Pine Ridge Indian Reservation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| (425 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Use mdy dates|date=January 2024}} |
|||
<!-- Infobox begins --> |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
| |
| name = |
||
| |
| official_name = Pine Ridge Indian Reservation |
||
| other_name = Oglala Lakota Reservation |
|||
|native_name = ''Wazí Aháŋhaŋ Oyáŋke'' |
|||
| native_name = {{native name|lkt|Wazí Aháŋhaŋ Oyáŋke}} |
|||
|nickname nlk/,kcm AN s;kavWNFKLSH*(Y6x47uglrwysgrs = Pine Ridge Rez |
|||
| nickname = |
|||
|settlement_type = [[Indian reservation|Reservation]] |
|||
| settlement_type = [[Indian reservation]] |
|||
|motto = |
|||
| |
| motto = |
||
| |
| image_skyline = |
||
| imagesize = |
|||
|image_caption = Badlands in the northern portion of Pine Ridge Indian Reservation |
|||
| image_caption = |
|||
|image_flag = Pine Ridge Flag.svg |
|||
| |
| image_flag = Pine Ridge Flag.svg |
||
| |
| flag_size = 140px |
||
| |
| image_seal = |
||
| |
| seal_size = |
||
| |
| image_shield = |
||
| |
| shield_size = |
||
| anthem = <br /><small>("{{lang|dak|[[The Star-Spangled Banner|Wapaha kiŋ kekah'boyaŋhan]]}}"<ref>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jk1LqWlZYOg Steven Wilson sings the National Anthem in Lakota]</ref> and "Lakota Flag Song" used for some occasions)</small> |
|||
|citylogo_size = |
|||
| |
| city_logo = |
||
| |
| citylogo_size = |
||
| |
| image_map = 2810R Pine Ridge Reservation Locator Map.svg |
||
| |
| mapsize = |
||
| |
| map_caption = Location of the reservation in [[South Dakota]] |
||
| |
| image_map1 = |
||
| |
| mapsize1 = |
||
| |
| map_caption1 = |
||
| |
| image_dot_map = |
||
| |
| dot_mapsize = |
||
| dot_map_caption = |
|||
|pushpin_map = |
|||
| dot_x = |
|||
|pushpin_label_position = <!-- the position of the pushpin label: left, right, top, bottom, none --> |
|||
| |
| dot_y = |
||
| |
| pushpin_map = |
||
| pushpin_label_position = <!-- the position of the pushpin label: left, right, top, bottom, none --> |
|||
|subdivision_type = Country |
|||
| pushpin_map_caption = |
|||
|subdivision_name = United States |
|||
| pushpin_mapsize = |
|||
|subdivision_type1 = State |
|||
| subdivision_type = Tribe |
|||
|subdivision_name1 = [[South Dakota]], [[Nebraska]] |
|||
| subdivision_name = [[Oglala Sioux]] |
|||
|subdivision_type2 = Counties |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = Country |
|||
|subdivision_name2 = [[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota|Oglala Lakota]], [[Jackson County, South Dakota|Jackson]], [[Bennett County, South Dakota|Bennett]], and [[Sheridan County, Nebraska|Sheridan County]] |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = [[United States]] |
|||
|subdivision_type3 = |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = States |
|||
|subdivision_name3 = |
|||
| subdivision_name2 = [[South Dakota]] (99%)<br>[[Nebraska]] (1%) |
|||
|subdivision_type4 = |
|||
| subdivision_type3 = Counties |
|||
|subdivision_name4 = |
|||
| subdivision_name3 = [[Bennett County, South Dakota|Bennett]] (all)<br>[[Jackson County, South Dakota|Jackson]] (half)<br>[[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota|Oglala Lakota]] (all)<br>[[Sheridan County, Nebraska|Sheridan]] (part) |
|||
|government_footnotes = |
|||
| subdivision_type4 = |
|||
|government_type = |
|||
| subdivision_name4 = |
|||
|leader_title = Governing Body |
|||
| seat_type = Headquarters |
|||
|leader_name = Tribal Council of the [[Oglala Lakota|Oglala Sioux Tribe]] |
|||
| |
| seat = [[Pine Ridge, South Dakota|Pine Ridge]] |
||
| government_footnotes = <ref>{{Cite web|title=Oglala Lakota Nation|url=https://www.oglalalakotanation.info/|access-date=2019-07-24|archive-date=2021-03-07|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210307124444/https://oglalalakotanation.info/|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
|leader_name1 = John Yellow Bird Steele<ref>http://rapidcityjournal.com/news/local/yellow-bird-steele-ousts-bryan-brewer-for-ost-presidency/article_0bea9173-7edc-5de9-93de-a1143f83414f.html</ref> |
|||
| government_type = |
|||
|leader_title2 = |
|||
| |
| leader_title = Governing Body |
||
| |
| leader_name = Tribal Council |
||
| |
| leader_title1 = President |
||
| leader_name1 = Frank Star Comes Out ([[Democratic Party (United States)|D]]) |
|||
|leader_title4 = |
|||
| leader_title2 = Vice-President |
|||
|leader_name4 = |
|||
| leader_name2 = [[Alicia Mousseau]] ([[Democratic Party (United States)|D]]) |
|||
|established_title = Established |
|||
|established_date |
| established_date = 1889 |
||
|established_title2 |
| established_title2 = <!-- Incorporated (town) --> |
||
|established_date2 |
| established_date2 = |
||
|established_title3 |
| established_title3 = <!-- Incorporated (city) --> |
||
|established_date3 |
| established_date3 = |
||
|area_magnitude |
| area_magnitude = |
||
|unit_pref |
| unit_pref = <!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired--> |
||
|area_footnotes |
| area_footnotes = |
||
|area_total_km2 |
| area_total_km2 = |
||
|area_land_km2 |
| area_land_km2 = |
||
|area_water_km2 |
| area_water_km2 = |
||
|area_total_sq_mi |
| area_total_sq_mi = 3,468.86 |
||
|area_land_sq_mi |
| area_land_sq_mi = |
||
|area_water_sq_mi |
| area_water_sq_mi = |
||
|area_water_percent |
| area_water_percent = |
||
|area_urban_km2 |
| area_urban_km2 = |
||
|area_urban_sq_mi |
| area_urban_sq_mi = |
||
|area_metro_km2 |
| area_metro_km2 = |
||
|area_metro_sq_mi |
| area_metro_sq_mi = |
||
|population_as_of |
| population_as_of = 2020 |
||
|population_footnotes |
| population_footnotes = <ref>{2020 OST DataBook}</ref> |
||
|population_note |
| population_note = |
||
|population_total |
| population_total = 32000 |
||
|population_density_km2 = |
| population_density_km2 = |
||
|population_density_sq_mi |
| population_density_sq_mi = auto |
||
|population_metro |
| population_metro = |
||
|population_density_metro_km2 |
| population_density_metro_km2 = |
||
|population_density_metro_sq_mi = |
| population_density_metro_sq_mi = |
||
|population_urban |
| population_urban = |
||
|population_density_urban_km2 |
| population_density_urban_km2 = |
||
|population_density_urban_sq_mi = |
| population_density_urban_sq_mi = |
||
|population_blank1_title |
| population_blank1_title = |
||
|population_blank1 |
| population_blank1 = |
||
|population_density_blank1_km2 = |
| population_density_blank1_km2 = |
||
| population_density_blank1_sq_mi = |
|||
|timezone |
| timezone = [[North American Mountain Time Zone|MST]] |
||
|utc_offset |
| utc_offset = -7 |
||
|timezone_DST |
| timezone_DST = [[Mountain Daylight Time|MDT]] |
||
|utc_offset_DST |
| utc_offset_DST = -6 |
||
|latd |
| latd = |
||
| latm = |
|||
|longd= |longm= |longs= |longEW= |
|||
| |
| lats = |
||
| |
| latNS = |
||
| |
| longd = |
||
| longm = |
|||
|postal_code_type = <!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... --> |
|||
| |
| longs = |
||
| |
| longEW = |
||
| elevation_footnotes = |
|||
|blank_name = |
|||
| |
| elevation_m = |
||
| |
| elevation_ft = |
||
| postal_code_type = <!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... --> |
|||
|blank1_info = |
|||
| |
| postal_code = |
||
| |
| area_code = |
||
| website = https://www.oglala.gov/ |
|||
}} <!-- Infobox ends --> |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
| blank_name_sec1 = GDP |
|||
| blank_info_sec1 = $330.8 Million (2018) |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''Pine Ridge Indian Reservation''' ( |
The '''Pine Ridge Indian Reservation''' ({{langx|lkt|Wazí Aháŋhaŋ Oyáŋke}}), also called '''Pine Ridge Agency''', is an [[Oglala Lakota]] [[Indian reservation]] located in the [[U.S. state]] of [[South Dakota]], with a small portion of it extending into [[Nebraska]]. Originally included within the territory of the [[Great Sioux Reservation]], Pine Ridge was created by the Act of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888. in the southwest corner of South Dakota on the Nebraska border. It consists of {{convert|3,468.85|mi2|km2|0|abbr=on}} of land area and is one of the largest reservations in the United States.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/biggest-indian-reservations-in-the-united-states.html|title=Biggest Indian Reservations In The United States|website=WorldAtlas|date=5 June 2018}}</ref> |
||
The reservation encompasses the entirety of [[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota| |
The reservation encompasses the entirety of [[Oglala Lakota County]] and [[Bennett County, South Dakota|Bennett County]], the southern half of [[Jackson County, South Dakota|Jackson County]], and a small section of [[Sheridan County, Nebraska|Sheridan County]] added by Executive Order No. 2980 of February 20, 1904. Of the 3,142 counties in the United States, these are among [[Lowest-income counties in the United States|the poorest]]. Only {{convert|84000|acre|km2}} of land are suitable for agriculture. The [[United States Census, 2000|2000 census]] population of the reservation was 15,521. A 2009 study by [[Colorado State University]] and accepted by the [[United States Department of Housing and Urban Development]] has estimated the resident population to reach 28,787.<ref>[http://www.hud.gov/offices/pih/ih/codetalk/onap/ihbgformula.cfm#2 "Indian Housing Block Grant Formula"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090414141829/http://www.hud.gov/offices/pih/ih/codetalk/onap/ihbgformula.cfm |date=2009-04-14 }}, U.S. Housing and Urban Development</ref> |
||
Pine Ridge is the site of several events that |
Pine Ridge is the site of several events that mark milestones in the history between the [[Sioux]] of the area and the [[Federal government of the United States|U.S. government]]. Stronghold Table, a [[mesa]] in what is today the [[Oglala]]-administered portion of [[Badlands National Park]], was the location of the last of the [[Ghost Dance]]s. U.S. authorities repressed this movement, eventually leading to the [[Wounded Knee Massacre]] on December 29, 1890. A mixed band of [[Miniconjou]] Lakota and [[Hunkpapa]] Sioux, led by [[Spotted Elk|Chief Spotted Elk]], sought sanctuary at Pine Ridge after fleeing the [[Standing Rock Agency]], where [[Sitting Bull]] had been killed during efforts to arrest him. The families were intercepted and attacked by a heavily armed detachment of the Seventh Cavalry, which killed many women and children as well as warriors. This was the last large engagement between U.S. forces and [[Indigenous peoples of the Americas|Native Americans]] and marked the end of the western frontier. |
||
Changes accumulated in the last quarter of the 20th century |
Changes accumulated in the last quarter of the 20th century: in 1971 the Oglala Sioux Tribe (OST) started [[Oglala Lakota College]], a [[Tribal colleges and universities|tribal college]], which offers 4-year degrees. In 1973 decades of discontent at the Pine Ridge Reservation resulted in a grassroots protest that escalated into the [[Wounded Knee Occupation|Wounded Knee Incident]], gaining national attention. Members of the Oglala Lakota, the [[American Indian Movement]] and supporters occupied the town in defiance of federal and state law enforcement in a protest that turned into an armed standoff lasting 71 days. This event inspired American Indians across the country and gradually led to changes at the reservation. It has revived some cultural traditions and encouraged language training. In 1981 [[Tim Giago]] (Lakota) started the ''[[Lakota Times]]'' at Pine Ridge. |
||
Located at the southern end of the [[Badlands]], the reservation is part of the [[mixed grass prairie]], an ecological transition zone between the short-grass and tall-grass prairies; all are part of the [[Great Plains]]. A great variety of plant and animal life flourishes on and adjacent to the reservation, including the endangered [[black-footed ferret]]. The area is also important in the field of [[paleontology]]; it contains deposits of [[Pierre Shale]] formed on the seafloor of the [[Western Interior Seaway]], evidence of the [[Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary|marine Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary]], and one of the largest deposits of fossils of extinct mammals from the [[Oligocene|Oligocene epoch]]. |
Located at the southern end of the [[Badlands]], the reservation is part of the [[mixed grass prairie]], an ecological transition zone between the short-grass and tall-grass prairies; all are part of the [[Great Plains]]. A great variety of plant and animal life flourishes on and adjacent to the reservation, including the endangered [[black-footed ferret]]. The area is also important in the field of [[paleontology]]; it contains deposits of [[Pierre Shale]] formed on the seafloor of the [[Western Interior Seaway]], evidence of the [[Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary|marine Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary]], and one of the largest deposits of fossils of extinct mammals from the [[Oligocene|Oligocene epoch]]. |
||
| Line 124: | Line 129: | ||
====Great Sioux Reservation==== |
====Great Sioux Reservation==== |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Great Sioux Reservation 1888 Map.png|thumb|[[Great Sioux Reservation]], 1888, established by [[Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868)]]]] |
||
[[File:Siouxreservationmap.png|thumb|A map showing the [[Great Sioux Reservation]], subsequent loss of land to the federal government, and current holdings of the various Sioux reservations]] |
|||
;Red Cloud Agency hi Im bsHFikcjqasFZHBS |
|||
As stipulated in the [[Fort Laramie Treaty (1868)]], the U.S. government built Indian agencies for the various Lakota and other Plains tribes. These were forerunners to the modern Indian reservations. The [[Red Cloud Agency]] was established for the Oglala Lakota in 1871 on the [[North Platte River]] in [[Wyoming Territory]]. The location was one mile (1.6 km) west of the present town of [[Henry, Nebraska]]. The location of the Red Cloud Agency was moved to two other locations before being settled at the present Pine Ridge location. Pine Ridge Reservation was originally part of the [[Great Sioux Reservation]] established by the [[Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868]]; it encompassed approximately 60 million contiguous acres (240,000 km<sup>2</sup>) of western [[South Dakota]] (all of what is now called [[West River (South Dakota)|West River]]), northern [[Nebraska]] and eastern [[Wyoming]]. |
|||
As stipulated in the [[Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868)]], the U.S. government built Indian agencies for the various Lakota and other Plains tribes.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Soulek |first=Lauren |date=2024-01-12 |title=Native American treaty law 101 |url=https://www.keloland.com/news/local-news/native-american-treaty-law-101/ |access-date=2024-01-13 |work=KELOLAND |language=en-US}}</ref> These were forerunners to the modern Indian reservations. The [[Red Cloud Agency]] was established for the Oglala Lakota in 1871 on the [[North Platte River]] in [[Wyoming Territory]]. The location was one mile (1.6 km) west of the present town of [[Henry, Nebraska]]. The location of the Red Cloud Agency was moved to two other locations before being settled at the present Pine Ridge location. Pine Ridge Reservation was originally part of the [[Great Sioux Reservation]] established by the 1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie. It encompassed approximately 60 million contiguous acres ({{convert|60|e6acre|km2|disp=out}}) of western [[South Dakota]] (all of what is now called [[West River (South Dakota)|West River]]), northern [[Nebraska]] and eastern [[Wyoming]]. |
|||
====Loss of the Black Hills==== |
|||
In 1874 [[George Armstrong Custer]] led the U.S. Army [[Custer's 1874 Black Hills Expedition|Black Hills Expedition]], which set out on July 2 from [[Fort Abraham Lincoln]] in the [[Dakota Territory]], with orders to travel to the previously uncharted [[Black Hills]] of [[South Dakota]]. Its mission was to look for suitable locations for a fort, find a route to the southwest, and to investigate the potential for gold mining. After his discovery of gold was made public, miners began migrating there illegally although it was reservation land. |
|||
====Exclusion of the Black Hills==== |
|||
"Custer's florid descriptions of the mineral and timber resources of the Black Hills, and the land's suitability for grazing and cultivation ... received wide circulation, and had the effect of creating an intense popular demand for the 'opening' of the Hills for settlement."<ref>''U.S. v Sioux Nation'' 448 U.S. 371 at 377.</ref> Initially the U.S. military tried to turn away trespassing miners and settlers. Eventually President Grant, the [[United States Secretary of the Interior|Secretary of the Interior]], and the [[Secretary of War]], "decided that the military should make no further resistance to the occupation of the Black Hills by miners."<ref name=ReferenceA>''U.S. v Sioux Nation'' 448 U.S. 371 at 378.</ref> These orders were to be enforced "quietly", and the President's decision was to remain "confidential."<ref name=ReferenceA/> |
|||
In 1874, [[George Armstrong Custer]] led the U.S. Army [[Custer's 1874 Black Hills Expedition|Black Hills Expedition]], which set out on July 2 from [[Fort Abraham Lincoln]] in the [[Dakota Territory]], with orders to travel to the previously uncharted [[Black Hills]] of [[South Dakota]]. Its mission was to look for suitable locations for a fort, find a route to the southwest, and to investigate the potential for gold mining. After the discovery of gold was made public, miners began invading Sioux Territory. |
|||
[[File:Indian Land for Sale.jpg|thumb|left|A 1911 ad offering former reservation land for sale. Most of the "[[Dawes Act|allotted Indian land]]" sold the previous year (1910) was Sioux land.]] |
|||
"Custer's florid descriptions of the mineral and timber resources of the Black Hills, and the land's suitability for grazing and cultivation ... received wide circulation, and had the effect of creating an intense popular demand for more settlers to invade the Black Hills."<ref>{{ussc|name=United States v. Sioux Nation |volume=448|page=371|pin=377|year=1980}}.</ref> Initially the U.S. military tried to turn away trespassing miners and settlers. Eventually President Grant, the [[United States Secretary of the Interior|Secretary of the Interior]], and the [[Secretary of War]], "decided that the military should make no further resistance to the occupation of the Black Hills by miners."<ref name=ReferenceA>''U.S. v. Sioux Nation'', 448 U.S. at 378.</ref> These orders were to be enforced "quietly", and the President's decision was to remain "confidential".<ref name=ReferenceA/> |
|||
[[File:Indian Land for Sale.jpg|thumb|left|upright|A 1911 ad offering former reservation land for sale. Most of the "[[Dawes Act|allotted Indian land]]" sold the previous year (1910) was Sioux land.]] |
|||
The consequent military expedition to remove the Sioux from the Black Hills included an attack on a major encampment of several bands on the Little Bighorn River. Led by General Custer, the attack ended in his defeat; it was an overwhelming victory of chiefs [[Sitting Bull]] and [[Crazy Horse]] over the [[7th Cavalry Regiment]], a conflict often called [[Battle of the Little Bighorn|Custer's Last Stand.]]<ref name="ReferenceB"/><ref>See generally {{cite book |last=Philbrick |first=Nathaniel |title=The Last Stand: Custer, Sitting Bull, and the Battle of the Little Bighorn |year=2010 |publisher=Viking |isbn=978-0-670-02172-7}}</ref> US forces were vastly outnumbered. |
|||
As more settlers and gold miners encroached upon the Black Hills, the Government determined it had to acquire the land from the Sioux, and appointed a commission to negotiate the purchase.<ref name="ReferenceB">''U.S. v. Sioux Nation'', 448 U.S. at 379.</ref> The negotiations failed, as the Sioux resisted giving up what they considered sacred land. The U.S. resorted to military force. They declared the Sioux Indians "hostile" for failing to obey an order to return from an off-reservation hunting expedition by a specific date. In the dead of winter, the Sioux found the overland travel was impossible.<ref>''U.S. v. Sioux Nation'', 448 U.S. at 379-380.</ref> |
|||
In 1876 the U.S. Congress decided to open up the Black Hills to development and break up the Great Sioux Reservation. In 1877, it passed an act to make 7.7 million acres (31,000 km<sup>2</sup>) of the [[Black Hills]] available for sale to [[Homestead Act|homesteaders]] and private interests. In 1889 Congress divided the remaining area of Great Sioux Reservation into five separate reservations, defining the boundaries of each in its Act of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888.<br> Pine Ridge was established at that time. |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
The consequent military expedition to remove the Sioux from the Black Hills included an attack on a major encampment of several bands on the Little Bighorn River. Led by General Custer, the attack ended in his defeat. It was an overwhelming victory of chiefs [[Sitting Bull]] and [[Crazy Horse]] over the [[7th Cavalry Regiment]], a conflict often called [[Battle of the Little Bighorn|Custer's Last Stand.]]<ref name="ReferenceB"/><ref>See generally {{cite book |last=Philbrick |first=Nathaniel |title=The Last Stand: Custer, Sitting Bull, and the Battle of the Little Bighorn |year=2010 |publisher=Viking |isbn=978-0-670-02172-7 |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780670021727 }}</ref> US forces were vastly outnumbered. |
|||
In 1876 the U.S. Congress decided to open up the Black Hills to development and break up the Great Sioux Reservation. In 1877, it passed an act to make 7.7 million acres (31,000 km<sup>2</sup>) of the Black Hills available for sale to [[Homestead Act|homesteaders]] and private interests. In 1889 Congress divided the remaining area of Great Sioux Reservation into five separate reservations, defining the boundaries of each in its Act of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888. Pine Ridge was established at that time. |
|||
====Wounded Knee Massacre==== |
====Wounded Knee Massacre==== |
||
{{Main|Wounded Knee Massacre}} |
{{Main|Wounded Knee Massacre}} |
||
[[File:Grabill - Survivors of Big Foots band.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Survivors of [[Wounded Knee Massacre]], 1891 (Title: ''What's left of Big Foot's band''). John C. Grabill]] |
[[File:Grabill - Survivors of Big Foots band - Survivors of Wounded Knee Massacre.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Survivors of [[Wounded Knee Massacre]], 1891 (Title: ''What's left of Big Foot's band''). John C. Grabill.]] |
||
The Wounded Knee Massacre occurred on December 29, 1890,<ref name=nps>{{cite web|url=http://tps.cr.nps.gov/nhl/detail.cfm?ResourceId=540&ResourceType=Site|title=National Historic Landmarks Program: Wounded Knee|publisher=[[National Park Service]]| |
The Wounded Knee Massacre occurred on December 29, 1890,<ref name=nps>{{cite web|url=http://tps.cr.nps.gov/nhl/detail.cfm?ResourceId=540&ResourceType=Site |title=National Historic Landmarks Program: Wounded Knee |publisher=[[National Park Service]] |access-date=2008-01-10 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080309200437/http://tps.cr.nps.gov/nhl/detail.cfm?ResourceId=540&ResourceType=Site |archive-date=2008-03-09 }}</ref> near Wounded Knee Creek ([[Lakota language|Lakota]]: ''Cankpe Opi Wakpala''). On the day before, a detachment of the [[7th Cavalry Regiment (United States)|U.S. 7th Cavalry Regiment]] commanded by Major [[Samuel Whitside|Samuel M. Whitside]] intercepted Spotted Elk's (Big Foot) band of [[Miniconjou]] Lakota and 38 [[Hunkpapa]] Lakota near [[Porcupine Butte]] and escorted them {{convert|5|mi|km}} westward to Wounded Knee Creek where they made camp. The rest of the 7th Cavalry Regiment, led by Colonel [[James W. Forsyth|James Forsyth]], surrounded the encampment, supported by four [[Hotchkiss gun]]s.<ref>{{cite web|last=Liggett|first=Lorie |title=Wounded Knee Massacre — An Introduction |publisher=Bowling Green State University |year=1998 |url=http://www.bgsu.edu/departments/acs/1890s/woundedknee/WKIntro.html |access-date=2007-03-02 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111205184809/http://www.bgsu.edu/departments/acs/1890s/woundedknee/WKIntro.html |archive-date=December 5, 2011}}</ref> |
||
On the morning of December 29, the troops went into the camp to disarm the Lakota. One version of events claims that during the process, a deaf tribesman named |
On the morning of December 29, 1890, the troops went into the camp to disarm the Lakota. One version of events claims that during the process, a deaf tribesman named Black Coyote was reluctant to give up his rifle, saying he had paid a lot for it.<ref>[http://www.lastoftheindependents.com/wounded.htm "Wounded Knee — Lakota"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100106003804/http://www.lastoftheindependents.com/wounded.htm |date=2010-01-06 }}, Native American Atrocities</ref> A scuffle over Black Coyote's rifle escalated and a shot was fired, which resulted in the 7th Cavalry opening firing indiscriminately from all sides, killing men, women, and children, as well as some of their fellow troopers. Those few Lakota warriors who still had weapons began shooting back at the troopers, who quickly suppressed the Lakota fire. The surviving Lakota fled, but U.S. cavalrymen pursued and killed many who were unarmed. |
||
In the end, U.S. forces killed at least 150 men, women, and children of the Lakota Sioux and wounded 51 (four men, and 47 women and children, some of whom died later); some estimates placed the number of dead at 300. Twenty-five troopers also died, and thirty-nine were wounded (six of the wounded would also die).<ref>Jack Utter, ''Wounded Knee & the Ghost Dance Tragedy,'' p. 25, National Woodlands Publishing Company; 1st edition (April 1991) ISBN |
In the end, U.S. forces killed at least 150 men, women, and children of the Lakota Sioux and wounded 51 (four men, and 47 women and children, some of whom died later); some estimates placed the number of dead at 300. Twenty-five troopers also died, and thirty-nine were wounded (six of the wounded would also die).<ref>Jack Utter, ''Wounded Knee & the Ghost Dance Tragedy,'' p. 25, National Woodlands Publishing Company; 1st edition (April 1991) {{ISBN|0-9628075-1-6}}</ref> Many Army deaths were believed to have been caused by [[friendly fire]], as the shooting took place at close range in chaotic conditions.<ref>{{cite web |last=Strom |first=Karen|author-link=Karen Strom |title=The Massacre at Wounded Knee |publisher=Karen Strom |year=1995 |url=http://www.hanksville.org/daniel/lakota/Wounded_Knee.html |access-date=25 August 2013}}</ref> |
||
The site has been designated a [[National Historic Landmark]] and is administered by the National Park Service.<ref name=nps/>{{clear}} |
The site has been designated a [[National Historic Landmark]] and is administered by the National Park Service.<ref name=nps/>{{clear}} |
||
| Line 155: | Line 161: | ||
====White Clay Extension==== |
====White Clay Extension==== |
||
[[File:Whiteclay Nebraska Taverm 1940.jpg|thumb| |
[[File:Whiteclay Nebraska Taverm 1940.jpg|thumb|A tavern in [[Whiteclay, Nebraska]], 1940]] |
||
{{main|Whiteclay, Nebraska}} |
{{main|Whiteclay, Nebraska}} |
||
In 1882, at the urging of [[Valentine McGillycuddy]] |
In 1882, at the urging of [[Valentine McGillycuddy]]—the US [[Indian Agent]] at the Pine President Agency—President [[Chester A. Arthur]] issued an [[executive order]] establishing the White Clay Extension, an area of land in Nebraska extending {{convert|5|mi|km}} south of the reservation's border and {{convert|10|mi|km}} wide approximately perpendicular to the road leading north into the town of Pine Ridge on the reservation.<ref>INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES Vol. I, Laws (Compiled to December 1, 1902) http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol1/HTML_files/NEB0861.html {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110805081736/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol1/HTML_files/NEB0861.html |date=2011-08-05 }}</ref> This road is today's [[Nebraska Highway 87]]. McGillycuddy lobbied for the buffer zone to prevent white peddlers from engaging in the illegal sale of "knives, guns, and alcohol" to the Oglala Lakota residents of Pine Ridge. |
||
A law passed in Congress in 1832 banned the sale of alcohol to Native Americans. The ban was ended in 1953 by Public Law 277, signed by President [[Dwight D. Eisenhower]]. The amended law gave Native American tribes the option of permitting or banning alcohol sales and consumption on their lands.<ref> |
A law passed in Congress in 1832 banned the sale of alcohol to Native Americans. The ban was ended in 1953 by Public Law 277, signed by President [[Dwight D. Eisenhower]]. The amended law gave Native American tribes the option of permitting or banning alcohol sales and consumption on their lands.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=eSBDF5_L3BgC&q=Alcohol+native+americans+dwight+eisenhower&pg=PA230|title=Historical Dictionary of the 1950s|first=James Stuart|last=Olson|date=February 13, 2000|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|isbn=9780313306198|via=Google Books}}</ref> The OST and many other tribes chose to exclude alcohol from their reservations because of the problems for their people. |
||
In 1887, when Congress enacted the [[Dawes Act|Dawes Severalty Act of 1887]] |
In 1887, when Congress enacted the [[Dawes Act|Dawes Severalty Act of 1887]]—breaking up the reservations and allotting a {{convert|160|acre|ha}} plot to the registered head of each family—the Whiteclay Extension was specifically exempted. On March 2, 1889, the U.S. Congress enacted the ''Great Sioux Agreement of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888,'' breaking up the [[Great Sioux Reservation]] and setting boundaries for the six reduced reservations. In this act, the White Clay Extension was incorporated again within the boundaries of the Pine Ridge Agency. "Provided, That the said tract of land in the State of Nebraska shall be reserved, by Executive order, only so long as it may be needed for the use and protection of the Indians receiving rations and annuities at the Pine Ridge Agency."<ref>''INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES'' Vol. I, Laws; Chapter 405, March 2, 1889. | 25 Stat., 888.[http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/vol1/HTML_files/SES0328.html] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120103204458/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol1/HTML_files/SES0328.html|date=2012-01-03}}</ref> |
||
On January 25, 1904, President [[Theodore Roosevelt]] signed an executive order returning the 50 |
On January 25, 1904, President [[Theodore Roosevelt]] signed an executive order returning the {{convert|50|sqmi|km2}} of the White Clay Extension to the public domain. The town of [[Whiteclay, Nebraska|Whiteclay]] in [[Sheridan County, Nebraska]], just over the border from the reservation, was founded in the former "Extension" zone. Merchants quickly started selling alcohol to the Oglala Sioux. |
||
{{blockquote|It is hereby ordered that the tract of country in the State of Nebraska "withdrawn from sale and set aside as an addition to the present Sioux Indian Reservation in the Territory of Dakota" by Executive order dated January 24, 1882, be, and the same hereby is, restored to the public domain.|President Theodore Roosevelt, January 25, 1904.<ref>United States. Office of Indian Affairs / Annual report of the commissioner of Indian affairs, for the year 1904 Part I [http://digicoll.library.wisc.edu/cgi-bin/History/History-idx?type=div&did=History.AnnRep04p1.i0030&isize=text]</ref>|}} |
|||
On February 20, 1904, Roosevelt amended the executive order to return |
On February 20, 1904, Roosevelt amended the executive order to return {{convert|1|sqmi|km2}} back to Pine Ridge: "the section of land embracing the Pine Ridge Boarding School irrigation ditch and the school pasture". |
||
====Bennett County Land dispute==== |
====Bennett County Land dispute==== |
||
In 1975 in ''Cook v. Parkinson'' 525 F.2d 120 (8th Cir. 1975) ruled that Bennett County was not considered part of the Pine Ridge Reservation. However, "the United States participated only as amicus before the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals in ''Cook v. Parkinson'', 525 F.2d 120 (8th Cir. 1975) and is not bound by that decision because it did not participate in the litigation. The United States was a party in ''United States v. Bennett County'', 394 F.2d 8 (8th Cir. 1968), in which the State of South Dakota had to obtain permission from the Department of Interior in order to fix roads or condemn property in Bennett County, consistent with the property's reservation status<ref name="villageearth.org">{{Cite web|url=http://archive.org/details/RespUOSpiritLakePineRidgeRosebud1|title=Reservation Boundary Disputes (Uinta, Pine Ridge, Rosebud, Devil's Lake)|date=March 8, 2003|via=Internet Archive}}</ref> as well as ''Putnam v. United States'' 248 F.2d 292 (8th Cir. 1957) which ruled that "Bennett County is within the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation created by the Act of Congress of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888." |
|||
No additional land changes were made within Pine Ridge until the U.S. Congress passed the Pine Ridge Act of May 27, 1910 (§1, 36 Stat. 440), by which most of the southeastern portion of Pine Ridge located within [[Bennett County, South Dakota|Bennett County]] was sold off. |
|||
:"... (T)he Secretary of the Interior be, and he is hereby authorized and directed, as hereinafter provided, to sell and dispose of all that portion of the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation, in the State of South Dakota, lying and being in Bennett County and described as follows ..." (Act of May 27, 1910, §1 (36 Stat. 440). |
|||
The Federal Government recognizes Bennett County as being entirely within the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation. In 2004, in State of South Dakota v. Acting Great Plains Regional Director, Bureau of Indian Affairs Docket Number IBIA3-24-A the State of South Dakota argued against an Oglala Sioux Tribal member's application to the BIA to return a 10-acre tract of land in Bennett County into Federal Trust arguing it was outside of the Boundary of the Pine Ridge Reservation. The judge ruled in favor of the applicant and Bureau of Indian Affairs' affirmant that Bennett County is indeed within the boundaries of the Reservation.<ref>{{Cite web|title=State of South Dakota and Bennett County, South Dakota v. Acting Great Plains Regional Director, Bureau of Indian Affair|date=October 3, 2018|url=https://www.oha.doi.gov/ibia/IbiaDecisions/39ibia/39ibia301.pdf}}</ref> |
|||
:"Provided that any Indian to whom allotments have been made on the tract to be ceded may, in case they elect to do so before said lands are offered for sale, relinquish same and select allotments in lieu thereof on the diminished reservation." |
|||
<ref>[http://ftp.resource.org/courts.gov/c/F2/525/525.F2d.120.75-1306.html ''UNITED STATES ex rel. COOK v. PARKINSON'']</ref> |
|||
The South Dakota Legislature determined the boundaries of Bennett County in 1909, while the land area was still part of the reservation.<ref>''Session laws By South Dakota,'' p. 428</ref> |
|||
"The United States participated only as amicus before the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals in Cook v. Parkinson, 525 F.2d 120 (8th Cir. 1975), a criminal case that discussed Bennett County as no longer being part of the Reservation. The United States is not bound by that decision because it did not participate in the litigation. The United States was part in United States v. Bennett County, 394 F.2d 8 (8th Cir. 1968), in which the State of South Dakota had to obtain permission from the Department of Interior in order to fix roads or condemn property Bennett County, consistent with the property's Reservation status."<ref>[http://villageearth.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/Resp_UO_SpiritLake_PineRidge_Rosebud-1.pdf ''Suzanne R. Schaeffer, Assistant Solicitor, Environment, Land and Minerals Branch, Division of Indian Affairs'']</ref> |
|||
====Indian Reorganization Act==== |
====Indian Reorganization Act==== |
||
{{main|Indian Reorganization Act}} |
{{main|Indian Reorganization Act}} |
||
