First aid: Difference between revisions
NotAG on AWB (talk | contribs) replace {{manual}} with {{how-to}} per TfD, replaced: {{Manual → {{how-to, typo(s) fixed: itsef → itself |
|||
| (685 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Emergency first response medical treatment}} |
|||
{{other uses}} |
|||
{{About|general first aid for humans|other uses}} |
|||
[[File:Sign first aid.svg|The universal first aid symbol|thumb|right]] |
|||
{{how-to|date=June 2022}} |
|||
[[File:US Navy 030322-M-6270B-010 A U.S. Navy Corpsman assigned to the 15th Marine Expeditionary Unit (Special Operations Capable) gives first aid to an injured Iraqi citizen.jpg|thumb|right|A [[US Navy]] corpsman gives first aid to an injured Iraqi citizen.]] |
|||
{{Use mdy dates|date=August 2021}} |
|||
[[File:ISO 7010 E003 - First aid sign.svg|The universal first aid symbol|thumb]] |
|||
[[File:US Navy 030322-M-6270B-010 A U.S. Navy Corpsman assigned to the 15th Marine Expeditionary Unit (Special Operations Capable) gives first aid to an injured Iraqi citizen.jpg|thumb|A [[US Navy]] corpsman gives first aid to an injured Iraqi citizen.]] |
|||
{{Portal|Medical}} |
{{Portal|Medical}} |
||
'''First aid''' is the assistance given to any person suffering a sudden [[illness]] or [[injury]],<ref>{{cite book|title=First aid manual: 9th edition|publisher=Dorling Kindersley|isbn=978 1 4053 3537 9|year=2009}}</ref> with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, and/or promote recovery. It includes initial intervention in a serious condition prior to professional medical help being available, such as performing [[CPR]] whilst awaiting an [[ambulance]], as well as the complete treatment of minor conditions, such as applying a plaster to a [[laceration|cut]]. First aid is generally performed by the [[layperson]], with many people trained in providing basic levels of first aid, and others willing to do so from acquired knowledge. [[Mental health first aid]] is an extension of the concept of first aid to cover mental health. |
|||
'''First aid''' is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with a [[medical emergency]],<ref>{{Cite book |title=First aid manual: 9th edition |publisher=Dorling Kindersley |year=2009 |isbn=978-1-4053-3537-9}}</ref> with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery until medical services arrive. First aid is generally performed by someone with basic medical or first response training. [[Mental health first aid]] is an extension of the concept of first aid to cover mental health,<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.mentalhealthfirstaid.org/ |title=Mental Health First Aid USA |date=2013-10-10 |website=Mental Health First Aid |access-date=2019-11-20}}</ref> while [[psychological first aid]] is used as early treatment of people who are at risk for developing [[Post-traumatic stress disorder|PTSD]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.nctsn.org/treatments-and-practices/psychological-first-aid-and-skills-for-psychological-recovery/about-pfa |title=About PFA |last=Peterson |first=Sarah |date=2018-01-30 |website=The National Child Traumatic Stress Network |access-date=2019-11-20}}</ref> Conflict first aid, focused on preservation and recovery of an individual's social or relationship well-being, is being piloted in [[Canada]]. |
|||
There are many situations which may require first aid, and many countries have legislation, regulation, or guidance which specifies a minimum level of first aid provision in certain circumstances. This can include specific training or equipment to be available in the workplace (such as an [[automated external defibrillator]]), the provision of specialist first aid cover at public gatherings, or mandatory first aid training within schools. First aid, however, does not necessarily require any particular equipment or prior knowledge, and can involve improvisation with materials available at the time, often by untrained persons.<ref>{{cite web|publisher=CPR Seattle|title=Duct tape for the win! Using household items for first aid needs.|url=http://www.cprseattle.com/blog/duct-tape-for-the-win}}</ref> |
|||
There are many situations that may require first aid, and many countries have legislation, regulation, or guidance, which specifies a minimum level of first aid provision in certain circumstances. This can include specific training or equipment to be available in the workplace (such as an [[Automated External Defibrillator|automated external defibrillator]]), the provision of specialist first aid cover at public gatherings, or mandatory first aid training within schools. Generally, five steps are associated with first aid: |
|||
First aid can be performed on all animals, although this article relates to the care of human patients. |
|||
# Assess the surrounding areas. |
|||
== History == |
|||
# Move to a safe surrounding (if not already; for example, road accidents are unsafe to be dealt with on roads). |
|||
[[File:Akhilleus Patroklos Antikensammlung Berlin F2278.jpg|thumb|left|The binding of a battlefield wound depicted on ancient Greek pottery]] |
|||
# Call for help: both professional medical help and people nearby who might help in first aid such as the compressions of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). |
|||
# Perform suitable first aid depending on the injury suffered by the casualty. |
|||
# Evaluate the casualty for any fatal signs of danger, or possibility of performing the first aid again. |
|||
==Early history and warfare== |
|||
Skills of what is now known as first aid have been recorded throughout history, especially in relation to [[warfare]], where the care of both [[injury|traumatic]] and medical cases is required in particularly large numbers. The [[bandage|bandaging]] of battle wounds is shown on [[Classical Greece|Classical Greek]] pottery from circa 500 BCE, whilst the [[parable of the Good Samaritan]] includes references to binding or dressing wounds.<ref name=early>{{cite journal|journal=The British Medical Journal|title=The earliest days of first aid|last=Pearn|first=John|year=1994|volume=309|page=1718|url=http://www.bmj.com/content/309/6970/1718?hwoasp=authn%3A1410435630%3A43629789%3A1452198704%3A0%3A0%3ACcwwDY32APVggSjWijUy6w%3D%3D|doi=10.1136/bmj.309.6970.1718}}</ref> There are numerous references to first aid performed within the [[Roman army]], with a system of first aid, supported by surgeons, field ambulances, and hospitals.<ref>{{cite journal|journal=JAMA Surgery|title=Blood in Our Streets: The Status and Evolution of Trauma Care Systems|last=Eastman|first=A Brent|year=1992|volume=127|issue=6|pages=677–681|url=http://archsurg.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=595395}}</ref> Roman legions had the specific role of capsarii, who were responsible for first aid such as bandaging, and are the forerunners of the modern [[combat medic]].<ref>{{cite journal|journal=ADF Health|title=A history of first aid and its role in armed forces|last=Efstathis|first=Vlas|url=http://www.defence.gov.au/Health/infocentre/journals/ADFHJ_nov99/ADFHealthNov99_1_1_42-44.pdf|date=November 1999}}</ref> |
|||
Skills of what is now known as first aid have been recorded throughout history, especially in relation to [[warfare]], where the care of both [[injury|traumatic]] and medical cases is required in particularly large numbers. The [[bandage|bandaging]] of battle wounds is shown on [[Classical Greece|Classical Greek]] pottery from {{circa|500 BC}}, whilst the [[parable of the Good Samaritan]] includes references to binding or dressing wounds.<ref name="early">{{Cite journal |last=[[John Hemsley Pearn|Pearn]] |first=John |year=1994 |title=The earliest days of first aid |journal=The British Medical Journal |volume=309 |issue=6970 |pages=1718–1720 |doi=10.1136/bmj.309.6970.1718 |pmc=2542683 |pmid=7820000 }}</ref> There are numerous references to first aid performed within the [[Roman army]], with a system of first aid supported by surgeons, field ambulances, and hospitals.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Eastman |first=A Brent |year=1992 |title=Blood in Our Streets: The Status and Evolution of Trauma Care Systems |journal=JAMA Surgery |volume=127 |issue=6 |pages=677–681 |doi=10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420060043008 |pmid=1596168}}</ref> Roman legions had the specific role of capsarii, who were responsible for first aid such as bandaging, and are the forerunners of the modern [[combat medic]].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Efstathis |first=Vlas |date=November 1999 |title=A history of first aid and its role in armed forces |url=http://www.defence.gov.au/Health/infocentre/journals/ADFHJ_nov99/ADFHealthNov99_1_1_42-44.pdf |url-status=live |journal=ADF Health |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141130145638/http://www.defence.gov.au/health/infocentre/journals/ADFHJ_nov99/ADFHealthNov99_1_1_42-44.pdf |archive-date=2014-11-30}}</ref> |
|||
Further examples occur through history, still mostly related to battle, with examples such as the [[Knights Hospitaller]] in the 11th century CE, providing care to pilgrims and knights in the [[Holy Land]].<ref name=medicinenet>{{cite web|url=http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=52749|title=First Aid: From Witchdoctors & Religious Knights to Modern Doctors|accessdate=March 23, 2011}}</ref> |
|||
Further examples occur through history, still mostly related to battle, with examples such as the [[Knights Hospitaller]] in the 11th century AD, providing care to pilgrims and knights in the [[Holy Land]].<ref name="medicinenet">{{Cite web |url=http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=52749 |title=First Aid: From Witchdoctors & Religious Knights to Modern Doctors |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120118055846/http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=52749 |archive-date=January 18, 2012 |access-date=March 23, 2011}}</ref> |
|||
===Formalization of life saving treatments=== |
===Formalization of life saving treatments=== |
||
During the late 18th century, [[drowning]] as a cause of death was a major concern amongst the population. |
During the late 18th century, [[drowning]] as a cause of death was a major concern amongst the population. In 1767, a society for the preservation of life from accidents in water was started in [[Amsterdam]], and in 1773, physician [[William Hawes (physician)|William Hawes]] began publicizing the power of [[artificial respiration]] as means of resuscitation of those who appeared drowned. This led to the formation, in 1774, of the [[Society for the Recovery of Persons Apparently Drowned]], later the [[Royal Humane Society]], who did much to promote resuscitation.<ref>New Scientist, Vol. 193 No. 2586 (13–19 Jan 2007), p. 50</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Price |first=John |title=Everyday Heroism: Victorian Constructions of the Heroic Civilian |publisher=Bloomsbury: London |year=2014 |isbn=978-1-4411066-5-0 |page=203}}</ref> |
||
[[Napoleon]]'s surgeon, [[Baron Dominique-Jean Larrey]], is credited with creating an ambulance corps |
[[Napoleon]]'s surgeon, [[Baron Dominique-Jean Larrey]], is credited with creating an ambulance corps, the ''[[ambulance volantes]]'', which included medical assistants, tasked to administer first aid in battle.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Baker |first1=David |last2=Cazalaà |first2=Jean-Bernard |last3=Carli |first3=Pierre |date=September 2005 |title=Resuscitation great. Larrey and Percy--a tale of two barons |journal=Resuscitation |volume=66 |issue=3 |pages=259–262 |doi=10.1016/j.resuscitation.2005.03.009 |issn=0300-9572 |pmid=15990216}}</ref> |
||
In 1859 [[Jean-Henri Dunant]] witnessed the aftermath of the [[Battle of Solferino]], and his work led to the formation of the [[International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement|Red Cross]], with a key stated aim of "aid to sick and |
In 1859, [[Switzerland|Swiss]] businessman [[Jean-Henri Dunant]] witnessed the aftermath of the [[Battle of Solferino]], and his work led to the formation of the [[International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement|Red Cross]], with a key stated aim of "aid to sick and wounded soldiers in the field".<ref name=medicinenet/> The [[Red Cross]] and [[Red crescent|Red Crescent]] are still the largest provider of first aid worldwide.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.redcross.org.uk/en/What-we-do/First-aid/Event-first-aid-and-ambulance-support |title=Event first aid and ambulance support |publisher=British Red Cross |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140908033750/http://www.redcross.org.uk/en/What-we-do/First-aid/Event-first-aid-and-ambulance-support |archive-date=2014-09-08}}</ref> |
||
[[File:Esmarch original.jpg|[[Esmarch bandage]] showing soldiers how to perform first aid|thumb |
[[File:Esmarch original.jpg|[[Esmarch bandage]] showing soldiers how to perform first aid|thumb]] |
||
In 1870, [[Prussia]]n military surgeon [[Friedrich von Esmarch]] introduced formalized first aid to the military, and first coined the term "erste hilfe" (translating to 'first aid'), including training for soldiers in the [[Franco-Prussian War]] on care for wounded comrades using pre-learnt bandaging and splinting skills, and making use of the [[Esmarch bandage]] which he designed.<ref name=early/> The bandage was issued as standard to the Prussian combatants, and also included aide-memoire pictures showing common uses. |
|||
