [[Darul Uloom Deoband]]. Nationally known figures such as [[Ram Prasad Bismil]] and [[Chandra Shekhar Azad]] were among the leaders of the movement in Uttar Pradesh, and [[Motilal Nehru]], [[Jawaharlal Nehru]], [[Madan Mohan Malaviya]] and [[Govind Ballabh Pant]] were important national leaders of the [[Indian National Congress]]. The [[All India Kisan Sabha]] was formed at the Lucknow session of the Congress on 11 April 1936, with the famous nationalist [[Sahajanand Saraswati]] elected as its first president,<ref>{{Cite book |last=Śekhara |first=Bandyopādhyāya |title=From Plassey to Partition: A History of Modern India |publisher=[[Orient Longman]] |year=2004 |isbn=978-8125025962 |page=407}}</ref> to address the longstanding grievances of the peasantry and mobilise them against the [[zamindari]] landlords attacks on their occupancy rights, thus sparking the Farmers movements in India.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Bandyopādhyāya |first=Śekhara |title=From Plassey to Partition: A History of Modern India |publisher=[[Orient Longman]] |year=2004 |isbn=978-8125025962 |page=406}}</ref> During the [[Quit India Movement]] of 1942, [[Ballia]] district overthrew the colonial authority and installed an independent administration under [[Chittu Pandey]]. Ballia became known as "Baghi Ballia" (Rebel Ballia) for this significant role in India's independence movement.<ref name="Chatterji2006">{{Cite book |last=Bankim Chandra Chatterji |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7Gmjn63ogDUC |title=Anandamath |publisher=Orient Paperbacks |year=2006 |isbn=978-8122201307 |page=168 |access-date=26 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528130144/http://books.google.com/books?id=7Gmjn63ogDUC |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Post-independence=== |
|||
After India's independence, the United Provinces were reorganised as Uttar Pradesh in 1957. The state has provided seven of India's prime ministers and is the source of the largest number of seats in the [[Lok Sabha]]. Despite its political influence, it poor economic development and administrative record, organised crime and corruption kept it amongst India's backward states. The state has been affected by repeated episodes of caste and communal violence.<ref>{{cite news|title=Communal violence|url=http://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/uttar-pradesh-tops-home-ministry-list-on-communal-violence-114080601639_1.html|accessdate=25 August 2014|work=[[Business Standard]]|agency=[[Kotak Mahindra Bank]]|publisher=[[Ananda Publishers]]|date=August 6, 2014}}</ref> In December, 1992 the [[Babri Mosque]] in [[Ayodhya]] was demolished by radical Hindu activists, leading to widespread violence across India.<ref name="communal violance">{{cite news|last=communal violence|first=in uttar pradesh|title=Communal conflicts in state|url=http://www.tehelka.com/what-led-to-the-muzaffarnagar-communal-riots/|accessdate=12 January 2014|newspaper=Tehalka}}</ref> In 1999, northern districts of the state were separated to form the state of [[Uttarakhand]].<ref name=seperation>{{cite book|last=Uttarakhand: Past, Present,|first=and Future|title=separation of uttarakhand|year=1995|publisher=Concept Publishing Company|page=391|url=http://books.google.co.in/books?id=alRh51xE_v0C&pg=PA391&lpg=PA391&dq=separation+of+uttarakhand&source=bl&ots=8nIurr8PZg&sig=afgXsaRygXC8tMqMwW5PnP2kUHM&hl=en&sa=X&ei=vd7SUpjtJonIrQfhlYDQBQ&ved=0CGMQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=separation%20of%20uttarakhand&f=false}}</ref> |
|||
==== Post-independence ==== |
|||
==Geography== |
|||
After India's independence, the United Provinces were renamed "Uttar Pradesh" ({{Lit|northern province}}), preserving UP as the abbreviation of the state's name,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Uttar Pradesh – States and Union Territories |url=http://www.archive.india.gov.in/knowindia/state_uts.php?id=28 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150715014814/http://www.archive.india.gov.in/knowindia/state_uts.php?id=28 |archive-date=15 July 2015 |access-date=14 July 2015 |website=Know India: National Portal of India}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=22 August 2007 |title=Uttar Pradesh |url=http://www.whatisindia.com/issues/uttarpra/uttar_general.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161012021112/http://www.whatisindia.com/issues/uttarpra/uttar_general.html |archive-date=12 October 2016 |access-date=8 October 2016 |publisher=What is India}}</ref> with the change coming into effect on 24 January 1950.<ref name="UPDay" /> The new state was formed after the merger of several princely states and territories, including the [[United Provinces of Agra and Oudh]], and the Delhi territory. The state has provided nine of India's prime ministers which is more than any other state and is the source of the largest number of seats in the [[Lok Sabha]]. Despite its political influence since ancient times, its poor record in economic development and administration, poor governance, organised crime and corruption have kept it among India's backward states. The state has been affected by repeated episodes of [[Caste-related violence in India|caste-related]] and [[communal violence]].<ref>{{Cite news |date=6 August 2014 |title=Communal violence |work=[[Business Standard]] |publisher=[[Ananda Publishers]] |agency=[[Kotak Mahindra Bank]] |url=http://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/uttar-pradesh-tops-home-ministry-list-on-communal-violence-114080601639_1.html |url-status=live |access-date=25 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140826115034/http://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/uttar-pradesh-tops-home-ministry-list-on-communal-violence-114080601639_1.html |archive-date=26 August 2014}}</ref> In December 1992 the disputed [[Demolition of the Babri Masjid|Babri Mosque]] located in [[Ayodhya]] was demolished by Hindu activists, leading to widespread violence across India.<ref name="communal violence">{{Cite news |last=communal violence |first=in uttar pradesh |title=Communal conflicts in state |work=Tehalka |url=http://www.tehelka.com/what-led-to-the-muzaffarnagar-communal-riots/ |url-status=dead |access-date=12 January 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140112232933/http://www.tehelka.com/what-led-to-the-muzaffarnagar-communal-riots/ |archive-date=12 January 2014}}</ref> In 2000, northern districts of the state were separated to form the state of [[Uttarakhand]].<ref name="separation">{{Cite book |last1=J. C. Aggarwal |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=alRh51xE_v0C&pg=PA391 |title=Uttarakhand: Past, Present, and Future |last2=S. P. Agrawal |date=1995 |publisher=Concept Publishing Company of India |isbn=978-8170225720 |page=391 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170324171535/https://books.google.com/books?id=alRh51xE_v0C&pg=PA391 |archive-date=24 March 2017 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Geography of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
[[File:Indo-Gangetic Plain.jpg|right|thumb|alt="photograph"|A part of the Gangetic Plain]] |
|||
Uttar Pradesh, with a total area of {{convert|243290|km2|sqmi|0}}, is India’s fifth largest state in terms of land area. It is situated on the northern spout of India and shares an international boundary with Nepal. The Himalayas border the state on the north,<ref name=land>{{cite web|title=Most critical factors|url=http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Land_830.aspx|publisher=Uttar Pradesh climate department|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> but the plains that cover most of the state are distinctly different from those high mountains.<ref name=Geography>{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh Geography|url=http://www.uponline.in/About/Profile/Geography/index.html|publisher=Uttar Pradesh State Profile|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> The larger [[Gangetic Plain]] region is in the north; it includes the Ganges-Yamuna [[Doab]], the Ghaghra plains, the Ganges plains and the [[Terai]].<ref name=Terai>{{cite web|title=The larger Gangetic Plain|url=http://www.gecafs.org/publications/Publications/IGP_Paper.pdf|publisher=Gecafs|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> The smaller [[Vindhya Range]] and plateau region is in the south.<ref name=autogenerated8>{{cite web|title=Gangetic Plains and Vindhya Hills and plateau.|url=http://zeenews.india.com/state-elections-2012/up/profile.html/2|publisher=[[Zee news]]|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> It is characterised by hard rock strata and a varied topography of hills, plains, valleys and plateaus. The [[Bhabhar]] tract gives place to the terai area which is covered with tall [[Saccharum ravennae|elephant grass]] and thick forests interspersed with [[marshes]] and [[swamps]].<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> The sluggish rivers of the bhabhar deepen in this area, their course running through a tangled mass of thick under growth. The terai runs parallel to the bhabhar in a thin strip. The entire alluvial plain is divide into three sub-regions.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> The first in the [[Eastern Uttar Pradesh|eastern]] tract consisting of 14 districts which are subject to periodical [[floods]] and [[droughts]] and have been classified as scarcity areas. These districts have the highest density of population which gives the lowest per capita land. The other two regions, the [[Central Uttar Pradesh|central]] and the [[Western Uttar Pradesh|western]] are comparatively better with a well-developed irrigation system.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> They suffer from water logging and large-scale user tracts.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005">{{cite book|author1=Gopal K. Bhargava|author2=Shankarlal C. Bhatt|title=Land and people of Indian states and union territories. 28. Uttar Pradesh|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=FCG5hGZ-hJsC&pg=PA31|accessdate=5 October 2012|year=2005|publisher=Gyan Publishing House|isbn=978-81-7835-384-5|pages=31–33}}</ref> In addition, the area is fairly arid. The state has more than 32 large and small rivers; of them, the Ganges, Yamuna, [[Saraswati river|Saraswati]], [[Sarayu]], [[Betwa]], and [[Ghaghara]] are larger and of religious importance in [[Hinduism]].<ref name=rivers>{{cite news|title=Rivers of Uttar Pradesh|url=http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/topiclist/Rivers-of-Uttar-Pradesh|publisher=[[The Economic Times]]|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
== Geography == |
|||
[[Tillage|Cultivation]] is intensive.<ref name=glossary>{{cite web|title=The Glossary of Meteorology|url=http://amsglossary.allenpress.com/glossary/preface2|publisher=Allen Press Inc.|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref> The [[valley]] areas have fertile and rich soil. There is intensive cultivation on terraced hill slopes, but irrigation facilities are deficient.<ref name=Irrigation>{{cite web|title=Potential Creation and Utilisation|url=http://irrigation.up.nic.in/aboutus_irrigation_potential.htm|publisher=Irrigation department U.P|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> The [[Siwalik Range]] which forms the southern foothills of the [[Himalayas]], slopes down into a boulder bed called 'bhadhar'.<ref name=Preface>{{cite web|title=Purports to define every important meteorological term likely to be found in the literature today.|url=http://amsglossary.allenpress.com/glossary/preface1|publisher=Allen Press,Inc.|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> The transitional belt running along the entire length of the state is called the terai and bhabhar area. It has rich forests, cutting across it are innumerable streams which swell into raging [[Torrent (stream)|torrents]] during the [[monsoon]].<ref name="Singh1998">{{cite book|author=Vir Singh|title=Mountain Ecosystems: A Scenario of Unsustainability|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=SX7ML4-0oGQC&pg=PA102|accessdate=27 July 2012|publisher=Indus Publishing|isbn=978-81-7387-081-1|pages=102–264}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Geography of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
[[File:Indo-Gangetic Plain.jpg|thumb|right|alt=The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain|A part of the Gangetic Plain]] |
|||
Uttar Pradesh, with a total area of {{convert|240928|km2|sqmi|0}}, is India's fourth-largest state in terms of land area and is roughly of same size as United Kingdom. It is situated on the northern spout of India and shares an international boundary with Nepal. The Himalayas border the state on the north,<ref name="land">{{Cite web |title=Most critical factors |url=http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Land_830.aspx |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121215063439/http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Land_830.aspx |archive-date=15 December 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Uttar Pradesh climate department}}</ref> but the plains that cover most of the state are distinctly different from those high mountains.<ref name="Geography">{{Cite web |title=Uttar Pradesh Geography |url=http://www.uponline.in/About/Profile/Geography/index.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120723070728/http://www.uponline.in/About/Profile/geography/index.html |archive-date=23 July 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Uttar Pradesh State Profile}}</ref> The larger [[Gangetic Plain]] region is in the north; it includes the [[Doab#The Doab|Ganges-Yamuna Doab]], the Ghaghra plains, the Ganges plains and the [[Terai]].<ref name="Terai">{{Cite web |title=The larger Gangetic Plain |url=http://www.gecafs.org/publications/Publications/IGP_Paper.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131226202743/http://www.gecafs.org/publications/Publications/IGP_Paper.pdf |archive-date=26 December 2013 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Gecafs}}</ref> The smaller [[Vindhya Range]] and plateau region are in the south.<ref name="autogenerated8">{{Cite web |title=Gangetic Plains and Vindhya Hills and plateau. |url=http://zeenews.india.com/state-elections-2012/up/profile.html/2 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120406104938/http://zeenews.india.com/state-elections-2012/up/profile.html/2 |archive-date=6 April 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=[[Zee news]]}}</ref> It is characterised by hard rock strata and a varied topography of hills, plains, valleys and plateaus. The [[Bhabar|Bhabhar]] tract gives place to the terai area which is covered with tall [[Saccharum ravennae|elephant grass]] and thick forests interspersed with [[marshes]] and [[swamps]].<ref name="Terai Area">{{Cite news |last=Anwar |first=Shakeel |date=16 August 2018 |title=List of major canals and dams in Uttar Pradesh |work=Dainik Jagran |agency=Jagran Prakashan Limited |url=https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/list-of-major-canals-and-dams-in-uttar-pradesh-1534427496-1 |access-date=21 June 2020 |archive-date=22 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200622130821/https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/list-of-major-canals-and-dams-in-uttar-pradesh-1534427496-1 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Bhabhar">{{Cite web |title=Indo–African Journal for Resource Management |url=http://thehaider.com/4.2.1.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220401145006/https://thehaider.com/4.2.1.pdf |archive-date=1 April 2022 |access-date=21 June 2020 |publisher=Indo–African Journal for Resource Management and Planning}}</ref> The sluggish rivers of the bhabhar deepen in this area, their course running through a tangled mass of thick undergrowth. The terai runs parallel to the bhabhar in a thin strip. The entire alluvial plain is divided into three sub-regions.<ref name="Great Plains">{{Cite news |last=Anwar |first=Shakeel |title=The Great Plains of India |work=Jagran Josh |publisher=Dainik Jagran |agency=Jagran Prakashan Private Limited |url=https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/the-great-plains-of-india-1448281967-1 |url-status=live |access-date=19 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171121224151/http://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/the-great-plains-of-india-1448281967-1 |archive-date=21 November 2017}}</ref> The first in the [[Eastern Uttar Pradesh|eastern]] tract consisting of 14 districts which are subject to periodical [[floods]] and [[droughts]] and have been classified as scarcity areas. These districts have the highest density of population which gives the lowest per capita land. The other two regions, the [[Central Uttar Pradesh|central]] and the [[Western Uttar Pradesh|western]], are comparatively better with a well-developed irrigation system.<ref name="Western - Eastern Irrigation">{{Cite journal |last=Clift |first=Charles |year=1977 |title=Progress of Irrigation in Uttar Pradesh: East-West Differences |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/4365953 |journal=Economic and Political Weekly |publisher=[[JSTOR]] |volume=12 |issue=39 |pages=A83–A90 |jstor=4365953 |access-date=19 October 2021 |archive-date=30 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211030043546/https://www.jstor.org/stable/4365953 |url-status=live }}</ref> They suffer from waterlogging and large-scale user tracts.<ref name="Meena">{{Cite book |last=R P Meena |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=I2fQDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT6 |title=Uttar Pradesh Current Affairs Yearbook 2020 |publisher=New Era Publication |page=6 |id=GGKEY:XTXLJ8SQZFE |access-date=19 May 2020 |archive-date=28 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240328164948/https://books.google.com/books?id=I2fQDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT6#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> In addition, the area is fairly arid. The state has more than 32 large and small rivers; of them, the [[Ganges|Ganga]], [[Yamuna]], [[Saraswati river|Saraswati]], [[Sarayu]], [[Betwa]], and [[Ghaghara]] are larger and of religious importance in [[Hinduism]].<ref name="rivers">{{Cite news |title=Rivers of Uttar Pradesh |work=[[The Economic Times]] |url=http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/topiclist/Rivers-of-Uttar-Pradesh |url-status=live |access-date=22 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130507013021/http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/topiclist/Rivers-of-Uttar-Pradesh |archive-date=7 May 2013}}</ref> |
|||
[[Tillage|Cultivation]] is intensive in the state.<ref name="glossary">{{Cite web |title=The Glossary of Meteorology |url=http://amsglossary.allenpress.com/glossary/preface2 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121005143046/http://amsglossary.allenpress.com/glossary/preface2 |archive-date=5 October 2012 |access-date=23 July 2012 |publisher=Allen Press Inc.}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh falls under three agro-climatic zones viz. Middle Gangetic Plains region (Zone–IV), Upper Gangetic Plains region (Zone–V) and Central Plateau and Hills region (Zone–VIII).<ref name="Agro-Climatic">{{Cite web |title=Agriculture Mechanization Guide for Uttar Pradesh |url=https://www.farmech.dac.gov.in/FarmerGuide/UP/index1.html#:~:text=The%20total%20geographical%20area%20of,68.5%25%20of%20cultivable%20area). |access-date=16 May 2021 |publisher=Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India |archive-date=16 May 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210516065713/https://www.farmech.dac.gov.in/FarmerGuide/UP/index1.html#:~:text=The%20total%20geographical%20area%20of,68.5%25%20of%20cultivable%20area). |url-status=live }}</ref> The [[valley]] areas have fertile and rich soil. There is intensive cultivation on terraced hill slopes, but irrigation facilities are deficient.<ref name="Irrigation">{{Cite web |title=Potential Creation and Utilisation |url=http://irrigation.up.nic.in/aboutus_irrigation_potential.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120213084300/http://irrigation.up.nic.in/aboutus_irrigation_potential.htm |archive-date=13 February 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Irrigation department U.P}}</ref> The [[Siwalik Range]] which forms the southern foothills of the [[Himalayas]], slopes down into a boulder bed called 'bhabhar'.<ref name="Preface">{{Cite web |title=Purports to define every important meteorological term likely to be found in the literature today. |url=http://amsglossary.allenpress.com/glossary/preface1 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120712214139/http://amsglossary.allenpress.com/glossary/preface1 |archive-date=12 July 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Allen Press, Inc.}}</ref> The transitional belt running along the entire length of the state is called the terai and bhabhar area. It has rich forests, cutting across it are innumerable streams which swell into raging [[Torrent (stream)|torrents]] during the [[monsoon]].<ref name="Singh1998">{{Cite book |last=Vir Singh |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SX7ML4-0oGQC&pg=PA102 |title=Mountain Ecosystems: A Scenario of Unsustainability |publisher=Indus Publishing |year=1998 |isbn=978-8173870811 |pages=102–264 |access-date=27 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528155028/http://books.google.com/books?id=SX7ML4-0oGQC&pg=PA102 |archive-date=28 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Climate=== |
|||
{{main|Climate of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
[[Image:Monsoon clouds Lucknow.JPG|thumb|alt=refer to adjacent text|Monsoon clouds over Lucknow]] |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has a humid subtropical climate and experiences four seasons.<ref name="Board2008" /> The winter in January and February is followed by summer between March and May and the monsoon season between June and September.<ref name=Climate>{{cite web|title=Climate change impacts|url=http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Climate_861.aspx|publisher=Uttar Pradesh climate department|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> Summers are extreme with temperatures fluctuating anywhere between 0 °C and 50 °C in parts of the state.<ref name=climate009>{{cite web|title=Climate|url=http://www.webindia123.com/uttar/index.htm|publisher=Uttar Prades:Land. Suni System (P) Ltd.|accessdate=5 August 2012}}</ref> The Gangetic plain varies from semiarid to sub-humid.<ref name=Climate/> The mean annual rainfall ranges from 650 mm in the southwest corner of the state to 1000 mm in the eastern and southeastern parts of the state.<ref name=rainfall>{{cite web|last=Government of Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow|first=Irrigation Department Uttar Pradesh|title=Average rainfall pattern of Uttar Pradesh|url=http://idup.gov.in/wps/portal/!ut/p/c0/04_SB8K8xLLM9MSSzPy8xBz9CP0os3ifUEcnYzdTEwMLVy8TA89gU38XT-8AIwM3A_2CbEdFAHA_W1g!|publisher= Irrigation Department Uttar Pradesh|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> Primarily a summer phenomenon, the Bay of Bengal branch of the [[Monsoon of India|Indian Monsoon]] is the major bearer of rain in most parts of state. It is the South-West Monsoon which brings most of the rain here, although rain due to the ''[[western disturbances]]'' and North-East Monsoon also contribute small quantities towards the overall precipitation of the state.<ref name="Board2008">{{cite book|author=Upkar Prakashan - Editorial Board|title=Uttar Pradesh General Knowledge|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=_ce8FpJzR-4C&pg=PA26|accessdate=9 March 2011|year=2008|publisher=Upkar Prakashan|isbn=978-81-7482-408-0|pages=26–}}</ref><ref name=WesDist>{{cite news|last=Sethi|first=Nitin|title=Met dept blames it on 'western disturbance'|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2007-02-13/india/27887812_1_met-dept-disturbance-rains|accessdate=9 March 2011|newspaper=The Times of India|date=13 February 2007}}</ref> |
|||
=== Climate === |
|||
{{Main|Climate of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
[[File:Sunset in Indirapuram Uttar Pradesh.jpg|thumb|left|alt=Early monsoon days in Lucknow|Monsoon clouds over [[Indirapuram]]]] |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has a humid subtropical climate and experiences four seasons.<ref name="Board2008" /> The winter in January and February is followed by summer between March and May and the monsoon season between June and September.<ref name="Climate">{{Cite web |title=Climate change impacts |url=http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Climate_861.aspx |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121115211430/http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Climate_861.aspx |archive-date=15 November 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Uttar Pradesh climate department}}</ref> Summers are extreme with temperatures fluctuating anywhere between {{Convert|0-50|C|F}} in parts of the state coupled with dry hot winds called the ''[[Loo (wind)|Loo]]''.<ref name="rana2007">{{Citation |last=S.V.S. Rana |title=Essentials of Ecology and Environmental Science |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IAPKG4LEBbQC |year=2007 |publisher=Prentice Hall of India |isbn=978-81-203-3300-0}}</ref> The Gangetic plain varies from semiarid to sub-humid.<ref name="Climate" /> The mean annual rainfall ranges from {{Convert|650|mm|in|abbr=in}} in the southwest corner of the state to {{Convert|1000|mm|in|abbr=in}} in the eastern and south eastern parts of the state.<ref name="rainfall">{{Cite web |last=Government of Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow |first=Irrigation Department Uttar Pradesh |title=Average rainfall pattern of Uttar Pradesh |url=http://idup.gov.in/wps/portal/!ut/p/c0/04_SB8K8xLLM9MSSzPy8xBz9CP0os3ifUEcnYzdTEwMLVy8TA89gU38XT-8AIwM3A_2CbEdFAHA_W1g! |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120824174636/http://idup.gov.in/wps/portal/!ut/p/c0/04_SB8K8xLLM9MSSzPy8xBz9CP0os3ifUEcnYzdTEwMLVy8TA89gU38XT-8AIwM3A_2CbEdFAHA_W1g! |archive-date=24 August 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Irrigation Department Uttar Pradesh}}</ref> Primarily a summer phenomenon, the Bay of Bengal branch of the [[Monsoon of India|Indian monsoon]] is the major bearer of rain in most parts of state. After summer it is the southwest monsoon which brings most of the rain here, while in winters rain due to the ''[[western disturbances]]'' and north-east monsoon also contribute small quantities towards the overall precipitation of the state.<ref name="Board2008">{{Cite book |last=Upkar Prakashan – Editorial Board |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_ce8FpJzR-4C&pg=PA26 |title=Uttar Pradesh General Knowledge |publisher=Upkar Prakashan |year=2008 |isbn=978-8174824080 |pages=26– |access-date=9 March 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130605095943/http://books.google.com/books?id=_ce8FpJzR-4C&pg=PA26 |archive-date=5 June 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="WesDist">{{Cite news |last=Sethi |first=Nitin |date=13 February 2007 |title=Met dept blames it on 'western disturbance' |work=[[The Times of India]] |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Met-dept-blames-it-on-western-disturbance/articleshow/1600979.cms |url-status=live |access-date=9 March 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110811031649/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2007-02-13/india/27887812_1_met-dept-disturbance-rains |archive-date=11 August 2011}}</ref> |
|||
{{Weather box |
{{Weather box |
||
|location = Uttar Pradesh |
|location = Uttar Pradesh |
||
| Line 238: | Line 252: | ||
|May sun = 316.2 |
|May sun = 316.2 |
||
|Jun sun = 186.0 |
|Jun sun = 186.0 |
||
|Jul sun = |
|Jul sun = 120.9 |
||
|Aug sun = 111.6 |
|Aug sun = 111.6 |
||
|Sep sun = 177.0 |
|Sep sun = 177.0 |
||
|Oct sun = 248 |
|Oct sun = 248.44 |
||
|Nov sun = 270.0 |
|Nov sun = 270.0 |
||
|Dec sun = 288.3 |
|Dec sun = 288.3 |
||
|year sun = |
|year sun = |
||
|source 1 =<ref>{{ |
|source 1 =<ref>{{Cite web |date=21 May 2012 |title=Local Weather Report |url=http://125.21.185.44/citywx/city_weather1.php?id=42369 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120501134209/http://125.21.185.44/citywx/city_weather1.php?id=42369 |archive-date=1 May 2012 |access-date=18 July 2012 |publisher=Local Weather Report and Forecast Department}}</ref>||date=June 2012 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
<!-- Two major cities are added from Western, Central and Eastern region of Uttar Pradesh --> |
|||
[[File:Anandabodhi.jpg|thumb|alt=refer to adjacent text|Anandabodhi tree in Jetavana Monastery, [[Sravasti]]]] |
|||
<!-- {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" |
|||
[[File:Tropaeolum majus.jpg|thumb|right|alt=Tropaeolum majus|A hybrid nasturtium (''[[Tropaeolum majus]]'') showing nectar spur, found mainly in [[Hardoi district]]]] |
|||
|+ Average high and low temperatures for some Uttar Pradesh cities (in Celsius) |
|||
<center> |
|||
|- |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
|||
! City |
|||
| colspan="13" style="text-align:center;font-size:120%;background:#E8EAFA;"|Average High and Low temperatures for various Uttar Pradesh Cities |
|||
! Jan |
|||
|- style="background:#e5afaa; color:#000" |
|||
! Feb |
|||
| '''City''' |
|||
! Mar |
|||
| '''Jan''' |
|||
! Apr |
|||
| '''Feb''' |
|||
! May |
|||
| '''Mar''' |
|||
! Jun |
|||
| '''Apr''' |
|||
! Jul |
|||
| '''May''' |
|||
! Aug |
|||
| '''Jun''' |
|||
! Sep |
|||
| '''Jul''' |
|||
! Oct |
|||
| '''Aug''' |
|||
! Nov |
|||
| '''Sep''' |
|||
! Dec |
|||
| '''Oct''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''Nov''' |
|||
| [[Lucknow]]<ref name="lucknowweather">{{Cite web |title=Weather Report & Forecast for Lucknow |url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/lucknow.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130208074134/http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/lucknow.htm |archive-date=8 February 2013 |access-date=5 October 2012 |publisher=India Meteorological Department}}</ref> |
|||
| '''Dec''' |
|||
| 23/7 |
|||
|- style="background:#f8f3ca; color:#000" |
|||
| 26/9 |
|||
|[[Lucknow]]<ref name=lucknowweather>{{cite web|title=Weather Report & Forecast for Lucknow|url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/lucknow.htm|publisher=India Meteorological Department|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| 32/14 |
||
| |
| 38/21 |
||
| |
| 41/24 |
||
| |
| 39/27 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 32/26 |
||
| |
| 33/24 |
||
| |
| 33/19 |
||
| |
| 26/12 |
||
| |
| 24/7 |
||
|- |
|||
| 79/53 |
|||
|[[Kanpur]]<ref name="kanpurweather">{{Cite web |title=Weather Report & Forecast for Kanpur |url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/kannur2.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140202134824/http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/kannur2.htm |archive-date=2 February 2014 |access-date=5 October 2012 |publisher=India Meteorological Department}}</ref> |
|||
| 75/45 |
|||
| 23/8 |
|||
|- style="background:#c5dfe1; color:#000" |
|||
| 25/10 |
|||
| [[Kanpur]]<ref name=kanpurweather>{{cite web|title=Weather Report & Forecast for Kanpur|url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/kannur2.htm|publisher=India Meteorological Department|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| 32/15 |
||
| |
| 38/21 |
||
| |
| 40/25 |
||
| |
| 39/27 |
||
| |
| 34/26 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 33/25 |
||
| |
| 32/19 |
||
| |
| 28/12 |
||
| |
| 24/8 |
||
|- |
|||
| 89/74 |
|||
|[[Ghaziabad]]<ref name="ghazForecast">{{Cite web |title=Weather Report & Forecast for Ghaziabad |url=http://www.weather.com/weather/wxclimatology/monthly/INXX0051 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131113174957/http://www.weather.com/weather/wxclimatology/monthly/INXX0051 |archive-date=13 November 2013 |access-date=24 September 2012 |publisher=India Meteorological Department}}</ref> |
|||
| 90/71 |
|||
| 21/7 |
|||
|- style="background:#f8f3ca; color:#000" |
|||
| 23/10 |
|||
| [[Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh|Ghaziabad]]<ref name=ghazForecast>{{cite web|title=Weather Report & Forecast for Ghaziabad|url=http://www.weather.com/weather/wxclimatology/monthly/INXX0051|publisher=India Meteorological Department|accessdate=24 September 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| 29/15 |
||
| |
| 36/21 |
||
| |
| 39/26 |
||
| |
| 38/28 |
||
| |
| 34/27 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 34/24 |
||
| |
| 33/19 |
||
| |
| 28/13 |
||
| |
| 23/8 |
||
|- |
|||
| 82/55 |
|||
|[[Allahabad]]<ref name="AllahabadForecast">{{Cite web |title=Weather Report & Forecast for Allahabaad |url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/allahabad2.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121031015105/http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/allahabad2.htm |archive-date=31 October 2012 |access-date=24 September 2012 |publisher=India Meteorological Department}}</ref> |
|||
| 73/46 |
|||
| 23/8 |
|||
|- style="background:#c5dfe1; color:#000" |
|||
| 27/11 |
|||
| [[Allahabad]]<ref name=AllahabadForecast>{{cite web|title=Weather Report & Forecast for Allahabaad|url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/allahabad2.htm|publisher=India Meteorological Department|accessdate=24 September 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| 33/17 |
||
| |
| 39/23 |
||
| |
| 42/27 |
||
| |
| 40/28 |
||
| |
| 34/26 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 33/25 |
||
| |
| 33/21 |
||
| |
| 30/14 |
||
| |
| 25/9 |
||
|- |
|||
| 86/57 |
|||
|[[Agra]]<ref name="agraweather">{{Cite web |title=Weather Report & Forecast for Agra |url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/agra2.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140202135110/http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/agra2.htm |archive-date=2 February 2014 |access-date=5 October 2012 |publisher=India Meteorological Department}}</ref> |
|||
| 77/49 |
|||
| 22/7 |
|||
|- style="background:#f8f3ca; color:#000" |
|||
| 24/11 |
|||
| [[Agra]]<ref name=agraweather>{{cite web|title=Weather Report & Forecast for Agra|url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/agra2.htm|publisher=India Meteorological Department|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| 32/16 |
||
| |
| 38/22 |
||
| |
| 42/27 |
||
| |
| 41/29 |
||
| |
| 35/26 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 34/24 |
||
| |
| 34/19 |
||
| |
| 29/13 |
||
| |
| 24/8 |
||
|- |
|||
| 85/55 |
|||
|[[Varanasi]]<ref name="varaweather">{{Cite web |title=Weather Report & Forecast for Varanasi |url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/varanasi2.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120709160100/http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/varanasi2.htm |archive-date=9 July 2012 |access-date=5 October 2012 |publisher=India Meteorological Department}}</ref> |
|||
| 75/47 |
|||
| 23/8 |
|||
|- style="background:#c5dfe1; color:#000" |
|||
| 27/11 |
|||
| [[Varanasi]]<ref name=varaweather>{{cite web|title=Weather Report & Forecast for Varanasi|url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/varanasi2.htm|publisher=India Meteorological Department|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| 33/16 |
||
| |
| 39/22 |
||
| |
| 41/27 |
||
| |
| 39/28 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 33/25 |
||
| |
| 32/21 |
||
| |
| 29/14 |
||
| |
| 24/9 |
||
|- |
|||
| 85/57 |
|||
|[[Gorakhpur]]<ref name="gorweather">{{Cite web |title=Weather Report & Forecast for Gorakhpur |url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/gorakhpur2.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100109193600/http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/gorakhpur2.htm |archive-date=9 January 2010 |access-date=5 October 2012 |publisher=India Meteorological Department}}</ref> |
|||
| 76/49 |
|||
| 23/9 |
|||
|- style="background:#f8f3ca; color:#000" |
|||
| 27/12 |
|||
| [[Gorakhpur]]<ref name=gorweather>{{cite web|title=Weather Report & Forecast for Gorakhpur|url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/gorakhpur2.htm|publisher=India Meteorological Department|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| 33/22 |
||
| |
| 39/25 |
||
| |
| 37/26 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 33/24 |
||
| |
| 33/21 |
||
| |
| 29/15 |
||
| |
| 24/11 |
||
| |
| 24/9 |
||
|- |
|||
| 76/51 |
|||
|[[Bareilly]]<ref name="bareiweather">{{Cite web |title=Weather Report & Forecast for Bareilly |url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/bareilly2.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120603055234/http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/bareilly2.htm |archive-date=3 June 2012 |access-date=5 October 2012 |publisher=India Meteorological Department}}</ref> |
|||
| 76/49 |
|||
| 22/8 |
|||
|- style="background:#c5dfe1; color:#000" |
|||
| 25/14 |
|||
| [[Bareilly]]<ref name=bareiweather>{{cite web|title=Weather Report & Forecast for Bareilly|url=http://www.imd.gov.in/section/climate/bareilly2.htm|publisher=India Meteorological Department|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| 31/16 |
||
| |
| 37/21 |
||
| |
| 41/25 |
||
| |
| 39/27 |
||
| |
| 34/26 |
||
| |
| 33/26 |
||
| |
| 33/24 |
||
| |
| 32/19 |
||
| |
| 28/13 |
||
| |
| 23/9 |
||
| |
|} --> |
||
The rain in Uttar Pradesh can vary from an annual average of {{Convert|170|cm|in|abbr=in}} in hilly areas to {{Convert|84|cm|in|abbr=in}} in [[Western Uttar Pradesh]].<ref name="Board2008" /> Given the concentration of most of this rainfall in the four months of the monsoon, excess rain can lead to floods and shortage to droughts. As such, these two phenomena, floods and droughts, commonly recur in the state. The climate of the Vindhya Range and [[plateau]] is subtropical with a mean annual rainfall between {{Convert|1000 and 1200|mm|in|abbr=in}}, most of which comes during the monsoon.<ref name="Climate" /> Typical summer months are from March to June, with maximum temperatures ranging from {{convert|30-38|C|F}}. There is a low relative humidity of around 20% and dust-laden winds blow throughout the season. In summer, hot winds called ''[[loo (wind)|loo]]'' blow all across Uttar Pradesh.<ref name="Board2008" /> |
|||
| 74/48 |
|||
|}</center> |
|||
The rain in U.P. can vary from an annual average of 170 cm in hilly areas to 84 cm in Western U.P.<ref name="Board2008"/> Given the concentration of most of this rainfall in the 4 months of Monsoon period, excess rain can lead to floods and shortage to droughts. As such, these two phenomena, floods and droughts, commonly recur in the state. The climate of the Vindhya Range and [[plateau]] is subtropical with a mean annual rainfall between 1000 and 1200 mm, most of which comes during the monsoon.<ref name=Climate/> Typical summer months are from March to June, with maximum temperatures ranging from {{convert|30|to|38|C|F}}. There is low relative humidity of around 20% and dust-laden winds blow throughout the season. In summers, hot winds called ''[[loo (wind)|loo]]'' blow all across Uttar Pradesh.<ref name="Board2008"/> |
|||
==Flora and fauna== |
=== Flora and fauna === |
||
{{See also|Pilibhit Tiger Reserve|Dudhwa National Park}} |
{{See also|Pilibhit Tiger Reserve|Dudhwa National Park}} |
||
{| class="toccolours" |
{| class="toccolours" style="margin:1em; float:right; width:25%" |
||
|+ '''State symbols of Uttar Pradesh'''<ref>{{ |
|+ '''State symbols of Uttar Pradesh'''<ref>{{Cite web |title=State Animal, Bird, Tree and Flower |url=http://www.pannatigerreserve.in/kids/state.htm |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141013002319/http://www.pannatigerreserve.in/kids/state.htm |archive-date=13 October 2014 |access-date=29 August 2014 |website=Panna Tiger Reserve}}</ref><ref name="dance">{{Cite web |title=Music & Dance |url=http://uptourism.gov.in/pages/top/experience/top-experience-music-and-dance |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170123210405/http://www.uptourism.gov.in/pages/top/experience/top-experience-music-and-dance |archive-date=23 January 2017 |access-date=3 March 2017 |website=uptourism.gov.in |publisher=Uttar Pradesh Tourism}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| '''State animal''' |
| '''State animal''' |
||
| [[Swamp deer]] [[File:The barasingha.jpg|50px]] |
| [[Swamp deer]] (''Rucervus duvaucelii'')|| [[File:The barasingha.jpg|50px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| '''State bird''' |
| '''State bird''' |
||
| [[Sarus crane]] || [[File:Grus antigone Luc viatour.jpg|50px]] |
| [[Sarus crane]] (''Antigone antigone'')|| [[File:Grus antigone Luc viatour.jpg|50px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| '''State tree''' |
| '''State tree''' |
||
| [[Saraca asoca|Ashoka]] || [[File: |
| [[Saraca asoca|Ashoka]] (''Saraca asoca'') || [[File:Ashoka (Polyalthia longifolia) flowers W IMG 7050.jpg|50px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| '''State flower''' |
| '''State flower''' |
||
| [[Butea monosperma|Palash]] || [[File:STS 001 Butea monosperma.jpg|50px]] |
| [[Butea monosperma|Palash]] (''Butea monosperma'') || [[File:STS 001 Butea monosperma.jpg|50px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| '''State |
| '''State dance''' |
||
| [[Kathak]] || [[File:Kathak 3511900193 986f6440f6 b retouched.jpg|50px]] |
| [[Kathak]] || [[File:Kathak 3511900193 986f6440f6 b retouched.jpg|50px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| '''State |
| '''State sport''' |
||
| [[Field hockey]] || [[File:Field hockey.jpg|50px]] |
| [[Field hockey]] || [[File:Field hockey.jpg|50px]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
Uttar Pradesh has an abundance of natural resources.<ref name="Flora">{{Cite web |title=Uttar Pradesh Forest Corporation |url=http://www.upforestcorporation.in/Default.aspx |url-status=unfit |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130120145111/http://www.upforestcorporation.in/Default.aspx |archive-date=20 January 2013 |access-date=23 July 2012 |publisher=Forest department uttar pradesh}}</ref> In 2011, the recorded forest area in the state was {{convert|16583|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} which is about 6.9% of the state's geographical area.<ref name="fsiwbforest">{{Cite web |title=Forest and tree resources in states and union territories: Uttar Pradesh |url=http://www.fsi.org.in/cover_2011/uttarapradesh.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131107201030/http://www.fsi.org.in/cover_2011/uttarapradesh.pdf |archive-date=7 November 2013 |access-date=4 March 2012 |website=India state of forest report 2009 |publisher=Forest Survey of India, Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India}}</ref> In spite of rapid deforestation and poaching of wildlife, a diverse flora and fauna continue to exist in the state. Uttar Pradesh is a [[habitat]] for 4.2% of all species of [[Algae]] recorded in India, 6.4% of [[Fungi]], 6.0% of [[Lichens]], 2.9% of [[Bryophytes]], 3.3% of [[Pteridophytes]], 8.7% of [[Gymnosperms]], 8.1% of [[Angiosperms]].<ref name="Plant Diversity">{{Cite web |title=Floral and Faunal Diversity of Uttar Pradesh |url=http://www.upsbdb.org/diversity-of-up.php |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190705034421/http://upsbdb.org/diversity-of-up.php |archive-date=5 July 2019 |access-date=22 May 2020 |publisher=Uttar Pradesh State Biodiversity Board}}</ref> Several species of trees, large and small [[mammals]], [[reptiles]], and insects are found in the belt of [[temperate]] upper mountainous forests. Medicinal plants are found in the wild<ref>{{Cite web |title=Aegyptica |url=http://bsienvis.nic.in/medi.htm#Balanites |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090506192204/http://bsienvis.nic.in/medi.htm |archive-date=6 May 2009 |access-date=21 September 2009 |publisher=Bsienvis.nic.in}}</ref> and are also grown in [[plantations]]. The [[Terai–Duar savanna and grasslands]] support cattle. Moist [[deciduous]] trees grow in the upper Gangetic plain, especially along its riverbanks. This plain supports a wide variety of plants and animals. The Ganges and its tributaries are the [[habitat]] of large and small reptiles, [[amphibians]], fresh-water fish, and crabs. [[Scrubland]] trees such as the [[Babool]] (''Vachellia nilotica'') and animals such as the [[Chinkara]] (''Gazella bennettii'') are found in the arid Vindhyas.<ref name="animals">{{Cite web |title=Bird Sanctuary |url=http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/wild_life/wild_life.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120704191031/http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/wild_life/wild_life.htm |archive-date=4 July 2012 |access-date=23 July 2012 |publisher=U.P tourism}}</ref><ref name="Predominant">{{Cite web |title=Sanctuary Park in U.P |url=http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/wild_life/places_of_interest.htm#Suhelva |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120718025605/http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/wild_life/places_of_interest.htm |archive-date=18 July 2012 |access-date=23 July 2012 |publisher=U.P tourism}}</ref> Tropical dry deciduous forests are found in all parts of the plains. Since much sunlight reaches the ground, shrubs and grasses are also abundant.<ref name="Vegetation and Flora">{{Cite web |title=Few patches of natural forest |url=http://upgov.nic.in/upwealth.aspx |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120520140217/http://upgov.nic.in/upwealth.aspx |archive-date=20 May 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=State government of Uttar Pradesh}}</ref> Large tracts of these forests have been cleared for cultivation. Tropical thorny forests, consisting of widely scattered thorny trees, mainly [[Acacia nilotica|babool]] are mostly found in the southwestern parts of the state.<ref name="Thorny Forest">{{Cite web |last=The Forests and biodiversity |first=in UP are important in many ways |title=Miscellaneous Statistics |url=http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Forest_838.aspx |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121115214704/http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Forest_838.aspx |archive-date=15 November 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Ministry of Environment and Forests}}</ref> |
