North Macedonia: Difference between revisions
Hellas 69 69 (talk | contribs) |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Altered title. Added work. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Nail123Real | #UCB_webform 1/3 |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{short description|Country in Southeast Europe}} |
||
{{About|the modern country||Macedonia (disambiguation)}} |
|||
<!-- NOTE TO EDITORS: DO NOT MODIFY THE COUNTRY NAMES USED IN THE INFOBOX BELOW WITHOUT FIRST DISCUSSING YOUR CHANGES ON THE DISCUSSION PAGE. FAILURE TO DO SO WILL RESULT IN YOUR EDITING PRIVILEGES BEING BLOCKED IMMEDIATELY WITHOUT ANY FURTHER WARNING. --><!-- BEGIN INFOBOX -->{{Infobox_Country| |
|||
{{pp-move}} |
|||
|native_name = {{lang|mk|''Република Македонија<br>Republika Makedonija''}} |
|||
{{pp|small=y}} |
|||
|conventional_long_name = Republic of Macedonia |
|||
{{Use British English|date=July 2022}} |
|||
|common_name = the Republic of Macedonia |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=May 2022}} |
|||
|image_flag = Flag of Macedonia.svg |
|||
{{Infobox country |
|||
|image_coat = Grb.gif |
|||
| conventional_long_name = Republic of North Macedonia |
|||
|image_map = LocationMacedonia.png |
|||
| common_name = North Macedonia |
|||
|national_motto = {{lang|mk|Слобода или смрт}}<br>([[Transliteration]]: {{lang|mk|''Sloboda ili smrt''}})<br>({{lang-en|Freedom or death}}) |
|||
| native_name = {{nowrap|{{native name|mk|Република Северна Македонија<wbr/>}}}}<br />{{nowrap|{{native name|sq|Republika e Maqedonisë së Veriut<wbr/>}}}} |
|||
|national_anthem = {{lang|mk|Денес Над Македонија}}<br>([[Transliteration]]: {{lang|mk|''Denes Nad Makedonija''}})<br>({{lang-en|[[Today over Macedonia]]}}) |
|||
| image_flag = Flag of North Macedonia.svg |
|||
|official_languages = [[Macedonian language|Macedonian]], [[Albanian language|Albanian]]<sup>1</sup> |
|||
| image_coat = Coat of arms of North Macedonia.svg |
|||
|capital = [[Skopje]] |
|||
| symbol_type = National emblem |
|||
| |
|||
| national_motto = |
|||
|latd=42 |latm=0 |latNS=N |longd=21 |longm=26 |longEW=E | |
|||
| national_anthem = {{nowrap|{{native name|mk|[[Denes nad Makedonija|Денес над Македонија]]|italics=no|nolink=yes}}}}<br />"Today over Macedonia"{{parabr}}{{center|[[File:Macedonia's national anthem (instrumental).ogg]]}} |
|||
|largest_city = [[Skopje]] |
|||
| image_map = Location Macedonia Europe.png |
|||
|government_type = [[Parliamentary democracy|Parliamentary]] [[republic]] |
|||
| map_caption = {{map caption|location_color=green|region=Europe|region_color=dark grey|legend=Location Macedonia Europe.png}} |
|||
|leader_title1 = [[President of the Republic of Macedonia|President]] |
|||
| capital = [[Skopje]] |
|||
|leader_title2 = [[Prime Minister of the Republic of Macedonia|Prime Minister]] |
|||
| religion_year = [[2021 North Macedonia census|2021]]<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/2022/2.1.22.10-mk-en.pdf/ |title=Попис на населението, домаќинствата и становите во Република Северна Македонија, 2021 – прв сет на податоци |access-date=7 July 2022 |archive-date=31 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220331074832/https://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/2022/2.1.22.10-mk-en.pdf }}</ref> |
|||
|leader_name1 = [[Branko Crvenkovski]] |
|||
| religion = {{unbulleted list |
|||
|leader_name2 = [[Nikola Gruevski]] |
|||
| 60.4% [[Christianity in North Macedonia|Christianity]] |
|||
|area_rank = 148th |
|||
| —46.1% [[Macedonian Orthodox Church – Ohrid Archbishopric|Eastern Orthodoxy]] |
|||
|area_magnitude = 1 E10 |
|||
| —14.3% Other [[Christian]] |
|||
|area= 25,333 |
|||
| 32.2% [[Islam in North Macedonia|Islam]] |
|||
|areami²=9,779 <!-- Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]] --> |
|||
| 0.1% [[Irreligion|No religion]] |
|||
|percent_water = 1.9% |
|||
| 0.1% [[Religion in North Macedonia|Other]] |
|||
|population_estimate = 2,034,000 |
|||
| 7.2% Data taken from administrative sources |
|||
|population_estimate_year = 2005 |
|||
|population_estimate_rank = 143rd |
|||
|population_census = |
|||
|population_census_year = |
|||
|population_density = 79 |
|||
|population_densitymi² = 205 <!-- Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]] --> |
|||
|population_density_rank = 110th |
|||
|GDP_PPP_year= 2005 |
|||
|GDP_PPP = $15.78 billion |
|||
|GDP_PPP_rank = 121st |
|||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = $7,645 |
|||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 80th |
|||
|sovereignty_type = [[History of the Republic of Macedonia#1990s|Independence]] |
|||
|sovereignty_note = From [[Yugoslavia]] |
|||
|established_event1 = Declared |
|||
|established_date1 = [[September 8]], [[1991]] |
|||
|HDI_year = 2003 |
|||
|HDI = 0.797 |
|||
|HDI_rank = 59th |
|||
|HDI_category = <font color="#FFCC00">medium</font> |
|||
|currency = [[Macedonian denar]] |
|||
|currency_code = MKD |
|||
|country_code = |
|||
|time_zone = [[Central European Time|CET]] |
|||
|utc_offset = +1 |
|||
|time_zone_DST = [[Central European Summer Time|CEST]] |
|||
|utc_offset_DST = +2 |
|||
|cctld = [[.mk]] |
|||
|calling_code = 389 |
|||
|footnotes = <sup>1</sup>[[Macedonian language|Macedonian]] is designated as the primary official language. As of June 2002, any language spoken by at least 20% of the population is also an official language - at present, only [[Albanian language|Albanian]] fulfils this requirement - but it can only be used as prescribed by law (e.g., issuing official documents, when communicating with government offices, in municipal self-government) and always in addition to Macedonian in [[Cyrillic alphabet|Cyrillic]]. In communities where over 20% of the population speak another language, that language can be used as a municipal official language along with Macedonian and any other official languages; such languages include [[Turkish language|Turkish]], [[Serbian language|Serbian]], [[Romany language|Romany]] and [[Aromanian language|Aromanian]]. |
|||
}}<!-- END INFOBOX --> |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''Republic of Macedonia''' ({{lang-mk|Република Македонија}} ''Republika Makedonija'', {{lang-sq|Republika e Maqedonisë}}), often referred to as '''Macedonia''', is an independent state on the [[Balkans|Balkan peninsula]] in southeastern [[Europe]]. This [[landlocked]] country borders [[Serbia]] to the north, [[Albania]] to the west, [[Greece]] to the south, and [[Bulgaria]] to the east. As the result of a [[Foreign relations of the Republic of Macedonia#Greece|naming dispute with Greece]], in 1993 it was admitted to the [[United Nations]] under the provisional name '''the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia''' ('''FYROM'''), pending resolution of the dispute.<ref>[http://www.un.org/documents/ga/res/47/a47r225.htm United Nations Resolution 225 (1993)]</ref> |
|||
| coordinates = {{Coord|42|0|N|21|26|E|type:city}} |
|||
| largest_city = capital |
|||
| official_languages = {{plainlist| |
|||
* {{nowrap|[[Macedonian language|Macedonian]]}}{{efn|name="language1"}} |
|||
* {{nowrap|[[Albanian language|Albanian]]}}{{efn|name="language2"}}}} |
|||
| languages2_type = {{ubl|Official regional languages}} |
|||
| languages2 = {{ubl|[[Turkish language|Turkish]]<ref name="auto1">{{cite web |url=http://www.stat.gov.mk/Publikacii/knigaX.pdf |title=Census final data |date=2002 |website=stat.gov.mk}}</ref>|[[Romani language|Romani]]|[[Serbian language|Serbian]]|[[Bosnian language|Bosnian]]|[[Aromanian language|Aromanian]]}} |
|||
| ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list |
|||
| 58.4% [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonians]] |
|||
| 24.3% [[Albanians in North Macedonia|Albanians]] |
|||
| 3.9% [[Turks in North Macedonia|Turks]] |
|||
| 2.5% [[Romani people in North Macedonia|Roma]] |
|||
| 1.3% [[Serbs in North Macedonia|Serbs]] |
|||
| 0.9% [[Bosniaks in North Macedonia|Bosniaks]] |
|||
| 0.5% [[Aromanians in North Macedonia|Aromanians]] (including [[Megleno-Romanians]]) |
|||
| 1.0% [[Demographics of North Macedonia|Other]] |
|||
| {{nowrap| 7.2% Did not participate}} |
|||
}} |
|||
| ethnic_groups_year = [[2021 North Macedonia census|2021]]<ref name="2021 census"/> |
|||
| demonym = {{hlist|Macedonian}} |
|||
| government_type = [[Unitary parliamentary republic]] |
|||
| leader_title1 = [[President of North Macedonia|President]] |
|||
| leader_name1 = [[Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova]] |
|||
| leader_title2 = [[Prime Minister of North Macedonia|Prime Minister]] |
|||
| leader_name2 = [[Hristijan Mickoski]] |
|||
| leader_title3 = [[List of Presidents of the Assembly of the Republic of North Macedonia|Chairman of the Assembly]] |
|||
| leader_name3 = [[Afrim Gashi]] |
|||
| legislature = [[Assembly of North Macedonia|Assembly]] |
|||
| sovereignty_type = Establishment history |
|||
| established_event1 = [[Socialist Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
| established_date1 = 2 August 1944 |
|||
| established_event2 = [[1991 Macedonian independence referendum|Independence referendum]] |
|||
| established_date2 = 8 September 1991 |
|||
| area_km2 = 25,436<ref name="SSO">[https://www.stat.gov.mk/OblastOpsto_en.aspx?id=1 Territorial Units]. ''State Statistical Office''.</ref> |
|||
| area_rank = 145th <!-- Area rank should match [[List of countries and dependencies by area]] --> |
|||
| area_sq_mi = 9,928 <!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]]--> |
|||
| percent_water = 1.1 |
|||
| population_census = {{decrease}} 1,836,713<ref name="2021 census">{{Cite web |title=State Statistical Office – News release: Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of North Macedonia, 2021 – first dataset ,2021 |url=https://www.stat.gov.mk/PrikaziSoopstenie_en.aspx?rbrtxt=146 |access-date=30 March 2022 |website=Stat.gov.mk}}</ref> |
|||
| population_estimate_year = 2019 |
|||
| population_estimate_rank = 147th |
|||
| population_census_year = 2021 |
|||
| population_density_km2 = 71.43 |
|||
| population_density_sq_mi = 185.0 <!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]]--> |
|||
| population_density_rank = 122nd |
|||
| GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $44.055 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.MK">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/October/weo-report?c=962,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2020&ey=2028&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2023 Edition. (MK) |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |website=IMF.org |date=10 October 2023 |access-date=13 October 2023}}</ref> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_year = 2023 |
|||
| GDP_PPP_rank = 130th |
|||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $21,391<ref name="IMFWEO.MK" /> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 75th |
|||
| GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $15.801 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.MK" /> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2023 |
|||
| GDP_nominal_rank = 143rd |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $7,672<ref name="IMFWEO.MK" /> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 90th |
|||
| Gini = 30.7 <!--number only--> |
|||
| Gini_year = 2019 |
|||
| Gini_change = decrease |
|||
| Gini_ref = <ref>{{cite web |title=Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey |url=https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/tessi190/default/table?lang=en|website=ec.europa.eu/eurostat |publisher=[[Eurostat]] |access-date=12 August 2021}}</ref> |
|||
| Gini_rank = |
|||
| HDI = 0.765 |
|||
| HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> |
|||
| HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| HDI_ref = <ref name="UNHDR">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2023/24|language=en|publisher=[[United Nations Development Programme]]|date=13 March 2024|access-date=13 March 2024}}</ref> |
|||
| HDI_rank = 83rd |
|||
| currency = [[Macedonian denar]] |
|||
| currency_code = MKD |
|||
| time_zone = [[Central European Time|CET]] |
|||
| utc_offset = +1 |
|||
| utc_offset_DST = +2 |
|||
| time_zone_DST = [[Central European Summer Time|CEST]] |
|||
| calling_code = [[Telephone numbers in North Macedonia|+389]] |
|||
| cctld = {{unbulleted list |[[.mk]] |[[.мкд]]}} |
|||
}} |
|||
'''North Macedonia''' ({{IPAc-en|ˌ|m|æ|s|ɪ|ˈ|d|oʊ|n|i|ə}} {{respell|MASS|ih|DOH|nee|ə}}),{{efn|{{langx|mk|Северна Македонија|Severna Makedonija}}, {{IPA-mk|ˈsɛvɛrna makɛˈdɔnija|pron}}; {{langx|sq|Maqedonia e Veriut}}, {{IPA-sq|macɛˈdɔnja ɛ vɛɾˈjut|pron}}}} officially the '''Republic of North Macedonia''',{{efn|{{Langx|mk|Република Северна Македонија|Republika Severna Makedonija}}, {{IPA-mk|rɛˈpublika ˈsɛvɛrna makɛˈdɔnija|pron}}; {{langx|sq|Republika e Maqedonisë së Veriut}}, {{IPA-sq|rɛˈpublika ɛ macɛˈdɔnis sə vɛɾˈjut|pron}}}} is a [[landlocked country]] in [[Southeast Europe]]. It shares land borders with [[Greece]] to the south, [[Albania]] to the west, [[Bulgaria]] to the east, [[Kosovo]]{{efn|name="Kosovo"}} to the northwest and [[Serbia]] to the north.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.mfa.gov.mk/default1.aspx?ItemID=288 |title=Basic Facts |website=North Macedonia, Ministry of Foreign Affairs |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081116102337/http://www.mfa.gov.mk/default1.aspx?ItemID=288 |archive-date= 16 November 2008 }}</ref> It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical [[Macedonia (region)|region of Macedonia]]. [[Skopje]], the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's population of 1.83 million. The majority of the residents are ethnic [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonians]], a [[South Slavs|South Slavic people]]. [[Albanians in North Macedonia|Albanians]] form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by [[Turks in North Macedonia|Turks]], [[Romani people in North Macedonia|Roma]], [[Serbs in North Macedonia|Serbs]], [[Bosniaks in North Macedonia|Bosniaks]], [[Aromanians in North Macedonia|Aromanians]] and a few other minorities. |
|||
The capital is [[Skopje]], with more than 600,000 inhabitants. It has a number of smaller cities, notably [[Bitola]], [[Prilep]], [[Tetovo]], [[Kumanovo]], [[Ohrid]], [[Veles (city)|Veles]], [[Štip]], and [[Strumica]]. It has more than 50 natural and artificial lakes and sixteen mountains higher than 2,000 meters (6,550 {{ft}}) above [[sea level]]. |
|||
The region's history begins with the [[Paeonia (kingdom)|kingdom of Paeonia]]. In the late sixth century BC, the area was subjugated by the Persian [[Achaemenid Empire]], then incorporated into the [[Macedonia (ancient kingdom)|Kingdom of Macedonia]] in the fourth century BC. The [[Roman Republic]] conquered the region in the second century BC and made it part of its larger province of [[Macedonia (Roman province)|Macedonia]]. The area remained part of the [[Byzantine Empire]], but was often raided and settled by [[Early Slavs|Slavic tribes]] beginning in the sixth century of the Christian era. Following [[Byzantine–Bulgarian wars|centuries of contention]] between the [[First Bulgarian Empire|Bulgarian]], Byzantine, and [[Serbian Empire]]s, it was part of the [[Ottoman Empire]] from the mid-14th until the early 20th century, when, following the [[Balkan Wars]] of 1912 and 1913, the modern territory of North Macedonia came under [[Kingdom of Serbia|Serbian]] rule. |
|||
The country is a member of the [[United Nations|UN]] and the [[Council of Europe]] and an associate member of [[La Francophonie]], the [[World Trade Organization]] (WTO), the [[Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe]]. Since December 2005 it is also a candidate for joining the [[European Union]] and has applied for [[NATO]] membership. |
|||
During the [[First World War]], the territory was ruled by Bulgaria. After the end of the war, it returned to Serbian rule as part of the newly formed [[Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes]]. During the [[World War II in Yugoslav Macedonia|Second World War]], it was again ruled by Bulgaria; and in 1945 it was established as a [[Socialist Republic of Macedonia|constituent state]] of [[Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia|communist Yugoslavia]], which it remained until [[1991 Macedonian independence referendum|its peaceful secession in 1991]]. The country became a member of the [[United Nations]] (UN) in 1993, but as a result of a [[Macedonia naming dispute|dispute with Greece]] over the [[Macedonia (terminology)|name "Macedonia"]], it was admitted under the provisional description "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (abbreviated as "FYR Macedonia" or "FYROM"). In 2018, the dispute was [[Prespa Agreement|resolved with an agreement]] that the country should rename itself "Republic of North Macedonia". This renaming came into effect in early 2019. |
|||
North Macedonia is also a member of [[NATO]], the [[Council of Europe]], the [[World Bank]], [[Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe|OSCE]], [[Central European Free Trade Agreement|CEFTA]], [[Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation|BSEC]] and the [[World Trade Organization|WTO]]. Since 2005, it has also been a [[Accession of North Macedonia to the European Union|candidate for joining the European Union]]. North Macedonia is an [[List of countries by GNI (nominal) per capita#Upper-middle-income group|upper-middle-income country]] according to the [[World Bank]]'s definitions<ref>{{cite web |title=The World Bank in North Macedonia |url=https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/northmacedonia |access-date=7 July 2022 |publisher=[[World Bank]]}}</ref> and has undergone considerable economic reform since its independence in developing an [[open economy]]. It is a [[developing country]], ranked 82nd on the [[Human Development Index]]; and provides [[social security]], a [[Health in North Macedonia|universal health care]] system, and free [[Education in North Macedonia|primary and secondary education]] to its citizens. |
|||
=={{anchor|Names|Etymology|Names and etymology}}Names and etymology==<!--linked--> |
|||
{{See also|Macedonia (terminology)|Macedonia naming dispute}} |
|||
<!--Avoid duplicating material here and in the "Naming dispute" subsection of the "Politics" section below--> |
|||
The state's name derives from the [[Ancient Greek language|Greek]] word {{wikt-lang|grc|Μακεδονία}} ({{lang|grc-Latn|Makedonía}}),<ref>[https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3D%2364599 Μακεδονία], Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Perseus</ref><ref name="Macedonia">[http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=Macedonia Macedonia], Online Etymology Dictionary</ref> a [[Macedon|kingdom]] (later, [[Macedonia (region)|region]]) named after the [[ancient Macedonians]]. Their name, {{wikt-lang|grc|Μακεδόνες}} ({{lang|grc-Latn|Makedónes}}), ultimately derives from the [[ancient Greek]] adjective {{lang|grc|[[Makednos|μακεδνός]]}} ({{lang|grc-Latn|makednós}}), meaning 'tall' or 'taper',<ref>[https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3D%2364596 μακεδνός], Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Perseus</ref> which shares the same root as the adjective {{wikt-lang|grc|μακρός}} ({{lang|grc-Latn|makrós}}, 'long, tall, high') in ancient Greek.<ref>[https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Dmakro%2Fs1 μακρός], Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Perseus</ref> The name is believed to have originally meant either 'highlanders' or 'the tall ones', possibly descriptive of the [[Ancient Macedonians|people]].<ref name="Macedonia"/><ref>[[Eugene N. Borza]], ''Makedonika'', Regina Books, {{ISBN|0-941690-65-2}}, p. 114: The "highlanders" or "Makedones" of the mountainous regions of western Macedonia are derived from northwest Greek stock; they were akin both to those who at an earlier time may have migrated south to become the historical "Dorians".</ref><ref>Nigel Guy Wilson (2009). ''Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece'', Routledge, p. 439: The latest archaeological findings have confirmed that Macedonia took its name from a tribe of tall, Greek-speaking people, the Makednoi.</ref> According to linguist [[Robert S. P. Beekes]], both terms are of [[pre-Greek substrate]] origin and cannot be explained in terms of Indo-European morphology.<ref>{{citation |first=Robert |last=Beekes |author-link=Robert S. P. Beekes |title=Etymological Dictionary of Greek |volume=II |page=894 |publisher=Brill |year=2010 |location=Leiden, Boston}}</ref> According to linguist Filip De Decker, Beekes's arguments are insufficiently supported.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=De Decker |first1=Filip |title=AN ETYMOLOGICAL CASE STUDY ON THE AND VOCABULARY IN ROBERT BEEKES'S NEW ETYMOLOGICAL DICTIONARY OF GREEK |journal=Studia Linguistica Universitatis Iagellonicae Cracoviensis |date=2016 |volume=133 |issue=2 |doi=10.4467/20834624SL.16.006.5152| issn = 1897-1059 }}</ref> |
|||
Apart from the [[theme (Byzantine district)|theme]] of [[Macedonia (theme)|Macedonia]], the name "Macedonia" was largely forgotten as a geographical denomination through the [[Macedonia (region)#Medieval Macedonia|Byzantine]] and [[North Macedonia under the Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] eras but was revived by [[Bulgarian irredentism|Bulgarian]] and [[Greek nationalism|Greek]] nationalist movements from the early 19th century onwards.<ref>"What is often overlooked is how [[Bulgarians]] and [[Greeks]] collaborated unknowingly from the middle decades of the 19th century onward in breathing new life into the geographical name Macedonia, which was all but forgotten during the [[Macedonia (region)#Medieval Macedonia|Byzantine]] and [[North Macedonia under the Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] periods. In the late Ottoman period, "Macedonia" as such did not exist as an administrative unit in the empire... [[Greek nationalism]], fixated on the continuity between ancient and modern Hellenes, was keen to project the name Macedonia as a way to assert the [[Macedonia (region)|Greek historical character of the area]]. In 1845, for instance, [[Alexander the Great|the story of Alexander]] was published in a Slavo-Macedonian dialect scripted in Greek characters... For their part, [[Bulgarian irredentism|Bulgarian nationalists]] readily accepted Macedonia as a regional denomination... Macedonia had become one of the "historic" Bulgarian lands... and "Macedonian Bulgarian" turned into a standard phrase." Dimitar Bechev, Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia, Scarecrow Press, 2009, {{ISBN|0-8108-6295-6}}, Introduction, p. VII.</ref><ref>"In the early 19th c. the modern Greeks with their Western-derived obsession with antiquity played a crucial role in reviving the classical name 'Macedonia' in the popular consciousness of the Balkan peoples. For a thousand years before that the name 'Macedonia' had meant different things for Westerners and Balkan Christians: for Westerners it always denoted the territories of the ancient Macedonians, but for the Greeks and all other Balkan Christians the name 'Macedonia' – if at all used – covered the territories of the former Byzantine theme 'Macedonia', situated between Adrianople (Edrine) and the river Nestos (Mesta) in classical and present-day Thrace. The central and northern parts of present-day 'geographic Macedonia' were traditionally called either 'Bulgaria' and 'Lower Moesia', but within a generation after Greek independence (gained in 1830) these names were replaced by 'Macedonia' in the minds of both Greeks and non-Greeks." Drezov K. (1999) Macedonian identity: an overview of the major claims. In: Pettifer J. (eds) The New Macedonian Question. St Antony's Series. Palgrave Macmillan, London, {{ISBN|0-230-53579-8}}, pp. 50–51.</ref><ref>"In 1813 Macedonia did not exist. A century later, it had become a hotly contested nationalist cause, a battlefield, and an obsession. What led to this dramatic transformation was modernity: a chilly wind of West European provenance that propelled to the Balkans concepts that few in the region understood, wanted or cared about. Among these, the idea of nationalism was the most potent, and the most lethal. Before the 1850s, Macedonia was a poverty-stricken province of the Ottoman Empire, where an Orthodox Christian and mostly peasant population speaking a variety of Slavonic idioms, Greek, or Vlach, was trying to eke out a modest living, and protect it from rapacious brigands and a decaying Ottoman administrative system. Religion was the only collective identity that most of them could make sense of, for ethnicity and language played little role in shaping their loyalties. But the winds of change quickly gathered momentum, and eventually shattered that multi-ethnic community, producing a 'Greek', or a 'Bulgarian', out of a 'Christian'." D. Livanios' review of Vemund Aarbakke, Ethnic Rivalry and the Quest for Macedonia, 1870–1913 in The Slavonic and East European Review, Vol. 83, No. 1 (Jan. 2005), pp. 141–142</ref> It was revived only in middle of the century, with the [[rise of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire]].<ref>''The ancient name 'Macedonia' disappeared during the period of Ottoman rule and was only restored in the nineteenth century originally as geographical term.'' The Oxford Handbook of the History of Nationalism, John Breuilly, Oxford University Press, 2013, {{ISBN|0-19-920919-7}}, p. 192.</ref><ref>"The region was not called "Macedonia" by the Ottomans, and the name "Macedonia" gained currency together with the ascendance of rival nationalism." Collective Memory, National Identity, and Ethnic Conflict: Greece, Bulgaria, and the Macedonian Question, Victor Roudometof, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2002, {{ISBN|0-275-97648-3}}, p. 89.</ref><ref>"The Greeks were amongst the first to define these lands since the beginning of the 19th century. For educated Greeks, Macedonia was the historical Greek land of kings Philip and Alexander the Great." John S. Koliopoulos, Thanos M. Veremis, Modern Greece: A History since 1821. A New History of Modern Europe, John Wiley & Sons, 2009, {{ISBN|1-4443-1483-1}}, p. 48.</ref> In the early 20th century the region was already a national cause, contested among Bulgarian, Greek, and [[Serbian nationalism|Serbian]] nationalists. During the [[interwar period]] the use of the name "Macedonia" was prohibited in the [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]], due to the implemented policy of [[Serbianisation]] of the local Slavic-speakers.<ref>Donald Bloxham, The Final Solution: A Genocide, OUP Oxford, 2009, {{ISBN|0-19-955033-6}}, p. 65.</ref><ref>Chris Kostov, Contested Ethnic Identity: The Case of Macedonian Immigrants in Toronto, Peter Lang, 2010, {{ISBN|3-0343-0196-0}}, p. 76.</ref> The name "Macedonia" was adopted officially for the first time at the end of the Second World War by the new [[Socialist Republic of Macedonia]], which became one of the six constituent countries of the [[Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]]. After the [[breakup of Yugoslavia]], this federal entity declared independence and changed its official name to the "Republic of Macedonia" in 1991. Prior to June 2018, the use of the name "Macedonia" was [[Macedonia naming dispute|disputed between Greece and the then-Republic of Macedonia]]. |
|||
The [[Prespa agreement]] of June 2018 saw the country change its name to the "Republic of North Macedonia" eight months later.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2018/06/greece-macedonia-sign-agreement-change-180617074429644.html |title=Greece and Macedonia sign agreement on name change |work=Al Jazeera |date=17 Jun 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2018/06/17/world/europe/greece-macedonia-name-dispute.html |title=Macedonia and Greece Sign Historic Deal on Name Change |last=Kitsantonis |first=Niki |date=17 June 2018 |work=The New York Times}}</ref> A non-binding<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cp24.com/world/macedonia-referendum-approves-name-change-but-turnout-low-1.4115262 |title=Macedonia: Referendum approves name change, but turnout low |first1=Konstantin |last1=Testorides |first2=Elena |last2=Becatoros |date=30 September 2018}}</ref> [[2018 Macedonian referendum|national referendum]] on the matter passed with 90% approval but did not reach the required 50% turnout amidst a boycott, leaving the final decision with parliament to ratify the result.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-45704860 |title=PM to press on with Macedonia name change |date=1 October 2018 |work=BBC}}</ref> Parliament approved of the name change on 19 October, reaching the required two-thirds majority needed to enact constitutional changes.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2018/oct/20/welcome-to-north-macedonia-parliament-votes-for-name-change |title=Welcome to North Macedonia: parliament votes for name change |last=Agencies |date=20 October 2018 |website=the Guardian}}</ref> The vote to amend the constitution and change the name of the country passed on 11 January 2019 in favour of the amendment.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-macedonia-name-parliament-idUSKCN1P5238 |title=Macedonia parliament agrees to change country's name |last=Casule |first=Kole |date=11 January 2019 |website=Reuters |access-date=17 August 2019}}</ref> The amendment entered into force on 12 February, following the ratification of the Prespa agreement and the Protocol on the Accession of North Macedonia to NATO by the [[Greek Parliament]].<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-47002865 |title=Greece vote settles 27-year Macedonia row |date=25 January 2019 |work=BBC|access-date=25 January 2019}}</ref> Despite the renaming, the country is unofficially referred to as "Macedonia" by most of its citizens and most local media outlets.{{citation needed|date=April 2020}} |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
{{ |
{{Main|History of North Macedonia}} |
||
{{See also|Historiography in North Macedonia}} |
|||
The lands governed by the Republic of Macedonia were previously the southernmost part of [[Yugoslavia]]. Its current borders were fixed shortly after [[World War II]] when the government of [[Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia|Yugoslavia]] established the ''Socialist Republic of Macedonia'', recognizing a [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonian]] ethnicity as distinct from the Serbs and as a separate nation within Yugoslavia. |
|||
=== Early history === |
|||
In the past, these lands came under a number of ancient states and former empires; [[Paionia]], the kingdom of ancient [[Macedon]] (which gave its name to the whole Macedonian region). It must be noted though, that the ancient kingdom of [[Macedon]] was centered in what is known today as [[Macedonia (Greece)|Greek Macedonia]] and its boundaries did not span north of the town [[Bitola]][http://www.cogsci.indiana.edu/farg/harry/geo/maced.htm].Later, in 146 BC, the area became part of the [[Roman Empire|Roman]] and [[Byzantine Empire|Byzantine]] empires, becoming Christian in the 3rd and 4th century. |
|||
{{Main|Paeonia (kingdom)|Macedonia (ancient kingdom)|Kingdom of Dardania|Roman Empire}} |
|||
[[File:PreMacedon.png|thumb|left|Tribal ethnes in the Southern Balkans prior to the expansion of Macedon]] |
|||
North Macedonia geographically roughly corresponds to the ancient [[Paeonia (kingdom)|kingdom of Paeonia]],<ref name=waterfield19>{{cite book |last1=Waterfield |first1=Robin |title=The Library, Books 16–20: Philip II, Alexander the Great, and the Successors |date=2019 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-875988-1 |page=428 |quote=Paeonia is roughly equivalent to the country currently known as the Republic of North Macedonia (the former FYROM).}}</ref><ref name=ovidbsl>{{cite book |author1=Ovid |editor1-last=Green |editor1-first=Peter |title=The Poems of Exile: Tristia and the Black Sea Letters |date=2005 |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-24260-9 |page=[https://archive.org/details/poemsofexiletris00ovid/page/319 319] |quote=Ovid was lax in his geography, not least over Paeonia (in fact roughly coextensive with the present Slav Republic of Macedonia). |url=https://archive.org/details/poemsofexiletris00ovid/page/319 }}</ref><ref name=roisman10>{{cite book |last1=Roisman |first1=Joseph |last2=Worthington |first2=Ian |title=A Companion to Ancient Macedonia |publisher=John Wiley and Sons |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-4051-7936-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lkYFVJ3U-BIC |page=13 |access-date=10 February 2016}}</ref><ref name=reames08>{{cite book |last1=Reames |first1=Jeanne |last2=Howe |first2=Timothy |title=Macedonian Legacies: Studies in Ancient Macedonian History and Culture in Honor of Eugene N. Borza |date=2008 |publisher=Regina Books |isbn=978-1-930053-56-4 |page=239 |quote=Having just conquered Paeonia (roughly where the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia is today).}}</ref><ref name=peshkopia15>{{cite book |last=Peshkopia |first=Ridvan |title=Conditioning Democratization: Institutional Reforms and EU Membership Conditionality in Albania and Macedonia |date=2015 |publisher=Anthem Press |isbn=978-0-85728-325-2 |page=189 |quote=Indeed, the territory of the Republic of Macedonia encompasses little of the ancient kingdom of Macedon, which, in most part, overlaps with the current region of the contemporary Greece, but the name Macedonia "flowed" northward with the creation of Roman region of Macedonia, after the Romans occupied Greece in 168 BC. Besides the former kingdom of Macedon, the Roman region included the territories of Paeonia, where the contemporary FYR Macedonia rests.}}</ref> which was located immediately north of the ancient [[Macedonia (ancient kingdom)|kingdom of Macedonia]].<ref name=strabo>Strabo, ''Geography'', [https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0239%3Abook%3D7%3Achapter%3Dfragments%3Asection%3D4 Book 7, Frg. 4:]</ref> Paeonia was inhabited by the [[Paeonians]], whilst the northwest was inhabited by the [[Dardani]] and the southwest by tribes known historically as the [[Enchelei|Enchelae]] both are considered [[Illyrian tribes|Illyrian]] and [[Pelagones]], and [[Lynkestis|Lyncestae]] which are generally regarded as [[Molossians|Molossian]] tribes of the northwestern [[Ancient Greece|Greek]] group.<ref name=willkes96>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4Nv6SPRKqs8C&pg=PA170 |title=The Illyrians |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-631-19807-9 |page=49 |last=Willkes |first=John |access-date=10 February 2016}}</ref><ref name=sealey76>{{cite book |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofgreekci0000seal |url-access=registration |quote=illyrian lychnitis. |last=Sealey |first=Raphael |title=A history of the Greek city states, ca. 700–338 B.C. |publisher=University of California Press |page=[https://archive.org/details/historyofgreekci0000seal/page/442 442] |year=1976 |isbn=978-0-520-03177-7}}</ref><ref name=evans07>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4CpYot4N2PUC&pg=RA1-PA13 |title=Macedonia |publisher=Bradt Travel Guides |last=Evans |first=Thammy |year=2007 |page=13 |isbn=978-1-84162-186-9}}</ref><ref name=borza92>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=614pd07OtfQC&pg=PA99 |last=Borza |first=Eugene N. |title=In the shadow of Olympus: the emergence of Macedon |publisher=Princeton University Press |pages=74–75 |isbn=978-0-691-00880-6 |year=1992}}</ref><ref name=lewis94>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vx251bK988gC&pg=RA6-PA750 |editor=Lewis, D.M. |display-editors=et al |title=The Cambridge ancient history: The fourth century B.C. |publisher=Cambridge University Press |pages=723–724 |isbn=978-0-521-23348-4 |year=1994 |access-date=10 February 2016}}</ref><ref name=caman3>The Cambridge Ancient History Volume 3, Part 3: The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman and N. G. L. Hammond, 1982, {{ISBN|0-521-23447-6}}, p. 284.</ref> The headwaters of the [[Axios river]] are mentioned by [[Homer]] as the home of the [[Paeonians]] allies of [[Troy]].<ref name=perseus>{{Cite web|url=http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/invalidquery.jsp?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0073:entry=entry=|title=No document found|website=Perseus.tufts.edu}}</ref> |
|||
In the late 6th century AD Byzantine control over the area disintegrated, and the region was submerged by the arrival from the north of pagan [[Sclaveni|Slavic]] tribes, that assimilated the preexisting Illyrian,Thracian, Greek and Latin-speaking inhabitants. In the 9th century the territory converted to Christianity through the evangelizing work of the [[Saints Cyril and Methodius]] and their disciples. In the same century the [[First Bulgarian Empire]] assumed control of most of the area. |
|||
In the late 6th century BC, the [[Achaemenid Persia]]ns under [[Darius the Great]] conquered the [[Paeonia (kingdom)|Paeonians]], incorporating what is today North Macedonia within their vast territories.{{sfn|Howe|Reames|2008|p=239}}{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2011|pp=135–138, 342–345}}<ref name=livius>{{cite web |url=https://www.livius.org/ia-in/influence/influence02.html |title=Persian influence on Greece (2) |access-date=17 December 2014 |archive-date=24 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200724223725/https://www.livius.org/ia-in/influence/influence02.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> Following the loss in the [[Second Persian invasion of Greece]] in 479 BC, the Persians eventually withdrew from their European territories, including from what is today North Macedonia. |
|||
The Byzantines reassumed full control of the [[Balkans]] by the early 11th century, but by the late 12th century Byzantine decline brought to the birth of the [[Second Bulgarian Empire]]. The empire early met with political difficulties, and [[Macedonia (region)|Macedonia]] fell once again in Byzantine control, and in the 14th century it became part of the [[Serbian Empire]], only to pass a few decades later in [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] hands, under whose rule it was to remain for five centuries. |
|||
[[File:Ancientbitola.jpg|thumb|[[Heraclea Lyncestis]], a city founded by [[Philip II of Macedon]] in the 4th century BC; ruins of the Byzantine "Small Basilica"]] |
|||
Following the two [[Balkan wars]] of 1912 and 1913 and the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, the region of [[Macedonia (region)|Macedonia]] was divided between [[Greece]], [[Bulgaria]] and [[Serbia]]. The territory of the present-day Republic of Macedonia was then named ''{{lang|sr|Južna Srbija}}'', "[[Stara Srbija|Southern Serbia]]". After the [[First World War]] Serbia joined the newly formed [[Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes]]. In 1929, the kingdom was officially renamed the [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]] and divided into provinces called [[banovina]]s. So called "Southern Serbia", including all of what is now the Republic of Macedonia, became a part of the [[Vardar Banovina]]. |
|||
[[Philip II of Macedon]] absorbed<ref name="Rome page 75">Warfare in the ancient world: from the Bronze Age to the fall of Rome. By Stefan G. Chrissanthos, p. 75</ref> the regions of [[Upper Macedonia]] (Lynkestis and Pelagonia) and the southern part of Paeonia ([[Deuriopus]]) into the kingdom of Macedon in 356 BC.<ref name=poulton00>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ppbuavUZKEwC&pg=PA187 |author=Poulton, Hugh |title=Who are the Macedonians? |publisher=C. Hurst & Co. Publishers |page=14 |date= 2000 |isbn=978-1-85065-534-3}}</ref> Philip's son [[Alexander the Great]] conquered the remainder of the region and incorporated it in his [[Macedonia (ancient kingdom)|empire]], reaching as far north as [[Scupi]], but the city and the surrounding area remained part of [[Kingdom of Dardania|Dardania]].<ref name=nurigiani67>Macedonia yesterday and today Author Giorgio Nurigiani, Publisher Teleurope, 1967 p. 77.</ref> After the death of Alexander, [[Celtic settlement of Southeast Europe|Celtic]] armies began to bear down on the southern regions, threatening the kingdom of Macedon. In 310 BC, they attacked the area, but were defeated.<ref>Stipčević, Aleksandar (1977). The Illyrians. Translated by Stojana Čulić Burton. Park Ridge, New Jersey: Noyes Press. p. 44.</ref> |
|||
In 1941, Yugoslavia was occupied by the [[Axis Powers]] and the Vardar Banovina was divided between [[Bulgaria]] and [[Italy|Italian]]-occupied [[Albania]]. Harsh rule by the occupying forces encouraged many Macedonians to support the Communist [[Partisans (Yugoslavia)|Partisan]] resistance movement of [[Josip Broz Tito]]. After the end of the [[Second World War]], when Tito became Yugoslavia's president, the ''People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia'' was established. The ''People's Republic of Macedonia'' became one of the six republics of the Yugoslav federation. Following the federation's renaming as the [[Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]] in 1963, the People's Republic of Macedonia was likewise renamed, becoming the ''Socialist Republic of Macedonia''. It dropped the "Socialist" from its name in 1991 when it peacefully seceded from Yugoslavia. A few very minor changes to its border with Serbia were agreed upon to resolve problems with the demarcation line between the two countries. |
|||
[[Roman Empire|The Romans]] established the [[Macedonia (Roman province)|province of Macedonia]] in 146 BC. By the time of [[Diocletian]], the province had been subdivided between ''Macedonia Prima'' ("first Macedonia") on the south, encompassing most of the kingdom of Macedon, and ''Macedonia Salutaris'' (meaning "wholesome Macedonia", known also as ''Macedonia Secunda'', "second Macedonia") on the north, encompassing partially Dardania and the whole of Paeonia; most of the country's modern boundaries fell within the latter, with the city of [[Stobi]] as its capital.<ref name=roisman549>A Companion to Ancient Macedonia, By Joseph Roisman and Ian Worthington, p. 549</ref> Roman expansion brought the Scupi area under Roman rule in the time of [[Domitian]] (81–96 AD), and it fell within the Province of [[Moesia]].<ref name=britannica>{{cite encyclopedia |url=https://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9068124/Skopje |title= Scopje |encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica |access-date=6 June 2011}}</ref> Whilst [[Greek language|Greek]] remained the dominant language in the eastern part of the Roman empire, especially south of the [[Jireček Line]], Latin spread to some extent in Macedonia.<ref name=christides07>A. F. Christidis (2007). ''A History of Ancient Greek: From the Beginnings to Late Antiquity'', Cambridge University Press, p. 351: "Despite Roman domination, there was no retreat on the part of Greek tradition in the eastern part of the empire, and only in Macedonia did Latin spread in some extent".</ref> |
|||
The country officially celebrates [[8 September]] [[1991]] as Independence day, with regard to the referendum, endorsing independence from Yugoslavia, albeit legalizing participation in future union of the former states of Yugoslavia. The Republic of Macedonia remained at peace through the [[Yugoslav wars]] of the early 1990s but was destabilized by the [[Kosovo War]] in 1999, when an estimated 360,000 [[Albanians|ethnic Albanian]] refugees from Kosovo took refuge in the country. Although they departed shortly after the war, soon after, [[Macedonian NLA|Albanian radicals]] on both sides of the border took up arms in pursuit of autonomy or independence for the Albanian-populated areas of the Republic. A [[Macedonian War|short war]] was fought between government and ethnic Albanian rebels, mostly in the north and west of the country, in March–June 2001. This war ended with the intervention of a [[North Atlantic Treaty Organization|NATO]] ceasefire monitoring force. In the [[Ohrid Agreement]], the government agreed to devolve greater political power and cultural recognition to the Albanian minority. The Albanian side agreed to give up any separatist demands and to fully recognise all Macedonian institutions. In addition, according to this accord the NLA was to disarm and hand over their weapons to a NATO force. In 2005, Macedonia was officially recognized, under the name Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, as a [[European Union]] candidate state. |
|||
=== Medieval period === |
|||
Another confusion that has just occurred recently is the debate over Alexander the Great's heritage. He was Greek-Macedonian which was the people of the region at the time. The Slavic race that now occupies most of FYR Macedonia did not settle in the region until centuries after Alexander's demise. |
|||
{{Further|Sclaveni|Byzantine Empire|First Bulgarian Empire|Bulgaria (theme)|Serbian Empire|Ottoman Vardar Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:66-manasses-chronicle.jpg|thumb|upright|left|Miniature from the [[Constantine Manasses|Manasses Chronicle]], depicting the defeat of [[Samuel of Bulgaria|Samuil]] by [[Basil II]] and the return of his blinded soldiers]] |
|||
==Politics== |
|||
<!--Please add new information into relevant articles of the series--> |
|||
{{morepolitics|country=the Republic of Macedonia}} |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia is a [[parliamentary democracy]] with an executive government composed of a coalition of parties from the unicameral legislature ({{lang|mk|Собрание, ''Sobranie''}}) and an independent judicial branch with a constitutional court. The Assembly is made up of 120 seats and the members are elected every four years. |
|||
[[Early Slavs|Slavic tribes]] settled in the Balkan region including North Macedonia by the late 6th century AD. They were led by [[Pannonian Avars]].<ref name="Little2007">{{cite book|editor=Lester K. Little|title=Plague and the End of Antiquity: The Pandemic of 541–750|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DKhLOd6gGlAC|year=2007|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-84639-4|pages=15, 24, 116, 118, 125, 286–287}}</ref><ref>Wright, David Curtis (1997). "The Hsiung-Nu-Hun Equation Revisited". ''Eurasian Studies Yearbook''. 69: 77–112.</ref><ref name=bü>{{cite journal |author1=Ulf Büntgen |author2=Vladimir S. Myglan |author3=Fredrik Charpentier Ljungqvist |author4=Michael McCormick |author5=Nicola Di Cosmo |author6=Michael Sigl |author7=Johann Jungclaus |author8=Sebastian Wagner |author9=Paul J. Krusic |author10=Jan Esper |author11=Jed O. Kaplan |author12=Michiel A. C. de Vaan |author13=Jürg Luterbacher |author14=Lukas Wacker |author15=Willy Tegel |author16=Alexander V. Kirdyanov |title=Cooling and societal change during the Late Antique Little Ice Age from 536 to around 660 AD |journal=Nature Geoscience |date=2016 |volume=9 |issue=3 |pages=231–236 |doi=10.1038/ngeo2652|bibcode=2016NatGe...9..231B |url=http://elib.sfu-kras.ru/handle/2311/27894 |issn = 1752-0894}}</ref> The Slavs settled on places of earlier settlements and probably merged later with the local populations to form mixed Byzantine-Slavic communities.<ref>Bintliff J.L. (2003), The ethnoarchaeology of a 'passive' ethnicity: The Arvanites of Central Greece, p. 142. In: Brown K.S., Hamilakis Y. (Eds.) The Usable Past. Greek Metahistories. Lanham-Boulder: Lexington Books. 129–144.</ref> Historical records document that in {{Circa|680}} a [[Bulgars|Bulgar]] ruler called [[Kuber]] led a group of largely Christians called [[Sermesianoi]], who were his subjects, and they settled in the region of [[Pelagonia]]. They may have consisted of Bulgars, Byzantines, Slavs and even Germanic tribes.<ref>D. Hupchick (2002) The Balkans: From Constantinople to Communism, Springer, p. 33, {{ISBN|0-312-29913-3}}.</ref> There is no more information of Kuber's life.<ref>{{Cite web|author=[[Florin Curta]]|url=https://archive.org/details/southeasterneuro0000curt|url-access=registration|title=Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250|website=Archive.org|year=2006 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|author=[[John Van Antwerp Fine Jr.]]|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Y0NBxG9Id58C|isbn=0-472-08149-7|title=The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century| year=1991 | publisher=University of Michigan Press }}</ref> [[Presian I of Bulgaria|Presian]]'s reign apparently coincides with the extension of Bulgarian control over the Slavic tribes in and around Macedonia. The Slavic tribes that settled in the region of Macedonia converted to Christianity around the 9th century during the reign of Tsar [[Boris I of Bulgaria]]. The [[Ohrid Literary School]] became one of the two major cultural centres of the First Bulgarian Empire, along with the [[Preslav Literary School]]. Established in Ohrid in 886 by Saint [[Clement of Ohrid]] on the order of Boris I, the Ohrid Literary School was involved in the spreading of the [[Cyrillic script]].<ref>{{Cite web|author=S. Runciman|url=http://www.promacedonia.org/en/sr/sr_app9.htm|title=A history of the First Bulgarian empire – Appendix 9|website=Promacedonia.org}}</ref> |
|||
The role of the President of the Republic is mostly ceremonial, with the real power resting in the hands of the President of the Government. The President is the commander-in-chief of the state armed forces and a president of the state Security Council. The President of the Republic is elected every five years and he or she can be elected twice at most. The current President is [[Branko Crvenkovski]]. |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
With the passage of a new law and elections held in 2005, local government functions are divided between 78 municipalities ({{lang|mk|општини, ''opštini''}}; [[singular]]: {{lang|mk|општина, ''opština''}}). The capital, [[Skopje]], is governed as a group of ten municipalities collectively referred to as "the City of Skopje". Municipalities in the Republic of Macedonia are units of local self-government. Neighbouring municipalities may establish cooperative arrangements. |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| image1 = St Sophia (Ohrid).jpg |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = |
|||
| image2 = Iglesia de San Pantaleón, Ohrid, Macedonia, 2014-04-17, DD 35 HDR.jpg |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = |
|||
| footer = [[Church of St. Sophia, Ohrid|Church of St. Sophia]], the first synod church of the [[Archbishopric of Ohrid]] (top). The [[Church of Saints Clement and Panteleimon]] (bottom). Both churches are located in [[Ohrid]]. |
|||
}} |
|||
After [[Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria]], the Byzantines took control of East Bulgaria. [[Samuel of Bulgaria|Samuil]] was proclaimed [[First Bulgarian Empire|Tsar of Bulgaria]]. He moved the capital to Skopje and then to Ohrid, which had been the cultural and military centre of southwestern Bulgaria since Boris I's rule. Samuil re-established Bulgarian power, but after several decades of conflicts, in 1014, the Byzantine Emperor [[Basil II]] defeated his armies, and within four years the Byzantines restored control over the Balkans (modern-day North Macedonia was included into a new province, called [[Bulgaria (theme)|Bulgaria]]). The rank of the autocephalous [[Bulgarian Patriarchate]] was lowered due to its subjugation to [[Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople|Constantinople]] and it was transformed into the [[Archbishopric of Ohrid]]. By the late 12th century, Byzantine decline saw the region contested by various political entities, including a brief [[Normans|Norman]] occupation in the 1080s.{{citation needed|date=January 2024}} |
|||
Judiciary power is exercised by courts, with the court system being headed by the Judicial Supreme Court, Constitutional Court and the Republican Judicial Council. The assembly appoints the judges. |
|||
In the early 13th century, a revived [[Second Bulgarian Empire|Bulgarian Empire]] gained control of the region. Plagued by political difficulties, the empire did not last, and the region came once again under Byzantine control in the early 14th century. In the 14th century, it became part of the [[Serbian Empire]]. Skopje became the capital of Tsar [[Stefan Dušan]]'s empire. Following Dušan's death, a weak successor appeared, and power struggles between nobles divided the Balkans once again. These events coincided with the entry of the [[Ottoman Turks]] into Europe. |
|||
The country's main political divergence is between the largely ethnically-based political parties representing the country's Slav majority and Albanian minority. The issue of the power balance between the two communities led to a brief war in 2001, following which a power-sharing agreement was reached. In August 2004, the Republic's parliament passed legislation redrawing local boundaries and giving greater local autonomy to ethnic Albanians in areas where they predominate. |
|||
===Ottoman period=== |
|||
After a troublesome pre-election campaign, the country saw a relatively calm and democratic [[Macedonian parliamentary election, 2006|change of government]] in the elections held on [[5 July]] [[2006]]. The elections were marked by a decisive victory of the centre-right party [[VMRO-DPMNE]] led by [[Nikola Gruevski]]. |
|||
{{Further|Ottoman Vardar Macedonia}} |
|||
The [[Kingdom of Prilep]] was one of the short-lived states that emerged from the collapse of the Serbian Empire in the 14th century, which was seized by the Ottomans at the end of the same century.<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=y2d6OHLqwEsC&pg=PA275 |title=The last Centuries of Byzantium, (1261–1453) |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1993 |isbn=978-0-521-43991-6 |page=500 |author1=Nicol, Donald Macgillivray |access-date=10 February 2016}}</ref> Gradually, all of the central Balkans were conquered by the [[Ottoman Empire]] and remained under its domination for five centuries as part of the province or [[Eyalet]] of [[Rumelia Eyalet|Rumelia]]. The name ''[[Rumelia]]'' ([[Turkish language|Turkish]]: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Turkish, referring to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Turks from the Byzantine Empire.<ref>[https://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9064407/Rumelia Encyclopædia Britannica – Rumelia] at Encyclopædia Britannica.com</ref> Over the centuries, Rumelia Eyalet was reduced in size through administrative reforms, until by the 19th century it consisted of a region of central Albania and western North Macedonia with its capital at Manastir or present-day [[Bitola]].<ref name=eb19>{{cite book |title=The Encyclopædia Britannica, or, Dictionary of arts, sciences ..., Volume 19 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TUEhAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA464 |page=464 |year=1859}}</ref> Rumelia Eyalet was abolished in 1867 and that territory of Macedonia subsequently became part of vilayets of [[Manastir Vilayet|Manastir]], [[Kosovo Vilayet|Kosova]] and [[Salonica Vilayet|Selanik]] until the end of Ottoman rule in 1912. With the beginning of the [[Bulgarian National Revival]] in the 19th century, many of the reformers were from this region, including the [[Miladinov brothers]],<ref name='Phillips'>{{cite book |last=Phillips |first=John |title=Macedonia: Warlords and Rebels in the Balkans |url=https://archive.org/details/macedoniawarlord00phil |url-access=limited |publisher=I.B. Tauris |year=2004 |isbn=978-1-86064-841-0 |page=[https://archive.org/details/macedoniawarlord00phil/page/n51 41]}}</ref> [[Rayko Zhinzifov|Rajko Žinzifov]], [[Yoakim Karchovski|Joakim Krčovski]],<ref>{{cite book |isbn=978-90-6143-311-8 |page=234 |title=Becoming Bulgarian: The articulation of Bulgarian identity in the nineteenth century in its international context: An intellectual history |last1=Sampimon |first1=Janette |year=2006|publisher=Pegasus }}</ref> [[Kiril Peychinovich|Kiril Pejčinoviḱ]]<ref>{{cite book |isbn=978-0-88033-149-4 |page=221 |quote=Peichinovich of Tetovo, Macedonia, author of one of the first Bulgarian books |title=The pen and the sword: Studies in Bulgarian history |last1=Clarke |first1=James Franklin |last2=Hupchick |first2=Dennis P. |year=1988|publisher=East European Monographs }}</ref> and others. The bishoprics of Skopje, [[Debar]], [[Bitola]], [[Ohrid]], [[Veles (city)|Veles]], and [[Strumica]] voted to join the [[Bulgarian Exarchate]] after it was established in 1870.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Crescent and the Eagle: Ottoman Rule, Islam and the Albanians, 1874–1913 |last=Gawrych |first=George |date=2006|page=28 |publisher=Bloomsbury Academic |isbn=978-1-84511-287-5}}</ref> |
|||
Gruevski's decision to include the [[Democratic Party of Albanians]] in the new government, instead of the [[Democratic Union for Integration]] - [[Party for Democratic Prosperity]] coalition which won the majority of the Albanian votes, triggered protests throughout the Albanian-dominated parts of the country. |
|||
=== Modern period === |
|||
==Foreign relations== |
|||
==== Macedonian autonomism ==== |
|||
{{main|Foreign relations of the Republic of Macedonia}} |
|||
{{See also|Bulgarian Millet|Autonomy for Macedonia and Adrianople regions|Macedonia for the Macedonians}} |
|||
[[File:Nikola Karev.jpg|thumb|upright|right|[[Nikola Karev]], head of the provisional government of the short-lived [[Kruševo Republic]] during the [[Ilinden uprising]]]] |
|||
[[File:Krushevo 1918.jpg|thumb|right|Celebration of the Ilinden Uprising in Kruševo during [[Bulgarian occupation of Serbia (World War I)|WWI Bulgarian occupation of Southern Serbia]].]] |
|||
Several movements whose goals were the establishment of an autonomous Macedonia, which would encompass the entire region of Macedonia, began to arise in the late 19th century; the earliest of these was the [[Bulgarian Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Committees]], later becoming Secret Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (SMARO). In 1905 it was renamed the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMARO), and after [[World War I]] the organisation separated into the [[Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization]] (IMRO) and the [[Internal Thracian Revolutionary Organisation]] (ITRO).<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1jSg3lxgSy8C&q=thracian+revolutionary+organization&pg=PA100|isbn=978-0-8108-5565-6|page=100|access-date=14 November 2011|title=Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia|last=Bechev|first=Dimitar|year=2009|publisher=Scarecrow Press }}</ref> |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia is a member of a number of international organisations such as the [[United Nations]], [[Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe]] [[Council of Europe]], associate member of [[La Francophonie]], [[World Trade Organization]] (WTO) etc. It is seeking to join [[NATO]] and the [[European Union]], although its accession to either is unlikely to occur before 2008 and 2012, respectively. In December 2005, the leaders of the EU formally named it as a [[Enlargement of the European Union|candidate country]] but did not set a date for starting entry talks. |
|||
In the early years of the organisation, membership eligibility was exclusive to Bulgarians, but later it was extended to all inhabitants of European Turkey regardless of ethnicity or religion.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6RveDmHbIv8C&pg=PA136 |title=Region, Regional Identity and Regionalism in Southeastern Europe |first1=Klaus |last1=Roth |first2=Ulf |last2=Brunnbauer |date=2008 |publisher=LIT Verlag Münster |via=Google Books |isbn=978-3-8258-1387-1}}</ref> The majority of its members were [[Macedonian Bulgarians]].<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AIET_7ji7YAC&pg=PA209 |title=History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey: Volume 2, Reform, Revolution, and Republic: The Rise of Modern Turkey 1808–1975 |last=Shaw |first=Stanford J. |publisher=Cambridge University Press |page=209 |date=1977 |isbn=978-0-521-29166-8}}</ref> In 1903, IMRO organised the [[Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising]] against the [[Ottoman Empire|Ottomans]], which after some initial successes, including the forming of the [[Kruševo Republic]], was crushed with much loss of life.<ref>There was even an attempt to form a kind of revolutionary government led by the socialist Nikola Karev. The Krushevo manifesto was declared, assuring the population that the uprising was against the Sultan and not against Muslims in general, and that all peoples would be included. As the population of Krushevo was two-thirds hellenised Vlachs and Patriarchist Slavs, this was a wise move. Despite these promises, the insurgent flew Bulgarian flags everywhere and in many places the uprising did entail attacks on Muslim Turks and Albanians who themselves organised for self-defence." Who are the Macedonians? Hugh Poulton, C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 1995, {{ISBN|1-85065-238-4}}, p. 57.</ref> The uprising and the forming of the Kruševo Republic are considered the cornerstone and precursors to the eventual establishment of the Macedonian state.<ref>In fact Macedonian historians as [[Blaze Ristovski]] have recognized, that the "government" of the "republic", nowadays a symbol of Macedonian statehood, was actually composed of people who identified themselves as "Greeks", "Vlachs" and "Bulgarians". "We, the People: Politics of National Peculiarity in Southeastern Europe" Diana Mishkova, Central European University Press, 2009, {{ISBN|963-9776-28-9}}, p. 124.</ref><ref>"The IMARO activists saw the future autonomous Macedonia as a multinational polity, and did not pursue the self-determination of Macedonian Slavs as a separate ethnicity. Therefore, Macedonian was an umbrella term covering Bulgarians, Turks, Greeks, Vlachs, Albanians, Serbs, Jews, and so on." Historical Dictionary of Macedonia, Historical Dictionaries of Europe, Dimitar Bechev, Scarecrow Press, 2009, {{ISBN|0-8108-6295-6}}, Introduction.</ref><ref>The political and military leaders of the Slavs of Macedonia at the turn of the century seem not to have heard the call for a separate Macedonian national identity; they continued to identify themselves in a national sense as Bulgarians rather than Macedonians.[...] (They) never seem to have doubted "the predominantly Bulgarian character of the population of Macedonia". "The Macedonian conflict: ethnic nationalism in a transnational world", Princeton University Press, Danforth, Loring M. 1997, {{ISBN|0-691-04356-6}}, p. 64.</ref> The leaders of the Ilinden uprising are celebrated as national heroes in North Macedonia. The names of IMRO revolutionaries like [[Gotse Delchev]], [[Pitu Guli]], [[Dame Gruev]] and [[Yane Sandanski]] were included into the lyrics of the national anthem of the state of North Macedonia "[[Denes nad Makedonija]]" ("Today over Macedonia"). The major national holiday of North Macedonia, the [[Republic Day (North Macedonia)|Republic Day]], is celebrated on 2 August, Ilinden (St. Elijah day), the day of the Ilinden uprising. |
|||
The [[United States Agency for International Development]] has underwritten a project called Macedonia Connects which has made the Republic of Macedonia the first all broadband wireless country its size or larger in the world. The Ministry of Education and Sciences reports that 461 schools (primary and secondary) are now connected to the internet. In addition, the Internet Service Provider named On.net has created a MESH Network to provide WIFI services in the 11 largest cities/towns in the country. |
|||
=== |
====Kingdom of Serbia==== |
||
{{See also|Second Balkan War|Serbianisation}} |
|||
Macedonia is represented abroad by embassies in the following countries: Albania, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Denmark, Egypt, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, the Netherlands, People's Republic of China, Poland, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, United Kingdom, United States, and the Vatican. |
|||
Following the two [[Balkan Wars]] of 1912 and 1913 and the [[dissolution of the Ottoman Empire]], most of its European-held territories were divided between Greece, Bulgaria and Serbia.{{sfn|Nicolle|2008|p=162}} Almost the territory that was to become North Macedonia was annexed by Serbia conforming to the [[Treaty of Bucharest (1913)|treaty of peace]] concluded at Bucharest.<ref name="Saucerman 1937 p. 195">{{cite book | last=Saucerman | first=S.B. | title=International Transfers of Territory in Europe with Names of the Affected Political Subdivisions| publisher=U.S. Government Printing Office | series=Department of State publication | year=1937 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KrJ9AAAAMAAJ&pg=PA195| page=195}}</ref> However, [[Strumica]] region was passed to Bulgaria. Following the partition, an anti-Bulgarian campaign was carried out in the areas under Serbian and Greek control.<ref name=Banac>{{cite book|url=https://archive.org/details/nationalquestion0000bana/page/317|title=The National Question in Yugoslavia. Origins, History, Politics|last=Banac|first=Ivo|publisher=Cornell University Press|year=1984|place=London and Ithaka|isbn=978-0-8014-1675-0}}</ref> As many as 641 Bulgarian schools and 761 churches were closed by the Serbs, while Exarchist clergy and teachers were expelled.<ref name=Banac/> The use of all [[Macedonian dialects]] and standard Bulgarian were proscribed.<ref name=Banac/> IMRO, together with local Albanians, organised the [[Ohrid–Debar uprising]] against the Serbian rule. Within a few days the rebels captured the towns of Gostivar, Struga and Ohrid, expelling the Serbian troops. According to the [[Carnegie Endowment for International Peace]] report, a Serbian army of 100,000 regulars suppressed the uprising. Many were killed and tens of thousands refugees fled to Bulgaria and Albania.<ref>{{cite book|last=Mojzes|first=Paul|title=Balkan Genocides: Holocaust and Ethnic Cleansing in the Twentieth Century|publisher=Rowman & Littlefield|date=2011|page=38|isbn=978-1-4422-0663-2}}</ref><ref>Йосиф Разсуканов, 85 години от Охриско-Дебърското въстание, в-к "Македония", брой 33, 16 септември 1998 г.</ref> |
|||
[[File:Balkan Wars Boundaries cleanup.jpg|thumb|The division of the Ottoman territories in Europe (including the [[Macedonia (region)|region of Macedonia]]) after the [[Balkan Wars]] according to the [[Treaty of Bucharest (1913)|Treaty of Bucharest]]]] |
|||
Macedonia also maintains consulates in Pristina, Kosovo; Thessaloniki, Greece; Toronto, Canada; Detroit, USA; Istanbul, Turkey and Podgorica, Montenegro. Macedonia also has permanent missions at the UN, NATO, EU, UNESCO, Council of Europe, and FAO headquarters. There is currently no representation in Taiwan (Republic of China) since 2001 when diplomatic relations were formally severed between the two countries and the Macedonian embassy in Beijing was reopened. |
|||
=== |
==== World War I ==== |
||
{{See also|Bulgarian occupation of Serbia (World War I)}} |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia generally has good relationships with [[Greece]]. However, the [[Foreign relations of the Republic of Macedonia#Greece|naming dispute]] inhibited the establishment of full diplomatic relations so far but has not prevented Greece and the Republic from engaging in military and security co-operation, cross-border investments, and cultural exchanges. The November 2005 [[European Commission]] report states that, ''"Relations with Greece have improved in the last few years. [[Greece]] is the most important investor in the country (57% of the total foreign investments) and trade has been constantly increasing."'' |
|||
During the [[First World War]], most of today's North Macedonia was part of the [[Bulgarian occupation of Serbia (World War I)|Bulgarian occupied zone of Serbia]] after the country was [[Serbian campaign|invaded]] by the [[Central Powers]] in the fall of 1915.<ref name="Banac" /> The region was known as the "Military Inspection Area of Macedonia" and was administered by a Bulgarian military commander.<ref name="Király Rothenberg 1985 p.2512">{{cite book|last1=Király|first1=B.K.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lGrfAAAAMAAJ|title=War and Society in East Central Europe: East central European society in World War I|last2=Rothenberg|first2=G.E.|publisher=Brooklyn College Press|year=1985|isbn=978-0-88033-089-3|series=Atlantic studies|page=377}}</ref> A policy of [[Bulgarisation]] of the region and its population was immediately initiated,<ref name="Gerwarth Horne 2013 p.150">{{cite book|last1=Gerwarth|first1=R.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lao-AAAAQBAJ|title=War in Peace: Paramilitary Violence in Europe After the Great War|last2=Horne|first2=J.|publisher=OUP Oxford|year=2013|isbn=978-0-19-968605-6|series=The Greater War|page=150}}</ref><ref name="Bianchi 2012 p.163">{{cite book|last=Bianchi|first=B.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ln1FLgEACAAJ|title=War crimes and crimes against humanity: violence against civilians on the eastern front (1914–1919)|publisher=UNICOPLI|year=2012|isbn=978-88-400-1579-8|series=Biblioteca di storia contemporanea|page=163|language=it}}</ref> during the period the IMRO arose from a clandestine organisation to serve as gendarmerie, taking control of the whole police structure, enforcing the Bulgarisation of the region.<ref name="Gerwarth Horne 2013 p.150"/> According to [[Robert Gerwarth]], the Bulgarian denationalisation policy, including its paramilitary aspect, was almost identical in its intent and execution to the Serbian policy that preceded it.<ref name="Gerwarth Horne 2013 p.150"/> |
|||
Former Greek foreign minister, M. Papakonstandinou, clearly expressed Athens' position towards the republic, "''Greek interests demand that this state survives. It must exist [...] This is the firm position of [both [[New Democracy (Greece)|ND]] and [[Panhellenic Socialist Movement|PASOK]]]."'' |
|||
(ref: Interview with the minister. In, 'Andi' (weekly socio-political journal), Nr 588, 13 October 1995). |
|||
Bulgarian language was to be exclusively used, [[Serbian Cyrillic alphabet|Serbian Cyrillic]] was forbidden, Serbian priests were arrested and deported, Serbian-sounding names had to be changed to Bulgarian ones,<ref name="Laffan 1989 p.252">{{cite book|last=Laffan|first=R.G.D.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_MwlAQAAMAAJ|title=The Serbs: The Guardians of the Gate|publisher=Dorset Press|year=1989|isbn=978-0-88029-413-3|series=Armenian Research Center collection|page=252}}</ref> school teachers were brought from Bulgaria while Serbian books were taken from schools and libraries and publicly destroyed.<ref name="Report of the Interallied Commission on the Violation of the Hague Convention p.2">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MxakAAAAMAAJ|title=Report of the Interallied Commission on the Violation of the Hague Convention|publisher=Imprimerie "Yougoslavia"|year=1919|page=22}}</ref> Adult males were sent to labour camps or forced to join the Bulgarian Army, representatives of the Serbian [[intelligentsia]] were deported or executed.<ref name="Bianchi 2012 p.163"/> According to [[Paul Mojzes]] the aim of the Bulgarian government was to create pure Bulgarian territories by denationalising the non-Bulgarian Slavic population of Macedonia.<ref name="Mojzes 2011 p.422">{{cite book|last=Mojzes|first=P.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KwW2O7v7CUcC|title=Balkan Genocides: Holocaust and Ethnic Cleansing in the Twentieth Century|publisher=Rowman & Littlefield|year=2011|isbn=978-1-4422-0663-2|page=42}}</ref> |
|||
Due to the dispute over the name, the [[United Nations]] agreed to a provisional name — "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (FYROM) ({{lang-mk|Поранешна Југословенска Република Македонија (ПЈРМ)}}) — when it became a member state in 1993 [http://www.un.org/documents/ga/res/47/a47r225.htm]. Most international organizations adopted the same convention, including the [[European Union]], [[NATO]], the [[International Monetary Fund]], the [[European Broadcasting Union]], and the [[International Olympic Committee]], among others. The [[European Union|EU]] recognises the country as the ''former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia'' (FYROM) and the negotiations with the EU are held using this reference [http://europa.eu.int/comm/enlargement/report_2005/pdf/package/sec_1425_final_en_analytical_report_mk.pdf]. |
|||
[[Image:Flag of Macedonia 1991-95.svg|thumb|The official [[flag of the Republic of Macedonia]] between 1992 and 1995]] |
|||
====Kingdom of Yugoslavia==== |
|||
However, an increasing number of countries have abandoned the [[United Nations]] provisional references and have recognised the country as the ''Republic of Macedonia'' instead. These include three of the five permanent [[UN Security Council]] members: the [[United States]], [[Russia]], and the [[People's Republic of China]], although as the UN name for the country is FYROM, the constitutional name is only used in relations where a state not recognizing it is not a party. |
|||
{{See also|South Serbia (1919–1922)|Vardar Banovina}} |
|||
After the capitulation of Bulgaria and the end of the First World War, the area returned under Belgrade control as part of the newly formed [[Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes]]<ref name="Naš rod">"Kraljevina Jugoslavija! Novi naziv naše države. No, mi smo itak med seboj vedno dejali Jugoslavija, četudi je bilo na vseh uradnih listih Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev. In tudi drugi narodi, kakor Nemci in Francozi, so pisali že prej v svojih listih mnogo o Jugoslaviji. 3. oktobra, ko je kralj Aleksander podpisal "Zakon o nazivu in razdelitvi kraljevine na upravna območja", pa je bil naslov kraljevine Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev za vedno izbrisan." (Naš rod ("Our Generation", a monthly Slovenian language periodical), Ljubljana 1929/30, št. 1, str. 22, letnik I.)</ref> and saw a reintroduction of anti-Bulgarian measures. Bulgarian teachers and clergy were expelled, Bulgarian language signs and books removed, and all Bulgarian organisations dissolved.<ref name=Banac/> Also after the [[Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine]], the Strumica region was annexed to Serbian Macedonia in 1919. |
|||
The Serbian government pursued a policy of forced [[Serbianisation]] in the region,<ref>{{Google books |id=ZMyZdvTympMC |page=123 |title=Dejan Djokić, Yugoslavism: histories of a failed idea, 1918–1992 }}</ref><ref>{{Google books |id=SGnKpNf2RbAC |page=20 |author=R. J. Crampton|title= Eastern Europe in the twentieth century – and after }}</ref> which included systematic suppression of Bulgarian activists, altering family surnames, internal colonisation, exploiting workers, and intense propaganda.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kroraina.com/knigi/en/ban/pww2.html#60 |title=An article by Dimiter Vlahov about the persecution of the Bulgarian population in Macedonia |publisher=newspaper "Balkanska federatsia", No. 140, 20 August 1930, Vienna, original in Bulgarian |access-date=3 August 2007}}</ref> To aid the implementation of this policy, some 50,000 Serbian army and [[Serbian Gendarmerie|gendarmerie]] were stationed in present-day North Macedonia.<ref name=Banac/> By 1940 about 280 Serbian colonies (comprising 4,200 families) were established as part of the government's internal colonisation program (initial plans envisaged 50,000 families settling in present-day North Macedonia).<ref name=Banac/> |
|||
From 1992 to 1995, the two countries also engaged in a dispute over the Republic's first flag, which incorporated the [[Vergina Sun]] symbol, a symbol of the ancient Kingdom of [[Macedon]]. Its adoption by the Republic of Macedonia, on [[3 July]] [[1992]], was seen as a reaction by Skopje to Athens' pressure to change the name. This aspect of the dispute was permanently resolved after an interim accord between the two states, when the flag was changed by an act of parliament, in October 1995. |
|||
In 1929, the Kingdom was officially renamed the [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]], and divided into provinces called [[Banovinas of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia|''banovinas'']]. South Serbia, including all of present-day North Macedonia, became the [[Vardar Banovina]] of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.<ref name=WOW>{{Google books |id=IGeJzd6BLU4C |page=43 |title=War of words: Washington tackles the Yugoslav conflict }}</ref> |
|||
===Bulgaria=== |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia maintains good relations with the Republic of [[Bulgaria]]. Bulgaria was the first country to recognize Macedonian independence. Many Macedonian students matriculate in Bulgarian universities. Bulgaria also supports the Macedonian bid to enter the EU and NATO. Bulgaria also donated tanks, artillery and other materials to the Macedonian army. |
|||
The [[Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization]] (IMRO) promoted the concept of an [[Independent Macedonia (IMRO)|Independent Macedonia]] in the [[interwar period]]. Its leaders—including [[Todor Alexandrov]], [[Aleksandar Protogerov]], and [[Ivan Mihailov]]—promoted independence of the Macedonian territory split between Serbia and Greece for the whole population, regardless of religion and ethnicity.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qMZaPjrHqYYC&q=Mihailov,%20Macedonia;%20A%20Switzerland%20%20Balkans%20%20bulgarian%20state&pg=PA127 |title=Balkan Strongmen: Dictators and Authoritarian Rulers of South Eastern Europe |first=Bernd Jürgen |last=Fischer |date=2007 |publisher=Purdue University Press |via=Google Books |isbn=978-1-55753-455-2}}</ref> The Bulgarian government of [[Alexander Malinov]] in 1918 offered to give [[Pirin Macedonia]] for that purpose after [[World War I]],<ref>Gerginov, Kr., Bilyarski, Ts. Unpublished documents for Todor Alexandrov's activities 1910–1919, magazine VIS, book 2, 1987, p. 214 – Гергинов, Кр. Билярски, Ц. Непубликувани документи за дейността на Тодор Александров 1910–1919, сп. ВИС, кн. 2 от 1987, с. 214.</ref> but the Great Powers did not adopt this idea because Serbia and Greece opposed it. In 1924, the [[Communist International]] (Comintern) suggested that all Balkan communist parties adopt a platform of a "[[United Macedonia]]" but the suggestion was rejected by the Bulgarian and Greek communists.<ref>Victor Roudometof, [https://books.google.com/books?id=Xoww453NVQMC&dq=%22united+macedonia%22&pg=PA100 ''Collective Memory, National Identity, and Ethnic Conflict: Greece, Bulgaria, and the Macedonian Question''], Praeger, 2002 p. 100</ref> |
|||
The basic problem in the relationship between the Republic of Macedonia and [[Bulgaria]] is the latter's refusal to recognise the existence of a separate Macedonian ethnicity, instead considering [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonians]] to be Bulgarians and their language as a regional "norm" based on local Bulgarian dialects [http://www.greekhelsinki.gr/pdf/cedime-se-bulgaria-macedonians.PDF]. Issues have been raised over what many Bulgarians view as appropriation and falsification of their history, and the treatment in Macedonia of people espousing a Bulgarian national identity. The pro-Bulgarian organization "Radko" for example (which was later banned by the Macedonian Constitutional Court) had been publicly harassed after they demonstrated in front of the Macedonian parliament and claimed that there is no Macedonian nation today, and the perpetrators were acclaimed as heroes by the media. [http://www.minelres.lv/minelres/archive/11032000-14:42:54-3629.html] |
|||
IMRO followed by starting an insurgent war in Vardar Macedonia, together with [[Macedonian Youth Secret Revolutionary Organization]], which also conducted guerrilla attacks against the Serbian administrative and army officials there. In 1923 in Stip, a paramilitary organisation called [[Association against Bulgarian Bandits]] was formed by Serbian [[chetniks]], IMRO renegades and [[Macedonian Federative Organization]] (MFO) members to oppose IMRO and MMTRO.<ref>{{cite web |author=Vassil Karloukovski |url=http://www.promacedonia.org/ag/ag_4_6.html |title=Гиза, Антони, "Балканските държави и Македония", Македонски Научен Институт София, 2001 г |publisher=Promacedonia.org |access-date=28 April 2010}}</ref> On 9 October 1934, IMRO member [[Vlado Chernozemski]] assassinated [[Alexander I of Yugoslavia]]. |
|||
===European Union candidacy and membership=== |
|||
The EU leaders on the meeting held in [[Thessaloniki]] in 2003 [http://www.stabilitypact.org/reg-conf/030621-thessaloniki/declaration.asp] promised western Balkan countries that they will become an integral part of the EU, once they meet the established criteria. As part of the [[enlargement of the European Union|ongoing efforts to expand its membership]], the [[European Union]] (EU) granted the Republic of Macedonia candidate status on [[17 December]] [[2005]], but with no promise of when such negotiations could start. [[France]] had made a budget deal as a condition for granting the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia candidate status and Greece agreed not to veto the decision on the premise that the name dispute will be resolved. The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia applied for full membership on [[22 March]] [[2004]]. [[Vlado Bučkovski]], then minister of defence and later prime minister, hailed the decision as a "one-way ticket" to the EU for his country. |
|||
The [[Macedonism|Macedonist]] ideas increased in Yugoslav Vardar Macedonia and among the left diaspora in Bulgaria during the interwar period. They were supported by the Comintern.<ref name="books.google.com">{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ilGfCIF4Ao4C&q=macedonism&pg=PA140 |title=Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia |first=Dimitar |last=Bechev |date=2009 |publisher=Scarecrow Press |via=Google Books |isbn=978-0-8108-6295-1}}</ref> In 1934, the Comintern issued a [[Resolution of the Comintern on the Macedonian question|special resolution]] in which for the first time directions were provided for recognising the existence of a separate Macedonian nation and Macedonian language.<ref>Duncan Perry, "The Republic of Macedonia: finding its way" in Karen Dawisha and Bruce Parrot (eds.), Politics, power and the struggle for Democracy in South-Eastern Europe, Cambridge University Press, 1997, pp. 228–229.</ref> |
|||
According to the EU, namely in accordance with its [[Copenhagen criteria]], the main obstacles towards eventual EU membership for Republic of Macedonia concern good relations with neighbouring countries and reforms to its judicial and police systems. Also, growth rate lags behind that of most EU members, unemployment is high, and foreign investment is relatively low. The [[decentralisation]] process imposed after the six-month conflict in 2001 still requires full implementation. In principle, the relatively low population and European characteristics of the Republic promise few strains on the EU budget. On a press conference held in March 2006, German chancellor [[Angela Merkel]] suggested a ''privileged partnership'' for potential members. Following the refusals of European constitution by the French and Dutch voters, EU is in a ''period of reflection'' (time to decide what to do next) that can last for several years. This decision seems to delay the prospect of EU membership for candidates like Croatia, the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia and Turkey for some period. French warned that they want strict application of the notion of ''absorption capacity'' for the EU - a concept which has existed since 1993 but which has rarely been highlighted. |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
==== World War II ==== |
|||
Another problem in the relations between the [[EU]] and the Republic of Macedonia is the EU visa regime with the country, fostering resentment and inhibiting progress on trade, business, education etc, contributing negatively to regional stability. [http://www.crisisgroup.org/home/index.cfm?id=3809&l=1]. |
|||
{{Main|World War II in Yugoslav Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:Liberation of Skopje.jpg|thumb|left|[[Dimitar Vlahov]], [[Mihajlo Apostolski]], [[Metodija Andonov-Čento]], [[Lazar Koliševski]] and others, greeted in Skopje on 20 November 1944, a week after its liberation<ref>Mitre Inadeski, Hronologija na Skopje: rabotničkoto i narodnoosloboditelnoto dviženje 1939–1945, tom 2, Arhiv, 1974, str. 181.</ref>]] |
|||
In February 2006, the Republic became the fourth member of the [[Central European Free Trade Agreement]] (CEFTA), joining [[Croatia]], [[Bulgaria]] and [[Romania]]. CEFTA acts as '[[sandbox]]' to encourage joint efforts for the integration of participating countries in Western European institutions and look for opportunities for close economic and political co-operation. |
|||
During World War II, Yugoslavia was occupied by the [[Axis powers]] from 1941 to 1945. The Vardar Banovina was divided between Bulgaria and Italian-occupied Albania. [[Bulgarian Action Committees]] were established to prepare the region for the new Bulgarian administration and army.<ref>[http://www.kroraina.com/knigi/bugarash/bccc_1941/index.html Bulgarian Campaign Committees in Macedonia – 1941] Dimitre Mičev</ref> The committees were mostly formed by former members of IMRO and Macedonian Youth Secret Revolutionary Organization (MYSRO, but some [[IMRO (United)]] former members also participated.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.kroraina.com/knigi/bugarash/bccc_1941/Chapter1_3.html|title=Forming of the Local Campaign Committees|work=kroraina.com}}</ref>{{sfn|Georgieva|Konechni|1998|p=223}} |
|||
A factor of outmost importance for the country's accession in EU, is that of the [[Foreign relations of the Republic of Macedonia#Greece|naming dispute]] with [[Greece]]. On [[August 29]], [[2006]], the [[Minister for Foreign Affairs (Greece)|Greek foreign minister]], Ms.[[Dora Bakoyannis]], affirmed that ''"...the [[Hellenic Parliament]], under any composition, will not ratify the accession of the neighbouring country to the [[EU]] and [[NATO]] if the name issue is not resolved beforehand."''<ref name=noEUsorry>{{cite web| url=http://www.greekembassy.org/Embassy/content/en/Article.aspx?office=1&folder=24&article=18371 | title=Embassy of Greece - Washington, DC | work=Answer of FM Ms. D. Bakoyannis regarding the FYROM name issue | accessmonthday= September 11 | accessyear=2006 |language= English}}</ref> |
|||
As leader of the Vardar Macedonian communists, [[Metodi Shatorov]] ("Sharlo") switched from the [[Yugoslav Communist Party]] to the [[Bulgarian Communist Party]]{{sfn|Georgieva|Konechni|1998|p=223}}<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=j_NbmSoRsRcC&q=Metodi+Shatorov+bulgarian+communist&pg=PA102 |title=Who are the Macedonians? |author=Hugh Poulton |publisher=C. Hurst & Co. Publishers |page=102 |isbn=978-1-85065-238-0 |year=1995 |access-date=10 February 2016}}</ref> and refused to start military action against the [[Bulgarian Army]].<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HjSsAAAAIAAJ&q=Metodi+Shatarov+bulgarian+communist&pg=PA130 |title=Bulgaria during the Second World War |publisher=Stanford University Press |year=1975 |isbn=978-0-8047-0870-8 |page=314 |last=Miller |first=Marshall Lee |access-date=10 February 2016}}</ref> The Bulgarian authorities, under German pressure,<ref>Bulgaria managed to save its entire 48,000-strong Jewish population during World War II from deportation to [[Nazi concentration camps]], but under German pressure those Jews from their newly annexed territories without Bulgarian citizenship were deported, such as those from Vardar Macedonia and [[Western Thrace]]. [http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?lang=en&ModuleId=10006804 ''The Holocaust in Macedonia: Deportation of Monastir Jewry''] [[United States Holocaust Memorial Museum]]</ref> were responsible for the round-up and deportation of over 7,000 Jews in Skopje and [[Bitola]].<ref>Mark Cohen, [http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?lang=en&ModuleId=10006803 The Holocaust in Macedonia: Deportation of Monastir Jewry], United States Holocaust Memorial Museum</ref> Harsh rule by the occupying forces encouraged many Vardar Macedonians to support the [[Yugoslav Partisans|Communist Partisan]] resistance movement of [[Josip Broz Tito]] after 1943,<ref group="lower-alpha">This policy changed after 1943 with the arrival of Tito's envoy Montenegrin Serb [[Svetozar Vukmanović]]-Tempo. He began in earnest to organise armed resistance to the Bulgarian rule and sharply criticised [[Metodi Shatorov|Sharlo]]'s pro-Bulgarian policy. At a meeting of the partisan brigades, as well as a group of battalions in the [[Resen, North Macedonia|Resen]] region on 21 December 1943, Tempo makes the following comments about Shatorov and the leadership of the MCP: "They thought that the Macedonian people were Bulgarians and that they were oppressed by the hegemony of Great Serbia and had to be transferred to Bulgaria. Their basic slogan is: 'All non-Macedonians out of Macedonia'. The capital ''J'' [Serbo-Croatian spelling of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavian, etc.] was deleted from all documents. In fact they did not want Yugoslavia, no matter where it stood politically. When the war started, the initial decision of this leadership was to be separate from Yugoslavia and from Tito. They declared that Macedonia would be free as soon as the Bulgarians came...."</ref> and the [[National Liberation War of Macedonia|National Liberation War]] ensued.<ref name="НОБ на Македонија">"НОБ на Македонија" Јован Поповски. Скопје, 1962</ref><ref name="Историја на МК">"Историја на Македонскиот Народ" Александар Стојановски, Иван Катарџиев, Данчо Зографски. Скопје, 1988</ref> |
|||
In Vardar Macedonia, after the [[Bulgarian coup d'état of 1944]], the Bulgarian troops, surrounded by German forces, fought their way back to the old borders of Bulgaria.<ref>''History of Bulgaria'', Petar Delev et al., 2001, p. 364</ref> Under the leadership of the new Bulgarian pro-Soviet government, four armies, 455,000 strong in total, were mobilised and reorganised. Most of them re-entered occupied Yugoslavia in early October 1944 and moved from [[Sofia]] to [[Niš]], Skopje and [[Pristina]] with the strategic task of blocking the German forces withdrawing from Greece.<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=A8X6UH58dlgC&pg=PA33 |title=Axis Forces in Yugoslavia 1941–45 |date=1995 |publisher=Bloomsbury |via=Google Books |isbn=978-1-85532-473-2 }}{{Dead link|date=July 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> The Bulgarian army would [[Nagykanizsa–Körmend Offensive|reach the Alps]] in Austria, participating in the expulsion of the Germans to the west, through Yugoslavia and Hungary. |
|||
*See also: [[Accession of the Republic of Macedonia to the European Union]] |
|||
Compelled by the [[Soviet Union]] with a view towards the creation of a large [[Yugoslavism|South Slav Federation]], in 1946 the new Communist government, led by [[Georgi Dimitrov]], agreed to give Bulgarian Macedonia to a [[United Macedonia]]. With the [[Bled agreement (1947)|Bled agreement]], in 1947 Bulgaria formally confirmed the envisioned unification of the Macedonian region, but postponed this act until after the formation of the future Federation.<ref>James Horncastle, The Macedonian Slavs in the Greek Civil War, 1944–1949, Rowman & Littlefield, 2019, {{ISBN|1-4985-8505-1}}, p. 167.</ref><ref>Andrew Rossos, Macedonia and the Macedonians: A History, Hoover Press, 2013, {{ISBN|0-8179-4883-X}}, p. 205.</ref> It was the first time it accepted the existence of a separate Macedonian ethnicity and language. After the [[Tito–Stalin split]] the region of Pirin Macedonia remained part of Bulgaria and later the Bulgarian Communist Party revised its view of the existence of a separate Macedonian nation and language. |
|||
==Administrative divisions== |
|||
[[Image:Macedonia municipalities.png|thumb|right|350px|Municipalities of the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
{{main|Municipalities of the Republic of Macedonia}} |
|||
==== Socialist Yugoslavia ==== |
|||
In August 2004, Macedonia was reorganized into 84 municipalities (''{{lang|mk|opštini}}''; sing. ''{{lang|mk|opština}}''), 10 of which comprise [[Greater Skopje]]. This is reduced from the previous 123 municipalities established in September, 1996. Prior to this, local government was organized into 34 administrative districts. |
|||
{{Main|Socialist Republic of Macedonia}} |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
[[File:Lazar Kolishevski left.jpg|thumb|160px|[[Lazar Koliševski]] was the political leader of SR Macedonia and briefly of SFR Yugoslavia.]] |
|||
==Geography== |
|||
{{main|Geography of the Republic of Macedonia}} |
|||
[[Image:Mk-map.png|thumb|300px|Map of the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
<!-- Unsourced image removed: [[Image:Macedonia.JPG|thumb|300px|Satellite view of the Republic of Macedonia]] --> |
|||
In December 1944, the [[Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia]] (ASNOM) proclaimed the People's Republic of Macedonia as part of the People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.<ref>Мичев, Добрин. Партизанското движение във Вардарска Македония, 1941–1944 г. сп. Македонски преглед, кн. 2, стр. 5–40.</ref> ASNOM remained an acting government until the end of the war. The Macedonian alphabet was codified by linguists of ASNOM, who based their alphabet on the phonetic alphabet of [[Vuk Stefanović Karadžić]] and the principles of [[Krste Misirkov|Krste Petkov Misirkov]]. During the [[Greek Civil War|civil war in Greece]] (1946–1949), Macedonian communist insurgents supported the Greek communists. Many refugees fled to the Socialist Republic of Macedonia from there. The state removed "Socialist" from its name in 1991 when it peacefully seceded from Yugoslavia. |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia is a [[landlocked]] country that is geographically clearly defined by a central valley formed by the Vardar river and framed along its borders by mountain ranges. |
|||
The new republic became one of the six republics of the Yugoslav federation. Following the federation's renaming as the [[Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]] in 1963, the People's Republic of Macedonia was likewise renamed the Socialist Republic of Macedonia.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.slvesnik.com.mk/Issues/0AF2E0456C964935B7705FB5BF6F31F9.pdf|title=Constitution of the Socialist Republic of Macedonia, 1974 – Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia}}</ref><ref>Устав Федеративне Народне Републике Југославије (1946), [http://sr.wikisource.org/wiki/%D0%A3%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B2_%D0%A4%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%B2%D0%BD%D0%B5_%D0%9D%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%BD%D0%B5_%D0%A0%D0%B5%D0%BF%D1%83%D0%B1%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B5_%D0%88%D1%83%D0%B3%D0%BE%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%98%D0%B5_%281946%29 sr.wikisource.org], retrieved on 19 October 2007. {{in lang|sh}}</ref><ref>Устав Социјалистичке Федеративне Републике Југославије (1963), [http://sr.wikisource.org/wiki/%D0%A3%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B2_%D0%A1%D0%BE%D1%86%D0%B8%D1%98%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%BA%D0%B5_%D0%A4%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%B2%D0%BD%D0%B5_%D0%A0%D0%B5%D0%BF%D1%83%D0%B1%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B5_%D0%88%D1%83%D0%B3%D0%BE%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%98%D0%B5_%281963%29 sr.wikisource.org], retrieved on 19 October 2007. {{in lang|sh}}</ref> |
|||
The Republic's terrain is mostly rugged, located between the [[Shara mountain|Šara]] and [[Rhodope mountains|Rhodope]], which frame the valley of the [[Vardar]] river. Three large lakes — [[Lake Ohrid]], [[Lake Prespa]] and [[Dojran Lake]] — lie on the southern borders of the Republic, bisected by the frontiers with Albania and Greece. Ohrid is considered the oldest lakes and biotopes in the world [http://www.moe.gov.mk/soer2/ohrid_a.htm]. The region is seismically active and has been the site of destructive earthquakes in the past, most recently in 1963 when [[Skopje]] was heavily damaged by a major earthquake, killing over 1,000. |
|||
==== Declaration of independence ==== |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia also has scenic mountains. They belong to two different ranges: Dinarska and Rodopska. The Dinarska range is the oldest with subsequent erosion; the Rodopska range is younger offering rugged, alpine sceneries. |
|||
North Macedonia officially celebrates 8 September 1991 as [[Independence Day (North Macedonia)|Independence day]] ({{langx|mk|Ден на независноста}}, ''Den na nezavisnosta''), with regard to [[1991 Macedonian independence referendum|the referendum endorsing independence from Yugoslavia]].<ref name=NS>[[Dieter Nohlen|Nohlen, D]] & Stöver, P (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p. 1278 {{ISBN|978-3-8329-5609-7}}</ref> The anniversary of the start of the [[Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising|Ilinden Uprising]] ([[Elijah|St. Elijah]]'s Day) on 2 August is also widely celebrated on an official level as the [[Republic Day (North Macedonia)|Day of the Republic]]. |
|||
Ten highest mountains in the Republic of Macedonia: |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Mount Korab]] || 2,764 m || 9,396 ft <!-- Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]] --> |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Shara Mountain]] || 2,747 m || 9,012 ft |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Baba Mountain]] || 2,601 m || 8,533 ft |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Jakupica]] || 2,540 m || 8,333 ft |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Nidze]] || 2,521 m || 8,271 ft |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Deshat]] || 2,373 m || 7,785 ft |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Galichica]] || 2,288 m || 7,507 ft |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Stogovo]] || 2,273 m || 7,457 ft |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Jablanica]] || 2,257 m || 7,405 ft |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Mount Bistra]] || 2,163 m || 7,096 ft |
|||
|} |
|||
[[Robert Badinter]], as the head of the [[Arbitration Commission of the Peace Conference on Yugoslavia]], recommended EC recognition in January 1992.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ejil.org/journal/Vol4/No1/art8-02.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050215223455/http://www.ejil.org/journal/Vol4/No1/art8-02.html |archive-date=15 February 2005 |title=Recognition of States: Annex 3 |access-date=28 April 2010 }}</ref> On 15 January 1992, Bulgaria was the first country to recognise the independence of the republic. |
|||
* See also: [[Mountains of the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
Macedonia remained at peace through the [[Yugoslav Wars]] of the early 1990s. A few very minor changes to its border with Yugoslavia were agreed upon to resolve problems with the demarcation line between the two countries. It was seriously destabilised by the [[Kosovo War]] in 1999, when an estimated 360,000 ethnic Albanian refugees from Kosovo took refuge in the country.<ref name="Thomas">{{cite book |last=Thomas |first=Nigel |ref=Thomas |year=2006 |publisher=Osprey Publishing |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=a7cOQ9Nch2AC |title=The Yugoslav Wars (2): Bosnia, Kosovo And Macedonia 1992–2001 |isbn=978-1-84176-964-6}}</ref> They departed shortly after the war, and [[Albanian nationalism|Albanian nationalists]] on both sides of the border took up arms soon after in pursuit of autonomy or independence for the Albanian-populated areas of Macedonia.<ref name="Thomas"/><ref name="news.bbc.co.uk"/> |
|||
==Economy== |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
{{main|Economy of the Republic of Macedonia}} |
|||
=== 21st century === |
|||
Today the Republic of Macedonia is considered a country with an intermediary-developed industry, with continuing growth of the industrial production. The process of transition in the economy was triggered in 1995. The government has signed arrangements with the IMF ([[International Monetary Fund]]) and [[World Bank]]. It has an open economy that is integrating into international trade, with a total trade-to-[[GDP]] ratio of 79.5%. The most important sectors are agriculture and industry. The service sector also grew in the past few years. Work force education and skills are competitive, but without adequate jobs leading to steady [[brain drain]]. The country's economic policy is to attract foreign investments and to increase employment rate. One of the biggest features of the country economy is the fiscal discipline which maintained stable course of the currency for a long period. The country also makes effort to develop Small and Medium-Size Enterprise sector. |
|||
==== 2001 insurgency ==== |
|||
{{Main|2001 insurgency in Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:2001 Macedonian insurgency map.svg|thumb|Map of operations during the 2001 insurgency]] |
|||
A [[2001 insurgency in Macedonia|conflict]] took place between the government and ethnic Albanian insurgents, mostly in the north and west of the country, between February and August 2001.<ref name="news.bbc.co.uk">{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/1231596.stm |work=BBC News |title=Who are the rebels? |date=20 March 2001}}</ref><ref name="stat.gov.mk2">{{cite web |title=Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Macedonia, 2002 – Book XIII, Skopje, 2005. |publisher=State Statistical Office of the Republic of Macedonia |url=http://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/kniga_13.pdf}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/kla-veterans-linked-to-latest--bout-of-violence-in-macedonia-686995.html |work=The Independent |location=London |title=KLA veterans linked to latest bout of violence in Macedonia |first=Justin |last=Huggler |date=12 March 2001 |access-date=4 April 2010 }}{{Dead link|date=September 2021 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> The war ended with the intervention of a [[NATO]] ceasefire monitoring force. Under the terms of the [[Ohrid Agreement]], the government agreed to devolve greater political power and cultural recognition to the Albanian minority.<ref>{{cite journal |url=http://www.ecmi.de/fileadmin/downloads/publications/JEMIE/2002/nr1/Focus1-2002Brunnbauer.pdf |title=The implementation of the Ohrid Agreement: Ethnic Macedonian resentments |first=Ulf |last=Brunnbauer |journal=Journal on Ethnopolitics and Minority Issues in Europe |issue=1/2002 |year=2002 |access-date=18 May 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923233057/http://www.ecmi.de/fileadmin/downloads/publications/JEMIE/2002/nr1/Focus1-2002Brunnbauer.pdf |archive-date=23 September 2015 }}</ref> The Albanian side agreed to abandon separatist demands and to recognise all Macedonian institutions fully. In addition, according to this accord, the [[National Liberation Army (North Macedonia)|NLA]] were to disarm and hand over their weapons to a NATO force.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://rtvfan.net/ria-novosti-clashes-between-macedonians-and-albanians-in-macedonia/ |title=Clashes between Macedonians and Albanians in Macedonia |date=5 May 2016 |website=rtvfan.net}}{{dead link|date=May 2019}}{{cbignore}}</ref> However the Macedonian security forces had two more armed confrontations with Albanian militant groups, in [[Operation Mountain Storm|2007]] and [[2015 Kumanovo clashes|2015]] respectively. |
|||
[[2012 Republic of Macedonia inter-ethnic violence|Inter-ethnic tensions]] flared in Macedonia in 2012, with incidents of violence between ethnic Albanians and Macedonians.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.rferl.org/content/macedonia_ethnic_albanians_protest_murder_suspect_arrests/24578167.html |title=In Macedonia, Ethnic Albanians Protest Arrests Of Murder Suspects |work=RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty |date=11 May 2012}}</ref> In April 2017, about 200 protesters - reportedly mostly from the conservative VMRO-DPMNE party, [[2017 storming of Macedonian Parliament|stormed]] the Macedonian Parliament in response to the election of Talat Xhaferi, an ethnic Albanian and former [[National Liberation Army (Macedonia)|National Liberation Army]] commander during the 2001 conflict, as the Speaker of the Assembly.<ref name="Service 2017 b496">{{cite web | last=Service | first=s Balkan | title=Protesters Attack Lawmakers After Storming Macedonia's Parliament | website=RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty | date=2017-04-27 | url=https://www.rferl.org/a/macedonian-parliament-stormed-zaev-injured-beaten-vmro-dpmne/28455833.html | access-date=2023-12-06}}</ref><ref name="the Guardian 2017 y829">{{cite web | title=Macedonia: protesters storm parliament and attack MPs | website=the Guardian | date=2017-04-27 | url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2017/apr/27/macedonia-protesters-storm-parliament-and-attack-mps | access-date=2023-12-06}}</ref> |
|||
Looking back, the country together with [[Montenegro]], [[Bosnia and Hercegovina]] and [[Kosovo]] belonged to the less developed regions in the former Yugoslavia. It suffered severe economic difficulties after independence, when the Yugoslav internal market collapsed and subsidies from Belgrade ended. In addition, it faced many of the same problems faced by other former socialist East European countries during the transition to a market economy. Its main land and rail exports route, through [[Serbia]], remains unreliable with high transit costs, thereby affecting the export of its formerly highly profitable, early vegetables market to Germany. |
|||
==== Antiquisation ==== |
|||
The outbreak of the [[Yugoslav wars]] and the imposition of sanctions on [[Serbia]] and [[Montenegro]] caused great damage to the Republic's economy, with Serbia constituting 60% of its markets prior to the disintegration of Yugoslavia. When Greece imposed a trade embargo on the Republic in 1994–95, the economy was also affected. Some relief was afforded by the end of the Bosnian war in November 1995 and the lifting of the Greek embargo, but the [[Kosovo War]] of 1999 and the 2001 Albanian crisis caused further destabilization. Since the end of the Greek embargo, [[Greece]] has become the most important business partner of the Republic of Macedonia. Many Greek companies have bought former state companies in the country, such as the oil refinery Okta, the baking company Zhito Luks, marble mine in [[Prilep]], textile facilities in [[Bitola]] etc. Other key partners are [[Germany]], [[Italy]] and [[Slovenia]]. |
|||
{{Main|Antiquisation|Macedonism}} |
|||
Upon its coming to power in 2006, but especially since the country's non-invitation to NATO in 2008, the VMRO-DPMNE government pursued a policy of "[[Macedonian nationalism#Post-independence period and Antiquisation|Antiquisation]]" ("Antikvizatzija") as a way of putting pressure on Greece as well as for the purposes of domestic identity-building.<ref name="Georgievski">"Ghosts of the past endanger Macedonia's future". Boris Georgievski, ''Balkan Insight'', 27 October 2009 [http://www.balkaninsight.com/en/article/ghosts-of-the-past-endanger-macedonia-s-future].</ref> Statues of [[Alexander the Great]] and [[Philip II of Macedon|Philip of Macedon]] have been erected in several cities across the country. Additionally, many pieces of public infrastructure, such as airports, highways, and stadiums were renamed after Alexander and Philip. These actions were seen as deliberate provocations in neighbouring Greece, exacerbating the dispute and further stalling the country's EU and NATO applications.<ref>''Greece slates Skopje's provocative Alexander statue'' Sinisa Jakov Marusic, Balkan Insight, 15 June 2011 [http://www.balkaninsight.com/en/article/greece-slates-skopje-s-provocative-alexander-statue]</ref> The policy has also attracted criticism domestically, as well as from EU diplomats,<ref name="Georgievski"/> and, following the Prespa agreement, it has been partly reversed after 2016 by the new [[SDSM]] government of North Macedonia.<ref>{{cite news |last=Marusic|first=Sinisa Jakov |date=15 June 2018 |title=Macedonia to Rename Divisive Statues That Irked Greece |url= https://balkaninsight.com/2018/06/15/divisive-skopje-2014-landmarks-find-new-purpose-06-14-2018/|work=BalkanInsight |location=Skopje|access-date=2 April 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Tagaris |first=Karolina |date=24 January 2018 |title=Macedonia to rename airport to help resolve name row with Greece, PM says |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-greece-macedonia-name-airport/macedonia-to-rename-airport-to-help-resolve-name-row-with-greece-pm-says-idUSKBN1FD2TS |work=[[Reuters]] |location= Davos|access-date=2 April 2019}}</ref> Moreover, per Prespa agreement both countries have acknowledged that their respective understanding of the terms "Macedonia" and "Macedonian" refers to a different historical context and cultural heritage. |
|||
The Macedonian economy has since made a sluggish recovery, though the extent of [[unemployment]], the [[grey market]], corruption and a relatively ineffective legal system keep growth rate low and cause significant problems. The Republic still has one of the lowest [[List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita|per capita GDPs]] in Europe. The official unemployment rate is 38%. The active population numbers 877,798 people with 318,096 of them unemployed. However, many of the employed go unreported, therefore it is more than likely that the unemployment rate is closer to 25%. This is reflected in the large [[grey market]], estimated at close to 20% of GDP<ref>The 2006 CIA Factbook [https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mk.html]</ref> |
|||
==== EU and NATO path ==== |
|||
Growth barely recovered in 2002 to 0.9%, then rose by 3.4% in 2003, 2.9% in 2004, and 3.7% in 2005. The past few years saw a significant rise in the economy and with the recent candidacy for the EU, the country should be making rapid progress. |
|||
{{Main|Macedonia naming dispute|Prespa agreement|Accession of North Macedonia to the European Union|North Macedonia–NATO relations|Bulgaria–North Macedonia relations}} |
|||
[[File:Потпишување на договорот за македонско-грчкиот спор (17.06.2018, Преспа) (42853677381).jpg|thumb|Symbolic signing of the Prespa agreement]] |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
{{main|Demographics of the Republic of Macedonia}} |
|||
In August 2017, what was then the Republic of Macedonia signed a [[Bulgaria–North Macedonia relations#Friendship treaty and beyond|friendship agreement]] with Bulgaria, aiming to end the "anti-Bulgarian ideology" in the country and to solve the historical issues between the two. |
|||
===Population=== |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia has a population of approximately 2,070,000 citizens, according to the last population [[census]] in 2002 with 58% of the population living in urban areas. Following is a list of the largest Macedonian cities according to the 1994 census data as more recent census does not list city populations [http://www.geohive.com/cntry/macedonia.php?diacrit=1] and municipalities according to the 2002 census data: [http://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/kniga_13.pdf] |
|||
Under the [[Prespa agreement]], signed with Greece on 17 June 2018, the country agreed to change its name to the Republic of North Macedonia and stop public use of the [[Vergina Sun]]. It retained the demonym "Macedonian", but clarified this as distinct from the Hellenistic Macedonian identity in northern Greece. The agreement included removal of irredentist material from textbooks and maps in both countries, and official UN recognition of the Slavic [[Macedonian language]]. It replaced the bilateral Interim Accord of 1995.<ref name="2018FinalAgreement">{{cite web|url=http://s.kathimerini.gr/resources/article-files/symfwnia-aggliko-keimeno.pdf|title=Final Agreement for the Settlement of Differences as Described in the United Nations Security Council Resolutions 817 (1993) and 845 (1993), the Termination of the Interim Accord of 1995, and the Establishment of a Strategic Partnership Between the Parties|website=Kathimerini.gr|access-date=13 June 2018}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
The withdrawal of the Greek veto, along with the signing the friendship agreement with Bulgaria, resulted in the European Union on 27 June approving the start of [[Accession of North Macedonia to the European Union|accession talks]], which were expected to take place in 2019, under the condition that the Prespa deal was implemented.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://balkaninsight.com/2018/06/27/eu-paves-the-road-for-macedonia-albania-accession-talks-06-27-2018/ |title=Macedonia, Albania Hail EU Approval for Accession Talks |first=Sinisa Jakov |last=Marusic |website=Balkan Insight |date=27 June 2018 |access-date=27 June 2018}}</ref> On 5 July, the Prespa agreement was ratified by the Macedonian parliament with 69 MPs voting in favour of it.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-greece-macedonia/macedonias-parliament-endorses-name-deal-with-greece-for-second-time-idUSKBN1JV1MP |title=Macedonia's parliament endorses name deal with Greece for second time |website=Reuters |date=5 July 2018 |access-date=6 July 2018}}</ref> On 12 July, [[NATO]] invited Macedonia to start accession talks in a bid to become the alliance's 30th member.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://balkaninsight.com/2018/07/11/nato-invites-macedonia-to-join-the-western-alliance-07-11-2018/ |title=NATO Invites Macedonia to Join the Western Alliance |first=Sinisa Jakov |last=Marusic |website=Balkan Insight |date=11 July 2018 |access-date=13 July 2018}}</ref> On 30 July, the parliament of Macedonia approved plans to hold a non-binding [[2018 Macedonian referendum|referendum on changing the country's name]], which took place on 30 September.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.sbs.com.au/news/macedonia-to-hold-name-change-referendum-on-september-30 |title=Macedonia to hold name-change referendum on September 30 |website=SBS News |date=30 July 2018 |access-date=31 July 2018}}</ref> Ninety-one percent of voters voted in favour with a 37% turnout,<ref>{{cite web |url=https://referendum.sec.mk/Referendum/Results?cs=en-US&r=r&rd=r1&eu=All&m=All |title=iVote Demokra – Integrated Election Information System of the State Election Commission of the Republic of Macedonia |website=referendum.sec.mk |access-date=14 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180930231415/https://referendum.sec.mk/Referendum/Results?cs=en-US&r=r&rd=r1&eu=All&m=All |archive-date=30 September 2018 }}</ref> but the referendum was not carried because of a constitutional requirement for a 50% turnout.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-macedonia-referendum-turnout/macedonia-name-referendum-fails-to-reach-turnout-threshold-election-commission-idUSKCN1MA0X2 |title=Macedonia name referendum fails to reach turnout threshold: election commission |website=Reuters |date=30 September 2018 |language=en |access-date=20 November 2019}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:North Macedonia Joins NATO.jpg|thumb|left|North Macedonia commemorates its accession to NATO at the US Department of State.]] |
|||
On 6 February 2019, the permanent representatives of NATO member states and Macedonian Foreign Affairs Minister Nikola Dimitrov, signed in [[Brussels]] the [[Accession of North Macedonia to NATO|accession protocol]] of North Macedonia into NATO.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-47139118 |title=Macedonia signs Nato accession deal |date=6 February 2019 |work=[[BBC News]]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.euractiv.com/section/enlargement/news/north-macedonia-minister-nato-not-eu-saved-name-change-deal |title=North Macedonia minister: NATO, not EU, saved name change deal |date=19 March 2019 |work=[[Euractiv]]}}</ref> The protocol was then ratified on 8 February by the Greek parliament, thus completing all the preconditions for putting into force the Prespa agreement. Subsequently, on 12 February the Macedonian government announced the formal activation of the constitutional amendments which effectively renamed the country as North Macedonia and informed accordingly the United Nations and its member states.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/un-notified-of-north-macedonia-s-name-change/29768586.html |title=UN Notified Of North Macedonia's Name Change |website=RFE/RL}}</ref><ref>{{Cite press release |url=https://www.gov.uk/government/news/foreign-secretary-statement-on-the-republic-of-north-macedonia |title=Foreign Secretary statement on the Republic of North Macedonia |publisher=Government of the United Kingdom |date=16 February 2019 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.dw.com/en/north-macedonia-name-change-enters-force/a-47487844 |title=North Macedonia name change enters force |work=Deustche Welle |date=12 February 2019 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> |
|||
In March 2020, after the ratification process by all NATO members was completed, North Macedonia [[North Macedonia–NATO relations|acceded to NATO]], becoming the 30th member state.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.dw.com/en/nato-north-macedonia-becomes-30th-member/a-52944781 |title=NATO: North Macedonia becomes 30th member |work=Deutsche Welle |date=27 March 2020 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natohq/news_174589.htm |title=North Macedonia joins NATO as 30th Ally |publisher=NATO |date=27 March 2020 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> The same month, the leaders of the [[European Union]] formally gave approval to North Macedonia to begin talks to join the EU.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/eu-leaders-give-final-approval-eu-membership-talks-macedonia-albania/30512156.html |title=EU Leaders Give Final OK To Begin North Macedonia, Albania Membership Talks |work=[[Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty]] |date=27 March 2020 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/23/eu-can-start-talks-with-albania-and-north-macedonia-over-joining |title=EU can start talks with Albania and North Macedonia over joining |agency=Reuters |work=The Guardian |date=23 March 2020 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> On 17 November 2020, Bulgaria refused to approve the European Union's negotiation framework for North Macedonia, effectively blocking the official start of accession talks with this country.<ref>{{cite news |title=Bulgaria blocks EU accession talks with North Macedonia |agency=Reuters |url=https://nationalpost.com/pmn/news-pmn/bulgaria-blocks-eu-accession-talks-with-north-macedonia |date=17 November 2020 |work=National Post |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> The explanation from the Bulgarian side was: no implementation of the friendship treaty from 2017, state-supported hate speech, minority claims, and an "ongoing nation-building process" based on historical negationism of the Bulgarian identity, culture and legacy in the broader [[Macedonia (region)|region of Macedonia]].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Foreign Minister Zaharieva: Bulgaria Cannot Approve EU Negotiating Framework with North Macedonia – Novinite.com – Sofia News Agency|url=https://www.novinite.com/articles/206579/Foreign+Minister+Zaharieva%3A+Bulgaria+Cannot+Approve+EU+Negotiating+Framework+with+North+Macedonia|access-date=10 December 2020|website=Novinite.com}}</ref> The veto received condemnation by intellectuals from both states<ref>{{Cite web|title=Bulgarian intellectuals: Unacceptable to deny Macedonian nation, language; green-light talks immediately |date=5 December 2020|url=https://english.republika.mk/news/balkans/bulgarian-intellectuals-unacceptable-to-deny-macedonian-nation-language-green-light-talks-immediately/|access-date=31 December 2020}}</ref> and criticism from international observers.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Bulgaria asks EU to stop 'fake' Macedonian identity|website=[[Deutsche Welle]]|url=https://www.dw.com/en/bulgaria-asks-eu-to-stop-fake-macedonian-identity/a-55020781|access-date=31 December 2020}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=Der Spiegel: Bulgaria Misuses Its Right of Veto for Nationalistic Purposes|url=https://www.novinite.com/articles/206604/Der+Spiegel%3A+Bulgaria+Misuses+Its+Right+of+Veto+for+Nationalistic+Purposes|work=novinite.com |date=19 November 2020 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |url=https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/1460787 |first=Tomasz |last=Kamusella |date=2021 |title=Bulgaria's Secret Empire: An Ultimatum to North Macedonia |pages=155–212 |journal=Journal of Balkan and Black Sea Studies |number=6}}</ref> |
|||
Protests broke out in [[2022 North Macedonia protests|July 2022]], organized by the opposition parties, over the French proposal for the [[Accession of North Macedonia to the European Union|accession of North Macedonia to the EU]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=North Macedonia: More violence reported at protests |url=https://news.yahoo.com/north-macedonia-47-police-officers-090041288.html |access-date=2022-07-08 |website=news.yahoo.com |date=6 July 2022 |language=en-GB}}</ref> The accession talks for the accession of North Macedonia to the EU officially began in the same month, after the French proposal was passed by the Assembly of North Macedonia.<ref>{{cite web|last=Casert|first=Raf|url=https://apnews.com/article/albania-ursula-von-der-leyen-european-union-edi-rama-c302c3fb6329185f30e6952a906b201a|title=EU starts membership talks with Albania, North Macedonia|work=[[Associated Press]]|date=19 July 2022|access-date=20 July 2022}}</ref> |
|||
The 2023 European Commission Progress Report has cited the unfulfilled constitutional changes, as the primary reasons for the blocking of the further country's accession path. The EU's intention regarding the country's accession seems unclear, excluding desire to maintain its geopolitical influence here, countering the Chinese and Russian impact in the Western Balkans.<ref>North Macedonia’s EU Trajectory amidst Geopolitical Dynamics. [https://china-cee.eu/2023/12/04/n-macedonias-eu-trajectory-amidst-geopolitical-dynamics/ China-CEE Institute, Weekly Briefing, Vol. 67. No. 1 (MK) November 2023.] |
|||
</ref> On 25 September 2024, the EU announced the separation of Albania from North Macedonia on the EU accession path, due to the disputes between North Macedonia and Bulgaria.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Restelica |first=Bleona |date=2024-09-26 |title=EU Separates Albania's Accession Path From North Macedonia |url=https://schengen.news/eu-separates-albanias-accession-path-from-north-macedonia/ |access-date=2024-09-26 |website=SchengenNews |language=en}}</ref> Following the decision, the EU opened negotiations on the first chapters with Albania separately on October 15, 2024. |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
