Expanded Disability Status Scale: Difference between revisions
→Results and clinical meaning: linked "ambulation" to the article "walking" |
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit iOS app edit App suggested edit App image add top |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Multiple sclerosis measure of severity}} |
|||
The Kurtzke '''Expanded Disability Status Scale''' (EDSS) is a method of quantifying disability in [[multiple sclerosis]].<ref name=Kurtzke>{{cite journal |author=Kurtzke JF |title=Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS) |journal=Neurology |volume=33 |issue=11 |pages=1444–52 |year=1983 |pmid=6685237 |doi=10.1212/WNL.33.11.1444}}</ref> The scale has been developed by [[John F. Kurtzke]]. |
|||
{{Infobox diagnostic |
|||
| name = Expanded Disability Status Scale |
|||
| image = |
|||
| alt = |
|||
| caption = |
|||
| pronounce = |
|||
| purpose =quantify disability in multiple sclerosis |
|||
| test of = |
|||
| based on = |
|||
| synonyms = |
|||
}} |
|||
[[File:Kurtzke_scale.jpg | thumb | right | alt=The Kurtzke Expanded Disability Scale. | The Kurtzke Expanded Disability Scale.]] |
|||
The Kurtzke '''Expanded Disability Status Scale''' (EDSS) is a method of quantifying disability in [[multiple sclerosis]].<ref name=Kurtzke>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kurtzke JF | title = Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS) | journal = Neurology | volume = 33 | issue = 11 | pages = 1444–52 | date = November 1983 | pmid = 6685237 | doi = 10.1212/WNL.33.11.1444 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="Piryonesi-2021">{{Cite journal|last1=Piryonesi|first1=S. Madeh|last2=Rostampour|first2=Sorour|last3=Piryonesi|first3=S. Abdurrahman|date=2021-04-01|title=Predicting falls and injuries in people with multiple sclerosis using machine learning algorithms|url=https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2021.102740|journal=Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders|volume=49|pages=102740|doi=10.1016/j.msard.2021.102740|issn=2211-0348|pmid=33450500|s2cid=231624230|via=}}</ref> The scale has been developed by [[John F. Kurtzke]].<ref name="Kurtzke" /> The EDSS is based on a neurological examination by a clinician. However, a number of versions have been developed which enable patient self-administration.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Collins CD, Ivry B, Bowen JD, Cheng EM, Dobson R, Goodin DS, Lechner-Scott J, Kappos L, Galea I | title = A comparative analysis of Patient-Reported Expanded Disability Status Scale tools | journal = Multiple Sclerosis | volume = 22 | issue = 10 | pages = 1349–58 | date = September 2016 | pmid = 26564998 | pmc = 5015760 | doi = 10.1177/1352458515616205 }}</ref> |
|||
The EDSS quantifies disability in eight Functional Systems (FS) by assigning a Functional System Score (FSS) in each of these functional systems. It consists of ordinal rating system ranging from 0 (normal neurological status) to 10 (death due to MS) in 0.5 increments interval (when reaching EDSS 1). The lower scale values of the EDSS measure impairments based on the neurological examination, while the upper range of the scale (> EDSS 6) measures handicaps of patients with MS. The determination of EDSS 4 – 6 is heavily dependent on aspects of walking ability.<ref name="Meyer-Moock-2014">{{Cite journal|last1=Meyer-Moock|first1=Sandra|last2=Feng|first2=You-Shan|last3=Maeurer|first3=Mathias|last4=Dippel|first4=Franz-Werner|last5=Kohlmann|first5=Thomas|date=2014-03-25|title=Systematic literature review and validity evaluation of the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) and the Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite (MSFC) in patients with multiple sclerosis|journal=BMC Neurology|volume=14|pages=58|doi=10.1186/1471-2377-14-58|issn=1471-2377|pmc=3986942|pmid=24666846 |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
The EDSS quantifies disability in eight Functional Systems (FS) and allows neurologists to assign a Functional System Score (FSS) in each of these. |
|||
The EDSS is the most widely used measurement tool to describe disease progression in patients with MS and to assess the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions in clinical trials.<ref name="Meyer-Moock-2014" /> Nonetheless, it has many criticisms,<ref name="Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health-2018">{{Cite book|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK533358/|title=Validity of Outcome Measures|date=May 2018|publisher=Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health|language=en}}</ref> including the fact that it has moderate intra-rater reliability (EDSS kappa values between 0.32 and 0.76 and between 0.23 and 0.58 for the individual FSs were reported), offers poor assessment of upper limb and cognitive function, and lacks linearity between score difference and clinical severity. Other limitations of EDSS include that it relies heavily on the evaluation of motor function and the ability to walk; as such, a patient who might not be able to walk but maintains full dexterity is classified toward the severe end of the scale. |
|||
Other validated assessment measures used in MS trials include the Timed 25-Foot Walk, the Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite, and the Short Form (36) Health Survey.<ref name="Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health-2018" /> |
|||
__TOC__ |
|||
==Functional systems== |
==Functional systems== |
||
| Line 40: | Line 59: | ||
*'''10.0:''' Death due to MS |
*'''10.0:''' Death due to MS |
||
== External links == |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [http://edss.neurol.ru/ Online EDSS calculator] |
|||
<references/> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{reflist}} |
|||
{{Multiple sclerosis}} |
{{Multiple sclerosis}} |
||
[[Category:Diagnostic neurology]] |
|||
[[Category:Multiple sclerosis]] |
[[Category:Multiple sclerosis]] |
||
[[Category:Neurology]] |
|||
[[Category:Medical scales]] |
[[Category:Medical scales]] |
||
Latest revision as of 01:52, 7 December 2024
| Expanded Disability Status Scale | |
|---|---|
| Purpose | quantify disability in multiple sclerosis |
The Kurtzke Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) is a method of quantifying disability in multiple sclerosis.[1][2] The scale has been developed by John F. Kurtzke.[1] The EDSS is based on a neurological examination by a clinician. However, a number of versions have been developed which enable patient self-administration.[3]
The EDSS quantifies disability in eight Functional Systems (FS) by assigning a Functional System Score (FSS) in each of these functional systems. It consists of ordinal rating system ranging from 0 (normal neurological status) to 10 (death due to MS) in 0.5 increments interval (when reaching EDSS 1). The lower scale values of the EDSS measure impairments based on the neurological examination, while the upper range of the scale (> EDSS 6) measures handicaps of patients with MS. The determination of EDSS 4 – 6 is heavily dependent on aspects of walking ability.[4]
The EDSS is the most widely used measurement tool to describe disease progression in patients with MS and to assess the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions in clinical trials.[4] Nonetheless, it has many criticisms,[5] including the fact that it has moderate intra-rater reliability (EDSS kappa values between 0.32 and 0.76 and between 0.23 and 0.58 for the individual FSs were reported), offers poor assessment of upper limb and cognitive function, and lacks linearity between score difference and clinical severity. Other limitations of EDSS include that it relies heavily on the evaluation of motor function and the ability to walk; as such, a patient who might not be able to walk but maintains full dexterity is classified toward the severe end of the scale.
