Rail Baltica: Difference between revisions
Took out Ventspils as it will not be a stop, as well as the maximum freight train lenght is 1050 m |
tunnel update |
||
| (304 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Railway network across the Baltic states}} |
|||
{{Infobox rail line |
{{Infobox rail line |
||
| name = Rail Baltica |
| name = '''Rail Baltica''' |
||
| |
| logo = File:Rail Baltica logo.png |
||
| |
| logo_width = 260px |
||
| |
| image = File:RBINFO (cropped).png |
||
| |
| image_width = 300px |
||
| caption = |
|||
| type = Public [[high-speed rail]]way |
|||
| system = Rail Baltica (European gauge railway) |
| system = Rail Baltica (European gauge railway) |
||
| tracks = [[Double track]] |
| tracks = [[Double track]] |
||
| locale = Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania |
| locale = Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland |
||
| routes = Tallinn–Pärnu–Riga–Riga International Airport–Panevėžys–Kaunas/Vilnius–Lithuania/Polish Border |
| routes = Tallinn–Pärnu–Riga–Riga International Airport–Panevėžys–Kaunas/Vilnius–Lithuania/Polish Border |
||
| gauge = |
| gauge = {{track gauge|sg|allk=on}} (primary) |
||
| electrification = |
| electrification = {{25 kV 50 Hz AC}} [[overhead line]]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/about-rail-baltica/tehnical-parametrs/|title=Technical Parameters|publisher=RB Rail AS|access-date=2017-10-11}}</ref> |
||
| |
| planopen = {{ubl|class=nowrap| |
||
|'''Partial:''' |
|||
| Design speed = 249 km/h (passenger); 120 km/h(freight) |
|||
|2028 |
|||
|'''Full:''' |
|||
|2030 |
|||
}} |
|||
| speed = {{ubl|class=nowrap| |
|||
|'''Passenger:''' |
|||
|{{convert|234|km/h|abbr=on|round=5}}<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.railbaltica.org/about-rail-baltica/tehnical-parametrs/ |website=Rail Baltica Global Project|title=Technical Parameters}}</ref> |
|||
|'''Freight:''' |
|||
|{{convert|120|km/h|abbr=on|round=5}} |
|||
}} |
|||
| signalling = ERTMS L2 |
|||
| website = {{URL|https://www.railbaltica.org/}} |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Rail Baltica''' is an under-construction rail infrastructure project that is intended to integrate the [[Baltic states]] in the European rail network.<ref name="about-rail-baltica">{{cite web | url=https://www.railbaltica.org/about-rail-baltica | title=Rail Baltica – Project of the Century |website=www.railbaltica.org}}</ref> Its purpose is to provide passenger and freight service between participating countries and improve rail connections between [[Central Europe|Central]] and [[Northern Europe|Northern]] Europe, specifically the area southeast of the [[Baltic Sea]]. It is also intended as a catalyst for building the economic corridor in [[Baltic region|Northeastern Europe]]. The project envisages a continuous rail link from [[Tallinn]] (Estonia) to [[Warsaw]] (Poland), consisting of links via [[Riga]] (Latvia), [[Kaunas]], and [[Vilnius]] (Lithuania). Its total length in the Baltic States is {{convert|870|km}}, with {{convert|213|km}} in Estonia, {{convert|265|km}} in Latvia, and {{convert|392|km}} in Lithuania.<ref name="alternative 6A approved">[https://www.railbaltica.org/route-alternative-approved-for-the-future-construction-of-the-rail-baltica-railway-from-kaunas-to-the-border-with-poland/ Route alternative approved for the future construction of the Rail Baltica railway from Kaunas to the border with Poland], railbaltica.org, 12 May 2022.</ref> Rail Baltica is one of the priority projects of the [[European Union]] (EU). It is part of the [[North Sea–Baltic Corridor]] of the [[Trans-European Transport Networks]] (TEN-T). |
|||
Rail Baltica will add the first large-scale mainline standard gauge railway in the area. Legacy [[Rail transport in Finland#History|rail networks in Finland]], [[Rail transport in Estonia#History|Estonia]], [[Latvian Railways#Railway history of Latvia|Latvia]] and [[Rail transport in Lithuania#History|Lithuania]] are mainly in [[Russian gauge]] (1,520 mm). These countries' first railways were built in the second half of the 19th century while part of the [[Russian Empire]]. While some railways were built or converted to narrow or standard gauge between [[World War I]] and [[World War II]] in the independent or German-occupied Baltic states, these were later converted back to Russian gauge under [[Military occupations by the Soviet Union |Soviet occupation]] rule after 1945. |
|||
}} |
|||
According to a study produced by [[Ernst & Young]], the measurable socio-economic benefits are estimated at €16.2 billion.<ref name=":2" />{{Rp|page=186}} The assessed GDP multiplier effect the Rail Baltica Global Project would create is an additional €2 billion.<ref name=":2" />{{Rp|page=203}} {{As of|2020|1}}, the high-speed railway connection from Tallinn to the Lithuanian-Polish border was expected to be completed by 2026.<ref name="TheBalticTimes">{{Cite web |url=https://www.baltictimes.com/implementation_of_rail_baltic_by_2026_remaining_target_for_rb_rail/ |title=Implementation of Rail Baltic by 2026 remaining target for RB Rail |work=The Baltic Times |date=7 January 2020|access-date=26 June 2020}}</ref> {{update after|2026}} In 2020, a private consortium claimed that it could open an undersea railway [[Helsinki–Tallinn Tunnel|tunnel between Tallinn and Helsinki]] by mid-2026,<ref name="Burroughs">{{update after|2026}}{{Cite news |url=https://www.railjournal.com/passenger/high-speed/finnish-regional-council-delays-finland-estonia-undersea-rail-tunnel/ |title=Finnish regional council delays Finland – Estonia undersea rail tunnel |author=David Burroughs |work=[[International Railway Journal]] |date=18 June 2020 |access-date=26 June 2020}}</ref> but this project has been put on hold indefinitely.<ref name=":4">{{cite web |last=Kapper |first=Külli |date=8 February 2024 |title=INTERVJUU > Soome minister: Tallinna ja Helsingi vaheline tunnel on ebarealistlik |trans-title=INTERVIEW > Minister of Finland: The tunnel between Tallinn and Helsinki is unrealistic |url=https://maailm.postimees.ee/7956112/intervjuu-soome-minister-tallinna-ja-helsingi-vaheline-tunnel-on-ebarealistlik |access-date=12 February 2024 |work=[[Postimees]] |language=et}}</ref> |
|||
'''''Rail Baltica''''' (in Estonia also known as '''''Rail Baltic'''''<ref>http://railbaltic.info/et/</ref> and the Baltic part referred to as the Rail Baltica Global Project) is a greenfield railway infrastructure project to link [[Finland]], [[Estonia]], [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]] and [[Poland]] with a European [[standard gauge]] rail line, providing passenger and freight service between the countries and improving rail connections between [[Central Europe|Central]] and [[Northern Europe|Northern]] Europe as well as acting as a catalyst for building the economic corridor in the Northeastern Europe. It envisages a continuous rail link from [[Tallinn]] ([[Estonia]]), to [[Warsaw]] ([[Poland]]), via [[Riga]] ([[Latvia]]) and [[Kaunas]] ([[Lithuania]]) with the link to [[Vilnius]] ([[Lithuania]]). Rail Baltica is one of the priority projects of the [[European Union]]: ''[[Trans-European Transport Networks]]'' (TEN-T). |
|||
== Overview == |
|||
Rail Baltica will be fully electrified, therefore any emissions will be avoided. The newest technologies and materials are going to be utilized in its construction. The line is planned avoiding the Natura 2000 protected areas as far as possible and without making a significant impact on other environmentally sensitive protected areas, and existing 1520mm gauge railway networking areas. Wherever necessary, noise protection barriers will be installed. Special animal passages will be built through the embankment<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/about-rail-baltica/|title=Rail Baltica – Project of the Century|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref>. |
|||
=== Proposed environmental impact === |
|||
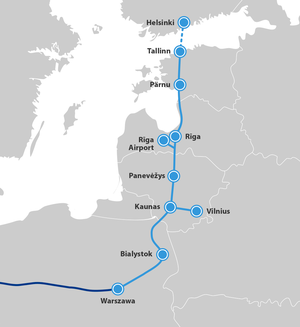
In the Baltics, Rail Baltica will enable both intermodality and multimodality. Plan includes three key multimodal freight terminals – in [[Muuga, Lääne-Viru County|Muuga]] ([[Estonia]]), [[Salaspils]] ([[Latvia]]) and [[Kaunas]] ([[Lithuania]]) – building synergies with existing 1520 mm railway system infrastructure, eight international passenger stations (in Tallinn, Pärnu, Riga, Riga Airport, Panevežys, Kaunas, Vilnius) with potential regional stations and connections to airports and seaports<ref name=":0" />. |