During the 1930s, President [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]]'s administration made changes in federal policy to improve conditions for American Indians. In response to complaints about corruption and injustices in the BIA management of reservations, Congress passed the [[Indian Reorganization Act]] of 1934, permitting tribal nations to reorganize with self-government. It encouraged them to adopt a model of elected representative governments and elected tribal chairmen or presidents, with written constitutions. While tribes welcomed taking back more control of their government, this change eroded the power and structure of the traditional hereditary leaders of the [[clan]] system. |
|||
In the 1930s, President [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]]'s administration made changes in federal policy to improve conditions for American Indians. In response to complaints about corruption and injustices in the BIA management of reservations, Congress passed the [[Indian Reorganization Act]] of 1934, permitting tribal nations to reorganize with self-government. It encouraged them to adopt a model of elected representative governments and elected tribal chairmen or presidents, with written constitutions. While tribes welcomed taking back more control of their government, this change eroded the power and structure of the traditional hereditary leaders of the [[clan]] system. |
|||
The Oglala Sioux Tribe developed a tribal government along democratic constitutional lines, with a chairman to be elected for a two-year term. This short term makes it difficult for leaders to accomplish longer-term projects, but the tribe has not changed its constitution. The BIA still has had the ability to oversee some tribal operations, including the police. Historically BIA tribal police were often assigned from other Indian tribes rather than representing local people and understanding their culture, which created tensions. Many traditionalists among the Oglala Lakota never supported the new style of government; tribal elders were still respected, and there were multiple lines of authority and influence among different groups on the reservation. Political factions also formed between those who were [[mixed race|mixed-bloods]] or had urban experiences, and those who were full-bloods and tended to be more traditional in practices and culture.<ref name=akim>[http://books.google.com/books?id=0OEzAiB8U6EC&pg=PA173&lpg=PA173&dq=Oglala+Sioux+Civil+Rights+Organization+%28OSCRO%29&source=bl&ots=rzJJ9pya80&sig=T8lZELkugTlECAnYPEebKtE82EA&hl=en&ei=rOAJTsCJMsOssAKQnrSyAQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=4&ved=0CCkQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=Oglala%20Sioux%20Civil%20Rights%20Organization%20%28OSCRO%29&f=false ''Ruling Pine Ridge: Oglala Lakota Politics from the IRA to Wounded Knee''], Texas Tech University Press, 2007</ref> |
|||
The Oglala Sioux Tribe developed a tribal government along democratic constitutional lines, with a chairman to be elected for a two-year term. This short term makes it difficult for leaders to accomplish longer-term projects, but the tribe has not changed its constitution. The BIA still has had the ability to oversee some tribal operations, including the police. Historically BIA tribal police were often assigned from other Indian tribes rather than representing local people and understanding their culture, which created tensions.<ref name=akim/> |
|||
The people continued to be under assimilation pressure: through the early part of the century, many children were sent away to Indian boarding schools where they were usually required to speak English and were prohibited from speaking Lakota; they were usually expected to practice Christianity rather than native religions. In the late 20th century, many of these institutions were found to have had staff who abused the children in their care.<ref name=PBS>[http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/weshallremain/the_films/episode_1_trailer "Wounded Knee"], ''We Shall Remain'', PBS: American Experience, accessed 29 June 2011</ref> |
|||
Many traditionalists among the Oglala Lakota never supported the new style of government. Tribal elders were still respected, and there were multiple lines of authority and influence among different groups on the reservation. Political factions also formed between those who were [[mixed race|mixed-bloods]] or had urban experiences, and those who were full-bloods and tended to be more traditional in practices and culture.<ref name=akim>[https://books.google.com/books?id=0OEzAiB8U6EC&dq=Oglala+Sioux+Civil+Rights+Organization+%28OSCRO%29&pg=PA173 ''Ruling Pine Ridge: Oglala Lakota Politics from the IRA to Wounded Knee''], Texas Tech University Press, 2007</ref> |
|||
The people continued to be under assimilation pressure: through the early part of the century, many children were sent away to Indian boarding schools where they were usually required to speak English and were prohibited from speaking Lakota. They were usually expected to practice Christianity rather than native religions. In the late 20th century, many of these institutions were found to have had staff who abused the children in their care.<ref name=PBS>[https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/weshallremain/the_films/episode_1_trailer "Wounded Knee"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170228145324/http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/weshallremain/the_films/episode_1_trailer |date=2017-02-28 }}, ''We Shall Remain'', PBS: American Experience, accessed 29 June 2011</ref> |
|||
====Taking of Badlands Bombing Range==== |
====Taking of Badlands Bombing Range==== |
||
[[File:Indian Head Buffalo Obverse.png|thumb|100px|right|[[Dewey Beard|A model for]] the [[Indian Head Nickel]], or Buffalo Nickel, had his home taken when the [[Badlands Bombing Range]] was seized.]] |
[[File:Indian Head Buffalo Obverse.png|thumb|100px|right|[[Dewey Beard|A model for]] the [[Indian Head Nickel]], or Buffalo Nickel, had his home taken when the [[Badlands Bombing Range]] was seized.]] |
||
In 1942 the federal government [[ |
In 1942 the federal government [[Takings Clause|took]] privately held Pine Ridge Indian Reservation land owned by tribal members in order to establish the [[Badlands Bombing Range]] of {{convert|341725|acre|km2}}. The largest portion is located in [[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota|Oglala Lakota County]]. It also leased communally held [[Oglala Sioux Tribe]] (OST) land for this defense installation. |
||
Among the 125 families evicted was that of Pat Cuny, an |
Among the 125 families evicted was that of Pat Cuny, an Oglala Sioux. He fought in World War II in the [[Battle of the Bulge]] after surviving torpedoing of his transport in the [[English Channel]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/article/the-83rd-infantry-division|title=The 83rd Infantry Division during World War II|website=encyclopedia.ushmm.org}}</ref> [[Dewey Beard]], a [[Miniconjou]] Sioux survivor of the Wounded Knee Massacre, who supported himself by raising horses on his {{convert|908|acre|km2|adj=on}} allotment received in 1907 was also evicted. The small federal payments were insufficient to enable such persons to buy new properties. In 1955, the 97-year-old Beard testified of earlier mistreatment at Congressional hearings about this project.<ref>Burnham: ''Indian Country, God's Country'', p.133</ref> He said, for "fifty years I have been kicked around. Today there is a hard winter coming. ... I might starve to death."{{Citation needed|date=January 2013}} |
||
Since 1960, the U.S. has returned portions{{Specify|acreage & dates?|date=January 2013}} of the bombing range to the OST. The 1968 Public Law 90-468 returned {{convert|202357|acre|km2}} to the OST and set aside former tribal lands as the [[Badlands National Monument]] |
Since 1960, the U.S. has returned portions{{Specify|acreage & dates?|date=January 2013}} of the bombing range to the OST. The 1968 Public Law 90-468 returned {{convert|202357|acre|km2}} to the OST and set aside former tribal lands as the [[Badlands National Monument]]. The smaller Air Force Retained Area is within the boundaries of the reservation.<ref name=ESTCP>{{cite web|date=September 1999|title=ESTCP Cost and Performance Report: Multi-Sensor Towed Array Detection System (MTADS) |url=http://www.serdp.org/Program-Areas/Munitions-Response/Land/Sensors/MR-199526 |publisher=U.S. Department of Defense |access-date=2013-01-20 |quote=The Reservation is located in the Southwest corner of South Dakota, with the largest part of the Bombing Range located in Oglala Lakota County. The Badlands Bombing Range (BBR) was a live fire range for over 30 years, and most recently was used as a training range for the Air National Guard. Since 1960, portions of the land have been returned to the Oglala Sioux Tribe (OST) in a step- wise fashion. In 1968, Congress enacted Public Law 90-468 returning 202,357 acres to the OST, and setting aside 136,882 acres of formerly held Tribal lands to form the Badlands National Monument, to be managed by the National Park Service. The U.S. Air Force still retains 2,486 acres of land on Bouquet Table within the Reservation boundaries. ... BBR I is a highly visible circular target composed of a 500-foot diameter circular earthberm, with a cross-hair berm inside the circle. ... BBR 1 ... within the National Park, is grassland grazed by both horses and cattle. |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131211180216/http://www.serdp.org/Program-Areas/Munitions-Response/Land/Sensors/MR-199526 |archive-date=2013-12-11 }}</ref> |
||
{{ |
{{blockquote|Understandably, many people now believe that the disruption of the time period 1973 –76 was instigated by the Wilson administration —and U.S. agents using that administration— to distract the people from these and other agreements being made about their land.|[[Peter Matthiessen]] [[In the Spirit of Crazy Horse]]| page 425 }} |
||
A 2008 USAF & OST agreement initiated "a three-month $1.6 million project to remove unexploded ordnance" from the bombing range |
A 2008, the USAF & OST agreement initiated "a three-month $1.6 million project to remove unexploded ordnance" from the bombing range.<ref name=Walker>{{cite web|last=Walker |first=Airman Kate |date=2011-10-12 |title=Ellsworth contractors work with tribe to destroy bombs |url=http://www.acc.af.mil/news/story.asp?id=123275231 |format=USAF news release |publisher=[[28th Bomb Wing]] Public Affairs |access-date=2013-01-20 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131216060433/http://www.acc.af.mil/news/story.asp?id=123275231 |archive-date=2013-12-16 }}</ref> |
||
====Wounded Knee Occupation==== |
|||
sup Im from japan |
|||
{{Main|Wounded Knee Occupation}} |
|||
In the early 1970s, tribal tensions rose and some members turned to the [[American Indian Movement]] (AIM) for help. Longstanding divisions on the reservation resulted from deep-seated political, ethnic and cultural differences. Many residents did not support the elected tribal government. Many residents were upset about what they described as the autocratic and repressive actions by the tribal president [[Dick Wilson (tribal chairman)|Dick Wilson]], elected in 1972. |
|||
On February 21, the tribal council was called into session to consider the removal of Wilson through [[Impeachment in the United States|impeachment]]. Five hundred Oglala members were in attendance. He was criticized for favoring family and friends with jobs and benefits, not consulting with the tribal council, and creating a private [[militia]], known as the [[Guardians of the Oglala Nation]] (GOONs), to suppress political opponents. He used tribal funds to pay for this force. Wilson's response was to screen a right wing propaganda film.<ref name="Koster 1974 https://archive.org/details/roadtowoundedkne00burn/page/224 224–225">{{Cite book|title=The Road to Wounded Knee|url=https://archive.org/details/roadtowoundedkne00burn|url-access=registration|last=Koster|first=John|publisher=Bantam Books|year=1974|location=New York, New York|pages=[https://archive.org/details/roadtowoundedkne00burn/page/224 224]–225}}</ref> |
|||
====Wounded Knee Incident==== |
|||
{{Main|Wounded Knee incident}} |
|||
In the early 1970s, tribal tensions rose and some members turned to the [[American Indian Movement]] (AIM) for help. Longstanding divisions on the reservation resulted from deep-seated political, ethnic and cultural differences. Many residents did not support the elected tribal government. Many residents were upset about what they described as the autocratic and repressive actions by the tribal president [[Dick Wilson (tribal chairman)|Dick Wilson]], elected in 1972. He was criticized for favoring family and friends with jobs and benefits, not consulting with the tribal council, and creating a private [[militia]], known as the [[Guardians of the Oglala Nation]] (GOONs), to suppress political opponents. He used tribal funds to pay for this force. |
|||
After |
After a series of meetings held in the Calico community near the Pine Ridge Agency, the old traditional chiefs and the Oglala Sioux Civil Rights Organization (OSCRO) called down to AIM in Rapid City and asked them to come to Pine Ridge. A meeting was arranged between Wilson and Russell Means. Five of Wilson's supporters cornered Means in the parking lot. Means escaped.<ref name="Koster 1974 https://archive.org/details/roadtowoundedkne00burn/page/224 224–225"/> Women elders such as [[Ellen Moves Camp]], founder of the Oglala Sioux Civil Rights Organization (OSCRO), called for action. They organized a public protest for the next day.<ref name=PBS/> |
||
About 200 AIM and Oglala Lakota activists occupied the hamlet of Wounded Knee on February 27, 1973. They demanded the removal of Wilson, restoration of treaty negotiations with the U.S. government, and correction of U.S. failures to enforce treaty rights. Visits by the U.S. senators from South Dakota, FBI agents and [[United States Department of Justice]] (DOJ) representatives, were attended by widespread media coverage, but the [[Richard Nixon]] administration was preoccupied internally with [[Watergate]].<ref name=PBS/> |
About 200 AIM and Oglala Lakota activists occupied the hamlet of Wounded Knee on February 27, 1973. They demanded the removal of Wilson, restoration of treaty negotiations with the U.S. government, and correction of U.S. failures to enforce treaty rights. Visits by the U.S. senators from South Dakota, FBI agents and [[United States Department of Justice]] (DOJ) representatives, were attended by widespread media coverage, but the [[Richard Nixon]] administration was preoccupied internally with [[Watergate]].<ref name=PBS/> |
||
As the events evolved, the activists at Wounded Knee had a 71-day armed stand-off with U.S. law enforcement. AIM leaders at the site were [[Russell Means]], [[Dennis Banks]] and Carter Camp |
As the events evolved, the activists at Wounded Knee had a 71-day armed stand-off with U.S. law enforcement. AIM leaders at the site were [[Russell Means]], [[Dennis Banks]], [[Clyde Bellecourt]], and Carter Camp. Traditional spiritual leaders of the Lakota, such as [[Frank Fools Crow]], were also prominent. Fools Crow led Oglala Lakota spiritual ceremonies and practice in their ways for participants.<ref name=PBS/> Joseph H. Trimbach of the FBI and Steve Frizell of DOJ led the government.<ref name=PBS/> |
||
Casualties of gunfire included a U.S. Marshal, who was seriously wounded and paralyzed; and the deaths of Frank Clearwater, a [[Cherokee]] from North Carolina, and Buddy Lamont, a local Oglala Lakota. After Lamont's death, the Oglala Lakota elders called an end to the occupation.<ref name=PBS/> Some Lakota have alleged that Ray Robinson, a [[civil rights]] activist, was killed during the Wounded Knee occupation, as he disappeared there.<ref name=RayRobinsonBackground>{{cite web|url=http://www.jfamr.org/ray.html|title=Widow Says Civil Rights Activist Killed During Wounded Knee Takeover|last=Walker|first=Carson|date=2004-01-16|work=Justice for Anna Mae and Ray| |
Casualties of gunfire included a U.S. Marshal, who was seriously wounded and paralyzed; and the deaths of Frank Clearwater, a [[Cherokee]] from North Carolina, and Buddy Lamont, a local Oglala Lakota. After Lamont's death, the Oglala Lakota elders called an end to the occupation.<ref name=PBS/> Some Lakota have alleged that [[Ray Robinson (activist)|Ray Robinson]], a [[civil rights]] activist, was killed during the Wounded Knee occupation, as he disappeared there.<ref name=RayRobinsonBackground>{{cite web|url=http://www.jfamr.org/ray.html|title=Widow Says Civil Rights Activist Killed During Wounded Knee Takeover|last=Walker|first=Carson|date=2004-01-16|work=Justice for Anna Mae and Ray|access-date=2007-10-27|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080705134626/http://www.jfamr.org/ray.html|archive-date=2008-07-05|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name=RayRobinsonSearch>{{cite web|url=http://www.rapidcityjournal.com/articles/2004/01/16/news/state/top/state01.txt |title=AIM case may help find man |last=Walker |first=Carson |date=2004-01-16 |work=Rapid City Journal |access-date=2007-10-27 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080909165337/http://www.rapidcityjournal.com/articles/2004/01/16/news/state/top/state01.txt |archive-date=2008-09-09 }}</ref> |
||
The stand-off ended, but Wilson remained in office. |
The stand-off ended, but Wilson remained in office. The U.S. government said it could not remove an elected tribal official as the Oglala Sioux Tribe had sovereignty.<ref name=PBS/> |
||
Ensuing open conflict between factions caused numerous deaths. The murder rate between March 1, 1973, and March 1, 1976, was 170 per 100,000; it was the highest in the country.<ref name=MurderStats>{{cite |
Ensuing open conflict between factions caused numerous deaths. The murder rate between March 1, 1973, and March 1, 1976, was 170 per 100,000; it was the highest in the country.<ref name=MurderStats>{{cite journal|url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10282580213090|last=Perry|first=Barbara|title=From ethnocide to ethnoviolence: Layers of native American victimization |journal=[[Contemporary Justice Review]]|volume=5 |issue=3 |pages=231–247 |year=2002|doi=10.1080/10282580213090 |s2cid=144629925 }}</ref> More than 60 opponents of the tribal government allegedly died violent deaths in the three years following the Wounded Knee Incident, a period called the "Reign of Terror" by many residents. Among those killed was Pedro Bissonette, executive director of the civil rights organization OSCRO.<ref>Banks, ''Ojibwa Warrior'', p. 286</ref> |
||
Residents accused officials of failing to try to solve the deaths.<ref>[[Peter Matthiessen]], ''In the Spirit of Crazy Horse,'' [[Penguin Books|Penguin]], 1992. {{ISBN|978-0-14-014456-7}}.</ref> In 2000, the FBI released a report regarding the 57 alleged unsolved violent deaths on Pine Ridge Reservation and accounted for most of the deaths, and disputed the claims of unsolved murders. The report stated that only 4 deaths were unsolved and that some deaths were not murders.<ref name=FBIDeathsReport>{{cite web|url=http://www.indiancountry.com/content.cfm?id=747 |title=Unsolved deaths debunked by FBI Case by case examination puts some rumors to rest |last=Melmer |first=David |work=Indian Country Today |date=2000-07-19 |access-date=2007-10-29 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060506041458/http://www.indiancountry.com/content.cfm?id=747 |archive-date=May 6, 2006 }}</ref><ref name=FBIDeathsReportAnnounce>{{cite web|url=http://minneapolis.fbi.gov/report.htm|title=Accounting For Native American Deaths, Pine Ridge Indian Reservation, South Dakota|author=staff|work=Federal Bureau of Investigation Minneapolis Division|date=May 2000|access-date=2007-10-29 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20070625072708/http://minneapolis.fbi.gov/report.htm |archive-date = 2007-06-25}}</ref> AIM representatives criticized the FBI report.<ref name=FBIDeathsReportRebuttal>{{cite web|url=http://ishgooda.org/peltier/pltr7.htm |title=INDIAN DEATHS |author=staff |work=Native News Online |date=2000-07-11 |access-date=2007-10-29 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071223035044/http://ishgooda.org/peltier/pltr7.htm |archive-date=2007-12-23 }}</ref> |
|||
====The Pine Ridge Shootout==== |
|||
During this period of increased violence, on June 26, 1975, the reservation was the site of an armed confrontation between AIM activists and the FBI and their allies, which became known as the 'Pine Ridge Shootout'.<ref name=TimeShootout>{{Cite news|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,913222,00.html|title=The Pine Ridge Shootout|work=[[TIME Magazine]]|accessdate=2007-10-27 | date=1975-07-07}}</ref> Two FBI agents, Jack R. Coler and Ronald A. Williams, and the AIM activist Joe Stuntz were killed. In two separate trials, the U.S. prosecuted participants in the firefight for the deaths of the agents. AIM members [[Robert Robideau]] and Dino Butler were acquitted after asserting that they had acted in self–defense. [[Leonard Peltier]] was extradited from Canada and tried separately because of the delay. He was convicted on two counts of first–degree murder for the deaths of the FBI agents<ref name=LeonardPeltierTrial>{{cite web|url=http://www.law.umkc.edu/faculty/projects/ftrials/peltier/peltieraccount.html|title=The Leonard Peltier Trial|work=University of Missouri — Kansas City School of Law|accessdate=2007-10-27}}</ref> and sentenced to two consecutive terms of life in prison, after a trial which is still contentious. He remains in prison. |
|||
====Pine Ridge Shootout==== |
|||
[[File:Agent_William's_Car.jpg|thumb|William's car riddled with bullets.]] |
|||
During this period of increased violence, on June 26, 1975, the reservation was the site of an armed confrontation between AIM activists and the FBI, which became known as the 'Pine Ridge Shootout'.<ref name=TimeShootout>{{Cite magazine|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,913222,00.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070226140819/http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,913222,00.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=February 26, 2007|title=The Pine Ridge Shootout|magazine=[[TIME Magazine]]|access-date=2007-10-27 | date=1975-07-07}}</ref> Two FBI agents, Jack R. Coler and Ronald A. Williams, were killed and executed at close range. The agents had been following a car when they were shot at by its occupants and others. AIM activist Joe Stuntz was later killed by responding police. Stuntz was found wearing Coler's FBI jacket.<ref name=TimeShootout/> |
|||
In two separate trials, the U.S. prosecuted participants in the firefight for the deaths of the agents. AIM members [[Robert Robideau]] and Dino Butler were acquitted after asserting that they had acted in self-defense. [[Leonard Peltier]] was extradited from Canada and tried separately because of the delay. He was convicted on two counts of first–degree murder for the deaths of the FBI agents,<ref name=LeonardPeltierTrial>{{cite web|url=http://www.law.umkc.edu/faculty/projects/ftrials/peltier/peltieraccount.html|title=The Leonard Peltier Trial|work=University of Missouri — Kansas City School of Law|access-date=2007-10-27|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071025005019/http://www.law.umkc.edu/faculty/projects/ftrials/peltier/peltieraccount.html|archive-date=2007-10-25}}</ref> and sentenced to two consecutive terms of life in prison. |
|||
====Murder of Anna Mae Aquash==== |
====Murder of Anna Mae Aquash==== |
||
{{main|Anna Mae Aquash}} |
{{main|Anna Mae Aquash}} |
||
On February 24, 1976, the body of [[Anna Mae Aquash]], a [[Mi'kmaq people|Mi'kmaq]] activist and the most prominent woman in AIM, was found in the far northeast corner of the Pine Ridge Reservation. Missing since December 1975, she had been shot execution-style. At the time, some AIM people said that she was a government informant, but the FBI has denied that. In 1974 AIM had discovered that Douglas Durham, then head of security, was an FBI informant. Three federal grand juries were called to hear testimony on the Aquash murder: in 1976, 1982 and 1994, but it was more than a quarter of a century before any suspects were indicted and tried for the crime. Two AIM members, Arlo Looking Cloud and John Graham, were convicted of her murder in 2004 and 2010 respectively, and sentenced to life in prison. Bruce Ellison, Leonard Peltier's lawyer since the 1970s, invoked his [[Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution|Fifth Amendment]] rights and refused to testify at the grand jury hearings on Looking Cloud or at his trial in 2004. At trial, the federal prosecutor referred to Ellison as a co-conspirator in the Aquash case.<ref>[http://www.jfamr.org/doc/appeal.pdf "Looking Cloud appeal decision"], Eighth Circuit Court</ref><ref>[http://www.timesonline.com/bct_news/news_details/article/1373/2010/december/10/woman-pleads-guilty-in-1975-sd-reservation-killing.html Nomaan Merchant, "SD jury convicts man in 1975 AIM activist's death"], Associated Press, ''Beaver County Times,'' December 11, 2010</ref> |
|||
On February 24, 1976, the body of [[Anna Mae Aquash]], a [[Mi'kmaq people|Mi'kmaq]] activist and the most prominent woman in AIM, was found in the far northeast corner of the Pine Ridge Reservation. Missing since December 1975, she had been shot execution-style. At the time, some AIM people said that she was a government informant, but the FBI has denied that. In 1974, AIM had discovered that Douglas Durham, then head of security, was an FBI informant. Three federal grand juries were called to hear testimony on the Aquash murder: in 1976, 1982 and 1994, but it was more than a quarter of a century before any suspects were indicted and tried for the crime.<ref name="web.archive.org">[https://web.archive.org/web/20190109204835/https://www.arthashastr.com/2019/01/quota-for-general-category-poor.html Nomaan Merchant, "SD jury convicts man in 1975 AIM activist's death"], Associated Press, ''Beaver County Times,'' December 11, 2010</ref> |
|||
===21st-century (2000 to present)=== |
|||
{{Further|Whiteclay, Nebraska}} |
|||
Two AIM members, [[Arlo Looking Cloud]] and [[John Graham (Canadian activist)|John Graham]], were convicted of her murder in 2004 and 2010 respectively, and sentenced to life in prison. Bruce Ellison, Leonard Peltier's lawyer since the 1970s, invoked his [[Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution|Fifth Amendment]] rights and refused to testify at the grand jury hearings on Looking Cloud, or at his trial in 2004. At trial, the federal prosecutor referred to Ellison as a co-conspirator in the Aquash case.<ref>[http://www.jfamr.org/doc/appeal.pdf "Looking Cloud appeal decision"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120308125102/http://www.jfamr.org/doc/appeal.pdf |date=2012-03-08 }}, Eighth Circuit Court</ref><ref name="web.archive.org"/> |
|||
===21st century=== |
|||
{{Further|The Battle for Whiteclay}} |
{{Further|The Battle for Whiteclay}} |
||
Alcoholism among residents has been a continuing problem in the life of the reservation since its founding. Since 1999, activists from the Pine Ridge Reservation, AIM and [[Nebraskans for Peace]] have worked to have beer sales shut down in nearby [[Whiteclay, Nebraska]], a border town selling millions of cans of beer annually, primarily to residents from the reservation in South Dakota, where alcohol possession and consumption is prohibited. In 2008 the documentary ''[[The Battle for Whiteclay]],'' about the toll of alcoholism and activists' efforts to control beer sales, was released, which has attracted wide attention. The Nebraska legislature allocated funds in late 2010 for increased police patrols in Pine Ridge by the county sheriff's office, based 22 miles away in Rushville. |
|||
Alcoholism among residents has been a continuing problem in the life of the reservation since its founding. Since 1999, activists from the Pine Ridge Reservation, AIM, and [[Nebraskans for Peace]] have worked to have beer sales shut down in nearby [[Whiteclay, Nebraska]], a border town. Whiteclay sells millions of cans of beer annually, primarily to residents from the reservation in South Dakota, where alcohol possession and consumption is prohibited. In 2008, the documentary ''[[The Battle for Whiteclay]],'' about the toll of alcoholism and activists' efforts to control beer sales, was released, which has attracted wide attention. The Nebraska legislature allocated funds in late 2010 for increased police patrols in Pine Ridge by the county sheriff's office, based {{convert|22|mi|km}} away in [[Rushville, Nebraska|Rushville]]. |
|||
While other tribes and reservations also prohibited alcohol at one time because of Native American vulnerability to abuse, many have since legalized its sales on their reservations. They use the revenues generated to improve health care and life on the reservation, and they prefer to directly control the regulation of alcohol sales and police its use. A 2007 survey found that 63% of federally recognized tribes in the lower 48 states have legalized liquor sales on their reservations.<ref name=Hughes/> They include the nearby [[Sicangu Oyate]] or Brulé Sioux at the [[Rosebud Indian Reservation]], also located in South Dakota. In 2006, the [[Omaha Nation]] in northeastern Nebraska started requiring payment of tribal license fees and sales taxes by liquor stores located in towns within its reservation boundaries in order to benefit in the revenues generated by alcohol sales.<ref name=Liquor>[http://h-net.msu.edu/cgi-bin/logbrowse.pl?trx=vx&list=H-AMINDIAN&month=0612&week=e&msg=3LoJIeU4HMsQCpZhNejOUQ&user=&pw= Paul Hammel, "Tribe's Liquor Tax May Restart Old Boundary Dispute,"], ''Omaha World-Herald'' (Nebraska), 28 December 2006, p. 03B, at H-Amindian Discussion Log, accessed 27 February 2012</ref> |
|||
While other tribes and reservations also prohibited alcohol at one time, many have since legalized its sales on their reservations. They use the revenues generated to improve health care and life on the reservation, and they prefer to directly control the regulation of alcohol sales and police its use. A 2007 survey found that 63% of federally recognized tribes in the lower 48 states have legalized liquor sales on their reservations.<ref name=Hughes/> They include the nearby [[Sicangu Oyate]] or Brulé Sioux at the [[Rosebud Indian Reservation]], also located in South Dakota. In 2006, the [[Omaha Nation]] in northeastern Nebraska started requiring payment of tribal license fees and sales taxes by liquor stores located in towns within its reservation boundaries in order to benefit in the revenues generated by alcohol sales.<ref name=Liquor>[http://h-net.msu.edu/cgi-bin/logbrowse.pl?trx=vx&list=H-AMINDIAN&month=0612&week=e&msg=3LoJIeU4HMsQCpZhNejOUQ&user=&pw= Paul Hammel, "Tribe's Liquor Tax May Restart Old Boundary Dispute,"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130524072934/http://h-net.msu.edu/cgi-bin/logbrowse.pl?trx=vx&list=H-AmIndian&month=0612&week=e&msg=3LoJIeU4HMsQCpZhNejOUQ&user=&pw= |date=2013-05-24 }}, ''Omaha World-Herald'' (Nebraska), 28 December 2006, p. 03B, at H-Amindian Discussion Log, accessed 27 February 2012</ref> |
|||
Activists at Pine Ridge have worked to persuade Nebraska to enforce its own laws and support the tribe's prohibition. In 2004 the [[Oglala Sioux Tribe]] voted down a referendum to legalize alcohol sales, and in 2006 the tribal council voted to maintain the ban on alcohol sales, rather than taking on the benefits and responsibility directly.<ref name=Hughes>[http://documents.jdsupra.com/4c1267de-b226-4e76-bd8a-4a2548169500.pdf James N. Hughes III, "Pine Ridge, Whiteclay and Indian Liquor Law"], Federal Indian Law Seminar, December 2010, p. 7, University of Nebraska College of Law, accessed 27 February 2012</ref> |
Activists at Pine Ridge have worked to persuade Nebraska to enforce its own laws and support the tribe's prohibition. In 2004 the [[Oglala Sioux Tribe]] voted down a referendum to legalize alcohol sales, and in 2006 the tribal council voted to maintain the ban on alcohol sales, rather than taking on the benefits and responsibility directly.<ref name=Hughes>[http://documents.jdsupra.com/4c1267de-b226-4e76-bd8a-4a2548169500.pdf James N. Hughes III, "Pine Ridge, Whiteclay and Indian Liquor Law"], Federal Indian Law Seminar, December 2010, p. 7, University of Nebraska College of Law, accessed 27 February 2012</ref> |
||
At a discussion at Bellevue University on April 2, 2010, [[Lance Morgan]], CEO of Ho-Chunk, Inc. |
At a discussion at Bellevue University on April 2, 2010, [[Lance Morgan]], CEO of Ho-Chunk, Inc.—the development corporation of the [[Winnebago Reservation]]—said the Oglala Sioux needed to concentrate on economic development. He believes that poverty is at the heart of its people's problems.<ref name=Abourezk>[http://battleforwhiteclay.org/?p=1486#more-1486 KEVIN ABOUREZK, "Winnebago business leader: Poverty at heart of Whiteclay debacle"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141216232906/http://battleforwhiteclay.org/?p=1486#more-1486 |date=2014-12-16 }}, ''Lincoln Journal Star,'' 7 April 2010, accessed 29 February 2012</ref> The Winnebago used revenues from a casino and alcohol sales at their reservation in eastern Nebraska to build an economic development corporation. It now employs 1,400 people in 26 subsidiaries. With its revenues, the Winnebago have been able to build a hospital, a new school and $1 million in new housing. Kevin Abourezk reported that [[Stew Magnuson]]—the author of ''The Death of [[Raymond Yellow Thunder]]'', a study of issues related to the Pine Ridge reservation and its border towns—described alcohol prohibition at the reservation "as a complete failure."<ref name=Abourezk/> Magnuson said, "Whenever you have prohibition, you're going to have places like Whiteclay."<ref name=Abourezk/> He thought prohibition contributed to bootlegging on the reservation. |
||
On February 9, 2012 the Oglala Sioux Tribe filed a lawsuit in U.S. District Court of Nebraska against the four liquor stores in Whiteclay, Nebraska, as well as the beverage distributors and the brewery companies who make it. The suit, ''Oglala Sioux Tribe v. Jason Schwarting, Licensee of Arrowhead Inn, Inc. et al'', |
On February 9, 2012, the Oglala Sioux Tribe filed a lawsuit in U.S. District Court of Nebraska against the four liquor stores in Whiteclay, Nebraska, as well as the beverage distributors and the brewery companies who make it. The suit, ''Oglala Sioux Tribe v. Jason Schwarting, Licensee of Arrowhead Inn, Inc. et al'', sought $500 million in damages for the "cost of health care, social services and child rehabilitation caused by chronic alcoholism on the reservation, which encompasses some of the nation's most impoverished counties."<ref name=Schulte>{{cite news|last=Schulte|first=Grant| title=Tribe suing beer companies for alcohol problems|url=http://www.boston.com/news/nation/articles/2012/02/09/tribe_to_sue_beer_companies_for_alcohol_problems/| agency=Associated Press|work=[[The Boston Globe]]|access-date=9 February 2012|date=9 February 2012}}{{dead link|date=March 2017}}</ref> The suit claims that the defendants knowingly and willingly sell excessive amounts of alcohol, knowing that most of it is smuggled onto the reservation, in violation of Pine Ridge Indian Reservation and Federal law. The defendants listed in the suit are the following:<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://dockets.justia.com/docket/nebraska/nedce/4:2012cv03027/58024|title=Oglala Sioux Tribe v. Jason Schwarting, et al|website=Justia Dockets & Filings}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/USCOURTS-ned-4_12-cv-03027/pdf/USCOURTS-ned-4_12-cv-03027-5.pdf|title=Oglala Sioux Tribe vs. Jason Schwarting, et al.|date=October 1, 2012}}</ref> |
||
*[[Anheuser-Busch InBev|Anheuser-Busch InBev Worldwide, Inc.]] |
*[[Anheuser-Busch InBev|Anheuser-Busch InBev Worldwide, Inc.]] |
||
*[[SAB Miller|SAB Miller d/b/a Miller Brewing Company]] |
*[[SAB Miller|SAB Miller d/b/a Miller Brewing Company]] |
||
| Line 241: | Line 252: | ||
*[[Miller Brewing Company|Miller Coors, LLC]] |
*[[Miller Brewing Company|Miller Coors, LLC]] |
||
*[[Pabst Brewing Company]] |
*[[Pabst Brewing Company]] |
||
*Pivo, Inc. d/b/a High Plains Budweiser. President, Treasurer:Jeffrey J. Scheinost. Secretary: Cynthia A. Scheinost. Director: Marykate Scheinost<ref> |
*Pivo, Inc. d/b/a High Plains Budweiser. President, Treasurer: Jeffrey J. Scheinost. Secretary: Cynthia A. Scheinost. Director: Marykate Scheinost<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=10004784|title=Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches}}</ref> |
||
*Dietrich Distributing Co., Inc. |
