Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta: Difference between revisions
Interactions |
consistent citation formatting |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 17 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens}} |
|||
{{cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc|display-authors=6}} |
|||
{{Infobox_gene}} |
{{Infobox_gene}} |
||
'''Glycogen synthase kinase |
'''Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta''', '''(GSK-3 beta)''', is an [[enzyme]] that in humans is encoded by the ''GSK3B'' [[gene]].<ref name="pmid7980435">{{cite journal | vauthors = Stambolic V, Woodgett JR | title = Mitogen inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta in intact cells via serine 9 phosphorylation | journal = The Biochemical Journal | volume = 303 | issue = Pt 3 | pages = 701–4 | date = November 1994 | pmid = 7980435 | pmc = 1137602 | doi = 10.1042/bj3030701 }}</ref><ref name="pmid10486203">{{cite journal | vauthors = Lau KF, Miller CC, Anderton BH, Shaw PC | title = Molecular cloning and characterization of the human glycogen synthase kinase-3beta promoter | journal = Genomics | volume = 60 | issue = 2 | pages = 121–8 | date = September 1999 | pmid = 10486203 | doi = 10.1006/geno.1999.5875 }}</ref> In mice, the enzyme is encoded by the Gsk3b gene.<ref name=hoeflich2000 /> Abnormal regulation and expression of GSK-3 beta is associated with an increased susceptibility towards [[bipolar disorder]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Luykx JJ, Boks MP, Terwindt AP, Bakker S, Kahn RS, Ophoff RA | title = The involvement of GSK3beta in bipolar disorder: integrating evidence from multiple types of genetic studies | journal = European Neuropsychopharmacology | volume = 20 | issue = 6 | pages = 357–68 | date = June 2010 | pmid = 20226637 | doi = 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.02.008 | s2cid = 43214075 }}</ref> |
||
== Function == |
== Function == |
||
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 ([[GSK-3]]) is a proline-directed [[Serine/threonine-specific protein kinase|serine-threonine kinase]] that was initially identified as a [[phosphorylation|phosphorylating]] and an inactivating agent of [[glycogen synthase]]. Two isoforms, alpha ([[GSK3A]]) and beta, show a high degree of amino acid homology.<ref name="pmid7980435" /> GSK3B is involved in energy metabolism, neuronal cell development, and body pattern formation.<ref name="pmid1333807">{{cite journal | vauthors = Plyte SE, Hughes K, Nikolakaki E, Pulverer BJ, Woodgett JR | title = Glycogen synthase kinase-3: functions in oncogenesis and development | journal = Biochimica et Biophysica Acta | volume = 1114 | issue = |
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 ([[GSK-3]]) is a proline-directed [[Serine/threonine-specific protein kinase|serine-threonine kinase]] that was initially identified as a [[phosphorylation|phosphorylating]] and an inactivating agent of [[glycogen synthase]]. Two isoforms, alpha ([[GSK3A]]) and beta, show a high degree of amino acid homology.<ref name="pmid7980435" /> GSK3B is involved in energy metabolism, neuronal cell development, and body pattern formation.<ref name="pmid1333807">{{cite journal | vauthors = Plyte SE, Hughes K, Nikolakaki E, Pulverer BJ, Woodgett JR | title = Glycogen synthase kinase-3: functions in oncogenesis and development | journal = Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer | volume = 1114 | issue = 2–3 | pages = 147–62 | date = December 1992 | pmid = 1333807 | doi = 10.1016/0304-419X(92)90012-N }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | title = Entrez Gene: GSK3B glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=2932}}</ref> It might be a new therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. |
||
== Disease relevance == |
|||
== Loss of function mutations == |
|||
[[Homozygous]] disruption of the |
[[Homozygous]] disruption of the Gsk3b locus in mice results in embryonic lethality during mid-gestation.<ref name=hoeflich2000 /> This lethality phenotype could be rescued by inhibition of [[tumor necrosis factor]].<ref name=hoeflich2000 /> |
||
Two SNPs at this gene, rs334558 (-50T/C) and rs3755557 (-1727A/T), are associated with efficacy of [[lithium (medication)|lithium]] treatment in [[bipolar disorder]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Iwahashi K, Nishizawa D, Narita S, Numajiri M, Murayama O, Yoshihara E, Onozawa Y, Nagahori K, Fukamauchi F, Ikeda K, Ishigooka J | title = Haplotype analysis of GSK-3β gene polymorphisms in bipolar disorder lithium responders and nonresponders | journal = Clinical Neuropharmacology | volume = 37 | issue = 4 | pages = 108–10 | date = 2013 | pmid = 24992082 | pmc = 4206383 | doi = 10.1097/WNF.0000000000000039 }}</ref> |
|||
== Signaling pathways == |
|||