== Geography == |
|||
{{Main|Geography of North Macedonia}} |
|||
{{see also|Geology of North Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:Mount Korab, Republic of Macedonia.jpg|thumb|[[Mount Korab]], the highest mountain in North Macedonia.]] |
|||
North Macedonia has a total area of {{cvt|25436|km2|0}}.<ref name="SSO"/> It lies between latitudes [[40th parallel north|40°]] and [[43rd parallel north|43° N]], and mostly between longitudes [[20th meridian east|20°]] and [[23rd meridian east|23° E]] (a small area lies east of 23°). North Macedonia has some {{cvt|748|km|0}} of boundaries, shared with [[Serbia]] ({{cvt|62|km|0|disp=or}}) to the North, [[Kosovo]] ({{cvt|159|km|0|disp=or}}) to the northwest, [[Bulgaria]] ({{cvt|148|km|0|disp=or}}) to the east, [[Greece]] ({{cvt|228|km|0|disp=or}}) to the south, and [[Albania]] ({{cvt|151|km|0|disp=or}}) to the west. It is a transit way for shipment of goods from Greece, through the Balkans, towards Eastern, Western and Central Europe and through Bulgaria to the east. It is part of the larger region of [[Macedonia (region)|Macedonia]], which also includes [[Greek Macedonia]] and the [[Blagoevgrad Province]] in southwestern Bulgaria. |
|||
North Macedonia is a [[landlocked country]] that is geographically clearly defined by a central valley formed by the Vardar river and framed along its borders by mountain ranges. The terrain is mostly rugged, located between the [[Šar Mountains]] and [[Osogovo]], which frame the valley of the [[Vardar]] river. Three large lakes—[[Lake Ohrid]], [[Lake Prespa]] and [[Dojran Lake]]—lie on the southern borders, bisected by the frontiers with Albania and Greece. Ohrid is considered to be one of the oldest lakes and biotopes in the world.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.moe.gov.mk/soer2/ohrid_a.htm |title=Macedonian Ministry of Environment |access-date=28 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080119010740/http://www.moe.gov.mk/soer2/ohrid_a.htm |archive-date=19 January 2008 }}</ref> The region is seismically active and has been the site of destructive earthquakes in the past, most recently in 1963 when Skopje was heavily damaged by a major earthquake, killing over 1,000.<ref name="BBC News 2011 v637">{{cite web | title=History of deadly earthquakes | website=BBC News | date=2011-03-11 | url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-12717980 | access-date=2023-12-05}}</ref> |
|||
North Macedonia also has scenic mountains. They belong to two different mountain ranges: the first is the Šar Mountains<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |author=Encyclopædia Britannica |url=https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/523838/Sar-Mountains |title=Britannica's article about Sar Mountains |encyclopedia=Britannica.com |access-date=28 April 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.euratlas.com/Atlasphys/Sarplanina2.htm |title=Sar Mountains on the Euratlas map of the Europe's most significant mountain ranges |publisher=Euratlas.com |access-date=28 April 2010}}</ref> that continues to the West Vardar/Pelagonia group of mountains ([[Baba Mountain, Macedonia|Baba Mountain]], [[Nidže]], [[Kožuf]] and [[Jakupica]]), also known as the [[Dinaric Alps|Dinaric range]]. The second range is the [[Osogovo]]–[[Belasica]] mountain chain, also known as the [[Rhodope Mountains|Rhodope range]]. The mountains belonging to the Šar Mountains and the West Vardar/Pelagonia range are younger and higher than the older mountains of the Osogovo-Belasica mountain group. [[Mount Korab]] of the Šar Mountains on the Albanian border, at {{cvt|2764|m}}, is the tallest mountain in North Macedonia. In North Macedonia there are 1,100 large sources of water. The rivers flow into three different basins: the Aegean, the [[Adriatic Sea|Adriatic]] and the [[Black Sea]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.mymacedonia.net/links/geography.htm |title=Macedonia |publisher=Mymacedonia.net |access-date=25 January 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101023070728/http://www.mymacedonia.net/links/geography.htm |archive-date=23 October 2010 }}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Matka2.jpg|thumb|right|[[Matka Canyon]]]] |
|||
The Aegean basin is the largest. It covers 87% of the territory of North Macedonia, which is {{convert|22075|km2|0|abbr=out}}. [[Vardar]], the largest river in this basin, drains 80% of the territory or {{convert|20459|km2|0|abbr=out}}. Its valley plays an important part in the economy and the communication system of the country. The Vardar Valley project is considered to be crucial for the strategic development of the country. The river [[Black Drin]] forms the Adriatic basin, which covers an area of about {{cvt|3320|km2|0}}, i.e., 13% of the territory. It receives water from Lakes Prespa and Ohrid. The Black Sea basin is the smallest with only {{cvt|37|km2|0}}. It covers the northern side of Mount [[Skopska Crna Gora]]. This is the source of the river [[Binačka Morava]], which joins the [[Great Morava|Morava]], and later, the [[Danube]], which flows into the Black Sea. North Macedonia has around fifty ponds and three natural lakes, [[Lake Ohrid]], [[Lake Prespa]] and [[Lake Dojran]]. In North Macedonia there are nine spa towns and resorts: Banište, Banja Bansko, Istibanja, Katlanovo, [[Kežovica]], Kosovrasti, Banja Kočani, Kumanovski Banji and Negorci.{{cn|date=December 2024}} |
|||
=== Climate === |
|||
{{See also|Geography of North Macedonia#Climate|l1=Climate of North Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:Koppen-Geiger Map MKD present.svg|thumb|[[Köppen–Geiger]] climate classification map for North Macedonia]] |
|||
Four different seasons are found in the country with warm and dry summers and moderately cold and snowy winters. The range of temperatures recorded throughout the year ranges from {{cvt|-20|C}} in winter, to {{cvt|40|C}} in summer. Low winter temperatures are influenced by winds from the north while heat seasons during summer arise due to the subtropical pressure of the Aegean Sea and climate influences from the [[Middle East]], with the latter causing dry periods.{{sfn|Georgieva|Konechni|1998|p=73}} There are three main climatic zones in the country: mildly [[continental climate|continental]] in the north, temperate [[Mediterranean climate|Mediterranean]] in the south and [[mountain climate|mountainous]] in the zones with high altitude.{{sfn|Georgieva|Konechni|1998|p=31}} Along the valleys of the Vardar and [[Strumica (river)|Strumica]] rivers, in the regions of [[Gevgelija]], [[Valandovo]], [[Dojran]], Strumica, and [[Radoviš]], the climate is temperate Mediterranean. The warmest regions are [[Demir Kapija]] and Gevgelija, where the temperature in July and August frequently exceeds {{cvt|40|C}}.<ref>{{cite book |script-title=mk:Клима и климатска регионализација во Република Македонија, "Географски разгледи"|trans-title=Climate and climatic regionalization in the Republic of Macedonia "Geographical postcards"|language=mk|first=Mihailo|last=Zikov|date=1995|number=30|location=Skopje}}</ref> |
|||
Average annual precipitation varies from {{cvt|1700|mm|1}} in the western mountainous area to {{cvt|500|mm|1}} in the eastern area. There is a low level of precipitation in the Vardar valley with {{cvt|500|mm|1}} of water per year.{{sfn|Georgieva|Konechni|1998|p=73}} The climate and irrigation diversity allow the cultivation of different plant types, including [[wheat]], [[corn]], [[potatoes]], poppies, peanuts, and [[rice]].{{sfn|Georgieva|Konechni|1998|p=2}} There are thirty main and regular weather stations in the country. |
|||
=== Biodiversity === |
|||
{{Main|Wildlife of North Macedonia}} |
|||
{{Multiple image |
|||
|align = right |
|||
|direction= |
|||
|width =170 |
|||
|image1 =Lynx lynx poing.jpg |
|||
|caption1 = [[Eurasian lynx]]. |
|||
|image2 =Sarplaninac front.jpg |
|||
|caption2= [[Šarplaninac|Šarplaninec]]. |
|||
}} |
|||
The flora of North Macedonia is represented by around 210 [[family (biology)|families]], 920 [[genus (biology)|genera]], and around 3,700 plant species. The most abundant group are the [[flowering plant]]s with around 3,200 species, followed by [[moss]]es (350 species) and [[fern]]s (42). |
|||
[[Phytogeography|Phytogeographically]], North Macedonia belongs to the Illyrian province of the [[Circumboreal Region]] within the [[Boreal Kingdom]]. According to the [[World Wide Fund for Nature]] (WWF) and the Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the [[European Environment Agency]], the territory of the Republic can be subdivided into four terrestrial [[ecoregion]]s: the [[Pindus Mountains mixed forests]], [[Balkan mixed forests]], [[Rodope montane mixed forests]], and [[Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests]].<ref name="DinersteinOlson2017">{{cite journal|last1=Dinerstein|first1=Eric|last2=Olson|first2=David|last3=Joshi|first3=Anup|last4=Vynne|first4=Carly|last5=Burgess|first5=Neil D.|last6=Wikramanayake|first6=Eric|last7=Hahn|first7=Nathan|last8=Palminteri|first8=Suzanne|last9=Hedao|first9=Prashant|last10=Noss|first10=Reed|last11=Hansen|first11=Matt|last12=Locke|first12=Harvey|last13=Ellis|first13=Erle C|last14=Jones|first14=Benjamin|last15=Barber|first15=Charles Victor|last16=Hayes|first16=Randy|last17=Kormos|first17=Cyril|last18=Martin|first18=Vance|last19=Crist|first19=Eileen|last20=Sechrest|first20=Wes|last21=Price|first21=Lori|last22=Baillie|first22=Jonathan E. M.|last23=Weeden|first23=Don|last24=Suckling|first24=Kierán|last25=Davis|first25=Crystal|last26=Sizer|first26=Nigel|last27=Moore|first27=Rebecca|last28=Thau|first28=David|last29=Birch|first29=Tanya|last30=Potapov|first30=Peter|last31=Turubanova|first31=Svetlana|last32=Tyukavina|first32=Alexandra|last33=de Souza|first33=Nadia|last34=Pintea|first34=Lilian|last35=Brito|first35=José C.|last36=Llewellyn|first36=Othman A.|last37=Miller|first37=Anthony G.|last38=Patzelt|first38=Annette|last39=Ghazanfar|first39=Shahina A.|last40=Timberlake|first40=Jonathan|last41=Klöser|first41=Heinz|last42=Shennan-Farpón|first42=Yara|last43=Kindt|first43=Roeland|last44=Lillesø|first44=Jens-Peter Barnekow|last45=van Breugel|first45=Paulo|last46=Graudal|first46=Lars|last47=Voge|first47=Maianna|last48=Al-Shammari|first48=Khalaf F.|last49=Saleem|first49=Muhammad|display-authors=1|title=An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm|journal=BioScience|volume=67|issue=6|year=2017|pages=534–545|issn=0006-3568|doi=10.1093/biosci/bix014|pmid=28608869|pmc=5451287}}</ref> North Macedonia had a 2019 [[Forest Landscape Integrity Index]] mean score of 7.42/10, ranking it 40th globally out of 172 countries.<ref name="FLII-Supplementary">{{cite journal|last1=Grantham|first1=H. S.|last2=Duncan|first2=A.|last3=Evans|first3=T. D.|last4=Jones|first4=K. R.|last5=Beyer|first5=H. L.|last6=Schuster|first6=R.|last7=Walston|first7=J.|last8=Ray|first8=J. C.|last9=Robinson|first9=J. G.|last10=Callow|first10=M.|last11=Clements|first11=T.|last12=Costa|first12=H. M.|last13=DeGemmis|first13=A.|last14=Elsen|first14=P. R.|last15=Ervin|first15=J.|last16=Franco|first16=P.|last17=Goldman|first17=E.|last18=Goetz|first18=S.|last19=Hansen|first19=A.|last20=Hofsvang|first20=E.|last21=Jantz|first21=P.|last22=Jupiter|first22=S.|last23=Kang|first23=A.|last24=Langhammer|first24=P.|last25=Laurance|first25=W. F.|last26=Lieberman|first26=S.|last27=Linkie|first27=M.|last28=Malhi|first28=Y.|last29=Maxwell|first29=S.|last30=Mendez|first30=M.|last31=Mittermeier|first31=R.|last32=Murray|first32=N. J.|last33=Possingham|first33=H.|last34=Radachowsky|first34=J.|last35=Saatchi|first35=S.|last36=Samper|first36=C.|last37=Silverman|first37=J.|last38=Shapiro|first38=A.|last39=Strassburg|first39=B.|last40=Stevens|first40=T.|last41=Stokes|first41=E.|last42=Taylor|first42=R.|last43=Tear|first43=T.|last44=Tizard|first44=R.|last45=Venter|first45=O.|last46=Visconti|first46=P.|last47=Wang|first47=S.|last48=Watson|first48=J. E. M.|display-authors=1|title=Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material|journal=Nature Communications|volume=11|issue=1|year=2020|page=5978|issn=2041-1723|doi=10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3|pmid=33293507|pmc=7723057|bibcode=2020NatCo..11.5978G }}</ref> |
|||
The native forest fauna is abundant and includes bears, [[wild boar]]s, wolves, foxes, squirrels, [[chamois]] and deer. The [[Eurasian lynx|lynx]] is found, very rarely, in the mountains of western Macedonia, while deer can be found in the region of [[Demir Kapija]]. Forest birds include the [[blackcap]], the [[grouse]], the [[black grouse]], the [[Eastern imperial eagle|imperial eagle]] and the forest owl. |
|||
The country has [[List of national parks in North Macedonia|four national park]]s: |
|||
{|class="wikitable sortable" style="margin: 1em auto;" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! Name |
|||
|colspan="4" align="center"| '''Largest Macedonian cities and municipalities''' |
|||
! Established |
|||
! Size |
|||
! class="unsortable" |Map |
|||
! class="unsortable" |Picture |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Mavrovo National Park|Mavrovo]] |
|||
|City|| Population || Coat<br/>of arms || Administrative division || Population |
|||
|style="text-align:center" |1948 |
|||
|- |
|||
|style="text-align:center" |731 km<sup>2</sup> |
|||
|[[Skopje]] || 444,000 || [[Image:MMCA(Skopje).png|25px]] || [[Greater Skopje]]||506,000 |
|||
|style="text-align:center; padding:0;"| |
|||
|- |
|||
{{location map|North Macedonia | relief = yes | label=|position=left|float=left|width=80|lat=41.7|long=20.77|caption=}} |
|||
|[[Bitola]] || 122,173 (1991) || [[Image:Bitola New coat.JPG|25px]] || [[Bitola municipality]]|| 105,000 |
|||
|style="text-align:center; padding:0;"|[[File:Mavrovo-Lake-Autumn.jpg|100px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Kumanovo]] || 71,000 || [[Image:MMCA(Kumanovo).png|20px]]|| [[Kumanovo municipality]] || 95,000 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Galičica]] |
|||
| [[Prilep]] || 68,000 || [[Image:MMCA(Prilep).png|25px]] || [[Prilep municipality]] || 86,000 |
|||
|style="text-align:center" |1958 |
|||
|style="text-align:center" |227 km<sup>2</sup> |
|||
|style="text-align:center; padding:0;"| |
|||
{{location map|North Macedonia | relief = yes |label=|position=left|float=left|width=80|lat=40.94|long=20.81|caption=}} |
|||
|style="text-align:center; padding:0;"|[[File:Galichitsa.jpg|100px]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Pelister National Park|Pelister]] |
|||
| [[Tetovo]] || 50,000 || [[Image:MMCA(Tetovo).png|25px]] || [[Tetovo municipality]] || 81,000 |
|||
|style="text-align:center" |1948 |
|||
|style="text-align:center" |125 km<sup>2</sup> |
|||
|style="text-align:center; padding:0;"| |
|||
{{location map|North Macedonia | relief = yes |label=|float=left|width=80|position=left|lat=41|long=21.18|caption=}} |
|||
|style="text-align:center; padding:0;"|[[File:Mount Pelister MK.jpg|100px]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Šar Mountains]] |
|||
| [[Gostivar]] || 46,000 || || [[Gostivar municipality]] || 76,000 |
|||
|style="text-align:center" |2021 |
|||
|style="text-align:center" |244 km<sup>2</sup><ref>{{Cite web |title=AFTER 27 YEARS, SHAR MOUNTAIN FINALLY DECLARED A NATIONAL PARK! |url=https://mes.org.mk/blog/%D0%BF%D0%BE%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%B5-27-%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%B8-%D1%88%D0%B0%D1%80-%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%B0-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B5%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%BE-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3/ |website=Македонско Еколошко Друштво |language=Macedonian}}</ref> |
|||
|style="text-align:center; padding:0;"| |
|||
{{location map|North Macedonia | relief = yes |label=|float=left|width=80|position=left|lat=42|long=21.05|caption=}} |
|||
|style="text-align:center; padding:0;"|[[File:Доброшки Езера (Шар Планина).jpg|100px]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|} |
|||
| [[Štip]] || 41,000 || [[Image:MMCA(Shtip).png|30px]] || [[Štip municipality]] || 63,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
== Politics == |
|||
| [[Ohrid]] || 41,000 || [[Image:MMCA(Ohrid).png|25px]] || [[Ohrid municipality]] || 55,000 |
|||
{{Main|Politics of North Macedonia}} |
|||
{{More citations needed|section|date=September 2020}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:left; float:right; margin-right:9px; margin-left:2px;" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| style="text-align:left;" | [[File:MK presidential office handover 2024 - Cropped.jpg|137px]] |
|||
| [[Veles (city)|Veles]] || 34,000 || [[Image:Amblem veles.jpg|20px]] || [[Veles municipality]] || 55,000 |
|||
| style="text-align:left;" | [[File:Hristijan Mickoski official portrait 2024 (cropped).jpg|149px]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| style="text-align:center;" | [[Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova|Gordana Siljanovska<br />Davkova]]<br />{{Small|[[President of North Macedonia|President]]}} |
|||
| [[Strumica]] || 55,000 || || [[Strumica municipality]] || 150,000 |
|||
| style="text-align:center;" | [[Hristijan Mickoski]]<br />{{Small|[[Prime Minister of North Macedonia|Prime Minister]]}} |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
* See also: [[List of cities in the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
North Macedonia is a [[parliamentary system|parliamentary democracy]] with an [[executive (government)|executive government]] composed of a coalition of parties from the [[unicameralism|unicameral legislature]] ({{lang|mk|Собрание}}, {{lang|mk-Latn|Sobranie}}; ''Assembly'' in English) and an independent [[judiciary|judicial branch]] with a [[constitutional court]]. The [[Assembly of North Macedonia|Assembly]] is made up of 120 seats and the members are elected every four years. The role of the [[President of North Macedonia|president]] is mostly ceremonial, with the real power resting in the hands of the [[Prime Minister of North Macedonia|prime minister]]. The president is the [[commander-in-chief]] of the state armed forces and a president of the [[National security|State Security]] Council. The president is elected every five years and he or she can be elected twice at most. |
|||
===Ethnicities=== |
|||
[[Image:MKD_muni_nonn(Ethnic).png|thumb|right|250px|Ethnic groups in the Republic of Macedonia, according to the 2002 census]] |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia is an ethnically diverse country. The largest ethnic group in the country are the [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonians]]. In the last population census, approximately 1,300,000 inhabitants declared themselves to be Macedonians, representing 64.2% of the total population. Approximately 500,000 inhabitants are declared as [[Albanians in the Republic of Macedonia|Albanians]], representing 25.2% of the population. They are concentrated mostly in the western and north-western part of the country. Smaller minorities include [[Turkish people|Turks]] (78,000 or 3.9%), [[Roma (people)|Roma]] (54,000 or 2.7%), [[Serbs]] (36,000 or 1.8%) and [[Aromanians]] called [[Vlachs]] in the census (9695 or 0.4%). [[Slavic Muslims]] called [[Bosniaks]] or [[Muslims by nationality|Muslims]] in the census represent 0.9% of total population and include [[Torbesh]], [[Gorani (Kosovo)|Gorans]] and [[Pomaks]]. Before independence, the census recognised them as [[Muslims by nationality]] and "Bosniaks", the current name, is quite controversial as most Macedonian Muslims have no connection with Bosnian Muslims or with Bosnia at all. In smaller numbers, many other minorities exist, namely [[Montenegrins]], [[Croats]], [[Slovenes]] (all constituting a small presence of people from the former Yugoslavia), [[Egyptians (Balkans)|Egyptians]], [[Circassians]], [[Greeks]], [[Bulgarians]] and others. These other minorities account for less than 2.5% of the population of the country. The Macedonian national census records most ethnic groups, but the smaller ones are not enumerated separately in the final report. |
|||
Since 2019, local government functions are divided between 80 [[Municipalities of North Macedonia|municipalities]] ({{lang|mk|општини}}, {{lang|mk-Latn|opštini}}; [[Grammatical number|singular]]: {{lang|mk|општина}}, {{lang|mk-Latn|opština}}).<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.stat.gov.mk/KlucniIndikatori_en.aspx |title=Key indicators |website=State Statistical Office |access-date=11 November 2022}}</ref> The capital, Skopje, is governed as a group of ten municipalities collectively referred to as the "City of Skopje". Municipalities in North Macedonia are units of local self-government. Neighbouring municipalities may establish co-operative arrangements. |
|||
===Languages=== |
|||
A wide variety of languages are spoken in the Republic of Macedonia, reflecting its ethnic diversity. The official and most widely spoken language is [[Macedonian language|Macedonian]], which belongs to the [[South Slavic languages|South Slavic]] language group. Structurally, it is closer to Bulgarian than to other [[Slavic languages|Slavonic langages]]. Its current form was codified after [[WWII]] and has accumulated a thriving literary tradition. |
|||
The country's main political divergence is between the largely ethnically based political parties representing the country's ethnic Macedonian majority and Albanian minority. The issue of the power balance between the two communities led to a brief war in 2001, following which a power-sharing agreement was reached. In August 2004, parliament passed legislation redrawing local boundaries and giving greater local autonomy to ethnic Albanians in areas where they predominate. |
|||
After a troublesome pre-election campaign, North Macedonia saw a relatively calm and democratic change of government in the [[2006 Macedonian parliamentary election|elections held on 5 July 2006]]. The elections were marked by a decisive victory of the centre-right party [[VMRO–DPMNE|VMRO-DPMNE]] led by [[Nikola Gruevski]]. Gruevski's decision to include the [[Democratic Party of Albanians]] in the new government, instead of the [[Democratic Union for Integration]]–[[Party for Democratic Prosperity]] coalition which won the majority of the Albanian votes, triggered protests throughout the parts of the country with a respective number of Albanian population. A dialogue was later established between the Democratic Union for Integration and the ruling VMRO-DMPNE party as an effort to talk about the disputes between the two parties and to support European and NATO aspirations of the country.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://limun.hr/en/main.aspx?id=127474 |title=Ahmeti accepts the invitation for dialog with Gruevski |publisher=Limun.hr |access-date=5 May 2009 |archive-date=25 February 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080225142712/http://limun.hr/en/main.aspx?id=127474 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
After the early parliamentary elections held in 2008, VMRO-DPMNE and Democratic Union for Integration formed a ruling coalition.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.setimes.com/cocoon/setimes/xhtml/en_GB/features/setimes/features/2008/07/08/feature-02 |title=VMRO-DPMNE and DUI form ruling coalition in Macedonia |publisher=SeTimes |access-date=28 April 2010}}</ref> In April 2009, presidential and local elections in the country were carried out peacefully, which was crucial for Macedonian aspirations to join the EU.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.irishtimes.com/newspaper/breaking/2009/0322/breaking39.htm |title=Macedonia elections pass off peacefully |newspaper=Irish Times |date=3 March 2009 |access-date=28 April 2010}}</ref> The ruling conservative VMRO-DPMNE party won a victory in the local elections and the candidate supported by the party, Gjorgi Ivanov, was elected as the new president. |
|||
In June 2017, [[Zoran Zaev]] of the [[Social Democratic Party of Macedonia|Social Democratic Party]], became the new prime minister six months after early elections. The new center-left government ended 11 years of conservative VMRO-DPMNE rule led by former prime minister Nikola Gruevski.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.dw.com/en/macedonia-gets-new-government-six-months-after-elections/a-39073477 |title=Macedonia gets new government six months after elections |work=Deutsche Welle |date=1 June 2017 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> |
|||
{{As of|2020|1|4}}, the acting prime minister of North Macedonia was [[Oliver Spasovski]] and the president of the Parliament was [[Talat Xhaferi]].<ref name="xhaferi">{{cite web |url=http://www.balkaneu.com/tension-in-skopje-talat-xhaferi-is-elected-assembly-speaker-in-a-situation-of-chaos/ |title=Tension in Skopje, Talat Xhaferi is elected Assembly Speaker in a situation of chaos |website=Balkaneu.com |date=27 April 2017 |language=en-US |access-date=31 August 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Macedonian Parliament's New Ethnic Albanian Speaker Enters Office |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/macedonia-parliament-speaker-xhaferi-enters-office/28466113.html |newspaper=Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty |date=3 May 2017 |language=en}}</ref> The election of Xhaferi was immediately met with protests led by VMRO-DPMNE, which was quickly handled by the police.<ref name="xhaferi"/> |
|||
The early parliamentary elections took place on 15 July 2020.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://europeanmovement.eu/news/em-north-macedonia-review-of-the-2020-parliamentary-elections-in-north-macedonia/ |title=EM North Macedonia: Review of the 2020 parliamentary elections in North Macedonia |publisher=European Movement International |date=22 July 2020 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> Zoran Zaev has served as the prime minister of the Republic of North Macedonia again since August 2020.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://vlada.mk/node/14652?ln=en-gb |title=President of the Government of the Republic of North Macedonia – Zoran Zaev |date=11 May 2018 |publisher=Government of the Republic of North Macedonia |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> [[Stevo Pendarovski]] was sworn in as North Macedonia's president in May 2019.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.euronews.com/2019/05/12/north-macedonia-s-new-president-stevo-pendarovski-takes-office|title = North Macedonia's new president Stevo Pendarovski takes office |work=euronews |first=Cristina Abellan |last=Matamoros |date = 12 May 2019 |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> Prime minister Zoran Zaev announced his resignation after his party, the Social Democratic Union, suffered losses in local elections in October 2021.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.dw.com/en/north-macedonia-prime-minister-zoran-zaev-resigns/a-59681002|title = North Macedonia Prime Minister Zoran Zaev resigns | DW |date=31 October 2021|website = [[Deutsche Welle]] |access-date=29 December 2021 }}</ref> In January 2022, [[Dimitar Kovačevski]] was elected as prime minister. The new coalition cabinet composed of Kovačevski's Social Democrats and two ethnic Albanian parties.<ref>{{cite news |title=North Macedonia's Kovacevski Approved As New PM |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/north-macedonia-elect-prime-minister--dimitar-kovacevski-/31657339.html |work=RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty |language=en}}</ref> [[Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova]] took office on 12 May 2024, becoming the country's first female president.<ref>{{cite web |title=North Macedonia's First Female President Sworn In, Declines To Use 'North' |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/north-macedonia-siljanovska-davkova-inauguration-greece-prespa/32943180.html |website=Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty |access-date=13 May 2024 |date=12 May 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Parliament, or Assembly ({{langx|mk|Собрание}}, {{lang|mk-Latn|Sobranie}}), is the country's legislative body. It makes, proposes and adopts laws. The [[Constitution of North Macedonia]] has been in use since shortly after the independence of the republic in 1991. It limits the power of the governments, both local and national. The military is also limited by the constitution. The constitution states that North Macedonia is a social free state, and that Skopje is the capital.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://eudo-citizenship.eu/NationalDB/docs/MAC%20Constitution%20(amended%20by%20XXX)%20eng.pdf |title=Constitution of the Republic of North Macedonia |access-date=17 April 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170110075847/http://eudo-citizenship.eu/NationalDB/docs/MAC%20Constitution%20(amended%20by%20XXX)%20eng.pdf |archive-date=10 January 2017}}</ref> The 120 members are elected for a mandate of four years through a general election. Each citizen aged 18 years or older can vote for one of the political parties. The current president of Parliament is [[Jovan Mitreski]] since 2024.<ref>{{cite web |title=Jovan Mitreski elected Parliament Speaker |url=https://mia.mk/en/story/jovan-mitreski-elected-parliament-speaker |website=Media Information Agency |access-date=13 May 2024 |date=26 January 2024}}</ref> |
|||
Executive power in North Macedonia is exercised by the Government, whose prime minister is the most politically powerful person in the country. The members of the government are chosen by the prime minister and there are ministers for each branch of the society. There are ministers for economy, finance, information technology, society, internal affairs, foreign affairs and other areas. The members of the Government are elected for a mandate of four years. Judiciary power is exercised by courts, with the court system being headed by the Judicial [[Supreme court]], Constitutional Court and the Republican Judicial Council. The assembly appoints the judges. |
|||
=== Naming dispute === |
|||
{{Main|Macedonia naming dispute}} |
|||
{{See also|Macedonia (terminology)}} |
|||
[[File:Flag of North Macedonia (1992–1995).svg|thumb|The flag of the then-Republic of Macedonia between 1992 and 1995, bearing the [[Vergina Sun]]]] |
|||
The use of the name "[[Macedonia (terminology)|Macedonia]]" was disputed between Greece and North Macedonia. The specific naming dispute was reignited after the [[breakup of Yugoslavia]] and the newly gained independence of the former Socialist Republic of Macedonia in 1991.<ref>Floudas, Demetrius Andreas; {{cite news |publisher=24 (1996) Journal of Political and Military Sociology, 285 |url=http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa3719/is_199601/ai_n8752910/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060127053906/http://www.findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa3719/is_199601/ai_n8752910 |archive-date=27 January 2006 |title=A Name for a Conflict or a Conflict for a Name? An Analysis of Greece's Dispute with FYROM |access-date=11 February 2008 |year=1996}}</ref> Greece opposed the use of the name without a geographical qualifier so as to avoid confusion with its own region of [[Greek Macedonia]] to the south.<ref>[http://www.mfa.gr/en/fyrom-name-issue/ FYROM Name Issue] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180113160107/https://www.mfa.gr/en/fyrom-name-issue/ |date=13 January 2018 }}, Hellenic Republic – Ministry of Foreign Affairs</ref> As some ethnic Greeks identify themselves as Macedonians, unrelated to the Slavic people who are associated with North Macedonia, Greece further objected to the use of the term ''Macedonian'' for the neighbouring country's largest ethnic group; it accused the country of appropriating symbols and figures that are historically considered parts of [[Culture of Greece|Greece's culture]] (such as [[Vergina Sun]] and [[Alexander the Great]]), and of promoting the [[irredentist]] concept of a [[United Macedonia]], which would include territories of Greece, Bulgaria, Albania, and Serbia.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://foreignpolicy.com/2018/09/25/its-time-for-macedonia-to-accept-compromise/ |title=It's Time for Macedonia to Accept Compromise |publisher=ForeignPolicy |date=25 September 2018 |access-date=13 February 2019}}</ref> |
|||
The UN adopted the provisional reference ''the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia'' ({{langx|mk|Поранешна Југословенска Република Македонија}}) when the country was admitted to the organisation in 1993.<ref name="UN">{{cite web |url=https://www.un.org/documents/ga/res/47/a47r225.htm |title=United Nations Resolution 225 (1993) |publisher=United Nations |date=8 April 1993 |access-date=28 April 2010}}</ref> The lower-cased "former" was chosen intentionally to display the provisionality of the name although most UN member countries soon abandoned the provisional reference and recognised the country as the ''Republic of Macedonia'' instead.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Birth of Classical Europe: A History from Troy to Augustine |first1=Peter |last1=Thonemann |first2=Simon |last2=Price |date=29 April 2010 |publisher=[[Penguin Books]] |pages=123–124}}</ref> Most international organisations adopted the same convention along with over 100 UN members and four of the five permanent [[United Nations Security Council|UN Security Council]] members.<ref>"[http://www.macedonian-heritage.gr/Opinion/comm_20050916Tziampiris.html Naming the solution]", ''[[Kathimerini]]'' English edition, 16 September 2005</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=European Commission |title=Background information – The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia |url=http://ec.europa.eu/comm/competition/international/bilateral/background/mk1_en.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071223150634/http://ec.europa.eu/comm/competition/international/bilateral/background/mk1_en.html |archive-date=23 December 2007 |access-date=1 October 2006 }}</ref> In the period between 1991 and 2019, the country's name was an ongoing issue in bilateral and international relations. The UN set up a negotiating process with a mediator, [[Matthew Nimetz]], and the two parties to try to mediate the dispute. Following the ratification of the Prespa agreement, most major international organisations welcomed the settlement of the long-standing dispute, and adopted the country's new name.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.un.org/press/en/2019/sgsm19460.doc.htm|title=Secretary-General Congratulates Greece, Republic of North Macedonia on Settling Long-Standing 'Name' Dispute, as Agreement Enters into Force |
|||
|website=[[United Nations]]|date=13 February 2019|access-date=2 April 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://eeas.europa.eu/delegations/republic-north-macedonia_en/1457/The%20Republic%20of%20North%20Macedonia%20and%20the%20EU|title=The Republic of North Macedonia and the EU|website=[[European External Action Service]]|date=12 May 2016|access-date=2 April 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natohq/topics_48830.htm?selectedLocale=en|title=Relations with the Republic of North Macedonia |website=[[NATO]]|date=15 February 2019|access-date=2 April 2019}}</ref> |
|||
=== Foreign relations === |
|||
{{Main|Foreign relations of North Macedonia}} |
|||
{{See also|List of diplomatic missions of North Macedonia}} |
|||
North Macedonia became a member state of the UN on 8 April 1993, eighteen months after its independence from Yugoslavia. It was referred to within the UN as "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia", until the resolution of the [[Macedonia naming dispute|long-running dispute]] with Greece about the country's name. |
|||
The major interest of the country is a full integration in the European and the [[wikt:transatlantic|Trans-Atlantic]] integration processes.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.ft.com/content/94fd64f4-3035-11e9-8744-e7016697f225 |title=Renamed Balkan country seeks closer ties with Nato, EU, PM says |newspaper=Financial Times|date=18 February 2019 |last1=Hopkins |first1=Valerie }}</ref> |
|||
North Macedonia is a member of the following international and regional organisations:<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.mfa.gov.mk/default1.aspx?ItemID=314 |title=North Macedonia, Ministry of foreign affairs |publisher=Mfa.gov.mk |access-date=5 May 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081116103843/http://www.mfa.gov.mk//default1.aspx?ItemID=314 |archive-date=16 November 2008}}</ref> [[IMF]] (since 1992), [[WHO]] (since 1993), [[EBRD]] (since 1993), [[Central European Initiative]] (since 1993), [[Council of Europe]] (since 1995), [[OSCE]] (since 1995), [[Southeast European Cooperative Initiative|SECI]] (since 1996), [[Organisation internationale de la Francophonie|La Francophonie]] (since 2001), [[WTO]] (since 2003), [[CEFTA]] (since 2006), and [[NATO]] (since 2020). |
|||
In 2005, the country was officially recognised as a [[European Union]] candidate state. |
|||
At the NATO [[2008 Bucharest summit]], Macedonia failed to gain an invitation to join the organisation because Greece vetoed the move after the dispute over the name issue.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.novinite.com/view_news.php?id=91875 |title=Bulgaria: Macedonia Remains Out of NATO Because of Greek Veto over Name Dispute – Novinite.com – Sofia News Agency |publisher=Novinite.com |date=3 April 2008 |access-date=5 May 2009}}</ref> The U.S. had previously expressed support for an invitation,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://thestar.com.my/news/story.asp?file=/2008/4/2/worldupdates/2008-04-02T203446Z_01_NOOTR_RTRMDNC_0_-328122-1&sec=Worldupdates |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080410030104/http://thestar.com.my/news/story.asp?file=%2F2008%2F4%2F2%2Fworldupdates%2F2008-04-02T203446Z_01_NOOTR_RTRMDNC_0_-328122-1&sec=Worldupdates |archive-date=10 April 2008 |title=Greece stands by NATO veto threat for Macedonia | work=The Star Online |publisher=Thestar.com.my |access-date=5 May 2009 }}</ref> but the summit then decided to extend an invitation only on condition of a resolution of the naming conflict with Greece. |
|||
In March 2009, the [[European Parliament]] expressed support for North Macedonia's EU candidacy and asked the EU Commission to grant the country a date for the start of accession talks by the end of 2009. The parliament also recommended a speedy lifting of the visa regime for Macedonian citizens.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.balkaninsight.com/en/article/ep-urges-accession-talks-for-macedonia |title=EP Urges Accession Talks For Macedonia |date=13 March 2009 |publisher=BalkanInsight.com |access-date=5 May 2009}}</ref> Prior to the Prespa agreement, the country failed to receive a start date for accession talks as a result of the naming dispute. However, after the Prespa agreement, North Macedonia became a member state of NATO on 27 March 2020. The EU's stance was similar to NATO's in that resolution of the naming dispute was a precondition for the start of accession talks. |
|||
In October 2012, the EU Enlargement Commissioner [[Štefan Füle]] proposed a start of accession negotiations with the country for the fourth time, while the previous efforts were blocked each time by Greece. At the same time Füle visited Bulgaria in a bid to clarify the state's position with respect to Macedonia. He established that Bulgaria had almost joined Greece in vetoing the accession talks. The Bulgarian position was that Sofia cannot grant an EU certificate to Skopje, which is systematically employing an ideology of hate towards Bulgaria.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.euractiv.com/enlargement/bulgaria-vetoes-macedonia-eu-acc-news-515809 |title=Bulgaria vetoes Macedonia's EU accession talks |work=euractiv.com|date=2 November 2012 }}</ref> |
|||
=== Military === |
|||
{{Main|Army of North Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:Macedonian_Soldiers_in_Kabul.jpg|thumb|right|Macedonian soldiers of the Special Operations Regiment in Kabul, Afghanistan.]] |
|||
The Army of the Republic of North Macedonia (ARSM) is led by the [[Chief of the General Staff (North Macedonia)|General Staff]], below which are the Operations Command, whose forces include the [[1st Mechanized Infantry Brigade (North Macedonia)|Mechanized Infantry Brigade]], the [[North Macedonia Air Brigade|Air Brigade]], the [[Special Operations Regiment (North Macedonia)|Special Operations Regiment]], and several independent battalions; the Training and Doctrine Command, which also oversees the [[Military Reserve Force (North Macedonia)|Military Reserve Force]]; and the Logistics Base. There is also an Honor Guard Battalion that is directly subordinated to the General Staff.<ref>{{cite web |title=STRUCTURE OF THE ARMY |work=Army of the Republic of North Macedonia |url=https://mil.mk/struktura-na-arm/?lang=en |access-date=12 February 2024 }}</ref> The ARSM has 8,000 active personnel and 4,850 reservists, as well as a military budget of US$235 million in 2022.<ref>{{Cite book |author=IISS |author-link=International Institute for Strategic Studies |date=2023 |title=The Military Balance 2023 |publisher=International Institute for Strategic Studies |pages=112–113 }}</ref> It has been a volunteer military since conscription was ended in 2007. North Macedonia has deployed troops to Afghanistan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Iraq, Kosovo, and Lebanon, as part of NATO, EU, or UN missions.<ref>{{cite web |title=North Macedonia |work=CIA World Factbook |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/north-macedonia/#military-and-security |access-date=12 February 2024 }}</ref> |
|||
The Ministry of Defence develops the Republic's defence strategy and assesses possible threats and risks. It is also responsible for the defence system, including training, readiness, equipment, and development, and for drawing up and presenting the defence budget.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.morm.gov.mk/morm/en/ARM/Defence-Structure.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100904165013/http://www.morm.gov.mk/morm/en/ARM/Defence-Structure.html|title=National Command Management|archive-date=4 September 2010}}</ref> |
|||
=== Human rights === |
|||
{{Main|Human rights in North Macedonia}} |
|||
North Macedonia is a signatory to the [[European Convention on Human Rights]] and the UN Geneva [[Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees]] and [[United Nations Convention Against Torture|Convention against Torture]], and the Constitution guarantees basic human rights to all Macedonian citizens. |
|||
According to human rights organisations, in 2003 there were suspected extrajudicial executions, threats against, and intimidation of, human rights activists and opposition journalists, and allegations of torture by the police.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/region/macedonia?page=2 |title=Amnesty International – Summary – Macedonia |publisher=Web.amnesty.org |access-date=6 June 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110518152631/http://www.amnesty.org/en/region/macedonia?page=2 |archive-date=18 May 2011}}</ref><ref name="hrw2006">{{cite web |url=https://www.hrw.org/legacy/campaigns/macedonia/ |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130414225403/http://www.hrw.org/legacy/campaigns/macedonia/ |title=Human Rights Watch – Defending Human Rights Worldwide |date=14 April 2013 |archive-date=14 April 2013 }}</ref> |
|||
== Administrative divisions == |
|||
{{Main|Statistical regions of North Macedonia|Municipalities of North Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:Map of urban and rural municipalities of North Macedonia en.svg|thumb|right|Rural/Urban municipalities]] |
|||
[[File:MSR.png|thumb|right|Statistical regions of North Macedonia]] |
|||
North Macedonia's statistical regions exist solely for legal and statistical purposes. The regions are: |
|||
* [[Eastern statistical region|Eastern]] |
|||
* [[Northeastern statistical region|Northeastern]] |
|||
* [[Pelagonia statistical region|Pelagonia]] |
|||
* [[Polog statistical region|Polog]] |
|||
* [[Skopje statistical region|Skopje]] |
|||
* [[Southeastern statistical region|Southeastern]] |
|||
* [[Southwestern statistical region|Southwestern]] |
|||
* [[Vardar statistical region|Vardar]] |
|||
In August 2004, the country was reorganised into 84 municipalities ({{lang|mk|opštini}}; sing. {{lang|mk|opština}}); 10 of the municipalities constitute the City of [[Skopje]], a distinct unit of local self-government and the country's capital. |
|||
Most of the current municipalities were unaltered or merely amalgamated from the previous 123 municipalities established in September 1996; others were consolidated and their borders changed. Prior to this, local government was organised into 34 administrative districts, communes, or counties (also opštini). |
|||
== Economy == |
|||
{{Main|Economy of North Macedonia}} |
|||
Ranked as the fourth "best reformatory state" out of 178 countries ranked by the [[World Bank]] in 2009, North Macedonia has undergone considerable economic reform since independence.<ref name="worldbank">{{cite web |url=http://lnweb90.worldbank.org/eca/eca.nsf/f27e125b8411fe0e852567d10013f34a/fffd3db0d7306bfd85256c250061ac88/$FILE/Macedonia%20Country%20Brief.pdf |title=Macedonia Country Brief |publisher=The World Bank |date=24 April 2009 |access-date=5 May 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181119132529/http://lnweb90.worldbank.org/eca/eca.nsf/f27e125b8411fe0e852567d10013f34a/fffd3db0d7306bfd85256c250061ac88/$FILE/Macedonia%20Country%20Brief.pdf |archive-date=19 November 2018 }}</ref> The country has developed an [[open economy]] with trade accounting for more than 90% of GDP in recent years. Since 1996, North Macedonia has witnessed steady, though slow, economic growth with GDP growing by 3.1% in 2005. This figure was projected to rise to an average of 5.2% in the 2006–2010 period.<ref name="worldbank-devdata">{{cite web |url=http://devdata.worldbank.org/AAG/mkd_aag.pdf |title=World Bank development data |access-date=28 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100308000321/http://devdata.worldbank.org/AAG/mkd_aag.pdf |archive-date=8 March 2010}}</ref> The government has proven successful in its efforts to combat inflation, with an [[inflation rate]] of only 3% in 2006 and 2% in 2007,<ref name="worldbank"/> and has implemented policies focused on attracting [[foreign direct investment|foreign investment]] and promoting the development of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). |
|||
[[File:Грозје - Вранец.jpg|thumb|Vineyard in North Macedonia]] |
|||
The current government introduced a [[flat tax]] system with the intention of making the country more attractive to foreign investment. The flat tax rate was 12% in 2007 and was further lowered to 10% in 2008.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.vlada.mk/english/News/December2006/ei8-12-2006.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080127122623/http://www.vlada.mk/english/News/December2006/ei8-12-2006.htm |archive-date=27 January 2008 |title=Government of the Republic of Macedonia |access-date=28 April 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nuwireinvestor.com/articles/macedonias-new-flat-tax-51002.aspx |title=Macedonia's Flat Tax |publisher=Nuwireinvestor.com |date=15 February 2007 |access-date=28 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100522141422/http://www.nuwireinvestor.com/articles/macedonias-new-flat-tax-51002.aspx |archive-date=22 May 2010}}</ref> |
|||
{{As of|2005|lc=y}} North Macedonia's [[unemployment|unemployment rate]] was 37.2%<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.worldbank.org.mk/ |title=Macedonian unemployment rate |publisher=Worldbank.org.mk |access-date=28 April 2010 |archive-date=2 March 2001 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20010302165747/http://www.worldbank.org.mk/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> and {{As of|2006|lc=y}} its [[poverty threshold|poverty rate]] was 22%.<ref name="worldbank-devdata"/> Due to a number of employment measures as well as the successful process of attracting multinational corporations, and according to the State Statistical Office of North Macedonia, the country's unemployment rate in the first quarter of 2015 decreased to 27.3%.<ref>State Statistical Office [http://www.stat.gov.mk/PrikaziSoopstenie_en.aspx?rbrtxt=98 Active population – Unemployment data]</ref> Government's policies and efforts in regards to foreign direct investments have resulted with the establishment of local subsidiaries of several world leading manufacturing companies, especially from the automotive industry, such as: [[Johnson Controls|Johnson Controls Inc.]], [[Van Hool|Van Hool NV]], [[Johnson Matthey|Johnson Matthey plc]], [[Lear Corporation|Lear Corp.]], [[Visteon|Visteon Corp.]], [[Kostal-Gruppe|Kostal GmbH]], [[Gentherm Incorporated|Gentherm Inc.]], [[Dräxlmaier Group]], [[Kromberg & Schubert]], [[Marquardt Group|Marquardt GmbH]], [[Amphenol|Amphenol Corp.]], [[Tekno Hose SpA]], [[KEMET Corporation|KEMET Corp.]], [[Key Safety Systems Inc.]], [[ODW-Elektrik GmbH]], etc. |
|||
In terms of GDP structure, {{As of|2013|lc=y}}, the manufacturing sector (including mining and construction)constituted the largest part of GDP at 21.4%, up from 21.1% in 2012. The trade, transportation and accommodation sector represents 18.2% of GDP in 2013, up from 16.7% in 2012, while agriculture represents 9.6%, up from 9.1% in the previous year.<ref>State Statistical Office [http://www.stat.gov.mk/PrikaziSoopstenie_en.aspx?id=32&rbr=1495 Gross domestic product 2013]</ref> |
|||
In terms of foreign trade, the largest sector contributing to the country's export in 2014 was "chemicals and related products" at 21.4%, followed by the "machinery and transport equipment" sector at 21.1%. North Macedonia's main import sectors in 2014 were "manufactured goods classified chiefly by material" with 34.2%, "machinery and transport equipment" with 18.7% and "mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials" with 14.4% of the total imports. Even 68.8% of the foreign trade in 2014 was done with the EU which makes the Union by far the largest trading partner of North Macedonia (23.3% with Germany, 7.9% with the UK, 7.3% with Greece, 6.2% with Italy, etc.). Almost 12% of the total external trade in 2014 was done with the Western Balkan countries.<ref>State Statistical Office [http://www.stat.gov.mk/PrikaziSoopstenie_en.aspx?id=78&rbr=1590 External trade volume 2014]</ref> In 2007, North Macedonia's information technology market increased 63.8% year on year, which was the fastest growing in the Adriatic region.<ref>[http://www.idc-cema.com/?showproduct=34598 "Investment in Government, Finance, and Telecom Sectors Makes Macedonia's IT Market the Fastest Growing in the Adriatic Region, Says IDC"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121022031748/http://idc-cema.com/?showproduct=34598 |date=22 October 2012 }}, ''IDC'' (global provider of market intelligence)</ref> |
|||
North Macedonia has one of the highest shares of people struggling financially, with 72% of its citizens stating that they could manage on their household's income only "with difficulty" or "with great difficulty", though North Macedonia, along with Croatia, was the only country in the Western Balkans to not report an increase in this statistic.<ref>[http://www.balkan-monitor.eu/files/BalkanMonitor-2010_Summary_of_Findings.pdf Gallup Balkan Monitor], 2010 {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121227084847/http://www.balkan-monitor.eu/files/BalkanMonitor-2010_Summary_of_Findings.pdf |date=27 December 2012 }}</ref> Corruption and a relatively ineffective legal system also act as significant restraints on successful [[economic development]]. North Macedonia still has one of the lowest [[List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita|per capita GDPs]] in Europe. Furthermore, the country's [[grey market]] is estimated at close to 20% of GDP.<ref>The 2006 [[The World Factbook|CIA Factbook]] [https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/north-macedonia/ CIA Factbook Macedonia]</ref> PPS GDP per capita stood at 36% of the EU average in 2017.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/tgm/table.do?tab=table&init=1&language=en&pcode=tec00114&plugin=1 |title=GDP per capita in PPS |publisher=Eurostat |access-date=18 May 2019 }}</ref> With a GDP per capita of US$9,157 at [[purchasing power parity]] and a [[List of countries by Human Development Index|Human Development Index]] of 0.701, North Macedonia is less developed and has a considerably smaller economy than most of the former Yugoslav states. |
|||
=== Trade === |
|||
The outbreak of the Yugoslav wars and the imposition of sanctions on [[Serbia and Montenegro]] caused great damage to the country's economy, with Serbia constituting 60% of its markets before the disintegration of Yugoslavia. When Greece imposed a [[trade embargo]] on the Republic in 1994–95, the economy was also affected. Some relief was afforded by the end of the [[Bosnian War]] in November 1995 and the lifting of the Greek embargo, but the [[Kosovo War]] of 1999 and the 2001 Albanian crisis caused further destabilisation. |
|||
Since the end of the Greek embargo, Greece has become the country's most important business partner. (See [[Greek investments in North Macedonia]].) Many Greek companies have bought former state companies in North Macedonia,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.greekembassy.org/embassy/Content/en/Article.aspx?office=1&folder=19&article=24108 |title=Greek investments in FYROM at 1 bil. Euros |publisher=Greekembassy.org |date=16 July 2008 |access-date=8 July 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100719013921/http://www.greekembassy.org/Embassy/Content/en/Article.aspx?office=1 |archive-date=19 July 2010}}</ref> such as the [[oil refinery]] Okta, the baking company Zhito Luks, a marble mine in [[Prilep]], textile facilities in Bitola, etc., and employ 20,000 people. The moving of business to North Macedonia in the oil sector has been caused by the rise of Greece in the oil markets.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.neweurope.eu/article/depa-sees-natural-gas-role-greece-exiting-crisis/ |title=DEPA sees natural gas role for Greece exiting from the crisis |date=3 April 2017 |work=New Europe |access-date=18 April 2017 |language=en-US |archive-date=19 April 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170419105856/https://www.neweurope.eu/article/depa-sees-natural-gas-role-greece-exiting-crisis/ }}</ref> |
|||
Other key partners are Germany, Italy, the United States, Slovenia, Austria and Turkey. |
|||
=== Tourism === |
|||
{{Main|Tourism in North Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:Church of St. John at Kaneo 6.jpg|thumb|The [[church of St. John at Kaneo]] and [[Lake Ohrid]], one of the most popular tourist destinations in North Macedonia]] |
|||
[[Tourism]] plays a significant role in the economy of North Macedonia accounting for 6.7% of its GDP in 2016. The annual income from tourism was estimated at 38.5 billion denars (€616 million) in that year.<ref>{{cite journal|first=Mirche|last=Jovanovski|title=Политичката криза не е добра реклама за туризмот|trans-title=The political crisis is not a good advertisement for tourism|journal=Ekonomija I Biznis|volume=19|issue=226|date=April 2017|pages=44–47}}</ref> Following its independence, the most serious negative impact on tourism performance occurred due to the armed conflicts taking place in 2001.<ref name="marinoski"/> The number of foreign visitors has been on the rise since, with a 14.6% increase in 2011.<ref name="tourism">{{cite web|title=The State of Tourism in Macedonia |url=http://makstack.com/2011/03/15/the-state-of-tourism-in-macedonia/ |publisher=Makstack |date=15 March 2011 |access-date=2 May 2020}}</ref> In 2019, North Macedonia received 1,184,963 tourist arrivals out of which 757,593 foreign.<ref name="State Statistical Office">{{cite web|url=http://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/2020/8.1.20.03_mk.pdf |script-title=mk:Туризам во декември 2019|trans-title=Tourism in December 2019|language=mk|publisher=State Statistical Office|access-date=2 May 2020}}</ref> Most numerous are tourists from [[Turkey]], neighboring Serbia, Greece and Bulgaria, [[Poland]] and other countries of Western Europe.<ref name="tourism2019">{{cite web|url=http://makstat.stat.gov.mk/PXWeb/pxweb/mk/MakStat/MakStat__TirizamUgostitel__Turizam/250_Turizam_RM_ZemjiMes_ml.px/table/tableViewLayout2/?rxid=7695dab9-15aa-4a0e-ac4b-75d3194ce355|script-title=mk:Број на туристи и ноќевања по земја на припадност, по месеци|trans-title=Number of tourists and nights spent by country of origin, by months|publisher=State Statistical Office|language=mk|date=2020|access-date=2 May 2020}}{{Dead link|date=July 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> The biggest bulk of tourists, approximately 60% of the million tourists that visited the country in 2017, was situated in Skopje and the southwestern region of the country.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://ako.mk/%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%98%D0%B0-%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%BE-%D1%82%D1%83%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%BA%D0%B0-%D0%B4%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%86/ |script-title=mk:Македонија како туристичка дестинација за 4 сезони|trans-title=Macedonia as a tourist destination for 4 seasons|work=Ako.mk|first=Ljupčo|last=Janevski|date=7 August 2018|language=mk|access-date=3 May 2020}}</ref> |
|||
The most significant tourism branches are lake tourism as there are three lakes in Ohrid, Prespa and Dojran and over 50 small glacial lakes of variable sizes, mountainous tourism as there are 16 mountains higher than 2,000 metres. Other forms of tourism also include rural and ecotourism, city tourism and [[cultural tourism]], represented through gastronomy, traditional music, cultural celebrations and cultural heritage sites.<ref name="marinoski">{{cite journal|title=Tourism in Macedonia in Changing Environment|journal=Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences|first1=Naume|last1=Marinoski|first2=Saso|last2=Korunovski|date=2012|volume=44|pages=19–31|doi=10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.05.001|doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
== Infrastructure == |
|||
=== Transport === |
|||
{{Main|Transport in North Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:North Macedonian Highway System.svg|thumb|Map of current and planned highways]] |
|||
North Macedonia (along with [[Montenegro]], [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]] and Kosovo) belongs to the less-developed southern region of the former Yugoslavia. It suffered severe economic difficulties after independence, when the Yugoslav [[Single market|internal market]] collapsed and subsidies from Belgrade ended. In addition, it faced many of the same problems faced by other former socialist [[Eastern Europe|East European]] countries during the transition to a [[market economy]]. Its main land and rail exports route, through Serbia, remains unreliable with high transit costs, thereby affecting the export of its formerly highly profitable, early vegetables market to Germany. |
|||
North Macedonia is a landlocked country in the middle of the Balkan peninsula, and the main transport links in the country are those that connect the different parts of the peninsula (trans-Balkan links). Particularly important is the connection between north–south and Vardar valley, which connects Greece with the rest of Europe. {{As of|2019}}, there were {{cvt|10,591|km|0}} of roads, of which about {{cvt|6000|km|-2}} were paved.<ref name=Bradt2019>{{cite book |author1=Thammy Evans |author2=Philip Briggs |title=North Macedonia |year=2019 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OZ2SDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA2 |page=2 |publisher=[[Bradt Travel Guides]] |isbn=9781784770846 |access-date=18 August 2024}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Автопатска делница Велес - Неготино - Демир Капија.JPG|thumb|left|[[European route E75]] in North Macedonia]] |
|||
{{As of|2019}}, the total length of the railway network in North Macedonia was {{Cvt|922|km|0}}.<ref name=Bradt2019/> Operated by [[Makedonski Železnici]], the most important railway line is the line on the border with Serbia–Kumanovo–Skopje–Veles–Gevgelija–border with Greece. Since 2001, the railway line Beljakovci has been built—the border with Bulgaria, which will get a direct connection Skopje-Sofia. The most important railway hub in the country is Skopje, while the other two are Veles and Kumanovo. |
|||
[[North Macedonia Post]] is the state-owned company for the provision of postal traffic. It was founded in 1992 as PTT Macedonia. In 1993 it was admitted to the [[Universal Postal Union|World Postal Union]] in 1997, PTT Macedonia was divided into Macedonian Telekom and Macedonian Post (later renamed North Macedonia Post). |
|||
As far as water transport is concerned, only lake traffic through Ohrid and Prespan Lake has been developed, mostly for tourist purposes. |
|||
There are officially 17 airports in North Macedonia, of which 11 are with solid substrates.<ref name=Bradt2019/> Two are international airports: [[Skopje International Airport]] and [[Ohrid St. Paul the Apostle Airport]].<ref name=Bradt2019/> |
|||
=== Education === |
|||
{{main|Education in North Macedonia}} |
|||
[[File:Ss. Cyril and Methodius University in Skopje 2.jpg|thumb|The [[Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje|Ss. Cyril and Methodius University]] in Skopje.]] |
|||
The higher levels of [[education]] can be obtained at one of the five state universities: [[Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje]], [[St. Clement of Ohrid University of Bitola]], [[Goce Delčev University of Štip]], [[State University of Tetova]] and [[University of Information Science and Technology "St. Paul The Apostle"]] in Ohrid. There are a number of private university institutions, such as the European University,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.oic.org.mk/ |title=Home |website=Oic.org.mk}}</ref> Slavic University in [[Sveti Nikole]], the [[South East European University]] and others. North Macedonia was ranked 58th in the [[Global Innovation Index]] in 2024.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Innovation Index 2024 : Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship |url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/ |access-date=2024-11-29 |website=www.wipo.int |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
The [[United States Agency for International Development]] has underwritten a project called ''Macedonia Connects'', which has made North Macedonia the first all-broadband wireless country in the world. The Ministry of Education and Sciences reports that 461 schools (primary and secondary) are now connected to the Internet.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.usaid.gov/ |title=U.S. Agency for International Development |publisher=Macedonia.usaid.gov |access-date=5 May 2009}}</ref> In addition, an [[Internet service provider]] (On.net), has created a MESH Network to provide WIFI services in the 11 largest cities/towns in the country. The national library of North Macedonia, [[National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid"]], is in Skopje. |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
== Demographics == |
|||
{{Main|Demographics of North Macedonia|List of cities in North Macedonia|Macedonians (ethnic group)|}} |
|||
<div class="noprint"> |
|||
{{bar box |
|||
|width =200px |
|||
|float =right |
|||
|title =Ethnic groups in 2021 |
|||
|titlebar= #ddd |
|||
|bars = |
|||
{{bar percent|'''Macedonians'''|red|58.44}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Albanians|black|24.30}} |
|||
{{bar percent|DNP/refused|orange|7.20}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Turks|violet|3.86}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Romani|blue|2.53}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Serbs|green|1.30}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Bosniaks|yellow|0.87}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Aromanians and Megleno-Romanians|brown|0.47}} |
|||
{{bar percent|other|purple|1.03}} |
|||
|caption= <small>The above table shows ethnic affiliation of the population according to the [[2021 North Macedonia census|2021 census]]:<ref name="2021 census"/></small> |
|||
}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
The results from the last [[2021 North Macedonia census|2021 census]] show a population of 1,836,713. The population density of the country is 72.2 persons per km<sup>2</sup> and the average age of the population is 40.08 years. 598,632 households were recorded with an average number of household members of 3.06. The gender balance of the country is 50.4% female to 49.6% male.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.stat.gov.mk/InfoGraphic/2022/Broshura-en-web.pdf |title= Census 2021 |author=<!--Not stated--> |date= |website= |publisher= Republic of North Macedonia State Statistical Office |access-date=17 April 2022 |quote=}}</ref> |
|||
Other languages including [[Albanian language|Albanian]], [[Turkish language|Turkish]], [[Serbian language|Serbian]], [[Aromanian language|Aromanian]], [[Romani language|Romani]], [[Megleno-Romanian language|Megleno-Romanian]], [[Circassian language|Circassian]], [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]], [[Greek language|Greek]] and others are spoken roughly in proportion with their associated ethnic groups. |
|||
Based on the 2021 census data, the largest ethnic group in the country are the ethnic [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonians]]. The second-largest group are the [[Albanians in North Macedonia|Albanians]], who dominated much of the northwestern part of the country. Following them, [[Turks in North Macedonia|Turks]] are the third-biggest ethnic group of the country where official census data put them close to 70,000 and unofficial estimates suggest numbers between 170,000 and 200,000. Some unofficial estimates indicate that there are possibly up to 260,000 [[Romani people in North Macedonia|Roma]].<ref>[http://europeandcis.undp.org/uploads/public/File/rbec_web/vgr/chapter1.1.pdf] [[United Nations Development Programme|UNDP's Regional Bureau for Europe]] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090325012943/http://europeandcis.undp.org/uploads/public/File/rbec_web/vgr/chapter1.1.pdf|date=25 March 2009}}</ref> |
|||
Macedonian is the only language designated as the country's official national language. Languages spoken by over 20% of the total population can be used for some official purposes, in some alowed areas (at present only Albanian fulfils this requirement), in municipalities where at least 20% of the population is from other ethnic minorities their individual languages are used for official purposes in local government. |
|||
===Religion=== |
===Religion=== |
||
{{Main|Religion in North Macedonia}} |
|||
{{Pie chart |
|||
|thumb = left |
|||
|caption = Religion in North Macedonia (2021)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/2022/2.1.22.10-mk-en.pdf/|title=Попис на населението, домаќинствата и становите во Република Северна Македонија, 2021 - прв сет на податоци|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220330231830/https://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/2022/2.1.22.10-mk-en.pdf/|language=mk|archive-date=30 March 2022|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
|label1 = [[Eastern Orthodox Church|Eastern Orthodoxy]] |
|||
|value1 = 46.1 |
|||
|color1 = Red |
|||
|label2 = [[Catholicism]] |
|||
|value2 = 0.4 |
|||
|color2 = Gold |
|||
|label3 = Other [[Christianity|Christian]] |
|||
|value3 = 13.9 |
|||
|color3 = DeepSkyBlue |
|||
|label4 = [[Islam]] |
|||
|value4 = 32.2 |
|||
|color4 = MediumSeaGreen |
|||
|label5 = None |
|||
|value5 = 0.1 |
|||
|color5 = Honeydew |
|||
|label6 = Others |
|||
|value6 = 7.3 |
|||
|color6 = Chartreuse |
|||
}} |
|||
[[Eastern Orthodox Church|Eastern Orthodox Christianity]] is the most practiced religion in North Macedonia, making up 46.1% of the population, the vast majority of whom belong to the [[Macedonian Orthodox Church]]. Various other Christian denominations account for 13.9% of the population. Muslims constitute 32.2% of the population. North Macedonia has the fifth-highest proportion of Muslims in Europe, after those of Kosovo (96%),<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/kosovo/ |title=CIA The World Factbook: Kosovo |publisher=CIA.gov |access-date=24 November 2016}}</ref> Turkey (90%),{{citation needed|date=August 2021}} Albania (59%),<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.instat.gov.al/media/177358/njoftim_per_media_-_fjala_e_drejtorit_te_instat_ines_nurja_per_rezultatet_finale_te_census_2011.pdf |title=Presentation of the main results of the Census of Population and Housing 2011. |access-date=15 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170326091156/http://www.instat.gov.al/media/177358/njoftim_per_media_-_fjala_e_drejtorit_te_instat_ines_nurja_per_rezultatet_finale_te_census_2011.pdf |archive-date=26 March 2017}}</ref> and Bosnia and Herzegovina (51%).<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/bosnia-and-herzegovina/ |title=CIA The World Factbook: Bosnia and Herzegovina |publisher=CIA.gov |access-date=24 November 2016}}</ref> |
|||
Most Muslims are Albanians, Turks, Romani or Bosniaks; few are [[Macedonian Muslims]]. The remaining 1.4% was determined to be "unaffiliated" by a 2010 Pew Research estimation.<ref name="Pew1">{{cite web |url=http://www.pewforum.org/2015/04/02/religious-projection-table/2010/percent/all/ |title=Religious Composition by Country, 2010–2050 |date=2 April 2015 |access-date=6 November 2016 |archive-date=2 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170802041823/http://www.pewforum.org/2015/04/02/religious-projection-table/2010/percent/all/ }}</ref> |
|||
There were 1,842 churches and 580 mosques in the country at the end of 2011.<ref name="dnevnik">{{cite news |url=http://www.dnevnik.com.mk/?ItemID=A080C78F46FF724BB7AA82A63C63251E |script-title=mk:Во Македонија има 1.842 цркви и 580 џамии |date=28 December 2011 |publisher=Dnevnik |language=mk |access-date=28 December 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120111014137/http://www.dnevnik.com.mk/?ItemID=A080C78F46FF724BB7AA82A63C63251E |archive-date=11 January 2012}}</ref> The Orthodox and Islamic religious communities have secondary religion schools in Skopje. There is an Orthodox [[Seminary|theological college]] in the capital. The Macedonian Orthodox Church has jurisdiction over 10 provinces (seven in the country and three abroad), has 10 bishops and about 350 priests. A total of 30,000 people are baptised in all the provinces every year. |
|||
The majority of the population belongs to the [[Macedonian Orthodox Church]] (64.7%). [[Muslim]]s comprise 33.3% of the population and other Christian denominations comprise 0.37%. The remainder (1.63%) is recorded as "unspecified" in the 2002 national census[https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mk.html]. Most of the native Albanians, Turks and Bosniaks are Muslims, as are a minority of the country's ethnic Slavic Macedonian population, known as [[Macedonian Muslims]]. |
|||
Altogether, there are more than 1200 churches and 400 mosques in the country. The Orthodox and Islamic religious communities have secondary religion schools in Skopje. There is an Orthodox Theological college in the capital. |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
====Macedonian Orthodox Church==== |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| image1 = Манастир Св Ђорђа.JPG |
|||
| width1 = 150 |
|||
| image2 = Kalkandelen - Alaca Cami R01.JPG |
|||
| width2 = 150 |
|||
| footer = [[Church of St. George, Staro Nagoričane|The Church of St. George]] in [[Kumanovo]] (left) and [[Šarena Džamija|Šarena Džamija Mosque]] in [[Tetovo]] (right) |
|||
}} |
|||
The Macedonian Orthodox Church, which declared [[autocephaly]] in 1967, remained unrecognised by the other Orthodox Churches until 2022 when it restored relations with the [[Serbian Orthodox Church]] and the [[Ecumenical Patriarchate]], which has been followed by recognition from other churches.<ref name=":1">{{Cite web |date=2022-06-12 |title=Συλλείτουργο Οικουμενικού Πατριάρχη-Αρχιεπισκόπου Αχρίδος στο Φανάρι |trans-title=Ecumenical Patriarch, Archbishop of Ohrid in the Phanar |url=https://www.orthodoxianewsagency.gr/patriarxeia/oikomeniko_patriarxio/sylleitourgo-oikoumenikou-patriarxi-arxiepiskopou-axridos-sto-fanari/ |access-date=2022-06-13 |website=Ορθοδοξία News Agency |language=el}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last= |date=16 May 2022 |title=Church of Serbia for North Macedonia: We are not under the influence or pressure of anyone |url=https://orthodoxtimes.com/church-of-serbia-for-north-macedonia-we-are-not-under-the-influence-or-pressure-of-anyone/ |access-date=2022-05-16 |website=Orthodox Times |language=en-US}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Macedonian Orthodox Church]] has issues with the [[Serbian Orthodox Church]] after the separation and self-declaration of autocephaly (not recognized by any other Orthodox churches) in 1967. After the negotiations between the two churches were suspended, the Serbian Orthodox Church recognized a schismatic group leaded by Zoran Vranishkovski (also known as [[Archbishop Jovan of Ohrid]], recognised by all other Eastern Orthodox Churches), a former Macedonian church bishop, as the [[Orthodox Ohrid Archbishopric]]. The reaction of the Macedonian Orthodox Church was to cut-off all relations with the clergy of the Ohrid Archbishopric and to prevent bishops of the Serbian Orthodox Church from entering the Republic of Macedonia. Bishop Jovan was jailed for 18 months for defaming the Macedonian Orthodox church and harming the religious feelings of local citizens. [http://www.iwpr.net/?p=bcr&s=f&o=257037&apc_state=henibcr200508]. |
|||
The reaction of the Macedonian Orthodox Church was to cut off all relations with the new Ohrid Archbishopric and to prevent bishops of the Serbian Orthodox Church from entering North Macedonia. Bishop Jovan was jailed for 18 months for "defaming the Macedonian Orthodox church and harming the religious feelings of local citizens" by distributing Serbian Orthodox church calendars and pamphlets.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iwpr.net/?p=bcr&s=f&o=257037&apc_state=henibcr200508 |title=Church Rivalry Threatens to Brim Over |publisher=Iwpr.net |access-date=5 May 2009}}</ref> |
|||
The Macedonian State Religion Commission denies the group to be registered as a religious group saying that only one group may be registered for each confession and that the name was not sufficiently distinct from that of the Macedonian Orthodox Church. The Macedonian church had acquired documents confirming direct involvement of the Serbian government in financing the activities of the group, seen as interference in the internal affairs of another sovereign state by the Macedonian President Crvenkovski. [http://www.m-p-c.org/Vesti/Serbian_Sponsorship.htm]. The Macedonian President also rejected the request of the Head of the Serbian Orthodox Church for abolition of Zoran Vranishkovski (set as a main condition for resumption of negotiations between two churches by the Serbian Patriarch). Vranishkovski is convicted of misappropriate usage of a large sum of money donated to the Macedonian Orthodox Church. [http://www.makfax.com.mk/look/novina/printer.tpl?IdLanguage=1&IdPublication=2&NrArticle=25141&NrIssue=43&NrSection=10] |
|||
[[File:Македонска ханукија - מקדוני חנוכייה - Macedonian Hanukkah menorah.jpg|thumb|A 19th-century silver [[Menorah (Hanukkah)|menorah]]]] |
|||
* See also: [[Human rights in the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
The [[Macedonian Greek Catholic Church|Macedonian Byzantine Catholic Church]] has approximately 11,000 adherents in North Macedonia. The Church was established in 1918, and is made up mostly of converts to Catholicism and their descendants. The Church is of the [[Byzantine Rite]] and is in communion with the Roman and [[Eastern Catholic Churches]]. Its liturgical worship is performed in Macedonian.<ref>{{Catholic-hierarchy|country|mk|Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of|21 January 2015}}</ref> |
|||
There is a small [[Protestant]] community. The most famous Protestant in the country is the late president [[Boris Trajkovski]]. He was from the [[Methodism|Methodist]] community, which is the largest and oldest Protestant church in the Republic, dating back to the late 19th century. Since the 1980s the Protestant community has grown, partly through new confidence and partly with outside missionary help.{{citation needed|date=September 2022}} |
|||
====Macedonian Byzantine Catholic Church==== |
|||
The [[History of the Jews in North Macedonia|country's Jewish community]], which numbered some 7,200 people on the eve of World War II, was almost entirely destroyed during the war: only 2% survived [[the Holocaust]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.balkanalysis.com/2007/03/14/macedonia%E2%80%99s-jewish-community-commemorates-the-holocaust-and-embraces-the-future/ |title=Blog Archives " Macedonia's Jewish Community Commemorates the Holocaust, and Embraces the Future |publisher=Balkanalysis.com |access-date=28 April 2010 |archive-date=24 October 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091024102459/http://www.balkanalysis.com/2007/03/14/macedonia%E2%80%99s-jewish-community-commemorates-the-holocaust-and-embraces-the-future/ }}</ref> |
|||
The [[Macedonian Greek Catholic Church|Macedonian Byzantine Catholic Church]] (also known as the ''Macedonian Greek Catholic Church'') has approximately 11,000 adherents in the Republic. The Church was established in 1918, and is made up mostly of converts to [[Roman Catholic Church|Catholicism]] and their descendents. The Church is a [[Byzantine Rite]] within the [[Roman Catholic Church]], and conducts its liturgy in [[Macedonian language|Macedonian]]. |
|||
After their liberation and the end of the War, most opted to emigrate to [[Israel]]. Today, the country's Jewish community numbers approximately 200 persons, almost all of whom live in Skopje. Most Macedonian Jews are [[Sephardi Jews|Sephardic]]—the descendants of 15th-century refugees who had been expelled from [[Alhambra Decree|Castile, Aragon]] and [[Persecution of Jews and Muslims by Manuel I of Portugal|Portugal]].{{citation needed|date=December 2019}} |
|||
====Jewish Community==== |
|||
===Languages=== |
|||
The [[Jewish]] community of the Republic of Macedonia, which numbered some 7,200 people on the eve of [[World War II]], was almost entirely destroyed during the war, with only 2% of Macedonian Jews surviving the [[Holocaust]]. After their liberation and the end of the war, most of them opted to emigrate to [[Israel]]. Today, the country's Jewish community numbers approximately 200 people, almost all of whom live in [[Skopje]]. Most Macedonian Jews are [[Sephardic]] - the descendants of 15th century refugees who had fled the [[Spanish Inquisition|Spanish]] and [[Portuguese Inquisition|Portuguese]] Inquisitions. |
|||
{{Main|Macedonian language|Languages of North Macedonia}} |
|||
{{See also|Political views on the Macedonian language}} |
|||
[[File:Makedonija - Jezicki sastav po naseljima 2002.gif|thumb|Linguistic map of North Macedonia, 2002 census]] |
|||
The national and official language in all aspects of the whole territory of North Macedonia and in its international relations is the [[Macedonian language]]. Since 2019 [[Albanian language|Albanian]] is co-official at a state level (excluding defense, central police and monetary policy).<ref>Dimitar Bechev (2019) Historical Dictionary of North Macedonia, Rowman & Littlefield, {{ISBN|9781538119624}}, p. XLVII.</ref> Macedonian belongs to the [[Eastern South Slavic|Eastern branch]] of the [[South Slavic languages|South Slavic language group]], while Albanian occupies an independent branch of the [[Indo-European languages|Indo-European family of languages]]. In municipalities where at least 20% of the population is part of another ethnic minority, those individual languages are used for official purposes in local government, alongside Macedonian and Albanian or just Macedonian. |
|||
Macedonian is closely related to and [[Mutual intelligibility|mutually intelligible]] with standard [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]]. It also has some similarities with standard [[Serbian language|Serbian]] and the intermediate [[Torlakian dialect|Torlakian]]/[[Shopi#Dialects|Shop]] dialects spoken mostly in southeastern Serbia and western Bulgaria (and by speakers in the northeastern corner of the country). The [[standard language]] was [[Codification (linguistics)|codified]] in the period following World War II and has accumulated a thriving literary tradition. |
|||
Besides Macedonian and Albanian, minority languages with substantial numbers of speakers are [[Turkish language|Turkish]] (including [[Balkan Gagauz Turkish language|Balkan Gagauz]]<ref name="Ethnologue">{{cite web |url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=MK |title=Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition |editor-last=Gordon |editor-first=Raymond G. Jr. |year=2005 |publisher=[[SIL International]] |access-date=3 November 2008}}</ref>), [[Romani language|Romani]], [[Serbian language|Serbian]]/[[Bosnian language|Bosnian]] and [[Aromanian language|Aromanian]] (including [[Megleno-Romanian language|Megleno-Romanian]]).<ref name="Eurominority">{{cite web |url=http://www.eurominority.eu/version/eng/minority-state2.asp?id_states=28 |title=Macedonia ethnic and linguistic minorities |publisher=Eurominority |access-date=7 November 2008 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130106233113/http://www.eurominority.eu/version/eng/minority-state2.asp?id_states=28 |archive-date=6 January 2013 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.eurominority.eu/version/maps/map-european-languages.asp |title=Map of the European languages |publisher=Eurominority |access-date=7 November 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160114185030/http://www.eurominority.eu/version/maps/map-european-languages.asp |archive-date=14 January 2016 }}</ref><ref name="Britannica">{{cite encyclopedia |url=http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/83/1983-004-1B1C7082.gif |title=Indo-European languages in contemporary Eurasia |encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |access-date=4 October 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081217180856/http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/83/1983-004-1B1C7082.gif |archive-date=17 December 2008}}</ref><ref name="BBC">{{cite web |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/languages/european_languages/countries/macedonia.shtml |title=BBC: Languages across Europe – Macedonia |publisher=BBC |access-date=7 November 2008}}</ref> [[Macedonian Sign Language]] is the primary language of those of the deaf community who did not pick up an oral language in childhood. |
|||
According to the last census, 1,344,815 citizens of North Macedonia declared that they spoke Macedonian, 507,989 declared Albanian, 71,757 Turkish, 38,528 Romani, 24,773 Serbian, 8,560 Bosnian, 6,884 Aromanian and 19,241 spoke other languages.<ref name="auto1"/> |
|||
* See also: [[Jews in the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
== |
===Cities=== |
||
{{Largest cities |
|||
| country = North Macedonia |
|||
| stat_ref = <ref name="PxWeb x960">{{cite web | title=Total resident population of the Republic of North Macedonia by ethnic affiliation, by settlement, Census 2021-PxWeb | website=PxWeb | url=https://makstat.stat.gov.mk/PXWeb/pxweb/en/MakStat/MakStat__Popisi__Popis2021__NaselenieVkupno__PodatociNaselenie/T1503P21.px/?rxid=9d39a8f4-4901-4025-9983-776064c2ddd6 | access-date=2023-12-05}}</ref> |
|||
| list_by_pop = <!-- link to the list of cities in the given country, if possible sorted by population --> |
|||
The Macedonian education system is consisted of: |
|||
| div_name = Region |
|||
| div_link = Statistical regions of North Macedonia{{!}}Region |
|||
| city_1 = Skopje | div_1 = Skopje Statistical Region{{!}}Skopje Statistical | pop_1 = 526,502 |img_1 = Skopje - Goce Delčev Bridge.jpg |
|||
* [[Kindergarten|pre-school education]] |
|||
| city_2 = Kumanovo | div_2 = Northeastern Statistical Region{{!}}Northeastern Statistical | pop_2 = 75,051 |img_2 = Куманово.jpg |
|||
* [[primary education]] |
|||
| city_3 = Bitola | div_3 = Pelagonia Statistical Region{{!}}Pelagonia Statistical | pop_3 = 69,287 |img_3 = Bitola to mount Baba.jpg |
|||
* [[secondary education]] |
|||
| city_4 = Prilep | div_4 = Pelagonia Statistical Region{{!}}Pelagonia Statistical | pop_4 = 63,308 |img_4 = Prilep from Towers of Marko.jpg |
|||
* [[higher education]] |
|||
| city_5 = Tetovo | div_5 = Polog Statistical Region{{!}}Polog Statistical | pop_5 = 63,176 |
|||
| city_6 = Štip | div_6 = Eastern Statistical Region{{!}}Eastern Statistical | pop_6 = 42,000 |
|||
| city_7 = Veles (city){{!}}Veles | div_7 = Vardar Statistical Region{{!}}Vardar Statistical | pop_7 = 40,664 |
|||
| city_8 = Ohrid | div_8 = Southwestern Statistical Region{{!}}Southwestern Statistical | pop_8 = 38 818 |
|||
| city_9 = Strumica | div_9 = Southeastern Statistical Region{{!}}Southeastern Statistical | pop_9 = 33,825 |
|||
| city_10 = Gostivar | div_10 = Polog Statistical Region{{!}}Polog Statistical | pop_10 = 32,814 |
|||
| city_11 = Kavadarci | div_11 = Vardar Statistical Region{{!}}Vardar Statistical | pop_11 = 32,038 |
|||
| city_12 = Kočani | div_12 = Eastern Statistical Region{{!}}Eastern Statistical | pop_12 = 24,632 |
|||
| city_13 = Kičevo | div_13 = Southwestern Statistical Region{{!}}Southwestern Statistical | pop_13 = 23,428 |
|||
| city_14 = Gevgelija | div_14 = Southeastern Statistical Region{{!}}Southeastern Statistical | pop_14 = 15,156 |
|||
| city_15 = Struga | div_15 = Southwestern Statistical Region{{!}}Southwestern Statistical | pop_15 = 15,009 |
|||
| city_16 = Radoviš | div_16 = Southeastern Statistical Region{{!}}Southeastern Statistical | pop_16 = 14,460 |
|||
| city_17 = Kriva Palanka | div_17 = Northeastern Statistical Region{{!}}Northeastern Statistical | pop_17 = 13,481 |
|||
| city_18 = Negotino | div_18 = Vardar Statistical Region{{!}}Vardar Statistical | pop_18 = 12,488 |
|||
| city_19 = Debar | div_19 = Southwestern Statistical Region{{!}}Southwestern Statistical | pop_19 = 11,735 |
|||
| city_20= Sveti Nikole | div_20 = Eastern Statistical Region{{!}}Eastern Statistical | pop_20 = 11,728 |
|||
}} |
|||
The higher levels of education can be obtained at one of the three state universities: [[Skopje University|Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje]], [[Bitola University|St. Clement of Ohrid University of Bitola]] and [[Tetovo University|State University of Tetovo]]. There is a number of private university institutions, such as the European University [http://www.oic.org.mk/en/Default-en.htm], the [[South East European University]] and others. |
|||
==Culture== |
==Culture== |
||
{{Main|Culture of North Macedonia|List of Macedonians (ethnic group)|Music of North Macedonia}} |
|||
:''See also: [[Macedonian culture (Slavic)]]'' |
|||
[[File:Tanec folk ensemble Macedonia 3.jpg|thumb|Folk dancers]] |
|||
North Macedonia has a rich cultural heritage in art, architecture, poetry and music. It has many ancient, protected religious sites. Poetry, cinema, and music festivals are held annually. [[Music of North Macedonia|Macedonian music]] styles developed under the strong influence of [[Byzantine music|Byzantine]] church music. North Macedonia has a significant number of preserved [[Byzantine art|Byzantine]] fresco paintings, mainly from the period between the 11th and 16th centuries. There are several thousands of square metres of [[fresco]] painting preserved, the major part of which is in very good condition and represent masterworks of the Macedonian school of ecclesiastical painting. |
|||
The most important cultural events in the country are the [[Ohrid Summer Festival]] of classical music and drama, the [[Struga Poetry Evenings]] which gather poets from more than 50 countries in the world, International Camera Festival in [[Bitola]], Open Youth Theatre and [[Skopje Jazz Festival]] in Skopje etc. |
|||
Macedonian music styles developed under the strong influence of Byzantine church music. |
|||
The National Opera opened in 1947, then named "Macedonian Opera", with a performance of ''[[Cavalleria rusticana]]'' under the direction of Branko Pomorisac. Every year, the May Opera Evenings are held in Skopje for around 20 nights. The first May Opera performance was that of [[Kiril Makedonski]]'s ''Tsar Samuil'' in May 1972.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.culture.in.mk/story.asp?id=19442&rub=35 |title=Macedonian Opera Marks 60th Anniversary. Culture – North Macedonia |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110727035755/http://www.culture.in.mk/story.asp?id=19442&rub=35 |archive-date=27 July 2011}}</ref> |
|||
The Republic of Macedonia is among the countries with the most beautiful preserved Byzantine fresco painting, mainly from the period between the 11th and 16th centuries. There are several thousands square metres of fresco painting preserved, the major part of which is in very good condition and represent masterworks of the Macedonian School of ecclesiastical painting. |
|||
===Cuisine=== |
|||
In the Republic of Macedonia the past meets the present. Its age-old architecture and monasteries and churches of exquisite beauty make an interesting contrast to the super modern new architecture. |
|||
{{Main|Macedonian cuisine}} |
|||
Most of the Macedonian monasteries, built in various periods, and particularly those built between the 11th and 15th–16th centuries, have been completely preserved until today. |
|||
[[File:Грав во тава(тафче гравче) (3).jpg|thumb|[[Tavče gravče]]]] |
|||
The Macedonian collection of icons, and in particular the Ohrid one, is among the most valuable collections in the world today. After the Sinai and the Moscow collection of icons, it is third in importance in Orthodoxy. From a Byzantological aspect, it is unique. |
|||
The country's cuisine is representative of that of the Balkans—reflecting [[Mediterranean cuisine|Mediterranean]] and [[Middle Eastern cuisine|Middle Eastern]] ([[Ottoman cuisine|Ottoman]]) influences, and to a lesser extent [[Italian cuisine|Italian]], [[German cuisine|German]] and Eastern European (especially [[Hungarian cuisine|Hungarian]]) ones.<ref name=friedman>{{citation |contribution=La cuisine macédonien |first1=Victor |last1=Friedman |first2=Veselka |last2=Palmer |title=Cuisines d'Orient et d'ailleurs |editor1-first=Michel |editor1-last=Aufray |editor2-first=Michel |editor2-last=Perret |publisher=Paris: INALCO/Grenoble: Glénant |year=1995 |pages=76–79 |url=http://mahimahi.uchicago.edu/media/faculty/vfriedm/094Friedman95.pdf |access-date=10 February 2016 |archive-date=14 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171014103901/http://mahimahi.uchicago.edu/media/faculty/vfriedm/094Friedman95.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> The relatively warm climate in North Macedonia provides excellent growth conditions for a variety of vegetables, herbs and fruits. Thus, Macedonian cuisine is particularly diverse. |
|||
The most important cultural events in the country are the [[Ohrid]] Summer festival of classical music and drama, the [[Struga]] Poetry evenings which gather poets from more than 50 countries in the world, Skopje May Opera Evenings, International Camera Festival in [[Bitola]], Open Youth Theatre and Jazz festivals in Skopje etc. |
|||
Macedonian cuisine is also noted for the diversity and quality of its [[dairy products]], wines, and local alcoholic beverages, such as [[rakija]]. [[Tavče gravče]] and [[mastika]] are considered the national dish and drink of North Macedonia, respectively. Some other important dishes include [[Šopska salad]], an appetiser and side dish that accompanies the main meal, [[ajvar]], stuffed peppers, [[pastrmajlija]] and others.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Culture and Food – Determining the Value of Food in Rural Tourism as an Important Part of the total Tourism Experience|first=Michael|last=Risteski|journal=XVI International Conference of Partner Institutions "Planning for Change"|publisher=La Fondation pour la Formation Hoteliere, Nestle Pro Gastronomia|year=2016}}</ref> |
|||
* [[List of Macedonians (ethnic group)|A list of famous ethnic Macedonians]] |
|||
* [[Music of the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
* [[Macedonian language]] |
|||
* [[Public holidays in the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
== |
===Sport=== |
||
[[File:SStandPhilipIIArena.jpg|thumb|[[Toše Proeski Arena]]]] |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
[[File:HC Vardar in Skopje.jpg|thumb|The welcoming ceremony for [[RK Vardar]] after winning the [[2016–17 EHF Champions League]]]] |
|||
Image:Ohridlake.jpg|[[Lake Ohrid]] |
|||
Image:Bogorodica.jpg|[[Saint Bogorodica Precista Monastery]] near [[Kichevo]] |
|||
[[Association football|Football]], [[handball]], and [[basketball]] are the most popular sports in North Macedonia. The [[North Macedonia national football team]] is controlled by the [[Football Federation of Macedonia]]. Their home stadium is the [[Toše Proeski Arena]]. In November 2003, to celebrate [[UEFA]]'s jubilee, [[Darko Pančev]] was selected as the [[UEFA Jubilee Awards|Golden Player]] of Macedonia as their most outstanding player of the past 50 years.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.uefa.com/uefa/news/Kind=256/newsId=130150.html|title=Golden Players take centre stage|date=29 November 2003|website=UEFA.com|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050317084104/http://www.uefa.com/uefa/news/Kind%3D256/newsId%3D130150.html|archive-date=17 March 2005|access-date=23 September 2020}}</ref> He was the winner of the [[European Golden Shoe|European Golden Boot]] award in 1991 and he is best known for scoring the winning penalty in the [[1991 European Cup Final]], bringing [[Red Star Belgrade]] the most prestigious trophy in European football for the first time in its 50-year existence. In 2020, the national team qualified for [[UEFA Euro 2020]] (held in 2021), their first major tournament in the country's history.<ref>{{cite news |title=North Macedonia qualify for Euro 2020, their first major tournament |url=https://www.beinsports.com/en/uefa-euro-2020-qualifying/news/north-macedonia-qualify-for-euro-2020-their-f/1582065/amp |access-date=12 November 2020 |publisher=beIN Sports |date=12 November 2020}}</ref> |
|||
Image:pelister.jpg|National park [[Pelister]] |
|||
Image:BitolaWinter.jpg|[[Bitola]] town |
|||
Handball is the other important team sport in the country. Macedonian clubs have enjoyed success in European competitions. [[RK Vardar]] won [[2016–17 EHF Champions League|2016–17]] and [[2018–19 EHF Champions League]], while [[Kometal Gjorče Petrov Skopje]] won the 2002 [[EHF Champions League|EHF Women's Champions League]]. The [[European Women's Handball Championship]] took place in 2008 in North Macedonia in Skopje and Ohrid; the [[North Macedonia women's national handball team|women's national team]] finished seventh place. The country's [[North Macedonia men's national handball team|men's national team]] has appeared in the European and World championships multiple times, with a best finish of fifth at the former ([[2012 European Men's Handball Championship|2012]]) and ninth at the latter ([[2015 World Men's Handball Championship|2015]]). |
|||
Image:KorabMountain.jpg|[[Mount Korab]] |
|||
Image:MountShara.jpg|[[Shara mountain]] |
|||
The [[North Macedonia men's national basketball team|North Macedonia national basketball team]] represents North Macedonia in international basketball. The team is run by the Basketball Federation of North Macedonia, the governing body of basketball in North Macedonia which was created in 1992 and joined FIBA in 1993. North Macedonia has participated in three [[EuroBasket]]s since then with its best finish at 4th place in [[EuroBasket 2011|2011]]. It plays its home games at the [[Boris Trajkovski Sports Center]] in Skopje. [[Pero Antić]] became the [[List of foreign NBA players|first Macedonian basketball player]] to play in the [[National Basketball Association]]. He also won three [[EuroLeague]] trophies. |
|||
Image:Nerezi.jpg|St. Panteleimon church near [[Skopje]] |
|||
Image:Architecture.jpg|[[Bitola]] town |
|||
In the summer months the [[Ohrid Swimming Marathon]] is an annual event on [[Lake Ohrid]] and during the winter months there is skiing in North Macedonia's winter sports centres. North Macedonia also takes part in the Olympic Games. Participation in the Games is organised by the [[Olympic Committee of North Macedonia]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.insidethegames.biz/articles/1077274/ioc-approve-name-change-to-north-macedonia-national-olympic-committee |title=IOC approve name change to North Macedonia National Olympic Committee |website= insidethegames.biz|date=27 March 2019 }}</ref> [[Magomed Ibragimov (wrestler, born 1974)|Magomed Ibragimov]] competed for Macedonia in the [[Wrestling at the 2000 Summer Olympics – Men's freestyle 85 kg|freestyle 85 kg competition]] at the [[2000 Summer Olympics]] and won the bronze medal, which was the first medal for independent country. Wrestlers [[Shaban Trstena]] and [[Shaban Sejdiu]] born in North Macedonia, as well as boxers [[Redžep Redžepovski]] and [[Ace Rusevski]], won Olympic medals as part of Yugoslav Olympic team. |
|||
Image:Panair Korab.jpg|[[Mount Korab]] – The highest mountain in the country |
|||
Image:Heraclea.jpg|Mosaic from [[Heraclea Lyncestis]] - near [[Bitola]] |
|||
===Cinema=== |
|||
Image:MountKorab.jpg|[[Mount Korab]] |
|||
{{Main|Cinema of North Macedonia}} |
|||
Image:Plaosnik1.jpg|St Panteleimon on the site of St. Clement’s Monastery, Plaosnik, [[Ohrid]] |
|||
[[File:Milcho Manchevski.JPG|thumb|right|[[Milcho Manchevski]] is a critically acclaimed Macedonian film and TV director who won the [[Golden Lion]] at [[Venice Film Festival]]]] |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
The [[history of film]] making in the country dates back over 110 years.{{citation needed|date=March 2016}} The first film to be produced on the territory of the present-day country was made in 1895 by [[Manakis brothers|Janaki and Milton Manaki]] in Bitola. Throughout the past century, the medium of film has depicted the history, culture and everyday life of the Macedonian people. Over the years many Macedonian films have been presented at film festivals around the world and several of these films have won prestigious awards. The first Macedonian feature film was ''Frosina'', released in 1952 and directed by [[Vojislav Nanović]].<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Terzin Stojčić|first=Marijana|date=2019|title=Seme istorije Kirila Cenevskog|journal=Kinoteka|volume=33|pages=54–57}}</ref> |
|||
The first feature film in colour was ''Miss Stone'', a movie about a Protestant missionary in Ottoman Macedonia. It was released in 1958. The highest grossing feature film in North Macedonia was ''[[Bal-Can-Can]]'', having been seen by over 500,000 people in its first year alone. In 1994, [[Milcho Manchevski]]'s film ''[[Before the Rain (1994 film)|Before the Rain]]'' was nominated for an [[Academy Award]] in the category of [[Academy Award for Best International Feature Film|Best International Feature Film]].<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|url=https://www.britannica.com/place/North-Macedonia/Cultural-life|title=North Macedonia – Cultural life|encyclopedia=Britannica|access-date=12 August 2019}}</ref> Manchevski continues to be the most prominent modern filmmaker in the country having subsequently written and directed ''[[Dust (2001 film)|Dust]]'' and ''[[Shadows (2007 film)|Shadows]]''. In 2020, the documentary ''[[Honeyland (2019 film)|Honeyland]]'' (2019) directed by [[Tamara Kotevska]] and Ljubomir Stefanov, received nominations in the categories for [[Academy Award for Best International Feature Film|Best International Feature Film]] and [[Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature|Best Documentary Feature]] at the [[92nd Academy Awards]], making it the first non-fictional film to receive a nomination in both categories.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Martinelli |first1=Marissa |title=Honeyland Just Made Oscar History |url=https://slate.com/culture/2020/01/oscars-2020-honeyland-international-documentary-north-macedonia.html |access-date=28 January 2020 |work=The Slate |date=13 January 2020}}</ref> |
|||
=== Media === |
|||
{{Main|Mass media in North Macedonia}} |
|||
The oldest newspaper in the country is ''[[Nova Makedonija]]'' from 1944. Other well known newspaper and magazines are: ''[[Utrinski vesnik]]'', {{Lang|mk-latn|[[Dnevnik (Skopje)|Dnevnik]]}}, ''Vest'', ''Fokus'', ''[[Večer (Skopje)|Večer]]'', ''[[Tea Moderna (magazine)|Tea Moderna]]'', ''[[Makedonsko Sonce]]'', and ''Koha''. Public channel is [[Macedonian Radio Television]] founded in 1993 by the [[Assembly of North Macedonia]]. [[TEKO TV]] (1989) from [[Štip]] is the first private television channel in the country. Other popular private channels are: [[Sitel (TV channel)|Sitel]], [[Kanal 5 (Macedonia)|Kanal 5]], [[Telma (TV channel)|Telma]], [[Alfa TV (TV channel Macedonia)|Alfa TV]], and [[Alsat-M]]. |
|||
===Public holidays=== |
|||
{{Main|Public holidays in North Macedonia}} |
|||
The main public holidays in North Macedonia are: |
|||
{|class="wikitable" |
|||
|- |
|||
! Date !! English name !! Macedonian name !! Remarks |
|||
|- |
|||
|1–2 January ||New Year ||Нова Година, ''Nova Godina'' || |
|||
|- |
|||
|7 January ||Christmas Day ([[Eastern Orthodox Church|Orthodox]]) ||Прв ден Божиќ, ''Prv den Božiḱ'' || |
|||
|- |
|||
|April/May ||[[Good Friday]] (Orthodox) ||Велики Петок, ''Veliki Petok'' ||Orthodox Easter and other Easter dates do not match; see: [[List of dates for Easter]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|April/May ||[[Easter Sunday]] (Orthodox) ||Прв ден Велигден, ''Prv den Veligden'' || |
|||
|- |
|||
|April/May ||[[Easter Monday]] (Orthodox) ||Втор ден Велигден, ''Vtor den Veligden'' || |
|||
|- |
|||
|1 May ||Labour Day ||Ден на трудот, ''Den na trudot'' || |
|||
|- |
|||
|24 May ||[[Saints Cyril and Methodius Day]] ||Св. Кирил и Методиј, Ден на сèсловенските просветители; ''Sv. Kiril i Metodij, Den na sèslovenskite prosvetiteli'' || |
|||
|- |
|||
|2 August ||[[Republic Day (North Macedonia)|Republic Day]] ||Ден на Републиката, ''Den na Republikata'' ||Day when the Republic was established in 1944, also [[Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising|Ilinden Uprising]] in 1903. |
|||
|- |
|||
|8 September ||[[Independence Day (North Macedonia)|Independence Day]] ||Ден на независноста, ''Den na nezavisnosta'' ||Day of independence from [[Yugoslavia]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|11 October ||[[Day of the Macedonian Uprising]] ||Ден на востанието, ''Den na vostanieto'' ||Beginning of Anti-fascist war during WWII in 1941 |
|||
|- |
|||
|23 October ||[[Day of the Macedonian Revolutionary Struggle (Holiday)]]||Ден на македонската револуционерна борба,''Den na makedonskata revolucionarna borba'' ||Day when the [[Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization]] (IMRO) was established in 1893. |
|||
|- |
|||
|1 Shawwal ||[[Eid ul-Fitr]] ||Рамазан Бајрам, ''Ramazan Bajram'' ||moveable, see: [[Islamic Calendar]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|8 December ||Saint [[Clement of Ohrid]] Day ||Св. Климент Охридски, ''Sv. Kliment Ohridski'' || |
|||
|} |
|||
Besides these, there are several major religious & minorities holidays. (See: ''[[Public holidays in North Macedonia]]'') |
|||
==Symbols== |
|||
{{See also|List of flags of North Macedonia|National symbols of North Macedonia}} |
|||
* '''Sun''': The official [[flag of North Macedonia]], adopted in 1995, is a yellow sun with eight broadening rays extending to the edges of the red field. |
|||
* '''Coat of arms''': After independence in 1991, North Macedonia retained the [[Coat of arms of North Macedonia|coat of arms]] adopted in 1946 by the People's Assembly of the People's Republic of Macedonia on its second extraordinary session held on 27 July 1946, later on altered by article 8 of the Constitution of the Socialist Federal Republic of Macedonia. The coat-of-arms is composed by a double bent garland of ears of wheat, tobacco and poppy, tied by a ribbon with the embroidery of a traditional folk costume. In the center of such a circular room there are mountains, rivers, lakes and the sun. All this is said to represent "the richness of our country, our struggle, and our freedom". |
|||
==International rankings== |
|||
{|class="wikitable" |
|||
|- |
|||
!Organisation |
|||
!Survey |
|||
!Ranking |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Institute for Economics and Peace]] |
|||
|[[Global Peace Index]] 2019<ref>{{cite web |title=Global Peace Index 2019 |url=http://visionofhumanity.org/app/uploads/2019/06/GPI-2019-web003.pdf |website=visionofhumanity.org |publisher=Institute of Economics & Peace |access-date=10 February 2020 |page=9 |archive-date=27 August 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190827155045/http://visionofhumanity.org/app/uploads/2019/06/GPI-2019-web003.pdf }}</ref> |
|||
|65 out of 163 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Reporters Without Borders]] |
|||
|Worldwide Press Freedom Index 2019<ref>{{cite web |title=Republic of North Macedonia – 2019 World Press Freedom Index |url=https://rsf.org/en/republic-north-macedonia |website=rsf.org |publisher=Reporters Without Borders |access-date=10 February 2020 |archive-date=14 January 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200114213439/https://rsf.org/en/republic-north-macedonia |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
|95 out of 180 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[The Heritage Foundation]]/[[The Wall Street Journal]] |
|||
|[[Index of Economic Freedom]] 2019<ref>{{cite web |title=Index of Economic Freedom 2019 |url=https://www.heritage.org/index/country/macedonia |website=heritage.org |publisher=The Heritage Foundation |access-date=10 February 2020}}</ref> |
|||
|33 out of 180 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Transparency International]] |
|||
|Corruption Perceptions Index 2019<ref>{{cite web |title=Corruption Perceptions Index 2019 |url=https://www.transparency.org/country/MKD |website=transparency.org |publisher=Transparency International |access-date=10 February 2020 |archive-date=11 April 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200411155258/https://www.transparency.org/country/MKD |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
|106 out of 180 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[United Nations Development Programme]] |
|||
|[[Human Development Index]] 2019<ref>{{cite web |title=2019 Human Development Index Ranking |url=http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/2019-human-development-index-ranking |website=hdr.undp.org |publisher=United Nations Development Programme |access-date=10 February 2020 |archive-date=16 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200516123624/http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/2019-human-development-index-ranking }}</ref> |
|||
|82 out of 189 |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[World Bank]] |
|||
|[[Ease of doing business index]] 2019<ref>{{cite web |title=Ease of doing business ranking |url=https://www.doingbusiness.org/content/dam/doingBusiness/media/Annual-Reports/English/DB2019-report_web-version.pdf |website=doingbusiness.org |publisher=World Bank |access-date=10 February 2020 |page=5}}</ref> |
|||
|10 out of 190 |
|||
|} |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{portal}} |
{{portal|North Macedonia}} |
||
* [[ |
* [[Outline of North Macedonia]] |
||
{{Clear}} |
|||
* [[Maps of the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
* [[Communications in the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
* [[Foreign relations of the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
* [[Military of the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
* [[Transportation in the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
* [[Public holidays in the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
==Notes== |
==Notes== |
||
{{notelist |
|||
<div class="references-small"><references/></div> |
|||
| notes = |
|||
{{efn |
|||
| name = Kosovo |
|||
| North Macedonia has recognised Kosovo since 9 October 2008.<ref>[http://www.mia.com.mk/default.aspx?vId=57722300&lId=2 Macedonia recognizes Kosovo] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081015121606/http://www.mia.com.mk/default.aspx?vId=57722300&lId=2 |date=15 October 2008 }}, Macedonian Information Agency, 9 October 2008</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
{{efn |
|||
| name = language1 |
|||
| National and official language in all aspects of the whole territory of the state and in its international relations. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{efn |
|||
| name = language2 |
|||
| Co-official language at a state level (excluding defence, central police and monetary policy) and in local self-government units where speakers are 20% or more. |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
==Bibliography== |
|||
{{Refbegin}} |
|||
* Brunnbauer, Ulf. "'Pro‐Serbians' vs. 'Pro‐Bulgarians': Revisionism in Post‐Socialist Macedonian Historiography." ''History Compass'' 3.1 (2005). [https://compass.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1478-0542.2005.00130.x online] |
|||
* Brunnbauer, Ulf. "Serving the Nation: Historiography in the Republic of Macedonia (FYROM) After Socialism." ''Historein'' 4 (2003): 161–182. [https://ejournals.epublishing.ekt.gr/index.php/historein/article/download/2176/2016 online] |
|||
* {{cite book|last1=Georgieva|first1=Valentina|last2=Konechni|first2=Sasha|title=Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia|url=https://archive.org/details/historicaldictio0000geor|url-access=registration|publisher=Scarecrow Press|year=1998|isbn=0-8108-3336-0}} |
|||
* Marinov, Tchavdar. "Historiographical Revisionism and Re-Articulation of Memory in the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia." ''Sociétés politiques comparées'' 25 (2010): 1-19. [https://fasopo.org/sites/default/files/article_n25.pdf online] |
|||
* {{cite book |last1=Mattioli |first1=Fabio |title=Dark Finance: Illiquidity and Authoritarianism at the Margins of Europe |date=2020 |publisher=Stanford University Press |isbn=978-1-5036-1294-5 |language=en}} |
|||
* {{cite book|first=David|last=Nicolle|title=The Ottomans: Empire of Faith|publisher=Thalamus Publishing|year=2008|isbn=978-1-902886-11-4}}* Tziampiris, Aristotle. "Greek Historiography and Slav-Macedonian National Identity." ''The Historical Review/La Revue Historique'' 8 (2011): 215-225. [https://ejournals.epublishing.ekt.gr/index.php/historicalReview/article/download/4064/3850 online] |
|||
{{Refend}} |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
* [https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/north-macedonia/ North Macedonia]. ''[[The World Factbook]]''. [[Central Intelligence Agency]]. |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{ |
{{Sister project links|North Macedonia|voy=North Macedonia|q=no}} |
||
<!--Wikipedia is not a link list nor a Web directory. If your link points to a site that does not cover many subjects about North Macedonia, it's most likely in the wrong place here and you should go and search for a more specific article.--> |
|||
* {{Official website|1=http://www.vlada.mk/}} |
|||
* [https://www.rferl.org/z/737 North Macedonia] from [[RFE/RL]] |
|||
* [https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-17550407 North Macedonia] from [[BBC News]] |
|||
* {{Wikiatlas|North Macedonia}} |
|||
* {{osmrelation-inline|53293|bullet=no}} |
|||
* [http://www.ifs.du.edu/ifs/frm_CountryProfile.aspx?Country=MK Key Development Forecasts for North Macedonia] from [[International Futures]] |
|||
{{Geographic location |
|||
*[http://www.exploringmacedonia.com/ ExploringMacedonia - National Tourism Portal] |
|||
|Northwest= {{flag|Kosovo}} |
|||
*[http://www.makedonika.com.mk Makedonika (multimedia encyclopedia about the Republic of Macedonia)] |
|||
|North= {{SRB}} |
|||
*[http://photo.macedonia.org/ Photos of the Republic of Macedonia] |
|||
|Northeast= |
|||
*[http://www.panoramio.com/map/#lt=41.607228&ln=21.626587&z=9&k=2&a=1 Photos of the Republic of Macedonia in Google Earth] |
|||
|West= {{ALB}} |
|||
*[http://digital.library.unt.edu/govdocs/crs/search.tkl?q=macedonia&search_crit=fulltext&search=Search&date1=Anytime&date2=Anytime&type=form Congressional Research Service (CRS) Reports regarding the Republic of Macedonia] |
|||
|Centre= {{flagicon|MKD}} [[Outline of North Macedonia|North Macedonia]] |
|||
* [http://macedonia.co.uk/ Macedonian Cultural and Information Centre] |
|||
|East= {{BGR}} |
|||
|Southwest= |
|||
|South= {{GRC}} |
|||
|Southeast= |
|||
}} |
|||
{{North Macedonia topics|state=collapsed}} |
|||
{{Navboxes |
|||
|list= |
|||
{{Sovereign states of Europe}} |
|||
{{Balkan countries}} |
|||
{{Council of Europe}} |
|||
{{European Union candidates}} |
|||
{{La Francophonie}} |
|||
{{OSCE}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{Coord|42|N|22|E|type:country_region:MK|display=title}} |
|||
{{Europe}} |
|||
{{EU countries and candidates}} |
|||
{{NATO}} |
|||
{{Slavic States}} |
|||
[[Category: |
[[Category:North Macedonia| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Balkan countries]] |
||
[[Category:Landlocked countries]] |
[[Category:Landlocked countries]] |
||
[[Category:Member states of the Council of Europe]] |
|||
[[Category:Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie]] |
|||
[[ar:مقدونيا]] |
|||
[[Category:Member states of the United Nations]] |
|||
[[roa-rup:Republica Machedonia]] |
|||
[[Category:Member states of NATO]] |
|||
[[ast:República de Macedonia]] |
|||
[[Category:Republics]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Makedonija Kiōng-hô-kok]] |
|||
[[Category:States and territories established in 1991]] |
|||
[[be:Рэспубліка Македонія]] |
|||
[[Category:1991 establishments in the Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
[[bs:Republika Makedonija]] |
|||
[[Category:Countries in Europe]] |
|||
[[br:Makedonia (Republik)]] |
|||
[[Category:Countries and territories where Albanian is an official language]] |
|||
[[bg:Република Македония]] |
|||
[[ca:República de Macedònia]] |
|||
[[cs:Republika Makedonie]] |
|||
[[cy:Gweriniaeth Macedonia]] |
|||
[[da:Makedonien]] |
|||
[[de:Mazedonien]] |
|||
[[et:Makedoonia]] |
|||
[[el:Πρώην Γιουγκοσλαβική Δημοκρατία της Μακεδονίας]] |
|||
[[es:República de Macedonia]] |
|||
[[eo:Respubliko de Makedonio]] |
|||
[[eu:Mazedoniako Errepublika]] |
|||
[[fa:مقدونیه]] |
|||
[[fr:Macédoine (pays)]] |
|||
[[fy:Masedoanje]] |
|||
[[gl:Macedonia - Македонија]] |
|||
[[ko:마케도니아 공화국]] |
|||
[[hy:Մակեդոնիա]] |
|||
[[hr:Makedonija]] |
|||
[[io:Macedonia]] |
|||
[[id:FYROM]] |
|||
[[is:Lýðveldið Makedónía]] |
|||
[[it:Repubblica di Macedonia]] |
|||
[[he:מקדוניה]] |
|||
[[ku:Komara Makedonyayê]] |
|||
[[lt:Makedonija]] |
|||
[[li:Macedonië (land)]] |
|||
[[hu:Macedónia]] |
|||
[[mk:Република Македонија]] |
|||
[[ms:Republik Macedonia]] |
|||
[[nl:Macedonië (land)]] |
|||
[[ne:म्यासेडोनिया]] |
|||
[[ja:マケドニア共和国]] |
|||
[[no:Republikken Makedonia]] |
|||
[[nn:Republikken Makedonia]] |
|||
[[ug:ماكېدونىيە]] |
|||
[[pam:Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
[[ps:مقدونيه]] |
|||
[[nds:Makedonien (Land)]] |
|||
[[pl:Macedonia]] |
|||
[[pt:República da Macedónia]] |
|||
[[ro:Republica Macedonia]] |
|||
[[rmy:Republika Makedoniya]] |
|||
[[ru:Республика Македония]] |
|||
[[se:Makedonia]] |
|||
[[sq:Ish Republika Jugosllave e Maqedonisë]] |
|||
[[scn:Macidonia (ex Ripubblica jugoslava di)]] |
|||
[[simple:Republic of Macedonia]] |
|||
[[sk:Macedónsko]] |
|||
[[sl:Makedonija]] |
|||
[[sr:Република Македонија]] |
|||
[[fi:Makedonian tasavalta]] |
|||
[[sv:Makedonien]] |
|||
[[tl:Republika ng Masedonya]] |
|||
[[tg:Ҷумҳурии Мақдуния]] |
|||
[[th:สาธารณรัฐมาซิโดเนีย]] |
|||
[[tr:Makedonya Cumhuriyeti]] |
|||
[[uk:Республіка Македонія]] |
|||
[[vo:Makedonän]] |
|||
[[fiu-vro:Makõdoonia]] |
|||
[[zh:馬其頓共和國]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 15:58, 1 January 2025
Republic of North Macedonia | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Денес над Македонија (Macedonian) "Today over Macedonia" | |
![Location of North Macedonia (green) in Europe (dark grey) – [Legend]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/35/Location_Macedonia_Europe.png/250px-Location_Macedonia_Europe.png) | |
| Capital and largest city | Skopje 42°0′N 21°26′E / 42.000°N 21.433°E |
| Official languages | |
| |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova | |
| Hristijan Mickoski | |
| Afrim Gashi | |
| Legislature | Assembly |
| Establishment history | |
| 2 August 1944 | |
| 8 September 1991 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 25,436[4] km2 (9,821 sq mi) (145th) |
• Water (%) | 1.1 |
| Population | |
• 2021 census | |
• Density | 71.43/km2 (185.0/sq mi) (122nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2019) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | high (83rd) |
| Currency | Macedonian denar (MKD) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | +389 |
| ISO 3166 code | MK |
| Internet TLD | |
North Macedonia (/ˌmæsɪˈdoʊniə/ MASS-ih-DOH-nee-ə),[c] officially the Republic of North Macedonia,[d] is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo[e] to the northwest and Serbia to the north.[8] It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's population of 1.83 million. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Roma, Serbs, Bosniaks, Aromanians and a few other minorities.
The region's history begins with the kingdom of Paeonia. In the late sixth century BC, the area was subjugated by the Persian Achaemenid Empire, then incorporated into the Kingdom of Macedonia in the fourth century BC. The Roman Republic conquered the region in the second century BC and made it part of its larger province of Macedonia. The area remained part of the Byzantine Empire, but was often raided and settled by Slavic tribes beginning in the sixth century of the Christian era. Following centuries of contention between the Bulgarian, Byzantine, and Serbian Empires, it was part of the Ottoman Empire from the mid-14th until the early 20th century, when, following the Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913, the modern territory of North Macedonia came under Serbian rule.
During the First World War, the territory was ruled by Bulgaria. After the end of the war, it returned to Serbian rule as part of the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. During the Second World War, it was again ruled by Bulgaria; and in 1945 it was established as a constituent state of communist Yugoslavia, which it remained until its peaceful secession in 1991. The country became a member of the United Nations (UN) in 1993, but as a result of a dispute with Greece over the name "Macedonia", it was admitted under the provisional description "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (abbreviated as "FYR Macedonia" or "FYROM"). In 2018, the dispute was resolved with an agreement that the country should rename itself "Republic of North Macedonia". This renaming came into effect in early 2019.
North Macedonia is also a member of NATO, the Council of Europe, the World Bank, OSCE, CEFTA, BSEC and the WTO. Since 2005, it has also been a candidate for joining the European Union. North Macedonia is an upper-middle-income country according to the World Bank's definitions[9] and has undergone considerable economic reform since its independence in developing an open economy. It is a developing country, ranked 82nd on the Human Development Index; and provides social security, a universal health care system, and free primary and secondary education to its citizens.
Names and etymology
The state's name derives from the Greek word Μακεδονία (Makedonía),[10][11] a kingdom (later, region) named after the ancient Macedonians. Their name, Μακεδόνες (Makedónes), ultimately derives from the ancient Greek adjective μακεδνός (makednós), meaning 'tall' or 'taper',[12] which shares the same root as the adjective μακρός (makrós, 'long, tall, high') in ancient Greek.[13] The name is believed to have originally meant either 'highlanders' or 'the tall ones', possibly descriptive of the people.[11][14][15] According to linguist Robert S. P. Beekes, both terms are of pre-Greek substrate origin and cannot be explained in terms of Indo-European morphology.[16] According to linguist Filip De Decker, Beekes's arguments are insufficiently supported.[17]
Apart from the theme of Macedonia, the name "Macedonia" was largely forgotten as a geographical denomination through the Byzantine and Ottoman eras but was revived by Bulgarian and Greek nationalist movements from the early 19th century onwards.[18][19][20] It was revived only in middle of the century, with the rise of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire.[21][22][23] In the early 20th century the region was already a national cause, contested among Bulgarian, Greek, and Serbian nationalists. During the interwar period the use of the name "Macedonia" was prohibited in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, due to the implemented policy of Serbianisation of the local Slavic-speakers.[24][25] The name "Macedonia" was adopted officially for the first time at the end of the Second World War by the new Socialist Republic of Macedonia, which became one of the six constituent countries of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. After the breakup of Yugoslavia, this federal entity declared independence and changed its official name to the "Republic of Macedonia" in 1991. Prior to June 2018, the use of the name "Macedonia" was disputed between Greece and the then-Republic of Macedonia.
The Prespa agreement of June 2018 saw the country change its name to the "Republic of North Macedonia" eight months later.[26][27] A non-binding[28] national referendum on the matter passed with 90% approval but did not reach the required 50% turnout amidst a boycott, leaving the final decision with parliament to ratify the result.[29] Parliament approved of the name change on 19 October, reaching the required two-thirds majority needed to enact constitutional changes.[30] The vote to amend the constitution and change the name of the country passed on 11 January 2019 in favour of the amendment.[31] The amendment entered into force on 12 February, following the ratification of the Prespa agreement and the Protocol on the Accession of North Macedonia to NATO by the Greek Parliament.[32] Despite the renaming, the country is unofficially referred to as "Macedonia" by most of its citizens and most local media outlets.[citation needed]
History
Early history