*Dietrich Distributing Co., Inc. President, Director, Treasurer: John D. Dietrich<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=0036293|title=Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches}}</ref> |
||
*Coors Distributing of West Nebraska d/b/a Coors of West Nebraska; President, Treasurer, Director: James K. Raymond, Treasurer, Director: Evelyn K. Raymond<ref> |
*Coors Distributing of West Nebraska d/b/a Coors of West Nebraska; President, Treasurer, Director: James K. Raymond, Treasurer, Director: Evelyn K. Raymond<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=0397377|title=Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches}}</ref> |
||
*Klemm Distributing Inc.: President: Robert (Bob) F. Klemm, Secretary: Barrett R. Klemm<ref> |
*Klemm Distributing Inc.: President: Robert (Bob) F. Klemm, Secretary: Barrett R. Klemm<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=0077496|title=Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches}}</ref> d/b/a Arrowhead Distributing, Inc.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://safer.fmcsa.dot.gov/query.asp?searchtype=ANY&query_type=queryCarrierSnapshot&query_param=USDOT&query_string=767865&Go.x=13&Go.y=8|title=SAFER Web - Company Snapshot KLEMM DISTRIBUTING INC|website=safer.fmcsa.dot.gov}}</ref> President: Patrick A, O'Neal. Secretary: Greg Burkholder, Treasurer: Kent O'Neal<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=10082213|title=Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches}}</ref> |
||
*Jason Schwarting d/b/a Arrowhead Inn, Inc. President: Jason Schwarting,<ref> |
*Jason Schwarting d/b/a Arrowhead Inn, Inc. President: Jason Schwarting,<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://caselaw.findlaw.com/ne-supreme-court/1231662.html|title=FindLaw's Supreme Court of Nebraska case and opinions.|website=Findlaw}}</ref> Secretary: Vic Clarke<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=10109732|title=Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches}}</ref> |
||
*Sanford Holdings, LLC d/b/a D&S Pioneer Service. Corporation Members: Doug Sanford, Steve Sanford<ref>State of Nebraska:https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=10109978</ref> |
*Sanford Holdings, LLC d/b/a D&S Pioneer Service. Corporation Members: Doug Sanford, Steve Sanford<ref>State of Nebraska:https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=10109978</ref> |
||
*Stuart J. Kozal d/b/a/ Jumping Eagle Inn. Owners: Stuart J. Kozal,<ref> |
*Stuart J. Kozal d/b/a/ Jumping Eagle Inn. Owners: Stuart J. Kozal,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.lcc.ne.gov/license_search/licsearch.cgi|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120114064155/http://www.lcc.ne.gov/license_search/licsearch.cgi|url-status=dead|title=Nebraska Liquor Control Commission | License Search|archive-date=January 14, 2012}}</ref> Lillie I. Norman<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.manta.com/g/mm3ydcl/lillie-norman|title=Manta}}</ref> |
||
*Clay M. Brehmer and Daniel J. Brehmer d/b/a State Line Liquor<ref>Before the Nebraska Liquor Control Commission[www.lcc.ne.gov/susp_fines/2011/December/53988.pdf]</ref> |
*Clay M. Brehmer and Daniel J. Brehmer d/b/a State Line Liquor<ref>Before the Nebraska Liquor Control Commission[www.lcc.ne.gov/susp_fines/2011/December/53988.pdf]</ref> |
||
On August 14, 2013, voters voted to end [[prohibition]] and legalize alcohol, so the tribe can use the profits for education and detoxification and treatment centers.<ref>{{cite |
On August 14, 2013, voters voted to end [[prohibition]] and legalize alcohol, so the tribe can use the profits for education and detoxification and treatment centers.<ref>{{cite news|title=VOTE TO LEGALIZE ALCOHOL ON SD'S PINE RIDGE PASSES|url=http://bigstory.ap.org/article/vote-legalize-alcohol-sds-pine-ridge-passes|agency=Associated Press|access-date=15 August 2013}}</ref> |
||
==Demographics== |
==Demographics== |
||
{{Expand section|date=June 2011}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| direction = horizontal |
|||
| image1 = Pat Cuny-Oglala Lakota.jpg |
|||
| width1 = 140 |
|||
| caption1 = Pat Cuny was a [[World War II]], combat veteran who served in the [[83rd Infantry Division (United States)|83rd Infantry Division]]; the liberators of [[Langenstein-Zwieberge|Langenstein concentration camp]] in [[Nazi Germany]]. |
|||
| image2 = Ola Mildred Rexroat.jpg |
|||
| width2 = 137 |
|||
| caption2 = Ola Mildred Rexroat was a pilot in the [[Women Airforce Service Pilots]] (WASP) during World War II an [[Air traffic controller]] and a recipient of the [[Congressional Gold Medal]]. |
|||
}} |
|||
In 2005 |
In a 2005 interview, [[Cecilia Fire Thunder]], the first female president of the [[Oglala Sioux Tribe]], noted, "[Sixty-eight] percent of the college graduates on the reservation are women. Seventy percent of the jobs are held by women. Over 90 percent of the jobs in our schools are held by women."<ref name=hurst>[http://www.rapidcityjournal.com/news/opinion/article_09432e04-144a-5acb-8929-97a26a896334.html Sam Hurst, "Cecilia Fire Thunder a 'person of character'"], ''Rapid City Journal'', 17 December 2005, accessed 13 June 2011</ref> |
||
* The [[2010 U.S. Census]] counted 18,834 individuals living on the Pine Ridge Reservation. The vast majority, 16,906, identified as [[Native Americans in the United States|American Indian]].<ref name="auto">{{Cite web|url=https://www.re-member.org/pine-ridge-reservation.aspx|title=Pine Ridge Indian Reservation Facts|website=Re-Member|access-date=2021-01-28|archive-date=2021-06-20|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210620204742/https://www.re-member.org/pine-ridge-reservation.aspx|url-status=dead}}</ref> Much of the non-Native population is found in the community of [[Martin, South Dakota]] |
|||
* As of 2011, population estimates of the reservation range from 28,000 to 40,000. Numerous enrolled members of the tribe live off the reservation.<ref name=Resroad/> |
|||
* |
* 89% of residents are unemployed.{{citation needed|date=June 2023}} |
||
* |
* 53.75% of the residents live below the Federal poverty level.<ref name="auto"/> |
||
* |
* Average per capita income in [[Oglala Lakota County]] is $8,768 and ranks as the "poorest" county in the nation.<ref name="auto"/> |
||
* The infant mortality rate is |
* The infant mortality rate is five times higher than the national average. |
||
* Native American amputation rates due to diabetes |
* Native American amputation rates due to diabetes are three to four times higher than the national average. |
||
* Death rate due to diabetes is |
* Death rate due to diabetes is three times higher than the national average. |
||
* Teen suicide is four times the national average. |
|||
* Life expectancy in 2007 was estimated to be 48 for males and 52 for females<ref>Kulkarni SC, Levin-Rector A, Ezzati M, Murray CJL. Falling behind: life expectancy in U.S. counties from 2000 to 2007 in an international context. Population Health Metrics. 2011; 9:16. A 1998 study estimated life expectancy in Oglala Lakota County was estimated to be the lowest of any county in the U.S.; Men — 56.5 years, Women — 66 years. Murray CJL, Michaud CM, McKenna MT, Marks JS. U.S. Patterns of Mortality by County and Race: 1965-1994: The U.S. Burden of Disease and Injury Monograph Series. Cambridge, Mass: Harvard Center for Population and Development Studies; 1998. Estimates of men at 48 years and women at 52 years are frequently reported as well, see [http://www.redcloudschool.org/history/072409_PineRidge_FactSheet.pdf "Pine Ridge Indian Reservation Demographics, 2009", Red Cloud Indian School]</ref> |
|||
* The average life expectancy on Pine Ridge is 66.81 years,<ref>{{ cite web | url=https://www.theguardian.com/society/2017/sep/29/pine-ridge-indian-reservation-south-dakota | title=Liquid genocide: alcohol destroyed Pine Ridge reservation - then they fought back | date=September 29, 2017 | work=The Guardian}}</ref> the lowest in the United States{{citation needed | reason=The CDC lists many other counties with far lower life expectancies, for example: Logan County, West Virginia with a life expectancy of 56.9|date=April 2024}}. In 2004, the average life expectancy was just 48 years for men and 52 years for women.<ref>{{ cite web | url=https://www.unpo.org/article.php?id=518 | title=Lakota: The Forgotten People of Pine Ridge | date=April 15, 2004 | publisher=Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO)}}</ref> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
==Notable leaders and residents== |
|||
[[File:Chief Bone Necklace-Oglala Lakota-1899 Heyn Photo.jpg|thumb|300px|Chief Bone Necklace (1899-Heyn Photo)]] |
|||
[[File:Ed McGaa Oglala Lakota-USMC.jpg|thumb|[[United States Marine Corps|U.S.M.C.]] pilot [[Ed McGaa]] (''Eagle Man''), and his co-pilot unfurl American flag on their [[F-4B Phantom]] fighter jet]] |
|||
*Albert Afraid of Hawk (1879-1900), an Oglala tribesman. In 1898, he became a member of [[Buffalo Bill]]'s Wild West Show. Prior to departing with that performance, he was present at the American Indian Congress in [[Omaha, Nebraska]], where all his known photographs were taken. In 1900, Afraid of Hawk was traveling along the east coast with Buffalo Bill’s Wild West Show. During that year, the show was presented at the fields in [[Danbury, Connecticut]]. One evening after the show's performance, Afraid of Hawk was taken ill. A local physician who took him to [[Danbury Hospital]]. It was felt that Albert was suffering from food poisoning, contracted from canned corn. He later succumbed to his illness on June 29, 1900. The interment was at Wooster Cemetery. One hundred and twelve years later, his remains were discovered by Robert Young, an employee of Wooster. Afraid of Hawk's corpse covered in a bison robe was relocated to Saint Mark's Episcopal Cemetery in [[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota|Rockyford]] for reburial.<ref>http://www.newstimes.com/local/article/Albert-Afraid-of-Hawk-s-last-ride-3848528.php</ref> |
|||
*[[American Horse]] ''Wašíčuŋ Tȟašúŋke'' (1840 – December 16, 1908) was a chieftain of the [[Oglala Lakota]] during the [[Sioux Wars]] of the 1870s. |
|||
*[[Amos Bad Heart Bull]]: [[Ledger Art]]ist and tribal historian; |
|||
* [[Crazy Horse|Chief Crazy Horse]]: war chief of the Oglala, c. 1870<ref>Kingsley M. Bray: ''Crazy Horse: A Lakota Life'', p. 153 ISBN 0-8061-3986-2</ref> |
|||
* [[SuAnne Big Crow]]: led Pine Ridge High School basketball team to state championship in 1989 |
|||
* Pat Cuny; an Oglala soldier in the [[83rd Infantry Division (United States)|83rd Infantry Division]], which fought in the [[Battle of the Bulge]] and liberated [[Langenstein-Zwieberge|Langenstein concentration camp]]; |
|||
*[[Ed McGaa]] (Eagle Man): author, attorney and a U.S. Marine Corps [[F-4B Phantom]] fighter pilot in [[Vietnam]], flew 110 [[Viet Nam War|combat missions]], received;8 [[Air Medal]]s, 2 [[Gallantry Cross (Vietnam)|Crosses of Gallantry]] and a recommendation for the [[Distinguished Flying Cross (United States)|Distinguished Flying Cross]].<ref>[http://lcweb2.loc.gov/diglib/vhp-stories/loc.natlib.afc2001001.28952/ Library of Congress: Veteran's History Project]</ref> |
|||
*[[Cecilia Fire Thunder]], first woman elected as president of the Oglala Sioux Tribe, 2004; promotes women's issues and revival of Lakota language |
|||
*[[Tim Giago]]; started the first independent Native American newspaper: ''Lakota Times'' (now ''[[Indian Country Today]]''), received a 1991 [[Nieman Fellowship]] at [[Harvard University]], and is a contributing writer to the ''[[Huffington Post]]''; |
|||
*[[Kicking Bear]], an Oglala who became a chief of the [[Miniconjou]] Lakota Sioux tribe. He fought in several battles during the [[Great Sioux War of 1876]], including the [[Battle of Little Big Horn]]. Also a holy man, he was active in the [[Ghost Dance]] religious movement of 1890, and had traveled with fellow Lakota [[Arnold Short Bull]] to visit the movement's leader, [[Wovoka]] (a Paiute holy man residing in Nevada). |
|||
*[[Eddie Little Sky]], actor; |
|||
*[[Little Wound]] (''Tȟaópi Čík’ala'': 1835–1899), Oglala chief. Following the death of his brother Bull Bear II in 1865 he became leader of the Kuinyan branch of the Kiyuksa band (Bear people).<ref>Sandoz, Mari: ''Crazy Horse: The Strange Man of the Oglalas'', Third edition [Updated with supplemental material] by Mari Sandoz and Vine Deloria. 2008, 512 p. ISBN 978-0-8032-1787-4 (p 470).</ref> |
|||
* Chief Long Wolf (1833–1892), warrior of [[Battle of the Little Bighorn]] and the [[Sioux Wars]]. He died at age 59 of bronchial pneumonia while taking part in the European tour of Buffalo Bill's Wild West Show. He shared the grave at [[West Brompton]]'s [[Brompton Cemetery|cemetery]] with a 17-month-old Sioux girl named White Star Ghost Dog believed to have fallen from her mother's arms while on horseback. 105 years later, a British woman named Elizabeth Knight traced his family and campaigned with them to have his remains returned to the land of his birth. In 1997, Long Wolf's coffin was finally moved to a new plot at Saint Ann's Cemetery in Wolf Creek. White Star Ghost Dog's coffin was also reinterred there.<ref>http://cgi.cnn.com/WORLD/9709/25/chief.long.wolf/</ref> |
|||
* [[Old Chief Smoke]] (''Šóta'': 1774-1864) an early Oglala chief and Shirt Wearer; |
|||
* [[Black Elk (Heȟáka Sápa)]] (1863-1950), an Oglala holy man, and second cousin to Crazy Horse. |
|||
[[File:Red Cloud3.jpg|thumb|left|[[Red Cloud|Chief Red Cloud]]: The [[Red Cloud Agency]] was originally established in [[Nebraska]] in 1873]]. |
|||
* [[Red Cloud|Chief Red Cloud]] (1822–1909), an Oglala chief, a respected warrior and statesman. From 1866 to 1868, he succeeded in closing the [[Bozeman Trail]], which passed through prime bison hunting grounds. At Pine Ridge, Red Cloud worked to establish a [[Jesuit]] school for Native American children. |
|||
*[[Spotted Elk|Chief Spotted Elk]]: called ''Big Foot'' by the U.S. soldiers. His band of Miniconjou Sioux were massacred at Wounded Knee in 1891.<ref>Helaine Silverman, D. Fairchild Ruggles: ''Cultural Heritage and Human Rights'', pp. 150-151; ISBN 978-0-387-76579-2</ref> |
|||
*[[Touch the Clouds]]: Oglala chief |
|||
*[[JoAnn Tall]], environmental activist at Pine Ridge, honored in 1993 for her opposition to [[uranium]] mining on the reservation |
|||
*[[Theresa Two Bulls]], first American Indian woman elected to the South Dakota legislature; state senator (2004–2008) and president of Oglala Sioux Tribe (2008–2010)<ref>[http://indiancountrynews.net/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=4988&Itemid=1 "Two Bulls to lead Oglala Sioux Tribe"], AP, ''News From Indian Country', November 2008, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> |
|||
* [[Dick Wilson (tribal chairman)|Richard Wilson]] (April 29, 1934 – January 31, 1990), tribal chairman from 1972–1976 during the [[Wounded Knee Incident]]; accused of suppressing political opposition with violence |
|||
*John Yellow Bird Steele, elected president of the Oglala Sioux Tribe six times from 1992-2010. |
|||
*[[Young Man Afraid Of His Horses]]: (''Tȟašúŋke Kȟokípȟapi'') (1830–1900). His name means "They fear his horse" or "His horse is feared," meaning the warrior was so renowned that the sight of his horse inspired fear. |
|||
* Charles Trimble, member of Oglala Lakota Nation and former Executive Director of the National Congress of American Indians. (1972–1978) |
|||
* [[Billy Mills|William Mervin "Billy" Mills]], also known as ''Makata Taka Hela'', is the second [[Native Americans in the United States|Native American]] to win an [[Olympic Games|Olympic]] [[gold medal]] and the only American ever to win the Olympic gold in the [[Athletics at the 1964 Summer Olympics - Men's 10000 metres|10,000 meter run]]. |
|||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
==Tribal government== |
==Tribal government== |
||
[[File:Oglala girl in front of a tipi.jpg|thumb|200px|Oglala girl in front of a tipi, |
[[File:Oglala girl in front of a tipi.jpg|thumb|200px|An Oglala girl in front of a tipi, 1891]] |
||
The reservation is |
The reservation is governed by the eighteen-member Oglala Sioux Tribal Council, who are elected officials rather than traditional [[clan]] life leaders, in accordance with the [[Indian Reorganization Act]] of 1934. The Executive Officers of the council are the President (also called Chairman), Vice President, Secretary, and Treasurer. Primary elections are held in October and the General election in November. |
||
The President and Vice-President are elected at large by voters to a term of office of |
The President and Vice-President are elected at large by voters to a term of office of two years; the Secretary and Treasurer are appointed by the Tribal Council. Council members serve a term of two years. There are nine election districts on the reservation. One representative is elected for each 1,000 tribe members. |
||
A Constitution was approved on January 15, 1936 with amendments approved |
A Constitution was approved on January 15, 1936, with amendments approved on December 24, 1969; December 3, 1985; July 11, 1997. |
||
===Politics=== |
===Politics=== |
||
While many residents have continued to struggle with the tribal government, BIA and other federal representatives, some have become more politically active in other ways. In 2002, the Pine Ridge Reservation was part of a statewide voter registration campaign organized by the Democratic Party. That year, Oglala Lakota candidates won offices in [[Bennett County]]; since the 1990s, Native Americans (mostly Lakota) have become a majority of the county's population. Charles Cummings was elected as county sheriff, Gerald 'Jed' Bettelyoun to one of the positions as county commissioner, and Sandy Flye became the first Native American elected to a seat on the county school board. Statewide turnout by Native Americans helped elect the Democratic candidate [[Tim Johnson (U.S. Senator)|Tim Johnson]] to the U.S. Senate by a narrow margin.<ref>[http://www.denverpost.com/Stories/0,1413,36%257E53%257E1095196%257E,00.html Gwen Florio, "Indians show political clout: Natives throng polls in 'white' S.D. county"], ''Denver Post'', 8 January 2003, accessed 8 June 2011</ref> |
While many residents have continued to struggle with the tribal government, BIA and other federal representatives, some have become more politically active in other ways. In 2002, the Pine Ridge Reservation was part of a statewide voter registration campaign organized by the Democratic Party. That year, Oglala Lakota candidates won offices in [[Bennett County]]; since the 1990s, Native Americans (mostly Lakota) have become a majority of the county's population. Charles Cummings was elected as county sheriff, Gerald 'Jed' Bettelyoun to one of the positions as county commissioner, and Sandy Flye became the first Native American elected to a seat on the county school board. Statewide turnout by Native Americans helped elect the Democratic candidate [[Tim Johnson (U.S. Senator)|Tim Johnson]] to the U.S. Senate by a narrow margin.<ref>[http://www.denverpost.com/Stories/0,1413,36%257E53%257E1095196%257E,00.html Gwen Florio, "Indians show political clout: Natives throng polls in 'white' S.D. county"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081116003953/http://www.denverpost.com/Stories/0%2C1413%2C36~53~1095196~%2C00.html |date=2008-11-16 }}, ''Denver Post'', 8 January 2003, accessed 8 June 2011</ref> |
||
In 1992, [[John Yellow Bird Steele]] was elected president of the OST, the first of what would become a record-setting seven terms as president.<ref>{{Cite book|last1=Reinhardt|first1=Akim D.|url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/71004236|title=Ruling Pine Ridge : Oglala Lakota politics from the IRA to Wounded Knee|last2=Kidwell|first2=Clara Sue|publisher=[[Texas Tech University Press]]|year=2007|isbn=978-0-89672-601-7|location=Lubbock|pages=220|oclc=71004236}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Reinhardt|first=Akim D.|url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/914715232|title=Welcome to the Oglala Nation : a documentary reader in Oglala Lakota political history|publisher=[[University of Nebraska Press]]|year=2015|isbn=978-0-8032-8436-4|location=Lincoln, NE|oclc=914715232}}</ref> Despite winning seven elections, Steele only won re-election once, in 2002.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Harlan|first=Bill|date=2002-11-20|title=Steele wins rare Oglala Tribe re-election|url=https://rapidcityjournal.com/news/steele-wins-rare-oglala-tribe-re-election/article_da9f2bed-fd57-5eda-84c3-57b2d6c46759.html|access-date=2020-12-06|website=[[Rapid City Journal]]|language=en}}</ref> In most cases, he was defeated when seeking re-election, only to come back and defeat his successor in the next election (or, in the case of the 2006 election, to defeat the person serving out the rest of his successor's term).<ref>{{Cite web|title=OGLALA SIOUX PRESIDENT JOHN YELLOW BIRD STEELE BIOGRAPHY|url=https://docs.house.gov/meetings/AP/AP06/20150324/102897/HHRG-114-AP06-Bio-SteeleJ-20150324.pdf|access-date=2020-11-29|website=[[United States House of Representatives]]}} {{PD-notice}}</ref> |
|||
In 2004 [[Cecilia Fire Thunder]] became the first woman elected president of the OST, defeating the incumbent and [[Russell Means]].<ref name=Giago/> In 2005 she led negotiations with Nebraska to strengthen law enforcement in [[Whiteclay, Nebraska]] by hiring more Oglala tribal police and having them deputized by Nebraska to patrol in the town. The town sells massive quantities of alcohol to the Lakota, although it is illegal on the reservation. The "historic agreement" was signed by Fire Thunder following approval by the tribal council, the Nebraska Governor [[Dave Heineman]] and State Attorney General [[Jon Bruning]].<ref name=APpatrol>[http://www.rapidcityjournal.com/news/local/top-stories/article_aba602e2-a06e-5dfb-9f3e-38465e9f5a66.html AP, "Two years after 'historic' agreement, no tribe patrols in Whiteclay"], ''Rapid City Journal'', 14 May 2007, accessed 13 June 2011</ref> |
In 2004, [[Cecilia Fire Thunder]] became the first woman elected president of the OST, defeating the incumbent Steele and [[Russell Means]].<ref name=Giago/> In 2005 she led negotiations with Nebraska to strengthen law enforcement in [[Whiteclay, Nebraska|Whiteclay]] by hiring more Oglala tribal police and having them deputized by Nebraska to patrol in the town. The town sells massive quantities of alcohol to the Lakota, although it is illegal on the reservation.{{dubious|date=February 2017}} The "historic agreement" was signed by Fire Thunder following approval by the tribal council, the Nebraska Governor [[Dave Heineman]] and State Attorney General [[Jon Bruning]].<ref name=APpatrol>[http://www.rapidcityjournal.com/news/local/top-stories/article_aba602e2-a06e-5dfb-9f3e-38465e9f5a66.html AP, "Two years after 'historic' agreement, no tribe patrols in Whiteclay"], ''Rapid City Journal'', 14 May 2007, accessed 13 June 2011</ref> |
||
On March 21, 2006, Fire Thunder announced her plan to bring a [[Planned Parenthood]] clinic to the reservation to improve health services to women. The South Dakota state legislature had recently passed a stringent abortion law.<ref name=Giago>{{Cite news |
On March 21, 2006, Fire Thunder announced her plan to bring a [[Planned Parenthood]] clinic to the reservation to improve health services to women. The South Dakota state legislature had recently passed a stringent abortion law.<ref name=Giago>{{Cite news |
||
| Line 327: | Line 299: | ||
| date =2006-03-21 |
| date =2006-03-21 |
||
| url =http://www.indianz.com/News/2006/013061.asp |
| url =http://www.indianz.com/News/2006/013061.asp |
||
| |
| access-date = 2007-10-05 }}</ref> In May 2006, the Oglala Sioux tribal council unanimously voted to ban all abortions on the reservation, regardless of the circumstances. The council also voted to suspend Fire Thunder for 20 days pending an impeachment hearing.<ref>{{Cite news |
||
| last =Melmer |
| last =Melmer |
||
| first =David |
| first =David |
||
| Line 334: | Line 306: | ||
| date =2006-06-05 |
| date =2006-06-05 |
||
| url =http://www.indiancountry.com/content.cfm?id=1096413086 |
| url =http://www.indiancountry.com/content.cfm?id=1096413086 |
||
| |
| access-date = 2007-10-05 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20070927172313/http://www.indiancountry.com/content.cfm?id=1096413086 |archive-date = 2007-09-27}}</ref> |
||
In November 2006, state voters reviewed the law passed by the state legislature, and they overwhelmingly defeated the ban on abortions without exceptions, by 55.57 percent to 44.43 percent. A ban with exceptions was proposed in 2008, and state voters rejected that by a margin of 55.21 percent to 44.79 percent.<ref>[http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2008/12/02/opinion/main4643908.shtml "Why Won't South Dakota Voters Ban Abortion?"], CBS News, 2 December 2008, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> |
On June 29, 2006, the tribal council voted to impeach Fire Thunder: it said that founding the clinic was outside her authority and she had failed to consult with them. Her two-year term would have expired in October 2006. In November 2006, state voters reviewed the law passed by the state legislature, and they overwhelmingly defeated the ban on abortions without exceptions, by 55.57 percent to 44.43 percent. A ban with exceptions was proposed in 2008, and state voters rejected that by a margin of 55.21 percent to 44.79 percent.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20081203235351/http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2008/12/02/opinion/main4643908.shtml "Why Won't South Dakota Voters Ban Abortion?"], CBS News, 2 December 2008, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> |
||
The U.S. Congress supported Fire Thunder's tribal law enforcement initiative, earmarking $200,000 over two years to pay for the increased cost of OST police patrols in Whiteclay. By May 2007, the tribe had spent none of the money. Fire Thunder's impeachment and tribal political conflict appeared to prevent its implementing the agreement.<ref name=APpatrol/> |
The U.S. Congress supported Fire Thunder's tribal law enforcement initiative, earmarking $200,000 over two years to pay for the increased cost of OST police patrols in Whiteclay. By May 2007, the tribe had spent none of the money. Fire Thunder's impeachment and tribal political conflict appeared to prevent its implementing the agreement.<ref name="APpatrol" /> During 2006 and 2007, tribal activists tried to blockade the road inside the reservation to confiscate beer being illegally brought in. The OST police chief complained of having insufficient money and staff to control the beer traffic.<ref name="Walker2">[http://battleforwhiteclay.org/?p=678#more-678 CARSON WALKER (Associated Press), "Pine Ridge blockade planned to nab bootleggers"], 13 May 2007, accessed 17 February 2012</ref> The tribe lost the earmarked funds and let the initiative lapse. |
||
In November 2008, [[Theresa Two Bulls]], a Democratic State Senator for South Dakota since 2004, became the second woman elected president of the OST. She succeeded Steele and defeated [[Russell Means]].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Crash|first=Tom|date=2008-12-04|title=Steele passes pipe on to Two Bulls {{!}} Lakota Times|url=https://www.lakotatimes.com/articles/steele-passes-pipe-on-to-two-bulls/|access-date=2020-12-06|website=Lakota Country Times}}</ref> When the reservation had a rash of [[suicide]]s in late 2009, she declared a state of emergency and organized a call-in to President [[Barack Obama]]. She organized services during a blizzard to assist residents in outlying areas on the reservation.<ref>[http://www.huffingtonpost.com/tim-giago/theresa-two-bulls-a-lady_b_417754.html Tim Giago, "Theresa Two Bulls: A lady of distinction"], ''Huffington Post'', 10 January 2010, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> |
|||
But, during 2006 and 2007, tribal activists tried to blockade the road inside the reservation to confiscate beer being illegally brought in. The OST police chief complained of having insufficient money and staff to control the beer traffic.<ref name=Walker>[http://battleforwhiteclay.org/?p=678#more-678 CARSON WALKER (Associated Press), "Pine Ridge blockade planned to nab bootleggers"], 13 May 2007, accessed 17 February 2012</ref> The tribe lost the earmarked funds and let the initiative lapse. |
|||
Steele was re-elected in 2010, defeating Two Bulls. [[Bryan Brewer]] was elected as Tribal president in November 2012, defeating the incumbent Steele with 52% of the vote. A retired educator and school administrator, he was new to tribal politics. He worked to develop housing and discourage alcoholism, even leading a protest against Whiteclay alcohol sales.<ref>[http://www.nativenewsnetwork.com/bryan-brewer-to-be-sworn-in-tomorrow-as-president-of-oglala-sioux-tribe.html Levi Rickert, "Bryan Brewer to be Sworn in Tomorrow as President of Oglala Sioux Tribe"], Native News Network, accessed 14 December 2012</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Ray|first=Charles Michael|date=2013-06-19|title=A Dry Reservation Clashes With Its Liquor Store Neighbors|url=https://www.wbur.org/npr/190365290/a-dry-reservation-clashes-with-its-liquor-store-neighbors|access-date=2020-12-05|website=WBUR|language=en}}</ref> The journalist Brian Ecoffey noted that Brewer represented a "new direction" for the tribe, as he had not held political office before.<ref>[http://www.indianz.com/News/2012/007928.asp Brandon Ecoffey, "Native Sun News: Oglala Sioux Tribe prepares for inauguration"], ''Native Sun News'', 6 December 2012, at Indianz.com, accessed 14 December 2012</ref> Steele then defeated Brewer in 2014, starting what would be Steele's last term.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Ecoffey|first=Brandon|date=2014-11-05|title=Native Sun News: Oglala Sioux Tribe chooses a new president|url=https://www.indianz.com/News/2014/11/05/native-sun-news-oglala-sioux-t-50.asp|access-date=2020-12-03|website=indianz.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=2014-11-05|title=Yellow Bird Steele elected leader of Oglala Sioux|url=https://www.mitchellrepublic.com/news/3607098-yellow-bird-steele-elected-leader-oglala-sioux|access-date=2020-12-03|website=The Mitchell Republic|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
In November 2008, [[Theresa Two Bulls]], a Democratic State Senator for South Dakota since 2004, became the second woman elected president of the OST. She succeeded John Yellow Bird Steele and defeated [[Russell Means]].<ref name=APelection>[http://indiancountrynews.net/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=4988&Itemid=1 "Two Bulls to lead Oglala Sioux Tribe"], AP, ''News From Indian Country'', November 2008, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> When the reservation had a rash of [[suicide]]s in late 2009, she declared a state of emergency and organized a call-in to President [[Barack Obama]]. She organized services during a blizzard to assist residents in outlying areas on the reservation.<ref>[http://www.huffingtonpost.com/tim-giago/theresa-two-bulls-a-lady_b_417754.html Tim Giago, "Theresa Two Bulls: A lady of distinction"], ''Huffington Post'', 10 January 2010, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> |
|||
[[Troy "Scott" Weston]] represented the Porcupine District in the 2010 and 2012 administrations; Weston was elected OST President in 2016 beating Steele, the incumbent, in a landslide victory. The ''Rapid City Journal'' reported that nearly 2/3 of voters at the polls cast their ballot for Weston.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://rapidcityjournal.com/news/election/pine-ridge-elects-new-tribal-president/article_a141249c-b408-5cd2-93f4-635a6424e118.html|title=Pine Ridge elects new tribal president|first=Mike Anderson Journal|last=staff|website=Rapid City Journal Media Group|date=November 9, 2016 }}</ref> |
|||
John Yellow Bird Steele was re-elected in 2010. Bryan Brewer was elected as Tribal president in November 2012, defeating the incumbent Steele with 52% of the vote. A retired educator and school administrator, he is new to tribal politics. He intends to work on developing housing and discouraging alcoholism.<ref>[http://www.nativenewsnetwork.com/bryan-brewer-to-be-sworn-in-tomorrow-as-president-of-oglala-sioux-tribe.html Levi Rickert, "Bryan Brewer to be Sworn in Tomorrow as President of Oglala Sioux Tribe"], Native News Network, accessed 14 December 2012</ref> The journalist Brian Ecoffey noted that Brewer represented a "new direction" for the tribe, as he had not held political office before.<ref>[http://www.indianz.com/News/2012/007928.asp Brandon Ecoffey, "Native Sun News: Oglala Sioux Tribe prepares for inauguration"], ''Native Sun News'', 6 December 2012, at Indianz.com, accessed 14 December 2012</ref> |
|||
In national elections, Pine Ridge is politically divided: the western half of the reservation (Oglala Lakota County) votes overwhelmingly Democratic at the national level, while the eastern half (Bennett and Jackson Counties) trends heavily Republican. In local politics, the Oglala are active in electing tribal members to the State House and Senate, with both Democrats and Republicans finding success on the reservation. |
|||
===Sovereignty=== |
|||
===Federal, state, and tribal law=== |
|||
The Oglala Sioux Tribe maintains legal jurisdiction over all crimes committed on the reservation by tribal members, non-reservation Indians, and those willing to relinquish authority to the tribal courts. [[Felony|Felony crimes]] and others which have been specifically assumed by the federal government, as defined by various acts of the U.S. Congress, are outside their jurisdiction and are prosecuted by the BIA and FBI. The ruling of the [[Supreme Court of the United States]] in ''Ex parte Crow Dog'' (1883) marked the high point of Indian sovereignty in law enforcement on reservations; since then federal legislation and subsequent Supreme Court decisions have reduced Native American sovereignty in this area.<ref>[http://www.americanbar.org/content/newsletter/publications/gp_solo_magazine_home/gp_solo_magazine_index/marshall.html Philip J. Prygoski: "From Marshall to Marshall: The Supreme Court's changing stance on tribal sovereignty"], ''Solo Magazine,'' American Bar Association</ref> |
The Oglala Sioux Tribe maintains legal jurisdiction over all crimes committed on the reservation by tribal members, non-reservation Indians, and those willing to relinquish authority to the tribal courts. [[Felony|Felony crimes]] and others which have been specifically assumed by the federal government, as defined by various acts of the U.S. Congress, are outside their jurisdiction and are prosecuted by the BIA and FBI. The ruling of the [[Supreme Court of the United States]] in ''Ex parte Crow Dog'' (1883) marked the high point of Indian sovereignty in law enforcement on reservations; since then federal legislation and subsequent Supreme Court decisions have reduced Native American sovereignty in this area.<ref>[http://www.americanbar.org/content/newsletter/publications/gp_solo_magazine_home/gp_solo_magazine_index/marshall.html Philip J. Prygoski: "From Marshall to Marshall: The Supreme Court's changing stance on tribal sovereignty"], ''Solo Magazine,'' American Bar Association</ref> |
||
[[Public Law 280]], enacted by Congress in 1953 and substantially amended in 1968, allows for states to assume jurisdiction on Indian reservations if approved by referendum by the affected reservations. In South Dakota, Public Law 280 is applied only to state highways running through reservations.<ref>Laurence French: ''Native American Justice,'' p.41, Rowman & Littlefield (2003) {{ISBN|0-8304-1575-0}}</ref> |
|||
Landmark cases affecting tribal criminal law include: |
|||
* |
*{{ussc|name=Ex parte Crow Dog|volume=109|page=556|pin=|year=1883|el=no}}: On August 5, 1881, Crow Dog, a [[Brulé|Brulé Lakota]] subchief, shot and killed the [[Oglala Lakota|Oglala]] principal chief Chief [[Spotted Tail]], on the [[Rosebud Indian Reservation]]. A [[grand jury]] was convened, and Crow Dog was tried and convicted in Dakota Territorial court in [[Deadwood, South Dakota]], and sentenced to death. In 1883 his lawyers petitioned for ''[[writ of habeas corpus|writs of habeas corpus]]'' and ''[[certiorari]]''; his case was argued in November 1883 before the U.S. Supreme Court. In a unanimous decision, the court ruled that, according to the provisions of the [[Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868)|Treaty of Fort Laramie]], the Dakota Territorial court had no jurisdiction over the Rosebud reservation; it overturned Crow Dog's conviction.<ref>{{ussc|name=Ex parte Crow Dog|volume=109|page=556|pin=|year=1883}}.</ref><ref>''Crow Dog's Case: American Indian Sovereignty, Tribal Law, and United States Law in the Nineteenth Century'' (Studies in North American Indian History) By Sidney L. Harring p. 107 Publisher: Cambridge University Press (February 25, 1994) {{ISBN|0-521-46715-2}}</ref><ref>''Famous American Crimes and Trials: 1860-1912'' by Frankie Y. Bailey, Steven M. Chermak p. 101-105 'Praeger Pub (October 2004) {{ISBN|0-275-98335-8}}</ref> In response to this ruling, Congress passed the [[Major Crimes Act]] in 1884, defining crimes that would be prosecuted under federal law. |