|||
Uttar Pradesh is known for its extensive [[Bird|avifauna]].<ref name="Avifauna">{{Cite web |title=Conservation of the Avifauna |url=http://ww.orientalbirdclub.org/publications/forktail/14pdfs/Javed-Dudwa.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/69LhYrtqy?url=http://ww.orientalbirdclub.org/publications/forktail/14pdfs/Javed-Dudwa.pdf |archive-date=22 July 2012 |access-date=20 July 2012 |publisher=[[Dudhwa National Park]]}}</ref> The most common birds which are found in the state are [[Columbidae|doves]], [[peafowl]], [[junglefowl]], [[black partridge]]s, [[house sparrow]]s, [[songbirds]], [[blue jay]]s, [[parakeet]]s, [[quail]]s, [[bulbul]]s, [[Knob-billed duck|comb ducks]], [[kingfisher]]s, [[woodpecker]]s, [[snipe]]s, and parrots. Bird sanctuaries in the state include [[Bakhira Sanctuary]], [[National Chambal Sanctuary]], [[Chandra Prabha Wildlife Sanctuary]], [[Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary]], [[Kaimoor Wildlife Sanctuary]], and [[Okhla Sanctuary]].<ref name="Bakhira">{{Cite web |title=Bakhira Bird Sanctuary |url=http://upforest.gov.in/StaticPages/bakhirabird_Home.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170204170352/http://upforest.gov.in/StaticPages/bakhirabird_Home.aspx |archive-date=4 February 2017 |access-date=4 February 2017 |website=upforest.gov.in |publisher=UP Forest and Wildlife Department }}</ref><ref name="Chambal Gharial">{{Cite web |title=National Chambal Gharial Wildlife Sanctuary |url=http://nationalchambalsanctuary.in/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170101110955/http://www.nationalchambalsanctuary.in/ |archive-date=1 January 2017 |access-date=4 February 2017 |publisher=National Chambal Sanctuary}}</ref><ref name="Chandra Prabha">{{Cite web |title=Chandra Prabha Wildlife Sanctuary And Picnic Spots |url=http://www.uptourism.gov.in/pages/top/explore/top-explore-chandra-prabha |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170204170953/http://www.uptourism.gov.in/pages/top/explore/top-explore-chandra-prabha |archive-date=4 February 2017 |access-date=4 February 2017 |website=uptourism.gov.in |publisher=Uttar Pradesh Tourism}}</ref><ref name="Hastinapur Wild Life">{{Cite web |title=Hastinapur Wild Life Sanctuary |url=http://upforest.gov.in/STATICpages/hastinapurwild_Home.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170204170724/http://upforest.gov.in/STATICpages/hastinapurwild_Home.aspx |archive-date=4 February 2017 |access-date=4 February 2017 |website=upforest.gov.in |publisher=P Forest and Wildlife Department }}</ref><ref name="Kaimoor Wild Life">{{Cite web |title=Kaimoor Wild Life Sanctuary |url=http://upforest.gov.in/StaticPages/kaimoorwildlife_Home.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170204171033/http://upforest.gov.in/StaticPages/kaimoorwildlife_Home.aspx |archive-date=4 February 2017 |access-date=4 February 2017 |website=upforest.gov.in |publisher=Forest and Wildlife Department Uttar Pradesh }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Inside Okhla Bird Sanctuary |url=http://upforest.gov.in/STATICpages/okhlabird_Home.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170204171135/http://upforest.gov.in/STATICpages/okhlabird_Home.aspx |archive-date=4 February 2017 |access-date=4 February 2017 |website=upforest.gov.in |publisher=UP Forest and Wildlife Department }}</ref> |
|||
{{Multiple image |
|||
| align = left |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| header = |
|||
| header_align = left/right/center |
|||
| header_background = |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| footer_align = left/right/center |
|||
| footer_background = |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| image1 = Ganges calling.jpg|thumb |
|||
| width1 = |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 =View of the [[Terai]] region |
|||
| image2 = Gavialis gangeticus, ZOO Praha 045.jpg|thumb |
|||
| width2 = |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 =[[Gharial]] (''Gavialis gangeticus'') is found in the [[Ganges river]] |
|||
}} |
|||
Other animals in the state include reptiles such as [[lizard]]s, [[cobra]]s, [[Bungarus|kraits]], and [[gharial]]s. Among the wide variety of fishes, the most common ones are [[Mahseer|mahaseer]] and [[trout]]. Some animal species have gone extinct in recent years, while others, like the lion from the Gangetic Plain, the [[rhinoceros]] from the [[Terai]] region, [[South Asian river dolphin|Ganges river dolphin]] primarily found in the Ganges have become [[Endangered species|endangered]].<ref name="S.k.agarwal">{{Cite book |last=S. K. Agarwal |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0UeDTX6HEK8C&pg=PA61 |title=Environment Biotechnology |publisher=APH Publishing |year=1998 |isbn=978-8131302941 |page=61 |access-date=25 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130523073400/http://books.google.com/books?id=0UeDTX6HEK8C&pg=PA61 |archive-date=23 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref> Many species are vulnerable to poaching despite regulation by the [[Government of Uttar Pradesh|government]].<ref name="fauna">{{Cite web |title=Processing of manuscripts of Fauna |url=http://zsi.gov.in/right_menu/Annual%20Meeting/Annual%20Meeting%202011-12/HQ/Fauna.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130505093620/http://zsi.gov.in/right_menu/Annual%20Meeting/Annual%20Meeting%202011-12/HQ/Fauna.pdf |archive-date=5 May 2013 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Indian Government}}</ref> |
|||
The state has an abundance of natural resources.<ref name=Flora>{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh Forest Corporation|url=http://www.upforestcorporation.in/Default.aspx|publisher=Forest department uttar pradesh|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref> In 2011 the recorded forest area in the state was {{convert|16583|sqkm|sqmi|abbr=on}} which is about 6.88% of the state's geographical area.<ref name="fsiwbforest">{{cite web|url=http://www.fsi.org.in/cover_2011/uttarapradesh.pdf|format=PDF|title=Forest and tree resources in states and union territories: Uttar Pradesh|work=India state of forest report 2009|publisher=Forest Survey of India, Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India|accessdate=4 March 2012}}</ref> In spite of rapid deforestation and poaching of wildlife, a diverse flora and fauna continue to exist in the state. Several species of trees, large and small [[mammals]], [[reptiles]], and insects are found in the belt of [[temperate]] upper mountainous forests. Medicinal plants are found in the wild<ref>{{cite web|url=http://bsienvis.nic.in/medi.htm#Balanites |title=Aegyptica |publisher=Bsienvis.nic.in |accessdate=21 September 2009}}</ref> and are also grown in [[plantations]]. The [[Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands]] support cattle. Moist [[deciduous]] trees grow in the upper Gangetic plain, especially along its riverbanks. This plain supports a wide variety of plants and animals. The Ganges and its tributaries are the [[habitat]] of large and small reptiles, [[amphibians]], fresh-water fish, and crabs. [[Scrubland]] trees such as the [[babool]] and animals such as the [[chinkara]] are found in the arid Vindhyas.<ref name=animals>{{cite web|title=Bird Sanctuary|url=http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/wild_life/wild_life.htm|publisher=U.P tourism|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref><ref name=Predominant>{{cite web|title=Sanctuary Park in U.P|url=http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/wild_life/places_of_interest.htm#Suhelva|publisher=U.P tourism|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
<gallery mode="nolines" heights="200px" widths="200px"> |
|||
Tropical dry deciduous forests are found in all parts of the plains. Since much sunlight reaches the ground, shrubs and grasses are also abundant.<ref name="Vegetation and Flora">{{cite web|title=Few patches of natural forest|url=http://upgov.nic.in/upwealth.aspx|publisher=State government of Uttar Pradesh|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> Large tracts of these forests have been cleared for cultivation. Tropical thorny forests, consisting of widely scattered thorny trees, mainly [[Acacia nilotica|babool]] are mostly found in the southwestern parts of the state.<ref name="Thorny Forest">{{cite web|last=The Forests and biodiversity|first=in UP are important in many ways|title=Miscellaneous Statistics|url=http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Forest_838.aspx|publisher= Ministry of Environment and Forests|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> These forests are confined to areas which have low annual rainfall (50–70 cm), a mean annual temperature of 25-27 °C and low humidity. |
|||
File:Anandabodhi.jpg|Anandabodhi tree (''[[Ficus religiosa]]'') in Jetavana Monastery, [[Sravasti]] |
|||
File:Tropaeolum majus.jpg|A hybrid nasturtium (''[[Tropaeolum majus]]'') showing nectar spur, found mainly in [[Hardoi district]] |
|||
File:Ganges River Dolphin cropped.jpg|An endangered [[Ganges river dolphin]] (''Platanista gangetica'') lives in the Ganges river |
|||
File:Ganges calling.jpg|View of the [[Terai]] region |
|||
File:Gavialis gangeticus, ZOO Praha 045.jpg|The threatened [[Gharial]] (''Gavialis gangeticus'') is a large fish-eating [[crocodilian]] found in the [[Ganges River]] |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
{{Anchor|Constituent regions}}{{Anchor|Regions and cities}} |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
== Divisions, districts and cities == |
|||
Uttar Pradesh is known for its extensive [[Bird|avifauna]].<ref name=Avifauna>{{cite web|title=Conservation of the Avifauna|url=http://ww.orientalbirdclub.org/publications/forktail/14pdfs/Javed-Dudwa.pdf|publisher=[[Dudhwa National Park]]|accessdate=20 July 2012}}</ref> The most common birds which are found in the state are [[Columbidae|doves]], [[Peafowl|peacocks]], [[junglefowl]], [[Black Partridge|black partridge]], [[House Sparrow|house sparrows]], [[songbirds]], [[Blue Jay|blue jays]], [[parakeet]]s, [[quail]]s, [[bulbul]]s, [[Knob-billed Duck|comb duck]]s, [[kingfisher]]s, [[woodpecker]]s, [[snipe]]s, and parrots. Bird sanctuaries in the state include [[Bakhira Sanctuary]], [[National Chambal Sanctuary]], [[Chandra Prabha Sanctuary]], [[Hastinapur Sanctuary]], [[Kaimoor Sanctuary]], and [[Okhla Sanctuary]].<ref name="Llc2010">{{cite book|author=Books Llc|title=Bird Sanctuaries of Uttar Pradesh: Okhla Sanctuary, Sandi Bird Sanctuary, Bakhira Sanctuary, Lakh Bahosi Sanctuary, Patna Bird Sanctuary|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=3R5KbwAACAAJ|accessdate=25 July 2012|date=26 July 2010|publisher=General Books LLC|isbn=978-1-157-17165-2|page=26}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Administrative divisions of Uttar Pradesh|List of districts of Uttar Pradesh|List of urban local bodies in Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
Other animals in the state include reptiles such as [[lizard]]s, [[cobra]]s, [[Bungarus|krait]]s, and [[gharial]]s. Among the wide variety of fishes, the most common ones are [[Mahseer|mahaseer]] and [[trout]]. Some animal species in Uttar Pradesh have gone extinct in recent years, while others, like the lion from the Gangetic Plain and the [[rhinoceros]] from the [[Terai|Terai region]], have become [[Endangered species|endangered]].<ref name="S.k.agarwal">{{cite book|author=S. K. Agarwal|title=Environment Biotechnology|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=0UeDTX6HEK8C&pg=PA61|accessdate=25 July 2012|publisher=APH Publishing|isbn=978-81-313-0294-1|page=61}}</ref> Many species are vulnerable to poaching despite regulation by the [[Government of Uttar Pradesh|government]].<ref name=fauna>{{cite web|title=Processing of manuscripts of Fauna|url=http://zsi.gov.in/right_menu/Annual%20Meeting/Annual%20Meeting%202011-12/HQ/Fauna.pdf|publisher=Indian Government|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
=={{anchor|Constituent regions}}{{anchor|Regions and cities}}Divisions, districts and cities== |
|||
{{Main|Divisions of Uttar Pradesh|Districts of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{See also|Western Uttar Pradesh|Eastern Uttar Pradesh|Central Uttar Pradesh}} |
{{See also|Western Uttar Pradesh|Eastern Uttar Pradesh|Central Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
[[File:Uttar Pradesh administrative divisions.svg|right|thumb| |
[[File:Uttar Pradesh administrative divisions.svg|right|thumb|200px|alt="Administrative Divisions"|[[Divisions of Uttar Pradesh]]]] |
||
Uttar Pradesh is divided into 75 [[Districts of Uttar Pradesh|districts]] under these 18 divisions:<ref name=divisions>{{cite web|title=State division of Uttar Pradesh|url=http://india.gov.in/knowindia/districts/andhra1.php?stateid=UP|publisher= Government of India|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Uttar Pradesh is divided into 75 districts under these 18 divisions:<ref name="divisions">{{Cite web |title=State division of Uttar Pradesh |url=http://india.gov.in/knowindia/districts/andhra1.php?stateid=UP |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120510202421/http://india.gov.in/knowindia/districts/andhra1.php?stateid=UP |archive-date=10 May 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Government of India}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- Divisions are added in region-wise order; Western, Central and Eastern.--> |
|||
{| style="margin-left:30px" |
{| style="margin-left:30px" |
||
| |
|||
{{col-begin}} |
{{col-begin}} |
||
{{col-break|width=57%}} |
{{col-break|width=57%}} |
||
| Line 448: | Line 448: | ||
|[[Moradabad division|Moradabad]] |
|[[Moradabad division|Moradabad]] |
||
|[[Bareilly division|Bareilly]] |
|[[Bareilly division|Bareilly]] |
||
|[[ |
|[[Meerut division|Meerut]] |
||
|[[Aligarh division|Aligarh]] |
|||
|[[Agra division|Agra]] |
|||
|[[Devipatan division|Devipatan]] |
|[[Devipatan division|Devipatan]] |
||
|[[Basti division|Basti]] |
|[[Basti division|Basti]] |
||
|[[Gorakhpur division|Gorakhpur]] |
|[[Gorakhpur division|Gorakhpur]] |
||
|[[Meerut division|Meerut]] |
|||
|[[Aligarh division|Aligarh]] |
|||
|[[Agra division|Agra]] |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{col-break}} |
{{col-break}} |
||
{{ordered list|start= |
{{ordered list|start=10 |
||
|[[Kanpur division|Kanpur]] |
|[[Kanpur division|Kanpur]] |
||
|[[ |
|[[Lucknow division|Lucknow]] |
||
|[[Ayodhya division|Ayodhya]] |
|||
|[[Azamgarh division|Azamgarh]] |
|[[Azamgarh division|Azamgarh]] |
||
|[[Jhansi division|Jhansi]] |
|[[Jhansi division|Jhansi]] |
||
|[[Chitrakoot division|Chitrakoot]] |
|[[Chitrakoot division|Chitrakoot]] |
||
|[[ |
|[[Prayagraj division|Prayagraj]] |
||
|[[Varanasi division|Varanasi]] |
|[[Varanasi division|Varanasi]] |
||
|[[Mirzapur division|Mirzapur]] |
|[[Mirzapur division|Mirzapur]] |
||
| Line 470: | Line 470: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
The following is a list of top |
The following is a list of top districts from state of Uttar Pradesh by population, ranked in respect of all India.<ref name="districts1">{{Cite web |title=Indian Districts by population |url=http://www.census2011.co.in/district.php |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110611224943/http://www.census2011.co.in/district.php |archive-date=11 June 2011 |access-date=5 October 2012 |website=2011 Census of India}}</ref> |
||
{| class="sortable |
{| class="wikitable sortable mw-collapsible" |
||
|- style="background:#ccc; text-align:center |
|- style="background:#ccc; text-align:center" |
||
! Rank !! District !! Population !! Growth |
! Rank (in India) !! District !! Population !! Growth Rate (%) !! Sex Ratio (Females per 1000 Males) !! Literacy Rate (%) |
||
|- style="vertical-align: |
|- style="vertical-align:middle; text-align:center" |
||
| |
| 13 || [[Prayagraj district|Prayagraj]]|| 5,954,391 || 20.63 || 901 || 72.32 |
||
|- style="vertical-align: |
|- style="vertical-align:middle; text-align:center" |
||
| 26 || [[Moradabad district|Moradabad]] || 4, |
| 26 || [[Moradabad district|Moradabad]] || 4,772,006 || 25.22 || 906 || 56.77 |
||
|- style="vertical-align: |
|- style="vertical-align:middle; text-align:center" |
||
| |
| 27 || [[Ghaziabad district|Ghaziabad]]|| 4,681,645 || 42.27 || 881 || 78.07 |
||
|- style="vertical-align: |
|- style="vertical-align:middle; text-align:center" |
||
| 30 || [[Azamgarh]] || 4, |
| 30 || [[Azamgarh district|Azamgarh]] || 4,613,913 || 17.11 || 1019 || 70.93 |
||
|- style="vertical-align: |
|- style="vertical-align:middle; text-align:center" |
||
| |
| 31 || [[Lucknow district|Lucknow]] || 4,589,838 || 25.82 || 917 || 77.29 |
||
|- style="vertical-align: |
|- style="vertical-align:middle; text-align:center" |
||
| |
| 32 || [[Kanpur Nagar district|Kanpur Nagar]] || 4,581,268 || 9.92 || 862 || 79.65 |
||
|- style="vertical-align:middle; text-align:center" |
|||
| 41 || [[Agra district|Agra]] || 4,418,797 || 22.05 || 868 || 71.58 |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:middle; text-align:center" |
|||
| 50 || [[Bareilly district|Bareilly]]|| 4,448,359 || 22.93% || 887 || 58.5 |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
Each district is governed by a [[district collector]] or District Magistrate, appointed either by the [[Indian Administrative Service]] or [[Uttar Pradesh Public Service Commission]].<ref name=panchayat/> Each district is divided into subdivisions, governed by a [[Sub-Divisional Magistrate|sub-divisional magistrate]], and again into [[Block (country subdivision)|Blocks]]. Blocks consists of [[panchayats]] (village councils) and town [[municipalities]].<ref name=blocks>{{cite web|title=Directory of district, sub division, panchayat samiti/ block and gram panchayats in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://panchayatiraj.up.nic.in/Acts%20And%20Rules%20Pdfs/Panchayat%20Raj%20Act_1947_ch6.57-70.pdf|work=Panchayati Raj Department|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> These blocks consists of urban units viz. [[census towns]] and rural units called [[gram panchayat]].<ref name=panchayat>{{cite web|title=Administration of block|url=http://panchayatiraj.up.nic.in/Acts%20And%20Rules%20Pdfs/Panchayat%20Raj%20Act_1947_ch4.38-50.pdf|work=Panchayati Raj Department|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Each district is governed by a District Magistrate, who is an [[Indian Administrative Service]] (IAS) officer appointed [[Government of Uttar Pradesh]] and reports to [[Divisional Commissioner]] of the division in which his district falls.<ref name="panchayat" /> The Divisional Commissioner is an IAS officer of high seniority. Each district is divided into subdivisions, governed by a [[Sub-Divisional Magistrate]], and again into [[Block (country subdivision)|Blocks]]. Blocks consists of [[panchayats]] (village councils) and town [[municipalities]].<ref name="blocks">{{Cite web |year=1947 |title=Panchayati Raj Act, 1947 – Chapter 6 – The Nyaya Panchayat |url=http://panchayatiraj.up.nic.in/Acts%20And%20Rules%20Pdfs/Panchayat%20Raj%20Act_1947_ch6.57-70.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304023420/http://panchayatiraj.up.nic.in/Acts%20And%20Rules%20Pdfs/Panchayat%20Raj%20Act_1947_ch6.57-70.pdf |archive-date=4 March 2016 |access-date=13 September 2017 |website=Department of Panchayati Raj, [[Government of Uttar Pradesh]]}}</ref> These blocks consists of urban units viz. [[census towns]] and rural units called [[gram panchayat]].<ref name="panchayat">{{Cite web |year=1947 |title=Panchayati Raj Act, 1947 |url=http://panchayatiraj.up.nic.in/Acts%20And%20Rules%20Pdfs/Panchayat%20Raj%20Act_1947_ch4.38-50.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170712165910/http://panchayatiraj.up.nic.in/Acts%20And%20Rules%20Pdfs/Panchayat%20Raj%20Act_1947_ch4.38-50.pdf |archive-date=12 July 2017 |access-date=16 August 2017 |website=Department of Panchayati Raj, [[Government of Uttar Pradesh]]}}</ref> |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has more [[List of most populous cities in India|metropolitan cities]] than any other state in India.<ref name="metropolitan cities">{{cite news|title=Development of 13 metropolitan cities in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://www.indianexpress.com/news/panels-to-draft-development-plans-for-13-cities/674326/|accessdate=13 July 2012|newspaper=The Indian Express|date=30 August 2010}}</ref><ref name="Metro cities">{{cite web|title=The area and density of metropolitan cities|url=http://urbanindia.nic.in/theministry/subordinateoff/tcpo/AREA_POP/CHAPTER-4.PDF|publisher=The Ministry of Urban Development|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> The absolute urban population of the state is 44.4 million, which constitutes 11.8% of the total urban population of India, the second highest of any state.<ref name="Population info">{{cite web|title=Provisional population totals, Census of India 2011 |url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/data_files/india/Rural_Urban_2011.pdf |publisher=Census of India 2011 |format=PDF |page=19 |accessdate=14 March 2012}}</ref> According to the 2011 census, there are 15 urban agglomerations with a population greater than 500,000.<ref name=Datasheet>{{cite web|title=Provisional population totals paper 1 of 2011 : Uttar Pradesh|url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/prov_data_products_up.html|publisher=Census of India 2011|accessdate=23 July 2012 }}</ref> There are 14 municipal corporations, while [[Noida]] is specially administered by a statuary authority.<ref name="GENERAL AMENDMENT">{{cite web|title=The Uttar Pradesh municipal corporation|url=http://sec.up.nic.in/acts_rules/MUNICIPAL%20CORPORATION_1959_eng/Municipal_Corp_Act_1959_chap1.pdf|publisher=Municipal corporation of Uttar Pradesh|accessdate=22 July 2012Pradesh}}</ref> |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has more [[List of most populous cities in India|metropolitan cities]] than any other state in India.<ref name="metropolitan cities">{{Cite news |date=30 August 2010 |title=Panels to draft development plans for 13 cities |work=[[The Indian Express]] |url=http://www.indianexpress.com/news/panels-to-draft-development-plans-for-13-cities/674326/ |access-date=13 July 2012}}</ref><ref name="Metro cities">{{Cite web |title=The area and density of metropolitan cities |url=http://urbanindia.nic.in/theministry/subordinateoff/tcpo/AREA_POP/CHAPTER-4.PDF |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121015142027/http://urbanindia.nic.in/theministry/subordinateoff/tcpo/AREA_POP/CHAPTER-4.PDF |archive-date=15 October 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=The Ministry of Urban Development}}</ref> The absolute urban population of the state is 44.4 million, which constitutes 11.8% of the total urban population of India, the second-highest of any state.<ref name="Population info">{{Cite web |title=Provisional population totals, Census of India 2011 |url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/data_files/india/Rural_Urban_2011.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120226224319/http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/data_files/india/Rural_Urban_2011.pdf |archive-date=26 February 2012 |access-date=14 March 2012 |publisher=Census of India 2011 |page=19}}</ref> According to the [[2011 Census of India|2011 census]], there are 15 urban agglomerations with a population greater than 500,000.<ref name="Datasheet">{{Cite web |title=Provisional population totals paper 1 of 2011 : Uttar Pradesh |url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/prov_data_products_up.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120427103412/http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/prov_data_products_up.html |archive-date=27 April 2012 |access-date=23 July 2012 |publisher=Census of India 2011}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has a complex system of municipalities. [[Nagar Nigam]] (Municipal Corporation) are urban local bodies in large cities such as Lucknow, Kanpur, Varanasi and cities having population more than 4 million.<ref name="UP Municipal">{{cite web | title= | url=https://cag.gov.in/uploads/download_audit_report/2021/5%20CHAPTER%20I-063076629450a19.40071813.pdf | access-date=10 July 2024}}</ref> These governed by a mayor and councilors elected from wards. [[Nagar Palika Parishad]] or Municipal Council, serves medium-sized towns like [[Bela Pratapgarh]], [[Jalaun]], or [[Bisalpur, Pilibhit|Bisalpur]] and are governed by a chairperson and councilors.<ref name="Palika">{{cite web | title= | url=https://www.indiacode.nic.in/bitstream/123456789/16228/1/Municipality_1916.pdf | access-date=10 July 2024}}</ref> [[Nagar Panchayat]] which operate in smaller towns and semi-urban areas like [[Badlapur, Jaunpur]], [[Bikapur]], or [[Chilkana Sultanpur]], are governed by a chairman and councilors.<ref name="Palika"/> There are 14 [[Municipal Corporations in India|Municipal Corporations]],<ref>{{Cite web |year=1959 |title=Uttar Pradesh Municipal Corporation Act, 1959 |url=http://www.janaagraha.org/asics/report/Uttar-Pradesh-Uttarakhand-Municipal-Corporation-Act-1959.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170816233237/http://www.janaagraha.org/asics/report/Uttar-Pradesh-Uttarakhand-Municipal-Corporation-Act-1959.pdf |archive-date=16 August 2017 |access-date=16 August 2017}}</ref><ref name="GENERAL AMENDMENT">{{Cite web |year=1959 |title=Uttar Pradesh Municipal Corporation Act, 1959 |url=http://sec.up.nic.in/acts_rules/MUNICIPAL%20CORPORATION_1959_eng/Municipal_Corp_Act_1959_chap1.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120324141206/http://sec.up.nic.in/acts_rules/MUNICIPAL%20CORPORATION_1959_eng/Municipal_Corp_Act_1959_chap1.pdf |archive-date=24 March 2012 |access-date=17 August 2017 |website=Uttar Pradesh State Election Commission}}</ref> while [[Noida]] and [[Greater Noida]] in [[Gautam Buddha Nagar district|Gautam Budha Nagar district]] are specially administered by statutory authorities under the Uttar Pradesh Industrial Development Act, 1976.<ref>{{Cite web |year=1976 |title=U.P. Industrial Development Act – 1976 (U.P. Act Number 6, of 1976) |url=http://www.noidaauthorityonline.com/UPIndAreaDevp.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170812211441/http://www.noidaauthorityonline.com/UPIndAreaDevp.pdf |archive-date=12 August 2017 |access-date=13 August 2017 |website=Noida Authority Online}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.greaternoida.com/files/attachments/inddevact.pdf|title=U.P. Industrial Development Act – 1976 (U.P. Act Number 6, of 1976)|year=1976|website=Greater Noida Authority|access-date=13 August 2017|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150511075823/http://www.greaternoida.com/files/attachments/inddevact.pdf|archive-date=11 May 2015}}</ref> |
|||
In 2011, state's cabinet ministers headed by the then Chief Minister [[Mayawati]] announced the separation of Uttar Pradesh into four different states of Purvanchal, Bundelkhand, Avadh Pradesh and Paschim Pradesh with twenty eight, seven, twenty three and seventeen districts respectively, later the proposal was turned down when [[Mulayam Singh Yadav]] lead [[Samajwadi Party]] came to power in the 2012 election.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/article2631472.ece | title=Maya splits U.P. poll scene wide open | publisher=[[The Hindu]] | date=16 November 2011 | accessdate=15 June 2013 | author=Khan, Atiq |location=Lucknow}}</ref> |
|||
In 2011, state's cabinet ministers headed by the then Chief Minister [[Mayawati]] announced the separation of Uttar Pradesh into four different states of Purvanchal, Bundelkhand, Avadh Pradesh and Paschim Pradesh with twenty-eight, seven, twenty-three and seventeen districts, respectively, later the proposal was turned down when the [[Akhilesh Yadav]]–lead [[Samajwadi Party]] came to power in the [[2012 Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly election|2012 election]].<ref>{{cite news | url=http://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/article2631472.ece | title=Maya splits U.P. poll scene wide open | newspaper=[[The Hindu]] | date=16 November 2011 | access-date=15 June 2013 | author=Khan, Atiq | location=Lucknow | url-status=live | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140112191630/http://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/article2631472.ece | archive-date=12 January 2014}}</ref> |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
{{main|Demographics of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
== Demographics == |
|||
{{See also|List of people from Uttar Pradesh|Pathans of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{Main|Demographics of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{IndiaCensusPop |
|||
{{See also|List of people from Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
| title= Population Growth |
|||
| 1951= 60274000 |
|||
{{ |
|||
| 1961= 70144000 |
|||
Pie chart|caption=Religion in Uttar Pradesh (2011)<ref name="religion census">{{cite news |last1=Number |first1=Religion |title=U.P religions by numbers |url=https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/religious-communities-census-2011-what-the-numbers-say/article7582284.ece |access-date=29 March 2020 |work=The Hindu |agency=The Hindu Group |issue=26 August 2015 |publisher=N. Ravi |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181115030444/https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/religious-communities-census-2011-what-the-numbers-say/article7582284.ece |archive-date=15 November 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
| 1971= 83849000 |
|||
|color8=black |
|||
| 1981= 105137000 |
|||
|color7=chartreuse |
|||
| 1991= 132062000 |
|||
|color6=gold |
|||
| 2001= 166198000 |
|||
|color5=brown |
|||
| 2011= 199581477 |
|||
|color4=blue |
|||
| estimate= |
|||
|color3=yellow |
|||
| estyear= |
|||
|color2=green |
|||
| estref= |
|||
|color1=darkorange |
|||
| footnote=Source:Census of India |
|||
|label8=Not stated |
|||
|label7=Other |
|||
|label6=[[Jainism]] |
|||
|label5=[[Buddhism]] |
|||
|label4=[[Christianity in Uttar Pradesh|Christianity]] |
|||
|label3=[[Sikhism]] |
|||
|label2=[[Islam in Uttar Pradesh|Islam]] |
|||
|label1=[[Hinduism]] |
|||
|value8=0.29 |
|||
|value7=0.01 |
|||
|value6=0.11 |
|||
|value5=0.10 |
|||
|value4=0.18 |
|||
|value3=0.32 |
|||
|value2=19.26 |
|||
|value1=79.73 |
|||
|thumb=left |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Pie chart|value1=80.16|value2=10.93|value3=5.42|value4=1.9|label1=[[Hindi]]|label2=[[Bhojpuri language|Bhojpuri]]|label3=[[Urdu]]|label4=[[Awadhi language|Awadhi]] |color1=Orange|color2=gold |color3=green|color4=maroon |value5=0.3 |label5=[[Punjabi language|Punjabi]]|color5=pink|caption=Languages of Uttar Pradesh from 2011 census<ref>{{cite web|url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011Census/Language_MTs.html|title=Table C-16: Language by States and Union Territories – Uttar Pradesh|website=censusindia.gov.in|access-date=24 February 2021|archive-date=24 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210224155157/https://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011Census/Language_MTs.html|url-status=live}}</ref>|value6=0.1|label6=[[Bengali language|Bengali]]|label7=Others|value7=1.19}} |
|||
{{bar box |
|||
|title=Religion in Uttar Pradesh |
|||
|titlebar=#Fcd116 |
|||
|left1=Religion |
|||
|right1=Percent |
|||
|float=right |
|||
|bars= |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Hindu]]|#FF6600|80.6}}<!-- Please do not change any of these numbers without adding a reference to back it up --> |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Islam]]|#009000|18.4}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Others|#808080|1}} |
|||
}}<ref name="census2001">{{cite web |
|||
| title = Census of India – Socio-cultural aspects |
|||
| publisher = Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India |
|||
| url = http://censusindia.gov.in/Census_Data_2001/Census_Data_Online/Social_and_cultural/Religion.aspx |
|||
| accessdate =2 March 2011}} |
|||
</ref> |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has a large population and a high population growth rate. From 1991 to 2001 its population increased by over 26%.<ref name=population>{{cite web|title=The density of population in U.P. |url=http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Overview_847.aspx |publisher=Environment and Related Issues Department U.P|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh is the [[List of states and union territories of India by population|most populous state in India]], with 199,581,477 people on 1 March 2011.<ref name=autogenerated7>{{cite web|title=Provisional population totals|url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/data_files/UP/7-pop-12-22.pdf|publisher=Census of India 2011|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref> The state contributes 16.16% of India's population. The population density is 828 people per square kilometre, making it one of the densest [[States and territories of India|states]] in the country.<ref name="GOI_2011"/> |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has a very large population and a high population growth rate. From 1991 to 2001 its population increased by over 26 per cent.<ref name=population>{{cite web |title=The density of population in U.P. |url=http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Overview_847.aspx |publisher=Environment and Related Issues Department U.P |access-date=23 July 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121215062041/http://upenvis.nic.in/Database/Overview_847.aspx |archive-date=15 December 2012}}</ref> It is the [[List of states and union territories of India by population|most populous state in India]], with 199,581,477 people on 1 March 2011.<ref name=autogenerated7>{{cite web|title=Provisional population totals|url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/data_files/UP/7-pop-12-22.pdf|publisher=Census of India 2011|access-date=23 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130207004512/http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/data_files/UP/7-pop-12-22.pdf|archive-date=7 February 2013}}</ref> The state contributes to 16.2 per cent of India's population. As of 2021, the estimated population of the state is around 240 million people.<ref name="Estimated 2021">{{cite news |last1=Rampal |first1=Nikhil |title=World population grew by a billion in past 12 yrs & 5% came from just UP & Bihar, data shows |url=https://theprint.in/india/world-population-hits-8-billion-india-highest-contributor-surpass-china-2023/1218281/ |access-date=1 May 2023 |work=ThePrint |agency=Printline Media Pvt. Ltd. |date=16 November 2022 |archive-date=1 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230501221830/https://theprint.in/india/world-population-hits-8-billion-india-highest-contributor-surpass-china-2023/1218281/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The population density is 828 people per square kilometre, making it one of the most densely populated [[States and territories of India|states]] in the country.<ref name="Statistics">{{cite web|title=Statistics of Uttar Pradesh|url=http://www.up.gov.in/upstateglance.aspx|website=up.gov.in|publisher=Government of Uttar Pradesh|access-date=12 April 2017|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170412224507/http://www.up.gov.in/upstateglance.aspx|archive-date=12 April 2017}}</ref> It has the largest [[scheduled caste]] population whereas [[List of Scheduled Tribes in India|scheduled tribes]] are less than 1 per cent of the total population.<ref name="Tribe">{{cite web |title=Scheduled castes and scheduled tribes |url=https://censusindia.gov.in/Census_And_You/scheduled_castes_and_sceduled_tribes.aspx |publisher=Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India |access-date=12 June 2020 |archive-date=27 April 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200427154205/http://censusindia.gov.in/Census_And_You/scheduled_castes_and_sceduled_tribes.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Indigenous">{{cite web |last1=Kaul |first1=Sudesh |title=Indigenous Peoples Policy Framework |url=http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/467821468035383950/pdf/IPP7630P14786400Box385405B00PUBLIC0.pdf |publisher=World Bank |access-date=12 June 2020 |archive-date=12 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200612181146/http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/467821468035383950/pdf/IPP7630P14786400Box385405B00PUBLIC0.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The [[sex ratio]] in 2011, at 908 women to 1000 men, was lower than the national figure of 933.<ref name="GOI_2011"/> The state's 2001–2011 decennial growth rate (including Uttrakhand) was 20.09%, higher than the national rate of 17.64%.<ref name=Decennial>{{cite web|title=Decennil growth of population by census |url=http://www.cwc.nic.in/Water_Data_Pocket_Book_2006/t9.01final.pdf|work=Census of India (2011)|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref><ref name=decennialgrowth>{{cite web|title=Decennial growth rate and density for 2011 at a glance for Uttar Pradesh and the districts: provisional population totals paper 1 of 2011 |url=http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/prov_data_products_up.html|work=Census of India(2011)|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has a large number of people living below the [[Poverty threshold|poverty line]].<ref name=poverty/> Estimates released by the Planning Commission for the year 2009-10 revealed that Uttar Pradesh had 59 million people below the poverty line, the most for any state in India.<ref name=poverty>{{cite web |title=The state with large no. of people living below poverty line|url=http://pib.nic.in/newsite/erelease.aspx?relid=49731 |work=Government of India|publisher=''Press Information Bureau|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref><ref name=commission>{{cite web|title=Number and Percentage of Population below poverty line by states - 2011-12|url=http://planningcommission.nic.in/news/pre_pov2307.pdf|website=http://planningcommission.nic.in/|publisher=Press Note on Poverty Estimates, 2011-12 , Government of India|accessdate=11 August 2014}}</ref> |
|||
The [[human sex ratio|sex ratio]] in 2011, at 912 women to 1000 men, was lower than the national figure of 943.<ref name="pc-census2011" /> The low sex ratio in Uttar Pradesh, is a result of various factors, such as [[sex-selective abortion]], [[female infanticide]], and discrimination against girls and women.<ref name="UP Foeticide">{{cite news |last1=Ara |first1=Ismat |title=Higher Female Foeticide, Targeted Harassment: UP's Population Control Bill May Be Dangerous |url=https://thewire.in/rights/rising-female-foeticide-targeted-harassment-ups-population-control-bill-may-be-dangerous |access-date=1 May 2023 |work=The Wire (India) |agency=Foundation for Independent Journalism (FIJ) |date=16 July 2021 |archive-date=1 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230501221117/https://thewire.in/rights/rising-female-foeticide-targeted-harassment-ups-population-control-bill-may-be-dangerous |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Uttar Pradesh21">{{cite news |last1=Rao |first1=Menaka |title=How one Uttar Pradesh district is using technology to prevent sex-selective abortions |url=https://scroll.in/pulse/828350/how-one-uttar-pradesh-district-is-using-technology-to-prevent-female-foeticide |access-date=1 May 2023 |work=Scroll.in |agency=Scroll Media Incorporation |date=16 February 2017 |archive-date=1 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230501221117/https://scroll.in/pulse/828350/how-one-uttar-pradesh-district-is-using-technology-to-prevent-female-foeticide |url-status=live }}</ref> The state's 2001–2011 decennial growth rate (including Uttrakhand) was 20.1 per cent, higher than the national rate of 17.64 per cent.<ref name=Decennial>{{cite web|title=Decennil growth of population by census|url=http://www.cwc.nic.in/Water_Data_Pocket_Book_2006/t9.01final.pdf|work=Census of India (2011)|access-date=5 October 2011|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090410021912/http://www.cwc.nic.in/Water_Data_Pocket_Book_2006/t9.01final.pdf|archive-date=10 April 2009}}</ref><ref name=decennialgrowth>{{cite web|title=Decennial growth rate and density for 2011 at a glance for Uttar Pradesh and the districts: provisional population totals paper 1 of 2011|url=http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/prov_data_products_up.html|work=Census of India(2011)|access-date=5 October 2011|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111007014159/http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/prov_data_products_up.html|archive-date=7 October 2011}}</ref> It has a large number of people living below the [[Poverty threshold|poverty line]].<ref name=poverty /> As per a [[World Bank]] document released in 2016, the pace of poverty reduction in the state has been slower than the rest of the country.<ref name="World Bank">{{cite web |title=Uttar Pradesh Poverty, Growth & Inequality |url=http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/187721467995647501/pdf/105884-BRI-P157572-ADD-SERIES-India-state-briefs-PUBLIC-UttarPradesh-Proverty.pdf |publisher=World Bank |access-date=23 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171116021320/http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/187721467995647501/pdf/105884-BRI-P157572-ADD-SERIES-India-state-briefs-PUBLIC-UttarPradesh-Proverty.pdf |archive-date=16 November 2017 |url-status=live}}</ref> Estimates released by the [[Reserve Bank of India]] for the year 2011–12 revealed that the state had 59 million (59819,000) people below the poverty line, the most for any state in India.<ref name=poverty>{{cite web|title=The state with large no. of peoples living below poverty line|url=http://pib.nic.in/newsite/erelease.aspx?relid=49731|work=Government of India|publisher=Press Information Bureau|access-date=5 October 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130208074013/http://pib.nic.in/newsite/erelease.aspx?relid=49731|archive-date=8 February 2013}}</ref><ref name=commission>{{cite web |url=http://planningcommission.nic.in/news/pre_pov2307.pdf |title=Press Note on Poverty Estimates, 2011–12 |website=Planning Commission |publisher=Government of India |access-date=11 August 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140628120737/http://planningcommission.nic.in/news/pre_pov2307.pdf |archive-date=28 June 2014|page=7}}</ref> The central and eastern districts in particular have very high levels of poverty. The state is also experiencing widening consumption inequality. As per the report of the [[Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation]] released in 2020, the state per capita income is below {{INRConvert|80|k}} per annum.<ref name="Annum">{{cite news |last1=Singh |first1=Hemant |title=Per Capita Income of Indian States 2019–20 |url=https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/per-capita-income-of-indian-states-1468997157-1 |access-date=23 May 2020 |work=Dainik Jagran |agency=Jagran Prakashan Limited |publisher=Jagran Josh |date=7 April 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190826043616/https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/per-capita-income-of-indian-states-1468997157-1 |archive-date=26 August 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
At the 2001 [[Demographics of India|Indian census]], about 80.6% of Uttar Pradesh's population was [[Hindu]], while [[Muslims]] made up around 18.4%, being the second-largest community and the largest minority group.<ref name=snapshot>{{cite web|title=A snapshot of population size, distribution, growth and socio economic characteristics of religious communities from Census 2001|url=http://www.censusindia.net/religiondata/presentation_on_religion.pdf|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070809024419/http://www.censusindia.net/religiondata/presentation_on_religion.pdf|archivedate=9 August 2007 |work=Census of India|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> The remainder consisted of [[Sikhs]], [[Buddhists]], Christians, and [[Jainism|Jains]].<ref>{{cite web| title = Census Reference Tables, C-Series Population by religious communities| work = Census of India| publisher = Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India| year = 2001|url= http://www.censusindia.gov.in/Census_Data_2001/Census_data_finder/C_Series/Population_by_religious_communities.htm |accessdate =12 July 2008}}</ref> The literacy rate of the state at the 2011 census was 70%, which was below the national average of 74%.<ref name="Literacy rate">{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh Profile |url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011census/censusinfodashboard/stock/profiles/en/IND009_Uttar%20Pradesh.pdf|publisher=Census of India 2011|accessdate=16 October 2010}}</ref><ref name="literacy rates">{{cite web|title=A comparison of the literacy rates|url=http://censusmp.gov.in/censusmp/All-PDF/6Literacy21.12.pdf|publisher=censusmp.gov.in|accessdate=16 October 2010}}</ref> The literacy rate for men is 79% and for women 59%. In 2001 the literacy rate in Uttar Pradesh stood at 56.27% overall, 67% for men and 43% for women.<ref name=Literacy>{{cite web|title=Literacy rate in Uttar Pradesh |url=http://www.census2011.co.in/census/state/uttar+pradesh.html|publisher=Census of India 2011|accessdate=16 October 2010}}</ref> |
|||