In 1870, [[Kingdom of Prussia|Prussian]] military surgeon [[Friedrich von Esmarch]] introduced formalized first aid to the military, and first coined the term "erste hilfe" (translating to 'first aid'), including training for soldiers in the [[Franco-Prussian War]] on care for wounded comrades using pre-learnt bandaging and splinting skills, and making use of the [[Esmarch bandage]] which he designed.<ref name=early/> The bandage was issued as standard to the Prussian combatants, and also included aide-memoire pictures showing common uses. |
|||
In 1872, the [[Venerable Order of Saint John|Order of Saint John of Jerusalem in England]] changed its focus from hospice care, and set out to start a system of practical medical help, starting with making a grant towards the establishment of Britain's first [[ambulance]] service. This was followed by creating its own wheeled transport litter in 1875 (the St John Ambulance), and in 1877 established the St John Ambulance Association (the forerunner of modern day [[St John Ambulance]]) "to train men and women for the benefit of the sick and wounded".<ref>Fletcher NC. The St John Ambulance Association: its history and its past in the ambulance movement. London: St John Ambulance Association, 1929:12–3.</ref> |
|||
In 1872, the [[Venerable Order of Saint John|Order of Saint John of Jerusalem in England]] changed its focus from hospice care, and set out to start a system of practical medical help, starting with making a grant towards the establishment of the UK's first [[ambulance]] service. This was followed by creating its own wheeled transport litter in 1875 (the St John Ambulance), and in 1877 established the St John Ambulance Association (the forerunner of modern-day [[St John Ambulance]]) "to train men and women for the benefit of the sick and wounded".<ref>Fletcher NC, The St John Ambulance Association: its history and its past in the ambulance movement. London: St John Ambulance Association, 1929:12–3.</ref> |
|||
Also in Britain, [[Peter Shepherd (British Army officer)|Surgeon-Major Peter Shepherd]] had seen the advantages of von Esmarch's new teaching of first aid, and introduced an equivalent programme for the British Army, and so being the first user of "first aid for the injured" in English, disseminating information through a series of lectures. Following this, in 1878, Shepherd and [[Francis Duncan|Colonel Francis Duncan]] took advantage of the newly charitable focus of St John,<ref name=early/> and established the concept of teaching first aid skills to civilians. The first classes were conducted in the hall of the Presbyterian school in Woolwich (near Woolwich barracks where Shepherd was based) using a comprehensive first aid curriculum. |
|||
Also in the UK, [[Peter Shepherd (British Army officer)|Surgeon-Major Peter Shepherd]] had seen the advantages of von Esmarch's new teaching of first aid, and introduced an equivalent programme for the British Army, and so being the first user of "first aid for the injured" in English, disseminating information through a series of lectures. Following this, in 1878, Shepherd and [[Francis Duncan|Colonel Francis Duncan]] took advantage of the newly charitable focus of St John,<ref name=early/> and established the concept of teaching first aid skills to civilians. The first classes were conducted in the hall of the Presbyterian school in Woolwich (near Woolwich barracks where Shepherd was based) using a comprehensive first aid curriculum. |
|||
First aid training began to spread through the [[British Empire]] through organisations such as St John, often starting, as in the UK, with high risk activities such as ports and railways.<ref>[http://www.sja.org.uk/history/victorian_britain.asp Industrial Revolution: St. John Ambulance], retrieved December 10, 2006.</ref> |
|||
First aid training began to spread through the [[British Empire]] through organisations such as St John, often starting, as in the UK, with high risk activities such as ports and railways.<ref>[http://www.sja.org.uk/history/victorian_britain.asp Industrial Revolution: St. John Ambulance] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070220111208/http://www.sja.org.uk/history/victorian_britain.asp |date=2007-02-20 }}, retrieved December 10, 2006.</ref> |
|||
==Aims== |
|||
The key aims of first aid can be summarized in three key points, sometimes known as 'the three P's':-<ref>{{cite web|title=Accidents and first aid|publisher=NHS Direct|url=http://www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk/articles/article.aspx?articleId=450|accessdate=2008-10-04 |archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20080503201513/http://www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk/articles/article.aspx?articleId=450 <!-- Bot retrieved archive --> |archivedate = 2008-05-03}}</ref> |
|||
* '''Preserve life''': the overriding aim of all medical care, including first aid, is to save lives and minimize the threat of death. |
|||
* '''Prevent further harm''': also sometimes called '''prevent the condition from worsening''', or '''danger of further injury''', this covers both external factors, such as moving a patient away from any cause of harm, and applying first aid techniques to prevent worsening of the condition, such as applying pressure to stop a bleed becoming dangerous. |
|||
* '''Promote recovery''': first aid also involves trying to start the recovery process from the illness or injury, and in some cases might involve completing a treatment, such as in the case of applying a plaster to a small wound. |
|||
The first recorded first aid training in the United States took place in [[Jermyn, Pennsylvania]] in 1899.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://jermynpa.com/community/history.php |title=Jermyn Pennsylvania - History |website=jermynpa.com |access-date=2024-09-10}}</ref> |
|||
==Key skills== |
|||
{{Unreferenced section|date=May 2010}} |
|||
[[File:Tongue-blocking-airways.png|right|thumb|300px|In case of tongue fallen backwards, blocking the airway, it is necessary to hyperextend the head and pull up the chin, so that the tongue lifts and clears the airway.]] |
|||
Certain skills are considered essential to the provision of first aid and are taught ubiquitously. Particularly the "[[ABC (medicine)|ABC]]"s of first aid, which focus on critical life-saving intervention, must be rendered before treatment of less serious injuries. <!-- Before editing this section to change circulation to Compressions, please read the article at ABC (medicine) -->ABC stands for ''Airway'', ''Breathing'', and ''Circulation''.<!-- Before editing this section to change Circulation to Compressions, please read the article at ABC (medicine) --> The same [[mnemonic]] is used by all [[emergency medicine|emergency health professionals]]. Attention must first be brought to the [[airway]] to [[basic airway management|ensure it is clear]]. [[airway obstructions|Obstruction]] ([[choking]]) is a life-threatening emergency. Following evaluation of the airway, a first aid attendant would determine adequacy of [[breath]]ing and provide [[rescue breathing]] if necessary. Assessment of [[Circulatory system|circulation]] is now not usually carried out for patients who are not breathing, with first aiders now trained to go straight to chest compressions (and thus providing artificial circulation) but [[pulse]] checks may be done on less serious patients. |
|||
== Main emergences that require first aid and their corresponding cares == |
|||
Some organizations add a fourth step of "D" for ''[[Bleeding|Deadly bleeding]]'' or ''[[Defibrillation]]'', while others consider this as part of the ''Circulation'' step. Variations on techniques to evaluate and maintain the ABCs depend on the skill level of the first aider. Once the ABCs are secured, first aiders can begin additional treatments, as required. Some organizations teach the same order of priority using the "3Bs": ''Breathing'', ''Bleeding'', and ''Bones'' (or "4Bs": ''Breathing'', ''Bleeding'', ''Brain'', and ''Bones''). While the ABCs and 3Bs are taught to be performed sequentially, certain conditions may require the consideration of two steps simultaneously. This includes the provision of both [[artificial respiration]] and [[cardiopulmonary resuscitation|chest compressions]] to someone who is not breathing and has no pulse, and the consideration of [[cervical spine]] injuries when ensuring an open airway. |
|||
List of some situations that require specific first aid, and information about them (in alphabetical order): |
|||
=== |
=== Bleeding === |
||
{{Main article|Emergency bleeding control#Wound management}} |
|||
In order to stay alive, all persons need to have an open airway—a clear passage where air can move in through the [[mouth]] or [[human nose|nose]] through the [[human pharynx|pharynx]] and down into the lungs, without obstruction. [[Conscious]] people will maintain their own airway automatically, but those who are unconscious (with a [[Glasgow coma scale|GCS]] of less than 8) may be unable to maintain a patent airway, as the part of the brain which automatically controls breathing in normal situations may not be functioning. |
|||
A '''bleeding''' or '''hemorrhage''' is the uncontrolled escape of blood from any vein or artery. |
|||
If the patient was breathing, a first aider would normally then place them in the [[recovery position]], with the patient leant over on their side, which also has the effect of clearing the tongue from the pharynx. It also avoids a common cause of death in unconscious patients, which is choking on regurgitated stomach contents. |
|||
In wounds that are caused by an external agent, there can be an additional risk of infection. |
|||
The airway can also become blocked through a foreign object becoming lodged in the pharynx or larynx, commonly called [[choking]]. The first aider will be taught to deal with this through a combination of ‘back slaps’ and ‘[[abdominal thrusts]]’. |
|||
=== Cardiac arrest (total stop of heartbeat) === |
|||
Once the airway has been opened, the first aider would assess to see if the patient is breathing. If there is no breathing, or the patient is not breathing normally, such as [[agonal breathing]], the first aider would undertake what is probably the most recognized first aid procedure—cardiopulmonary resuscitation or CPR, which involves breathing for the patient, and manually massaging the heart to promote blood flow around the body. |
|||
{{For|the proper sequence of first aid reactions to a cardiac arrest|Cardiopulmonary resuscitation#Order of CPR in a first aid sequence}}{{For|the cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) practice itself|Cardiopulmonary resuscitation#Compressions with rescue breaths}} |
|||
A '''cardiac arrest''' is the complete stop of heart function. |
|||
===Promoting recovery=== |
|||
The first aider is also likely to be trained in dealing with injuries such as [[wounds|cuts]], [[Abrasion (medical)|grazes]] or [[bone fracture]]. They may be able to deal with the situation in its entirety (a small adhesive bandage on a paper cut), or may be required to maintain the condition of something like a broken bone, until the next stage of definitive care (usually an [[ambulance]]) arrives. |
|||
== |
=== Choking === |
||
{{Main article|Choking#Basic treatment (first aid)}} |
|||
A '''choking''' is an obstruction in the airway |
|||
=== Diabetes, hyperglycemia === |
|||
{{Main article|Hyperglycemia#Treatment}} |
|||
A '''hyperglycemia''' or '''hyperglycaemia''' is an excessive level of blood sugars. |
|||
=== Diabetes, hypoglycemia === |
|||
{{Main article|Diabetic hypoglycemia#Treatment}} |
|||
A '''hypoglycemia''' or '''hypoglycaemia''' is an excessive fall of blood sugars in a diabetic patient. |
|||
It almost always occurs because of a problem with a medication to reduce the sugar level in blood. |
|||
=== Drowning === |
|||
{{For|first aid in a victim of drowning|Drowning#First aid}}{{For|the possible reactions when a victim is drowning|Drowning#Rescue}} |
|||
A '''drowning''' is a suffocation into a liquid substance. |
|||
First aid for drowning are very similar to those for cardiorespiratory arrest, but starting with 2 initial ventilations. |
|||
=== Infarction of the heart === |
|||
{{Main article|Management of acute coronary syndrome#Patient-dependent initial measures}} |
|||
A '''cardiac infarction''' is the sudden lack of blood supply to the heart, normally because of a problem in one of its arteries. |
|||
=== Stroke === |
|||
{{Main article|FAST (stroke)}} |
|||
A '''stroke''' is a sudden lack of blood supply to the brain. |
|||
==Aims of first aid== |
|||
The primary goal of first aid is to prevent death or serious injury from worsening. The key aims of first aid can be summarized with the acronym of 'the three Ps':<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk/articles/article.aspx?articleId=450 |title=Accidents and first aid |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080503201513/http://www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk/articles/article.aspx?articleId=450 |archive-date=2008-05-03 |access-date=2008-10-04}}</ref> |
|||
* '''Preserve life:''' The overriding aim of all medical care which includes first aid, is to save lives and minimize the threat of death. First aid done correctly should help reduce the patient's level of [[Pain management|pain]] and calm them down during the evaluation and treatment process. |
|||
