Ceilândia: Difference between revisions
ajuste+ |
|||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 33 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Multiple issues| |
|||
{{Lead too short|date=May 2023}} |
|||
{{POV|date=May 2023}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
|name |
| name = Ceilândia |
||
|settlement_type |
| settlement_type = [[Administrative region (Brazil)|Administrative region]] |
||
|official_name |
| official_name = ''Região Administrativa de Ceilândia''<br>Administrative Region of Ceilândia |
||
|nickname |
| nickname = Cei |
||
|motto |
| motto = |
||
|image_skyline |
| image_skyline = {{multiple image |
||
| border = infobox |
|||
|imagesize = |
|||
| total_width = 290 |
|||
|image_caption = |
|||
| image_style = border:1; |
|||
|image_flag = Bandeira de Ceilândia.png |
|||
| perrow = 1/2/2/2 |
|||
|image_seal = |
|||
| image1 = Ceilândia.jpg |
|||
|image_map = Distrito Federal RA Ceilandia.svg |
|||
| image2 = Letreiro de Ceilândia.jpg |
|||
|mapsize = |
|||
| image3 = Brasília-Reservatório-Elevado-de-Ceilândia-8.jpg |
|||
|map_caption = Localization of Ceilândia in Federal District |
|||
| image4 = Feira Central de Ceilândia (2).jpg |
|||
|pushpin_map = Brazil |
|||
| image5 = Com quase R$ 168 milhões em recursos, Ceilândia completa 52 anos - 52775057520.jpg |
|||
|pushpin_map_size = 250 |
|||
| image6 = Casa do Cantador.jpg |
|||
|pushpin_map_caption = Localization of Ceilândia in Brazil |
|||
}} |
|||
|subdivision_type = [[List of countries|Country]] |
|||
| imagesize = |
|||
|subdivision_type1 = [[Regions of Brazil|Region]] |
|||
| image_caption = '''Clockwise from top:''' City view, Water Tower, Bus terminal, [[Casa do Cantador]], Fair, Ceilândia sign |
|||
|subdivision_type2 = [[States of Brazil|State]] |
|||
| image_flag = Bandeira de Ceilândia.svg |
|||
|subdivision_name = {{flag|Brazil}} |
|||
| image_seal = |
|||
|subdivision_name1 = [[Central-West Region, Brazil|Central-West]] |
|||
| image_map = Distrito Federal RA Ceilandia.svg |
|||
|subdivision_name2 = [[Image:Bandeira do Distrito Federal.svg|border|22px]] [[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]] |
|||
| |
| mapsize = |
||
| map_caption = Localization of Ceilândia in Federal District |
|||
|leader_name = Aridelson Sebastião de Almeida |
|||
| |
| pushpin_map = Brazil |
||
| pushpin_map_caption = Localization of Ceilândia in Brazil |
|||
|established_date = March 27, 1971 |
|||
| subdivision_type = [[List of sovereign states|Country]] |
|||
|area_magnitude = |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = [[Regions of Brazil|Region]] |
|||
|area_total_km2 = 230.30 |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = [[States of Brazil|State]] |
|||
|area_land_km2 = |
|||
| subdivision_name = {{flag|Brazil}} |
|||
|area_water_km2 = |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Central-West Region, Brazil|Central-West]] |
|||
|area_water_percent = |
|||
| subdivision_name2 = [[Image:Bandeira do Distrito Federal (Brasil).svg|border|22px]] [[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]] |
|||
|area_urban_km2 = |
|||
| leader_title = [[Regional administrator]] |
|||
|area_metro_km2 = |
|||
| leader_name = Vilson José de Oliveira<ref name=adm>{{cite web|url = http://www.ceilandia.df.gov.br/category/sobre-a-ra/perfil-do-administrador/ | title = Perfil do administrador | language = Portuguese | publisher = Administração Regional de Ceilândia, DF | access-date = 2015-01-01}}</ref> |
|||
|population_as_of = 2010 |
|||
| established_title = Founded |
|||
|population_note = |
|||
| established_date = {{start date and age|1971|3|27}} |
|||
|population_footnotes = <ref name=totalpop>{{cite web | url = http://www.codeplan.df.gov.br/sites/200/216/00000472.pdf | title = Pesquisa Distrital por Amostra de Domicílios - 2010/2011 | language = Portuguese | publisher = [[Codeplan]] | accessdate = 2012-08-20 | deadurl = yes | archiveurl = https://web.archive.org/web/20120217082058/http://www.codeplan.df.gov.br/sites/200/216/00000472.pdf | archivedate = 2012-02-17 | df = }}</ref> |
|||
| area_magnitude = |
|||
|population_total = 398374 |
|||
| area_total_km2 = 230.30 |
|||
|population_urban = |
|||
| area_land_km2 = |
|||