Pharmacological inhibition of [[MAPK3|ERK1/2]] restores GSK-3 beta activity and protein synthesis levels in a model of [[tuberous sclerosis]].<ref name="pmid28646232">{{cite journal | vauthors = Pal R, Bondar VV, Adamski CJ, Rodney GG, Sardiello M | title = Inhibition of ERK1/2 Restores GSK3β Activity and Protein Synthesis Levels in a Model of Tuberous Sclerosis | journal = Scientific Reports | volume = 7 | issue = 1 | pages = 4174 | date = June 2017 | pmid = 28646232 | pmc = 5482840 | doi = 10.1038/s41598-017-04528-5 | bibcode = 2017NatSR...7.4174P }}</ref> |
|||
== Interactions == |
== Interactions == |
||
GSK3B has been shown to [[Protein-protein interaction|interact]] with: |
GSK3B has been shown to [[Protein-protein interaction|interact]] with: |
||
* [[KIAA1211L]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.ebi.ac.uk |
* [[KIAA1211L]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.ebi.ac.uk |title=EMBL European Bioinformatics Institute|last=EMBL-EBI|website=www.ebi.ac.uk.|language=en|access-date=2017-04-26}}</ref> |
||
* [[ATP2A2]]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gonnot F, Boulogne L, Brun C, Dia M, Gouriou Y, Bidaux G, Chouabe C, Crola Da Silva C, Ducreux S, Pillot B, Kaczmarczyk A, Leon C, Chanon S, Perret C, Sciandra F, Dargar T, Gache V, Farhat F, Sebbag L, Bochaton T, Thibault H, Ovize M, Paillard M, Gomez L | title = SERCA2 phosphorylation at serine 663 is a key regulator of Ca<sup>2+</sup> homeostasis in heart diseases | journal = Nature Communications | volume = 14 | issue = 1 | pages = 3346 | date = June 2023 | pmid = 37291092 | pmc = 10250397 | doi = 10.1038/s41467-023-39027-x }}</ref> |
|||
{{div col|colwidth=20em}} |
{{div col|colwidth=20em}} |
||
* [[AKAP11]],<ref name = pmid12147701/> |
* [[AKAP11]],<ref name = pmid12147701/> |
||
* [[AXIN1]],<ref name = pmid12511557/><ref name = pmid9734785>{{cite journal | vauthors = Nakamura T, Hamada F, Ishidate T, Anai K, Kawahara K, Toyoshima K, Akiyama T | title = Axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt signalling pathway, interacts with beta-catenin, GSK-3beta and APC and reduces the beta-catenin level | journal = Genes to Cells | volume = 3 | issue = 6 | pages = 395–403 | date = |
* [[AXIN1]],<ref name = pmid12511557/><ref name = pmid9734785>{{cite journal | vauthors = Nakamura T, Hamada F, Ishidate T, Anai K, Kawahara K, Toyoshima K, Akiyama T | title = Axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt signalling pathway, interacts with beta-catenin, GSK-3beta and APC and reduces the beta-catenin level | journal = Genes to Cells | volume = 3 | issue = 6 | pages = 395–403 | date = June 1998 | pmid = 9734785 | doi = 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1998.00198.x | s2cid = 10875463 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
* [[AXIN2]],<ref name = pmid10966653>{{cite journal | vauthors = von Kries JP, Winbeck G, Asbrand C, Schwarz-Romond T, Sochnikova N, Dell'Oro A, Behrens J, Birchmeier W | title = Hot spots in beta-catenin for interactions with LEF-1, conductin and APC | journal = Nature Structural Biology | volume = 7 | issue = 9 | pages = 800–7 | date = |
* [[AXIN2]],<ref name = pmid10966653>{{cite journal | vauthors = von Kries JP, Winbeck G, Asbrand C, Schwarz-Romond T, Sochnikova N, Dell'Oro A, Behrens J, Birchmeier W | title = Hot spots in beta-catenin for interactions with LEF-1, conductin and APC | journal = Nature Structural Biology | volume = 7 | issue = 9 | pages = 800–7 | date = September 2000 | pmid = 10966653 | doi = 10.1038/79039 | s2cid = 40432152 }}</ref><ref name = pmid12183362>{{cite journal | vauthors = Schwarz-Romond T, Asbrand C, Bakkers J, Kühl M, Schaeffer HJ, Huelsken J, Behrens J, Hammerschmidt M, Birchmeier W | title = The ankyrin repeat protein Diversin recruits Casein kinase Iepsilon to the beta-catenin degradation complex and acts in both canonical Wnt and Wnt/JNK signaling | journal = Genes & Development | volume = 16 | issue = 16 | pages = 2073–84 | date = August 2002 | pmid = 12183362 | pmc = 186448 | doi = 10.1101/gad.230402 }}</ref> |
||
* [[Androgen receptor|AR]],<ref name = pmid15178691>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wang L, Lin HK, Hu YC, Xie S, Yang L, Chang C | title = Suppression of androgen receptor-mediated transactivation and cell growth by the glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in prostate cells | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 279 | issue = 31 | pages = 32444–52 | date = |
* [[Androgen receptor|AR]],<ref name = pmid15178691>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wang L, Lin HK, Hu YC, Xie S, Yang L, Chang C | title = Suppression of androgen receptor-mediated transactivation and cell growth by the glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in prostate cells | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 279 | issue = 31 | pages = 32444–52 | date = July 2004 | pmid = 15178691 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.M313963200 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