||
*[[Major Crimes Act]] |
*[[Major Crimes Act]], 18 U.S.C. § 1: Congress gave federal authorities concurrent jurisdiction over seven major crimes committed on a reservation, regardless of whether one of the parties was Indian. This legislation reduced the criminal jurisdiction previously held by tribal courts.<ref>Carrie E. Garrow, Sarah Deer: ''Tribal Criminal Law and Procedure'', p.87, AltaMira Press (2004) {{ISBN|978-0-7591-0718-2}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.justice.gov/archives/jm/criminal-resource-manual-679-major-crimes-act-18-usc-1153|title=679. The Major Crimes Act—18 U.S.C. § 1153|date=February 19, 2015|website=www.justice.gov}}</ref> |
||
* |
*{{ussc|name=United States v. Quiver|volume=241|page=602|pin=|year=1916|el=no}}: Congress left to the Indian Tribal Courts jurisdiction over all crimes not taken by the Federal government.<ref>{{ussc|name=United States v. Quiver|volume=241|page=602|pin=|year=1916}}.</ref><ref>U.S. Department of the Interior, ''Federal Indian Law'' (pp 319–20, (1958).</ref> |
||
*''[[Iron Crow v. Oglala Sioux Tribe]]'', 231 F. |
*''[[Iron Crow v. Oglala Sioux Tribe]]'', 231 [[F.2d]] 89 (8th Cir. 1956): Indian Tribal Courts have inherent jurisdiction over all matters not taken over by the Federal government.<ref>{{cite court |litigants=Iron Crow v. Oglala Sioux Tribe |vol=231 |reporter=F.2d |opinion=89 |court=8th Cir. |date=1956 |url=https://law.justia.com/cases/federal/appellate-courts/F2/231/89/374603/ |access-date=2018-05-22 }}</ref><ref>National Indian Law Library, American Association of Law Libraries, United States. ''Supreme Court Landmark Indian Law Cases: Landmark Indian law cases,'' p.432, Fred B Rothman & Co (2003) {{ISBN|0-8377-0157-0}}</ref> |
||
* |
*{{ussc|name=Oliphant v. Suquamish Indian Tribe|volume=435|page=191|pin=|year=1978|el=no}}: Indian Tribes do not have inherent criminal jurisdiction over non-Indians absent Congressional authority.<ref>{{ussc|name=Oliphant v. Suquamish Indian Tribe|volume=435|page=191|pin=|year=1978}}.</ref> |
||
* |
*{{ussc|name=United States v. Wheeler|link=United States v. Wheeler (1978)|volume=435|page=313|pin=|year=1978|el=no}}: Indian Tribes have inherent powers to punish offenses against Tribal laws when committed by Tribal members.<ref>{{ussc|name=United States v. Wheeler|link=United States v. Wheeler (1978)|volume=435|page=313|pin=|year=1978}}</ref> |
||
====Law enforcement==== |
|||
[[File:Sioux Indian police lined up on horseback in front of Pine Ridge Agency buildings, Dakota Territory, 08-09-1882 - NARA - 519143.jpg|thumb|Sioux Indian police lined up on horseback in front of Pine Ridge Agency buildings, Dakota Territory, August 9, 1882]] |
|||
In traditional Sioux society, law enforcement was performed by members of the warrior societies, such as the Kit Foxes, Badgers and Crow Owners, known as the ''akicitas.'' They maintained order in camp and during communal buffalo hunts. Each band would appoint one society as the official ''akicita'' group for the year.<ref>Royal B. Hassrick: ''The Sioux: Life and Customs of a Warrior Society'', p. 16, University of Oklahoma Press (1988) ISBN 978-0-8061-2140-6</ref> This custom prevailed for a short time after the Sioux were forced onto the reservations. In 1878 Congress authorized the formation of an Indian police force to provide law enforcement in [[Indian territory]] and upon reservations. They were superseded by police assigned and managed by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA). The BIA police force is composed of members of various Native American tribes from throughout the United States, and personnel often do not belong to the nations they oversee. |
|||
In traditional Sioux society, law enforcement was performed by members of the warrior societies, such as the Kit Foxes, Badgers and Crow Owners, known as the ''akicitas.'' They maintained order in camp and during communal buffalo hunts. Each band would appoint one society as the official ''akicita'' group for the year.<ref>Royal B. Hassrick: ''The Sioux: Life and Customs of a Warrior Society'', p. 16, University of Oklahoma Press (1988) {{ISBN|978-0-8061-2140-6}}</ref> This custom prevailed for a short time after the Sioux were forced onto the reservations. |
|||
Since the late 1970s, the Oglala Sioux Tribe has received Federal funding to maintain its own reservation police, supplemented by BIA personnel. The FBI has jurisdiction for any [[felony]] crimes committed upon the reservation. After the reservation police respond to the initial call, a BIA police person initiates the investigation and notifies the FBI.<ref>Vine Deloria, Clifford M. Lytle: ''American Indians, American Justice,'' p. 183, University of Texas Press (1983) ISBN 978-0-292-73834-8</ref> |
|||
In 1878, Congress authorized the formation of an Indian police force to provide law enforcement in [[Indian territory]] and upon reservations. They were superseded by police assigned and managed by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA). The BIA police force is composed of members of various Native American tribes from throughout the United States, and personnel often do not belong to the nations they oversee. |
|||
The OST is developing a new Tribal Justice Center, to include the tribal courts and a [[restorative justice]] courtroom. The latter concept relates to traditional Lakota ideas about restoring the victim and offender to balance within the community. In practice, it is intended to bring together the affected parties in facilitated communication, together with members of the community; to settle on a form of reparation or compensation by the offender that is satisfactory to the victim, which may include money, public apology, and/or community service work; and to bring the offender quickly back within the community with its support for the future. As the process is being used at [[Kahnawake]], a [[Mohawk people|Mohawk]] reserve in Canada, the [[First Nation]] community works to intervene and settle issues before arrest.<ref name=Haslip>[http://www.murdoch.edu.au/elaw/issues/v9n1/haslip91.html Susan Haslip, "The (Re)Introduction of Restorative Justice in Kahnawake: 'Beyond Indigenization'"], ''E Law,'' Vol. 9 No. 1 (March 2002), Murdoch University, accessed 3 June 2011</ref> |
|||
Since the late 1970s, the Oglala Sioux Tribe has received Federal funding to maintain its own reservation police, supplemented by BIA personnel. The FBI has jurisdiction for any [[felony]] crimes committed upon the reservation. After the reservation police respond to the initial call, a BIA police person initiates the investigation and notifies the FBI.<ref>Vine Deloria, [[Clifford M. Lytle]]: ''American Indians, American Justice,'' p. 183, University of Texas Press (1983) {{ISBN|978-0-292-73834-8}}</ref> |
|||
The OST is developing a new Tribal Justice Center, to include the tribal courts and a [[restorative justice]] courtroom. The latter concept relates to traditional Lakota ideas about restoring the victim and offender to balance within the community. In practice, it is intended to bring together the affected parties in facilitated communication, together with members of the community; to settle on a form of reparation or compensation by the offender that is satisfactory to the victim, which may include money, public apology, and/or community service work; and to bring the offender quickly back within the community with its support for the future. As the process is being used at [[Kahnawake]], a [[Mohawk people|Mohawk]] reserve in Canada, the [[First Nations in Canada|First Nation]] community works to intervene and settle issues before arrest.<ref name=Haslip>[http://www.murdoch.edu.au/elaw/issues/v9n1/haslip91.html Susan Haslip, "The (Re)Introduction of Restorative Justice in Kahnawake: 'Beyond Indigenization'"], ''E Law,'' Vol. 9 No. 1 (March 2002), Murdoch University, accessed 3 June 2011</ref> |
|||
==Social issues and economy== |
==Social issues and economy== |
||
[[File:Pine Ridge Indian Health Service Hospital.jpg|300px|thumb|Pine Ridge Indian Health Service Hospital]] |
[[File:Pine Ridge Indian Health Service Hospital.jpg|300px|thumb|Pine Ridge Indian Health Service Hospital]] |
||
Pine Ridge is the eighth-largest reservation in the United States and it is the poorest. The population of Pine Ridge suffer health conditions, including high [[mortality rate]]s, [[Major depressive disorder|depression]], [[alcoholism]], [[drug abuse]], [[malnutrition]] and [[diabetes]], among others. Reservation access to health care is limited compared to urban areas, and it is not sufficient. Unemployment on the reservation hovers between 80% and 85%, and 49% of the population live below the [[Poverty in the United States|federal poverty level]].<ref>[http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=16000US4649660&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U_DP3&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U&-_lang=en&-_sse=on "Pine Ridge CDP, South Dakota — DP-3. Profile of Selected Economic Characteristics: 2000"] U.S. Census Bureau.</ref> Many of the families have no electricity, telephone, running water, or sewage systems; and many use [[wood stove]]s to heat their homes, depleting limited wood resources. |
Pine Ridge is the eighth-largest reservation in the United States and it is the poorest. The population of Pine Ridge suffer health conditions, including high [[mortality rate]]s, [[Major depressive disorder|depression]], [[alcoholism]], [[drug abuse]], [[malnutrition]] and [[diabetes]], among others. Reservation access to health care is limited compared to urban areas, and it is not sufficient. Unemployment on the reservation hovers between 80% and 85%, and 49% of the population live below the [[Poverty in the United States|federal poverty level]].<ref>[http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=16000US4649660&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U_DP3&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U&-_lang=en&-_sse=on "Pine Ridge CDP, South Dakota — DP-3. Profile of Selected Economic Characteristics: 2000"] {{Webarchive|url=https://archive.today/20200212042051/http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=16000US4649660&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U_DP3&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U&-_lang=en&-_sse=on |date=2020-02-12 }} U.S. Census Bureau.</ref> {{clarify|date=March 2018}} Many of the families have no electricity, telephone, running water, or sewage systems; and many use [[wood stove]]s to heat their homes, depleting limited wood resources. |
||
===Health and healthcare=== |
===Health and healthcare=== |
||
The population on Pine Ridge has among the shortest [[life expectancy|life expectancies]] of any group in the Western Hemisphere: approximately 47 years for males and 52 years for females in 2004. The [[infant mortality rate]] is five times the United States national average, and the adolescent [[suicide]] rate is four times the United States national average. Members of the reservation suffer from a disproportionately high rate of poverty and [[alcoholism]].<ref name=Resroad>Williams, Matthew. "[https://web.archive.org/web/20110226192801/http://www.time.com/time/photogallery/0,29307,2048598_2235606,00.html Reservation Road"], ''[[TIME (magazine)|TIME]]''. Retrieved on February 26, 2011.</ref> By 2011, a [[Gangs in the United States|gang culture]] formed among Native American teenagers on the reservation.<ref>Williams, Matthew. "[https://web.archive.org/web/20110224033748/http://www.time.com/time/photogallery/0,29307,2048598,00.html Urban Jungle on the Reservation]." ''[[TIME (magazine)|TIME]]''. Retrieved on February 26, 2011.</ref> Young residents leave the reservation for larger cities. |
|||
{{Expand section|date=May 2011}} |
|||
The population on Pine Ridge has among the shortest [[life expectancy|life expectancies]] of any group in the Western Hemisphere: approximately 47 years for males and 52 years for females. The [[infant mortality rate]] is five times the United States national average, and the adolescent [[suicide]] rate is four times the United States national average. Members of the reservation suffer from a disproportionately high rate of poverty and [[alcoholism]].<ref name=Resroad>Williams, Matthew. "[http://www.time.com/time/photogallery/0,29307,2048598_2235606,00.html Reservation Road"], ''[[TIME (magazine)|TIME]]''. Retrieved on February 26, 2011.</ref> By 2011, a [[Gangs in the United States|gang culture]] formed among Native American teenagers on the reservation.<ref>Williams, Matthew. "[http://www.time.com/time/photogallery/0,29307,2048598,00.html Urban Jungle on the Reservation]." ''[[TIME (magazine)|TIME]]''. Retrieved on February 26, 2011.</ref> Young residents leave the reservation for larger cities. When they return to the reservation, they bring gang culture with them. |
|||
The Pine Ridge Comprehensive Health Facility is the on-reservation hospital run by the [[Indian Health Service]]. The 110,000 |
The Pine Ridge Comprehensive Health Facility is the on-reservation hospital run by the [[Indian Health Service]]. The {{convert|110,000|sqft|m2}} inpatient hospital also has an outpatient clinic, dental clinic, and a surgery suite. The emergency room is staffed by two physicians as well as two physician assistants and a hospitalist in triage. The "Sick Kids" clinic is also based at the facility, with pediatricians on staff. During the [[COVID-19 pandemic in the United States|Covid-19 pandemic]], the hospital increased its capacity to provide respiratory and critical care, with assistance from [[Stanford University|Stanford Center for Innovation in Global Health]].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Jensen|first=Anpotowin|date=2021-03-29|title=Stanford Medicine team aids Lakota Nation in fighting COVID-19|url=https://scopeblog.stanford.edu/2021/03/29/stanford-medicine-team-aids-lakota-nation-in-fighting-covid-19/|access-date=2022-01-02|website=Scope|language=en-US}}</ref> |
||
In June 2011, the OST broke ground on a long-planned 60-bed nursing home facility, to be completed within two years. It was developed in cooperation with the federal government |
In June 2011, the OST broke ground on a long-planned 60-bed nursing home facility, to be completed within two years. It was developed in cooperation with the federal government, the states of Nebraska and South Dakota. In October 2016, the Oglala Lakota Nursing Home, $6.5-million, 80-bed nursing home for the care of their elderly, opened in White Clay, South Dakota.<ref name="rooks">[https://web.archive.org/web/20161027054618/http://indiancountrytodaymedianetwork.com/2016/10/24/oglala-lakota-nursing-bringing-elders-home-166184 David Rooks, "Oglala Lakota Nursing Bringing the Elders Home"], ''Indian Country Today,'' 24 October 2016; accessed 24 October 2016</ref> The tribe borrowed money for a loan for the facility from the Mdewakanton Shakopee tribe, agreeing to "an independent advisory board and an experienced outside management firm."<ref name="rooks"/> It is working with Native American Health Management, LLC (NAHM), to gain training for staff and oversight of operations until people gain experience. |
||
====Alcoholism==== |
====Alcoholism==== |
||
{{Update|section|date=February 2017}} |
|||
Because of historic problems with alcohol use by its members, the Oglala Sioux Tribe has prohibited the sale and possession of alcohol on the Pine Ridge Reservation since 1832. The exception was a brief period in the 1970s when on-reservation sales were tried. The town of [[Whiteclay, Nebraska]] (just over the South Dakota-Nebraska border) has approximately 12 residents and four liquor stores, which sold over 4.9 million 12-ounce cans of beer in 2010 almost exclusively to Oglala Lakota from the reservation. This contributes to widespread alcoholism on the reservation, which is estimated to affect 85 percent of the families.<ref name=Woodward/> Tribal police estimate that 90 percent of the crimes are alcohol-related.<ref name=Woodward/> |
|||
{{See also|Alcohol and Native Americans}} |
|||
Alcoholism is widespread on the reservation, affecting an estimated 85 percent of the families.<ref name=Woodward/> Tribal police estimate that 90 percent of the crimes are alcohol-related.<ref name=Woodward/> |
|||
Because of historic problems with alcohol use by its members, the Oglala Sioux Tribe has prohibited the sale and possession of alcohol on the Pine Ridge Reservation since 1832. The exception was a brief period in the 1970s when on-reservation sales were tried. The town of [[Whiteclay, Nebraska]] (just over the South Dakota-Nebraska border), previously had approximately 12 residents and four liquor stores, which sold over 4.9 million 12-ounce cans of beer in 2010 almost exclusively to Oglala Lakota from the reservation (nearly 170 cans per person). The Whiteclay liquor stores were shut down by the state of Nebraska in 2017, though the store owners are appealing to have the stores reopened.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Kent|first1=Jim|title=With Alcoholism Rampant On Nearby Reservation, Nebraska Shuts Town's Liquor Stores|url=https://www.npr.org/sections/thesalt/2017/05/11/527832897/with-alcoholism-rampant-on-nearby-reservation-nebraska-shuts-towns-liquor-stores|website=npr.org|publisher=National Public Radio|access-date=19 December 2017}}</ref> |
|||
=====Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder===== |
|||
[[Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder]] (FASD) is a spectrum of anatomical structural anomalies, and behavioral, neurocognitive disabilities resulting from the exposure of a fetus to alcohol in the womb. The most severe manifestation within this spectrum is [[Fetal Alcohol Syndrome]] (FAS).<ref>Hoyme HE, May PA, Kalberg WO, Kodituwakku P, ''et al.'' "A practical clinical approach to diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: clarification of the 1996 institute of medicine criteria", ''Pediatrics'', 2005 Jan;115(1):39-47. PMID 15629980 Free article</ref> One in four children born on the reservation are diagnosed with either FASD or FAS.<ref>''Congressional Record,'' V. 146, Pt. 10, July 10, 2000 to July 17, 2000 By Congress, p.13912</ref> |
|||
[[Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder]] (FASD) is a spectrum of anatomical structural anomalies, and behavioral, neurocognitive disabilities resulting from the exposure of a fetus to alcohol in the womb. The most severe manifestation within this spectrum is [[Fetal Alcohol Syndrome|fetal alcohol syndrome]] (FAS).<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Hoyme | first1 = HE | last2 = May | first2 = PA | last3 = Kalberg | first3 = WO | last4 = Kodituwakku | first4 = P | display-authors = etal | year = 2005 | title = A practical clinical approach to diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: clarification of the 1996 institute of medicine criteria | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 115 | issue = 1| pages = 39–47 | pmid = 15629980 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2004-0259 | pmc = 1380311 }}</ref> A quarter of the children born on the reservation are diagnosed with either FASD or FAS, resulting in lifelong challenges.<ref>''Congressional Record,'' V. 146, Pt. 10, July 10, 2000 to July 17, 2000 By Congress, p.13912</ref> |
|||
===Education=== |
|||
{{Expand section|date=May 2011}} |
|||
The state of education on the reservation is severely lacking in multiple areas. The school drop-out rate is over 70%, and the teacher turnover rate is eight times that of the U.S. national average. [[Red Cloud Indian School]] is located in the area. |
|||
===Education=== |
|||
In 1971 the tribe founded the [[Oglala Lakota College]], one of the earliest [[Tribal colleges and universities|tribal colleges]] in the nation, and part of Native American institution building of the last 40 years. First started as a two-year community college, it has expanded to offer 4-year baccalaureate degrees, as well as a master's in Lakota leadership. It is operated by tribal people, with a tribal board. In 2011, it had an enrollment of 1,400.<ref>[http://www.olc.edu/about/ About: "Oglala Lakota College"] Official Website, 2001-2010</ref> Since 1994, tribal colleges have been classified as [[land-grant college]]s by the U.S. Congress. |
|||
The state of education on the reservation is severely lacking in multiple areas. The school drop-out rate is{{when|date=December 2022}} over 70%, and the teacher turnover rate is eight times that of the U.S. national average.{{citation needed|date=December 2022}} |
|||
In 1971 the tribe founded the [[Oglala Lakota College]], one of the earliest [[Tribal colleges and universities|tribal colleges]] in the nation, and part of Native American institution building of the last 40 years. First started as a two-year community college, it has expanded to offer four-year baccalaureate degrees, as well as a master's in Lakota leadership. It is operated by tribal people, with a tribal board. In 2011, it had an enrollment of 1,400.<ref>[http://www.olc.edu/about/ About: "Oglala Lakota College"] Official Website, 2001-2010</ref> Since 1994, tribal colleges have been classified as [[land-grant college]]s by the U.S. Congress. |
|||
Among its courses has been "Aboriginal [[Restorative Justice]]", taught by Harley and Sue Eagle ([[Saulteaux]] and [[Sioux#Linguistics|Dakota]]), program coordinators of the Oglala Lakota Nation [[Mennonite]] Central Committee Voluntary Service Unit. Since the early 2000s (decade), they have been called upon at the reservation to use restorative justice in many situations, as did previous coordinators.<ref>[http://www.restorativejustice.org/10fulltext/eagleharley "A Journey in Aboriginal Restorative Justice"], ''Conciliation Quarterly'', Vol. 20 No. 3, March 2002, reprinted with permission of Mennonite Conciliation Service at Restorative Justice Online Website, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> The OST's commitment to using this process is reflected in its planning for a restorative justice courtroom in the new tribal justice center. |
|||
[[Oglala Lakota County School District]] (formerly the Shannon County School District) serves all areas in Oglala Lakota County.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/DC20BLK/st46_sd/county/c46102_oglala_lakota/DC20BLK_C46102.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP (INDEX): Oglala Lakota County, SD|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]|accessdate=2023-01-01}} - [https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/PL20/st46_sd/schooldistrict_maps/c46102_oglala_lakota/DC20SD_C46102_SD2MS.txt See text list]</ref> It includes: |
|||
;Schools operating on the Reservation: |
|||
*[[Lakota Tech High School]] |
|||
*American Horse School (K-8) |
|||
*Batesland Elementary School (preK-8th) |
*Batesland Elementary School (preK-8th) |
||
*Crazy Horse School (K-12th) [http://www.crazyhorse.k12.sd.us/] |
|||
*Lakota Waldorf School |
|||
*Little Wound School |
|||
*Loneman Day School (Isnawica Owayawa) |
|||
*Porcupine School |
|||
*Red Shirt School |
*Red Shirt School |
||
*Rockyford Elementary School |
*Rockyford Elementary School |
||
*Wolf Creek Elementary School |
*Wolf Creek Elementary School |
||
*Wounded Knee District School |
|||
[[Bennett County School District 03-1]] serves areas in Bennett County.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/PL20/st46_sd/schooldistrict_maps/c46007_bennett/DC20SD_C46007.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Bennett County, SD|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]|accessdate=2023-01-01}}</ref> |
|||
*Little Wound High School |
|||
*Shannon County Virtual High School |
|||
The [[Kadoka School District 36-2]] serves the portion of Jackson County that is a part of the reservation.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/PL20/st46_sd/schooldistrict_maps/c46071_jackson/DC20SD_C46071.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Jackson County, SD|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]|accessdate=2023-01-01}}</ref> |
|||
*Pine Ridge School (K-12) |
|||
The portion in Sheridan County, Nebraska is zoned to [[Gordon-Rushville Public Schools]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/PL20/st31_ne/schooldistrict_maps/c31161_sheridan/DC20SD_C31161.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Sheridan County, NE|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]|accessdate=2023-01-01}}</ref> |
|||
[[Bureau of Indian Education]] (BIE)-operated and affiliated schools include: |
|||
*[[Crazy Horse School]] (K-12th)<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.crazyhorse.k12.sd.us/|title=Home|website=www.crazyhorse.k12.sd.us}}</ref> |
|||
*[[Little Wound School]] (K-12) |
|||
*[[Pine Ridge School]] (K-12) |
|||
*American Horse School (K-8)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.bie.edu/schools/directory/american-horse-school|title=American Horse School|publisher=[[Bureau of Indian Education]]|accessdate=2021-08-01}}</ref> |
|||
*Porcupine School (K-8)<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.bie.edu/schools/directory/pahin-sinte-owayawa-school-porcupine-school|title=BIE Schools Directory | Bureau of Indian Education}}</ref> |
|||
*Wounded Knee District School<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.bie.edu/schools/directory/wounded-knee-district-school|title=BIE Schools Directory | Bureau of Indian Education}}</ref> |
|||
Other K-12 Schools operating on the Reservation include: |
|||
*Lakota Waldorf School |
|||
*Loneman Day School (Isnawica Owayawa) |
|||
*Head Start at Oglala Lakota College |
*Head Start at Oglala Lakota College |
||
Private schools include: |
|||
*[[Red Cloud Indian School]] that consists of three schools: Our Lady of Lourdes School (K–8), Red Cloud Elementary (K-8) and Red Cloud High School. |
|||
*Red Cloud Indian School |
|||
*Our Lady of Lourdes School - (K-8th) [http://www.redcloudschool.org/ourladyoflourdes/] |
|||
==== Lakota Immersion Childcare ==== |
|||
*Red Cloud High School - operated by the Jesuits [http://www.redcloudschool.org/page.aspx?pid=397] |
|||
Globally, there are currently only 2,000 [[Lakota language]] speakers, and fewer than 1,000 at Pine Ridge.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.minneapolisfed.org/publications/community-dividend/early-childhood-native-language-immersion-develops-minds-revitalizes-cultures|title=Early childhood Native language immersion develops minds, revitalizes cultures {{!}} Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis|last=Grunewald|first=Rob|website=www.minneapolisfed.org|access-date=2018-11-19}}</ref> The age of the average Lakota speaker is 60, making it a "critically endangered" language.<ref name="The Seattle Times">{{Cite news|url=https://www.seattletimes.com/nation-world/lakota-language-immersion-for-toddlers-aims-to-revive-sioux-culture/|title=Lakota language immersion for toddlers aims to revive Sioux culture|date=2012-10-20|work=The Seattle Times|access-date=2018-11-19|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.usnews.com/news/best-states/south-dakota/articles/2018-06-04/lakota-language-immersion-expanding-in-rapid-city|title=Lakota Language Immersion Expanding in Rapid City|work=U.S. News|access-date=19 November 2018}}</ref> |
|||
In the fall of 2012, a new program was founded to combat the loss of the language and create a young generation of fluent Lakota speakers. Peter Hill, a former elementary teacher at the reservation who speaks Lakota, started the early childcare language immersion program from his own basement, initially serving five students with crowdsourced funding.<ref name="The Seattle Times"/><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.csmonitor.com/EqualEd/2018/0228/To-keep-the-Dakota-language-alive-a-young-woman-looks-to-preschoolers|title=To keep the Dakota language alive, a young woman looks to preschoolers|date=2018-02-28|work=[[The Christian Science Monitor]]|access-date=2018-11-19|issn=0882-7729}}</ref><ref name="Lockett">{{Cite news|url=http://listen.sdpb.org/post/pine-ridge-immersions-program-creates-lakota-speakers|title=Pine Ridge Immersions Program Creates Lakota Speakers|last=Lockett|first=Chynna|access-date=2018-11-19|language=en}}</ref> In the program, students and teachers speak exclusively Lakota, with children eventually learning English as a second language. Over the last six years, the childcare program has expanded significantly to serve students ages one to five, and has additionally begun offering kindergarten and first grade.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://theoutline.com/post/3615/lakota-modern-language-peter-hill?zd=1&zi=tkutosw7|title=How do you say "smartphone" in Lakota?|work=The Outline|access-date=2018-11-19|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Citation|last=carletoncollege|title=Lakota Language Initiative at Pine Ridge|date=2017-11-29|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5NevgPgVvEU| archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211117/5NevgPgVvEU| archive-date=2021-11-17 | url-status=live|access-date=2018-11-19}}{{cbignore}}</ref> A continuing challenge for the school is creating teaching materials, since textbooks and other teaching resources are not typically printed in Lakota. Thus, creating new materials like children's books, apps, or videos, as well as translation of existing works into the language is crucial.<ref name="Lockett"/> |
|||
Beyond the immersion childcare, other efforts are underway to bring Lakota into community members' lives in relevant ways: basketball games are frequently announced in Lakota, after new words were coined and the coach began using them in practices and drills with the teams. The first news website written entirely in Lakota was launched in 2016.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.dailyyonder.com/first-ever-lakota-news-website-helps-keep-language-alive-and-relevant/2016/06/14/13574/|title=First-Ever Lakota News Website Helps Keep Language Alive and Relevant - Daily Yonder|website=www.dailyyonder.com|date=14 June 2016|language=en-US|access-date=2018-11-19}}</ref> |
|||
===Economy=== |
===Economy=== |
||
{{Update|section|date=February 2017}} |
|||
[[File:Kevin pourier.jpg|thumb|left|Kevin Pourier, contemporary Oglala artist, maintains a studio in the Medicine Root District of Pine Ridge]] |
|||
[[File:Kevin pourier.jpg|thumb|Kevin Pourier, contemporary Oglala artist, maintains a studio in the Medicine Root District of Pine Ridge.]] |
|||
As of 2011, the reservation has little economic development or industry. No banks or discount stores are located on the reservation.<ref name=Resroad/> But, its people receive $80 million annually in federal monies, such as Social Security and veterans benefits; they spend most of this money largely in stores located off the reservation in Nebraska border towns, so it creates no benefit for the tribe. As the journalist Stephanie Woodward noted, little money changes hands within the reservation.<ref name=Woodward/> As an example of the money that goes outside the reservation to border towns, the owner of Whiteclay's grocery store, Arrowhead Foods, said he "did more than a million dollars in business last year, with an entirely Native American clientele."<ref name=Woodward>[http://100r.org/2012/02/gold-mines-in-hell/ Stephanie Woodward, "Gold Mines in Hell"], 100Reporters, February 2012</ref> Similarly, Nebraska State Senator [[LeRoy J. Louden]], whose district includes Whiteclay, noted the recent construction of a Wal-Mart superstore at [[Chadron, Nebraska]], another border town. He said, "That store was built because of the reservation."<ref name=Woodward/> |
|||
As of 2011, the reservation has little economic development or industry. No discount stores are located on the reservation.<ref name=Resroad/> Though its people receive $80 million per annum in federal monies, such as Social Security and veterans benefits, most of this money is spent largely in stores located off the reservation in Nebraska border towns, creating no net benefit for the tribe. As the journalist Stephanie Woodward noted, little money changes hands within the reservation.<ref name=Woodward/> |
|||
As an example of the money that goes outside the reservation to border towns, the owner of Whiteclay's grocery store, Arrowhead Foods, said he "did more than a million dollars in business last year, with an entirely Native American clientele."<ref name=Woodward>[http://100r.org/2012/02/gold-mines-in-hell/ Stephanie Woodward, "Gold Mines in Hell"], 100Reporters, February 2012</ref> Similarly, Nebraska State Senator [[LeRoy J. Louden]], whose district includes Whiteclay, noted the recent construction of a [[Walmart]] superstore at [[Chadron, Nebraska]], another border town. He said, "That store was built because of the reservation."<ref name=Woodward/> |
|||
The tribe has prohibited sale and consumption of alcohol on the reservation, but Pine Ridge residents support four liquor stores at Whiteclay, which in 2010 paid federal and state excise taxes (included in liquor’s sale price) of $413,932, according to the state liquor commission.<ref name=Woodward/> Some residents have argued that the continuing rate of alcoholism on the reservation shows the failure of the prohibition policy. They say that if the tribe legalized alcohol sales, it could keep much of the revenues now flowing to Nebraska and to state and federal taxes, and use such monies to bolster the reservation's economy and health care services, including building a much-needed detoxification facility and rehab services. |
|||
The tribe has prohibited the sale and consumption of alcohol on the reservation. Still, Pine Ridge residents support four liquor stores across reservation borders in the town of [[Whiteclay, Nebraska]] In 2010, these businesses paid $413,932 in federal and state excise taxes on the sale of liquor, according to the Nebraska State Liquor Commission.<ref name=Woodward/> Some residents have argued that the climbing rate of alcoholism on the reservation shows the failure of the prohibition policy. They argue that if the tribe legalized alcohol sales, it could keep much of their people's wealth from flowing to Nebraska, allowing for such monies to instead be directed toward the reservation's economy and health care services and new projects like building a detoxification facility and rehab clinic. |
|||
Despite the lack of formal employment opportunities on Pine Ridge, considerable agricultural production is taking place on the reservation, yet only a small percentage of the tribe directly benefit from this, as land is leased to agricultural producers. According to the [[USDA]], in 2002 there was nearly $33 million in receipts from agricultural production on Pine Ridge. Less than one-third of that income went to members of the tribe.<ref>[http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/amindian.pdf USDA 2002 "Census of Agriculture for Native American Reservations"]</ref> |
|||
Despite the lack of formal employment opportunities on Pine Ridge, considerable agricultural production takes place on the reservation. Only a small percentage of the tribe directly benefits from agriculture, as land is leased to agricultural producers. According to the [[USDA]], in 2002 there was nearly $33 million in receipts from agricultural production on Pine Ridge. Less than one-third of that income went to members of the tribe.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/amindian.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070615033245/http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/amindian.pdf|url-status=dead|title=USDA 2002 "Census of Agriculture for Native American Reservations"|archive-date=June 15, 2007}}</ref> |
|||
Most employment on the reservation is provided by community institutions, such as Oglala Lakota College, a tribal college, and other schools; the [[Bureau of Indian Affairs]] (BIA); and the U.S. [[Indian Health Service]] (IHS). In June 2011, the tribe broke ground for a 60-bed nursing home facility, developed in collaboration with state officials from South Dakota and Nebraska. Its costs are to be covered by the federal government.<ref>[http://www.oglalalakotanation.org/OLN/Photos_Nursing_Home_Groundbreaking.html "OST Breaks Ground for Nursing Home Facility"], Oglala Lakota Nation website, accessed 7 July 2011</ref> The tribe is working on a justice center and has advertised an art competition for works for its spaces, to include the tribal courts and a [[restorative justice]] courtroom. |