|population_density_km2 = 1729.8 |
|||
| |
| area_water_km2 = |
||
| area_water_percent = |
|||
|timezone = [[UTC-3]] |
|||
| |
| area_urban_km2 = |
||
| area_metro_km2 = |
|||
|timezone_DST = [[UTC-2]] |
|||
| population_as_of = 2010 |
|||
|utc_offset_DST = -2 |
|||
| population_note = |
|||
|coordinates = {{coord|15|49|09|S|48|06|30|W|region:BR|display=inline}} |
|||
| population_footnotes = <ref name=totalpop>{{cite web | url = http://www.codeplan.df.gov.br/sites/200/216/00000472.pdf | title = Pesquisa Distrital por Amostra de Domicílios - 2010/2011 | language = Portuguese | publisher = [[Codeplan]] | access-date = 2012-08-20 | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120217082058/http://www.codeplan.df.gov.br/sites/200/216/00000472.pdf | archive-date = 2012-02-17 }}</ref> |
|||
|elevation_m = 1000 |
|||
| population_total = 398374 |
|||
|area_code = +55 61 |
|||
| population_urban = |
|||
|postal_code_type = Postal Code (CEP) |
|||
| population_density_km2 = 1729.8 |
|||
|postal_code = 72200-000 |
|||
| population_demonym = Ceilandense |
|||
|blank_name = |
|||
| |
| timezone = [[Time in Brazil|BRT]] |
||
| utc_offset = −3 |
|||
|website = [http://www.ceilandia.df.gov.br/ www.ceilandia.df.gov.br] |
|||
| |
| timezone_DST = |
||
| utc_offset_DST = |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|15|49|09|S|48|06|30|W|region:BR-DF|display=title,inline}} |
|||
| elevation_m = 1000 |
|||
| area_code = +55 61 |
|||
| postal_code_type = Postal Code (CEP) |
|||
| postal_code = 72200-000 |
|||
| blank_name = |
|||
| blank_info = |
|||
| website = [http://www.ceilandia.df.gov.br/ www.ceilandia.df.gov.br] |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Ceilândia''' ({{IPA|pt|seiˈlɐn.dʒiɐ}}) is an [[Administrative region (Brazil)|administrative region]] in the [[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]] in [[Brazil]]. It is bordered by [[Brazlândia]] to the north, [[Taguatinga, Federal District|Taguatinga]] to the east, and [[Samambaia, Federal District|Samambaia]] and [[Sol Nascente/Pôr do Sol|Sol Nascente/Por do Sol]] to the south. With about 398,374 inhabitants, it is the administrative region of largest population in the Federal District.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Patriolino' |first='Luana |date=2021-03-27 |title=Cidade mais populosa do DF, Ceilândia chega aos 50 anos com economia própria |url=https://www.correiobraziliense.com.br/cidades-df/2021/03/4914419-cidade-mais-populosa-do-df-ceilandia-chega-aos-50-anos-com-economia-propria.html |access-date=2023-06-12 |website=Cidades DF |language=pt-BR}}</ref> Ceilândia was created in 1971 by Hélio Prates da Silveira,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Ceilândia: 41 anos de história, tradição e modernidade! |url=https://www.unodc.org/lpo-brazil/pt/crime/jovemdeexpressao/noticias2012/03/27-aniversario-da-ceilandia.html |access-date=2023-06-12 |website=www.unodc.org}}</ref> originally created as the "CEI" ({{langx|pt|Campanha de Erradicação de Invasões|translation=Invasions Eradication Campaign}}) in 1969, a campaign to combat irregular settlements near Brasília. |
|||
'''Ceilândia''' is an [[Administrative region (Brazil)|administrative region]] in the [[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]], [[Brazil]]. With about 398,374 inhabitants, it is the administrative region of largest population in the Federal District. |
|||
Located 26 kilometers (16 mi) from downtown [[Brasília]], and linked by a four-lane highway, Ceilândia occupies an area of 230.30 square kilometers (88.92 sq mi) and is in one of the most privileged hydrographic areas of the Federal District. It has several streams forming its boundaries and is in the basin of the Descoberto River, which supplies 60% of the water to the population of the Federal District. |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
Ceilândia was created by the government in the 1970s to keep people from moving into Brasília and setting up [[shanty town]]s. The root of the name Ceilândia is 'CEI' ({{lang-pt|Centro de Erradicação de Invasões}}: Squatters Eradication Center).{{Citation needed|date=August 2008}} |
|||
=== Early history === |
|||