* [[Beta-catenin|CTNNB1]],<ref name = pmid11251183>{{cite journal | vauthors = Davies G, Jiang WG, Mason MD | title = The interaction between beta-catenin, GSK3beta and APC after motogen induced cell-cell dissociation, and their involvement in signal transduction pathways in prostate cancer | journal = International Journal of Oncology | volume = 18 | issue = 4 | pages = 843–7 | date = |
* [[Beta-catenin|CTNNB1]],<ref name = pmid11251183>{{cite journal | vauthors = Davies G, Jiang WG, Mason MD | title = The interaction between beta-catenin, GSK3beta and APC after motogen induced cell-cell dissociation, and their involvement in signal transduction pathways in prostate cancer | journal = International Journal of Oncology | volume = 18 | issue = 4 | pages = 843–7 | date = April 2001 | pmid = 11251183 | doi = 10.3892/ijo.18.4.843 }}</ref><ref name = pmid10330181>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kishida S, Yamamoto H, Hino S, Ikeda S, Kishida M, Kikuchi A | title = DIX domains of Dvl and axin are necessary for protein interactions and their ability to regulate beta-catenin stability | journal = Molecular and Cellular Biology | volume = 19 | issue = 6 | pages = 4414–22 | date = June 1999 | pmid = 10330181 | pmc = 104400 | doi = 10.1128/mcb.19.6.4414 }}</ref> |
||
* [[DNM1L]],<ref name = pmid9731200>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hong YR, Chen CH, Cheng DS, Howng SL, Chow CC | title = Human dynamin-like protein interacts with the glycogen synthase kinase 3beta | journal = Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications | volume = 249 | issue = 3 | pages = 697–703 | date = |
* [[DNM1L]],<ref name = pmid9731200>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hong YR, Chen CH, Cheng DS, Howng SL, Chow CC | title = Human dynamin-like protein interacts with the glycogen synthase kinase 3beta | journal = Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications | volume = 249 | issue = 3 | pages = 697–703 | date = August 1998 | pmid = 9731200 | doi = 10.1006/bbrc.1998.9253 }}</ref> |
||
*[[MACF1]]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wu X, Shen QT, Oristian DS, Lu CP, Zheng Q, Wang HW, Fuchs E | title = Skin stem cells orchestrate directional migration by regulating microtubule-ACF7 connections through GSK3β | journal = Cell | volume = 144 | issue = 3 | pages = 341–52 | date = |
*[[MACF1]]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wu X, Shen QT, Oristian DS, Lu CP, Zheng Q, Wang HW, Fuchs E | title = Skin stem cells orchestrate directional migration by regulating microtubule-ACF7 connections through GSK3β | journal = Cell | volume = 144 | issue = 3 | pages = 341–52 | date = February 2011 | pmid = 21295697 | pmc = 3050560 | doi = 10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.033 }}</ref> |
||
* [[MUC1]],<ref name = pmid9819408>{{cite journal | vauthors = Li Y, Bharti A, Chen D, Gong J, Kufe D | title = Interaction of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta with the DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated antigen and beta-catenin | journal = Molecular and Cellular Biology | volume = 18 | issue = 12 | pages = 7216–24 | date = |
* [[MUC1]],<ref name = pmid9819408>{{cite journal | vauthors = Li Y, Bharti A, Chen D, Gong J, Kufe D | title = Interaction of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta with the DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated antigen and beta-catenin | journal = Molecular and Cellular Biology | volume = 18 | issue = 12 | pages = 7216–24 | date = December 1998 | pmid = 9819408 | pmc = 109303 | doi = 10.1128/mcb.18.12.7216 }}</ref><ref name = pmid11152665>{{cite journal | vauthors = Li Y, Kuwahara H, Ren J, Wen G, Kufe D | title = The c-Src tyrosine kinase regulates signaling of the human DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated antigen with GSK3 beta and beta-catenin | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 276 | issue = 9 | pages = 6061–4 | date = March 2001 | pmid = 11152665 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.C000754200 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
* [[Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3|SMAD3]]<ref name = pmid18172167>{{cite journal | vauthors = Guo X, Ramirez A, Waddell DS, Li Z, Liu X, Wang XF | title = Axin and GSK3- control Smad3 protein stability and modulate TGF- signaling | journal = Genes & Development | volume = 22 | issue = 1 | pages = 106–20 | date = |
* [[Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3|SMAD3]]<ref name = pmid18172167>{{cite journal | vauthors = Guo X, Ramirez A, Waddell DS, Li Z, Liu X, Wang XF | title = Axin and GSK3- control Smad3 protein stability and modulate TGF- signaling | journal = Genes & Development | volume = 22 | issue = 1 | pages = 106–20 | date = January 2008 | pmid = 18172167 | pmc = 2151009 | doi = 10.1101/gad.1590908 }}</ref> |