* '''Prevent further harm:''' Prevention of further harm includes addressing both external factors, such as moving a patient away from any cause of harm, and applying first aid techniques to prevent worsening of the condition, such as applying pressure to stop a bleed from becoming dangerous. |
|||
* '''Promote recovery:''' First aid also involves trying to start the recovery process from the illness or injury, and in some cases might involve completing a treatment, such as in the case of applying a plaster to a small wound. |
|||
First aid is not medical treatment, and cannot be compared with what a trained medical professional provides. First aid involves making common sense decisions in the best interest of an injured person. |
|||
==Setting the priorities== |
|||
A first aid intervention would follow an order, which would try to attend in the best manner the main threats for the life and mobility of the victim. |
|||
There are some first aid protocols (such as ATLS, BATLS and SAFE-POINT) that define which are the priorities and the correct execution of the steps for saving human life. A major benefit of the use of official protocols is that they require minimum resources, time and skills, and have a great degree of success. |
|||
=== ABCDE and csABCDE general protocol === |
|||
The '''ABCDE''' method is the general protocol of first aid and implies a quite general view.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Thim |first1=Troels |last2=Krarup |first2=Niels Henrik Vinther |last3=Grove |first3=Erik Lerkevang |last4=Rohde |first4=Claus Valter |last5=Løfgren |first5=Bo |date=2012-01-31 |title=Initial assessment and treatment with the Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure (ABCDE) approach |journal=International Journal of General Medicine |language=English |volume=5 |pages=117–121 |doi=10.2147/IJGM.S28478 |pmc=3273374 |pmid=22319249 |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
It was initially developed by Dr Peter Safar in the 1950s. But it has received some modifications, improvements and variations that were intended for more specific contexts. For example: it has been completed with improvements from the ATLS (Advanced Trauma Life Support) version of the American College of Surgeons<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last1=Schmidt |first1=Oliver I. |last2=Gahr |first2=Ralf H. |last3=Gosse |first3=Andreas |last4=Heyde |first4=Christoph E. |date=2009-03-03 |title=ATLS(R) and damage control in spine trauma |journal=World Journal of Emergency Surgery: WJES |volume=4 |pages=9 |doi=10.1186/1749-7922-4-9 |issn=1749-7922 |pmc=2660300 |pmid=19257904 |doi-access=free}}</ref> and the BATLS (Battlefield Advanced Trauma Life Support) version of the British Army.<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal |last1=Hodgetts |first1=T. J. |last2=Mahoney |first2=P. F. |last3=Russell |first3=M. Q. |last4=Byers |first4=M. |date=October 2006 |title=ABC to ABC: redefining the military trauma paradigm |journal=Emergency Medicine Journal |volume=23 |issue=10 |pages=745–746 |doi=10.1136/emj.2006.039610 |issn=1472-0213 |pmc=2579588 |pmid=16988297}}</ref> |
|||
As a result, the mnemonic of the steps of this protocol is '''ABCDE''', or its improved version '''(cs)ABCDE''' (sometimes called '''xABCDE''', the words in the mnemonic may vary), which represent:<ref>{{Cite web |last=NotSan |title=xABCDE untersuchung Rettungsdienst |url=https://notsan.info/index.php?content_id=8 |website=notsan.info |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20241120112312/https://notsan.info/index.php?content_id=8 |archive-date=November 20, 2024 |language=de}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Certain |first1=Lucas |last2=Rostirola |first2=João Vitor Cerávolo |last3=Pereira |first3=Juliana Silva |last4=Rostirola |first4=Gabriela Cerávolo |last5=Estevam |first5=Barbara Canto |last6=Vieira |first6=Carla Caroline Aguiar |last7=da Silva |first7=Israel |last8=da Silva |first8=Jussara Aparecida Rodrigues |last9=Schevenin |first9=Juliana de Cássia |last10=de Oliveira |first10=Ana Barbara Regiani |last11=Franceli |first11=Amanda Bonamichi |last12=Lisboa |first12=Camila Emanuele Camargo |last13=Benites |first13=Bruno Deltreggia |date=2023-07-01 |title=First immediate transfusion at a prehospital environment in Latin America: A case report |journal=Hematology, Transfusion and Cell Therapy |series=Diversity in Classical Hematology Research |volume=45 |issue=Suppl 2 |pages=S153–S156 |doi=10.1016/j.htct.2021.08.007 |issn=2531-1379 |pmc=10433293 |pmid=34862155}}</ref><br/> |
|||
—An attached first part (named as "cs" or "x", or in any other way) that will always mention stopping the critical losses of blood and managing with a special and careful treatment to patients with serious damages at the spine that threaten their future mobility: |
|||
* '''catastrophic-bleeding''' (stopping urgently the massive external bleedings, as it is marked in the BATLS version). |
|||
* '''spine-protection''' (previous examination of the spine, and careful preventive treatment for its damages, as it is marked in the ATLS version). |
|||
—The ABCDE protocol itself: |
|||
*'''Airway''' (clearing airways). |
|||
*'''Breathing''' (ensuring respiration). |
|||
* '''Circulation''' (ensuring effective cardiac output).<br />Any '''Defibrillation''' process for a [[Cardiopulmonary resuscitation#Compressions with rescue breaths|cardiac arrest]] (total stop of heartbeat) would be included here, or in 'Disability' (as a double mnemonic 'D'). |
|||
* '''Disability''' (neurological condition, level of glucose can also be examined). |
|||
* '''Exposure''' (or 'Evaluate': other questions in an overall examination of the patient, environment). |
|||
=== ABC and CABD cardiopulmonary resuscitation protocol === |
|||
This protocol (originally named as '''ABC''') is a simplified version or concrete application of the previous csABCDE (or ABCDE) protocol, that focuses in the use of [[Cardiopulmonary resuscitation#Compressions with rescue breaths|cardio-pulmonary resuscitation]]. The American Heart Association and the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation teach it as a reference.<ref>{{Cite web |last=American Heart Association (AHA) |date=2015 |title=Highlights of the Guidelines for CPR and ECC |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190203102957/http://eccguidelines.heart.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/2015-AHA-Guidelines-Highlights-English.pdf.heart.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/2015-AHA-Guidelines-Highlights-English.pdf |archive-url= |access-date=2024-12-01}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Field |first1=John M. |last2=Hazinski |first2=Mary Fran |last3=Sayre |first3=Michael R. |last4=Chameides |first4=Leon |last5=Schexnayder |first5=Stephen M. |last6=Hemphill |first6=Robin |last7=Samson |first7=Ricardo A. |last8=Kattwinkel |first8=John |last9=Berg |first9=Robert A. |last10=Bhanji |first10=Farhan |last11=Cave |first11=Diana M. |last12=Jauch |first12=Edward C. |last13=Kudenchuk |first13=Peter J. |last14=Neumar |first14=Robert W. |last15=Peberdy |first15=Mary Ann |date=2010-11-02 |title=Part 1: Executive Summary: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care |url=https://ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970889 |journal=Circulation |language=en |volume=122 |issue=18 Suppl 3 |pages=S640-56 |doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970889 |pmid=20956217 |issn=0009-7322}}</ref> |
|||
Its current mnemonic is '''CABD''' (an improvement in the sequence for most of the cases): |
|||
* '''Circulation''' or Chest '''Compressions.''' |
|||
* '''Airway''': attempt to open the airway (using a head-tilt and chin-lift technique; not in the case of babies, which require avoid tilting the head). |
|||
* '''Breathing''' or Rescue '''Breaths'''. |
|||
* '''Defibrillation''': use of an automated external defibrillator to recover heart function. |
|||
=== Wider protocols === |
|||
These are the protocols that do not only deal with direct care to the victim but they also mention other complementary tasks (before and later). |
|||
==== European protocol ==== |
|||
This method has been studied and employed for a long time in many European countries, as France.<ref>{{cite web |last=Croix-Rouge francaise |title=Les 4 étapes pour porter secours |url=http://croix-rouge.fr/Je-me-forme/Particuliers/Les-6-gestes-de-base/Les-4-etapes-pour-porter-secours |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230522153855/http://croix-rouge.fr/Je-me-forme/Particuliers/Les-6-gestes-de-base/Les-4-etapes-pour-porter-secours |access-date=2024-10-30 |archive-date=May 22, 2023 |language=fr-FR}}<!-- auto-translated from French by Module:CS1 translator --></ref> It is a reference, of a certain reputation, that could be applied solely or to a certain degree, usually combining it with the common csABCDE (ABCDE) method or its simplified CABD (ABC) variant about [[Cardiopulmonary resuscitation#Compressions with rescue breaths|cardio-pulmonary resuscitation]]. The European method has a wider range than them, and their steps include tasks that are previous to the first aid techniques themselves. |
|||
These are its steps (with no official mnemonic that helps to remember them): |
|||
* '''Protection''' for patients and rescuers. If dangers are present, the patient would be moved to a safer place with a careful management of any detected spinal injury. |
|||
* '''Evaluation''' of the patient (looking for priorities as critical bleeding and cardiac arrest). |
|||
* '''Alerting''' to medical services and bystanders. |
|||
* '''Performing''' the first aid practices. The '''CABD (or ABC)''' method for [[Cardiopulmonary resuscitation#Compressions with rescue breaths|cardio-pulmonary resuscitation]] and many details of the wider '''csABCDE (or ABCDE)''' method would be included in this step. |
|||
=== Other mentionable protocols === |
|||
Some other known protocols that could be mentioned in many contexts (in alphabetical order): |
|||
'''AMEGA protocol''' |
|||
{{anchor|AMEGA}}It is similar to the European protocol, because it also has a wider range<ref>Furst, J., [https://web.archive.org/web/20231022015347/http://firstaidforfree.com/what-does-amega-stand-for-in-first-aid/ What does AMEGA stand for in first aid?], updated 12 July 2019, accessed 24 January 2022</ref> than the common csABCDE (or ABCDE) protocol, and includes other tasks that are previous to the first aid techniques themselves. The order of the steps is changed, and the experience with it is lesser, but it adds the idea of a posterior 'aftermath' phase. |
|||
The mnemonic AMEGA refers to: |
|||
* ''Assess'' the situation, looking for risks. |
|||
* ''Make safe'' the situation, after having identified the risks. |
|||
* ''Emergency aid''. Performing the first aid practices. |
|||
* ''Get help''. Asking for emergency help to medical services and bystanders. |
|||
* ''Aftermath''. The aftermath tasks include recording and reporting, continued care of patients and the welfare of responders and the replacement of used first aid kit elements. |
|||
'''ATLS and BATLS protocols'''{{See also|Advanced trauma life support|BATLS}} |
|||
{{anchor|ATLS and BATLS}}They are basically the common [[First aid#ABCDE and cAsBCDE protocol|ABCDE and csABCDE protocol]], but focusing in particular aspects. |
|||
The ATLS (Advanced Trauma Life Support) version<ref name=":0" /> was developed by the American College of Surgeons, focusing in the particular needs of trauma and specifically in the spinal injuries. And the BATLS (Battlefield Advanced Trauma Life Support) version<ref name=":1" /> is an improvement for the British Army that added the concept of 'catastrophic bleeding'. |
|||
The preference for one or another among all these protocols can depend on the context and the audience. |
|||
==== Check, Call and Care protocol ==== |
|||
{{anchor|Check, Call and Care}}It comes from Red Cross<ref>{{Cite web |last=American Red Cross |title=Check, Call, Care: 3 Emergency Actions Steps to Take to Save Lives |url=http://redcross.org/take-a-class/resources/articles/the-three-cs-of-first-aid-check-call-care|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20241111144154/http://redcross.org/take-a-class/resources/articles/the-three-cs-of-first-aid-check-call-care |archive-date=November 11, 2024 }}</ref> and, as the European protocol, has a wider range than the common csABCDE (ABCDE) method. So it could be seen as a simplification of the European protocol, and, especially, easier to remember as a guide for most of cases. |
|||
It mentions the following steps: |
|||
* ''Check'' the scene for safety of the rescuer and others, and check the patient's condition. |
|||
* ''Call'' to emergency medical services. |
|||
* ''Care'' the patient. |
|||
==== SAFE-POINT protocol ==== |
|||
{{anchor|SAFE-POINT}}Another European protocol, which appeared in the field of construction of Czech Republic to react to any emergence .<ref>{{Cite web |last=safe-point.cz |title=SAFE-Point: 6 steps to save life |url=http://safe-point.cz/index.php/6-kroku-k-zachrane-zivota-2/ |language=Czech}}</ref> |
|||
Their steps (which have not any mnemonic) are: |
|||
* ''Safety of the rescuers.'' |
|||
* ''Calling'' to emergency telephone number. |
|||
* ''Bleeding'': treating the massive bleedings. |
|||
* ''Freeing the airways''. |
|||
* ''Resuscitation'': applying cardiopulmonary resuscitation. |
|||
* ''Keeping warm'' to the patient. |
|||
== Key basic skills == |
|||
Certain skills are considered essential to the provision of first aid and are taught ubiquitously. |
|||
=== Displacement skills === |
|||