In 1969, after only nine years of existence, Brasília already had 79,128 people living in shacks ([[favela]]s), out of a population of 500 thousand inhabitants in all the Federal District. In that year a seminar took place in Brasília concerning social problems of the Federal District. The shanty dwellers were the most serious problem. The Governor at that time, Hélio Prates da Silveira, decided to eradicate the shanty towns and a commission was formed. |
|||
Ceilândia was originally created by the government in the 1970s as a campaign by then governor Hélio Prates da Silveira to keep people from moving into [[Brasília]] and setting up invasions.<ref>{{Cite web |last=PODER360 |date=2021-03-27 |title=Ceilândia, implantada no apartheid de Brasília, completa 50 anos |url=https://www.poder360.com.br/brasil/ceilandia-regiao-mais-populosa-do-df-completa-50-anos-neste-sabado/ |access-date=2023-06-12 |website=Poder360 |language=pt-br}}</ref> The root of the name Ceilândia is "CEI" ({{langx|pt|Campanha de Erradicação de Invasões: Invasions Eradication Campaign}}).<ref>{{Cite web |last=Brasília |first=Histórias de |date=2020-03-27 |title=A origem de Ceilândia |url=https://historiasdebrasilia.com/2020/03/27/a-origem-de-ceilandia/ |access-date=2023-06-12 |website=Histórias de Brasília |language=pt-BR}}</ref> The campaign was created by Hélio Prates da Silveira to prevent people from invading Brasilia, and to combat irregular settlements in the region.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Brasília |first=Histórias de |date=2020-03-27 |title=A origem de Ceilândia |url=https://historiasdebrasilia.com/2020/03/27/a-origem-de-ceilandia/ |access-date=2024-01-04 |website=Histórias de Brasília |language=pt-BR}}</ref> |
|||
In 1969, after only nine years of existence, the Federal District already had 79,128 people living in [[irregular occupations]], out of a population of 500 thousand inhabitants in all of the Federal District. In that year a seminar took place in Brasília concerning social problems of the Federal District. Invasion dwellers were the most serious problem. |
|||
17619 lots were laid out and in 1970 the first construction began. In nine months the transfer of the families was concluded with the streets opened In the beginning it was dramatic. The population had no water, no public lighting, no public transport and fought against the dust, the mud and the [[flash flood]]s. |
|||
17619 lots were laid out and in 1970 the first construction began. In nine months the transfer of the families was concluded with the streets opening. The population had no water, no public lighting, and no public transport and struggled against dust, mud and [[flash flood]]s. |
|||
Today Ceilândia is the largest electoral college of the Federal District and the most populous city, with more inhabitants than the Pilot Plan. It occupies a total of 91 residential squares laid out like Brasília, intercalated by areas for local commerce, churches and schools. There are also some special areas that are set aside to provide community services. |
|||
[[Image:Casa do Cantador.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Partial view of the [[Casa do Cantador]], one of the symbols of the city.]] |
|||
Ceilândia was founded on March 27, 1971, receiving the status of administrative region, according to Law 49, of October 25, 1989. |
|||
=== Recent developments === |
|||
Today Ceilândia is the largest electoral college of the Federal District and the most populous city, with more inhabitants than the Brasília. It occupies a total of 91 residential squares laid out like Brasília, intercalated by areas for local commerce, churches and schools. There are also some special areas that are set aside to provide community services. |
|||
[[Image:Casa do Cantador.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Partial view of the [[Casa do Cantador]], one of its symbols]] |
|||
An active commercial center, it has 4,500 commercial establishments and 1,600 small industries. The economically active population is more than 160,000 people. |
An active commercial center, it has 4,500 commercial establishments and 1,600 small industries. The economically active population is more than 160,000 people. |
||
Two important locals of Ceilandia are |