As per [[2011 Census of India|2011 census]], Uttar Pradesh, the most populous state in India, is home to the highest numbers of both Hindus and Muslims.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.deccanherald.com/content/497347/muslim-population-grew-faster-census.html|title=Muslim population grew faster: Census|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150827035701/http://www.deccanherald.com/content/497347/muslim-population-grew-faster-census.html|archive-date=27 August 2015}}</ref> The literacy rate of the state at the 2011 census was 67.7 per cent, which was below the national average of 74 per cent.<ref name="Literacy rate">{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh Profile|url=http://censusindia.gov.in/2011census/censusinfodashboard/stock/profiles/en/IND009_Uttar%20Pradesh.pdf|publisher=Census of India 2011|access-date=16 October 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130208074636/http://censusindia.gov.in/2011census/censusinfodashboard/stock/profiles/en/IND009_Uttar%20Pradesh.pdf|archive-date=8 February 2013}}</ref><ref name="literacy rates">{{cite web |title= A comparison of the literacy rates |url= http://censusmp.gov.in/censusmp/All-PDF/6Literacy21.12.pdf |publisher= censusmp.gov.in |access-date= 16 October 2010 |url-status= live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120417110338/http://censusmp.gov.in/censusmp/All-PDF/6Literacy21.12.pdf |archive-date= 17 April 2012}}</ref> The literacy rate for men is 79 per cent and for women 59 per cent. In 2001 the literacy rate in the state stood at 56 per cent overall, 67 per cent for men and 43 per cent for women.<ref name=Literacy>{{cite web |title= Literacy rate in Uttar Pradesh |url= http://www.census2011.co.in/census/state/uttar+pradesh.html |publisher= Census of India 2011 |access-date= 16 October 2010 |url-status= live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110430133506/http://www.census2011.co.in/census/state/uttar+pradesh.html |archive-date= 30 April 2011}}</ref> A report based on a [[Central Statistics Office (India)|National Statistical Office]] (NSO) survey{{Efn|name=remark1|National Sample Survey from July 2017 to June 2018 provides state-wise details of literacy rates among persons aged seven and above.}} revealed that Uttar Pradesh's literacy rate is 73 per cent, less than the national average of 77.7 per cent. According to the report, in the rural region, the literacy rate among men is 80.5 per cent and women is 60.4 per cent, while in urban areas, the literacy rate among men is 86.8 per cent and women is 74.9 per cent.<ref name="NSO">{{cite news |title=UP literacy rate poor than national average: Report |url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/education/up-literacy-rate-poor-than-national-average-report/story-04cd30glcG2IchqkB0TLaJ.html |access-date=20 June 2021 |work=Hindustan Times |agency=HT Media Ltd |date=8 September 2020 |archive-date=24 June 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210624203635/https://www.hindustantimes.com/education/up-literacy-rate-poor-than-national-average-report/story-04cd30glcG2IchqkB0TLaJ.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
[[Hindi language|Hindi]] is the only state-wide official language of Uttar Pradesh. People of Uttar Pradesh regard their language a very important part of their cultural identity.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005">{{cite book|author1=Gopal K. Bhargava |author2=Shankarlal C. Bhatt|title=Land and people of Indian states and union territories. 28. Uttar Pradesh |url=http://books.google.com/books?id=FCG5hGZ-hJsC&pg=PA31|accessdate=5 October 2012|year=2005|publisher=Gyan Publishing House |isbn=978-81-7835-384-5|page=43}}</ref> Hindi is spoken as the first language by 89.43% of the population.<ref name="classic language">{{cite web|title=The real classical language|url=http://www.columbia.edu/|publisher=Columbia University|accessdate=5 October 2012}}</ref> Most people in Uttar Pradesh speak a dialect of [[Hindustani language|Hindustani]], which in its written forms is referred to as [[Urdu language|Urdu]] and [[Hindi language|Hindi]].<ref name="Official Language">{{cite web|last=Compliance of the constitutional and legal provisions|title=Functions of the department of official language|url=http://rajbhasha.nic.in/MenuContent.aspx?t=endol-aboutus|publisher=Department of Official Language|accessdate=27 June 2011}}</ref><ref name="Official Languages">{{cite web|title=Official language - Constitutional/Statutory Provisions|url=http://india.gov.in/knowindia/profile.php?id=33|publisher=The National Portal of India|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[Hindi]] is the primary official language and is spoken by the majority of the population.<ref name="2011lang">{{cite web |url = http://www.nclm.nic.in/shared/linkimages/NCLM52ndReport.pdf |title = Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 52nd report (July 2014 to June 2015) |pages = 49–53 |publisher = Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India |access-date = 16 February 2016 |url-status = dead |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20161115133948/http://nclm.nic.in/shared/linkimages/NCLM52ndReport.pdf |archive-date = 15 November 2016}}</ref> [[Bhojpuri language|Bhojpuri]] is the second most spoken language of the state,<ref name="Experts">{{Cite book |last=Experts |first=Disha |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4D44EAAAQBAJ&dq=bhojpuri+second+language+uttar+pradesh&pg=PA117 |title=Amazing Uttar Pradesh – General Knowledge for UPPSC, UPSSSC & other Competitive Exams |date=1 July 2020 |publisher=Disha Publications |isbn=978-93-90486-72-4|access-date=11 September 2022 |archive-date=27 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230427232733/https://books.google.com/books?id=4D44EAAAQBAJ&dq=bhojpuri+second+language+uttar+pradesh&pg=PA117 |url-status=live }}</ref> it is spoken by almost 11 per cent of the population. Most people speak regional languages classified as dialects of Hindi in the census. These include [[Awadhi language|Awadhi]] spoken in [[Awadh]] in central Uttar Pradesh, Bhojpuri spoken in [[Purvanchal]] in eastern Uttar Pradesh, and [[Braj Bhasha]] spoken in the [[Braj]] region in Western Uttar Pradesh. These languages have also been recognised by the state government for official use in their respective regions. [[Urdu]] is given the status of a second official language, spoken by 5.4 per cent of the population.<ref name="2011lang" /><ref name="census2011-langreport" /> [[English language|English]] is used as a means of communication for education, commerce, and governance. It is commonly spoken and employed as a language of instruction in educational institutions, as well as for conducting business transactions and managing administrative affairs. Other notable languages spoken in the state include [[Punjabi language|Punjabi]] (0.3 per cent) and [[Bengali language|Bengali]] (0.1 per cent).<ref name="census2011-langreport">{{cite web |title=Language – India, States and Union Territories |url=http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011Census/C-16_25062018_NEW.pdf |work=Census of India 2011 |publisher=Office of the Registrar General |pages=13–14 |access-date=21 November 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181114073412/http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011Census/C-16_25062018_NEW.pdf |archive-date=14 November 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
A large number of other dialects exist. Five distinct dialect regions have been identified. The [[Western Uttar Pradesh|western]] part of the state, [[Rohilkhand]] and the upper [[Doab]], is home to the speakers of [[Khari Boli]]. The lower Doab, which is referred as Braj Bhumi, or the land of Braj, is home to the speakers of [[Braj Bhasha]]. Further south, the [[Bundelkhand]] region people speaks [[Bundelkhandi]]. In central Uttar Pradesh, people speak the [[Awadhi language|Awadhi]] dialect and [[Bhojpuri language|Bhojpuri]] is spoken in the east. Indian states are defined on the languages they spoke, and eastern Uttar Pradesh primarily speaks Bhojpuri and their culture is identical to Bihar. This creates no central identity of Uttar Pradesh.<ref name=awadhi>{{cite web|title=The story of an Awadhi|url=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Db_bmy0bwUg|publisher=[[YouTube]]|accessdate=20 July 2012}}</ref><ref name=language>{{cite web|title=Awadhi diaect|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=hif|publisher=Ethnologue-Languages of the world|accessdate=20 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
{{Largest Metropolitan Areas of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{-}} |
|||
== |
== Governance and administration == |
||
{{Main|Government of Uttar Pradesh| |
{{Main|Government of Uttar Pradesh|Vidhan Bhavan, Lucknow}} |
||
[[File:Vidhan Sabha (at day).jpg|left|thumb|alt=refer caption|Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha), the lower house of the bicameral legislature]] |
|||
{{See also|Uttar Pradesh legislative assembly election, 2012}} |
|||
The state is governed by a [[parliamentary system]] of [[representative democracy]]. Uttar Pradesh is one of the seven states in India, where the state legislature is bicameral, comprising two houses: the [[Vidhan Sabha]] (Legislative Assembly) and the [[Vidhan Parishad]] (Legislative Council).<ref name="vidhan parishad">{{cite web|url=http://legislativebodiesinindia.nic.in/UttarPradesh-LC.htm|title=Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Parishad structure|website=Legislative Bodies of India|publisher=[[Government of India]]|access-date=19 September 2017|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160417175655/http://legislativebodiesinindia.nic.in/UttarPradesh-LC.htm|archive-date=17 April 2016}}</ref><ref name="Vidhan Sabha">{{cite web|url=http://legislativebodiesinindia.nic.in/UTTAR%20PRADESH.htm|title=Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Sabha structure|website=Legislative Bodies of India|publisher=[[Government of India]]|access-date=19 September 2017|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160417175232/http://legislativebodiesinindia.nic.in/UTTAR%20PRADESH.htm|archive-date=17 April 2016}}</ref> The [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly|Legislative Assembly]] consists of 404 members who are elected for five-year terms. The [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council|Legislative Council]] is a permanent body of 100 members with one-third (33 members) retiring every two years. The state sends the largest number of legislators to the national Parliament.<ref name="elections">{{cite web|url=http://www.aljazeera.com/news/asia/2012/02/2012286478579763.html|title=Legislative elections in Uttar Pradesh|last=Four other states seen as a barometer of support for the federal government.|publisher=[[Al Jazeera Arabic|Al Jazeera]]|access-date=8 February 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120210194222/http://www.aljazeera.com/news/asia/2012/02/2012286478579763.html|archive-date=10 February 2012}}</ref> The state contributes 80 seats to [[Lok Sabha]], the lower house of the [[Indian Parliament]], and 31 seats to [[Rajya Sabha]], the upper house.<ref name="Grover1989">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fRqrO0Hx0Y0C&pg=PA37|title=Legislative Council in State Legislatures|first=Verinder|last=Grover|publisher=Deep & Deep Publications|isbn=978-8171001934|pages=37–255|access-date=27 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528132659/http://books.google.com/books?id=fRqrO0Hx0Y0C&pg=PA37|archive-date=28 May 2013|year=1989}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://rajyasabha.nic.in/rsnew/rsat_work/chapter-2.pdf|title=Composition of Rajya Sabha|work=Rajya Sabha|publisher=Rajya Sabha Secretariat|location=New Delhi|pages=24–25|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160305020442/http://rajyasabha.nic.in/rsnew/rsat_work/chapter-2.pdf|archive-date=5 March 2016|url-status=dead|access-date=15 February 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Allahabad high court.jpg|thumb|alt=refer to adjacent text|[[Allahabad High Court]] is the fourth oldest high court of India]] |
|||
Since Uttar Pradesh sends the largest number of legislators to the national Parliament, it is often considered to be one of the most important states with respect to Indian politics.<ref name=elections>{{cite web|last=Four other states seen as barometer of support for federal government.|title=Legislative elections in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://www.aljazeera.com/news/asia/2012/02/2012286478579763.html|publisher=[[Al Jazeera]]|accessdate=8 February 2012}}</ref> The state contributes 80 seats to the [[Lok Sabha]] and 35 seats to the [[Rajya Sabha]] of the [[Indian Parliament]].<ref name="Grover1989">{{cite book|author=Verinder Grover|title=Legislative Council in State Legislatures|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=fRqrO0Hx0Y0C&pg=PA37|accessdate=27 July 2012|publisher=Deep & Deep Publications|isbn=978-81-7100-193-4|pages=37–255}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url= http://rajyasabha.nic.in/rsnew/rsat_work/chapter-2.pdf|format=PDF|title=Composition of Rajya Sabha |work=Rajya Sabha|publisher=Rajya Sabha Secretariat |location=New Delhi |pages=24–25 |accessdate=15 February 2012}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has been called India's under-achiever, because it has provided India with eight prime ministers while remaining a poor state.<ref name="politically crucial state">{{cite web|title=UP: the nerve centre of politics|url=http://zeenews.india.com/state-elections-2012/up/issues.html|publisher=[[Zee news]]|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
The state's legislative body is divided into two significant parts: [[Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Parishad]]<ref name="vidhan parishad">{{cite web|title=UP vidhan parishad|url=http://legislativebodiesinindia.nic.in/UttarPradesh-LC.htm|publisher=Government of India|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> and [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly|Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Sabha]].<ref name="Vidhan Sabha">{{cite web|title=UP vidhan sabha structure|url=http://legislativebodiesinindia.nic.in/UTTAR%20PRADESH.htm|publisher=Government of India|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> The state is governed through a [[parliamentary system]] of [[representative democracy]], a feature the state shares with other Indian states. The Governor is the [[head of state]] and is appointed by the [[President of India]]. The leader of the party or coalition with a majority in the Legislative Assembly is appointed as the Chief Minister by the Governor, and the Council of Ministers are appointed by the Governor on the advice of the Chief Minister. In the 2012 election, the largest number of seats went to the [[Samajwadi Party]] with 224 seats.<ref name="election result">{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh 2012 Election Result|url=http://zeenews.india.com/state-elections-2012/up/uttar-pradesh-akhilesh-wins-the-battle-royale_762475.html|publisher=[[Zee News]]|accessdate=7 March 2012}}</ref> At the local level, the state has a large number of village councils (''[[panchayat]]s''), which are similar to those found in other Indian states. The administration in each district is headed by a [[District Magistrate (India)|District Magistrate]] who belongs to the [[Indian Administrative Service]] and is assisted by a number of officers belonging to state services.<ref name=judiciary/> |
|||
The [[Government of Uttar Pradesh]] is a [[Democracy|democratically]] elected body in India with the [[List of governors of Uttar Pradesh|governor]] as its constitutional head and is appointed by the [[president of India]] for a five-year term.<ref>{{cite web |title= Role of The Governor |url= http://upgovernor.gov.in/upgovernor.gov.in/roleofgov.htm |website= upgovernor.gov.in |publisher= Raj Bhavan Uttar Pradesh |access-date= 17 March 2017 |url-status= dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20170407230227/http://www.upgovernor.gov.in/upgovernor.gov.in/roleofgov.htm |archive-date= 7 April 2017}}</ref> The leader of the party or coalition with a majority in the Legislative Assembly is appointed as the [[List of chief ministers of Uttar Pradesh|chief minister]] by the governor, and the council of ministers is appointed by the governor on the advice of the chief minister. The governor remains a ceremonial head of the state, while the chief minister and his council are responsible for day-to-day government functions. The Council of Ministers consists of Cabinet Ministers and Ministers of State (MoS). The Secretariat headed by the [[Chief Secretary (India)|Chief Secretary]] assists the council of ministers. The Chief Secretary is also the administrative head of the government. Each government department is headed by a minister, who is assisted by an [[Additional Chief Secretary (India)|Additional Chief Secretary]] or a [[Principal Secretary (India)|Principal Secretary]], who is usually an officer of [[Indian Administrative Service]] (IAS), the Additional Chief Secretary/Principal Secretary serves as the administrative head of the department they are assigned to. Each department also has officers of the rank of Secretary, Special Secretary, Joint Secretary etc. assisting the Minister and the [[Additional Chief Secretary (India)|Additional Chief Secretary]]/[[Principal Secretary (India)|Principal Secretary]].<ref name=":2">{{Cite web |title=Constitutional Setup |url=http://up.gov.in/upconstitution.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170831000649/http://up.gov.in/upconstitution.aspx |archive-date=31 August 2017 |access-date=30 August 2017 |website=[[Government of Uttar Pradesh]]}}</ref><ref name=":64">{{Cite book |last=Laxmikanth |first=M. |title=Governance in India |publisher=McGraw Hill Education |year=2014 |isbn=978-9339204785 |edition=2nd |location=[[Noida]] |pages=4.3–4.5}}</ref> |
|||
Judges and judicial officers are appointed non-politically and under strict rules regarding [[tenure]] to help maintain constitutional independence from the government.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> This theoretically allows the judiciary to interpret the law based solely on the legislation enacted by Parliament without other influences on their decisions. The [[Superintendent of Police (India)|Deputy Commissioner of Police]], an officer belonging to the [[Indian Police Service]] and assisted by the officers of the Uttar Pradesh Police Service, is entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining law and order and related issues in each district.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> The [[Deputy Conservator of Forests (India)|Deputy Conservator of Forests]], an officer belonging to the [[Indian Forest Service]], also serves the government.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> Sectoral development in the districts is looked after by the district head of each development department such as the Department of Public Works, Health, Education, Agriculture, Animal Husbandry, etc.<ref name=judiciary>{{cite web|title=Judiciary in the state|url=http://www.allahabadnagarnigam.in/Hindi/download_hindifont_hin.htm|publisher=Allahabad Nagar Nigam|accessdate=17 February 2011}}</ref> |
|||
For administration, the state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts. [[Divisional Commissioner]], an IAS officer is the head of administration on the divisional level.<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":42">{{Cite book|title=Indian Administration |last=Maheshwari |first=S.R. |publisher=Orient Blackswan Private Ltd. |year=2000 |isbn=978-8125019886 |location=[[New Delhi]] |pages=563–572 |edition=6th}}</ref><ref name=":52">{{Cite book |title=Revenue administration in India: A case study of Bihar |last=Singh |first=G.P. |publisher=Mittal Publications|year=1993 |isbn=978-8170993810|location=[[Delhi]] |pages=26–129}}</ref> The administration in each district is headed by a [[District collector|District Magistrate]], who is also an IAS officer, and is assisted by several officers belonging to state services.<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":022">{{Cite web|url=http://uphome.gov.in/DM-UP-Contact.htm|title=Contact Details of Commissioners and District Magistrates of U.P.|website=[[Department of Home (Uttar Pradesh)|Department of Home and Confidential]], [[Government of Uttar Pradesh]]|access-date=15 August 2017|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170816061300/http://uphome.gov.in/DM-UP-Contact.htm|archive-date=16 August 2017}}</ref> District Magistrate being the head of the district administration, is responsible for maintaining law and order and providing public services in the district. At the block level, the Block Development Officer (BDO) is responsible for the overall development of the [[Block (district subdivision)|block]]. The [[Uttar Pradesh Police]] is headed by an IPS officer of the rank of [[Director general of police]]. A [[Superintendent of Police]], an IPS officer assisted by the officers of the Uttar Pradesh Police Service, is entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining law and order and related issues in each district. The Divisional Forest Officer, an officer belonging to the [[Indian Forest Service]] manages the forests, environment, and wildlife of the district, assisted by the officers of [[Provincial Forest Service (Uttar Pradesh)|Provincial Forest Service]] and Uttar Pradesh Forest Subordinate Service.<ref name="Provincial_Forest">{{cite web |title=LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS |url=https://forest.uk.gov.in/uploads/fbd/1637060091.pdf |publisher=Government of Uttarakhand |access-date=8 July 2024}}</ref> |
|||
The judiciary in the state consists of the [[Allahabad High Court]] in [[Allahabad]], the [[Lucknow]] Bench of [[Allahabad High Court]], district courts namely the ''District court of Etawah'', the district court of Kanpur Dehat and district courts in each districts as ''Uttar Pradesh Judiciary'', session courts in each district or Sessions Division, lower courts and judges at the taluka level.<ref name=courts/> The [[President of India]] appoints the chief justice of the High Court of the Uttar Pradesh judiciary on the advice of the chief justice of the [[Supreme Court of India]] as well as the Governor of Uttar Pradesh.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> Other judges are appointed by the chief justice of the high court of the judiciary of Uttar Pradesh on the advice of the Chief Justice.<ref name=courts>{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh judiciary|url=http://www.mapsofindia.com/uttar-pradesh/local-government/judiciary.html|publisher=Maps of India|accessdate=19 September 2012}}</ref><ref name=Constitution>{{cite web|title=Constitutional setup|url=http://www.upgov.nic.in/upconstitution.aspx|publisher=[[Government of Uttar Pradesh]]|accessdate=19 September 2012}}</ref> ''Subordinate Judicial Service'' is another vital part of the judiciary of Uttar Pradesh. The subordinate judiciary or the district courts are categorized into two divisions viz. Uttar Pradesh civil judicial services and Uttar Pradesh higher judicial service.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> While the Uttar Pradesh civil judicial services comprises the Civil Judges (Junior Division)/Judicial Magistraes and civil judges (Senior Division)/Chief Judicial Magistrate, the Uttar Pradesh higher judicial service comprises civil and sessions judges. The Subordinate judicial service of the judiciary at Uttar Pradesh is controlled by the District Judge.<ref name="BhargavaBhatt2005"/> The district court of Etawah and district court of Kanpur Dehat of Uttar Pradesh serves as the subordinate judicial service of the state.<ref name="Civil Judiciary">{{cite web|title=Subordinate Civil Judiciary in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://www.allahabadhighcourt.in/event/TheHistoryRoleSubordinateJudiciaryBBPrasad.pdf|publisher=[[Allahabad High Court]]|accessdate=19 September 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Allahabad high court.jpg|right|thumb|alt=refer caption|Allahabad High Court]] |
|||
The judiciary in the state consists of the [[Allahabad High Court]] in [[Prayagraj]], the [[Lucknow]] Bench of [[Allahabad High Court]], district courts and session courts in each district or Sessions Division, and lower courts at the [[tehsil]] level.<ref name=":2" /><ref name="courts">{{cite web|url=http://www.mapsofindia.com/uttar-pradesh/local-government/judiciary.html|title=Uttar Pradesh judiciary|publisher=Maps of India|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120904072538/http://www.mapsofindia.com/uttar-pradesh/local-government/judiciary.html|archive-date=4 September 2012|url-status=dead|access-date=19 September 2012}}</ref> The president of India appoints the chief justice of the High Court of the Uttar Pradesh judiciary on the advice of the [[Chief Justice of India|Chief Justice]] of the [[Supreme Court of India]] as well as the governor of Uttar Pradesh.<ref name=":2" /><ref name="Appointment">{{cite web |title=The Uttar Pradesh Judicial Service Rules, 2001 |url=http://www.allahabadhighcourt.in/rules/TheUttarPradeshJudicialServiceRules2001.pdf |publisher=Allahabad High Court |access-date=19 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191024015107/http://allahabadhighcourt.in/rules/TheUttarPradeshJudicialServiceRules2001.pdf |archive-date=24 October 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> Subordinate Judicial Service, categorised into two divisions viz. Uttar Pradesh civil judicial services and Uttar Pradesh higher judicial service are another vital part of the judiciary of Uttar Pradesh.<ref name=":2"/><ref name="presiding" /> While the Uttar Pradesh civil judicial services comprise the Civil Judges (Junior Division)/Judicial Magistrates and civil judges (Senior Division)/Chief Judicial Magistrate, the Uttar Pradesh higher judicial service comprises civil and sessions judges.<ref name=":2" /> The Subordinate judicial service (viz. The district court of [[Etawah]] and the district court of Kanpur Dehat) of the judiciary at Uttar Pradesh is controlled by the District Judge.<ref name=":2" /><ref name="presiding"><!--?REPEAT1?-->{{cite web |last1=Bind |first1=Basini Prasad |title=The History and Role of Subordinate Civil Judiciary in Uttar Pradesh |url=http://www.allahabadhighcourt.in/event/TheHistoryRoleSubordinateJudiciaryBBPrasad.pdf |publisher=Allahabad High Court |access-date=19 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130508214410/http://www.allahabadhighcourt.in/event/TheHistoryRoleSubordinateJudiciaryBBPrasad.pdf |archive-date=8 May 2013 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Civil Judiciary"><!--?REPEAT2?-->{{cite web |url=http://www.allahabadhighcourt.in/event/TheHistoryRoleSubordinateJudiciaryBBPrasad.pdf |title=Subordinate Civil Judiciary in Uttar Pradesh |publisher=[[Allahabad High Court]]|access-date=19 September 2012|url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130508214410/http://www.allahabadhighcourt.in/event/TheHistoryRoleSubordinateJudiciaryBBPrasad.pdf |archive-date=8 May 2013}}</ref> |
|||
Politics in Uttar Pradesh has been dominated by four political parties – the [[Samajwadi Party]], the [[Bahujan Samaj Party]], the [[Bharatiya Janata Party]], and the [[Indian National Congress]]. The political landscape of the state is often characterized by intense competition and [[Political polarization|polarization]], leading to [[Caste-related violence in India|caste-based tensions]] and [[Communal violence|communal conflicts]].<ref name="State Tensions">{{cite news |last1=Salam |first1=Ziya Us |title=Casteism and social apartheid the norm in Uttar Pradesh |url=https://frontline.thehindu.com/cover-story/social-apartheid-is-the-norm/article32882917.ece |access-date=1 November 2024 |work=The Frontline |agency=The Hindu |date=20 October 2020}}</ref> Critics often suggest that despite Uttar Pradesh's significant political legacy of producing eight [[Prime Minister of India|Prime Ministers]], the state continues to struggle with issues that hinder its overall advancement.<ref name="politically crucial state">{{cite web|title=UP: the nerve center of politics|url=http://zeenews.india.com/state-elections-2012/up/issues.html|publisher=[[Zee news]]|access-date=22 July 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120524062808/http://zeenews.india.com/state-elections-2012/up/issues.html|archive-date=24 May 2012}}</ref> |
|||
==Crime== |
|||
According to the [[National Crime Records Bureau]], Uttar Pradesh has the highest number of crimes among any state in India, but due to its high population, the actual per capita crime rate is low.<ref>{{cite web|author=Pervez Iqbal Siddiqui|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-10-30/lucknow/30338628_1_crime-incidents-population-kidnapping-and-abduction-cases |title=UP tops in crime, low on 'criminality'|work=Times of India |date=30 October 2011 |accessdate=14 September 2013}}</ref> Because of this, the NCRB states that UP is the third safest state in the country to live in. The value of human development index in Uttar Pradesh has steadily increased over time.<ref name=HDI>{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh Human Development Report|url=http://hdr.undp.org/en/reports/national/asiathepacific/india/name,20179,en.html|publisher=Uttar Pradesh Human Development|accessdate=18 June 2007}}</ref><ref name=growth>{{cite news|title=Impressive growth in UP|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-10-22/india/30310270_1_poor-states-bjp-ruled-states-social-inclusion|publisher=[[Times of India]]|accessdate= 22 October 2011|date=22 October 2011}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has the second largest [[Indian Police Service|Civil police]] force with 107,840 members, accounting for 9.5% of the total civil police in the country.<ref name="armed force">{{cite web|last=Shafi|first=Alam|title=The strength of Armed Police in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://ncrb.nic.in/CII2010/cii-2010/Chapter%2017.pdf|publisher=[[National Crime Records Bureau]]|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref><ref name=Highlight>{{cite web|title=Highlight of criminal statistics|url=http://mospi.nic.in/Mospi_New/upload/statistical_year_book_2011/SECTOR-6-MISCELLANEOUS%20SECTOR/CH-37-CRIME%20STATISTICS/CRIME%20STATISTICS-WRITEUP.pdf|publisher=Ministry of statics and progra implementation|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
=== |
=== Crime and accidents === |
||
According to the [[National Human Rights Commission of India]] (NHRC), Uttar Pradesh tops the list of states of [[Encounter killings by police|encounter killings]] and custodial deaths.<ref name="Express">{{cite news |last1=Sarda |first1=Kanu |title=In Custody: Six died daily in four months |url=https://www.newindianexpress.com/thesundaystandard/2018/aug/19/in-custody-six-died-daily-in-four-months-1859555.html |access-date=7 June 2020 |work=The New Indian Express |agency=Express Publications (Madurai) Limited D |date=19 August 2018 |archive-date=7 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200607174117/https://www.newindianexpress.com/thesundaystandard/2018/aug/19/in-custody-six-died-daily-in-four-months-1859555.html |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2014, the state recorded 365 judicial deaths out of a total 1,530 deaths recorded in the country.<ref name="deaths">{{cite news |last1=Sandhu |first1=Kamaljit Kaur |title=More bad news for Yogi Adityanath as data show UP tops crime chart |url=https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/more-bad-news-for-yogi-adityanath-as-data-show-up-tops-crime-chart-1189660-2018-03-14 |access-date=20 May 2020 |work=India Today |agency=Living Media India Limited |date=14 May 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190828232341/https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/more-bad-news-for-yogi-adityanath-as-data-show-up-tops-crime-chart-1189660-2018-03-14 |archive-date=28 August 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> NHRC further said, of the over 30,000 murders registered in the country in 2016, Uttar Pradesh had 4,889 cases.<ref name="NHRC">{{cite news |last1=Rao |first1=Phalguni |title=NHRC registered 1,782 fake encounter cases between 2000–2017; Uttar Pradesh alone accounts for 44.55% |url=https://www.firstpost.com/india/nhrc-registered-1782-fake-encounter-cases-between-2000-2017-uttar-pradesh-alone-accounts-for-44-55-4332125.html |access-date=7 June 2020 |work=Firstpost |agency=Network 18 |archive-date=7 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200607175917/https://www.firstpost.com/india/nhrc-registered-1782-fake-encounter-cases-between-2000-2017-uttar-pradesh-alone-accounts-for-44-55-4332125.html |url-status=live }}</ref> A data from [[Minister of Home Affairs (India)|Minister of Home Affairs]] (MHA) avers, [[Bareilly]] recorded the highest number of custodial death at 25, followed by [[Agra]] (21), [[Allahabad]] (19) and [[Varanasi]] (9). [[National Crime Records Bureau]] (NCRB) data from 2011 says, the state has the highest number of crimes among any state in India, but due to its [[Population density|high population]], the actual per capita crime rate is low.<ref>{{cite web|author=Pervez Iqbal Siddiqui|url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/lucknow/UP-tops-in-crime-low-on-criminality/articleshow/10537316.cms|title=UP tops in crime, low on 'criminality'|date=30 October 2011|access-date=14 September 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131226121729/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-10-30/lucknow/30338628_1_crime-incidents-population-kidnapping-and-abduction-cases|archive-date=26 December 2013|work=[[The Times of India]]|url-status=live}}</ref> The state also continues to top the list of states with maximum [[Religious violence in India|communal violence]] incidents. An analysis of Ministers of State of Home Affairs states (2014), 23 per cent of all incidents of communal violence in India took place in the state.<ref name="rise violence">{{cite news |title=Uttar Pradesh tops the list of communal violence hit states in 2017: Govt |url=https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/uttar-pradesh-tops-the-list-of-communal-violence-hit-states-in-2017-govt/articleshow/63300833.cms?from=mdr |access-date=20 May 2020 |work=The Economic Times |agency=Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. |date=14 March 2018 |archive-date=25 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210225120204/https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/uttar-pradesh-tops-the-list-of-communal-violence-hit-states-in-2017-govt/articleshow/63300833.cms?from=mdr |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="violence raise">{{cite news |last1=Sharma |first1=Neeta |title=Communal Violence Goes Up In Country, Uttar Pradesh Still Tops List |url=https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/communal-violence-goes-up-in-country-uttar-pradesh-still-tops-list-1823917 |access-date=20 May 2020 |publisher=NDTV |agency=New Delhi Television Limited |date=14 March 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190812005415/https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/communal-violence-goes-up-in-country-uttar-pradesh-still-tops-list-1823917 |archive-date=12 August 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> According to a research assembled by [[State Bank of India]], Uttar Pradesh failed to improve its [[Human Development Index]] (HDI) ranking over a period of 27 years (1990–2017).<ref name="SBI">{{cite web |title= Human Development Index Across Indian States: Is the Glass Still Half Empty? |url=https://sbi.co.in/documents/13958/14472/Ecowrap_20190308.pdf |publisher=State Bank of India |access-date=20 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200406004223/https://sbi.co.in/documents/13958/14472/Ecowrap_20190308.pdf |archive-date=6 April 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> Based on sub-national human development index data for [[List of Indian states and union territories by Human Development Index|Indian states]] from 1990 to 2017, the report also stated that the value of human development index has steadily increased over time from 0.39 in 1990 to 0.59 in 2017.<ref name="Index">{{cite news |last1=Chauhan |first1=Saurabh |title=UP fails to improve human development index ranking in 27 years |url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/lucknow/up-fails-to-improve-human-development-index-ranking-in-27-years/story-RJM0f3tD9hiQ3mAE62VVaL.html |access-date=20 May 2020 |work=Hindustan Times |agency=HT Media Ltd |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200126140936/https://www.hindustantimes.com/lucknow/up-fails-to-improve-human-development-index-ranking-in-27-years/story-RJM0f3tD9hiQ3mAE62VVaL.html |archive-date=26 January 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="HDI">{{cite web|url=http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/india_uttar_pradesh_2007.pdf|title=Uttar Pradesh Human Development Report|date=December 2008|website=[[United Nations Development Programme]]|access-date=13 September 2017|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170709020534/http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/india_uttar_pradesh_2007.pdf|archive-date=9 July 2017}}</ref><ref name="growth">{{cite news|url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/India-Human-Development-Report-raps-Gujarat-praises-UP-and-Bihar/articleshow/10446060.cms|title=India Human Development Report report raps Gujarat, praises UP and Bihar|date=22 October 2011|work=[[The Times of India]]|access-date=13 September 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131226114722/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-10-22/india/30310270_1_poor-states-bjp-ruled-states-social-inclusion|archive-date=26 December 2013|url-status=live}}</ref> The [[Uttar Pradesh Police]], governed by the [[Department of Home and Confidential]], is the largest [[police]] force in the world.<ref name="armed force">{{cite web|last=Shafi |first=Alam |title=The strength of Armed Police in Uttar Pradesh |url=http://ncrb.nic.in/CII2010/cii-2010/Chapter%2017.pdf |publisher=[[National Crime Records Bureau]] |access-date=23 July 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111110085726/http://ncrb.nic.in/CII2010/cii-2010/Chapter%2017.pdf |archive-date=10 November 2011}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://uppolice.gov.in/pages/en/topmenu/about-us/en-general-information|title=General Information|website=Uttar Pradesh Police|access-date=6 September 2017|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170906042425/https://uppolice.gov.in/pages/en/topmenu/about-us/en-general-information|archive-date=6 September 2017}}</ref><ref name=Highlight>{{cite web|title=Highlight of criminal statistics|url=http://mospi.nic.in/Mospi_New/upload/statistical_year_book_2011/SECTOR-6-MISCELLANEOUS%20SECTOR/CH-37-CRIME%20STATISTICS/CRIME%20STATISTICS-WRITEUP.pdf|publisher=Ministry of statistics and program implementation|access-date=22 July 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121120103625/http://mospi.nic.in/Mospi_New/upload/statistical_year_book_2011/SECTOR-6-MISCELLANEOUS%20SECTOR/CH-37-CRIME%20STATISTICS/CRIME%20STATISTICS-WRITEUP.pdf|archive-date=20 November 2012}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|2006 Varanasi bombings|2007 Uttar Pradesh bombings|2010 Varanasi bombing}} |
|||
[[File:Dashashwamedha ghat on the Ganga, Varanasi.jpg|thumb|alt=ghat on the edge of Gnaga river|Ghat on the Ganges, where the 2010 Varanasi bombing occurred]] |
|||
Since 2006, there have been a number of terrorist attacks, including explosions in a landmark holy place, a court and a temple. The [[2006 Varanasi bombings]] were a series of bombings that occurred across the [[Hinduism|Hindu]] holy city of [[Varanasi]] on 7 March 2006. At least 28 people were killed and as many as 101 others were injured.<ref name=bomb09>{{cite news|title=A powerful bomb placed in|url=http://zeenews.india.com/news/uttar-pradesh/delhi-blast-raid-at-huji-militant-s-house-in-up_730458.html|accessdate=20 July 2012|publisher=[[Zee news]]|date=20 July 2012}}</ref> The blasts occurred simultaneously shortly after 18:00 IST. The first blast took place at 18:20 in the crowded [[Sankat Mochan Hanuman Temple (Varanasi)|Sankat Mochan Hanuman Temple]] near the [[Banaras Hindu University]].<ref name=bombing>{{cite web|title=Sankat Mochan Hanuman temple blast|url=http://in.rediff.com/news/2006/mar/07up.htm|publisher='[[Rediff.com]]|accessdate=14 July 2012}}</ref><ref name=bombing>{{cite web|title=A Recall of the 2006 Blasts in Varanasi on March 7|url=http://www.southasiaanalysis.org/%5Cpapers43%5Cpaper4216.html|publisher=South Asia analysis|accessdate=7 December 2010}}</ref> Other blasts followed at the [[Varanasi Cantonment Railway Station]] near the waiting area next to the travel office. Initially, another blast was reported inside the stationary Shivganga Express bound for [[Delhi]].<ref name=autogenerated2>{{cite web|title=Varanasi railway station blast|url=http://in.rediff.com/news/2006/mar/07up.htm|publisher=[[Rediff.com]]|accessdate=14 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Uttar Pradesh also reported the highest number of deaths – 41,746 – due to road accidents till December 2022, according to "Road Accidents in India" report of [[Ministry of Road Transport and Highways|Union Ministry of Road Transport and Highways]].<ref name="Road Deaths">{{cite news |title=UP sees 6.5% rise in road accidents, 4% in fatalities this yr, says govt data |url=https://indianexpress.com/article/india/up-road-accidents-up-6-5-this-yr-fatalities-rise-4-9051922/#:~:text=The%20report%20shows%20that%20a,injured%20and%2021%2C227%20people%20died. |access-date=1 November 2024 |work=Express News Service |agency=The Indian Express |date=3 December 2023}}</ref><ref name="Highest">{{cite news |last1=Chauhan |first1=Arvind |title=At 23,219, UP reports highest number of road, rail accident |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/agra/at-23219-up-reports-highest-number-of-road-rail-accident-deaths/articleshow/56394327.cms |access-date=7 June 2020 |work=The Times of India |agency=The Times Group |publisher=Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. |date=7 January 2017 |archive-date=18 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200618182651/https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/agra/at-23219-up-reports-highest-number-of-road-rail-accident-deaths/articleshow/56394327.cms |url-status=live }}</ref> The [[Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation|UP Transport Department]] report also indicates that the primary cause of road accident fatalities was over-speeding, which accounted for 40 per cent of deaths. Drunken driving contributed to 10 per cent of fatalities, while 12 per cent of deaths were due to driving on the wrong side. Additionally, 10 per cent of accident deaths were caused by the use of mobile phones, and 5 per cent resulted from running red lights. The remaining 23 per cent of deaths were attributed to factors such as losing control of the vehicle, drowsiness, poor road visibility, and engineering defects.<ref>{{cite news|title=An accident reported every two hours in UP: Fatal accidents in the state|url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/lucknow/an-accident-reported-every-two-hours-in-up-fatal-accidents-in-the-state/story-qfPeclssrDuZGulc7ETNUJ.html|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170505113620/http://www.hindustantimes.com/lucknow/an-accident-reported-every-two-hours-in-up-fatal-accidents-in-the-state/story-qfPeclssrDuZGulc7ETNUJ.html|archive-date=5 May 2017}}</ref> |
|||
In the afternoon of 23 November 2007, within a span of 25 minutes, six consecutive serial blasts occurred in the Lucknow, Varanasi, and Faizabad courts, in which 28 people were killed and several others injured.<ref name=RDX>{{cite news|title=Uttar Pradesh blasts, RDX use confirmed|url=http://news.webindia123.com/news/Articles/India/20071125/832278.html|accessdate=4 August 2012|publisher=Web India|date=25 November 2007}}</ref> The blasts came a week after the Uttar Pradesh police and central security agencies busted [[Jaish-e-Mohammed]] terrorists who had planned to abduct [[Rahul Gandhi]]. The [[Indian Mujahidin]] has claimed responsibility of these blasts in an email sent to TV stations five minutes before the blast.<ref name="blast responsible">{{cite news|title=Varanasi blast|url=http://www.ndtv.com/article/india/varanasi-blast-18-month-old-killed-25-injured-71186|accessdate=15 July 2012|publisher=[[NDTV]]|date=7 December 2010}}</ref><ref name="2007 bombing">{{cite news|last=Swami|first=Praveen|title=Uttar Pradesh bombings mark new phase|url=http://www.hindu.com/2007/11/25/stories/2007112555861000.htm|accessdate=20 July 2012|work=[[The Hindu]]|date= 25 November 2007}}</ref> The first blast occurred in the premises of the Varanasi [[civil court]] and collectorate between 13:05 and 13:07. Two successive blasts occurred in the Faizabad district court around 13:12 and 13:15, closely followed by one at Lucknow at 13:32. Bombs were explicitly targeted at the lawyers who were working in the courts.<ref name=bombings>{{cite news|last=Swami|first=Praveen|title=Wiretap warning on Uttar Pradesh bombings went in vain|url=http://hindu.com/2007/12/26/stories/2007122653691200.htm|accessdate=20 July 2012|work=[[The Hindu]]|date=26 December 2007}}</ref> |
|||