North Macedonia geographically roughly corresponds to the ancient kingdom of Paeonia,[33][34][35][36][37] which was located immediately north of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia.[38] Paeonia was inhabited by the Paeonians, whilst the northwest was inhabited by the Dardani and the southwest by tribes known historically as the Enchelae both are considered Illyrian and Pelagones, and Lyncestae which are generally regarded as Molossian tribes of the northwestern Greek group.[39][40][41][42][43][44] The headwaters of the Axios river are mentioned by Homer as the home of the Paeonians allies of Troy.[45]
In the late 6th century BC, the Achaemenid Persians under Darius the Great conquered the Paeonians, incorporating what is today North Macedonia within their vast territories.[46][47][48] Following the loss in the Second Persian invasion of Greece in 479 BC, the Persians eventually withdrew from their European territories, including from what is today North Macedonia.

Philip II of Macedon absorbed[49] the regions of Upper Macedonia (Lynkestis and Pelagonia) and the southern part of Paeonia (Deuriopus) into the kingdom of Macedon in 356 BC.[50] Philip's son Alexander the Great conquered the remainder of the region and incorporated it in his empire, reaching as far north as Scupi, but the city and the surrounding area remained part of Dardania.[51] After the death of Alexander, Celtic armies began to bear down on the southern regions, threatening the kingdom of Macedon. In 310 BC, they attacked the area, but were defeated.[52]
The Romans established the province of Macedonia in 146 BC. By the time of Diocletian, the province had been subdivided between Macedonia Prima ("first Macedonia") on the south, encompassing most of the kingdom of Macedon, and Macedonia Salutaris (meaning "wholesome Macedonia", known also as Macedonia Secunda, "second Macedonia") on the north, encompassing partially Dardania and the whole of Paeonia; most of the country's modern boundaries fell within the latter, with the city of Stobi as its capital.[53] Roman expansion brought the Scupi area under Roman rule in the time of Domitian (81–96 AD), and it fell within the Province of Moesia.[54] Whilst Greek remained the dominant language in the eastern part of the Roman empire, especially south of the Jireček Line, Latin spread to some extent in Macedonia.[55]
Medieval period

