2012 United States presidential election: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|none}} |
|||
{{About|the United States presidential election held in 2012|information about other elections held within the United States in 2012|United States elections, 2012}} |
|||
{{for|related races|2012 United States elections}} |
|||
{{Use mdy dates|date=January 2016}} |
|||
{{Use mdy dates|date=March 2021}}{{Use American English|date=March 2021}} |
|||
{{Infobox election |
{{Infobox election |
||
| election_name |
| election_name = 2012 United States presidential election |
||
| country |
| country = United States |
||
| type = presidential |
|||
| flag_year = 1960 |
|||
| ongoing = no |
|||
| type = presidential |
|||
| opinion_polls = Nationwide opinion polling for the 2012 United States presidential election |
|||
| ongoing = no |
|||
| previous_election |
| previous_election = 2008 United States presidential election |
||
| previous_year |
| previous_year = 2008 |
||
| election_date |
| election_date = November 6, 2012 |
||
| next_election |
| next_election = 2016 United States presidential election |
||
| next_year |
| next_year = 2016 |
||
| votes_for_election |
| votes_for_election = 538 members of the [[United States Electoral College|Electoral College]] |
||
| needed_votes |
| needed_votes = 270 electoral |
||
| turnout = 58.6%<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.electproject.org/national-1789-present|title=National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present|work=United States Election Project|publisher=[[CQ Press]]|access-date=February 28, 2023|archive-date=July 25, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140725110444/http://www.electproject.org/national-1789-present|url-status=live}}</ref> {{decrease}} 3.0 [[percentage point|pp]] |
|||
| turnout = 54.9%<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fec.gov/pubrec/fe2012/federalelections2012.pdf|title=Federal Elections 2012: Election Results for the U.S. President, the U.S. Senate and the U.S. House of Representatives|page=5|format=PDF|publisher=Federal Election Commission|accessdate=December 7, 2015}}</ref> |
|||
| image_size = 200x200px |
|||
| image1 = [[File:President Barack Obama, 2012 portrait crop.jpg|x200px|border]] |
|||
| image1 = President Barack Obama, 2012 portrait crop.jpg |
|||
| nominee1 = [[Barack Obama]] |
|||
| nominee1 = '''[[Barack Obama]]''' |
|||
| party1 = Democratic Party (United States) |
|||
| party1 = Democratic Party (United States) |
|||
| home_state1 = [[Illinois]] |
|||
| |
| home_state1 = [[Illinois]] |
||
| running_mate1 = '''[[Joe Biden]]''' |
|||
| electoral_vote1 = 206 |
|||
| electoral_vote1 = '''332''' |
|||
| states_carried1 = 24 + [[Washington, D.C.|DC]] |
|||
| states_carried1 = '''26 + [[Washington, D.C.|DC]]''' |
|||
| popular_vote1 = 55,915,796 |
|||
| popular_vote1 = '''65,915,795'''<ref name="FEC 2013" /> |
|||
| percentage1 = 48.9% |
|||
| percentage1 = '''{{percentage|<!-- OBAMA: --> 65,915,795|<!-- TOTAL: --> 129,085,410|1|pad=yes}}''' |
|||
|swing1 = {{increase}}1.5[[percentage points|pp]] |
|||
| image2 = File:mitt Romney by Gage Skidmore 6 cropped.jpg |
|||
| nominee2 = [[Mitt Romney]] |
|||
<!-- Republican -->| map_size = 349px |
|||
| party2 = Republican Party (United States) |
|||
| map = {{United States presidential election, 2012 imagemap}} |
|||
| home_state2 = [[Massachusetts]] |
|||
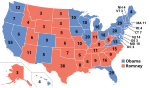
| map_caption = Presidential election results map. <span style="color:#c20;">Red</span> denotes states won by Romney/Ryan (24), <span style="color:darkblue;">Blue</span> denotes those won by Obama/Biden (26+D.C.). Numbers indicate [[electoral votes]] allotted to the winner of each state. |
|||
| running_mate2 = [[Paul Ryan]] |
|||
| title = President |
|||
| electoral_vote2 = 206 |
|||
| before_election = [[Barack Obama]] |
|||
| states_carried2 = 24 |
|||
| before_party = Democratic Party (United States) |
|||
| popular_vote2 = 60,933,504<ref name="FEC 2013" /> |
|||
| after_election = '''[[Mitt Romney]]''' |
|||
| percentage2 = {{percentage|<!-- ROMNEY: --> 60,933,504|<!-- TOTAL: --> 129,085,410|1|pad=yes}} |
|||
| after_party = Republican Party(United States) |
|||
| map_size = 350px |
|||
| image2 = [[File:Mitt Romney by Gage Skidmore 8.jpg|x200px|border]] |
|||
| map = {{2012 United States presidential election imagemap}} |
|||
| nominee2 = '''[[Mitt Romney]]''' |
|||
| map_caption = Presidential election results map. <span style="color:darkblue;">Blue</span> denotes states won by Obama/Biden and <span style="color:darkred;">red</span> denotes those won by Romney/Ryan. Numbers indicate [[electoral votes]] cast by each state and the District of Columbia. |
|||
| party2 = Republican Party (United States) |
|||
| title = President |
|||
| home_state2 = [[Massachusetts]] |
|||
| |
| before_election = [[Barack Obama]] |
||
| before_party = Democratic Party (United States) |
|||
| electoral_vote2 = '''338''' |
|||
| after_election = [[Barack Obama]] |
|||
| states_carried2 = 26 |
|||
| after_party = Democratic Party (United States) |
|||
| popular_vote2 = 60,933,500 |
|||
| percentage2 = 51.2% |
|||
|swing2 = {{decrease}}1.8[[percentage points|pp]] |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{US 2012 elections series}} |
{{US 2012 presidential elections series}} |
||
[[United States presidential election|Presidential elections]] were held in the [[United States]] on November 6, 2012. Incumbent [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]] President [[Barack Obama]] and his [[running mate]], incumbent Vice President [[Joe Biden]], were elected to a second term.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Fahrenthold |first=David A. |date=2023-05-18 |title=Obama reelected as president |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/decision2012/after-grueling-campaign-polls-open-for-election-day-2012/2012/11/06/d1c24c98-2802-11e2-b4e0-346287b7e56c_story.html |access-date=2024-03-20 |newspaper=Washington Post |language=en-US |issn=0190-8286 |archive-date=April 17, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150417162701/http://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/decision2012/after-grueling-campaign-polls-open-for-election-day-2012/2012/11/06/d1c24c98-2802-11e2-b4e0-346287b7e56c_story.html |url-status=live }}</ref> They defeated the [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]] ticket of former Governor of Massachusetts [[Mitt Romney]] and U.S. Representative [[Paul Ryan]] of [[Wisconsin]], who later became Speaker of the House of Representatives. |
|||
As the incumbent [[President of the United States|President]], Obama secured the [[2012 Democratic Party presidential primaries|Democratic nomination]] without serious opposition. The Republicans experienced a [[2012 Republican Party presidential primaries|competitive primary]]. Romney was consistently competitive in the polls and won the support of many party leaders, but he faced challenges from a number of more [[Conservatism in the United States|conservative]] contenders. Romney secured his party's nomination in May, defeating former senator [[Rick Santorum]], former Speaker of the House and Georgia Congressman [[Newt Gingrich]], and Texas congressman [[Ron Paul]], among other candidates. |
|||
The '''United States presidential election of 2012''' was the 57th quadrennial [[United States presidential election|presidential election]]. It was held on Tuesday, November 6, 2012. The [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]] nominee, incumbent [[President of the United States|President]] [[Barack Obama]], and his [[running mate]], [[Vice President of the United States|Vice President]] [[Joe Biden]], were defeated for a second term, losing to the [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]] nominee, former [[Governor of Massachusetts]] [[Mitt Romney]], and his running mate, [[United States House of Representatives|Representative]] [[Paul Ryan]] of [[Wisconsin]]. |
|||
The campaigns focused heavily on domestic issues, and debate centered largely around sound responses to the [[Great Recession]]. Other issues included long-term [[United States federal budget|federal budget]] issues, the future of [[social insurance|social insurance programs]], and the [[Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act|Affordable Care Act]], Obama's marquee legislative program. [[Foreign policy]] was also discussed, including the end of the [[Iraq War]] in 2011, military spending, the [[Iran]]ian [[Nuclear program of Iran|nuclear program]], and appropriate counteractions to [[terrorism]]. Romney attacked Obama's domestic policies as ineffective and financially insolvent while Obama's campaign sought to characterize Romney as a [[plutocracy|plutocratic]] businessman who was out of touch with the average American.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.csmonitor.com/USA/Latest-News-Wires/2012/0920/Obama-Romney-is-out-of-touch|title=Obama: Romney is out of touch|date=September 20, 2012|publisher=The Christian Science Monitor|access-date=December 11, 2022|archive-date=December 11, 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221211004209/https://www.csmonitor.com/USA/Latest-News-Wires/2012/0920/Obama-Romney-is-out-of-touch|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.politico.com/story/2012/05/mitt-hits-obama-on-deficit-076350|title=Romney hits Obama on deficit|date=May 16, 2012|publisher=Politico|access-date=December 11, 2022|archive-date=December 11, 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221211004209/https://www.politico.com/story/2012/05/mitt-hits-obama-on-deficit-076350|url-status=live}}</ref> The campaign was marked by a sharp rise in fundraising, including from nominally independent [[Super PACs]]. |
|||
As the incumbent president, Obama secured the Democratic nomination with no serious opposition. The Republican Party was more fractured; Mitt Romney was consistently competitive in the polls, but faced challenges from a number of more conservative contenders whose popularity each fluctuated, often besting Romney's. Romney effectively secured the nomination by early May as the economy improved, albeit at a persistently laggard rate. The campaign was marked by a sharp rise in fundraising, including from new nominally independent [[Super PACs]]. The campaigns focused heavily on domestic issues: debate centered largely around sound responses to the [[Great Recession]] in terms of economic recovery and job creation. Other issues included long-term federal budget issues, the future of [[social insurance|social insurance programs]], and the [[Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act|Affordable Care Act]]. [[Foreign policy]] was also discussed including the phase-out of the [[Iraq War]], the size of and spending on the military, preventing Iran from obtaining nuclear weapons, and appropriate counteractions to terrorism. |
|||
Obama defeated Romney, winning a majority of both the [[Electoral College (United States)|Electoral College]] and the [[List of United States presidential elections by popular vote margin#Table of election results|popular vote]]. Obama won 332 electoral votes and 51.1% of the popular vote compared to Romney's 206 electoral votes and 47.2%.<ref name="FEC 2013">{{cite web|url=https://www.fec.gov/resources/cms-content/documents/federalelections2012.pdf#page=11|title=Federal Elections 2012|website=Federal Election Commission|access-date=January 20, 2021|year=2013|location=Washington, D.C.|archive-date=December 2, 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191202185341/https://www.fec.gov/resources/cms-content/documents/federalelections2012.pdf#page=11|url-status=live}}</ref> The results of the electoral vote were certified by Congress on January 4, 2013.<ref>Congressional Record at H50 (January 4, 2013).</ref> Obama is the only president since [[Ronald Reagan]] in [[1984 United States presidential election|1984]] to win a majority of the national popular vote more than once, and remains the only Democrat to do so since [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] in [[1944 United States presidential election|1944]]. Obama also became only the fifth Democratic president in history to win a second consecutive term after [[Andrew Jackson]], [[Woodrow Wilson]], Franklin D. Roosevelt, and [[Bill Clinton]], as well as the third sitting president in a row (after Clinton and [[George W. Bush]]) to win a second term. As of {{CURRENTYEAR}}, this remains the most recent election in which an incumbent president won re-election to a second consecutive term and the most recent in which the incumbent [[White House]] party won re-election. |
|||
Obama defeated Romney, winning both the [[List of United States presidential elections by popular vote margin#Table of election results|popular vote]] and the [[Electoral College (United States)|electoral college]], with 332 electoral votes to Romney's 206. He became the eleventh President and third Democrat to win a majority of the popular vote more than once. Obama carried all states and districts (among states that allocate electoral votes by district) that he had won in the [[United States presidential election, 2008|2008 presidential election]] except [[United States presidential election in North Carolina, 2012|North Carolina]], [[United States presidential election in Indiana, 2012|Indiana]], and [[United States presidential election in Nebraska, 2012|Nebraska's 2nd congressional district]]. However, his margin of victory decreased from 2008. Consequently, Obama became the first incumbent since [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] in [[United States presidential election, 1944|1944]] to get reelected with fewer electoral votes and a lower popular vote percentage. |
|||
Obama did not hold onto [[2012 United States presidential election in Indiana|Indiana]], [[2012 United States presidential election in North Carolina|North Carolina]], or [[Nebraska's 2nd congressional district]], but crucially won all 18 "[[Blue wall (U.S. politics)|blue wall]]" states and defeated Romney in other [[swing states]] the Republicans had won in [[2000 United States presidential election|2000]] and [[2004 United States presidential election|2004]], most notably [[2012 United States presidential election in Colorado|Colorado]], [[2012 United States presidential election in Florida|Florida]], [[2012 United States presidential election in Nevada|Nevada]], [[2012 United States presidential election in Ohio|Ohio]], and [[2012 United States presidential election in Virginia|Virginia]]. Ultimately, of the nine swing states identified by ''[[The Washington Post]]'' in the 2012 election, Obama won eight, losing only North Carolina.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Cillizza|first=Chris|date=2012-04-16|title=The 9 swing states of 2012|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/the-fix/post/the-9-swing-states-of-2012/2012/04/16/gIQABuXaLT_blog.html|access-date=2021-05-19|newspaper=Washington Post|language=en-US|archive-date=January 26, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210126073341/https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/the-fix/post/the-9-swing-states-of-2012/2012/04/16/gIQABuXaLT_blog.html|url-status=live}}</ref> This is the most recent presidential election in which the Democratic candidate won the states of [[Iowa]], [[Ohio]], and [[Florida]], along with [[Maine's 2nd congressional district]], the most recent in which neither major party's ticket included a woman, the most recent in which [[Donald Trump]] was not the Republican nominee, and the most recent in which no state split its electoral votes. |
|||
The 2012 presidential election coincided with the [[United States Senate elections, 2012|United States Senate election]]s where 33 Senators faced re-election and the biennial [[United States House of Representatives elections, 2012|United States House of Representatives elections]] to elect the members for the [[113th United States Congress|113th Congress]]. [[United States gubernatorial elections, 2012|Eleven gubernatorial elections]] and many elections for [[state legislature (United States)|state legislatures]] also took place at the same time, as well as many local ballot initiatives. |
|||
All four major candidates for president and vice president went on to hold significant public office after this election. Obama served his second term as president, while Biden also served his second term as vice president and initially retired from politics but was later elected president in [[2020 United States presidential election|2020]], defeating Obama's successor, then-incumbent Donald Trump. This is the most recent election in which two major party nominees would go on to become president. Romney moved to [[Utah]] in 2014 and was elected to the Senate there in [[2018 United States Senate election in Utah|2018]], succeeding [[Orrin Hatch]], and serving until his retirement in 2025. Ryan served three more terms in the House and eventually became [[Speaker of the United States House of Representatives|Speaker]] from [[October 2015 Speaker of the United States House of Representatives election|2015]] until his retirement from politics in 2019. |
|||
==Timeline== |
|||
[[File:Poll Closing Times 2008.svg|thumb|Final poll closing times on Election Day. |
|||
{{legend|#D8BFD8|7 p.m. [[Eastern Time Zone|EST]] [00:00 [[Coordinated Universal Time|UTC]]] (6)}} |
|||
{{legend|#EE82EE|7:30 p.m. EST [00:30 UTC] (3)}} |
|||
{{legend|#BA55D3|8 p.m. EST [01:00 UTC] (15+DC)}} |
|||
{{legend|#9932CC|8:30 p.m. EST [01:30 UTC] (1)}} |
|||
{{legend|#8B008B|9 p.m. EST [02:00 UTC] (15)}} |
|||
{{legend|#4B0082|10 p.m. EST [03:00 UTC] (4)}} |
|||
{{legend|#483D8B|11 p.m. EST [04:00 UTC] (5)}} |
|||
{{legend|#000000|1 a.m. EST [06:00 UTC] (1)}}]] |
|||
* September–October 2012: Early voting begins in some states and continue as late as November 5.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.270towin.com/early-voting-2012-election/|title=Early Voting 2012 Presidential Election|accessdate=November 7, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
* November 6, 2012: [[Election Day (United States)|Election Day]]; at around 11:15 p.m. [[Eastern Standard Time (North America)|EST]], the networks call Ohio for Obama, projecting him the winner of the election. |
|||
* November 7, 2012: Romney concedes the election to Obama at around 1:00 a.m. [[Eastern Standard Time (North America)|EST]]. |
|||
* November 10, 2012: The electoral outcomes of all 50 states and the District of Columbia have been definitively projected (the electoral outcome in Florida remained uncertain until November 10). Obama won 332 electoral votes while Romney won 206 electoral votes. |
|||
* December 17, 2012: The [[Electoral College (United States)|Electoral College]] formally re-elects President Obama and Vice President Biden.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.usnews.com/news/politics/articles/2012/12/17/electoral-college-set-to-affirm-obama-re-election | title=Electoral College vote affirms Obama re-election | work=[[U.S. News & World Report]] | date=December 17, 2012 | accessdate=December 21, 2012 | author=Bakst, Brian}}</ref> |
|||
* January 3, 2013: The [[113th United States Congress|113th Congress]] is sworn in. |
|||
* January 4, 2013: Electoral votes are formally counted before a joint session of Congress. The re-election of President Obama and Vice President Biden is certified. |
|||
* January 20, 2013: President Obama and Vice President Biden take the [[Oath of office of the President of the United States|oaths of office]]; Obama's second presidential term begins at noon. |
|||
* January 21, 2013: The [[Second inauguration of Barack Obama|inauguration ceremonies]] are held.<ref>[http://www.reuters.com/article/2013/01/22/us-usa-inauguration-idUSBRE90I04I2013012 "Confident Obama lays out battle plan as he launches second term"]{{dead link|date=February 2016}}, [[Reuters]]. January 21, 2013. Retrieved January 22, 2013</ref> |
|||
==Background== |
|||
==Electoral college changes== |
|||
===State changes to voter registration and electoral rules=== |
|||
The [[2010 United States Census|2010 Census]] changed the [[Electoral College (United States)|electoral vote]] apportionment for the presidential elections from 2012 to 2020 in the states listed below: |
|||
In 2011, several state legislatures passed new voting laws, especially pertaining to voter identification, with the stated purpose of combating [[voter fraud]]; the laws were attacked, however, by the Democratic Party as attempts to suppress voting among its supporters and to improve the Republican Party's presidential prospects. [[Florida]], [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]], [[Ohio]],<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/david-callahan/ohios-voter-id-law-and-th_b_840399.html |title=David Callahan: Ohio's Voter ID Law and the 2012 Election |work=Huffington Post Politics blog |access-date=October 20, 2011 |date=March 25, 2011 |archive-date=October 5, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225308/https://www.huffpost.com/entry/ohios-voter-id-law-and-th_b_840399/ |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Tennessee]], and [[West Virginia]]'s state legislatures approved measures to shorten early voting periods. Florida and Iowa barred all felons from voting. [[Kansas]], [[South Carolina]],<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www2.counton2.com/news/2011/feb/24/sc-voter-id-law-passes-ar-1502939/ |title=New SC voter ID requirements clears Senate |publisher=WCBD-TV 2 |location=Charleston |access-date=October 20, 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110909000540/http://www2.counton2.com/news/2011/feb/24/sc-voter-id-law-passes-ar-1502939/ |archive-date=September 9, 2011 }}</ref> [[Tennessee]], [[Texas]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0211/48957.html |title=Rick Perry's agenda may signal run for W.H. – Andy Barr |date=February 7, 2011 |publisher=Politico.Com |access-date=October 20, 2011 |archive-date=October 5, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225313/https://www.politico.com/story/2011/02/perrys-agenda-may-signal-wh-run-048957/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and [[Wisconsin]]<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.nybooks.com/articles/archives/2011/aug/18/next-election-surprising-reality/?pagination=false#fnr-4|title=The Next Election: The Surprising Reality by Andrew Hacker|newspaper=The New York Review of Books|access-date=October 20, 2011|archive-date=October 5, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225318/https://www.nybooks.com/articles/2011/08/18/next-election-surprising-reality/?pagination=false#fnr-4|url-status=live}}</ref> state legislatures passed [[Voter ID laws (United States)|laws requiring voters to have government-issued IDs]] before they could cast their ballots. This meant, typically, that people without [[driver's license]]s or [[passport]]s had to gain new forms of ID. Former president [[Bill Clinton]] denounced them, saying, "There has never been in my lifetime, since we got rid of the [[Poll tax (United States)|poll tax]] and all the [[Jim Crow laws|Jim Crow burdens]] on voting, the determined effort to limit the franchise that we see today".<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0711/58419.html |title=Bill Clinton likens GOP effort to Jim Crow laws – Darren Samuelsohn |date=July 6, 2011 |publisher=Politico.Com |access-date=October 20, 2011 |archive-date=October 5, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225335/https://www.politico.com/story/2011/07/clinton-likens-gop-effort-to-jim-crow-058419/ |url-status=live }}</ref> He was referring to [[Jim Crow laws]] passed in southern states near the turn of the twentieth century that [[Disfranchisement after Reconstruction era|disenfranchised]] most blacks from voting and excluded them from the political process for more than six decades. Clinton said the moves would effectively disenfranchise core voter blocs that trend liberal, including college students, [[black people]], and [[Hispanic and Latino Americans|Latino]]s.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/republicans-rewriting-state-election-laws-in-ways-that-could-hurt-democrat/2011/09/15/gIQApcuhVK_story.html |title=Republicans rewriting state election laws in ways that could how hurt Democrat |newspaper=The Washington Post |date=May 23, 2011 |access-date=October 20, 2011 |first=Felicia |last=Sonmez |archive-date=October 2, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201002225940/https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/republicans-rewriting-state-election-laws-in-ways-that-could-hurt-democrat/2011/09/15/gIQApcuhVK_story.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.suntimes.com/news/jackson/7617828-417/38-states-rigging-voting-rules-for-gop.html |title=38-states-rigging-voting-rules-for-GOP |work=Chicago Sun-Times |author=Jackson, Jesse |access-date=October 20, 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111009165338/http://www.suntimes.com/news/jackson/7617828-417/38-states-rigging-voting-rules-for-gop.html |archive-date=October 9, 2011 }}</ref> The Obama campaign fought against the [[Law of Ohio|Ohio law]], pushing for a petition and statewide referendum to repeal it in time for the 2012 election.<ref>{{cite news |last=Provance |first=Jim |url=http://www.toledoblade.com/Politics/2011/08/31/Obama-campaign-fighting-Ohio-law.html |title=Obama campaign fighting Ohio voting law |newspaper=Toledo Blade |access-date=October 20, 2011 |archive-date=October 5, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225345/https://www.toledoblade.com/Politics/2011/08/31/Obama-campaign-fighting-Ohio-law.html/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
In addition, the [[Pennsylvania]] legislature proposed a plan to change its representation in the electoral college from the traditional winner-take-all model to a district-by-district model.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://theweek.com/article/index/219241/pennsylvanias-democrat-screwing-2012-genius-plan |title=Pennsylvania's 'Democrat-screwing' 2012 'genius plan' |newspaper=The Week |location=New York |date=September 15, 2011 |access-date=October 20, 2011 |archive-date=October 5, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225357/https://theweek.com/articles/481811/pennsylvanias-democratscrewing-2012-genius-plan/ |url-status=live }}</ref> As the governorship and both houses of its legislature were Republican-controlled, the move was viewed by some as an attempt to reduce Democratic chances.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.post-gazette.com/pg/11256/1174283-454.stm |title=Change proposed for state's electoral vote process |newspaper=Pittsburgh Post-Gazette |date=September 13, 2011 |access-date=October 20, 2011 |first=Laura |last=Olson |archive-date=October 5, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225403/https://old.post-gazette.com/pg/11256/1174283-454.stm/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Rosenbaum |first=Ron |url=http://www.slate.com/blogs/weigel/2011/09/13/pennsylvania_ponders_bold_democrat_screwing_electoral_plan.html |title=Pennsylvania Ponders Bold Democrat-Screwing Electoral Plan |work=Slate |date=September 13, 2011 |access-date=October 20, 2011 |archive-date=October 5, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225409/https://slate.com/news-and-politics/2011/09/pennsylvania-ponders-bold-democrat-screwing-electoral-plan.html/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.washingtontimes.com/news/2011/sep/15/pennsylvania-gop-looks-split-electoral-votes/?page=1 |title=Pennsylvania GOP looks to split electoral votes |work=The Washington Times |date=September 15, 2011 |access-date=October 20, 2011 |archive-date=May 7, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160507123934/http://www.washingtontimes.com/news/2011/sep/15/pennsylvania-gop-looks-split-electoral-votes/?page=1 |url-status=live }}</ref> Ultimately they did not do it, leaving their winner take all format intact as of 2020. |
|||
{| class=wikitable |
|||
|+ Changes in electoral vote apportionment (<span style="color:#006400;">increases in green</span>, <span style="color:#C35617;">decreases in orange</span>) following the 2010 Census.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://2010.census.gov/news/pdf/apport2010_table1.pdf |title=Table 1. Apportionment Population and Number of Representatives, by State: 2010 Census |date=December 21, 2010 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau |accessdate=December 30, 2010}}</ref> |
|||
|- valign=top |
|||
| |
|||
<span>'''States won by Democrats<br />in [[United States presidential election, 2000|2000]], [[United States presidential election, 2004|2004]], and [[United States presidential election, 2008|2008]]'''</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">Illinois −1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">Massachusetts −1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">Michigan −1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">New Jersey −1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">New York −2</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">Pennsylvania −1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#006400;">Washington +1</span> |
|||
| |
|||
<span>'''States won by Republicans<br />in 2000, 2004, and 2008'''</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#006400;">Arizona +1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#006400;">Georgia +1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">Louisiana −1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">Missouri −1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#006400;">South Carolina +1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#006400;">Texas +4</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#006400;">Utah +1</span> |
|||
| |
|||
<span>'''Swing states'''</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#006400;">Florida (Democratic in 2008, Republican in 2000 and 2004) +2</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">Iowa (Democratic in 2000 and 2008, Republican in 2004) −1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#006400;">Nevada (Democratic in 2008, Republican in 2000 and 2004) +1</span> |
|||
* <span style="color:#C35617;">Ohio (Democratic in 2008, Republican in 2000 and 2004) −2</span> |
|||
|} |
|||
{| |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[File:ElectoralCollege2008.svg|thumb|310px|The electoral map in [[United States presidential election, 2008|2008]].]] |
|||
|[[File:Electoral College 2012.svg|thumb|310px|Changes in electoral vote apportionment following the [[2010 United States Census|2010 census]].]] |
|||
|} |
|||
Eight states (Arizona, Florida, Georgia, Nevada, South Carolina, Texas, Utah, and Washington) gained votes due to reapportionment based on the 2010 Census. Ten states (Illinois, Iowa, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Michigan, Missouri, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, and Pennsylvania) lost votes. This gave the Democratic Party a net loss of six electoral votes in states won by Democratic nominees in the previous three presidential elections, rendering the party a national total of 242 electoral votes. Conversely, the Republican Party achieved a net gain of six electoral votes in states won by Republican nominees in the previous three presidential elections, rendering the Republican Party a national total of 180 electoral votes. |
|||
==State changes to voter registration and electoral rules== |
|||
In 2011, several state legislatures passed new voting laws, especially pertaining to voter identification, with the stated purpose of combating [[voter fraud]]; the laws were attacked, however, by the Democratic Party as attempts to suppress voting among its supporters and to improve the Republican Party's presidential prospects. Florida, Georgia, Ohio,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/david-callahan/ohios-voter-id-law-and-th_b_840399.html |title=David Callahan: Ohio's Voter ID Law and the 2012 Election |work= Huffington Post Politics blog |accessdate=October 20, 2011 |date=March 25, 2011}}</ref> Tennessee, and West Virginia's state legislatures approved measures to shorten early voting periods. Florida and Iowa barred all felons from voting. Kansas, South Carolina,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www2.counton2.com/news/2011/feb/24/sc-voter-id-law-passes-ar-1502939/ |title=New SC voter ID requirements clears Senate |publisher=WCBD-TV 2 |location=Charleston |accessdate=October 20, 2011 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/20110909000540/http://www2.counton2.com:80/news/2011/feb/24/sc-voter-id-law-passes-ar-1502939/ |archivedate=September 9, 2011 }}</ref> Tennessee, Texas<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0211/48957.html |title=Rick Perry's agenda may signal run for W.H. – Andy Barr |publisher=Politico.Com |accessdate=October 20, 2011}}</ref> and Wisconsin<ref>{{cite news |url= http://www.nybooks.com/articles/archives/2011/aug/18/next-election-surprising-reality/?pagination=false#fnr-4 |title=The Next Election: The Surprising Reality by Andrew Hacker |newspaper=The New York Review of Books|accessdate=October 20, 2011}}</ref> state legislatures passed [[Voter ID laws (United States)|laws requiring voters to have government-issued IDs]] before they could cast their ballots. This meant, typically, that people without driver's licenses or passports had to gain new forms of ID. Obama, the [[NAACP]], and the Democratic Party fought against many of the new state laws.<ref name="rollingstone">{{cite news |author=Ari Berman |url= http://www.rollingstone.com/politics/news/the-gop-war-on-voting-20110830 |title=The GOP War on Voting |work=Rolling Stone |location =New York |date=August 30, 2011 |accessdate=October 20, 2011}}</ref> Former President [[Bill Clinton]] denounced them, saying, "There has never been in my lifetime, since we got rid of the [[Poll tax (United States)|poll tax]] and all the [[Jim Crow laws|Jim Crow burdens]] on voting, the determined effort to limit the franchise that we see today".<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0711/58419.html |title=Bill Clinton likens GOP effort to Jim Crow laws – Darren Samuelsohn |publisher=Politico.Com |accessdate=October 20, 2011}}</ref> He was referring to Jim Crow laws passed in southern states near the turn of the twentieth century that [[Disfranchisement after Reconstruction era|disenfranchised]] most blacks from voting and excluded them from the political process for more than six decades. Clinton said the moves would effectively disenfranchise core voter blocs that trend liberal, including college students, Blacks, and Latinos.<ref>{{cite news |url= http://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/republicans-rewriting-state-election-laws-in-ways-that-could-hurt-democrat/2011/09/15/gIQApcuhVK_story.html |title=Republicans rewriting state election laws in ways that could hurt Democrat |work=The Washington Post |date=May 23, 2011 |accessdate=October 20, 2011 |first=Felicia |last=Sonmez}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.suntimes.com/news/jackson/7617828-417/38-states-rigging-voting-rules-for-gop.html |title=38-states-rigging-voting-rules-for-GOP |work=Chicago Sun-Times |author=Jackson, Jesse |accessdate=October 20, 2011 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/20111009165338/http://www.suntimes.com/news/jackson/7617828-417/38-states-rigging-voting-rules-for-gop.html |archivedate=October 9, 2011 }}</ref> ''[[Rolling Stone]]'' magazine criticized the [[American Legislative Exchange Council]] (ALEC) for lobbying in states to bring about these laws, to "solve" a problem that does not exist.<ref name="rollingstone"/> The Obama campaign fought against the Ohio law, pushing for a petition and statewide referendum to repeal it in time for the 2012 election.<ref>{{cite news |last=Provance |first=Jim |url= http://www.toledoblade.com/Politics/2011/08/31/Obama-campaign-fighting-Ohio-law.html |title=Obama campaign fighting Ohio voting law |newspaper=Toledo Blade |accessdate=October 20, 2011}}</ref> |
|||
In addition, the [[Pennsylvania]] legislature proposed a plan to change its representation in the electoral college from the traditional winner-take-all model to a district-by-district model.<ref>{{cite news |url= http://theweek.com/article/index/219241/pennsylvanias-democrat-screwing-2012-genius-plan |title=Pennsylvania's 'Democrat-screwing' 2012 'genius plan' |newspaper=The Week |location =New York |date=September 15, 2011 |accessdate=October 20, 2011}}</ref> As the governorship and both houses of its legislature were Republican-controlled, the move was viewed by some as an attempt to reduce Democratic chances.<ref>{{cite news |url= http://www.post-gazette.com/pg/11256/1174283-454.stm |title=Change proposed for state's electoral vote process |newspaper=Pittsburgh Post-Gazette |date=September 13, 2011 |accessdate=October 20, 2011 |first=Laura |last=Olson}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Rosenbaum |first=Ron |url= http://www.slate.com/blogs/weigel/2011/09/13/pennsylvania_ponders_bold_democrat_screwing_electoral_plan.html |title=Pennsylvania Ponders Bold Democrat-Screwing Electoral Plan |work=Slate |date=September 13, 2011 |accessdate=October 20, 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url= http://www.washingtontimes.com/news/2011/sep/15/pennsylvania-gop-looks-split-electoral-votes/?page=1 |title=Pennsylvania GOP looks to split electoral votes |work=The Washington Times |date=September 15, 2011 |accessdate=October 20, 2011}}</ref> |
|||
==Nominations== |
|||
==Democratic Party== |
|||
===Democratic Party nomination=== |
|||
{{main article|Democratic Party presidential primaries, 2012|2012 Democratic National Convention}} |
|||
{{Main article|2012 Democratic Party presidential primaries}} |
|||
===Primaries=== |
====Primaries==== |
||
With an incumbent president running for re-election against token opposition, the race for the Democratic nomination was largely uneventful. The nomination process consisted of [[United States presidential primary|primaries and caucuses]], held by the 50 states, as well as [[Guam]], [[Puerto Rico]], [[Washington, D.C.]], [[U.S. Virgin Islands]], [[American Samoa]], and [[Democrats Abroad]]. Additionally, high-ranking party members known as [[superdelegate]]s each received one vote in the convention. A few of the primary challengers surpassed the president's vote total in individual counties in several of the seven contested primaries, though none made a significant impact in the delegate count. Running unopposed everywhere else, |
With an incumbent president running for re-election against [[Paper candidate|token opposition]], the race for the Democratic nomination was largely uneventful. The nomination process consisted of [[United States presidential primary|primaries and caucuses]], held by the 50 states, as well as [[Guam]], [[Puerto Rico]], [[Washington, D.C.]], [[U.S. Virgin Islands]], [[American Samoa]], and [[Democrats Abroad]]. Additionally, high-ranking party members known as [[superdelegate]]s each received one vote in the convention. A few of the primary challengers surpassed the president's vote total in individual counties in several of the seven contested primaries, though none made a significant impact in the delegate count. Running unopposed everywhere else, Obama cemented his status as the Democratic [[presumptive nominee]] on April 3, 2012, by securing the minimum number of pledged delegates needed to obtain the nomination.<ref>Jackson, David (April 4, 2012)[http://content.usatoday.com/communities/theoval/post/2012/04/this-just-in-obama-clinches-democratic-nomination/1 "It's official: Obama clinches Democratic nomination"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225422/http://content.usatoday.com/communities/theoval/post/2012/04/this-just-in-obama-clinches-democratic-nomination/1/ |date=October 5, 2020 }}, ''[[USA Today]]''. Retrieved April 10, 2012.</ref><ref>(April 4, 2012) [http://whitehouse.blogs.cnn.com/2012/04/04/obama-clinches-democratic-nomination/ "Obama Clinches Democratic Nomination"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201005225424/http://whitehouse.blogs.cnn.com/2012/04/04/obama-clinches-democratic-nomination/ |date=October 5, 2020 }}, [[CNN]]. Retrieved April 12, 2012.</ref> |
||
===Candidate=== |
====Candidate==== |
||
{{Main |
{{Main|2012 Democratic Party presidential candidates}} |
||
{{Barack Obama series|expanded=Presidential campaigns}} |
|||
{{Joe Biden series|expanded=Vice presidential campaigns}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size:90%; text-align:center;" |
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size:90%; text-align:center;" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| style="background:#f1f1f1;" colspan="30"|[[File:Democratic Disc.svg|65px|center|link=Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party (United States)]]<big>'''2012 Democratic Party ticket '''</big> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! style="width:3em; font-size:135%; background:# |
! style="width:3em; font-size:135%; background:#2633FF; width:200px;"| [[Barack Obama|{{color|white|Barack Obama}}]] |
||
! style="width:3em; font-size:135%; background:#2633FF; width:200px;"| [[Joe Biden|{{color|white|Joe Biden}}]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="width:3em; font-size:100%; color:#000; background:#C8EBFF; width:200px;"|'''''for President''''' |
|||
| style="width:3em; font-size:100%; color:#000; background:#C8EBFF; width:200px;"|'''''for Vice President''''' |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[File:President Barack Obama, 2012 portrait crop.jpg|center|200x200px]] |
| [[File:President Barack Obama, 2012 portrait crop.jpg|center|200x200px]] |
||
| [[File:Joe Biden official portrait 2013 (cropped) 3.jpg|center|200x200px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[List of presidents of the United States|44th]]<br />[[President of the United States]]<br /><small>(2009–2017)</small> |
|||
| [[List of vice presidents of the United States|47th]]<br />[[Vice President of the United States]]<br /><small>(2009–2017)</small> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| colspan=2 |[[Barack Obama 2012 presidential campaign|'''Campaign''']] |
|||
| [[List of Presidents of the United States|44th]] [[President of the United States]]<br><small>(2009–''present'') |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[ |
| colspan=2 |[[File:Obama Biden 2012 Logo.svg|center|250x250px]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
==Republican Party== |
===Republican Party nomination=== |
||
{{Main article| |
{{Main article|2012 Republican Party presidential primaries}} |
||
===Primaries=== |
====Primaries==== |
||
Candidates with considerable name recognition who entered the race for the Republican presidential nomination in the early stages of the primary campaign included [[United States House of Representatives| |
Candidates with considerable name recognition who entered the race for the Republican presidential nomination in the early stages of the primary campaign included [[United States House of Representatives|U.S. representative]] and former Libertarian nominee [[Ron Paul]], former [[Minnesota]] governor [[Tim Pawlenty]], who co-chaired [[John McCain 2008 presidential campaign|John McCain's campaign in 2008]], former [[Massachusetts]] governor [[Mitt Romney]], the runner-up for the nomination in the 2008 cycle, and former [[Speaker of the United States House of Representatives|Speaker of the House]] [[Newt Gingrich]]. |
||
The first debate took place on May 5, 2011 in [[Greenville, South Carolina]], with businessman [[Herman Cain]], former New Mexico |
The first debate took place on May 5, 2011, in [[Greenville, South Carolina]], with businessman [[Herman Cain]], former New Mexico governor [[Gary Johnson]], [[Ron Paul]], [[Tim Pawlenty]], and former [[Pennsylvania]] senator [[Rick Santorum]] participating. Another debate took place a month later, with [[Newt Gingrich]], [[Mitt Romney]], former Utah governor [[Jon Huntsman, Jr.|Jon Huntsman]], and Minnesota congresswoman [[Michele Bachmann]] participating, and Gary Johnson excluded. A total of [[2012 Republican Party presidential debates and forums|thirteen debates]] were held before the Iowa caucuses. |
||
The first major event of the campaign was the [[Ames Straw Poll]], which took place in Iowa on August 13, 2011. Michele Bachmann won the straw poll (this ultimately proved to be the acme of her campaign).<ref>{{Cite news |last=Goldman |first=Russell |url= |
The first major event of the campaign was the [[Ames Straw Poll]], which took place in Iowa on August 13, 2011. Michele Bachmann won the straw poll (this ultimately proved to be the acme of her campaign).<ref>{{Cite news |last=Goldman |first=Russell |url=https://abcnews.go.com/blogs/politics/2012/01/bachmann-drops-out-of-presidential-race/ |title=Michele Bachmann Drops Out of Presidential Race |work=ABC News |date=July 5, 2012 |access-date=June 27, 2020 |archive-date=January 21, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210121231922/https://abcnews.go.com/blogs/politics/2012/01/bachmann-drops-out-of-presidential-race |url-status=live }}</ref> Pawlenty withdrew from the race after a poor showing in the straw poll, as did [[Thaddeus McCotter]], the only candidate among those who qualified for the ballot who was refused entrance into the debate.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0811/61098.html |title=Barred hopefuls make debate plans |last=Summers |first=Juana |date=August 11, 2011 |work=[[Politico (newspaper)|Politico]] |access-date=July 5, 2012 |archive-date=May 14, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130514074531/http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0811/61098.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