Between 2006 and 2010, the state has been hit with three terrorist attacks, including explosions in a landmark holy place, a court and a temple. The [[2006 Varanasi bombings]] were a series of bombings that occurred across the [[Hinduism|Hindu]] holy city of [[Varanasi]] on 7 March 2006. At least 28 people were killed and as many as 101 others were injured.<ref name=bomb09>{{cite news|title=A powerful bomb placed in|url=http://zeenews.india.com/news/uttar-pradesh/delhi-blast-raid-at-huji-militant-s-house-in-up_730458.html|access-date=20 July 2012|publisher=[[Zee news]]|date=20 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120129235043/http://zeenews.india.com/news/uttar-pradesh/delhi-blast-raid-at-huji-militant-s-house-in-up_730458.html|archive-date=29 January 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Sankat Mochan Hanuman temple blast|url=http://in.rediff.com/news/2006/mar/07up.htm|work='[[Rediff.com]]|access-date=14 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160809032928/http://in.rediff.com/news/2006/mar/07up.htm|archive-date=9 August 2016}}</ref> In the afternoon of 23 November 2007, within a span of 25 minutes, six consecutive [[2007 Uttar Pradesh bombings|serial blasts]] occurred in the Lucknow, Varanasi, and Faizabad courts, in which 28 people were killed.<ref name="blast responsible">{{cite news|title=Varanasi blast|url=http://www.ndtv.com/article/india/varanasi-blast-18-month-old-killed-25-injured-71186|access-date=15 July 2012|publisher=[[NDTV]]|date=7 December 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121212033140/http://www.ndtv.com/article/india/varanasi-blast-18-month-old-killed-25-injured-71186|archive-date=12 December 2012}}</ref><ref name="2007 bombing">{{cite news|last=Swami|first=Praveen|title=Uttar Pradesh bombings mark new phase|url=http://www.hindu.com/2007/11/25/stories/2007112555861000.htm|access-date=20 July 2012|work=[[The Hindu]]|date=25 November 2007|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120126061742/http://www.hindu.com/2007/11/25/stories/2007112555861000.htm|archive-date=26 January 2012}}</ref><ref name=bombings>{{cite news|last=Swami|first=Praveen|title=Wiretap warning on Uttar Pradesh bombings went in vain|url=http://hindu.com/2007/12/26/stories/2007122653691200.htm|access-date=20 July 2012|work=[[The Hindu]]|date=26 December 2007|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080304213229/http://www.hindu.com/2007/12/26/stories/2007122653691200.htm|archive-date=4 March 2008}}</ref> Another blast occurred on 7 December 2010, the [[2010 Varanasi bombing|blast]] occurred at Sheetla Ghat in Varanasi in which more than 38 people were killed.<ref name="people killed">{{cite news|title=Massive terror attacks|url=http://www.thesundayindian.com/en/story/massive-terror-attacks-in-india-in-the-last-20-years/14/26333/|access-date=20 July 2012|publisher=The Sunday Indian|date=25 November 2011|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130606090350/http://www.thesundayindian.com/en/story/massive-terror-attacks-in-india-in-the-last-20-years/14/26333/|archive-date=6 June 2013}}</ref><ref name="terror attack">{{cite web|title=Chronology of recent terror attacks|url=http://in.news.yahoo.com/chronology-recent-terror-attacks-india-153913362.html|publisher=[[Yahoo]]|access-date=13 July 2011|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110717155321/http://in.news.yahoo.com/chronology-recent-terror-attacks-india-153913362.html|archive-date=17 July 2011}}</ref> In February 2016, a series of bomb blasts occurred at the Jhakarkati Bus Station in [[Kanpur]], killing 2 people and injuring more than 30.<ref name="Kanpur16">{{cite news |title=Freak blast sets panic alarm ringing |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/kanpur/freak-blast-sets-panic-alarm-ringing/articleshow/4230409.cms |access-date=2 May 2023 |work=The Times of India |agency=The Times Group |publisher=Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. |date=5 March 2009 |archive-date=2 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230502183426/https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/kanpur/freak-blast-sets-panic-alarm-ringing/articleshow/4230409.cms |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
On 7 December 2010, another [[2010 Varanasi bombing|blast]] occurred at Sheetla Ghat, adjacent to the main [[Dashashwamedh Ghat]], in which more than 38 people were killed and several others injured.<ref name="people killed">{{cite news|title=Massive terror attacks|url=http://www.thesundayindian.com/en/story/massive-terror-attacks-in-india-in-the-last-20-years/14/26333/|accessdate=20 July 2012|publisher=The Sunday Indian|date=25 November 2011}}</ref> The blast came a day after the anniversary of the 1992 [[Babri Masjid demolition]], in which a mosque was demolished at [[Ayodhya]] leading to nationwide religious riots that killed over 2,000 people.<ref name="terror attack">{{cite web|title=Chronology of recent terror attacks|url=http://in.news.yahoo.com/chronology-recent-terror-attacks-india-153913362.html|publisher=[[Yahoo]]|accessdate=13 July 2011}}</ref> |
|||
==Economy== |
== Economy == |
||
{{Main|Economy of Uttar Pradesh}} |
{{Main|Economy of Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
{{See also|List of |
{{See also|List of urban agglomerations in Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="float:right; width:260px; margin:0 0 1em 1em; background:#f4f5f6; border:#c6c7c8 solid; font-size:90%" |
|||
[[File:A Busy road in Main Market.JPG|thumb|left|alt=refer to caption|Roadside vendors in a town. A large proportion of residents are employed in the informal sector.]] |
|||
| colspan=2 style="background:#c2d6e5; text-align:center"| '''Net State Domestic Product at Factor Cost at Current Prices (2011–12 Base)''' |
|||
{| class="wikitable" cellspacing="1" style="float:right; width:260px; margin:0 0 1em 1em; background:#f4f5f6; border:#c6c7c8 solid; font-size:90%;" |
|||
| colspan="2" style="background:#c2d6e5; text-align:center;"| '''Net State Domestic Product at Factor Cost at Current Prices (2004–05 Base)<ref name=rbinsdpstat>{{cite web |
|||
| url = http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/PublicationsView.aspx?id=13592| title = Net state domestic product at factor cost—state-wise (at current prices) |date=15 September 2011 |
|||
| accessdate =7 February 2012|work=Handbook of statistics on Indian economy| publisher = [[Reserve Bank of India]] |
|||
}}</ref>''' |
|||
figures in [[crore]]s of [[Indian rupee |
figures in [[crore]]s of [[Indian rupee]]s |
||
|- |
|||
! Year || Net State Domestic Product |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! Year || Net State Domestic Product<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://updes.up.nic.in/STATE%20ACC%20STATISTICS/State%20Domestic%20Product/GSDP%20at%20current%202014-15.pdf|title=Gross State Domestic Product by Economic Activity (crore Rs) Uttar Pradesh|website=Directorate of Economics and Statistics, [[Government of Uttar Pradesh]]|access-date=11 January 2018|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180112042957/http://updes.up.nic.in/STATE%20ACC%20STATISTICS/State%20Domestic%20Product/GSDP%20at%20current%202014-15.pdf|archive-date=12 January 2018}}</ref> |
|||
| 2004–2005 || 229,074 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 2011–12 || 532,218 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 2015–16 || 1,137,808 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 2016–17 || 1,288,700 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|2017–18 |
|||
| 2008–2009 || 384,718 |
|||
|1,446,000<ref name=":0">{{cite web|url=http://www.prsindia.org/uploads/media/State%20Budget%202018-19/Uttar%20Pradesh%20Budget%20Analysis%202018-19.pdf|title=Uttar Pradesh Budget Analysis 2018–19|last=Khullar|first=Vatsal|date=20 February 2018|website=[[PRS Legislative Research]]|access-date=28 March 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180221100915/http://www.prsindia.org/uploads/media/State%20Budget%202018-19/Uttar%20Pradesh%20Budget%20Analysis%202018-19.pdf|archive-date=21 February 2018|url-status=dead}}</ref> {{Small|(est.)}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| 2009–2010 || 453,020 |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
[[File:Common Indian Sunflower.jpg|left|thumb|alt=Common sunflower farming in [[Lambhua]], Sultanpur|Sown saplings of [[common sunflower]]s; located in the rich fertile [[Indo-Gangetic Plain]], agriculture is the largest employment generator in the state.]] |
|||
In terms of [[Net domestic product|net state domestic product]] (NSDP), Uttar Pradesh holds the third largest economy (2011–2012) in India, with an NSDP of {{INRConvert|7080|b}}.<ref name="Financial Year 2011">{{cite web|title=The Federal States of India|url=http://unidow.com/india%20home%20eng/statewise_gdp.html|publisher=The VMW Analytic Services|accessdate=1 August 2012}}</ref><ref name="Planning Commission Government of India">{{Cite journal|title=Current NSDP status of state|url=http://planningcommission.nic.in/data/datatable/0904/tab_104.pdf|publisher=Planning Commission Government of India|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> Agriculture is the leading occupation in Uttar Pradesh.<ref name=resources>{{cite web|title=The state profile|url=http://www.phdcci.in/admin/userfiles/file/Research-Bureau/Uttar-Pradesh.pdf|publisher=PHD Chember|accessdate=20 September 2012}}</ref> Wheat is the state's principal food crop and [[sugarcane]] is the main commercial crop.<ref name=Policy/> About 70% of India's sugar comes from Uttar Pradesh. State industries are localised in the Kanpur region, the fertile [[purvanchal]] lands and the Noida region. The [[Mughalsarai]] is home to a number of major [[locomotive]] plants. Major manufacturing products include engineering products, electronics, electrical equipment, cables, steel, leather, textiles, jewellery, frigates, automobiles, railway coaches, and wagons. More [[Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises|small-scale industrial units]] are situated in Uttar Pradesh than in any other state, with 12 percent of over 2.3 million units.<ref name=resources/> With 359 manufacturing clusters cement is top sector of [[Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises|SMEs]] in UP.<ref name="ET-20130620-SMEs">{{cite web | url=http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/emerging-businesses/sme-policy-trends/smes-employ-close-to-40-of-indias-workforce-but-contribute-only-17-to-gdp/articleshow/20496337.cms?curpg=2 | title=SMEs employ close to 40% of India's workforce, but contribute only 17% to GDP | work=The Economic TImes| date=9 Jun 2013<!--, 05.00AM IST -->| accessdate=20 June 2013 | author=Malini Goyal}}</ref> |
|||
In terms of [[Net domestic product|net state domestic product]] (NSDP), Uttar Pradesh is the [[List of Indian states and union territories by GDP|fourth-largest]] economy in India, with an estimated gross state domestic product of {{INRConvert|14.89|lc}},<ref name=":0"/> contributing 8.4% of India's gross domestic product.<ref name="RBI2023">{{cite web | title= TABLE 27: GROSS STATE DOMESTIC PRODUCT| url=https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/Publications/PDFs/27T_15112023E301A02422494F73BFAFD6CDD84EEEAE.PDF | access-date=12 April 2024}}</ref> According to the report generated by India Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF), in 2014–15, Uttar Pradesh has accounted for 19% share in the country's total food grain output.<ref name="IBEF2015">{{cite web |url=https://www.ibef.org/download/Uttar%20Pradesh-November-2015.pdf |title=Uttar Pradesh: A Rainbow Land |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |year=2015 |website=ibef.org |publisher=[[India Brand Equity Foundation]] |access-date=13 May 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180921230048/https://www.ibef.org/download/Uttar%20Pradesh-November-2015.pdf |archive-date=21 September 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> About 70% of India's sugar comes from Uttar Pradesh. Sugarcane is the most important cash crop as the state is country's largest producer of sugar.<ref name="IBEF2015" /> As per the report generated by Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA), total sugarcane production in India was estimated to be 28.3 million tonnes in the fiscal ending September 2015 which includes 10.47 million tonnes from Maharashtra and 7.35 million tonnes from Uttar Pradesh.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.indiansugar.com/NewsDetails.aspx?nid=4584|title=Indian sugar mills association|website=indiansugar.com|access-date=8 August 2016|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160826083928/http://www.indiansugar.com/NewsDetails.aspx?nid=4584|archive-date=26 August 2016}}</ref> |
|||
With 359 manufacturing clusters, cement is the top sector of [[Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises|SMEs]] in Uttar Pradesh.<ref name="ET-20130620-SMEs">{{cite web | url=http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/emerging-businesses/sme-policy-trends/smes-employ-close-to-40-of-indias-workforce-but-contribute-only-17-to-gdp/articleshow/20496337.cms?curpg=2 | title=SMEs employ close to 40% of India's workforce, but contribute only 17% to GDP | work=The Economic Times | date=9 June 2013| access-date=20 June 2013 | first=Malini | last=Goyal | url-status=live | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161231062949/http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/emerging-businesses/sme-policy-trends/smes-employ-close-to-40-of-indias-workforce-but-contribute-only-17-to-gdp/articleshow/20496337.cms?curpg=2 | archive-date=31 December 2016}}</ref> The Uttar Pradesh Financial Corporation (UPFC) was established in 1954 under the SFCs Act of 1951 mainly to develop small- and medium-scale industries in the state.<ref name="UPFC">{{cite web|title=Details of financing & limits of accommodation|url=http://www.ijest.info/docs/IJEST10-02-07-13.pdf|publisher=UPFC India|access-date=22 July 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120530154018/http://www.ijest.info/docs/IJEST10-02-07-13.pdf|archive-date=30 May 2012|url-status=live}}</ref> The UPFC also provides working capital to existing units with a soundtrack record and to new units under a single window scheme.<ref name="statements">{{cite web|title=A statement of the categories of documents that are held by the Corporation.|url=http://www.upfcindia.com/rti/manual-vi.pdf|publisher=Uttar Pradesh Financial Corporation|access-date=9 July 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121116014458/http://www.upfcindia.com/rti/manual-vi.pdf|archive-date=16 November 2012}}</ref> In July 2012, due to financial constraints and directions from the state government, lending activities were suspended except for State Government Schemes.<ref name="budget">{{cite web|title=The budget allocated to each of its agency|url=http://www.upfcindia.com/rti/manual-xi.pdf|publisher=UPFC India|access-date=22 July 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121116014535/http://www.upfcindia.com/rti/manual-xi.pdf|archive-date=16 November 2012}}</ref> The state has reported total private investment worth over Rs. 25,081 crores during the years of 2012 and 2016.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.business-standard.com/article/politics/private-investment-under-akhilesh-government-more-than-doubles-116032700361_1.html|title=Private investment under Akhilesh government more than doubles|last=Rawat|first=Virendra Singh|newspaper=Business Standard India|date=27 March 2016|access-date=8 August 2016|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160820114551/http://www.business-standard.com/article/politics/private-investment-under-akhilesh-government-more-than-doubles-116032700361_1.html|archive-date=20 August 2016}}</ref> According to a 2015 report by the World Bank on the [[Indian states ranking by ease of doing business|Ease of Doing Business in India]], Uttar Pradesh was ranked among the top 10 states and was the first among the northern states.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/slideshows/economy/world-bank-survey-indias-top-10-states-on-the-ease-of-doing-business-ranking/10-uttar-pradesh/slideshow/48970813.cms|title=10. Uttar Pradesh – World Bank Survey: India's top 10 states on the ease of doing business ranking – The Economic Times|access-date=8 August 2016|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160623140228/http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/slideshows/economy/world-bank-survey-indias-top-10-states-on-the-ease-of-doing-business-ranking/10-uttar-pradesh/slideshow/48970813.cms|archive-date=23 June 2016}}</ref> |
|||
According to the Uttar Pradesh Budget Documents (2019–20), Uttar Pradesh's debt burden is 29.8 per cent of the [[Gross domestic product|GSDP]].<ref name="Debt HT">{{cite news |last1=Raghuvanshi |first1=Umesh |title=Finance commission asks Uttar Pradesh to bring down its debt burden |url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/finance-commission-asks-up-to-bring-down-its-debt-burden/story-ySZwu16DTAU6bsnzfbEBHP.html |access-date=24 May 2020 |work=Hindustan Times |agency=HT Media Ltd |date=23 October 2019 |archive-date=18 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200518022214/https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/finance-commission-asks-up-to-bring-down-its-debt-burden/story-ySZwu16DTAU6bsnzfbEBHP.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The state's total financial debt stood at {{INRConvert|2.09|lc}} in 2011.<ref name="debt burden">{{cite news |date=14 June 2011 |title=State slipping into debt burden |newspaper=[[The Times of India]] |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/pune/state-slipping-into-debt-burden/articleshow/8840055.cms |url-status=live |access-date=14 June 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130506234001/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-06-14/pune/29656552_1_debt-burden-white-paper-finance-minister |archive-date=6 May 2013}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has not been able to witness double-digit economic growth despite consistent attempts over the years.<ref name="Debt HT" /> The GSDP is estimated to have grown 7 per cent in 2017–18 and 6.5 per cent in 2018–19 which is about 10 per cent of India's GDP. According to a survey conducted by the [[Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy]] (CMIE), Uttar Pradesh's [[unemployment rate]] increased 11.4 percentage points, rising to 21.5 per cent in April 2020.<ref name="Unemployment">{{cite news |title=Unemployment in Uttar Pradesh increased 11.4 pct points, rose to 21.5% in Apr 2020: CMIE Survey |url=https://www.livemint.com/news/india/unemployment-in-uttar-pradesh-increased-11-4-pct-points-rose-to-21-5-in-apr-2020-cmie-survey-11588316047392.html |access-date=5 June 2020 |work=[[Mint (newspaper)|Mint]] |agency=HT Media |date=1 May 2020 |archive-date=5 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200605165040/https://www.livemint.com/news/india/unemployment-in-uttar-pradesh-increased-11-4-pct-points-rose-to-21-5-in-apr-2020-cmie-survey-11588316047392.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has the largest number of [[Human migration|net migrants]] migrating out of the state.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Jha |first1=Abhishek |last2=Kawoosa |first2=Vijdan Mohammad |title=What the 2011 census data on migration tells us |url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/delhi-news/migration-from-up-bihar-disproportionately-high/story-K3WAio8TrrvBhd22VbAPLN.html |access-date=31 July 2020 |work=Hindustan Times |agency=HT Media |date=26 July 2019 |archive-date=14 August 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200814073603/https://www.hindustantimes.com/delhi-news/migration-from-up-bihar-disproportionately-high/story-K3WAio8TrrvBhd22VbAPLN.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The 2011 census data on migration shows that nearly 14.4 million (14.7%) people had migrated out of Uttar Pradesh.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Edwin |first1=Tina |title=Migrants seem to prefer neighbouring States for livelihood |url=https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/migrants-seem-to-prefer-neighbouring-states-for-livelihood/article28762755.ece |access-date=31 July 2020 |work=Business Line |agency=Kasturi and Sons Limited |publisher=The Hindu Group |date=30 July 2019 |archive-date=25 October 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201025025600/https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/migrants-seem-to-prefer-neighbouring-states-for-livelihood/article28762755.ece |url-status=live }}</ref> Marriage was cited as the predominant reason for migration among females. Among males, the most important reason for migration was work and employment.<ref name="Reasons">{{cite web |title=Census of India 2001 – Data Highlights |url=https://censusindia.gov.in/Data_Products/Data_Highlights/Data_Highlights_link/data_highlights_D1D2D3.pdf |publisher=Government of India |access-date=31 July 2020 |archive-date=1 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201101020548/https://censusindia.gov.in/Data_Products/Data_Highlights/Data_Highlights_link/data_highlights_D1D2D3.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Uttar Pradesh continues to have regional disparities, particularly with the western districts of the state showing higher development indicators such as per capita district development product (PCDDP) and gross district development product (GDDP) compared to other regions.<ref name="TOI_Regions">{{cite web | last=Singh | first=Mahendra | title=Eastern UP, not Bundelkhand, most backward: Govt data | website=The Times of India | date=21 October 2013 | url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/eastern-up-not-bundelkhand-most-backward-govt-data/articleshow/24453834.cms | access-date=10 July 2024}}</ref> Due to inadequate infrastructure and a dense population, [[Eastern Uttar Pradesh]] ([[Purvanchal]]) faces notable socio-economic disparities.<ref name="NG Journal">{{cite journal | last1=Tiwari | first1=Anil Kumar | last2=Pandey | first2=Ravindra K. | last3=Sharma | first3=Vishwambhar Nath | title=A study of disparities in the socio-economic development of eastern Uttar Pradesh, India | journal=National Geographical Journal of India | volume=67 | issue=4 | date=31 December 2021 | issn=0027-9374 | pages=438–446 | doi=10.48008/ngji.1789 | url=https://ngji.in/index.php/ngji/article/view/299#:~:text=Eastern%20Uttar%20Pradesh%2C%20an%20economically,disparity%20in%20socio%2Deconomic%20development. | access-date=10 July 2024}}</ref> For 2021–22 the GDDP for Purvanchal it is ₹5.37 lakh crore, while for [[Western Uttar Pradesh]] it is ₹9.44 lakh crore. For the [[Bundelkhand]] and [[Central Uttar Pradesh]] regions, the GDDP remained ₹99,029.34 crore and ₹3.36 lakh crore, respectively. As of 2021–22, the per capita annual income in eastern districts is about one-fourth of the national average at ₹12,741 while the state's average stood at ₹17,349.<ref name="HT Data">{{cite web | last=Raghuvanshi | first=Umesh | title=Regional disparities persist, west U.P. far ahead of east | website=Hindustan Times | date=7 September 2023 | url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/lucknow-news/uttar-pradesh-s-regional-disparities-western-districts-lead-in-development-indicators-eastern-districts-lag-behind-101694030468889.html | access-date=10 July 2024}}</ref> |
|||
In 2009–10, the [[tertiary sector of the economy]] (service industries) was the largest contributor to the gross domestic product of the state, contributing 44.8% of the state domestic product compared to 44% from the primary sector (agriculture, forestry, and tourism) and 11.2% from the secondary sector (industrial and manufacturing).<ref name=Investment>{{cite web|title=Investment climate of a state|url=http://www.ibef.org/download/Uttar_Pradesh_060710.pdf|publisher=IBEF organization|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref><ref name="Service sector">{{cite news|title=Service sector over the present crisis|url=http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2009-03-14/news/28471008_1_service-sector-gdp-growth-enterprises |work=[[The Economic Times]]|accessdate=14 March 2009|date=14 March 2009}}</ref> During the 11th five-year plan (2007–2012), the average [[Gross domestic product|gross state domestic product]] (GSDP) growth rate was 7.28%, lower than 15.5%, the average for all states of the country.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.moneycontrol.com/news/economy/only-5-states-exceed-11th-plan-growth-targets-govt_584266.html|title=Only 5 states exceed 11th Plan growth targets: Govt: Ruled by CNBC TV18 News|date=13 May 2011|work=[[CNBC]] TV18-MoneyControl Post}}</ref><ref name="State Finances">{{cite web|title=RBI releases Study on State Finances 2009-10|url=http://rbi.org.in/scripts/BS_PressReleaseDisplay.aspx?prid=22105|publisher=''[[Reserve Bank of India]]'' (RBI)|accessdate=22 February 2010}}</ref> The state’s per capita GSDP was {{INRConvert|29417}}, lower than the national per capita GSDP of {{INRConvert|60972}}.<ref name="Ministry of statistics and Program Implementation Govt. Of India">{{Cite journal|title=Ministry of statistics and Program Implementation|url=http://mospi.nic.in/Mospi_New/upload/State_wise_SDP_2004-05_14mar12.pdf|publisher=Ministry of statistics and Program Implementation Govt. Of India}}</ref> The state's total financial debt stood at {{INRConvert|2000|b}} in 2011.<ref name="debt burden">{{cite news|title=State slipping into debt burden|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-06-14/pune/29656552_1_debt-burden-white-paper-finance-minister|publisher=[[Times of India]]|accessdate=14 Jun 2011|date=14 June 2011}}</ref> Labour efficiency is higher at an index of 26 than the national average of 25. The economy also benefits from the state's tourism industry.<ref name="Small Scale Industries">{{cite web|title=Small scale industries and other small trades.|url=http://indiabudget.nic.in/ub2004-05(I)/eb/sbe84.pdf|publisher=Ministry of Small Scale Industries|accessdate=17 January 2008}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:IT Park, Noida, Uttar Pradesh (2011-06-18).jpg|thumb|alt=refer caption|[[Business park|IT Parks]] in Noida, which are known for their infrastructure and services, as well as high-end housing complexes.<ref name="IT parks">{{cite news|last1=IT park|first1=Infrastructure and|date=4 January 2016|title=Noida-Greater Noida's world class infrastructure to be highlighted in UP Pravasi Diwas|work=[[The Times of India]]|agency=Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd|url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/noida/Noida-Greater-Noidas-world-class-infrastructure-to-be-highlighted-in-UP-Pravasi-Diwas/articleshow/50433022.cms|url-status=live|access-date=2 April 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170131081352/http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/noida/Noida-Greater-Noidas-world-class-infrastructure-to-be-highlighted-in-UP-Pravasi-Diwas/articleshow/50433022.cms|archive-date=31 January 2017}}</ref>]] |
|||
In 2009–10, the [[tertiary sector of the economy]] (service industries) was the largest contributor to the gross domestic product of the state, contributing 44.8 per cent of the state domestic product compared to 44 per cent from the primary sector (agriculture, forestry, and tourism) and 11.2 per cent from the secondary sector (industrial and manufacturing).<ref name="Investment">{{cite web|title=Investment climate of a state|url=http://www.ibef.org/download/Uttar_Pradesh_060710.pdf|publisher=IBEF organization|access-date=22 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130510142802/http://www.ibef.org/download/Uttar_Pradesh_060710.pdf|archive-date=10 May 2013}}</ref><ref name="Service sector">{{cite news|title=Service sector over the present crisis|url=http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2009-03-14/news/28471008_1_service-sector-gdp-growth-enterprises|work=[[The Economic Times]]|access-date=14 March 2009|date=14 March 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130507005546/http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2009-03-14/news/28471008_1_service-sector-gdp-growth-enterprises|archive-date=7 May 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref> [[Noida]], [[Meerut]], and [[Agra]] rank as the top 3 districts with the highest per capita income, whereas [[Lucknow]] and [[Kanpur]] rank 7th and 9th in per capita income.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Statistical Diary of Uttar Pradesh |url=https://updes.up.nic.in/updes/data/sdiaryenglish/files/diary%20eng%202021_merged.pdf |access-date=2 October 2023 |archive-date=4 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231004145340/https://updes.up.nic.in/updes/data/sdiaryenglish/files/diary%20eng%202021_merged.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> During the 11th five-year plan (2007–2012), the average [[Gross domestic product|gross state domestic product]] (GSDP) growth rate was 7.3 per cent, lower than 15.5 per cent, the average for all states of the country.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.moneycontrol.com/news/economy/only-5-states-exceed-11th-plan-growth-targets-govt_584266.html|title=Only 5 states exceed 11th Plan growth targets: Govt: Ruled by CNBC TV18 News|date=13 May 2011|work=[[CNBC]] TV18-MoneyControl Post|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130605114827/http://www.moneycontrol.com/news/economy/only-5-states-exceed-11th-plan-growth-targets-govt_584266.html|archive-date=5 June 2013}}</ref><ref name="State Finances">{{cite web|title=RBI releases Study on State Finances 2009–10 |url=http://rbi.org.in/scripts/BS_PressReleaseDisplay.aspx?prid=22105 |publisher=[[Reserve Bank of India]] (RBI) |access-date=22 February 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100225162108/http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/BS_PressReleaseDisplay.aspx?prid=22105 |archive-date=25 February 2010}}</ref> The state's per capita GSDP was {{INRConvert|29417}}, lower than the national per capita GSDP of {{INRConvert|60972}}.<ref name="Ministry of statistics and Program Implementation Govt. Of India">{{Cite report|title=Ministry of statistics and Program Implementation |url=http://mospi.nic.in/Mospi_New/upload/State_wise_SDP_2004-05_14mar12.pdf |publisher=Ministry of statistics and Program Implementation Govt. Of India |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304023256/http://mospi.nic.in/Mospi_New/upload/State_wise_SDP_2004-05_14mar12.pdf |archive-date= 4 March 2016}}</ref> Labor efficiency is higher at an index of 26 than the national average of 25. Textiles and sugar refining, both long-standing industries in Uttar Pradesh, employ a significant proportion of the state's total factory labour. The economy also benefits from the state's tourism industry.<ref name="Small Scale Industries">{{cite web|title=Small scale industries and other small trades.|url=http://indiabudget.nic.in/ub2004-05(I)/eb/sbe84.pdf|publisher=Ministry of Small Scale Industries|access-date=17 January 2008|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090410141303/http://indiabudget.nic.in/ub2004-05(I)/eb/sbe84.pdf|archive-date=10 April 2009}}</ref> |
|||
== Transportation == |
|||
The state is attracting [[foreign direct investment]] which has mostly come in the software and electronics fields; Noida and Lucknow is becoming a major hub for the information technology (IT) industry. [[Sonebhadra]], a district in [[eastern Uttar Pradesh]], has large-scale industries. Its southern region is known as the "Energy Capital of India".<ref name=Introduction>{{cite web|title=Western part of the coalfield|url=http://ncl.gov.in/new/profile1.htm|publisher=Northern Coalfields Limited|accessdate=8 July 2008}}</ref> In May 2013 Uttar Pradesh had the largest number of mobile subscribers in the country, a total of 121.60 million mobile phone connections out of 861.66 million in India, according to the telecom regulator, Telecom Regulatory Authority of India [[TRAI]].<ref name="Mobile subscribers">{{cite web|last=Report by|first=TRAI|title=Monthly press release|url=http://www.trai.gov.in/WriteReadData/WhatsNew/Documents/Monthly_press_release_February_2013_16april2013.pdf|work=Telecom Regulatory Authority of India|publisher=[[TRAI]]|accessdate=23 May 2013}}</ref><ref name="Press Trust">{{cite news|last=Mobile subscriber|first=in UP|title=State with most cellphone users in India|url=http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/industry-and-economy/info-tech/up-tn-have-most-cellphone-users-in-india-trai/article4686660.ece|accessdate=23 May 2013|newspaper=The Hindu Business line}}</ref><ref name="Cell phone users">{{cite news|title=Most cell phone users state of India|url=http://www.indianexpress.com/news/up-has-most-cell-phone-users-in-india-trai/1111876/|accessdate=23 May 2013|newspaper=Indian Express|date=6 May 2013}}</ref><ref name=Subscribers>{{cite news|title=Uttar Pradesh top in mobile penetration|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2013-05-06/telecom/39064013_1_telecom-subscriber-base-connections-cell-phone|accessdate=23 May 2013|newspaper=The Times of India|date=6 May 2013}}</ref> |
|||
==Transportation== |
|||
{{Further|List of state highways in Uttar Pradesh|List of airports in Uttar Pradesh|Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation}} |
{{Further|List of state highways in Uttar Pradesh|List of airports in Uttar Pradesh|Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation}} |
||
[[File:Delhi Noida Direct flyway (Uttar Pradesh - 2011-06-18).jpg|left|thumb|A section of Delhi–Noida Direct Flyway]] |
|||
[[File:Terminal-2, Lucknow International airport.jpg|thumb|Terminal-2 at [[Amausi Airport|CCS International Airport]], [[Lucknow]]]] |
|||
The state has the largest railway network in the country but in relative terms has only sixth-highest railway density despite its plain topography and largest population. {{As of|2015}}, there were {{convert|9,077|km|mi|0|abbr=on}} of rail in the state.<ref name="route length">{{cite web|title=total railway route length uttar pradesh|url=http://lko.railnet.gov.in/|publisher=Northern Railways Lucknow Division|access-date=22 July 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120814075641/http://lko.railnet.gov.in/|archive-date=14 August 2012}}</ref><ref name="Network">{{cite web |title=The Network |url=https://indianrailways.gov.in/railwayboard/uploads/directorate/stat_econ/IRSP_2015-16/Year_Book_Eng/9.pdf |publisher=Ministry of Railways |access-date=28 June 2024}}</ref> The railway network in the state is controlled by two divisions of the [[Indian Railways]] viz. North Central Railway and North Eastern Railway. Allahabad is the headquarters of the [[North Central Railway zone|North Central Railway]]<ref name="North Central Railway">{{cite web|title=North Central Railway-The Allahabad Division|url=http://www.ncr.indianrailways.gov.in/view_section.jsp?lang=0&id=0,1,396,403|publisher=Indian Railways Portal CMS Team|access-date=22 February 2011|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140318062507/http://ncr.indianrailways.gov.in/view_section.jsp?lang=0&id=0,1,396,403|archive-date=18 March 2014}}</ref> and [[Gorakhpur]] is the headquarters of the [[North Eastern Railway zone|North Eastern Railway]].<ref name="North-Eastern Railways">{{cite web|title=the Portal of Indian Railways|url=http://www.ner.indianrailways.gov.in/|publisher=[[Indian Railways]]|access-date=14 April 2011|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110411221732/http://www.ner.indianrailways.gov.in/|archive-date=11 April 2011}}</ref><ref name="security system">{{cite news|title=Equipment arrives for integrated security system|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/North-Eastern-Railway|newspaper=[[The Times of India]]|access-date=22 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130514093655/http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/North-Eastern-Railway|archive-date=14 May 2013}}</ref> Lucknow and Moradabad serve as divisional Headquarters of the Northern Railway Division. [[Lucknow Swarna Shatabdi Express]], the second fastest [[Shatabdi Express]] train, connects the Indian capital of [[New Delhi railway station|New Delhi]] to [[Lucknow Charbagh railway station|Lucknow]] while [[Kanpur–New Delhi Shatabdi Express|Kanpur Shatabdi Express]], connects New Delhi to [[Kanpur Central railway station|Kanpur Central]]. This was the first train in India to get the new German [[LHB coaches]].<ref name="train">{{cite news|title=Lucknow New Delhi Shatabdi Express|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/Lucknow-New-Delhi-Shatabdi-Express|access-date=28 July 2012|work=[[The Times of India]]|date=2 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120926075420/http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/Lucknow-New-Delhi-Shatabdi-Express|archive-date=26 September 2012}}</ref> The railway stations of [[Prayagraj Junction]], [[Agra Cantonment]], Lucknow Charbagh, [[Gorakhpur Junction]], Kanpur Central, [[Mathura Junction]] and [[Varanasi Junction]] are included in the Indian Railways list of 50 world-class railway stations.<ref name="Railway Budget">{{cite web|title=Introducing the Railway Budget 2011–12|url=http://www.indianrailways.gov.in/railwayboard/uploads/directorate/finance_budget/RailBudget_11-12/RailBudget_2011-12.pdf|publisher=[[Indian Railways]]|access-date=22 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160512215003/http://www.indianrailways.gov.in/railwayboard/uploads/directorate/finance_budget/RailBudget_11-12/RailBudget_2011-12.pdf|archive-date=12 May 2016}}</ref> The [[Lucknow Metro]], along with the [[Kanpur Metro]] (Orange line), are rapid transit systems that serve Lucknow and Kanpur, respectively. |
|||
[[File:Lkoshat.jpg|thumb|alt="photograph"|[[Lucknow Swarna Shatabdi Express|Lucknow Shatabdi]] near New Delhi]] |
|||
The state has excellent [[civil aviation]] infrastructure with [[Chaudhary Charan Singh International Airport]] in Lucknow and [[Varanasi Airport|Lal Bahadur Shastri International Airport]] in Varanasi, providing international service.<ref name=Airports>{{cite web|title=contributing to economic growth and prosperity of the nation|url=http://www.aai.aero/allAirports/varanasi_generalinfo.jsp|publisher=Airports Authority of India|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> and four domestic airports located at Agra, Allahabad, Gorakhpur and Kanpur. The Lucknow Airport is the second busiest airport in North India after the [[Indira Gandhi International Airport]], New Delhi. The state has also proposed creating the [[Taj International Airport]] at Kurikupa near Hirangaon, [[Tundla]] in [[Firozabad district]].<ref>http://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/lucknow/up-to-seek-dgca-nod-for-taj-airport/article1-1080013.aspx</ref><ref>http://paper.hindustantimes.com/epaper/viewer.aspx</ref> An international Airport is also proposed at [[Kushinagar]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/kushinagar-international-airport-to-get-ready-for-take-off-113010700012_1.html|title=Kushinagar international airport to get ready for take-off|publisher=Virendra Singh Rawat|date= January 7, 2013}}</ref> |
|||
The state has a large, multimodal transportation system with the largest road network in the country.<ref name="ROAD NETWORK"><!--?REPEAT1?-->{{cite web |last=Investment Promotion & Infrastructure Development Cell |title=Road |url=http://dipp.nic.in/English/Investor/Investers_Gudlines/roads.pdf |publisher=Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion |access-date=7 January 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111014170737/http://dipp.nic.in/English/Investor/Investers_Gudlines/roads.pdf |archive-date=14 October 2011}}</ref> It has 42 national highways, with a total length of {{Convert|4942|km|abbr=in}} comprising 8.9 per cent of the total national highways length in India.<ref name="NH Share">{{cite web |title=Basic Road Statistics, 2018 - 19 |url=https://morth.nic.in/sites/default/files/Basic%20Road%20Statistics%20in%20India-2018-19.pdf |publisher=Ministry of Road Transport and Highways of India |access-date=28 June 2024}}</ref> The [[Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation]] (UPSRTC) was established in 1972 to provide transportation in the state with connecting services to adjoining states.<ref>{{cite web|title=Road network|url=http://www.ibef.org/download/uttar_pradesh_190111.pdf|publisher=India Brand Equity Foundation|access-date=22 July 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120907052302/http://www.ibef.org/download/uttar_pradesh_190111.pdf|archive-date=7 September 2012}}</ref> The UPSRTC’s current fleet consists of 11,238 buses operating on 2,762 routes across a total distance of {{cvt|768,065|km}} throughout the state, generating an average daily income of {{INRConvert|16|c|lk=|year=2023}}.<ref name="Fleet_Profite">{{cite news |title=UPSRTC to replace 45% of its existing fleet with e-buses |url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/lucknow-news/upsrtc-to-replace-45-of-its-existing-fleet-with-ebuses-101719244472805.html |access-date=24 August 2024 |work=[[Hindustan Times]] |date=Jun 24, 2024}}</ref> Despite its extensive operation, many of UPSRTC buses are now outdated and unreliable, raising concerns about their condition and the impact on passenger safety.<ref name="Fleets">{{cite news |last1=Dash |first1=Deepak |title=UPSRTC has set a new record by registering the highest profit among all state transport undertakings |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/up-creates-record-registering-highest-profit-among-all-state-transport-undertakings/articleshow/68586093.cms |access-date=24 August 2024 |work=Times of India |agency=The Times Group |date=March 26, 2019}}</ref> All cities are connected to [[State highways in India|state highways]], and all district headquarters are being connected with four lane roads which carry traffic between major centres within the state. One of them is [[Agra–Lucknow Expressway]], which is a {{Convert|302|km|abbr=in}} [[controlled-access highway]] constructed by [[Uttar Pradesh Expressways Industrial Development Authority|UPEIDA]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Welcome :: U.P. Expressways Industrial Development Authority|url=http://www.upeida.in/project_8.htm|website=upeida.in|access-date=26 July 2016|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160712131932/http://www.upeida.in/project_8.htm|archive-date=12 July 2016}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has the highest road density in India – {{Convert|1027|km|abbr=in}} per {{Convert|1000|km2|sqmi|abbr=in}} – and the largest surfaced urban-road network in the country – {{Convert|50721|km|abbr=in}}.<ref>{{cite web|title=Pervasive road network of Uttar Pradesh|url=http://planningcommission.nic.in/plans/stateplan/upsdr/vol-2/Chap_b8.pdf|publisher=Planning commission, Government of India|access-date=20 September 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121222090850/http://planningcommission.nic.in/plans/stateplan/upsdr/vol-2/Chap_b8.pdf|archive-date=22 December 2012}}</ref> |
|||
The state has the largest railway network in the country and the sixth highest railway density. As 0f 2011, there were {{convert|8546|km|mi|0|abbr=on}} of rail in the state.<ref name="route length">{{cite web|title=total railway route length uttar pradesh|url=http://lko.railnet.gov.in/|publisher=Northern Railways Lucknow Division|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> Allahabad is the headquarters of the [[North Central Railway Zone|North Central Railway]]<ref name="North Central Railway">{{cite web|title=North Central Railway-The Allahabad Division|url=http://www.ncr.indianrailways.gov.in/view_section.jsp?lang=0&id=0,1,396,403|publisher=Indian Railways Portal CMS Team|accessdate=22 February 2011}}</ref> and [[Gorakhpur]] is the headquarters of the [[North Eastern Railway Zone|North Eastern Railway]].<ref name="North-Eastern Railways">{{cite web|title=the Portal of Indian Railways|url=http://www.ner.indianrailways.gov.in/|publisher=[[Indian Railways]]|accessdate=14 April 2011}}</ref><ref name="security system">{{cite news|title=Equipment arrives for integrated security system|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/North-Eastern-Railway|publisher=[[Times of india]]|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> Other than Zonal Headquarters of Allahabad and Gorakhpur, Lucknow and Moradabad serve as divisional Headquarters of the Northern Railway Division. [[Lucknow Swarna Shatabdi Express]], the second fastest [[shatabdi]] train, connects the Indian capital of [[New Delhi Railway Station|New Delhi]] to [[Charbagh Railway Station|Lucknow]]. This was the first train in India to get the new German LHB coaches.<ref name=train>{{cite news|title=Lucknow New Delhi Shatabdi Express|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/Lucknow-New-Delhi-Shatabdi-Express|accessdate=28 July 2012|work=[[The Times of India]]|date=2 July 2012}}</ref> The railway stations of [[Charbagh Railway Station|Lucknow NR]], [[Kanpur Central]], [[Varanasi Junction]], [[Agra Cantt]], [[Gorakhpur]] and Mathura Junction were included in the Indian Railways list of 50 world-class railway stations.<ref name="Railway Budget">{{cite web|title=Introducing the Railway Budget 2011-12|url=http://www.indianrailways.gov.in/railwayboard/uploads/directorate/finance_budget/RailBudget_11-12/RailBudget_2011-12.pdf|publisher=[[Indian Railways]]|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