|||
Most employment on the reservation is provided by community institutions, such as the tribal Oglala Lakota College, and other schools; the [[Bureau of Indian Affairs]] (BIA); and the U.S. [[Indian Health Service]] (IHS). In October 2016, the tribe opened an 80-bed nursing home; at full operation, it should employ 100 staff. The tribe is working on building a justice center and has advertised an art competition to decorate its spaces, including the tribal courts and a [[restorative justice]] courtroom. |
|||
Various enterprises are owned by the Oglala Sioux tribe. These include the Prairie Wind Casino, a Parks and Recreation Department, guided hunting, and cattle ranching and farming.<ref name=OSTCommunityProfile>{{cite web|url=http://www.mnisose.org/profiles/oglala.htm|title=Oglala Sioux Tribe Community Environmental Profile|author=staff|year=1997|work=Mni Sose Intertribal Water Rights Coalition, Inc.|accessdate=2007-10-26}}</ref> The Oglala Sioux Tribe also operates the White River Visitor Center near the [[Badlands National Park]].<ref name=NPSBadlands>{{cite web|url=http://www.nps.gov/badl/planyourvisit/hours.htm|title=Badlands National Park Operating Hours & Seasons|author=staff|date=current|work=U.S. Department of the Interior|accessdate=2007-10-26}}</ref> There is one radio station, [[KILI|KILI-FM]] in [[Porcupine, South Dakota|Porcupine]]. |
|||
Enterprises owned by the Oglala Sioux tribe include the Prairie Wind Casino, a Parks and Recreation Department, guided hunting, and cattle ranching and farming.<ref name=OSTCommunityProfile>{{cite web|url=http://www.mnisose.org/profiles/oglala.htm|title=Oglala Sioux Tribe Community Environmental Profile|author=staff|year=1997|work=Mni Sose Intertribal Water Rights Coalition, Inc.|access-date=2007-10-26|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071018231642/http://www.mnisose.org/profiles/oglala.htm|archive-date=2007-10-18}}</ref> The Oglala Sioux Tribe also operates the White River Visitor Center near the [[Badlands National Park]].<ref name=NPSBadlands>{{cite web|url=http://www.nps.gov/badl/planyourvisit/hours.htm|title=Badlands National Park Operating Hours & Seasons|author=staff|work=U.S. Department of the Interior|access-date=2007-10-26}}</ref> It has one radio station, [[KILI|KILI-FM]] in [[Porcupine, South Dakota|Porcupine]]. |
|||
In 1973 at the time of the Wounded Knee Incident, not one Native American worked for a South Dakota newspaper. In 1981 the Lakota [[journalist]] [[Tim Giago]] founded and published the independent ''[[Lakota Times]]'' on the reservation. (Most such newspapers have been owned by tribes.)<ref name=carrier>[http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?f=/c/a/2007/12/23/INVHTSVHP.DTL#ixzz1QhzrerHL Jim Carrier, "South Dakota Indian journalist gave voices to a people long ignored"], ''San Francisco Chronicle,'' 23 December 2007, accessed 29 June 2011</ref> He renamed it ''[[Indian Country Today]]'' in 1992, as he was providing more national coverage of Native American news. In 1998 he sold the paper to the [[Oneida Nation]]; it was then the largest independent Native American paper in the country. He founded the [[Native American Journalists Association]] (NAJA) and has worked to recruit Native American students into journalism through its foundation, as well as to establish Indian studies in journalism schools.<ref name=free>[http://www.nieman.harvard.edu/reports/article/100616/Freedom-of-the-Press-in-Indian-Country.aspx Tim Giago, "Freedom of the Press in Indian Country"], ''Nieman Reports: Covering Indian Country,'' Fall 2005, accessed 29 June 2011</ref> |
|||
In 1973 at the time of the Wounded Knee Incident, not one Native American worked for a South Dakota newspaper. In 1981 the Lakota [[journalist]] [[Tim Giago]] founded and published the independent ''[[Lakota Times]]'' on the reservation. (Most such newspapers have been owned by tribal governments.)<ref name=carrier>[http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?f=/c/a/2007/12/23/INVHTSVHP.DTL#ixzz1QhzrerHL Jim Carrier, "South Dakota Indian journalist gave voices to a people long ignored"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091011124341/http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?f=%2Fc%2Fa%2F2007%2F12%2F23%2FINVHTSVHP.DTL |date=2009-10-11 }}, ''San Francisco Chronicle,'' 23 December 2007, accessed 29 June 2011</ref> He renamed it ''[[Indian Country Today]]'' in 1992, as he was providing more national coverage of Native American news.<ref name=free/> |
|||
Connie Smith started the ''[[Lakota Country Times]]'', a weekly newspaper which she owns. It is the official legal newspaper for the Pine Ridge and Rosebud reservations. It also publishes material online. In 2009 it won first place for general excellence of its website from NAJA, and in 2010 won three prizes, including two for best articles.<ref>[http://www.lakotacountrytimes.com/ "Lakota Country Times Staff Win Three Awards"], ''Lakota Country Times'', 4 August 2010, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> |
|||
In 1998 he sold the paper to the [[Oneida Nation]]; it was then the largest independent Native American paper in the country. It continues to operate the paper as part of a media network; ''Indian Country Today'' features regular political coverage that notes the increasing number of Native Americans gaining office at the local and state levels. Giago founded the [[Native American Journalists Association]] (NAJA) and has worked to recruit Native American students into journalism through its foundation, as well as to establish Indian studies in journalism schools.<ref name=free>[http://www.nieman.harvard.edu/reports/article/100616/Freedom-of-the-Press-in-Indian-Country.aspx Tim Giago, "Freedom of the Press in Indian Country"], ''Nieman Reports: Covering Indian Country,'' Fall 2005, accessed 29 June 2011</ref> |
|||
Lakota Federal Credit Union, established to serve the financial needs of residents of the reservation, was established in 2012.<ref>{{cite press release|publisher=[[National Credit Union Administration]]|date=August 29, 2012|title=NCUA Charters Lakota Federal Credit Union|url=http://www.ncua.gov/News/Pages/NW20120829LakotaFCU.aspx}}</ref> |
|||
Connie Smith started the ''[[Lakota Country Times]],'' a weekly newspaper which she owns. It is the official legal newspaper for the Pine Ridge and Rosebud reservations. It also publishes material online. In 2009 it won first place for general excellence of its website from NAJA, and in 2010 won three prizes, including two for best articles.<ref>[http://www.lakotacountrytimes.com/ "Lakota Country Times Staff Win Three Awards"], ''Lakota Country Times'', 4 August 2010, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> |
|||
Lakota Federal Credit Union, established to serve the financial needs of residents of the reservation, was established in 2012.<ref>{{cite press release|publisher=[[National Credit Union Administration]] |date=August 29, 2012 |title=NCUA Charters Lakota Federal Credit Union |url=http://www.ncua.gov/News/Pages/NW20120829LakotaFCU.aspx |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120901213626/http://www.ncua.gov/News/Pages/NW20120829LakotaFCU.aspx |archive-date=September 1, 2012 }}</ref> |
|||
====Industrial hemp==== |
====Industrial hemp==== |
||
[[File:Bloc de chanvre ep 15cm.gif|thumb |
[[File:Bloc de chanvre ep 15cm.gif|thumb|[[Industrial hemp]] is used to make [[Hempcrete]], a material used for building [[concrete block]]s, as well as other products. The Oglala were denied their [[Sovereignty|sovereign right]] to grow industrial hemp by the [[federal government of the United States]].]] |
||
After doing research and noting the worldwide market for hemp, in July 1998, the Tribal Council approved '[[industrial hemp]] agriculture' for the reservation. With demand high for the crop, three Lakota farmers, Tom Cook, his wife Afraid of Bear and American Horse grandson of [[American Horse|Chief American Horse]] formed the Slim Butte Land-Use Association.<ref name=clarren>[http://www.hcn.org/issues/221/11044/print_view Rebecca Clarren, "Seed in the ground"], ''High Country News'', n.d., accessed 5 June 2011</ref> To emphasize the issue of Sioux sovereignty in land use, they publicly announced the first planting of industrial hemp seeds on April 29, 2000, on the 132nd anniversary of the signing of the 1868 Fort Laramie Treaty, which established the reservation. The Association believed production of industrial hemp-based concrete could help solve the severe shortage of suitable dwellings on the reservation, as it is a sustainable construction material, and work for the unemployed. Hemp can also be processed to yield oil for cooking and other products.<ref>[http://www.hempology.org/CURRENT%20HISTORY/SIOUX%20HEMP%20ARTICLE%20%26%20PIX%20HTML/2000%3BSIOUX%20PLANT%20HEMP.html OGLALA SIOUX TRIBE PLANTS INDUSTRIAL HEMP CROP], Hempology</ref> |
After doing research and noting the worldwide market for hemp, in July 1998, the Tribal Council approved '[[industrial hemp]] agriculture' for the reservation. With demand high for the crop, three Lakota farmers, Tom Cook, his wife Loretta Afraid of Bear and American Horse, grandson of [[American Horse|Chief American Horse]], formed the Slim Butte Land-Use Association.<ref name=clarren>[http://www.hcn.org/issues/221/11044/print_view Rebecca Clarren, "Seed in the ground"], ''High Country News'', n.d., accessed 5 June 2011</ref> To emphasize the issue of Sioux sovereignty in land use, they publicly announced the first planting of industrial hemp seeds on April 29, 2000, on the 132nd anniversary of the signing of the 1868 Fort Laramie Treaty, which established the reservation. The Association believed production of industrial hemp-based concrete could help solve the severe shortage of suitable dwellings on the reservation, as it is a sustainable construction material, and work for the unemployed. Hemp can also be processed to yield oil for cooking and other products.<ref>[http://www.hempology.org/CURRENT%20HISTORY/SIOUX%20HEMP%20ARTICLE%20%26%20PIX%20HTML/2000%3BSIOUX%20PLANT%20HEMP.html OGLALA SIOUX TRIBE PLANTS INDUSTRIAL HEMP CROP], Hempology</ref> |
||
Congress in 1968 prohibited the cultivation of ''[[Cannabis]]''-related crops, including [[hemp]], as part of anti-drug legislation, although hemp does not have the psychoactive properties of [[Cannabis (drug)|cannabis as a drug]]. Industrial hemp is legal in Canada.<ref name=pov/> The law in the U.S. is enforced by the [[Drug Enforcement Administration]]. In August 2000 and July 2001, federal DEA agents destroyed industrial hemp crops on the Pine Ridge reservation.<ref name=pov>[ |
Congress in 1968 prohibited the cultivation of ''[[Cannabis]]''-related crops, including [[hemp]], as part of anti-drug legislation, although hemp does not have the psychoactive properties of [[Cannabis (drug)|cannabis as a drug]]. Industrial hemp is legal in Canada.<ref name=pov/> The law in the U.S. is enforced by the [[Drug Enforcement Administration]] (DEA). In August 2000 and July 2001, federal DEA agents destroyed industrial hemp crops on the Pine Ridge reservation.<ref name=pov>[https://www.pbs.org/pov/standing/film_description.php "Standing Silent Nation: Film Description"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151019103857/http://www.pbs.org/pov/standing/film_description.php |date=2015-10-19 }}, ''POV'', PBS, 3 July 2007, accessed 5 June 2011</ref> After the raid destroyed his crops, the farmer [[Alex White Plume]]<ref name=pov/> appealed a DEA court order that prohibited his growing the crop, but the 8th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed the district court ruling in ''United States v. White Plume'' (8th Cir. 2006), that the Lakota had to comply with DEA registration process and get a permit to cultivate hemp.<ref name=brokaw>[http://indiancountrynews.net/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=885&Itemid=33 Chet Brokaw, "Fight with DEA over hemp leaves White Plume broke"], ''Indian Country News'', July 2007, accessed 5 June 2011</ref> The former crop is currently growing wild in the area.<ref name=fuller2012/> |
||
The [[North Dakota]] legislature has authorized hemp growing statewide and issued the nation's first two state licenses to grow hemp. The licensed farmers may face DEA legal problems if they do not acquire DEA permits. As the DEA had not yet acted on their requests, in June 2007 the men filed a lawsuit seeking federal court permission to grow the crop without being subject to federal criminal charges.<ref name=brokaw/> |
The [[North Dakota]] legislature has authorized hemp growing statewide and issued the nation's first two state licenses to grow hemp. The licensed farmers may face DEA legal problems if they do not acquire DEA permits. As the DEA had not yet acted on their requests, in June 2007 the men filed a lawsuit seeking federal court permission to grow the crop without being subject to federal criminal charges.<ref name=brokaw/> |
||
{{clear}} |
|||
====Private enterprise at Pine Ridge==== |
====Private enterprise at Pine Ridge==== |
||
Members of the tribe have developed |
Members of the tribe have developed a variety of private enterprises, from arts to modern technologies. Numerous artists maintain private studios and use diverse media in both traditional Lakota artforms, such as [[parfleche]] and beadwork, and contemporary styles. |
||
Oglala are becoming involved |
The Oglala are becoming involved in start-up tech companies, such as Lakota Solar Enterprises (LSE), started on the Pine Ridge Reservation in 2006 by Henry Red Cloud (a fifth-generation descendant of Chief Red Cloud) with help from the non-profit org Trees, Water and People. Lakota Solar Enterprises is active in education and training for the advancement of renewable and sustainable energy and technology with a focus of bringing employment opportunities to members of OST as well as other tribal nations throughout the United States. Such technologies include: solar heating and electricity; compressed earth blocks for structural use; geothermal heating; solar assisted irrigated farming, cellulose insulation, and wind generated power. |
||
==Tourism |
==Tourism== |
||
[[File:Chief Little Wound and Family.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Little Wound|Chief Little Wound]] with his wife and son |
[[File:Chief Little Wound and Family.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Little Wound|Chief Little Wound]] with his wife and son, 1899]] |
||
(1899 Heyn Photo)]] |
|||
*'''History''': |
|||
**'''Wounded Knee Massacre and burial site'''. The events at Wounded Knee represents a significant event in Native American and United States history; it was the last significant clash between Native Americans and U.S. troops and was considered to be the closing of the Western Frontier. The trail that Spotted Elk and his band took on the reservation is marked with signs, including the spot where they surrendered to U.S. troops and were escorted to a site by Wounded Knee Creek. |
|||
**'''Stronghold Table''': a remote mesa in what is now the Stronghold (South) Unit of [[Badlands National Park]], which is administered by the tribe. Site of the last [[Ghost Dance]]s prior to the Wounded Knee Massacre. |
|||
**'''Red Cloud Cemetery''': location of the grave of Chief Red Cloud, as well as [[Bloody Knife]] (1840–1876), Chief of the Indian Scouts of the 7th Cavalry under General George Armstrong Custer. Bloody Knife was killed at the Battle of the Little Bighorn while assigned to Major [[Marcus Reno]]'s detachment. |
|||
=== History === |
|||
*'''Cultural tourism''': |
|||
**'''Oglala Lakota Nation Pow Wow''', an annual [[Pow wow]] featuring dancers from various parts of the U.S. |
|||
*Wounded Knee Massacre and burial site. The events at Wounded Knee represents a significant event in Native American and United States history; it was the last significant clash between Native Americans and U.S. troops and was considered to be the closing of the Western Frontier. The trail that Spotted Elk and his band took on the reservation is marked with signs, including the spot where they surrendered to U.S. troops and were escorted to a site by Wounded Knee Creek. |
|||
**'''Badlands Ranch Resort''': Started as private enterprise, it was purchased in July 2009 by the Oglala Sioux Tribe. Located at the base of Badlands National Park, the resort features an RV park, cabins and rooms in the main lodge. |
|||
*Stronghold Table: a remote mesa in what is now the Stronghold (South) Unit of [[Badlands National Park]], which is administered by the tribe. Site of the last [[Ghost Dance]]s prior to the Wounded Knee Massacre. |
|||
*Red Cloud Cemetery: location of the grave of Chief Red Cloud, as well as [[Bloody Knife]] (1840–1876), Chief of the Indian Scouts of the 7th Cavalry under General George Armstrong Custer. Bloody Knife was killed at the Battle of the Little Bighorn while assigned to Major [[Marcus Reno]]'s detachment. |
|||
=== Cultural tourism === |
|||
*Oglala Lakota Nation Pow Wow, an annual [[pow wow]] featuring dancers from various parts of the U.S. |
|||
*Badlands Ranch Resort: Started as private enterprise, it was purchased in July 2009 by the Oglala Sioux Tribe. It is located at the base of Badlands National Park. |
|||
=== Ecotourism === |
|||
*'''[[Ecotourism]]''': |
|||
The Oglala Sioux Park & Recreation Authority offers eco-tours and hunting trips on the reservation as well as engaging in wildlife conservation work. |
The Oglala Sioux Park & Recreation Authority offers eco-tours and hunting trips on the reservation as well as engaging in wildlife conservation work. |
||
* |
*Geology: The Badlands (''Makhóšiča'')- formed by erosion, represent over 65 million years of the earth's geological history starting from the late Cretaceous when the entire middle of the United States was covered by the Western Interior Seaway. The Pine Ridge area contain one of the largest deposits of mammal fossils from the [[Oligocene|Oligocene epoch]]. |
||
* |
*Paleontology: One of the most complete fossil accumulations in North America is found within the badlands. The rocks and fossils preserve evidence of ancient ecosystems and give scientists clues about how early mammal species lived. |
||
* |
*Flora: Pine Ridge is located in the [[Great Plains]] region, which encompasses the nation's largest grassland ecosystem. the northern portion of the reservation and Badlands National Park contain one of the largest expanses of [[mixed grass prairie]] in the United States. |
||
*Fauna: In addition to bison, the reservation is also home to [[pronghorn]] (''Antilocapra americana'').<ref>Hawes, Alex. "Pronghorns — Survivors of the American Savanna," ''Zoogoer,'' November/December 2001</ref> There is a colony of endangered [[black-footed ferret]], the only ferret native to North America, in the [[Conata Basin]], which is also home to [[black-tailed prairie dog]]s. |
|||
*[[White River (Missouri River)|White River]]: A [[Missouri River]] tributary that flows {{convert|580|mi|km}}<ref name=NHD>{{cite web|publisher=United States Geological Survey|title=National Hydrography Dataset |url=http://viewer.nationalmap.gov/viewer/ |access-date=March 30, 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120329155652/http://viewer.nationalmap.gov/viewer/ |archive-date=March 29, 2012 }}</ref> through [[Nebraska]] and [[South Dakota]]. A variety of fish species suitable for [[Recreational fishing|sportfishing]] live in the river.{{citation needed|date=February 2018}} |
|||
=== Casino === |
|||
*'''Casino''': Prairie Wind Casino which began operation in 1994 in three doublewide trailers, was upgraded with the completion of a $20 million casino, a 78-room hotel and a full-service restaurant in early 2007. The casino provides 250 jobs, most held by tribal residents, with revenues helping support education and social welfare efforts.<ref name=NewPrairieWind>{{cite web|url=http://www.rapidcityjournal.com/articles/2007/05/10/news/top/news00h_prairie_wind_casino_feature.txt|title=New complex ups ante for Prairie Wind Casino|last=Daly|first=Dan|date=2007-05-10|work=Rapid City Journal|accessdate=2007-10-26}}</ref> |
|||
Prairie Wind Casino, which began operation in 1994 in three doublewide trailers, was upgraded with the completion of a $20 million casino, a 78-room hotel and a full-service restaurant in early 2007. The casino provides 250 jobs, most held by tribal residents, with revenues helping support education and social welfare efforts.<ref name=NewPrairieWind>{{cite web|url=http://www.rapidcityjournal.com/articles/2007/05/10/news/top/news00h_prairie_wind_casino_feature.txt|title=New complex ups ante for Prairie Wind Casino|last=Daly|first=Dan|date=2007-05-10|work=Rapid City Journal|access-date=2007-10-26}}{{dead link|date=March 2017}}</ref> |
|||
{{Wide image|Badlands National Park Butte.jpg|1200px|A type of [[mesa]] found in the [[Badlands National Park]] and along the northern border of the reservation}} |
{{Wide image|Badlands National Park Butte.jpg|1200px|A type of [[mesa]] found in the [[Badlands National Park]] and along the northern border of the reservation}} |
||
== |
==Geography== |
||
[[File:Badlands in South Dakota.jpg|thumb|[[Badlands]] in the northern portion of Pine Ridge Indian Reservation]] |
|||
<center>{{Weather box |
|||
Located in southwest South Dakota, the reservation takes {{convert|3400|sqmi|sqkm}} of space. The nearest urban center, [[Rapid City, South Dakota]], is {{convert|120|mi|km}} from the center of the reservation.<ref name="Resroad" /> |
|||
The most [[Pole of inaccessibility|inland point in North America]] is located within the reservation, near the town of [[Allen, South Dakota|Allen]], and is {{convert|1650|km|mi|abbr=on}} from the nearest coastline. |
|||
[[Bennett County, South Dakota|Bennett County]] and [[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota|Oglala Lakota County]] make up much of the reservation.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/DC20BLK/st46_sd/county/c46007_bennett/DC20BLK_C46007.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP (INDEX): Bennett County, SD|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]|accessdate=2023-01-03}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/DC20BLK/st46_sd/county/c46102_oglala_lakota/DC20BLK_C46102.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Oglala Lakota County, SD|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]|accessdate=2023-01-03}}</ref> The reservation takes up the southern portion of [[Jackson County, South Dakota|Jackson County]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/DC20BLK/st46_sd/county/c46071_jackson/DC20BLK_C46071.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Jackson County, SD|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]|accessdate=2023-01-03}}</ref> A small portion is in [[Sheridan County, Nebraska]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/DC20BLK/st31_ne/county/c31161_sheridan/DC20BLK_C31161.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Sheridan County, NE|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]|accessdate=2022-12-30|page=2 (PDF p. 3/71)}}</ref> |
|||
=== Topography === |
|||
[[File:White River SD map 1.jpg|thumb|The [[White River (Missouri River)|White River]] and multiple tributaries cut across the reservation]] |
|||
The [[topography]] is generally rolling [[mixed grass prairie]], interspersed in various location, especially to the north, into typical [[badlands]] topography. The higher elevations of the prairie are covered by wind blown sands that form [[dune]]s, [[Blowout (geology)|blowouts]], and thin [[Sand sheet|sheets]]. The southern part of the reservation is crossed by Pine Ridge, which is probably a [[fault scarp]], and which supports the growth of scattered pine and cedar trees. Well-developed sandhills are the dominant features along the southern boundary of the reservation, which extend into the [[Sand Hills (Nebraska)|sandhills region of Nebraska]].<ref>Status of Mineral Resource Information for the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation [http://www1.eere.energy.gov/tribalenergy/guide/pdfs/pine_ridge_12.pdf]</ref> |
|||
Only {{convert|84000|acre|km2}} of the more than {{convert|2|e6acre|km2}} of the reservation are considered land suitable for agricultural uses, and the climate, soil and water conditions are challenging. Many farmers among the Lakota can do little more than gain a subsistence living from the land.<ref name="pov" /> |
|||
The White River flows through the reservation. It was named for the water's white-gray color, a result of eroded sand, clay, and volcanic ash carried by the river.<ref>Benke and Cushing, p. 445</ref> Draining a basin of about {{convert|10200|mi2|km2|-3}}, the stream flows through a region of sparsely populated hills, plateaus, and [[badland]]s.<ref>Benke and Cushing, p. 449</ref> It flows west to east through the reservation. |
|||
===Geology=== |
|||
Deposition of sediments in the Badlands began 69 million years ago when an ancient sea, the [[Western Interior Seaway]], stretched across what is now the [[Great Plains]]. After the sea retreated, successive land environments, including rivers and flood plains, continued to deposit sediments. Although the major period of deposition ended 28 million years ago, significant erosion of the Badlands did not begin until half a million years ago. |
|||
=== Climate === |
|||
{{Weather box |
|||
|location = Weather Station: Porcupine 11 N, ~17.0 miles Elevation: 2820 feet (-353 ft from town of Pine Ridge) |
|location = Weather Station: Porcupine 11 N, ~17.0 miles Elevation: 2820 feet (-353 ft from town of Pine Ridge) |
||
|single line = y |
|single line = y |
||
| Line 514: | Line 533: | ||
|Dec precipitation inch = .38 |
|Dec precipitation inch = .38 |
||
|year precipitation inch = 16.64|date=June 2011 |
|year precipitation inch = 16.64|date=June 2011 |
||
|source=NOAA<ref>http://www4.ncdc.noaa.gov/cgi-win/wwcgi.dll?WWDI~StnSrch</ref> |
|source=NOAA<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www4.ncdc.noaa.gov/cgi-win/wwcgi.dll?WWDI~StnSrch |title=Archived copy |access-date=2018-11-29 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20041030121728/http://www4.ncdc.noaa.gov/cgi-win/wwcgi.dll?WWDI~StnSrch |archive-date=2004-10-30 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
}} |
|||
}} </center> |
|||
==Geography and topography== |
|||
[[File:White River SD map 1.jpg|thumb|left|The [[White River (Missouri River)|White River]] and multiple tributaries cut across the reservation]] |
|||
'''Geography'''<br> |
|||
The reservation, located in southwest South Dakota, takes {{convert|3400|sqmi|sqkm}} of space. The nearest urban center, [[Rapid City, South Dakota]], is {{convert|120|mi|km}} from the center of the reservation.<ref name=Resroad/><br> |
|||
'''Topography'''<br> |
|||
The [[topography]] is generally rolling [[mixed grass prairie]], interspersed in various location, especially to the north, into typical [[badlands]] topography. The higher elevations of the prairie are covered by wind blown sands that form [[dune]]s, [[Blowout (geology)|blowouts]], and thin [[Sand sheet|sheets]]. The southern part of the reservation is crossed by Pine Ridge, which is probably a [[fault scarp]], and which supports the growth of scattered pine and cedar trees. Well-developed sandhills are the dominant features along the southern boundary of the reservation, which extend into the [[Sand Hills (Nebraska)|sandhills region of Nebraska]].<ref>Status of Mineral Resource Information for the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation [http://www1.eere.energy.gov/tribalenergy/guide/pdfs/pine_ridge_12.pdf]</ref> Only {{convert|84000|acre|km2}} of the more than {{convert|2|e6acre|km2}} of the reservation are considered land suitable for agricultural uses, and the climate, soil and water conditions are challenging. Many farmers among the Lakota can do little more than gain a subsistence living from the land.<ref name=pov/> |
|||
The White River flows through the reservation. It was named for the water's white-gray color, a result of eroded sand, clay, and volcanic ash carried by the river.<ref>Benke and Cushing, p. 445</ref> Draining a basin of about {{convert|10200|mi2|km2|-3}}, the stream flows through a region of sparsely populated hills, plateaus, and [[badland]]s.<ref>Benke and Cushing, p. 449</ref> It flows west to east through the reservation. |
|||
==Geology== |
|||
Deposition of sediments in the Badlands began 69 million years ago when an ancient sea, the [[Western Interior Seaway]], stretched across what is now the [[Great Plains]]. After the sea retreated, successive land environments, including rivers and flood plains, continued to deposit sediments. Although the major period of deposition ended 28 million years ago, significant erosion of the Badlands did not begin until half a million years ago. |
|||
==Flora and fauna== |
==Flora and fauna== |
||
[[File:Buffalo Herd grazing South Dakota.jpg|thumb|A herd of [[bison]] (''tȟatȟáŋka'') grazing on the [[mixed grass prairie]], |
[[File:Buffalo Herd grazing South Dakota.jpg|thumb|A herd of [[bison]] (''tȟatȟáŋka'') grazing on the [[mixed grass prairie]], 1948. The Oglala today maintain a herd on the reservation.]] |
||
'''Flora'''<br> |
|||
=== Flora === |
|||
The [[mixed grass prairie]] contains both ankle-high and waist-high grasses, and fills a transitional zone between the moister tall-grass prairie to the east and the more arid short-grass prairie to the west. |
The [[mixed grass prairie]] contains both ankle-high and waist-high grasses, and fills a transitional zone between the moister tall-grass prairie to the east and the more arid short-grass prairie to the west. |
||
Biologists have identified more than 400 different plant species growing in Badlands National Park. Each plant species is adapted to survive the conditions prevalent in the mixed-grass prairie ecosystem. The climate here is one of extremes: hot, cold, dry, windy and stormy with blizzards, floods, droughts, and fires. Grasses dominate the landscape.<ref>[http://www.nps.gov/badl/naturescience/prairies.htm "Badlands: Prairies"], National Park Service</ref> |
Biologists have identified more than 400 different plant species growing in Badlands National Park. Each plant species is adapted to survive the conditions prevalent in the mixed-grass prairie ecosystem. The climate here is one of extremes: hot, cold, dry, windy and stormy with blizzards, floods, droughts, and fires. Grasses dominate the landscape.<ref>[http://www.nps.gov/badl/naturescience/prairies.htm "Badlands: Prairies"], National Park Service</ref> |
||
The short-grass and tall-grass prairies intergrade just east of an irregular line that runs from northern Texas through Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska, northwestward into west-central North Dakota and South Dakota. The perimeter is not well defined because of the array of short-stature, intermediate, and tall-grass species that make up an [[ecotone]] between the short-grass and tall-grass prairies (Bragg and Steuter 1996). In general, the mixed-grass prairie is characterized by the warm-season grasses of the short-grass prairie to the west and the cool- and warm-season grasses, which grow much taller, to the east. Because of this ecotonal mixing, the number of plant species found in mixed-grass prairies exceeds that in other prairie types.<ref>[http://www.npwrc.usgs.gov/resource/habitat/grlands/grasses.htm "Habitat: Grasslands"], United States Geological Service</ref> Since 2000, [[hemp]] has grown wild here, following a failed attempt in growing it commercially, as a local ordinance allows. The attempt was shut down by the DEA and several other agencies.<ref name=fuller2012>{{cite journal|last=Fuller|first=Alexandra|title=Life After Wounded Knee|url=http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2012/08/pine-ridge/fuller-text?source=link_tw20120718ngm-pineridge&utm_source=Twitter&utm_medium=Social&utm_content=link_tw20120718ngm-pineridge&utm_campaign=Content|journal=National Geographic|date=August 2012|volume=222|issue=2|page=p. 38|accessdate=8 August 2012}}</ref> |
|||
The short-grass and tall-grass prairies intergrade just east of an irregular line that runs from northern Texas to Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska, northwestward into west-central North Dakota and South Dakota. The perimeter is not well defined because of the array of short-stature, intermediate, and tall-grass species that make up an [[ecotone]] between the short-grass and tall-grass prairies (Bragg and Steuter 1996). In general, the mixed-grass prairie is characterized by the warm-season grasses of the short-grass prairie to the west and the cool- and warm-season grasses, which grow much taller, to the east. Because of this ecotonal mixing, the number of plant species found in mixed-grass prairies exceeds that in other prairie types.<ref>[http://www.npwrc.usgs.gov/resource/habitat/grlands/grasses.htm "Habitat: Grasslands"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100614024851/http://www.npwrc.usgs.gov/resource/habitat/grlands/grasses.htm |date=2010-06-14 }}, United States Geological Service</ref> Since 2000, [[hemp]] has grown wild here, following a failed attempt in growing it commercially, as a local ordinance allows. The attempt was shut down by the DEA and several other agencies.<ref name=fuller2012>{{cite journal|last=Fuller|first=Alexandra|title=Life After Wounded Knee|url=http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2012/08/pine-ridge/fuller-text?source=link_tw20120718ngm-pineridge|journal=National Geographic|date=August 2012|volume=222|issue=2|page=38|access-date=8 August 2012}}{{dead link|date=November 2023|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> |
|||
'''Fauna'''<br> |
|||
The mixed grass prairie is home to a variety of animals. In Badlands National Park, scientists have recorded the presence of 37 mammal species, 9 reptile species, 6 amphibian species, 206 bird species, and 69 butterfly species.<ref>[http://www.nps.gov/badl/naturescience/animals.htm National Park Service]</ref> The rare [[swift fox]] and endangered [[black footed ferret]] are among two of the various mammal species found in the Badlands region. Both species feed on the [[Black-tailed prairie dog]] |
|||
=== Fauna === |
|||
The mixed grass prairie is home to a variety of animals. In Badlands National Park, scientists have recorded the presence of 37 mammal species, nine reptile species, six amphibian species, 206 bird species, and 69 butterfly species.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.nps.gov/badl/naturescience/animals.htm|title=National Park Service}}</ref> The rare [[swift fox]] and endangered [[black footed ferret]] are among two of the various mammal species found in the Badlands region. Both species feed on the [[black-tailed prairie dog]]. |
|||
==Transportation== |
==Transportation== |
||
===Roads=== |
|||
[[File:Pine Ridge Reservation Road System FDOT.jpg|thumb|300px|Major roads through Jackson and Oglala Lakota Counties]] |
[[File:Pine Ridge Reservation Road System FDOT.jpg|thumb|300px|Major roads through Jackson and Oglala Lakota Counties]] |
||
* {{jct|I|90|state=SD}} passes east to west through Jackson County and Pennington County just north of the reservation with multiple exits in both counties |
|||
[[File:I-90.svg|left|40px]] |
|||
* {{jct|US|18|state=SD}} is an east–west [[U.S. highway]] which passes through the reservation. The western terminus is in [[Orin, Wyoming]], at an interchange with [[Interstate 25]]. Its eastern terminus of U.S. 18 is in downtown [[Milwaukee, Wisconsin]].<ref name=ends>{{Cite web|url=http://usends.com/10-19/018/018.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141006154246/http://usends.com/10-19/018/018.html|url-status=dead|title=Endpoints of U.S. highways|archive-date=October 6, 2014}}</ref> However, U.S. 18 runs [[Concurrency (road)|concurrent]] with other U.S. routes from its western terminus to [[Mule Creek Junction, Wyoming]]. U.S. 18 is one of the original [[United States highway]]s of 1926. |
|||
[[Interstate 90]]: passes east to west through Jackson County and Pennington County just north of the reservation with multiple exits in both counties |
|||