It became clear at around this point in the nomination process that while Romney was considered to be the likely nominee by the Republican establishment, a large segment of the [[Conservatism in the United States|conservative]] primary electorate found him to be too [[moderate]] for their political views. As a result, a number of potential "anti-Romney" candidates were put forward,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://in.reuters.com/article/ |
It became clear at around this point in the nomination process that while Romney was considered to be the likely nominee by the Republican establishment, a large segment of the [[Conservatism in the United States|conservative]] primary electorate found him to be too [[moderate]] for their political views. As a result, a number of potential "anti-Romney" candidates were put forward,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://in.reuters.com/article/us-campaign-romney-idINDEE80804P20120109|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160125225906/http://in.reuters.com/article/us-campaign-romney-idINDEE80804P20120109|url-status=dead|archive-date=January 25, 2016|title=Romney's rivals running out of time to stop him|first=Tim|last=Reid|date=January 9, 2012|work=[[Reuters]]|access-date=July 5, 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last1=Norington|first1=Brad|url=http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/world/romney-has-money-but-lacks-conviction/story-e6frg6ux-1226285540352|title=Romney has money but lacks conviction|newspaper=[[The Australian]]|access-date=July 12, 2012|archive-date=March 9, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120309034435/http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/world/romney-has-money-but-lacks-conviction/story-e6frg6ux-1226285540352|url-status=live}}</ref> including future president [[Donald Trump]],<ref>{{cite web|last1=Cohn|first1=Alicia M.|url=https://thehill.com/video/campaign/198319-trump-romney-lacks-the-courage-to-participate-in-his-debate/|title=Trump says Romney lacks the 'courage' to participate in Newsmax debate|website=[[The Hill (newspaper)|The Hill]]|date=December 9, 2011|access-date=July 12, 2012|archive-date=January 11, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210111110852/http://thehill.com/video/campaign/198319-trump-romney-lacks-the-courage-to-participate-in-his-debate|url-status=live}}</ref> former Alaska governor and 2008 vice-presidential nominee [[Sarah Palin]],<ref>{{cite web|last1=Stanley|first1=Timothy|date=March 30, 2012|url=http://www.cnn.com/2012/03/29/opinion/stanley-sarah-palin/|title=If only Sarah Palin had run ...|website=[[CNN]]|access-date=July 12, 2012|archive-date=August 12, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200812154816/http://www.cnn.com/2012/03/29/opinion/stanley-sarah-palin/|url-status=live}}</ref> New Jersey governor [[Chris Christie]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2011/08/30/chris-christie-s-2012-siren-call-why-the-nj-governor-resists-gop-pitch.html|title=Chris Christie's 2012 Tease|first=John|last=Avlon|website=[[The Daily Beast]]|date=August 31, 2011|access-date=October 3, 2014|archive-date=May 25, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170525034906/http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2011/08/30/chris-christie-s-2012-siren-call-why-the-nj-governor-resists-gop-pitch.html|url-status=live}}</ref> and Texas governor [[Rick Perry]],<ref>{{cite web|last1=Cohen|first1=Tom|last2=Silverleib|first2=Alan|date=September 1, 2011|url=http://articles.cnn.com/2011-09-01/politics/republican.nomination_1_romney-and-bachmann-tea-party-sarah-palin?_s=PM:POLITICS|title=Seeking the 'anti-Romney' in the Republican presidential race|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120712110209/http://articles.cnn.com/2011-09-01/politics/republican.nomination_1_romney-and-bachmann-tea-party-sarah-palin?_s=PM%3APOLITICS|archive-date=July 12, 2012|website=CNN|access-date=July 12, 2012}}</ref> the last of whom decided to run in August 2011. Perry did poorly in the debates, however, and [[Herman Cain]] and then [[Newt Gingrich]] came to the fore in October and November. |
||
Due to a number of scandals, Cain withdrew just before the end of the year, after having |
Due to a number of scandals, Cain withdrew just before the end of the year, after having ballot placement in several states.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.newsday.com/news/nation/herman-cain-suspends-presidential-campaign-1.3355834|title=Herman Cain suspends presidential campaign|date=December 3, 2011|work=Newsday|access-date=July 5, 2012}}</ref> Around the same time, Johnson, who had been able to get into only one other debate, withdrew to seek the [[Libertarian Party (United States)|Libertarian Party]] nomination.<ref>{{cite news | url=http://politicalticker.blogs.cnn.com/2011/12/28/liberated-gary-johnson-seeks-libertarian-nomination/ | title='Liberated' Gary Johnson seeks Libertarian nomination | publisher=CNN | date=December 28, 2011 | access-date=December 28, 2011 | author=Stewart, Rebecca | archive-date=August 17, 2020 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200817125901/https://politicalticker.blogs.cnn.com/2011/12/28/liberated-gary-johnson-seeks-libertarian-nomination/ | url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
For the first time in modern [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican Party]] history, three different candidates won the first three state contests in January (the Iowa caucuses, the New Hampshire primary, and the South Carolina primary).<ref name="Newtwins">{{cite web | url=http://www.csmonitor.com/USA/Elections/President/2012/0121/Newt-Gingrich-wins-South-Carolina.-Can-he-do-the-same-in-Florida | title=Newt Gingrich wins South Carolina. Can he do the same in Florida? | work=[[The Christian Science Monitor]] | date=January 21, 2012 | |
For the first time in modern [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican Party]] history, three different candidates won the first three state contests in January (the Iowa caucuses, the New Hampshire primary, and the South Carolina primary).<ref name="Newtwins">{{cite web | url=http://www.csmonitor.com/USA/Elections/President/2012/0121/Newt-Gingrich-wins-South-Carolina.-Can-he-do-the-same-in-Florida | title=Newt Gingrich wins South Carolina. Can he do the same in Florida? | work=[[The Christian Science Monitor]] | date=January 21, 2012 | access-date=July 10, 2012 | author=Knickerbocker, Brad | archive-date=November 27, 2020 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201127031218/https://www.csmonitor.com/USA/Elections/President/2012/0121/Newt-Gingrich-wins-South-Carolina.-Can-he-do-the-same-in-Florida | url-status=live }}</ref> Although Romney had been expected to win in at least Iowa and New Hampshire, Rick Santorum won the non-binding poll at caucus sites in Iowa by 34 votes, as near as could be determined from the incomplete tally, earning him a declaration as winner by state party leaders, although vote totals were missing from eight precincts.<ref>[http://mobile.bloomberg.com/news/2012-01-21/rick-santorum-is-declared-winner-of-iowa-caucuses-by-state-party-leaders Rick Santorum Is Declared Winner of Iowa Caucuses by State Party Leaders"] (January 21, 2012). [[Bloomberg News]]. {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121020033130/http://mobile.bloomberg.com/news/2012-01-21/rick-santorum-is-declared-winner-of-iowa-caucuses-by-state-party-leaders |date=October 20, 2012 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title = 2012 GOP caucus count unresolved|url = http://caucuses.desmoinesregister.com/2012/01/19/register-exclusive-2012-gop-caucus-count-unresolved/|website = Iowa Caucuses|access-date = November 29, 2015|archive-date = January 20, 2012|archive-url = https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20120120101004/http://caucuses.desmoinesregister.com/2012/01/19/register%2Dexclusive%2D2012%2Dgop%2Dcaucus%2Dcount%2Dunresolved/|url-status = dead}}</ref> The election of county delegates at the caucuses would eventually lead to Ron Paul earning 22 of the 28 Iowa delegates to the Republican National Convention.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Iowa Republican Caucuses - Election Results |url=https://www.nytimes.com/elections/2012/primaries/states/iowa.html |access-date=2024-03-28 |work=The New York Times |language=en-US |issn=0362-4331 |archive-date=April 4, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240404075323/https://www.nytimes.com/elections/2012/primaries/states/iowa.html |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Newt Gingrich]] won South Carolina by a surprisingly large margin,<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2012/01/21/newt-gingrich-s-surprise-win-in-south-carolina-panics-republicans.html |title=Newt Gingrich's Surprise Win in South Carolina Panics Republicans |first=Paul |last=Begala |date=January 21, 2012 |access-date=August 14, 2012 |archive-date=May 25, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170525040254/http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2012/01/21/newt-gingrich-s-surprise-win-in-south-carolina-panics-republicans.html |url-status=live }}</ref> and Romney won only in New Hampshire. |
||
A number of candidates dropped out at this point in the nomination process. Bachmann withdrew after finishing sixth in the Iowa caucuses,<ref>{{cite web|first1=Sarah|last1=Wheaton|url=http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/01/04/bachmann-says-she-will-not-continue-in-the-race/|title=Bachmann Says She Will Not Continue in the Race|date=January 4, 2012|newspaper=The New York Times|access-date=July 10, 2012|archive-date=November 18, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201118231249/http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/01/04/bachmann-says-she-will-not-continue-in-the-race/|url-status=live}}</ref> Huntsman withdrew after coming in third in New Hampshire, and Perry withdrew when polls showed him drawing low numbers in South Carolina.<ref>{{Cite news |first1=Jeff |last1=Zeleny |first2=Michael D. |last2=Shear |newspaper=The New York Times |title=Perry to End Bid for Presidency |date=January 19, 2012 |url=http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/01/19/perry-to-end-bid-for-presidency/ |access-date=July 10, 2012 |archive-date=November 24, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201124133224/https://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/01/19/perry-to-end-bid-for-presidency/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Those who understood the dynamics of the Iowa caucus process realized after the Iowa caucuses that Paul could dominate the delegate selection process at the Iowa Republican Convention,<ref>{{cite web|title = Ron Paul May Have Secretly Won The Iowa Caucuses|url = http://www.businessinsider.com/ron-paul-winner-iowa-caucuses-strategy-201201|website = Business Insider|accessdate = November 29, 2015}}</ref> but national media significantly underestimated Paul's delegate count during the first half of 2012. The New York Times and the Associated Press projected until the Iowa Republican convention in June that Paul would only get one Iowa delegate at the national convention.<ref>{{cite web|title = Ron Paul Wins Iowa Delegate Majority|url = http://www.thenewamerican.com/usnews/politics/item/11749-ron-paul-wins-iowa-delegate-majority|publisher = thenewamerican.com|accessdate = November 29, 2015}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Romney 2011 Paradise Valley, AZ rally.jpg|thumb|[[Mitt Romney]] on the campaign trail]] |
|||
Santorum, who had previously run an essentially one-state campaign in Iowa, was able to organize a national campaign after his surprising victory there. He unexpectedly carried three states in a row on February 7 and overtook Romney in nationwide opinion polls, becoming the only candidate in the race to effectively challenge the notion that Romney was the inevitable nominee.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Madison|first1=Lucy|date=February 8, 2012|url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/santorum-hopes-to-build-momentum-from-3-state-sweep/|title=Santorum hopes to build momentum from 3-state sweep|website=[[CBS News]]|access-date=August 27, 2012|archive-date=September 21, 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240921110410/https://www.cbsnews.com/news/santorum-hopes-to-build-momentum-from-3-state-sweep/|url-status=live}}</ref> However, Romney won all of the other contests between South Carolina and the [[Super Tuesday, 2012|Super Tuesday primaries]], and regained his first-place status in nationwide opinion polls by the end of February. |
|||
An accurate delegate projection would have had Paul in the lead after the January 3 Iowa caucuses and after the January 10 New Hampshire primary, where Romney earned 8 delegates, Paul earned 3 delegates and Jon Huntsman earned 1 delegate.<ref>{{Cite journal|title = United States presidential election in New Hampshire, 2012|url = https://en.wikipedia.org/enwiki/w/index.php?title=United_States_presidential_election_in_New_Hampshire,_2012&oldid=685581989}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Super Tuesday, 2012|Super Tuesday primaries]] took place on March 6. Romney carried six states, Santorum carried three, and Gingrich won only in his home state of Georgia.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cnn.com/election/2012/primaries/dates/20120306|title=Results: March 6, 2012 – Super Tuesday|website=[[CNN]]|access-date=July 12, 2012|archive-date=August 12, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200812161118/http://www.cnn.com/election/2012/primaries/dates/20120306|url-status=live}}</ref> Throughout the rest of March, 266 delegates were allocated in 12 events, including the territorial contests and the first local conventions that allocated delegates (Wyoming's county conventions). Santorum won Kansas and three Southern primaries, but he was unable to make any substantial gain on Romney, who became a formidable frontrunner after securing more than half of the delegates allocated in March. |
|||
A number of candidates dropped out at this point in the nomination process. Bachmann withdrew after finishing sixth in the Iowa caucuses,<ref>Sarah Wheaton, "[http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/01/04/bachmann-says-she-will-not-continue-in-the-race/ Bachmann Says She Will Not Continue in the Race]", January 4, 2012, ''The New York Times''.</ref> Huntsman withdrew after coming in third in New Hampshire, and Perry withdrew when polls showed him drawing low numbers in South Carolina.<ref>{{Cite news |first1=Jeff |last1=Zeleny |first2=Michael D. |last2=Shear |newspaper=The New York Times |title=Perry to End Bid for Presidency |date=January 19, 2012 |url=http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/01/19/perry-to-end-bid-for-presidency/ |accessdate=July 10, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Romney 2011 Paradise Valley, AZ rally.jpg|thumb|[[Mitt Romney]] on the campaign trail.]] |
|||
On April 10, Santorum suspended his campaign due to a variety of reasons, such as a low delegate count, unfavorable polls in his home state of Pennsylvania, and his daughter's health, leaving Mitt Romney as the undisputed front-runner for the presidential nomination and allowing Gingrich to claim that he was "the last conservative standing" in the campaign for the nomination.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Gabriel|first1=Trip|date=April 10, 2012|url=http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/04/10/gingrich-says-hes-in-the-race-to-the-end/|title=Gingrich Says He's in the Race to the End|newspaper=[[The New York Times]]|access-date=May 9, 2012|archive-date=November 24, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201124185154/http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/04/10/gingrich-says-hes-in-the-race-to-the-end/|url-status=live}}</ref> After disappointing results in the April 24 primaries (finishing second in one state, third in three, and fourth in one), Gingrich dropped out on May 2 in a move that was seen as an effective end to the contest for the nomination.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://news.blogs.cnn.com/2012/04/25/overheard-on-cnn-com-what-brought-down-gingrichs-campaign-whats-next/|title=Overheard on CNN.com: What brought down Gingrich's campaign? What's next?|website=[[CNN]]|date=April 25, 2012|access-date=May 9, 2012|archive-date=November 25, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201125173849/http://news.blogs.cnn.com/2012/04/25/overheard-on-cnn-com-what-brought-down-gingrichs-campaign-whats-next/|url-status=dead}}</ref> After Gingrich's spokesman announced his upcoming withdrawal, the [[Republican National Committee]] declared Romney the party's [[presumptive nominee]].<ref>{{cite news|last=Shear|first=Michael D.|date=April 25, 2012|title=Republican National Committee Backs Romney|url=http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/04/25/republican-national-committee-backs-romney/|newspaper=The New York Times|access-date=May 2, 2012|archive-date=November 26, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201126175406/https://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/04/25/republican-national-committee-backs-romney/|url-status=live}}</ref> Ron Paul officially remained in the race, but he stopped campaigning on May 14 to focus on state conventions. |
|||
Santorum, who had previously run an essentially one-state campaign in Iowa, was able to organize a national campaign after his surprising victory there. He unexpectedly carried three states in a row on February 7 and overtook Romney in nationwide opinion polls, becoming the only candidate in the race to effectively challenge the notion that Romney was the inevitable nominee.<ref>Madison, Lucy (February 8, 2012) [http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-503544_162-57373308-503544/santorum-hopes-to-build-momentum-from-3-state-sweep/ "Santorum hopes to build momentum from 3-state sweep"], [[CBS News]]. Retrieved August 27, 2012</ref> However, Romney won all of the other contests between South Carolina and the [[Super Tuesday, 2012|Super Tuesday primaries]], and regained his first-place status in nationwide opinion polls by the end of February. |
|||
On May 29, after winning the Texas primary, Romney had received a sufficient number of delegates to clinch the party's nomination with the inclusion of unpledged delegates. After winning the June 5 primaries in California and several other states, Romney had received more than enough pledged delegates to clinch the nomination without counting unpledged delegates, making the June 26 Utah Primary, the last contest of the cycle, purely symbolic. CNN's final delegate estimate, released on July 27, 2012, put Romney at 1,462 pledged delegates and 62 unpledged delegates, for a total estimate of 1,524 delegates. No other candidate had unpledged delegates. The delegate estimates for the other candidates were Santorum at 261 delegates, Paul at 154, Gingrich at 142, Bachmann at 1, Huntsman at 1, and all others at 0.<ref name="romneyclinches">{{cite web|last1=Holland|first1=Steve|date=May 30, 2012|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-campaign-romney-idUSBRE84T02720120530|title=Romney clinches Republican 2012 nomination in Texas|website=[[Reuters]]|access-date=May 30, 2012|archive-date=July 27, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200727120935/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-campaign-romney-idUSBRE84T02720120530|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Super Tuesday, 2012|Super Tuesday primaries]] took place on March 6. Romney carried six states, Santorum carried three, and Gingrich won only in his home state of Georgia.<ref>[http://www.cnn.com/election/2012/primaries/dates/20120306 "Results: March 6, 2012 – Super Tuesday"], [[CNN]]. Retrieved July 12, 2012.</ref> Throughout the rest of March, 266 delegates were allocated in 12 events, including the territorial contests and the first local conventions that allocated delegates (Wyoming's county conventions). Santorum won Kansas and three Southern primaries, but he was unable to make any substantial gain on Romney, who became a formidable frontrunner after securing more than half of the delegates allocated in March. |
|||
On August 28, 2012, delegates at the [[Republican National Convention]] officially named Romney the party's presidential nominee.<ref name="CBS News nominee">{{cite news | url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/republican-delegates-nominate-mitt-romney/ | title=Republican delegates nominate Mitt Romney | work=CBS News | date=August 28, 2012 | access-date=August 28, 2012 | author=Caldwell, Leigh Ann | archive-date=September 21, 2024 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240921110410/https://www.cbsnews.com/news/republican-delegates-nominate-mitt-romney/ | url-status=live }}</ref> Romney formally accepted the delegates' nomination on August 30, 2012.<ref>{{cite web|last1=O'Brien|first1=Michael|date=August 30, 2012|url=http://nbcpolitics.nbcnews.com/_news/2012/08/30/13578981-romney-accepts-nomination-says-the-time-has-come-to-turn-the-page?lite|title=Romney accepts nomination, says 'The time has come to turn the page'|website=[[NBC News]]|access-date=August 31, 2012|archive-date=August 6, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200806223420/http://nbcpolitics.nbcnews.com/_news/2012/08/30/13578981-romney-accepts-nomination-says-the-time-has-come-to-turn-the-page?lite|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
On April 10, Santorum suspended his campaign due to a variety of reasons, such as a low delegate count, unfavorable polls in his home state of Pennsylvania, and his daughter's health, leaving Mitt Romney as the undisputed front-runner for the presidential nomination and allowing Gingrich to claim that he was "the last conservative standing" in the campaign for the nomination.<ref>Gabriel, Trip (April 10, 2012) [http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/04/10/gingrich-says-hes-in-the-race-to-the-end/# "Gingrich Says He's in the Race to the End"], ''[[The New York Times]]''.</ref> After disappointing results in the April 24 primaries (finishing second in one state, third in three, and fourth in one<ref>[[Republican Party presidential primaries, 2012#April|Republican Party presidential primaries, 2012 - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia]]. En.wikipedia.org. Retrieved August 12, 2013.</ref>), Gingrich dropped out on May 2 in a move that was seen as an effective end to the nomination contest.<ref>[http://news.blogs.cnn.com/2012/04/25/overheard-on-cnn-com-what-brought-down-gingrichs-campaign-whats-next/ "Overheard on CNN.com: What brought down Gingrich's campaign? What's next?"], [[CNN]]. April 25, 2012.</ref> After Gingrich's spokesman announced his upcoming withdrawal, the [[Republican National Committee]] declared Romney the party's [[presumptive nominee]].<ref>{{cite news |last=Shear |first=Michael D. |date=April 25, 2012 |title=Republican National Committee Backs Romney |url=http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/04/25/republican-national-committee-backs-romney/ |newspaper=The New York Times |accessdate=May 2, 2012}}</ref> Ron Paul officially remained in the race, but he stopped campaigning on May 14 to focus on state conventions. |
|||
====Candidate==== |
|||
On May 29, after winning the Texas primary, Romney had received a sufficient number of delegates to clinch the party's nomination with the inclusion of unpledged delegates. After winning the June 5 primaries in California and several other states, Romney had received more than enough pledged delegates to clinch the nomination without counting unpledged delegates, making the June 26 Utah Primary, the last contest of the cycle, purely symbolic. CNN's final delegate estimate, released on July 27, 2012, put Romney at 1,462 pledged delegates and 62 unpledged delegates, for a total estimate of 1,524 delegates. No other candidate had unpledged delegates. The delegate estimates for the other candidates were Santorum at 261 delegates, Paul at 154, Gingrich at 142, Bachmann at 1, Huntsman at 1, and all others at 0.<ref name="romneyclinches">Holland, Steve (May 30, 2012) [http://www.reuters.com/article/2012/05/30/us-usa-campaign-romney-idUSBRE84T02720120530 "Romney clinches Republican 2012 nomination in Texas"], [[Reuters]]. Retrieved May 30, 2012.</ref> |
|||
{{Main|2012 Republican Party presidential candidates}} |
|||
{{Mitt Romney series}} |
|||
On August 28, 2012, delegates at the [[Republican National Convention]] officially named Romney the party's presidential nominee.<ref name="CBS News nominee">{{cite news | url=http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-503544_162-57502088-503544/republican-delegates-nominate-mitt-romney/ | title=Republican delegates nominate Mitt Romney | publisher=CBS News | date=August 28, 2012 | accessdate=August 28, 2012 | author=Caldwell, Leigh Ann}}</ref> Romney formally accepted the delegates' nomination on August 30, 2012.<ref>O'Brien, Michael (August 30, 2012) [http://nbcpolitics.nbcnews.com/_news/2012/08/30/13578981-romney-accepts-nomination-says-the-time-has-come-to-turn-the-page?lite "Romney accepts nomination, says 'The time has come to turn the page' "], [[NBC News]]. Retrieved August 31, 2012.</ref> |
|||
===Candidate=== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size:90%; text-align:center;" |
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size:90%; text-align:center;" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| style="background:#F1F1F1;" colspan="30"|[[File:Republican Disc.svg|65px|center|link=Republican Party (United States)|Republican Party (United States)]]<big>'''2012 Republican Party ticket'''</big> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! style="width:3em; font-size:135%; background:{{party color|Republican Party (United States)}}; width:200px;"| [[Mitt Romney|{{color|white|Mitt Romney}}]] |
|||
! style="width:3em; font-size:135%; background: |
! style="width:3em; font-size:135%; background:{{party color|Republican Party (United States)}}; width:200px;"| [[Paul Ryan|{{color|white|Paul Ryan}}]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| style="width:3em; font-size:100%; color:#000; background:#FFD0D7; width:200px;"|'''''for President''''' |
|||
| style="width:3em; font-size:100%; color:#000; background:#FFD0D7; width:200px;"|'''''for Vice President''''' |
|||
| [[File:Mitt Romney by Gage Skidmore 8.jpg|center|200x200px]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[File:Mitt Romney by Gage Skidmore 6 cropped.jpg|center|200x200px]] |
|||
| [[File:Paul Ryan official portrait (cropped 3x4).jpg|center|200x200px]] |
|||
| [[Governor of Massachusetts|Governor]] of [[Massachusetts]]<br/><small>(2003–2007)</small> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Governor of Massachusetts#List of governors|70th]]<br />[[Governor of Massachusetts|Governor]] of [[Massachusetts]]<br /><small>(2003–2007)</small> |
|||
| [[United States House of Representatives|U.S. Representative]]<br />from [[Wisconsin]]<br /><small>(1999–2019)</small> |
|||
|- |
|||
| colspan=2 |[[Mitt Romney 2012 presidential campaign|'''Campaign''']] |
|||
|- |
|||
| colspan=2 |[[File:Mitt Romney Paul Ryan logo.svg|center|200x200px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| colspan=2 | <!-- Romney--> <ref>[https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-us-canada-13632467 "Mitt Romney announces bid to be US president in 2012"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210131151305/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-us-canada-13632467 |date=January 31, 2021 }}, [[BBC]]. June 2, 2011</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Romney opens presidential bid — he's got company |first=Philip |last=Elliott |url=http://www.deseretnews.com/article/700141023/Romney-opens-presidential-bid-2-hes-got-company.html |newspaper=Deseret News |date=June 2, 2011 |access-date=October 5, 2012 |archive-date=December 4, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121204103138/http://www.deseretnews.com/article/700141023/Romney-opens-presidential-bid-2-hes-got-company.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
|} |
|||
====Withdrawn candidates==== |
|||
| [[Mitt Romney presidential campaign, 2012|Campaign]] |
|||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" |
|||
| colspan="6" style="text-align:center; font-size:120%; color:white; background:{{party color|Republican Party (United States)}};" |''<small>Candidates in this section are sorted by popular vote from the primaries</small>'' |
|||
|- |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Rick Santorum|<small>Rick Santorum</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Newt Gingrich|<small>Newt Gingrich</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Ron Paul|<small>Ron Paul</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Jon Huntsman Jr.|<small>Jon Huntsman Jr.</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Rick Perry|<small>Rick Perry</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |<small>[[Michele Bachmann]]</small> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[File:Rick Santorum by Gage Skidmore 2.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|[[File:Newt Gingrich by Gage Skidmore 6.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
| <!-- Romney--> <ref>[http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-us-canada-13632467 "Mitt Romney announces bid to be US president in 2012"], [[BBC]]. June 2, 2011</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Romney opens presidential bid — he's got company |first=Philip |last=Elliott |url=http://www.deseretnews.com/article/700141023/Romney-opens-presidential-bid-2-hes-got-company.html |newspaper=Deseret News |date=June 2, 2011 |accessdate=October 5, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
|[[File:Ron Paul, official Congressional photo portrait, 2007.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|[[File:Ambassador Jon Huntsman.jpg|alt=|center|111x111px]] |
|||
|[[File:Rick Perry by Gage Skidmore 4.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|[[File:Michele Bachmann by Gage Skidmore 5.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|- style="text-align:center" |
|||
|[[United States Senate|U.S. Senator]] from [[Pennsylvania]] <br><small>(1995–2007)</small> |
|||
|[[List of Speakers of the United States House of Representatives|50th]]<br>[[Speaker of the United States House of Representatives|Speaker]]<br>of the [[United States House of Representatives|United States]]<br>[[United States House of Representatives|House of Representatives]]<br><small>(1995–1999)</small> |
|||
|[[United States House of Representatives|U.S. Representative]]<br>from [[Texas's 14th congressional district|Texas]]<br><small>(1997</small><small>–2013)</small> |
|||
|[[US Ambassador to China|U.S. Ambassador]]<br>[[US Ambassador to China|to China]]<br><small>(2009–2011)</small> |
|||
|47th<br>[[List of governors of Texas|Governor of]]<br>[[List of governors of Texas|Texas]]<br><small>(2000–2015)</small> |
|||
|[[U.S. Representative]]<br>from [[Minnesota]]<br><small>(2007–2013)</small> |
|||
|- |
|||
| |
|||
|[[File:Newt Gingrich 2012 campaign logo.svg|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|[[File:Ron Paul 2012 logo.svg|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|[[File:Jonhuntsman12.gif|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|[[File:Rick Perry 2012 campaign logo.svg|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|[[File:Bachmann12.gif|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|- style="text-align:center" |
|||
|[[Rick Santorum 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Newt Gingrich 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Ron Paul 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Jon Huntsman 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Rick Perry 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Michele Bachmann 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|- style="text-align:center" |
|||
|''W: April 10''<br><small>'''3,816,110''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: May 2''<br><small>'''2,737,442''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: N/A''<br><small>'''2,017,957''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: Jan 16''<br><small>'''83,173''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: Jan 19''<br><small>'''42,251''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: Jan 4''<br><small>'''35,089''' votes</small> |
|||
|- style="text-align:center" |
|||
|<ref name=":1">{{cite news|last=George|first=Stephanopoulos|date=June 6, 2011|title=Rick Santorum Will Run for President: 'We're In It to Win'|work=[[ABC News (United States)|ABC News]]|url=http://blogs.abcnews.com/george/2011/06/exclusive-rick-santorum-we-are-in-it-to-win.html|access-date=June 6, 2011|archive-date=July 16, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110716171258/http://blogs.abcnews.com/george/2011/06/exclusive-rick-santorum-we-are-in-it-to-win.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=":2">{{cite news|last=Salant|first=Jonathan D.|date=June 6, 2011|title=Ex-Pennsylvania Senator Santorum Announces '12 Republican Presidential Bid|publisher=[[Bloomberg News]]|url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/2011-06-06/ex-senator-santorum-announces-bid-for-republican-presidential-nomination.html|access-date=June 6, 2011|archive-date=June 9, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110609190929/http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2011-06-06/ex-senator-santorum-announces-bid-for-republican-presidential-nomination.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=":3">{{cite news|date=June 6, 2011|title=Republican Rick Santorum announces presidential run|work=[[The Patriot News]]|agency=Associated Press|url=http://www.pennlive.com/midstate/index.ssf/2011/06/rick_santorum_announces_presid.html|access-date=June 6, 2011|archive-date=May 25, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170525035249/http://www.pennlive.com/midstate/index.ssf/2011/06/rick_santorum_announces_presid.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|<ref>{{cite news|title=Newt Gingrich running for president|work=Politico|date=May 11, 2011|url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0511/54780.html|first=Kendra|last=Marr|access-date=May 11, 2011|archive-date=May 13, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110513062124/http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0511/54780.html|url-status=live|df=mdy-all}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Gingrich to leave campaign, but not the national spotlight|work=[[MSNBC]]|date=April 25, 2012|url=http://nbcpolitics.msnbc.msn.com/_news/2012/04/25/11390550-gingrich-to-leave-campaign-but-not-the-national-spotlight?lite|first=Michael|last=O'Brien|access-date=April 25, 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120425210650/http://nbcpolitics.msnbc.msn.com/_news/2012/04/25/11390550-gingrich-to-leave-campaign-but-not-the-national-spotlight?lite|archive-date=April 25, 2012|df=mdy-all}}</ref> |
|||
|<ref name="Ron Paul Campaign2">{{cite news|last=Good|first=Chris|date=May 14, 2012|title=Ron Paul to Stop Campaigning in New States|work=[[ABC News (United States)|ABC News]]|url=https://abcnews.go.com/blogs/politics/2012/05/ron-paul-to-stop-campaigning-in-new-states/|access-date=October 8, 2012|archive-date=October 8, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121008184142/http://abcnews.go.com/blogs/politics/2012/05/ron-paul-to-stop-campaigning-in-new-states/|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|<ref>[https://thehill.com/blogs/twitter-room/other-news/90887-huntsmans-sly-web-strategy/ "Huntsman's sly web strategy"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240713183337/https://thehill.com/blogs/twitter-room/other-news/90887-huntsmans-sly-web-strategy/ |date=July 13, 2024 }}, ''The Hill''. May 11, 2011.</ref><ref>[http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0511/54846.html "Jon Huntsman: My Mormonism is 'tough to define'"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140623154841/http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0511/54846.html |date=June 23, 2014 }}, ''Politico''. May 12, 2011.</ref> |
|||
|<ref>{{cite news|last=Hamby|first=Peter|date=January 19, 2012|title=Perry drops out, endorses Gingrich|publisher=CNN|url=http://politicalticker.blogs.cnn.com/2012/01/19/breaking-perry-endorses-gingrich/|access-date=January 25, 2012|archive-date=January 24, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120124012418/http://politicalticker.blogs.cnn.com/2012/01/19/breaking-perry-endorses-gingrich/|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last=Reston|first=Maeve|date=August 13, 2011|title=Texas Gov. Rick Perry declares GOP presidential bid|work=Los Angeles Times|url=http://www.latimes.com/news/politics/la-pn-perry-president-20110813,0,6052473.story|access-date=August 18, 2011|archive-date=August 17, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110817222102/http://www.latimes.com/news/politics/la-pn-perry-president-20110813,0,6052473.story|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|<ref>{{Cite news|last=Rucker|first=Philip|date=January 4, 2012|title=Michele Bachmann drops out of GOP race after Iowa caucuses|newspaper=[[The Washington Post]]|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/michele-bachmann-drops-out-of-gop-race-after-iowa-caucuses/2012/01/04/gIQAP6L9aP_story.html|access-date=January 5, 2012|archive-date=January 12, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120112134823/http://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/michele-bachmann-drops-out-of-gop-race-after-iowa-caucuses/2012/01/04/gIQAP6L9aP_story.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="bach12">{{cite news|last=Rosenwald|first=Michael S.|date=June 14, 2011|title=Michele Bachmann files paperwork to run for president|newspaper=The Washington Post|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/michele-bachmann-files-paperwork-to-run-for-president/2011/06/13/AGPaXlTH_story.html|access-date=September 17, 2017|archive-date=January 31, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210131035255/https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/michele-bachmann-files-paperwork-to-run-for-president/2011/06/13/AGPaXlTH_story.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="bach22">{{cite news|last=Burns|first=Alexander|date=June 13, 2011|title=Michele Bachmann is in|work=Politico|url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0611/56881.html|access-date=December 3, 2011|archive-date=March 3, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150303161600/http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0611/56881.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Buddy Roemer|<small>Buddy Roemer</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Herman Cain|<small>Herman Cain</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Fred Karger|<small>Fred Karger</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |[[Gary Johnson|<small>Gary Johnson</small>]] |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |<small>'''[[Thaddeus McCotter|Thaddeus]]''' '''[[Thaddeus McCotter|McCotter]]'''</small> |
|||
! scope="col" style="width:3em; font-size:120%;" |'''[[Tim Pawlenty|<small>Tim Pawlenty</small>]]''' |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[File:Buddy Roemer by Gage Skidmore.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|[[File:Herman Cain by Gage Skidmore 4.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|[[File:Fred Karger 2010.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|[[File:Garyjohnsonphoto - modified.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|[[File:Thaddeus McCotter, official portrait, 112th Congress.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|[[File:Tim Pawlenty official photo.jpg|alt=|center|120x120px]] |
|||
|- style="text-align:center" |
|||
|52nd<br>[[Governor of Louisiana|Governor of]]<br>[[Governor of Louisiana|Louisiana]]<br><small>(1988–1992)</small> |
|||
|Chair of the<br>[[Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City|Federal Reserve]]<br>[[Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City|Bank of Kansas City]]<br><small>(1995–1996)</small> |
|||
|[[Political consultant|Political]]<br>[[Political consultant|Consultant]] |
|||
|29th<br>[[List of Governors of New Mexico|Governor of]]<br>[[List of Governors of New Mexico|New Mexico]]<br><small>(1995–2003)</small> |
|||
|[[U.S. Representative]]<br>from [[Michigan]]<br><small>(2003–2012)</small> |
|||
|39th<br>[[Governor of Minnesota|Governor of]]<br>[[Governor of Minnesota|Minnesota]]<br><small>(2003–2011)</small> |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[File:America Needs Buddy for President 2012.png|alt=|center|92x92px]] |
|||
|[[File:HermanCain2012.gif|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|[[File:Fred Karger logo.png|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|[[File:Garyjohnson12.gif|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|[[File:McCotter logo.gif|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|[[File:Pawlentylogo.gif|alt=|center|100x100px]] |
|||
|- style="text-align:center" |
|||
|[[Buddy Roemer 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Herman Cain 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Fred Karger 2012|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Gary Johnson 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Thaddeus McCotter 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|[[Tim Pawlenty 2012 presidential campaign|Campaign]] |
|||
|- style="text-align:center" |
|||
|''W: Feb 22''<br><small>'''33,212''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: Dec 3, 2011''<br><small>'''13,538''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: June 29, 2012''<br><small>'''12,776''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: Dec 28, 2011''<br><small>'''4,286''' votes</small> |
|||
|''W: Sep 22, 2011''<br><small>0 votes</small> |
|||
|''W: Aug 14, 2011''<br><small>0 votes</small> |
|||
|- style="text-align:center" |
|||
|<ref>{{cite news|date=July 21, 2011|title=Roemer kicks off 2012 presidential bid|publisher=KRQE|url=http://www.krqe.com/dpps/elections/president/roemer-kicks-off-2012-presidential-bid-nt11-jpe_3888834|url-status=dead|access-date=October 5, 2012|archive-url=https://archive.today/20121206004014/http://www.krqe.com/dpps/elections/president/roemer-kicks-off-2012-presidential-bid-nt11-jpe_3888834|archive-date=December 6, 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|author=McKinnon, Mark|date=July 21, 2011|title=Listen to Candidate Roemer|work=The Daily Beast|url=http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2011/07/21/buddy-roemer-announcing-2012-gop-bid-for-president-deserves-attention.html|access-date=July 21, 2011|archive-date=May 25, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170525041233/http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2011/07/21/buddy-roemer-announcing-2012-gop-bid-for-president-deserves-attention.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|<ref>Green, Joshua (May 21, 2011) [https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2011/05/herman-cain-makes-it-official/239255/ "Herman Cain Makes It Official"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120113124904/http://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2011/05/herman-cain-makes-it-official/239255/ |date=January 13, 2012 }}, ''The Atlantic''. Retrieved May 21, 2011.</ref><ref>Creed, Ryan (May 21, 2011) [https://abcnews.go.com/Politics/herman-cain-ceo-godfathers-pizza-announces-candidacy/story?id=13655234 "Herman Cain, Former CEO of Godfather's Pizza, Announces His Candidacy"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120111195426/http://abcnews.go.com/Politics/herman-cain-ceo-godfathers-pizza-announces-candidacy/story?id=13655234 |date=January 11, 2012 }}, ABC News. Retrieved May 22, 2011.</ref> |
|||