If there are dangers around (such as fire, electric dangers or others) the patient has to be moved to a safe place,<ref name=":2" /><ref>{{Cite web |last=Community Emergency Response Team of L.A. |date=2024-10-31 |title=Lifts and carries |url=https://cert-la.com/cert-training-education/lifts-carries/ |website=CERTLA}}</ref> where providing the required first aid procedures is possible. |
|||
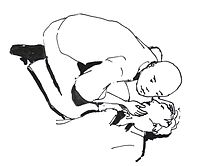
—'''In case of a possible severe spinal injury:''' when a patient seems to have a possible serious injury in the spinal cord (in the backbone, either at the neck part or the back part), that patient must not be moved except if that is necessary, and, when necessary, it must be done as little as possible and very carefully (see mentions about this type of injury in the gallery of drawings below). These precautions avoid many risks of causing further damages for the patient's mobility in the future. |
|||
Usually, the patient needs to end up lying down, in a face-up position, on a sufficiently firm surface (for example, on the floor, which allows to perform the chest compressions of cardiopulmonary resuscitation). |
|||
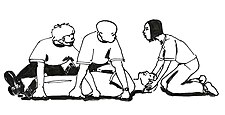
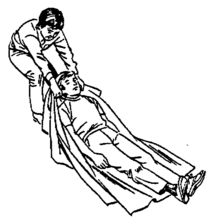
{{Gallery|File:Recovery_position_maneuver.jpg|—A victim with a serious injury in the spine (in the back or the neck), which indicates a risk to the future mobility, can be carefully transferred by several rescuers that work coordinately.<br />The victim’s head and back would be held in the same position they were.|File:Rautek-maneuver.png|—When there is a victim with a serious injury in the spine (in the back or the neck) and a rescuer without instruments, the rescuer can try to carry the victim carefully through the Rautek maneuver (as in the picture), trying to keep victim’s head and back in the same position they were.<br />The victim's head can be supported on the rescuer to try to soften the movements.|File:Blanket-Pull.png|—A victim without a serious injury in the spine (in the back or the neck) can be pulled through the floor, which is easier on a blanket, carpet or another tissue located under most of the body.<br />—Carrying on a base to victims with a suspected spinal injury would require to place them carefully, while keeping their head and back in the same position they were, on a higher or much thicker base (as a litter or mattress), for a better displacement.|width=225|height=225|align=center|title=Displacement of victims to a safe place}} |
|||
=== Checking skills === |
|||
They evaluate the condition of the victim,<ref name=":2">{{Cite book |last=American Red Cross |title=CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers |year=2016 |edition=2nd}}</ref> first attending to the main threats for life. |
|||
The preferred initial way of checking consist of asking, commonly by touching the patient in one of his shoulders and shouting something, such as: "can you hear me?" |
|||
In some cases, the victim has a wound that bleeds abundantly, which requires its own additional treatment to stop the blood loss (usually, it would begin by keeping the wound pressed). |
|||
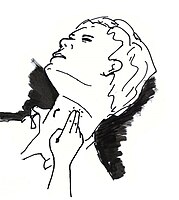
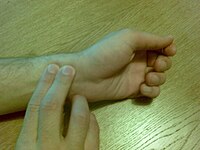
If the patient does not react, the heartbeats can be checked in the carotid pulse: placing two fingers on any side of the neck (on the left or the right side), near his head. In cases where checking the carotid pulse is impossible, heartbeats can be perceived in the radial pulse: placing two fingers on a wrist, under the part of the thumb, and applying moderate pressure. Breathing can also be checked additionally, placing an ear on the mouth and, at the same time, watching the chest rising by the effect of the air. It is recommended not to waste too much time of first aid in checking (professional rescuers are taught to take 10 seconds in it). |
|||
{{Gallery|File:Carotidian_pulse_(clear).jpg|Checking of heartbeats in the carotid pulse.<br/>This is usually the fastest method of checking the patient's condition.|File:Pulse2.jpg|Verification of heartbeats in the radial pulse, pressing moderately on a wrist, under the part of the thumb.|File:Checking_respiration3.jpg|Check of patient's breathing, listening the air inside of the mouth and watching the chest swelling.|width=200|height=200|align=center|title=Check of patient's condition}} |
|||
=== Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) === |
|||
{{For|the proper sequence of first aid reactions to a cardiac arrest|Cardiopulmonary resuscitation#Order of CPR in a first aid sequence}}{{For|cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) practice|Cardiopulmonary resuscitation#Compressions with rescue breaths}} |
|||
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the method of first aid for treating victims of cardiac arrest (complete stop of heartbeat). |
|||
{{Multiple images |
|||
| direction = horizontal |
|||
| image1 = Ratownik medyczny, defibrylacja.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = Traditional maneuvers of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) have included in the present the use of automatic defibrillators. |
|||
| align = center |
|||
| width1 = 230 |
|||
| header = Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) |
|||
}} |
|||
=== Airway, Breathing, and Circulation skills === |
|||
[[File:Tongue blocking airway.svg|right|thumb|300px|In case of tongue fallen backwards, blocking the airway, it is necessary to hyperextend the head and pull up the chin, so that the tongue lifts and clears the airway.]]<!-- Before editing this section to change circulation to Compressions, please read the article at ABC (medicine) --> |
|||
ABC method stands for ''Airway'', ''Breathing'', and ''Circulation''.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Eisenburger |first1=Philip |last2=Safar |first2=Peter |year=1999 |title=Life supporting first aid training of the public—review and recommendations |journal=Resuscitation |volume=41 |issue=1 |pages=3–18 |doi=10.1016/S0300-9572(99)00034-9 |pmid=10459587}}</ref><!-- Before editing this section to change Circulation to Compressions, please read the article at ABC (medicine) --> The same [[mnemonic]] is used by [[emergency medicine|emergency health professionals]]. |
|||
It is focused on critical life-saving intervention, and it must be rendered before treatment of less serious injuries. |
|||
Attention must first be brought to the [[airway]] to [[basic airway management|ensure it is clear]]. An [[airway obstructions|obstruction]] (choking) is a life-threatening emergency. If an object blocks the airway, it requires [[Choking#General strategy: "five and five"|anti-choking procedures]]. Following any evaluation of the airway, a first aid attendant would determine adequacy of [[breath]]ing and provide [[rescue breathing]] if necessary. |
|||
Assessment of [[Circulatory system|circulation]] is now not usually carried out for patients who are not breathing, with first aiders now trained to go straight to chest compressions (and thus providing artificial circulation) but [[pulse]] checks may be done on less serious patients. |
|||
Some organizations add a fourth step of "D" for ''[[Bleeding|Deadly bleeding]]'' or ''[[Defibrillation]]'', while others consider this as part of the ''Circulation'' step simply referred as Disability. Variations on techniques to evaluate and maintain the ABCs depend on the skill level of the first aider. Once the ABCs are secured, first aiders can begin additional treatments or examination, as required if they possess the proper training (such as measuring pupil dilation).<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.resus.org.uk/resuscitation-guidelines/abcde-approach/ |title=Guidelines and Guidance: The ABCDE approach |website=Resuscitation Council (UK) |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050812085403/http://www.resus.org.uk/pages/alsABCDE.htm |archive-date=12 August 2005 |access-date=2 May 2019}}</ref> |
|||
Some organizations teach the same order of priority using the "3Bs": ''Breathing'', ''Bleeding'', and ''Bones'' (or "4Bs": ''Breathing'', ''Bleeding'', ''Burns'', and ''Bones''). While the ABCs and 3Bs are taught to be performed sequentially, certain conditions may require the consideration of two steps simultaneously. This includes the provision of both [[artificial respiration]] and [[cardiopulmonary resuscitation|chest compressions]] to someone who is not breathing and has no pulse, and the consideration of [[cervical spine]] injuries when ensuring an open airway. |
|||
==== Preserving life ==== |
|||
The patient must have an open airway—that is, an unobstructed passage that allows air to travel from the open [[mouth]] or uncongested [[human nose|nose]], down through the [[human pharynx|pharynx]] and into the lungs. [[Conscious]] people maintain their own airway automatically, but those who are unconscious (with a [[Glasgow coma scale|GCS]] of less than 8) may be unable to do so, as the part of the brain that manages spontaneous breathing may not be functioning. |
|||
Whether conscious or not, the patient may be placed in the [[recovery position]], laying on their side. In addition to relaxing the patient, this can have the effect of clearing the tongue from the [[pharynx]]. It also avoids a common cause of death in unconscious patients, which is choking on regurgitated stomach contents. |
|||
The airway can also become blocked by a foreign object. To dislodge the object and solve the choking case, the first aider may use [[Choking#General strategy: "five and five"|anti-choking methods]] (such as 'back slaps' and 'abdominal thrusts'). |
|||
Once the airway has been opened, the first aider would reassess the patient's breathing. If there is no breathing, or the patient is not breathing normally (e.g., [[agonal breathing]]), the first aider would initiate [[Cardiopulmonary resuscitation|CPR]], which attempts to restart the patient's breathing by forcing air into the lungs. They may also manually massage the heart to promote blood flow around the body. |
|||
If the choking person is an infant, the first aider may use [[Choking#Infants|anti-choking methods for babies.]] During that procedure, series of five strong blows are delivered on the infant's upper back after placing the infant's face in the aider's forearm. If the infant is able to cough or cry, no breathing assistance should be given. Chest thrusts can also be applied with two fingers on the lower half of the middle of the chest. Coughing and crying indicate the airway is open and the foreign object will likely to come out from the force the coughing or crying produces.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000048.htm|title=Choking - infant under 1 year: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia|website=medlineplus.gov}}</ref> |
|||
A first responder should know how to use an [[Automated external defibrillator|Automatic External Defibrillator]] (AED) in the case of a person having a sudden cardiac arrest. The survival rate of those who have a cardiac arrest outside of the hospital is low. Permanent brain damage sets in after five minutes of no oxygen delivery, so rapid action on the part of the rescuer is necessary. An AED is a device that can examine a heartbeat and produce electric shocks to restart the heart.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Nessel |first=Edward H. |date=2012 |title=Treating Sudden Cardiac Arrest and the Use of Automated External Defibrillators in the Community Setting |url=https://www.thefreelibrary.com/Treating+sudden+cardiac+arrest+and+the+use+of+automated+external...-a0285436339 |journal=AAMA Journal |volume=25 |page=9}}</ref> |
|||
A first aider should be prepared to quickly deal with less severe problems such as [[wounds|cuts]], [[Abrasion (medical)|grazes]] or [[bone fracture]]. They may be able to completely resolve a situation if they have the proper training and equipment. For situations that are more severe, complex or dangerous, a first aider might need to do the best they can with the equipment they have, and wait for an ambulance to arrive at the scene. |
|||
== First aid kits == |
|||
[[File:A first aid box.jpg|thumb|A first aid box]] |
|||
A [[first aid kit]] consists of a strong, durable bag or transparent plastic box. They are commonly identified with a white cross on a green background. A first aid kit does not have to be bought ready-made. The advantage of ready-made first aid kits are that they have well organized compartments and familiar layouts. |
|||
===Contents=== |
|||
There is no universal agreement upon the list for the contents of a first aid kit. The UK Health and Safety Executive stress that the contents of workplace first aid kits will vary according to the nature of the work activities.<ref>First aid at work: The Health and Safety (First-Aid) Regulations 1981. Guidance on Regulations L74</ref> As an example of possible contents of a kit, [[British Standards|British Standard]] BS 8599 ''First Aid Kits for the Workplace''<ref>BS 8599-1:2011 BSI 2011</ref> lists the following items: |
|||
{{div col | colwidth=25em}} |
|||
*Information leaflet |
|||
*Medium [[Asepsis|sterile dressing]]s |
|||
*Large sterile dressings |
|||
*Bandages |
|||
*Triangular dressings |
|||
*Safety pins |
|||
*Adhesive dressings |
|||
*Sterile wet wipes |
|||
*Microporous tape |
|||
*[[Nitrile]] gloves |
|||
*Face shield |
|||
*Foil blanket |
|||
*Burn dressings |
|||
*Clothing shears |
|||
*Conforming bandages |
|||
*Finger dressing |
|||
*Antiseptic cream |
|||
*Scissors |
|||
*[[Tweezers]] |
|||