* {{jct|SD|44|state=SD}}, also known as the "Rimrock Highway" or "Rimrock Drive" connects [[Rapid City, South Dakota]], with [[U.S. Highway 385]] at Pactola Junction, just north of [[Pactola Lake]]. One of the most scenic drives in the [[Black Hills]], SD 44 follows Rapid Creek, a blue-ribbon trout fishery, much of the way, and also follows much of the alignment of the old [[Rapid City, Black Hills and Western Railroad]], also known as the Crouch Line. SD 44 passes through the Jackson County portion of the reservation |
|||
[[File:US 18.svg|left|40px]]:[[United States Route 18]] is an east–west [[U.S. highway]] which passes through the reservation. The western terminus is in [[Orin, Wyoming]] at an interchange with [[Interstate 25]]. Its eastern terminus of U.S. 18 is in downtown [[Milwaukee, Wisconsin]].<ref name=ends>[http://usends.com/10-19/018/018.html Endpoints of U.S. highways]</ref> However, U.S. 18 runs [[Concurrency (road)|concurrent]] with other U.S. routes from its western terminus to [[Mule Creek Junction, Wyoming]]. U.S. 18 is one of the original [[United States highway]]s of 1926. |
|||
* {{jct|SD|73|state=SD}} (not shown on FDOT map) is a state route that runs north to south through the Jackson County portion of the reservation. It begins at the [[Nebraska]] border north of [[Merriman, Nebraska]], as a continuation of [[Nebraska Highway 61]]. It runs to the North Dakota border, where it continues as North Dakota Highway 49. It is 250 miles (402 kilometers) in length. |
|||
[[File:SD 44.svg|left|40px]]:'''South Dakota Highway 44''', also known as the "Rimrock Highway" or "Rimrock Drive" connects [[Rapid City, South Dakota]] with [[U.S. Highway 385]] at Pactola Junction, just north of [[Pactola Lake]]. One of the most scenic drives in the [[Black Hills]], SD 44 follows Rapid Creek, a blue-ribbon trout fishery, much of the way, and also follows much of the alignment of the old [[Rapid City, Black Hills and Western Railroad]], also known as the Crouch Line. SD 44 passes through the Jackson County portion of the reservation |
|||
* {{jct|SD|407|state=SD}} (not shown on FDOT map) is a short [[state highway]] in [[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota|Oglala Lakota County]] which turns into [[Nebraska Highway 87]] (N-87), SD 407-N-87, serves as a connector route between [[U.S. Route 18 (South Dakota)|U.S. Route 18]] (U.S. 18) in [[Pine Ridge, South Dakota]], and [[U.S. Route 20 (Nebraska)|U.S. 20]] in [[Rushville, Nebraska]]. |
|||
[[File:SD 407.svg|left|40px]]: '''South Dakota Highway 407''' (not shown on FDOT map) is a short [[state highway]] in [[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota|Oglala Lakota County]] which turns into [[Nebraska Highway 87]] (N-87), SD 407-N-87, serves as a connector route between [[U.S. Route 18 (South Dakota)|U.S. Route 18]] (U.S. 18) in [[Pine Ridge, South Dakota]] and [[U.S. Route 20 (Nebraska)|U.S. 20]] in [[Rushville, Nebraska]]. |
|||
===Airports=== |
|||
[[File:Cessna172-CatalinaTakeOff.JPG|left|40px]]'''Airports''' |
|||
[[Pine Ridge Airport]], owned by the Oglala Sioux Tribe, is located two miles (3 km) east of the town of Pine Ridge. The unattended airport has four asphalt runways; runways 12&30 are {{convert|5000|x|60|ft|m|abbr=on}}, runways 6&24 (currently closed) are {{convert|3003|x|50|ft|m|abbr=on}}. The airport is in poor repair and is used predominately for government flights.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.airnav.com/airport/KIEN|title=AirNav: KIEN - Pine Ridge Airport|website=www.airnav.com}}</ref> The nearest commercial airport to Pine Ridge is [[Chadron Municipal Airport]] (CDR / KCDR) in [[Chadron, Nebraska]], approximately {{convert|30|mi|km}} south. The nearest major airport is [[Rapid City Regional Airport]], in Rapid City, South Dakota, approximately {{convert|80|mi|km}} NE. The closest international airport is [[Denver International Airport]] in [[Denver, Colorado]] approximately {{convert|240|mi|km}} SW. |
|||
===Public transportation=== |
|||
'''Pine Ridge Airport''', owned by the Oglala Sioux Tribe is located two miles (3 km) east of the town of Pine Ridge. The unattended airport has four asphalt runways; runways 12&30 are 5000 x 60 ft. (1524 x 18 m), runways 6&24 (currently closed) are 3003 x 50 ft. (915 x 15 m). The airport is in poor repair and is used prdominately for government flights.<ref>[http://www.airnav.com/airport/KIEN FAA records as supplied by AirNav.com]</ref> The nearest commercial airport to Pine Ridge is [[Chadron Municipal Airport]] (CDR / KCDR) in [[Chadron, Nebraska]] approximately {{convert|30|mi|km}} south. The nearest major airport is [[Rapid City Regional Airport]], in Rapid City, South Dakota approximately {{convert|80|mi|km}} NE. The closest international airport is [[Denver International Airport]] in [[Denver, Colorado]] approximately {{convert|240|mi|km}} SW. |
|||
On January 30, 2009, the Oglala Sioux Tribe of Pine Ridge held the grand opening of their public transportation system, a bus service with multiple vehicles to cover the entire reservation.<ref>[http://www.lakotacountrytimes.com/news/2009-01-15/front_page/003.html Lil Witt, "Oglala Sioux Transit grand opening Jan. 30"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110713182221/http://www.lakotacountrytimes.com/news/2009-01-15/front_page/003.html |date=2011-07-13 }}, ''Lakota Country Times'', 15 January 2009, accessed 29 May 2011</ref> |
|||
'''Public transportation'''<br> |
|||
On January 30, 2009, the Oglala Sioux Tribe of Pine Ridge held the grand opening of their public transportation system, a bus service with multiple vehicles to cover the entire reservation.<ref>[http://www.lakotacountrytimes.com/news/2009-01-15/front_page/003.html Lil Witt, "Oglala Sioux Transit grand opening Jan. 30"], ''Lakota Country Times'', 15 January 2009, accessed 29 May 2011</ref> |
|||
==Communities== |
==Communities== |
||
[[File:Allen, South Dakota.jpg|thumb |
[[File:Allen, South Dakota.jpg|thumb|[[Allen, South Dakota]], on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation.]] |
||
<div style="float:left; width:400px;"> |
|||
Nebraska |
===Nebraska=== |
||
*[[Whiteclay, Nebraska|Whiteclay]] |
*[[Whiteclay, Nebraska|Whiteclay]] |
||
South Dakota: |
|||
===South Dakota=== |
|||
*[[Allen, South Dakota|Allen]] |
*[[Allen, South Dakota|Allen]] |
||
*[[Batesland, South Dakota|Batesland]] |
*[[Batesland, South Dakota|Batesland]] |
||
| Line 572: | Line 582: | ||
*[[Wanblee, South Dakota|Wanblee]] |
*[[Wanblee, South Dakota|Wanblee]] |
||
*[[Wounded Knee, South Dakota|Wounded Knee]] |
*[[Wounded Knee, South Dakota|Wounded Knee]] |
||
</div><div style="float:right; width:400px;"> |
|||
</div>{{Clear}} |
|||
==Notable leaders and residents== |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{Portal|Indigenous peoples of North America|South Dakota}} |
|||
* |
|||
{{Commons category|Pine Ridge Indian Reservation}} |
|||
*Albert Afraid of Hawk (1879-1900, Oglala). member of [[Buffalo Bill]]'s ''Wild West Show''. |
|||
* [[American Horse]] (''Wašícuŋ Tašuŋke''), an [[Oglala Lakota]] chief during the [[Sioux Wars]] of the 1870s. |
|||
* [[Amos Bad Heart Bull]] (''Waŋblí Wapaha''), a [[ledger art]]ist and tribal historian |
|||
* [[SuAnne Big Crow]] (1974-1992) led the Pine Ridge High School basketball team to state championship in 1989 |
|||
* [[William "Hawk" Birdshead]], ([[Oglala]], [[Hunkpapa]], [[Cheyenne]], [[Arapaho]]) philanthropist, suicide prevention, award winning filmmaker |
|||
* [[Black Elk]] (Heȟaka Sapa; 1863–1950), an Oglala holy man, and second cousin to Crazy Horse |
|||
* [[Alice Blue Legs]], (1925–2003) master quillworker |
|||
* [[Regina Brave]], an [[Oglala Lakota]] activist |
|||
* [https://www.imdb.com/name/nm1129746/?ref%20=fn%20al%20nm%201 Tokala Clifford], actor |
|||
* [[Crazy Horse|Chief Crazy Horse]] (''Tašuŋke Witko''), war chief of the Oglala, c. 1870<ref>Kingsley M. Bray: ''Crazy Horse: A Lakota Life'', p. 153 {{ISBN|0-8061-3986-2}}</ref> |
|||
* |
|||
* |
|||
[[File:Pat Cuny-Oglala Lakota.jpg|thumb|Pat Cuny served in the [[83rd Infantry Division (United States)|83rd Infantry Division]] in [[World War II|WWII]].]] |
|||
[[File:Ed McGaa Oglala Lakota-USMC.jpg|thumb|[[United States Marine Corps|U.S.M.C.]] pilot [[Ed McGaa]] (Eagle Man) and his co-pilot unfurl the US flag on their [[F-4B Phantom]] fighter jet.]] |
|||
* Pat Cuny (Oglala), [[83rd Infantry Division (United States)|83rd Infantry Division]] US Soldier |
|||
* [[Sarah Eagle Heart]], [[Emmy Awards|Emmy Award]]-winning producer, writer, and activist |
|||
* |
|||
* [[Cecilia Fire Thunder]], first woman elected as president of the Oglala Sioux Tribe |
|||
* [[Tim Giago]] (1934-2022) Newspaper Publisher, Writer |
|||
*Brady Jandreau, former rodeo rider and star of [[The Rider (film)|''The Rider'']] (2017) |
|||
* [[Kicking Bear]] (Oglala), chief of the [[Miniconjou]] Lakota Sioux tribe. |
|||
* [[Eddie Little Sky]], actor. |
|||
* [[Little Wound]] (''Taópi Čík'ala'': 1835–1899, Oglala). |
|||
* Chief Long Wolf (1833–1892), warrior of [[Battle of the Little Bighorn]] and the [[Sioux Wars]]. |
|||
* [[Old Chief Smoke]] (''Šóta''; 1774–1864), an early Oglala chief and Shirt Wearer |
|||
* |
|||
* [[Red Cloud|Chief Red Cloud]] (1822–1909, Oglala), a chief |
|||
*[[Philip N. Hogen]], [[United States Attorney for the District of South Dakota]] 1981–1991 |
|||
*[[Ed McGaa]] (Eagle Man), author, attorney and veteran |
|||
* [[Ola Mildred Rexroat]], only Native American pilot in the [[Women Airforce Service Pilots]] |
|||
*[[Billy Mills|William Mervin "Billy" Mills]], also known as ''Makata Taka Hela'', is the second [[Native Americans in the United States|Native American]] to win an [[Olympic Games|Olympic]] [[gold medal]] and the only American ever to win the Olympic gold in the [[Athletics at the 1964 Summer Olympics - Men's 10000 metres|10,000 meter run]] |
|||
** |
|||
** |
|||
** |
|||
** |
|||
* |
|||
* [[Sean Sherman]], food educator, caterer, author of ''[[The Sioux Chef's Indigenous Kitchen]]'' |
|||
* [[Teton Saltes]], Member of the Oglala Sioux Tribe and NFL offensive lineman |
|||
* [[Spotted Elk|Chief Spotted Elk]], called ''Big Foot'' by the U.S. soldiers. His band of Miniconjou Sioux were massacred at Wounded Knee in 1890.<ref>Helaine Silverman, [[D. Fairchild Ruggles]]: ''Cultural Heritage and Human Rights'', pp. 150-151; {{ISBN|978-0-387-76579-2}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Touch the Clouds]], Oglala chief |
|||
* [[JoAnn Tall]], environmental activist at Pine Ridge |
|||
* [[Theresa Two Bulls]], legislature, state senator (2004–2008), president of Oglala Sioux Tribe (2008–2010)<ref>[http://indiancountrynews.net/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=4988&Itemid=1 "Two Bulls to lead Oglala Sioux Tribe"], AP, ''News From Indian Country'', November 2008, accessed 8 July 2011</ref> |
|||
* [[Dick Wilson (tribal chairman)|Richard Wilson]] (April 29, 1934 – January 31, 1990), tribal chairman (1972 to 1976) during the [[Wounded Knee Incident]] |
|||
* John Yellow Bird Steele, President of the Oglala Sioux Tribe (1992-2010) |
|||
* [[They Even Fear His Horses]] (''Tȟašúŋke Kȟokípȟapi'') (1836–1893) |
|||
* Charles Trimble (Oglala Lakota Nation), activist and former executive director of the National Congress of American Indians (1972–1978) |
|||
* |
|||
* |
|||
* |
|||
* |
|||
* |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 583: | Line 642: | ||
==Further reading== |
==Further reading== |
||
* |
* Glover, Vic (2004), ''Keeping Heart on Pine Ridge.'' Natives Voices. {{ISBN|978-1-57067-165-4}}. |
||
* |
* [[Chris Hedges|Hedges, Chris]] and [[Joe Sacco]] (2012). ''Days of Destruction, Days of Revolt.'' Nation Books. {{ISBN|978-1-56858-824-7}}. |
||
* Laughland, Oliver and Tom Silverstone. "[https://www.theguardian.com/society/2017/sep/29/pine-ridge-indian-reservation-south-dakota Liquid genocide: alcohol destroyed Pine Ridge reservation - then they fought back.]" ''[[The Guardian]].'' September 29, 2017. |
|||
* Magnuson, Stew (2009), ''The Death of Raymond Yellow Thunder: And Other True Stories from the Nebraska–Pine Ridge Border Towns'', Texas Tech University Press, ISBN 978-0-89672-634-5. |
|||
* |
* Magnuson, Stew (2009), ''The Death of Raymond Yellow Thunder: And Other True Stories from the Nebraska–Pine Ridge Border Towns'', Texas Tech University Press, {{ISBN|978-0-89672-634-5}}. |
||
* Reinhardt, Akim D. (2007), [https://books.google.com/books?id=0OEzAiB8U6ECdq ''Ruling Pine Ridge: Oglala Lakota Politics from the IRA to Wounded Knee.''] Texas Tech University Press, 2007. {{ISBN|978-0-89672-601-7}}. |
|||
* Wagoner, Paula L. (2002) ''They Treated Us Just Like Indians: The Worlds of Bennett County, South Dakota,'' University of Nebraska Press |
* Wagoner, Paula L. (2002) ''They Treated Us Just Like Indians: The Worlds of Bennett County, South Dakota,'' University of Nebraska Press |
||
==External links== |
|||
*[http://aaronhuey.com/#/pine-ridge-(national-geographic-magazine)/Press_NG_cover Extensive photo essay on Pine Ridge made for National Geographic Magazine] |
*[http://aaronhuey.com/#/pine-ridge-(national-geographic-magazine)/Press_NG_cover Extensive photo essay on Pine Ridge made for National Geographic Magazine] |
||
*[https://www.ted.com/talks/aaron_huey_america_s_native_prisoners_of_war TED talk about Pine Ridge] |
|||
*[http://www.oglalalakotanation.org Official website of the Oglala Sioux tribe/Pine Ridge Reservation] |
|||
*[http://www.lakotacountrytimes.com ''The Lakota Country Times''] |
|||
*[http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/amindian.pdf USDA 2002 Census of Agriculture for Native American Reservations] |
|||
*[http://www.usccr.gov/pubs/sac/sd0300/main.htm ''Native Americans in South Dakota: An Erosion of Confidence in the Justice System''], South Dakota Advisory Commission to U.S. Commission on Civil Rights, 2000 |
*[http://www.usccr.gov/pubs/sac/sd0300/main.htm ''Native Americans in South Dakota: An Erosion of Confidence in the Justice System''], South Dakota Advisory Commission to U.S. Commission on Civil Rights, 2000 |
||
*Starita, Joe (2002) [https://books.google.com/books?id=2aVjEAAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+Dull+Knifes+of+Pine+Ridge&hl=en&newbks=1&newbks_redir=0&source=gb_mobile_search&ovdme=1&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwivzZ24v5mJAxU2ElkFHSNACPQQ6AF6BAgHEAM#v=onepage&q=The%20Dull%20Knifes%20of%20Pine%20Ridge&f=false ''The Dull Knifes of Pine Ridge : A Lakota Odyssey''], University of Nebraska Press. |
|||
*[http://www.friendsofpineridgereservation.org Friends of Pine Ridge Reservation] |
|||
*[http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTTable?_bm=y&-context=dt&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U&-CHECK_SEARCH_RESULTS=N&-CONTEXT=dt&-mt_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_P001&-tree_id=4001&-transpose=N&-all_geo_types=N&-redoLog=true&-_caller=geoselect&-geo_id=25000US2810&-geo_id=NBSP&-search_results=15000US311619405001&-format=&-fully_or_partially=N&-_lang=en&-show_geoid=Y Pine Ridge Reservation and Off-Reservation Trust Land, South Dakota/Nebraska] United States Census Bureau |
|||
*{{dmoz|Regional/North_America/United_States/South_Dakota/Localities/P/Pine_Ridge_Reservation|Pine Ridge Reservation}} |
|||
*[http://www.ted.com/talks/aaron_huey.html TED talk about Pine Ridge] |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{Coord|43|21|12|N|102|05|21|W|scale:1000000|display=title}} |
|||
{{Commons category|Pine Ridge Indian Reservation}} |
|||
'''Community websites''' |
|||
*[https://oglalalakotanation.info/ Official website of the Oglala Sioux tribe/Pine Ridge Reservation] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210504181457/https://oglalalakotanation.info/ |date=2021-05-04 }} |
|||
*''[https://www.lakotatimes.com/ The Lakota Country Times]'' |
|||
*[https://friendsofpineridgereservation.org/ Friends of Pine Ridge Reservation] |
|||
'''Databases''' |
|||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20070615033245/http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/amindian.pdf USDA 2002 Census of Agriculture for Native American Reservations] |
|||
*[https://www.census.gov Pine Ridge Reservation and Off-Reservation Trust Land, South Dakota/Nebraska] United States Census Bureau |
|||
{{Coord|43|21|12|N|102|05|21|W|scale:1000000|display=title}} |
|||
{{Pine Ridge Indian Reservation}} |
|||
{{Navboxes|list= |
|||
{{Native Americans in Nebraska}} |
|||
{{Indian reservations in South Dakota}} |
{{Indian reservations in South Dakota}} |
||
{{Bennett County, South Dakota}} |
|||
{{Jackson County, South Dakota}} |
|||
{{Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota}} |
{{Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota}} |
||
{{Sheridan County, Nebraska}} |
|||
{{United States political divisions}} |
|||
{{Lakota people}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pine Ridge Indian Reservation}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pine Ridge Indian Reservation}} |
||
[[Category:American Indian reservations in South Dakota]] |
|||
[[Category:Pine Ridge Indian Reservation| ]] |
[[Category:Pine Ridge Indian Reservation| ]] |
||
[[Category:American Indian reservations in South Dakota]] |
|||
[[Category:Badlands of the United States]] |
|||
[[Category:Federally recognized tribes in the United States]] |
|||
[[Category:Geography of Bennett County, South Dakota]] |
[[Category:Geography of Bennett County, South Dakota]] |
||
[[Category:Geography of Jackson County, South Dakota]] |
|||
[[Category:Geography of Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota]] |
[[Category:Geography of Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota]] |
||
[[Category:Geography of Jackson County, South Dakota]] |
|||
[[Category:Geography of Sheridan County, Nebraska]] |
[[Category:Geography of Sheridan County, Nebraska]] |
||
[[Category:Native American tribes in South Dakota]] |
[[Category:Native American tribes in South Dakota]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Oglala]] |
||
[[Category:Sioux Wars]] |
[[Category:Sioux Wars]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:States and territories established in 1889]] |
||
[[Category:1889 establishments in Dakota Territory]] |
|||
[[Category:Lakota]] Sup dues |
|||
Latest revision as of 08:29, 3 January 2025
Pine Ridge Indian Reservation
Wazí Aháŋhaŋ Oyáŋke (Lakota) Oglala Lakota Reservation | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: ("Wapaha kiŋ kekah'boyaŋhan"[1] and "Lakota Flag Song" used for some occasions) | |
 Location of the reservation in South Dakota | |
| Tribe | Oglala Sioux |
| Country | United States |
| States | South Dakota (99%) Nebraska (1%) |
| Counties | Bennett (all) Jackson (half) Oglala Lakota (all) Sheridan (part) |
| Headquarters | Pine Ridge |
| Government | |
| • Governing Body | Tribal Council |
| • President | Frank Star Comes Out (D) |
| • Vice-President | Alicia Mousseau (D) |
| Area | |
• Total | 8,984.3 km2 (3,468.86 sq mi) |
| Population (2020)[3] | |
• Total | 32,000 |
| • Density | 3.6/km2 (9.2/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-7 (MST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-6 (MDT) |
| GDP | $330.8 Million (2018) |
| Website | https://www.oglala.gov/ |
The Pine Ridge Indian Reservation (Lakota: Wazí Aháŋhaŋ Oyáŋke), also called Pine Ridge Agency, is an Oglala Lakota Indian reservation located in the U.S. state of South Dakota, with a small portion of it extending into Nebraska. Originally included within the territory of the Great Sioux Reservation, Pine Ridge was created by the Act of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888. in the southwest corner of South Dakota on the Nebraska border. It consists of 3,468.85 sq mi (8,984 km2) of land area and is one of the largest reservations in the United States.[4]
The reservation encompasses the entirety of Oglala Lakota County and Bennett County, the southern half of Jackson County, and a small section of Sheridan County added by Executive Order No. 2980 of February 20, 1904. Of the 3,142 counties in the United States, these are among the poorest. Only 84,000 acres (340 km2) of land are suitable for agriculture. The 2000 census population of the reservation was 15,521. A 2009 study by Colorado State University and accepted by the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development has estimated the resident population to reach 28,787.[5]
Pine Ridge is the site of several events that mark milestones in the history between the Sioux of the area and the U.S. government. Stronghold Table, a mesa in what is today the Oglala-administered portion of Badlands National Park, was the location of the last of the Ghost Dances. U.S. authorities repressed this movement, eventually leading to the Wounded Knee Massacre on December 29, 1890. A mixed band of Miniconjou Lakota and Hunkpapa Sioux, led by Chief Spotted Elk, sought sanctuary at Pine Ridge after fleeing the Standing Rock Agency, where Sitting Bull had been killed during efforts to arrest him. The families were intercepted and attacked by a heavily armed detachment of the Seventh Cavalry, which killed many women and children as well as warriors. This was the last large engagement between U.S. forces and Native Americans and marked the end of the western frontier.
Changes accumulated in the last quarter of the 20th century: in 1971 the Oglala Sioux Tribe (OST) started Oglala Lakota College, a tribal college, which offers 4-year degrees. In 1973 decades of discontent at the Pine Ridge Reservation resulted in a grassroots protest that escalated into the Wounded Knee Incident, gaining national attention. Members of the Oglala Lakota, the American Indian Movement and supporters occupied the town in defiance of federal and state law enforcement in a protest that turned into an armed standoff lasting 71 days. This event inspired American Indians across the country and gradually led to changes at the reservation. It has revived some cultural traditions and encouraged language training. In 1981 Tim Giago (Lakota) started the Lakota Times at Pine Ridge.
Located at the southern end of the Badlands, the reservation is part of the mixed grass prairie, an ecological transition zone between the short-grass and tall-grass prairies; all are part of the Great Plains. A great variety of plant and animal life flourishes on and adjacent to the reservation, including the endangered black-footed ferret. The area is also important in the field of paleontology; it contains deposits of Pierre Shale formed on the seafloor of the Western Interior Seaway, evidence of the marine Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, and one of the largest deposits of fossils of extinct mammals from the Oligocene epoch.
History
[edit]19th century
[edit]Great Sioux Reservation
[edit]
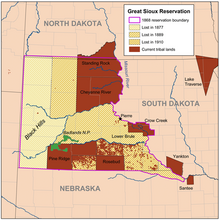
As stipulated in the Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868), the U.S. government built Indian agencies for the various Lakota and other Plains tribes.[6] These were forerunners to the modern Indian reservations. The Red Cloud Agency was established for the Oglala Lakota in 1871 on the North Platte River in Wyoming Territory. The location was one mile (1.6 km) west of the present town of Henry, Nebraska. The location of the Red Cloud Agency was moved to two other locations before being settled at the present Pine Ridge location. Pine Ridge Reservation was originally part of the Great Sioux Reservation established by the 1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie. It encompassed approximately 60 million contiguous acres (240,000 km2) of western South Dakota (all of what is now called West River), northern Nebraska and eastern Wyoming.
Exclusion of the Black Hills
[edit]In 1874, George Armstrong Custer led the U.S. Army Black Hills Expedition, which set out on July 2 from Fort Abraham Lincoln in the Dakota Territory, with orders to travel to the previously uncharted Black Hills of South Dakota. Its mission was to look for suitable locations for a fort, find a route to the southwest, and to investigate the potential for gold mining. After the discovery of gold was made public, miners began invading Sioux Territory.
"Custer's florid descriptions of the mineral and timber resources of the Black Hills, and the land's suitability for grazing and cultivation ... received wide circulation, and had the effect of creating an intense popular demand for more settlers to invade the Black Hills."[7] Initially the U.S. military tried to turn away trespassing miners and settlers. Eventually President Grant, the Secretary of the Interior, and the Secretary of War, "decided that the military should make no further resistance to the occupation of the Black Hills by miners."[8] These orders were to be enforced "quietly", and the President's decision was to remain "confidential".[8]

As more settlers and gold miners encroached upon the Black Hills, the Government determined it had to acquire the land from the Sioux, and appointed a commission to negotiate the purchase.[9] The negotiations failed, as the Sioux resisted giving up what they considered sacred land. The U.S. resorted to military force. They declared the Sioux Indians "hostile" for failing to obey an order to return from an off-reservation hunting expedition by a specific date. In the dead of winter, the Sioux found the overland travel was impossible.[10]
The consequent military expedition to remove the Sioux from the Black Hills included an attack on a major encampment of several bands on the Little Bighorn River. Led by General Custer, the attack ended in his defeat. It was an overwhelming victory of chiefs Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse over the 7th Cavalry Regiment, a conflict often called Custer's Last Stand.[9][11] US forces were vastly outnumbered.
In 1876 the U.S. Congress decided to open up the Black Hills to development and break up the Great Sioux Reservation. In 1877, it passed an act to make 7.7 million acres (31,000 km2) of the Black Hills available for sale to homesteaders and private interests. In 1889 Congress divided the remaining area of Great Sioux Reservation into five separate reservations, defining the boundaries of each in its Act of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888. Pine Ridge was established at that time.
Wounded Knee Massacre
[edit]
The Wounded Knee Massacre occurred on December 29, 1890,[12] near Wounded Knee Creek (Lakota: Cankpe Opi Wakpala). On the day before, a detachment of the U.S. 7th Cavalry Regiment commanded by Major Samuel M. Whitside intercepted Spotted Elk's (Big Foot) band of Miniconjou Lakota and 38 Hunkpapa Lakota near Porcupine Butte and escorted them 5 miles (8.0 km) westward to Wounded Knee Creek where they made camp. The rest of the 7th Cavalry Regiment, led by Colonel James Forsyth, surrounded the encampment, supported by four Hotchkiss guns.[13]
On the morning of December 29, 1890, the troops went into the camp to disarm the Lakota. One version of events claims that during the process, a deaf tribesman named Black Coyote was reluctant to give up his rifle, saying he had paid a lot for it.[14] A scuffle over Black Coyote's rifle escalated and a shot was fired, which resulted in the 7th Cavalry opening firing indiscriminately from all sides, killing men, women, and children, as well as some of their fellow troopers. Those few Lakota warriors who still had weapons began shooting back at the troopers, who quickly suppressed the Lakota fire. The surviving Lakota fled, but U.S. cavalrymen pursued and killed many who were unarmed.
In the end, U.S. forces killed at least 150 men, women, and children of the Lakota Sioux and wounded 51 (four men, and 47 women and children, some of whom died later); some estimates placed the number of dead at 300. Twenty-five troopers also died, and thirty-nine were wounded (six of the wounded would also die).[15] Many Army deaths were believed to have been caused by friendly fire, as the shooting took place at close range in chaotic conditions.[16]
The site has been designated a National Historic Landmark and is administered by the National Park Service.[12]
20th century
[edit]White Clay Extension
[edit]
In 1882, at the urging of Valentine McGillycuddy—the US Indian Agent at the Pine President Agency—President Chester A. Arthur issued an executive order establishing the White Clay Extension, an area of land in Nebraska extending 5 miles (8.0 km) south of the reservation's border and 10 miles (16 km) wide approximately perpendicular to the road leading north into the town of Pine Ridge on the reservation.[17] This road is today's Nebraska Highway 87. McGillycuddy lobbied for the buffer zone to prevent white peddlers from engaging in the illegal sale of "knives, guns, and alcohol" to the Oglala Lakota residents of Pine Ridge.
A law passed in Congress in 1832 banned the sale of alcohol to Native Americans. The ban was ended in 1953 by Public Law 277, signed by President Dwight D. Eisenhower. The amended law gave Native American tribes the option of permitting or banning alcohol sales and consumption on their lands.[18] The OST and many other tribes chose to exclude alcohol from their reservations because of the problems for their people.
In 1887, when Congress enacted the Dawes Severalty Act of 1887—breaking up the reservations and allotting a 160 acres (65 ha) plot to the registered head of each family—the Whiteclay Extension was specifically exempted. On March 2, 1889, the U.S. Congress enacted the Great Sioux Agreement of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888, breaking up the Great Sioux Reservation and setting boundaries for the six reduced reservations. In this act, the White Clay Extension was incorporated again within the boundaries of the Pine Ridge Agency. "Provided, That the said tract of land in the State of Nebraska shall be reserved, by Executive order, only so long as it may be needed for the use and protection of the Indians receiving rations and annuities at the Pine Ridge Agency."[19]
On January 25, 1904, President Theodore Roosevelt signed an executive order returning the 50 square miles (130 km2) of the White Clay Extension to the public domain. The town of Whiteclay in Sheridan County, Nebraska, just over the border from the reservation, was founded in the former "Extension" zone. Merchants quickly started selling alcohol to the Oglala Sioux.
It is hereby ordered that the tract of country in the State of Nebraska "withdrawn from sale and set aside as an addition to the present Sioux Indian Reservation in the Territory of Dakota" by Executive order dated January 24, 1882, be, and the same hereby is, restored to the public domain.
— President Theodore Roosevelt, January 25, 1904.[20]
On February 20, 1904, Roosevelt amended the executive order to return 1 square mile (2.6 km2) back to Pine Ridge: "the section of land embracing the Pine Ridge Boarding School irrigation ditch and the school pasture".
Bennett County Land dispute
[edit]In 1975 in Cook v. Parkinson 525 F.2d 120 (8th Cir. 1975) ruled that Bennett County was not considered part of the Pine Ridge Reservation. However, "the United States participated only as amicus before the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals in Cook v. Parkinson, 525 F.2d 120 (8th Cir. 1975) and is not bound by that decision because it did not participate in the litigation. The United States was a party in United States v. Bennett County, 394 F.2d 8 (8th Cir. 1968), in which the State of South Dakota had to obtain permission from the Department of Interior in order to fix roads or condemn property in Bennett County, consistent with the property's reservation status[21] as well as Putnam v. United States 248 F.2d 292 (8th Cir. 1957) which ruled that "Bennett County is within the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation created by the Act of Congress of March 2, 1889, 25 Stat. 888."
The Federal Government recognizes Bennett County as being entirely within the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation. In 2004, in State of South Dakota v. Acting Great Plains Regional Director, Bureau of Indian Affairs Docket Number IBIA3-24-A the State of South Dakota argued against an Oglala Sioux Tribal member's application to the BIA to return a 10-acre tract of land in Bennett County into Federal Trust arguing it was outside of the Boundary of the Pine Ridge Reservation. The judge ruled in favor of the applicant and Bureau of Indian Affairs' affirmant that Bennett County is indeed within the boundaries of the Reservation.[22]
Indian Reorganization Act
[edit]In the 1930s, President Franklin D. Roosevelt's administration made changes in federal policy to improve conditions for American Indians. In response to complaints about corruption and injustices in the BIA management of reservations, Congress passed the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934, permitting tribal nations to reorganize with self-government. It encouraged them to adopt a model of elected representative governments and elected tribal chairmen or presidents, with written constitutions. While tribes welcomed taking back more control of their government, this change eroded the power and structure of the traditional hereditary leaders of the clan system.
The Oglala Sioux Tribe developed a tribal government along democratic constitutional lines, with a chairman to be elected for a two-year term. This short term makes it difficult for leaders to accomplish longer-term projects, but the tribe has not changed its constitution. The BIA still has had the ability to oversee some tribal operations, including the police. Historically BIA tribal police were often assigned from other Indian tribes rather than representing local people and understanding their culture, which created tensions.[23]
Many traditionalists among the Oglala Lakota never supported the new style of government. Tribal elders were still respected, and there were multiple lines of authority and influence among different groups on the reservation. Political factions also formed between those who were mixed-bloods or had urban experiences, and those who were full-bloods and tended to be more traditional in practices and culture.[23]
The people continued to be under assimilation pressure: through the early part of the century, many children were sent away to Indian boarding schools where they were usually required to speak English and were prohibited from speaking Lakota. They were usually expected to practice Christianity rather than native religions. In the late 20th century, many of these institutions were found to have had staff who abused the children in their care.[24]
Taking of Badlands Bombing Range
[edit]
In 1942 the federal government took privately held Pine Ridge Indian Reservation land owned by tribal members in order to establish the Badlands Bombing Range of 341,725 acres (1,382.91 km2). The largest portion is located in Oglala Lakota County. It also leased communally held Oglala Sioux Tribe (OST) land for this defense installation.
Among the 125 families evicted was that of Pat Cuny, an Oglala Sioux. He fought in World War II in the Battle of the Bulge after surviving torpedoing of his transport in the English Channel.[25] Dewey Beard, a Miniconjou Sioux survivor of the Wounded Knee Massacre, who supported himself by raising horses on his 908-acre (3.67 km2) allotment received in 1907 was also evicted. The small federal payments were insufficient to enable such persons to buy new properties. In 1955, the 97-year-old Beard testified of earlier mistreatment at Congressional hearings about this project.[26] He said, for "fifty years I have been kicked around. Today there is a hard winter coming. ... I might starve to death."[citation needed]
Since 1960, the U.S. has returned portions[specify] of the bombing range to the OST. The 1968 Public Law 90-468 returned 202,357 acres (818.91 km2) to the OST and set aside former tribal lands as the Badlands National Monument. The smaller Air Force Retained Area is within the boundaries of the reservation.[27]
Understandably, many people now believe that the disruption of the time period 1973 –76 was instigated by the Wilson administration —and U.S. agents using that administration— to distract the people from these and other agreements being made about their land.
— Peter Matthiessen In the Spirit of Crazy Horse, page 425
A 2008, the USAF & OST agreement initiated "a three-month $1.6 million project to remove unexploded ordnance" from the bombing range.[28]
Wounded Knee Occupation
[edit]In the early 1970s, tribal tensions rose and some members turned to the American Indian Movement (AIM) for help. Longstanding divisions on the reservation resulted from deep-seated political, ethnic and cultural differences. Many residents did not support the elected tribal government. Many residents were upset about what they described as the autocratic and repressive actions by the tribal president Dick Wilson, elected in 1972.