Slavic tribes settled in the Balkan region including North Macedonia by the late 6th century AD. They were led by Pannonian Avars.[56][57][58] The Slavs settled on places of earlier settlements and probably merged later with the local populations to form mixed Byzantine-Slavic communities.[59] Historical records document that in c. 680 a Bulgar ruler called Kuber led a group of largely Christians called Sermesianoi, who were his subjects, and they settled in the region of Pelagonia. They may have consisted of Bulgars, Byzantines, Slavs and even Germanic tribes.[60] There is no more information of Kuber's life.[61][62] Presian's reign apparently coincides with the extension of Bulgarian control over the Slavic tribes in and around Macedonia. The Slavic tribes that settled in the region of Macedonia converted to Christianity around the 9th century during the reign of Tsar Boris I of Bulgaria. The Ohrid Literary School became one of the two major cultural centres of the First Bulgarian Empire, along with the Preslav Literary School. Established in Ohrid in 886 by Saint Clement of Ohrid on the order of Boris I, the Ohrid Literary School was involved in the spreading of the Cyrillic script.[63]
After Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria, the Byzantines took control of East Bulgaria. Samuil was proclaimed Tsar of Bulgaria. He moved the capital to Skopje and then to Ohrid, which had been the cultural and military centre of southwestern Bulgaria since Boris I's rule. Samuil re-established Bulgarian power, but after several decades of conflicts, in 1014, the Byzantine Emperor Basil II defeated his armies, and within four years the Byzantines restored control over the Balkans (modern-day North Macedonia was included into a new province, called Bulgaria). The rank of the autocephalous Bulgarian Patriarchate was lowered due to its subjugation to Constantinople and it was transformed into the Archbishopric of Ohrid. By the late 12th century, Byzantine decline saw the region contested by various political entities, including a brief Norman occupation in the 1080s.[citation needed]
In the early 13th century, a revived Bulgarian Empire gained control of the region. Plagued by political difficulties, the empire did not last, and the region came once again under Byzantine control in the early 14th century. In the 14th century, it became part of the Serbian Empire. Skopje became the capital of Tsar Stefan Dušan's empire. Following Dušan's death, a weak successor appeared, and power struggles between nobles divided the Balkans once again. These events coincided with the entry of the Ottoman Turks into Europe.
Ottoman period
The Kingdom of Prilep was one of the short-lived states that emerged from the collapse of the Serbian Empire in the 14th century, which was seized by the Ottomans at the end of the same century.[64] Gradually, all of the central Balkans were conquered by the Ottoman Empire and remained under its domination for five centuries as part of the province or Eyalet of Rumelia. The name Rumelia (Turkish: Rumeli) means "Land of the Romans" in Turkish, referring to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Turks from the Byzantine Empire.[65] Over the centuries, Rumelia Eyalet was reduced in size through administrative reforms, until by the 19th century it consisted of a region of central Albania and western North Macedonia with its capital at Manastir or present-day Bitola.[66] Rumelia Eyalet was abolished in 1867 and that territory of Macedonia subsequently became part of vilayets of Manastir, Kosova and Selanik until the end of Ottoman rule in 1912. With the beginning of the Bulgarian National Revival in the 19th century, many of the reformers were from this region, including the Miladinov brothers,[67] Rajko Žinzifov, Joakim Krčovski,[68] Kiril Pejčinoviḱ[69] and others. The bishoprics of Skopje, Debar, Bitola, Ohrid, Veles, and Strumica voted to join the Bulgarian Exarchate after it was established in 1870.[70]
Modern period
Macedonian autonomism