|||
Rail Baltica will be an [[Railway electrification system|electric railway]], motivated by a desire to reduce [[Greenhouse gas|carbon emissions]]. The railway has been planned to avoid [[Natura 2000]] protected areas, in addition to minimising impacts on other environmentally sensitive protected areas and existing 1,520 mm gauge railway networking areas. Wherever necessary, noise protection barriers will be installed. Special [[cattle creep|animal passages]] will be built through the embankment.<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |url=http://www.railbaltica.org/about-rail-baltica/ |title=Rail Baltica – Project of the Century |website=www.railbaltica.org |language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref> |
|||
=== Stations === |
|||
Rail Baltica in three Baltic States will be built as a new, private-owned, fast conventional double-track (quadruple track if the railway will run freight trains) electrified and ERTMS-equipped railway line with maximum design speed 249 km/h for passenger trains and 120 km/h for freight trains. The new railway line will be designed with 1435 mm gauge. Other key technical parameters: |
|||
The railway project will enable [[Intermodal freight transport|intermodality]] and [[Multimodal transport|multimodality]], i.e. transportation of freight through two or more methods of transportation. Rail Baltica includes plans for three multimodal freight terminals located in [[Muuga Harbour]] (Estonia), [[Salaspils]] (Latvia), and [[Kaunas]] (Lithuania). This is intended to create synergies with the existing 1,520 mm railway system infrastructure. There will be seven international passenger stations—in [[Ülemiste railway station|Tallinn]], [[Pärnu railway station|Pärnu]], [[Riga Central Station|Riga]], Riga Airport, [[Panevežys]], [[Kaunas railway station|Kaunas]], and [[Vilnius railway station|Vilnius]]—with potential regional stations and connections to airports and seaports.<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
The section from [[Helsinki]] to Tallinn will be operated by existing commercial [[Ferry|ferries]]. A proposed [[Helsinki to Tallinn Tunnel]] was considered to provide a rail link between the two cities.<ref>{{cite news |date=31 October 2008 |title=Helsinki-Tallinn Rail Tunnel Link? |work=YLE News |url=http://yle.fi/news/id86525.html |access-date=11 May 2008 |archive-date=4 April 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080404204947/http://www.yle.fi/news/id86525.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> At the end of April 2021, governments of Estonia and Finland signed a [[memorandum of understanding]] committing themselves to cooperation in the area of transport. In February 2024, the tunnel was judged by Finnish [[Minister of Transport and Communications (Finland)|Minister of Transport and Communications]], [[Lulu Ranne]] to be unrealistic and that it was not on the agenda of the government.<ref name=":4" /> |
|||
* The maximum freight train length will be 1050 m |
|||
* The maximum axle load – 25 tonnes |
|||
* There should be no level crossing with roads and with 1520 mm railways for the Rail Baltica infrastructure |
|||
* For maintenance and emergency servieces access to the main line should be every two or three km and in specific areas. |
|||
* The railway will have ballasted track |
|||
* Its energy system should be 2x25kV |
|||
* Its double track side should be right-hand running |
|||
* ERTMS - Level 2, Baseline 3<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.latviannews.lv/business/11978/|title=Latviannews.lv|website=www.latviannews.lv|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref> |
|||
* Loading gauge should be Swedish SE-C. |
|||
===Parameters=== |
|||
Its parameters are according to the EU Technical Specifications for Interoperability (TSI – P2, F1)<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.era.europa.eu/core-activities/interoperability/pages/technicalspecifications.aspx|title=Technical specifications for interoperability|website=www.era.europa.eu|language=en-us|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref>. |
|||
[[File:Rail-baltica-poland-v-max.svg|thumb|360x360px|Rail Baltica max speed in Poland (2018)]] |
|||
Rail Baltica will be built as a new, publicly owned, fast conventional double-track railway. If the railway runs freight trains, it will be quadruple-track. It will be electrified and equipped with the [[European Rail Traffic Management System]] (ERTMS) for signalling and communications. The maximum [[design speed]] is {{convert|249|km/h|abbr=on}} for passenger trains, while the maximum operational speed will be {{convert|234|km/h|abbr=on}}.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.railbaltica.org/about-rail-baltica/tehnical-parametrs/ |website=Rail Baltica Global Project|title=Technical Parameters}}</ref> For freight trains, the maximum design speed is {{convert|120|km/h|abbr=on}}. The new railway line will be designed with a {{railgauge|1435mm}} gauge. Other key technical parameters include:<ref>{{Cite web|date=2018-04-11|title=Rail Baltica - Design Guidelines|url=https://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/Elodie_Faivre_RBGF2018_Day2.pdf|access-date=2022-01-28|website=www.railbaltica.org}}</ref> |
|||
* The maximum freight train length will be {{convert|1,050|m|abbr=on}}. |
|||
* The maximum [[axle load]] will be {{convert|25|t}}. |
|||
* No [[level crossing]]s with roads. |
|||
* No [[flat crossing]]s with the {{railgauge|1520mm}} ([[Russian gauge]]) rail network. |
|||
* For maintenance and emergency services, access to the main line should be every {{convert|2–3|km|abbr=on}} and in specific areas. |
|||
* The railway will have ballasted track. |
|||
* Its energy system should be [[25 kV AC railway electrification|25 kV]]. |
|||
* Its double track side should be [[left- and right-hand traffic|right-hand running]]. |
|||
* It is [[ERTMS]] Level 2, Baseline 3. |
|||
The network's parameters are in accordance with the EU Technical Specifications for Interoperability (TSI – P2, F1).<ref>{{Cite web|date=2018-05-03|title=Rail Baltica Design Guidelines Approved {{!}} Rail Baltica|url=https://www.railbaltica.org/rail-baltica-design-guidelines-approved/|access-date=2022-01-28|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=|first=|date=October 2018|title=Technical Specifications for Interoperability|url=https://www.era.europa.eu/activities/technical-specifications-interoperability_en|access-date=2022-01-28|website=[[European Union Agency for Railways]]|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
The planning phase of Rail Baltica implementation in the Baltics took place from 2010 till 2017. The design phase started in 2016 with design activities at the Riga Central Passenger Station and the Riga International Airport passenger station in Latvia to be continued till 2023. Meanwhile, the construction of the Rail Baltica infrastructure is planned to start in 2019 and should be completed in 2026<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/video/rail-baltica-is-your-future/|title=Rail Baltica is your future {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref><ref name=":1">{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Intergovernmental_Agreement_2017.pdf|title=AGREEMENT OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE RAIL BALTIC/RAIL BALTICA RAILWAY CONNECTION|last=|first=|date=|website=|archive-url=|archive-date=|dead-url=|access-date=}}</ref>. |
|||
The design phase began in 2016, with design activities at the Riga Central Passenger Station and the Riga International Airport passenger station in Latvia to be continued until 2023. Meanwhile, the construction of the Rail Baltica infrastructure started in 2019, the first operations should start on some of the sections by 2028 and the overall corridor should be completed by 2030.<ref name="about-rail-baltica"/><ref name="auto">{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/video/rail-baltica-is-your-future/|title=Rail Baltica is your future {{!}} Rail Baltica |website=www.railbaltica.org |language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref><ref name=":1">{{Cite web |url=http://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Intergovernmental_Agreement_2017.pdf|title=AGREEMENT OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE RAIL BALTIC/RAIL BALTICA RAILWAY CONNECTION}}</ref> |