On February 21, the tribal council was called into session to consider the removal of Wilson through impeachment. Five hundred Oglala members were in attendance. He was criticized for favoring family and friends with jobs and benefits, not consulting with the tribal council, and creating a private militia, known as the Guardians of the Oglala Nation (GOONs), to suppress political opponents. He used tribal funds to pay for this force. Wilson's response was to screen a right wing propaganda film.[29]
After a series of meetings held in the Calico community near the Pine Ridge Agency, the old traditional chiefs and the Oglala Sioux Civil Rights Organization (OSCRO) called down to AIM in Rapid City and asked them to come to Pine Ridge. A meeting was arranged between Wilson and Russell Means. Five of Wilson's supporters cornered Means in the parking lot. Means escaped.[29] Women elders such as Ellen Moves Camp, founder of the Oglala Sioux Civil Rights Organization (OSCRO), called for action. They organized a public protest for the next day.[24]
About 200 AIM and Oglala Lakota activists occupied the hamlet of Wounded Knee on February 27, 1973. They demanded the removal of Wilson, restoration of treaty negotiations with the U.S. government, and correction of U.S. failures to enforce treaty rights. Visits by the U.S. senators from South Dakota, FBI agents and United States Department of Justice (DOJ) representatives, were attended by widespread media coverage, but the Richard Nixon administration was preoccupied internally with Watergate.[24]
As the events evolved, the activists at Wounded Knee had a 71-day armed stand-off with U.S. law enforcement. AIM leaders at the site were Russell Means, Dennis Banks, Clyde Bellecourt, and Carter Camp. Traditional spiritual leaders of the Lakota, such as Frank Fools Crow, were also prominent. Fools Crow led Oglala Lakota spiritual ceremonies and practice in their ways for participants.[24] Joseph H. Trimbach of the FBI and Steve Frizell of DOJ led the government.[24]
Casualties of gunfire included a U.S. Marshal, who was seriously wounded and paralyzed; and the deaths of Frank Clearwater, a Cherokee from North Carolina, and Buddy Lamont, a local Oglala Lakota. After Lamont's death, the Oglala Lakota elders called an end to the occupation.[24] Some Lakota have alleged that Ray Robinson, a civil rights activist, was killed during the Wounded Knee occupation, as he disappeared there.[30][31]
The stand-off ended, but Wilson remained in office. The U.S. government said it could not remove an elected tribal official as the Oglala Sioux Tribe had sovereignty.[24] Ensuing open conflict between factions caused numerous deaths. The murder rate between March 1, 1973, and March 1, 1976, was 170 per 100,000; it was the highest in the country.[32] More than 60 opponents of the tribal government allegedly died violent deaths in the three years following the Wounded Knee Incident, a period called the "Reign of Terror" by many residents. Among those killed was Pedro Bissonette, executive director of the civil rights organization OSCRO.[33]
Residents accused officials of failing to try to solve the deaths.[34] In 2000, the FBI released a report regarding the 57 alleged unsolved violent deaths on Pine Ridge Reservation and accounted for most of the deaths, and disputed the claims of unsolved murders. The report stated that only 4 deaths were unsolved and that some deaths were not murders.[35][36] AIM representatives criticized the FBI report.[37]
Pine Ridge Shootout
[edit]
During this period of increased violence, on June 26, 1975, the reservation was the site of an armed confrontation between AIM activists and the FBI, which became known as the 'Pine Ridge Shootout'.[38] Two FBI agents, Jack R. Coler and Ronald A. Williams, were killed and executed at close range. The agents had been following a car when they were shot at by its occupants and others. AIM activist Joe Stuntz was later killed by responding police. Stuntz was found wearing Coler's FBI jacket.[38]
In two separate trials, the U.S. prosecuted participants in the firefight for the deaths of the agents. AIM members Robert Robideau and Dino Butler were acquitted after asserting that they had acted in self-defense. Leonard Peltier was extradited from Canada and tried separately because of the delay. He was convicted on two counts of first–degree murder for the deaths of the FBI agents,[39] and sentenced to two consecutive terms of life in prison.
Murder of Anna Mae Aquash
[edit]On February 24, 1976, the body of Anna Mae Aquash, a Mi'kmaq activist and the most prominent woman in AIM, was found in the far northeast corner of the Pine Ridge Reservation. Missing since December 1975, she had been shot execution-style. At the time, some AIM people said that she was a government informant, but the FBI has denied that. In 1974, AIM had discovered that Douglas Durham, then head of security, was an FBI informant. Three federal grand juries were called to hear testimony on the Aquash murder: in 1976, 1982 and 1994, but it was more than a quarter of a century before any suspects were indicted and tried for the crime.[40]
Two AIM members, Arlo Looking Cloud and John Graham, were convicted of her murder in 2004 and 2010 respectively, and sentenced to life in prison. Bruce Ellison, Leonard Peltier's lawyer since the 1970s, invoked his Fifth Amendment rights and refused to testify at the grand jury hearings on Looking Cloud, or at his trial in 2004. At trial, the federal prosecutor referred to Ellison as a co-conspirator in the Aquash case.[41][40]
21st century
[edit]Alcoholism among residents has been a continuing problem in the life of the reservation since its founding. Since 1999, activists from the Pine Ridge Reservation, AIM, and Nebraskans for Peace have worked to have beer sales shut down in nearby Whiteclay, Nebraska, a border town. Whiteclay sells millions of cans of beer annually, primarily to residents from the reservation in South Dakota, where alcohol possession and consumption is prohibited. In 2008, the documentary The Battle for Whiteclay, about the toll of alcoholism and activists' efforts to control beer sales, was released, which has attracted wide attention. The Nebraska legislature allocated funds in late 2010 for increased police patrols in Pine Ridge by the county sheriff's office, based 22 miles (35 km) away in Rushville.
While other tribes and reservations also prohibited alcohol at one time, many have since legalized its sales on their reservations. They use the revenues generated to improve health care and life on the reservation, and they prefer to directly control the regulation of alcohol sales and police its use. A 2007 survey found that 63% of federally recognized tribes in the lower 48 states have legalized liquor sales on their reservations.[42] They include the nearby Sicangu Oyate or Brulé Sioux at the Rosebud Indian Reservation, also located in South Dakota. In 2006, the Omaha Nation in northeastern Nebraska started requiring payment of tribal license fees and sales taxes by liquor stores located in towns within its reservation boundaries in order to benefit in the revenues generated by alcohol sales.[43]
Activists at Pine Ridge have worked to persuade Nebraska to enforce its own laws and support the tribe's prohibition. In 2004 the Oglala Sioux Tribe voted down a referendum to legalize alcohol sales, and in 2006 the tribal council voted to maintain the ban on alcohol sales, rather than taking on the benefits and responsibility directly.[42]
At a discussion at Bellevue University on April 2, 2010, Lance Morgan, CEO of Ho-Chunk, Inc.—the development corporation of the Winnebago Reservation—said the Oglala Sioux needed to concentrate on economic development. He believes that poverty is at the heart of its people's problems.[44] The Winnebago used revenues from a casino and alcohol sales at their reservation in eastern Nebraska to build an economic development corporation. It now employs 1,400 people in 26 subsidiaries. With its revenues, the Winnebago have been able to build a hospital, a new school and $1 million in new housing. Kevin Abourezk reported that Stew Magnuson—the author of The Death of Raymond Yellow Thunder, a study of issues related to the Pine Ridge reservation and its border towns—described alcohol prohibition at the reservation "as a complete failure."[44] Magnuson said, "Whenever you have prohibition, you're going to have places like Whiteclay."[44] He thought prohibition contributed to bootlegging on the reservation.
On February 9, 2012, the Oglala Sioux Tribe filed a lawsuit in U.S. District Court of Nebraska against the four liquor stores in Whiteclay, Nebraska, as well as the beverage distributors and the brewery companies who make it. The suit, Oglala Sioux Tribe v. Jason Schwarting, Licensee of Arrowhead Inn, Inc. et al, sought $500 million in damages for the "cost of health care, social services and child rehabilitation caused by chronic alcoholism on the reservation, which encompasses some of the nation's most impoverished counties."[45] The suit claims that the defendants knowingly and willingly sell excessive amounts of alcohol, knowing that most of it is smuggled onto the reservation, in violation of Pine Ridge Indian Reservation and Federal law. The defendants listed in the suit are the following:[46][47]
- Anheuser-Busch InBev Worldwide, Inc.
- SAB Miller d/b/a Miller Brewing Company
- Molson Coors Brewing Company
- Miller Coors, LLC
- Pabst Brewing Company
- Pivo, Inc. d/b/a High Plains Budweiser. President, Treasurer: Jeffrey J. Scheinost. Secretary: Cynthia A. Scheinost. Director: Marykate Scheinost[48]
- Dietrich Distributing Co., Inc. President, Director, Treasurer: John D. Dietrich[49]
- Coors Distributing of West Nebraska d/b/a Coors of West Nebraska; President, Treasurer, Director: James K. Raymond, Treasurer, Director: Evelyn K. Raymond[50]
- Klemm Distributing Inc.: President: Robert (Bob) F. Klemm, Secretary: Barrett R. Klemm[51] d/b/a Arrowhead Distributing, Inc.[52] President: Patrick A, O'Neal. Secretary: Greg Burkholder, Treasurer: Kent O'Neal[53]
- Jason Schwarting d/b/a Arrowhead Inn, Inc. President: Jason Schwarting,[54] Secretary: Vic Clarke[55]
- Sanford Holdings, LLC d/b/a D&S Pioneer Service. Corporation Members: Doug Sanford, Steve Sanford[56]
- Stuart J. Kozal d/b/a/ Jumping Eagle Inn. Owners: Stuart J. Kozal,[57] Lillie I. Norman[58]
- Clay M. Brehmer and Daniel J. Brehmer d/b/a State Line Liquor[59]
On August 14, 2013, voters voted to end prohibition and legalize alcohol, so the tribe can use the profits for education and detoxification and treatment centers.[60]
Demographics
[edit]In a 2005 interview, Cecilia Fire Thunder, the first female president of the Oglala Sioux Tribe, noted, "[Sixty-eight] percent of the college graduates on the reservation are women. Seventy percent of the jobs are held by women. Over 90 percent of the jobs in our schools are held by women."[61]
- The 2010 U.S. Census counted 18,834 individuals living on the Pine Ridge Reservation. The vast majority, 16,906, identified as American Indian.[62] Much of the non-Native population is found in the community of Martin, South Dakota
- 89% of residents are unemployed.[citation needed]
- 53.75% of the residents live below the Federal poverty level.[62]
- Average per capita income in Oglala Lakota County is $8,768 and ranks as the "poorest" county in the nation.[62]
- The infant mortality rate is five times higher than the national average.
- Native American amputation rates due to diabetes are three to four times higher than the national average.
- Death rate due to diabetes is three times higher than the national average.
- Teen suicide is four times the national average.
- The average life expectancy on Pine Ridge is 66.81 years,[63] the lowest in the United States[citation needed]. In 2004, the average life expectancy was just 48 years for men and 52 years for women.[64]
Tribal government
[edit]
The reservation is governed by the eighteen-member Oglala Sioux Tribal Council, who are elected officials rather than traditional clan life leaders, in accordance with the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934. The Executive Officers of the council are the President (also called Chairman), Vice President, Secretary, and Treasurer. Primary elections are held in October and the General election in November.
The President and Vice-President are elected at large by voters to a term of office of two years; the Secretary and Treasurer are appointed by the Tribal Council. Council members serve a term of two years. There are nine election districts on the reservation. One representative is elected for each 1,000 tribe members.
A Constitution was approved on January 15, 1936, with amendments approved on December 24, 1969; December 3, 1985; July 11, 1997.
Politics
[edit]While many residents have continued to struggle with the tribal government, BIA and other federal representatives, some have become more politically active in other ways. In 2002, the Pine Ridge Reservation was part of a statewide voter registration campaign organized by the Democratic Party. That year, Oglala Lakota candidates won offices in Bennett County; since the 1990s, Native Americans (mostly Lakota) have become a majority of the county's population. Charles Cummings was elected as county sheriff, Gerald 'Jed' Bettelyoun to one of the positions as county commissioner, and Sandy Flye became the first Native American elected to a seat on the county school board. Statewide turnout by Native Americans helped elect the Democratic candidate Tim Johnson to the U.S. Senate by a narrow margin.[65]
In 1992, John Yellow Bird Steele was elected president of the OST, the first of what would become a record-setting seven terms as president.[66][67] Despite winning seven elections, Steele only won re-election once, in 2002.[68] In most cases, he was defeated when seeking re-election, only to come back and defeat his successor in the next election (or, in the case of the 2006 election, to defeat the person serving out the rest of his successor's term).[69]
In 2004, Cecilia Fire Thunder became the first woman elected president of the OST, defeating the incumbent Steele and Russell Means.[70] In 2005 she led negotiations with Nebraska to strengthen law enforcement in Whiteclay by hiring more Oglala tribal police and having them deputized by Nebraska to patrol in the town. The town sells massive quantities of alcohol to the Lakota, although it is illegal on the reservation.[dubious – discuss] The "historic agreement" was signed by Fire Thunder following approval by the tribal council, the Nebraska Governor Dave Heineman and State Attorney General Jon Bruning.[71]
On March 21, 2006, Fire Thunder announced her plan to bring a Planned Parenthood clinic to the reservation to improve health services to women. The South Dakota state legislature had recently passed a stringent abortion law.[70] In May 2006, the Oglala Sioux tribal council unanimously voted to ban all abortions on the reservation, regardless of the circumstances. The council also voted to suspend Fire Thunder for 20 days pending an impeachment hearing.[72]
On June 29, 2006, the tribal council voted to impeach Fire Thunder: it said that founding the clinic was outside her authority and she had failed to consult with them. Her two-year term would have expired in October 2006. In November 2006, state voters reviewed the law passed by the state legislature, and they overwhelmingly defeated the ban on abortions without exceptions, by 55.57 percent to 44.43 percent. A ban with exceptions was proposed in 2008, and state voters rejected that by a margin of 55.21 percent to 44.79 percent.[73]
The U.S. Congress supported Fire Thunder's tribal law enforcement initiative, earmarking $200,000 over two years to pay for the increased cost of OST police patrols in Whiteclay. By May 2007, the tribe had spent none of the money. Fire Thunder's impeachment and tribal political conflict appeared to prevent its implementing the agreement.[71] During 2006 and 2007, tribal activists tried to blockade the road inside the reservation to confiscate beer being illegally brought in. The OST police chief complained of having insufficient money and staff to control the beer traffic.[74] The tribe lost the earmarked funds and let the initiative lapse.
In November 2008, Theresa Two Bulls, a Democratic State Senator for South Dakota since 2004, became the second woman elected president of the OST. She succeeded Steele and defeated Russell Means.[75] When the reservation had a rash of suicides in late 2009, she declared a state of emergency and organized a call-in to President Barack Obama. She organized services during a blizzard to assist residents in outlying areas on the reservation.[76]
Steele was re-elected in 2010, defeating Two Bulls. Bryan Brewer was elected as Tribal president in November 2012, defeating the incumbent Steele with 52% of the vote. A retired educator and school administrator, he was new to tribal politics. He worked to develop housing and discourage alcoholism, even leading a protest against Whiteclay alcohol sales.[77][78] The journalist Brian Ecoffey noted that Brewer represented a "new direction" for the tribe, as he had not held political office before.[79] Steele then defeated Brewer in 2014, starting what would be Steele's last term.[80][81]
Troy "Scott" Weston represented the Porcupine District in the 2010 and 2012 administrations; Weston was elected OST President in 2016 beating Steele, the incumbent, in a landslide victory. The Rapid City Journal reported that nearly 2/3 of voters at the polls cast their ballot for Weston.[82]
In national elections, Pine Ridge is politically divided: the western half of the reservation (Oglala Lakota County) votes overwhelmingly Democratic at the national level, while the eastern half (Bennett and Jackson Counties) trends heavily Republican. In local politics, the Oglala are active in electing tribal members to the State House and Senate, with both Democrats and Republicans finding success on the reservation.
Federal, state, and tribal law
[edit]The Oglala Sioux Tribe maintains legal jurisdiction over all crimes committed on the reservation by tribal members, non-reservation Indians, and those willing to relinquish authority to the tribal courts. Felony crimes and others which have been specifically assumed by the federal government, as defined by various acts of the U.S. Congress, are outside their jurisdiction and are prosecuted by the BIA and FBI. The ruling of the Supreme Court of the United States in Ex parte Crow Dog (1883) marked the high point of Indian sovereignty in law enforcement on reservations; since then federal legislation and subsequent Supreme Court decisions have reduced Native American sovereignty in this area.[83]
Public Law 280, enacted by Congress in 1953 and substantially amended in 1968, allows for states to assume jurisdiction on Indian reservations if approved by referendum by the affected reservations. In South Dakota, Public Law 280 is applied only to state highways running through reservations.[84]
Landmark cases affecting tribal criminal law include:
- Ex parte Crow Dog, 109 U.S. 556 (1883): On August 5, 1881, Crow Dog, a Brulé Lakota subchief, shot and killed the Oglala principal chief Chief Spotted Tail, on the Rosebud Indian Reservation. A grand jury was convened, and Crow Dog was tried and convicted in Dakota Territorial court in Deadwood, South Dakota, and sentenced to death. In 1883 his lawyers petitioned for writs of habeas corpus and certiorari; his case was argued in November 1883 before the U.S. Supreme Court. In a unanimous decision, the court ruled that, according to the provisions of the Treaty of Fort Laramie, the Dakota Territorial court had no jurisdiction over the Rosebud reservation; it overturned Crow Dog's conviction.[85][86][87] In response to this ruling, Congress passed the Major Crimes Act in 1884, defining crimes that would be prosecuted under federal law.
- Major Crimes Act, 18 U.S.C. § 1: Congress gave federal authorities concurrent jurisdiction over seven major crimes committed on a reservation, regardless of whether one of the parties was Indian. This legislation reduced the criminal jurisdiction previously held by tribal courts.[88][89]
- United States v. Quiver, 241 U.S. 602 (1916): Congress left to the Indian Tribal Courts jurisdiction over all crimes not taken by the Federal government.[90][91]
- Iron Crow v. Oglala Sioux Tribe, 231 F.2d 89 (8th Cir. 1956): Indian Tribal Courts have inherent jurisdiction over all matters not taken over by the Federal government.[92][93]
- Oliphant v. Suquamish Indian Tribe, 435 U.S. 191 (1978): Indian Tribes do not have inherent criminal jurisdiction over non-Indians absent Congressional authority.[94]
- United States v. Wheeler, 435 U.S. 313 (1978): Indian Tribes have inherent powers to punish offenses against Tribal laws when committed by Tribal members.[95]
Law enforcement
[edit]
In traditional Sioux society, law enforcement was performed by members of the warrior societies, such as the Kit Foxes, Badgers and Crow Owners, known as the akicitas. They maintained order in camp and during communal buffalo hunts. Each band would appoint one society as the official akicita group for the year.[96] This custom prevailed for a short time after the Sioux were forced onto the reservations.
In 1878, Congress authorized the formation of an Indian police force to provide law enforcement in Indian territory and upon reservations. They were superseded by police assigned and managed by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA). The BIA police force is composed of members of various Native American tribes from throughout the United States, and personnel often do not belong to the nations they oversee.
Since the late 1970s, the Oglala Sioux Tribe has received Federal funding to maintain its own reservation police, supplemented by BIA personnel. The FBI has jurisdiction for any felony crimes committed upon the reservation. After the reservation police respond to the initial call, a BIA police person initiates the investigation and notifies the FBI.[97]
The OST is developing a new Tribal Justice Center, to include the tribal courts and a restorative justice courtroom. The latter concept relates to traditional Lakota ideas about restoring the victim and offender to balance within the community. In practice, it is intended to bring together the affected parties in facilitated communication, together with members of the community; to settle on a form of reparation or compensation by the offender that is satisfactory to the victim, which may include money, public apology, and/or community service work; and to bring the offender quickly back within the community with its support for the future. As the process is being used at Kahnawake, a Mohawk reserve in Canada, the First Nation community works to intervene and settle issues before arrest.[98]
Social issues and economy
[edit]
Pine Ridge is the eighth-largest reservation in the United States and it is the poorest. The population of Pine Ridge suffer health conditions, including high mortality rates, depression, alcoholism, drug abuse, malnutrition and diabetes, among others. Reservation access to health care is limited compared to urban areas, and it is not sufficient. Unemployment on the reservation hovers between 80% and 85%, and 49% of the population live below the federal poverty level.[99] [clarification needed] Many of the families have no electricity, telephone, running water, or sewage systems; and many use wood stoves to heat their homes, depleting limited wood resources.
Health and healthcare
[edit]The population on Pine Ridge has among the shortest life expectancies of any group in the Western Hemisphere: approximately 47 years for males and 52 years for females in 2004. The infant mortality rate is five times the United States national average, and the adolescent suicide rate is four times the United States national average. Members of the reservation suffer from a disproportionately high rate of poverty and alcoholism.[100] By 2011, a gang culture formed among Native American teenagers on the reservation.[101] Young residents leave the reservation for larger cities.
The Pine Ridge Comprehensive Health Facility is the on-reservation hospital run by the Indian Health Service. The 110,000 square feet (10,000 m2) inpatient hospital also has an outpatient clinic, dental clinic, and a surgery suite. The emergency room is staffed by two physicians as well as two physician assistants and a hospitalist in triage. The "Sick Kids" clinic is also based at the facility, with pediatricians on staff. During the Covid-19 pandemic, the hospital increased its capacity to provide respiratory and critical care, with assistance from Stanford Center for Innovation in Global Health.[102]
In June 2011, the OST broke ground on a long-planned 60-bed nursing home facility, to be completed within two years. It was developed in cooperation with the federal government, the states of Nebraska and South Dakota. In October 2016, the Oglala Lakota Nursing Home, $6.5-million, 80-bed nursing home for the care of their elderly, opened in White Clay, South Dakota.[103] The tribe borrowed money for a loan for the facility from the Mdewakanton Shakopee tribe, agreeing to "an independent advisory board and an experienced outside management firm."[103] It is working with Native American Health Management, LLC (NAHM), to gain training for staff and oversight of operations until people gain experience.
Alcoholism
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (February 2017) |
Alcoholism is widespread on the reservation, affecting an estimated 85 percent of the families.[104] Tribal police estimate that 90 percent of the crimes are alcohol-related.[104]
Because of historic problems with alcohol use by its members, the Oglala Sioux Tribe has prohibited the sale and possession of alcohol on the Pine Ridge Reservation since 1832. The exception was a brief period in the 1970s when on-reservation sales were tried. The town of Whiteclay, Nebraska (just over the South Dakota-Nebraska border), previously had approximately 12 residents and four liquor stores, which sold over 4.9 million 12-ounce cans of beer in 2010 almost exclusively to Oglala Lakota from the reservation (nearly 170 cans per person). The Whiteclay liquor stores were shut down by the state of Nebraska in 2017, though the store owners are appealing to have the stores reopened.[105]
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) is a spectrum of anatomical structural anomalies, and behavioral, neurocognitive disabilities resulting from the exposure of a fetus to alcohol in the womb. The most severe manifestation within this spectrum is fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS).[106] A quarter of the children born on the reservation are diagnosed with either FASD or FAS, resulting in lifelong challenges.[107]
Education
[edit]The state of education on the reservation is severely lacking in multiple areas. The school drop-out rate is[when?] over 70%, and the teacher turnover rate is eight times that of the U.S. national average.[citation needed]
In 1971 the tribe founded the Oglala Lakota College, one of the earliest tribal colleges in the nation, and part of Native American institution building of the last 40 years. First started as a two-year community college, it has expanded to offer four-year baccalaureate degrees, as well as a master's in Lakota leadership. It is operated by tribal people, with a tribal board. In 2011, it had an enrollment of 1,400.[108] Since 1994, tribal colleges have been classified as land-grant colleges by the U.S. Congress.
Oglala Lakota County School District (formerly the Shannon County School District) serves all areas in Oglala Lakota County.[109] It includes:
- Lakota Tech High School
- Batesland Elementary School (preK-8th)
- Red Shirt School
- Rockyford Elementary School
- Wolf Creek Elementary School
Bennett County School District 03-1 serves areas in Bennett County.[110]
The Kadoka School District 36-2 serves the portion of Jackson County that is a part of the reservation.[111]
The portion in Sheridan County, Nebraska is zoned to Gordon-Rushville Public Schools.[112]
Bureau of Indian Education (BIE)-operated and affiliated schools include:
- Crazy Horse School (K-12th)[113]
- Little Wound School (K-12)
- Pine Ridge School (K-12)
- American Horse School (K-8)[114]
- Porcupine School (K-8)[115]
- Wounded Knee District School[116]
Other K-12 Schools operating on the Reservation include:
- Lakota Waldorf School
- Loneman Day School (Isnawica Owayawa)
- Head Start at Oglala Lakota College
Private schools include:
- Red Cloud Indian School that consists of three schools: Our Lady of Lourdes School (K–8), Red Cloud Elementary (K-8) and Red Cloud High School.
Lakota Immersion Childcare
[edit]Globally, there are currently only 2,000 Lakota language speakers, and fewer than 1,000 at Pine Ridge.[117] The age of the average Lakota speaker is 60, making it a "critically endangered" language.[118][119]
In the fall of 2012, a new program was founded to combat the loss of the language and create a young generation of fluent Lakota speakers. Peter Hill, a former elementary teacher at the reservation who speaks Lakota, started the early childcare language immersion program from his own basement, initially serving five students with crowdsourced funding.[118][120][121] In the program, students and teachers speak exclusively Lakota, with children eventually learning English as a second language. Over the last six years, the childcare program has expanded significantly to serve students ages one to five, and has additionally begun offering kindergarten and first grade.[122][123] A continuing challenge for the school is creating teaching materials, since textbooks and other teaching resources are not typically printed in Lakota. Thus, creating new materials like children's books, apps, or videos, as well as translation of existing works into the language is crucial.[121]
Beyond the immersion childcare, other efforts are underway to bring Lakota into community members' lives in relevant ways: basketball games are frequently announced in Lakota, after new words were coined and the coach began using them in practices and drills with the teams. The first news website written entirely in Lakota was launched in 2016.[124]
Economy
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (February 2017) |

As of 2011, the reservation has little economic development or industry. No discount stores are located on the reservation.[100] Though its people receive $80 million per annum in federal monies, such as Social Security and veterans benefits, most of this money is spent largely in stores located off the reservation in Nebraska border towns, creating no net benefit for the tribe. As the journalist Stephanie Woodward noted, little money changes hands within the reservation.[104]
As an example of the money that goes outside the reservation to border towns, the owner of Whiteclay's grocery store, Arrowhead Foods, said he "did more than a million dollars in business last year, with an entirely Native American clientele."[104] Similarly, Nebraska State Senator LeRoy J. Louden, whose district includes Whiteclay, noted the recent construction of a Walmart superstore at Chadron, Nebraska, another border town. He said, "That store was built because of the reservation."[104]
The tribe has prohibited the sale and consumption of alcohol on the reservation. Still, Pine Ridge residents support four liquor stores across reservation borders in the town of Whiteclay, Nebraska In 2010, these businesses paid $413,932 in federal and state excise taxes on the sale of liquor, according to the Nebraska State Liquor Commission.[104] Some residents have argued that the climbing rate of alcoholism on the reservation shows the failure of the prohibition policy. They argue that if the tribe legalized alcohol sales, it could keep much of their people's wealth from flowing to Nebraska, allowing for such monies to instead be directed toward the reservation's economy and health care services and new projects like building a detoxification facility and rehab clinic.
Despite the lack of formal employment opportunities on Pine Ridge, considerable agricultural production takes place on the reservation. Only a small percentage of the tribe directly benefits from agriculture, as land is leased to agricultural producers. According to the USDA, in 2002 there was nearly $33 million in receipts from agricultural production on Pine Ridge. Less than one-third of that income went to members of the tribe.[125]
Most employment on the reservation is provided by community institutions, such as the tribal Oglala Lakota College, and other schools; the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA); and the U.S. Indian Health Service (IHS). In October 2016, the tribe opened an 80-bed nursing home; at full operation, it should employ 100 staff. The tribe is working on building a justice center and has advertised an art competition to decorate its spaces, including the tribal courts and a restorative justice courtroom.
Enterprises owned by the Oglala Sioux tribe include the Prairie Wind Casino, a Parks and Recreation Department, guided hunting, and cattle ranching and farming.[126] The Oglala Sioux Tribe also operates the White River Visitor Center near the Badlands National Park.[127] It has one radio station, KILI-FM in Porcupine.
In 1973 at the time of the Wounded Knee Incident, not one Native American worked for a South Dakota newspaper. In 1981 the Lakota journalist Tim Giago founded and published the independent Lakota Times on the reservation. (Most such newspapers have been owned by tribal governments.)[128] He renamed it Indian Country Today in 1992, as he was providing more national coverage of Native American news.[129]
In 1998 he sold the paper to the Oneida Nation; it was then the largest independent Native American paper in the country. It continues to operate the paper as part of a media network; Indian Country Today features regular political coverage that notes the increasing number of Native Americans gaining office at the local and state levels. Giago founded the Native American Journalists Association (NAJA) and has worked to recruit Native American students into journalism through its foundation, as well as to establish Indian studies in journalism schools.[129]
Connie Smith started the Lakota Country Times, a weekly newspaper which she owns. It is the official legal newspaper for the Pine Ridge and Rosebud reservations. It also publishes material online. In 2009 it won first place for general excellence of its website from NAJA, and in 2010 won three prizes, including two for best articles.[130]
Lakota Federal Credit Union, established to serve the financial needs of residents of the reservation, was established in 2012.[131]
Industrial hemp
[edit]
After doing research and noting the worldwide market for hemp, in July 1998, the Tribal Council approved 'industrial hemp agriculture' for the reservation. With demand high for the crop, three Lakota farmers, Tom Cook, his wife Loretta Afraid of Bear and American Horse, grandson of Chief American Horse, formed the Slim Butte Land-Use Association.[132] To emphasize the issue of Sioux sovereignty in land use, they publicly announced the first planting of industrial hemp seeds on April 29, 2000, on the 132nd anniversary of the signing of the 1868 Fort Laramie Treaty, which established the reservation. The Association believed production of industrial hemp-based concrete could help solve the severe shortage of suitable dwellings on the reservation, as it is a sustainable construction material, and work for the unemployed. Hemp can also be processed to yield oil for cooking and other products.[133]
Congress in 1968 prohibited the cultivation of Cannabis-related crops, including hemp, as part of anti-drug legislation, although hemp does not have the psychoactive properties of cannabis as a drug. Industrial hemp is legal in Canada.[134] The law in the U.S. is enforced by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). In August 2000 and July 2001, federal DEA agents destroyed industrial hemp crops on the Pine Ridge reservation.[134] After the raid destroyed his crops, the farmer Alex White Plume[134] appealed a DEA court order that prohibited his growing the crop, but the 8th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed the district court ruling in United States v. White Plume (8th Cir. 2006), that the Lakota had to comply with DEA registration process and get a permit to cultivate hemp.[135] The former crop is currently growing wild in the area.[136]
The North Dakota legislature has authorized hemp growing statewide and issued the nation's first two state licenses to grow hemp. The licensed farmers may face DEA legal problems if they do not acquire DEA permits. As the DEA had not yet acted on their requests, in June 2007 the men filed a lawsuit seeking federal court permission to grow the crop without being subject to federal criminal charges.[135]
Private enterprise at Pine Ridge
[edit]Members of the tribe have developed a variety of private enterprises, from arts to modern technologies. Numerous artists maintain private studios and use diverse media in both traditional Lakota artforms, such as parfleche and beadwork, and contemporary styles.
The Oglala are becoming involved in start-up tech companies, such as Lakota Solar Enterprises (LSE), started on the Pine Ridge Reservation in 2006 by Henry Red Cloud (a fifth-generation descendant of Chief Red Cloud) with help from the non-profit org Trees, Water and People. Lakota Solar Enterprises is active in education and training for the advancement of renewable and sustainable energy and technology with a focus of bringing employment opportunities to members of OST as well as other tribal nations throughout the United States. Such technologies include: solar heating and electricity; compressed earth blocks for structural use; geothermal heating; solar assisted irrigated farming, cellulose insulation, and wind generated power.
Tourism
[edit]
History
[edit]- Wounded Knee Massacre and burial site. The events at Wounded Knee represents a significant event in Native American and United States history; it was the last significant clash between Native Americans and U.S. troops and was considered to be the closing of the Western Frontier. The trail that Spotted Elk and his band took on the reservation is marked with signs, including the spot where they surrendered to U.S. troops and were escorted to a site by Wounded Knee Creek.
- Stronghold Table: a remote mesa in what is now the Stronghold (South) Unit of Badlands National Park, which is administered by the tribe. Site of the last Ghost Dances prior to the Wounded Knee Massacre.
- Red Cloud Cemetery: location of the grave of Chief Red Cloud, as well as Bloody Knife (1840–1876), Chief of the Indian Scouts of the 7th Cavalry under General George Armstrong Custer. Bloody Knife was killed at the Battle of the Little Bighorn while assigned to Major Marcus Reno's detachment.
Cultural tourism
[edit]- Oglala Lakota Nation Pow Wow, an annual pow wow featuring dancers from various parts of the U.S.
- Badlands Ranch Resort: Started as private enterprise, it was purchased in July 2009 by the Oglala Sioux Tribe. It is located at the base of Badlands National Park.
Ecotourism
[edit]The Oglala Sioux Park & Recreation Authority offers eco-tours and hunting trips on the reservation as well as engaging in wildlife conservation work.
- Geology: The Badlands (Makhóšiča)- formed by erosion, represent over 65 million years of the earth's geological history starting from the late Cretaceous when the entire middle of the United States was covered by the Western Interior Seaway. The Pine Ridge area contain one of the largest deposits of mammal fossils from the Oligocene epoch.
- Paleontology: One of the most complete fossil accumulations in North America is found within the badlands. The rocks and fossils preserve evidence of ancient ecosystems and give scientists clues about how early mammal species lived.
- Flora: Pine Ridge is located in the Great Plains region, which encompasses the nation's largest grassland ecosystem. the northern portion of the reservation and Badlands National Park contain one of the largest expanses of mixed grass prairie in the United States.
- Fauna: In addition to bison, the reservation is also home to pronghorn (Antilocapra americana).[137] There is a colony of endangered black-footed ferret, the only ferret native to North America, in the Conata Basin, which is also home to black-tailed prairie dogs.