Several movements whose goals were the establishment of an autonomous Macedonia, which would encompass the entire region of Macedonia, began to arise in the late 19th century; the earliest of these was the Bulgarian Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Committees, later becoming Secret Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (SMARO). In 1905 it was renamed the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMARO), and after World War I the organisation separated into the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO) and the Internal Thracian Revolutionary Organisation (ITRO).[71]
In the early years of the organisation, membership eligibility was exclusive to Bulgarians, but later it was extended to all inhabitants of European Turkey regardless of ethnicity or religion.[72] The majority of its members were Macedonian Bulgarians.[73] In 1903, IMRO organised the Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising against the Ottomans, which after some initial successes, including the forming of the Kruševo Republic, was crushed with much loss of life.[74] The uprising and the forming of the Kruševo Republic are considered the cornerstone and precursors to the eventual establishment of the Macedonian state.[75][76][77] The leaders of the Ilinden uprising are celebrated as national heroes in North Macedonia. The names of IMRO revolutionaries like Gotse Delchev, Pitu Guli, Dame Gruev and Yane Sandanski were included into the lyrics of the national anthem of the state of North Macedonia "Denes nad Makedonija" ("Today over Macedonia"). The major national holiday of North Macedonia, the Republic Day, is celebrated on 2 August, Ilinden (St. Elijah day), the day of the Ilinden uprising.
Kingdom of Serbia
Following the two Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913 and the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, most of its European-held territories were divided between Greece, Bulgaria and Serbia.[78] Almost the territory that was to become North Macedonia was annexed by Serbia conforming to the treaty of peace concluded at Bucharest.[79] However, Strumica region was passed to Bulgaria. Following the partition, an anti-Bulgarian campaign was carried out in the areas under Serbian and Greek control.[80] As many as 641 Bulgarian schools and 761 churches were closed by the Serbs, while Exarchist clergy and teachers were expelled.[80] The use of all Macedonian dialects and standard Bulgarian were proscribed.[80] IMRO, together with local Albanians, organised the Ohrid–Debar uprising against the Serbian rule. Within a few days the rebels captured the towns of Gostivar, Struga and Ohrid, expelling the Serbian troops. According to the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace report, a Serbian army of 100,000 regulars suppressed the uprising. Many were killed and tens of thousands refugees fled to Bulgaria and Albania.[81][82]