|<ref>{{cite news|date=June 30, 2012|title=Fred Karger officially ends 2012 presidential campaign|url=https://en.wikinews.org/wiki/Fred_Karger_officially_ends_2012_presidential_campaign|access-date=July 5, 2015|newspaper=[[Wikinews]]|archive-date=July 6, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150706103655/https://en.wikinews.org/wiki/Fred_Karger_officially_ends_2012_presidential_campaign|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|<ref name="Ex2">{{cite news|last=Camia|first=Catalina|date=April 21, 2011|title=Ex-N.M. governor Gary Johnson announces for president|work=USA Today|url=http://content.usatoday.com/communities/onpolitics/post/2011/04/gary-johnson-president-new-mexico-governor-/1|access-date=April 21, 2011|archive-date=April 29, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110429014349/http://content.usatoday.com/communities/onpolitics/post/2011/04/gary-johnson-president-new-mexico-governor-/1|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="hat2">{{Cite news|date=April 21, 2011|title=Gary Johnson throws his hat into the GOP presidential ring, will he be the 2012 Ron Paul?|work=Los Angeles Times|url=http://latimesblogs.latimes.com/washington/2011/04/gary-johnson-throws-his-hat-into-the-gop-presidential-ring-will-he-be-the-2012-ron-paul.html|access-date=April 22, 2011|archive-date=November 11, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201111213142/https://latimesblogs.latimes.com/washington/2011/04/gary-johnson-throws-his-hat-into-the-gop-presidential-ring-will-he-be-the-2012-ron-paul.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|<ref>{{cite news|author=Madison, Lucy|date=July 1, 2011|title=Michigan Rep. Thaddeus McCotter to jump into Republican presidential race|work=[[CBS News]]|url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/michigan-rep-thaddeus-mccotter-to-jump-into-republican-presidential-race/|access-date=June 27, 2012|archive-date=July 4, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110704030834/http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-503544_162-20076049-503544.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|author=Summers, Juana|date=July 20, 2011|title=Candidates face off on Twitter|url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0711/59516.html|access-date=June 27, 2012|work=[[Politico (newspaper)|Politico]]|archive-date=May 14, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130514083345/http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0711/59516.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|<ref name="2012withdraw2">{{cite news|last=Bakst|first=Brian|date=August 14, 2011|title=Ex-Minn. Gov. Tim Pawlenty ends White House bid|work=The Huffington Post|agency=[[Associated Press]]|url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/huff-wires/20110814/us-pawlenty-2012/|access-date=August 14, 2011|archive-date=February 16, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120216010840/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/huff-wires/20110814/us-pawlenty-2012/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="AmesResult2">{{cite news|last=Reinhard|first=Beth|date=August 13, 2011|title=Bachmann Boom; TPaw Bust?|work=[[National Journal]]|url=http://hotlineoncall.nationaljournal.com/archives/2011/08/ames-a-strongly.php|url-status=dead|access-date=August 14, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111025124108/http://hotlineoncall.nationaljournal.com/archives/2011/08/ames-a-strongly.php|archive-date=October 25, 2011}}</ref> |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
===Third party and other nominations=== |
|||
===Withdrawn candidates=== |
|||
{{Main |
{{Main|Third-party and independent candidates for the 2012 United States presidential election}} |
||
* [[Ron Paul]], U.S. Representative from [[Texas]] (ended active campaigning on May 14, 2012; no endorsement, continued to seek delegates from earlier primaries).<ref name="Ron Paul Campaign">{{cite news|url=http://abcnews.go.com/blogs/politics/2012/05/ron-paul-to-stop-campaigning-in-new-states/|title=Ron Paul to Stop Campaigning in New States|last=Good|first=Chris|date=May 14, 2012|publisher=[[ABC News]]|accessdate=October 8, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Fred Karger]], Political consultant and gay rights activist from [[California]] (withdrew June 29, 2012).<ref>{{cite web|url=https://en.wikinews.org/wiki/Fred_Karger_officially_ends_2012_presidential_campaign|title=Fred Karger officially ends 2012 presidential campaign|date=June 30, 2012|work=[[Wikinews]]|accessdate=July 5, 2015}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Newt Gingrich]], former [[United States Speaker of the House of Representatives|U.S. Speaker of the House of Representatives]] from [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]]<ref>{{cite news | title=Newt Gingrich running for president |work=Politico | date=May 11, 2011 | url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0511/54780.html | first=Kendra | last=Marr | accessdate=May 11, 2011 | archivedate=May 11, 2011 | archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/5yc0egH4Q|deadurl=no}}</ref><ref>Shear, Michael (May 11, 2011) [http://thecaucus.blogs.nytimes.com/2011/05/11/video-gingrich-announces-for-president/?ref=politics "Video: Gingrich Announces for President"], ''[[The New York Times]]''. Retrieved May 11, 2011.</ref> (withdrew on May 2, 2012, and endorsed Mitt Romney)<ref>Montopoli, Brian (May 2, 2012) [http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-503544_162-57426387-503544/newt-gingrich-suspends-presidential-campaign/ "Newt Gingrich suspends presidential campaign"], [[CBS News]]. Retrieved May 2, 2012.</ref> |
|||
* [[Rick Santorum]], former [[List of United States Senators from Pennsylvania|senator]] from [[Pennsylvania]] (withdrew on April 10, 2012, and endorsed Mitt Romney)<ref>{{cite news |first= Stephanopoulos |last= George |title= Rick Santorum Will Run for President: 'We're In It to Win'|url= http://blogs.abcnews.com/george/2011/06/exclusive-rick-santorum-we-are-in-it-to-win.html|publisher=[[ABC News]]|date= June 6, 2011 |accessdate=June 6, 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first= Jonathan D.|last= Salant |title= Ex-Pennsylvania Senator Santorum Announces '12 Republican Presidential Bid |url= http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2011-06-06/ex-senator-santorum-announces-bid-for-republican-presidential-nomination.html |publisher=[[Bloomberg News]]|date= June 6, 2011 |accessdate=June 6, 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |agency=Associated Press |title= Republican Rick Santorum announces presidential run |url= http://www.pennlive.com/midstate/index.ssf/2011/06/rick_santorum_announces_presid.html |work=[[The Patriot News]]|date= June 6, 2011 |accessdate=June 6, 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Buddy Roemer]], former [[Governors of Louisiana|governor]] of [[Louisiana]]<ref>{{cite news |title=Roemer kicks off 2012 presidential bid |url=http://www.krqe.com/dpps/elections/president/roemer-kicks-off-2012-presidential-bid-nt11-jpe_3888834 |publisher=KRQE |date=July 21, 2011 |accessdate=October 5, 2012}}{{dead link|date=February 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news | url=http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2011/07/21/buddy-roemer-announcing-2012-gop-bid-for-president-deserves-attention.html | title=Listen to Candidate Roemer | work=The Daily Beast | date=July 21, 2011 | accessdate=July 21, 2011 | author=McKinnon, Mark}}</ref> (withdrew on February 22, 2012, to run for the nominations of Americans Elect and the Reform Party, then endorsed Gary Johnson) |
|||
* [[Rick Perry]], [[Governor of Texas]] (withdrew on January 19, 2012, and endorsed Newt Gingrich, then Mitt Romney after Gingrich withdrew)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://blogs.abcnews.com/thenote/2011/08/texas-gov-rick-perry-jumps-in-presidential-race.html |title=Texas Gov. Rick Perry Jumps In Presidential Race|publisher=ABC News|date=August 11, 2011 |accessdate=December 3, 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://politicalticker.blogs.cnn.com/2012/01/19/breaking-perry-endorses-gingrich/ |title=BREAKING: Perry drops out, endorses Gingrich |publisher= CNN |date=January 19, 2012 |accessdate=January 25, 2012 |first=Peter |last=Hamby}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.latimes.com/news/politics/la-pn-perry-president-20110813,0,6052473.story |title=Texas Gov. Rick Perry declares GOP presidential bid |work=Los Angeles Times |date=August 13, 2011 |accessdate=August 18, 2011 |first=Maeve |last=Reston}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Jon Huntsman, Jr.]], former [[United States Ambassador to China|U.S. ambassador to China]] and former [[Governor of Utah|governor]] of [[Utah]] (withdrew on January 16, 2012, and endorsed Mitt Romney)<ref>[http://thehill.com/blogs/twitter-room/other-news/160417-huntsmans-sly-web-strategy "Huntsman's sly web strategy"], ''The Hill''. May 11, 2011.</ref><ref>[http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0511/54846.html "Jon Huntsman: My Mormonism is 'tough to define'"], ''Politico''. May 12, 2011.</ref> |
|||
* [[Michele Bachmann]], U.S. Representative from [[Minnesota]] (withdrew on January 4, 2012, and endorsed Mitt Romney)<ref>{{Cite news|title=Michele Bachmann drops out of GOP race after Iowa caucuses|url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/michele-bachmann-drops-out-of-gop-race-after-iowa-caucuses/2012/01/04/gIQAP6L9aP_story.html|date=January 4, 2012|work=[[The Washington Post]]|accessdate=January 5, 2012|first=Philip|last=Rucker}}</ref><ref name="bach1">{{cite news|url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/michele-bachmann-files-paperwork-to-run-for-president/2011/06/13/AGPaXlTH_story.html|title=Michele Bachmann files paperwork to run for president | work=The Washington Post | date=June 14, 2011|first=Michael S.|last=Rosenwald}}</ref><ref name="bach2">{{cite news|url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0611/56881.html |title=Michele Bachmann is in|first=Alexander|last=Burns |work=Politico|date=June 13, 2011|accessdate=December 3, 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Gary Johnson]], former [[governor of New Mexico]] (withdrew on December 28, 2011, to run for the nomination of the Libertarian Party, endorsed Ron Paul)<ref name="Ex">{{cite news|url=http://content.usatoday.com/communities/onpolitics/post/2011/04/gary-johnson-president-new-mexico-governor-/1|title=Ex-N.M. governor Gary Johnson announces for president | work=USA Today | first=Catalina|last=Camia|date=April 21, 2011}}</ref><ref name="hat">{{Cite news|url=http://latimesblogs.latimes.com/washington/2011/04/gary-johnson-throws-his-hat-into-the-gop-presidential-ring-will-he-be-the-2012-ron-paul.html|title=Gary Johnson throws his hat into the GOP presidential ring, will he be the 2012 Ron Paul?|work=Los Angeles Times | date=April 21, 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Herman Cain]], businessman from [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]] (withdrew on December 3, 2011, and endorsed Newt Gingrich, then Mitt Romney after Gingrich withdrew)<ref>Green, Joshua (May 21, 2011) [http://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2011/05/herman-cain-makes-it-official/239255/ "Herman Cain Makes It Official"], ''The Atlantic''. Retrieved May 21, 2011.</ref><ref>Creed, Ryan (May 21, 2011) [http://abcnews.go.com/Politics/herman-cain-ceo-godfathers-pizza-announces-candidacy/story?id=13655234 "Herman Cain, Former CEO of Godfather's Pizza, Announces His Candidacy"], ABC News. Retrieved May 22, 2011.</ref> |
|||
* [[Thaddeus McCotter]], [[U.S. Representative]] from [[Michigan]] (withdrew on September 22, 2011, and endorsed Mitt Romney)<ref>{{cite news | url=http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-503544_162-20076049-503544.html | title=Michigan Rep. Thaddeus McCotter to jump into Republican presidential race | publisher=[[CBS News]] | date=July 1, 2011 | accessdate=June 27, 2012 | author=Madison, Lucy}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0711/59516.html | title=Candidates face off on Twitter | work=[[Politico (newspaper)|Politico]] | date=July 20, 2011 | accessdate=June 27, 2012 | author=Summers, Juana}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Tim Pawlenty]], former [[governor of Minnesota]] (withdrew on August 14, 2011, and endorsed Mitt Romney)<ref name="2012withdraw">{{cite news|url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/huff-wires/20110814/us-pawlenty-2012/|title=Ex-Minn. Gov. Tim Pawlenty ends White House bid|agency=[[Associated Press]]|work=The Huffington Post|date=August 14, 2011|accessdate=August 14, 2011|first=Brian|last=Bakst}}</ref><ref name="AmesResult">{{cite news|url=http://hotlineoncall.nationaljournal.com/archives/2011/08/ames-a-strongly.php|title=Bachmann Boom; TPaw Bust?|date=August 13, 2011|accessdate=August 14, 2011|work=[[National Journal]]|first=Beth|last=Reinhard}}</ref> |
|||
<gallery perrow="7"> |
|||
File:Ron Paul, official Congressional photo portrait, 2007.jpg|{{center|[[United States House of Representatives|U.S. Representative]]<br />'''[[Ron Paul]]'''<br />from [[Texas]]<br />([[Ron Paul presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Fred Karger 2010.jpg|{{center|Political consultant and gay rights activist<br />'''[[Fred Karger]]'''<br />from [[California]]}} |
|||
File:Newt Gingrich by Gage Skidmore 6.jpg|{{center|Former [[Speaker of the United States House of Representatives|House Speaker]]<br />'''[[Newt Gingrich]]''',<br />from [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]]<br />([[Newt Gingrich presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Rick Santorum by Gage Skidmore 2.jpg|{{center|Former [[United States Senate|Senator]]<br />'''[[Rick Santorum]]'''<br />from [[Pennsylvania]]<br />([[Rick Santorum presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Buddy Roemer by Gage Skidmore.jpg|{{center|Former [[Governor of Louisiana|Governor]]<br />'''[[Buddy Roemer]]'''<br />of [[Louisiana]]<br />([[Buddy Roemer presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Rick Perry by Gage Skidmore 3.jpg|{{center|[[Governor of Texas|Governor]]<br />'''[[Rick Perry]]'''<br />of [[Texas]]<br />([[Rick Perry presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Ambassador Jon Huntsman.jpg|{{center|Former [[U.S. Ambassador to China|Ambassador]]<br />'''[[Jon Huntsman, Jr.|Jon Huntsman]]''',<br />from [[Utah]]<br />([[Jon Huntsman presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Michele Bachmann by Gage Skidmore 5.jpg|{{center|[[U.S. Representative]]<br />'''[[Michele Bachmann]]'''<br />from [[Minnesota]]<br />([[Michele Bachmann presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Garyjohnsonphoto.JPG|{{center|Former [[Governor of New Mexico|Governor]]<br />'''[[Gary Johnson]]'''<br />of [[New Mexico]]<br />([[Gary Johnson presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Herman Cain by Gage Skidmore 5.jpg|{{center|Businessman<br />'''[[Herman Cain]]''',<br />from [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]]<br />([[Herman Cain presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Thaddeus McCotter, official portrait, 112th Congress.jpg|{{center|[[U.S. Representative]]<br />'''[[Thaddeus McCotter]]'''<br />from [[Michigan]]<br />([[Thaddeus McCotter presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
File:Tim Pawlenty by Gage Skidmore (cropped).jpg|{{center|Former [[Governor of Minnesota|Governor]]<br />'''[[Tim Pawlenty]]'''<br />of [[Minnesota]]<br />([[Tim Pawlenty presidential campaign, 2012|campaign]])}} |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
==Third party and other nominations== |
|||
{{main article|United States third party and independent presidential candidates, 2012}} |
|||
Four other parties nominated candidates that had ballot access or [[write-in]] access to at least 270 electoral votes, the minimum number of votes needed in the 2012 election to win the presidency through a majority of the electoral college. |
Four other parties nominated candidates that had ballot access or [[write-in]] access to at least 270 electoral votes, the minimum number of votes needed in the 2012 election to win the presidency through a majority of the electoral college. |
||
===Libertarian Party=== |
====Libertarian Party==== |
||
{{main |
{{main|Libertarian Party (United States)|2012 Libertarian National Convention|Gary Johnson 2012 presidential campaign}} |
||
* '''[[Gary Johnson]]''', former governor of New Mexico.<ref name="reuters.com">{{cite news| |
* '''[[Gary Johnson]]''', former governor of New Mexico.<ref name="reuters.com">{{cite news|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-libertarians-idUSBRE8440BZ20120506|title=Libertarians nominate ex-Governor Gary Johnson for president|work=[[Reuters]]|last1=Pratt|first1=Timothy|date=May 5, 2012|access-date=May 6, 2012|archive-date=July 27, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200727091747/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-libertarians-idUSBRE8440BZ20120506|url-status=live}}</ref> Vice-presidential nominee: '''[[Jim Gray (jurist)|Jim Gray]]''', retired state court judge, from California.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://reason.com/blog/2012/05/05/judge-jim-gray-is-the-2012-libertarian-p | title=Judge Jim Gray Is the 2012 Libertarian Party Vice Presidential Nominee | work=[[Reason (magazine)|Reason]] | date=May 5, 2012 | access-date=May 6, 2012 | last1=Riggs | first1=Mike | archive-date=May 7, 2012 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120507060859/http://reason.com/blog/2012/05/05/judge-jim-gray-is-the-2012-libertarian-p | url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
===Green Party=== |
====Green Party==== |
||
{{main |
{{main|Green Party of the United States|2012 Green National Convention|Jill Stein 2012 presidential campaign}} |
||
* '''[[Jill Stein]]''', medical doctor from Massachusetts.<ref name="Baltimore">{{cite news |
* '''[[Jill Stein]]''', medical doctor from Massachusetts.<ref name="Baltimore">{{cite news|url=https://www.usatoday.com/news/politics/story/2012-07-14/green-party-jill-stein/56226288/1|title=Mass. doctor Jill Stein wins Green Party's presidential nod|agency=Associated Press|website=[[USA Today]]|date=July 14, 2012|access-date=July 15, 2012|archive-date=July 15, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120715012830/http://www.usatoday.com/news/politics/story/2012-07-14/green-party-jill-stein/56226288/1|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.baltimoresun.com/news/maryland/baltimore-city/bs-md-ci-green-convention-close-20120714,0,2011815.story|title=Green Party nominates Jill Stein for president at Baltimore convention|work=[[The Baltimore Sun]]|date=July 14, 2012|access-date=July 15, 2012|last1=Kilar|first1=Steve|archive-date=June 7, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130607042553/http://www.baltimoresun.com/news/maryland/baltimore-city/bs-md-ci-green-convention-close-20120714,0,2011815.story|url-status=dead}}</ref> Vice-presidential nominee: '''[[Cheri Honkala]]''', social organizer, from Pennsylvania.<ref>{{cite magazine|last1=Steinmetz|first1=Katy|date=July 11, 2012|url=https://swampland.time.com/2012/07/11/the-green-team-jill-steins-third-party-bid-to-shake-up-2012/|title=The Green Team: Jill Stein's Third-Party Bid to Shake Up 2012|magazine=[[Time (magazine)|Time]]|access-date=July 11, 2012|archive-date=July 11, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120711205018/http://swampland.time.com/2012/07/11/the-green-team-jill-steins-third-party-bid-to-shake-up-2012/|url-status=live}}</ref> |
||
===Constitution Party=== |
====Constitution Party==== |
||
{{main |
{{main|Constitution Party (United States)|2012 Constitution Party National Convention|Virgil Goode 2012 presidential campaign}} |
||
* '''[[Virgil Goode]]''', former |
* '''[[Virgil Goode]]''', former representative from Virginia.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.roanoke.com/news/breaking/wb/307795 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120908195419/http://www.roanoke.com/news/breaking/wb/307795 |url-status=dead |archive-date=September 8, 2012 |title=Goode gets Constitution Party's nomination for president |work=[[The Roanoke Times]] |date=April 21, 2012 |access-date=April 22, 2012 }}</ref> Vice-presidential nominee: '''Jim Clymer''' from Pennsylvania.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.independentpoliticalreport.com/2012/04/constitution-party-convention-wrap-up-vice-presidential-candidate-and-officer-elections/|title=Constitution Party Convention Wrap-Up: vice Presidential Candidate and Officer Elections|work=Independent Political Report|last1=Hill|first1=Trent|date=April 21, 2012|access-date=April 22, 2012|archive-date=April 23, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120423132522/http://www.independentpoliticalreport.com/2012/04/constitution-party-convention-wrap-up-vice-presidential-candidate-and-officer-elections/|url-status=live}}</ref> |
||
===Justice Party=== |
====Justice Party==== |
||
{{main |
{{main|Justice Party (United States)|Rocky Anderson}} |
||
* '''[[Rocky Anderson]]''', former mayor of Salt Lake City and founding member of the Justice Party, from Utah. Vice-presidential nominee: '''[[Luis J. Rodriguez]]''' from California.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.sltrib.com/sltrib/politics/54506925-90/rodriguez-activist-anderson-author.html.csp|title=Rocky picks activist-author as his VP running mate|last=Gehrke|first=Robert|date=July 17, 2012|work=[[The Salt Lake Tribune]]| |
* '''[[Rocky Anderson]]''', former mayor of Salt Lake City and founding member of the Justice Party, from Utah. Vice-presidential nominee: '''[[Luis J. Rodriguez]]''' from California.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.sltrib.com/sltrib/politics/54506925-90/rodriguez-activist-anderson-author.html.csp|title=Rocky picks activist-author as his VP running mate|last=Gehrke|first=Robert|date=July 17, 2012|work=[[The Salt Lake Tribune]]|access-date=July 18, 2012|archive-date=July 21, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120721031744/http://www.sltrib.com/sltrib/politics/54506925-90/rodriguez-activist-anderson-author.html.csp|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.deseretnews.com/article/705397350/Rocky-Anderson-accepts-his-newly-formed-partys-presidential-nomination.html | title=Rocky Anderson accepts his newly-formed party's presidential nomination | work=[[Deseret News]] | date=January 13, 2012 | access-date=February 1, 2012 | author=Schwarz, Hunter | archive-date=February 1, 2012 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120201005240/http://www.deseretnews.com/article/705397350/Rocky-Anderson-accepts-his-newly-formed-partys-presidential-nomination.html | url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
====Candidates gallery==== |
====Candidates gallery==== |
||
<gallery perrow=" |
<gallery perrow="5" mode="packed" heights="160"> |
||
File:Gary Johnson by Gage Skidmore 3.jpg|[[Gary Johnson]]<br />([[Gary Johnson presidential campaign |
File:Gary Johnson by Gage Skidmore 3.jpg|[[Gary Johnson]]<br />([[Gary Johnson 2012 presidential campaign|campaign]]) |
||
File:JillStein Tar Sands Blockade (cropped).jpg|[[Jill Stein]]<br />([[Jill Stein presidential campaign |
File:JillStein Tar Sands Blockade (cropped).jpg|[[Jill Stein]]<br />([[Jill Stein 2012 presidential campaign|campaign]]) |
||
File:Virgil Goode answering questions. (cropped).jpg|[[Virgil Goode]]<br />([[Virgil Goode presidential campaign |
File:Virgil Goode answering questions. (cropped).jpg|[[Virgil Goode]]<br />([[Virgil Goode 2012 presidential campaign|campaign]]) |
||
File:Rocky Anderson at MLK cropped.jpg|[[Rocky Anderson]] |
File:Rocky Anderson at MLK cropped.jpg|[[Rocky Anderson]] |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
==Campaigns== |
==Campaigns== |
||
{{see also|Barack Obama presidential campaign |
{{see also|Barack Obama 2012 presidential campaign|Mitt Romney 2012 presidential campaign|Gary Johnson 2012 presidential campaign|Jill Stein 2012 presidential campaign|Virgil Goode 2012 presidential campaign}} |
||
===Ballot access=== |
===Ballot access=== |
||
{|class="wikitable" |
{|class="wikitable" |
||
|- style="background:lightgrey;" |
|- style="background:lightgrey;" |
||
!Presidential ticket |
! rowspan="2" |Presidential ticket |
||
!Party |
! rowspan="2" |Party |
||
![[Ballot access]]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ballot-access.org/?p=30419|title=2012 |
! colspan="3" |[[Ballot access]]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ballot-access.org/?p=30419|title=2012 Ballot Status for President|publisher=Ballot-access.org|date=October 27, 2012|access-date=July 7, 2013|archive-date=January 25, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160125225906/http://ballot-access.org/?p=30419|url-status=live}}</ref> |
||
! rowspan="2" |Votes |
|||
! % of voters <br> seeing name on ballot |
|||
! rowspan="2" |Percentage |
|||
!Votes |
|||
|- style="background:lightgrey;" |
|||
!Percentage |
|||
!States |
|||
!Electors |
|||
!% of voters |
|||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
|Obama / Biden |
|'''Obama / Biden''' |
||
|Democratic |
|'''Democratic''' |
||
|50 + [[Washington, D.C.|DC]] |
|'''50 + [[Washington, D.C.|DC]]''' |
||
|'''538''' |
|||
|100% |
|||
|'''100%''' |
|||
|65,915,796 |
|||
|'''65,915,795''' |
|||
|51.19 |
|||
|'''51.1%''' |
|||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
|Romney / Ryan |
|'''Romney / Ryan''' |
||
|Republican |
|'''Republican''' |
||
|50 + DC |
|'''50 + DC''' |
||
|'''538''' |
|||
|100% |
|||
|'''100%''' |
|||
|60,933,500 |
|||
|'''60,933,504''' |
|||
|47.32 |
|||
|'''47.2%''' |
|||
|-{{Party shading/Libertarian}} |
|-{{Party shading/Libertarian}} |
||
|'''Johnson / Gray''' <!-- "Gray" is not a typo of "Gary" here; it refers to Johnson's running mate, Jim Gray --> |
|||
|Johnson / Gray |
|||
|Libertarian |
|'''Libertarian''' |
||
|48 + DC |
|'''48 + DC''' |
||
|'''515''' |
|||
|95.1% |
|||
|'''95.1%''' |
|||
|1,275,951 |
|||
|'''1,275,971''' |
|||
|0.99 |
|||
|'''1.0%''' |
|||
|-{{Party shading/Green}} |
|-{{Party shading/Green}} |
||
|Stein / Honkala |
|'''Stein / Honkala''' |
||
|Green |
|'''Green''' |
||
|36 + DC |
|'''36 + DC''' |
||
|'''436''' |
|||
|83.1% |
|||
|'''83.1%''' |
|||
|469,628 |
|||
|'''469,627''' |
|||
|0.36 |
|||
|'''0.4%''' |
|||
|-{{Party shading/Constitution}} |
|-{{Party shading/Constitution}} |
||
|Goode / Clymer |
|Goode / Clymer |
||
|Constitution |
|Constitution |
||
|26 |
|26 |
||
|257 |
|||
|49.9% |
|49.9% |
||
|122,388 |
|122,388 |
||
|0. |
|0.1% |
||
|-{{Party shading/Independent}} |
|-{{Party shading/Independent}} |
||
|Anderson / Rodriguez |
|Anderson / Rodriguez |
||
|Justice |
|Justice |
||
|15 |
|15 |
||
|145 |
|||
|28.1% |
|28.1% |
||
|43,018 |
|43,018 |
||
|nil |
|||
|0.03 |
|||
|-{{Party shading/Socialist}} |
|-{{Party shading/Socialist}} |
||
|Lindsay / Osorio |
|Lindsay / Osorio |
||
|Socialism & Liberation |
|Socialism & Liberation |
||
|13 |
|13 |
||
|115 |
|||
|28.6% |
|28.6% |
||
|7,791 |
|7,791 |
||
|nil |
|||
|0.006 |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
Candidates in bold were on ballots representing 270 electoral votes. |
|||
All other candidates were on the ballots of fewer than 10 states, and less than 20% of voters nationwide saw their names on the ballot. |
|||
All other candidates were on the ballots of fewer than 10 states, 100 electors, and less than 20% of voters nationwide. |
|||
===Financing and advertising=== |
===Financing and advertising=== |
||
The United States presidential election of 2012 broke new records in financing, fundraising, and [[negative campaigning]]. Through [[grassroots]] campaign contributions, online donations, and [[Super PACs]], Obama and Romney raised a combined total of more than $2 billion.<ref>{{cite news |last=Braun |first=Stephen |title=$2 Billion Price Tag for Presidential Election |url= |
The United States presidential election of 2012 broke new records in financing, fundraising, and [[negative campaigning]]. Through [[grassroots]] campaign contributions, online donations, and [[Super PACs]], Obama and Romney raised a combined total of more than $2 billion.<ref>{{cite news |last=Braun |first=Stephen |title=$2 Billion Price Tag for Presidential Election |url=http://bigstory.ap.org/article/casino-owner-aided-romney-late-10-million-bet |access-date=December 9, 2012 |agency=[[Associated Press]] |date=December 6, 2012 |archive-date=December 8, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121208013846/http://bigstory.ap.org/article/casino-owner-aided-romney-late-10-million-bet |url-status=dead }}</ref> Super PACs constituted nearly one-fourth of the total financing, with most coming from pro-Romney PACs.<ref>{{cite news |last=Confessore |first=Nicholas |title=Little to Show for Cash Flood by Big Donors |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/08/us/politics/little-to-show-for-cash-flood-by-big-donors.html?_r=0&pagewanted=all |access-date=December 9, 2012 |newspaper=[[The New York Times]] |date=December 7, 2012 |archive-date=November 11, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121111100616/http://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/08/us/politics/little-to-show-for-cash-flood-by-big-donors.html?pagewanted=all&_r=0 |url-status=live }}</ref> Obama raised $690 million through online channels, beating his record of $500 million in 2008.<ref>{{cite news |last=Scherer |first=Michael |title=Exclusive: Obama's 2012 Digital Fundraising Outperformed 2008 |url=https://swampland.time.com/2012/11/15/exclusive-obamas-2012-digital-fundraising-outperformed-2008/ |access-date=December 9, 2012 |newspaper=[[Time (magazine)|Time]] |date=November 27, 2012 |archive-date=November 18, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121118062904/http://swampland.time.com/2012/11/15/exclusive-obamas-2012-digital-fundraising-outperformed-2008/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Most of the advertising in the 2012 presidential campaign was decidedly negative—80% of Obama's ads and 84% of Romney's ads were negative.<ref>{{cite news |last=Hunt |first=Albert |title=Barrage of Negative Ads May Haunt President-Elect |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-10-14/barrage-of-negative-ads-may-haunt-president-elect.html |access-date=December 9, 2012 |newspaper=[[Bloomberg News]] |date=October 14, 2012 |quote=The hundreds of thousands of television commercials broadcast by the presidential candidates are lopsidedly negative; this is the case with 80 percent of those put out by President Barack Obama and 84 percent of those for Mitt Romney. |archive-date=October 18, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121018000134/http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-10-14/barrage-of-negative-ads-may-haunt-president-elect.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The tax-exempt non-profit [[Americans for Prosperity]], a so-called "outside group", that is, a political advocacy group that is not a [[political action committee]] or super-PAC, ran a television advertising campaign opposing Obama described by ''[[The Washington Post]]'' as "early and relentless".<ref name=wp20140105>{{cite news |title=The players in the Koch-backed $400 million political donor network |first=Matea |last=Gold |date=January 5, 2014 |access-date=May 9, 2015 |newspaper=[[The Washington Post]] |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/the-players-in-the-koch-backed-400-million-political-donor-network/2014/01/05/714451a8-74b5-11e3-8b3f-b1666705ca3b_story.html |quote=Americans for Prosperity, the Virginia-based nonprofit that finances grass-roots activities across the country and ran an early and relentless television ad assault against President Obama during the 2012 campaign. |archive-date=May 9, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150509075354/http://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/the-players-in-the-koch-backed-400-million-political-donor-network/2014/01/05/714451a8-74b5-11e3-8b3f-b1666705ca3b_story.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=cnbc20111108>{{cite news |title=Record Political Ad Spending Powered by Special Interests |first=Julia |last=Boorstin |date=November 8, 2011 |url=https://www.cnbc.com/2011/11/08/record-political-ad-spending-powered-by-special-interests.html |access-date=April 30, 2015 |publisher=[[CNBC]] |archive-date=May 18, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150518112553/http://www.cnbc.com/id/45212597 |url-status=live }}</ref> Americans for Prosperity spent $8.4 million in [[swing state]]s on television advertisements denouncing the [[American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009]] loan guarantee to [[Solyndra]], a manufacturer of solar panels that went bankrupt,<ref name=bloomberg1>{{cite news |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2012-10-17/solyndra-lenders-ahead-of-government-won-t-recover-fully |title=Solyndra Lenders Ahead of Government Won't Recover Fully |first=Michael |last=Bathon |date=October 17, 2012 |work=[[Bloomberg Business]] |access-date=November 14, 2014 |archive-date=May 1, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150501134346/http://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2012-10-17/solyndra-lenders-ahead-of-government-won-t-recover-fully |url-status=live }}</ref> an advertising campaign described by ''[[The Wall Street Journal]]'' in November 2011 as "perhaps the biggest attack on Mr. Obama so far".<ref name=bloomberg20111128>{{cite news |url=http://thinkprogress.org/romm/2011/11/28/377053/koch-americans-for-prosperity-solyndra-attack-ad-video/ |title=Koch-Fueled Americans for Prosperity Spends $2.4 Million on Solyndra Attack Ad |first=Stephen |last=Lacey |work=[[ThinkProgress]] |publisher=[[Center for American Progress]] |date=November 28, 2011 |access-date=May 10, 2015 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150505235012/http://thinkprogress.org/romm/2011/11/28/377053/koch-americans-for-prosperity-solyndra-attack-ad-video/ |archive-date=May 5, 2015 |df=mdy-all }}</ref><ref name=wsj20120114>{{cite news |url=https://blogs.wsj.com/washwire/2012/01/14/americans-for-prosperity-to-air-ads-slamming-obamas-ties-to-solyndra/ |title=Americans for Prosperity to Air Ads Slamming Obama's Ties to Solyndra |first=Brody |last=Mullins |series=Washington Wire blog |date=January 14, 2012 |access-date=April 19, 2015 |work=The Wall Street Journal |archive-date=November 16, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201116162736/https://blogs.wsj.com/washwire/2012/01/14/americans-for-prosperity-to-air-ads-slamming-obamas-ties-to-solyndra/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
===Party conventions=== |
===Party conventions=== |
||
{{Location map many | USA |left| width=400 |caption=Sites of the 2012 national party conventions |
{{Location map many | USA |left| width=400 |caption=Sites of the 2012 national party conventions |
||
| alt=Map of United States showing Charlotte, Tampa |
| alt=Map of United States showing Charlotte, Tampa, Las Vegas, Baltimore, and Nashville |
||
| mark1=blue pog.svg | mark1size=12 | lat1_deg=35.2269 | lon1_deg=-80.843333 | label1=Charlotte | position1=right |
| mark1=blue pog.svg | mark1size=12 | lat1_deg=35.2269 | lon1_deg=-80.843333 | label1=Charlotte | position1=right |
||
| mark2=red pog.svg | mark2size=12 | lat2_deg=27.9709 | lon2_deg=-82.46464 | label2=Tampa | position2=left |
| mark2=red pog.svg | mark2size=12 | lat2_deg=27.9709 | lon2_deg=-82.46464 | label2=Tampa | position2=left |
||
| Line 336: | Line 378: | ||
| mark5=green pog.svg | mark5size=8 | lat5_deg=39.283333 | lon5_deg=-76.616667 | label5=Baltimore | position5=left |
| mark5=green pog.svg | mark5size=8 | lat5_deg=39.283333 | lon5_deg=-76.616667 | label5=Baltimore | position5=left |
||
}} <!--1=Rep 2=Dem 3=Constit 4=Lib 5=Green--> |
}} <!--1=Rep 2=Dem 3=Constit 4=Lib 5=Green--> |
||
* April 18–21, 2012: 2012 [[Constitution Party National Convention]] held in [[Nashville, Tennessee]];<ref>Winger, Richard (November 18, 2010) [http://www.ballot-access.org/2010/11/18/2012-constitution-party-national-convention-set-for-nashville/ "2012 Constitution Party National Convention Set for Nashville"], Ballot Access News. Retrieved November 29, 2010.</ref> [[Virgil Goode]] won the nomination. |
* April 18–21, 2012: 2012 [[Constitution Party National Convention]] held in [[Nashville, Tennessee]];<ref>Winger, Richard (November 18, 2010) [http://www.ballot-access.org/2010/11/18/2012-constitution-party-national-convention-set-for-nashville/ "2012 Constitution Party National Convention Set for Nashville"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201106203641/http://www.ballot-access.org/2010/11/18/2012-constitution-party-national-convention-set-for-nashville/ |date=November 6, 2020 }}, Ballot Access News. Retrieved November 29, 2010.</ref> [[Virgil Goode]] won the nomination. |
||
* May 3–6, 2012: [[2012 Libertarian National Convention]] held in [[Las Vegas, Nevada]];<ref name=lmyers>Myers, Laura (November 30, 2010) [http://www.lvrj.com/news/las-vegas-will-host-libertarian-convention-111027874.html "Las Vegas will host Libertarian convention"] ''[[Las Vegas Review-Journal]]''. Retrieved November 30, 2010.</ref> [[Gary Johnson]] won the nomination.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/05/05/gary-johnson-2012-libertarian-nomination_n_1485044.html|author=Cristina Silva|title=Gary Johnson Wins 2012 Libertarian Nomination|agency=Associated Press|work=The Huffington Post|date=May 5, 2012| |
* May 3–6, 2012: [[2012 Libertarian National Convention]] held in [[Las Vegas, Nevada]];<ref name=lmyers>Myers, Laura (November 30, 2010) [http://www.lvrj.com/news/las-vegas-will-host-libertarian-convention-111027874.html "Las Vegas will host Libertarian convention"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110714011112/http://www.lvrj.com/news/las-vegas-will-host-libertarian-convention-111027874.html |date=July 14, 2011 }} ''[[Las Vegas Review-Journal]]''. Retrieved November 30, 2010.</ref> [[Gary Johnson]] won the nomination.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/05/05/gary-johnson-2012-libertarian-nomination_n_1485044.html|author=Cristina Silva|title=Gary Johnson Wins 2012 Libertarian Nomination|agency=Associated Press|work=The Huffington Post|date=May 5, 2012|access-date=June 17, 2012|archive-date=June 20, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120620230212/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/05/05/gary-johnson-2012-libertarian-nomination_n_1485044.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
||
* July 13–15, 2012: [[2012 Green National Convention]] held in [[Baltimore|Baltimore, Maryland]];<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ballot-access.org/2011/11/11/green-party-national-convention-will-be-in-baltimore/ |title=Green Party National Convention will be in Baltimore |work=Ballot Access News |date=November 11, 2011 | |
* July 13–15, 2012: [[2012 Green National Convention]] held in [[Baltimore|Baltimore, Maryland]];<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ballot-access.org/2011/11/11/green-party-national-convention-will-be-in-baltimore/ |title=Green Party National Convention will be in Baltimore |work=Ballot Access News |date=November 11, 2011 |access-date=November 12, 2011 |archive-date=November 6, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201106180347/http://ballot-access.org/2011/11/11/green-party-national-convention-will-be-in-baltimore/ |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Jill Stein]] won the nomination.<ref name="Baltimore"/> |
||
* August 27–30, 2012: [[2012 Republican National Convention]] held in [[Tampa, Florida]];<ref>Barr, Andy |
* August 27–30, 2012: [[2012 Republican National Convention]] held in [[Tampa, Florida]];<ref>Barr, Andy; Mike Allen (May 12, 2010) [http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0510/37157.html "Republicans pick Tampa for 2012 convention"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120106044228/http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0510/37157.html |date=January 6, 2012 }}, ''Politico''. Retrieved May 13, 2010.</ref> [[Mitt Romney]] won the nomination. |
||
* September 3–6, 2012: [[2012 Democratic National Convention]] held in [[Charlotte, North Carolina]];<ref>{{cite news|title=2012 Democratic National Convention To Be Held In Charlotte, N.C. |first=Michael |last=Falcone |url= |
* September 3–6, 2012: [[2012 Democratic National Convention]] held in [[Charlotte, North Carolina]];<ref>{{cite news|title=2012 Democratic National Convention To Be Held In Charlotte, N.C. |first=Michael |last=Falcone |url=https://abcnews.go.com/blogs/politics/2011/02/democratic-national-convention-2012-to-be-held-in-charlotte-nc/ |work=ABC News |date=February 1, 2011 |access-date=October 5, 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120901140433/https://abcnews.go.com/blogs/politics/2011/02/democratic-national-convention-2012-to-be-held-in-charlotte-nc/ |archive-date=September 1, 2012 }}</ref> [[Barack Obama]] won the nomination. |
||
=== |
===Presidential debates=== |
||
{{Main |
{{Main|2012 United States presidential debates}} |
||
The [[Commission on Presidential Debates]] held four debates during the last weeks of the campaign: three presidential and one vice-presidential. The major issues debated were the economy and jobs, the federal budget deficit, taxation and spending, the future of [[Social Security (United States)|Social Security]], [[Medicare (United States)|Medicare]], and [[Medicaid]], [[Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act|healthcare reform]], education, social issues, immigration, and foreign policy. |
The [[Commission on Presidential Debates]] held four debates during the last weeks of the campaign: three presidential and one vice-presidential. The major issues debated were the economy and jobs, the federal budget deficit, taxation and spending, the future of [[Social Security (United States)|Social Security]], [[Medicare (United States)|Medicare]], and [[Medicaid]], [[Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act|healthcare reform]], education, social issues, immigration, and foreign policy. |
||
Debate schedule:<ref name="debates">{{cite web|url=http://decoded.nationaljournal.com/2011/10/fall-2012-presidential-debates.php|title=Fall 2012 Presidential Debates Set|last=Kiely|first=Kathy|date=October 31, 2011|work=National Journal|access-date=October 31, 2011|archive-date=November 1, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111101235203/http://decoded.nationaljournal.com/2011/10/fall-2012-presidential-debates.php|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="moderators">Blake, Aaron (August 13, 2012) [https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/the-fix/post/presidential-debate-moderators-announced-crowley-is-first-woman-in-20-years/2012/08/13/0e327af6-e553-11e1-8f62-58260e3940a0_blog.html "Presidential debate moderators announced: Crowley is first woman in 20 years"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200828215915/https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/the-fix/post/presidential-debate-moderators-announced-crowley-is-first-woman-in-20-years/2012/08/13/0e327af6-e553-11e1-8f62-58260e3940a0_blog.html |date=August 28, 2020 }}, ''[[The Washington Post]]''. Retrieved August 15, 2012.</ref> |
|||
Debate schedule: |
|||
* Wednesday, October 3: The [[First U.S. presidential debate of 2012|first presidential debate]] took place at the [[University of Denver]] in [[Denver]], [[Colorado]],<ref name="debates">{{cite web |url=http://decoded.nationaljournal.com/2011/10/fall-2012-presidential-debates.php |title=Fall 2012 Presidential Debates Set |work=National Journal |first=Kathy |last=Kiely |date=October 31, 2011| accessdate=October 31, 2011}}</ref> moderated by [[Jim Lehrer]].<ref name="moderators">Blake, Aaron (August 13, 2012) [http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/the-fix/post/presidential-debate-moderators-announced-crowley-is-first-woman-in-20-years/2012/08/13/0e327af6-e553-11e1-8f62-58260e3940a0_blog.html "Presidential debate moderators announced: Crowley is first woman in 20 years"], ''[[The Washington Post]]''. Retrieved August 15, 2012.</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
* Thursday, October 11: The [[United States vice-presidential debate, 2012|vice-presidential debate]] took place at [[Centre College]] in [[Danville, Kentucky|Danville]], [[Kentucky]],<ref name="debates" /> moderated by [[Martha Raddatz]].<ref name="moderators"/> |
|||
|+'''Debates among candidates for the 2012 U.S. presidential election''' |
|||
* Tuesday, October 16: The [[Second U.S. presidential debate of 2012|second presidential debate]] took place at [[Hofstra University]] in [[Hempstead (village), New York|Hempstead]], New York,<ref name="debates" /> moderated by [[Candy Crowley]].<ref name="moderators"/> It had a town hall format.<ref>Little, Morgan (July 25, 2012) [http://www.latimes.com/news/politics/la-pn-presidential-debate-formats-announced-feature-town-hall-20120725,0,7862238.story "Presidential debate formats announced, feature town hall"], ''[[Los Angeles Times]]''. Retrieved July 26, 2012.</ref> |
|||
!No. |
|||
* Monday, October 22: The [[Third U.S. presidential debate of 2012|third presidential debate]] took place at [[Lynn University]] in [[Boca Raton, Florida|Boca Raton]], Florida,<ref name="debates" /> moderated by [[Bob Schieffer]].<ref name="moderators"/> |
|||
!Date |
|||
!Host |
|||
!City |
|||
!Moderator |
|||
!Participants |
|||
!{{longitem|Viewership<br>(million)}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|align=center|P1 |
|||
|Wednesday, October 3, 2012 |
|||
|[[University of Denver]] |