- White River: A Missouri River tributary that flows 580 miles (930 km)[138] through Nebraska and South Dakota. A variety of fish species suitable for sportfishing live in the river.[citation needed]
Casino
[edit]Prairie Wind Casino, which began operation in 1994 in three doublewide trailers, was upgraded with the completion of a $20 million casino, a 78-room hotel and a full-service restaurant in early 2007. The casino provides 250 jobs, most held by tribal residents, with revenues helping support education and social welfare efforts.[139]
Geography
[edit]
Located in southwest South Dakota, the reservation takes 3,400 square miles (8,800 km2) of space. The nearest urban center, Rapid City, South Dakota, is 120 miles (190 km) from the center of the reservation.[100]
The most inland point in North America is located within the reservation, near the town of Allen, and is 1,650 km (1,030 mi) from the nearest coastline.
Bennett County and Oglala Lakota County make up much of the reservation.[140][141] The reservation takes up the southern portion of Jackson County.[142] A small portion is in Sheridan County, Nebraska.[143]
Topography
[edit]
The topography is generally rolling mixed grass prairie, interspersed in various location, especially to the north, into typical badlands topography. The higher elevations of the prairie are covered by wind blown sands that form dunes, blowouts, and thin sheets. The southern part of the reservation is crossed by Pine Ridge, which is probably a fault scarp, and which supports the growth of scattered pine and cedar trees. Well-developed sandhills are the dominant features along the southern boundary of the reservation, which extend into the sandhills region of Nebraska.[144]
Only 84,000 acres (340 km2) of the more than 2 million acres (8,100 km2) of the reservation are considered land suitable for agricultural uses, and the climate, soil and water conditions are challenging. Many farmers among the Lakota can do little more than gain a subsistence living from the land.[134]
The White River flows through the reservation. It was named for the water's white-gray color, a result of eroded sand, clay, and volcanic ash carried by the river.[145] Draining a basin of about 10,200 square miles (26,000 km2), the stream flows through a region of sparsely populated hills, plateaus, and badlands.[146] It flows west to east through the reservation.
Geology
[edit]Deposition of sediments in the Badlands began 69 million years ago when an ancient sea, the Western Interior Seaway, stretched across what is now the Great Plains. After the sea retreated, successive land environments, including rivers and flood plains, continued to deposit sediments. Although the major period of deposition ended 28 million years ago, significant erosion of the Badlands did not begin until half a million years ago.
Climate
[edit]| Climate data for Weather Station: Porcupine 11 N, ~17.0 miles Elevation: 2820 feet (-353 ft from town of Pine Ridge) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 33.0 (0.6) |
39.2 (4.0) |
48.5 (9.2) |
59.4 (15.2) |
70.0 (21.1) |
80.3 (26.8) |
88.0 (31.1) |
87.6 (30.9) |
78.0 (25.6) |
64.4 (18.0) |
45.6 (7.6) |
36.2 (2.3) |
59.1 (15.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 6.9 (−13.9) |
12.0 (−11.1) |
20.2 (−6.6) |
30.0 (−1.1) |
42.4 (5.8) |
51.9 (11.1) |
57.8 (14.3) |
55.2 (12.9) |
43.2 (6.2) |
30.1 (−1.1) |
17.7 (−7.9) |
8.7 (−12.9) |
34.0 (1.1) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | .40 (10) |
.47 (12) |
1.00 (25) |
1.90 (48) |
2.81 (71) |
2.95 (75) |
2.66 (68) |
1.57 (40) |
1.35 (34) |
1.43 (36) |
.60 (15) |
.38 (9.7) |
16.64 (423) |
| Source: NOAA[147] | |||||||||||||
Flora and fauna
[edit]
Flora
[edit]The mixed grass prairie contains both ankle-high and waist-high grasses, and fills a transitional zone between the moister tall-grass prairie to the east and the more arid short-grass prairie to the west.
Biologists have identified more than 400 different plant species growing in Badlands National Park. Each plant species is adapted to survive the conditions prevalent in the mixed-grass prairie ecosystem. The climate here is one of extremes: hot, cold, dry, windy and stormy with blizzards, floods, droughts, and fires. Grasses dominate the landscape.[148]
The short-grass and tall-grass prairies intergrade just east of an irregular line that runs from northern Texas to Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska, northwestward into west-central North Dakota and South Dakota. The perimeter is not well defined because of the array of short-stature, intermediate, and tall-grass species that make up an ecotone between the short-grass and tall-grass prairies (Bragg and Steuter 1996). In general, the mixed-grass prairie is characterized by the warm-season grasses of the short-grass prairie to the west and the cool- and warm-season grasses, which grow much taller, to the east. Because of this ecotonal mixing, the number of plant species found in mixed-grass prairies exceeds that in other prairie types.[149] Since 2000, hemp has grown wild here, following a failed attempt in growing it commercially, as a local ordinance allows. The attempt was shut down by the DEA and several other agencies.[136]
Fauna
[edit]The mixed grass prairie is home to a variety of animals. In Badlands National Park, scientists have recorded the presence of 37 mammal species, nine reptile species, six amphibian species, 206 bird species, and 69 butterfly species.[150] The rare swift fox and endangered black footed ferret are among two of the various mammal species found in the Badlands region. Both species feed on the black-tailed prairie dog.
Transportation
[edit]Roads
[edit]
 I-90 passes east to west through Jackson County and Pennington County just north of the reservation with multiple exits in both counties
I-90 passes east to west through Jackson County and Pennington County just north of the reservation with multiple exits in both counties US 18 is an east–west U.S. highway which passes through the reservation. The western terminus is in Orin, Wyoming, at an interchange with Interstate 25. Its eastern terminus of U.S. 18 is in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin.[151] However, U.S. 18 runs concurrent with other U.S. routes from its western terminus to Mule Creek Junction, Wyoming. U.S. 18 is one of the original United States highways of 1926.
US 18 is an east–west U.S. highway which passes through the reservation. The western terminus is in Orin, Wyoming, at an interchange with Interstate 25. Its eastern terminus of U.S. 18 is in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin.[151] However, U.S. 18 runs concurrent with other U.S. routes from its western terminus to Mule Creek Junction, Wyoming. U.S. 18 is one of the original United States highways of 1926. SD 44, also known as the "Rimrock Highway" or "Rimrock Drive" connects Rapid City, South Dakota, with U.S. Highway 385 at Pactola Junction, just north of Pactola Lake. One of the most scenic drives in the Black Hills, SD 44 follows Rapid Creek, a blue-ribbon trout fishery, much of the way, and also follows much of the alignment of the old Rapid City, Black Hills and Western Railroad, also known as the Crouch Line. SD 44 passes through the Jackson County portion of the reservation
SD 44, also known as the "Rimrock Highway" or "Rimrock Drive" connects Rapid City, South Dakota, with U.S. Highway 385 at Pactola Junction, just north of Pactola Lake. One of the most scenic drives in the Black Hills, SD 44 follows Rapid Creek, a blue-ribbon trout fishery, much of the way, and also follows much of the alignment of the old Rapid City, Black Hills and Western Railroad, also known as the Crouch Line. SD 44 passes through the Jackson County portion of the reservation SD 73 (not shown on FDOT map) is a state route that runs north to south through the Jackson County portion of the reservation. It begins at the Nebraska border north of Merriman, Nebraska, as a continuation of Nebraska Highway 61. It runs to the North Dakota border, where it continues as North Dakota Highway 49. It is 250 miles (402 kilometers) in length.
SD 73 (not shown on FDOT map) is a state route that runs north to south through the Jackson County portion of the reservation. It begins at the Nebraska border north of Merriman, Nebraska, as a continuation of Nebraska Highway 61. It runs to the North Dakota border, where it continues as North Dakota Highway 49. It is 250 miles (402 kilometers) in length. SD 407 (not shown on FDOT map) is a short state highway in Oglala Lakota County which turns into Nebraska Highway 87 (N-87), SD 407-N-87, serves as a connector route between U.S. Route 18 (U.S. 18) in Pine Ridge, South Dakota, and U.S. 20 in Rushville, Nebraska.
SD 407 (not shown on FDOT map) is a short state highway in Oglala Lakota County which turns into Nebraska Highway 87 (N-87), SD 407-N-87, serves as a connector route between U.S. Route 18 (U.S. 18) in Pine Ridge, South Dakota, and U.S. 20 in Rushville, Nebraska.
Airports
[edit]Pine Ridge Airport, owned by the Oglala Sioux Tribe, is located two miles (3 km) east of the town of Pine Ridge. The unattended airport has four asphalt runways; runways 12&30 are 5,000 ft × 60 ft (1,524 m × 18 m), runways 6&24 (currently closed) are 3,003 ft × 50 ft (915 m × 15 m). The airport is in poor repair and is used predominately for government flights.[152] The nearest commercial airport to Pine Ridge is Chadron Municipal Airport (CDR / KCDR) in Chadron, Nebraska, approximately 30 miles (48 km) south. The nearest major airport is Rapid City Regional Airport, in Rapid City, South Dakota, approximately 80 miles (130 km) NE. The closest international airport is Denver International Airport in Denver, Colorado approximately 240 miles (390 km) SW.
Public transportation
[edit]On January 30, 2009, the Oglala Sioux Tribe of Pine Ridge held the grand opening of their public transportation system, a bus service with multiple vehicles to cover the entire reservation.[153]
Communities
[edit]
Nebraska
[edit]South Dakota
[edit]- Allen
- Batesland
- Kyle
- Manderson-White Horse Creek
- Oglala
- Pine Ridge
- Porcupine
- Wakpamni Lake
- Wanblee
- Wounded Knee
Notable leaders and residents
[edit]- Albert Afraid of Hawk (1879-1900, Oglala). member of Buffalo Bill's Wild West Show.
- American Horse (Wašícuŋ Tašuŋke), an Oglala Lakota chief during the Sioux Wars of the 1870s.
- Amos Bad Heart Bull (Waŋblí Wapaha), a ledger artist and tribal historian
- SuAnne Big Crow (1974-1992) led the Pine Ridge High School basketball team to state championship in 1989
- William "Hawk" Birdshead, (Oglala, Hunkpapa, Cheyenne, Arapaho) philanthropist, suicide prevention, award winning filmmaker
- Black Elk (Heȟaka Sapa; 1863–1950), an Oglala holy man, and second cousin to Crazy Horse
- Alice Blue Legs, (1925–2003) master quillworker
- Regina Brave, an Oglala Lakota activist
- Tokala Clifford, actor
- Chief Crazy Horse (Tašuŋke Witko), war chief of the Oglala, c. 1870[154]


- Pat Cuny (Oglala), 83rd Infantry Division US Soldier
- Sarah Eagle Heart, Emmy Award-winning producer, writer, and activist
- Cecilia Fire Thunder, first woman elected as president of the Oglala Sioux Tribe
- Tim Giago (1934-2022) Newspaper Publisher, Writer
- Brady Jandreau, former rodeo rider and star of The Rider (2017)
- Kicking Bear (Oglala), chief of the Miniconjou Lakota Sioux tribe.
- Eddie Little Sky, actor.
- Little Wound (Taópi Čík'ala: 1835–1899, Oglala).
- Chief Long Wolf (1833–1892), warrior of Battle of the Little Bighorn and the Sioux Wars.
- Old Chief Smoke (Šóta; 1774–1864), an early Oglala chief and Shirt Wearer
- Chief Red Cloud (1822–1909, Oglala), a chief
- Philip N. Hogen, United States Attorney for the District of South Dakota 1981–1991
- Ed McGaa (Eagle Man), author, attorney and veteran
- Ola Mildred Rexroat, only Native American pilot in the Women Airforce Service Pilots
- William Mervin "Billy" Mills, also known as Makata Taka Hela, is the second Native American to win an Olympic gold medal and the only American ever to win the Olympic gold in the 10,000 meter run
- Sean Sherman, food educator, caterer, author of The Sioux Chef's Indigenous Kitchen
- Teton Saltes, Member of the Oglala Sioux Tribe and NFL offensive lineman
- Chief Spotted Elk, called Big Foot by the U.S. soldiers. His band of Miniconjou Sioux were massacred at Wounded Knee in 1890.[155]
- Touch the Clouds, Oglala chief
- JoAnn Tall, environmental activist at Pine Ridge
- Theresa Two Bulls, legislature, state senator (2004–2008), president of Oglala Sioux Tribe (2008–2010)[156]
- Richard Wilson (April 29, 1934 – January 31, 1990), tribal chairman (1972 to 1976) during the Wounded Knee Incident
- John Yellow Bird Steele, President of the Oglala Sioux Tribe (1992-2010)
- They Even Fear His Horses (Tȟašúŋke Kȟokípȟapi) (1836–1893)
- Charles Trimble (Oglala Lakota Nation), activist and former executive director of the National Congress of American Indians (1972–1978)
References
[edit]- ^ Steven Wilson sings the National Anthem in Lakota
- ^ "Oglala Lakota Nation". Archived from the original on March 7, 2021. Retrieved July 24, 2019.
- ^ {2020 OST DataBook}
- ^ "Biggest Indian Reservations In The United States". WorldAtlas. June 5, 2018.
- ^ "Indian Housing Block Grant Formula" Archived 2009-04-14 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Housing and Urban Development
- ^ Soulek, Lauren (January 12, 2024). "Native American treaty law 101". KELOLAND. Retrieved January 13, 2024.
- ^ United States v. Sioux Nation, 448 U.S. 371, 377 (1980).
- ^ a b U.S. v. Sioux Nation, 448 U.S. at 378.
- ^ a b U.S. v. Sioux Nation, 448 U.S. at 379.
- ^ U.S. v. Sioux Nation, 448 U.S. at 379-380.
- ^ See generally Philbrick, Nathaniel (2010). The Last Stand: Custer, Sitting Bull, and the Battle of the Little Bighorn. Viking. ISBN 978-0-670-02172-7.
- ^ a b "National Historic Landmarks Program: Wounded Knee". National Park Service. Archived from the original on March 9, 2008. Retrieved January 10, 2008.
- ^ Liggett, Lorie (1998). "Wounded Knee Massacre — An Introduction". Bowling Green State University. Archived from the original on December 5, 2011. Retrieved March 2, 2007.
- ^ "Wounded Knee — Lakota" Archived 2010-01-06 at the Wayback Machine, Native American Atrocities
- ^ Jack Utter, Wounded Knee & the Ghost Dance Tragedy, p. 25, National Woodlands Publishing Company; 1st edition (April 1991) ISBN 0-9628075-1-6
- ^ Strom, Karen (1995). "The Massacre at Wounded Knee". Karen Strom. Retrieved August 25, 2013.
- ^ INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES Vol. I, Laws (Compiled to December 1, 1902) http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol1/HTML_files/NEB0861.html Archived 2011-08-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Olson, James Stuart (February 13, 2000). Historical Dictionary of the 1950s. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 9780313306198 – via Google Books.
- ^ INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES Vol. I, Laws; Chapter 405, March 2, 1889. | 25 Stat., 888.[1] Archived 2012-01-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United States. Office of Indian Affairs / Annual report of the commissioner of Indian affairs, for the year 1904 Part I [2]
- ^ "Reservation Boundary Disputes (Uinta, Pine Ridge, Rosebud, Devil's Lake)". March 8, 2003 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ "State of South Dakota and Bennett County, South Dakota v. Acting Great Plains Regional Director, Bureau of Indian Affair" (PDF). October 3, 2018.
- ^ a b Ruling Pine Ridge: Oglala Lakota Politics from the IRA to Wounded Knee, Texas Tech University Press, 2007
- ^ a b c d e f g "Wounded Knee" Archived 2017-02-28 at the Wayback Machine, We Shall Remain, PBS: American Experience, accessed 29 June 2011
- ^ "The 83rd Infantry Division during World War II". encyclopedia.ushmm.org.
- ^ Burnham: Indian Country, God's Country, p.133
- ^ "ESTCP Cost and Performance Report: Multi-Sensor Towed Array Detection System (MTADS)". U.S. Department of Defense. September 1999. Archived from the original on December 11, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
The Reservation is located in the Southwest corner of South Dakota, with the largest part of the Bombing Range located in Oglala Lakota County. The Badlands Bombing Range (BBR) was a live fire range for over 30 years, and most recently was used as a training range for the Air National Guard. Since 1960, portions of the land have been returned to the Oglala Sioux Tribe (OST) in a step- wise fashion. In 1968, Congress enacted Public Law 90-468 returning 202,357 acres to the OST, and setting aside 136,882 acres of formerly held Tribal lands to form the Badlands National Monument, to be managed by the National Park Service. The U.S. Air Force still retains 2,486 acres of land on Bouquet Table within the Reservation boundaries. ... BBR I is a highly visible circular target composed of a 500-foot diameter circular earthberm, with a cross-hair berm inside the circle. ... BBR 1 ... within the National Park, is grassland grazed by both horses and cattle.
- ^ Walker, Airman Kate (October 12, 2011). "Ellsworth contractors work with tribe to destroy bombs". 28th Bomb Wing Public Affairs. Archived from the original (USAF news release) on December 16, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ a b Koster, John (1974). The Road to Wounded Knee. New York, New York: Bantam Books. pp. 224–225.
- ^ Walker, Carson (January 16, 2004). "Widow Says Civil Rights Activist Killed During Wounded Knee Takeover". Justice for Anna Mae and Ray. Archived from the original on July 5, 2008. Retrieved October 27, 2007.
- ^ Walker, Carson (January 16, 2004). "AIM case may help find man". Rapid City Journal. Archived from the original on September 9, 2008. Retrieved October 27, 2007.
- ^ Perry, Barbara (2002). "From ethnocide to ethnoviolence: Layers of native American victimization". Contemporary Justice Review. 5 (3): 231–247. doi:10.1080/10282580213090. S2CID 144629925.
- ^ Banks, Ojibwa Warrior, p. 286
- ^ Peter Matthiessen, In the Spirit of Crazy Horse, Penguin, 1992. ISBN 978-0-14-014456-7.
- ^ Melmer, David (July 19, 2000). "Unsolved deaths debunked by FBI Case by case examination puts some rumors to rest". Indian Country Today. Archived from the original on May 6, 2006. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- ^ staff (May 2000). "Accounting For Native American Deaths, Pine Ridge Indian Reservation, South Dakota". Federal Bureau of Investigation Minneapolis Division. Archived from the original on June 25, 2007. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- ^ staff (July 11, 2000). "INDIAN DEATHS". Native News Online. Archived from the original on December 23, 2007. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- ^ a b "The Pine Ridge Shootout". TIME Magazine. July 7, 1975. Archived from the original on February 26, 2007. Retrieved October 27, 2007.
- ^ "The Leonard Peltier Trial". University of Missouri — Kansas City School of Law. Archived from the original on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 27, 2007.
- ^ a b Nomaan Merchant, "SD jury convicts man in 1975 AIM activist's death", Associated Press, Beaver County Times, December 11, 2010
- ^ "Looking Cloud appeal decision" Archived 2012-03-08 at the Wayback Machine, Eighth Circuit Court
- ^ a b James N. Hughes III, "Pine Ridge, Whiteclay and Indian Liquor Law", Federal Indian Law Seminar, December 2010, p. 7, University of Nebraska College of Law, accessed 27 February 2012
- ^ Paul Hammel, "Tribe's Liquor Tax May Restart Old Boundary Dispute," Archived 2013-05-24 at the Wayback Machine, Omaha World-Herald (Nebraska), 28 December 2006, p. 03B, at H-Amindian Discussion Log, accessed 27 February 2012
- ^ a b c KEVIN ABOUREZK, "Winnebago business leader: Poverty at heart of Whiteclay debacle" Archived 2014-12-16 at the Wayback Machine, Lincoln Journal Star, 7 April 2010, accessed 29 February 2012
- ^ Schulte, Grant (February 9, 2012). "Tribe suing beer companies for alcohol problems". The Boston Globe. Associated Press. Retrieved February 9, 2012.[dead link]
- ^ "Oglala Sioux Tribe v. Jason Schwarting, et al". Justia Dockets & Filings.
- ^ "Oglala Sioux Tribe vs. Jason Schwarting, et al" (PDF). October 1, 2012.
- ^ "Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches".
- ^ "Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches".
- ^ "Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches".
- ^ "Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches".
- ^ "SAFER Web - Company Snapshot KLEMM DISTRIBUTING INC". safer.fmcsa.dot.gov.
- ^ "Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches".
- ^ "FindLaw's Supreme Court of Nebraska case and opinions". Findlaw.
- ^ "Nebraska Secretary of State - Corporation and Business Entity Searches".
- ^ State of Nebraska:https://www.nebraska.gov/sos/corp/corpsearch.cgi?acct-number=10109978
- ^ "Nebraska Liquor Control Commission | License Search". Archived from the original on January 14, 2012.
- ^ "Manta".
- ^ Before the Nebraska Liquor Control Commission[www.lcc.ne.gov/susp_fines/2011/December/53988.pdf]
- ^ "VOTE TO LEGALIZE ALCOHOL ON SD'S PINE RIDGE PASSES". Associated Press. Retrieved August 15, 2013.
- ^ Sam Hurst, "Cecilia Fire Thunder a 'person of character'", Rapid City Journal, 17 December 2005, accessed 13 June 2011
- ^ a b c "Pine Ridge Indian Reservation Facts". Re-Member. Archived from the original on June 20, 2021. Retrieved January 28, 2021.
- ^ "Liquid genocide: alcohol destroyed Pine Ridge reservation - then they fought back". The Guardian. September 29, 2017.
- ^ "Lakota: The Forgotten People of Pine Ridge". Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO). April 15, 2004.
- ^ Gwen Florio, "Indians show political clout: Natives throng polls in 'white' S.D. county" Archived 2008-11-16 at the Wayback Machine, Denver Post, 8 January 2003, accessed 8 June 2011
- ^ Reinhardt, Akim D.; Kidwell, Clara Sue (2007). Ruling Pine Ridge : Oglala Lakota politics from the IRA to Wounded Knee. Lubbock: Texas Tech University Press. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-89672-601-7. OCLC 71004236.
- ^ Reinhardt, Akim D. (2015). Welcome to the Oglala Nation : a documentary reader in Oglala Lakota political history. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-8436-4. OCLC 914715232.
- ^ Harlan, Bill (November 20, 2002). "Steele wins rare Oglala Tribe re-election". Rapid City Journal. Retrieved December 6, 2020.
- ^ "OGLALA SIOUX PRESIDENT JOHN YELLOW BIRD STEELE BIOGRAPHY" (PDF). United States House of Representatives. Retrieved November 29, 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b "Giago: Oglala Sioux President on State Abortion Law". Indianz.Com. March 21, 2006. Retrieved October 5, 2007.
- ^ a b AP, "Two years after 'historic' agreement, no tribe patrols in Whiteclay", Rapid City Journal, 14 May 2007, accessed 13 June 2011
- ^ Melmer, David (June 5, 2006). "Fire Thunder suspended and abortions banned on Pine Ridge". Indian Country Today. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved October 5, 2007.
- ^ "Why Won't South Dakota Voters Ban Abortion?", CBS News, 2 December 2008, accessed 8 July 2011
- ^ CARSON WALKER (Associated Press), "Pine Ridge blockade planned to nab bootleggers", 13 May 2007, accessed 17 February 2012
- ^ Crash, Tom (December 4, 2008). "Steele passes pipe on to Two Bulls | Lakota Times". Lakota Country Times. Retrieved December 6, 2020.
- ^ Tim Giago, "Theresa Two Bulls: A lady of distinction", Huffington Post, 10 January 2010, accessed 8 July 2011
- ^ Levi Rickert, "Bryan Brewer to be Sworn in Tomorrow as President of Oglala Sioux Tribe", Native News Network, accessed 14 December 2012
- ^ Ray, Charles Michael (June 19, 2013). "A Dry Reservation Clashes With Its Liquor Store Neighbors". WBUR. Retrieved December 5, 2020.
- ^ Brandon Ecoffey, "Native Sun News: Oglala Sioux Tribe prepares for inauguration", Native Sun News, 6 December 2012, at Indianz.com, accessed 14 December 2012
- ^ Ecoffey, Brandon (November 5, 2014). "Native Sun News: Oglala Sioux Tribe chooses a new president". indianz.com. Retrieved December 3, 2020.
- ^ "Yellow Bird Steele elected leader of Oglala Sioux". The Mitchell Republic. November 5, 2014. Retrieved December 3, 2020.
- ^ staff, Mike Anderson Journal (November 9, 2016). "Pine Ridge elects new tribal president". Rapid City Journal Media Group.
- ^ Philip J. Prygoski: "From Marshall to Marshall: The Supreme Court's changing stance on tribal sovereignty", Solo Magazine, American Bar Association
- ^ Laurence French: Native American Justice, p.41, Rowman & Littlefield (2003) ISBN 0-8304-1575-0
- ^ Ex parte Crow Dog, 109 U.S. 556 (1883).
- ^ Crow Dog's Case: American Indian Sovereignty, Tribal Law, and United States Law in the Nineteenth Century (Studies in North American Indian History) By Sidney L. Harring p. 107 Publisher: Cambridge University Press (February 25, 1994) ISBN 0-521-46715-2
- ^ Famous American Crimes and Trials: 1860-1912 by Frankie Y. Bailey, Steven M. Chermak p. 101-105 'Praeger Pub (October 2004) ISBN 0-275-98335-8
- ^ Carrie E. Garrow, Sarah Deer: Tribal Criminal Law and Procedure, p.87, AltaMira Press (2004) ISBN 978-0-7591-0718-2
- ^ "679. The Major Crimes Act—18 U.S.C. § 1153". www.justice.gov. February 19, 2015.
- ^ United States v. Quiver, 241 U.S. 602 (1916).
- ^ U.S. Department of the Interior, Federal Indian Law (pp 319–20, (1958).
- ^ Iron Crow v. Oglala Sioux Tribe, 231 F.2d 89 (8th Cir. 1956).
- ^ National Indian Law Library, American Association of Law Libraries, United States. Supreme Court Landmark Indian Law Cases: Landmark Indian law cases, p.432, Fred B Rothman & Co (2003) ISBN 0-8377-0157-0
- ^ Oliphant v. Suquamish Indian Tribe, 435 U.S. 191 (1978).
- ^ United States v. Wheeler, 435 U.S. 313 (1978)
- ^ Royal B. Hassrick: The Sioux: Life and Customs of a Warrior Society, p. 16, University of Oklahoma Press (1988) ISBN 978-0-8061-2140-6
- ^ Vine Deloria, Clifford M. Lytle: American Indians, American Justice, p. 183, University of Texas Press (1983) ISBN 978-0-292-73834-8
- ^ Susan Haslip, "The (Re)Introduction of Restorative Justice in Kahnawake: 'Beyond Indigenization'", E Law, Vol. 9 No. 1 (March 2002), Murdoch University, accessed 3 June 2011
- ^ "Pine Ridge CDP, South Dakota — DP-3. Profile of Selected Economic Characteristics: 2000" Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today U.S. Census Bureau.
- ^ a b c Williams, Matthew. "Reservation Road", TIME. Retrieved on February 26, 2011.
- ^ Williams, Matthew. "Urban Jungle on the Reservation." TIME. Retrieved on February 26, 2011.
- ^ Jensen, Anpotowin (March 29, 2021). "Stanford Medicine team aids Lakota Nation in fighting COVID-19". Scope. Retrieved January 2, 2022.
- ^ a b David Rooks, "Oglala Lakota Nursing Bringing the Elders Home", Indian Country Today, 24 October 2016; accessed 24 October 2016
- ^ a b c d e f Stephanie Woodward, "Gold Mines in Hell", 100Reporters, February 2012
- ^ Kent, Jim. "With Alcoholism Rampant On Nearby Reservation, Nebraska Shuts Town's Liquor Stores". npr.org. National Public Radio. Retrieved December 19, 2017.
- ^ Hoyme, HE; May, PA; Kalberg, WO; Kodituwakku, P; et al. (2005). "A practical clinical approach to diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: clarification of the 1996 institute of medicine criteria". Pediatrics. 115 (1): 39–47. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-0259. PMC 1380311. PMID 15629980.
- ^ Congressional Record, V. 146, Pt. 10, July 10, 2000 to July 17, 2000 By Congress, p.13912
- ^ About: "Oglala Lakota College" Official Website, 2001-2010
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP (INDEX): Oglala Lakota County, SD" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved January 1, 2023. - See text list
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Bennett County, SD" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved January 1, 2023.
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Jackson County, SD" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved January 1, 2023.
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Sheridan County, NE" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved January 1, 2023.
- ^ "Home". www.crazyhorse.k12.sd.us.
- ^ "American Horse School". Bureau of Indian Education. Retrieved August 1, 2021.
- ^ "BIE Schools Directory | Bureau of Indian Education".
- ^ "BIE Schools Directory | Bureau of Indian Education".
- ^ Grunewald, Rob. "Early childhood Native language immersion develops minds, revitalizes cultures | Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis". www.minneapolisfed.org. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^ a b "Lakota language immersion for toddlers aims to revive Sioux culture". The Seattle Times. October 20, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^ "Lakota Language Immersion Expanding in Rapid City". U.S. News. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^ "To keep the Dakota language alive, a young woman looks to preschoolers". The Christian Science Monitor. February 28, 2018. ISSN 0882-7729. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^ a b Lockett, Chynna. "Pine Ridge Immersions Program Creates Lakota Speakers". Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^ "How do you say "smartphone" in Lakota?". The Outline. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^ carletoncollege (November 29, 2017), Lakota Language Initiative at Pine Ridge, archived from the original on November 17, 2021, retrieved November 19, 2018
- ^ "First-Ever Lakota News Website Helps Keep Language Alive and Relevant - Daily Yonder". www.dailyyonder.com. June 14, 2016. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^ "USDA 2002 "Census of Agriculture for Native American Reservations"" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 15, 2007.
- ^ staff (1997). "Oglala Sioux Tribe Community Environmental Profile". Mni Sose Intertribal Water Rights Coalition, Inc. Archived from the original on October 18, 2007. Retrieved October 26, 2007.
- ^ staff. "Badlands National Park Operating Hours & Seasons". U.S. Department of the Interior. Retrieved October 26, 2007.
- ^ Jim Carrier, "South Dakota Indian journalist gave voices to a people long ignored" Archived 2009-10-11 at the Wayback Machine, San Francisco Chronicle, 23 December 2007, accessed 29 June 2011
- ^ a b Tim Giago, "Freedom of the Press in Indian Country", Nieman Reports: Covering Indian Country, Fall 2005, accessed 29 June 2011
- ^ "Lakota Country Times Staff Win Three Awards", Lakota Country Times, 4 August 2010, accessed 8 July 2011
- ^ "NCUA Charters Lakota Federal Credit Union" (Press release). National Credit Union Administration. August 29, 2012. Archived from the original on September 1, 2012.
- ^ Rebecca Clarren, "Seed in the ground", High Country News, n.d., accessed 5 June 2011
- ^ OGLALA SIOUX TRIBE PLANTS INDUSTRIAL HEMP CROP, Hempology
- ^ a b c d "Standing Silent Nation: Film Description" Archived 2015-10-19 at the Wayback Machine, POV, PBS, 3 July 2007, accessed 5 June 2011
- ^ a b Chet Brokaw, "Fight with DEA over hemp leaves White Plume broke", Indian Country News, July 2007, accessed 5 June 2011
- ^ a b Fuller, Alexandra (August 2012). "Life After Wounded Knee". National Geographic. 222 (2): 38. Retrieved August 8, 2012.[dead link]
- ^ Hawes, Alex. "Pronghorns — Survivors of the American Savanna," Zoogoer, November/December 2001
- ^ "National Hydrography Dataset". United States Geological Survey. Archived from the original on March 29, 2012. Retrieved March 30, 2011.
- ^ Daly, Dan (May 10, 2007). "New complex ups ante for Prairie Wind Casino". Rapid City Journal. Retrieved October 26, 2007.[dead link]
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP (INDEX): Bennett County, SD" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Oglala Lakota County, SD" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Jackson County, SD" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Sheridan County, NE" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. p. 2 (PDF p. 3/71). Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ^ Status of Mineral Resource Information for the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation [3]
- ^ Benke and Cushing, p. 445
- ^ Benke and Cushing, p. 449
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on October 30, 2004. Retrieved November 29, 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Badlands: Prairies", National Park Service
- ^ "Habitat: Grasslands" Archived 2010-06-14 at the Wayback Machine, United States Geological Service
- ^ "National Park Service".
- ^ "Endpoints of U.S. highways". Archived from the original on October 6, 2014.
- ^ "AirNav: KIEN - Pine Ridge Airport". www.airnav.com.
- ^ Lil Witt, "Oglala Sioux Transit grand opening Jan. 30" Archived 2011-07-13 at the Wayback Machine, Lakota Country Times, 15 January 2009, accessed 29 May 2011
- ^ Kingsley M. Bray: Crazy Horse: A Lakota Life, p. 153 ISBN 0-8061-3986-2
- ^ Helaine Silverman, D. Fairchild Ruggles: Cultural Heritage and Human Rights, pp. 150-151; ISBN 978-0-387-76579-2
- ^ "Two Bulls to lead Oglala Sioux Tribe", AP, News From Indian Country, November 2008, accessed 8 July 2011
Further reading
[edit]- Glover, Vic (2004), Keeping Heart on Pine Ridge. Natives Voices. ISBN 978-1-57067-165-4.
- Hedges, Chris and Joe Sacco (2012). Days of Destruction, Days of Revolt. Nation Books. ISBN 978-1-56858-824-7.
- Laughland, Oliver and Tom Silverstone. "Liquid genocide: alcohol destroyed Pine Ridge reservation - then they fought back." The Guardian. September 29, 2017.
- Magnuson, Stew (2009), The Death of Raymond Yellow Thunder: And Other True Stories from the Nebraska–Pine Ridge Border Towns, Texas Tech University Press, ISBN 978-0-89672-634-5.
- Reinhardt, Akim D. (2007), Ruling Pine Ridge: Oglala Lakota Politics from the IRA to Wounded Knee. Texas Tech University Press, 2007. ISBN 978-0-89672-601-7.
- Wagoner, Paula L. (2002) They Treated Us Just Like Indians: The Worlds of Bennett County, South Dakota, University of Nebraska Press
- Extensive photo essay on Pine Ridge made for National Geographic Magazine
- TED talk about Pine Ridge
- Native Americans in South Dakota: An Erosion of Confidence in the Justice System, South Dakota Advisory Commission to U.S. Commission on Civil Rights, 2000
- Starita, Joe (2002) The Dull Knifes of Pine Ridge : A Lakota Odyssey, University of Nebraska Press.
External links
[edit]Community websites
- Official website of the Oglala Sioux tribe/Pine Ridge Reservation Archived 2021-05-04 at the Wayback Machine
- The Lakota Country Times
- Friends of Pine Ridge Reservation
Databases
- Pine Ridge Indian Reservation
- American Indian reservations in South Dakota
- Badlands of the United States
- Federally recognized tribes in the United States
- Geography of Bennett County, South Dakota
- Geography of Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota
- Geography of Jackson County, South Dakota
- Geography of Sheridan County, Nebraska
- Native American tribes in South Dakota
- Oglala
- Sioux Wars
- States and territories established in 1889
- 1889 establishments in Dakota Territory