|||
The section from [[Helsinki]] to Tallinn will be operated by existing commercial [[Ferry|ferries]]. In the future a proposed [[Helsinki to Tallinn Tunnel]] could provide a rail link between the two cities.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://yle.fi/news/id86525.html| work=YLE News| title=Helsinki-Tallinn Rail Tunnel Link?| date=31 October 2008}}</ref> The length of the railway between Tallinn and Warsaw will be at least {{convert|950|km}}. Total length of the Baltic railway part: 870 km. |
|||
The overall length of the railway between Tallinn and Warsaw will be at least {{convert|950|km|abbr=on}}, while the length within the Baltic States proper will be {{convert|870|km|abbr=on}}.<ref name="alternative 6A approved"/> |
|||
==Status== |
==Status== |
||
In 2017, all three Baltic parliaments ratified the Inter-Governmental Agreement for the Rail Baltica project, thereby confirming their long-term commitment to the |
In 2017, all three Baltic parliaments ratified the Inter-Governmental Agreement for the Rail Baltica project, thereby confirming their long-term commitment to the project.<ref name=":1" /> In addition, Rail Baltica Global Project's [[cost-benefit analysis]] was delivered by [[Ernst & Young]] and [[Atkins International]] experts, based on the European Union's CBA guidelines. The analysis showed that the project was financially feasible and viable, and its measurable benefits would outweigh the costs.<ref name=":2">{{Cite web |last=EY |title=Rail Baltica Global Project Cost-Benefit Analysis Final Report |url=http://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/RB_CBA_FINAL_REPORT_0405.pdf |website=www.railbaltica.org}}</ref> |
||
In August 2016, the spatial planning for the entire Rail Baltica railway line was approved in Latvia by the decision of the Latvian Government. This was followed by the approval of the Lithuanian Government in January 2017 for their respective section from Kaunas to the border with Latvia. The route for the section from Kaunas to the border with Poland, known as Rail Baltica I, is subject to the results of an Upgrade Feasibility Study. On 14 February 2018, the Ministry of Public Administration of the Republic of Estonia approved the spatial plan for the line in Estonia, leading to the setting of the final route and preliminary design of the railway in the country. With Estonia's decision, the spatial territorial planning and preliminary technical design of the Rail Baltica railway in the Baltic states was finalised.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/route-setting-and-spatial-territorial-planning-for-rail-baltica-railway-finalised-in-all-three-baltic-states/|title=Route setting and spatial territorial planning for Rail Baltica railway finalised in all three Baltic states {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:RB_infografiki_Karte_EN.jpg|thumb|365x365px|Map of Rail Baltica with stations]] |
|||
The Rail Baltica project has entered the design phase in all three Baltic States with the approval of the Detailed Design Guidelines for Rail Baltica, continuing the work on the consolidated preliminary technical design, tendering the detailed technical design services, preparing BIM strategy. On March 20, the first Rail Baltica construction design and supervision contract of Rail Baltica's Riga International Airport railway station, related infrastructure and viaduct was signed by "Eiropas Dzelzceļa līnijas" SIA and the winner of the open International tneder – partnership of suppliers from three countries "PROSIV" ("Sintagma" (Italy), "Prodex" (Slovakia) and "Vektors T" (Latvia))<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://edzl.lv/en/news/the-first-rail-baltica-construction-design-and-supervision-contract-signed-in-the-baltics.html|title=The first Rail Baltica construction design and supervision contract signed in the Baltics - Edzl|website=edzl.lv|language=lv|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref>. During the Rail Baltica Global Forum 2018, the project implementers introduced the plans for the Rail Baltica design phase to around 500 suppliers from 24 countries<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/forum/programme|title=Rail Baltica Global Forum 2018, 10-11 April, Tallinn, Estonia|website=www.railbaltica.org|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref>. |
|||
The Rail Baltica project entered the design phase in all three Baltic States with the approval of detailed design guidelines. Certain sections have finished consolidating preliminary technical design, tendering the detailed technical design services, and preparing a [[Building information modeling|BIM strategy]]. On 20 March 2018, the first Rail Baltica construction design and supervision contract—for Rail Baltica's Riga International Airport railway station, related infrastructure, and viaduct—was signed by Eiropas Dzelzceļa līnijas SIA and PROSIV, the winner of the open international tender and a partnership of suppliers from three countries: Prodex (Slovakia), Sintagma (Italy), and Vektors T (Latvia).<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://edzl.lv/en/news/the-first-rail-baltica-construction-design-and-supervision-contract-signed-in-the-baltics.html|title=The first Rail Baltica construction design and supervision contract signed in the Baltics - Edzl|website=edzl.lv|language=lv|access-date=2018-05-24|archive-date=2018-08-06|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180806145647/http://edzl.lv/en/news/the-first-rail-baltica-construction-design-and-supervision-contract-signed-in-the-baltics.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
In 2018, it is planned to finalise the long-term Business Plan, Operational Plan, the Upgraded Feasibility Study of the European gauge railway line from Kaunas to Lithuanian/Polish border, Infrastructure Management Study and other studies related to commercialisation and supply materials<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/annual-press-conference-of-the-rail-baltica-implementers-2/|title=Annual Press Conference of the Rail Baltica implementers {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref>. |
|||
In 2018, studies related to commercialisation and supply materials were finalised, including a long-term business plan, an operational plan, an infrastructure management study, and an upgraded feasibility study of the European gauge railway line from Kaunas to the Lithuanian–Polish border.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/annual-press-conference-of-the-rail-baltica-implementers-2/|title=Annual Press Conference of the Rail Baltica implementers {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref> In 2019, the first cornerstone of Rail Baltica was laid in Estonia to mark the beginning of construction of the [[Saustinõmme]] viaduct. Also, detailed technical design contracts were signed for the following sections: Tallinn–Rapla and Pärnu–Rapla in Estonia, Kaunas–Ramygala and Ramygala–Latvian/Lithuanian border in Lithuania, and Vangaži–Salaspils–Misa and the main line through Riga in Latvia.<ref name="Interactive map">{{Cite web|title=Interactive map|url=https://www.railbaltica.org/info/en/interactive-map|access-date=2020-09-21|website=www.railbaltica.org}}</ref> With the contracts signed, geotechnical research was started in different sections of the railway in order to gather information about the soil. |
|||
In 2020, the development of detailed technical design had progressed to cover {{Convert|643|km|abbr=on}} of the main track, which included all railway sections in Estonia and Latvia as well as sections from Kaunas to the Latvian/Lithuanian border in Lithuania.<ref name="Interactive map"/> |
|||