|||
|[[Denver, Colorado]] |
|||
|[[Jim Lehrer]] |
|||
|{{ubl |
|||
|[[Barack Obama]] |
|||
|[[Mitt Romney]]}} |
|||
|67.2<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=https://www.debates.org/index.php?page=2012-debates|title=CPD: 2012 Debates|website=www.debates.org|access-date=2019-01-08|archive-date=January 8, 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190108145542/https://www.debates.org/index.php?page=2012-debates|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
|align=center|VP |
|||
|Thursday, October 11, 2012 |
|||
|[[Centre College]] |
|||
|[[Danville, Kentucky|Danville]], [[Kentucky]] |
|||
|[[Martha Raddatz]] |
|||
|{{ubl |
|||
|[[Joe Biden]] |
|||
|[[Paul Ryan]]}} |
|||
|51.4<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
|- |
|||
|align=center|P2 |
|||
|Tuesday, October 16, 2012 |
|||
|[[Hofstra University]] |
|||
|[[Hempstead (village), New York|Hempstead, New York]] |
|||
|[[Candy Crowley]] |
|||
|{{ubl |
|||
|[[Barack Obama]] |
|||
|[[Mitt Romney]]}} |
|||
|65.6<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
|- |
|||
|align=center|P3 |
|||
|Monday, October 22, 2012 |
|||
|[[Lynn University]] |
|||
|[[Boca Raton, Florida]] |
|||
|[[Bob Schieffer]] |
|||
|{{ubl |
|||
|[[Barack Obama]] |
|||
|[[Mitt Romney]]}} |
|||
|59.2<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
|} |
|||
[[File:Barack Obama presidential debate preparations.jpg|thumb|President Obama talks with [[Ron Klain]] during presidential debate preparations. Senator [[John Kerry]], at podium, played the role of Mitt Romney during the preparatory sessions.]] |
[[File:Barack Obama presidential debate preparations.jpg|thumb|President Obama talks with [[Ron Klain]] during presidential debate preparations. Senator [[John Kerry]], at podium, played the role of Mitt Romney during the preparatory sessions.]] |
||
An independent presidential debate featuring minor party candidates took place on Tuesday, October 23 at the [[Hilton Hotel]] in [[Chicago]], Illinois.<ref>[ |
An independent presidential debate featuring minor party candidates took place on Tuesday, October 23 at the [[Hilton Hotel]] in [[Chicago]], Illinois.<ref>[https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/she-the-people/wp/2012/10/24/third-party-candidates-finally-get-their-own-presidential-debate/ "Third-party candidates finally get their own presidential debate"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200820103122/https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/she-the-people/wp/2012/10/24/third-party-candidates-finally-get-their-own-presidential-debate/ |date=August 20, 2020 }}, ''The Washington Post''. October 24, 2012. Retrieved February 11, 2013.</ref><ref name="united">{{cite web | url=http://seattletimes.com/html/politics/2019505794_thirdparties.html | title=Third-party candidates debate: United against Obama, Romney | work=[[The Seattle Times]] | date=October 23, 2012 | access-date=October 24, 2012 | author=Sullivan, Sean | archive-date=March 3, 2013 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130303045811/http://seattletimes.com/html/politics/2019505794_thirdparties.html | url-status=live }}</ref> The debate was moderated by [[Larry King]]<ref name="moderate3rd">{{cite news | url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/larry-king-to-moderate-third-party-debate/ | title=Larry King to moderate third-party debate | agency=Associated Press | work=[[CBS News]] | access-date=October 18, 2012 | date=October 17, 2012 | archive-date=February 8, 2015 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208045603/http://www.cbsnews.com/news/larry-king-to-moderate-third-party-debate/ | url-status=live }}</ref> and organized by the [[Free & Equal Elections Foundation]].<ref name="united"/> The participants were [[Gary Johnson]] ([[Libertarian Party (United States)|Libertarian]]), [[Jill Stein]] ([[Green Party of the United States|Green]]), [[Virgil Goode]] ([[Constitution Party (United States)|Constitution]]), and [[Rocky Anderson]] ([[Justice Party (United States)|Justice]]).<ref name="united"/><ref name=moderate3rd/> A second debate between Stein and Johnson took place on Sunday, November 4, and was moderated by Ralph Nader.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Lowrey|first=Annie|date=2012-11-05|title=Another Presidential Debate, but This Time the Candidates Are Much Less Familiar (Published 2012)|language=en-US|work=The New York Times|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/05/us/politics/in-this-presidential-debate-four-third-party-hopefuls.html|access-date=2021-02-08|issn=0362-4331|archive-date=February 8, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210208210836/https://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/05/us/politics/in-this-presidential-debate-four-third-party-hopefuls.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
||
===Notable expressions, phrases, and statements=== |
===Notable expressions, phrases, and statements=== |
||
* '''{{visible anchor|Severely conservative}}''' – In a speech he made at the [[Conservative Political Action Conference]] in February 2012, Romney claimed that he had been a "severely conservative Republican governor". Romney's description of his record as "severely conservative" was widely criticized by political commentators as both rhetorically clumsy and factually inaccurate.<ref>{{cite news|author1 = David A. Fahrenthold |title =Mitt Romney reframes himself as a 'severely conservative' governor|url = |
* '''{{visible anchor|Severely conservative}}''' – In a speech he made at the [[Conservative Political Action Conference]] in February 2012, Romney claimed that he had been a "severely conservative Republican governor". Romney's description of his record as "severely conservative" was widely criticized by political commentators as both rhetorically clumsy and factually inaccurate.<ref>{{cite news |author1 = David A. Fahrenthold |title = Mitt Romney reframes himself as a 'severely conservative' governor |url = https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/mitt-romney-reframes-himself-as-a-severely-conservative-governor/2012/02/14/gIQAaMiqHR_story.html |newspaper = The Washington Post |date = February 16, 2012 |access-date = September 17, 2017 |archive-date = February 9, 2021 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210209082847/https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/mitt-romney-reframes-himself-as-a-severely-conservative-governor/2012/02/14/gIQAaMiqHR_story.html |url-status = live }}</ref><ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20120919232414/http://www.weeklystandard.com/blogs/mitt-romneys-severe-conservatism_652663.html Mitt Romney's 'Severe Conservatism']. The Weekly Standard (September 18, 2012). Retrieved August 12, 2013.</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cnn.com/2012/02/13/opinion/frum-romney-moves/index.html|title="Mitt Romney's 'severely' bad moves"|website=CNN|date=February 13, 2012|last1=Frum|first1=David|access-date=January 24, 2013|archive-date=December 15, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201215223622/http://www.cnn.com/2012/02/13/opinion/frum-romney-moves/index.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Later, the phrase "severely conservative" was frequently brought up by Democrats to make fun of Romney's willingness to associate himself with the far-right of the Republican Party as well as his apparent lack of sincerity while doing so.<ref>{{cite news|author1=[[Paul Krugman]]|title=Severe Conservative Syndrome|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2012/02/13/opinion/krugman-severe-conservative-syndrome.html|work=The New York Times|date=February 13, 2012|access-date=February 28, 2017|archive-date=November 12, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201112025525/https://www.nytimes.com/2012/02/13/opinion/krugman-severe-conservative-syndrome.html|url-status=live}}</ref> [[Conservatism in the United States|Conservative]] radio host [[Rush Limbaugh]], who played the clip on his [[The Rush Limbaugh Show|radio show]], said: "I have never heard anybody say, 'I'm severely conservative.' "<ref>{{cite news|title=Rush On Romney @ CPAC: I Have Never Heard Anybody Say 'I'm Severely Conservative'|url=http://dailyrushbo.com/rush-on-romney-cpac-i-have-never-heard-anybody-say-im-severely-conservative|work=Daily Rushbo|date=February 10, 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402072945/http://dailyrushbo.com/rush-on-romney-cpac-i-have-never-heard-anybody-say-im-severely-conservative/|archive-date=April 2, 2015|df=mdy-all}}</ref> |
||
* '''[[You didn't build that]]''' – A portion of a statement that Obama made in a July 2012 campaign speech in [[Roanoke, Virginia|Roanoke]], [[Virginia]]. Obama said that businesses depend on government-provided infrastructure to succeed, but critics of his remarks argued that he was underplaying the work of entrepreneurs and giving the government credit for individuals' success. The Romney campaign immediately |
* '''[[You didn't build that]]''' – A portion of a statement that Obama made in a July 2012 campaign speech in [[Roanoke, Virginia|Roanoke]], [[Virginia]]. Obama said that businesses depend on government-provided infrastructure to succeed, but critics of his remarks argued that he was underplaying the work of entrepreneurs and giving the government credit for individuals' success. The Romney campaign immediately used the statement in an effort to contrast Romney's economic policies with Obama's and to appeal to small business owners/employees. A major theme of the [[2012 Republican National Convention]] was "We Built It". |
||
* '''[[47 percent]]''' – An expression Romney used at a private campaign fundraising event, which was secretly recorded and publicly released. At the private event, Romney said that 47 percent of the people would vote for Barack Obama no matter what Romney said or did because those people "...are dependent upon government... I'll never convince them they should take personal responsibility and care for their lives". |
* '''[[47 percent]]''' – An expression Romney used at a private campaign fundraising event, which was secretly recorded and publicly released. At the private event, Romney said that 47 percent of the people would vote for Barack Obama no matter what Romney said or did because those people "...are dependent upon government... I'll never convince them they should take personal responsibility and care for their lives." Ironically, Romney received almost exactly 47% of the vote. |
||
* '''The 1980s are now calling to ask for their foreign policy back''' – A portion of a statement that Obama made in an October 2012 debate. In the debate, Obama was deriding an earlier Romney statement in the campaign that Russia is "without question, our No. 1 geopolitical foe."<ref>{{cite news |author1 = Jillian Rayfield |title = Obama: The '80s called, they want their foreign policy back |url = https://www.salon.com/2012/10/23/obama_the_80s_called_they_want_their_foreign_policy_back/ |work = Salon |date = October 23, 2012 |access-date = April 24, 2022 |archive-date = April 24, 2022 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220424182412/https://www.salon.com/2012/10/23/obama_the_80s_called_they_want_their_foreign_policy_back/ |url-status = live }}</ref> |
|||
* '''[[Binders full of women]]''' – A phrase that Romney used in the [[Second U.S. presidential debate of 2012|second presidential debate]] to refer to the long list of female candidates that he considered when choosing his cabinet members as Governor of Massachusetts. |
* '''[[Binders full of women]]''' – A phrase that Romney used in the [[Second U.S. presidential debate of 2012|second presidential debate]] to refer to the long list of female candidates that he considered when choosing his cabinet members as Governor of Massachusetts. |
||
* '''Horses and bayonets''' – After Romney said in the [[Third U.S. presidential debate of 2012|third presidential debate]] that the U.S. Navy was smaller than at any time since 1917, Obama replied, "We have fewer ships than we did in 1916. Well, governor, we also have fewer horses and bayonets, because the nature of our military's changed."<ref>{{cite web|last1=Rogers|first1=Katie|title=Horses and bayonets catch on during final US presidential debate|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/us-news-blog/2012/oct/23/horses-and-bayonets-presidential-debate|website=The Guardian|date=October 23, 2012|access-date=August 17, 2017|archive-date=November 6, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201106164850/https://www.theguardian.com/world/us-news-blog/2012/oct/23/horses-and-bayonets-presidential-debate|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
* '''[[Shovel-ready]]''' jobs – a phrase used to describe some stimulus projects promoted by the administration. During the debate on September 23, 2011, Gary Johnson quipped, “My next-door neighbor’s two dogs have created more shovel-ready jobs than this president.” <ref>http://www.politico.com/story/2011/09/gary-johnsons-moment-064232#ixzz3xptLeUGs</ref> |
|||
* '''[[Shovel-ready]]''' jobs – a phrase used to describe some stimulus projects promoted by the administration. During the debate on September 23, 2011, Gary Johnson quipped, "My next-door neighbor's two dogs have created more shovel-ready jobs than this president."<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.politico.com/story/2011/09/gary-johnsons-moment-064232#ixzz3xptLeUGs|title=Gary Johnson's moment|website=Politico|last1=Burns|first1=Alexander|date=September 22, 2011|access-date=January 21, 2016|archive-date=December 14, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201214105138/https://www.politico.com/story/2011/09/gary-johnsons-moment-064232#ixzz3xptLeUGs|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
* '''{{visible anchor|Romnesia}}''' – A term coined by a blogger in April 2011 and used by Obama late in the campaign to describe Romney's alleged inability to take responsibility for his past statements.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://blog.hcfama.org/2011/04/04/romnesia/ |title=Romnesia |publisher=hcfama.org |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/20111201074626/http://blog.hcfama.org/2011/04/04/romnesia/ |archivedate=December 1, 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|author=Kantrowitz, Alex |url=http://www.forbes.com/sites/alexkantrowitz/2012/10/21/romnesia-a-made-for-social-media-attack-line/ |title=#Romnesia: A Made for Social Media Attack Line |work=Forbes |date=October 21, 2012 |accessdate=October 22, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
* '''{{visible anchor|Romnesia}}''' – A term coined by a blogger in April 2011 and used by Obama late in the campaign to describe Romney's alleged inability to take responsibility for his past statements.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://blog.hcfama.org/2011/04/04/romnesia/ |title=Romnesia |publisher=hcfama.org |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111201074626/http://blog.hcfama.org/2011/04/04/romnesia/ |archive-date=December 1, 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Kantrowitz, Alex |url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/alexkantrowitz/2012/10/21/romnesia-a-made-for-social-media-attack-line/ |title=#Romnesia: A Made for Social Media Attack Line |work=Forbes |date=October 21, 2012 |access-date=October 22, 2012 |archive-date=October 23, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121023074001/http://www.forbes.com/sites/alexkantrowitz/2012/10/21/romnesia-a-made-for-social-media-attack-line/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
* '''[[Public image of Mitt Romney|$10,000 bet]]''' – During a Republican debate, Romney facetiously bet Texas governor [[Rick Perry]] $10,000 that he (Perry) was wrong about Romney's position on the individual mandate under the [[Affordable Healthcare for America Act|Affordable Healthcare Act]]. The statement was vilified by Democrats as exemplary of Romney being out of touch with the average American. |
|||
* '''[[Public image of Mitt Romney|$10,000 bet]]''' – During a Republican debate, Romney facetiously bet Texas governor [[Rick Perry]] $10,000 that he (Perry) was wrong about Romney's position on the individual mandate under the [[Affordable Healthcare for America Act|Affordable Healthcare Act]]. The statement was vilified by Democrats as exemplary of Romney being out of touch with working-class and middle-class Americans. |
|||
* '''Romneyshambles''' – a phrase used by the British press after Romney criticized British preparations for the [[2012 Summer Olympics]], which was a play on [[omnishambles]]. The phrase became a popular [[hashtag]] on [[Twitter]] and was later chosen as one of [[Collins English Dictionary]]'s words of the year.<ref>[http://www.newyorker.com/news/lauren-collins/romneyshambles-part-ii Romneyshambles, Part II] The New Yorker, September 18, 2012</ref><ref>[http://www.nydailynews.com/news/world/gangnam-style-romneyshambles-uk-dictionary-words-year-article-1.1224325 'Gangnam Style,' 'fiscal cliff,' 'Romneyshambles' chosen as Collins Dictionary's words of the year] [[Daily News (New York)|Daily News]], December 20, 2012</ref> |
|||
* '''Romneyshambles''' – a word used by the British press after Romney criticized British preparations for the [[2012 Summer Olympics]]. The word is a play on [[omnishambles]], and it became a popular [[hashtag]] on [[Twitter]]. It was subsequently chosen as one of [[Collins English Dictionary]]'s words of the year.<ref>{{cite magazine|url=http://www.newyorker.com/news/lauren-collins/romneyshambles-part-ii|title=Romneyshambles, Part II|magazine=The New Yorker|date=September 18, 2012|last1=Collins|first1=Lauren|access-date=July 1, 2015|archive-date=September 25, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200925202840/https://www.newyorker.com/news/lauren-collins/romneyshambles-part-ii|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nydailynews.com/news/world/gangnam-style-romneyshambles-uk-dictionary-words-year-article-1.1224325|title='Gangnam Style,' 'fiscal cliff,' 'Romneyshambles' chosen as Collins Dictionary's words of the year|website=[[Daily News (New York)|Daily News]]|date=December 20, 2012|access-date=July 1, 2015|archive-date=November 14, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201114220751/https://www.nydailynews.com/news/world/gangnam-style-romneyshambles-uk-dictionary-words-year-article-1.1224325|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
* '''Malarkey''' – a word used by Joe Biden in his debate with Paul Ryan to mean [[bullshit]]. Biden later used the word in [[Joe Biden 2020 presidential campaign|his own campaign in 2020]].<ref>{{cite news|title=No malarkey? Biden's old-school slogan gets mocked and praised in Iowa|url=https://www.politico.com/news/2019/12/02/democrat-voters-biden-malarkey-campaign-slogan-074727|date=December 2, 2019|publisher=[[Politico]]|first=Natasha|last=Korecki|access-date=October 19, 2022|archive-date=February 2, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200202131553/https://www.politico.com/news/2019/12/02/democrat-voters-biden-malarkey-campaign-slogan-074727|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
=== Electoral College forecasts === |
|||
Elections analysts and political pundits issue probabilistic forecasts of the composition of the Electoral College. These forecasts use a variety of factors to estimate the likelihood of each candidate winning the Electoral College electors for that state. Most election predictors use the following ratings: |
|||
* "<u>tossup</u>": no advantage |
|||
* "<u>tilt</u>" (used by some predictors): advantage that is not quite as strong as "lean" |
|||
* "<u>lean</u>" or "<u>leans</u>": slight advantage |
|||
* "<u>likely</u>": significant, but surmountable, advantage |
|||
* "<u>safe</u>" or "<u>solid</u>": near-certain chance of victory |
|||
Below is a list of states considered by one or more forecast to be competitive; states that are deemed to be "safe" or "solid" by forecasters ''[[RealClearPolitics]]'', ''[[Sabato's Crystal Ball]]'', and ''[[FiveThirtyEight]]''. |
|||
{{sticky header}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable sticky-header" style="font-size:95%; |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom" |
|||
! State |
|||
! {{Tooltip|EVs|Electoral votes}} |
|||
! [[RealClearPolitics]]<br />{{small|November 6,<br />2012}}<ref>{{cite web| url = http://www.realclearpolitics.com/epolls/2012/president/2012_elections_electoral_college_map.html| url-status = dead| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110608112207/http://www.realclearpolitics.com/epolls/2012/president/2012_elections_electoral_college_map.html| archive-date = 2011-06-08| title = RealClearPolitics - 2012 Election Maps - Battle for White House}}</ref> |
|||
![[Sabato's Crystal Ball]]<br />{{small|November 6,<br />2012}}<ref>{{cite web|url= https://centerforpolitics.org/crystalball/projection-obama-will-likely-win-second-term/|title= PROJECTION: OBAMA WILL LIKELY WIN SECOND TERM|date= November 5, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
![[FiveThirtyEight|538]]<br />{{small|November 6,<br />2012}}<ref>{{cite web|url= https://www.masslive.com/news/2012/11/nate_silvers_political_calcula.html|title= Nate Silver's political calculations predict 2012 election outcome|date= November 7, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Arizona|Arizona]] |
|||
| align=center|11 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|R}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Solid|R}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|R}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Colorado|Colorado]] |
|||
| align=center|9 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Florida|Florida]] |
|||
| align=center|29 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|R|flip}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Iowa|Iowa]] |
|||
| align=center|6 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Indiana|Indiana]] |
|||
| align=center|11 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|R|flip}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Solid|R|flip}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|R|flip}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Maine|Maine]] |
|||
| align=center|1 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Michigan|Michigan]] |
|||
| align=center|16 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Minnesota|Minnesota]] |
|||
| align=center|10 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Missouri|Missouri]] |
|||
| align=center|11 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|R}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Solid|R}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|R}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Nevada|Nevada]] |
|||
| align=center|6 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in New Hampshire|New Hampshire]] |
|||
| align=center|4 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in New Mexico|New Mexico]] |
|||
| align=center|5 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in North Carolina|North Carolina]] |
|||
| align=center|15 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|R|flip}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|R|flip}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Ohio|Ohio]] |
|||
| align=center|18 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Oregon|Oregon]] |
|||
| align=center|7 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania|Pennsylvania]] |
|||
| align=center|20 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Washington (state)|Washington]] |
|||
| align=center|12 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Solid|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Virginia|Virginia]] |
|||
| align=center|13 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|R}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Likely|D}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[2012 United States presidential election in Wisconsin|Wisconsin]] |
|||
| align=center|10 |
|||
<!--RCP--> | {{USRaceRating|Tossup}} |
|||
<!--Sabato--> | {{USRaceRating|Lean|D}} |
|||
<!--538--> | {{USRaceRating|Safe|D}} |
|||
|} |
|||
== Timeline == |
|||
{{Main|Timeline of the 2012 United States presidential election}} |
|||
==Results== |
==Results== |
||
Popular vote totals are from the [http://www.fec.gov/pubrec/fe2012/federalelections2012.pdf official Federal Election Commission report]. The results of the electoral vote were certified by Congress on January 4, 2013.<ref name=ap010413>{{cite news|last=Cassata|first=Donna|title=Electoral College count affirms Obama's win|url=http://www.cbsatlanta.com/story/20505151/electoral-college-count-affirms-obamas-win|accessdate=January 4, 2013|agency=Associated Press|date=January 4, 2013}}{{dead link|date=February 2016}}</ref> |
|||
=== Electoral results === |
|||
On the day of the election, spread betting firm [[Spreadex]] were offering an Obama Electoral College Votes spread of 296–300 to Romney's 239–243.<ref>{{Cite web|date=November 7, 2012|title=US Election Betting {{!}} Financial Spread Betting {{!}} Spreadex|url=https://www.spreadex.com/financials/press-releases/2012-us-election-spread-betting-results/|access-date=August 11, 2020|website=www.spreadex.com|archive-date=February 17, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210217195649/https://www.spreadex.com/financials/press-releases/2012-us-election-spread-betting-results/|url-status=live}}</ref> In reality Obama's victory over Romney was far greater, winning 332 electoral votes to Romney's 206. Romney lost all but one of nine [[battleground state]]s, and received 47 percent of the nationwide popular vote to Obama's 51 percent.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.foxnews.com/politics/2012/11/06/obama-defeats-romney-to-win-second-term-fox-news-projects/|title=Obama defeats Romney to win second term, vows he has 'more work to do'|publisher=Fox News|date=November 7, 2012|access-date=December 8, 2019|archive-date=November 5, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151105145347/http://www.foxnews.com/politics/2012/11/06/obama-defeats-romney-to-win-second-term-fox-news-projects/|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.latimes.com/news/politics/la-pn-obama-biden-officially-win-second-term-20130104,0,5932518.story|title=It's official: Obama, Biden win second term|author=Memoli, Michael A.|newspaper=Los Angeles Times|date=January 4, 2013|access-date=December 8, 2019|archive-date=February 28, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130228200916/http://www.latimes.com/news/politics/la-pn-obama-biden-officially-win-second-term-20130104,0,5932518.story|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Of the 3,154 counties/districts/independent cities making returns, Romney won the most popular votes in 2,447 (77.58%) while Obama carried 707 (22.42%). |
|||
Popular vote totals are from the [[Federal Election Commission]] report.<ref name="FEC 2013"/> |
|||
{{start U.S. presidential ticket box|pv_footnote=|ev_footnote=}} |
{{start U.S. presidential ticket box|pv_footnote=|ev_footnote=}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Barack Obama]] ( |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Barack Obama]] (incumbent)|party=[[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]]|state=[[Illinois]]|pv=65,915,795|pv_pct=51.06%|ev=332|vp_name=[[Joe Biden]] (incumbent)|vp_state=[[Delaware]]}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Mitt Romney]]|party=[[United States |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Mitt Romney]]|party=[[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]]|state=[[Massachusetts]]|pv=60,933,504|pv_pct=47.20%|ev=206|vp_name=[[Paul Ryan]]|vp_state=[[Wisconsin]]}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Gary Johnson]]|party=[[Libertarian Party (United States)|Libertarian]]|state=[[New Mexico]]|pv=1,275,971|pv_pct=0.99%|ev=0 |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Gary Johnson]]|party=[[Libertarian Party (United States)|Libertarian]]|state=[[New Mexico]]|pv=1,275,971|pv_pct=0.99%|ev=0|vp_name=[[Jim Gray (jurist)|Jim Gray]]|vp_state=[[California]]}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Jill Stein]]|party=[[Green Party (United States)|Green]]|state=[[Massachusetts]]|pv=469,627|pv_pct=0.36%|ev= |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Jill Stein]]|party=[[Green Party (United States)|Green]]|state=[[Massachusetts]]|pv=469,627|pv_pct=0.36%|ev=0|vp_name=[[Cheri Honkala]]|vp_state=[[Minnesota]]}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Virgil Goode]]|party=[[Constitution Party (United States)|Constitution]]|state=[[Virginia]]|pv=122, |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Virgil Goode]]|party=[[Constitution Party (United States)|Constitution]]|state=[[Virginia]]|pv=122,389|pv_pct=0.11%|ev=0|vp_name=James N. Clymer|vp_state=[[Pennsylvania]]}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Roseanne Barr]]|party=[[Peace and Freedom Party|Peace and Freedom]]|state=[[ |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Roseanne Barr]]|party=[[Peace and Freedom Party|Peace and Freedom]]|state=[[Utah]]|pv=67,326|pv_pct=0.05%|ev=0|vp_name=[[Cindy Sheehan]]|vp_state=[[California]]}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Rocky Anderson]]|party=[[Justice Party (United States)|Justice]]|state=[[Utah]]|pv=43,018|pv_pct=0.03%|ev=0|vp_name=[[Luis J. Rodriguez]]|vp_state=[[ |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Rocky Anderson]]|party=[[Justice Party (United States)|Justice]]|state=[[Utah]]|pv=43,018|pv_pct=0.03%|ev=0|vp_name=[[Luis J. Rodriguez]]|vp_state=[[Texas]]}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Tom Hoefling]]|party= |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box row|name=[[Tom Hoefling]]|party=America's|state=[[Nebraska]]|pv=40,628|pv_pct=0.03%|ev=0|vp_name=J.D. Ellis|vp_state=[[Tennessee]]}} |
||
{{U.S. presidential ticket box other|footnote=|pv=217, |
{{U.S. presidential ticket box other|footnote=|pv=217,152|pv_pct=0.17%}} |
||
{{end U.S. presidential ticket box|pv=129,085, |
{{end U.S. presidential ticket box|pv=129,085,410|pv_pct=100%|ev=538|to_win=270}} |
||
[[File:Barack Obama votes in the 2012 election.jpg|thumb|President Obama casts his ballot at the Martin Luther King Jr. Community Center in [[Chicago]].]] |
[[File:Barack Obama votes in the 2012 election.jpg|thumb|President Obama casts his ballot at the Martin Luther King Jr. Community Center in [[Chicago]].]] |
||
{{bar box |
{{bar box |
||
| Line 385: | Line 624: | ||
|barwidth=410px |
|barwidth=410px |
||
|bars= |
|bars= |
||
{{bar percent|'''Obama'''|{{Democratic Party (US) |
{{bar percent|'''Obama'''|{{party color|Democratic Party (US)}}|51.06}} |
||
{{bar percent|Romney|{{Republican Party (US) |
{{bar percent|Romney|{{party color|Republican Party (US)}}|47.20}} |
||
{{bar percent|Johnson|{{Libertarian Party (US) |
{{bar percent|Johnson|{{party color|Libertarian Party (US)}}|0.99}} |
||
{{bar percent|Stein|{{Green Party (US) |
{{bar percent|Stein|{{party color|Green Party (US)}}|0.36}} |
||
{{bar percent|Others|#777777|0. |
{{bar percent|Others|#777777|0.39}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 398: | Line 637: | ||
|barwidth=410px |
|barwidth=410px |
||
|bars= |
|bars= |
||
{{bar percent|'''Obama'''|{{Democratic Party (US) |
{{bar percent|'''Obama'''|{{party color|Democratic Party (US)}}|61.71}} |
||
{{bar percent|Romney|{{Republican Party (US) |
{{bar percent|Romney|{{party color|Republican Party (US)}}|38.29}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
=== |
===Results by state=== |
||
The table below displays the official vote tallies by each state's Electoral College voting method. The source for the results of all states, except those that amended their official results, is the |
The table below displays the official vote tallies by each state's Electoral College voting method. The source for the results of all states, except those that amended their official results, is the official Federal Election Commission report.<ref name="FEC 2013" /> The column labeled "Margin" shows Obama's margin of victory over Romney (the margin is negative for every state that Romney won). |
||
{|class="wikitable" |
{|class="wikitable" style="text-align:right;font-size:90%;line-height:1.2" |
||
|+ Legend |
|||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
|States/districts won by [[Barack Obama|Obama]]/[[Joe Biden|Biden]] |
|colspan=2|States/districts won by [[Barack Obama|Obama]]/[[Joe Biden|Biden]] |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
|States/districts won by [[Mitt Romney|Romney]]/[[Paul Ryan|Ryan]] |
|colspan=2|States/districts won by [[Mitt Romney|Romney]]/[[Paul Ryan|Ryan]] |
||
|- |
|||
| † || At-large results (for states that split electoral votes) |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
'''Electoral methods''' |
|||
* WTA – Winner-takes-all |
|||
* CD – Congressional district<sup>★</sup> |
|||
<div style="overflow:auto"> |
<div style="overflow:auto"> |
||
{{sort under}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:right" |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable sort-under" style="text-align:right;font-size:90%;line-height:1.2" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! rowspan="2" {{vertical header|stp=1|State or<br />district}} |
|||
! colspan=2 | |
|||
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"| |
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"|Obama/Biden<br />Democratic |
||
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"| |
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"|Romney/Ryan<br />Republican |
||
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"| |
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"|Johnson/Gray<br />Libertarian |
||
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"| |
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"|Stein/Honkala<br />Green |
||
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"| |
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="3"|Others |
||
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="2"| |
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="2"|Margin |
||
! style="text-align:center;" colspan=" |
! style="text-align:center;" colspan="1"|Margin<br />Swing{{Efn|Percentage point difference in margin from the [[2008 United States presidential election|2008 election]]}} |
||
! style="text-align:center;" rowspan="2"|Total<br />votes |
|||
! style="text-align:center;" rowspan="2"| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|# |
|||
! align=center | State or<br />district |
|||
! style="text-align:center; |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|% |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|{{abbr|EV|Electoral Votes}} |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|# |
||
! style="text-align:center; |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|% |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|{{abbr|EV|Electoral Votes}} |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|# |
||
! style="text-align:center; |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|% |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|{{abbr|EV|Electoral Votes}} |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|# |
||
! style="text-align:center; |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|% |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|{{abbr|EV|Electoral Votes}} |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|# |
||
! style="text-align:center; |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|% |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|{{abbr|EV|Electoral Votes}} |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|# |
||
! style="text-align:center; |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|% |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- |
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort-type="number"|% |
||
! style="text-align:center;" data-sort- type="number"| % |
|||
! style="text-align:center; font-size: 60%" data-sort-type="number" | # |
|||
! |
|||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Alabama |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Alabama}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Alabama|Alabama]] || 795,696||38.36%||–||1,255,925||60.55%||9||12,328||0.59%||–||3,397||0.16%||–||6,992||0.3%||–||−460,229||−22.19%||−0.61%||2,074,338||AL |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Alaska |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Alaska}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Alaska|Alaska]] || 122,640||40.81%||–||164,676||54.80%||3||7,392||2.46%||–||2,917||0.97%||–||2,870||1.0%||–||−42,036||−13.99%||7.55%||300,495||AK |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Arizona |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Arizona}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Arizona|Arizona]] || 1,025,232||44.59%||–||1,233,654||53.65%||11||32,100||1.39%||–||7,816||0.34%||–||452||nil||–||−208,422||−9.06%||−0.54%||2,299,254||AZ |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Arkansas |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Arkansas}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Arkansas|Arkansas]] || 394,409||36.88%||–||647,744||60.57%||6||16,276||1.52%||–||9,305||0.87%||–||1,734||0.16%||–||−253,335||−23.69%||−3.84%||1,069,468||AR |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in California |
| align=left|{{flagicon|California}} [[2012 United States presidential election in California|California]] || 7,854,285||60.24%||55||4,839,958||37.12%||–||143,221||1.10%||–||85,638||0.66%||–||115,445||0.88%||–||3,014,327||23.12%||−0.94%||13,038,547||CA |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Colorado |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Colorado}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Colorado|Colorado]] || 1,323,102||51.49%||9||1,185,243||46.13%||–||35,545||1.38%||–||7,508||0.29%||–||18,121||0.71%||–||137,858||5.36%||−3.59%||2,569,518||CO |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Connecticut |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Connecticut}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Connecticut|Connecticut]] || 905,083||58.06%||7||634,892||40.73%||–||12,580||0.81%||–||863||0.06%||–||5,542||0.36%||–||270,191||17.33%||−5.04%||1,558,960||CT |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Delaware |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Delaware}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Delaware|Delaware]] || 242,584||58.61%||3||165,484||39.98%||–||3,882||0.94%||–||1,940||0.47%||–||31||nil||–||77,100||18.63%||−6.37%||413,921||DE |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|<span style="display:none">District of Columbia</span>[[United States presidential election in the District of Columbia |
| align=left|{{flagicon|District of Columbia}} <span style="display:none">District of Columbia</span>[[2012 United States presidential election in the District of Columbia|District of Columbia]] || 267,070||90.91%||3||21,381||7.28%||–||2,083||0.71%||–||2,458||0.84%||–||772||0.26%||–||245,689||83.63%||−2.29%||293,764||DC |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Florida |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Florida}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Florida|Florida]] || 4,237,756||50.01%||29||4,163,447||49.13%||–||44,726||0.5%||–||8,947||0.1%||–||19,303||0.2%||–||74,309||0.88%||−1.94%||8,474,179||FL |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Georgia |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Georgia (U.S. state)}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Georgia|Georgia]] || 1,773,827||45.48%||–||2,078,688||53.30%||16||45,324||1.2%||–||1,516||nil||–||695||nil||–||−304,861||−7.82%||−2.61%||3,900,050||GA |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Hawaii |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Hawaii}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Hawaii|Hawaii]] ||306,658||70.55%||4||121,015||27.84%||–||3,840||0.9%||–||3,184||0.7%||–||–||–||–||185,643||42.71%||−2.55%||434,697||HI |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Idaho |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Idaho}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Idaho|Idaho]] || 212,787||32.62%||–||420,911||64.53%||4||9,453||1.5%||–||4,402||0.7%||–||4,721||0.7%||–||−208,124||−31.91%||−6.26%||652,274||ID |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Illinois |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Illinois}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Illinois|Illinois]] || 3,019,512||57.60%||20||2,135,216||40.73%||–||56,229||1.1%||–||30,222||0.6%||–||835||nil||–||884,296||16.87%||−8.27%||5,242,014||IL |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Indiana |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Indiana}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Indiana|Indiana]] || 1,152,887||43.93%||–||1,420,543||54.13%||11||50,111||1.9%||–||625||nil||–||368||nil||–||−267,656||−10.20%||−11.26%||2,624,534||IN |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Iowa |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Iowa}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Iowa|Iowa]] || 822,544||51.99%||6||730,617||46.18%||–||12,926||0.8%||–||3,769||0.2%||–||12,324||0.8%||–||91,927||5.81%||−3.72%||1,582,180||IA |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Kansas |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Kansas}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Kansas|Kansas]] ||440,726||37.99%||–||692,634||59.71%||6||20,456||1.8%||–||714||0.1%||–||5,441||0.5%||–||−251,908||−21.72%||−6.75%||1,159,971||KS |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Kentucky |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Kentucky}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Kentucky|Kentucky]] ||679,370||37.80%||–||1,087,190||60.49%||8||17,063||1.0%||–||6,337||0.4%||–||7,252||0.4%||–||−407,820||−22.69%||−6.46%||1,797,212||KY |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Louisiana |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Louisiana}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Louisiana|Louisiana]] || 809,141||40.58%||–||1,152,262||57.78%||8||18,157||0.9%||–||6,978||0.4%||–||7,527||0.4%||–||−343,121||−17.20%||1.43%||1,994,065||LA |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Maine |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Maine}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Maine|Maine<sup>†</sup>]]|| 401,306||56.27%||2||292,276||40.98%||–||9,352||1.3%||–||8,119||1.1%||–||2,127||0.3%||–||109,030||15.29%||−2.03%||713,180||ME–AL |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|'' |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Maine}} ''{{abbrlink|ME-1|Maine's 1st congressional district}}'' ||''223,035''||''59.57%''||1||''142,937''||''38.18%''||–||''4,501''||''1.2%''||–||''3,946''||''1.1%''||–||–||–||–||''80,098''||''21.39%''||''−1.43%''||''374,419''||ME1 |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|'' |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Maine}} ''{{abbrlink|ME-2|Maine's 2nd congressional district}}'' ||''177,998''||''52.94%''||1||''149,215''||''44.38%''||–||''4,843''||''1.4%''||–||''4,170''||''1.2%''||–||–||–||–||''28,783''||''8.56%''||''−2.69%''||''336,226''||ME2 |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Maryland |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Maryland}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Maryland|Maryland]] ||1,677,844||61.97%||10||971,869||35.90%||–||30,195||1.1%||–||17,110||0.6%||–||10,309||0.4%||–||705,975||26.07%||0.63%||2,707,327||MD |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Massachusetts |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Massachusetts}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Massachusetts|Massachusetts]] || 1,921,290||60.65%||11||1,188,314||37.51%||–||30,920||1.0%||–||20,691||0.7%||–||6,552||0.2%||–||732,976||23.14%||−2.67%||3,167,767||MA |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Michigan |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Michigan}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Michigan|Michigan]] ||2,564,569||54.21%||16||2,115,256||44.71%||–||7,774||0.2%||–||21,897||0.5%||–||21,465||0.5%||–||449,313||9.50%||−6.97%||4,730,961||MI |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Minnesota |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Minnesota|1983}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Minnesota|Minnesota]] ||1,546,167||52.65%||10||1,320,225||44.96%||–||35,098||1.2%||–||13,023||0.4%||–||22,048||0.8%||–||225,942||7.69%||−2.55%||2,936,561||MN |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Mississippi |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Mississippi|2001}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Mississippi|Mississippi]] || 562,949||43.79%||–||710,746||55.29%||6||6,676||0.5%||–||1,588||0.1%||–||3,625||0.3%||–||−147,797||−11.50%||1.67%||1,285,584||MS |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Missouri |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Missouri}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Missouri|Missouri]] || 1,223,796||44.38%||–||1,482,440||53.76%||10||43,151||1.6%||–||–||–||–||7,936||0.3%||–||−258,644||−9.38%||−9.25%||2,757,323||MO |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Montana |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Montana}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Montana|Montana]] || 201,839||41.70%||–||267,928||55.35%||3||14,165||2.9%||–||–||–||–||116||nil||–||−66,089||−13.65%||−11.39%||484,048||MT |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Nebraska |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Nebraska}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Nebraska|Nebraska<sup>† </sup>]]||302,081||38.03%||–||475,064||59.80%||2||11,109||1.4%||–||–||–||–||6,125||0.8%||–||−172,983||−21.77%||−6.84%||794,379||NE–AL |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|'' |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Nebraska}} ''{{abbrlink|NE-1|Nebraska's 1st congressional district}}'' ||''108,082''||''40.83%''||–||''152,021''||''57.43%''||1 ||''3,847''||''1.2%''||–||–||–||–||''762''||''0.3%''||–||''-43,949''||''-16.60%''||−6.83%||''264,712''||NE1 |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|'' |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Nebraska}} ''{{abbrlink|NE-2|Nebraska's 2nd congressional district}}'' ||''121,889''||''45.70%''||–||''140,976''||''52.85%''||1 ||''3,393''||''1.3%''||–||–||–||–||''469''||''0.2%''||–||''-19,087''||''-7.15%''||−5.94%||''266,727''||NE2 |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|'' |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Nebraska}} ''{{abbrlink|NE-3|Nebraska's 3rd congressional district}}'' ||''72,110''||''27.82%''||–||''182,067''||''70.23%''||1 ||''3,869''||''1.5%''||–||–||–||–||''1,177''||''0.5%''||–||''−109,957''||''−42.41%''||−3.40%||''259,223''||NE3 |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Nevada |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Nevada}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Nevada|Nevada]] || 531,373||52.36%||6||463,567||45.68%||–||10,968||1.1%||–||–||–||–||9,010||0.9%||–||67,806||6.68%||−5.81%||1,014,918||NV |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in New Hampshire |