World War I
During the First World War, most of today's North Macedonia was part of the Bulgarian occupied zone of Serbia after the country was invaded by the Central Powers in the fall of 1915.[80] The region was known as the "Military Inspection Area of Macedonia" and was administered by a Bulgarian military commander.[83] A policy of Bulgarisation of the region and its population was immediately initiated,[84][85] during the period the IMRO arose from a clandestine organisation to serve as gendarmerie, taking control of the whole police structure, enforcing the Bulgarisation of the region.[84] According to Robert Gerwarth, the Bulgarian denationalisation policy, including its paramilitary aspect, was almost identical in its intent and execution to the Serbian policy that preceded it.[84]
Bulgarian language was to be exclusively used, Serbian Cyrillic was forbidden, Serbian priests were arrested and deported, Serbian-sounding names had to be changed to Bulgarian ones,[86] school teachers were brought from Bulgaria while Serbian books were taken from schools and libraries and publicly destroyed.[87] Adult males were sent to labour camps or forced to join the Bulgarian Army, representatives of the Serbian intelligentsia were deported or executed.[85] According to Paul Mojzes the aim of the Bulgarian government was to create pure Bulgarian territories by denationalising the non-Bulgarian Slavic population of Macedonia.[88]
Kingdom of Yugoslavia
After the capitulation of Bulgaria and the end of the First World War, the area returned under Belgrade control as part of the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes[89] and saw a reintroduction of anti-Bulgarian measures. Bulgarian teachers and clergy were expelled, Bulgarian language signs and books removed, and all Bulgarian organisations dissolved.[80] Also after the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine, the Strumica region was annexed to Serbian Macedonia in 1919.
The Serbian government pursued a policy of forced Serbianisation in the region,[90][91] which included systematic suppression of Bulgarian activists, altering family surnames, internal colonisation, exploiting workers, and intense propaganda.[92] To aid the implementation of this policy, some 50,000 Serbian army and gendarmerie were stationed in present-day North Macedonia.[80] By 1940 about 280 Serbian colonies (comprising 4,200 families) were established as part of the government's internal colonisation program (initial plans envisaged 50,000 families settling in present-day North Macedonia).[80]
In 1929, the Kingdom was officially renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, and divided into provinces called banovinas. South Serbia, including all of present-day North Macedonia, became the Vardar Banovina of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.[93]
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO) promoted the concept of an Independent Macedonia in the interwar period. Its leaders—including Todor Alexandrov, Aleksandar Protogerov, and Ivan Mihailov—promoted independence of the Macedonian territory split between Serbia and Greece for the whole population, regardless of religion and ethnicity.[94] The Bulgarian government of Alexander Malinov in 1918 offered to give Pirin Macedonia for that purpose after World War I,[95] but the Great Powers did not adopt this idea because Serbia and Greece opposed it. In 1924, the Communist International (Comintern) suggested that all Balkan communist parties adopt a platform of a "United Macedonia" but the suggestion was rejected by the Bulgarian and Greek communists.[96]
IMRO followed by starting an insurgent war in Vardar Macedonia, together with Macedonian Youth Secret Revolutionary Organization, which also conducted guerrilla attacks against the Serbian administrative and army officials there. In 1923 in Stip, a paramilitary organisation called Association against Bulgarian Bandits was formed by Serbian chetniks, IMRO renegades and Macedonian Federative Organization (MFO) members to oppose IMRO and MMTRO.[97] On 9 October 1934, IMRO member Vlado Chernozemski assassinated Alexander I of Yugoslavia.
The Macedonist ideas increased in Yugoslav Vardar Macedonia and among the left diaspora in Bulgaria during the interwar period. They were supported by the Comintern.[98] In 1934, the Comintern issued a special resolution in which for the first time directions were provided for recognising the existence of a separate Macedonian nation and Macedonian language.[99]
World War II

During World War II, Yugoslavia was occupied by the Axis powers from 1941 to 1945. The Vardar Banovina was divided between Bulgaria and Italian-occupied Albania. Bulgarian Action Committees were established to prepare the region for the new Bulgarian administration and army.[101] The committees were mostly formed by former members of IMRO and Macedonian Youth Secret Revolutionary Organization (MYSRO, but some IMRO (United) former members also participated.[102][103]
As leader of the Vardar Macedonian communists, Metodi Shatorov ("Sharlo") switched from the Yugoslav Communist Party to the Bulgarian Communist Party[103][104] and refused to start military action against the Bulgarian Army.[105] The Bulgarian authorities, under German pressure,[106] were responsible for the round-up and deportation of over 7,000 Jews in Skopje and Bitola.[107] Harsh rule by the occupying forces encouraged many Vardar Macedonians to support the Communist Partisan resistance movement of Josip Broz Tito after 1943,[f] and the National Liberation War ensued.[108][109]
In Vardar Macedonia, after the Bulgarian coup d'état of 1944, the Bulgarian troops, surrounded by German forces, fought their way back to the old borders of Bulgaria.[110] Under the leadership of the new Bulgarian pro-Soviet government, four armies, 455,000 strong in total, were mobilised and reorganised. Most of them re-entered occupied Yugoslavia in early October 1944 and moved from Sofia to Niš, Skopje and Pristina with the strategic task of blocking the German forces withdrawing from Greece.[111] The Bulgarian army would reach the Alps in Austria, participating in the expulsion of the Germans to the west, through Yugoslavia and Hungary.
Compelled by the Soviet Union with a view towards the creation of a large South Slav Federation, in 1946 the new Communist government, led by Georgi Dimitrov, agreed to give Bulgarian Macedonia to a United Macedonia. With the Bled agreement, in 1947 Bulgaria formally confirmed the envisioned unification of the Macedonian region, but postponed this act until after the formation of the future Federation.[112][113] It was the first time it accepted the existence of a separate Macedonian ethnicity and language. After the Tito–Stalin split the region of Pirin Macedonia remained part of Bulgaria and later the Bulgarian Communist Party revised its view of the existence of a separate Macedonian nation and language.
Socialist Yugoslavia

In December 1944, the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (ASNOM) proclaimed the People's Republic of Macedonia as part of the People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.[114] ASNOM remained an acting government until the end of the war. The Macedonian alphabet was codified by linguists of ASNOM, who based their alphabet on the phonetic alphabet of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and the principles of Krste Petkov Misirkov. During the civil war in Greece (1946–1949), Macedonian communist insurgents supported the Greek communists. Many refugees fled to the Socialist Republic of Macedonia from there. The state removed "Socialist" from its name in 1991 when it peacefully seceded from Yugoslavia.
The new republic became one of the six republics of the Yugoslav federation. Following the federation's renaming as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in 1963, the People's Republic of Macedonia was likewise renamed the Socialist Republic of Macedonia.[115][116][117]
Declaration of independence
North Macedonia officially celebrates 8 September 1991 as Independence day (Macedonian: Ден на независноста, Den na nezavisnosta), with regard to the referendum endorsing independence from Yugoslavia.[118] The anniversary of the start of the Ilinden Uprising (St. Elijah's Day) on 2 August is also widely celebrated on an official level as the Day of the Republic.
Robert Badinter, as the head of the Arbitration Commission of the Peace Conference on Yugoslavia, recommended EC recognition in January 1992.[119] On 15 January 1992, Bulgaria was the first country to recognise the independence of the republic.
Macedonia remained at peace through the Yugoslav Wars of the early 1990s. A few very minor changes to its border with Yugoslavia were agreed upon to resolve problems with the demarcation line between the two countries. It was seriously destabilised by the Kosovo War in 1999, when an estimated 360,000 ethnic Albanian refugees from Kosovo took refuge in the country.[120] They departed shortly after the war, and Albanian nationalists on both sides of the border took up arms soon after in pursuit of autonomy or independence for the Albanian-populated areas of Macedonia.[120][121]
21st century
2001 insurgency
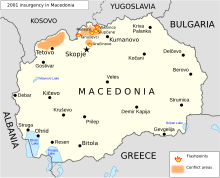
A conflict took place between the government and ethnic Albanian insurgents, mostly in the north and west of the country, between February and August 2001.[121][122][123] The war ended with the intervention of a NATO ceasefire monitoring force. Under the terms of the Ohrid Agreement, the government agreed to devolve greater political power and cultural recognition to the Albanian minority.[124] The Albanian side agreed to abandon separatist demands and to recognise all Macedonian institutions fully. In addition, according to this accord, the NLA were to disarm and hand over their weapons to a NATO force.[125] However the Macedonian security forces had two more armed confrontations with Albanian militant groups, in 2007 and 2015 respectively.
Inter-ethnic tensions flared in Macedonia in 2012, with incidents of violence between ethnic Albanians and Macedonians.[126] In April 2017, about 200 protesters - reportedly mostly from the conservative VMRO-DPMNE party, stormed the Macedonian Parliament in response to the election of Talat Xhaferi, an ethnic Albanian and former National Liberation Army commander during the 2001 conflict, as the Speaker of the Assembly.[127][128]
Antiquisation
Upon its coming to power in 2006, but especially since the country's non-invitation to NATO in 2008, the VMRO-DPMNE government pursued a policy of "Antiquisation" ("Antikvizatzija") as a way of putting pressure on Greece as well as for the purposes of domestic identity-building.[129] Statues of Alexander the Great and Philip of Macedon have been erected in several cities across the country. Additionally, many pieces of public infrastructure, such as airports, highways, and stadiums were renamed after Alexander and Philip. These actions were seen as deliberate provocations in neighbouring Greece, exacerbating the dispute and further stalling the country's EU and NATO applications.[130] The policy has also attracted criticism domestically, as well as from EU diplomats,[129] and, following the Prespa agreement, it has been partly reversed after 2016 by the new SDSM government of North Macedonia.[131][132] Moreover, per Prespa agreement both countries have acknowledged that their respective understanding of the terms "Macedonia" and "Macedonian" refers to a different historical context and cultural heritage.
EU and NATO path

In August 2017, what was then the Republic of Macedonia signed a friendship agreement with Bulgaria, aiming to end the "anti-Bulgarian ideology" in the country and to solve the historical issues between the two.
Under the Prespa agreement, signed with Greece on 17 June 2018, the country agreed to change its name to the Republic of North Macedonia and stop public use of the Vergina Sun. It retained the demonym "Macedonian", but clarified this as distinct from the Hellenistic Macedonian identity in northern Greece. The agreement included removal of irredentist material from textbooks and maps in both countries, and official UN recognition of the Slavic Macedonian language. It replaced the bilateral Interim Accord of 1995.[133]
The withdrawal of the Greek veto, along with the signing the friendship agreement with Bulgaria, resulted in the European Union on 27 June approving the start of accession talks, which were expected to take place in 2019, under the condition that the Prespa deal was implemented.[134] On 5 July, the Prespa agreement was ratified by the Macedonian parliament with 69 MPs voting in favour of it.[135] On 12 July, NATO invited Macedonia to start accession talks in a bid to become the alliance's 30th member.[136] On 30 July, the parliament of Macedonia approved plans to hold a non-binding referendum on changing the country's name, which took place on 30 September.[137] Ninety-one percent of voters voted in favour with a 37% turnout,[138] but the referendum was not carried because of a constitutional requirement for a 50% turnout.[139]