||
* [[NOTCH1]],<ref name = pmid12123574>{{cite journal | vauthors = Foltz DR, Santiago MC, Berechid BE, Nye JS | title = Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta modulates notch signaling and stability | journal = Current Biology | volume = 12 | issue = 12 | pages = 1006–11 | date = |
* [[NOTCH1]],<ref name = pmid12123574>{{cite journal | vauthors = Foltz DR, Santiago MC, Berechid BE, Nye JS | title = Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta modulates notch signaling and stability | journal = Current Biology | volume = 12 | issue = 12 | pages = 1006–11 | date = June 2002 | pmid = 12123574 | doi = 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00888-6 | s2cid = 15884556 | doi-access = free | bibcode = 2002CBio...12.1006F }}</ref> |
||
* [[NOTCH2]],<ref name = pmid12794074>{{cite journal | vauthors = Espinosa L, Inglés-Esteve J, Aguilera C, Bigas A | title = Phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta down-regulates Notch activity, a link for Notch and Wnt pathways | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 278 | issue = 34 | pages = 32227–35 | date = |
* [[NOTCH2]],<ref name = pmid12794074>{{cite journal | vauthors = Espinosa L, Inglés-Esteve J, Aguilera C, Bigas A | title = Phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta down-regulates Notch activity, a link for Notch and Wnt pathways | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 278 | issue = 34 | pages = 32227–35 | date = August 2003 | pmid = 12794074 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.M304001200 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
* [[P53]],<ref name = pmid12048243>{{cite journal | vauthors = Watcharasit P, Bijur GN, Zmijewski JW, Song L, Zmijewska A, Chen X, Johnson GV, Jope RS | title = Direct, activating interaction between glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and p53 after DNA damage | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 99 | issue = 12 | pages = 7951–5 | date = |
* [[P53]],<ref name = pmid12048243>{{cite journal | vauthors = Watcharasit P, Bijur GN, Zmijewski JW, Song L, Zmijewska A, Chen X, Johnson GV, Jope RS | title = Direct, activating interaction between glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and p53 after DNA damage | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 99 | issue = 12 | pages = 7951–5 | date = June 2002 | pmid = 12048243 | pmc = 123001 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.122062299 | bibcode = 2002PNAS...99.7951W | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
* [[PRKAR2A]],<ref name = pmid12147701>{{cite journal | vauthors = Tanji C, Yamamoto H, Yorioka N, Kohno N, Kikuchi K, Kikuchi A | title = A-kinase anchoring protein AKAP220 binds to glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta ) and mediates protein kinase A-dependent inhibition of GSK-3beta | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 277 | issue = 40 | pages = 36955–61 | date = |
* [[PRKAR2A]],<ref name = pmid12147701>{{cite journal | vauthors = Tanji C, Yamamoto H, Yorioka N, Kohno N, Kikuchi K, Kikuchi A | title = A-kinase anchoring protein AKAP220 binds to glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta ) and mediates protein kinase A-dependent inhibition of GSK-3beta | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 277 | issue = 40 | pages = 36955–61 | date = October 2002 | pmid = 12147701 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.M206210200 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
* [[SGK3]],<ref name = pmid12054501>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dai F, Yu L, He H, Chen Y, Yu J, Yang Y, Xu Y, Ling W, Zhao S | title = Human serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase-like kinase (SGKL) phosphorylates glycogen syntheses kinase 3 beta (GSK-3beta) at serine-9 through direct interaction | journal = Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications | volume = 293 | issue = 4 | pages = 1191–6 | date = May 2002 | pmid = 12054501 | doi = 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00349-2 }}</ref> and |
* [[SGK3]],<ref name = pmid12054501>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dai F, Yu L, He H, Chen Y, Yu J, Yang Y, Xu Y, Ling W, Zhao S | title = Human serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase-like kinase (SGKL) phosphorylates glycogen syntheses kinase 3 beta (GSK-3beta) at serine-9 through direct interaction | journal = Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications | volume = 293 | issue = 4 | pages = 1191–6 | date = May 2002 | pmid = 12054501 | doi = 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00349-2 }}</ref> and |
||