By passenger traffic in India, [[Chaudhary Charan Singh International Airport]] in Lucknow and [[Lal Bahadur Shastri Airport]] in Varanasi, are the major international airports and the main gateway to the state.<ref name="Airports">{{cite web |title=contributing to economic growth and prosperity of the nation |url=http://www.aai.aero/allAirports/varanasi_generalinfo.jsp |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120629091735/http://www.aai.aero/allAirports/varanasi_generalinfo.jsp |archive-date=29 June 2012 |access-date=22 July 2012 |publisher=Airports Authority of India}}</ref> Another international airport has been built at [[Kushinagar]]. However, since its inauguration, [[Kushinagar International Airport]] has not yet seen any outbound flights to international destinations.<ref name="Kushinagar IA">{{cite web | last=Kumar | first=Mayank | title=The over-promise of Uttar Pradesh's Kushinagar International Airport | website=The Hindu | date=30 November 2023 | url=https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/the-over-promise-of-uttar-pradeshs-kushinagar-international-airport/article67591556.ece | access-date=5 April 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=7 January 2013 |title=Kushinagar international airport to get ready for take-off |url=http://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/kushinagar-international-airport-to-get-ready-for-take-off-113010700012_1.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140521031503/http://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/kushinagar-international-airport-to-get-ready-for-take-off-113010700012_1.html |archive-date=21 May 2014 |publisher=Virendra Singh Rawat}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has six domestic airports located at [[Agra Airport|Agra]], [[Allahabad Airport|Allahabad]], [[Bareilly Airport|Bareilly]], [[Hindon Airport|Ghaziabad]], [[Gorakhpur Airport|Gorakhpur]] and [[Kanpur Airport|Kanpur]].<ref name="DFCCIL">{{Cite web |title=DFCCIL |url=https://dfccil.com/Home/DynemicPages?MenuId=76 |access-date=2 October 2023 |website=dfccil.com |archive-date=1 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200701102211/https://dfccil.com/Home/DynemicPages?MenuId=76 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |date=9 March 2021 |title=UP gets its 8th airport|work=mint |url=https://www.livemint.com/news/india/up-gets-its-8th-airport-check-flight-routes-fare-and-other-details-11615267509248.html |access-date=24 April 2021 |archive-date=24 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210424073306/https://www.livemint.com/news/india/up-gets-its-8th-airport-check-flight-routes-fare-and-other-details-11615267509248.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Under the collaboration with [[Airports Authority of India|civilian aviation authority]], these domestic airports are primarily used by the [[Indian Air Force]] for operational flexibility, especially during emergencies or natural disasters. The [[Noida International Airport]] is proposed to be built near [[Jewar]] in [[Gautam Buddha Nagar]], district.<ref>{{cite web |date=21 June 2013 |title=UP to seek DGCA nod for Taj airport |url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/lucknow/up-to-seek-dgca-nod-for-taj-airport/article1-1080013.aspx |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402155751/http://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/lucknow/up-to-seek-dgca-nod-for-taj-airport/article1-1080013.aspx |archive-date=2 April 2015 |access-date=29 July 2015 |work=Hindustan Times}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Hindustan Times e-Paper |url=http://paper.hindustantimes.com/epaper/viewer.aspx |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140608140626/http://paper.hindustantimes.com/epaper/viewer.aspx |archive-date=8 June 2014 |access-date=29 July 2015 |work=Hindustan Times}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last1=Mishra |first1=Mihir |date=24 June 2017 |title=Jewar to be second airport in Delhi NCR |work=The Economic Times |url=https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/transportation/airlines-/-aviation/jewar-to-be-second-airport-in-delhi-ncr/articleshow/59296768.cms |url-status=live |access-date=11 August 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180811133947/https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/transportation/airlines-/-aviation/jewar-to-be-second-airport-in-delhi-ncr/articleshow/59296768.cms |archive-date=11 August 2018}}</ref> |
|||
The state has a large, multimodal transportation system with the largest road network in the country.<ref name="ROAD NETWORK">{{cite web|first=Statutes and Institutional Structure|title=Investment Promotion & Infrastructure Development Cell|url=http://dipp.nic.in/English/Investor/Investers_Gudlines/roads.pdf|publisher=Department of Industrial policy and promotion|accessdate=7 January 2012}}</ref> The state is well connected to its nine neighboring states and almost all other parts of India through the [[National Highway (India)|national highways]] (NH). It boasts 42 national highways, with a total length of 4,942 km (9.6% of the total NH length in India). The [[Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation]] was established in 1972 to provide economical, reliable, and comfortable transportation in the state with connecting services to adjoining states<ref name=road>{{cite web|title=Road network|url=http://www.ibef.org/download/uttar_pradesh_190111.pdf|publisher=India Brand Equity Foundation|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> and boasts as being the only State Transport Corporation that runs in profit in the entire nation. All cities are connected to [[State Highway (India)|state highways]], which carry traffic between major centres within the state. Other district roads and village roads provide villages accessibility to meet their social needs as also the means to transport agriculture produce from village to nearby markets. Major district roads provide a secondary function of linking between main roads and rural roads.<ref name="road networks">{{cite web|last=Roads in India are divided into the categories|first=For the purpose of management and administration,|title=One of the largest road networks in the Country|url=http://dipp.nic.in/English/Investor/Investers_Gudlines/roads.pdf|publisher=Department of Industrial policy and promotion|accessdate=22 July 2012}}</ref> Uttar Pradesh has the seventh-highest road density in India, (1,027 km per 1000 km<sup>2</sup>) and the largest surfaced urban-road network in the country (50,721 km).<ref name=road>{{cite web|title=Pervasive road network of Uttar Pradesh|url=http://planningcommission.nic.in/plans/stateplan/upsdr/vol-2/Chap_b8.pdf|publisher=Planning commission, Government of India|accessdate=20 September 2012}}</ref> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
The Noida International Airport |
|||
==Sports== |
|||
== Sports == |
|||
{{See also|Indian Grand Prix|Uttar Pradesh Cricket Association}} |
{{See also|Indian Grand Prix|Uttar Pradesh Cricket Association}} |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Force india Buddh.jpg|thumb|left|alt=refer caption|[[Force India]] racing at [[Buddh International Circuit]]]] |
||
Traditional sports, now played mostly as a pastime, include [[wrestling]], [[Swimming (sport)|swimming]], [[kabaddi]], and track-sports or [[List of water sports|water-sports]] played according to local traditional rules and without modern equipment. Some sports are designed to display martial skills such as using a sword or 'Pata' (stick).<ref name="Rao2005">{{cite book|first=Mohan|last=Rao|title=From Population Control To Reproductive Health: Malthusian Arithmetic|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9p1cojMJUtkC&pg=PA244|access-date=26 July 2012|year=2005|publisher=Sage Publications|isbn=978-0761932697|pages=244–246|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130604230402/http://books.google.com/books?id=9p1cojMJUtkC&pg=PA244|archive-date=4 June 2013}}</ref> Due to a lack of organised patronage and requisite facilities, these sports survive mostly as individuals' hobbies or local competitive events. Among modern sports, [[field hockey]] is popular and Uttar Pradesh has produced top-level players in India, such as Nitin Kumar. and Lalit Kumar Upadhyay.<ref name=player>{{cite web|title=Hapless victim of a TV sting, this hockey player is now a rising star|url=http://www.indianexpress.com/news/hapless-victim-of-a-tv-sting-this-hockey-player-is-now-a-rising-star/938634/|work=[[The Indian Express]]|date=19 April 2012 |access-date=29 June 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Popular sports in Uttar Pradesh are both traditional and modern sports of mainly European origin. Athletes from the state have included the field hockey player [[Dhyan Chand]], Olympic shooter Nawab Mian, volleyball player Sanjiv Balian, and the wrestler Anuj.<ref name=ACHIEVEMENTS:>{{cite web|title=District Sports Office|url=http://muzaffarnagar.nic.in/sports.htm|publisher=District sport office|accessdate=29 Jun 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Recently, [[cricket]] has become more popular than [[field hockey]].<ref name="Cricket Legacy">{{cite news |title=Uttar Pradesh: Sports |url=https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/uttar-pradesh-sports-1371707833-1 |access-date=19 October 2021 |work=Jagran Josh |publisher=Jagran Prakashan Limited |date=29 July 2013 |archive-date=29 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211029170917/https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/uttar-pradesh-sports-1371707833-1 |url-status=live }}</ref> Uttar Pradesh won its first [[Ranji Trophy]] tournament in February 2006, beating [[Bengal]] in the final.<ref name="Ranji Trophy">{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh win Ranji Trophy|url=http://www.rediff.com/cricket/report/ranji-up/20060202.htm|work=[[Rediff.com]]|access-date=2 February 2006|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121019103708/http://www.rediff.com/cricket/report/ranji-up/20060202.htm|archive-date=19 October 2012}}</ref> [[Shaheed Vijay Singh Pathik Sports Complex]] is a newly built international cricket stadium with a capacity of around 20,000 spectators.<ref>{{cite web |title=UP to get one more cricket stadium by 2011 |url=http://zeenews.india.com/sports/cricket/up-to-get-one-more-cricket-stadium-by-2011_25512.html |url-status=deviated |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130524011021/http://zeenews.india.com/sports/cricket/up-to-get-one-more-cricket-stadium-by-2011_25512.html |archive-date=24 May 2013 |access-date=2 February 2006 |publisher=First Published:PTI, Friday, 27 November 2009, 21:26}}</ref> Wrestling has deep roots in Uttar Pradesh, with many [[akhara]]s (traditional wrestling schools) spread across the state.<ref name="Kushti">{{cite web | last=Singh | first=Prithviraj | title=Akhara body caught in successor row after UP mahant's 'murder', 1 group claims leader is elected | website=ThePrint | date=24 October 2021 | url=https://theprint.in/india/akhara-body-caught-in-successor-row-after-up-mahants-murder-1-group-claims-leader-is-elected/755933/ | access-date=6 May 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Traditional sports, now played mostly as a pastime, include [[wrestling]], [[Swimming (sport)|swimming]], [[kabaddi]], and track- or [[List of water sports|water-sports]] played according to local traditional rules and without modern equipment. Some sports are designed to display martial skills such as using a sword or 'Pata' (stick).<ref name="Rao2005">{{cite book|author=Mohan Rao|title=From Population Control To Reproductive Health: Malthusian Arithmetic|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=9p1cojMJUtkC&pg=PA244|accessdate=26 July 2012|date=6 January 2005|publisher=Sage Publications|isbn=978-0-7619-3269-7|pages=244–246}}</ref> Due to lack of organised patronage and requisite facilities, these sports survive mostly as individuals' hobbies or local competitive events. Among modern sports, [[field hockey]] is popular and Uttar Pradesh has produced some of the finest players in India, including Dhyan Chand and, more recently, Nitin Kumar<ref name="state hockey">{{cite web|title=Indian Hockey Player|url=http://www.stick2hockey.com/View-Bio-Data/Nitin%20Kumar/48.html|publisher=stick2hockey|accessdate=31 December 2010}}</ref> and Lalit Kumar Upadhyay.<ref name=player>{{cite web|title=Hapless victim of a TV sting, this hockey player is now a rising star|url=http://www.indianexpress.com/news/hapless-victim-of-a-tv-sting-this-hockey-player-is-now-a-rising-star/938634/|work=[[The Indian Express]]|accessdate=29 Jun 2012}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Uttar Pradesh football team]] (UPFS) serves as the governing body for football in Uttar Pradesh. It holds authority over the Uttar Pradesh football team and is officially affiliated with the [[All India Football Federation]].<ref name="Football Sangh">{{cite web | title=District Football Association Kanpur – Uttar Pradesh Football Sangh | website=Uttar Pradesh Football Sangh | url=https://uttarpradeshfootballsangh.com/kanpur-football-association/ | access-date=5 April 2024}}</ref> The UPFS participates in sending state teams to compete in all National Football Championships organised by the All India Football Federation.<ref name="Official AIFF">{{cite web | title=Arunachal Pradesh to host Final Rounds of 77th National Football Championship for Santosh Trophy | website=Official Website of All India Football Federation | date=6 September 2023 | url=https://www.the-aiff.com/article/arunachal-pradesh-to-host-final-rounds-of-77th-national-football-championship-for-santosh-trophy | access-date=5 April 2024}}</ref> Additionally, the UPFS oversees two Mandal Football Associations: the Aligarh Football Association and the Kanpur Football Association.<ref name="UPFS">{{cite web | title=About Us – Uttar Pradesh Football Sangh | website=Uttar Pradesh Football Sangh | url=https://uttarpradeshfootballsangh.com/about-us/ | access-date=5 April 2024}}</ref> The Uttar Pradesh Badminton Association is a sports body affiliated to [[Badminton Association of India]] responsible for overseeing players representing Uttar Pradesh at the national level.<ref name="TOI_2023">{{cite web | title=Up Players Dominate In Badminton C'ship | website=The Times of India | date=22 June 2023 | url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/lucknow/up-players-dominate-in-badminton-cship/articleshow/101177761.cms | access-date=5 April 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Recently, [[cricket]] has become more popular than field [[hockey]]. Uttar Pradesh won its first [[Ranji Trophy]] tournament in February 2006, beating [[Bengal]] in the final.<ref name="Ranji Trophy">{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh win Ranji Trophy|url=http://www.rediff.com/cricket/report/ranji-up/20060202.htm|publisher=[[Rediff.com]]|accessdate=2 February 2006}}</ref> It can also boast of routinely having 3 or 4 players on the national side. [[Green Park Stadium]] in [[Kanpur]], the only internationally recognised cricket stadium in the state, has witnessed some of India's most famous victories. [[Uttar Pradesh Cricket Association]] (UPCA) has headquarter in Kanpur. [[Faizabad Sports Complex]] is another sports venue in Uttar Pradesh which includes [[Faizabad International Sports Stadium]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://news.oneindia.in/2006/06/20/faizabad-to-get-international-standard-sports-complex-1150814208.html|title=Faizabad to get international standard sports complex |publisher=India Language Portal|accessdate=2 February 2006}}</ref> [[Greater Noida Cricket Stadium]] is another newly built international cricket stadium.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://zeenews.india.com/sports/cricket/up-to-get-one-more-cricket-stadium-by-2011_25512.html|title=UP to get one more cricket stadium by 2011|publisher=First Published:PTI, Friday, 27 November 2009, 21:26|accessdate=2 February 2006}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Buddh International Circuit]] hosted |
The [[Buddh International Circuit]] hosted India's inaugural [[List of Formula One Grands Prix|F1 Grand Prix]] race on 30 October 2011.<ref name="Indian Grand Prix">{{cite news|title=The Buddh International Circuit (BIC), which played host to India's first Formula One Grand Prix|url=http://ibnlive.in.com/news/buddh-circuit-wins-global-award/203294-5-24.html|access-date=14 July 2012|publisher=[[CNN-IBN]]|date=18 November 2011|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111222055639/http://ibnlive.in.com/news/buddh-circuit-wins-global-award/203294-5-24.html|archive-date=22 December 2011}}</ref> Races were only held three times before being cancelled due to falling attendance and lack of government support. The government of Uttar Pradesh considered [[Formula One]] to be entertainment and not a sport, and thus imposed taxes on the event and participants.<ref name="bbc.co.uk">{{cite news | url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-24659690 | work=BBC News | title=Why India's Formula 1 Grand Prix is under threat | date=24 October 2013 | url-status=live | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131027223718/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-24659690 | archive-date=27 October 2013}}</ref> |
||
==Education== |
== Education == |
||
{{Main|Education in Uttar Pradesh}} |
{{Main|Education in Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
{{See also|List of institutions of higher education in Uttar Pradesh |
{{See also|List of institutions of higher education in Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
[[File:Chattar Manzil 2005.jpg|thumb|right|alt=refer caption|[[Central Drug Research Institute]], an autonomous multidisciplinary research institute]] |
|||
[[File:JRHU - Main Building.jpg|thumb|left|alt=World's first school for handicap|[[Jagadguru Rambhadracharya Handicapped University|JRHU]] is a world's first school for handicap]] |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has a |
Uttar Pradesh has a prolonged tradition of education, although historically it was primarily confined to the elite class and religious schools.<ref name=schools>{{cite news|title=Islamic religious schools|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/keyword/madrassas|archive-url=https://archive.today/20130103081247/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/keyword/madrassas|url-status=dead|archive-date=3 January 2013|newspaper=[[The Times of India]]|access-date=25 April 2003}}</ref> Sanskrit-based learning formed the major part of education from the [[Vedic period|Vedic]] to the [[Gupta period]]s. As cultures travelled through the region they brought their bodies of knowledge with them, adding [[Pali]], [[Persian language|Persian]] and [[Arabic]] scholarship to the community. These formed the core of Hindu-Buddhist-Muslim education until the rise of British colonialism. The present schools-to-university system of education owes its inception and development in the state (as in the rest of the country) to foreign [[Christian missionaries]] and the [[British Empire|British colonial administration]].<ref name="Education System">{{cite web|title=British colonial administration system in state education system|url=http://www.upeducation.net/|publisher=State Education Board|access-date=25 April 2003|url-status=usurped|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030421195013/http://upeducation.net/|archive-date=21 April 2003}}</ref> Schools in the state are either managed by the government or by private trusts. [[Hindi]] is used as a medium of instruction in most of the schools except those affiliated to the [[Central Board of Secondary Education|CBSE]] or the council for [[Indian Certificate of Secondary Education|ICSE]] boards.<ref name=Facts>{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh Facts & Figures|url=http://www.upeducation.net/Facts/|publisher=Uttar Pradesh education department|access-date=16 October 2010|url-status=usurped|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110403071219/http://www.upeducation.net/facts/|archive-date=3 April 2011}}</ref> Under the [[10+2+3 plan]], after completing secondary school, students typically enroll for two years in a [[junior college]], also known as pre-university, or in schools with a higher secondary facility affiliated with the [[Board of High School and Intermediate Education Uttar Pradesh|Uttar Pradesh Board of High School and Intermediate Education]] (commonly referred to as U.P. Board) or a central board. Students choose from one of three streams, namely [[liberal arts]], commerce, or science. Upon completing the required coursework, students may enrol in general or professional degree programs. In a study done by [[Child Rights and You]] (CRY) and the Centre for Budgets, Governance, and Accountability (CBGA), Uttar Pradesh spent ₹9,167 per [[Student|pupil]], which is below the national average of ₹12,768.<ref name="pupil ratio">{{cite web | last=Jain | first=Isha | title=At Rs 9, 167, UP spends least on per child school education, reveals study | website=The Times of India | date=12 May 2017 | url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/education/news/at-rs-9-167-up-spends-least-on-per-child-school-education-reveals-study/articleshow/58646292.cms | access-date=9 July 2024}}</ref> The pupil/teacher ratio is 39:1,{{efn|One teacher for every 39 students}} lower than the national average of 23:1.<ref name="NBER Report">{{cite web | last=Balani | first=Khushboo | title=Uttar Pradesh has India's largest population of children, but least teachers per student | website=Scroll.in | date=7 January 2017 | url=https://scroll.in/article/825966/uttar-pradesh-has-indias-largest-population-of-children-but-least-teachers-per-student | access-date=9 July 2024}}</ref> According to the [[National Bureau of Economic Research]], the state reported the second-highest teacher [[absenteeism]] (31 percent) in rural public schools among 19 surveyed states.<ref name="NBER Data">{{cite web | title= The Fiscal Cost Of Weak Governance: Evidence From Teacher Absence In India| url=https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w20299/w20299.pdf#page=31 | access-date=9 July 2024}}</ref> According to an answer given by the [[Minister of Education (India)|Union Education Minister]] in 2020 in the Lok Sabha, about 17.1 percent of all elementary teacher posts in government schools in Uttar Pradesh are vacant. In terms of absolute numbers, the figure stands at 210,000.<ref name="Vacant posts">{{cite web | title=17% of teaching posts in govt schools vacant | website=The Times of India | date=20 September 2020 | url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/17-of-teaching-posts-in-govt-schools-vacant/articleshow/78212162.cms | access-date=9 July 2024}}</ref> In February 2024, the [[Uttar Pradesh government]] informed [[Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly|legislative assembly]] that, 85,152 posts of headmasters and assistant teachers are vacant in the state.<ref name="Deccan Herald">{{cite web | title=85,152 posts of headmasters and assistant teachers are vacant in Uttar Pradesh, says state government | website=Deccan Herald | date=6 February 2024 | url=https://www.deccanherald.com/india/uttar-pradesh/85152-posts-of-headmasters-and-assistant-teachers-are-vacant-in-uttar-pradesh-says-state-government-2881920 | access-date=9 July 2024}}</ref> |
||
[[File:La Martiniere, lucknow 39.jpg|thumb|left|alt=refer caption|La Martiniere, Lucknow]] |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has more than 45 universities,<ref name="universities">{{cite web|url=http://www.educationinfoindia.com/Universities/U-up.htm|title=List of universities|website=Education info India|access-date=13 September 2017|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170411015723/http://www.educationinfoindia.com/Universities/U-up.htm|archive-date=11 April 2017}}</ref> including six [[Central University, India|central universities]], twenty eight [[State university (India)|state universities]], eight [[Deemed university|deemed universities]], two [[IITs]] in [[Indian Institute of Technology (BHU) Varanasi|Varanasi]] and [[Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur|Kanpur]], [[AIIMS Gorakhpur]] and [[AIIMS Rae Bareli]], an [[Indian Institutes of Management|IIM]] in [[Indian Institute of Management Lucknow|Lucknow]]<ref name=Universities>{{cite web|title=List of Universities in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://www.upeducation.net/universities/|publisher=Education department of U.P|access-date=27 June 2012|url-status=usurped|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120621081900/http://www.upeducation.net/universities/|archive-date=21 June 2012}}</ref><ref name=IIM>{{cite web|title=Official Website of IIM Lucknow|url=http://www.iiml.ac.in/|publisher=[[IIM Lucknow]]|access-date=11 April 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120413144029/http://www.iiml.ac.in/|archive-date=13 April 2012|url-status=live}}</ref> Founded in 1845, [[La Martiniere Lucknow|La Martinière Girls' College]] in Lucknow, stands as one of the oldest schools in India.<ref>{{cite web|title=India's Best Schools, 2014|url=http://www.rediff.com/getahead/report/career-indias-best-schools-of-2014/20140922.htm|work=Rediff.com|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150722053415/http://www.rediff.com/getahead/report/career-indias-best-schools-of-2014/20140922.htm|archive-date=22 July 2015}}</ref> Located in Amethi, [[Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Petroleum Technology]] (RGIPT), provides education and training in [[Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics|STEM]] fields, particularly emphasizing the petroleum industry. With deemed university status, the RGIPT awards degrees in its own right. [[King George's Medical University]] (KGMU), located in Lucknow, is an institution for medical education, research, and healthcare services. [[Integral University (Lucknow)|The Integral University]], a state level institution, was established by the [[Government of Uttar Pradesh|Uttar Pradesh Government]] to provide education in different technical, [[applied science]], and other [[Academic discipline|disciplines]].<ref name=institution>{{cite web|title=The Integral University Lucknow state level institution|url=http://www.upeducation.net/universities/Integral_University/|publisher=Government of Uttar Pradesh|access-date=28 June 2012|url-status=usurped|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120107225558/http://www.upeducation.net/universities/Integral_University/|archive-date=7 January 2012}}</ref> The [[Central Institute of Higher Tibetan Studies]] was founded as an autonomous organisation by the national [[Ministry of Culture (India)|ministry of culture]]. [[Jagadguru Rambhadracharya Handicapped University]] is the only university established exclusively for the disabled in the world.<ref name="jansatta">{{cite news | publisher=Jansatta Express | language=hi | first=Dikshit| last=Ragini| title= चित्रकूट: दुनिया का प्रथम विकलांग विश्वविद्यालय |trans-title=Chitrakuta: The world's first handicapped university | date = 10 July 2007}}</ref> |
|||
As of 2023, the state has 573 public libraries.<ref name="Libraries">{{cite web |title=No. of public libraries in different States and Union Territories |url=http://rrrlf.nic.in/Docs/pdf/PUBLIC_LIBRARY_DATA.pdf |publisher=Ministry of Culture, Government of India |access-date=8 July 2024}}</ref><ref name="Library network">{{cite web |title=Public Library network |url=https://www.library.up.gov.in/Pages/public_library_network/en |publisher=Government of Uttar Pradesh |access-date=8 July 2024}}</ref> Established in 1875, [[Maulana Azad Library]] is one of the oldest and is the largest university library in Asia. [[Rampur Raza Library]] is a repository of Indo-Islamic cultural heritage established in the last decades of the 18th century.<ref name="Library network"/> It was established in 1774 by nawab [[Faizullah Khan]] and now an autonomous body under the [[Ministry of Culture]].<ref name="public libraries">{{cite web |title=Top libraries of UP |url=https://www.library.up.gov.in/home/toplibrary/en |publisher=Government of Uttar Pradesh |access-date=8 July 2024}}</ref> [[Thornhill Mayne Memorial]] also known as Allahabad Public Library, has an approximate collection of 125,000 books, 40 types of magazines, and 28 different newspapers in Hindi, English, Urdu and Bangla and it also contains 21 [[Arabic]] manuscripts.<ref name="Thornhill">{{cite web | title=Public library witnesses 37% increase in readers | website=The Times of India | date=23 September 2014 | url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/allahabad/Public-library-witnesses-37-increase-in-readers/articleshow/43224473.cms | access-date=8 July 2024}}</ref> A large number of Indian scholars are educated at different universities in Uttar Pradesh. Notable scholars who were born, worked or studied in the geographic area of the state include [[Harivansh Rai Bachchan]], [[Motilal Nehru]], [[Harish Chandra]] and [[Indira Gandhi]].<ref name="scholars">{{cite web | title=List of Famous Freedom Fighters from Uttar Pradesh | website=Jagranjosh.com | date=4 September 2018 | url=https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/list-of-famous-freedom-fighters-from-uttar-pradesh-1536056996-1 | access-date=6 May 2024}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Chattar Manzil 2005.jpg|thumb|270px|alt=Educational institute|[[Central Drug Research Institute]], an autonomous multidisciplinary research institute]] |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
== Tourism == |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has more than 30 universities,<ref name=universities>{{cite web|title=List of universities|url=http://www.educationinfoindia.com/Universities/U-up.htm|publisher=Education department of india|accessdate=16 October 2010}}</ref> including 4 [[Central University, India|central universities]], 20 [[State university (India)|state universities]], 8 [[Deemed university|deemed universities]], 2 [[IITs]], 1 [[Indian Institutes of Management|IIM]] in [[Lucknow]], 1 [[National Institutes of Technology|NIT]] in [[Allahabad]] and several polytechnics, engineering colleges and [[industrial training institute]]s.<ref name=Universities>{{cite web|title=List of Universities in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://www.upeducation.net/universities/|publisher=Education department of U.P|accessdate=27 Jun 2012}}</ref> Prestigious institutes like the [[Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences]], [[Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur]],<ref name=IIT>{{cite news|title=Kanpur schools welcome IIT Council formula|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/IIT-Kanpur|publisher=[[The Times of India]]|accessdate=27 Jun 2012}}</ref> [[Indian Institute of Technology (BHU) Varanasi]], the [[Indian Institute of Management Lucknow]], [[Indian Institute of Information Technology, Allahabad]], [[Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology Allahabad]], and the [[Harcourt Butler Technological Institute]] are known worldwide for their quality education and research in their respective fields.<ref name=IIM>{{cite web|title=Official Website of IIM Lucknow|url=http://www.iiml.ac.in/|publisher=[[IIM Lucknow]]|accessdate=11 April 2012}}</ref> The presence of such institutions provides the students of the state with ample opportunities for higher education.<ref name="IIM students">{{cite news|title=IIM-Lucknow sends country's first team to global agribusiness meet|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2012-06-28/lucknow/32456320_1_iim-lucknow-management-lucknow-global-colleges|publisher=[[The Times of India]]|accessdate=28 Jun 2012|date=28 June 2012}}</ref><ref name=Agri-biz>{{cite web|title=IIM Lucknow students shine at International Agri-biz symposium in Shanghai|url=http://www.mbauniverse.com/article/id/5953/IIM-Lucknow-agribusiness-summit|publisher=MBA Universe|accessdate=28 June 2012}}</ref> Other universities in the state include [[Gautam Buddha University]], [[Banaras Hindu University]], [[Purvanchal University]], [[Aligarh Muslim University]], [[Deen Dayal Upadhyay Gorakhpur University]], [[Allahabad University|University of Allahabad]], [[Indian Veterinary Research Institute]] [[Bareilly]], [[Institute of Management Technology, Ghaziabad|IMT Ghaziabad]], [[Gautam Buddha Technical University]], [[M.J.P. Rohilkhand University]], [[Narendra Dev University of Agriculture and Technology]], [[Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University]], and [[Chhatrapati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University|King George's Medical University]].<ref name=autogenerated9>{{cite web|title=List of Universities in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://www.upeducation.net/universities/|publisher=Government of Uttar Pradesh|accessdate=28 June 2012}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Tourism in Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{See also|Kumbh Mela|Architecture of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
[[File:Kumbh Mela 2013 Sangam, Allahabd.jpg|left|thumb|alt=refer caption|[[Kumbh Mela]] at [[Triveni Sangam|Sangam, Allahabad, 2013]]]] |
|||
Uttar Pradesh ranks first in domestic tourist arrivals among all states of India.<ref name="Board2010">{{cite book |author=Upkar Prakashan – Editorial Board |title=Uttar Pradesh General Knowledge |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_ce8FpJzR-4C&pg=PA46 |access-date=26 July 2012 |year= 2010 |publisher=Upkar Prakashan |isbn=978-8174824080 |pages=46–287 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528155016/http://books.google.com/books?id=_ce8FpJzR-4C&pg=PA46 |archive-date=28 May 2013}}</ref><ref name=Tourism>{{cite journal |title=Performance of Tourist Centres in Uttar Pradesh: An Evaluation Using Data Envelopment Analysis |url=http://asci.org.in/journal/Vol.40(2010-11)/40_1_Masood%20H%20Siddiqui.pdf |publisher=Administrative Staff College of India |journal=ASCI Journal of Management |volume=40 |issue=1 |first1=Masood H. |last1=Siddiqui |first2=Shalini N. |last2=Tripathi |year=2011 |access-date=22 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160804081245/http://asci.org.in/journal/Vol.40(2010-11)/40_1_Masood%20H%20Siddiqui.pdf |archive-date=4 August 2016 |url-status=live}}</ref> Some 44,000 foreign tourists arrived in the state in 2021, and almost 110 million domestic tourists.<ref>{{cite web |title=Uttar Pradesh |url=https://www.ibef.org/states/uttar-pradesh |publisher=India Brand Equity Foundation |access-date=22 January 2023 |archive-date=22 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230122094328/https://www.ibef.org/states/uttar-pradesh |url-status=live }}</ref> The Taj Mahal attracts some 7 million people a year,<!--<ref>{{cite news |title=Archaeological Survey of India Agra working on compiling visual archives on Taj Mahal |date=29 November 2015 |url=http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2015-11-29/news/68644851_1_agra-circle-taj-mahal-asi |newspaper=The Economic Times |access-date=16 January 2016 |archive-date=23 April 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160423233109/http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2015-11-29/news/68644851_1_agra-circle-taj-mahal-asi |url-status=dead}}</ref>--> earning almost {{INRConvert|78|c|lk=on}} in ticket sales in 2018–19.<ref>{{cite news |date=10 July 2019 |last1=Sharma |first1=Aman |title=Tourists up at Taj Mahal and Red Fort but Qutub Minar loses its No.2 Spot |url=https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/tourists-up-at-taj-mahal-and-red-fort-but-qutub-minar-loses-its-no-2-spot/articleshow/70152555.cms |access-date=29 March 2020 |work=[[The Economic Times]] |agency=Bennett, Coleman & Co. |publisher=[[The Times Group]] |ref=grow |archive-date=18 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200318151817/https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/tourists-up-at-taj-mahal-and-red-fort-but-qutub-minar-loses-its-no-2-spot/articleshow/70152555.cms |url-status=live }}</ref> The state is home to three [[World Heritage Sites]]: the [[Taj Mahal]],<ref>{{cite web |title=Taj Mahal |url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/252 |website=UNESCO World Heritage Centre |access-date=22 January 2023 |archive-date=27 August 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160827000214/https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/252 |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Agra Fort]],<ref>{{cite web |title=Agra Fort |url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/251 |website=UNESCO World Heritage Centre |access-date=22 January 2023 |archive-date=17 July 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100717221242/https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/251/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and the nearby [[Fatehpur Sikri]].<ref>{{cite web |title=Fatehpur Sikri |url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/255 |website=UNESCO World Heritage Centre |access-date=22 January 2023 |archive-date=14 May 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110514052508/https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/255 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
[[Religious tourism]] plays a significant role in the state's economy. [[Varanasi]] is a major religious hub and one of the seven sacred cities (''[[Sapta Puri]]'') in [[Hinduism]] and [[Jainism]].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Fouberg |first1=Erin H. |last2=Moseley |first2=William G. |title=Understanding World Geography |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |location=New York |page=173 |isbn=9781119473169 |oclc=1066742384 |year=2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Eck |first=Diana |author-link=Diana Eck |title=Banaras, the City of Light |publisher=Alfred Knopf Inc, [Columbia University Press] |orig-year=1981 |page=324 |year=2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Parry |first=Jonathan P. |title=Death in Banaras |series=Lewis Henry Morgan Lectures |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2000 |orig-year=1994 |page=1 |isbn=9780521466257 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=r10f4uwzcosC}}</ref><!-- Domestic tourists most commonly visit for religious purposes while foreign tourists visit for ghats along the river Ganges.--> [[Vrindavan]] is considered to be a holy place for [[Vaishnavism]].<ref name="Hawley">{{cite book |surname=Hawley |given=John Stratton |title=Krishna's Playground: Vrindavan in the 21st Century |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2020 |isbn=978-0190123987 |place=Oxford}}</ref><ref name="Madan">{{cite book |last=Gopal |first=Madan |url=https://archive.org/details/indiathroughages00mada |title=India through the ages |publisher=Publication Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, Government of India |year=1990 |editor=K.S. Gautam |page=[https://archive.org/details/indiathroughages00mada/page/176 176]}}</ref> [[Shravasti|Sravasti]] generally considered as revered sites in [[Buddhism]], believed to be where the Buddha taught many of his ''[[Suttas]]'' (sermons).<ref name="PIB 2019">{{cite web | title=Ministry of Tourism presents its latest webinar on "In the Footsteps of the Buddha" under Dekho Apna Desh Webinar Series | website=Press Information Bureau | date=7 February 2019 | url=https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=1653937 | ref={{sfnref | Press Information Bureau| 2019}} | access-date=6 May 2024}}</ref> Owing to the belief as to the birthplace of [[Rama]], [[Ayodhya]] (Awadh) has been regarded as one of the seven most important pilgrimage sites.<ref name=Paramasivan>{{cite book |last=Paramasivan |first=Vasudha |chapter=Yah Ayodhya Vah Ayodhya: Earthly and Cosmic Journeys in the Anand-lahari |editor=Heidi R. M. Pauwels |title=Patronage and Popularisation, Pilgrimage and Procession |publisher=Otto Harrassowitz Verlag |year=2009 |isbn=978-3-447-05723-3 |pages=101–116}}</ref><ref name=AboutDistrict>{{cite web |title=District Ayodhya – Government of Uttar Pradesh: City Of Lord Rama: India |url=https://ayodhya.nic.in/ |access-date=10 August 2021|archive-date=8 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201108190706/https://ayodhya.nic.in/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://ayodhya.nic.in/about-district/ |title=About District |website=District Ayodhya – Government of Uttar Pradesh |access-date=22 January 2023 |archive-date=9 November 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191109061219/https://ayodhya.nic.in/about-district/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Millions gather at [[Prayagraj]] to take part in the [[Magh Mela]] festival on the banks of the Ganges.<ref name="MacLean2008">{{cite book|first=Kama |last=MacLean |title=Pilgrimage and Power: The Kumbh Mela in Allahabad, 1765–1954|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MALacgnsroMC|access-date=25 July 2012|year= 2008|publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0195338942|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130527022328/http://books.google.com/books?id=MALacgnsroMC |archive-date=27 May 2013}}</ref> This festival is organised on a larger scale every 12th year and is called the [[Kumbh Mela]], where over 10 million Hindu pilgrims congregate in one of the largest gatherings of people in the world.<ref name="Magh Mela">{{cite news |title=Hindus gather for the Kumbh Mela at the Ganges in India and Maha Shivaratri in Allahabad |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/picturegalleries/worldnews/7222387/pictures-Hindus-gather-for-the-Kumbh-Mela-in-India-and-Maha-Shivaratri-in-Nepal.html |work=The Daily Telegraph |location=London |access-date=25 January 2011 |date=12 February 2010|url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110127012405/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/picturegalleries/worldnews/7222387/pictures-Hindus-gather-for-the-Kumbh-Mela-in-India-and-Maha-Shivaratri-in-Nepal.html |archive-date=27 January 2011}}</ref> |
|||
[[Integral University (Lucknow)|The Integral University]], a state level institution, was established by the [[Government of Uttar Pradesh|Uttar Pradesh Government]] to provide education in different technical, [[applied science]], and other [[Academic discipline|disciplines]].<ref name=institution>{{cite web|title=The Integral University Lucknow state level institution|url=http://www.upeducation.net/universities/Integral_University/|publisher=Government of Uttar Pradesh|accessdate=28 June 2012}}</ref> The [[Central Institute of Higher Tibetan Studies]] was founded as an autonomous organisation by the national [[Ministry of Culture (India)|ministry of culture]]. [[Jagadguru Rambhadracharya Handicapped University]] is the only university established exclusively for the disabled in the world.<ref name="jansatta">{{cite news | publisher=Jansatta Express | language=Hindi | first=Dikshit| last=Ragini| title= चित्रकूट: दुनिया का प्रथम विकलांग विश्वविद्यालय | trans_title = Chitrakuta: The world's first handicapped university | date = 10 July 2007}}</ref> A large number of Indian scholars are educated at different universities in Uttar Pradesh. Notable scholars who were born, worked or studied in the geographic area of the state include [[Harivansh Rai Bachchan]], [[Motilal Nehru]], [[Harish Chandra]] and [[Indira Gandhi]]. |
|||
Buddhist attractions in Uttar Pradesh include [[stupas]] and [[monasteries]]. The historically important towns of [[Sarnath]] where [[Gautama Buddha]] gave his first sermon after his enlightenment and died at [[Kushinagar]]; both of which are important pilgrimage sites for [[Buddhists]].<ref name=SARNATH>{{cite web|title=Sarnath General Information|url=http://varanasi.nic.in/tourist/tourist7.html |publisher=Tourism department of Varanasi |access-date=8 July 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120508235741/http://varanasi.nic.in/tourist/tourist7.html|archive-date=8 May 2012}}</ref> Also at Sarnath are the [[Pillars of Ashoka]] and the [[Lion Capital of Ashoka]], both important archaeological artefacts with national significance. At a distance of {{Convert|80|km|abbr=in}} from Varanasi, [[Ghazipur district|Ghazipur]] is famous not only for its [[Ghat]]s on the Ganges but also for the tomb of [[Lord Cornwallis]], the 18th-century Governor of [[East India Company]] ruled [[Bengal Presidency]]. The tomb is maintained by the [[Archaeological Survey of India]].<ref name="Joon">{{cite book |first=Sanjeev |last=Joon |title=Complete Guide for SSC|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=E9YfW2709psC&pg=RA2-PA93|access-date=25 July 2012 |publisher=Tata McGraw-Hill Education |isbn=978-0070706453|page=255|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528151112/http://books.google.com/books?id=E9YfW2709psC&pg=RA2-PA93 |archive-date=28 May 2013}}</ref> [[Jhansi Fort]], located in the city of [[Jhansi]], is closely associated with the "First War of Indian Independence", also known as the "Great Rebellion" or the [[Indian Rebellion of 1857]].<ref name="Jhansi_Fort">{{cite web |title=Jhansi Fort |url=https://jhansi.nic.in/forts/ |publisher=Government of Uttar Pradesh |access-date=29 November 2023 |archive-date=23 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230323181613/https://jhansi.nic.in/forts/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The fort is constructed in accordance with medieval Indian military architecture, featuring thick walls, bastions, and various structures within its complex. The architecture reflects a blend of Hindu and Islamic styles.<ref name="UP_Monuments">{{cite web |title=Ticketed Monuments – Uttar Pradesh jhansi Fort |url=https://asi.nic.in/jhansi-fort/ |publisher=Archaeological Survey of India |access-date=29 November 2023 |archive-date=5 December 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231205043357/https://asi.nic.in/jhansi-fort/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
==Tourism== |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
{{Main|Tourism in Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{See also|Kumbh Mela|Taj Mahal|Architecture of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
[[File:Kumbh Mela 2013 Sangam, Allahabd.jpg|thumb|right|alt= Kumbh Mela is biggest religious gathering| Kumbh Mela 2013 at Sangam, Allahabad]] |
|||
Uttar Pradesh ranks first in domestic tourist arrivals with more than 71 million,<ref name="Board2010">{{cite book|author=Upkar Prakashan - Editorial Board|title=Uttar Pradesh General Knowledge|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=_ce8FpJzR-4C&pg=PA46|accessdate=26 July 2012|date=1 September 2010|publisher=Upkar Prakashan|isbn=978-81-7482-408-0|pages=46–287}}</ref><ref name=Tourism>{{cite web|title=Performance of Tourist Centres in Uttar Pradesh|url=http://journal.asci.org.in/Vol.40(2010–11)/40_1_Masood%20H%20Siddiqui.pdf|publisher=Uttar Pradesh Tourist Department|date=8 July 2012}}</ref> owing to its rich and varied [[topography]], vibrant culture, festivals, monuments, ancient places of worship, and [[List of Buddhist temples|viharas]]. Thousands gather at [[Allahabad]] to take part in the [[Magh Mela]] festival on the banks of the Ganges.<ref name="MacLean2008">{{cite book|author=Kama MacLean|title=Pilgrimage and Power: The Kumbh Mela in Allahabad, 1765-1954|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=MALacgnsroMC|accessdate=25 July 2012|date=29 August 2008|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-533894-2}}</ref> This festival is organised on a larger scale every 12th year and is called the [[Kumbha Mela]], where over 10 million Hindu pilgrims congregate in one of the largest gatherings of people in the world.<ref name="Magh Mela">{{cite news|title=Hindus gather for the Kumbh Mela at the Ganges in India and Maha Shivaratri in Allahabad|url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/picturegalleries/worldnews/7222387/pictures-Hindus-gather-for-the-Kumbh-Mela-in-India-and-Maha-Shivaratri-in-Nepal.html|publisher=[[The Daily Telegraph]]|accessdate=25 January 2011|date=12 February 2010}}</ref> |
|||
== Healthcare == |
|||