Two important locals of Ceilandia are the ''{{lang|pt|Caixa d'Água}}'' (Water Tower), and the ''{{lang|pt|[[Casa do Cantador]]}}'' (House of the Singer), a cultural center dedicated to the artists of [[Northeast Region, Brazil|Northeast Brazil]].<ref>{{Cite web |last= |date=2018-03-27 |title=História de Ceilândia se mistura com o Nordeste |url=https://www.correiobraziliense.com.br/app/noticia/meu-lugar/ceilandia/2018/03/27/noticias_meulugarceilandia,668919/historia-de-ceilandia-se-mistura-com-o-nordeste.shtml |access-date=2024-01-04 |website=Acervo |language=pt-BR}}</ref> The building was designed by [[Oscar Niemeyer]] and completed in 1986. |
||
==Ceilândia and its fairs== |
==Ceilândia and its fairs== |
||
Ceilândia is considered the second largest "Northeastern city" outside the Brazilian Northeast Region (the first one is [[São Paulo]]). About 70% of the population is of Northeastern origin. The presence of the Northeast culture can be seen in the number of open-air fairs (13 in all). |
Ceilândia is considered the second largest "Northeastern city" outside the Brazilian Northeast Region (the first one is [[São Paulo]]).<ref>{{Cite web |last=Ribeiro |first=Raquel Martins |date=2018-09-09 |title=Sabores e ritmos de Ceilândia: o reduto nordestino da capital federal {{!}} Metrópoles |url=https://www.metropoles.com/entretenimento/sabores-e-ritmos-de-ceilandia-o-reduto-nordestino-da-capital-federal |access-date=2024-01-04 |website=www.metropoles.com |language=pt-BR}}</ref> About 70% of the population is of Northeastern origin.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Flávio |first=Lúcio |date=2020-01-05 |title=Ceilândia ganha título de Capital da Cultura Nordestina no DF |url=https://www.agenciabrasilia.df.gov.br/2020/01/05/ceilandia-ganha-titulo-de-capital-da-cultura-nordestina-no-distrito-federal/ |access-date=2023-01-04 |website=Agência Brasília}}</ref> The presence of the Northeast culture can be seen in the number of open-air fairs (13 in all). The fairs (''{{lang|pt|feiras-livres}}'') were also an alternative for the workers that did not find space in the economy of the Federal District. In most of them, fruits, foods, clothes and footwear are commercialized. The Fair of the Producer ({{lang|pt|Feira do Produtor e Atacadista de Ceilândia}}) sells wholesale and supplies almost 50% of the Federal District.{{No source|date=January 2024}} |
||
The Central Fair ({{lang|pt|Feira Permanente de Ceilândia}}), is the largest of all. It occupies an area of seven thousand square meters and sells household articles, tools, electric appliances, fruits, vegetables, and poultry. It is located next to the ''{{lang|pt|Caixa d'Água}}'' (Water Tower) - the symbol of Ceilândia. Another fair is the {{lang|pt|Feira do Rolo}}. |
|||
The fairs (''{{lang|pt|feiras-livres}}'') are also an alternative for the workers that did not find space in the economy of the Federal District. In most of them, fruits, foods, clothes and footwear are commercialized. The Fair of the Producer ({{lang|pt|Feira do Produtor e Atacadista de Ceilândia}}) sells wholesale and supplies almost 50% of the Federal District. |
|||
== Sports == |
|||
The Central Fair ({{lang|pt|Feira Permanente de Ceilândia}}), is the largest of all. It occupies an area of seven thousand square meters and sells household articles, tools, electric appliances, fruits, vegetables, and poultry. It is located next to the ''{{lang|pt|Caixa d'Água}}'' (Water Tower) - the symbol of Ceilândia. |
|||
=== Venues === |
|||
But the most peculiar fair, without doubt, is the {{lang|pt|Feira do Rolo}}, where one can find almost everything, new or used, entire or broken, and things there can be sold or exchanged. |
|||
* Estádio Maria de Lourdes Abadia |
|||
=== Clubs === |
|||
* Football |
|||
** [[Ceilândia Esporte Clube]] |
|||
== Transportation == |
|||
Ceilândia is served by several highways connecting it to [[Brasília]] |
|||
* DF-075 (Estrada Parque Núcleo Bandeirante - EPNB); |
|||
* DF-085 (Estrada Parque Taguatinga - EPTG, or "Linha Verde"); |
|||
* DF-095 (Estrada Parque Ceilândia - EPCL, or "Via Estrutural"). |
|||
=== Metro === |
|||