On 6 February 2019, the permanent representatives of NATO member states and Macedonian Foreign Affairs Minister Nikola Dimitrov, signed in Brussels the accession protocol of North Macedonia into NATO.[140][141] The protocol was then ratified on 8 February by the Greek parliament, thus completing all the preconditions for putting into force the Prespa agreement. Subsequently, on 12 February the Macedonian government announced the formal activation of the constitutional amendments which effectively renamed the country as North Macedonia and informed accordingly the United Nations and its member states.[142][143][144]
In March 2020, after the ratification process by all NATO members was completed, North Macedonia acceded to NATO, becoming the 30th member state.[145][146] The same month, the leaders of the European Union formally gave approval to North Macedonia to begin talks to join the EU.[147][148] On 17 November 2020, Bulgaria refused to approve the European Union's negotiation framework for North Macedonia, effectively blocking the official start of accession talks with this country.[149] The explanation from the Bulgarian side was: no implementation of the friendship treaty from 2017, state-supported hate speech, minority claims, and an "ongoing nation-building process" based on historical negationism of the Bulgarian identity, culture and legacy in the broader region of Macedonia.[150] The veto received condemnation by intellectuals from both states[151] and criticism from international observers.[152][153][154]
Protests broke out in July 2022, organized by the opposition parties, over the French proposal for the accession of North Macedonia to the EU.[155] The accession talks for the accession of North Macedonia to the EU officially began in the same month, after the French proposal was passed by the Assembly of North Macedonia.[156]
The 2023 European Commission Progress Report has cited the unfulfilled constitutional changes, as the primary reasons for the blocking of the further country's accession path. The EU's intention regarding the country's accession seems unclear, excluding desire to maintain its geopolitical influence here, countering the Chinese and Russian impact in the Western Balkans.[157] On 25 September 2024, the EU announced the separation of Albania from North Macedonia on the EU accession path, due to the disputes between North Macedonia and Bulgaria.[158] Following the decision, the EU opened negotiations on the first chapters with Albania separately on October 15, 2024.
Geography

North Macedonia has a total area of 25,436 km2 (9,821 sq mi).[4] It lies between latitudes 40° and 43° N, and mostly between longitudes 20° and 23° E (a small area lies east of 23°). North Macedonia has some 748 km (465 mi) of boundaries, shared with Serbia (62 km or 39 mi) to the North, Kosovo (159 km or 99 mi) to the northwest, Bulgaria (148 km or 92 mi) to the east, Greece (228 km or 142 mi) to the south, and Albania (151 km or 94 mi) to the west. It is a transit way for shipment of goods from Greece, through the Balkans, towards Eastern, Western and Central Europe and through Bulgaria to the east. It is part of the larger region of Macedonia, which also includes Greek Macedonia and the Blagoevgrad Province in southwestern Bulgaria.
North Macedonia is a landlocked country that is geographically clearly defined by a central valley formed by the Vardar river and framed along its borders by mountain ranges. The terrain is mostly rugged, located between the Šar Mountains and Osogovo, which frame the valley of the Vardar river. Three large lakes—Lake Ohrid, Lake Prespa and Dojran Lake—lie on the southern borders, bisected by the frontiers with Albania and Greece. Ohrid is considered to be one of the oldest lakes and biotopes in the world.[159] The region is seismically active and has been the site of destructive earthquakes in the past, most recently in 1963 when Skopje was heavily damaged by a major earthquake, killing over 1,000.[160]
North Macedonia also has scenic mountains. They belong to two different mountain ranges: the first is the Šar Mountains[161][162] that continues to the West Vardar/Pelagonia group of mountains (Baba Mountain, Nidže, Kožuf and Jakupica), also known as the Dinaric range. The second range is the Osogovo–Belasica mountain chain, also known as the Rhodope range. The mountains belonging to the Šar Mountains and the West Vardar/Pelagonia range are younger and higher than the older mountains of the Osogovo-Belasica mountain group. Mount Korab of the Šar Mountains on the Albanian border, at 2,764 m (9,068 ft), is the tallest mountain in North Macedonia. In North Macedonia there are 1,100 large sources of water. The rivers flow into three different basins: the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.[163]

The Aegean basin is the largest. It covers 87% of the territory of North Macedonia, which is 22,075 square kilometres (8,523 sq mi). Vardar, the largest river in this basin, drains 80% of the territory or 20,459 square kilometres (7,899 sq mi). Its valley plays an important part in the economy and the communication system of the country. The Vardar Valley project is considered to be crucial for the strategic development of the country. The river Black Drin forms the Adriatic basin, which covers an area of about 3,320 km2 (1,282 sq mi), i.e., 13% of the territory. It receives water from Lakes Prespa and Ohrid. The Black Sea basin is the smallest with only 37 km2 (14 sq mi). It covers the northern side of Mount Skopska Crna Gora. This is the source of the river Binačka Morava, which joins the Morava, and later, the Danube, which flows into the Black Sea. North Macedonia has around fifty ponds and three natural lakes, Lake Ohrid, Lake Prespa and Lake Dojran. In North Macedonia there are nine spa towns and resorts: Banište, Banja Bansko, Istibanja, Katlanovo, Kežovica, Kosovrasti, Banja Kočani, Kumanovski Banji and Negorci.[citation needed]
Climate

Four different seasons are found in the country with warm and dry summers and moderately cold and snowy winters. The range of temperatures recorded throughout the year ranges from −20 °C (−4 °F) in winter, to 40 °C (104 °F) in summer. Low winter temperatures are influenced by winds from the north while heat seasons during summer arise due to the subtropical pressure of the Aegean Sea and climate influences from the Middle East, with the latter causing dry periods.[164] There are three main climatic zones in the country: mildly continental in the north, temperate Mediterranean in the south and mountainous in the zones with high altitude.[165] Along the valleys of the Vardar and Strumica rivers, in the regions of Gevgelija, Valandovo, Dojran, Strumica, and Radoviš, the climate is temperate Mediterranean. The warmest regions are Demir Kapija and Gevgelija, where the temperature in July and August frequently exceeds 40 °C (104 °F).[166]
Average annual precipitation varies from 1,700 mm (66.9 in) in the western mountainous area to 500 mm (19.7 in) in the eastern area. There is a low level of precipitation in the Vardar valley with 500 mm (19.7 in) of water per year.[164] The climate and irrigation diversity allow the cultivation of different plant types, including wheat, corn, potatoes, poppies, peanuts, and rice.[167] There are thirty main and regular weather stations in the country.
Biodiversity
The flora of North Macedonia is represented by around 210 families, 920 genera, and around 3,700 plant species. The most abundant group are the flowering plants with around 3,200 species, followed by mosses (350 species) and ferns (42).
Phytogeographically, North Macedonia belongs to the Illyrian province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) and the Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the European Environment Agency, the territory of the Republic can be subdivided into four terrestrial ecoregions: the Pindus Mountains mixed forests, Balkan mixed forests, Rodope montane mixed forests, and Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests.[168] North Macedonia had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.42/10, ranking it 40th globally out of 172 countries.[169]
The native forest fauna is abundant and includes bears, wild boars, wolves, foxes, squirrels, chamois and deer. The lynx is found, very rarely, in the mountains of western Macedonia, while deer can be found in the region of Demir Kapija. Forest birds include the blackcap, the grouse, the black grouse, the imperial eagle and the forest owl.
The country has four national parks:
| Name | Established | Size | Map | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mavrovo | 1948 | 731 km2 | 
| |
| Galičica | 1958 | 227 km2 | 
| |
| Pelister | 1948 | 125 km2 | 
| |
| Šar Mountains | 2021 | 244 km2[170] | 
|
Politics
This section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2020) |

|

|
| Gordana Siljanovska Davkova President |
Hristijan Mickoski Prime Minister |
North Macedonia is a parliamentary democracy with an executive government composed of a coalition of parties from the unicameral legislature (Собрание, Sobranie; Assembly in English) and an independent judicial branch with a constitutional court. The Assembly is made up of 120 seats and the members are elected every four years. The role of the president is mostly ceremonial, with the real power resting in the hands of the prime minister. The president is the commander-in-chief of the state armed forces and a president of the State Security Council. The president is elected every five years and he or she can be elected twice at most.
Since 2019, local government functions are divided between 80 municipalities (општини, opštini; singular: општина, opština).[171] The capital, Skopje, is governed as a group of ten municipalities collectively referred to as the "City of Skopje". Municipalities in North Macedonia are units of local self-government. Neighbouring municipalities may establish co-operative arrangements.
The country's main political divergence is between the largely ethnically based political parties representing the country's ethnic Macedonian majority and Albanian minority. The issue of the power balance between the two communities led to a brief war in 2001, following which a power-sharing agreement was reached. In August 2004, parliament passed legislation redrawing local boundaries and giving greater local autonomy to ethnic Albanians in areas where they predominate.
After a troublesome pre-election campaign, North Macedonia saw a relatively calm and democratic change of government in the elections held on 5 July 2006. The elections were marked by a decisive victory of the centre-right party VMRO-DPMNE led by Nikola Gruevski. Gruevski's decision to include the Democratic Party of Albanians in the new government, instead of the Democratic Union for Integration–Party for Democratic Prosperity coalition which won the majority of the Albanian votes, triggered protests throughout the parts of the country with a respective number of Albanian population. A dialogue was later established between the Democratic Union for Integration and the ruling VMRO-DMPNE party as an effort to talk about the disputes between the two parties and to support European and NATO aspirations of the country.[172]
After the early parliamentary elections held in 2008, VMRO-DPMNE and Democratic Union for Integration formed a ruling coalition.[173] In April 2009, presidential and local elections in the country were carried out peacefully, which was crucial for Macedonian aspirations to join the EU.[174] The ruling conservative VMRO-DPMNE party won a victory in the local elections and the candidate supported by the party, Gjorgi Ivanov, was elected as the new president.
In June 2017, Zoran Zaev of the Social Democratic Party, became the new prime minister six months after early elections. The new center-left government ended 11 years of conservative VMRO-DPMNE rule led by former prime minister Nikola Gruevski.[175]
As of 4 January 2020[update], the acting prime minister of North Macedonia was Oliver Spasovski and the president of the Parliament was Talat Xhaferi.[176][177] The election of Xhaferi was immediately met with protests led by VMRO-DPMNE, which was quickly handled by the police.[176]
The early parliamentary elections took place on 15 July 2020.[178] Zoran Zaev has served as the prime minister of the Republic of North Macedonia again since August 2020.[179] Stevo Pendarovski was sworn in as North Macedonia's president in May 2019.[180] Prime minister Zoran Zaev announced his resignation after his party, the Social Democratic Union, suffered losses in local elections in October 2021.[181] In January 2022, Dimitar Kovačevski was elected as prime minister. The new coalition cabinet composed of Kovačevski's Social Democrats and two ethnic Albanian parties.[182] Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova took office on 12 May 2024, becoming the country's first female president.[183]
Parliament, or Assembly (Macedonian: Собрание, Sobranie), is the country's legislative body. It makes, proposes and adopts laws. The Constitution of North Macedonia has been in use since shortly after the independence of the republic in 1991. It limits the power of the governments, both local and national. The military is also limited by the constitution. The constitution states that North Macedonia is a social free state, and that Skopje is the capital.[184] The 120 members are elected for a mandate of four years through a general election. Each citizen aged 18 years or older can vote for one of the political parties. The current president of Parliament is Jovan Mitreski since 2024.[185]
Executive power in North Macedonia is exercised by the Government, whose prime minister is the most politically powerful person in the country. The members of the government are chosen by the prime minister and there are ministers for each branch of the society. There are ministers for economy, finance, information technology, society, internal affairs, foreign affairs and other areas. The members of the Government are elected for a mandate of four years. Judiciary power is exercised by courts, with the court system being headed by the Judicial Supreme court, Constitutional Court and the Republican Judicial Council. The assembly appoints the judges.
Naming dispute

The use of the name "Macedonia" was disputed between Greece and North Macedonia. The specific naming dispute was reignited after the breakup of Yugoslavia and the newly gained independence of the former Socialist Republic of Macedonia in 1991.[186] Greece opposed the use of the name without a geographical qualifier so as to avoid confusion with its own region of Greek Macedonia to the south.[187] As some ethnic Greeks identify themselves as Macedonians, unrelated to the Slavic people who are associated with North Macedonia, Greece further objected to the use of the term Macedonian for the neighbouring country's largest ethnic group; it accused the country of appropriating symbols and figures that are historically considered parts of Greece's culture (such as Vergina Sun and Alexander the Great), and of promoting the irredentist concept of a United Macedonia, which would include territories of Greece, Bulgaria, Albania, and Serbia.[188]
The UN adopted the provisional reference the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (Macedonian: Поранешна Југословенска Република Македонија) when the country was admitted to the organisation in 1993.[189] The lower-cased "former" was chosen intentionally to display the provisionality of the name although most UN member countries soon abandoned the provisional reference and recognised the country as the Republic of Macedonia instead.[190] Most international organisations adopted the same convention along with over 100 UN members and four of the five permanent UN Security Council members.[191][192] In the period between 1991 and 2019, the country's name was an ongoing issue in bilateral and international relations. The UN set up a negotiating process with a mediator, Matthew Nimetz, and the two parties to try to mediate the dispute. Following the ratification of the Prespa agreement, most major international organisations welcomed the settlement of the long-standing dispute, and adopted the country's new name.[193][194][195]
Foreign relations
North Macedonia became a member state of the UN on 8 April 1993, eighteen months after its independence from Yugoslavia. It was referred to within the UN as "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia", until the resolution of the long-running dispute with Greece about the country's name.
The major interest of the country is a full integration in the European and the Trans-Atlantic integration processes.[196]
North Macedonia is a member of the following international and regional organisations:[197] IMF (since 1992), WHO (since 1993), EBRD (since 1993), Central European Initiative (since 1993), Council of Europe (since 1995), OSCE (since 1995), SECI (since 1996), La Francophonie (since 2001), WTO (since 2003), CEFTA (since 2006), and NATO (since 2020).
In 2005, the country was officially recognised as a European Union candidate state.
At the NATO 2008 Bucharest summit, Macedonia failed to gain an invitation to join the organisation because Greece vetoed the move after the dispute over the name issue.[198] The U.S. had previously expressed support for an invitation,[199] but the summit then decided to extend an invitation only on condition of a resolution of the naming conflict with Greece.
In March 2009, the European Parliament expressed support for North Macedonia's EU candidacy and asked the EU Commission to grant the country a date for the start of accession talks by the end of 2009. The parliament also recommended a speedy lifting of the visa regime for Macedonian citizens.[200] Prior to the Prespa agreement, the country failed to receive a start date for accession talks as a result of the naming dispute. However, after the Prespa agreement, North Macedonia became a member state of NATO on 27 March 2020. The EU's stance was similar to NATO's in that resolution of the naming dispute was a precondition for the start of accession talks.
In October 2012, the EU Enlargement Commissioner Štefan Füle proposed a start of accession negotiations with the country for the fourth time, while the previous efforts were blocked each time by Greece. At the same time Füle visited Bulgaria in a bid to clarify the state's position with respect to Macedonia. He established that Bulgaria had almost joined Greece in vetoing the accession talks. The Bulgarian position was that Sofia cannot grant an EU certificate to Skopje, which is systematically employing an ideology of hate towards Bulgaria.[201]
Military

The Army of the Republic of North Macedonia (ARSM) is led by the General Staff, below which are the Operations Command, whose forces include the Mechanized Infantry Brigade, the Air Brigade, the Special Operations Regiment, and several independent battalions; the Training and Doctrine Command, which also oversees the Military Reserve Force; and the Logistics Base. There is also an Honor Guard Battalion that is directly subordinated to the General Staff.[202] The ARSM has 8,000 active personnel and 4,850 reservists, as well as a military budget of US$235 million in 2022.[203] It has been a volunteer military since conscription was ended in 2007. North Macedonia has deployed troops to Afghanistan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Iraq, Kosovo, and Lebanon, as part of NATO, EU, or UN missions.[204]
The Ministry of Defence develops the Republic's defence strategy and assesses possible threats and risks. It is also responsible for the defence system, including training, readiness, equipment, and development, and for drawing up and presenting the defence budget.[205]
Human rights
North Macedonia is a signatory to the European Convention on Human Rights and the UN Geneva Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees and Convention against Torture, and the Constitution guarantees basic human rights to all Macedonian citizens.
According to human rights organisations, in 2003 there were suspected extrajudicial executions, threats against, and intimidation of, human rights activists and opposition journalists, and allegations of torture by the police.[206][207]
Administrative divisions


North Macedonia's statistical regions exist solely for legal and statistical purposes. The regions are:
In August 2004, the country was reorganised into 84 municipalities (opštini; sing. opština); 10 of the municipalities constitute the City of Skopje, a distinct unit of local self-government and the country's capital.
Most of the current municipalities were unaltered or merely amalgamated from the previous 123 municipalities established in September 1996; others were consolidated and their borders changed. Prior to this, local government was organised into 34 administrative districts, communes, or counties (also opštini).
Economy
Ranked as the fourth "best reformatory state" out of 178 countries ranked by the World Bank in 2009, North Macedonia has undergone considerable economic reform since independence.[208] The country has developed an open economy with trade accounting for more than 90% of GDP in recent years. Since 1996, North Macedonia has witnessed steady, though slow, economic growth with GDP growing by 3.1% in 2005. This figure was projected to rise to an average of 5.2% in the 2006–2010 period.[209] The government has proven successful in its efforts to combat inflation, with an inflation rate of only 3% in 2006 and 2% in 2007,[208] and has implemented policies focused on attracting foreign investment and promoting the development of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).

The current government introduced a flat tax system with the intention of making the country more attractive to foreign investment. The flat tax rate was 12% in 2007 and was further lowered to 10% in 2008.[210][211] as of 2005[update] North Macedonia's unemployment rate was 37.2%[212] and as of 2006[update] its poverty rate was 22%.[209] Due to a number of employment measures as well as the successful process of attracting multinational corporations, and according to the State Statistical Office of North Macedonia, the country's unemployment rate in the first quarter of 2015 decreased to 27.3%.[213] Government's policies and efforts in regards to foreign direct investments have resulted with the establishment of local subsidiaries of several world leading manufacturing companies, especially from the automotive industry, such as: Johnson Controls Inc., Van Hool NV, Johnson Matthey plc, Lear Corp., Visteon Corp., Kostal GmbH, Gentherm Inc., Dräxlmaier Group, Kromberg & Schubert, Marquardt GmbH, Amphenol Corp., Tekno Hose SpA, KEMET Corp., Key Safety Systems Inc., ODW-Elektrik GmbH, etc.
In terms of GDP structure, as of 2013[update], the manufacturing sector (including mining and construction)constituted the largest part of GDP at 21.4%, up from 21.1% in 2012. The trade, transportation and accommodation sector represents 18.2% of GDP in 2013, up from 16.7% in 2012, while agriculture represents 9.6%, up from 9.1% in the previous year.[214]
In terms of foreign trade, the largest sector contributing to the country's export in 2014 was "chemicals and related products" at 21.4%, followed by the "machinery and transport equipment" sector at 21.1%. North Macedonia's main import sectors in 2014 were "manufactured goods classified chiefly by material" with 34.2%, "machinery and transport equipment" with 18.7% and "mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials" with 14.4% of the total imports. Even 68.8% of the foreign trade in 2014 was done with the EU which makes the Union by far the largest trading partner of North Macedonia (23.3% with Germany, 7.9% with the UK, 7.3% with Greece, 6.2% with Italy, etc.). Almost 12% of the total external trade in 2014 was done with the Western Balkan countries.[215] In 2007, North Macedonia's information technology market increased 63.8% year on year, which was the fastest growing in the Adriatic region.[216]
North Macedonia has one of the highest shares of people struggling financially, with 72% of its citizens stating that they could manage on their household's income only "with difficulty" or "with great difficulty", though North Macedonia, along with Croatia, was the only country in the Western Balkans to not report an increase in this statistic.[217] Corruption and a relatively ineffective legal system also act as significant restraints on successful economic development. North Macedonia still has one of the lowest per capita GDPs in Europe. Furthermore, the country's grey market is estimated at close to 20% of GDP.[218] PPS GDP per capita stood at 36% of the EU average in 2017.[219] With a GDP per capita of US$9,157 at purchasing power parity and a Human Development Index of 0.701, North Macedonia is less developed and has a considerably smaller economy than most of the former Yugoslav states.
Trade
The outbreak of the Yugoslav wars and the imposition of sanctions on Serbia and Montenegro caused great damage to the country's economy, with Serbia constituting 60% of its markets before the disintegration of Yugoslavia. When Greece imposed a trade embargo on the Republic in 1994–95, the economy was also affected. Some relief was afforded by the end of the Bosnian War in November 1995 and the lifting of the Greek embargo, but the Kosovo War of 1999 and the 2001 Albanian crisis caused further destabilisation.
Since the end of the Greek embargo, Greece has become the country's most important business partner. (See Greek investments in North Macedonia.) Many Greek companies have bought former state companies in North Macedonia,[220] such as the oil refinery Okta, the baking company Zhito Luks, a marble mine in Prilep, textile facilities in Bitola, etc., and employ 20,000 people. The moving of business to North Macedonia in the oil sector has been caused by the rise of Greece in the oil markets.[221]
Other key partners are Germany, Italy, the United States, Slovenia, Austria and Turkey.
Tourism

Tourism plays a significant role in the economy of North Macedonia accounting for 6.7% of its GDP in 2016. The annual income from tourism was estimated at 38.5 billion denars (€616 million) in that year.[222] Following its independence, the most serious negative impact on tourism performance occurred due to the armed conflicts taking place in 2001.[223] The number of foreign visitors has been on the rise since, with a 14.6% increase in 2011.[224] In 2019, North Macedonia received 1,184,963 tourist arrivals out of which 757,593 foreign.[225] Most numerous are tourists from Turkey, neighboring Serbia, Greece and Bulgaria, Poland and other countries of Western Europe.[226] The biggest bulk of tourists, approximately 60% of the million tourists that visited the country in 2017, was situated in Skopje and the southwestern region of the country.[227]
The most significant tourism branches are lake tourism as there are three lakes in Ohrid, Prespa and Dojran and over 50 small glacial lakes of variable sizes, mountainous tourism as there are 16 mountains higher than 2,000 metres. Other forms of tourism also include rural and ecotourism, city tourism and cultural tourism, represented through gastronomy, traditional music, cultural celebrations and cultural heritage sites.[223]
Infrastructure
Transport

North Macedonia (along with Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo) belongs to the less-developed southern region of the former Yugoslavia. It suffered severe economic difficulties after independence, when the Yugoslav internal market collapsed and subsidies from Belgrade ended. In addition, it faced many of the same problems faced by other former socialist East European countries during the transition to a market economy. Its main land and rail exports route, through Serbia, remains unreliable with high transit costs, thereby affecting the export of its formerly highly profitable, early vegetables market to Germany.
North Macedonia is a landlocked country in the middle of the Balkan peninsula, and the main transport links in the country are those that connect the different parts of the peninsula (trans-Balkan links). Particularly important is the connection between north–south and Vardar valley, which connects Greece with the rest of Europe. As of 2019[update], there were 10,591 km (6,581 mi) of roads, of which about 6,000 km (3,700 mi) were paved.[228]

As of 2019[update], the total length of the railway network in North Macedonia was 922 km (573 mi).[228] Operated by Makedonski Železnici, the most important railway line is the line on the border with Serbia–Kumanovo–Skopje–Veles–Gevgelija–border with Greece. Since 2001, the railway line Beljakovci has been built—the border with Bulgaria, which will get a direct connection Skopje-Sofia. The most important railway hub in the country is Skopje, while the other two are Veles and Kumanovo.
North Macedonia Post is the state-owned company for the provision of postal traffic. It was founded in 1992 as PTT Macedonia. In 1993 it was admitted to the World Postal Union in 1997, PTT Macedonia was divided into Macedonian Telekom and Macedonian Post (later renamed North Macedonia Post).
As far as water transport is concerned, only lake traffic through Ohrid and Prespan Lake has been developed, mostly for tourist purposes.
There are officially 17 airports in North Macedonia, of which 11 are with solid substrates.[228] Two are international airports: Skopje International Airport and Ohrid St. Paul the Apostle Airport.[228]
Education

The higher levels of education can be obtained at one of the five state universities: Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje, St. Clement of Ohrid University of Bitola, Goce Delčev University of Štip, State University of Tetova and University of Information Science and Technology "St. Paul The Apostle" in Ohrid. There are a number of private university institutions, such as the European University,[229] Slavic University in Sveti Nikole, the South East European University and others. North Macedonia was ranked 58th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.[230]
The United States Agency for International Development has underwritten a project called Macedonia Connects, which has made North Macedonia the first all-broadband wireless country in the world. The Ministry of Education and Sciences reports that 461 schools (primary and secondary) are now connected to the Internet.[231] In addition, an Internet service provider (On.net), has created a MESH Network to provide WIFI services in the 11 largest cities/towns in the country. The national library of North Macedonia, National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", is in Skopje.
Demographics
The results from the last 2021 census show a population of 1,836,713. The population density of the country is 72.2 persons per km2 and the average age of the population is 40.08 years. 598,632 households were recorded with an average number of household members of 3.06. The gender balance of the country is 50.4% female to 49.6% male.[232]
Based on the 2021 census data, the largest ethnic group in the country are the ethnic Macedonians. The second-largest group are the Albanians, who dominated much of the northwestern part of the country. Following them, Turks are the third-biggest ethnic group of the country where official census data put them close to 70,000 and unofficial estimates suggest numbers between 170,000 and 200,000. Some unofficial estimates indicate that there are possibly up to 260,000 Roma.[233]
Religion
Religion in North Macedonia (2021)[234]
Eastern Orthodox Christianity is the most practiced religion in North Macedonia, making up 46.1% of the population, the vast majority of whom belong to the Macedonian Orthodox Church. Various other Christian denominations account for 13.9% of the population. Muslims constitute 32.2% of the population. North Macedonia has the fifth-highest proportion of Muslims in Europe, after those of Kosovo (96%),[235] Turkey (90%),[citation needed] Albania (59%),[236] and Bosnia and Herzegovina (51%).[237] Most Muslims are Albanians, Turks, Romani or Bosniaks; few are Macedonian Muslims. The remaining 1.4% was determined to be "unaffiliated" by a 2010 Pew Research estimation.[238]
There were 1,842 churches and 580 mosques in the country at the end of 2011.[239] The Orthodox and Islamic religious communities have secondary religion schools in Skopje. There is an Orthodox theological college in the capital. The Macedonian Orthodox Church has jurisdiction over 10 provinces (seven in the country and three abroad), has 10 bishops and about 350 priests. A total of 30,000 people are baptised in all the provinces every year.
The Macedonian Orthodox Church, which declared autocephaly in 1967, remained unrecognised by the other Orthodox Churches until 2022 when it restored relations with the Serbian Orthodox Church and the Ecumenical Patriarchate, which has been followed by recognition from other churches.[240][241]
The reaction of the Macedonian Orthodox Church was to cut off all relations with the new Ohrid Archbishopric and to prevent bishops of the Serbian Orthodox Church from entering North Macedonia. Bishop Jovan was jailed for 18 months for "defaming the Macedonian Orthodox church and harming the religious feelings of local citizens" by distributing Serbian Orthodox church calendars and pamphlets.[242]

The Macedonian Byzantine Catholic Church has approximately 11,000 adherents in North Macedonia. The Church was established in 1918, and is made up mostly of converts to Catholicism and their descendants. The Church is of the Byzantine Rite and is in communion with the Roman and Eastern Catholic Churches. Its liturgical worship is performed in Macedonian.[243]
There is a small Protestant community. The most famous Protestant in the country is the late president Boris Trajkovski. He was from the Methodist community, which is the largest and oldest Protestant church in the Republic, dating back to the late 19th century. Since the 1980s the Protestant community has grown, partly through new confidence and partly with outside missionary help.[citation needed]
The country's Jewish community, which numbered some 7,200 people on the eve of World War II, was almost entirely destroyed during the war: only 2% survived the Holocaust.[244]
After their liberation and the end of the War, most opted to emigrate to Israel. Today, the country's Jewish community numbers approximately 200 persons, almost all of whom live in Skopje. Most Macedonian Jews are Sephardic—the descendants of 15th-century refugees who had been expelled from Castile, Aragon and Portugal.[citation needed]
Languages

The national and official language in all aspects of the whole territory of North Macedonia and in its international relations is the Macedonian language. Since 2019 Albanian is co-official at a state level (excluding defense, central police and monetary policy).[245] Macedonian belongs to the Eastern branch of the South Slavic language group, while Albanian occupies an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. In municipalities where at least 20% of the population is part of another ethnic minority, those individual languages are used for official purposes in local government, alongside Macedonian and Albanian or just Macedonian.
Macedonian is closely related to and mutually intelligible with standard Bulgarian. It also has some similarities with standard Serbian and the intermediate Torlakian/Shop dialects spoken mostly in southeastern Serbia and western Bulgaria (and by speakers in the northeastern corner of the country). The standard language was codified in the period following World War II and has accumulated a thriving literary tradition.
Besides Macedonian and Albanian, minority languages with substantial numbers of speakers are Turkish (including Balkan Gagauz[246]), Romani, Serbian/Bosnian and Aromanian (including Megleno-Romanian).[247][248][249][250] Macedonian Sign Language is the primary language of those of the deaf community who did not pick up an oral language in childhood.
According to the last census, 1,344,815 citizens of North Macedonia declared that they spoke Macedonian, 507,989 declared Albanian, 71,757 Turkish, 38,528 Romani, 24,773 Serbian, 8,560 Bosnian, 6,884 Aromanian and 19,241 spoke other languages.[1]
Cities
| Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Skopje  Kumanovo |
1 | Skopje | Skopje Statistical | 526,502 | 11 | Kavadarci | Vardar Statistical | 32,038 |  Bitola  Prilep |
| 2 | Kumanovo | Northeastern Statistical | 75,051 | 12 | Kočani | Eastern Statistical | 24,632 | ||
| 3 | Bitola | Pelagonia Statistical | 69,287 | 13 | Kičevo | Southwestern Statistical | 23,428 | ||
| 4 | Prilep | Pelagonia Statistical | 63,308 | 14 | Gevgelija | Southeastern Statistical | 15,156 | ||
| 5 | Tetovo | Polog Statistical | 63,176 | 15 | Struga | Southwestern Statistical | 15,009 | ||
| 6 | Štip | Eastern Statistical | 42,000 | 16 | Radoviš | Southeastern Statistical | 14,460 | ||
| 7 | Veles | Vardar Statistical | 40,664 | 17 | Kriva Palanka | Northeastern Statistical | 13,481 | ||
| 8 | Ohrid | Southwestern Statistical | 38 818 | 18 | Negotino | Vardar Statistical | 12,488 | ||
| 9 | Strumica | Southeastern Statistical | 33,825 | 19 | Debar | Southwestern Statistical | 11,735 | ||
| 10 | Gostivar | Polog Statistical | 32,814 | 20 | Sveti Nikole | Eastern Statistical | 11,728 | ||
Culture

North Macedonia has a rich cultural heritage in art, architecture, poetry and music. It has many ancient, protected religious sites. Poetry, cinema, and music festivals are held annually. Macedonian music styles developed under the strong influence of Byzantine church music. North Macedonia has a significant number of preserved Byzantine fresco paintings, mainly from the period between the 11th and 16th centuries. There are several thousands of square metres of fresco painting preserved, the major part of which is in very good condition and represent masterworks of the Macedonian school of ecclesiastical painting.
The most important cultural events in the country are the Ohrid Summer Festival of classical music and drama, the Struga Poetry Evenings which gather poets from more than 50 countries in the world, International Camera Festival in Bitola, Open Youth Theatre and Skopje Jazz Festival in Skopje etc. The National Opera opened in 1947, then named "Macedonian Opera", with a performance of Cavalleria rusticana under the direction of Branko Pomorisac. Every year, the May Opera Evenings are held in Skopje for around 20 nights. The first May Opera performance was that of Kiril Makedonski's Tsar Samuil in May 1972.[252]
Cuisine

The country's cuisine is representative of that of the Balkans—reflecting Mediterranean and Middle Eastern (Ottoman) influences, and to a lesser extent Italian, German and Eastern European (especially Hungarian) ones.[253] The relatively warm climate in North Macedonia provides excellent growth conditions for a variety of vegetables, herbs and fruits. Thus, Macedonian cuisine is particularly diverse.
Macedonian cuisine is also noted for the diversity and quality of its dairy products, wines, and local alcoholic beverages, such as rakija. Tavče gravče and mastika are considered the national dish and drink of North Macedonia, respectively. Some other important dishes include Šopska salad, an appetiser and side dish that accompanies the main meal, ajvar, stuffed peppers, pastrmajlija and others.[254]
Sport


Football, handball, and basketball are the most popular sports in North Macedonia. The North Macedonia national football team is controlled by the Football Federation of Macedonia. Their home stadium is the Toše Proeski Arena. In November 2003, to celebrate UEFA's jubilee, Darko Pančev was selected as the Golden Player of Macedonia as their most outstanding player of the past 50 years.[255] He was the winner of the European Golden Boot award in 1991 and he is best known for scoring the winning penalty in the 1991 European Cup Final, bringing Red Star Belgrade the most prestigious trophy in European football for the first time in its 50-year existence. In 2020, the national team qualified for UEFA Euro 2020 (held in 2021), their first major tournament in the country's history.[256]
Handball is the other important team sport in the country. Macedonian clubs have enjoyed success in European competitions. RK Vardar won 2016–17 and 2018–19 EHF Champions League, while Kometal Gjorče Petrov Skopje won the 2002 EHF Women's Champions League. The European Women's Handball Championship took place in 2008 in North Macedonia in Skopje and Ohrid; the women's national team finished seventh place. The country's men's national team has appeared in the European and World championships multiple times, with a best finish of fifth at the former (2012) and ninth at the latter (2015).
The North Macedonia national basketball team represents North Macedonia in international basketball. The team is run by the Basketball Federation of North Macedonia, the governing body of basketball in North Macedonia which was created in 1992 and joined FIBA in 1993. North Macedonia has participated in three EuroBaskets since then with its best finish at 4th place in 2011. It plays its home games at the Boris Trajkovski Sports Center in Skopje. Pero Antić became the first Macedonian basketball player to play in the National Basketball Association. He also won three EuroLeague trophies.
In the summer months the Ohrid Swimming Marathon is an annual event on Lake Ohrid and during the winter months there is skiing in North Macedonia's winter sports centres. North Macedonia also takes part in the Olympic Games. Participation in the Games is organised by the Olympic Committee of North Macedonia.[257] Magomed Ibragimov competed for Macedonia in the freestyle 85 kg competition at the 2000 Summer Olympics and won the bronze medal, which was the first medal for independent country. Wrestlers Shaban Trstena and Shaban Sejdiu born in North Macedonia, as well as boxers Redžep Redžepovski and Ace Rusevski, won Olympic medals as part of Yugoslav Olympic team.
Cinema