* [[TSC2]].<ref name = pmid12511557>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mak BC, Takemaru K, Kenerson HL, Moon RT, Yeung RS | title = The tuberin-hamartin complex negatively regulates beta-catenin signaling activity | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 278 | issue = 8 | pages = 5947–51 | date = |
* [[TSC2]].<ref name = pmid12511557>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mak BC, Takemaru K, Kenerson HL, Moon RT, Yeung RS | title = The tuberin-hamartin complex negatively regulates beta-catenin signaling activity | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 278 | issue = 8 | pages = 5947–51 | date = February 2003 | pmid = 12511557 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.C200473200 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name = pmid16959574>{{cite journal | vauthors = Inoki K, Ouyang H, Zhu T, Lindvall C, Wang Y, Zhang X, Yang Q, Bennett C, Harada Y, Stankunas K, Wang CY, He X, MacDougald OA, You M, Williams BO, Guan KL | title = TSC2 integrates Wnt and energy signals via a coordinated phosphorylation by AMPK and GSK3 to regulate cell growth | journal = Cell | volume = 126 | issue = 5 | pages = 955–68 | date = September 2006 | pmid = 16959574 | doi = 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.055 | s2cid = 16047397 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
{{Div col end}} |
{{Div col end}} |
||
| Line 40: | Line 50: | ||
{{reflist|35em|refs= |
{{reflist|35em|refs= |
||
<ref name="hoeflich2000">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin O, Woodgett JR | title = Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation | journal = Nature | volume = 406 | issue = 6791 | pages = 86–90 | |
<ref name="hoeflich2000">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin O, Woodgett JR | title = Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation | journal = Nature | volume = 406 | issue = 6791 | pages = 86–90 | date = July 2000 | pmid = 10894547 | doi = 10.1038/35017574 | bibcode = 2000Natur.406...86H | s2cid = 205007364 }}{{closed access}}</ref> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 46: | Line 56: | ||
== Further reading == |
== Further reading == |
||
{{refbegin|35em}} |
{{refbegin|35em}} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Turenne GA, Price BD | title = Glycogen synthase kinase3 beta phosphorylates serine 33 of p53 and activates p53's transcriptional activity | journal = BMC Cell Biology | volume = 2 | pages = 12 | year = 2001 | pmid = 11483158 | pmc = 35361 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2121-2-12 | |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Turenne GA, Price BD | title = Glycogen synthase kinase3 beta phosphorylates serine 33 of p53 and activates p53's transcriptional activity | journal = BMC Cell Biology | volume = 2 | pages = 12 | year = 2001 | pmid = 11483158 | pmc = 35361 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2121-2-12 | doi-access = free }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Plyte SE, Hughes K, Nikolakaki E, Pulverer BJ, Woodgett JR | title = Glycogen synthase kinase-3: functions in oncogenesis and development | journal = Biochimica et Biophysica Acta | volume = 1114 | issue = |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Plyte SE, Hughes K, Nikolakaki E, Pulverer BJ, Woodgett JR | title = Glycogen synthase kinase-3: functions in oncogenesis and development | journal = Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer | volume = 1114 | issue = 2–3 | pages = 147–62 | date = December 1992 | pmid = 1333807 | doi = 10.1016/0304-419X(92)90012-N }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Morishima-Kawashima M, Hasegawa M, Takio K, Suzuki M, Yoshida H, Watanabe A, Titani K, Ihara Y | title = Hyperphosphorylation of tau in PHF | journal = Neurobiology of Aging | volume = 16 | issue = 3 | pages = 365–71; discussion 371–80 | year = 1995 | pmid = 7566346 | doi = 10.1016/0197-4580(95)00027-C }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Morishima-Kawashima M, Hasegawa M, Takio K, Suzuki M, Yoshida H, Watanabe A, Titani K, Ihara Y | title = Hyperphosphorylation of tau in PHF | journal = Neurobiology of Aging | volume = 16 | issue = 3 | pages = 365–71; discussion 371–80 | year = 1995 | pmid = 7566346 | doi = 10.1016/0197-4580(95)00027-C | s2cid = 22471158 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Jope RS, Bijur GN | title = Mood stabilizers, glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and cell survival | journal = Molecular Psychiatry | volume = 7 |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Jope RS, Bijur GN | title = Mood stabilizers, glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and cell survival | journal = Molecular Psychiatry | volume = 7 | pages = S35-45 | year = 2002 | issue = Suppl 1 | pmid = 11986994 | doi = 10.1038/sj.mp.4001017 | doi-access = free }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Bhat