*Cotton |
|||
{{div col end}} |
|||
== Training principles == |
|||
[[File:Suicide-prague.jpg|thumb|First aid scenario training in progress]] |
[[File:Suicide-prague.jpg|thumb|First aid scenario training in progress]] |
||
Basic principles, such as knowing to use an adhesive bandage or applying direct pressure on a bleed, are often acquired passively through life experiences. However, to provide effective, life-saving first aid interventions requires instruction and practical training. This is especially true where it relates to potentially fatal illnesses and injuries, such as those that require [[cardiopulmonary resuscitation]] (CPR); these procedures may be invasive, and carry a risk of further injury to the patient and the provider. As with any training, it is more useful if it occurs ''before'' an actual [[emergency]], and in many countries, emergency ambulance dispatchers may give basic first aid instructions over the phone while the ambulance is on the way. |
|||
Basic principles, such as knowing the use of adhesive bandage or applying direct pressure on a bleed, are often acquired passively through life experiences. However, to provide effective, life-saving first aid interventions requires instruction and practical training. This is especially true where it relates to potentially fatal illnesses and injuries, such as those that require CPR; these procedures may be invasive, and carry a risk of further injury to the patient and the provider. As with any training, it is more useful if it occurs ''before'' an actual [[emergency]]. And, in many countries, calling emergency medical services allows listening basic first aid instructions over the phone while the ambulance is on the way. |
|||
Training is generally provided by attending a course, typically leading to certification. Due to regular changes in procedures and protocols, based on updated clinical knowledge, and to maintain skill, attendance at regular refresher courses or re-certification is often necessary. First aid training is often available through community organizations such as the [[Red Cross]] and [[St. John Ambulance]], or through commercial providers, who will train people for a fee. This commercial training is most common for training of employees to perform first aid in their workplace. Many community organizations also provide a commercial service, which complements their community programmes. |
Training is generally provided by attending a course, typically leading to certification. Due to regular changes in procedures and protocols, based on updated clinical knowledge, and to maintain skill, attendance at regular refresher courses or re-certification is often necessary. First aid training is often available through community organizations such as the [[Red Cross]] and [[St. John Ambulance]], or through commercial providers, who will train people for a fee. This commercial training is most common for training of employees to perform first aid in their workplace. Many community organizations also provide a commercial service, which complements their community programmes. |
||
1.Junior level certificate [[Basic Life Support]] |
|||
===Specific disciplines=== |
|||
There are several types of first aid (and first aider) which require specific additional training. These are usually undertaken to fulfill the demands of the work or activity undertaken. |
|||
2.Senior level certificate |
|||
* '''Aquatic/Marine first aid''' is usually practiced by professionals such as [[lifeguards]], professional [[mariner]]s or in [[diver rescue]], and covers the specific problems which may be faced after water-based rescue and/or delayed [[MedEvac]]. |
|||
3.Special certificate |
|||
=== Types of first aid which require training === |
|||
[[File:Resusci Anne - CPR dummy.jpg|thumb|Shown here is an example of a way for people to practice CPR in a safe and reliable manner.]]There are several types of first aid (and first aider) that require specific additional training. These are usually undertaken to fulfill the demands of the work or activity undertaken. |
|||
* '''Aquatic/Marine first aid''' is usually practiced by professionals such as [[lifeguards]], professional [[sailor|mariner]]s or in [[diver rescue]], and covers the specific problems which may be faced after water-based rescue or delayed [[MedEvac]]. |
|||
* '''[[Battlefield medicine|Battlefield first aid]]''' takes into account the specific needs of treating wounded [[combatants]] and [[non-combatants]] during [[armed conflict]]. |
* '''[[Battlefield medicine|Battlefield first aid]]''' takes into account the specific needs of treating wounded [[combatants]] and [[non-combatants]] during [[armed conflict]]. |
||
* Conflict First Aid focuses on support for stability and recovery of personal, social, group or system well-being and to address circumstantial safety needs. |
|||
* '''[[Hyperbaric medicine|Hyperbaric]] first aid''' may be practiced by [[Scuba diving|SCUBA diving]] professionals, who need to treat conditions such as [[decompression sickness|the bends]]. |
|||
* '''[[ |
* '''[[Hyperbaric medicine|Hyperbaric]] first aid''' may be practiced by [[underwater diving]] professionals, who need to treat conditions such as [[decompression sickness]]. |
||
*'''[[Oxygen therapy|Oxygen]] first aid''' is the providing of oxygen to casualties with conditions resulting in [[hypoxia (medical)|hypoxia]]. It is also a standard first aid procedure for underwater diving incidents where gas bubble formation in the tissues is possible. |
|||
* '''[[Wilderness first aid]]''' is the provision of first aid under conditions where the arrival of emergency responders or the evacuation of an injured person may be delayed due to constraints of terrain, weather, and available persons or equipment. It may be necessary to care for an injured person for several hours or days. |
|||
*'''[[Wilderness first aid]]''' is the provision of first aid under conditions where the arrival of [[emergency responders]] or the evacuation of an injured person may be delayed due to constraints of terrain, weather, and available persons or equipment. It may be necessary to care for an injured person for several hours or days. |
|||
* '''[[Mental health first aid]]''' is taught independently of physical first aid. How to support someone experiencing a mental health problem or in a crisis situation. Also how to identify the first signs of someone developing mental ill health and guide people towards appropriate help. |
|||
*'''[[Mental health first aid]]''' is taught independently of physical first aid. How to support someone experiencing a mental health problem or in a crisis situation. Also how to identify the first signs of someone developing mental ill health and guide people towards appropriate help. |
|||
[[File:First aider in parade.jpg|First aider of the [[British Red Cross]] accompanies parade of morris dancers at the [[Knutsford]] Royal May Day, Knutsford, Cheshire, England, 2012|thumb]] |
|||
==First aid services== |
== First aid services == |
||
Some people undertake specific training in order to provide first aid at public or private events, during filming, or other places where people gather. They may be designated as a ''first aider'', or use some other title. This role may be undertaken on a voluntary basis, with organisations such as the [[Red Cross]] society and [[St John Ambulance|St. John Ambulance]],<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.sja.org.uk/sja/first-aid-advice/what-to-do-as-a-first-aider/the-role-of-a-first-aider.aspx |title=Role of a First Aider - First Aid - St John Ambulance |website=www.sja.org.uk |access-date=2019-11-20}}</ref> or as paid employment with a medical contractor. |
|||
[[File:First aider in parade.jpg|First aider of the [[British Red Cross]] accompanies parade of morris dancers at the [[Knutsford]] Royal May Day 2012|thumb|right]] |
|||
Some people undertake specific training in order to provide first aid at public or private events, during filming, or other places where people gather. They may be designated as a '''first aider''', or use some other title. This role may be undertaken on a voluntary basis, with an organisation such as the Red Cross, or as paid employment with a medical contractor. |
|||
People performing a first aid role, whether in a professional or voluntary capacity, are often expected to have a high level of first aid training. |
People performing a first aid role, whether in a professional or voluntary capacity, are often expected to have a high level of first aid training and are often uniformed. |
||
==Symbols== |
==Symbols== |
||
{{ |
{{further|Emblems of the Red Cross#Use of the emblems}} |
||
Although commonly associated with first aid, the symbol of a red cross is an official protective symbol of the [[Red Cross]]. According to the [[Geneva Conventions]] and other international laws, the use of this and [[International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement#Protection symbols vs. organizational emblems|similar symbols]] is reserved for official agencies of the '''[[International Red Cross and Red Crescent]]''', and as a protective emblem for medical personnel and facilities in combat situations. Use by any other person or organization is illegal, and may lead to prosecution. |
Although commonly associated with first aid, the symbol of a red cross is an official protective symbol of the [[Red Cross]]. According to the [[Geneva Conventions]] and other international laws, the use of this and [[International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement#Protection symbols vs. organizational emblems|similar symbols]] is reserved for official agencies of the '''[[International Red Cross and Red Crescent]]''', and as a protective emblem for medical personnel and facilities in combat situations. Use by any other person or organization is illegal, and may lead to prosecution. |
||
| Line 87: | Line 318: | ||
Some organizations may make use of the [[Star of Life]], although this is usually reserved for use by ambulance services, or may use symbols such as the [[Maltese Cross]], like the [[Order of Malta Ambulance Corps]] and [[St John Ambulance]]. Other symbols may also be used. |
Some organizations may make use of the [[Star of Life]], although this is usually reserved for use by ambulance services, or may use symbols such as the [[Maltese Cross]], like the [[Order of Malta Ambulance Corps]] and [[St John Ambulance]]. Other symbols may also be used. |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Star of life2.svg|[[Star of Life]] |
|||
File:Sign_first_aid.svg|[[International Organization for Standardization|ISO]] First aid symbol |
|||
File:CivilDefence.svg|[[Civil defense]] |
|||
File:St. Andrews First Aid.png|St. Andrew's first aid badge |
|||
File: |
File:Flag of the Red Crystal.svg|Emblem of the [[Emblems of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement#Red Crystal|Red Crystal]] |
||
File:Flag of the Red Crescent.svg|Emblem of the [[Emblems of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement#Red Crescent|Red Crescent]] |
|||
File:Maltese-Cross-Heraldry.svg|The [[Maltese cross]] |
|||
File:Flag of the Red Cross.svg|Emblem of the [[Emblems of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement#Red Cross|Red Cross]] |
|||
File:Star_of_life2.svg|The [[Star of life]] |
|||
File:ISO 7010 E003 - Crescent Symbol.svg|ISO First Aid Symbol ([[ISO 7010#Crescent variant|Crescent variant]]) |
|||
File:CivilDefence.svg|[[Civil defence]] |
|||
File:ISO 7010 E003 - First aid sign.svg|[[ISO 7010|ISO First Aid Symbol]] |
|||
File:Maltese-Cross-Heraldry.svg|[[Maltese cross|Maltese or Amalfi Cross]] |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
==Conditions that often require first aid== |
|||
''Also see [[medical emergency]].'' |
|||
* [[Altitude sickness]], which can begin in susceptible people at altitudes as low as 5,000 feet, can cause potentially fatal [[High altitude cerebral edema|swelling of the brain]] or [[High altitude pulmonary edema|lungs]].<ref name=MedicalProblems>{{cite journal |author=Cymerman, A; Rock, PB |title=Medical Problems in High Mountain Environments. A Handbook for Medical Officers |publisher=US Army Research Inst. of Environmental Medicine Thermal and Mountain Medicine Division Technical Report |volume=USARIEM-TN94-2 |url=http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/7976 |accessdate=2009-03-05}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Anaphylaxis]], a life-threatening condition in which the airway can become constricted and the patient may go into [[shock (circulatory)|shock]]. The reaction can be caused by a systemic allergic reaction to [[allergen]]s such as insect bites or peanuts. Anaphylaxis is initially treated with injection of [[epinephrine]]. |
|||
* [[Battle]]field first aid—This protocol refers to treating shrapnel, gunshot wounds, burns, bone fractures, etc. as seen either in the ‘traditional’ battlefield setting or in an area subject to damage by large-scale weaponry, such as a [[bomb]] blast. |
|||
* [[Bone fracture]], a break in a bone initially treated by stabilizing the fracture with a [[splint (medical)|splint]]. |
|||
* [[Burn (injury)|Burns]], which can result in damage to tissues and loss of body fluids through the burn site. |
|||
* [[Cardiac Arrest]], which will lead to death unless CPR preferably combined with an AED is started within minutes. There is often no time to wait for the emergency services to arrive as 92 percent of people suffering a sudden cardiac arrest die before reaching hospital according to the American Heart Association. |