In Estonia, discussions about environmental impact assessment were started and meetings were planned until the end of 2020. During the discussions, people were invited to ask questions regarding the project's environmental impact, while various technical solutions were presented.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Kõrvek: Conducting Rail Baltica's environmental impact assessment discussions electronically has proven itself useful {{!}} Rail Baltica|url=https://www.railbaltica.org/korvek-conducting-rail-balticas-environmental-impact-assessment-discussions-electronically-has-proven-itself-useful/|access-date=2020-09-21|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US}}</ref> |
|||
In Latvia, the Riga Central Station construction was officially started with ceremonies on 23 November 2020.<ref>{{Cite web|title=The Start of Construction of Rail Baltica Central Hub in Riga {{!}} Rail Baltica|url=https://www.railbaltica.org/the-start-of-construction-of-rail-baltica-central-hub-in-riga/|access-date=2020-12-01|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en}}</ref> On the 3rd of February 2021, the project implementer of Riga Airport Station was also chosen; construction began in May 2021 and is ongoing {{as of|2023|7|lc=on}}.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-07-05 |title=At Riga International Airport, the construction of the Rail Baltica passenger terminal's reinforced concrete structures and railway platforms is underway {{!}} Rail Baltica |url=https://www.railbaltica.org/at-riga-international-airport-the-construction-of-the-rail-baltica-passenger-terminals-reinforced-concrete-structures-and-railway-platforms-is-underway/ |access-date=2023-12-06 |website=www.railbaltica.org |language=en-US}}</ref> Talks with [[NGO]]s in Riga were started to discuss technical solutions within the city, especially for infrastructure elements such as crossings and overpasses.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Publiskā diskusija "Rail Baltica kā projekts Rīgas attīstībai" {{!}} Rail Baltica|url=https://www.railbaltica.org/lv/publiskaja-diskusija-rail-baltica-ka-projekts-rigas-attistibai/|access-date=2020-09-21|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=lv-LV}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Russian invasion of Ukraine]] has raised the importance of this European project, because of the connectivity across Europe that it will create, for civilian and military travel. Lithuania has a new commission to speed construction within the cities (freight terminal facilities and passenger depot). Estonia faces cost increases and construction delays.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.railway-technology.com/features/how-rail-baltica-is-making-progress/#catfish |title=How Rail Baltica is making progress |work=Railway Technology |first=Andrew |last=Tunnicliffe |date=March 7, 2023 |quote=In addition, projected costs for the multi-billion-Euro project continue to rise above initial estimates. At the end of 2022, it was reported costs for the Estonia section alone were expected to be €1.8bn, almost double what had originally been projected. Speaking to Estonia’s daily newspaper, Postimees, Anvar Salomets, Chair of the board at RB Eesti, acknowledged the difficulties this section had faced, saying: “It is indeed the case that the design of the main route of the railway has proved difficult.” |access-date=June 30, 2023 }}</ref> |
|||
{{As of|2023}}, the project completion is scheduled for 2030, with services starting in 2028 on some sections.<ref name="railbaltica-about">[https://www.railbaltica.org/about-rail-baltica/ Rail Baltica – Project of the Century"] on the Rail Baltica official website, accessed on 26 April 2023.</ref> |
|||
=== Project implementers === |
=== Project implementers === |
||
The Rail Baltica project is being implemented by the three Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. [[Finland]] announced in February 2019 that it will also join the project.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://news.err.ee/907106/finland-to-formally-join-rail-baltica-joint-venture|title=Finland to formally join Rail Baltica joint venture|last=[[Estonian Public Broadcasting]]|first=BNS {{!}}|date=2019-02-03|website=ERR|language=en|access-date=2019-02-15}}</ref><ref name=":3">{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/finland-to-join-the-rail-baltica-joint-ventures-as-a-shareholder/|title=Finland to join the Rail Baltica Joint Ventures as a shareholder {{!}} Rail Baltica|date=2019-02-05|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2019-02-15}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.railtech.com/policy/2019/02/04/finland-to-become-shareholder-of-rail-baltica/|title=Finland will take part in Rail Baltica|date=2019-02-04|website=RailTech.com|language=en-GB|access-date=2019-02-15}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://emerging-europe.com/news/finland-hops-on-board-rail-baltica/|title=Finland hops on board Rail Baltica|last=Shah|first=Shakhil|date=2019-02-05|website=Emerging Europe|access-date=2019-02-15}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:RB_Project_Structure-copy-1.png|thumb|360x360px|Rail Baltica Project Structure]] |
|||
The Rail Baltica project is being implemented by the three Baltic States – Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. |
|||
The |
The beneficiaries of the Rail Baltica project are ministries of the three Baltic States: Estonia's Ministry of Economic Affairs and Communications, Latvia's Ministry of Transport, and Lithuania's Ministry of Transport and Communications. In 2014, they established RB Rail AS, a joint venture that acts as the main coordinator and project implementer for the project. Its main business is the design, construction, and marketing of the railway. RB Rail AS also submits EU financing proposals for the Rail Baltica purchasing body for all parties for the procurement of studies, plans, designs for the Global Project, sub-systems (control, command, and signalling and energy/electrification), raw materials, key components, and cross-border track sections.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/project-implementers/main-coordinator/|title=Main Coordinator|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref> |
||
Rail Baltic Estonia OU |
Rail Baltic Estonia OU in Estonia, Eiropas Dzelzceļa līnijas SIA in Latvia, and Rail Baltica statyba UAB and LtgInfra in Lithuania are the national implementing bodies.<ref name=":3" /> All construction carried out by the implementing bodies is done under the supervision of RB Rail AS and is based on common procurement principles, rules, and contract templates.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/project-implementers/|title=Project Implementers|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref> |
||
===Financing=== |
===Financing=== |
||
[[File:RB_Project_Structure-copy-1.png|thumb|360x360px|Rail Baltica project structure]] |
|||
The total estimated cost of the Rail Baltica Global project is 5.8 billion euro in all three Baltic States according to the Cost-Benefit Study carried out by EY in 2017. |
|||
A feasibility study of Rail Baltica in the three Baltic States carried out by [[AECOM]] in May 2011 estimated a cost of €3.6 billion for the railway and proved that Rail Baltica is economically viable. Based on that study, key political and practical decisions—both on the national and EU level—were made to implement Rail Baltica.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/AECOM_Rail_Baltica_Final_Report_Executive_Summary_31_05_11_FINAL_v2.pdf|title=Rail Baltica Final Report}}</ref> |
|||
Since the AECOM study, the project has grown to include additional elements to the Rail Baltica Global Project for better connectivity, passenger mobility, and inter-modality. These additions include routing the Rail Baltica passenger mainline through the Riga International Airport and the construction of the airport passenger station (Latvia), the Kaunas–Vilnius connection (Lithuania), an improved connection in Kaunas (Lithuania), and the construction of the Ülemiste–Tallinn airport tram line (Estonia). Moreover, the preparation of environmental impact assessments, spatial planning, and some preliminary designs has provided better investment estimations for the project.<ref name=":2" /> |
|||