The historically important towns of [[Sarnath]] and [[Kushinagar]] are located not far from Varanasi.<ref name=SARNATH>{{cite web|title=SARNATH GENERAL INFORMATION|url=http://varanasi.nic.in/tourist/tourist7.html|publisher=Tourism department of Varanasi|accessdate=8 July 2012}}</ref> [[Gautama Buddha]] gave his first sermon after his enlightenment at Sarnath and died at Kushinagar; both are important pilgrimage sites for [[Buddhists]]. Also at Sarnath are the [[Ashoka pillar|Pillars of Ashoka]] and the [[Lion Capital of Ashoka]], both important archaeological artifacts with national significance. At a distance of 80 km from Varanasi, [[Ghazipur district|Ghazipur]] is famous not only for its Ganges Ghats but also for the tomb of the British potentate [[Lord Cornwallis]], maintained by the [[Archeological Survey of India]].<ref name="Joon">{{cite book|author=Sanjeev Joon|title=Complete Guide for SSC|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=E9YfW2709psC&pg=RA2-PA93|accessdate=25 July 2012|publisher=Tata McGraw-Hill Education|isbn=978-0-07-070645-3|page=255}}</ref> |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| perrow = 1 |
|||
| total_width = 225 |
|||
| caption_align = center |
|||
| image_style = border:none; |
|||
| background color = |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| image1 = District Hospital.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = {{font|text=|District Hospital, [[Kanpur Dehat district|Kanpur Dehat]]}} |
|||
}} |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has a mix of [[Publicly funded health care|public]] as well as private healthcare infrastructure. Public healthcare in Uttar Pradesh is provided through a grid of primary health centers, [[community health centers]], [[district hospital]]s, and [[medical colleges]]. Although an extensive network of public and private sector healthcare providers has been built, the available [[Healthcare in India|health infrastructure]] is inadequate to meet the demand for health services in the state.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Anand |first1=Manjaree |title=Health status and health care services in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar: A comparative study |journal=Indian Journal of Public Health |date=1 July 2014 |volume=58 |issue=3 |pages=174–9 |doi=10.4103/0019-557X.138624 |pmid=25116823|issn=0019-557X|doi-access=free}}</ref> In 15 years to 2012–13, the population increased by more than 25 per cent. The public health centres, which are the frontline of the government's health care system, decreased by 8 per cent.<ref name="health">{{cite web|url=http://www.censusindia.gov.in/vital_statistics/AHSBulletins/AHS_Factsheets_2012-13/FACTSHEET-UTTAR_PRADESH.pdf|title=Annual Health Survey 2012–13 Fact Sheet – Uttar Pradesh|year=2013|website=Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner|publisher=[[Ministry of Home Affairs (India)|Ministry of Home Affairs]], [[Government of India]]|access-date=13 September 2017|ref=health|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171113214808/http://www.censusindia.gov.in/vital_statistics/AHSBulletins/AHS_Factsheets_2012-13/FACTSHEET-UTTAR_PRADESH.pdf|archive-date=13 November 2017}}</ref> Smaller sub-centres, the first point of public contact, increased by no more than 2 per cent over the 25 years to 2015, a period when the population grew by more than 51 per cent.<ref name="health" /> The state is also facing challenges such as a shortage of healthcare professionals, increasing cost of healthcare, a lack of essential medicines and equipment, the mushrooming of private healthcare and a lack of planning.<ref name="WHO">{{cite news |last1=Perappadan |first1=Bindu Shajan |title=India facing critical shortage of healthcare providers: WHO |url=https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/india-facing-critical-shortage-of-healthcare-providers-who/article27096738.ece |access-date=17 June 2020 |work=The Hindu |agency=The Hindu Group |date=11 May 2019 |archive-date=17 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200617151333/https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/india-facing-critical-shortage-of-healthcare-providers-who/article27096738.ece |url-status=live }}</ref> The number of doctors registered with State Medical Councils or the [[Medical Council of India]] in Uttar Pradesh was 77,549.<ref name="Doctors">{{cite web |title=Doctors Registered |url=https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/171/AU3334.pdf?source=pqals |publisher=The Ministry Of Health And Family Welfare |access-date=30 July 2024}}</ref> {{As of|2019}}, the number of government hospital in rural and urban areas of Uttar Pradesh stood at 4,442 with 39,104 beds and 193 with 37,156 beds respectively. The average population served per government hospital stands at 47,782 individuals.<ref name="Hospitals">{{cite web |title=State/UT wise Number of Government Hospitals |url=https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/171/AU3295.pdf?source=pqals |publisher=Directorate General of State Health Services |access-date=30 July 2024}}</ref> {{As of|December 2023}}, [[Out-of-pocket expense|Out-of-pocket expenditures]] in Uttar Pradesh is {{INRConvert|60883|c}}, highest in India.<ref name="OOP">{{cite web |title=Out Of Pocket Expenditure Data |url=https://sansad.in/getFile/annex/262/AU263.pdf?source=pqars |publisher=Department Of Health And Family Welfare |access-date=31 July 2024}}</ref> |
|||
A newborn in Uttar Pradesh is expected to live four years fewer than in the neighbouring state of [[Bihar]], five years fewer than in [[Haryana]] and seven years fewer than in [[Himachal Pradesh]]. The state contributed to the largest share of almost all [[Contagious disease|communicable]] and noncommunicable disease deaths, including 48 per cent of all [[typhoid]] deaths (2014); 17 per cent of cancer deaths and 18 per cent of [[tuberculosis]] deaths (2015).<ref name="health" /> Its [[maternal mortality]] ratio is higher than the national average at 285 maternal deaths for every 100,000 live births (2021), with 64.2 per cent of pregnant women unable to access minimum [[ante-natal care]].<ref name="Maternal">{{cite web |title=Maternal & Adolescent Healthcare |url=https://main.mohfw.gov.in/sites/default/files/03Chapter.pdf |publisher=Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW) |access-date=30 July 2024}}</ref><ref name="NITI">{{cite web |title=Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) (Per 100000 Live Births) |url=https://niti.gov.in/content/maternal-mortality-ratio-mmr-100000-live-births |publisher=NITI Aayog |access-date=24 May 2020 |archive-date=15 January 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200115010734/http://niti.gov.in/content/maternal-mortality-ratio-mmr-100000-live-births |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref name="Mortality">{{cite news |last1=Rao |first1=Menaka |title=Uttar Pradesh has a free ambulance service for pregnant women but substandard hospitals |url=https://scroll.in/pulse/827874/uttar-pradesh-has-a-free-ambulance-service-for-pregnant-women-but-substandard-hospitals |access-date=24 May 2020 |work=Scroll.in |agency=Scroll Media Inc, US |date=8 February 2017 |archive-date=28 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200928064649/https://scroll.in/pulse/827874/uttar-pradesh-has-a-free-ambulance-service-for-pregnant-women-but-substandard-hospitals |url-status=live }}</ref> Around 42 per cent of pregnant women, more than 1.5 million, [[Home birth|deliver babies at home]]. About two-thirds (61 per cent) of childbirths at home in the state are unsafe.<ref name="Health and Family">{{cite web|url=http://www.uhrc.in/downloads/Reports/up.pdf|title=State of Urban Health in Uttar Pradesh – Urban Health Resource Center|website=[[Urban Health Resource Centre]]|publisher=[[Ministry of Health and Family Welfare]], [[Government of India]]|access-date=14 August 2017|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170722150012/http://www.uhrc.in/downloads/Reports/up.pdf|archive-date=22 July 2017}}</ref> It has the highest [[child mortality]] indicators,<ref name="Child mortality">{{cite web |title=Estimates of mortality indicators |url=https://www.censusindia.gov.in/vital_statistics/SRS_Report_2017/11.%20Chap%204-Estimates%20of%20Mortality%20Indicators-2017.pdf |publisher=Census of India |access-date=24 May 2020 |archive-date=14 November 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191114040231/http://www.censusindia.gov.in/vital_statistics/SRS_Report_2017/11.%20Chap%204-Estimates%20of%20Mortality%20Indicators-2017.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> from the [[neonatal mortality rate]] to the under-five mortality rate of 64 children who die per 1,000 live births before five years of age, 35 die within a month of birth, and 50 do not complete a year of life.<ref name="Rural">{{cite web|url=http://wcd.nic.in/sites/default/files/RHS_1.pdf|title=Rural Health Statistics 2014–15|year=2015|website=[[Ministry of Health and Family Welfare]], [[Government of India]]|access-date=13 September 2017|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170829050157/http://wcd.nic.in/sites/default/files/RHS_1.pdf|archive-date=29 August 2017}}</ref> |
|||
Lucknow, the capital of the state, has several beautiful historical [[monument]]s such as [[Bara Imambara]] and [[Chhota Imambara]].<ref name=Monuments>{{cite web|title=List of Monuments - Uttar Pradesh|url=http://asi.nic.in/asi_monu_alphalist_uttarpradesh_lucknow.asp|publisher=Archeological Survey of India|date=8 July 2012}}</ref><ref name="Bara Imambara">{{cite web|title=The historical monument called Bara Imambara of Lucknow that is also known as Asfi Imambara|url=http://www.lucknow.org.uk/tourist-attractions/bara-imambara.html|publisher=Lucknow online news|accessdate=8 July 2012}}</ref> It has also preserved the damaged complex of the Oudh-period [[British Resident]]'s quarters, which are being restored. Uttar Pradesh gives access to three [[World Heritage Sites]]: the [[Taj Mahal]], [[Agra Fort]], and the nearby [[Fatehpur Sikri]]. Varanasi is an ancient city famous for its [[ghats]].<ref name=Ghats>{{cite web|title=Varanasi Ghats On the banks of the river Ganga|url=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pcwE4XIyrG0|publisher=[[YouTube]]|accessdate=8 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
To promote tourism, the [[Ministry of Tourism (India)|Directorate of Tourism]] was established in the 1972 with a Director General who is an [[Indian Administrative Service|I.A.S.]] officer. In 1974 the Uttar Pradesh State Tourism Development Corporation was established to look after the commercial tourist activities.<ref name=autogenerated10>{{cite web|title=The Tourism Development Policy|url=http://www.up-tourism.com/about_tourism.htm|publisher=Department of Tourism, Uttar Pradesh|accessdate=8 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
==Culture== |
== Culture == |
||
{{Main|Culture of Uttar Pradesh}} |
{{Main|Culture of Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
===Language and literature=== |
=== Language and literature === |
||
{{Main|Languages of Uttar Pradesh}} |
{{Main|Languages of Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
[[File:Kurukshetra.jpg|thumb|The battle of Kurukshetra, folio from the Mahabharata]] |
|||
Several texts and hymns of the Vedic literature were composed in Uttar Pradesh. The festival of ''[[Guru Purnima]]'' is dedicated to Sage [[Vyasa]], and also known as ''Vyasa Purnima'' as it is the day which is believed to be his birthday and also the day he divided the Vedas.<ref name=ci>{{cite book|title=Awakening Indians to India|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=AIU4LzftaPAC&pg=PA167&dq=%22Guru+Purnima%22+-inpublisher:icon&cd=8#v=onepage&q=%22Guru%20Purnima%22%20-inpublisher%3Aicon&f=false|year=2008 |publisher=Chinmaya Mission|isbn=81-7597-434-6|page=167|accessdate=5 August 2012}}</ref> There is a long literary and folk Hindi language tradition in the state. In the 19th and 20th century, Hindi literature was modernised by authors such as [[Jaishankar Prasad]], [[Maithili Sharan Gupt]], [[Munshi Premchand]], [[Suryakant Tripathi Nirala]], [[Babu Gulabrai]], [[Sachchidananda Vatsyayan|Sachchidananda Hirananda Vatsyayan 'Agyeya']], [[Rahul Sankrityayan]], [[Harivansh Rai Bachchan]], [[Dharamvir Bharati]], [[Subhadra Kumari Chauhan]], [[Mahavir Prasad Dwivedi]], [[Swami Sahajanand Saraswati]], [[Dushyant Kumar]], [[Hazari Prasad Dwivedi]], [[Acharya Kuber Nath Rai]], [[Bharatendu Harishchandra]], [[Kamleshwar Prasad Saxena]], [[Shivmangal Singh Suman]], [[Mahadevi Varma]], and [[Vibhuti Narain Rai]].<ref name=authors>{{cite web|title=The Indus Valley Civilization|url=http://www.hindunet.org/hindu_history/ancient/indus/indus_civ.html|publisher=The Hindu universe|accessdate=8 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Kurukshetra.jpg|thumb|left|The [[battle of Kurukshetra]], folio from the Mahabharata]] |
|||
The state is sometimes called the 'Hindi heartland of India'.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.newkerala.com/topstory-fullnews-67268.html |title=Three indian children to attend J8 summit in Rome.:. newkerala.com Online News |publisher=New kerala|accessdate=21 September 2009}}</ref> [[Hindi]] became the language of state administration with the Uttar Pradesh Official Language Act of 1951. A 1989 amendment to the act added [[Urdu]] as another native language of the state.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://uplegassembly.nic.in/UPLL.HTML |title=Uttar Pradesh Legislature |publisher=U.P assembly |accessdate=21 September 2009}}</ref> Linguistically, the state spreads across the Central, East-Central, and Eastern zones of the [[Indo-Aryan languages]], the major native languages of the state being [[Awadhi]], [[Bhojpuri]], [[Bundeli]], [[Braj Bhasha]], [[Kannauji]] and the vernacular form of [[Khariboli]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=bfy |title=Ethnologue report for language code: bfy |publisher=Ethnologue|accessdate=21 September 2009}}</ref> |
|||
Several texts and hymns of the Vedic literature were composed in Uttar Pradesh. Renowned Indian writers who have resided in Uttar Pradesh were [[Kabir]], [[Ravidas]], and [[Tulsidas]], who wrote much of his ''Ram Charit Manas'' in Varanasi. The festival of ''[[Guru Purnima]]'' is dedicated to Sage [[Vyasa]], and also known as ''Vyasa Purnima'' as it is the day which is believed to be his birthday and also the day he divided the Vedas.<ref name="ci">{{cite book |title=Awakening Indians to India |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AIU4LzftaPAC&pg=PA167 |year=2008 |publisher=Chinmaya Mission |isbn=978-8175974340 |page=167 |access-date=5 August 2012 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130528135339/http://books.google.com/books?id=AIU4LzftaPAC&pg=PA167&dq=%22Guru+Purnima%22+-inpublisher%3Aicon&cd=8#v=onepage&q=%22Guru%20Purnima%22%20-inpublisher%3Aicon&f=false |archive-date=28 May 2013}}</ref> |
|||
===Music and dance=== |
|||
Uttar Pradesh has produced musicians, including [[Anup Jalota]], [[Baba Sehgal]], [[Girija Devi]], [[Gopal Shankar Misra]], [[Hari Prasad Chaurasia]], [[Kishan Maharaj]], [[Vikash Maharaj]]<ref>{{cite web|last1=Varanasi District|website=http://www.varanasi.nic.in}}</ref>[[Naushad Ali]], [[Ravi Shankar]], [[Shubha Mudgal]], [[Siddheshwari Devi]], [[Talat Mehmood]], and [[Ustad Bismillah Khan]]. The [[Ghazal]] singer [[Begum Akhtar]] was a native of Uttar Pradesh. The region's folk heritage includes songs called rasiya (especially popular in [[Braj]]), which celebrate the divine love of [[Radha]] and [[Krishna]]. Other forms of music are [[kajari]], [[sohar]], [[qawwali]], [[rasiya]], [[thumri]], birha, [[chaiti]], and [[sawani]]. Traditional dance and musical styles are taught at the [[Bhatkhande Music Institute|Bhatkhande Music Institute University]] in Lucknow, named after the musician [[Pandit Vishnu Narayan Bhatkhande]].<ref name=Institute>{{cite web|title=Bhatkhande music institute|url=http://www.upeducation.net/universities/Bhatkhande_Music_Institute/|publisher=Uttar Pradesh Education Department|accessdate=25 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[Hindi]] became the language of state administration with the Uttar Pradesh Official Language Act of 1951.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://uplegassembly.nic.in/UPLL.HTML |title=Uttar Pradesh Legislature |publisher=U.P assembly |access-date=21 September 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090619093010/http://www.uplegassembly.nic.in/UPLL.HTML |archive-date=19 June 2009}}</ref> A 1989 amendment to the act added [[Urdu]], as an additional language of the state.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.lawsofindia.org/pdf/uttar_pradesh/1989/1989UP28.pdf |title=The Uttar Pradesh Official Language (Amendment) Act, 1989 |access-date=7 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190707095531/http://www.lawsofindia.org/pdf/uttar_pradesh/1989/1989UP28.pdf |archive-date=7 July 2019 |url-status=usurped}}</ref> Linguistically, the state spreads across the Central, East-Central, and Eastern zones of the [[Indo-Aryan languages|Indo Aryan languages]]. The major Hindi languages of the state are [[Awadhi language|Awadhi]], [[Bagheli language|Bagheli]], [[Bundeli]], [[Braj Bhasha]], [[Kannauji]], and [[Hindustani language|Hindustani]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=bfy |title=Ethnologue report for language code: bfy |publisher=Ethnologue |access-date=21 September 2009 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090416015135/http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=bfy |archive-date=16 April 2009}}</ref> [[Bhojpuri language|Bhojpuri]], an [[Eastern Indo-Aryan languages|Eastern Indo Aryan language]], is also spoken in the state.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Frawley |first=William |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sl_dDVctycgC&dq=Bhojpuri+eastern+indo+aryan+language&pg=PA481 |title=International Encyclopedia of Linguistics: 4-Volume Set |date=May 2003 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-513977-8|access-date=11 September 2022 |archive-date=27 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230427232735/https://books.google.com/books?id=sl_dDVctycgC&dq=Bhojpuri+eastern+indo+aryan+language&pg=PA481 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
[[Kathak]], a classical dance form, owes its origin to the state of Uttar Pradesh.<ref name=Dance>{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh Folk Music on Harmonica|url=http://www.youtube.com/watch?gl=US&v=CQAa0F83oRM|publisher=[[YouTube]]|accessdate=23 June 2012 }}</ref> The dance form is connected to classical Hindustani music where the rhythmic nimbleness of the feet is accompanied by the [[Tabla]] or [[Pakhawaj]].<ref>{{cite web|title=North Indian: Kathak|url=http://www.worldartswest.org/plm/guide/printablepages/kathak.pdf|publisher=Dance style loacator|accessdate=23 June 2012}}</ref> Two schools of this dance form, [[Lucknow gharana (tabla)|Lucknow gharana]] and [[Benares gharana]], are situated in Uttar Pradesh.<ref name=gharana>{{cite web|title=Lucknow gharana, developed with Kathak.|url=http://www.hindustaniclassical.com/lucknow.asp|publisher=Hindustani classical music|accessdate=23 July 2012}}</ref><ref name="benaras gharna">{{cite web|title=Benaras Gharana, traditional style and way of teaching and performing Indian classical music.|url=http://www.benaresmusicacademy.com/page-1|publisher=Benares music academy|accessdate=23 June 2012}}</ref> |
|||
=== |
=== Music and dance === |
||
{{Main|Music of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
[[File:Saraswati festival Varanasi-2.JPG|thumb|left|alt=Hindu goddess Saraswati|Saraswati festival, in which people worship the [[Devi|goddess]] of [[knowledge]], music, [[arts]], and science]] |
|||
With each district of Uttar Pradesh having its unique music and tradition, traditional folk music in Uttar Pradesh has been categorised in three different ways including music transmitted orally, music with unknown composers and music performed by custom. During the [[Medieval India|medieval]] period, two distinct types of music began to emerge in Uttar Pradesh. One was the courtly music, which received support from cities like Agra, [[Fatehpur Sikri]], Lucknow, Jaunpur, Varanasi, and [[Banda, Uttar Pradesh|Banda]]. The other was the religious music stemming from the [[Bhakti movement|Bhakti Cult]], which thrived in places like Mathura, Vrindavan, and Ayodhya.<ref name="Hindustani Music">{{cite web | title=Visit the land of the Taj for some Hindustani music & dance | website=The Economic Times | date=10 March 2016 | url=https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/magazines/travel/visit-the-land-of-the-taj-for-some-hindustani-music-dance/articleshow/51288777.cms?from=mdr | access-date=6 May 2024}}</ref> The popular folk music of Uttar Pradesh includes sohar, which is sung to celebrate the birth of a child. Evolved into the form of semi-classical singing, [[Kajari]] sung during the rainy season, and its singing style is closely associated the Benares gharana.<ref name="Kajari Origin">{{cite web | title=List of Folk Music of Uttar Pradesh | website=Jagranjosh.com | date=12 July 2018 | url=https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/list-of-folk-music-of-uttar-pradesh-1531391804-1 | access-date=6 May 2024}}</ref> [[Ghazal]], [[Thumri]] and [[Qawwali]] which is a form of [[Sufi poetry]] is popular in the Awadh region, [[Rasiya]] (especially popular in [[Braj]]), which celebrate the divine love of [[Radha]] and [[Krishna]]. [[Khayal]] is a form of semi-classical singing which comes from the courts of Awadh. Other forms of music are [[Biraha]], [[Chaiti]], [[Chowtal]], [[Alha-Khand|Alha]], and [[Sawani]].<ref name="Hindustani Music"/> |
|||
[[File:India - Varanasi sun greet - 0270.jpg|thumb|alt=Evening salute to sun|[[Hindu]] priest saluting the sun in the Ganges, [[Varanasi]]]] |
|||
[[Diwali]] (celebrated between mid-October and mid-December) and [[Rama Navami]] are popular festivals in Uttar Pradesh. [[Kumbh Mela]], organised in the month of [[Maagha]] (Feb-March), is a major festival held every three years in rotation at Allahabad, [[Haridwar]], [[Ujjain]], on the river Ganges and [[Nasik]] on the [[Godavari river]].<ref name=Mela>{{cite web|title=Kumbh Mela - India|url=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WqvzEjgYTFA|publisher=[[YouTube]]|accessdate=18 July 2012}}</ref> [[Lath mar Holi]] is a local celebration of the Hindu festival of Holi. It takes place well before the actual Holi in the town of [[Barsana]] near Mathura. [[Taj Mahotsav]], held annually at Agra, is a colorful display of the culture of the Braj area.<ref name="Braj Holi">{{cite news|title=The Braj Holi: Legend in real life|url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/News-Feed/lifestyle/The-Braj-Holi-Legend-in-real-life/Article1-675341.aspx|accessdate=13 July 2012|work=[[Hindustan Times]]|date=19 March 2011}}</ref> [[Vesak|Buddha Purnima]], which marks the birth of [[Gautama Buddha]], is a major Hindu and Buddhist festival, while Christmas is celebrated by the minority Christian population. Other festivals are [[Vijayadashami]], [[Makar Sankranti]], [[Vasant Panchami]], [[Ayudha Puja]], Ganga Mahotsava, [[Janmashtami]], Sardhana Christian Fair, [[Maha Shivaratri]], [[Mahavir Jayanti]], [[Moharram]], [[Mawlid|Bārah Wafāṭ]], [[Eid ul-Fitr|Eid]], [[Eid ul-Adha|Bakreed]], [[Chhath|Chhath puja]], [[Lucknow Mahotsav]], [[Kabob]] and [[Hanuman Jayanti]].<ref name=traditions>{{cite web|title=The glorious traditions and mythological legacy|url=http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/varanasi/fair_festival.htm|publisher=Department of tourism U.P |accessdate=18 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[Kathak]], a classical dance form, owes its origin to the state of Uttar Pradesh.<ref name="walker100">{{cite book |first=Margaret E. |last=Walker |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nC83DAAAQBAJ&pg=PA100 |title=India's Kathak Dance in Historical Perspective |publisher=Routledge |year=2016 |isbn=978-1-317-11737-7 |pages=100–102}}</ref> [[Ramlila]] is one of the oldest dramatic folk dances; it depicts the life of the Hindu deity [[Rama]] and is performed during festivals such as [[Vijayadashami]].<ref name="Schechner Hess 1977">{{cite journal | last1=Schechner | first1=Richard | last2=Hess | first2=Linda | title=The Ramlila of Ramnagar [India] | journal=The Drama Review: TDR | publisher=The MIT Press | volume=21 | issue=3 | year=1977 | pages=51–82 | doi=10.2307/1145152 | jstor=1145152 }}</ref> [[Nautanki]] is a traditional form of folk theatre that originated in Uttar Pradesh. It typically portrays a variety of themes ranging from historical and mythological tales to social and political commentary.<ref name="Nautanki">{{cite web | last=Goyal | first=Shikha | title=List of Folk Dances of Different States in India | website=Jagranjosh.com | date=3 January 2022 | url=https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/lists-of-states-and-folk-dances-of-india-1466770456-1 | access-date=6 May 2024}}</ref> In the [[gharana]] dance form, both the [[Lucknow gharana|Lucknow]] and the [[Benares gharana|Benares]] gharanas are situated in the state.<ref>{{cite news |title=Kathak: The cultural gem of Uttar Pradesh |url=https://www.thestatesman.com/travel/kathak-cultural-gem-uttar-pradesh-1503037669.html |access-date=22 January 2023 |work=The Statesman |date=10 January 2022 |archive-date=22 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230122175009/https://www.thestatesman.com/travel/kathak-cultural-gem-uttar-pradesh-1503037669.html |url-status=live }}</ref><!--[[Ajrara gharana]], [[Farrukhabad gharana]] too, maybe, if they can be cited--> [[Charkula]] is popular dance of the Braj region.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Charkula Dance |url=http://www.charkula.com/dance_charkula.asp |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200126222148/http://charkula.com/dance_charkula.asp |archive-date=26 January 2020 |access-date=27 January 2023 |website=Charkula}}</ref> |
|||
===Cuisine=== |
|||
=== Fairs and festivals === |
|||
[[File:Vegetarian Curry.jpeg|thumb|right|Uttar Pradeshi thali with [[naan]], [[Dal|sultani dal]], [[raita]], and [[shahi paneer]]]] |
|||
[[Chhath|Chhath Puja]] is the biggest festival of [[Purvanchal|eastern Uttar Pradesh]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=18 October 2021 |title=Chhath puja and the centrality of the Purvanchal community in Delhi politics |url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/analysis/chhath-puja-and-the-centrality-of-the-purvanchal-community-in-delhi-politics-101634568992424.html |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230101210315/https://www.hindustantimes.com/analysis/chhath-puja-and-the-centrality-of-the-purvanchal-community-in-delhi-politics-101634568992424.html |archive-date=1 January 2023 |access-date=6 September 2022 |website=Hindustan Times}}</ref> The [[Kumbh Mela]], organised in the month of [[Maagha]] (February—March), is a major festival held every twelve years in rotation at Prayagraj on the river Ganges.<ref name=maclean2003>{{cite journal |title=Making the Colonial State Work for You: The Modern Beginnings of the Ancient Kumbh Mela in Allahabad |last=Maclean |first=Kama |journal=The Journal of Asian Studies |year=2003 |volume=62 |pages=873–905 |number=3 |doi=10.2307/3591863 |jstor=3591863 |s2cid=162404242 }}</ref> [[Lathmar Holi]] is a local celebration of the Hindu festival of [[Holi]]. It takes place well before the actual Holi in the town of [[Barsana]] near Mathura.<ref>{{cite news |title=What is Lathmar Holi? Why is it celebrated? |publisher=India Today |url=http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/why-is-lathmar-holi-celebrated-in-barsana-and-nandgaon/1/624875.html |date=21 March 2016 |accessdate=6 December 2017 |archive-date=5 November 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171105044957/http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/why-is-lathmar-holi-celebrated-in-barsana-and-nandgaon/1/624875.html |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Taj Mahotsav]], held annually at Agra, is a colourful display of the culture of the Braj area.<ref name="Braj Holi">{{cite news |date=19 March 2011 |title=The Braj Holi: Legend in real life |work=[[Hindustan Times]] |url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/entertainment/the-braj-holi-legend-in-real-life/story-KolfzC30FW5KEZtKs5v9gN.html |url-status=live |access-date=13 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110322041343/http://www.hindustantimes.com/News-Feed/lifestyle/The-Braj-Holi-Legend-in-real-life/Article1-675341.aspx |archive-date=22 March 2011}}</ref> [[Dev Deepawali (Varanasi)|Ganga Mahotsav]], a festival of [[Kartik Purnima]], is celebrated fifteen days after Diwali.<ref name=traditions>{{cite web|title=The glorious traditions and mythological legacy |url=http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/varanasi/fair_festival.htm |publisher=Department of tourism U.P |access-date=18 July 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120629052417/http://www.up-tourism.com/destination/varanasi/fair_festival.htm |archive-date=29 June 2012}}</ref> |
|||
=== Cuisine === |
|||
{{Main|Cuisine of Uttar Pradesh}} |
{{Main|Cuisine of Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
[[Image:Vegetarian Curry.jpeg|alt=photograph|thumb|200px|Uttar Pradeshi thali with [[naan]], [[dal|sultani dal]], [[raita]], and [[shahi paneer]]]] |
|||
A typical day-to-day traditional vegetarian meal of Uttar Pradesh, like any other North Indian [[thali]], consists of [[roti]] (flatbread), [[chawal]], [[dal]], [[sabji]], raita and [[papad]]. Many people still drink the traditional drink chaach (traditional [[ Butter milk]]) with meals. On festive occasions, usually 'tava' (flat pan for roti) is considered inauspicious, and instead fried foods are consumed. A typical festive thali consists of Puri, Kachauri, sabji, pulav, [[Popadum|papad]], [[raita]], salad and desserts (such as sewai or [[Kheer]]). |
|||
[[Mughlai cuisine]] is a style of cooking developed in the [[Indian subcontinent]] by the {{linktext|imperial}} kitchens of the [[Mughal Empire]]. It represents the cooking styles used in [[North India]], especially Uttar Pradesh, and has been strongly influenced by [[Central Asian cuisine]]. [[Awadhi cuisine]] from the city of [[Lucknow]] consists of both vegetarian and non-vegetarian dishes. It has been greatly influenced by Mughlai cuisine.<ref>{{cite news |title=How is Awadhi Cuisine different from Mughlai Cuisine |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/food-news/how-is-awadhi-cuisine-different-from-mughlai-cuisine/photostory/88918225.cms |access-date=22 January 2023 |work=The Times of India |date=16 January 2022 |archive-date=22 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230122175602/https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/food-news/how-is-awadhi-cuisine-different-from-mughlai-cuisine/photostory/88918225.cms |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Many communities have their own particular style of cuisines, such as the Jains, Kayasths and Muslims. There are also certain sub-regional delicacies. Awadhi cuisine is world famous for dishes such as [[kebab]], [[biryani]], [[keema]] and [[nihari]]. Sweets occupy an important place in the Hindu diet and are eaten at social ceremonies. People make distinctive [[Confectionery|sweetmeats]] from milk products, including khurchan, [[peda]], [[gulabjamun]], [[petha]], makkhan malai, and [[chamcham]]. The [[chaat]] in Lucknow and Banarasi [[Paan]] is known across India for its flavour and ingredients.<ref name=paan>{{cite news|title=Banarasi paan or tobacco|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/Banarasi-paan-or-tobacco|accessdate=14 July 2012|work=[[The Times of India]]|date=28 April 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[Bhojpuri cuisine]] is a style of food preparation common in the districts located near the Bihar border. Bhojpuri foods are mostly mild and tend to be less hot in terms of spices used. The cuisine consists of both vegetable and meat dishes.<ref name="Bhojpuri Cuisine">{{cite web | title=Bhojpuri: सवाद के सरताज ह फुटेहरी, रउआ सभे खइले जरूर होखब! | website=News18 हिंदी | date=24 May 2021 | url=https://hindi.news18.com/news/bhojpuri-news/footehari-litti-chokha-is-desi-food-of-purvanchal-is-very-tasty-3598250.html | language=hi | access-date=8 July 2024}}</ref> |
|||
[[Awadhi cuisine]] is from the city of [[Lucknow]]. The cuisine consists of both vegetarian and non-vegetarian dishes. [[Awadh]] has been greatly influenced by [[Mughlai cuisine|Mughal cooking techniques]], and the cuisine of Lucknow bears similarities to those of [[Central Asia]], [[Kashmir]], [[Punjab region|Punjab]] and [[Hyderabad, India|Hyderabad]]; and the city is known for [[Nawabi]] foods.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://books.google.nl/books?id=v-2TyjzZhZEC&pg=PA10&lpg=PA10&dq=central+asian+influence+on+mughal+cuisine&source=bl&ots=lAKSebyjQh&sig=h5POMzB7tweY280fb245Pbj4R1k&hl=nl&sa=X&ei=vbKKU_6zDseYO-GggYAL&ved=0CDwQ6AEwCDgK|title=Royal Mughal Ladies and Their Contributions|accessdate=1 June 2014}}</ref> |
|||
The [[bawarchi]]s and rakabdars of Awadh gave birth to the [[Dum Pukht|dum style of cooking]] or the art of cooking over a slow fire, which has become synonymous with Lucknow today. Their spread consisted of elaborate dishes like [[kebabs]], [[korma]]s, [[biryani]], kaliya, [[Kulcha|nahari-kulchas]], zarda, sheermal, [[Roti|roomali rotis]], and [[Paratha|warqi parathas]]. The richness of Awadh cuisine lies not only in the variety of cuisine but also in the ingredients used like [[mutton]], [[paneer]], and rich spices including [[cardamom]] and [[saffron]]. |
|||
== See also == |
|||
[[Mughlai cuisine]] is a style of cooking developed in the [[Indian subcontinent]] by the [[wikt:imperial|imperial]] kitchens of the [[Mughal Empire]]. It represents the cooking styles used in [[North India]] (especially Uttar Pradesh. The cuisine is strongly influenced by the [[Central Asian Cuisine|cuisine of Central Asia]], and has in turn strongly similarities to the regional cuisines of [[Kashmiri cuisine|Kashmir]] and the [[Punjabi cuisine|Punjab]] region.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://books.google.nl/books?id=v-2TyjzZhZEC&pg=PA10&lpg=PA10&dq=central+asian+influence+on+mughal+cuisine&source=bl&ots=lAKSebyjQh&sig=h5POMzB7tweY280fb245Pbj4R1k&hl=nl&sa=X&ei=vbKKU_6zDseYO-GggYAL&ved=0CDwQ6AEwCDgK|title=Royal Mughal Ladies and Their Contributions|accessdate=1 June 2014}}</ref> |
|||
{{Portal|India}} |
|||
The tastes of Mughlai cuisine vary from extremely mild to spicy, and is often associated with a distinctive [[aroma]] and the taste of ground and whole spices. |
|||
* [[List of people from Uttar Pradesh]] |
|||
* [[Outline of India]] |
|||
* [[UP Gaurav Samman]] |
|||
== Explanatory notes == |
|||
===Dress=== |
|||
{{notelist}} |
|||
The people of Uttar Pradesh dress in a variety of traditional and Western styles.<ref name=Costumes>{{cite web|title=Costumes of Uttar Pradesh|url=http://www.indfy.com/uttar-pradesh/dresses.html|publisher=Indify|accessdate=1 October 2012}}</ref> Traditional styles of dress include colourful draped garments – such as [[sari]] for women and [[dhoti]] or [[lungi]] for men – and tailored clothes such as [[salwar kameez]] for women and [[kurta]]-[[pajamas|pyjama]] for men.<ref name=Costumes/> Men often sport head-gear like [[topi]] or [[pagri]].<ref name=Costumes/> [[Sherwani]] is a more formal male dress and is frequently worn along with [[chooridar]] on festive occasions. European-style trousers and shirts are also common among the men.{{r|Costumes}} |
|||
== |
== References == |
||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
A number of newspapers and periodicals are published in Hindi, English, and Urdu. ''[[The Pioneer (Indian newspaper)|The Pioneer]]'' was founded in [[Allahabad]] in 1865 by George Allen.<ref name=dasgupta>{{cite journal|doi=10.1017/S0026749X00015092|author=Das Gupta, Uma|year= 1977|title=The Indian Press 1870–1880: A Small World of Journalism|url=http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=2701888|journal=Modern Asian Studies|volume=11|issue=2|pages=213–235|format=see pages 233–234|jstor=311549|ref=harv}}</ref> ''[[Amar Ujala]]'', ''[[Dainik Bhaskar]]'', and ''[[Dainik Jagran]]'', have a wide circulation, with local editions published from several important cities. Major English language newspapers which are published and sold in large numbers are ''[[The Telegraph (Calcutta)|The Telegraph]]'', ''[[The Times of India]]'', ''[[Hindustan Times]]'', ''[[The Hindu]]'', ''[[The Statesman]]'', ''[[The Indian Express]]'', and ''[[Asian Age]]''. Some prominent financial dailies like ''[[The Economic Times]]'', ''[[The Financial Express (India)|Financial Express]]'', ''[[Business Line]]'', and ''[[Business Standard]]'' are widely circulated. Vernacular newspapers such as those in [[Hindi]], [[Nepali language|Nepali]], [[Gujarati language|Gujarati]], [[Oriya language|Oriya]], [[Urdu]], and [[Punjabi language|Punjabi]] are also read by a select readership. |
|||
== External links == |
|||
[[Doordarshan]] is the state-owned television broadcaster. Multi system operators provide a mix of Hindi, English, Bengali, Nepali and international channels via [[Cable television|cable]]. [[:Category:24-hour television news channels|Hindi 24-hour television news channels]] are ''[[NDTV India]]'', ''[[DD News]]'', ''Zee News Uttar Pradesh'', ''[[Jan TV]]'', ''IBN-7'', and ''[[ABP News]]''. ''[[All India Radio]]'' is a public radio station. There are 32 private [[frequency modulation|FM]] stations available in major cities like Lucknow, Kanpur, Varanasi, Allahabad, Agra, and Noida.<ref name="RADIO STATIONS">{{cite web|title=Radio Stations in Uttar Pradesh, India|url=http://www.asiawaves.net/india/uttar-pradesh-radio.htm|publisher=Asiawaves|accessdate=14 July 2012}}</ref><ref name="FM Stations">{{cite web|title=Indian FM Stations Statewise|url=http://fmstations.bharatiyamobile.com/Indian-FM-Stations-Statewise.php?state=Uttar+Pradesh&location=Aligarh|publisher=Bharatiya mobile|accessdate=14 July 2012}}</ref> Cell phone providers include ''[[Vodafone Essar|Vodafone]]'', ''[[Bharti Airtel|Airtel]]'', ''[[BSNL]]'', ''[[Reliance Communications]]'', ''[[Uninor]]'', ''[[Aircel]]'',''[[Tata Indicom]]'', ''[[Idea Cellular]]'', and ''[[Tata DoCoMo]]''. Broadband internet is available in select towns and cities and is provided by the state-run BSNL and by private companies.<ref name=cellular>{{cite web|title=Uttar Pradesh (East)|url=http://www.india-cellular.com/UPE-page.html|publisher=India cellular phone industry|accessdate=14 July 2012}}</ref> [[Dial-up access]] is provided throughout the state by BSNL and other providers.<ref name="dial up">{{cite web|title=Internet Service Provider|url=http://www.datainfocom.in/services/isp.htm|publisher=Data Infocom Limited|accessdate=14 July 2012}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- {{No more links}} |
|||
Please be cautious about adding more external links. |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{portal|India|Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
*[[Outline of India]] |
|||
*[[List of Chief Ministers of Uttar Pradesh]] |
|||
*[[List of Governors of Uttar Pradesh]] |
|||
*[[List of people from Uttar Pradesh]] |
|||
*[[Nawabganj Bird Sanctuary]] |
|||
*[[Brijwood]] |
|||
Wikipedia is not a collection of links and should not be used for advertising. |
|||
==References== |
|||
http://leadtech.in/infoelection/index.php/lok-sabha-elections-2014-/2598-lok-sabha-election-result-2014.html |
|||
Excessive or inappropriate links will be removed. |
|||
{{Reflist|30em}} |
|||
See [[Wikipedia:External links]] and [[Wikipedia:Spam]] for details. |
|||
If there are already suitable links, propose additions or replacements on |
|||
the article's talk page, or submit your link to the relevant category at |
|||
the Open Directory Project (dmoz.org) and link there using {{Dmoz}}. |
|||
--> |
|||
; Government |
|||
* {{Official website}} |
|||
* [https://www.uptourism.gov.in/en Official tourism site] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230127065629/https://uptourism.gov.in/en |date=27 January 2023 }} |
|||
; [https://e-district.info/ General information] |
|||
* {{GovPubs|Uttar%20Pradesh}} |
|||
* {{Britannica|620898|Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
* {{Wikiatlas|Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
* {{osmrelation-inline|1942587}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{Commons category}} |
|||
{{wikivoyage|Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
* [http://up.gov.in/ Uttar Pradesh Government Website] |
|||
* [http://www.up-tourism.com/ Department of Tourism, Government of Uttar Pradesh] |
|||
* {{dmoz|Regional/Asia/India/Uttar_Pradesh|Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
* [http://www.rainrays.com/topic_list?cat_id=200 Uttar Pradesh Districts] |
|||
* [http://www.indiamapatlas.com/uttar-pradesh/district/ Uttar Pradesh Districts Map] |
|||
{{Geographic location |
{{Geographic location |
||
|Centre = Uttar Pradesh |
|Centre = Uttar Pradesh |
||
|North = [[Uttarakhand]] |
|North = [[Uttarakhand]] |
||
|Northeast = [[ |
|Northeast = [[Sudurpashchim Province]], [[Lumbini Province]] and [[Gandaki Province]], {{flag|Nepal}} |
||
|East = [[Bihar]] |
|East = [[Bihar]] |
||
|Southeast = [[Jharkhand]]<br />[[Chhattisgarh]] |
|Southeast = [[Jharkhand]]<br />[[Chhattisgarh]] |
||
| Line 712: | Line 728: | ||
|Northwest = [[Himachal Pradesh]]<br />[[Haryana]]<br />[[Delhi]] |
|Northwest = [[Himachal Pradesh]]<br />[[Haryana]]<br />[[Delhi]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Navboxes |
|||
|title = Articles related to Uttar Pradesh |
|||
{{India}} |
|||
|list = |
|||
{{Uttar Pradesh}} |
{{Uttar Pradesh}} |
||
{{Universities in Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{Hydrography of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{Uttar Pradesh topics}} |
{{Uttar Pradesh topics}} |
||
{{Hydrography of Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{Protected areas in Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{Hindu temples in Uttar Pradesh}} |
|||
{{States and territories of India}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Subject bar |commons=yes |commons-search=Category:Uttar Pradesh |n=yes |n-search=Category:Uttar Pradesh |wikt=yes |b=yes |q=yes |s=yes |v=yes |voy=yes |d=yes }} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Uttar Pradesh| ]] |
[[Category:Uttar Pradesh| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:North India|*]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:1950 establishments in India]] |
||
[[Category:Countries and territories where Hindi is an official language]] |
|||
[[Category:Countries and territories where Urdu is an official language]] |
|||
[[Category:States and territories established in 1950]] |
|||
[[Category:States and union territories of India]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 11:05, 22 December 2024
Uttar Pradesh (/ˌʊtər prəˈdɛʃ/ UUT-ər prə-DESH;[13] Hindi: [ˈʊtːəɾ pɾəˈdeːʃ]; abbr. UP) is a state in northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world – more populous than all but four other countries outside of India (China, US, Indonesia, and Pakistan)[14] – and accounting for 16.5 percent of the population of India or around 3 percent of the total world population. The state is bordered by Rajasthan to the west, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Delhi to the northwest, Uttarakhand and Nepal to the north, Bihar to the east, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand to the south. It is the fourth-largest Indian state by area covering 243,286 km2 (93,933 sq mi), accounting for 7.3 percent of the total area of India. Lucknow serves as the state capital, with Prayagraj being the judicial capital. It is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts.
Uttar Pradesh was established in 1950 after India had become a republic. It is a successor to the United Provinces, established in 1935 by renaming the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh, in turn established in 1902 from the North-Western Provinces and the Oudh Province. Though long known for sugar production, the state's economy is now dominated by the services industry. The service sector comprises travel and tourism, hotel industry, real estate, insurance and financial consultancies. The economy of Uttar Pradesh is the third-largest state economy in India, with ₹18.63 lakh crore (US$220 billion) in gross domestic product and a per capita GSDP of ₹68,810 (US$810).[9] The High Court of the state is located in Prayagraj. The state contributes 80 seats to the lower house Lok Sabha and 31 seats and the upper house Rajya Sabha.
On 9 November 2000, a new state, Uttaranchal (now Uttarakhand), was created from Uttar Pradesh's western Himalayan hill region. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges and its tributary Yamuna, meet at the Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj, a Hindu pilgrimage site. Other notable rivers are Gomti and Saryu. The forest cover in the state is 6.1 percent of the state's geographical area. The cultivable area is 82 percent of the total geographical area, and the net area sown is 68.5 percent of the cultivable area.[15]
Inhabitants of the state are called Awadhi, Brajwasi, or Bundeli, depending upon their region of origin. Hinduism is practised by more than three-fourths of the population, followed by Islam. Hindi is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state, along with Urdu. Uttar Pradesh was home to most of the mainstream political entities that existed in ancient and medieval India including the Maurya Empire, Harsha Empire, Gupta Empire, Pala Empire, Delhi Sultanate and Mughal Empire as well as many other empires. At the time of the Indian independence movement in the early 20th century, there were three major princely states in Uttar Pradesh – Ramgadi, Rampur and Benares and served as a focal point for the 1857 rebellion against British rule. The state houses several holy Hindu temples and pilgrimage centres. Along with several historical, natural and religious tourist destinations, including Agra, Aligarh, Ayodhya, Bareilly, Gorakhpur, Kanpur, Kushinagar, Lucknow, Mathura, Meerut, Prayagraj, Varanasi, and Vrindavan, Uttar Pradesh is also home to three World Heritage sites.