Ceilândia is served by the following [[Federal District Metro (Brazil)|Federal District Metro]] stations, and is expected to have two more stations.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Braziliense |first=Correio |date=2024-01-19 |title=Metrô-DF abre licitação para obras de expansão em Ceilândia |url=https://www.correiobraziliense.com.br/cidades-df/2024/01/6789602-metro-df-abre-licitacao-para-obras-de-expansao-em-ceilandia.html |access-date=2024-01-24 |website=Cidades DF |language=pt-BR}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Ceilândia Sul station]] |
|||
* [[Ceilândia Centro station]] |
|||
* [[Ceilândia Norte station]] |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[Brasília]] |
|||
*[[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]] |
|||
*[[List of administrative regions of the Federal District (Brazil)|List of administrative regions of the Federal District]] |
*[[List of administrative regions of the Federal District (Brazil)|List of administrative regions of the Federal District]] |
||
| Line 92: | Line 128: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{commons category|Ceilândia}} |
{{commons category|Ceilândia}} |
||
* [http://www.ceilandia.df.gov.br/ |
* [http://www.ceilandia.df.gov.br/ Regional Administration of Ceilândia website] |
||
* [http://www.df.gov.br/ |
* [http://www.df.gov.br/ Government of the Federal District website] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140625040004/http://df.gov.br/ |date=2014-06-25 }} |
||
{{Administrative regions of Federal District}} |
{{Administrative regions of Federal District}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ceilandia}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ceilandia}} |
||
[[Category:Administrative regions |
[[Category:Administrative regions in the Federal District (Brazil)]] |
||
Latest revision as of 18:37, 21 October 2024
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Ceilândia | |
|---|---|
| Região Administrativa de Ceilândia Administrative Region of Ceilândia | |
Clockwise from top: City view, Water Tower, Bus terminal, Casa do Cantador, Fair, Ceilândia sign | |
| Nickname: Cei | |
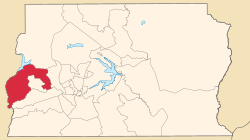 Localization of Ceilândia in Federal District | |
| Coordinates: 15°49′09″S 48°06′30″W / 15.81917°S 48.10833°W | |
| Country | |
| Region | Central-West |
| State | |
| Founded | March 27, 1971 |
| Government | |
| • Regional administrator | Vilson José de Oliveira[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 230.30 km2 (88.92 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,000 m (3,000 ft) |
| Population (2010)[2] | |
• Total | 398,374 |
| • Density | 1,729.8/km2 (4,480/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Ceilandense |
| Time zone | UTC−3 (BRT) |
| Postal Code (CEP) | 72200-000 |
| Area code | +55 61 |
| Website | www.ceilandia.df.gov.br |
Ceilândia (Portuguese pronunciation: [seiˈlɐn.dʒiɐ]) is an administrative region in the Federal District in Brazil. It is bordered by Brazlândia to the north, Taguatinga to the east, and Samambaia and Sol Nascente/Por do Sol to the south. With about 398,374 inhabitants, it is the administrative region of largest population in the Federal District.[3] Ceilândia was created in 1971 by Hélio Prates da Silveira,[4] originally created as the "CEI" (Portuguese: Campanha de Erradicação de Invasões, lit. 'Invasions Eradication Campaign') in 1969, a campaign to combat irregular settlements near Brasília.
History
[edit]Early history
[edit]Ceilândia was originally created by the government in the 1970s as a campaign by then governor Hélio Prates da Silveira to keep people from moving into Brasília and setting up invasions.[5] The root of the name Ceilândia is "CEI" (Portuguese: Campanha de Erradicação de Invasões: Invasions Eradication Campaign).[6] The campaign was created by Hélio Prates da Silveira to prevent people from invading Brasilia, and to combat irregular settlements in the region.[7]
In 1969, after only nine years of existence, the Federal District already had 79,128 people living in irregular occupations, out of a population of 500 thousand inhabitants in all of the Federal District. In that year a seminar took place in Brasília concerning social problems of the Federal District. Invasion dwellers were the most serious problem.