RV, Budd SL | title = GSK3beta signalling: casting a wide net in Alzheimer's disease | journal = Neuro-Signals | volume = 11 | issue = 5 | pages = 251–61 | year = 2003 | pmid = 12566926 | doi = 10.1159/000067423 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Bhat RV, Budd SL | title = GSK3beta signalling: casting a wide net in Alzheimer's disease | journal = Neuro-Signals | volume = 11 | issue = 5 | pages = 251–61 | year = 2003 | pmid = 12566926 | doi = 10.1159/000067423 | s2cid = 13650262 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Wang W, Li M, Wang Y, Li Q, Deng G, Wan J, Yang Q, Chen Q, Wang J | title = GSK-3β inhibitor TWS119 attenuates rtPA-induced hemorrhagic transformation and activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway after acute ischemic stroke in rats | journal = Molecular Neurobiology | volume = 53 | issue = 10 | pages = 7028–7036 | date = December 2016 | pmid = 26671619 | pmc = 4909586 | doi = 10.1007/s12035-015-9607-2 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Nadri C, Kozlovsky N, Agam G | title = [Schizophrenia, neurodevelopment and glycogen synthase kinase-3] | journal = Harefuah | volume = 142 | issue = 8–9 | pages = 636–42, 644 | date = September 2003 | pmid = 14518171 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Mulholland DJ, Dedhar S, Wu H, Nelson CC | title = PTEN and GSK3beta: key regulators of progression to androgen-independent prostate cancer | journal = Oncogene | volume = 25 | issue = 3 | pages = 329–37 | date = January 2006 | pmid = 16421604 | doi = 10.1038/sj.onc.1209020 | doi-access = free }} |
|||
{{refend}} |
{{refend}} |
||
== External links == |
|||
* [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/pdbe-kb/proteins/P49841 PDBe-KB] provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3B) |
|||
{{PDB Gallery|geneid=2932}} |
{{PDB Gallery|geneid=2932}} |
||
{{Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases}} |
{{Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases}} |
||
{{Enzymes}} |
{{Enzymes}} |
||
{{Portal bar| |
{{Portal bar|Biology|border=no}} |
||
[[Category:Protein kinases]] |
[[Category:Protein kinases]] |
||
Latest revision as of 16:52, 22 May 2024
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, (GSK-3 beta), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSK3B gene.[5][6] In mice, the enzyme is encoded by the Gsk3b gene.[7] Abnormal regulation and expression of GSK-3 beta is associated with an increased susceptibility towards bipolar disorder.[8]
Function
[edit]Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a proline-directed serine-threonine kinase that was initially identified as a phosphorylating and an inactivating agent of glycogen synthase. Two isoforms, alpha (GSK3A) and beta, show a high degree of amino acid homology.[5] GSK3B is involved in energy metabolism, neuronal cell development, and body pattern formation.[9][10] It might be a new therapeutic target for ischemic stroke.
Disease relevance
[edit]Homozygous disruption of the Gsk3b locus in mice results in embryonic lethality during mid-gestation.[7] This lethality phenotype could be rescued by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor.[7]
Two SNPs at this gene, rs334558 (-50T/C) and rs3755557 (-1727A/T), are associated with efficacy of lithium treatment in bipolar disorder.[11]
Signaling pathways
[edit]Pharmacological inhibition of ERK1/2 restores GSK-3 beta activity and protein synthesis levels in a model of tuberous sclerosis.[12]
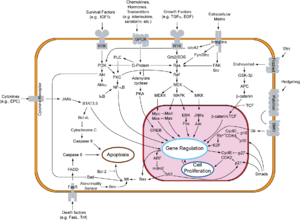
Interactions
[edit]GSK3B has been shown to interact with:
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000082701 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022812 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b Stambolic V, Woodgett JR (November 1994). "Mitogen inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta in intact cells via serine 9 phosphorylation". The Biochemical Journal. 303 (Pt 3): 701–4. doi:10.1042/bj3030701. PMC 1137602. PMID 7980435.
- ^ Lau KF, Miller CC, Anderton BH, Shaw PC (September 1999). "Molecular cloning and characterization of the human glycogen synthase kinase-3beta promoter". Genomics. 60 (2): 121–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5875. PMID 10486203.
- ^ a b c Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin O, Woodgett JR (July 2000). "Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation". Nature. 406 (6791): 86–90. Bibcode:2000Natur.406...86H. doi:10.1038/35017574. PMID 10894547. S2CID 205007364.

- ^ Luykx JJ, Boks MP, Terwindt AP, Bakker S, Kahn RS, Ophoff RA (June 2010). "The involvement of GSK3beta in bipolar disorder: integrating evidence from multiple types of genetic studies". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 20 (6): 357–68. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.02.008. PMID 20226637. S2CID 43214075.