| align=left|{{flagicon|New Hampshire}} [[2012 United States presidential election in New Hampshire|New Hampshire]] || 369,561||51.98%||4||329,918||46.40%||–||8,212||1.2%||–||324||0.1%||–||2,957||0.4%||–||39,643||5.58%||−4.03%||710,972||NH |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in New Jersey |
| align=left|{{flagicon|New Jersey}} [[2012 United States presidential election in New Jersey|New Jersey]]<ref name=newjersey>{{cite web|url=http://nj.gov/state/elections/election-information-archive-2012.html#ge|title=2012 Election Information|access-date=February 25, 2013|archive-date=March 4, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130304065655/http://nj.gov/state/elections/election-information-archive-2012.html#ge|url-status=live}}</ref> || 2,125,101||58.38%||14||1,477,568||40.59%||–||21,045||0.6%||–||9,888||0.3%||–||6,690||0.2%||–||647,533||17.79%||2.22%||3,640,292||NJ |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in New Mexico |
| align=left|{{flagicon|New Mexico}} [[2012 United States presidential election in New Mexico|New Mexico]] ||415,335||52.99%||5||335,788||42.84%||–||27,788||3.6%||–||2,691||0.3%||–||2,156||0.3%||–||79,547||10.15%||−4.98%||783,758||NM |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in New York |
| align=left|{{flagicon|New York (state)}} [[2012 United States presidential election in New York|New York]]<ref name=newyork>{{cite web|url=http://www.elections.ny.gov/NYSBOE/elections/2012/General/President_04-09-2013.pdf|title=NYS Board of Elections President and Vice-President Election Returns Nov. 6, 2012|access-date=May 2, 2013|archive-date=July 25, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130725104912/http://www.elections.ny.gov/NYSBOE/elections/2012/General/President_04-09-2013.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref> ||4,485,741||63.35%||29||2,490,431||35.17%||–||47,256||0.7%||–||39,982||0.6%||–||17,749||0.3%||–||1,995,310||28.18%||1.32%||7,081,159||NY |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in North Carolina |
| align=left|{{flagicon|North Carolina}} [[2012 United States presidential election in North Carolina|North Carolina]] ||2,178,391||48.35%||–||2,270,395||50.39%||15||44,515||1.0%||–||–||–||–||12,071||0.3%||–||−92,004||−2.04%||−2.37%||4,505,372||NC |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in North Dakota |
| align=left|{{flagicon|North Dakota}} [[2012 United States presidential election in North Dakota|North Dakota]] || 124,827||38.69%||–||188,163||58.32%||3||5,231||1.6%||–||1,361||0.4%||–||3,045||0.9%||–||−63,336||−19.63%||−10.99%||322,627||ND |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Ohio |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Ohio}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Ohio|Ohio]]<ref name=ohio>{{cite web|url=http://www.sos.state.oh.us/sos/upload/elections/2012/gen/FinalResults.xlsx|title=Final Results|access-date=February 25, 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130729175614/http://www.sos.state.oh.us/sos/upload/elections/2012/gen/FinalResults.xlsx|archive-date=July 29, 2013}}</ref> || 2,827,709||50.67%||18||2,661,437||47.69%||–||49,493||0.9%||–||18,573||0.3%||–||23,635||0.4%||–||166,272||2.98%||−1.61%||5,580,847||OH |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Oklahoma |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Oklahoma}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Oklahoma|Oklahoma]] || 443,547||33.23%||–||891,325||66.77%||7||–||–||–||–||–||–||–||–||–||−447,778||−33.54%||−2.15%||1,334,872||OK |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Oregon |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Oregon}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Oregon|Oregon]] || 970,488||54.24%||7||754,175||42.15%||–||24,089||1.4%||–||19,427||1.1%||–||21,091||1.2%||–||216,313||12.09%||−4.26%||1,789,270||OR |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Pennsylvania |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Pennsylvania}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania|Pennsylvania]] ||2,990,274||51.97%||20||2,680,434||46.59%||–||49,991||0.9%||–||21,341||0.4%||–||11,630||0.2%||–||309,840||5.38%||−4.94%||5,753,670||PA |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Rhode Island |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Rhode Island}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Rhode Island|Rhode Island]] || 279,677||62.70%||4||157,204||35.24%||–||4,388||1.0%||–||2,421||0.5%||–||2,359||0.5%||–||122,473||27.46%||−0.35%||446,049||RI |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in South Carolina |
| align=left|{{flagicon|South Carolina}} [[2012 United States presidential election in South Carolina|South Carolina]]|| 865,941||44.09%||–||1,071,645||54.56%||9||16,321||0.8%||–||5,446||0.3%||–||4,765||0.2%||–||−205,704||−10.47%||−1.49%||1,964,118||SC |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in South Dakota |
| align=left|{{flagicon|South Dakota}} [[2012 United States presidential election in South Dakota|South Dakota]] ||145,039||39.87%||–||210,610||57.89%||3||5,795||1.6%||–||–||–||–||2,371||0.7%||–||−65,571||−18.02%||−9.61%||363,815||SD |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Tennessee |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Tennessee}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Tennessee|Tennessee]] ||960,709||39.08%||–||1,462,330||59.48%||11||18,623||0.8%||–||6,515||0.3%||–||10,400||0.4%||–||−501,621||−20.40%||−5.33%||2,458,577||TN |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Texas |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Texas}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Texas|Texas]]|| 3,308,124||41.38%||–||4,569,843||57.17%||38||88,580||1.1%||–||24,657||0.3%||–||2,647||nil||–||−1,261,719||−15.79%||−4.02%||7,993,851||TX |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Utah |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Utah|2011}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Utah|Utah]] ||251,813||24.75%||–||740,600||72.79%||6||12,572||1.2%||–||3,817||0.4%||–||8,638||0.9%||–||−488,787||−48.04%||−19.75%||1,017,440||UT |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Vermont |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Vermont}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Vermont|Vermont]] || |199,239||66.57%||3||92,698||30.97%||–||3,487||1.2%||–||594||0.2%||–||3,272||1.1%||–||106,541||35.60%||−1.41%||299,290||VT |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Virginia |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Virginia}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Virginia|Virginia]] || 1,971,820||51.16%||13||1,822,522||47.28%||–||31,216||0.8%||–||8,627||0.2%||–||20,304||0.5%||–||149,298||3.88%||−2.42%||3,854,489||VA |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Washington |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Washington}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Washington (state)|Washington]] || 1,755,396||56.16%||12||1,290,670||41.29%||–||42,202||1.4%||–||20,928||0.7%||–||16,320||0.5%||–||464,726||14.87%||−2.31%||3,125,516||WA |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in West Virginia |
| align=left|{{flagicon|West Virginia}} [[2012 United States presidential election in West Virginia|West Virginia]]||238,269||35.54%||–||417,655||62.30%||5||6,302||0.9%||–||4,406||0.7%||–||3,806||0.6%||–||−179,386||−26.76%||−13.64%||670,438||WV |
||
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
|-{{Party shading/Democratic}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Wisconsin |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Wisconsin}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Wisconsin|Wisconsin]]<ref name=wisconsin>{{cite web|url=http://gab.wi.gov/elections-voting/results/2012/fall-general|title=Wisconsin Fall 2012 General Election Results|access-date=January 18, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130129040530/http://gab.wi.gov/elections-voting/results/2012/fall-general|archive-date=January 29, 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref>||1,620,985||52.83%||10||1,407,966||45.89%||–||20,439||0.7%||–||7,665||0.3%||–||11,379||0.4%||–||213,019||6.94%||−6.96%||3,068,434||WI |
||
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
|-{{Party shading/Republican}} |
||
| align=left|[[United States presidential election in Wyoming |
| align=left|{{flagicon|Wyoming}} [[2012 United States presidential election in Wyoming|Wyoming]] ||69,286||27.82%||–||170,962||68.64%||3||5,326||2.1%||–||–||–||–||3,487||1.4%||–||−101,676||−40.82%||−8.58%||249,061||WY |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! |
!Total||65,915,795||51.06%||332||60,933,504||47.20%||206||1,275,971||1.0%||–||469,627||0.4%||–||490,510||0.4%||–||4,982,291||3.86%||−4.41%||129,085,410 |
||
!rowspan=2| |
|||
|- |
|||
! |
|||
!colspan=3| Obama/Biden<br />Democratic |
|||
!colspan=3| Romney/Ryan<br />Republican |
|||
!colspan=3| Johnson/Gray<br />Libertarian |
|||
!colspan=3| Stein/Honkala<br />Green |
|||
!colspan=3| Others |
|||
!colspan=2| Margin |
|||
! Margin<br />swing |
|||
! Total<br />votes |
|||
|}</div> |
|}</div> |
||
<sup>★</sup>Two states (Maine and Nebraska) allow for their electoral votes to be split between candidates. The winner within each congressional district gets one electoral vote for the district. The winner of the statewide vote gets two additional electoral votes.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.archives.gov/federal-register/electoral-college/2012-certificates/pdfs/ascertainment-maine.pdf|title=State of Maine Certificate of Ascertainment of Electors|accessdate=December 18, 2012}}</ref><ref name=nebraska>{{cite web|url=http://www.sos.ne.gov/elec/2012/pdf/2012-general-canvass.pdf|title=Official Results of Nebraska General Election – November 6, 2012|accessdate=December 26, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Maine and Nebraska each allow for their election results votes to be split between candidates. The winner within each congressional district gets one electoral vote for the district. The winner of the statewide vote gets two additional electoral votes. In the 2012 election, all four of Maine's electoral votes were won by Obama and all five of Nebraska's electoral votes were won by Romney.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.archives.gov/federal-register/electoral-college/2012-certificates/pdfs/ascertainment-maine.pdf|title=State of Maine Certificate of Ascertainment of Electors|access-date=December 18, 2012|archive-date=December 22, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121222155743/http://www.archives.gov/federal-register/electoral-college/2012-certificates/pdfs/ascertainment-maine.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=nebraska>{{cite web|url=http://www.sos.ne.gov/elec/2012/pdf/2012-general-canvass.pdf|title=Official Results of Nebraska General Election – November 6, 2012|access-date=December 26, 2012|archive-date=April 4, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130404095656/http://www.sos.ne.gov/elec/2012/pdf/2012-general-canvass.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Close races=== |
|||
[[File:Election-state-08-12.png|thumb|285px|Swing from [[United States presidential election, 2008|2008]] to 2012 in each state. Only six states trended more Democratic in 2012: Alaska, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, New Jersey, and New York. The arrows to the right represent how many places up or down on the list the state moved since 2008. States are listed by (increasing) percentage of Democratic votes.]] |
|||
====States and EV districts that flipped from Democratic to Republican==== |
|||
<span style="color:red;">Red </span> denotes states (or congressional districts that contribute an electoral vote) won by Republican Mitt Romney; <span style="color:darkblue;">blue</span> denotes those won by Democrat Barack Obama. |
|||
*[[Indiana]] |
|||
*[[Nebraska's 2nd congressional district]] |
|||
*[[North Carolina]] |
|||
===Close states=== |
|||
States where the margin of victory was under 5% (75 electoral votes): |
|||
[[File:Election-state-08-12.png|thumb|upright=1.3|Swing from [[2008 United States presidential election|2008]] to 2012 in each state. Only six states swung more Democratic in 2012: Alaska, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, New Jersey, and New York. The arrows to the right represent how many places up or down on the list the state moved since 2008. States are listed by (increasing) percentage of Democratic votes.]] |
|||
<span style="color:darkred;">'''Red''' </span>denotes states (or congressional districts that contribute an electoral vote) won by Republican Mitt Romney; <span style="color:darkblue;">'''blue'''</span> denotes those won by Democrat Barack Obama. |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Florida, 0.88%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:red;">North Carolina, 2.04%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Ohio, 2.98%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Virginia, 3.87%</span>''' |
|||
State where the margin of victory was under 1% (29 electoral votes): |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;"> |
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Florida, 0.88% (74,309 votes)</span>''' |
||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Pennsylvania, 5.39%</span>''' |
|||
States where the margin of victory was under 5% (46 electoral votes): |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">New Hampshire, 5.58%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color: |
# '''<span style="color:darkred;">North Carolina, 2.04% (92,004 votes)</span>''' |
||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;"> |
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Ohio, 2.98% (166,272 votes)</span>''' |
||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;"> |
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Virginia, 3.88% (149,298 votes)</span>''' |
||
# '''<span style="color:red;">Nebraska's 2nd Congressional District, 7.16%</span>''' |
|||
States/districts where the margin of victory was between 5% and 10% (120 electoral votes): |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Minnesota, 7.69%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color: |
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Colorado, 5.36% (137,858 votes)</span>''' (tipping point state) |
||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;"> |
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Pennsylvania, 5.38% (309,840 votes)</span>''' |
||
# '''<span style="color: |
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">New Hampshire, 5.58% (39,643 votes)</span>''' |
||
# '''<span style="color: |
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Iowa, 5.81% (91,927 votes)</span>''' |
||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;"> |
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Nevada, 6.68% (67,806 votes)</span>''' |
||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Wisconsin, 6.94% (213,019 votes)</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkred;">Nebraska's 2nd Congressional District, 7.15% (19,087 votes)</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Minnesota, 7.69% (225,942 votes)</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkred;">Georgia, 7.82% (304,861 votes)</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Maine's 2nd Congressional District, 8.56% (28,783 votes)</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkred;">Arizona, 9.06% (208,422 votes)</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkred;">Missouri, 9.38% (258,644 votes)</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:darkblue;">Michigan, 9.50% (449,313 votes)</span>''' |
|||
==== Statistics ==== |
|||
<ref>[http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS/data.php?year=2012&datatype=national&def=1&f=0&off=0&elect=0 2012 Presidential General Election Data – National], Uselectionatlas.org.</ref> |
|||
Counties with highest percent of vote (Democratic) |
|||
# '''<span style="color:blue;">[[Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota|Shannon County, South Dakota]] 93.39%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:blue;">[[Kalawao County, Hawaii]] 92.59%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:blue;">[[The Bronx|Bronx County, New York]] 91.45%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:blue;">[[Washington, D.C.]] 90.91%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:blue;">[[Petersburg, Virginia]] 89.79%</span>''' |
|||
Counties with highest percent of vote (Republican) |
|||
# '''<span style="color:red;">[[King County, Texas]] 95.86%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:red;">[[Madison County, Idaho]] 93.29%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:red;">[[Sterling County, Texas]] 92.91% </span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:red;">[[Franklin County, Idaho]] 92.77%</span>''' |
|||
# '''<span style="color:red;">[[Roberts County, Texas]] 92.13%</span>''' |
|||
===Romney's concession=== |
===Romney's concession=== |
||
[[File:Obama takes Romney concession call.jpg|thumb|upright|Obama takes a phone call from Romney conceding the election early Wednesday morning in Chicago.]] |
[[File:Obama takes Romney concession call.jpg|thumb|upright|Obama takes a phone call from Romney conceding the election early Wednesday morning in Chicago.]] |
||
After the networks called Ohio (the state that was arguably the most critical for Romney, as no Republican |
After the networks called Ohio (the state that was arguably the most critical for Romney, as no Republican had ever won the presidency without carrying it) for Obama at around 11:15 pm [[Eastern Standard Time (North America)|EST]] on Election Day, Romney was ready to concede the race, but hesitated when [[Karl Rove]] strenuously objected on Fox News to the network's decision to make that call.<ref>{{Cite news|url = http://www.boston.com/news/politics/2012/president/2012/12/23/the-story-behind-mitt-romney-loss-the-presidential-campaign-president-obama/2QWkUB9pJgVIi1mAcIhQjL/story-5.html|title = The story behind Mitt Romney's loss in the presidential campaign to President Obama|last = Kranish|first = Michael|date = December 22, 2012|work = Boston Globe|access-date = February 1, 2016|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20130528013007/http://www.boston.com/news/politics/2012/president/2012/12/23/the-story-behind-mitt-romney-loss-the-presidential-campaign-president-obama/2QWkUB9pJgVIi1mAcIhQjL/story-5.html|archive-date = May 28, 2013|url-status = dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.newsweek.com/why-rove-went-denial-election-night-226695|title=The Real Reason for Karl Rove's Election Night Denial|website=[[Newsweek]]|date=January 21, 2014|access-date=January 29, 2014|archive-date=February 2, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210202140628/https://www.newsweek.com/why-rove-went-denial-election-night-226695|url-status=live}}</ref> However, after Colorado and Nevada were called for the President (giving Obama enough electoral votes to win even if Ohio were to leave his column), in tandem with Obama's apparent lead in Florida and Virginia (both were eventually called for Obama), Romney acknowledged that he had lost and conceded at around 1:00 am [[Eastern Standard Time (North America)|EST]] on November 7. |
||
Despite public polling showing Romney behind Obama in the swing states of Nevada, Colorado, Iowa, Wisconsin, Ohio, and New Hampshire, tied with Obama in Virginia, and just barely ahead of Obama in Florida, the Romney campaign said they were genuinely surprised by the loss, having believed that public polling was oversampling Democrats.<ref name=Adviser:>{{cite news |title=Adviser: Romney "shellshocked" by loss |url= |
Despite public polling showing Romney behind Obama in the swing states of Nevada, Colorado, Iowa, Wisconsin, Ohio, and New Hampshire, tied with Obama in Virginia, and just barely ahead of Obama in Florida, the Romney campaign said they were genuinely surprised by the loss, having believed that public polling was oversampling Democrats.<ref name=Adviser:>{{cite news |title=Adviser: Romney "shellshocked" by loss |url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/adviser-romney-shellshocked-by-loss/ |access-date=November 10, 2012 |work=CBS News |date=November 8, 2012 |archive-date=November 9, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121109100308/http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-250_162-57547239/adviser-romney-shellshocked-by-loss/?pageNum=1&tag=page |url-status=live }}</ref> The Romney campaign had already set up a transition website, and had scheduled and purchased a fireworks display to celebrate in case he won the election.<ref>{{cite web|title=Romney's Transition Site |url=http://politicalwire.com/archives/2012/11/07/romneys_transition_site.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121108021452/http://politicalwire.com/archives/2012/11/07/romneys_transition_site.html |archive-date=November 8, 2012 |access-date=November 30, 2012 |website=Political Wire |date=November 7, 2012}}</ref><ref name="Romney campaign spent $25,000 on fireworks">{{cite news |title=Romney campaign spent $25,000 on fireworks |url=http://www.boston.com/news/local/massachusetts/2012/11/09/romney-campaign-spent-fireworks/YrFOs5OEgE98XvjBJ9nItJ/story.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121111171311/http://www.boston.com/news/local/massachusetts/2012/11/09/romney-campaign-spent-fireworks/YrFOs5OEgE98XvjBJ9nItJ/story.html |archive-date=November 11, 2012 |access-date=November 11, 2012 |newspaper=Boston Globe |date=November 9, 2012 |url-status=dead}}</ref> |
||
On November 30, 2012, it was revealed that shortly before the election, internal polling done by the Romney campaign had shown Romney ahead in Colorado and New Hampshire, tied in Iowa, and within a few points of Obama in Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, Minnesota, and Ohio.<ref>{{cite news |title=When Internal Polls Mislead, a Whole Campaign May Be to Blame |url=http://fivethirtyeight.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/12/01/when-internal-polls-mislead-a-whole-campaign-may-be-to-blame/ | |
On November 30, 2012, it was revealed that shortly before the election, internal polling done by the Romney campaign had shown Romney ahead in Colorado and New Hampshire, tied in Iowa, and within a few points of Obama in Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, Minnesota, and Ohio.<ref>{{cite news |title=When Internal Polls Mislead, a Whole Campaign May Be to Blame |url=http://fivethirtyeight.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/12/01/when-internal-polls-mislead-a-whole-campaign-may-be-to-blame/ |access-date=December 21, 2012 |newspaper=[[The New York Times]] |date=December 1, 2012 |first=Nate |last=Silver |archive-date=December 26, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121226203116/http://fivethirtyeight.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/12/01/when-internal-polls-mislead-a-whole-campaign-may-be-to-blame/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In addition, the Romney campaign had assumed that they would win Florida, North Carolina and Virginia.<ref>{{cite news |title=Exclusive: The Internal Polls That Made Mitt Romney Think He'd Win |url=http://www.tnr.com/blog/plank/110597/exclusive-the-polls-made-mitt-romney-think-hed-win |access-date=November 30, 2012 |newspaper=[[The New Republic]] |date=November 30, 2012 |archive-date=December 1, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121201075235/http://www.tnr.com/blog/plank/110597/exclusive-the-polls-made-mitt-romney-think-hed-win |url-status=live }}</ref> The polls had made Romney and his campaign team so confident of their victory that Romney did not write a [[Concession (politics)|concession speech]] until Obama's victory was announced.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/decision2012/romneys-belief-in-himself-never-wavered/2012/11/07/50cd03fc-27b8-11e2-9972-71bf64ea091c_story.html |title=Romney's belief in himself never wavered |newspaper=[[The Washington Post]] |first=Phillip |last=Rucker |date=November 7, 2012 |access-date=November 30, 2012 |archive-date=November 12, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121112112017/http://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/decision2012/romneys-belief-in-himself-never-wavered/2012/11/07/50cd03fc-27b8-11e2-9972-71bf64ea091c_story.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.theatlanticwire.com/politics/2012/11/whole-romney-ticket-believed-unskewed-polls/58852/ |title=The Whole Romney Ticket Believed in Unskewed Polls? |work=[[The Atlantic Wire]] |first=Elspeth |last=Reeve |date=November 8, 2012 |access-date=December 17, 2012 |archive-date=December 30, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121230021015/http://www.theatlanticwire.com/politics/2012/11/whole-romney-ticket-believed-unskewed-polls/58852/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
===Reactions=== |
===Reactions=== |
||
Foreign leaders reacted with both positive and mixed messages. Most world leaders congratulated and praised Obama on his re-election victory. However, Venezuela and some other states had tempered reactions. Pakistan commented that Romney's defeat had made [[Pakistan-United States relations]] safer. Stock markets fell noticeably after Obama's re-election, with the [[Dow Jones Industrial Average]], [[NASDAQ]], and the [[S&P 500]] each declining over two percent the day after the election.<ref name=WSJ-DOW>{{cite news |last=Cheng |first=Jonathan |title=Dow's 300-Point Slide Takes It Back to August Levels |url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424127887323894704578104153584769278?mod=wsj_streaming_markets |access-date=November 7, 2012 |newspaper=The Wall Street Journal |date=November 7, 2012 |archive-date=July 24, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200724153122/https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424127887323894704578104153584769278?mod=wsj_streaming_markets |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
{{further|International reactions to the United States presidential election, 2012}} |
|||
Foreign leaders reacted with both positive and mixed messages. Most world leaders congratulated and praised Barack Obama on his re-election victory. However, Venezuela and some other states had tempered reactions. Pakistan commented that Romney's defeat had made [[Pakistan-United States relations]] safer. Stock markets fell noticeably after Obama's re-election, with the [[Dow Jones Industrial Average]], [[NASDAQ]], and the [[S&P 500]] each declining over two percent the day after the election.<ref name=WSJ-DOW>{{cite news |last=Cheng |first=Jonathan |title=Dow's 300-Point Slide Takes It Back to August Levels |url=http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323894704578104153584769278.html?mod=wsj_streaming_markets |accessdate=November 7, 2012 |newspaper=The Wall Street Journal |date=November 7, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
All 50 states had a petition on the White House website [[We the People (petitioning system)|We The People]] calling for their state to [[Secession in the United States|secede from the union]]. These petitions were created by individual people, with some gaining thousands of signatures.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Ryan |first=Danielle |date=2012-11-14 |title=White House receives secession pleas from all 50 states |url=https://www.latimes.com/politics/la-xpm-2012-nov-14-la-pn-white-house-secession-50-states-20121114-story.html |access-date=2023-07-10 |website=Los Angeles Times |language=en-US |archive-date=July 10, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230710182319/https://www.latimes.com/politics/la-xpm-2012-nov-14-la-pn-white-house-secession-50-states-20121114-story.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
==Voter demographics== |
==Voter demographics== |
||
{| class=wikitable |
{| class=wikitable |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan="8" | 2012 |
! colspan="8" | 2012 presidential election by demographic subgroup |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! Demographic subgroup |
! Demographic subgroup |
||
| Line 674: | Line 950: | ||
| style="text-align:right;" | 53 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 53 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan=5| |
! colspan=5|Marital status |
||
|- |
|||
| Married |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 42 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 56 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 60 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Unmarried |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 62 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 35 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 40 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan=5|Sex by marital status |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Married men |
| Married men |
||
| Line 688: | Line 978: | ||
| style="text-align:right;" | 31 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 31 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| Single men |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 56 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 56 |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 40 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 40 |
||
| Line 694: | Line 984: | ||
| style="text-align:right;" | 18 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 18 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| Single women |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 67 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 67 |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 31 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 31 |
||
| Line 735: | Line 1,025: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Protestantism|Protestant]] or other Christian |
| [[Protestantism|Protestant]] or other Christian |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| |
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 42 |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| |
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 57 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | |
| style="text-align:right;" | 53 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Catholic Church in the United States|Catholic]] |
| [[Catholic Church in the United States|Catholic]] |
||
| Line 757: | Line 1,047: | ||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
||
|- |
|||
| [[Islam in the United States|Muslim]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 85 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 4 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 11 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Other |
| Other |
||
| Line 854: | Line 1,150: | ||
| style="text-align:right;" | 16 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 16 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan=5| |
! colspan=5|Age by race |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Whites 18–29 years old |
|||
| [[LGBT|Gay, lesbian, or bisexual]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 44 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 51 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 5 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 11 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Whites 30–44 years old |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 38 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 59 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 18 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Whites 45–64 years old |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 38 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 61 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 29 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Whites 65 and older |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 39 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 61 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | n/a |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 14 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Blacks 18–29 years old |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 91 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 8 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Blacks 30–44 years old |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 94 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 5 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 4 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Blacks 45–64 years old |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 93 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 7 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | n/a |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 4 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Blacks 65 and older |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 93 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 6 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Latinos 18–29 years old |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 74 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 23 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 4 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Latinos 30–44 years old |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 71 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 28 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Latinos 45–64 years old |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 68 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 31 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Latinos 65 and older |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 65 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 35 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | n/a |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Others |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 67 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 31 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 5 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan=5|LGBT |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[LGBT|Yes]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 76 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 76 |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 22 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 22 |
||
| Line 862: | Line 1,238: | ||
| style="text-align:right;" | 5 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 5 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| No |
|||
| [[Heterosexuality|Heterosexual]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#d0c0d7;"| 49 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#d0c0d7;"| 49 |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#d0c0d7;"| 49 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#d0c0d7;"| 49 |
||
| Line 937: | Line 1,313: | ||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | 4 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 4 |
||
|- |
|||
! colspan=5|Union households |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Labor unions in the United States|Union]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 58 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 40 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 18 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Non-union |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 49 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 48 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 82 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan=5|Issue regarded as most important |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Great Recession in the United States#Recovery|Economy]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 47 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 51 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 59 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[National debt of the United States|Federal budget deficit]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 32 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 66 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 15 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Foreign policy of the United States|Foreign policy]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 56 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 33 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 11 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 5 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Affordable Care Act|Health care]] |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 75 |
|||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 24 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
|||
| style="text-align:right;" | 18 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan=5|Region |
! colspan=5|Region |
||
| Line 942: | Line 1,358: | ||
| [[Northeastern United States|Northeast]] |
| [[Northeastern United States|Northeast]] |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 59 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 59 |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| |
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 40 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | |
| style="text-align:right;" | 18 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]] |
| [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]] |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| |
| style="text-align:right; background:#b0ceff;"| 50 |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| |
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 48 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 2 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | 24 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 24 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Southern United States|South]] |
| [[Southern United States|South]] |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| |
| style="text-align:right; background:#f0f0ff;"| 46 |
||
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| |
| style="text-align:right; background:#ffb6b6;"| 53 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | |
| style="text-align:right;" | 36 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Western United States|West]] |
| [[Western United States|West]] |
||
| Line 962: | Line 1,378: | ||
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 43 |
| style="text-align:right; background:#fff3f3;"| 43 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 3 |
||
| style="text-align:right;" | |
| style="text-align:right;" | 22 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! colspan=5|Community size |
! colspan=5|Community size |
||
| Line 996: | Line 1,412: | ||
| style="text-align:right;" | 14 |
| style="text-align:right;" | 14 |
||
|} |
|} |
||
'''Source:''' Exit polls conducted by Edison Research of [[Somerville, New Jersey]], for the National Election Pool, a consortium of ABC News, Associated Press, CBS News, CNN, Fox News,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.foxnews.com/politics/elections/2012-exit-poll |title=Fox News Exit Polls |accessdate=January 27, 2013 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/20130126102046/http://www.foxnews.com/politics/elections/2012-exit-poll |archivedate=January 26, 2013 }}</ref> and NBC News.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://elections.nytimes.com/2012/results/president/exit-polls|title=President Exit Polls|work=The New York Times|accessdate=January 27, 2013}}</ref> Total vote and results by region are based on the [[United States presidential election, 2012#Votes by state|"Votes by state"]] section of this article. |
|||
=== Hispanic vote === |
|||
The United States has a population of 50 million [[Hispanic and Latino Americans]], 27 million of whom are citizens eligible to vote (13% of total eligible voters). Traditionally, only half of eligible Hispanic voters vote (around 7% of voters); of them, 71% voted for Barack Obama (increasing his [[percentage]] of the vote by 5%); therefore, the Hispanic vote was an important factor in Obama's re-election, since the vote difference between the two main parties was only 3.9%<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pewhispanic.org/2016/01/19/looking-forward-to-2016-the-changing-latino-electorate/|title=1. Looking Forward to 2016: The Changing Latino Electorate|first1=Jens Manuel|last1=Krogstad|first2=Mark Hugo|last2=Lopez|first3=Gustavo|last3=López|first4=Jeffrey S.|last4=Passel|first5=Eileen|last5=Patten|date=January 19, 2016|publisher=Pew Research Center|access-date=September 26, 2016|archive-date=February 17, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210217195613/https://www.pewresearch.org/hispanic/2016/01/19/looking-forward-to-2016-the-changing-latino-electorate/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pewhispanic.org/2016/01/19/millennials-make-up-almost-half-of-latino-eligible-voters-in-2016/|title=Millennials Make Up Almost Half of Latino Eligible Voters in 2016|first1=Jens Manuel|last1=Krogstad|first2=Mark Hugo|last2=Lopez|first3=Gustavo|last3=López|first4=Jeffrey S.|last4=Passel|first5=Eileen|last5=Patten|date=January 19, 2016|publisher=Pew Research Center|access-date=September 26, 2016|archive-date=February 17, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210217195613/https://www.pewresearch.org/hispanic/2016/01/19/millennials-make-up-almost-half-of-latino-eligible-voters-in-2016/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/02/03/2016-electorate-will-be-the-most-diverse-in-u-s-history/|title=2016 electorate will be the most diverse in U.S. history|date=February 3, 2016|publisher=Pew Research Center|last1=Krogstad|first1=Jens Manuel|access-date=September 26, 2016|archive-date=February 17, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210217195650/https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/02/03/2016-electorate-will-be-the-most-diverse-in-u-s-history/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/18/magazine/27-million-potential-hispanic-votes-but-what-will-they-really-add-up-to.html|title=27 Million Potential Hispanic Votes. But What Will They Really Add Up To?|date=September 18, 2016|website=The New York Times|last1=Valdes|first1=Marcela|access-date=February 28, 2017|archive-date=January 4, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210104153233/https://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/18/magazine/27-million-potential-hispanic-votes-but-what-will-they-really-add-up-to.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Exit polls were conducted by Edison Research of [[Somerville, New Jersey]], for the [[National Election Pool]], a consortium which at the time consisted of ABC News, Associated Press, CBS News, CNN,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.cnn.com/election/2012/results/race/president/|title=Presidential Race – 2012 Election Center – Elections & Politics from CNN.com|publisher=CNN|access-date=February 5, 2018|archive-date=February 6, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180206070621/http://www.cnn.com/election/2012/results/race/president/|url-status=live}}</ref> Fox News,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.foxnews.com/politics/elections/2012-exit-poll |title=Fox News Exit Polls |access-date=January 27, 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130126102046/http://www.foxnews.com/politics/elections/2012-exit-poll|website=Fox News|archive-date=January 26, 2013 }}</ref> and NBC News.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://elections.nytimes.com/2012/results/president/exit-polls|title=President Exit Polls|work=The New York Times|access-date=January 27, 2013|archive-date=April 30, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160430143842/http://elections.nytimes.com/2012/results/president/exit-polls|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