History
Prehistory
Modern human hunter-gatherers have been in Uttar Pradesh[16][17][18] since between around[19] 85,000 and 72,000 years ago. There have also been prehistorical finds in the state from the Middle and Upper Paleolithic dated to 21,000–31,000 years old[20] and Mesolithic/Microlithic hunter-gatherer settlement, near Pratapgarh, from around 10550–9550 BCE. Villages with domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats and evidence of agriculture began as early as 6000 BCE, and gradually developed between c. 4000 and 1500 BCE beginning with the Indus Valley Civilisation and Harappa culture to the Vedic period and extending into the Iron Age.[21][22][23]
Ancient and classical period
Out of the sixteen mahajanapadas (lit. 'great realms') or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India, seven fell entirely within the present-day boundaries of the state.[24] The kingdom of Kosala, in the Mahajanapada era, was also located within the regional boundaries of modern-day Uttar Pradesh.[25] According to Hinduism, the divine King Rama of the Ramayana epic reigned in Ayodhya, the capital of Kosala.[26] Krishna, another divine king of Hindu legend, who plays a key role in the Mahabharata epic and is revered as the eighth reincarnation (Avatar) of the Hindu god Vishnu, is said to have been born in the city of Mathura.[25] The aftermath of the Kurukshetra War is believed to have taken place in the area between the Upper Doab and Delhi, (in what was Kuru Mahajanapada), during the reign of the Pandava King Yudhishthira. The kingdom of the Kurus corresponds to the Black and Red Ware and Painted Gray Ware culture and the beginning of the Iron Age in northwest India, around 1000 BCE.[25]
Control over Gangetic plains region was of vital importance to the power and stability of all of India's major empires, including the Maurya (320–200 BCE), Kushan (100–250 CE), Gupta (350–600), and Gurjara-Pratihara (650–1036) empires.[27] Following the Huns' invasions that broke the Gupta empire, the Ganges-Yamuna Doab saw the rise of Kannauj.[28] During the reign of Harshavardhana (590–647), the Kannauj empire reached its zenith.[28] It spanned from Punjab in the north and Gujarat in the west to Bengal in the east and Odisha in the south.[25] It included parts of central India, north of the Narmada River and it encompassed the entire Indo-Gangetic Plain.[29] Many communities in various parts of India claim descent from the migrants of Kannauj.[30] Soon after Harshavardhana's death, his empire disintegrated into many kingdoms, which were invaded and ruled by the Gurjara-Pratihara empire, which challenged Bengal's Pala Empire for control of the region.[29] Kannauj was several times invaded by the South Indian Rashtrakuta dynasty, from the 8th century to the 10th century.[31][32] After the fall of the Pala empire, the Chero dynasty ruled from the 12th century to the 18th century.[33]
Delhi Sultanate
Uttar Pradesh was partially or entirely ruled by the Delhi Sultanate for 320 years (1206–1526). Five dynasties ruled over the Delhi Sultanate sequentially: the Mamluk dynasty (1206–90), the Khalji dynasty (1290–1320), the Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1414), the Sayyid dynasty (1414–51), and the Lodi dynasty (1451–1526).[34][35]
The first Sultan of Delhi, Qutb ud-Din Aibak, conquered some parts of Uttar Pradesh, including Meerut, Aligarh, and Etawah. His successor, Iltutmish, expanded the Sultanate's rule over Uttar Pradesh by defeating the King of Kannauj. During the reign of Sultan Balban, the Mamluk dynasty faced numerous rebellions in the state, but he was able to suppress them and establish his authority. Alauddin Khilji, extended his conquests to various regions in the state, including Varanasi and Prayagraj. Apart from the rulers, the Delhi Sultanate era also saw the growth of Sufism in Uttar Pradesh. Sufi saints, such as Nizamuddin Auliya and Qutbuddin Bakhtiar Kaki, lived during this period and their teachings had a significant impact on the people of the region. Sultanat era in the state also witnessed the construction of mosques and tombs, including the Atala Masjid in Jaunpur, the Jama Masjid in Fatehpur Sikri, and the Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq's Tomb in Tughlaqabad.[36][37]
Medieval and early modern period
In the 16th century, Babur, a Timurid descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan from Fergana Valley (modern-day Uzbekistan), swept across the Khyber Pass and founded the Mughal Empire, covering India, along with modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and Bangladesh.[38] The Mughals were descended from Persianised Central Asian Turks (with significant Mongol admixture). In the Mughal era, Uttar Pradesh became the heartland of the empire.[30] Mughal emperors Babur and Humayun ruled from Delhi.[39][40] In 1540 an Afghan, Sher Shah Suri, took over the reins of Uttar Pradesh after defeating the Mughal King Humanyun.[41] Sher Shah and his son Islam Shah ruled Uttar Pradesh from their capital at Gwalior.[42] After the death of Islam Shah Suri, his prime minister Hemu became the de facto ruler of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and the western parts of Bengal. He was bestowed the title of Hemchandra Vikramaditya (title of Vikramāditya adopted from Vedic period) at his formal coronation took place at Purana Qila in Delhi on 7 October 1556. A month later, Hemu died in the Second Battle of Panipat, and Uttar Pradesh came under Emperor Akbar's rule.[43] Akbar ruled from Agra and Fatehpur Sikri.[44]
In the 18th century, after the fall of Mughal authority, the power vacuum was filled by the Maratha Empire, in the mid-18th century, the Maratha army invaded the Uttar Pradesh region, which resulted in Rohillas losing control of Rohilkhand to the Maratha forces led by Raghunath Rao and Malha Rao Holkar. The conflict between Rohillas and Marathas came to an end on 18 December 1788 with the arrest of Ghulam Qadir, the grandson of Najeeb-ud-Daula, who was defeated by the Maratha general Mahadaji Scindia. In 1803–04, following the Second Anglo-Maratha War, when the British East India Company defeated the Maratha Empire, much of the region came under British suzerainty.[45]
British India era
| Timeline of reorganisation and name changes of UP[46] | |
|---|---|
| 1807 | Ceded and Conquered Provinces |
| 14 November 1834 | Presidency of Agra |
| 1 January 1836 | North-Western Provinces |
| 3 April 1858 | Oudh taken under British control, Delhi taken away from NWP and merged into Punjab |
| 1 April 1871 | Ajmer, Merwara & Kekri made separate commissioner-ship |
| 15 February 1877 | Oudh added to North-Western Provinces |
| 22 March 1902 | Renamed United Provinces of Agra and Oudh |
| 3 January 1921 | Renamed United Provinces of British India |
| 1 April 1937 | Renamed United Provinces |
| 1 April 1946 | Self rule granted |
| 15 August 1947 | Part of independent India |
| 24 January 1950 | Renamed Uttar Pradesh |
| 9 November 2000 | Uttaranchal state, now known as Uttarakhand, created from part of Uttar Pradesh |
Starting from Bengal in the second half of the 18th century, a series of battles for north Indian lands finally gave the British East India Company accession over the state's territories.[47] Ajmer and Jaipur kingdoms were also included in this northern territory, which was named the "North-Western Provinces" (of Agra). Although UP later became the fifth-largest state of India, NWPA was one of the smallest states of the British Indian empire.[48] Its capital shifted twice between Agra and Allahabad.[49]
Due to dissatisfaction with British rule, a serious rebellion erupted in various parts of North India, which became known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857; Bengal regiment's sepoy stationed at Meerut cantonment, Mangal Pandey, is widely considered as its starting point.[50] After the revolt failed, the British divided the most rebellious regions by reorganising their administrative boundaries, splitting the Delhi region from 'NWFP of Agra' and merging it with Punjab Province, while the Ajmer–Marwar region was merged with Rajputana and Oudh was incorporated into the state. The new state was called the North Western Provinces of Agra and Oudh, which in 1902 was renamed as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh.[51] It was commonly referred to as the United Provinces or its acronym UP.[52][53]
In 1920, the capital of the province was shifted from Allahabad to Lucknow.[54] The high court continued to be at Allahabad, but a bench was established at Lucknow.[55] Allahabad continues to be an important administrative base of today's Uttar Pradesh and has several administrative headquarters.[56] Uttar Pradesh continued to be central to Indian politics and was especially important in modern Indian history as a hotbed of the Indian independence movement. The state hosted modern educational institutions such as the Aligarh Muslim University, Banaras Hindu University and Darul Uloom Deoband. Nationally known figures such as Ram Prasad Bismil and Chandra Shekhar Azad were among the leaders of the movement in Uttar Pradesh, and Motilal Nehru, Jawaharlal Nehru, Madan Mohan Malaviya and Govind Ballabh Pant were important national leaders of the Indian National Congress. The All India Kisan Sabha was formed at the Lucknow session of the Congress on 11 April 1936, with the famous nationalist Sahajanand Saraswati elected as its first president,[57] to address the longstanding grievances of the peasantry and mobilise them against the zamindari landlords attacks on their occupancy rights, thus sparking the Farmers movements in India.[58] During the Quit India Movement of 1942, Ballia district overthrew the colonial authority and installed an independent administration under Chittu Pandey. Ballia became known as "Baghi Ballia" (Rebel Ballia) for this significant role in India's independence movement.[59]
Post-independence
After India's independence, the United Provinces were renamed "Uttar Pradesh" (lit. 'northern province'), preserving UP as the abbreviation of the state's name,[60][61] with the change coming into effect on 24 January 1950.[1] The new state was formed after the merger of several princely states and territories, including the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh, and the Delhi territory. The state has provided nine of India's prime ministers which is more than any other state and is the source of the largest number of seats in the Lok Sabha. Despite its political influence since ancient times, its poor record in economic development and administration, poor governance, organised crime and corruption have kept it among India's backward states. The state has been affected by repeated episodes of caste-related and communal violence.[62] In December 1992 the disputed Babri Mosque located in Ayodhya was demolished by Hindu activists, leading to widespread violence across India.[63] In 2000, northern districts of the state were separated to form the state of Uttarakhand.[64]
Geography

Uttar Pradesh, with a total area of 240,928 square kilometres (93,023 sq mi), is India's fourth-largest state in terms of land area and is roughly of same size as United Kingdom. It is situated on the northern spout of India and shares an international boundary with Nepal. The Himalayas border the state on the north,[65] but the plains that cover most of the state are distinctly different from those high mountains.[66] The larger Gangetic Plain region is in the north; it includes the Ganges-Yamuna Doab, the Ghaghra plains, the Ganges plains and the Terai.[67] The smaller Vindhya Range and plateau region are in the south.[68] It is characterised by hard rock strata and a varied topography of hills, plains, valleys and plateaus. The Bhabhar tract gives place to the terai area which is covered with tall elephant grass and thick forests interspersed with marshes and swamps.[69][70] The sluggish rivers of the bhabhar deepen in this area, their course running through a tangled mass of thick undergrowth. The terai runs parallel to the bhabhar in a thin strip. The entire alluvial plain is divided into three sub-regions.[71] The first in the eastern tract consisting of 14 districts which are subject to periodical floods and droughts and have been classified as scarcity areas. These districts have the highest density of population which gives the lowest per capita land. The other two regions, the central and the western, are comparatively better with a well-developed irrigation system.[72] They suffer from waterlogging and large-scale user tracts.[73] In addition, the area is fairly arid. The state has more than 32 large and small rivers; of them, the Ganga, Yamuna, Saraswati, Sarayu, Betwa, and Ghaghara are larger and of religious importance in Hinduism.[74]
Cultivation is intensive in the state.[75] Uttar Pradesh falls under three agro-climatic zones viz. Middle Gangetic Plains region (Zone–IV), Upper Gangetic Plains region (Zone–V) and Central Plateau and Hills region (Zone–VIII).[76] The valley areas have fertile and rich soil. There is intensive cultivation on terraced hill slopes, but irrigation facilities are deficient.[77] The Siwalik Range which forms the southern foothills of the Himalayas, slopes down into a boulder bed called 'bhabhar'.[78] The transitional belt running along the entire length of the state is called the terai and bhabhar area. It has rich forests, cutting across it are innumerable streams which swell into raging torrents during the monsoon.[79]
Climate

Uttar Pradesh has a humid subtropical climate and experiences four seasons.[80] The winter in January and February is followed by summer between March and May and the monsoon season between June and September.[81] Summers are extreme with temperatures fluctuating anywhere between 0–50 °C (32–122 °F) in parts of the state coupled with dry hot winds called the Loo.[82] The Gangetic plain varies from semiarid to sub-humid.[81] The mean annual rainfall ranges from 650 mm (26 inches) in the southwest corner of the state to 1,000 mm (39 inches) in the eastern and south eastern parts of the state.[83] Primarily a summer phenomenon, the Bay of Bengal branch of the Indian monsoon is the major bearer of rain in most parts of state. After summer it is the southwest monsoon which brings most of the rain here, while in winters rain due to the western disturbances and north-east monsoon also contribute small quantities towards the overall precipitation of the state.[80][84]
| Climate data for Uttar Pradesh | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.9 (85.8) |
31.9 (89.4) |
35.4 (95.7) |
37.7 (99.9) |
36.9 (98.4) |
31.7 (89.1) |
28.4 (83.1) |
27.4 (81.3) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.4 (88.5) |
30.1 (86.2) |
28.9 (84.0) |
31.6 (88.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 11.0 (51.8) |
12.1 (53.8) |
15.8 (60.4) |
19.9 (67.8) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.2 (72.0) |
21.6 (70.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
18.5 (65.3) |
14.4 (57.9) |
11.5 (52.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 0 (0) |
3 (0.1) |
2 (0.1) |
11 (0.4) |
40 (1.6) |
138 (5.4) |
163 (6.4) |
129 (5.1) |
155 (6.1) |
68 (2.7) |
28 (1.1) |
4 (0.2) |
741 (29.2) |
| Average precipitation days | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 3.3 | 10.9 | 17.0 | 16.2 | 10.9 | 5.0 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 67.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 291.4 | 282.8 | 300.7 | 303.0 | 316.2 | 186.0 | 120.9 | 111.6 | 177.0 | 248.44 | 270.0 | 288.3 | 2,896.34 |
| Source: [85] | |||||||||||||
The rain in Uttar Pradesh can vary from an annual average of 170 cm (67 inches) in hilly areas to 84 cm (33 inches) in Western Uttar Pradesh.[80] Given the concentration of most of this rainfall in the four months of the monsoon, excess rain can lead to floods and shortage to droughts. As such, these two phenomena, floods and droughts, commonly recur in the state. The climate of the Vindhya Range and plateau is subtropical with a mean annual rainfall between 1,000 and 1,200 mm (39 and 47 inches), most of which comes during the monsoon.[81] Typical summer months are from March to June, with maximum temperatures ranging from 30–38 °C (86–100 °F). There is a low relative humidity of around 20% and dust-laden winds blow throughout the season. In summer, hot winds called loo blow all across Uttar Pradesh.[80]
Flora and fauna
| State animal | Swamp deer (Rucervus duvaucelii) | |
| State bird | Sarus crane (Antigone antigone) | 
|
| State tree | Ashoka (Saraca asoca) | |
| State flower | Palash (Butea monosperma) | |
| State dance | Kathak | 
|
| State sport | Field hockey |
Uttar Pradesh has an abundance of natural resources.[88] In 2011, the recorded forest area in the state was 16,583 km2 (6,403 sq mi) which is about 6.9% of the state's geographical area.[89] In spite of rapid deforestation and poaching of wildlife, a diverse flora and fauna continue to exist in the state. Uttar Pradesh is a habitat for 4.2% of all species of Algae recorded in India, 6.4% of Fungi, 6.0% of Lichens, 2.9% of Bryophytes, 3.3% of Pteridophytes, 8.7% of Gymnosperms, 8.1% of Angiosperms.[90] Several species of trees, large and small mammals, reptiles, and insects are found in the belt of temperate upper mountainous forests. Medicinal plants are found in the wild[91] and are also grown in plantations. The Terai–Duar savanna and grasslands support cattle. Moist deciduous trees grow in the upper Gangetic plain, especially along its riverbanks. This plain supports a wide variety of plants and animals. The Ganges and its tributaries are the habitat of large and small reptiles, amphibians, fresh-water fish, and crabs. Scrubland trees such as the Babool (Vachellia nilotica) and animals such as the Chinkara (Gazella bennettii) are found in the arid Vindhyas.[92][93] Tropical dry deciduous forests are found in all parts of the plains. Since much sunlight reaches the ground, shrubs and grasses are also abundant.[94] Large tracts of these forests have been cleared for cultivation. Tropical thorny forests, consisting of widely scattered thorny trees, mainly babool are mostly found in the southwestern parts of the state.[95]
Uttar Pradesh is known for its extensive avifauna.[96] The most common birds which are found in the state are doves, peafowl, junglefowl, black partridges, house sparrows, songbirds, blue jays, parakeets, quails, bulbuls, comb ducks, kingfishers, woodpeckers, snipes, and parrots. Bird sanctuaries in the state include Bakhira Sanctuary, National Chambal Sanctuary, Chandra Prabha Wildlife Sanctuary, Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary, Kaimoor Wildlife Sanctuary, and Okhla Sanctuary.[97][98][99][100][101][102]
Other animals in the state include reptiles such as lizards, cobras, kraits, and gharials. Among the wide variety of fishes, the most common ones are mahaseer and trout. Some animal species have gone extinct in recent years, while others, like the lion from the Gangetic Plain, the rhinoceros from the Terai region, Ganges river dolphin primarily found in the Ganges have become endangered.[103] Many species are vulnerable to poaching despite regulation by the government.[104]
-
Anandabodhi tree (Ficus religiosa) in Jetavana Monastery, Sravasti
-
A hybrid nasturtium (Tropaeolum majus) showing nectar spur, found mainly in Hardoi district
-
An endangered Ganges river dolphin (Platanista gangetica) lives in the Ganges river
-
View of the Terai region
-
The threatened Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) is a large fish-eating crocodilian found in the Ganges River
Divisions, districts and cities
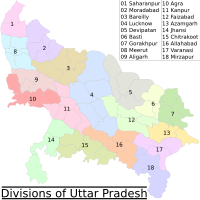
Uttar Pradesh is divided into 75 districts under these 18 divisions:[105]
The following is a list of top districts from state of Uttar Pradesh by population, ranked in respect of all India.[106]
| Rank (in India) | District | Population | Growth Rate (%) | Sex Ratio (Females per 1000 Males) | Literacy Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Prayagraj | 5,954,391 | 20.63 | 901 | 72.32 |
| 26 | Moradabad | 4,772,006 | 25.22 | 906 | 56.77 |
| 27 | Ghaziabad | 4,681,645 | 42.27 | 881 | 78.07 |
| 30 | Azamgarh | 4,613,913 | 17.11 | 1019 | 70.93 |
| 31 | Lucknow | 4,589,838 | 25.82 | 917 | 77.29 |
| 32 | Kanpur Nagar | 4,581,268 | 9.92 | 862 | 79.65 |
| 41 | Agra | 4,418,797 | 22.05 | 868 | 71.58 |
| 50 | Bareilly | 4,448,359 | 22.93% | 887 | 58.5 |
Each district is governed by a District Magistrate, who is an Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officer appointed Government of Uttar Pradesh and reports to Divisional Commissioner of the division in which his district falls.[107] The Divisional Commissioner is an IAS officer of high seniority. Each district is divided into subdivisions, governed by a Sub-Divisional Magistrate, and again into Blocks. Blocks consists of panchayats (village councils) and town municipalities.[108] These blocks consists of urban units viz. census towns and rural units called gram panchayat.[107]
Uttar Pradesh has more metropolitan cities than any other state in India.[109][110] The absolute urban population of the state is 44.4 million, which constitutes 11.8% of the total urban population of India, the second-highest of any state.[111] According to the 2011 census, there are 15 urban agglomerations with a population greater than 500,000.[112] Uttar Pradesh has a complex system of municipalities. Nagar Nigam (Municipal Corporation) are urban local bodies in large cities such as Lucknow, Kanpur, Varanasi and cities having population more than 4 million.[113] These governed by a mayor and councilors elected from wards. Nagar Palika Parishad or Municipal Council, serves medium-sized towns like Bela Pratapgarh, Jalaun, or Bisalpur and are governed by a chairperson and councilors.[114] Nagar Panchayat which operate in smaller towns and semi-urban areas like Badlapur, Jaunpur, Bikapur, or Chilkana Sultanpur, are governed by a chairman and councilors.[114] There are 14 Municipal Corporations,[115][116] while Noida and Greater Noida in Gautam Budha Nagar district are specially administered by statutory authorities under the Uttar Pradesh Industrial Development Act, 1976.[117][118]
In 2011, state's cabinet ministers headed by the then Chief Minister Mayawati announced the separation of Uttar Pradesh into four different states of Purvanchal, Bundelkhand, Avadh Pradesh and Paschim Pradesh with twenty-eight, seven, twenty-three and seventeen districts, respectively, later the proposal was turned down when the Akhilesh Yadav–lead Samajwadi Party came to power in the 2012 election.[119]
Demographics
Uttar Pradesh has a very large population and a high population growth rate. From 1991 to 2001 its population increased by over 26 per cent.[122] It is the most populous state in India, with 199,581,477 people on 1 March 2011.[123] The state contributes to 16.2 per cent of India's population. As of 2021, the estimated population of the state is around 240 million people.[124] The population density is 828 people per square kilometre, making it one of the most densely populated states in the country.[125] It has the largest scheduled caste population whereas scheduled tribes are less than 1 per cent of the total population.[126][127]
The sex ratio in 2011, at 912 women to 1000 men, was lower than the national figure of 943.[11] The low sex ratio in Uttar Pradesh, is a result of various factors, such as sex-selective abortion, female infanticide, and discrimination against girls and women.[128][129] The state's 2001–2011 decennial growth rate (including Uttrakhand) was 20.1 per cent, higher than the national rate of 17.64 per cent.[130][131] It has a large number of people living below the poverty line.[132] As per a World Bank document released in 2016, the pace of poverty reduction in the state has been slower than the rest of the country.[133] Estimates released by the Reserve Bank of India for the year 2011–12 revealed that the state had 59 million (59819,000) people below the poverty line, the most for any state in India.[132][134] The central and eastern districts in particular have very high levels of poverty. The state is also experiencing widening consumption inequality. As per the report of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation released in 2020, the state per capita income is below ₹80,000 (US$940) per annum.[135]
As per 2011 census, Uttar Pradesh, the most populous state in India, is home to the highest numbers of both Hindus and Muslims.[136] The literacy rate of the state at the 2011 census was 67.7 per cent, which was below the national average of 74 per cent.[137][138] The literacy rate for men is 79 per cent and for women 59 per cent. In 2001 the literacy rate in the state stood at 56 per cent overall, 67 per cent for men and 43 per cent for women.[139] A report based on a National Statistical Office (NSO) survey[a] revealed that Uttar Pradesh's literacy rate is 73 per cent, less than the national average of 77.7 per cent. According to the report, in the rural region, the literacy rate among men is 80.5 per cent and women is 60.4 per cent, while in urban areas, the literacy rate among men is 86.8 per cent and women is 74.9 per cent.[140]
Hindi is the primary official language and is spoken by the majority of the population.[8] Bhojpuri is the second most spoken language of the state,[141] it is spoken by almost 11 per cent of the population. Most people speak regional languages classified as dialects of Hindi in the census. These include Awadhi spoken in Awadh in central Uttar Pradesh, Bhojpuri spoken in Purvanchal in eastern Uttar Pradesh, and Braj Bhasha spoken in the Braj region in Western Uttar Pradesh. These languages have also been recognised by the state government for official use in their respective regions. Urdu is given the status of a second official language, spoken by 5.4 per cent of the population.[8][142] English is used as a means of communication for education, commerce, and governance. It is commonly spoken and employed as a language of instruction in educational institutions, as well as for conducting business transactions and managing administrative affairs. Other notable languages spoken in the state include Punjabi (0.3 per cent) and Bengali (0.1 per cent).[142]
Governance and administration

The state is governed by a parliamentary system of representative democracy. Uttar Pradesh is one of the seven states in India, where the state legislature is bicameral, comprising two houses: the Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) and the Vidhan Parishad (Legislative Council).[143][144] The Legislative Assembly consists of 404 members who are elected for five-year terms. The Legislative Council is a permanent body of 100 members with one-third (33 members) retiring every two years. The state sends the largest number of legislators to the national Parliament.[145] The state contributes 80 seats to Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Indian Parliament, and 31 seats to Rajya Sabha, the upper house.[146][147]
The Government of Uttar Pradesh is a democratically elected body in India with the governor as its constitutional head and is appointed by the president of India for a five-year term.[148] The leader of the party or coalition with a majority in the Legislative Assembly is appointed as the chief minister by the governor, and the council of ministers is appointed by the governor on the advice of the chief minister. The governor remains a ceremonial head of the state, while the chief minister and his council are responsible for day-to-day government functions. The Council of Ministers consists of Cabinet Ministers and Ministers of State (MoS). The Secretariat headed by the Chief Secretary assists the council of ministers. The Chief Secretary is also the administrative head of the government. Each government department is headed by a minister, who is assisted by an Additional Chief Secretary or a Principal Secretary, who is usually an officer of Indian Administrative Service (IAS), the Additional Chief Secretary/Principal Secretary serves as the administrative head of the department they are assigned to. Each department also has officers of the rank of Secretary, Special Secretary, Joint Secretary etc. assisting the Minister and the Additional Chief Secretary/Principal Secretary.[149][150]
For administration, the state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts. Divisional Commissioner, an IAS officer is the head of administration on the divisional level.[149][151][152] The administration in each district is headed by a District Magistrate, who is also an IAS officer, and is assisted by several officers belonging to state services.[149][153] District Magistrate being the head of the district administration, is responsible for maintaining law and order and providing public services in the district. At the block level, the Block Development Officer (BDO) is responsible for the overall development of the block. The Uttar Pradesh Police is headed by an IPS officer of the rank of Director general of police. A Superintendent of Police, an IPS officer assisted by the officers of the Uttar Pradesh Police Service, is entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining law and order and related issues in each district. The Divisional Forest Officer, an officer belonging to the Indian Forest Service manages the forests, environment, and wildlife of the district, assisted by the officers of Provincial Forest Service and Uttar Pradesh Forest Subordinate Service.[154]

The judiciary in the state consists of the Allahabad High Court in Prayagraj, the Lucknow Bench of Allahabad High Court, district courts and session courts in each district or Sessions Division, and lower courts at the tehsil level.[149][155] The president of India appoints the chief justice of the High Court of the Uttar Pradesh judiciary on the advice of the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India as well as the governor of Uttar Pradesh.[149][156] Subordinate Judicial Service, categorised into two divisions viz. Uttar Pradesh civil judicial services and Uttar Pradesh higher judicial service are another vital part of the judiciary of Uttar Pradesh.[149][157] While the Uttar Pradesh civil judicial services comprise the Civil Judges (Junior Division)/Judicial Magistrates and civil judges (Senior Division)/Chief Judicial Magistrate, the Uttar Pradesh higher judicial service comprises civil and sessions judges.[149] The Subordinate judicial service (viz. The district court of Etawah and the district court of Kanpur Dehat) of the judiciary at Uttar Pradesh is controlled by the District Judge.[149][157][158]
Politics in Uttar Pradesh has been dominated by four political parties – the Samajwadi Party, the Bahujan Samaj Party, the Bharatiya Janata Party, and the Indian National Congress. The political landscape of the state is often characterized by intense competition and polarization, leading to caste-based tensions and communal conflicts.[159] Critics often suggest that despite Uttar Pradesh's significant political legacy of producing eight Prime Ministers, the state continues to struggle with issues that hinder its overall advancement.[160]
Crime and accidents
According to the National Human Rights Commission of India (NHRC), Uttar Pradesh tops the list of states of encounter killings and custodial deaths.[161] In 2014, the state recorded 365 judicial deaths out of a total 1,530 deaths recorded in the country.[162] NHRC further said, of the over 30,000 murders registered in the country in 2016, Uttar Pradesh had 4,889 cases.[163] A data from Minister of Home Affairs (MHA) avers, Bareilly recorded the highest number of custodial death at 25, followed by Agra (21), Allahabad (19) and Varanasi (9). National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data from 2011 says, the state has the highest number of crimes among any state in India, but due to its high population, the actual per capita crime rate is low.[164] The state also continues to top the list of states with maximum communal violence incidents. An analysis of Ministers of State of Home Affairs states (2014), 23 per cent of all incidents of communal violence in India took place in the state.[165][166] According to a research assembled by State Bank of India, Uttar Pradesh failed to improve its Human Development Index (HDI) ranking over a period of 27 years (1990–2017).[167] Based on sub-national human development index data for Indian states from 1990 to 2017, the report also stated that the value of human development index has steadily increased over time from 0.39 in 1990 to 0.59 in 2017.[168][169][170] The Uttar Pradesh Police, governed by the Department of Home and Confidential, is the largest police force in the world.[171][172][173]
Uttar Pradesh also reported the highest number of deaths – 41,746 – due to road accidents till December 2022, according to "Road Accidents in India" report of Union Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.[174][175] The UP Transport Department report also indicates that the primary cause of road accident fatalities was over-speeding, which accounted for 40 per cent of deaths. Drunken driving contributed to 10 per cent of fatalities, while 12 per cent of deaths were due to driving on the wrong side. Additionally, 10 per cent of accident deaths were caused by the use of mobile phones, and 5 per cent resulted from running red lights. The remaining 23 per cent of deaths were attributed to factors such as losing control of the vehicle, drowsiness, poor road visibility, and engineering defects.[176]
Between 2006 and 2010, the state has been hit with three terrorist attacks, including explosions in a landmark holy place, a court and a temple. The 2006 Varanasi bombings were a series of bombings that occurred across the Hindu holy city of Varanasi on 7 March 2006. At least 28 people were killed and as many as 101 others were injured.[177][178] In the afternoon of 23 November 2007, within a span of 25 minutes, six consecutive serial blasts occurred in the Lucknow, Varanasi, and Faizabad courts, in which 28 people were killed.[179][180][181] Another blast occurred on 7 December 2010, the blast occurred at Sheetla Ghat in Varanasi in which more than 38 people were killed.[182][183] In February 2016, a series of bomb blasts occurred at the Jhakarkati Bus Station in Kanpur, killing 2 people and injuring more than 30.[184]
Economy
| Net State Domestic Product at Factor Cost at Current Prices (2011–12 Base)
figures in crores of Indian rupees | |
| Year | Net State Domestic Product[185] |
|---|---|
| 2011–12 | 532,218 |
| 2015–16 | 1,137,808 |
| 2016–17 | 1,288,700 |
| 2017–18 | 1,446,000[186] (est.) |

In terms of net state domestic product (NSDP), Uttar Pradesh is the fourth-largest economy in India, with an estimated gross state domestic product of ₹14.89 lakh crore (US$170 billion),[186] contributing 8.4% of India's gross domestic product.[187] According to the report generated by India Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF), in 2014–15, Uttar Pradesh has accounted for 19% share in the country's total food grain output.[188] About 70% of India's sugar comes from Uttar Pradesh. Sugarcane is the most important cash crop as the state is country's largest producer of sugar.[188] As per the report generated by Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA), total sugarcane production in India was estimated to be 28.3 million tonnes in the fiscal ending September 2015 which includes 10.47 million tonnes from Maharashtra and 7.35 million tonnes from Uttar Pradesh.[189]
With 359 manufacturing clusters, cement is the top sector of SMEs in Uttar Pradesh.[190] The Uttar Pradesh Financial Corporation (UPFC) was established in 1954 under the SFCs Act of 1951 mainly to develop small- and medium-scale industries in the state.[191] The UPFC also provides working capital to existing units with a soundtrack record and to new units under a single window scheme.[192] In July 2012, due to financial constraints and directions from the state government, lending activities were suspended except for State Government Schemes.[193] The state has reported total private investment worth over Rs. 25,081 crores during the years of 2012 and 2016.[194] According to a 2015 report by the World Bank on the Ease of Doing Business in India, Uttar Pradesh was ranked among the top 10 states and was the first among the northern states.[195]
According to the Uttar Pradesh Budget Documents (2019–20), Uttar Pradesh's debt burden is 29.8 per cent of the GSDP.[196] The state's total financial debt stood at ₹2.09 lakh crore (US$24 billion) in 2011.[197] Uttar Pradesh has not been able to witness double-digit economic growth despite consistent attempts over the years.[196] The GSDP is estimated to have grown 7 per cent in 2017–18 and 6.5 per cent in 2018–19 which is about 10 per cent of India's GDP. According to a survey conducted by the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), Uttar Pradesh's unemployment rate increased 11.4 percentage points, rising to 21.5 per cent in April 2020.[198] Uttar Pradesh has the largest number of net migrants migrating out of the state.[199] The 2011 census data on migration shows that nearly 14.4 million (14.7%) people had migrated out of Uttar Pradesh.[200] Marriage was cited as the predominant reason for migration among females. Among males, the most important reason for migration was work and employment.[201] Uttar Pradesh continues to have regional disparities, particularly with the western districts of the state showing higher development indicators such as per capita district development product (PCDDP) and gross district development product (GDDP) compared to other regions.[202] Due to inadequate infrastructure and a dense population, Eastern Uttar Pradesh (Purvanchal) faces notable socio-economic disparities.[203] For 2021–22 the GDDP for Purvanchal it is ₹5.37 lakh crore, while for Western Uttar Pradesh it is ₹9.44 lakh crore. For the Bundelkhand and Central Uttar Pradesh regions, the GDDP remained ₹99,029.34 crore and ₹3.36 lakh crore, respectively. As of 2021–22, the per capita annual income in eastern districts is about one-fourth of the national average at ₹12,741 while the state's average stood at ₹17,349.[204]

In 2009–10, the tertiary sector of the economy (service industries) was the largest contributor to the gross domestic product of the state, contributing 44.8 per cent of the state domestic product compared to 44 per cent from the primary sector (agriculture, forestry, and tourism) and 11.2 per cent from the secondary sector (industrial and manufacturing).[206][207] Noida, Meerut, and Agra rank as the top 3 districts with the highest per capita income, whereas Lucknow and Kanpur rank 7th and 9th in per capita income.[208] During the 11th five-year plan (2007–2012), the average gross state domestic product (GSDP) growth rate was 7.3 per cent, lower than 15.5 per cent, the average for all states of the country.[209][210] The state's per capita GSDP was ₹29,417 (US$340), lower than the national per capita GSDP of ₹60,972 (US$710).[211] Labor efficiency is higher at an index of 26 than the national average of 25. Textiles and sugar refining, both long-standing industries in Uttar Pradesh, employ a significant proportion of the state's total factory labour. The economy also benefits from the state's tourism industry.[212]
Transportation

The state has the largest railway network in the country but in relative terms has only sixth-highest railway density despite its plain topography and largest population. As of 2015[update], there were 9,077 km (5,640 mi) of rail in the state.[213][214] The railway network in the state is controlled by two divisions of the Indian Railways viz. North Central Railway and North Eastern Railway. Allahabad is the headquarters of the North Central Railway[215] and Gorakhpur is the headquarters of the North Eastern Railway.[216][217] Lucknow and Moradabad serve as divisional Headquarters of the Northern Railway Division. Lucknow Swarna Shatabdi Express, the second fastest Shatabdi Express train, connects the Indian capital of New Delhi to Lucknow while Kanpur Shatabdi Express, connects New Delhi to Kanpur Central. This was the first train in India to get the new German LHB coaches.[218] The railway stations of Prayagraj Junction, Agra Cantonment, Lucknow Charbagh, Gorakhpur Junction, Kanpur Central, Mathura Junction and Varanasi Junction are included in the Indian Railways list of 50 world-class railway stations.[219] The Lucknow Metro, along with the Kanpur Metro (Orange line), are rapid transit systems that serve Lucknow and Kanpur, respectively.
The state has a large, multimodal transportation system with the largest road network in the country.[220] It has 42 national highways, with a total length of 4,942 km (3,071 miles) comprising 8.9 per cent of the total national highways length in India.[221] The Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (UPSRTC) was established in 1972 to provide transportation in the state with connecting services to adjoining states.[222] The UPSRTC’s current fleet consists of 11,238 buses operating on 2,762 routes across a total distance of 768,065 km (477,253 mi) throughout the state, generating an average daily income of ₹16 crore (US$1.9 million).[223] Despite its extensive operation, many of UPSRTC buses are now outdated and unreliable, raising concerns about their condition and the impact on passenger safety.[224] All cities are connected to state highways, and all district headquarters are being connected with four lane roads which carry traffic between major centres within the state. One of them is Agra–Lucknow Expressway, which is a 302 km (188 miles) controlled-access highway constructed by UPEIDA.[225] Uttar Pradesh has the highest road density in India – 1,027 km (638 miles) per 1,000 km2 (390 square miles) – and the largest surfaced urban-road network in the country – 50,721 km (31,517 miles).[226]
By passenger traffic in India, Chaudhary Charan Singh International Airport in Lucknow and Lal Bahadur Shastri Airport in Varanasi, are the major international airports and the main gateway to the state.[227] Another international airport has been built at Kushinagar. However, since its inauguration, Kushinagar International Airport has not yet seen any outbound flights to international destinations.[228][229] Uttar Pradesh has six domestic airports located at Agra, Allahabad, Bareilly, Ghaziabad, Gorakhpur and Kanpur.[230][231] Under the collaboration with civilian aviation authority, these domestic airports are primarily used by the Indian Air Force for operational flexibility, especially during emergencies or natural disasters. The Noida International Airport is proposed to be built near Jewar in Gautam Buddha Nagar, district.[232][233][234]
The Noida International Airport
Sports

Traditional sports, now played mostly as a pastime, include wrestling, swimming, kabaddi, and track-sports or water-sports played according to local traditional rules and without modern equipment. Some sports are designed to display martial skills such as using a sword or 'Pata' (stick).[235] Due to a lack of organised patronage and requisite facilities, these sports survive mostly as individuals' hobbies or local competitive events. Among modern sports, field hockey is popular and Uttar Pradesh has produced top-level players in India, such as Nitin Kumar. and Lalit Kumar Upadhyay.[236]
Recently, cricket has become more popular than field hockey.[237] Uttar Pradesh won its first Ranji Trophy tournament in February 2006, beating Bengal in the final.[238] Shaheed Vijay Singh Pathik Sports Complex is a newly built international cricket stadium with a capacity of around 20,000 spectators.[239] Wrestling has deep roots in Uttar Pradesh, with many akharas (traditional wrestling schools) spread across the state.[240]
The Uttar Pradesh football team (UPFS) serves as the governing body for football in Uttar Pradesh. It holds authority over the Uttar Pradesh football team and is officially affiliated with the All India Football Federation.[241] The UPFS participates in sending state teams to compete in all National Football Championships organised by the All India Football Federation.[242] Additionally, the UPFS oversees two Mandal Football Associations: the Aligarh Football Association and the Kanpur Football Association.[243] The Uttar Pradesh Badminton Association is a sports body affiliated to Badminton Association of India responsible for overseeing players representing Uttar Pradesh at the national level.[244]
The Buddh International Circuit hosted India's inaugural F1 Grand Prix race on 30 October 2011.[245] Races were only held three times before being cancelled due to falling attendance and lack of government support. The government of Uttar Pradesh considered Formula One to be entertainment and not a sport, and thus imposed taxes on the event and participants.[246]
Education

Uttar Pradesh has a prolonged tradition of education, although historically it was primarily confined to the elite class and religious schools.[247] Sanskrit-based learning formed the major part of education from the Vedic to the Gupta periods. As cultures travelled through the region they brought their bodies of knowledge with them, adding Pali, Persian and Arabic scholarship to the community. These formed the core of Hindu-Buddhist-Muslim education until the rise of British colonialism. The present schools-to-university system of education owes its inception and development in the state (as in the rest of the country) to foreign Christian missionaries and the British colonial administration.[248] Schools in the state are either managed by the government or by private trusts. Hindi is used as a medium of instruction in most of the schools except those affiliated to the CBSE or the council for ICSE boards.[249] Under the 10+2+3 plan, after completing secondary school, students typically enroll for two years in a junior college, also known as pre-university, or in schools with a higher secondary facility affiliated with the Uttar Pradesh Board of High School and Intermediate Education (commonly referred to as U.P. Board) or a central board. Students choose from one of three streams, namely liberal arts, commerce, or science. Upon completing the required coursework, students may enrol in general or professional degree programs. In a study done by Child Rights and You (CRY) and the Centre for Budgets, Governance, and Accountability (CBGA), Uttar Pradesh spent ₹9,167 per pupil, which is below the national average of ₹12,768.[250] The pupil/teacher ratio is 39:1,[b] lower than the national average of 23:1.[251] According to the National Bureau of Economic Research, the state reported the second-highest teacher absenteeism (31 percent) in rural public schools among 19 surveyed states.[252] According to an answer given by the Union Education Minister in 2020 in the Lok Sabha, about 17.1 percent of all elementary teacher posts in government schools in Uttar Pradesh are vacant. In terms of absolute numbers, the figure stands at 210,000.[253] In February 2024, the Uttar Pradesh government informed legislative assembly that, 85,152 posts of headmasters and assistant teachers are vacant in the state.[254]

Uttar Pradesh has more than 45 universities,[255] including six central universities, twenty eight state universities, eight deemed universities, two IITs in Varanasi and Kanpur, AIIMS Gorakhpur and AIIMS Rae Bareli, an IIM in Lucknow[256][257] Founded in 1845, La Martinière Girls' College in Lucknow, stands as one of the oldest schools in India.[258] Located in Amethi, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Petroleum Technology (RGIPT), provides education and training in STEM fields, particularly emphasizing the petroleum industry. With deemed university status, the RGIPT awards degrees in its own right. King George's Medical University (KGMU), located in Lucknow, is an institution for medical education, research, and healthcare services. The Integral University, a state level institution, was established by the Uttar Pradesh Government to provide education in different technical, applied science, and other disciplines.[259] The Central Institute of Higher Tibetan Studies was founded as an autonomous organisation by the national ministry of culture. Jagadguru Rambhadracharya Handicapped University is the only university established exclusively for the disabled in the world.[260]
As of 2023, the state has 573 public libraries.[261][262] Established in 1875, Maulana Azad Library is one of the oldest and is the largest university library in Asia. Rampur Raza Library is a repository of Indo-Islamic cultural heritage established in the last decades of the 18th century.[262] It was established in 1774 by nawab Faizullah Khan and now an autonomous body under the Ministry of Culture.[263] Thornhill Mayne Memorial also known as Allahabad Public Library, has an approximate collection of 125,000 books, 40 types of magazines, and 28 different newspapers in Hindi, English, Urdu and Bangla and it also contains 21 Arabic manuscripts.[264] A large number of Indian scholars are educated at different universities in Uttar Pradesh. Notable scholars who were born, worked or studied in the geographic area of the state include Harivansh Rai Bachchan, Motilal Nehru, Harish Chandra and Indira Gandhi.[265]
Tourism

Uttar Pradesh ranks first in domestic tourist arrivals among all states of India.[266][267] Some 44,000 foreign tourists arrived in the state in 2021, and almost 110 million domestic tourists.[268] The Taj Mahal attracts some 7 million people a year, earning almost ₹78 crore (US$9.1 million) in ticket sales in 2018–19.[269] The state is home to three World Heritage Sites: the Taj Mahal,[270] Agra Fort,[271] and the nearby Fatehpur Sikri.[272]
Religious tourism plays a significant role in the state's economy. Varanasi is a major religious hub and one of the seven sacred cities (Sapta Puri) in Hinduism and Jainism.[273][274][275] Vrindavan is considered to be a holy place for Vaishnavism.[276][277] Sravasti generally considered as revered sites in Buddhism, believed to be where the Buddha taught many of his Suttas (sermons).[278] Owing to the belief as to the birthplace of Rama, Ayodhya (Awadh) has been regarded as one of the seven most important pilgrimage sites.[279][280][281] Millions gather at Prayagraj to take part in the Magh Mela festival on the banks of the Ganges.[282] This festival is organised on a larger scale every 12th year and is called the Kumbh Mela, where over 10 million Hindu pilgrims congregate in one of the largest gatherings of people in the world.[283]
Buddhist attractions in Uttar Pradesh include stupas and monasteries. The historically important towns of Sarnath where Gautama Buddha gave his first sermon after his enlightenment and died at Kushinagar; both of which are important pilgrimage sites for Buddhists.[284] Also at Sarnath are the Pillars of Ashoka and the Lion Capital of Ashoka, both important archaeological artefacts with national significance. At a distance of 80 km (50 miles) from Varanasi, Ghazipur is famous not only for its Ghats on the Ganges but also for the tomb of Lord Cornwallis, the 18th-century Governor of East India Company ruled Bengal Presidency. The tomb is maintained by the Archaeological Survey of India.[285] Jhansi Fort, located in the city of Jhansi, is closely associated with the "First War of Indian Independence", also known as the "Great Rebellion" or the Indian Rebellion of 1857.[286] The fort is constructed in accordance with medieval Indian military architecture, featuring thick walls, bastions, and various structures within its complex. The architecture reflects a blend of Hindu and Islamic styles.[287]
Healthcare
Uttar Pradesh has a mix of public as well as private healthcare infrastructure. Public healthcare in Uttar Pradesh is provided through a grid of primary health centers, community health centers, district hospitals, and medical colleges. Although an extensive network of public and private sector healthcare providers has been built, the available health infrastructure is inadequate to meet the demand for health services in the state.[288] In 15 years to 2012–13, the population increased by more than 25 per cent. The public health centres, which are the frontline of the government's health care system, decreased by 8 per cent.[289] Smaller sub-centres, the first point of public contact, increased by no more than 2 per cent over the 25 years to 2015, a period when the population grew by more than 51 per cent.[289] The state is also facing challenges such as a shortage of healthcare professionals, increasing cost of healthcare, a lack of essential medicines and equipment, the mushrooming of private healthcare and a lack of planning.[290] The number of doctors registered with State Medical Councils or the Medical Council of India in Uttar Pradesh was 77,549.[291] As of 2019[update], the number of government hospital in rural and urban areas of Uttar Pradesh stood at 4,442 with 39,104 beds and 193 with 37,156 beds respectively. The average population served per government hospital stands at 47,782 individuals.[292] As of December 2023[update], Out-of-pocket expenditures in Uttar Pradesh is ₹60,883 crore (US$7.1 billion), highest in India.[293]
A newborn in Uttar Pradesh is expected to live four years fewer than in the neighbouring state of Bihar, five years fewer than in Haryana and seven years fewer than in Himachal Pradesh. The state contributed to the largest share of almost all communicable and noncommunicable disease deaths, including 48 per cent of all typhoid deaths (2014); 17 per cent of cancer deaths and 18 per cent of tuberculosis deaths (2015).[289] Its maternal mortality ratio is higher than the national average at 285 maternal deaths for every 100,000 live births (2021), with 64.2 per cent of pregnant women unable to access minimum ante-natal care.[294][295][296] Around 42 per cent of pregnant women, more than 1.5 million, deliver babies at home. About two-thirds (61 per cent) of childbirths at home in the state are unsafe.[297] It has the highest child mortality indicators,[298] from the neonatal mortality rate to the under-five mortality rate of 64 children who die per 1,000 live births before five years of age, 35 die within a month of birth, and 50 do not complete a year of life.[299]
Culture
Language and literature

Several texts and hymns of the Vedic literature were composed in Uttar Pradesh. Renowned Indian writers who have resided in Uttar Pradesh were Kabir, Ravidas, and Tulsidas, who wrote much of his Ram Charit Manas in Varanasi. The festival of Guru Purnima is dedicated to Sage Vyasa, and also known as Vyasa Purnima as it is the day which is believed to be his birthday and also the day he divided the Vedas.[300]
Hindi became the language of state administration with the Uttar Pradesh Official Language Act of 1951.[301] A 1989 amendment to the act added Urdu, as an additional language of the state.[302] Linguistically, the state spreads across the Central, East-Central, and Eastern zones of the Indo Aryan languages. The major Hindi languages of the state are Awadhi, Bagheli, Bundeli, Braj Bhasha, Kannauji, and Hindustani.[303] Bhojpuri, an Eastern Indo Aryan language, is also spoken in the state.[304]
Music and dance
With each district of Uttar Pradesh having its unique music and tradition, traditional folk music in Uttar Pradesh has been categorised in three different ways including music transmitted orally, music with unknown composers and music performed by custom. During the medieval period, two distinct types of music began to emerge in Uttar Pradesh. One was the courtly music, which received support from cities like Agra, Fatehpur Sikri, Lucknow, Jaunpur, Varanasi, and Banda. The other was the religious music stemming from the Bhakti Cult, which thrived in places like Mathura, Vrindavan, and Ayodhya.[305] The popular folk music of Uttar Pradesh includes sohar, which is sung to celebrate the birth of a child. Evolved into the form of semi-classical singing, Kajari sung during the rainy season, and its singing style is closely associated the Benares gharana.[306] Ghazal, Thumri and Qawwali which is a form of Sufi poetry is popular in the Awadh region, Rasiya (especially popular in Braj), which celebrate the divine love of Radha and Krishna. Khayal is a form of semi-classical singing which comes from the courts of Awadh. Other forms of music are Biraha, Chaiti, Chowtal, Alha, and Sawani.[305]
Kathak, a classical dance form, owes its origin to the state of Uttar Pradesh.[307] Ramlila is one of the oldest dramatic folk dances; it depicts the life of the Hindu deity Rama and is performed during festivals such as Vijayadashami.[308] Nautanki is a traditional form of folk theatre that originated in Uttar Pradesh. It typically portrays a variety of themes ranging from historical and mythological tales to social and political commentary.[309] In the gharana dance form, both the Lucknow and the Benares gharanas are situated in the state.[310] Charkula is popular dance of the Braj region.[311]
Fairs and festivals

Chhath Puja is the biggest festival of eastern Uttar Pradesh.[312] The Kumbh Mela, organised in the month of Maagha (February—March), is a major festival held every twelve years in rotation at Prayagraj on the river Ganges.[313] Lathmar Holi is a local celebration of the Hindu festival of Holi. It takes place well before the actual Holi in the town of Barsana near Mathura.[314] Taj Mahotsav, held annually at Agra, is a colourful display of the culture of the Braj area.[315] Ganga Mahotsav, a festival of Kartik Purnima, is celebrated fifteen days after Diwali.[316]
Cuisine
Mughlai cuisine is a style of cooking developed in the Indian subcontinent by the imperial kitchens of the Mughal Empire. It represents the cooking styles used in North India, especially Uttar Pradesh, and has been strongly influenced by Central Asian cuisine. Awadhi cuisine from the city of Lucknow consists of both vegetarian and non-vegetarian dishes. It has been greatly influenced by Mughlai cuisine.[317]
Bhojpuri cuisine is a style of food preparation common in the districts located near the Bihar border. Bhojpuri foods are mostly mild and tend to be less hot in terms of spices used. The cuisine consists of both vegetable and meat dishes.[318]
See also
Explanatory notes
References
- ^ a b "United Province, UP was notified in Union gazette on January 24, 1950". The New Indian Express. 2 May 2017. Archived from the original on 8 May 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh District". up.gov.in. Government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 15 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ "List of districts in Uttar Pradesh". archive.india.gov.in. Government of India. Archived from the original on 26 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ PTI (20 July 2019). "Anandiben Patel made UP governor, Lal ji Tandon to replace her in Madhya Pradesh". India Today. Archived from the original on 20 July 2019. Retrieved 20 July 2019.