The Feasibility study of Rail Baltica in the three Baltic States carried out by AECOM in 2011 had estimated cost of 3.6 billion euro for the railway and proved that Rail Baltica is economically viable. Based on that study, key political and practical decisions – both on the national and EU level – were made to implement Rail Baltica<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/AECOM_Rail_Baltica_Final_Report_Executive_Summary_31_05_11_FINAL_v2.pdf|title=Rail Baltica Final Report|last=|first=|date=|website=|archive-url=|archive-date=|dead-url=|access-date=}}</ref>. |
|||
Thus, in April 2017, the overall cost of the Rail Baltica Global Project implementation in all three countries—including the construction of the Kaunas–Vilnius section—was estimated to be €5.8 billion, according to a cost-benefit study carried out by [[Ernst & Young]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://news.err.ee/587839/rail-baltic-to-cost-5-8-billion|title=Rail Baltic to cost €5.8 billion|last=ERR|date=3 April 2017|website=ERR}}</ref> According to the analysis, the project's economic feasibility and social benefits were still proved, providing the necessary updated parameters for continued EU and national co-financing of the project.<ref name=":2" /> |
|||
Since the AECOM study the project has matured, and essential elements have subsequently been added to the Rail Baltica Global Project for better connectivity, passenger mobility and inter-modality. Additions to the Global Project include routing the Rail Baltica passenger mainline through the Riga International Airport and construction of the airport passenger station (Latvia), the Kaunas–Vilnius connection (Lithuania), an improved connection in Kaunas city (Lithuania), and construction of the tram line “Ülemiste-Tallinn airport” (Estonia). Moreover, the Environmental Impact Assessments, spatial planning and some preliminary designs have been prepared allowing to better estimate the investments needed for the project<ref name=":2" />. |
|||
The project's profitability lies in its wider socio-economic benefits, which Ernst & Young estimated to be around €16.22 billion.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://news.err.ee/591968/analysis-rail-baltic-project-to-have-3-96-billion-gap|title=Analysis: Rail Baltic project to have €3.96 billion gap|last=ERR|date=25 April 2017|website=ERR}}</ref> In addition, several immeasurable (mostly catalytic) benefits would be created through regional integration, such as tourism development, new business creation, increased attractiveness to FDI, access to new export markets, technological transfer, and innovation. |
|||
Thus, in April 2017, the overall cost of the Rail Baltica Global Project implementation in three countries, including the construction of the Kaunas-Vilnius section, was estimated at about €5.8 billion.<ref>[https://news.err.ee/587839/rail-baltic-to-cost-5-8-billion Rail Baltic to cost €5.8 billion]</ref> According to the According to the Ernst & Young (EY) cost-benefit analysis, the project's economic feasibility and benefits society will gain was proved, providing the necessary updated parameters for continued EU and national co-financing of the project<ref name=":2" />. |
|||
The project is financed by the member states, the [[European Union]] [[TEN-T]] budget, and the Structural and Cohesion Funds provided to the EU New Member States.<ref>{{cite press release |title=Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T): selection of projects for the TEN-T multi-annual programme 2007–2013 and the annual TEN-T programme 2007 |publisher=European Union |url= http://europa.eu/rapid/pressReleasesAction.do?reference=MEMO/07/491&format=HTML&aged=0&language=EN&guiLanguage=en |date=21 November 2007}}</ref> By the start of 2018, the three Baltic States and RB Rail AS had received two grants totaling €765 million designed under the [[Connecting Europe Facility|CEF]] for the construction of the Rail Baltica railway. On 13 July 2018, a third grant agreement was signed for an additional €130 million, of which €110 million was CEF contribution.<ref>{{cite web |title=Third CEF Grant Agreement for Rail Baltica Global project signed |url=http://www.railbaltica.org/third-cef-grant-agreement-for-rail-baltica-global-project-signed/ |website=Rail Baltica |access-date=23 July 2018}}</ref> In July 2020, another CEF funding was received, amounting to €216 million for construction, technical design, and planning works.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Rail Baltica receives next round of funding {{!}} Rail Baltica|url=https://www.railbaltica.org/rail-baltica-receives-next-round-of-funding/|access-date=2020-09-21|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US}}</ref> In total, the project has received around €1.2 billion from the EU and national funds. |
|||
The project's profitability lies in its wider socio-economic benefits, which are estimated by EY at around €16.22 billion.<ref>[https://news.err.ee/591968/analysis-rail-baltic-project-to-have-3-96-billion-gap Analysis: Rail Baltic project to have €3.96 billion gap]</ref> In addition, there will be several immeasurable (mostly, catalytic) benefits that would be created by Rail Baltica through regional integration, tourism development, new business creation, increased attractiveness to FDI, access to new export markets, technological transfer, innovation, etc. |
|||
In October 2023 Rail Baltica joint venture of the Baltic States, RB Rail AS, announced the signing of an additional cross-border Grant Agreement for Connecting Europe Facility (CEF) funding, which amounted to 928 million euros CEF support. This substantial funding, combined with national co-financing from the three Baltic States, will exceed 1.1 billion euros, enabling necessary activities for further high-speed infrastructure development.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://eng.lsm.lv/article/economy/transport/18.10.2023-rail-baltica-cleared-to-receive-another-billion-euros.a528342/|title=Rail Baltica cleared to receive another billion euros|website=Public broadcasting of Latvia|date=18 October 2023}}</ref> |
|||
The project is financed by the member states and the [[European Union]] TEN-T budget, and the Structural and Cohesion Funds provided to the EU New Member States.<ref>{{cite press release |title=Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T): selection of projects for the TEN-T multi-annual programme 2007–2013 and the annual TEN-T programme 2007 |publisher=European Union |url= http://europa.eu/rapid/pressReleasesAction.do?reference=MEMO/07/491&format=HTML&aged=0&language=EN&guiLanguage=en |date=21 November 2007}}</ref> By the start of 2018, the three Baltic States and RB RAIL AS have received two grants designed under the CEF for the construction of the Rail Baltica railway, having signed Grant Agreements with a total value of 765 million euros. |
|||
Financial contributions from CEF and national countries (in millions of euros), April 2017: |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
!In total |
|||
!765 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Estonia |
|||
|229 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Latvia |
|||
|295 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Lithuania |
|||
|242 |
|||
|} |
|||
===Route and standard=== |
===Route and standard=== |
||
[[File:Rail Baltica.svg|thumb|upright=1.2|Rail Baltica in Poland]] |
|||
In 2011, the three Baltic States agreed on a route connecting Tallinn, [[Pärnu]], Riga, [[Panevėžys]], and Kaunas.<ref name="Press report on route in Lithuania">{{cite web |url=http://www.baltic-course.com/eng/transport/?doc=38760 |title=Rail Baltica's fate to become clearer by the end of May |date=March 2011 |format=PDF}}</ref> A feasibility study for this option estimated the line will cost about €3.68 billion in total.<ref name="Project Rail Baltica would cost EUR 3.68 bln">{{cite web |url=http://www.baltic-course.com/eng/transport/?doc=42701 |title=Project Rail Baltica would cost EUR 3.68 bln |date=June 2011}}</ref> |
|||