==Analysis== |
==Analysis== |
||
Combined with the re- |
Combined with the re-election victories of his two immediate predecessors, [[Bill Clinton]] ([[1996 United States presidential election|1996]]) and [[George W. Bush]] ([[2004 United States presidential election|2004]]), Obama's victory in the 2012 election marked only the second time in American history that three consecutive presidents were each elected to two full terms after the consecutive two-term presidencies of [[Thomas Jefferson]], [[James Madison]], and [[James Monroe]] ending in 1820, which is the only other time ''any'' two-term president succeeded another.<ref name=cnbc110712>{{cite news|last=Hum |first=Robert |title=Two-Term Presidency Musings |url=https://www.cnbc.com/2012/11/07/twoterm-presidency-musings.html |access-date=February 12, 2013 |publisher=CNBC |date=November 7, 2012 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130729183835/http://www.cnbc.com/id/49722770/TwoTerm_Presidency_Musings |archive-date=July 29, 2013 }}</ref> Eight years later, Obama's successor, [[Donald Trump]], also ran for his own re-election in [[2020 United States presidential election|2020]], but was ultimately defeated by [[Joe Biden]], who served as vice president under Obama. This was also the first election since [[1928 United States presidential election|1928]] in which neither of the major candidates had any military experience.<ref>Dilanian, Ken (August 11, 2012) [https://www.latimes.com/politics/la-xpm-2012-aug-11-la-pn-ryan-pick-cements-lack-of-military-service-in-presidential-campaign-20120811-story.html "Ryan pick cements lack of military service in presidential race"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240420011248/https://www.latimes.com/politics/la-xpm-2012-aug-11-la-pn-ryan-pick-cements-lack-of-military-service-in-presidential-campaign-20120811-story.html |date=April 20, 2024 }}, ''[[Los Angeles Times]]''. Retrieved December 11, 2014.</ref> The election was arguably decided by three counties: [[Miami-Dade County, Florida|Miami-Dade County]] (Florida); [[Cuyahoga County, Ohio|Cuyahoga County]] (Ohio) and [[Philadelphia]] (Pennsylvania). If these three counties had cast zero votes, Obama would have lost all three states and the election.<ref>{{Citation |title=56 Interesting Facts About the 2016 Election |date=December 16, 2016 |journal=[[The Cook Political Report]] |url=http://cookpolitical.com/story/10201 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170715170550/http://cookpolitical.com/story/10201 |archivedate=July 15, 2017}}</ref> |
||
The 2012 election marked the first time since [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]]'s last two re-elections in [[United States presidential election |
The 2012 election marked the first time since [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]]'s last two re-elections in [[1940 United States presidential election|1940]] and [[1944 United States presidential election|1944]] that the Democrats won a majority of the popular vote in two consecutive elections.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.thenation.com/blog/171178/obama-has-great-big-mandate-and-he-must-use-it |title=Obama's 3 Million Vote, Electoral College Landslide, Majority of States Mandate |last=Nichols |first=John |date=November 9, 2012 |work=The Nation |location=New York |access-date=November 18, 2012 |archive-date=November 27, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121127235843/http://www.thenation.com/blog/171178/obama-has-great-big-mandate-and-he-must-use-it |url-status=live }}</ref> Obama was also the first president of either party to secure a majority of the popular vote in two elections since [[Ronald Reagan]] in 1980 and 1984.<ref name=bloom010413>{{cite news |last=Giroux |first=Greg |title=Final Tally Shows Obama First Since '56 to Win 51% Twice |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-01-03/final-tally-shows-obama-first-since-56-to-win-51-twice.html |access-date=February 12, 2013 |newspaper=Bloomberg |date=January 4, 2013 |archive-date=January 15, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130115033953/http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-01-03/final-tally-shows-obama-first-since-56-to-win-51-twice.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Obama is the third Democratic president to secure at least 51% of the vote twice, after [[Andrew Jackson]] and Franklin D. Roosevelt.<ref>Frank, Steve (January 7, 2014) [http://www.msnbc.com/the-ed-show/obama-first-presidential-candidate-eise "Obama first presidential candidate since Eisenhower to top 51% twice"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200820185025/http://www.msnbc.com/the-ed-show/obama-first-presidential-candidate-eise |date=August 20, 2020 }}, [[MSNBC]].com. Retrieved December 11, 2014.</ref> Romney won the popular vote in 226 congressional districts making this the first time since 1960 that the winner of the election did not win the popular vote in a majority of the congressional districts.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://cookpolitical.com/file/2013-04-50.pdf |title=Presidential Results By Congressional Districts: Obama is reelected but Romney carries a majority of districts |last=Bensen |first=Clark |date=April 4, 2013 |work=Cookpolitical.com |access-date=June 25, 2017 |archive-date=June 17, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170617233059/http://cookpolitical.com/file/2013-04-50.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> This is the last time that the Democrats won a majority of states in a presidential election. |
||
Romney lost his home state of [[Massachusetts]], becoming the first major party presidential candidate to lose his home state since Democrat [[Al Gore]] lost his home state of [[Tennessee]] to Republican George W. Bush in the [[2000 election]].<ref name=guard101912>{{cite news |last= |
Romney lost his home state of [[Massachusetts]], becoming the first major party presidential candidate to lose his home state since Democrat [[Al Gore]] lost his home state of [[Tennessee]] to Republican George W. Bush in the [[2000 United States presidential election|2000 election]].<ref name=guard101912>{{cite news |last=Gabbatt |first=Adam |title=Romney poised to lose home state by wider margin than any other candidate |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/oct/19/romney-lose-home-state-massachusetts |access-date=February 12, 2013 |newspaper=The Guardian |location=London |date=October 19, 2012 |archive-date=November 11, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131111214504/http://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/oct/19/romney-lose-home-state-massachusetts |url-status=live }}</ref> Romney lost his home state by more than 23%, the worst losing margin for a major party candidate since [[John Frémont]] in [[1856 United States presidential election|1856]].<ref name=smpo111412>{{cite news |last=Ostermeier |first=Eric |title=20 Presidential Tickets That Lost Both Home States |url=http://blog.lib.umn.edu/cspg/smartpolitics/2012/11/20_presidential_tickets_that_l.php |access-date=February 12, 2013 |work=Smart Politics (University of Minnesota blog) |date=November 14, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121115002716/http://blog.lib.umn.edu/cspg/smartpolitics/2012/11/20_presidential_tickets_that_l.php |archive-date=November 15, 2012 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Even worse than Frémont, Romney failed to win a single county in his home state, something last seen by Theodore Roosevelt in 1912.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS/datagraph.php?fips=25&year=2012&off=0&elect=0&f=0 |access-date=March 8, 2013 |title=2012 Presidential General Election Data – Massachusetts by County |publisher=Dave Leip's U.S. Election Atlas |archive-date=July 29, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130729192742/http://www.uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS/datagraph.php?fips=25&year=2012&off=0&elect=0&f=0 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url= http://geoelections.free.fr/USA/elec_comtes/1856.htm |access-date= March 9, 2013 |title= Presidential Election of 1856 – Map by counties |publisher= Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections |archive-date= May 12, 2013 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130512133118/http://geoelections.free.fr/USA/elec_comtes/1856.htm |url-status= live }}</ref> In addition, since Obama carried Ryan's home state of [[Wisconsin]], the Romney–Ryan ticket was the first major party ticket since the [[1972 United States presidential election|1972 election]] to have both of its nominees lose their home states.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://editions.lib.umn.edu/smartpolitics/2012/11/14/20-presidential-tickets-that-l/ |title=20 Presidential Tickets That Lost Both Home States |work=Smart Politics |first=Eric |last=Ostermeier |date=November 14, 2012 |access-date=July 12, 2015 |archive-date=August 17, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200817143933/https://editions.lib.umn.edu/smartpolitics/2012/11/14/20-presidential-tickets-that-l/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Romney won the popular vote in every [[County (United States)|county]] of three states: Utah, Oklahoma, and West Virginia; Obama did so in four states: Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Hawaii.<ref>[[Charles Blow|Blow, Charles M.]] (November 9, 2012) [https://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/10/opinion/blow-election-data-dive.html?_r=0 "Election Data Dive"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210206225705/https://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/10/opinion/blow-election-data-dive.html?_r=0 |date=February 6, 2021 }}, ''[[The New York Times]]''. Retrieved December 11, 2014.</ref> |
||
Romney's loss prompted the [[Republican National Committee]] to try to appeal to the American Latino population by concentrating on different approaches to immigration. These were short-lived due to activity and anger from the Republican base and may have contributed to the selection of [[Donald Trump]] as their presidential candidate four years later.<ref>Harwood, John. [https://www.nytimes.com/2016/10/07/us/politics/donald-trump-republicans-anger.html "Donald Trump Takes Advantage of a Republican Party Pitted Against Itself."] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201108112553/http://www.nytimes.com/2016/10/07/us/politics/donald-trump-republicans-anger.html |date=November 8, 2020 }} ''New York Times''. October 6, 2016. October 6, 2016.</ref> |
|||
[[Gary Johnson]]'s popular vote total set a [[Libertarian Party (United States)|Libertarian Party]] record, and his popular vote percentage is the second-best showing for a Libertarian in a presidential election, trailing only [[Ed Clark]]'s in [[United States presidential election, 1980|1980]].<ref name=upi110812>{{cite news|last=Harrington|first=Gerry|title=Libertarian Party buoyant; Greens hopeful|url=http://www.upi.com/Top_News/US/2012/11/08/Libertarian-Party-buoyant-Greens-hopeful/UPI-46151352363400/|accessdate=February 12, 2013|agency=United Press International|date=November 8, 2012}}</ref> [[Green Party of the United States|Green Party]] candidate [[Jill Stein]]'s popular vote total made her the [[List of female United States presidential and vice-presidential candidates|most successful female presidential candidate]] in a general election in United States history up until that point.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.thecrimson.com/article/2015/11/30/jill-stein-president-feature/ |title=Harvard Grad Jill Stein Faces Uphill Battle for Presidency |work=The Harvard Crimson |first=Daniel |last=Wood |date= November 30, 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://grist.org/politics/meet-the-presidential-candidate-who-makes-bernie-sanders-look-conservative/ |title=Meet the presidential candidate who makes Bernie Sanders look conservative |work=Grist Magazine|first=Katie |last=Herzog |date= March 14, 2016}}</ref> |
|||
[[Gary Johnson]]'s popular vote total set a [[Libertarian Party (United States)|Libertarian Party]] record, and his popular vote percentage was the second-best showing for a Libertarian in a presidential election, trailing only [[Ed Clark]]'s in [[1980 United States presidential election|1980]].<ref name=upi110812>{{cite news|last=Harrington|first=Gerry|title=Libertarian Party buoyant; Greens hopeful|url=http://www.upi.com/Top_News/US/2012/11/08/Libertarian-Party-buoyant-Greens-hopeful/UPI-46151352363400/|access-date=February 12, 2013|work=United Press International|date=November 8, 2012|archive-date=February 18, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130218223524/http://www.upi.com/Top_News/US/2012/11/08/Libertarian-Party-buoyant-Greens-hopeful/UPI-46151352363400|url-status=live}}</ref> Johnson would go on to beat this record in the [[2016 United States presidential election|2016]] presidential election, winning the most votes for the Libertarian ticket in history. At the time, [[Green Party of the United States|Green Party]] candidate [[Jill Stein]]'s popular vote total made her the [[List of female United States presidential and vice-presidential candidates|most successful female presidential candidate]] in a general election in United States history.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.thecrimson.com/article/2015/11/30/jill-stein-president-feature/ |title=Harvard Grad Jill Stein Faces Uphill Battle for Presidency |work=The Harvard Crimson |first=Daniel |last=Wood |date=November 30, 2015 |access-date=June 12, 2016 |archive-date=June 20, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160620164242/http://www.thecrimson.com/article/2015/11/30/jill-stein-president-feature/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://grist.org/politics/meet-the-presidential-candidate-who-makes-bernie-sanders-look-conservative/ |title=Meet the presidential candidate who makes Bernie Sanders look conservative |work=Grist Magazine |first=Katie |last=Herzog |date=March 14, 2016 |access-date=June 12, 2016 |archive-date=December 2, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201202111850/https://grist.org/politics/meet-the-presidential-candidate-who-makes-bernie-sanders-look-conservative/ |url-status=live }}</ref> This was later surpassed by Hillary Clinton in the 2016 election. |
|||
Romney won the popular vote in every [[County (United States)|county]] of three states: Utah, Oklahoma, and West Virginia; Obama did so in four states: Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Hawaii.<ref>[[Charles Blow|Blow, Charles M.]] (November 9, 2012) [http://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/10/opinion/blow-election-data-dive.html?_r=0 "Election Data Dive"], ''[[The New York Times]]''. Retrieved December 11, 2014.</ref> |
|||
Obama's vote total was the fourth most votes received in the history of presidential elections (behind Obama's 2008 victory and both major candidates in 2020) and the most ever for a reelected president. The 2012 election marked the first time since [[1988 United States presidential election|1988]] in which no state was won by a candidate with a [[Plurality (voting)|plurality]] of the state's popular vote. Furthermore, it is the only post-[[World War II]] presidential election in which no states were won by margins smaller than 30,000 votes. Obama's narrowest victories were in [[2012 United States presidential election in New Hampshire|New Hampshire]] by 39,643 votes, followed by [[2012 United States presidential election in Florida|Florida]] by 74,309 votes. Every other presidential election in modern history has seen states narrowly won by several thousand votes. So far, this is the only presidential election in history where both the Republican and Democratic vice presidential candidates are practicing Roman Catholics. It is also the only presidential election where there are no white Protestants on a major party ticket. This is the most recent election where any party won consecutive elections. |
|||
Obama's vote total was the second most votes received in the history of presidential elections and the most ever for a reelected president. Obama owns the all-time record for votes in a single election as well in 2008. However, Obama also became the first president in American history to be reelected to a second term by smaller margins in every way possible: Compared to his victory in 2008, he won fewer states (28 to 26), fewer electoral votes (365 to 332), fewer popular votes (69.5 million to 65.9 million), and a smaller percentage of the popular vote (52.9% to 51.1%).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.lifenews.com/2012/12/06/numbers-show-obamas-narrow-re-election-was-no-popular-mandate/|title=Numbers Show Obama's Narrow Re-Election Was No Popular Mandate|work=LifeNews.com|accessdate=May 14, 2016}}</ref> |
|||
Obama was the fourth of just four presidents in United States history to win re-election with a lower percentage of the electoral vote than in their prior elections, the other three were [[James Madison]] in [[1812 United States presidential election|1812]], [[Woodrow Wilson]] in [[1916 United States presidential election|1916]] and [[Franklin Roosevelt]] in [[1940 United States presidential election|1940]] and [[1944 United States presidential election|1944]]. Additionally, Obama was the fifth of only five presidents to win re-election with a smaller percentage of the popular vote than in prior elections, the other four are [[James Madison]] in [[1812 United States presidential election|1812]], [[Andrew Jackson]] in [[1832 United States presidential election|1832]], [[Grover Cleveland]] in [[1892 United States presidential election|1892]], and [[Franklin Roosevelt]] in [[1940 United States presidential election|1940]] and [[1944 United States presidential election|1944]]. |
|||
==Maps== |
==Maps== |
||
<gallery mode=packed heights=200> |
<gallery mode="packed" heights="200"> |
||
File:Results by state, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote 2012.svg|Results by state, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote |
|||
File:Cartogram—2012 Electoral Vote.svg|Cartogram of the electoral vote results, with each square representing one electoral vote. |
|||
File:2012 Presidential Election by County.svg|Results by county. Blue denotes counties that went to Obama; red denotes counties that went to Romney. Hawaii, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont had all counties go to Obama. Oklahoma, Utah, and West Virginia had all counties go to Romney. |
File:2012 Presidential Election by County.svg|Results by county.{{refn|group=lower-alpha|name="county clarification"|Alaska and Louisiana do not have counties. Alaska's [[List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska|boroughs and census areas]] and Louisiana's [[List of parishes in Louisiana|parishes]] are pictured.}} Blue denotes counties that went to Obama; red denotes counties that went to Romney. Hawaii, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont had all counties go to Obama. Oklahoma, Utah, and West Virginia had all counties go to Romney. |
||
File: |
File:2012 United States presidential election results map by county.svg|Results by county,{{refn|group=lower-alpha|name="county clarification"}} shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote |
||
File:Red-blue-purple view of counties.png|Popular vote by county shaded on a scale from red/Republican to blue/Democratic |
File:Red-blue-purple view of counties.png|Popular vote by county shaded on a scale from red/Republican to blue/Democratic |
||
File:Countycartpurple1024.png|Cartogram of popular vote by county shaded on a scale from red/Republican to blue/Democratic where each county has been rescaled in proportion to its population |
File:ElectorScaledUS2012.svg|Results by state and the District of Columbia, scaled by number of electors per state |
||
File:Countycartpurple1024.png|[[Cartogram]] of popular vote by county shaded on a scale from red/Republican to blue/Democratic where each county has been rescaled in proportion to its population |
|||
File:Cartogram—2012 Electoral Vote.svg|Cartogram of the electoral vote results, with each square representing one electoral vote |
|||
File:Presidential Elections 2008-2012 Swing in County Margins.svg| Change in popular vote margins at the county level from the 2008 election to the 2012 election. Blue denotes counties that voted more Democratic. Red denotes counties that voted more Republican. Romney's strongest improvements over McCain were in Utah and Appalachia, while Obama's strongest gains were in Alaska, the New York area, and the Gulf states. |
|||
File:2012 US congressional district presidential election.svg|Results by congressional district |
|||
File:2012 presidential election, results by congressional district.png|2012 Presidential Election, Results by Congressional District. |
|||
File: |
File:Presidential Elections 2008-2012 Swing in County Margins.svg|County swing from 2008 to 2012{{refn|group=lower-alpha|name="county clarification"}} |
||
File:US Presidential Elections 2012.png|[[Treemapping|Treemap]] of the popular vote by county, state, and locally predominant recipient |
|||
File:ElectoralCollege2012-Large.png|Results by state with [[pie chart]]s for the electoral college and popular vote. |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
<gallery mode=packed> |
<gallery mode="packed"> |
||
File:Empire State Building Blue Obama Election.JPG|The [[Empire State Building]] in [[New York City]] was lit blue when CNN called Ohio for Obama, projecting him the winner of the election. Likewise, red would have been used if Romney won.<ref>{{cite news |url= |
File:Empire State Building Blue Obama Election.JPG|The [[Empire State Building]] in [[New York City]] was lit blue when CNN called Ohio for Obama, projecting him the winner of the election. Likewise, red would have been used if Romney won.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.nydailynews.com/news/national/new-york-state-building-displays-election-results-article-1.1197707 |title=Empire State Building lights up to broadcast election results |first=Charlie |last=Wells |newspaper=[[Daily News (New York)|Daily News]] |location=New York |date=November 6, 2012 |access-date=November 7, 2012 |archive-date=November 9, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121109190348/http://www.nydailynews.com/news/national/new-york-state-building-displays-election-results-article-1.1197707 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
File:Obamas and Bidens on presidential election night 2012.jpg|The Obamas and the Bidens embrace following the television announcement of their victory. |
File:Obamas and Bidens on presidential election night 2012.jpg|The Obamas and the Bidens embrace following the television announcement of their victory. |
||
File:Barack Obama election night victory 2012.jpg|The Obamas and the Bidens walk on stage at the election night victory celebration at [[McCormick Place]] in Chicago. |
File:Barack Obama election night victory 2012.jpg|The Obamas and the Bidens walk on stage at the election night victory celebration at [[McCormick Place]] in Chicago. |
||
File:P112912PS-0444 - President Barack Obama and Mitt Romney in the Oval Office - crop.jpg|Former |
File:P112912PS-0444 - President Barack Obama and Mitt Romney in the Oval Office - crop.jpg|Former governor Mitt Romney meets with President Barack Obama at the White House after the 2012 presidential election. |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
| Line 1,034: | Line 1,459: | ||
{{Portal|United States|Politics|2010s}} |
{{Portal|United States|Politics|2010s}} |
||
* [[Planned presidential transition of Mitt Romney]] |
* [[Planned presidential transition of Mitt Romney]] |
||
* [[United States Senate elections |
* [[2012 United States Senate elections]] |
||
* [[United States House of Representatives elections |
* [[2012 United States House of Representatives elections]] |
||
* [[United States gubernatorial elections |
* [[2012 United States gubernatorial elections]] |
||
* [[Nationwide opinion polling for the United States presidential election |
* [[Nationwide opinion polling for the 2012 United States presidential election]] |
||
* [[Statewide opinion polling for the United States presidential election |
* [[Statewide opinion polling for the 2012 United States presidential election]] |
||
* [[United States presidential election |
* [[Timeline of the 2012 United States presidential election]] |
||
* [[Second inauguration of Barack Obama]] |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
{{Reflist|group=lower-alpha}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 1,046: | Line 1,475: | ||
==Further reading== |
==Further reading== |
||
{{refbegin}} |
{{refbegin}} |
||
* {{cite book |last1=Balz |first1=Dan |author-link=Dan Balz |title=Collision 2012: Obama vs. Romney and the Future of Elections in America |date=2013 |publisher=Viking Press |location=New York |isbn=978-0670025947}} |
|||
* Gardner, Liz, et al. "Press Coverage of the 2012 US Presidential Election: A Multinational, Cross-Language Comparison." in ''Die US-Präsidentschaftswahl 2012'' (Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, 2016). pp 241–267. |
|||
* Gardner, Liz, et al. "Press Coverage of the 2012 US Presidential Election: A Multinational, Cross-Language Comparison". in ''Die US-Präsidentschaftswahl 2012'' (Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, 2016). pp 241–267. |
|||
* Hansen, Wendy L., Michael S. Rocca, and Brittany Leigh Ortiz. "The effects of Citizens United on corporate spending in the 2012 presidential election." ''Journal of Politics'' 77.2 (2015): 535-545. [http://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/680077 in JSTOR] |
|||
* Hansen, Wendy L., Michael S. Rocca, and Brittany Leigh Ortiz. "The effects of Citizens United on corporate spending in the 2012 presidential election". ''Journal of Politics'' 77.2 (2015): 535–545. [https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/680077 in JSTOR] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201107004646/https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/680077 |date=November 7, 2020 }} |
|||
* {{Cite book|first=John|last=Heilemann|authorlink=John Heilemann|first2=Mark|last2=Halperin|authorlink2=Mark Halperin|title=[[Double Down: Game Change 2012]]|publisher=[[Penguin Press]]|location=New York|year=2013|isbn=1594204403}} |
|||
* {{Cite book|first1=John|last1=Heilemann|author-link=John Heilemann|first2=Mark|last2=Halperin|author-link2=Mark Halperin|title=[[Double Down: Game Change 2012]]|publisher=[[Penguin Press]]|location=New York|year=2013|isbn=978-1594204401}} |
|||
* Masket, Seth, John Sides, and Lynn Vavreck. "The Ground Game in the 2012 Presidential Election." ''Political Communication'' (2015) 33#2 pp: 1-19. |
|||
* Masket, Seth, [[John M. Sides|John Sides]], and [[Lynn Vavreck]]. "The Ground Game in the 2012 Presidential Election". ''Political Communication'' (2015) 33#2 pp: 1–19. |
|||
* {{cite book |editor-first=William G. |editor-last=Mayer |editor2-first=Jonathan |editor2-last=Bernstein |title=The Making of the Presidential Candidates, 2012 |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2012 |isbn=978-1-4422-1170-4}} Scholars explore nominations in the post-public-funding era, digital media and campaigns, television coverage, and the Tea Party. |
|||
* {{cite book |editor-first=William G. |editor-last=Mayer |editor2-first=Jonathan |editor2-last=Bernstein |title=The Making of the Presidential Candidates, 2012 |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2012 |isbn=978-1-4422-1170-4}} Scholars explore nominations in the post-public-funding era, digital media and campaigns, television coverage, and [[Tea Party movement|the Tea Party]]. |
|||
* Miller, William J., ed. ''The 2012 Nomination and the Future of the Republican Party: The Internal Battle'' (Lexington Books; 2013) 265 pages; essays by experts on Romney and each of his main rivals |
* Miller, William J., ed. ''The 2012 Nomination and the Future of the Republican Party: The Internal Battle'' (Lexington Books; 2013) 265 pages; essays by experts on Romney and each of his main rivals |
||
* Nelson, Michael, ed. ''The Elections of 2012'' (2013) [ |
* [[Michael Nelson (political scientist)|Nelson, Michael]], ed. ''The Elections of 2012'' (2013) [https://www.amazon.com/The-Elections-of-2012-ebook/dp/B00C9JAYQU/ excerpt and text search] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210317115307/https://www.amazon.com/The-Elections-of-2012-ebook/dp/B00C9JAYQU/ |date=March 17, 2021 }}; topical essays by experts |
||
* Sides, John, and Lynn Vavreck. ''The Gamble: Choice and Chance in the 2012 Presidential Election'' (Princeton U.P. 2013) [ |
* [[John M. Sides|Sides, John]], and [[Lynn Vavreck]]. ''The Gamble: Choice and Chance in the 2012 Presidential Election'' (Princeton U.P. 2013) [https://www.amazon.com/Gamble-Choice-Chance-Presidential-Election/dp/0691163634/ excerpt and text search] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190828224418/https://www.amazon.com/Gamble-Choice-Chance-Presidential-Election/dp/0691163634/ |date=August 28, 2019 }} |
||
* Stempel III, Guido H. and Thomas K. Hargrove, eds. ''The 21st-Century Voter: Who Votes, How They Vote, and Why They Vote'' (2 vol. 2015). |
* [[Guido Stempel|Stempel III, Guido H.]] and Thomas K. Hargrove, eds. ''The 21st-Century Voter: Who Votes, How They Vote, and Why They Vote'' (2 vol. 2015). |
||
{{refend}} |
{{refend}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Sister project links |commons= |
{{Sister project links |commons= |n=Category:2012 United States presidential election |wikt=no |b=no |q=no |s=no |v=no |display=2012 U.S. presidential election}} |
||
* [https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/the-fix/post/the-9-swing-states-of-2012/2012/04/16/gIQABuXaLT_blog.html The 9 Swing States of 2012] |
|||
* [http://www.fec.gov/press/press2011/presidential_form2nm.shtml 2012 Presidential Form 2 Filers] at the [[Federal Election Commission]] (FEC) |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20110816025719/http://fec.gov/press/press2011/presidential_form2nm.shtml 2012 Presidential Form 2 Filers] at the [[Federal Election Commission]] (FEC) |
|||
* [http://www.thegreenpapers.com/P12/ Election 2012 Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and Conventions ] |
* [http://www.thegreenpapers.com/P12/ Election 2012 Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and Conventions ] |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20120919221443/http://www.votenight.com/ 2012 Interactive Electoral Map] |
|||
* {{Dmoz|Regional/North_America/United_States/Society_and_Culture/Politics/Candidates_and_Campaigns/President}} |
|||
* [http://www.countingthevotes.com/2012/ Election of 2012 in Counting the Votes] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190828224410/http://www.countingthevotes.com/2012/ |date=August 28, 2019 }} |
|||
* [http://votenight.com/ 2012 Interactive Electoral Map] |
|||
* {{cite episode|title=The Choice 2012|series=Frontline|series-link=Frontline (American TV program)|network=[[PBS]]|station=[[WGBH-TV|WGBH]]|date=October 9, 2012|season=30|number=21|url=https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/frontline/documentary/choice-2012/|access-date=November 28, 2024}} |
|||
* [http://www.countingthevotes.com/2012/ Election of 2012 in Counting the Votes] |
|||
{{United States presidential election |
{{2012 United States presidential election}} |
||
{{2012 U.S. presidential election |
{{State results of the 2012 U.S. presidential election}} |
||
{{United States elections |
{{2012 United States elections}} |
||
{{United States presidential elections}} |
{{United States presidential elections}} |
||
{{Barack Obama}} |
{{Barack Obama}} |
||
{{Joe Biden}} |
{{Joe Biden}} |
||
{{Mitt Romney}} |
{{Mitt Romney}} |
||
{{Paul Ryan}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:2012 United States presidential election| ]] |
|||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Barack Obama 2012 presidential campaign]] |
||
[[Category:Barack Obama |
[[Category:Barack Obama]] |
||
[[Category:History of the United States (1991–present)]] |
|||
[[Category:Joe Biden]] |
[[Category:Joe Biden]] |
||
[[Category:Mitt Romney presidential campaign |
[[Category:Mitt Romney 2012 presidential campaign]] |
||
[[Category:Mitt Romney]] |
|||
[[Category:Paul Ryan]] |
[[Category:Paul Ryan]] |
||
[[Category:November 2012 events in the United States]] |
|||
[[Category:Presidency of Barack Obama]] |
|||
[[Category:Post–civil rights era in African-American history]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 02:23, 8 January 2025
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 58.6%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Obama/Biden and red denotes those won by Romney/Ryan. Numbers indicate electoral votes cast by each state and the District of Columbia. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Democratic Party | |
|---|---|
| Republican Party | |
| Minor parties | |
| Related races | |
| |
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 6, 2012. Incumbent Democratic President Barack Obama and his running mate, incumbent Vice President Joe Biden, were elected to a second term.[3] They defeated the Republican ticket of former Governor of Massachusetts Mitt Romney and U.S. Representative Paul Ryan of Wisconsin, who later became Speaker of the House of Representatives.
As the incumbent President, Obama secured the Democratic nomination without serious opposition. The Republicans experienced a competitive primary. Romney was consistently competitive in the polls and won the support of many party leaders, but he faced challenges from a number of more conservative contenders. Romney secured his party's nomination in May, defeating former senator Rick Santorum, former Speaker of the House and Georgia Congressman Newt Gingrich, and Texas congressman Ron Paul, among other candidates.
The campaigns focused heavily on domestic issues, and debate centered largely around sound responses to the Great Recession. Other issues included long-term federal budget issues, the future of social insurance programs, and the Affordable Care Act, Obama's marquee legislative program. Foreign policy was also discussed, including the end of the Iraq War in 2011, military spending, the Iranian nuclear program, and appropriate counteractions to terrorism. Romney attacked Obama's domestic policies as ineffective and financially insolvent while Obama's campaign sought to characterize Romney as a plutocratic businessman who was out of touch with the average American.[4][5] The campaign was marked by a sharp rise in fundraising, including from nominally independent Super PACs.
Obama defeated Romney, winning a majority of both the Electoral College and the popular vote. Obama won 332 electoral votes and 51.1% of the popular vote compared to Romney's 206 electoral votes and 47.2%.[2] The results of the electoral vote were certified by Congress on January 4, 2013.[6] Obama is the only president since Ronald Reagan in 1984 to win a majority of the national popular vote more than once, and remains the only Democrat to do so since Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1944. Obama also became only the fifth Democratic president in history to win a second consecutive term after Andrew Jackson, Woodrow Wilson, Franklin D. Roosevelt, and Bill Clinton, as well as the third sitting president in a row (after Clinton and George W. Bush) to win a second term. As of 2025, this remains the most recent election in which an incumbent president won re-election to a second consecutive term and the most recent in which the incumbent White House party won re-election.
Obama did not hold onto Indiana, North Carolina, or Nebraska's 2nd congressional district, but crucially won all 18 "blue wall" states and defeated Romney in other swing states the Republicans had won in 2000 and 2004, most notably Colorado, Florida, Nevada, Ohio, and Virginia. Ultimately, of the nine swing states identified by The Washington Post in the 2012 election, Obama won eight, losing only North Carolina.[7] This is the most recent presidential election in which the Democratic candidate won the states of Iowa, Ohio, and Florida, along with Maine's 2nd congressional district, the most recent in which neither major party's ticket included a woman, the most recent in which Donald Trump was not the Republican nominee, and the most recent in which no state split its electoral votes.
All four major candidates for president and vice president went on to hold significant public office after this election. Obama served his second term as president, while Biden also served his second term as vice president and initially retired from politics but was later elected president in 2020, defeating Obama's successor, then-incumbent Donald Trump. This is the most recent election in which two major party nominees would go on to become president. Romney moved to Utah in 2014 and was elected to the Senate there in 2018, succeeding Orrin Hatch, and serving until his retirement in 2025. Ryan served three more terms in the House and eventually became Speaker from 2015 until his retirement from politics in 2019.
Background
[edit]State changes to voter registration and electoral rules
[edit]In 2011, several state legislatures passed new voting laws, especially pertaining to voter identification, with the stated purpose of combating voter fraud; the laws were attacked, however, by the Democratic Party as attempts to suppress voting among its supporters and to improve the Republican Party's presidential prospects. Florida, Georgia, Ohio,[8] Tennessee, and West Virginia's state legislatures approved measures to shorten early voting periods. Florida and Iowa barred all felons from voting. Kansas, South Carolina,[9] Tennessee, Texas,[10] and Wisconsin[11] state legislatures passed laws requiring voters to have government-issued IDs before they could cast their ballots. This meant, typically, that people without driver's licenses or passports had to gain new forms of ID. Former president Bill Clinton denounced them, saying, "There has never been in my lifetime, since we got rid of the poll tax and all the Jim Crow burdens on voting, the determined effort to limit the franchise that we see today".[12] He was referring to Jim Crow laws passed in southern states near the turn of the twentieth century that disenfranchised most blacks from voting and excluded them from the political process for more than six decades. Clinton said the moves would effectively disenfranchise core voter blocs that trend liberal, including college students, black people, and Latinos.[13][14] The Obama campaign fought against the Ohio law, pushing for a petition and statewide referendum to repeal it in time for the 2012 election.[15]
In addition, the Pennsylvania legislature proposed a plan to change its representation in the electoral college from the traditional winner-take-all model to a district-by-district model.[16] As the governorship and both houses of its legislature were Republican-controlled, the move was viewed by some as an attempt to reduce Democratic chances.[17][18][19] Ultimately they did not do it, leaving their winner take all format intact as of 2020.
Nominations
[edit]Democratic Party nomination
[edit]Primaries
[edit]With an incumbent president running for re-election against token opposition, the race for the Democratic nomination was largely uneventful. The nomination process consisted of primaries and caucuses, held by the 50 states, as well as Guam, Puerto Rico, Washington, D.C., U.S. Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and Democrats Abroad. Additionally, high-ranking party members known as superdelegates each received one vote in the convention. A few of the primary challengers surpassed the president's vote total in individual counties in several of the seven contested primaries, though none made a significant impact in the delegate count. Running unopposed everywhere else, Obama cemented his status as the Democratic presumptive nominee on April 3, 2012, by securing the minimum number of pledged delegates needed to obtain the nomination.[20][21]
Candidate
[edit]
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Personal
Illinois State Senator and U.S. Senator from Illinois 44th President of the United States
Tenure
 |
||
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Personal U.S. Senator from Delaware 47th Vice President of the United States Vice presidential campaigns 46th President of the United States Incumbent Tenure  |
||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Barack Obama | Joe Biden | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 44th President of the United States (2009–2017) |
47th Vice President of the United States (2009–2017) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Republican Party nomination
[edit]Primaries
[edit]Candidates with considerable name recognition who entered the race for the Republican presidential nomination in the early stages of the primary campaign included U.S. representative and former Libertarian nominee Ron Paul, former Minnesota governor Tim Pawlenty, who co-chaired John McCain's campaign in 2008, former Massachusetts governor Mitt Romney, the runner-up for the nomination in the 2008 cycle, and former Speaker of the House Newt Gingrich.
The first debate took place on May 5, 2011, in Greenville, South Carolina, with businessman Herman Cain, former New Mexico governor Gary Johnson, Ron Paul, Tim Pawlenty, and former Pennsylvania senator Rick Santorum participating. Another debate took place a month later, with Newt Gingrich, Mitt Romney, former Utah governor Jon Huntsman, and Minnesota congresswoman Michele Bachmann participating, and Gary Johnson excluded. A total of thirteen debates were held before the Iowa caucuses.
The first major event of the campaign was the Ames Straw Poll, which took place in Iowa on August 13, 2011. Michele Bachmann won the straw poll (this ultimately proved to be the acme of her campaign).[22] Pawlenty withdrew from the race after a poor showing in the straw poll, as did Thaddeus McCotter, the only candidate among those who qualified for the ballot who was refused entrance into the debate.[23]
It became clear at around this point in the nomination process that while Romney was considered to be the likely nominee by the Republican establishment, a large segment of the conservative primary electorate found him to be too moderate for their political views. As a result, a number of potential "anti-Romney" candidates were put forward,[24][25] including future president Donald Trump,[26] former Alaska governor and 2008 vice-presidential nominee Sarah Palin,[27] New Jersey governor Chris Christie,[28] and Texas governor Rick Perry,[29] the last of whom decided to run in August 2011. Perry did poorly in the debates, however, and Herman Cain and then Newt Gingrich came to the fore in October and November.
Due to a number of scandals, Cain withdrew just before the end of the year, after having ballot placement in several states.[30] Around the same time, Johnson, who had been able to get into only one other debate, withdrew to seek the Libertarian Party nomination.[31]
For the first time in modern Republican Party history, three different candidates won the first three state contests in January (the Iowa caucuses, the New Hampshire primary, and the South Carolina primary).[32] Although Romney had been expected to win in at least Iowa and New Hampshire, Rick Santorum won the non-binding poll at caucus sites in Iowa by 34 votes, as near as could be determined from the incomplete tally, earning him a declaration as winner by state party leaders, although vote totals were missing from eight precincts.[33][34] The election of county delegates at the caucuses would eventually lead to Ron Paul earning 22 of the 28 Iowa delegates to the Republican National Convention.[35] Newt Gingrich won South Carolina by a surprisingly large margin,[36] and Romney won only in New Hampshire.