|||
* [[Choking]], blockage of the airway which can quickly result in death due to lack of [[oxygen]] if the patient’s trachea is not cleared, for example by the [[Heimlich Maneuver]]. |
|||
* [[Childbirth]]. |
|||
* [[Cramp]]s in muscles due to lactic acid build up caused either by inadequate oxygenation of muscle or lack of water or salt. |
|||
* [[Diving disorders]], [[drowning]] or [[asphyxiation]].<ref name=Longphre>{{cite journal |last=Longphre |first=John M. |author2=Petar J. DeNoble |author3=Richard E. Moon |author4=Richard D. Vann |author5= John J. Freiberger |title=First aid normobaric oxygen for the treatment of recreational diving injuries. |journal=Undersea and Hyperbaric Medicine |volume=34 |issue=1 |pages=43–49 |year=2007 |issn=1066-2936 |oclc=26915585 |pmid=17393938 |url=http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/5514 |accessdate=2009-03-05 }}</ref> |
|||
* Gender-specific conditions, such as [[dysmenorrhea]] and [[testicular torsion]]. |
|||
* [[Myocardial infarction|Heart attack]], or inadequate blood flow to the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle. |
|||
* Heat stroke, also known as sunstroke or [[hyperthermia]], which tends to occur during heavy exercise in high humidity, or with inadequate water, though it may occur spontaneously in some chronically ill persons. Sunstroke, especially when the victim has been unconscious, often causes major damage to body systems such as brain, kidney, liver, gastric tract. [[Coma|Unconsciousness for more than two hours]] usually leads to permanent disability. Emergency treatment involves rapid cooling of the patient. |
|||
* [[Hair tourniquet]] a condition where a hair or other thread becomes tied around a toe or finger tightly enough to cut off blood flow. |
|||
* [[Heat syncope]], another stage in the same process as heat stroke, occurs under similar conditions as heat stroke and is not distinguished from the latter by some authorities. |
|||
* Heavy bleeding, treated by applying pressure (manually and later with a [[pressure bandage]]) to the wound site and elevating the limb if possible. |
|||
* [[Hyperglycemia]] ([[diabetic coma]]) and [[Hypoglycemia]] ([[insulin shock]]). |
|||
* [[Hypothermia]], or Exposure, occurs when a person’s core body temperature falls below 33.7 °C (92.6 °F). First aid for a mildly hypothermic patient includes rewarming, which can be achieved by wrapping the affected person in a blanket, and providing warm drinks, such as soup, and high energy food, such as chocolate.<ref>{{cite web|publisher=British Red Cross|url=http://www.redcross.org.uk/en/What-we-do/First-aid/Everyday-First-Aid/Hypothermia|title=Everyday First Aid - Hypothermia}}</ref>However, rewarming a severely hypothermic person could result in a fatal [[arrhythmia]], an irregular heart rhythm.<ref name=sterba>{{cite journal |author=Sterba, JA |title=Field Management of Accidental Hypothermia during Diving |journal=[[US Naval Experimental Diving Unit Technical Report]] |volume=NEDU-1-90 |year=1990 |url=http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/4248 |accessdate=2013-03-15 }}</ref> |
|||
* Insect and animal [[bite (medicine)|bites]] and stings. |
|||
* [[Joint dislocation]]. |
|||
* [[Poison]]ing, which can occur by injection, inhalation, absorption, or ingestion. |
|||
* [[Seizures]], or a malfunction in the electrical activity in the brain. Three types of seizures include a grand mal (which usually features convulsions as well as temporary respiratory abnormalities, change in skin complexion, etc.) and petit mal (which usually features twitching, rapid blinking, and/or fidgeting as well as altered consciousness and temporary respiratory abnormalities). |
|||
* [[Strain (injury)|Muscle strains]] and [[Sprain]]s, a temporary [[dislocation]] of a [[joint (anatomy)|joint]] that immediately reduces automatically but may result in ligament damage. |
|||
* [[Stroke]], a temporary loss of blood supply to the brain. |
|||
* [[Toothache]], which can result in severe pain and loss of the tooth but is rarely life-threatening, unless over time the infection spreads into the bone of the jaw and starts [[osteomyelitis]]. |
|||
* [[Wound]]s and [[bleeding]], including [[laceration]]s, [[incision]]s and [[Abrasion (medical)|abrasions]], [[Gastrointestinal bleeding]], [[Avulsion injury|avulsions]] and [[Pneumothorax|Sucking chest wounds]], treated with an [[occlusive dressing]] to let air out but not in. |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{ |
{{reflist|30em}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
| Line 133: | Line 337: | ||
<!-- If you're looking at this bit of the page, with the intention of inserting the name of your first aid training business, organisation or club, and maybe a link too, then you are most likely wasting your time. You are not the first person to think of this, and on average your link will be deleted in less than an hour. It won't reach loads of people, and it doesn't do anything to improve your Google rating or anything similar. --> |
<!-- If you're looking at this bit of the page, with the intention of inserting the name of your first aid training business, organisation or club, and maybe a link too, then you are most likely wasting your time. You are not the first person to think of this, and on average your link will be deleted in less than an hour. It won't reach loads of people, and it doesn't do anything to improve your Google rating or anything similar. --> |
||
* [http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/FirstAidIndex/FirstAidIndex First Aid Guide at the Mayo Clinic] |
* [http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/FirstAidIndex/FirstAidIndex First Aid Guide at the Mayo Clinic] |
||
* [http://www. |
* [http://www.redcross.org.uk/first-aid/first-aid-apps/ First aid from the British Red Cross] – including first aid tips and first aid training information |
||
* [http://www. |
* [http://www.sja.org.uk/get-advice/free-first-aid-app/ First aid from St John Ambulance] – first aid information and advice |
||
<!-- PROMOTIONAL LINKS INSERTED HERE WILL BE DELETED --> |
<!-- PROMOTIONAL LINKS INSERTED HERE WILL BE DELETED --> |
||
{{First aid|state=expand}} |
|||
{{First aid|state=}} |
|||
{{Emergency medicine}} |
{{Emergency medicine}} |
||
{{Lifesaving and Lifeguarding}} |
{{Lifesaving and Lifeguarding}} |
||
{{Underwater diving|divsaf}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:First Aid}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:First Aid}} |
||
<!--Categories--> |
<!--Categories--> |
||
[[Category:First aid| ]] |
[[Category:First aid| ]] |
||
[[Category:Scoutcraft]] |
|||
[[Category:Self care]] |
|||
[[Category:Emergency medical services]] |
[[Category:Emergency medical services]] |
||
[[Category:Lifesaving]] |
[[Category:Lifesaving]] |
||
[[Category:Scoutcraft]] |
|||
[[Category:Self-care]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 09:06, 3 January 2025
This article contains instructions, advice, or how-to content. (June 2022) |


First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with a medical emergency,[1] with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery until medical services arrive. First aid is generally performed by someone with basic medical or first response training. Mental health first aid is an extension of the concept of first aid to cover mental health,[2] while psychological first aid is used as early treatment of people who are at risk for developing PTSD.[3] Conflict first aid, focused on preservation and recovery of an individual's social or relationship well-being, is being piloted in Canada.
There are many situations that may require first aid, and many countries have legislation, regulation, or guidance, which specifies a minimum level of first aid provision in certain circumstances. This can include specific training or equipment to be available in the workplace (such as an automated external defibrillator), the provision of specialist first aid cover at public gatherings, or mandatory first aid training within schools. Generally, five steps are associated with first aid:
- Assess the surrounding areas.
- Move to a safe surrounding (if not already; for example, road accidents are unsafe to be dealt with on roads).
- Call for help: both professional medical help and people nearby who might help in first aid such as the compressions of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
- Perform suitable first aid depending on the injury suffered by the casualty.
- Evaluate the casualty for any fatal signs of danger, or possibility of performing the first aid again.
Early history and warfare
[edit]Skills of what is now known as first aid have been recorded throughout history, especially in relation to warfare, where the care of both traumatic and medical cases is required in particularly large numbers. The bandaging of battle wounds is shown on Classical Greek pottery from c. 500 BC, whilst the parable of the Good Samaritan includes references to binding or dressing wounds.[4] There are numerous references to first aid performed within the Roman army, with a system of first aid supported by surgeons, field ambulances, and hospitals.[5] Roman legions had the specific role of capsarii, who were responsible for first aid such as bandaging, and are the forerunners of the modern combat medic.[6]
Further examples occur through history, still mostly related to battle, with examples such as the Knights Hospitaller in the 11th century AD, providing care to pilgrims and knights in the Holy Land.[7]
Formalization of life saving treatments
[edit]During the late 18th century, drowning as a cause of death was a major concern amongst the population. In 1767, a society for the preservation of life from accidents in water was started in Amsterdam, and in 1773, physician William Hawes began publicizing the power of artificial respiration as means of resuscitation of those who appeared drowned. This led to the formation, in 1774, of the Society for the Recovery of Persons Apparently Drowned, later the Royal Humane Society, who did much to promote resuscitation.[8][9]
Napoleon's surgeon, Baron Dominique-Jean Larrey, is credited with creating an ambulance corps, the ambulance volantes, which included medical assistants, tasked to administer first aid in battle.[10]
In 1859, Swiss businessman Jean-Henri Dunant witnessed the aftermath of the Battle of Solferino, and his work led to the formation of the Red Cross, with a key stated aim of "aid to sick and wounded soldiers in the field".[7] The Red Cross and Red Crescent are still the largest provider of first aid worldwide.[11]

In 1870, Prussian military surgeon Friedrich von Esmarch introduced formalized first aid to the military, and first coined the term "erste hilfe" (translating to 'first aid'), including training for soldiers in the Franco-Prussian War on care for wounded comrades using pre-learnt bandaging and splinting skills, and making use of the Esmarch bandage which he designed.[4] The bandage was issued as standard to the Prussian combatants, and also included aide-memoire pictures showing common uses.
In 1872, the Order of Saint John of Jerusalem in England changed its focus from hospice care, and set out to start a system of practical medical help, starting with making a grant towards the establishment of the UK's first ambulance service. This was followed by creating its own wheeled transport litter in 1875 (the St John Ambulance), and in 1877 established the St John Ambulance Association (the forerunner of modern-day St John Ambulance) "to train men and women for the benefit of the sick and wounded".[12]
Also in the UK, Surgeon-Major Peter Shepherd had seen the advantages of von Esmarch's new teaching of first aid, and introduced an equivalent programme for the British Army, and so being the first user of "first aid for the injured" in English, disseminating information through a series of lectures. Following this, in 1878, Shepherd and Colonel Francis Duncan took advantage of the newly charitable focus of St John,[4] and established the concept of teaching first aid skills to civilians. The first classes were conducted in the hall of the Presbyterian school in Woolwich (near Woolwich barracks where Shepherd was based) using a comprehensive first aid curriculum.
First aid training began to spread through the British Empire through organisations such as St John, often starting, as in the UK, with high risk activities such as ports and railways.[13]
The first recorded first aid training in the United States took place in Jermyn, Pennsylvania in 1899.[14]
Main emergences that require first aid and their corresponding cares
[edit]List of some situations that require specific first aid, and information about them (in alphabetical order):
Bleeding
[edit]A bleeding or hemorrhage is the uncontrolled escape of blood from any vein or artery.
In wounds that are caused by an external agent, there can be an additional risk of infection.
Cardiac arrest (total stop of heartbeat)
[edit]A cardiac arrest is the complete stop of heart function.
Choking
[edit]A choking is an obstruction in the airway
Diabetes, hyperglycemia
[edit]A hyperglycemia or hyperglycaemia is an excessive level of blood sugars.
Diabetes, hypoglycemia
[edit]A hypoglycemia or hypoglycaemia is an excessive fall of blood sugars in a diabetic patient.
It almost always occurs because of a problem with a medication to reduce the sugar level in blood.
Drowning
[edit]A drowning is a suffocation into a liquid substance.