Other validated assessment measures used in MS trials include the Timed 25-Foot Walk, the Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite, and the Short Form (36) Health Survey.[5]
Functional systems
[edit]Kurtzke defines functional systems as follows:[1]
Results and clinical meaning
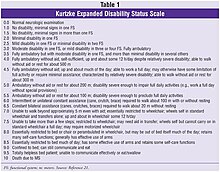
[edit]EDSS steps 1.0 to 4.5 refer to people with MS who are fully ambulatory. EDSS steps 5.0 to 9.5 are defined by the impairment to ambulation.
The clinical meaning of each possible result is the following:
- 0.0: Normal Neurological Exam
- 1.0: No disability, minimal signs in 1 FS
- 1.5: No disability, minimal signs in more than 1 FS
- 2.0: Minimal disability in 1 FS
- 2.5: Mild disability in 1 or Minimal disability in 2 FS
- 3.0: Moderate disability in 1 FS or mild disability in 3 - 4 FS, though fully ambulatory
- 3.5: Fully ambulatory but with moderate disability in 1 FS and mild disability in 1 or 2 FS; or moderate disability in 2 FS; or mild disability in 5 FS
- 4.0: Fully ambulatory without aid, up and about 12hrs a day despite relatively severe disability. Able to walk without aid 500 meters
- 4.5: Fully ambulatory without aid, up and about much of day, able to work a full day, may otherwise have some limitations of full activity or require minimal assistance. Relatively severe disability. Able to walk without aid 300 meters
- 5.0: Ambulatory without aid for about 200 meters. Disability impairs full daily activities
- 5.5: Ambulatory for 100 meters, disability precludes full daily activities
- 6.0: Intermittent or unilateral constant assistance (cane, crutch or brace) required to walk 100 meters with or without resting
- 6.5: Constant bilateral support (cane, crutch or braces) required to walk 20 meters without resting
- 7.0: Unable to walk beyond 5 meters even with aid, essentially restricted to wheelchair, wheels self, transfers alone; active in wheelchair about 12 hours a day
- 7.5: Unable to take more than a few steps, restricted to wheelchair, may need aid to transfer; wheels self, but may require motorized chair for full day's activities
- 8.0: Essentially restricted to bed, chair, or wheelchair, but may be out of bed much of day; retains self care functions, generally effective use of arms
- 8.5: Essentially restricted to bed much of day, some effective use of arms, retains some self care functions
- 9.0: Helpless bed patient, can communicate and eat
- 9.5: Unable to communicate effectively or eat/swallow
- 10.0: Death due to MS
External links
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Kurtzke JF (November 1983). "Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS)". Neurology. 33 (11): 1444–52. doi:10.1212/WNL.33.11.1444. PMID 6685237.
- ^ Piryonesi, S. Madeh; Rostampour, Sorour; Piryonesi, S. Abdurrahman (2021-04-01). "Predicting falls and injuries in people with multiple sclerosis using machine learning algorithms". Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders. 49: 102740. doi:10.1016/j.msard.2021.102740. ISSN 2211-0348. PMID 33450500. S2CID 231624230.
- ^ Collins CD, Ivry B, Bowen JD, Cheng EM, Dobson R, Goodin DS, Lechner-Scott J, Kappos L, Galea I (September 2016). "A comparative analysis of Patient-Reported Expanded Disability Status Scale tools". Multiple Sclerosis. 22 (10): 1349–58. doi:10.1177/1352458515616205. PMC 5015760. PMID 26564998.
- ^ a b Meyer-Moock, Sandra; Feng, You-Shan; Maeurer, Mathias; Dippel, Franz-Werner; Kohlmann, Thomas (2014-03-25). "Systematic literature review and validity evaluation of the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) and the Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite (MSFC) in patients with multiple sclerosis". BMC Neurology. 14: 58. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-14-58. ISSN 1471-2377. PMC 3986942. PMID 24666846.
- ^ a b Validity of Outcome Measures. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. May 2018.