17619 lots were laid out and in 1970 the first construction began. In nine months the transfer of the families was concluded with the streets opening. The population had no water, no public lighting, and no public transport and struggled against dust, mud and flash floods.
Ceilândia was founded on March 27, 1971, receiving the status of administrative region, according to Law 49, of October 25, 1989.
Recent developments
[edit]Today Ceilândia is the largest electoral college of the Federal District and the most populous city, with more inhabitants than the Brasília. It occupies a total of 91 residential squares laid out like Brasília, intercalated by areas for local commerce, churches and schools. There are also some special areas that are set aside to provide community services.

An active commercial center, it has 4,500 commercial establishments and 1,600 small industries. The economically active population is more than 160,000 people.
Two important locals of Ceilandia are the Caixa d'Água (Water Tower), and the Casa do Cantador (House of the Singer), a cultural center dedicated to the artists of Northeast Brazil.[8] The building was designed by Oscar Niemeyer and completed in 1986.
Ceilândia and its fairs
[edit]Ceilândia is considered the second largest "Northeastern city" outside the Brazilian Northeast Region (the first one is São Paulo).[9] About 70% of the population is of Northeastern origin.[10] The presence of the Northeast culture can be seen in the number of open-air fairs (13 in all). The fairs (feiras-livres) were also an alternative for the workers that did not find space in the economy of the Federal District. In most of them, fruits, foods, clothes and footwear are commercialized. The Fair of the Producer (Feira do Produtor e Atacadista de Ceilândia) sells wholesale and supplies almost 50% of the Federal District.[citation needed]
The Central Fair (Feira Permanente de Ceilândia), is the largest of all. It occupies an area of seven thousand square meters and sells household articles, tools, electric appliances, fruits, vegetables, and poultry. It is located next to the Caixa d'Água (Water Tower) - the symbol of Ceilândia. Another fair is the Feira do Rolo.
Sports
[edit]Venues
[edit]- Estádio Maria de Lourdes Abadia
Clubs
[edit]- Football
Transportation
[edit]Ceilândia is served by several highways connecting it to Brasília
- DF-075 (Estrada Parque Núcleo Bandeirante - EPNB);
- DF-085 (Estrada Parque Taguatinga - EPTG, or "Linha Verde");
- DF-095 (Estrada Parque Ceilândia - EPCL, or "Via Estrutural").
Metro
[edit]Ceilândia is served by the following Federal District Metro stations, and is expected to have two more stations.[11]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Perfil do administrador" (in Portuguese). Administração Regional de Ceilândia, DF. Retrieved 2015-01-01.
- ^ "Pesquisa Distrital por Amostra de Domicílios - 2010/2011" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Codeplan. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-02-17. Retrieved 2012-08-20.
- ^ Patriolino', 'Luana (2021-03-27). "Cidade mais populosa do DF, Ceilândia chega aos 50 anos com economia própria". Cidades DF (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2023-06-12.
- ^ "Ceilândia: 41 anos de história, tradição e modernidade!". www.unodc.org. Retrieved 2023-06-12.
- ^ PODER360 (2021-03-27). "Ceilândia, implantada no apartheid de Brasília, completa 50 anos". Poder360 (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2023-06-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Brasília, Histórias de (2020-03-27). "A origem de Ceilândia". Histórias de Brasília (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2023-06-12.
- ^ Brasília, Histórias de (2020-03-27). "A origem de Ceilândia". Histórias de Brasília (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2024-01-04.
- ^ "História de Ceilândia se mistura com o Nordeste". Acervo (in Brazilian Portuguese). 2018-03-27. Retrieved 2024-01-04.
- ^ Ribeiro, Raquel Martins (2018-09-09). "Sabores e ritmos de Ceilândia: o reduto nordestino da capital federal | Metrópoles". www.metropoles.com (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2024-01-04.
- ^ Flávio, Lúcio (2020-01-05). "Ceilândia ganha título de Capital da Cultura Nordestina no DF". Agência Brasília. Retrieved 2023-01-04.
- ^ Braziliense, Correio (2024-01-19). "Metrô-DF abre licitação para obras de expansão em Ceilândia". Cidades DF (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2024-01-24.