The history of film making in the country dates back over 110 years.[citation needed] The first film to be produced on the territory of the present-day country was made in 1895 by Janaki and Milton Manaki in Bitola. Throughout the past century, the medium of film has depicted the history, culture and everyday life of the Macedonian people. Over the years many Macedonian films have been presented at film festivals around the world and several of these films have won prestigious awards. The first Macedonian feature film was Frosina, released in 1952 and directed by Vojislav Nanović.[258]
The first feature film in colour was Miss Stone, a movie about a Protestant missionary in Ottoman Macedonia. It was released in 1958. The highest grossing feature film in North Macedonia was Bal-Can-Can, having been seen by over 500,000 people in its first year alone. In 1994, Milcho Manchevski's film Before the Rain was nominated for an Academy Award in the category of Best International Feature Film.[259] Manchevski continues to be the most prominent modern filmmaker in the country having subsequently written and directed Dust and Shadows. In 2020, the documentary Honeyland (2019) directed by Tamara Kotevska and Ljubomir Stefanov, received nominations in the categories for Best International Feature Film and Best Documentary Feature at the 92nd Academy Awards, making it the first non-fictional film to receive a nomination in both categories.[260]
Media
The oldest newspaper in the country is Nova Makedonija from 1944. Other well known newspaper and magazines are: Utrinski vesnik, Dnevnik, Vest, Fokus, Večer, Tea Moderna, Makedonsko Sonce, and Koha. Public channel is Macedonian Radio Television founded in 1993 by the Assembly of North Macedonia. TEKO TV (1989) from Štip is the first private television channel in the country. Other popular private channels are: Sitel, Kanal 5, Telma, Alfa TV, and Alsat-M.
Public holidays
The main public holidays in North Macedonia are:
| Date | English name | Macedonian name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–2 January | New Year | Нова Година, Nova Godina | |
| 7 January | Christmas Day (Orthodox) | Прв ден Божиќ, Prv den Božiḱ | |
| April/May | Good Friday (Orthodox) | Велики Петок, Veliki Petok | Orthodox Easter and other Easter dates do not match; see: List of dates for Easter |
| April/May | Easter Sunday (Orthodox) | Прв ден Велигден, Prv den Veligden | |
| April/May | Easter Monday (Orthodox) | Втор ден Велигден, Vtor den Veligden | |
| 1 May | Labour Day | Ден на трудот, Den na trudot | |
| 24 May | Saints Cyril and Methodius Day | Св. Кирил и Методиј, Ден на сèсловенските просветители; Sv. Kiril i Metodij, Den na sèslovenskite prosvetiteli | |
| 2 August | Republic Day | Ден на Републиката, Den na Republikata | Day when the Republic was established in 1944, also Ilinden Uprising in 1903. |
| 8 September | Independence Day | Ден на независноста, Den na nezavisnosta | Day of independence from Yugoslavia |
| 11 October | Day of the Macedonian Uprising | Ден на востанието, Den na vostanieto | Beginning of Anti-fascist war during WWII in 1941 |
| 23 October | Day of the Macedonian Revolutionary Struggle (Holiday) | Ден на македонската револуционерна борба,Den na makedonskata revolucionarna borba | Day when the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO) was established in 1893. |
| 1 Shawwal | Eid ul-Fitr | Рамазан Бајрам, Ramazan Bajram | moveable, see: Islamic Calendar |
| 8 December | Saint Clement of Ohrid Day | Св. Климент Охридски, Sv. Kliment Ohridski |
Besides these, there are several major religious & minorities holidays. (See: Public holidays in North Macedonia)
Symbols
- Sun: The official flag of North Macedonia, adopted in 1995, is a yellow sun with eight broadening rays extending to the edges of the red field.
- Coat of arms: After independence in 1991, North Macedonia retained the coat of arms adopted in 1946 by the People's Assembly of the People's Republic of Macedonia on its second extraordinary session held on 27 July 1946, later on altered by article 8 of the Constitution of the Socialist Federal Republic of Macedonia. The coat-of-arms is composed by a double bent garland of ears of wheat, tobacco and poppy, tied by a ribbon with the embroidery of a traditional folk costume. In the center of such a circular room there are mountains, rivers, lakes and the sun. All this is said to represent "the richness of our country, our struggle, and our freedom".
International rankings
| Organisation | Survey | Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Institute for Economics and Peace | Global Peace Index 2019[261] | 65 out of 163 |
| Reporters Without Borders | Worldwide Press Freedom Index 2019[262] | 95 out of 180 |
| The Heritage Foundation/The Wall Street Journal | Index of Economic Freedom 2019[263] | 33 out of 180 |
| Transparency International | Corruption Perceptions Index 2019[264] | 106 out of 180 |
| United Nations Development Programme | Human Development Index 2019[265] | 82 out of 189 |
| World Bank | Ease of doing business index 2019[266] | 10 out of 190 |
See also
Notes
- ^ National and official language in all aspects of the whole territory of the state and in its international relations.
- ^ Co-official language at a state level (excluding defence, central police and monetary policy) and in local self-government units where speakers are 20% or more.
- ^ Macedonian: Северна Македонија, romanized: Severna Makedonija, pronounced [ˈsɛvɛrna makɛˈdɔnija]; Albanian: Maqedonia e Veriut, pronounced [macɛˈdɔnja ɛ vɛɾˈjut]
- ^ Macedonian: Република Северна Македонија, romanized: Republika Severna Makedonija, pronounced [rɛˈpublika ˈsɛvɛrna makɛˈdɔnija]; Albanian: Republika e Maqedonisë së Veriut, pronounced [rɛˈpublika ɛ macɛˈdɔnis sə vɛɾˈjut]
- ^ North Macedonia has recognised Kosovo since 9 October 2008.[267]
- ^ This policy changed after 1943 with the arrival of Tito's envoy Montenegrin Serb Svetozar Vukmanović-Tempo. He began in earnest to organise armed resistance to the Bulgarian rule and sharply criticised Sharlo's pro-Bulgarian policy. At a meeting of the partisan brigades, as well as a group of battalions in the Resen region on 21 December 1943, Tempo makes the following comments about Shatorov and the leadership of the MCP: "They thought that the Macedonian people were Bulgarians and that they were oppressed by the hegemony of Great Serbia and had to be transferred to Bulgaria. Their basic slogan is: 'All non-Macedonians out of Macedonia'. The capital J [Serbo-Croatian spelling of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavian, etc.] was deleted from all documents. In fact they did not want Yugoslavia, no matter where it stood politically. When the war started, the initial decision of this leadership was to be separate from Yugoslavia and from Tito. They declared that Macedonia would be free as soon as the Bulgarians came...."
References
- ^ a b "Census final data" (PDF). stat.gov.mk. 2002.
- ^ a b c "State Statistical Office – News release: Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of North Macedonia, 2021 – first dataset ,2021". Stat.gov.mk. Retrieved 30 March 2022.
- ^ "Попис на населението, домаќинствата и становите во Република Северна Македонија, 2021 – прв сет на податоци" (PDF). Archived from the original on 31 March 2022. Retrieved 7 July 2022.
- ^ a b Territorial Units. State Statistical Office.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2023 Edition. (MK)". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. 10 October 2023. Retrieved 13 October 2023.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey". ec.europa.eu/eurostat. Eurostat. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ "Basic Facts". North Macedonia, Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 16 November 2008.
- ^ "The World Bank in North Macedonia". World Bank. Retrieved 7 July 2022.
- ^ Μακεδονία, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek–English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ a b Macedonia, Online Etymology Dictionary
- ^ μακεδνός, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek–English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ μακρός, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek–English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ Eugene N. Borza, Makedonika, Regina Books, ISBN 0-941690-65-2, p. 114: The "highlanders" or "Makedones" of the mountainous regions of western Macedonia are derived from northwest Greek stock; they were akin both to those who at an earlier time may have migrated south to become the historical "Dorians".
- ^ Nigel Guy Wilson (2009). Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece, Routledge, p. 439: The latest archaeological findings have confirmed that Macedonia took its name from a tribe of tall, Greek-speaking people, the Makednoi.
- ^ Beekes, Robert (2010), Etymological Dictionary of Greek, vol. II, Leiden, Boston: Brill, p. 894
- ^ De Decker, Filip (2016). "AN ETYMOLOGICAL CASE STUDY ON THE AND VOCABULARY IN ROBERT BEEKES'S NEW ETYMOLOGICAL DICTIONARY OF GREEK". Studia Linguistica Universitatis Iagellonicae Cracoviensis. 133 (2). doi:10.4467/20834624SL.16.006.5152. ISSN 1897-1059.
- ^ "What is often overlooked is how Bulgarians and Greeks collaborated unknowingly from the middle decades of the 19th century onward in breathing new life into the geographical name Macedonia, which was all but forgotten during the Byzantine and Ottoman periods. In the late Ottoman period, "Macedonia" as such did not exist as an administrative unit in the empire... Greek nationalism, fixated on the continuity between ancient and modern Hellenes, was keen to project the name Macedonia as a way to assert the Greek historical character of the area. In 1845, for instance, the story of Alexander was published in a Slavo-Macedonian dialect scripted in Greek characters... For their part, Bulgarian nationalists readily accepted Macedonia as a regional denomination... Macedonia had become one of the "historic" Bulgarian lands... and "Macedonian Bulgarian" turned into a standard phrase." Dimitar Bechev, Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia, Scarecrow Press, 2009, ISBN 0-8108-6295-6, Introduction, p. VII.
- ^ "In the early 19th c. the modern Greeks with their Western-derived obsession with antiquity played a crucial role in reviving the classical name 'Macedonia' in the popular consciousness of the Balkan peoples. For a thousand years before that the name 'Macedonia' had meant different things for Westerners and Balkan Christians: for Westerners it always denoted the territories of the ancient Macedonians, but for the Greeks and all other Balkan Christians the name 'Macedonia' – if at all used – covered the territories of the former Byzantine theme 'Macedonia', situated between Adrianople (Edrine) and the river Nestos (Mesta) in classical and present-day Thrace. The central and northern parts of present-day 'geographic Macedonia' were traditionally called either 'Bulgaria' and 'Lower Moesia', but within a generation after Greek independence (gained in 1830) these names were replaced by 'Macedonia' in the minds of both Greeks and non-Greeks." Drezov K. (1999) Macedonian identity: an overview of the major claims. In: Pettifer J. (eds) The New Macedonian Question. St Antony's Series. Palgrave Macmillan, London, ISBN 0-230-53579-8, pp. 50–51.
- ^ "In 1813 Macedonia did not exist. A century later, it had become a hotly contested nationalist cause, a battlefield, and an obsession. What led to this dramatic transformation was modernity: a chilly wind of West European provenance that propelled to the Balkans concepts that few in the region understood, wanted or cared about. Among these, the idea of nationalism was the most potent, and the most lethal. Before the 1850s, Macedonia was a poverty-stricken province of the Ottoman Empire, where an Orthodox Christian and mostly peasant population speaking a variety of Slavonic idioms, Greek, or Vlach, was trying to eke out a modest living, and protect it from rapacious brigands and a decaying Ottoman administrative system. Religion was the only collective identity that most of them could make sense of, for ethnicity and language played little role in shaping their loyalties. But the winds of change quickly gathered momentum, and eventually shattered that multi-ethnic community, producing a 'Greek', or a 'Bulgarian', out of a 'Christian'." D. Livanios' review of Vemund Aarbakke, Ethnic Rivalry and the Quest for Macedonia, 1870–1913 in The Slavonic and East European Review, Vol. 83, No. 1 (Jan. 2005), pp. 141–142
- ^ The ancient name 'Macedonia' disappeared during the period of Ottoman rule and was only restored in the nineteenth century originally as geographical term. The Oxford Handbook of the History of Nationalism, John Breuilly, Oxford University Press, 2013, ISBN 0-19-920919-7, p. 192.
- ^ "The region was not called "Macedonia" by the Ottomans, and the name "Macedonia" gained currency together with the ascendance of rival nationalism." Collective Memory, National Identity, and Ethnic Conflict: Greece, Bulgaria, and the Macedonian Question, Victor Roudometof, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2002, ISBN 0-275-97648-3, p. 89.
- ^ "The Greeks were amongst the first to define these lands since the beginning of the 19th century. For educated Greeks, Macedonia was the historical Greek land of kings Philip and Alexander the Great." John S. Koliopoulos, Thanos M. Veremis, Modern Greece: A History since 1821. A New History of Modern Europe, John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 1-4443-1483-1, p. 48.
- ^ Donald Bloxham, The Final Solution: A Genocide, OUP Oxford, 2009, ISBN 0-19-955033-6, p. 65.
- ^ Chris Kostov, Contested Ethnic Identity: The Case of Macedonian Immigrants in Toronto, Peter Lang, 2010, ISBN 3-0343-0196-0, p. 76.
- ^ "Greece and Macedonia sign agreement on name change". Al Jazeera. 17 June 2018.
- ^ Kitsantonis, Niki (17 June 2018). "Macedonia and Greece Sign Historic Deal on Name Change". The New York Times.
- ^ Testorides, Konstantin; Becatoros, Elena (30 September 2018). "Macedonia: Referendum approves name change, but turnout low".
- ^ "PM to press on with Macedonia name change". BBC. 1 October 2018.
- ^ Agencies (20 October 2018). "Welcome to North Macedonia: parliament votes for name change". the Guardian.
- ^ Casule, Kole (11 January 2019). "Macedonia parliament agrees to change country's name". Reuters. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- ^ "Greece vote settles 27-year Macedonia row". BBC. 25 January 2019. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- ^ Waterfield, Robin (2019). The Library, Books 16–20: Philip II, Alexander the Great, and the Successors. Oxford University Press. p. 428. ISBN 978-0-19-875988-1.
Paeonia is roughly equivalent to the country currently known as the Republic of North Macedonia (the former FYROM).
- ^ Ovid (2005). Green, Peter (ed.). The Poems of Exile: Tristia and the Black Sea Letters. University of California Press. p. 319. ISBN 978-0-520-24260-9.
Ovid was lax in his geography, not least over Paeonia (in fact roughly coextensive with the present Slav Republic of Macedonia).
- ^ Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (2010). A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. John Wiley and Sons. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-4051-7936-2. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ Reames, Jeanne; Howe, Timothy (2008). Macedonian Legacies: Studies in Ancient Macedonian History and Culture in Honor of Eugene N. Borza. Regina Books. p. 239. ISBN 978-1-930053-56-4.
Having just conquered Paeonia (roughly where the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia is today).
- ^ Peshkopia, Ridvan (2015). Conditioning Democratization: Institutional Reforms and EU Membership Conditionality in Albania and Macedonia. Anthem Press. p. 189. ISBN 978-0-85728-325-2.
Indeed, the territory of the Republic of Macedonia encompasses little of the ancient kingdom of Macedon, which, in most part, overlaps with the current region of the contemporary Greece, but the name Macedonia "flowed" northward with the creation of Roman region of Macedonia, after the Romans occupied Greece in 168 BC. Besides the former kingdom of Macedon, the Roman region included the territories of Paeonia, where the contemporary FYR Macedonia rests.
- ^ Strabo, Geography, Book 7, Frg. 4:
- ^ Willkes, John (1996). The Illyrians. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-631-19807-9. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ Sealey, Raphael (1976). A history of the Greek city states, ca. 700–338 B.C.. University of California Press. p. 442. ISBN 978-0-520-03177-7.
illyrian lychnitis.
- ^ Evans, Thammy (2007). Macedonia. Bradt Travel Guides. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-84162-186-9.
- ^ Borza, Eugene N. (1992). In the shadow of Olympus: the emergence of Macedon. Princeton University Press. pp. 74–75. ISBN 978-0-691-00880-6.
- ^ Lewis, D.M.; et al., eds. (1994). The Cambridge ancient history: The fourth century B.C. Cambridge University Press. pp. 723–724. ISBN 978-0-521-23348-4. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History Volume 3, Part 3: The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman and N. G. L. Hammond, 1982, ISBN 0-521-23447-6, p. 284.
- ^ "No document found". Perseus.tufts.edu.
- ^ Howe & Reames 2008, p. 239.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2011, pp. 135–138, 342–345.
- ^ "Persian influence on Greece (2)". Archived from the original on 24 July 2020. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ Warfare in the ancient world: from the Bronze Age to the fall of Rome. By Stefan G. Chrissanthos, p. 75
- ^ Poulton, Hugh (2000). Who are the Macedonians?. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. p. 14. ISBN 978-1-85065-534-3.
- ^ Macedonia yesterday and today Author Giorgio Nurigiani, Publisher Teleurope, 1967 p. 77.
- ^ Stipčević, Aleksandar (1977). The Illyrians. Translated by Stojana Čulić Burton. Park Ridge, New Jersey: Noyes Press. p. 44.
- ^ A Companion to Ancient Macedonia, By Joseph Roisman and Ian Worthington, p. 549
- ^ "Scopje". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 6 June 2011.
- ^ A. F. Christidis (2007). A History of Ancient Greek: From the Beginnings to Late Antiquity, Cambridge University Press, p. 351: "Despite Roman domination, there was no retreat on the part of Greek tradition in the eastern part of the empire, and only in Macedonia did Latin spread in some extent".
- ^ Lester K. Little, ed. (2007). Plague and the End of Antiquity: The Pandemic of 541–750. Cambridge University Press. pp. 15, 24, 116, 118, 125, 286–287. ISBN 978-0-521-84639-4.
- ^ Wright, David Curtis (1997). "The Hsiung-Nu-Hun Equation Revisited". Eurasian Studies Yearbook. 69: 77–112.
- ^ Ulf Büntgen; Vladimir S. Myglan; Fredrik Charpentier Ljungqvist; Michael McCormick; Nicola Di Cosmo; Michael Sigl; Johann Jungclaus; Sebastian Wagner; Paul J. Krusic; Jan Esper; Jed O. Kaplan; Michiel A. C. de Vaan; Jürg Luterbacher; Lukas Wacker; Willy Tegel; Alexander V. Kirdyanov (2016). "Cooling and societal change during the Late Antique Little Ice Age from 536 to around 660 AD". Nature Geoscience. 9 (3): 231–236. Bibcode:2016NatGe...9..231B. doi:10.1038/ngeo2652. ISSN 1752-0894.
- ^ Bintliff J.L. (2003), The ethnoarchaeology of a 'passive' ethnicity: The Arvanites of Central Greece, p. 142. In: Brown K.S., Hamilakis Y. (Eds.) The Usable Past. Greek Metahistories. Lanham-Boulder: Lexington Books. 129–144.
- ^ D. Hupchick (2002) The Balkans: From Constantinople to Communism, Springer, p. 33, ISBN 0-312-29913-3.
- ^ Florin Curta (2006). "Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250". Archive.org.
- ^ John Van Antwerp Fine Jr. (1991). The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08149-7.
- ^ S. Runciman. "A history of the First Bulgarian empire – Appendix 9". Promacedonia.org.
- ^ Nicol, Donald Macgillivray (1993). The last Centuries of Byzantium, (1261–1453). Cambridge University Press. p. 500. ISBN 978-0-521-43991-6. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica – Rumelia at Encyclopædia Britannica.com
- ^ The Encyclopædia Britannica, or, Dictionary of arts, sciences ..., Volume 19. 1859. p. 464.
- ^ Phillips, John (2004). Macedonia: Warlords and Rebels in the Balkans. I.B. Tauris. p. 41. ISBN 978-1-86064-841-0.
- ^ Sampimon, Janette (2006). Becoming Bulgarian: The articulation of Bulgarian identity in the nineteenth century in its international context: An intellectual history. Pegasus. p. 234. ISBN 978-90-6143-311-8.
- ^ Clarke, James Franklin; Hupchick, Dennis P. (1988). The pen and the sword: Studies in Bulgarian history. East European Monographs. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-88033-149-4.
Peichinovich of Tetovo, Macedonia, author of one of the first Bulgarian books
- ^ Gawrych, George (2006). The Crescent and the Eagle: Ottoman Rule, Islam and the Albanians, 1874–1913. Bloomsbury Academic. p. 28. ISBN 978-1-84511-287-5.
- ^ Bechev, Dimitar (2009). Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia. Scarecrow Press. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-8108-5565-6. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- ^ Roth, Klaus; Brunnbauer, Ulf (2008). Region, Regional Identity and Regionalism in Southeastern Europe. LIT Verlag Münster. ISBN 978-3-8258-1387-1 – via Google Books.
- ^ Shaw, Stanford J. (1977). History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey: Volume 2, Reform, Revolution, and Republic: The Rise of Modern Turkey 1808–1975. Cambridge University Press. p. 209. ISBN 978-0-521-29166-8.
- ^ There was even an attempt to form a kind of revolutionary government led by the socialist Nikola Karev. The Krushevo manifesto was declared, assuring the population that the uprising was against the Sultan and not against Muslims in general, and that all peoples would be included. As the population of Krushevo was two-thirds hellenised Vlachs and Patriarchist Slavs, this was a wise move. Despite these promises, the insurgent flew Bulgarian flags everywhere and in many places the uprising did entail attacks on Muslim Turks and Albanians who themselves organised for self-defence." Who are the Macedonians? Hugh Poulton, C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 1995, ISBN 1-85065-238-4, p. 57.
- ^ In fact Macedonian historians as Blaze Ristovski have recognized, that the "government" of the "republic", nowadays a symbol of Macedonian statehood, was actually composed of people who identified themselves as "Greeks", "Vlachs" and "Bulgarians". "We, the People: Politics of National Peculiarity in Southeastern Europe" Diana Mishkova, Central European University Press, 2009, ISBN 963-9776-28-9, p. 124.
- ^ "The IMARO activists saw the future autonomous Macedonia as a multinational polity, and did not pursue the self-determination of Macedonian Slavs as a separate ethnicity. Therefore, Macedonian was an umbrella term covering Bulgarians, Turks, Greeks, Vlachs, Albanians, Serbs, Jews, and so on." Historical Dictionary of Macedonia, Historical Dictionaries of Europe, Dimitar Bechev, Scarecrow Press, 2009, ISBN 0-8108-6295-6, Introduction.
- ^ The political and military leaders of the Slavs of Macedonia at the turn of the century seem not to have heard the call for a separate Macedonian national identity; they continued to identify themselves in a national sense as Bulgarians rather than Macedonians.[...] (They) never seem to have doubted "the predominantly Bulgarian character of the population of Macedonia". "The Macedonian conflict: ethnic nationalism in a transnational world", Princeton University Press, Danforth, Loring M. 1997, ISBN 0-691-04356-6, p. 64.
- ^ Nicolle 2008, p. 162.
- ^ Saucerman, S.B. (1937). International Transfers of Territory in Europe with Names of the Affected Political Subdivisions. Department of State publication. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 195.
- ^ a b c d e f g Banac, Ivo (1984). The National Question in Yugoslavia. Origins, History, Politics. London and Ithaka: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-1675-0.
- ^ Mojzes, Paul (2011). Balkan Genocides: Holocaust and Ethnic Cleansing in the Twentieth Century. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 38. ISBN 978-1-4422-0663-2.
- ^ Йосиф Разсуканов, 85 години от Охриско-Дебърското въстание, в-к "Македония", брой 33, 16 септември 1998 г.
- ^ Király, B.K.; Rothenberg, G.E. (1985). War and Society in East Central Europe: East central European society in World War I. Atlantic studies. Brooklyn College Press. p. 377. ISBN 978-0-88033-089-3.
- ^ a b c Gerwarth, R.; Horne, J. (2013). War in Peace: Paramilitary Violence in Europe After the Great War. The Greater War. OUP Oxford. p. 150. ISBN 978-0-19-968605-6.
- ^ a b Bianchi, B. (2012). War crimes and crimes against humanity: violence against civilians on the eastern front (1914–1919). Biblioteca di storia contemporanea (in Italian). UNICOPLI. p. 163. ISBN 978-88-400-1579-8.
- ^ Laffan, R.G.D. (1989). The Serbs: The Guardians of the Gate. Armenian Research Center collection. Dorset Press. p. 252. ISBN 978-0-88029-413-3.
- ^ Report of the Interallied Commission on the Violation of the Hague Convention. Imprimerie "Yougoslavia". 1919. p. 22.
- ^ Mojzes, P. (2011). Balkan Genocides: Holocaust and Ethnic Cleansing in the Twentieth Century. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 42. ISBN 978-1-4422-0663-2.
- ^ "Kraljevina Jugoslavija! Novi naziv naše države. No, mi smo itak med seboj vedno dejali Jugoslavija, četudi je bilo na vseh uradnih listih Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev. In tudi drugi narodi, kakor Nemci in Francozi, so pisali že prej v svojih listih mnogo o Jugoslaviji. 3. oktobra, ko je kralj Aleksander podpisal "Zakon o nazivu in razdelitvi kraljevine na upravna območja", pa je bil naslov kraljevine Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev za vedno izbrisan." (Naš rod ("Our Generation", a monthly Slovenian language periodical), Ljubljana 1929/30, št. 1, str. 22, letnik I.)
- ^ Dejan Djokić, Yugoslavism: histories of a failed idea, 1918–1992, p. 123, at Google Books
- ^ Eastern Europe in the twentieth century – and after, p. 20, at Google Books
- ^ "An article by Dimiter Vlahov about the persecution of the Bulgarian population in Macedonia". newspaper "Balkanska federatsia", No. 140, 20 August 1930, Vienna, original in Bulgarian. Retrieved 3 August 2007.
- ^ War of words: Washington tackles the Yugoslav conflict, p. 43, at Google Books
- ^ Fischer, Bernd Jürgen (2007). Balkan Strongmen: Dictators and Authoritarian Rulers of South Eastern Europe. Purdue University Press. ISBN 978-1-55753-455-2 – via Google Books.
- ^ Gerginov, Kr., Bilyarski, Ts. Unpublished documents for Todor Alexandrov's activities 1910–1919, magazine VIS, book 2, 1987, p. 214 – Гергинов, Кр. Билярски, Ц. Непубликувани документи за дейността на Тодор Александров 1910–1919, сп. ВИС, кн. 2 от 1987, с. 214.
- ^ Victor Roudometof, Collective Memory, National Identity, and Ethnic Conflict: Greece, Bulgaria, and the Macedonian Question, Praeger, 2002 p. 100
- ^ Vassil Karloukovski. "Гиза, Антони, "Балканските държави и Македония", Македонски Научен Институт София, 2001 г". Promacedonia.org. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ Bechev, Dimitar (2009). Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-6295-1 – via Google Books.
- ^ Duncan Perry, "The Republic of Macedonia: finding its way" in Karen Dawisha and Bruce Parrot (eds.), Politics, power and the struggle for Democracy in South-Eastern Europe, Cambridge University Press, 1997, pp. 228–229.
- ^ Mitre Inadeski, Hronologija na Skopje: rabotničkoto i narodnoosloboditelnoto dviženje 1939–1945, tom 2, Arhiv, 1974, str. 181.
- ^ Bulgarian Campaign Committees in Macedonia – 1941 Dimitre Mičev
- ^ "Forming of the Local Campaign Committees". kroraina.com.
- ^ a b Georgieva & Konechni 1998, p. 223.
- ^ Hugh Poulton (1995). Who are the Macedonians?. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. p. 102. ISBN 978-1-85065-238-0. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ Miller, Marshall Lee (1975). Bulgaria during the Second World War. Stanford University Press. p. 314. ISBN 978-0-8047-0870-8. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ Bulgaria managed to save its entire 48,000-strong Jewish population during World War II from deportation to Nazi concentration camps, but under German pressure those Jews from their newly annexed territories without Bulgarian citizenship were deported, such as those from Vardar Macedonia and Western Thrace. The Holocaust in Macedonia: Deportation of Monastir Jewry United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
- ^ Mark Cohen, The Holocaust in Macedonia: Deportation of Monastir Jewry, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
- ^ "НОБ на Македонија" Јован Поповски. Скопје, 1962
- ^ "Историја на Македонскиот Народ" Александар Стојановски, Иван Катарџиев, Данчо Зографски. Скопје, 1988
- ^ History of Bulgaria, Petar Delev et al., 2001, p. 364
- ^ Axis Forces in Yugoslavia 1941–45. Bloomsbury. 1995. ISBN 978-1-85532-473-2 – via Google Books.[permanent dead link]
- ^ James Horncastle, The Macedonian Slavs in the Greek Civil War, 1944–1949, Rowman & Littlefield, 2019, ISBN 1-4985-8505-1, p. 167.
- ^ Andrew Rossos, Macedonia and the Macedonians: A History, Hoover Press, 2013, ISBN 0-8179-4883-X, p. 205.
- ^ Мичев, Добрин. Партизанското движение във Вардарска Македония, 1941–1944 г. сп. Македонски преглед, кн. 2, стр. 5–40.
- ^ "Constitution of the Socialist Republic of Macedonia, 1974 – Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia" (PDF).
- ^ Устав Федеративне Народне Републике Југославије (1946), sr.wikisource.org, retrieved on 19 October 2007. (in Serbo-Croatian)
- ^ Устав Социјалистичке Федеративне Републике Југославије (1963), sr.wikisource.org, retrieved on 19 October 2007. (in Serbo-Croatian)
- ^ Nohlen, D & Stöver, P (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, p. 1278 ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7
- ^ "Recognition of States: Annex 3". Archived from the original on 15 February 2005. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ a b Thomas, Nigel (2006). The Yugoslav Wars (2): Bosnia, Kosovo And Macedonia 1992–2001. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84176-964-6.
- ^ a b "Who are the rebels?". BBC News. 20 March 2001.
- ^ "Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Macedonia, 2002 – Book XIII, Skopje, 2005" (PDF). State Statistical Office of the Republic of Macedonia.
- ^ Huggler, Justin (12 March 2001). "KLA veterans linked to latest bout of violence in Macedonia". The Independent. London. Retrieved 4 April 2010.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Brunnbauer, Ulf (2002). "The implementation of the Ohrid Agreement: Ethnic Macedonian resentments" (PDF). Journal on Ethnopolitics and Minority Issues in Europe (1/2002). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ^ "Clashes between Macedonians and Albanians in Macedonia". rtvfan.net. 5 May 2016.[dead link]
- ^ "In Macedonia, Ethnic Albanians Protest Arrests Of Murder Suspects". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. 11 May 2012.
- ^ Service, s Balkan (27 April 2017). "Protesters Attack Lawmakers After Storming Macedonia's Parliament". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Retrieved 6 December 2023.
- ^ "Macedonia: protesters storm parliament and attack MPs". the Guardian. 27 April 2017. Retrieved 6 December 2023.
- ^ a b "Ghosts of the past endanger Macedonia's future". Boris Georgievski, Balkan Insight, 27 October 2009 [1].
- ^ Greece slates Skopje's provocative Alexander statue Sinisa Jakov Marusic, Balkan Insight, 15 June 2011 [2]
- ^ Marusic, Sinisa Jakov (15 June 2018). "Macedonia to Rename Divisive Statues That Irked Greece". BalkanInsight. Skopje. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ Tagaris, Karolina (24 January 2018). "Macedonia to rename airport to help resolve name row with Greece, PM says". Reuters. Davos. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ "Final Agreement for the Settlement of Differences as Described in the United Nations Security Council Resolutions 817 (1993) and 845 (1993), the Termination of the Interim Accord of 1995, and the Establishment of a Strategic Partnership Between the Parties" (PDF). Kathimerini.gr. Retrieved 13 June 2018.
- ^ Marusic, Sinisa Jakov (27 June 2018). "Macedonia, Albania Hail EU Approval for Accession Talks". Balkan Insight. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
- ^ "Macedonia's parliament endorses name deal with Greece for second time". Reuters. 5 July 2018. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ^ Marusic, Sinisa Jakov (11 July 2018). "NATO Invites Macedonia to Join the Western Alliance". Balkan Insight. Retrieved 13 July 2018.
- ^ "Macedonia to hold name-change referendum on September 30". SBS News. 30 July 2018. Retrieved 31 July 2018.
- ^ "iVote Demokra – Integrated Election Information System of the State Election Commission of the Republic of Macedonia". referendum.sec.mk. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 14 October 2018.
- ^ "Macedonia name referendum fails to reach turnout threshold: election commission". Reuters. 30 September 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "Macedonia signs Nato accession deal". BBC News. 6 February 2019.
- ^ "North Macedonia minister: NATO, not EU, saved name change deal". Euractiv. 19 March 2019.
- ^ "UN Notified Of North Macedonia's Name Change". RFE/RL.
- ^ "Foreign Secretary statement on the Republic of North Macedonia" (Press release). Government of the United Kingdom. 16 February 2019. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "North Macedonia name change enters force". Deustche Welle. 12 February 2019. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "NATO: North Macedonia becomes 30th member". Deutsche Welle. 27 March 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "North Macedonia joins NATO as 30th Ally". NATO. 27 March 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "EU Leaders Give Final OK To Begin North Macedonia, Albania Membership Talks". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 27 March 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "EU can start talks with Albania and North Macedonia over joining". The Guardian. Reuters. 23 March 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "Bulgaria blocks EU accession talks with North Macedonia". National Post. Reuters. 17 November 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "Foreign Minister Zaharieva: Bulgaria Cannot Approve EU Negotiating Framework with North Macedonia – Novinite.com – Sofia News Agency". Novinite.com. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ^ "Bulgarian intellectuals: Unacceptable to deny Macedonian nation, language; green-light talks immediately". 5 December 2020. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- ^ "Bulgaria asks EU to stop 'fake' Macedonian identity". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- ^ "Der Spiegel: Bulgaria Misuses Its Right of Veto for Nationalistic Purposes". novinite.com. 19 November 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ Kamusella, Tomasz (2021). "Bulgaria's Secret Empire: An Ultimatum to North Macedonia". Journal of Balkan and Black Sea Studies (6): 155–212.
- ^ "North Macedonia: More violence reported at protests". news.yahoo.com. 6 July 2022. Retrieved 8 July 2022.
- ^ Casert, Raf (19 July 2022). "EU starts membership talks with Albania, North Macedonia". Associated Press. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
- ^ North Macedonia’s EU Trajectory amidst Geopolitical Dynamics. China-CEE Institute, Weekly Briefing, Vol. 67. No. 1 (MK) November 2023.
- ^ Restelica, Bleona (26 September 2024). "EU Separates Albania's Accession Path From North Macedonia". SchengenNews. Retrieved 26 September 2024.
- ^ "Macedonian Ministry of Environment". Archived from the original on 19 January 2008. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "History of deadly earthquakes". BBC News. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica. "Britannica's article about Sar Mountains". Britannica.com. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "Sar Mountains on the Euratlas map of the Europe's most significant mountain ranges". Euratlas.com. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "Macedonia". Mymacedonia.net. Archived from the original on 23 October 2010. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- ^ a b Georgieva & Konechni 1998, p. 73.
- ^ Georgieva & Konechni 1998, p. 31.
- ^ Zikov, Mihailo (1995). Клима и климатска регионализација во Република Македонија, "Географски разгледи" [Climate and climatic regionalization in the Republic of Macedonia "Geographical postcards"] (in Macedonian). Skopje.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Georgieva & Konechni 1998, p. 2.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ "AFTER 27 YEARS, SHAR MOUNTAIN FINALLY DECLARED A NATIONAL PARK!". Македонско Еколошко Друштво (in Macedonian).
- ^ "Key indicators". State Statistical Office. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "Ahmeti accepts the invitation for dialog with Gruevski". Limun.hr. Archived from the original on 25 February 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "VMRO-DPMNE and DUI form ruling coalition in Macedonia". SeTimes. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "Macedonia elections pass off peacefully". Irish Times. 3 March 2009. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "Macedonia gets new government six months after elections". Deutsche Welle. 1 June 2017. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ a b "Tension in Skopje, Talat Xhaferi is elected Assembly Speaker in a situation of chaos". Balkaneu.com. 27 April 2017. Retrieved 31 August 2017.
- ^ "Macedonian Parliament's New Ethnic Albanian Speaker Enters Office". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 3 May 2017.
- ^ "EM North Macedonia: Review of the 2020 parliamentary elections in North Macedonia". European Movement International. 22 July 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "President of the Government of the Republic of North Macedonia – Zoran Zaev". Government of the Republic of North Macedonia. 11 May 2018. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ Matamoros, Cristina Abellan (12 May 2019). "North Macedonia's new president Stevo Pendarovski takes office". euronews. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "North Macedonia Prime Minister Zoran Zaev resigns | DW". Deutsche Welle. 31 October 2021. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "North Macedonia's Kovacevski Approved As New PM". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty.
- ^ "North Macedonia's First Female President Sworn In, Declines To Use 'North'". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 12 May 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Constitution of the Republic of North Macedonia" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 January 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2017.
- ^ "Jovan Mitreski elected Parliament Speaker". Media Information Agency. 26 January 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Floudas, Demetrius Andreas; "A Name for a Conflict or a Conflict for a Name? An Analysis of Greece's Dispute with FYROM". 24 (1996) Journal of Political and Military Sociology, 285. 1996. Archived from the original on 27 January 2006. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- ^ FYROM Name Issue Archived 13 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Hellenic Republic – Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- ^ "It's Time for Macedonia to Accept Compromise". ForeignPolicy. 25 September 2018. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- ^ "United Nations Resolution 225 (1993)". United Nations. 8 April 1993. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ Thonemann, Peter; Price, Simon (29 April 2010). The Birth of Classical Europe: A History from Troy to Augustine. Penguin Books. pp. 123–124.
- ^ "Naming the solution", Kathimerini English edition, 16 September 2005
- ^ European Commission. "Background information – The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia". Archived from the original on 23 December 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2006.
- ^ "Secretary-General Congratulates Greece, Republic of North Macedonia on Settling Long-Standing 'Name' Dispute, as Agreement Enters into Force". United Nations. 13 February 2019. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ "The Republic of North Macedonia and the EU". European External Action Service. 12 May 2016. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ "Relations with the Republic of North Macedonia". NATO. 15 February 2019. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ Hopkins, Valerie (18 February 2019). "Renamed Balkan country seeks closer ties with Nato, EU, PM says". Financial Times.
- ^ "North Macedonia, Ministry of foreign affairs". Mfa.gov.mk. Archived from the original on 16 November 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "Bulgaria: Macedonia Remains Out of NATO Because of Greek Veto over Name Dispute – Novinite.com – Sofia News Agency". Novinite.com. 3 April 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "Greece stands by NATO veto threat for Macedonia". The Star Online. Thestar.com.my. Archived from the original on 10 April 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "EP Urges Accession Talks For Macedonia". BalkanInsight.com. 13 March 2009. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "Bulgaria vetoes Macedonia's EU accession talks". euractiv.com. 2 November 2012.
- ^ "STRUCTURE OF THE ARMY". Army of the Republic of North Macedonia. Retrieved 12 February 2024.
- ^ IISS (2023). The Military Balance 2023. International Institute for Strategic Studies. pp. 112–113.
- ^ "North Macedonia". CIA World Factbook. Retrieved 12 February 2024.
- ^ "National Command Management". Archived from the original on 4 September 2010.
- ^ "Amnesty International – Summary – Macedonia". Web.amnesty.org. Archived from the original on 18 May 2011. Retrieved 6 June 2011.
- ^ "Human Rights Watch – Defending Human Rights Worldwide". 14 April 2013. Archived from the original on 14 April 2013.
- ^ a b "Macedonia Country Brief" (PDF). The World Bank. 24 April 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ a b "World Bank development data" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 March 2010. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "Government of the Republic of Macedonia". Archived from the original on 27 January 2008. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "Macedonia's Flat Tax". Nuwireinvestor.com. 15 February 2007. Archived from the original on 22 May 2010. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "Macedonian unemployment rate". Worldbank.org.mk. Archived from the original on 2 March 2001. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ State Statistical Office Active population – Unemployment data
- ^ State Statistical Office Gross domestic product 2013
- ^ State Statistical Office External trade volume 2014
- ^ "Investment in Government, Finance, and Telecom Sectors Makes Macedonia's IT Market the Fastest Growing in the Adriatic Region, Says IDC" Archived 22 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, IDC (global provider of market intelligence)
- ^ Gallup Balkan Monitor, 2010 Archived 27 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The 2006 CIA Factbook CIA Factbook Macedonia
- ^ "GDP per capita in PPS". Eurostat. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- ^ "Greek investments in FYROM at 1 bil. Euros". Greekembassy.org. 16 July 2008. Archived from the original on 19 July 2010. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- ^ "DEPA sees natural gas role for Greece exiting from the crisis". New Europe. 3 April 2017. Archived from the original on 19 April 2017. Retrieved 18 April 2017.
- ^ Jovanovski, Mirche (April 2017). "Политичката криза не е добра реклама за туризмот" [The political crisis is not a good advertisement for tourism]. Ekonomija I Biznis. 19 (226): 44–47.
- ^ a b Marinoski, Naume; Korunovski, Saso (2012). "Tourism in Macedonia in Changing Environment". Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences. 44: 19–31. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.05.001.
- ^ "The State of Tourism in Macedonia". Makstack. 15 March 2011. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- ^ Туризам во декември 2019 [Tourism in December 2019] (PDF) (in Macedonian). State Statistical Office. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- ^ Број на туристи и ноќевања по земја на припадност, по месеци [Number of tourists and nights spent by country of origin, by months] (in Macedonian). State Statistical Office. 2020. Retrieved 2 May 2020.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Janevski, Ljupčo (7 August 2018). Македонија како туристичка дестинација за 4 сезони [Macedonia as a tourist destination for 4 seasons]. Ako.mk (in Macedonian). Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- ^ a b c d Thammy Evans; Philip Briggs (2019). North Macedonia. Bradt Travel Guides. p. 2. ISBN 9781784770846. Retrieved 18 August 2024.
- ^ "Home". Oic.org.mk.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index 2024 : Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship". www.wipo.int. Retrieved 29 November 2024.
- ^ "U.S. Agency for International Development". Macedonia.usaid.gov. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "Census 2021" (PDF). Republic of North Macedonia State Statistical Office. Retrieved 17 April 2022.
- ^ [3] UNDP's Regional Bureau for Europe Archived 25 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Попис на населението, домаќинствата и становите во Република Северна Македонија, 2021 - прв сет на податоци" (in Macedonian). Archived from the original on 30 March 2022.
- ^ "CIA The World Factbook: Kosovo". CIA.gov. Retrieved 24 November 2016.
- ^ "Presentation of the main results of the Census of Population and Housing 2011" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 March 2017. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "CIA The World Factbook: Bosnia and Herzegovina". CIA.gov. Retrieved 24 November 2016.
- ^ "Religious Composition by Country, 2010–2050". 2 April 2015. Archived from the original on 2 August 2017. Retrieved 6 November 2016.
- ^ Во Македонија има 1.842 цркви и 580 џамии (in Macedonian). Dnevnik. 28 December 2011. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- ^ "Συλλείτουργο Οικουμενικού Πατριάρχη-Αρχιεπισκόπου Αχρίδος στο Φανάρι" [Ecumenical Patriarch, Archbishop of Ohrid in the Phanar]. Ορθοδοξία News Agency (in Greek). 12 June 2022. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- ^ "Church of Serbia for North Macedonia: We are not under the influence or pressure of anyone". Orthodox Times. 16 May 2022. Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ^ "Church Rivalry Threatens to Brim Over". Iwpr.net. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of". Catholic-Hierarchy.org. David M. Cheney. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ "Blog Archives " Macedonia's Jewish Community Commemorates the Holocaust, and Embraces the Future". Balkanalysis.com. Archived from the original on 24 October 2009. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ Dimitar Bechev (2019) Historical Dictionary of North Macedonia, Rowman & Littlefield, ISBN 9781538119624, p. XLVII.
- ^ Gordon, Raymond G. Jr., ed. (2005). "Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition". SIL International. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- ^ "Macedonia ethnic and linguistic minorities". Eurominority. Archived from the original on 6 January 2013. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ^ "Map of the European languages". Eurominority. Archived from the original on 14 January 2016. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ^ "Indo-European languages in contemporary Eurasia". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Archived from the original on 17 December 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
- ^ "BBC: Languages across Europe – Macedonia". BBC. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ^ "Total resident population of the Republic of North Macedonia by ethnic affiliation, by settlement, Census 2021-PxWeb". PxWeb. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- ^ "Macedonian Opera Marks 60th Anniversary. Culture – North Macedonia". Archived from the original on 27 July 2011.
- ^ Friedman, Victor; Palmer, Veselka (1995), "La cuisine macédonien", in Aufray, Michel; Perret, Michel (eds.), Cuisines d'Orient et d'ailleurs (PDF), Paris: INALCO/Grenoble: Glénant, pp. 76–79, archived from the original (PDF) on 14 October 2017, retrieved 10 February 2016
- ^ Risteski, Michael (2016). "Culture and Food – Determining the Value of Food in Rural Tourism as an Important Part of the total Tourism Experience". XVI International Conference of Partner Institutions "Planning for Change". La Fondation pour la Formation Hoteliere, Nestle Pro Gastronomia.
- ^ "Golden Players take centre stage". UEFA.com. 29 November 2003. Archived from the original on 17 March 2005. Retrieved 23 September 2020.
- ^ "North Macedonia qualify for Euro 2020, their first major tournament". beIN Sports. 12 November 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- ^ "IOC approve name change to North Macedonia National Olympic Committee". insidethegames.biz. 27 March 2019.
- ^ Terzin Stojčić, Marijana (2019). "Seme istorije Kirila Cenevskog". Kinoteka. 33: 54–57.
- ^ "North Macedonia – Cultural life". Britannica. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- ^ Martinelli, Marissa (13 January 2020). "Honeyland Just Made Oscar History". The Slate. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ^ "Global Peace Index 2019" (PDF). visionofhumanity.org. Institute of Economics & Peace. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 August 2019. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ "Republic of North Macedonia – 2019 World Press Freedom Index". rsf.org. Reporters Without Borders. Archived from the original on 14 January 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ "Index of Economic Freedom 2019". heritage.org. The Heritage Foundation. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ "Corruption Perceptions Index 2019". transparency.org. Transparency International. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ "2019 Human Development Index Ranking". hdr.undp.org. United Nations Development Programme. Archived from the original on 16 May 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ "Ease of doing business ranking" (PDF). doingbusiness.org. World Bank. p. 5. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ Macedonia recognizes Kosovo Archived 15 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Macedonian Information Agency, 9 October 2008
Bibliography
- Brunnbauer, Ulf. "'Pro‐Serbians' vs. 'Pro‐Bulgarians': Revisionism in Post‐Socialist Macedonian Historiography." History Compass 3.1 (2005). online
- Brunnbauer, Ulf. "Serving the Nation: Historiography in the Republic of Macedonia (FYROM) After Socialism." Historein 4 (2003): 161–182. online
- Georgieva, Valentina; Konechni, Sasha (1998). Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 0-8108-3336-0.
- Marinov, Tchavdar. "Historiographical Revisionism and Re-Articulation of Memory in the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia." Sociétés politiques comparées 25 (2010): 1-19. online
- Mattioli, Fabio (2020). Dark Finance: Illiquidity and Authoritarianism at the Margins of Europe. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-1-5036-1294-5.
- Nicolle, David (2008). The Ottomans: Empire of Faith. Thalamus Publishing. ISBN 978-1-902886-11-4.* Tziampiris, Aristotle. "Greek Historiography and Slav-Macedonian National Identity." The Historical Review/La Revue Historique 8 (2011): 215-225. online
Further reading
External links
- Official website
- North Macedonia from RFE/RL
- North Macedonia from BBC News
 Wikimedia Atlas of North Macedonia
Wikimedia Atlas of North Macedonia Geographic data related to North Macedonia at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to North Macedonia at OpenStreetMap- Key Development Forecasts for North Macedonia from International Futures
- North Macedonia
- Balkan countries
- Landlocked countries
- Member states of the Council of Europe
- Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
- Member states of the United Nations
- Member states of NATO
- Republics
- States and territories established in 1991
- 1991 establishments in the Republic of Macedonia
- Countries in Europe
- Countries and territories where Albanian is an official language