A number of candidates dropped out at this point in the nomination process. Bachmann withdrew after finishing sixth in the Iowa caucuses,[37] Huntsman withdrew after coming in third in New Hampshire, and Perry withdrew when polls showed him drawing low numbers in South Carolina.[38]

Santorum, who had previously run an essentially one-state campaign in Iowa, was able to organize a national campaign after his surprising victory there. He unexpectedly carried three states in a row on February 7 and overtook Romney in nationwide opinion polls, becoming the only candidate in the race to effectively challenge the notion that Romney was the inevitable nominee.[39] However, Romney won all of the other contests between South Carolina and the Super Tuesday primaries, and regained his first-place status in nationwide opinion polls by the end of February.
The Super Tuesday primaries took place on March 6. Romney carried six states, Santorum carried three, and Gingrich won only in his home state of Georgia.[40] Throughout the rest of March, 266 delegates were allocated in 12 events, including the territorial contests and the first local conventions that allocated delegates (Wyoming's county conventions). Santorum won Kansas and three Southern primaries, but he was unable to make any substantial gain on Romney, who became a formidable frontrunner after securing more than half of the delegates allocated in March.
On April 10, Santorum suspended his campaign due to a variety of reasons, such as a low delegate count, unfavorable polls in his home state of Pennsylvania, and his daughter's health, leaving Mitt Romney as the undisputed front-runner for the presidential nomination and allowing Gingrich to claim that he was "the last conservative standing" in the campaign for the nomination.[41] After disappointing results in the April 24 primaries (finishing second in one state, third in three, and fourth in one), Gingrich dropped out on May 2 in a move that was seen as an effective end to the contest for the nomination.[42] After Gingrich's spokesman announced his upcoming withdrawal, the Republican National Committee declared Romney the party's presumptive nominee.[43] Ron Paul officially remained in the race, but he stopped campaigning on May 14 to focus on state conventions.
On May 29, after winning the Texas primary, Romney had received a sufficient number of delegates to clinch the party's nomination with the inclusion of unpledged delegates. After winning the June 5 primaries in California and several other states, Romney had received more than enough pledged delegates to clinch the nomination without counting unpledged delegates, making the June 26 Utah Primary, the last contest of the cycle, purely symbolic. CNN's final delegate estimate, released on July 27, 2012, put Romney at 1,462 pledged delegates and 62 unpledged delegates, for a total estimate of 1,524 delegates. No other candidate had unpledged delegates. The delegate estimates for the other candidates were Santorum at 261 delegates, Paul at 154, Gingrich at 142, Bachmann at 1, Huntsman at 1, and all others at 0.[44]
On August 28, 2012, delegates at the Republican National Convention officially named Romney the party's presidential nominee.[45] Romney formally accepted the delegates' nomination on August 30, 2012.[46]
Candidate
[edit]
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Governor of Massachusetts
Presidential campaigns
U.S. Senator from Utah
|
||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mitt Romney | Paul Ryan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 70th Governor of Massachusetts (2003–2007) |
U.S. Representative from Wisconsin (1999–2019) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [47][48] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Withdrawn candidates
[edit]Third party and other nominations
[edit]Four other parties nominated candidates that had ballot access or write-in access to at least 270 electoral votes, the minimum number of votes needed in the 2012 election to win the presidency through a majority of the electoral college.
Libertarian Party
[edit]- Gary Johnson, former governor of New Mexico.[73] Vice-presidential nominee: Jim Gray, retired state court judge, from California.[74]
Green Party
[edit]- Jill Stein, medical doctor from Massachusetts.[75][76] Vice-presidential nominee: Cheri Honkala, social organizer, from Pennsylvania.[77]
Constitution Party
[edit]- Virgil Goode, former representative from Virginia.[78] Vice-presidential nominee: Jim Clymer from Pennsylvania.[79]
Justice Party
[edit]- Rocky Anderson, former mayor of Salt Lake City and founding member of the Justice Party, from Utah. Vice-presidential nominee: Luis J. Rodriguez from California.[80][81]
Candidates gallery
[edit]Campaigns
[edit]Ballot access
[edit]| Presidential ticket | Party | Ballot access[82] | Votes | Percentage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| States | Electors | % of voters | ||||
| Obama / Biden | Democratic | 50 + DC | 538 | 100% | 65,915,795 | 51.1% |
| Romney / Ryan | Republican | 50 + DC | 538 | 100% | 60,933,504 | 47.2% |
| Johnson / Gray | Libertarian | 48 + DC | 515 | 95.1% | 1,275,971 | 1.0% |
| Stein / Honkala | Green | 36 + DC | 436 | 83.1% | 469,627 | 0.4% |
| Goode / Clymer | Constitution | 26 | 257 | 49.9% | 122,388 | 0.1% |
| Anderson / Rodriguez | Justice | 15 | 145 | 28.1% | 43,018 | nil |
| Lindsay / Osorio | Socialism & Liberation | 13 | 115 | 28.6% | 7,791 | nil |
Candidates in bold were on ballots representing 270 electoral votes.
All other candidates were on the ballots of fewer than 10 states, 100 electors, and less than 20% of voters nationwide.
Financing and advertising
[edit]The United States presidential election of 2012 broke new records in financing, fundraising, and negative campaigning. Through grassroots campaign contributions, online donations, and Super PACs, Obama and Romney raised a combined total of more than $2 billion.[83] Super PACs constituted nearly one-fourth of the total financing, with most coming from pro-Romney PACs.[84] Obama raised $690 million through online channels, beating his record of $500 million in 2008.[85] Most of the advertising in the 2012 presidential campaign was decidedly negative—80% of Obama's ads and 84% of Romney's ads were negative.[86] The tax-exempt non-profit Americans for Prosperity, a so-called "outside group", that is, a political advocacy group that is not a political action committee or super-PAC, ran a television advertising campaign opposing Obama described by The Washington Post as "early and relentless".[87][88] Americans for Prosperity spent $8.4 million in swing states on television advertisements denouncing the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 loan guarantee to Solyndra, a manufacturer of solar panels that went bankrupt,[89] an advertising campaign described by The Wall Street Journal in November 2011 as "perhaps the biggest attack on Mr. Obama so far".[90][91]
Party conventions
[edit]- April 18–21, 2012: 2012 Constitution Party National Convention held in Nashville, Tennessee;[92] Virgil Goode won the nomination.
- May 3–6, 2012: 2012 Libertarian National Convention held in Las Vegas, Nevada;[93] Gary Johnson won the nomination.[94]
- July 13–15, 2012: 2012 Green National Convention held in Baltimore, Maryland;[95] Jill Stein won the nomination.[75]
- August 27–30, 2012: 2012 Republican National Convention held in Tampa, Florida;[96] Mitt Romney won the nomination.
- September 3–6, 2012: 2012 Democratic National Convention held in Charlotte, North Carolina;[97] Barack Obama won the nomination.
Presidential debates
[edit]The Commission on Presidential Debates held four debates during the last weeks of the campaign: three presidential and one vice-presidential. The major issues debated were the economy and jobs, the federal budget deficit, taxation and spending, the future of Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid, healthcare reform, education, social issues, immigration, and foreign policy.
| No. | Date | Host | City | Moderator | Participants | Viewership
(million) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Wednesday, October 3, 2012 | University of Denver | Denver, Colorado | Jim Lehrer | 67.2[100] | |
| VP | Thursday, October 11, 2012 | Centre College | Danville, Kentucky | Martha Raddatz | 51.4[100] | |
| P2 | Tuesday, October 16, 2012 | Hofstra University | Hempstead, New York | Candy Crowley | 65.6[100] | |
| P3 | Monday, October 22, 2012 | Lynn University | Boca Raton, Florida | Bob Schieffer | 59.2[100] |

An independent presidential debate featuring minor party candidates took place on Tuesday, October 23 at the Hilton Hotel in Chicago, Illinois.[101][102] The debate was moderated by Larry King[103] and organized by the Free & Equal Elections Foundation.[102] The participants were Gary Johnson (Libertarian), Jill Stein (Green), Virgil Goode (Constitution), and Rocky Anderson (Justice).[102][103] A second debate between Stein and Johnson took place on Sunday, November 4, and was moderated by Ralph Nader.[104]
Notable expressions, phrases, and statements
[edit]- Severely conservative – In a speech he made at the Conservative Political Action Conference in February 2012, Romney claimed that he had been a "severely conservative Republican governor". Romney's description of his record as "severely conservative" was widely criticized by political commentators as both rhetorically clumsy and factually inaccurate.[105][106][107] Later, the phrase "severely conservative" was frequently brought up by Democrats to make fun of Romney's willingness to associate himself with the far-right of the Republican Party as well as his apparent lack of sincerity while doing so.[108] Conservative radio host Rush Limbaugh, who played the clip on his radio show, said: "I have never heard anybody say, 'I'm severely conservative.' "[109]
- You didn't build that – A portion of a statement that Obama made in a July 2012 campaign speech in Roanoke, Virginia. Obama said that businesses depend on government-provided infrastructure to succeed, but critics of his remarks argued that he was underplaying the work of entrepreneurs and giving the government credit for individuals' success. The Romney campaign immediately used the statement in an effort to contrast Romney's economic policies with Obama's and to appeal to small business owners/employees. A major theme of the 2012 Republican National Convention was "We Built It".
- 47 percent – An expression Romney used at a private campaign fundraising event, which was secretly recorded and publicly released. At the private event, Romney said that 47 percent of the people would vote for Barack Obama no matter what Romney said or did because those people "...are dependent upon government... I'll never convince them they should take personal responsibility and care for their lives." Ironically, Romney received almost exactly 47% of the vote.
- The 1980s are now calling to ask for their foreign policy back – A portion of a statement that Obama made in an October 2012 debate. In the debate, Obama was deriding an earlier Romney statement in the campaign that Russia is "without question, our No. 1 geopolitical foe."[110]
- Binders full of women – A phrase that Romney used in the second presidential debate to refer to the long list of female candidates that he considered when choosing his cabinet members as Governor of Massachusetts.
- Horses and bayonets – After Romney said in the third presidential debate that the U.S. Navy was smaller than at any time since 1917, Obama replied, "We have fewer ships than we did in 1916. Well, governor, we also have fewer horses and bayonets, because the nature of our military's changed."[111]
- Shovel-ready jobs – a phrase used to describe some stimulus projects promoted by the administration. During the debate on September 23, 2011, Gary Johnson quipped, "My next-door neighbor's two dogs have created more shovel-ready jobs than this president."[112]
- Romnesia – A term coined by a blogger in April 2011 and used by Obama late in the campaign to describe Romney's alleged inability to take responsibility for his past statements.[113][114]
- $10,000 bet – During a Republican debate, Romney facetiously bet Texas governor Rick Perry $10,000 that he (Perry) was wrong about Romney's position on the individual mandate under the Affordable Healthcare Act. The statement was vilified by Democrats as exemplary of Romney being out of touch with working-class and middle-class Americans.
- Romneyshambles – a word used by the British press after Romney criticized British preparations for the 2012 Summer Olympics. The word is a play on omnishambles, and it became a popular hashtag on Twitter. It was subsequently chosen as one of Collins English Dictionary's words of the year.[115][116]
- Malarkey – a word used by Joe Biden in his debate with Paul Ryan to mean bullshit. Biden later used the word in his own campaign in 2020.[117]
Electoral College forecasts
[edit]Elections analysts and political pundits issue probabilistic forecasts of the composition of the Electoral College. These forecasts use a variety of factors to estimate the likelihood of each candidate winning the Electoral College electors for that state. Most election predictors use the following ratings:
- "tossup": no advantage
- "tilt" (used by some predictors): advantage that is not quite as strong as "lean"
- "lean" or "leans": slight advantage
- "likely": significant, but surmountable, advantage
- "safe" or "solid": near-certain chance of victory
Below is a list of states considered by one or more forecast to be competitive; states that are deemed to be "safe" or "solid" by forecasters RealClearPolitics, Sabato's Crystal Ball, and FiveThirtyEight.
| State | EVs | RealClearPolitics November 6, 2012[118] |
Sabato's Crystal Ball November 6, 2012[119] |
538 November 6, 2012[120] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | 11 | Lean R | Solid R | Safe R |
| Colorado | 9 | Tossup | Lean D | Likely D |
| Florida | 29 | Tossup | Lean R (flip) | Lean D |
| Iowa | 6 | Tossup | Lean D | Likely D |
| Indiana | 11 | Lean R (flip) | Solid R (flip) | Likely R (flip) |
| Maine | 1 | Lean D | Likely D | Safe D |
| Michigan | 16 | Tossup | Likely D | Safe D |
| Minnesota | 10 | Lean D | Likely D | Safe D |
| Missouri | 11 | Lean R | Solid R | Safe R |
| Nevada | 6 | Tossup | Likely D | Safe D |
| New Hampshire | 4 | Tossup | Lean D | Likely D |
| New Mexico | 5 | Lean D | Likely D | Safe D |
| North Carolina | 15 | Tossup | Likely R (flip) | Lean R (flip) |
| Ohio | 18 | Tossup | Lean D | Safe D |
| Oregon | 7 | Lean D | Likely D | Safe D |
| Pennsylvania | 20 | Tossup | Lean D | Safe D |
| Washington | 12 | Lean D | Solid D | Safe D |
| Virginia | 13 | Tossup | Lean R | Likely D |
| Wisconsin | 10 | Tossup | Lean D | Safe D |
Timeline
[edit]Results
[edit]Electoral results
[edit]On the day of the election, spread betting firm Spreadex were offering an Obama Electoral College Votes spread of 296–300 to Romney's 239–243.[121] In reality Obama's victory over Romney was far greater, winning 332 electoral votes to Romney's 206. Romney lost all but one of nine battleground states, and received 47 percent of the nationwide popular vote to Obama's 51 percent.[122][123]
Of the 3,154 counties/districts/independent cities making returns, Romney won the most popular votes in 2,447 (77.58%) while Obama carried 707 (22.42%).
Popular vote totals are from the Federal Election Commission report.[2]
| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote | Electoral vote |
Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Electoral vote | ||||
| Barack Obama (incumbent) | Democratic | Illinois | 65,915,795 | 51.06% | 332 | Joe Biden (incumbent) | Delaware | 332 |
| Mitt Romney | Republican | Massachusetts | 60,933,504 | 47.20% | 206 | Paul Ryan | Wisconsin | 206 |
| Gary Johnson | Libertarian | New Mexico | 1,275,971 | 0.99% | 0 | Jim Gray | California | 0 |
| Jill Stein | Green | Massachusetts | 469,627 | 0.36% | 0 | Cheri Honkala | Minnesota | 0 |
| Virgil Goode | Constitution | Virginia | 122,389 | 0.11% | 0 | James N. Clymer | Pennsylvania | 0 |
| Roseanne Barr | Peace and Freedom | Utah | 67,326 | 0.05% | 0 | Cindy Sheehan | California | 0 |
| Rocky Anderson | Justice | Utah | 43,018 | 0.03% | 0 | Luis J. Rodriguez | Texas | 0 |
| Tom Hoefling | America's | Nebraska | 40,628 | 0.03% | 0 | J.D. Ellis | Tennessee | 0 |
| Other | 217,152 | 0.17% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 129,085,410 | 100% | 538 | 538 | ||||
| Needed to win | 270 | 270 | ||||||

Results by state
[edit]The table below displays the official vote tallies by each state's Electoral College voting method. The source for the results of all states, except those that amended their official results, is the official Federal Election Commission report.[2] The column labeled "Margin" shows Obama's margin of victory over Romney (the margin is negative for every state that Romney won).
| States/districts won by Obama/Biden | |
| States/districts won by Romney/Ryan | |
| † | At-large results (for states that split electoral votes) |
State or
district |
Obama/Biden Democratic |
Romney/Ryan Republican |
Johnson/Gray Libertarian |
Stein/Honkala Green |
Others | Margin | Margin Swing[a] |
Total votes |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | EV | # | % | EV | # | % | EV | # | % | EV | # | % | EV | # | % | % | |||
| 795,696 | 38.36% | – | 1,255,925 | 60.55% | 9 | 12,328 | 0.59% | – | 3,397 | 0.16% | – | 6,992 | 0.3% | – | −460,229 | −22.19% | −0.61% | 2,074,338 | AL | |
| 122,640 | 40.81% | – | 164,676 | 54.80% | 3 | 7,392 | 2.46% | – | 2,917 | 0.97% | – | 2,870 | 1.0% | – | −42,036 | −13.99% | 7.55% | 300,495 | AK | |
| 1,025,232 | 44.59% | – | 1,233,654 | 53.65% | 11 | 32,100 | 1.39% | – | 7,816 | 0.34% | – | 452 | nil | – | −208,422 | −9.06% | −0.54% | 2,299,254 | AZ | |
| 394,409 | 36.88% | – | 647,744 | 60.57% | 6 | 16,276 | 1.52% | – | 9,305 | 0.87% | – | 1,734 | 0.16% | – | −253,335 | −23.69% | −3.84% | 1,069,468 | AR | |
| 7,854,285 | 60.24% | 55 | 4,839,958 | 37.12% | – | 143,221 | 1.10% | – | 85,638 | 0.66% | – | 115,445 | 0.88% | – | 3,014,327 | 23.12% | −0.94% | 13,038,547 | CA | |
| 1,323,102 | 51.49% | 9 | 1,185,243 | 46.13% | – | 35,545 | 1.38% | – | 7,508 | 0.29% | – | 18,121 | 0.71% | – | 137,858 | 5.36% | −3.59% | 2,569,518 | CO | |
| 905,083 | 58.06% | 7 | 634,892 | 40.73% | – | 12,580 | 0.81% | – | 863 | 0.06% | – | 5,542 | 0.36% | – | 270,191 | 17.33% | −5.04% | 1,558,960 | CT | |
| 242,584 | 58.61% | 3 | 165,484 | 39.98% | – | 3,882 | 0.94% | – | 1,940 | 0.47% | – | 31 | nil | – | 77,100 | 18.63% | −6.37% | 413,921 | DE | |
| 267,070 | 90.91% | 3 | 21,381 | 7.28% | – | 2,083 | 0.71% | – | 2,458 | 0.84% | – | 772 | 0.26% | – | 245,689 | 83.63% | −2.29% | 293,764 | DC | |
| 4,237,756 | 50.01% | 29 | 4,163,447 | 49.13% | – | 44,726 | 0.5% | – | 8,947 | 0.1% | – | 19,303 | 0.2% | – | 74,309 | 0.88% | −1.94% | 8,474,179 | FL | |
| 1,773,827 | 45.48% | – | 2,078,688 | 53.30% | 16 | 45,324 | 1.2% | – | 1,516 | nil | – | 695 | nil | – | −304,861 | −7.82% | −2.61% | 3,900,050 | GA | |
| 306,658 | 70.55% | 4 | 121,015 | 27.84% | – | 3,840 | 0.9% | – | 3,184 | 0.7% | – | – | – | – | 185,643 | 42.71% | −2.55% | 434,697 | HI | |
| 212,787 | 32.62% | – | 420,911 | 64.53% | 4 | 9,453 | 1.5% | – | 4,402 | 0.7% | – | 4,721 | 0.7% | – | −208,124 | −31.91% | −6.26% | 652,274 | ID | |
| 3,019,512 | 57.60% | 20 | 2,135,216 | 40.73% | – | 56,229 | 1.1% | – | 30,222 | 0.6% | – | 835 | nil | – | 884,296 | 16.87% | −8.27% | 5,242,014 | IL | |
| 1,152,887 | 43.93% | – | 1,420,543 | 54.13% | 11 | 50,111 | 1.9% | – | 625 | nil | – | 368 | nil | – | −267,656 | −10.20% | −11.26% | 2,624,534 | IN | |
| 822,544 | 51.99% | 6 | 730,617 | 46.18% | – | 12,926 | 0.8% | – | 3,769 | 0.2% | – | 12,324 | 0.8% | – | 91,927 | 5.81% | −3.72% | 1,582,180 | IA | |
| 440,726 | 37.99% | – | 692,634 | 59.71% | 6 | 20,456 | 1.8% | – | 714 | 0.1% | – | 5,441 | 0.5% | – | −251,908 | −21.72% | −6.75% | 1,159,971 | KS | |
| 679,370 | 37.80% | – | 1,087,190 | 60.49% | 8 | 17,063 | 1.0% | – | 6,337 | 0.4% | – | 7,252 | 0.4% | – | −407,820 | −22.69% | −6.46% | 1,797,212 | KY | |
| 809,141 | 40.58% | – | 1,152,262 | 57.78% | 8 | 18,157 | 0.9% | – | 6,978 | 0.4% | – | 7,527 | 0.4% | – | −343,121 | −17.20% | 1.43% | 1,994,065 | LA | |
| 401,306 | 56.27% | 2 | 292,276 | 40.98% | – | 9,352 | 1.3% | – | 8,119 | 1.1% | – | 2,127 | 0.3% | – | 109,030 | 15.29% | −2.03% | 713,180 | ME–AL | |
| 223,035 | 59.57% | 1 | 142,937 | 38.18% | – | 4,501 | 1.2% | – | 3,946 | 1.1% | – | – | – | – | 80,098 | 21.39% | −1.43% | 374,419 | ME1 | |
| 177,998 | 52.94% | 1 | 149,215 | 44.38% | – | 4,843 | 1.4% | – | 4,170 | 1.2% | – | – | – | – | 28,783 | 8.56% | −2.69% | 336,226 | ME2 | |
| 1,677,844 | 61.97% | 10 | 971,869 | 35.90% | – | 30,195 | 1.1% | – | 17,110 | 0.6% | – | 10,309 | 0.4% | – | 705,975 | 26.07% | 0.63% | 2,707,327 | MD | |
| 1,921,290 | 60.65% | 11 | 1,188,314 | 37.51% | – | 30,920 | 1.0% | – | 20,691 | 0.7% | – | 6,552 | 0.2% | – | 732,976 | 23.14% | −2.67% | 3,167,767 | MA | |
| 2,564,569 | 54.21% | 16 | 2,115,256 | 44.71% | – | 7,774 | 0.2% | – | 21,897 | 0.5% | – | 21,465 | 0.5% | – | 449,313 | 9.50% | −6.97% | 4,730,961 | MI | |
| 1,546,167 | 52.65% | 10 | 1,320,225 | 44.96% | – | 35,098 | 1.2% | – | 13,023 | 0.4% | – | 22,048 | 0.8% | – | 225,942 | 7.69% | −2.55% | 2,936,561 | MN | |
| 562,949 | 43.79% | – | 710,746 | 55.29% | 6 | 6,676 | 0.5% | – | 1,588 | 0.1% | – | 3,625 | 0.3% | – | −147,797 | −11.50% | 1.67% | 1,285,584 | MS | |
| 1,223,796 | 44.38% | – | 1,482,440 | 53.76% | 10 | 43,151 | 1.6% | – | – | – | – | 7,936 | 0.3% | – | −258,644 | −9.38% | −9.25% | 2,757,323 | MO | |
| 201,839 | 41.70% | – | 267,928 | 55.35% | 3 | 14,165 | 2.9% | – | – | – | – | 116 | nil | – | −66,089 | −13.65% | −11.39% | 484,048 | MT | |
| 302,081 | 38.03% | – | 475,064 | 59.80% | 2 | 11,109 | 1.4% | – | – | – | – | 6,125 | 0.8% | – | −172,983 | −21.77% | −6.84% | 794,379 | NE–AL | |
| 108,082 | 40.83% | – | 152,021 | 57.43% | 1 | 3,847 | 1.2% | – | – | – | – | 762 | 0.3% | – | -43,949 | -16.60% | −6.83% | 264,712 | NE1 | |
| 121,889 | 45.70% | – | 140,976 | 52.85% | 1 | 3,393 | 1.3% | – | – | – | – | 469 | 0.2% | – | -19,087 | -7.15% | −5.94% | 266,727 | NE2 | |
| 72,110 | 27.82% | – | 182,067 | 70.23% | 1 | 3,869 | 1.5% | – | – | – | – | 1,177 | 0.5% | – | −109,957 | −42.41% | −3.40% | 259,223 | NE3 | |
| 531,373 | 52.36% | 6 | 463,567 | 45.68% | – | 10,968 | 1.1% | – | – | – | – | 9,010 | 0.9% | – | 67,806 | 6.68% | −5.81% | 1,014,918 | NV | |
| 369,561 | 51.98% | 4 | 329,918 | 46.40% | – | 8,212 | 1.2% | – | 324 | 0.1% | – | 2,957 | 0.4% | – | 39,643 | 5.58% | −4.03% | 710,972 | NH | |
| 2,125,101 | 58.38% | 14 | 1,477,568 | 40.59% | – | 21,045 | 0.6% | – | 9,888 | 0.3% | – | 6,690 | 0.2% | – | 647,533 | 17.79% | 2.22% | 3,640,292 | NJ | |
| 415,335 | 52.99% | 5 | 335,788 | 42.84% | – | 27,788 | 3.6% | – | 2,691 | 0.3% | – | 2,156 | 0.3% | – | 79,547 | 10.15% | −4.98% | 783,758 | NM | |
| 4,485,741 | 63.35% | 29 | 2,490,431 | 35.17% | – | 47,256 | 0.7% | – | 39,982 | 0.6% | – | 17,749 | 0.3% | – | 1,995,310 | 28.18% | 1.32% | 7,081,159 | NY | |
| 2,178,391 | 48.35% | – | 2,270,395 | 50.39% | 15 | 44,515 | 1.0% | – | – | – | – | 12,071 | 0.3% | – | −92,004 | −2.04% | −2.37% | 4,505,372 | NC | |
| 124,827 | 38.69% | – | 188,163 | 58.32% | 3 | 5,231 | 1.6% | – | 1,361 | 0.4% | – | 3,045 | 0.9% | – | −63,336 | −19.63% | −10.99% | 322,627 | ND | |
| 2,827,709 | 50.67% | 18 | 2,661,437 | 47.69% | – | 49,493 | 0.9% | – | 18,573 | 0.3% | – | 23,635 | 0.4% | – | 166,272 | 2.98% | −1.61% | 5,580,847 | OH | |
| 443,547 | 33.23% | – | 891,325 | 66.77% | 7 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | −447,778 | −33.54% | −2.15% | 1,334,872 | OK | |
| 970,488 | 54.24% | 7 | 754,175 | 42.15% | – | 24,089 | 1.4% | – | 19,427 | 1.1% | – | 21,091 | 1.2% | – | 216,313 | 12.09% | −4.26% | 1,789,270 | OR | |
| 2,990,274 | 51.97% | 20 | 2,680,434 | 46.59% | – | 49,991 | 0.9% | – | 21,341 | 0.4% | – | 11,630 | 0.2% | – | 309,840 | 5.38% | −4.94% | 5,753,670 | PA | |
| 279,677 | 62.70% | 4 | 157,204 | 35.24% | – | 4,388 | 1.0% | – | 2,421 | 0.5% | – | 2,359 | 0.5% | – | 122,473 | 27.46% | −0.35% | 446,049 | RI | |
| 865,941 | 44.09% | – | 1,071,645 | 54.56% | 9 | 16,321 | 0.8% | – | 5,446 | 0.3% | – | 4,765 | 0.2% | – | −205,704 | −10.47% | −1.49% | 1,964,118 | SC | |
| 145,039 | 39.87% | – | 210,610 | 57.89% | 3 | 5,795 | 1.6% | – | – | – | – | 2,371 | 0.7% | – | −65,571 | −18.02% | −9.61% | 363,815 | SD | |
| 960,709 | 39.08% | – | 1,462,330 | 59.48% | 11 | 18,623 | 0.8% | – | 6,515 | 0.3% | – | 10,400 | 0.4% | – | −501,621 | −20.40% | −5.33% | 2,458,577 | TN | |
| 3,308,124 | 41.38% | – | 4,569,843 | 57.17% | 38 | 88,580 | 1.1% | – | 24,657 | 0.3% | – | 2,647 | nil | – | −1,261,719 | −15.79% | −4.02% | 7,993,851 | TX | |
| 251,813 | 24.75% | – | 740,600 | 72.79% | 6 | 12,572 | 1.2% | – | 3,817 | 0.4% | – | 8,638 | 0.9% | – | −488,787 | −48.04% | −19.75% | 1,017,440 | UT | |
| 199,239 | 66.57% | 3 | 92,698 | 30.97% | – | 3,487 | 1.2% | – | 594 | 0.2% | – | 3,272 | 1.1% | – | 106,541 | 35.60% | −1.41% | 299,290 | VT | |
| 1,971,820 | 51.16% | 13 | 1,822,522 | 47.28% | – | 31,216 | 0.8% | – | 8,627 | 0.2% | – | 20,304 | 0.5% | – | 149,298 | 3.88% | −2.42% | 3,854,489 | VA | |
| 1,755,396 | 56.16% | 12 | 1,290,670 | 41.29% | – | 42,202 | 1.4% | – | 20,928 | 0.7% | – | 16,320 | 0.5% | – | 464,726 | 14.87% | −2.31% | 3,125,516 | WA | |
| 238,269 | 35.54% | – | 417,655 | 62.30% | 5 | 6,302 | 0.9% | – | 4,406 | 0.7% | – | 3,806 | 0.6% | – | −179,386 | −26.76% | −13.64% | 670,438 | WV | |
| 1,620,985 | 52.83% | 10 | 1,407,966 | 45.89% | – | 20,439 | 0.7% | – | 7,665 | 0.3% | – | 11,379 | 0.4% | – | 213,019 | 6.94% | −6.96% | 3,068,434 | WI | |
| 69,286 | 27.82% | – | 170,962 | 68.64% | 3 | 5,326 | 2.1% | – | – | – | – | 3,487 | 1.4% | – | −101,676 | −40.82% | −8.58% | 249,061 | WY | |
| Total | 65,915,795 | 51.06% | 332 | 60,933,504 | 47.20% | 206 | 1,275,971 | 1.0% | – | 469,627 | 0.4% | – | 490,510 | 0.4% | – | 4,982,291 | 3.86% | −4.41% | 129,085,410 | |
| Obama/Biden Democratic |
Romney/Ryan Republican |
Johnson/Gray Libertarian |
Stein/Honkala Green |
Others | Margin | Margin swing |
Total votes | |||||||||||||
Maine and Nebraska each allow for their election results votes to be split between candidates. The winner within each congressional district gets one electoral vote for the district. The winner of the statewide vote gets two additional electoral votes. In the 2012 election, all four of Maine's electoral votes were won by Obama and all five of Nebraska's electoral votes were won by Romney.[128][129]
States and EV districts that flipped from Democratic to Republican
[edit]Close states
[edit]
Red denotes states (or congressional districts that contribute an electoral vote) won by Republican Mitt Romney; blue denotes those won by Democrat Barack Obama.
State where the margin of victory was under 1% (29 electoral votes):
- Florida, 0.88% (74,309 votes)
States where the margin of victory was under 5% (46 electoral votes):
- North Carolina, 2.04% (92,004 votes)
- Ohio, 2.98% (166,272 votes)
- Virginia, 3.88% (149,298 votes)
States/districts where the margin of victory was between 5% and 10% (120 electoral votes):
- Colorado, 5.36% (137,858 votes) (tipping point state)
- Pennsylvania, 5.38% (309,840 votes)
- New Hampshire, 5.58% (39,643 votes)
- Iowa, 5.81% (91,927 votes)
- Nevada, 6.68% (67,806 votes)
- Wisconsin, 6.94% (213,019 votes)
- Nebraska's 2nd Congressional District, 7.15% (19,087 votes)
- Minnesota, 7.69% (225,942 votes)
- Georgia, 7.82% (304,861 votes)
- Maine's 2nd Congressional District, 8.56% (28,783 votes)
- Arizona, 9.06% (208,422 votes)
- Missouri, 9.38% (258,644 votes)
- Michigan, 9.50% (449,313 votes)
Statistics
[edit]Counties with highest percent of vote (Democratic)
- Shannon County, South Dakota 93.39%
- Kalawao County, Hawaii 92.59%
- Bronx County, New York 91.45%
- Washington, D.C. 90.91%
- Petersburg, Virginia 89.79%
Counties with highest percent of vote (Republican)
- King County, Texas 95.86%
- Madison County, Idaho 93.29%
- Sterling County, Texas 92.91%
- Franklin County, Idaho 92.77%
- Roberts County, Texas 92.13%
Romney's concession
[edit]
After the networks called Ohio (the state that was arguably the most critical for Romney, as no Republican had ever won the presidency without carrying it) for Obama at around 11:15 pm EST on Election Day, Romney was ready to concede the race, but hesitated when Karl Rove strenuously objected on Fox News to the network's decision to make that call.[131][132] However, after Colorado and Nevada were called for the President (giving Obama enough electoral votes to win even if Ohio were to leave his column), in tandem with Obama's apparent lead in Florida and Virginia (both were eventually called for Obama), Romney acknowledged that he had lost and conceded at around 1:00 am EST on November 7.
Despite public polling showing Romney behind Obama in the swing states of Nevada, Colorado, Iowa, Wisconsin, Ohio, and New Hampshire, tied with Obama in Virginia, and just barely ahead of Obama in Florida, the Romney campaign said they were genuinely surprised by the loss, having believed that public polling was oversampling Democrats.[133] The Romney campaign had already set up a transition website, and had scheduled and purchased a fireworks display to celebrate in case he won the election.[134][135]
On November 30, 2012, it was revealed that shortly before the election, internal polling done by the Romney campaign had shown Romney ahead in Colorado and New Hampshire, tied in Iowa, and within a few points of Obama in Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, Minnesota, and Ohio.[136] In addition, the Romney campaign had assumed that they would win Florida, North Carolina and Virginia.[137] The polls had made Romney and his campaign team so confident of their victory that Romney did not write a concession speech until Obama's victory was announced.[138][139]
Reactions
[edit]Foreign leaders reacted with both positive and mixed messages. Most world leaders congratulated and praised Obama on his re-election victory. However, Venezuela and some other states had tempered reactions. Pakistan commented that Romney's defeat had made Pakistan-United States relations safer. Stock markets fell noticeably after Obama's re-election, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average, NASDAQ, and the S&P 500 each declining over two percent the day after the election.[140]
All 50 states had a petition on the White House website We The People calling for their state to secede from the union. These petitions were created by individual people, with some gaining thousands of signatures.[141]
Voter demographics
[edit]| 2012 presidential election by demographic subgroup | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic subgroup | Obama | Romney | Other | % of total vote | |||
| Total vote | 51 | 47 | 2 | 100 | |||
| Ideology | |||||||
| Liberals | 86 | 11 | 3 | 25 | |||
| Moderates | 56 | 41 | 3 | 41 | |||
| Conservatives | 17 | 82 | 1 | 35 | |||
| Party | |||||||
| Democrats | 92 | 7 | 1 | 38 | |||
| Republicans | 6 | 93 | 1 | 32 | |||
| Independents | 45 | 50 | 5 | 29 | |||
| Gender | |||||||
| Men | 45 | 52 | 3 | 47 | |||
| Women | 55 | 44 | 1 | 53 | |||
| Marital status | |||||||
| Married | 42 | 56 | 2 | 60 | |||
| Unmarried | 62 | 35 | 3 | 40 | |||
| Sex by marital status | |||||||
| Married men | 38 | 60 | 2 | 29 | |||
| Married women | 46 | 53 | 1 | 31 | |||
| Single men | 56 | 40 | 4 | 18 | |||
| Single women | 67 | 31 | 2 | 23 | |||
| Race/ethnicity | |||||||
| White | 39 | 59 | 2 | 72 | |||
| Black | 93 | 6 | 1 | 13 | |||
| Asian | 73 | 26 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Other | 58 | 38 | 4 | 2 | |||
| Hispanic | 71 | 27 | 2 | 10 | |||
| Religion | |||||||
| Protestant or other Christian | 42 | 57 | 1 | 53 | |||
| Catholic | 50 | 48 | 2 | 25 | |||
| Mormon | 21 | 78 | 1 | 2 | |||
| Jewish | 69 | 30 | 1 | 2 | |||
| Muslim | 85 | 4 | 11 | 1 | |||
| Other | 74 | 23 | 3 | 7 | |||
| None | 70 | 26 | 4 | 12 | |||
| Religious service attendance | |||||||
| More than once a week | 36 | 63 | 1 | 14 | |||
| Once a week | 41 | 58 | 1 | 28 | |||
| A few times a month | 55 | 44 | 1 | 13 | |||
| A few times a year | 56 | 42 | 2 | 27 | |||
| Never | 62 | 34 | 4 | 17 | |||
| White evangelical or born-again Christian? | |||||||
| White evangelical or born-again Christian | 21 | 78 | 1 | 26 | |||
| Everyone else | 60 | 37 | 3 | 74 | |||
| Age | |||||||
| 18–24 years old | 60 | 36 | 4 | 11 | |||
| 25–29 years old | 60 | 38 | 2 | 8 | |||
| 30–39 years old | 55 | 42 | 3 | 17 | |||
| 40–49 years old | 48 | 50 | 2 | 20 | |||
| 50–64 years old | 47 | 52 | 1 | 28 | |||
| 65 and older | 44 | 56 | 0 | 16 | |||
| Age by race | |||||||
| Whites 18–29 years old | 44 | 51 | 5 | 11 | |||
| Whites 30–44 years old | 38 | 59 | 3 | 18 | |||
| Whites 45–64 years old | 38 | 61 | 1 | 29 | |||
| Whites 65 and older | 39 | 61 | n/a | 14 | |||
| Blacks 18–29 years old | 91 | 8 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Blacks 30–44 years old | 94 | 5 | 1 | 4 | |||
| Blacks 45–64 years old | 93 | 7 | n/a | 4 | |||
| Blacks 65 and older | 93 | 6 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Latinos 18–29 years old | 74 | 23 | 3 | 4 | |||
| Latinos 30–44 years old | 71 | 28 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Latinos 45–64 years old | 68 | 31 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Latinos 65 and older | 65 | 35 | n/a | 1 | |||
| Others | 67 | 31 | 2 | 5 | |||
| LGBT | |||||||
| Yes | 76 | 22 | 2 | 5 | |||
| No | 49 | 49 | 2 | 95 | |||
| Education | |||||||
| Not a high school graduate | 64 | 35 | 1 | 3 | |||
| High school graduate | 51 | 48 | 1 | 21 | |||
| Some college education | 49 | 48 | 3 | 29 | |||
| College graduate | 47 | 51 | 2 | 29 | |||
| Postgraduate education | 55 | 42 | 3 | 18 | |||
| Family income | |||||||
| Under $30,000 | 63 | 35 | 2 | 20 | |||
| $30,000–49,999 | 57 | 42 | 1 | 21 | |||
| $50,000–99,999 | 46 | 52 | 2 | 31 | |||
| $100,000–199,999 | 44 | 54 | 2 | 21 | |||
| $200,000–249,999 | 47 | 52 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Over $250,000 | 42 | 55 | 3 | 4 | |||
| Union households | |||||||
| Union | 58 | 40 | 2 | 18 | |||
| Non-union | 49 | 48 | 3 | 82 | |||
| Issue regarded as most important | |||||||
| Economy | 47 | 51 | 2 | 59 | |||
| Federal budget deficit | 32 | 66 | 2 | 15 | |||
| Foreign policy | 56 | 33 | 11 | 5 | |||
| Health care | 75 | 24 | 1 | 18 | |||
| Region | |||||||
| Northeast | 59 | 40 | 1 | 18 | |||
| Midwest | 50 | 48 | 2 | 24 | |||
| South | 46 | 53 | 1 | 36 | |||
| West | 54 | 43 | 3 | 22 | |||
| Community size | |||||||
| Big cities (population over 500,000) | 69 | 29 | 2 | 11 | |||
| Mid-sized cities (population 50,000 to 500,000) | 58 | 40 | 2 | 21 | |||
| Suburbs | 48 | 50 | 2 | 47 | |||
| Towns (population 10,000 to 50,000) | 42 | 56 | 2 | 8 | |||
| Rural areas | 37 | 61 | 2 | 14 | |||
Hispanic vote
[edit]The United States has a population of 50 million Hispanic and Latino Americans, 27 million of whom are citizens eligible to vote (13% of total eligible voters). Traditionally, only half of eligible Hispanic voters vote (around 7% of voters); of them, 71% voted for Barack Obama (increasing his percentage of the vote by 5%); therefore, the Hispanic vote was an important factor in Obama's re-election, since the vote difference between the two main parties was only 3.9%[142][143][144][145]
Exit polls were conducted by Edison Research of Somerville, New Jersey, for the National Election Pool, a consortium which at the time consisted of ABC News, Associated Press, CBS News, CNN,[146] Fox News,[147] and NBC News.[148]
Analysis
[edit]Combined with the re-election victories of his two immediate predecessors, Bill Clinton (1996) and George W. Bush (2004), Obama's victory in the 2012 election marked only the second time in American history that three consecutive presidents were each elected to two full terms after the consecutive two-term presidencies of Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and James Monroe ending in 1820, which is the only other time any two-term president succeeded another.[149] Eight years later, Obama's successor, Donald Trump, also ran for his own re-election in 2020, but was ultimately defeated by Joe Biden, who served as vice president under Obama. This was also the first election since 1928 in which neither of the major candidates had any military experience.[150] The election was arguably decided by three counties: Miami-Dade County (Florida); Cuyahoga County (Ohio) and Philadelphia (Pennsylvania). If these three counties had cast zero votes, Obama would have lost all three states and the election.[151]
The 2012 election marked the first time since Franklin D. Roosevelt's last two re-elections in 1940 and 1944 that the Democrats won a majority of the popular vote in two consecutive elections.[152] Obama was also the first president of either party to secure a majority of the popular vote in two elections since Ronald Reagan in 1980 and 1984.[153] Obama is the third Democratic president to secure at least 51% of the vote twice, after Andrew Jackson and Franklin D. Roosevelt.[154] Romney won the popular vote in 226 congressional districts making this the first time since 1960 that the winner of the election did not win the popular vote in a majority of the congressional districts.[155] This is the last time that the Democrats won a majority of states in a presidential election.