The planning phase of Rail Baltica took place from 2010 to 2017.{{citation needed|date=October 2022}} In 2011, the three Baltic States agreed on a route connecting Tallinn, [[Pärnu]], Riga, [[Panevėžys]], and Kaunas.<ref name="Press report on route in Lithuania">{{cite web |url=http://www.baltic-course.com/eng/transport/?doc=38760 |title=Rail Baltica's fate to become clearer by the end of May |date=March 2011 |format=PDF}}</ref> A feasibility study for this option estimated the line would cost about €3.68 billion in total.<ref name="Project Rail Baltica would cost EUR 3.68 bln">{{cite web |url=http://www.baltic-course.com/eng/transport/?doc=42701 |title=Project Rail Baltica would cost EUR 3.68 bln |date=June 2011}}</ref> |
|||
During the planning of the location of the project route in the Baltic States, a conceptual agreement among the three countries was reached that the railway should be as straight as possible, as this provides the highest benefits at the lowest cost. The shorter and more direct the route is, the faster traffic it can ensure, which economically has the highest advantage compared to its alternatives. This was confirmed by an AECOM study in 2013.{{citation needed|date=October 2022}} |
|||
Initially two options were considered. Both options included an upgrade of the existing railway (with [[standard gauge]]) to {{convert|160|km/h|abbr=on}} for the stretch that runs from Warsaw via [[Białystok]] and [[Ełk]] to [[Trakiszki]],<ref name="feasibility EU"/> followed by a new railway with standard gauge Trakiszki–Kaunas. For the remainder of the route to Tallinn two different options were considered: |
|||
* Option one was to upgrade the existing railway from [[Joniškis]] via Riga and [[Tartu]] to Tallinn to 160 km/h, keeping the current [[Russian gauge]] and state-owned, and a new railway from Kaunas–Joniškis with 160 km/h, also at Russian gauge and state-owned. Because of the [[break of gauge]] at Kaunas, passengers would have to change trains there. For freight, a reloading facility or a [[bogie exchange]] station would be placed near Kaunas. This option was already completed as Rail Baltica I. |
|||
* Option two was a new railway with {{convert|200|km/h|abbr=on}} speed standard gauge (with 3kV DC, the same voltage as in Poland) from Kaunas via Joniškis to Riga, as above, but then continuing in a shorter, straighter line via [[Pärnu]] to Tallinn.<ref name="feasibility EU">{{cite web |url= http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/sources/docgener/evaluation/railbaltica/concl_en.PDF |title=Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways |date=January 2007 |format=PDF |author=European Commission, Directorate-General for Regional Policy}}</ref> This option was chosen as the preferred route. |
|||
Initially, two options were considered. Both options included upgrading the existing [[standard gauge]] railway to enable travel speeds of up to {{convert|160|km/h|abbr=on}} along the stretch in Poland from Warsaw via [[Białystok]] and [[Ełk]] to [[Trakiszki]],<ref name="feasibility EU"/> followed by a new railway with standard gauge from Trakiszki to Kaunas. For the remainder of the route to Tallinn, two different options were considered: |
|||
During the planning of the location of the project route in the Baltic States a conceptual agreement among the three Baltic States was reached that it should be as straight as possible as it provides the highest benefits at the lowest cost. The shorter and more direct the route is, the faster traffic it is possible to ensure, which economically has the highest advantage compared to its alternatives. This was confirmed by the AECOM study in 2013, analysing the four possible options of the location of the route in all three Baltic countries. |
|||
# The first option was to upgrade the existing state-owned Tallinn–[[Tartu]]–Riga–[[Joniškis]] railway to 160 km/h (maintaining its [[Russian gauge]]) and build a new state-owned railway from Joniškis–Kaunas with 160 km/h, also at Russian gauge. However, because of the [[break of gauge]] at Kaunas, passengers would have to change trains there. For freight, a reloading facility or a [[bogie exchange]] station would be placed near Kaunas. This option was already completed as Rail Baltica I.{{citation needed|date=October 2022}} |
|||
# The second option was a new standard gauge railway with {{convert|200|km/h|abbr=on}} speed and 3 kV DC power (the same voltage as in Poland) from Kaunas via Joniškis to Riga, as above, but then continuing in a shorter, straighter line via [[Pärnu]] to Tallinn.<ref name="feasibility EU">{{cite web |url= http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/sources/docgener/evaluation/railbaltica/concl_en.PDF |title=Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways |date=January 2007 |work=European Commission, Directorate-General for Regional Policy}}</ref> This option was chosen as the preferred route. The existing Lelle–Pärnu line in Estonia was permanently closed for passenger operations on 9 December 2018,<ref>{{cite web |url=https://bnn-news.com/estonia-to-close-railway-line-and-wait-for-rail-baltica-193449 |title=Estonia to close railway line and wait for Rail Baltica|website=Baltic News Network|date=6 November 2018}}</ref> as it required a €17 million refurbishment.<ref>[https://news.err.ee/874854/tallinn-parnu-railway-line-to-be-closed-permanently-in-december ERR News. ''Tallinn-Pärnu railway line to be closed permanently in December.''] news.err.ee accessed 7 June 2019</ref> |
|||
The [[Šiauliai]]–Latvian border rail section (using broad gauge) was newly built and scheduled to be finished in 2015{{Update inline|date=May 2023}} with an estimated cost of €270 million. In Latvia, the existing railway upgrade between Riga and Valka was finished in 2016 at a cost of €97 million. The EU contributed about 25% of the cost for the three parts.{{citation needed|date=October 2022}} |
|||
In 2017, the Parliaments of the three Baltic States ratified the intergovernmental Agreement on Rail Baltica stating "route" shall be from Tallinn though Pärnu–Riga–Panevezys–Kaunas to the Lithuanian/Polish state border with a connection of Vilnius–Kaunas as a part of the railway<ref name=":1" /> and defining the design speed 240 km/h for passenger travel. Now the Rail Baltica Global Project route is aligned from Tallinn till Kaunas with already built European gauge railway line section from Kaunas-Lithuanian/Polish border being subject to the results of the Upgrade Feasibility Study<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/rail-baltica-route-setting-in-the-baltics/|title=Rail Baltica Route Setting in the Baltics {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref>. Nevertheless, in April 2018 the Ministries of the three Baltic States approved the Design Guidelines of Rail Baltica, which states that the maximum design speed will be 249 km/h and maximum operational speed should be 234 km/h<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/rail-baltica-design-guidelines-approved/|title=Rail Baltica Design Guidelines Approved {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref>. |
|||
=== Construction (2017–present) === |
|||
===Rail Baltica I=== |
|||
[[File:RB_infografiki_Karte_EN.jpg|thumb|365x365px|Map of Rail Baltica with stations]] |
|||
The name Rail Baltica is also sometimes used to mean the first phase of European gauge railway construction from the Poland-Lithuania border to Kaunas in Lithuania. It was inaugurated on October 16, 2015. The project, which built European standard-gauge one track alongside the existing Russian gauge tracks, cost €380m. The 119 km line accommodates diesel trains, with passenger trains running at up to 120 km/h and freight trains at up to 80 km/h. Higher speeds will depend on future electrification and a new signal system. In June 2016, [[Lithuanian Railways]] and [[Przewozy Regionalne]] started weekend passenger train service between Kaunas and [[Białystok]].[[Rail Baltica#cite note-6|<sup>[6]</sup>]][[Rail Baltica#cite note-7|<sup>[7]</sup>]] |
|||
[[File:Rail Baltica future tracks at Ülemiste.jpg|thumb|Construction of Rail Baltica tracks at [[Ülemiste station]] in [[Tallinn]]]] |
|||
[[File:Construction of Ülemiste station, Rail Baltica.jpg|thumb|Construction of Rail Baltica's Ülemiste railway terminal in Tallinn; the current railway station can be seen on the far right]] |
|||