First aid for drowning are very similar to those for cardiorespiratory arrest, but starting with 2 initial ventilations.
Infarction of the heart
[edit]A cardiac infarction is the sudden lack of blood supply to the heart, normally because of a problem in one of its arteries.
Stroke
[edit]A stroke is a sudden lack of blood supply to the brain.
Aims of first aid
[edit]The primary goal of first aid is to prevent death or serious injury from worsening. The key aims of first aid can be summarized with the acronym of 'the three Ps':[15]
- Preserve life: The overriding aim of all medical care which includes first aid, is to save lives and minimize the threat of death. First aid done correctly should help reduce the patient's level of pain and calm them down during the evaluation and treatment process.
- Prevent further harm: Prevention of further harm includes addressing both external factors, such as moving a patient away from any cause of harm, and applying first aid techniques to prevent worsening of the condition, such as applying pressure to stop a bleed from becoming dangerous.
- Promote recovery: First aid also involves trying to start the recovery process from the illness or injury, and in some cases might involve completing a treatment, such as in the case of applying a plaster to a small wound.
First aid is not medical treatment, and cannot be compared with what a trained medical professional provides. First aid involves making common sense decisions in the best interest of an injured person.
Setting the priorities
[edit]A first aid intervention would follow an order, which would try to attend in the best manner the main threats for the life and mobility of the victim.
There are some first aid protocols (such as ATLS, BATLS and SAFE-POINT) that define which are the priorities and the correct execution of the steps for saving human life. A major benefit of the use of official protocols is that they require minimum resources, time and skills, and have a great degree of success.
ABCDE and csABCDE general protocol
[edit]The ABCDE method is the general protocol of first aid and implies a quite general view.[16]
It was initially developed by Dr Peter Safar in the 1950s. But it has received some modifications, improvements and variations that were intended for more specific contexts. For example: it has been completed with improvements from the ATLS (Advanced Trauma Life Support) version of the American College of Surgeons[17] and the BATLS (Battlefield Advanced Trauma Life Support) version of the British Army.[18]
As a result, the mnemonic of the steps of this protocol is ABCDE, or its improved version (cs)ABCDE (sometimes called xABCDE, the words in the mnemonic may vary), which represent:[19][20]
—An attached first part (named as "cs" or "x", or in any other way) that will always mention stopping the critical losses of blood and managing with a special and careful treatment to patients with serious damages at the spine that threaten their future mobility:
- catastrophic-bleeding (stopping urgently the massive external bleedings, as it is marked in the BATLS version).
- spine-protection (previous examination of the spine, and careful preventive treatment for its damages, as it is marked in the ATLS version).
—The ABCDE protocol itself:
- Airway (clearing airways).
- Breathing (ensuring respiration).
- Circulation (ensuring effective cardiac output).
Any Defibrillation process for a cardiac arrest (total stop of heartbeat) would be included here, or in 'Disability' (as a double mnemonic 'D'). - Disability (neurological condition, level of glucose can also be examined).
- Exposure (or 'Evaluate': other questions in an overall examination of the patient, environment).
ABC and CABD cardiopulmonary resuscitation protocol
[edit]This protocol (originally named as ABC) is a simplified version or concrete application of the previous csABCDE (or ABCDE) protocol, that focuses in the use of cardio-pulmonary resuscitation. The American Heart Association and the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation teach it as a reference.[21][22]
Its current mnemonic is CABD (an improvement in the sequence for most of the cases):
- Circulation or Chest Compressions.
- Airway: attempt to open the airway (using a head-tilt and chin-lift technique; not in the case of babies, which require avoid tilting the head).
- Breathing or Rescue Breaths.
- Defibrillation: use of an automated external defibrillator to recover heart function.
Wider protocols
[edit]These are the protocols that do not only deal with direct care to the victim but they also mention other complementary tasks (before and later).
European protocol
[edit]This method has been studied and employed for a long time in many European countries, as France.[23] It is a reference, of a certain reputation, that could be applied solely or to a certain degree, usually combining it with the common csABCDE (ABCDE) method or its simplified CABD (ABC) variant about cardio-pulmonary resuscitation. The European method has a wider range than them, and their steps include tasks that are previous to the first aid techniques themselves.
These are its steps (with no official mnemonic that helps to remember them):
- Protection for patients and rescuers. If dangers are present, the patient would be moved to a safer place with a careful management of any detected spinal injury.
- Evaluation of the patient (looking for priorities as critical bleeding and cardiac arrest).
- Alerting to medical services and bystanders.
- Performing the first aid practices. The CABD (or ABC) method for cardio-pulmonary resuscitation and many details of the wider csABCDE (or ABCDE) method would be included in this step.
Other mentionable protocols
[edit]Some other known protocols that could be mentioned in many contexts (in alphabetical order):
AMEGA protocol
It is similar to the European protocol, because it also has a wider range[24] than the common csABCDE (or ABCDE) protocol, and includes other tasks that are previous to the first aid techniques themselves. The order of the steps is changed, and the experience with it is lesser, but it adds the idea of a posterior 'aftermath' phase.
The mnemonic AMEGA refers to:
- Assess the situation, looking for risks.
- Make safe the situation, after having identified the risks.
- Emergency aid. Performing the first aid practices.
- Get help. Asking for emergency help to medical services and bystanders.
- Aftermath. The aftermath tasks include recording and reporting, continued care of patients and the welfare of responders and the replacement of used first aid kit elements.
ATLS and BATLS protocols
They are basically the common ABCDE and csABCDE protocol, but focusing in particular aspects.
The ATLS (Advanced Trauma Life Support) version[17] was developed by the American College of Surgeons, focusing in the particular needs of trauma and specifically in the spinal injuries. And the BATLS (Battlefield Advanced Trauma Life Support) version[18] is an improvement for the British Army that added the concept of 'catastrophic bleeding'.
The preference for one or another among all these protocols can depend on the context and the audience.
Check, Call and Care protocol
[edit]It comes from Red Cross[25] and, as the European protocol, has a wider range than the common csABCDE (ABCDE) method. So it could be seen as a simplification of the European protocol, and, especially, easier to remember as a guide for most of cases.
It mentions the following steps:
- Check the scene for safety of the rescuer and others, and check the patient's condition.
- Call to emergency medical services.
- Care the patient.
SAFE-POINT protocol
[edit]Another European protocol, which appeared in the field of construction of Czech Republic to react to any emergence .[26]
Their steps (which have not any mnemonic) are:
- Safety of the rescuers.
- Calling to emergency telephone number.
- Bleeding: treating the massive bleedings.
- Freeing the airways.
- Resuscitation: applying cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- Keeping warm to the patient.
Key basic skills
[edit]Certain skills are considered essential to the provision of first aid and are taught ubiquitously.
Displacement skills
[edit]If there are dangers around (such as fire, electric dangers or others) the patient has to be moved to a safe place,[27][28] where providing the required first aid procedures is possible.
—In case of a possible severe spinal injury: when a patient seems to have a possible serious injury in the spinal cord (in the backbone, either at the neck part or the back part), that patient must not be moved except if that is necessary, and, when necessary, it must be done as little as possible and very carefully (see mentions about this type of injury in the gallery of drawings below). These precautions avoid many risks of causing further damages for the patient's mobility in the future.
Usually, the patient needs to end up lying down, in a face-up position, on a sufficiently firm surface (for example, on the floor, which allows to perform the chest compressions of cardiopulmonary resuscitation).
-
—A victim with a serious injury in the spine (in the back or the neck), which indicates a risk to the future mobility, can be carefully transferred by several rescuers that work coordinately.
The victim’s head and back would be held in the same position they were. -
—When there is a victim with a serious injury in the spine (in the back or the neck) and a rescuer without instruments, the rescuer can try to carry the victim carefully through the Rautek maneuver (as in the picture), trying to keep victim’s head and back in the same position they were.
The victim's head can be supported on the rescuer to try to soften the movements. -
—A victim without a serious injury in the spine (in the back or the neck) can be pulled through the floor, which is easier on a blanket, carpet or another tissue located under most of the body.
—Carrying on a base to victims with a suspected spinal injury would require to place them carefully, while keeping their head and back in the same position they were, on a higher or much thicker base (as a litter or mattress), for a better displacement.
Checking skills
[edit]They evaluate the condition of the victim,[27] first attending to the main threats for life.
The preferred initial way of checking consist of asking, commonly by touching the patient in one of his shoulders and shouting something, such as: "can you hear me?"
In some cases, the victim has a wound that bleeds abundantly, which requires its own additional treatment to stop the blood loss (usually, it would begin by keeping the wound pressed).
If the patient does not react, the heartbeats can be checked in the carotid pulse: placing two fingers on any side of the neck (on the left or the right side), near his head. In cases where checking the carotid pulse is impossible, heartbeats can be perceived in the radial pulse: placing two fingers on a wrist, under the part of the thumb, and applying moderate pressure. Breathing can also be checked additionally, placing an ear on the mouth and, at the same time, watching the chest rising by the effect of the air. It is recommended not to waste too much time of first aid in checking (professional rescuers are taught to take 10 seconds in it).
-
Checking of heartbeats in the carotid pulse.
This is usually the fastest method of checking the patient's condition. -
Verification of heartbeats in the radial pulse, pressing moderately on a wrist, under the part of the thumb.
-
Check of patient's breathing, listening the air inside of the mouth and watching the chest swelling.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
[edit]Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the method of first aid for treating victims of cardiac arrest (complete stop of heartbeat).
Airway, Breathing, and Circulation skills
[edit]
ABC method stands for Airway, Breathing, and Circulation.[29] The same mnemonic is used by emergency health professionals.
It is focused on critical life-saving intervention, and it must be rendered before treatment of less serious injuries.
Attention must first be brought to the airway to ensure it is clear. An obstruction (choking) is a life-threatening emergency. If an object blocks the airway, it requires anti-choking procedures. Following any evaluation of the airway, a first aid attendant would determine adequacy of breathing and provide rescue breathing if necessary.
Assessment of circulation is now not usually carried out for patients who are not breathing, with first aiders now trained to go straight to chest compressions (and thus providing artificial circulation) but pulse checks may be done on less serious patients.
Some organizations add a fourth step of "D" for Deadly bleeding or Defibrillation, while others consider this as part of the Circulation step simply referred as Disability. Variations on techniques to evaluate and maintain the ABCs depend on the skill level of the first aider. Once the ABCs are secured, first aiders can begin additional treatments or examination, as required if they possess the proper training (such as measuring pupil dilation).[30]
Some organizations teach the same order of priority using the "3Bs": Breathing, Bleeding, and Bones (or "4Bs": Breathing, Bleeding, Burns, and Bones). While the ABCs and 3Bs are taught to be performed sequentially, certain conditions may require the consideration of two steps simultaneously. This includes the provision of both artificial respiration and chest compressions to someone who is not breathing and has no pulse, and the consideration of cervical spine injuries when ensuring an open airway.
Preserving life
[edit]The patient must have an open airway—that is, an unobstructed passage that allows air to travel from the open mouth or uncongested nose, down through the pharynx and into the lungs. Conscious people maintain their own airway automatically, but those who are unconscious (with a GCS of less than 8) may be unable to do so, as the part of the brain that manages spontaneous breathing may not be functioning.
Whether conscious or not, the patient may be placed in the recovery position, laying on their side. In addition to relaxing the patient, this can have the effect of clearing the tongue from the pharynx. It also avoids a common cause of death in unconscious patients, which is choking on regurgitated stomach contents.
The airway can also become blocked by a foreign object. To dislodge the object and solve the choking case, the first aider may use anti-choking methods (such as 'back slaps' and 'abdominal thrusts').
Once the airway has been opened, the first aider would reassess the patient's breathing. If there is no breathing, or the patient is not breathing normally (e.g., agonal breathing), the first aider would initiate CPR, which attempts to restart the patient's breathing by forcing air into the lungs. They may also manually massage the heart to promote blood flow around the body.