- ^ Plyte SE, Hughes K, Nikolakaki E, Pulverer BJ, Woodgett JR (December 1992). "Glycogen synthase kinase-3: functions in oncogenesis and development". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer. 1114 (2–3): 147–62. doi:10.1016/0304-419X(92)90012-N. PMID 1333807.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: GSK3B glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta".
- ^ Iwahashi K, Nishizawa D, Narita S, Numajiri M, Murayama O, Yoshihara E, et al. (2013). "Haplotype analysis of GSK-3β gene polymorphisms in bipolar disorder lithium responders and nonresponders". Clinical Neuropharmacology. 37 (4): 108–10. doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000039. PMC 4206383. PMID 24992082.
- ^ Pal R, Bondar VV, Adamski CJ, Rodney GG, Sardiello M (June 2017). "Inhibition of ERK1/2 Restores GSK3β Activity and Protein Synthesis Levels in a Model of Tuberous Sclerosis". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 4174. Bibcode:2017NatSR...7.4174P. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-04528-5. PMC 5482840. PMID 28646232.
- ^ EMBL-EBI. "EMBL European Bioinformatics Institute". www.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ Gonnot F, Boulogne L, Brun C, Dia M, Gouriou Y, Bidaux G, et al. (June 2023). "SERCA2 phosphorylation at serine 663 is a key regulator of Ca2+ homeostasis in heart diseases". Nature Communications. 14 (1): 3346. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-39027-x. PMC 10250397. PMID 37291092.
- ^ a b Tanji C, Yamamoto H, Yorioka N, Kohno N, Kikuchi K, Kikuchi A (October 2002). "A-kinase anchoring protein AKAP220 binds to glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta ) and mediates protein kinase A-dependent inhibition of GSK-3beta". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (40): 36955–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206210200. PMID 12147701.
- ^ a b Mak BC, Takemaru K, Kenerson HL, Moon RT, Yeung RS (February 2003). "The tuberin-hamartin complex negatively regulates beta-catenin signaling activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (8): 5947–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200473200. PMID 12511557.
- ^ Nakamura T, Hamada F, Ishidate T, Anai K, Kawahara K, Toyoshima K, et al. (June 1998). "Axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt signalling pathway, interacts with beta-catenin, GSK-3beta and APC and reduces the beta-catenin level". Genes to Cells. 3 (6): 395–403. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2443.1998.00198.x. PMID 9734785. S2CID 10875463.
- ^ von Kries JP, Winbeck G, Asbrand C, Schwarz-Romond T, Sochnikova N, Dell'Oro A, et al. (September 2000). "Hot spots in beta-catenin for interactions with LEF-1, conductin and APC". Nature Structural Biology. 7 (9): 800–7. doi:10.1038/79039. PMID 10966653. S2CID 40432152.
- ^ Schwarz-Romond T, Asbrand C, Bakkers J, Kühl M, Schaeffer HJ, Huelsken J, et al. (August 2002). "The ankyrin repeat protein Diversin recruits Casein kinase Iepsilon to the beta-catenin degradation complex and acts in both canonical Wnt and Wnt/JNK signaling". Genes & Development. 16 (16): 2073–84. doi:10.1101/gad.230402. PMC 186448. PMID 12183362.
- ^ Wang L, Lin HK, Hu YC, Xie S, Yang L, Chang C (July 2004). "Suppression of androgen receptor-mediated transactivation and cell growth by the glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in prostate cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (31): 32444–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313963200. PMID 15178691.
- ^ Davies G, Jiang WG, Mason MD (April 2001). "The interaction between beta-catenin, GSK3beta and APC after motogen induced cell-cell dissociation, and their involvement in signal transduction pathways in prostate cancer". International Journal of Oncology. 18 (4): 843–7. doi:10.3892/ijo.18.4.843. PMID 11251183.
- ^ Kishida S, Yamamoto H, Hino S, Ikeda S, Kishida M, Kikuchi A (June 1999). "DIX domains of Dvl and axin are necessary for protein interactions and their ability to regulate beta-catenin stability". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (6): 4414–22. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.6.4414. PMC 104400. PMID 10330181.
- ^ Hong YR, Chen CH, Cheng DS, Howng SL, Chow CC (August 1998). "Human dynamin-like protein interacts with the glycogen synthase kinase 3beta". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 249 (3): 697–703. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9253. PMID 9731200.
- ^ Wu X, Shen QT, Oristian DS, Lu CP, Zheng Q, Wang HW, et al. (February 2011). "Skin stem cells orchestrate directional migration by regulating microtubule-ACF7 connections through GSK3β". Cell. 144 (3): 341–52. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.033. PMC 3050560. PMID 21295697.