In 2017, the parliaments of the three Baltic States ratified the intergovernmental agreement on Rail Baltica, stating that the "route shall be from Tallinn through Pärnu–Riga–Panevėžys–Kaunas to the Lithuanian/Polish state border with a connection of Vilnius–Kaunas as a part of the railway"<ref name=":1" /> and defining a design speed of 240 km/h for passenger travel. Thus, the Rail Baltica Global Project route was aligned from Tallinn until Kaunas, with the pre-existing European gauge railway line section from Kaunas to the Lithuanian/Polish border being subject to the results of the Upgrade Feasibility Study.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/rail-baltica-route-setting-in-the-baltics/|title=Rail Baltica Route Setting in the Baltics {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref> Nevertheless, in April 2018, the Ministries of the three Baltic States approved the design guidelines of Rail Baltica, which state that the maximum design speed will be 249 km/h and maximum operational speed should be 234 km/h.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/rail-baltica-design-guidelines-approved/|title=Rail Baltica Design Guidelines Approved {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref> |
|||
In Estonia and Latvia, implementation of the Rail Baltica I project contained upgrade of the existing rail lines in the region.<ref>https://ec.europa.eu/inea/ten-t/ten-t-projects/projects-by-priority-project/priority-project-27</ref> The {{convert|66|km}} long Russian gauge line from Tartu to [[Valga, Estonia|Valga]] (on the Latvian border) in Estonia was renovated between 2008 and 2010. The work was done by the Finnish [[VR Group]] for a cost of €40M.<ref name="MidTermReview">{{cite web |title=Mid-Term Review |format=PDF, 65 MB |work=Detailed report from 2010 |pages=161–172 (PDF) |url= http://ec.europa.eu/transport/wcm/infrastructure/ten-t_map_project_portfolio.pdf |year=2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite press release |title=VR-Track wins superstructure renovation contract for Tartu-Valga track |author=VR Group |location=Finland |url=http://www.vrgroup.fi/vakiolinkit/VRinforms/news_119.html |date=28 April 2008 }}{{dead link|date=April 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> |
|||
For the Kaunas (Jiesia)–Lithuanian/Polish border section, a 78.1 km route named "alternative 6A" was approved in May 2022 by the Lithuanian Ministry of Transport and Communications, taking into account the opinion of the majority of the local residents.<ref name="alternative 6A approved"/><ref>{{Cite web | url=https://sumin.lrv.lt/uploads/sumin/documents/files/02_SPAV%20ataskaita_%20Tekstiniai%20priedai.pdf | title=Tekstiniai Priedai (Text Attachments) (planning document comparing several alternative routes for the Kaunas (Jiesia) - Lithuanian-Polish border section) | via=[[Government of Lithuania]] | date=February 2022 | access-date=2022-05-18 | archive-date=2022-03-31 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220331120311/https://sumin.lrv.lt/uploads/sumin/documents/files/02_SPAV%20ataskaita_%20Tekstiniai%20priedai.pdf | url-status=dead }}</ref> This optimal route is the shortest among the alternatives which were proposed and the most remote from the urban areas. |
|||
The Polish section of Rail Baltica is being upgraded to allow passenger trains to run at 200 km/h.<ref>{{cite news |first=Jakub |last=Madrjas |title=Zmieniona koncepcja Rail Baltiki w Polsce. Nowy przebieg i obwodnica Białegostoku |trans-title=Amended concept of Rail Baltica in Poland. New route and Białystok bypass |url=https://www.rynek-kolejowy.pl/wiadomosci/zmieniona-koncepcja-rail-baltica-w-polsce-nowy-przebieg-i-obwodnica-bialegostoku-95187.html |website=Rynek Kolejowy |date=24 January 2020 |language=pl }}</ref> The Ełk–state border section may be built to allow 250 km/h and may be electrified using the 25 kV AC system.<ref>{{cite news |first=Jakub |last=Madrjas |title=Adamczyk: Zmieniamy projekt Rail Baltica na prośbę Komisji Europejskiej. Będzie 250 km/h? |trans-title=Adamczyk: following European Commission request, we amend Rail Baltica project. Will there be 250 km/h? |url=https://www.rynek-kolejowy.pl/wiadomosci/adamczyk-zmieniamy-projekt-rail-baltica-na-prosbe-komisji-europejskiej-bedzie-250-kmh-92903.html |website=Rynek Kolejowy |date=25 July 2019 |language=pl }}</ref> |
|||
On 29 February 2024, construction on the Rail Baltica Riga Central Railway Station reached the rooftop, which was celebrated with a ceremony according to Latvian tradition. This train station is expected to become the busiest in the Baltics once Rail Baltica is fully operational.<ref>{{Cite web |title=The rooftop ceremony of Rail Baltica at Riga Central Station was celebrated |author= |work=baltictimes.com |date=1 March 2024 |access-date=19 April 2024 |url= https://www.baltictimes.com/the_rooftop_ceremony_of_rail_baltica_at_riga_central_station_was_celebrated/}}</ref> |
|||
===Rail Baltica I=== |
|||
The name "Rail Baltica" is also sometimes used to mean the first phase of European gauge railway construction from the Poland/Lithuania border to Kaunas in Lithuania. It was inaugurated on 16 October 2015. The project, which built one track at European standard-gauge alongside the existing Russian gauge tracks, cost €380 million. The 119 km line accommodates diesel trains, with passenger trains running at up to 120 km/h and freight trains at up to 80 km/h. Higher speeds will depend on future electrification, a new signal system, and more level crossing gates. In June 2016, [[Lithuanian Railways]] and [[Polregio]] started weekend passenger train service between Kaunas and [[Białystok]].<ref>{{cite news|title=Lithuanian, Polish railways to launch Kaunas-Bialystok passenger route in June|publisher=[[The Baltic Course]] |url= http://www.baltic-course.com/eng/good_for_business/?doc=121482 |date=31 May 2016}}</ref> |
|||
In Estonia and Latvia, implementation of the Rail Baltica I project included upgrades of the existing rail lines in the region.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://ec.europa.eu/inea/en/ten-t/ten-t-projects/projects-by-priority-project/priority-project-27|title=Priority Project 27|website=Innovation and Networks Executive Agency - European Commission}}</ref> The {{convert|66|km|mi|adj=mid|-long}} Russian gauge line from Tartu to [[Valga, Estonia|Valga]] (on the Latvian border) in Estonia was renovated between 2008 and 2010. The work was done by the Finnish [[VR Group]] for a cost of €40 million.<ref name="MidTermReview">{{cite web |title=Mid-Term Review |format=PDF, 65 MB |work=Detailed report from 2010 |pages=161–172 (PDF) |url=http://ec.europa.eu/transport/wcm/infrastructure/ten-t_map_project_portfolio.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121103110640/http://ec.europa.eu/transport/wcm/infrastructure/ten-t_map_project_portfolio.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=2012-11-03 |year=2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite press release |title=VR-Track wins superstructure renovation contract for Tartu-Valga track |author=VR Group |location=Finland |url=http://www.vrgroup.fi/vakiolinkit/VRinforms/news_119.html |date=28 April 2008 }}{{dead link|date=April 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> |
|||
The [[Šiauliai]]-to-Latvian border rail section (using broad gauge) will be newly-built and to be finished in 2015 with an estimated cost of €270M. In Latvia, the existing railway upgrade between Riga and Valka at the cost of €97M was finished 2016. The EU will contribute about 25% of the cost for the three parts. |
|||
== |
==Benefits== |
||
The Baltic railway infrastructure will be connected to the European railway corridor, ensuring high-speed passenger travel and freight movement. Rail Baltica creates the possibility to shift the major freight transport in the regions from road to rail, which is currently being transported towards Russia and then north by heavy trucks. In the case of Poland, trucks follow local roads and directly cross the villages of [[Podlaskie Voivodeship]].{{citation needed|date=December 2015}} |
|||
[[File:RB_infografiks_EN-01.jpg|thumb|390x390px|Rail Baltica timeline]] |
[[File:RB_infografiks_EN-01.jpg|thumb|390x390px|Rail Baltica timeline]] |
||