If the choking person is an infant, the first aider may use anti-choking methods for babies. During that procedure, series of five strong blows are delivered on the infant's upper back after placing the infant's face in the aider's forearm. If the infant is able to cough or cry, no breathing assistance should be given. Chest thrusts can also be applied with two fingers on the lower half of the middle of the chest. Coughing and crying indicate the airway is open and the foreign object will likely to come out from the force the coughing or crying produces.[31]
A first responder should know how to use an Automatic External Defibrillator (AED) in the case of a person having a sudden cardiac arrest. The survival rate of those who have a cardiac arrest outside of the hospital is low. Permanent brain damage sets in after five minutes of no oxygen delivery, so rapid action on the part of the rescuer is necessary. An AED is a device that can examine a heartbeat and produce electric shocks to restart the heart.[32]
A first aider should be prepared to quickly deal with less severe problems such as cuts, grazes or bone fracture. They may be able to completely resolve a situation if they have the proper training and equipment. For situations that are more severe, complex or dangerous, a first aider might need to do the best they can with the equipment they have, and wait for an ambulance to arrive at the scene.
First aid kits
[edit]
A first aid kit consists of a strong, durable bag or transparent plastic box. They are commonly identified with a white cross on a green background. A first aid kit does not have to be bought ready-made. The advantage of ready-made first aid kits are that they have well organized compartments and familiar layouts.
Contents
[edit]There is no universal agreement upon the list for the contents of a first aid kit. The UK Health and Safety Executive stress that the contents of workplace first aid kits will vary according to the nature of the work activities.[33] As an example of possible contents of a kit, British Standard BS 8599 First Aid Kits for the Workplace[34] lists the following items:
- Information leaflet
- Medium sterile dressings
- Large sterile dressings
- Bandages
- Triangular dressings
- Safety pins
- Adhesive dressings
- Sterile wet wipes
- Microporous tape
- Nitrile gloves
- Face shield
- Foil blanket
- Burn dressings
- Clothing shears
- Conforming bandages
- Finger dressing
- Antiseptic cream
- Scissors
- Tweezers
- Cotton
Training principles
[edit]
Basic principles, such as knowing the use of adhesive bandage or applying direct pressure on a bleed, are often acquired passively through life experiences. However, to provide effective, life-saving first aid interventions requires instruction and practical training. This is especially true where it relates to potentially fatal illnesses and injuries, such as those that require CPR; these procedures may be invasive, and carry a risk of further injury to the patient and the provider. As with any training, it is more useful if it occurs before an actual emergency. And, in many countries, calling emergency medical services allows listening basic first aid instructions over the phone while the ambulance is on the way.
Training is generally provided by attending a course, typically leading to certification. Due to regular changes in procedures and protocols, based on updated clinical knowledge, and to maintain skill, attendance at regular refresher courses or re-certification is often necessary. First aid training is often available through community organizations such as the Red Cross and St. John Ambulance, or through commercial providers, who will train people for a fee. This commercial training is most common for training of employees to perform first aid in their workplace. Many community organizations also provide a commercial service, which complements their community programmes.
1.Junior level certificate Basic Life Support
2.Senior level certificate
3.Special certificate
Types of first aid which require training
[edit]
There are several types of first aid (and first aider) that require specific additional training. These are usually undertaken to fulfill the demands of the work or activity undertaken.
- Aquatic/Marine first aid is usually practiced by professionals such as lifeguards, professional mariners or in diver rescue, and covers the specific problems which may be faced after water-based rescue or delayed MedEvac.
- Battlefield first aid takes into account the specific needs of treating wounded combatants and non-combatants during armed conflict.
- Conflict First Aid focuses on support for stability and recovery of personal, social, group or system well-being and to address circumstantial safety needs.
- Hyperbaric first aid may be practiced by underwater diving professionals, who need to treat conditions such as decompression sickness.
- Oxygen first aid is the providing of oxygen to casualties with conditions resulting in hypoxia. It is also a standard first aid procedure for underwater diving incidents where gas bubble formation in the tissues is possible.
- Wilderness first aid is the provision of first aid under conditions where the arrival of emergency responders or the evacuation of an injured person may be delayed due to constraints of terrain, weather, and available persons or equipment. It may be necessary to care for an injured person for several hours or days.
- Mental health first aid is taught independently of physical first aid. How to support someone experiencing a mental health problem or in a crisis situation. Also how to identify the first signs of someone developing mental ill health and guide people towards appropriate help.

First aid services
[edit]Some people undertake specific training in order to provide first aid at public or private events, during filming, or other places where people gather. They may be designated as a first aider, or use some other title. This role may be undertaken on a voluntary basis, with organisations such as the Red Cross society and St. John Ambulance,[35] or as paid employment with a medical contractor.
People performing a first aid role, whether in a professional or voluntary capacity, are often expected to have a high level of first aid training and are often uniformed.
Symbols
[edit]Although commonly associated with first aid, the symbol of a red cross is an official protective symbol of the Red Cross. According to the Geneva Conventions and other international laws, the use of this and similar symbols is reserved for official agencies of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent, and as a protective emblem for medical personnel and facilities in combat situations. Use by any other person or organization is illegal, and may lead to prosecution.
The internationally accepted symbol for first aid is the white cross on a green background shown below.
Some organizations may make use of the Star of Life, although this is usually reserved for use by ambulance services, or may use symbols such as the Maltese Cross, like the Order of Malta Ambulance Corps and St John Ambulance. Other symbols may also be used.
-
Emblem of the Red Crystal
-
Emblem of the Red Crescent
-
Emblem of the Red Cross
-
ISO First Aid Symbol (Crescent variant)
References
[edit]- ^ First aid manual: 9th edition. Dorling Kindersley. 2009. ISBN 978-1-4053-3537-9.
- ^ "Mental Health First Aid USA". Mental Health First Aid. October 10, 2013. Retrieved November 20, 2019.
- ^ Peterson, Sarah (January 30, 2018). "About PFA". The National Child Traumatic Stress Network. Retrieved November 20, 2019.
- ^ a b c Pearn, John (1994). "The earliest days of first aid". The British Medical Journal. 309 (6970): 1718–1720. doi:10.1136/bmj.309.6970.1718. PMC 2542683. PMID 7820000.
- ^ Eastman, A Brent (1992). "Blood in Our Streets: The Status and Evolution of Trauma Care Systems". JAMA Surgery. 127 (6): 677–681. doi:10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420060043008. PMID 1596168.
- ^ Efstathis, Vlas (November 1999). "A history of first aid and its role in armed forces" (PDF). ADF Health. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 30, 2014.
- ^ a b "First Aid: From Witchdoctors & Religious Knights to Modern Doctors". Archived from the original on January 18, 2012. Retrieved March 23, 2011.
- ^ New Scientist, Vol. 193 No. 2586 (13–19 Jan 2007), p. 50
- ^ Price, John (2014). Everyday Heroism: Victorian Constructions of the Heroic Civilian. Bloomsbury: London. p. 203. ISBN 978-1-4411066-5-0.
- ^ Baker, David; Cazalaà, Jean-Bernard; Carli, Pierre (September 2005). "Resuscitation great. Larrey and Percy--a tale of two barons". Resuscitation. 66 (3): 259–262. doi:10.1016/j.resuscitation.2005.03.009. ISSN 0300-9572. PMID 15990216.
- ^ "Event first aid and ambulance support". British Red Cross. Archived from the original on September 8, 2014.
- ^ Fletcher NC, The St John Ambulance Association: its history and its past in the ambulance movement. London: St John Ambulance Association, 1929:12–3.
- ^ Industrial Revolution: St. John Ambulance Archived 2007-02-20 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved December 10, 2006.
- ^ "Jermyn Pennsylvania - History". jermynpa.com. Retrieved September 10, 2024.
- ^ "Accidents and first aid". Archived from the original on May 3, 2008. Retrieved October 4, 2008.
- ^ Thim, Troels; Krarup, Niels Henrik Vinther; Grove, Erik Lerkevang; Rohde, Claus Valter; Løfgren, Bo (January 31, 2012). "Initial assessment and treatment with the Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure (ABCDE) approach". International Journal of General Medicine. 5: 117–121. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S28478. PMC 3273374. PMID 22319249.
- ^ a b Schmidt, Oliver I.; Gahr, Ralf H.; Gosse, Andreas; Heyde, Christoph E. (March 3, 2009). "ATLS(R) and damage control in spine trauma". World Journal of Emergency Surgery: WJES. 4: 9. doi:10.1186/1749-7922-4-9. ISSN 1749-7922. PMC 2660300. PMID 19257904.
- ^ a b Hodgetts, T. J.; Mahoney, P. F.; Russell, M. Q.; Byers, M. (October 2006). "ABC to ABC: redefining the military trauma paradigm". Emergency Medicine Journal. 23 (10): 745–746. doi:10.1136/emj.2006.039610. ISSN 1472-0213. PMC 2579588. PMID 16988297.
- ^ NotSan. "xABCDE untersuchung Rettungsdienst". notsan.info (in German). Archived from the original on November 20, 2024.
- ^ Certain, Lucas; Rostirola, João Vitor Cerávolo; Pereira, Juliana Silva; Rostirola, Gabriela Cerávolo; Estevam, Barbara Canto; Vieira, Carla Caroline Aguiar; da Silva, Israel; da Silva, Jussara Aparecida Rodrigues; Schevenin, Juliana de Cássia; de Oliveira, Ana Barbara Regiani; Franceli, Amanda Bonamichi; Lisboa, Camila Emanuele Camargo; Benites, Bruno Deltreggia (July 1, 2023). "First immediate transfusion at a prehospital environment in Latin America: A case report". Hematology, Transfusion and Cell Therapy. Diversity in Classical Hematology Research. 45 (Suppl 2): S153 – S156. doi:10.1016/j.htct.2021.08.007. ISSN 2531-1379. PMC 10433293. PMID 34862155.
- ^ American Heart Association (AHA) (2015). "Highlights of the Guidelines for CPR and ECC" (PDF). Retrieved December 1, 2024.
- ^ Field, John M.; Hazinski, Mary Fran; Sayre, Michael R.; Chameides, Leon; Schexnayder, Stephen M.; Hemphill, Robin; Samson, Ricardo A.; Kattwinkel, John; Berg, Robert A.; Bhanji, Farhan; Cave, Diana M.; Jauch, Edward C.; Kudenchuk, Peter J.; Neumar, Robert W.; Peberdy, Mary Ann (November 2, 2010). "Part 1: Executive Summary: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care". Circulation. 122 (18 Suppl 3): S640-56. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970889. ISSN 0009-7322. PMID 20956217.
- ^ Croix-Rouge francaise. "Les 4 étapes pour porter secours" (in French). Archived from the original on May 22, 2023. Retrieved October 30, 2024.
- ^ Furst, J., What does AMEGA stand for in first aid?, updated 12 July 2019, accessed 24 January 2022
- ^ American Red Cross. "Check, Call, Care: 3 Emergency Actions Steps to Take to Save Lives". Archived from the original on November 11, 2024.
- ^ safe-point.cz. "SAFE-Point: 6 steps to save life" (in Czech).
- ^ a b American Red Cross (2016). CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers (2nd ed.).
- ^ Community Emergency Response Team of L.A. (October 31, 2024). "Lifts and carries". CERTLA.
- ^ Eisenburger, Philip; Safar, Peter (1999). "Life supporting first aid training of the public—review and recommendations". Resuscitation. 41 (1): 3–18. doi:10.1016/S0300-9572(99)00034-9. PMID 10459587.
- ^ "Guidelines and Guidance: The ABCDE approach". Resuscitation Council (UK). Archived from the original on August 12, 2005. Retrieved May 2, 2019.
- ^ "Choking - infant under 1 year: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov.
- ^ Nessel, Edward H. (2012). "Treating Sudden Cardiac Arrest and the Use of Automated External Defibrillators in the Community Setting". AAMA Journal. 25: 9.
- ^ First aid at work: The Health and Safety (First-Aid) Regulations 1981. Guidance on Regulations L74
- ^ BS 8599-1:2011 BSI 2011
- ^ "Role of a First Aider - First Aid - St John Ambulance". www.sja.org.uk. Retrieved November 20, 2019.
External links
[edit]- First Aid Guide at the Mayo Clinic
- First aid from the British Red Cross – including first aid tips and first aid training information
- First aid from St John Ambulance – first aid information and advice