- ^ Li Y, Bharti A, Chen D, Gong J, Kufe D (December 1998). "Interaction of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta with the DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated antigen and beta-catenin". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (12): 7216–24. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.12.7216. PMC 109303. PMID 9819408.
- ^ Li Y, Kuwahara H, Ren J, Wen G, Kufe D (March 2001). "The c-Src tyrosine kinase regulates signaling of the human DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated antigen with GSK3 beta and beta-catenin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (9): 6061–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000754200. PMID 11152665.
- ^ Guo X, Ramirez A, Waddell DS, Li Z, Liu X, Wang XF (January 2008). "Axin and GSK3- control Smad3 protein stability and modulate TGF- signaling". Genes & Development. 22 (1): 106–20. doi:10.1101/gad.1590908. PMC 2151009. PMID 18172167.
- ^ Foltz DR, Santiago MC, Berechid BE, Nye JS (June 2002). "Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta modulates notch signaling and stability". Current Biology. 12 (12): 1006–11. Bibcode:2002CBio...12.1006F. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00888-6. PMID 12123574. S2CID 15884556.
- ^ Espinosa L, Inglés-Esteve J, Aguilera C, Bigas A (August 2003). "Phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta down-regulates Notch activity, a link for Notch and Wnt pathways". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (34): 32227–35. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304001200. PMID 12794074.
- ^ Watcharasit P, Bijur GN, Zmijewski JW, Song L, Zmijewska A, Chen X, et al. (June 2002). "Direct, activating interaction between glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and p53 after DNA damage". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (12): 7951–5. Bibcode:2002PNAS...99.7951W. doi:10.1073/pnas.122062299. PMC 123001. PMID 12048243.
- ^ Dai F, Yu L, He H, Chen Y, Yu J, Yang Y, et al. (May 2002). "Human serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase-like kinase (SGKL) phosphorylates glycogen syntheses kinase 3 beta (GSK-3beta) at serine-9 through direct interaction". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 293 (4): 1191–6. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00349-2. PMID 12054501.
- ^ Inoki K, Ouyang H, Zhu T, Lindvall C, Wang Y, Zhang X, et al. (September 2006). "TSC2 integrates Wnt and energy signals via a coordinated phosphorylation by AMPK and GSK3 to regulate cell growth". Cell. 126 (5): 955–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.055. PMID 16959574. S2CID 16047397.
Further reading
[edit]- Turenne GA, Price BD (2001). "Glycogen synthase kinase3 beta phosphorylates serine 33 of p53 and activates p53's transcriptional activity". BMC Cell Biology. 2: 12. doi:10.1186/1471-2121-2-12. PMC 35361. PMID 11483158.
- Plyte SE, Hughes K, Nikolakaki E, Pulverer BJ, Woodgett JR (December 1992). "Glycogen synthase kinase-3: functions in oncogenesis and development". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer. 1114 (2–3): 147–62. doi:10.1016/0304-419X(92)90012-N. PMID 1333807.
- Morishima-Kawashima M, Hasegawa M, Takio K, Suzuki M, Yoshida H, Watanabe A, et al. (1995). "Hyperphosphorylation of tau in PHF". Neurobiology of Aging. 16 (3): 365–71, discussion 371–80. doi:10.1016/0197-4580(95)00027-C. PMID 7566346. S2CID 22471158.
- Jope RS, Bijur GN (2002). "Mood stabilizers, glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and cell survival". Molecular Psychiatry. 7 (Suppl 1): S35-45. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001017. PMID 11986994.
- Bhat RV, Budd SL (2003). "GSK3beta signalling: casting a wide net in Alzheimer's disease". Neuro-Signals. 11 (5): 251–61. doi:10.1159/000067423. PMID 12566926. S2CID 13650262.
- Wang W, Li M, Wang Y, Li Q, Deng G, Wan J, et al. (December 2016). "GSK-3β inhibitor TWS119 attenuates rtPA-induced hemorrhagic transformation and activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway after acute ischemic stroke in rats". Molecular Neurobiology. 53 (10): 7028–7036. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9607-2. PMC 4909586. PMID 26671619.
- Nadri C, Kozlovsky N, Agam G (September 2003). "[Schizophrenia, neurodevelopment and glycogen synthase kinase-3]". Harefuah. 142 (8–9): 636–42, 644. PMID 14518171.
- Mulholland DJ, Dedhar S, Wu H, Nelson CC (January 2006). "PTEN and GSK3beta: key regulators of progression to androgen-independent prostate cancer". Oncogene. 25 (3): 329–37. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209020. PMID 16421604.
External links
[edit]- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3B)