- ^ "The Governor of Uttar Pradesh". uplegisassembly.gov.in. Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly. Archived from the original on 3 May 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh | History, Government, Map, & Population | Britannica". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 1 April 2020. Retrieved 24 March 2023.
- ^ "List of Highest Mountain Peaks State-wise". Wordpandit. 29 July 2017. Archived from the original on 24 March 2023. Retrieved 24 March 2023.
- ^ a b c "Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 52nd report (July 2014 to June 2015)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. pp. 49–53. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 November 2016. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- ^ a b "Handbook of Statistics of Indian States 2021–22" (PDF). Reserve Bank of India. pp. 37–42. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 11 February 2022.
- ^ "Sub-national HDI – Area Database". Global Data Lab. Institute for Management Research, Radboud University. Archived from the original on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 25 September 2018.
- ^ a b "Census 2011 (Final Data) – Demographic details, Literate Population (Total, Rural & Urban)" (PDF). planningcommission.gov.in. Planning Commission, Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 January 2018. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- ^ "Sex ratio of State and Union Territories of India as per National Health survey (2019–2021)". Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, India. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 26 April 2022.
- ^ Kopf, Dan; Varathan, Preeti (11 October 2017). "If Uttar Pradesh were a country". Quartz India. Archived from the original on 22 June 2019. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
- ^ "Agriculture" (PDF). niti.gov.in. NITI Aayog. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 October 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2021.
- ^ Virendra N. Misra, Peter Bellwood (1985). Recent Advances in Indo-Pacific Prehistory: proceedings of the international symposium held at Poona. BRILL. p. 69. ISBN 9004075127. Archived from the original on 3 March 2018. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ Bridget Allchin, Frank Raymond Allchin (1982). The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan. Cambridge University Press. p. 58. ISBN 052128550X. Archived from the original on 25 March 2017. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ Hasmukhlal Dhirajlal Sankalia; Shantaram Bhalchandra Deo; Madhukar Keshav Dhavalikar (1985). Studies in Indian Archaeology: Professor H.D. Sankalia Felicitation Volume. Popular Prakashan. p. 96. ISBN 978-0861320882. Archived from the original on 24 March 2017.
- ^ Confidence limits for the age are 85 (±11) and 72 (±8) thousand years ago.
- ^ Gibling, Sinha; Sinha, Roy; Roy, Tandon; Tandon, Jain; Jain, M (2008). "Quaternary fluvial and eolian deposits on the Belan river, India: paleoclimatic setting of Paleolithic to Neolithic archeological sites over the past 85,000 years". Quaternary Science Reviews. 27 (3–4): 391. Bibcode:2008QSRv...27..391G. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.11.001. ISSN 0277-3791. S2CID 129392697.
- ^ Kenneth A. R. Kennedy (2000). God-apes and Fossil Men. University of Michigan Press. p. 263. ISBN 0472110136. Archived from the original on 24 March 2017. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ Bridget Allchin, Frank Raymond Allchin (1982). The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan. Cambridge University Press. p. 119. ISBN 052128550X. Archived from the original on 3 March 2018. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ Misra, V N (November 2001). "Prehistoric human colonization of India". Journal of Biosciences. 26 (4 Supp). Indian Academy of Sciences: 491–531. doi:10.1007/bf02704749. PMID 11779962. S2CID 26248907. Archived from the original on 7 October 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh – History". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 1 April 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2020.
A systematic history of India and the area of Uttar Pradesh dates to the end of the 7th century BCE, when 16 mahajanapadas (great states) in northern India were contending for supremacy. Of those, seven fell entirely within the present-day boundaries of Uttar Pradesh.
- ^ a b c d Sailendra Nath Sen (1999). Ancient Indian History And Civilization. New Age International. pp. 105–106. ISBN 978-8122411980. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ William Buck (2000). Ramayana. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-8120817203. Archived from the original on 4 June 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ Richard White (2010). The Middle Ground: Indians, Empires, and Republics in the Great Lakes Region, 1650–1815. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1107005624. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ a b Marshall Cavendish Corporation (2007). World and Its Peoples: Eastern and Southern Asia. Marshall Cavendish. pp. 331–335. ISBN 978-0761476313. Archived from the original on 5 June 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ a b Pran Nath Chopra (2003). A Comprehensive History of Ancient India. Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. p. 196. ISBN 978-8120725034. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ a b John Stewart Bowman (2000). Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture. Columbia University Press. p. 273. ISBN 978-0231110044. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- ^ The History of India by Kenneth Pletcher p. 102
- ^ The City in South Asia by James Heitzman p. 37
- ^ Singh, Pradyuman (19 January 2021). Bihar General Knowledge Digest. Prabhat Prakashan. ISBN 978-9352667697.
- ^ * Srivastava, Ashirvadi Lal (1929). The Sultanate of Delhi 711–1526 A D. Shiva Lal Agarwala & Company. Archived from the original on 8 April 2016. Retrieved 29 April 2018.
- ^ Islam; Bosworth (1998). History of Civilizations of Central Asia. UNESCO. pp. 269–291. ISBN 978-9231034671. Archived from the original on 28 March 2024. Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- ^ "Atala Masjid". District Jaunpur, Government of Uttar Pradesh. 20 June 2017. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ Datta, Rangan (22 July 2022). "The tomb of Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq". Telegraph India. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ "The Islamic World to 1600: Rise of the Great Islamic Empires (The Mughal Empire)". Archived from the original on 27 September 2011.
- ^ Annemarie Schimmel (2004). The Empire of the Great Mughals: History, Art and Culture. Reaktion Books. ISBN 978-1861891853. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ Babur (Emperor of Hindustan); Dilip Hiro (2006). Babur Nama: Journal of Emperor Babur. Penguin Books India. ISBN 978-0144001491. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ Carlos Ramirez-Faria (2007). Concise Encyclopedia of World History. Atlantic Publishers & Dist. p. 171. ISBN 978-8126907755. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- ^ Stronge, Susan (2012). Mughal Hindustan is renowned for its opulence. London: The Arts of the Sikh Kingdoms. p. 255. ISBN 9788174366962. Archived from the original on 16 February 2017. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ Ashvini Agrawal (1983). Studies in Mughal History. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 30–46. ISBN 978-8120823266. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2012.
- ^ Fergus Nicoll, Shah Jahan: The Rise and Fall of the Mughal Emperor (2009)
- ^ Mayaram, Shail (2003). Against history, against state: counterperspectives from the margins Cultures of history. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0231127318.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Day: How the state was born 67 years back". 3 May 2017. Archived from the original on 3 May 2017. Retrieved 3 May 2017.
- ^ Gyanesh Kudaisya (1994). Region, nation, "heartland": Uttar Pradesh in India's body-politic. LIT Verlag Münster. pp. 126–376. ISBN 978-3825820978.
- ^ K. Sivaramakrishnan (1999). Modern Forests: Statemaking and Environmental Change in Colonial Eastern India. Stanford University Press. pp. 240–276. ISBN 978-0804745567. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- ^ Ashutosh Joshi (2008). Town Planning Regeneration of Cities. New India Publishing. p. 237. ISBN 978-8189422820. Archived from the original on 3 March 2018.
- ^ Rudrangshu Mukherjee (2005). Mangal Pandey: brave martyr or accidental hero?. Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0143032564. Archived from the original on 5 June 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ United Provinces of Agra and Oudh (India); D.L. Drake-Brockman (1934). District Gazetteers of the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh: supp.D.Pilibhit District. Supdt., Government Press, United Provinces. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ Dilip K. Chakrabarti (1997). Colonial Indology: sociopolitics of the ancient Indian past. Michigan: Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers Pvt. Ltd. p. 257. ISBN 978-8121507509. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- ^ Bernard S. Cohn (1996). Colonialism and Its Forms of Knowledge: The British in India. Princeton University Press. p. 189. ISBN 978-0691000435. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- ^ Clare M. Wilkinson-Weber (1999). Embroidering Lives: Women's Work and Skill in the Lucknow Embroidery Industry. SUNY Press. p. 18. ISBN 978-0791440872. Archived from the original on 28 March 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- ^ Mathur, Prakash Narain. "A History of the Lucknow Bench Of The Allahabad High Court" (PDF). Allahabad High Court. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- ^ K. Balasankaran Nair (2004). Law of Contempt of Court in India. Atlantic Publishers & Dist. p. 320. ISBN 978-8126903597. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- ^ Śekhara, Bandyopādhyāya (2004). From Plassey to Partition: A History of Modern India. Orient Longman. p. 407. ISBN 978-8125025962.
- ^ Bandyopādhyāya, Śekhara (2004). From Plassey to Partition: A History of Modern India. Orient Longman. p. 406. ISBN 978-8125025962.
- ^ Bankim Chandra Chatterji (2006). Anandamath. Orient Paperbacks. p. 168. ISBN 978-8122201307. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh – States and Union Territories". Know India: National Portal of India. Archived from the original on 15 July 2015. Retrieved 14 July 2015.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh". What is India. 22 August 2007. Archived from the original on 12 October 2016. Retrieved 8 October 2016.
- ^ "Communal violence". Business Standard. Ananda Publishers. Kotak Mahindra Bank. 6 August 2014. Archived from the original on 26 August 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ communal violence, in uttar pradesh. "Communal conflicts in state". Tehalka. Archived from the original on 12 January 2014. Retrieved 12 January 2014.
- ^ J. C. Aggarwal; S. P. Agrawal (1995). Uttarakhand: Past, Present, and Future. Concept Publishing Company of India. p. 391. ISBN 978-8170225720. Archived from the original on 24 March 2017.
- ^ "Most critical factors". Uttar Pradesh climate department. Archived from the original on 15 December 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Geography". Uttar Pradesh State Profile. Archived from the original on 23 July 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "The larger Gangetic Plain" (PDF). Gecafs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Gangetic Plains and Vindhya Hills and plateau". Zee news. Archived from the original on 6 April 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ Anwar, Shakeel (16 August 2018). "List of major canals and dams in Uttar Pradesh". Dainik Jagran. Jagran Prakashan Limited. Archived from the original on 22 June 2020. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ "Indo–African Journal for Resource Management" (PDF). Indo–African Journal for Resource Management and Planning. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 April 2022. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ Anwar, Shakeel. "The Great Plains of India". Jagran Josh. Dainik Jagran. Jagran Prakashan Private Limited. Archived from the original on 21 November 2017. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ Clift, Charles (1977). "Progress of Irrigation in Uttar Pradesh: East-West Differences". Economic and Political Weekly. 12 (39). JSTOR: A83 – A90. JSTOR 4365953. Archived from the original on 30 October 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2021.
- ^ R P Meena. Uttar Pradesh Current Affairs Yearbook 2020. New Era Publication. p. 6. GGKEY:XTXLJ8SQZFE. Archived from the original on 28 March 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ "Rivers of Uttar Pradesh". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 7 May 2013. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "The Glossary of Meteorology". Allen Press Inc. Archived from the original on 5 October 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ "Agriculture Mechanization Guide for Uttar Pradesh". Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India. Archived from the original on 16 May 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2021.
- ^ "Potential Creation and Utilisation". Irrigation department U.P. Archived from the original on 13 February 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Purports to define every important meteorological term likely to be found in the literature today". Allen Press, Inc. Archived from the original on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ Vir Singh (1998). Mountain Ecosystems: A Scenario of Unsustainability. Indus Publishing. pp. 102–264. ISBN 978-8173870811. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2012.
- ^ a b c d Upkar Prakashan – Editorial Board (2008). Uttar Pradesh General Knowledge. Upkar Prakashan. pp. 26–. ISBN 978-8174824080. Archived from the original on 5 June 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2011.
- ^ a b c "Climate change impacts". Uttar Pradesh climate department. Archived from the original on 15 November 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ S.V.S. Rana (2007), Essentials of Ecology and Environmental Science, Prentice Hall of India, ISBN 978-81-203-3300-0
- ^ Government of Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow, Irrigation Department Uttar Pradesh. "Average rainfall pattern of Uttar Pradesh". Irrigation Department Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 24 August 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ Sethi, Nitin (13 February 2007). "Met dept blames it on 'western disturbance'". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2011.
- ^ "Local Weather Report". Local Weather Report and Forecast Department. 21 May 2012. Archived from the original on 1 May 2012. Retrieved 18 July 2012.
- ^ "State Animal, Bird, Tree and Flower". Panna Tiger Reserve. Archived from the original on 13 October 2014. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- ^ "Music & Dance". uptourism.gov.in. Uttar Pradesh Tourism. Archived from the original on 23 January 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Forest Corporation". Forest department uttar pradesh. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ "Forest and tree resources in states and union territories: Uttar Pradesh" (PDF). India state of forest report 2009. Forest Survey of India, Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 November 2013. Retrieved 4 March 2012.
- ^ "Floral and Faunal Diversity of Uttar Pradesh". Uttar Pradesh State Biodiversity Board. Archived from the original on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 22 May 2020.
- ^ "Aegyptica". Bsienvis.nic.in. Archived from the original on 6 May 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2009.
- ^ "Bird Sanctuary". U.P tourism. Archived from the original on 4 July 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ "Sanctuary Park in U.P". U.P tourism. Archived from the original on 18 July 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ "Few patches of natural forest". State government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 20 May 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ The Forests and biodiversity, in UP are important in many ways. "Miscellaneous Statistics". Ministry of Environment and Forests. Archived from the original on 15 November 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Conservation of the Avifauna" (PDF). Dudhwa National Park. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 20 July 2012.
- ^ "Bakhira Bird Sanctuary". upforest.gov.in. UP Forest and Wildlife Department. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- ^ "National Chambal Gharial Wildlife Sanctuary". National Chambal Sanctuary. Archived from the original on 1 January 2017. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- ^ "Chandra Prabha Wildlife Sanctuary And Picnic Spots". uptourism.gov.in. Uttar Pradesh Tourism. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- ^ "Hastinapur Wild Life Sanctuary". upforest.gov.in. P Forest and Wildlife Department. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- ^ "Kaimoor Wild Life Sanctuary". upforest.gov.in. Forest and Wildlife Department Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- ^ "Inside Okhla Bird Sanctuary". upforest.gov.in. UP Forest and Wildlife Department. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- ^ S. K. Agarwal (1998). Environment Biotechnology. APH Publishing. p. 61. ISBN 978-8131302941. Archived from the original on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- ^ "Processing of manuscripts of Fauna" (PDF). Indian Government. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 May 2013. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "State division of Uttar Pradesh". Government of India. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Indian Districts by population". 2011 Census of India. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ^ a b "Panchayati Raj Act, 1947" (PDF). Department of Panchayati Raj, Government of Uttar Pradesh. 1947. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2017. Retrieved 16 August 2017.
- ^ "Panchayati Raj Act, 1947 – Chapter 6 – The Nyaya Panchayat" (PDF). Department of Panchayati Raj, Government of Uttar Pradesh. 1947. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ "Panels to draft development plans for 13 cities". The Indian Express. 30 August 2010. Retrieved 13 July 2012.
- ^ "The area and density of metropolitan cities" (PDF). The Ministry of Urban Development. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Provisional population totals, Census of India 2011" (PDF). Census of India 2011. p. 19. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 February 2012. Retrieved 14 March 2012.
- ^ "Provisional population totals paper 1 of 2011 : Uttar Pradesh". Census of India 2011. Archived from the original on 27 April 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ https://cag.gov.in/uploads/download_audit_report/2021/5%20CHAPTER%20I-063076629450a19.40071813.pdf. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b https://www.indiacode.nic.in/bitstream/123456789/16228/1/Municipality_1916.pdf. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ "Uttar Pradesh Municipal Corporation Act, 1959" (PDF). 1959. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 August 2017. Retrieved 16 August 2017.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Municipal Corporation Act, 1959" (PDF). Uttar Pradesh State Election Commission. 1959. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
- ^ "U.P. Industrial Development Act – 1976 (U.P. Act Number 6, of 1976)" (PDF). Noida Authority Online. 1976. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 August 2017. Retrieved 13 August 2017.
- ^ "U.P. Industrial Development Act – 1976 (U.P. Act Number 6, of 1976)" (PDF). Greater Noida Authority. 1976. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 13 August 2017.
- ^ Khan, Atiq (16 November 2011). "Maya splits U.P. poll scene wide open". The Hindu. Lucknow. Archived from the original on 12 January 2014. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
- ^ Number, Religion. "U.P religions by numbers". The Hindu. No. 26 August 2015. N. Ravi. The Hindu Group. Archived from the original on 15 November 2018. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ^ "Table C-16: Language by States and Union Territories – Uttar Pradesh". censusindia.gov.in. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ "The density of population in U.P." Environment and Related Issues Department U.P. Archived from the original on 15 December 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ "Provisional population totals" (PDF). Census of India 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 February 2013. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ Rampal, Nikhil (16 November 2022). "World population grew by a billion in past 12 yrs & 5% came from just UP & Bihar, data shows". ThePrint. Printline Media Pvt. Ltd. Archived from the original on 1 May 2023. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ^ "Statistics of Uttar Pradesh". up.gov.in. Government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 12 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ "Scheduled castes and scheduled tribes". Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 27 April 2020. Retrieved 12 June 2020.
- ^ Kaul, Sudesh. "Indigenous Peoples Policy Framework" (PDF). World Bank. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 June 2020. Retrieved 12 June 2020.
- ^ Ara, Ismat (16 July 2021). "Higher Female Foeticide, Targeted Harassment: UP's Population Control Bill May Be Dangerous". The Wire (India). Foundation for Independent Journalism (FIJ). Archived from the original on 1 May 2023. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ^ Rao, Menaka (16 February 2017). "How one Uttar Pradesh district is using technology to prevent sex-selective abortions". Scroll.in. Scroll Media Incorporation. Archived from the original on 1 May 2023. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ^ "Decennil growth of population by census" (PDF). Census of India (2011). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 April 2009. Retrieved 5 October 2011.
- ^ "Decennial growth rate and density for 2011 at a glance for Uttar Pradesh and the districts: provisional population totals paper 1 of 2011". Census of India(2011). Archived from the original on 7 October 2011. Retrieved 5 October 2011.
- ^ a b "The state with large no. of peoples living below poverty line". Government of India. Press Information Bureau. Archived from the original on 8 February 2013. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Poverty, Growth & Inequality" (PDF). World Bank. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 November 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ "Press Note on Poverty Estimates, 2011–12" (PDF). Planning Commission. Government of India. p. 7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 June 2014. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- ^ Singh, Hemant (7 April 2020). "Per Capita Income of Indian States 2019–20". Dainik Jagran. Jagran Josh. Jagran Prakashan Limited. Archived from the original on 26 August 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ "Muslim population grew faster: Census". Archived from the original on 27 August 2015.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Profile" (PDF). Census of India 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 February 2013. Retrieved 16 October 2010.
- ^ "A comparison of the literacy rates" (PDF). censusmp.gov.in. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 April 2012. Retrieved 16 October 2010.
- ^ "Literacy rate in Uttar Pradesh". Census of India 2011. Archived from the original on 30 April 2011. Retrieved 16 October 2010.
- ^ "UP literacy rate poor than national average: Report". Hindustan Times. HT Media Ltd. 8 September 2020. Archived from the original on 24 June 2021. Retrieved 20 June 2021.
- ^ Experts, Disha (1 July 2020). Amazing Uttar Pradesh – General Knowledge for UPPSC, UPSSSC & other Competitive Exams. Disha Publications. ISBN 978-93-90486-72-4. Archived from the original on 27 April 2023. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ a b "Language – India, States and Union Territories" (PDF). Census of India 2011. Office of the Registrar General. pp. 13–14. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 November 2018. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Parishad structure". Legislative Bodies of India. Government of India. Archived from the original on 17 April 2016. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Sabha structure". Legislative Bodies of India. Government of India. Archived from the original on 17 April 2016. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- ^ Four other states seen as a barometer of support for the federal government. "Legislative elections in Uttar Pradesh". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 10 February 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- ^ Grover, Verinder (1989). Legislative Council in State Legislatures. Deep & Deep Publications. pp. 37–255. ISBN 978-8171001934. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2012.
- ^ "Composition of Rajya Sabha" (PDF). Rajya Sabha. New Delhi: Rajya Sabha Secretariat. pp. 24–25. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2012.
- ^ "Role of The Governor". upgovernor.gov.in. Raj Bhavan Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 7 April 2017. Retrieved 17 March 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Constitutional Setup". Government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 31 August 2017. Retrieved 30 August 2017.
- ^ Laxmikanth, M. (2014). Governance in India (2nd ed.). Noida: McGraw Hill Education. pp. 4.3 – 4.5. ISBN 978-9339204785.
- ^ Maheshwari, S.R. (2000). Indian Administration (6th ed.). New Delhi: Orient Blackswan Private Ltd. pp. 563–572. ISBN 978-8125019886.
- ^ Singh, G.P. (1993). Revenue administration in India: A case study of Bihar. Delhi: Mittal Publications. pp. 26–129. ISBN 978-8170993810.
- ^ "Contact Details of Commissioners and District Magistrates of U.P." Department of Home and Confidential, Government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 16 August 2017. Retrieved 15 August 2017.
- ^ "LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS" (PDF). Government of Uttarakhand. Retrieved 8 July 2024.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh judiciary". Maps of India. Archived from the original on 4 September 2012. Retrieved 19 September 2012.
- ^ "The Uttar Pradesh Judicial Service Rules, 2001" (PDF). Allahabad High Court. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 October 2019. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ a b Bind, Basini Prasad. "The History and Role of Subordinate Civil Judiciary in Uttar Pradesh" (PDF). Allahabad High Court. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 May 2013. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ "Subordinate Civil Judiciary in Uttar Pradesh" (PDF). Allahabad High Court. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 May 2013. Retrieved 19 September 2012.
- ^ Salam, Ziya Us (20 October 2020). "Casteism and social apartheid the norm in Uttar Pradesh". The Frontline. The Hindu. Retrieved 1 November 2024.
- ^ "UP: the nerve center of politics". Zee news. Archived from the original on 24 May 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ Sarda, Kanu (19 August 2018). "In Custody: Six died daily in four months". The New Indian Express. Express Publications (Madurai) Limited D. Archived from the original on 7 June 2020. Retrieved 7 June 2020.
- ^ Sandhu, Kamaljit Kaur (14 May 2018). "More bad news for Yogi Adityanath as data show UP tops crime chart". India Today. Living Media India Limited. Archived from the original on 28 August 2019. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ Rao, Phalguni. "NHRC registered 1,782 fake encounter cases between 2000–2017; Uttar Pradesh alone accounts for 44.55%". Firstpost. Network 18. Archived from the original on 7 June 2020. Retrieved 7 June 2020.
- ^ Pervez Iqbal Siddiqui (30 October 2011). "UP tops in crime, low on 'criminality'". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 14 September 2013.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh tops the list of communal violence hit states in 2017: Govt". The Economic Times. Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. 14 March 2018. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ Sharma, Neeta (14 March 2018). "Communal Violence Goes Up In Country, Uttar Pradesh Still Tops List". NDTV. New Delhi Television Limited. Archived from the original on 12 August 2019. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ "Human Development Index Across Indian States: Is the Glass Still Half Empty?" (PDF). State Bank of India. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ Chauhan, Saurabh. "UP fails to improve human development index ranking in 27 years". Hindustan Times. HT Media Ltd. Archived from the original on 26 January 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Human Development Report" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. December 2008. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 July 2017. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ "India Human Development Report report raps Gujarat, praises UP and Bihar". The Times of India. 22 October 2011. Archived from the original on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ Shafi, Alam. "The strength of Armed Police in Uttar Pradesh" (PDF). National Crime Records Bureau. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 November 2011. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
- ^ "General Information". Uttar Pradesh Police. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- ^ "Highlight of criminal statistics" (PDF). Ministry of statistics and program implementation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 November 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "UP sees 6.5% rise in road accidents, 4% in fatalities this yr, says govt data". Express News Service. The Indian Express. 3 December 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2024.
- ^ Chauhan, Arvind (7 January 2017). "At 23,219, UP reports highest number of road, rail accident". The Times of India. Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. The Times Group. Archived from the original on 18 June 2020. Retrieved 7 June 2020.
- ^ "An accident reported every two hours in UP: Fatal accidents in the state". Archived from the original on 5 May 2017.
- ^ "A powerful bomb placed in". Zee news. 20 July 2012. Archived from the original on 29 January 2012. Retrieved 20 July 2012.
- ^ "Sankat Mochan Hanuman temple blast". 'Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 9 August 2016. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
- ^ "Varanasi blast". NDTV. 7 December 2010. Archived from the original on 12 December 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2012.
- ^ Swami, Praveen (25 November 2007). "Uttar Pradesh bombings mark new phase". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 26 January 2012. Retrieved 20 July 2012.
- ^ Swami, Praveen (26 December 2007). "Wiretap warning on Uttar Pradesh bombings went in vain". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 4 March 2008. Retrieved 20 July 2012.
- ^ "Massive terror attacks". The Sunday Indian. 25 November 2011. Archived from the original on 6 June 2013. Retrieved 20 July 2012.
- ^ "Chronology of recent terror attacks". Yahoo. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ "Freak blast sets panic alarm ringing". The Times of India. Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. The Times Group. 5 March 2009. Archived from the original on 2 May 2023. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ^ "Gross State Domestic Product by Economic Activity (crore Rs) Uttar Pradesh" (PDF). Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 January 2018. Retrieved 11 January 2018.
- ^ a b Khullar, Vatsal (20 February 2018). "Uttar Pradesh Budget Analysis 2018–19" (PDF). PRS Legislative Research. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 February 2018. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- ^ "TABLE 27: GROSS STATE DOMESTIC PRODUCT" (PDF). Retrieved 12 April 2024.
- ^ a b "Uttar Pradesh: A Rainbow Land" (PDF). ibef.org. India Brand Equity Foundation. 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 September 2018. Retrieved 13 May 2019.
- ^ "Indian sugar mills association". indiansugar.com. Archived from the original on 26 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ Goyal, Malini (9 June 2013). "SMEs employ close to 40% of India's workforce, but contribute only 17% to GDP". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 31 December 2016. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ^ "Details of financing & limits of accommodation" (PDF). UPFC India. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 May 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "A statement of the categories of documents that are held by the Corporation" (PDF). Uttar Pradesh Financial Corporation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 November 2012. Retrieved 9 July 2012.
- ^ "The budget allocated to each of its agency" (PDF). UPFC India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 November 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ Rawat, Virendra Singh (27 March 2016). "Private investment under Akhilesh government more than doubles". Business Standard India. Archived from the original on 20 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ "10. Uttar Pradesh – World Bank Survey: India's top 10 states on the ease of doing business ranking – The Economic Times". Archived from the original on 23 June 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ a b Raghuvanshi, Umesh (23 October 2019). "Finance commission asks Uttar Pradesh to bring down its debt burden". Hindustan Times. HT Media Ltd. Archived from the original on 18 May 2020. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- ^ "State slipping into debt burden". The Times of India. 14 June 2011. Archived from the original on 6 May 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2011.
- ^ "Unemployment in Uttar Pradesh increased 11.4 pct points, rose to 21.5% in Apr 2020: CMIE Survey". Mint. HT Media. 1 May 2020. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ Jha, Abhishek; Kawoosa, Vijdan Mohammad (26 July 2019). "What the 2011 census data on migration tells us". Hindustan Times. HT Media. Archived from the original on 14 August 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- ^ Edwin, Tina (30 July 2019). "Migrants seem to prefer neighbouring States for livelihood". Business Line. The Hindu Group. Kasturi and Sons Limited. Archived from the original on 25 October 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- ^ "Census of India 2001 – Data Highlights" (PDF). Government of India. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- ^ Singh, Mahendra (21 October 2013). "Eastern UP, not Bundelkhand, most backward: Govt data". The Times of India. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ Tiwari, Anil Kumar; Pandey, Ravindra K.; Sharma, Vishwambhar Nath (31 December 2021). "A study of disparities in the socio-economic development of eastern Uttar Pradesh, India". National Geographical Journal of India. 67 (4): 438–446. doi:10.48008/ngji.1789. ISSN 0027-9374. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ Raghuvanshi, Umesh (7 September 2023). "Regional disparities persist, west U.P. far ahead of east". Hindustan Times. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ IT park, Infrastructure and (4 January 2016). "Noida-Greater Noida's world class infrastructure to be highlighted in UP Pravasi Diwas". The Times of India. Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. Archived from the original on 31 January 2017. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- ^ "Investment climate of a state" (PDF). IBEF organization. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 May 2013. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Service sector over the present crisis". The Economic Times. 14 March 2009. Archived from the original on 7 May 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "Statistical Diary of Uttar Pradesh" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 October 2023. Retrieved 2 October 2023.
- ^ "Only 5 states exceed 11th Plan growth targets: Govt: Ruled by CNBC TV18 News". CNBC TV18-MoneyControl Post. 13 May 2011. Archived from the original on 5 June 2013.
- ^ "RBI releases Study on State Finances 2009–10". Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Archived from the original on 25 February 2010. Retrieved 22 February 2010.
- ^ Ministry of statistics and Program Implementation (PDF) (Report). Ministry of statistics and Program Implementation Govt. Of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016.
- ^ "Small scale industries and other small trades" (PDF). Ministry of Small Scale Industries. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 April 2009. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- ^ "total railway route length uttar pradesh". Northern Railways Lucknow Division. Archived from the original on 14 August 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "The Network" (PDF). Ministry of Railways. Retrieved 28 June 2024.
- ^ "North Central Railway-The Allahabad Division". Indian Railways Portal CMS Team. Archived from the original on 18 March 2014. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
- ^ "the Portal of Indian Railways". Indian Railways. Archived from the original on 11 April 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ^ "Equipment arrives for integrated security system". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 14 May 2013. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Lucknow New Delhi Shatabdi Express". The Times of India. 2 July 2012. Archived from the original on 26 September 2012. Retrieved 28 July 2012.
- ^ "Introducing the Railway Budget 2011–12" (PDF). Indian Railways. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 May 2016. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ Investment Promotion & Infrastructure Development Cell. "Road" (PDF). Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 October 2011. Retrieved 7 January 2012.
- ^ "Road network" (PDF). India Brand Equity Foundation. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 September 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "UPSRTC to replace 45% of its existing fleet with e-buses". Hindustan Times. 24 June 2024. Retrieved 24 August 2024.
- ^ Dash, Deepak (26 March 2019). "UPSRTC has set a new record by registering the highest profit among all state transport undertakings". Times of India. The Times Group. Retrieved 24 August 2024.
- ^ "Welcome :: U.P. Expressways Industrial Development Authority". upeida.in. Archived from the original on 12 July 2016. Retrieved 26 July 2016.
- ^ "Pervasive road network of Uttar Pradesh" (PDF). Planning commission, Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 December 2012. Retrieved 20 September 2012.
- ^ "contributing to economic growth and prosperity of the nation". Airports Authority of India. Archived from the original on 29 June 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ Kumar, Mayank (30 November 2023). "The over-promise of Uttar Pradesh's Kushinagar International Airport". The Hindu. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "Kushinagar international airport to get ready for take-off". Virendra Singh Rawat. 7 January 2013. Archived from the original on 21 May 2014.
- ^ "DFCCIL". dfccil.com. Archived from the original on 1 July 2020. Retrieved 2 October 2023.
- ^ "UP gets its 8th airport". mint. 9 March 2021. Archived from the original on 24 April 2021. Retrieved 24 April 2021.
- ^ "UP to seek DGCA nod for Taj airport". Hindustan Times. 21 June 2013. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ^ "Hindustan Times e-Paper". Hindustan Times. Archived from the original on 8 June 2014. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ^ Mishra, Mihir (24 June 2017). "Jewar to be second airport in Delhi NCR". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 11 August 2018. Retrieved 11 August 2018.
- ^ Rao, Mohan (2005). From Population Control To Reproductive Health: Malthusian Arithmetic. Sage Publications. pp. 244–246. ISBN 978-0761932697. Archived from the original on 4 June 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- ^ "Hapless victim of a TV sting, this hockey player is now a rising star". The Indian Express. 19 April 2012. Retrieved 29 June 2012.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh: Sports". Jagran Josh. Jagran Prakashan Limited. 29 July 2013. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2021.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh win Ranji Trophy". Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 19 October 2012. Retrieved 2 February 2006.
- ^ "UP to get one more cricket stadium by 2011". First Published:PTI, Friday, 27 November 2009, 21:26. Archived from the original on 24 May 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2006.
- ^ Singh, Prithviraj (24 October 2021). "Akhara body caught in successor row after UP mahant's 'murder', 1 group claims leader is elected". ThePrint. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ "District Football Association Kanpur – Uttar Pradesh Football Sangh". Uttar Pradesh Football Sangh. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "Arunachal Pradesh to host Final Rounds of 77th National Football Championship for Santosh Trophy". Official Website of All India Football Federation. 6 September 2023. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "About Us – Uttar Pradesh Football Sangh". Uttar Pradesh Football Sangh. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "Up Players Dominate In Badminton C'ship". The Times of India. 22 June 2023. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "The Buddh International Circuit (BIC), which played host to India's first Formula One Grand Prix". CNN-IBN. 18 November 2011. Archived from the original on 22 December 2011. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
- ^ "Why India's Formula 1 Grand Prix is under threat". BBC News. 24 October 2013. Archived from the original on 27 October 2013.
- ^ "Islamic religious schools". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 3 January 2013. Retrieved 25 April 2003.
- ^ "British colonial administration system in state education system". State Education Board. Archived from the original on 21 April 2003. Retrieved 25 April 2003.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Facts & Figures". Uttar Pradesh education department. Archived from the original on 3 April 2011. Retrieved 16 October 2010.
- ^ Jain, Isha (12 May 2017). "At Rs 9, 167, UP spends least on per child school education, reveals study". The Times of India. Retrieved 9 July 2024.
- ^ Balani, Khushboo (7 January 2017). "Uttar Pradesh has India's largest population of children, but least teachers per student". Scroll.in. Retrieved 9 July 2024.
- ^ "The Fiscal Cost Of Weak Governance: Evidence From Teacher Absence In India" (PDF). Retrieved 9 July 2024.
- ^ "17% of teaching posts in govt schools vacant". The Times of India. 20 September 2020. Retrieved 9 July 2024.
- ^ "85,152 posts of headmasters and assistant teachers are vacant in Uttar Pradesh, says state government". Deccan Herald. 6 February 2024. Retrieved 9 July 2024.
- ^ "List of universities". Education info India. Archived from the original on 11 April 2017. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ "List of Universities in Uttar Pradesh". Education department of U.P. Archived from the original on 21 June 2012. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
- ^ "Official Website of IIM Lucknow". IIM Lucknow. Archived from the original on 13 April 2012. Retrieved 11 April 2012.
- ^ "India's Best Schools, 2014". Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 22 July 2015.
- ^ "The Integral University Lucknow state level institution". Government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 7 January 2012. Retrieved 28 June 2012.
- ^ Ragini, Dikshit (10 July 2007). "चित्रकूट: दुनिया का प्रथम विकलांग विश्वविद्यालय" [Chitrakuta: The world's first handicapped university] (in Hindi). Jansatta Express.
- ^ "No. of public libraries in different States and Union Territories" (PDF). Ministry of Culture, Government of India. Retrieved 8 July 2024.
- ^ a b "Public Library network". Government of Uttar Pradesh. Retrieved 8 July 2024.
- ^ "Top libraries of UP". Government of Uttar Pradesh. Retrieved 8 July 2024.
- ^ "Public library witnesses 37% increase in readers". The Times of India. 23 September 2014. Retrieved 8 July 2024.
- ^ "List of Famous Freedom Fighters from Uttar Pradesh". Jagranjosh.com. 4 September 2018. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ Upkar Prakashan – Editorial Board (2010). Uttar Pradesh General Knowledge. Upkar Prakashan. pp. 46–287. ISBN 978-8174824080. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- ^ Siddiqui, Masood H.; Tripathi, Shalini N. (2011). "Performance of Tourist Centres in Uttar Pradesh: An Evaluation Using Data Envelopment Analysis" (PDF). ASCI Journal of Management. 40 (1). Administrative Staff College of India. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 August 2016. Retrieved 22 March 2019.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh". India Brand Equity Foundation. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ Sharma, Aman (10 July 2019). "Tourists up at Taj Mahal and Red Fort but Qutub Minar loses its No.2 Spot". The Economic Times. The Times Group. Bennett, Coleman & Co. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ^ "Taj Mahal". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ "Agra Fort". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ "Fatehpur Sikri". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ Fouberg, Erin H.; Moseley, William G. (2018). Understanding World Geography. New York: John Wiley & Sons. p. 173. ISBN 9781119473169. OCLC 1066742384.
- ^ Eck, Diana (2013) [1981]. Banaras, the City of Light. Alfred Knopf Inc, [Columbia University Press]. p. 324.
- ^ Parry, Jonathan P. (2000) [1994]. Death in Banaras. Lewis Henry Morgan Lectures. Cambridge University Press. p. 1. ISBN 9780521466257.
- ^ Hawley, John Stratton (2020). Krishna's Playground: Vrindavan in the 21st Century. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0190123987.
- ^ Gopal, Madan (1990). K.S. Gautam (ed.). India through the ages. Publication Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, Government of India. p. 176.
- ^ "Ministry of Tourism presents its latest webinar on "In the Footsteps of the Buddha" under Dekho Apna Desh Webinar Series". Press Information Bureau. 7 February 2019. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ Paramasivan, Vasudha (2009). "Yah Ayodhya Vah Ayodhya: Earthly and Cosmic Journeys in the Anand-lahari". In Heidi R. M. Pauwels (ed.). Patronage and Popularisation, Pilgrimage and Procession. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 101–116. ISBN 978-3-447-05723-3.
- ^ "District Ayodhya – Government of Uttar Pradesh: City Of Lord Rama: India". Archived from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ "About District". District Ayodhya – Government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 9 November 2019. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ MacLean, Kama (2008). Pilgrimage and Power: The Kumbh Mela in Allahabad, 1765–1954. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195338942. Archived from the original on 27 May 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- ^ "Hindus gather for the Kumbh Mela at the Ganges in India and Maha Shivaratri in Allahabad". The Daily Telegraph. London. 12 February 2010. Archived from the original on 27 January 2011. Retrieved 25 January 2011.
- ^ "Sarnath General Information". Tourism department of Varanasi. Archived from the original on 8 May 2012. Retrieved 8 July 2012.
- ^ Joon, Sanjeev. Complete Guide for SSC. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. 255. ISBN 978-0070706453. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- ^ "Jhansi Fort". Government of Uttar Pradesh. Archived from the original on 23 March 2023. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ "Ticketed Monuments – Uttar Pradesh jhansi Fort". Archaeological Survey of India. Archived from the original on 5 December 2023. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ Anand, Manjaree (1 July 2014). "Health status and health care services in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar: A comparative study". Indian Journal of Public Health. 58 (3): 174–9. doi:10.4103/0019-557X.138624. ISSN 0019-557X. PMID 25116823.
- ^ a b c "Annual Health Survey 2012–13 Fact Sheet – Uttar Pradesh" (PDF). Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner. Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 November 2017. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ Perappadan, Bindu Shajan (11 May 2019). "India facing critical shortage of healthcare providers: WHO". The Hindu. The Hindu Group. Archived from the original on 17 June 2020. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- ^ "Doctors Registered" (PDF). The Ministry Of Health And Family Welfare. Retrieved 30 July 2024.
- ^ "State/UT wise Number of Government Hospitals" (PDF). Directorate General of State Health Services. Retrieved 30 July 2024.
- ^ "Out Of Pocket Expenditure Data" (PDF). Department Of Health And Family Welfare. Retrieved 31 July 2024.
- ^ "Maternal & Adolescent Healthcare" (PDF). Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW). Retrieved 30 July 2024.
- ^ "Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) (Per 100000 Live Births)". NITI Aayog. Archived from the original on 15 January 2020. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- ^ Rao, Menaka (8 February 2017). "Uttar Pradesh has a free ambulance service for pregnant women but substandard hospitals". Scroll.in. Scroll Media Inc, US. Archived from the original on 28 September 2020. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- ^ "State of Urban Health in Uttar Pradesh – Urban Health Resource Center" (PDF). Urban Health Resource Centre. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 July 2017. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
- ^ "Estimates of mortality indicators" (PDF). Census of India. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 November 2019. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- ^ "Rural Health Statistics 2014–15" (PDF). Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 August 2017. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ Awakening Indians to India. Chinmaya Mission. 2008. p. 167. ISBN 978-8175974340. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Legislature". U.P assembly. Archived from the original on 19 June 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2009.
- ^ "The Uttar Pradesh Official Language (Amendment) Act, 1989" (PDF). Archived from the original on 7 July 2019. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ "Ethnologue report for language code: bfy". Ethnologue. Archived from the original on 16 April 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2009.
- ^ Frawley, William (May 2003). International Encyclopedia of Linguistics: 4-Volume Set. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-513977-8. Archived from the original on 27 April 2023. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ a b "Visit the land of the Taj for some Hindustani music & dance". The Economic Times. 10 March 2016. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ "List of Folk Music of Uttar Pradesh". Jagranjosh.com. 12 July 2018. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ Walker, Margaret E. (2016). India's Kathak Dance in Historical Perspective. Routledge. pp. 100–102. ISBN 978-1-317-11737-7.
- ^ Schechner, Richard; Hess, Linda (1977). "The Ramlila of Ramnagar [India]". The Drama Review: TDR. 21 (3). The MIT Press: 51–82. doi:10.2307/1145152. JSTOR 1145152.
- ^ Goyal, Shikha (3 January 2022). "List of Folk Dances of Different States in India". Jagranjosh.com. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ "Kathak: The cultural gem of Uttar Pradesh". The Statesman. 10 January 2022. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ "Charkula Dance". Charkula. Archived from the original on 26 January 2020. Retrieved 27 January 2023.
- ^ "Chhath puja and the centrality of the Purvanchal community in Delhi politics". Hindustan Times. 18 October 2021. Archived from the original on 1 January 2023. Retrieved 6 September 2022.
- ^ Maclean, Kama (2003). "Making the Colonial State Work for You: The Modern Beginnings of the Ancient Kumbh Mela in Allahabad". The Journal of Asian Studies. 62 (3): 873–905. doi:10.2307/3591863. JSTOR 3591863. S2CID 162404242.
- ^ "What is Lathmar Holi? Why is it celebrated?". India Today. 21 March 2016. Archived from the original on 5 November 2017. Retrieved 6 December 2017.
- ^ "The Braj Holi: Legend in real life". Hindustan Times. 19 March 2011. Archived from the original on 22 March 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2012.
- ^ "The glorious traditions and mythological legacy". Department of tourism U.P. Archived from the original on 29 June 2012. Retrieved 18 July 2012.
- ^ "How is Awadhi Cuisine different from Mughlai Cuisine". The Times of India. 16 January 2022. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ "Bhojpuri: सवाद के सरताज ह फुटेहरी, रउआ सभे खइले जरूर होखब!". News18 हिंदी (in Hindi). 24 May 2021. Retrieved 8 July 2024.
External links
- Government
- Official website

- Official tourism site Archived 27 January 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- Uttar Pradesh web resources provided by GovPubs at the University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Uttar Pradesh at the Encyclopædia Britannica
 Wikimedia Atlas of Uttar Pradesh
Wikimedia Atlas of Uttar Pradesh Geographic data related to Uttar Pradesh at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Uttar Pradesh at OpenStreetMap