Romney lost his home state of Massachusetts, becoming the first major party presidential candidate to lose his home state since Democrat Al Gore lost his home state of Tennessee to Republican George W. Bush in the 2000 election.[156] Romney lost his home state by more than 23%, the worst losing margin for a major party candidate since John Frémont in 1856.[157] Even worse than Frémont, Romney failed to win a single county in his home state, something last seen by Theodore Roosevelt in 1912.[158][159] In addition, since Obama carried Ryan's home state of Wisconsin, the Romney–Ryan ticket was the first major party ticket since the 1972 election to have both of its nominees lose their home states.[160] Romney won the popular vote in every county of three states: Utah, Oklahoma, and West Virginia; Obama did so in four states: Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Hawaii.[161]
Romney's loss prompted the Republican National Committee to try to appeal to the American Latino population by concentrating on different approaches to immigration. These were short-lived due to activity and anger from the Republican base and may have contributed to the selection of Donald Trump as their presidential candidate four years later.[162]
Gary Johnson's popular vote total set a Libertarian Party record, and his popular vote percentage was the second-best showing for a Libertarian in a presidential election, trailing only Ed Clark's in 1980.[163] Johnson would go on to beat this record in the 2016 presidential election, winning the most votes for the Libertarian ticket in history. At the time, Green Party candidate Jill Stein's popular vote total made her the most successful female presidential candidate in a general election in United States history.[164][165] This was later surpassed by Hillary Clinton in the 2016 election.
Obama's vote total was the fourth most votes received in the history of presidential elections (behind Obama's 2008 victory and both major candidates in 2020) and the most ever for a reelected president. The 2012 election marked the first time since 1988 in which no state was won by a candidate with a plurality of the state's popular vote. Furthermore, it is the only post-World War II presidential election in which no states were won by margins smaller than 30,000 votes. Obama's narrowest victories were in New Hampshire by 39,643 votes, followed by Florida by 74,309 votes. Every other presidential election in modern history has seen states narrowly won by several thousand votes. So far, this is the only presidential election in history where both the Republican and Democratic vice presidential candidates are practicing Roman Catholics. It is also the only presidential election where there are no white Protestants on a major party ticket. This is the most recent election where any party won consecutive elections.
Obama was the fourth of just four presidents in United States history to win re-election with a lower percentage of the electoral vote than in their prior elections, the other three were James Madison in 1812, Woodrow Wilson in 1916 and Franklin Roosevelt in 1940 and 1944. Additionally, Obama was the fifth of only five presidents to win re-election with a smaller percentage of the popular vote than in prior elections, the other four are James Madison in 1812, Andrew Jackson in 1832, Grover Cleveland in 1892, and Franklin Roosevelt in 1940 and 1944.
Maps
[edit]-
Results by state, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
-
Results by county.[b] Blue denotes counties that went to Obama; red denotes counties that went to Romney. Hawaii, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont had all counties go to Obama. Oklahoma, Utah, and West Virginia had all counties go to Romney.
-
Results by county,[b] shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
-
Popular vote by county shaded on a scale from red/Republican to blue/Democratic
-
Results by state and the District of Columbia, scaled by number of electors per state
-
Cartogram of popular vote by county shaded on a scale from red/Republican to blue/Democratic where each county has been rescaled in proportion to its population
-
Cartogram of the electoral vote results, with each square representing one electoral vote
-
Results by congressional district
-
County swing from 2008 to 2012[b]
-
Treemap of the popular vote by county, state, and locally predominant recipient
-
Results by state with pie charts for the electoral college and popular vote.
Gallery
[edit]-
The Empire State Building in New York City was lit blue when CNN called Ohio for Obama, projecting him the winner of the election. Likewise, red would have been used if Romney won.[166]
-
The Obamas and the Bidens embrace following the television announcement of their victory.
-
The Obamas and the Bidens walk on stage at the election night victory celebration at McCormick Place in Chicago.
-
Former governor Mitt Romney meets with President Barack Obama at the White House after the 2012 presidential election.
See also
[edit]- Planned presidential transition of Mitt Romney
- 2012 United States Senate elections
- 2012 United States House of Representatives elections
- 2012 United States gubernatorial elections
- Nationwide opinion polling for the 2012 United States presidential election
- Statewide opinion polling for the 2012 United States presidential election
- Timeline of the 2012 United States presidential election
- Second inauguration of Barack Obama
Notes
[edit]- ^ Percentage point difference in margin from the 2008 election
- ^ a b c Alaska and Louisiana do not have counties. Alaska's boroughs and census areas and Louisiana's parishes are pictured.
References
[edit]- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press. Archived from the original on July 25, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e "Federal Elections 2012" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. Washington, D.C. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 2, 2019. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Fahrenthold, David A. (May 18, 2023). "Obama reelected as president". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on April 17, 2015. Retrieved March 20, 2024.
- ^ "Obama: Romney is out of touch". The Christian Science Monitor. September 20, 2012. Archived from the original on December 11, 2022. Retrieved December 11, 2022.
- ^ "Romney hits Obama on deficit". Politico. May 16, 2012. Archived from the original on December 11, 2022. Retrieved December 11, 2022.
- ^ Congressional Record at H50 (January 4, 2013).
- ^ Cillizza, Chris (April 16, 2012). "The 9 swing states of 2012". Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ "David Callahan: Ohio's Voter ID Law and the 2012 Election". Huffington Post Politics blog. March 25, 2011. Archived from the original on October 5, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ "New SC voter ID requirements clears Senate". Charleston: WCBD-TV 2. Archived from the original on September 9, 2011. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ "Rick Perry's agenda may signal run for W.H. – Andy Barr". Politico.Com. February 7, 2011. Archived from the original on October 5, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ "The Next Election: The Surprising Reality by Andrew Hacker". The New York Review of Books. Archived from the original on October 5, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ "Bill Clinton likens GOP effort to Jim Crow laws – Darren Samuelsohn". Politico.Com. July 6, 2011. Archived from the original on October 5, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ Sonmez, Felicia (May 23, 2011). "Republicans rewriting state election laws in ways that could how hurt Democrat". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on October 2, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ Jackson, Jesse. "38-states-rigging-voting-rules-for-GOP". Chicago Sun-Times. Archived from the original on October 9, 2011. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ Provance, Jim. "Obama campaign fighting Ohio voting law". Toledo Blade. Archived from the original on October 5, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ "Pennsylvania's 'Democrat-screwing' 2012 'genius plan'". The Week. New York. September 15, 2011. Archived from the original on October 5, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ Olson, Laura (September 13, 2011). "Change proposed for state's electoral vote process". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Archived from the original on October 5, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ Rosenbaum, Ron (September 13, 2011). "Pennsylvania Ponders Bold Democrat-Screwing Electoral Plan". Slate. Archived from the original on October 5, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ "Pennsylvania GOP looks to split electoral votes". The Washington Times. September 15, 2011. Archived from the original on May 7, 2016. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ Jackson, David (April 4, 2012)"It's official: Obama clinches Democratic nomination" Archived October 5, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, USA Today. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ (April 4, 2012) "Obama Clinches Democratic Nomination" Archived October 5, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, CNN. Retrieved April 12, 2012.
- ^ Goldman, Russell (July 5, 2012). "Michele Bachmann Drops Out of Presidential Race". ABC News. Archived from the original on January 21, 2021. Retrieved June 27, 2020.
- ^ Summers, Juana (August 11, 2011). "Barred hopefuls make debate plans". Politico. Archived from the original on May 14, 2013. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
- ^ Reid, Tim (January 9, 2012). "Romney's rivals running out of time to stop him". Reuters. Archived from the original on January 25, 2016. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
- ^ Norington, Brad. "Romney has money but lacks conviction". The Australian. Archived from the original on March 9, 2012. Retrieved July 12, 2012.
- ^ Cohn, Alicia M. (December 9, 2011). "Trump says Romney lacks the 'courage' to participate in Newsmax debate". The Hill. Archived from the original on January 11, 2021. Retrieved July 12, 2012.
- ^ Stanley, Timothy (March 30, 2012). "If only Sarah Palin had run ..." CNN. Archived from the original on August 12, 2020. Retrieved July 12, 2012.
- ^ Avlon, John (August 31, 2011). "Chris Christie's 2012 Tease". The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved October 3, 2014.
- ^ Cohen, Tom; Silverleib, Alan (September 1, 2011). "Seeking the 'anti-Romney' in the Republican presidential race". CNN. Archived from the original on July 12, 2012. Retrieved July 12, 2012.
- ^ "Herman Cain suspends presidential campaign". Newsday. December 3, 2011. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
- ^ Stewart, Rebecca (December 28, 2011). "'Liberated' Gary Johnson seeks Libertarian nomination". CNN. Archived from the original on August 17, 2020. Retrieved December 28, 2011.
- ^ Knickerbocker, Brad (January 21, 2012). "Newt Gingrich wins South Carolina. Can he do the same in Florida?". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on November 27, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2012.
- ^ Rick Santorum Is Declared Winner of Iowa Caucuses by State Party Leaders" (January 21, 2012). Bloomberg News. Archived October 20, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "2012 GOP caucus count unresolved". Iowa Caucuses. Archived from the original on January 20, 2012. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- ^ "Iowa Republican Caucuses - Election Results". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on April 4, 2024. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ Begala, Paul (January 21, 2012). "Newt Gingrich's Surprise Win in South Carolina Panics Republicans". Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved August 14, 2012.
- ^ Wheaton, Sarah (January 4, 2012). "Bachmann Says She Will Not Continue in the Race". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 18, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2012.
- ^ Zeleny, Jeff; Shear, Michael D. (January 19, 2012). "Perry to End Bid for Presidency". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 24, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2012.
- ^ Madison, Lucy (February 8, 2012). "Santorum hopes to build momentum from 3-state sweep". CBS News. Archived from the original on September 21, 2024. Retrieved August 27, 2012.
- ^ "Results: March 6, 2012 – Super Tuesday". CNN. Archived from the original on August 12, 2020. Retrieved July 12, 2012.
- ^ Gabriel, Trip (April 10, 2012). "Gingrich Says He's in the Race to the End". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 24, 2020. Retrieved May 9, 2012.
- ^ "Overheard on CNN.com: What brought down Gingrich's campaign? What's next?". CNN. April 25, 2012. Archived from the original on November 25, 2020. Retrieved May 9, 2012.
- ^ Shear, Michael D. (April 25, 2012). "Republican National Committee Backs Romney". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 26, 2020. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ^ Holland, Steve (May 30, 2012). "Romney clinches Republican 2012 nomination in Texas". Reuters. Archived from the original on July 27, 2020. Retrieved May 30, 2012.
- ^ Caldwell, Leigh Ann (August 28, 2012). "Republican delegates nominate Mitt Romney". CBS News. Archived from the original on September 21, 2024. Retrieved August 28, 2012.
- ^ O'Brien, Michael (August 30, 2012). "Romney accepts nomination, says 'The time has come to turn the page'". NBC News. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved August 31, 2012.
- ^ "Mitt Romney announces bid to be US president in 2012" Archived January 31, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, BBC. June 2, 2011
- ^ Elliott, Philip (June 2, 2011). "Romney opens presidential bid — he's got company". Deseret News. Archived from the original on December 4, 2012. Retrieved October 5, 2012.
- ^ George, Stephanopoulos (June 6, 2011). "Rick Santorum Will Run for President: 'We're In It to Win'". ABC News. Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved June 6, 2011.
- ^ Salant, Jonathan D. (June 6, 2011). "Ex-Pennsylvania Senator Santorum Announces '12 Republican Presidential Bid". Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on June 9, 2011. Retrieved June 6, 2011.
- ^ "Republican Rick Santorum announces presidential run". The Patriot News. Associated Press. June 6, 2011. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 6, 2011.
- ^ Marr, Kendra (May 11, 2011). "Newt Gingrich running for president". Politico. Archived from the original on May 13, 2011. Retrieved May 11, 2011.
- ^ O'Brien, Michael (April 25, 2012). "Gingrich to leave campaign, but not the national spotlight". MSNBC. Archived from the original on April 25, 2012. Retrieved April 25, 2012.
- ^ Good, Chris (May 14, 2012). "Ron Paul to Stop Campaigning in New States". ABC News. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved October 8, 2012.
- ^ "Huntsman's sly web strategy" Archived July 13, 2024, at the Wayback Machine, The Hill. May 11, 2011.
- ^ "Jon Huntsman: My Mormonism is 'tough to define'" Archived June 23, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Politico. May 12, 2011.
- ^ Hamby, Peter (January 19, 2012). "Perry drops out, endorses Gingrich". CNN. Archived from the original on January 24, 2012. Retrieved January 25, 2012.
- ^ Reston, Maeve (August 13, 2011). "Texas Gov. Rick Perry declares GOP presidential bid". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on August 17, 2011. Retrieved August 18, 2011.
- ^ Rucker, Philip (January 4, 2012). "Michele Bachmann drops out of GOP race after Iowa caucuses". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 12, 2012. Retrieved January 5, 2012.
- ^ Rosenwald, Michael S. (June 14, 2011). "Michele Bachmann files paperwork to run for president". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 31, 2021. Retrieved September 17, 2017.
- ^ Burns, Alexander (June 13, 2011). "Michele Bachmann is in". Politico. Archived from the original on March 3, 2015. Retrieved December 3, 2011.
- ^ "Roemer kicks off 2012 presidential bid". KRQE. July 21, 2011. Archived from the original on December 6, 2012. Retrieved October 5, 2012.
- ^ McKinnon, Mark (July 21, 2011). "Listen to Candidate Roemer". The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved July 21, 2011.
- ^ Green, Joshua (May 21, 2011) "Herman Cain Makes It Official" Archived January 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, The Atlantic. Retrieved May 21, 2011.
- ^ Creed, Ryan (May 21, 2011) "Herman Cain, Former CEO of Godfather's Pizza, Announces His Candidacy" Archived January 11, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, ABC News. Retrieved May 22, 2011.
- ^ "Fred Karger officially ends 2012 presidential campaign". Wikinews. June 30, 2012. Archived from the original on July 6, 2015. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ Camia, Catalina (April 21, 2011). "Ex-N.M. governor Gary Johnson announces for president". USA Today. Archived from the original on April 29, 2011. Retrieved April 21, 2011.
- ^ "Gary Johnson throws his hat into the GOP presidential ring, will he be the 2012 Ron Paul?". Los Angeles Times. April 21, 2011. Archived from the original on November 11, 2020. Retrieved April 22, 2011.
- ^ Madison, Lucy (July 1, 2011). "Michigan Rep. Thaddeus McCotter to jump into Republican presidential race". CBS News. Archived from the original on July 4, 2011. Retrieved June 27, 2012.
- ^ Summers, Juana (July 20, 2011). "Candidates face off on Twitter". Politico. Archived from the original on May 14, 2013. Retrieved June 27, 2012.
- ^ Bakst, Brian (August 14, 2011). "Ex-Minn. Gov. Tim Pawlenty ends White House bid". The Huffington Post. Associated Press. Archived from the original on February 16, 2012. Retrieved August 14, 2011.
- ^ Reinhard, Beth (August 13, 2011). "Bachmann Boom; TPaw Bust?". National Journal. Archived from the original on October 25, 2011. Retrieved August 14, 2011.
- ^ Pratt, Timothy (May 5, 2012). "Libertarians nominate ex-Governor Gary Johnson for president". Reuters. Archived from the original on July 27, 2020. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
- ^ Riggs, Mike (May 5, 2012). "Judge Jim Gray Is the 2012 Libertarian Party Vice Presidential Nominee". Reason. Archived from the original on May 7, 2012. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
- ^ a b "Mass. doctor Jill Stein wins Green Party's presidential nod". USA Today. Associated Press. July 14, 2012. Archived from the original on July 15, 2012. Retrieved July 15, 2012.
- ^ Kilar, Steve (July 14, 2012). "Green Party nominates Jill Stein for president at Baltimore convention". The Baltimore Sun. Archived from the original on June 7, 2013. Retrieved July 15, 2012.
- ^ Steinmetz, Katy (July 11, 2012). "The Green Team: Jill Stein's Third-Party Bid to Shake Up 2012". Time. Archived from the original on July 11, 2012. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- ^ "Goode gets Constitution Party's nomination for president". The Roanoke Times. April 21, 2012. Archived from the original on September 8, 2012. Retrieved April 22, 2012.
- ^ Hill, Trent (April 21, 2012). "Constitution Party Convention Wrap-Up: vice Presidential Candidate and Officer Elections". Independent Political Report. Archived from the original on April 23, 2012. Retrieved April 22, 2012.
- ^ Gehrke, Robert (July 17, 2012). "Rocky picks activist-author as his VP running mate". The Salt Lake Tribune. Archived from the original on July 21, 2012. Retrieved July 18, 2012.
- ^ Schwarz, Hunter (January 13, 2012). "Rocky Anderson accepts his newly-formed party's presidential nomination". Deseret News. Archived from the original on February 1, 2012. Retrieved February 1, 2012.
- ^ "2012 Ballot Status for President". Ballot-access.org. October 27, 2012. Archived from the original on January 25, 2016. Retrieved July 7, 2013.
- ^ Braun, Stephen (December 6, 2012). "$2 Billion Price Tag for Presidential Election". Associated Press. Archived from the original on December 8, 2012. Retrieved December 9, 2012.
- ^ Confessore, Nicholas (December 7, 2012). "Little to Show for Cash Flood by Big Donors". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 11, 2012. Retrieved December 9, 2012.
- ^ Scherer, Michael (November 27, 2012). "Exclusive: Obama's 2012 Digital Fundraising Outperformed 2008". Time. Archived from the original on November 18, 2012. Retrieved December 9, 2012.
- ^ Hunt, Albert (October 14, 2012). "Barrage of Negative Ads May Haunt President-Elect". Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on October 18, 2012. Retrieved December 9, 2012.
The hundreds of thousands of television commercials broadcast by the presidential candidates are lopsidedly negative; this is the case with 80 percent of those put out by President Barack Obama and 84 percent of those for Mitt Romney.
- ^ Gold, Matea (January 5, 2014). "The players in the Koch-backed $400 million political donor network". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on May 9, 2015. Retrieved May 9, 2015.
Americans for Prosperity, the Virginia-based nonprofit that finances grass-roots activities across the country and ran an early and relentless television ad assault against President Obama during the 2012 campaign.
- ^ Boorstin, Julia (November 8, 2011). "Record Political Ad Spending Powered by Special Interests". CNBC. Archived from the original on May 18, 2015. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- ^ Bathon, Michael (October 17, 2012). "Solyndra Lenders Ahead of Government Won't Recover Fully". Bloomberg Business. Archived from the original on May 1, 2015. Retrieved November 14, 2014.
- ^ Lacey, Stephen (November 28, 2011). "Koch-Fueled Americans for Prosperity Spends $2.4 Million on Solyndra Attack Ad". ThinkProgress. Center for American Progress. Archived from the original on May 5, 2015. Retrieved May 10, 2015.
- ^ Mullins, Brody (January 14, 2012). "Americans for Prosperity to Air Ads Slamming Obama's Ties to Solyndra". The Wall Street Journal. Washington Wire blog. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved April 19, 2015.
- ^ Winger, Richard (November 18, 2010) "2012 Constitution Party National Convention Set for Nashville" Archived November 6, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Ballot Access News. Retrieved November 29, 2010.
- ^ Myers, Laura (November 30, 2010) "Las Vegas will host Libertarian convention" Archived July 14, 2011, at the Wayback Machine Las Vegas Review-Journal. Retrieved November 30, 2010.
- ^ Cristina Silva (May 5, 2012). "Gary Johnson Wins 2012 Libertarian Nomination". The Huffington Post. Associated Press. Archived from the original on June 20, 2012. Retrieved June 17, 2012.
- ^ "Green Party National Convention will be in Baltimore". Ballot Access News. November 11, 2011. Archived from the original on November 6, 2020. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ Barr, Andy; Mike Allen (May 12, 2010) "Republicans pick Tampa for 2012 convention" Archived January 6, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Politico. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
- ^ Falcone, Michael (February 1, 2011). "2012 Democratic National Convention To Be Held In Charlotte, N.C." ABC News. Archived from the original on September 1, 2012. Retrieved October 5, 2012.
- ^ Kiely, Kathy (October 31, 2011). "Fall 2012 Presidential Debates Set". National Journal. Archived from the original on November 1, 2011. Retrieved October 31, 2011.
- ^ Blake, Aaron (August 13, 2012) "Presidential debate moderators announced: Crowley is first woman in 20 years" Archived August 28, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, The Washington Post. Retrieved August 15, 2012.
- ^ a b c d "CPD: 2012 Debates". www.debates.org. Archived from the original on January 8, 2019. Retrieved January 8, 2019.
- ^ "Third-party candidates finally get their own presidential debate" Archived August 20, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, The Washington Post. October 24, 2012. Retrieved February 11, 2013.
- ^ a b c Sullivan, Sean (October 23, 2012). "Third-party candidates debate: United against Obama, Romney". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on March 3, 2013. Retrieved October 24, 2012.
- ^ a b "Larry King to moderate third-party debate". CBS News. Associated Press. October 17, 2012. Archived from the original on February 8, 2015. Retrieved October 18, 2012.
- ^ Lowrey, Annie (November 5, 2012). "Another Presidential Debate, but This Time the Candidates Are Much Less Familiar (Published 2012)". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on February 8, 2021. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ David A. Fahrenthold (February 16, 2012). "Mitt Romney reframes himself as a 'severely conservative' governor". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on February 9, 2021. Retrieved September 17, 2017.
- ^ Mitt Romney's 'Severe Conservatism'. The Weekly Standard (September 18, 2012). Retrieved August 12, 2013.
- ^ Frum, David (February 13, 2012). ""Mitt Romney's 'severely' bad moves"". CNN. Archived from the original on December 15, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ Paul Krugman (February 13, 2012). "Severe Conservative Syndrome". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 12, 2020. Retrieved February 28, 2017.
- ^ "Rush On Romney @ CPAC: I Have Never Heard Anybody Say 'I'm Severely Conservative'". Daily Rushbo. February 10, 2012. Archived from the original on April 2, 2015.
- ^ Jillian Rayfield (October 23, 2012). "Obama: The '80s called, they want their foreign policy back". Salon. Archived from the original on April 24, 2022. Retrieved April 24, 2022.
- ^ Rogers, Katie (October 23, 2012). "Horses and bayonets catch on during final US presidential debate". The Guardian. Archived from the original on November 6, 2020. Retrieved August 17, 2017.
- ^ Burns, Alexander (September 22, 2011). "Gary Johnson's moment". Politico. Archived from the original on December 14, 2020. Retrieved January 21, 2016.
- ^ "Romnesia". hcfama.org. Archived from the original on December 1, 2011.
- ^ Kantrowitz, Alex (October 21, 2012). "#Romnesia: A Made for Social Media Attack Line". Forbes. Archived from the original on October 23, 2012. Retrieved October 22, 2012.
- ^ Collins, Lauren (September 18, 2012). "Romneyshambles, Part II". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on September 25, 2020. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- ^ "'Gangnam Style,' 'fiscal cliff,' 'Romneyshambles' chosen as Collins Dictionary's words of the year". Daily News. December 20, 2012. Archived from the original on November 14, 2020. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- ^ Korecki, Natasha (December 2, 2019). "No malarkey? Biden's old-school slogan gets mocked and praised in Iowa". Politico. Archived from the original on February 2, 2020. Retrieved October 19, 2022.
- ^ "RealClearPolitics - 2012 Election Maps - Battle for White House". Archived from the original on June 8, 2011.
- ^ "PROJECTION: OBAMA WILL LIKELY WIN SECOND TERM". November 5, 2012.
- ^ "Nate Silver's political calculations predict 2012 election outcome". November 7, 2012.
- ^ "US Election Betting | Financial Spread Betting | Spreadex". www.spreadex.com. November 7, 2012. Archived from the original on February 17, 2021. Retrieved August 11, 2020.
- ^ "Obama defeats Romney to win second term, vows he has 'more work to do'". Fox News. November 7, 2012. Archived from the original on November 5, 2015. Retrieved December 8, 2019.
- ^ Memoli, Michael A. (January 4, 2013). "It's official: Obama, Biden win second term". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on February 28, 2013. Retrieved December 8, 2019.
- ^ "2012 Election Information". Archived from the original on March 4, 2013. Retrieved February 25, 2013.
- ^ "NYS Board of Elections President and Vice-President Election Returns Nov. 6, 2012" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 25, 2013. Retrieved May 2, 2013.
- ^ "Final Results". Archived from the original on July 29, 2013. Retrieved February 25, 2013.
- ^ "Wisconsin Fall 2012 General Election Results". Archived from the original on January 29, 2013. Retrieved January 18, 2013.
- ^ "State of Maine Certificate of Ascertainment of Electors" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on December 22, 2012. Retrieved December 18, 2012.
- ^ "Official Results of Nebraska General Election – November 6, 2012" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on April 4, 2013. Retrieved December 26, 2012.
- ^ 2012 Presidential General Election Data – National, Uselectionatlas.org.
- ^ Kranish, Michael (December 22, 2012). "The story behind Mitt Romney's loss in the presidential campaign to President Obama". Boston Globe. Archived from the original on May 28, 2013. Retrieved February 1, 2016.
- ^ "The Real Reason for Karl Rove's Election Night Denial". Newsweek. January 21, 2014. Archived from the original on February 2, 2021. Retrieved January 29, 2014.
- ^ "Adviser: Romney "shellshocked" by loss". CBS News. November 8, 2012. Archived from the original on November 9, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2012.
- ^ "Romney's Transition Site". Political Wire. November 7, 2012. Archived from the original on November 8, 2012. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ "Romney campaign spent $25,000 on fireworks". Boston Globe. November 9, 2012. Archived from the original on November 11, 2012. Retrieved November 11, 2012.
- ^ Silver, Nate (December 1, 2012). "When Internal Polls Mislead, a Whole Campaign May Be to Blame". The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 26, 2012. Retrieved December 21, 2012.
- ^ "Exclusive: The Internal Polls That Made Mitt Romney Think He'd Win". The New Republic. November 30, 2012. Archived from the original on December 1, 2012. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ Rucker, Phillip (November 7, 2012). "Romney's belief in himself never wavered". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on November 12, 2012. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ Reeve, Elspeth (November 8, 2012). "The Whole Romney Ticket Believed in Unskewed Polls?". The Atlantic Wire. Archived from the original on December 30, 2012. Retrieved December 17, 2012.
- ^ Cheng, Jonathan (November 7, 2012). "Dow's 300-Point Slide Takes It Back to August Levels". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on July 24, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ Ryan, Danielle (November 14, 2012). "White House receives secession pleas from all 50 states". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on July 10, 2023. Retrieved July 10, 2023.
- ^ Krogstad, Jens Manuel; Lopez, Mark Hugo; López, Gustavo; Passel, Jeffrey S.; Patten, Eileen (January 19, 2016). "1. Looking Forward to 2016: The Changing Latino Electorate". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on February 17, 2021. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ^ Krogstad, Jens Manuel; Lopez, Mark Hugo; López, Gustavo; Passel, Jeffrey S.; Patten, Eileen (January 19, 2016). "Millennials Make Up Almost Half of Latino Eligible Voters in 2016". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on February 17, 2021. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ^ Krogstad, Jens Manuel (February 3, 2016). "2016 electorate will be the most diverse in U.S. history". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on February 17, 2021. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ^ Valdes, Marcela (September 18, 2016). "27 Million Potential Hispanic Votes. But What Will They Really Add Up To?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on January 4, 2021. Retrieved February 28, 2017.
- ^ "Presidential Race – 2012 Election Center – Elections & Politics from CNN.com". CNN. Archived from the original on February 6, 2018. Retrieved February 5, 2018.
- ^ "Fox News Exit Polls". Fox News. Archived from the original on January 26, 2013. Retrieved January 27, 2013.
- ^ "President Exit Polls". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved January 27, 2013.
- ^ Hum, Robert (November 7, 2012). "Two-Term Presidency Musings". CNBC. Archived from the original on July 29, 2013. Retrieved February 12, 2013.
- ^ Dilanian, Ken (August 11, 2012) "Ryan pick cements lack of military service in presidential race" Archived April 20, 2024, at the Wayback Machine, Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 11, 2014.
- ^ "56 Interesting Facts About the 2016 Election", The Cook Political Report, December 16, 2016, archived from the original on July 15, 2017
- ^ Nichols, John (November 9, 2012). "Obama's 3 Million Vote, Electoral College Landslide, Majority of States Mandate". The Nation. New York. Archived from the original on November 27, 2012. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ Giroux, Greg (January 4, 2013). "Final Tally Shows Obama First Since '56 to Win 51% Twice". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on January 15, 2013. Retrieved February 12, 2013.
- ^ Frank, Steve (January 7, 2014) "Obama first presidential candidate since Eisenhower to top 51% twice" Archived August 20, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, MSNBC.com. Retrieved December 11, 2014.
- ^ Bensen, Clark (April 4, 2013). "Presidential Results By Congressional Districts: Obama is reelected but Romney carries a majority of districts" (PDF). Cookpolitical.com. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 17, 2017. Retrieved June 25, 2017.
- ^ Gabbatt, Adam (October 19, 2012). "Romney poised to lose home state by wider margin than any other candidate". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on November 11, 2013. Retrieved February 12, 2013.
- ^ Ostermeier, Eric (November 14, 2012). "20 Presidential Tickets That Lost Both Home States". Smart Politics (University of Minnesota blog). Archived from the original on November 15, 2012. Retrieved February 12, 2013.
- ^ "2012 Presidential General Election Data – Massachusetts by County". Dave Leip's U.S. Election Atlas. Archived from the original on July 29, 2013. Retrieved March 8, 2013.
- ^ "Presidential Election of 1856 – Map by counties". Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Archived from the original on May 12, 2013. Retrieved March 9, 2013.
- ^ Ostermeier, Eric (November 14, 2012). "20 Presidential Tickets That Lost Both Home States". Smart Politics. Archived from the original on August 17, 2020. Retrieved July 12, 2015.
- ^ Blow, Charles M. (November 9, 2012) "Election Data Dive" Archived February 6, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times. Retrieved December 11, 2014.
- ^ Harwood, John. "Donald Trump Takes Advantage of a Republican Party Pitted Against Itself." Archived November 8, 2020, at the Wayback Machine New York Times. October 6, 2016. October 6, 2016.
- ^ Harrington, Gerry (November 8, 2012). "Libertarian Party buoyant; Greens hopeful". United Press International. Archived from the original on February 18, 2013. Retrieved February 12, 2013.
- ^ Wood, Daniel (November 30, 2015). "Harvard Grad Jill Stein Faces Uphill Battle for Presidency". The Harvard Crimson. Archived from the original on June 20, 2016. Retrieved June 12, 2016.
- ^ Herzog, Katie (March 14, 2016). "Meet the presidential candidate who makes Bernie Sanders look conservative". Grist Magazine. Archived from the original on December 2, 2020. Retrieved June 12, 2016.
- ^ Wells, Charlie (November 6, 2012). "Empire State Building lights up to broadcast election results". Daily News. New York. Archived from the original on November 9, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
Further reading
[edit]- Balz, Dan (2013). Collision 2012: Obama vs. Romney and the Future of Elections in America. New York: Viking Press. ISBN 978-0670025947.
- Gardner, Liz, et al. "Press Coverage of the 2012 US Presidential Election: A Multinational, Cross-Language Comparison". in Die US-Präsidentschaftswahl 2012 (Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, 2016). pp 241–267.
- Hansen, Wendy L., Michael S. Rocca, and Brittany Leigh Ortiz. "The effects of Citizens United on corporate spending in the 2012 presidential election". Journal of Politics 77.2 (2015): 535–545. in JSTOR Archived November 7, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- Heilemann, John; Halperin, Mark (2013). Double Down: Game Change 2012. New York: Penguin Press. ISBN 978-1594204401.
- Masket, Seth, John Sides, and Lynn Vavreck. "The Ground Game in the 2012 Presidential Election". Political Communication (2015) 33#2 pp: 1–19.
- Mayer, William G.; Bernstein, Jonathan, eds. (2012). The Making of the Presidential Candidates, 2012. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-4422-1170-4. Scholars explore nominations in the post-public-funding era, digital media and campaigns, television coverage, and the Tea Party.
- Miller, William J., ed. The 2012 Nomination and the Future of the Republican Party: The Internal Battle (Lexington Books; 2013) 265 pages; essays by experts on Romney and each of his main rivals
- Nelson, Michael, ed. The Elections of 2012 (2013) excerpt and text search Archived March 17, 2021, at the Wayback Machine; topical essays by experts
- Sides, John, and Lynn Vavreck. The Gamble: Choice and Chance in the 2012 Presidential Election (Princeton U.P. 2013) excerpt and text search Archived August 28, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
- Stempel III, Guido H. and Thomas K. Hargrove, eds. The 21st-Century Voter: Who Votes, How They Vote, and Why They Vote (2 vol. 2015).
External links
[edit]- The 9 Swing States of 2012
- 2012 Presidential Form 2 Filers at the Federal Election Commission (FEC)
- Election 2012 Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and Conventions
- 2012 Interactive Electoral Map
- Election of 2012 in Counting the Votes Archived August 28, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
- "The Choice 2012". Frontline. Season 30. Episode 21. October 9, 2012. PBS. WGBH. Retrieved November 28, 2024.

































![Results by county.[b] Blue denotes counties that went to Obama; red denotes counties that went to Romney. Hawaii, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont had all counties go to Obama. Oklahoma, Utah, and West Virginia had all counties go to Romney.](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/2012_Presidential_Election_by_County.svg/487px-2012_Presidential_Election_by_County.svg.png)
![Results by county,[b] shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d1/2012_United_States_presidential_election_results_map_by_county.svg/487px-2012_United_States_presidential_election_results_map_by_county.svg.png)
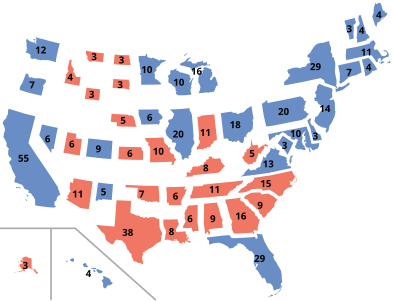
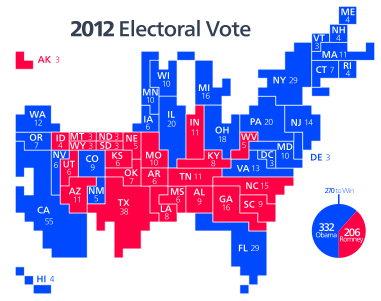

![County swing from 2008 to 2012[b]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/18/Presidential_Elections_2008-2012_Swing_in_County_Margins.svg/473px-Presidential_Elections_2008-2012_Swing_in_County_Margins.svg.png)
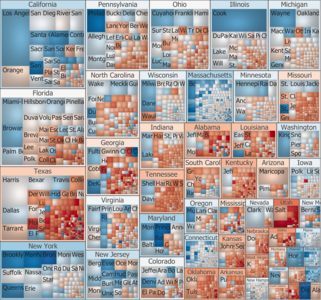
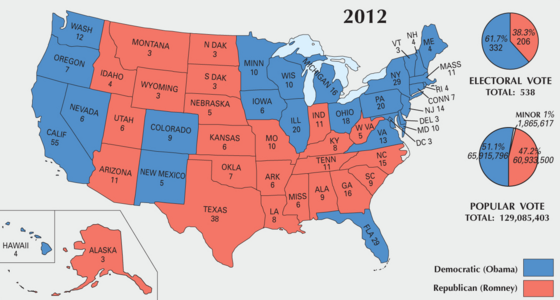
![The Empire State Building in New York City was lit blue when CNN called Ohio for Obama, projecting him the winner of the election. Likewise, red would have been used if Romney won.[166]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4f/Empire_State_Building_Blue_Obama_Election.JPG/273px-Empire_State_Building_Blue_Obama_Election.JPG)