Rail Baltica will bring vast opportunities to the region. It will act as a powerful catalyst for sustainable economic growth in the Baltic States, will provide a new standard of passenger and freight mobility, sustainable employment and educational opportunities, an environmentally sustainable infrastructure, new opportunities for multimodal freight logistics development, new intermodal transport solutions for passengers, a new value platform for digitalization and innovation. Rail Baltica will ensure safety and performance improvements<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/benefits/|title=Benefits {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref><ref name=":2" />. |
|||
According to the 2017 cost-benefit study by Ernst & Young, the benefits from Rail Baltica are calculated to be: |
|||
According to the Cost-Benefit Study (2017), due to construction of Rail Baltica, there will be 7.1 billion Euro saved in climate change and noise reduction, relevant track traffic flow shift to railways – 30-40%, 13 000 jobs created during the construction phase, 5.3 billion euro saved for passenger and freight travel, 5.3 million passenger hours saved and 400 human lives saved in 29 years<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.railbaltica.org/video/rail-baltica-is-your-future/|title=Rail Baltica is your future {{!}} Rail Baltica|website=www.railbaltica.org|language=en-US|access-date=2018-05-24}}</ref>. |
|||
* €7.1 billion saved in climate change and noise reduction |
|||
All in total, measurable socio-economic benefits are estimated at 16.2 billion euro. The assessed GDP multiplier effect the Rail Baltica Global Project would create is an additional 2 billion euro. There will be substantial unmeasurable benefits<ref name=":2" />. |
|||
* 30–40% relevant truck traffic flow shifted to railways |
|||
* 13,000 jobs created during the construction phase |
|||
* €5.3 billion saved for passenger and freight travel |
|||
* 5.3 million passenger hours saved |
|||
* 400 human lives saved in 29 years |
|||
All in total, measurable socio-economic benefits are estimated at €16.2 billion. The assessed GDP multiplier effect the Rail Baltica Global Project would create is an additional €2 billion. It is also claimed there will be "substantial unmeasurable benefits".<ref name=":2" /> |
|||
==Criticisms== |
|||
[[File:A 3 billion euro mistake in Rail Baltica Cost-Benefit Analysis.svg|thumb|Average Baltic Vehicle fleet composition projection and Ernst & Young assumptions for justifying Rail Baltica|450px|Graph showing the claimed 3 billion euro mistake in Rail Baltica Cost-Benefit Analysis]] |
|||
In late April 2022, implementers of the Rail Baltica project presented the progress at the European Parliament where the strategic and geopolitical security importance of the project was stressed repeatedly in reference to the [[2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine]].<ref>[https://www.railbaltica.org/rail-baltica-global-project-progress-presented-at-the-european-parliament-necessity-of-swift-implementation-of-rail-baltica-and-eu-added-value-clearer-than-ever/ ''Rail Baltica global project progress presented at the European Parliament: necessity of swift implementation of Rail Baltica and EU added value clearer than ever''] (26 April 2022)</ref> |
|||
Criticism started after a feasibility study by [[AECOM]] was published, with the government of Lithuania keen to include a link to Vilnius.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Barrow|first1=Keith|title=Governments edge towards consensus on Rail Baltica|url=http://www.railjournal.com/index.php/main-line/governments-edge-towards-consensus-on-rail-baltica.html|work=International Rail Journal|date=11 March 2014|language=en-gb}}</ref> The mayor of [[Tartu]], Estonia's second largest city, called for the city to be included in the route.<ref>{{cite news|title=Current Rail Baltic route through Latvia publicly approved|url=https://news.err.ee/119874/current-rail-baltic-route-through-latvia-publicly-approved|work=ERR|date=30 November 2016|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Tartu-Valga Rail Baltic Route Should Be Considered, Says Tartu Mayor|url=http://news.err.ee/111389/tartu-valga-rail-baltic-route-should-be-considered-says-tartu-mayor|work=ERR|date=17 January 2014|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
==Criticism== |
|||
In 2017 several Estonian environmental groups claimed that the lack of public participation on the decision made by Baltic governments and building of a new line, rather than upgrading the existing network, is in conflict with the [[Aarhus Convention]].<ref>{{cite news|title=Estonian ex-PM: Ratification of Rail Baltic accord will result in litigation|url=https://www.baltictimes.com/estonian_ex-pm__ratification_of_rail_baltic_accord_will_result_in_litigation|work=Baltic Times|date=15 June 2017|language=en}}</ref> The [[:ee:Eesti Rooma Klubi|Estonian Association]] for the [[Club of Rome]] advised the government to abandon the Rail Baltica route.<ref>{{cite news|title=Eesti Rooma Klubi soovitab Rail Balticust loobuda|url=https://www.err.ee/322052/eesti-rooma-klubi-soovitab-rail-balticust-loobuda|work=ERR|date=15 November 2013|language=et}}</ref> Problems in the environmental assessment programme have also been claimed.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Arumäe|first1=Liisu|title=Expert says Rail Baltica endangers Tallinn drinking water|url=https://news.postimees.ee/2589316/expert-says-rail-baltica-endangers-tallinn-drinking-water|work=Postimees|date=7 November 2013|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
Criticism started after the feasibility study published by [[AECOM]] in 2011, with the government of Lithuania keen to include a link to Vilnius.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Barrow|first1=Keith|title=Governments edge towards consensus on Rail Baltica|url=http://www.railjournal.com/index.php/main-line/governments-edge-towards-consensus-on-rail-baltica.html|work=International Rail Journal|date=11 March 2014|language=en-gb}}</ref> The mayor of [[Tartu]], Estonia's second-largest city, called for the city to be included in the route.<ref>{{cite news|title=Current Rail Baltic route through Latvia publicly approved|url=https://news.err.ee/119874/current-rail-baltic-route-through-latvia-publicly-approved|work=ERR|date=30 November 2016|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Tartu-Valga Rail Baltic Route Should Be Considered, Says Tartu Mayor|url=http://news.err.ee/111389/tartu-valga-rail-baltic-route-should-be-considered-says-tartu-mayor|work=ERR|date=17 January 2014|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
In 2013, the [[:et:Eesti Rooma Klubi|Estonian Association]] for the [[Club of Rome]] advised the government to abandon the Rail Baltica route.<ref>{{cite news|title=Eesti Rooma Klubi soovitab Rail Balticust loobuda|url=https://www.err.ee/322052/eesti-rooma-klubi-soovitab-rail-balticust-loobuda|work=ERR|date=15 November 2013|language=et}}</ref> Problems in the environmental assessment programme have also been claimed.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Arumäe|first1=Liisu|title=Expert says Rail Baltica endangers Tallinn drinking water|url=https://news.postimees.ee/2589316/expert-says-rail-baltica-endangers-tallinn-drinking-water|work=Postimees|date=7 November 2013|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
In 2016 and 2017, three open letters <ref>[[:et:101 kiri|Open letter of 101 public persons requesting Estonian government to stop Rail Baltic]]</ref><ref>[[:et:152 kiri|Open letter of 152 public persons requesting Estonian government to stop Rail Baltic]]</ref><ref>[[:et:222 kiri|Open letter of 222 public persons requesting Estonian government to stop Rail Baltic]]</ref> were composed in Estonia by public persons including scientists, academics, and architects who called on the Estonian government and parliament to stop the project in its planned form. The main arguments in these letters were that the new track as a greenfield project will cause too much damage to nature and does not essentially improve the travelling possibilities. |
|||
In 2017, two Estonian environmental groups claimed that the lack of public participation on the decision made by Baltic governments and building of a new line, rather than upgrading the existing network, is in conflict with the [[Aarhus Convention]].<ref>{{cite news|title=Estonian ex-PM: Ratification of Rail Baltic accord will result in litigation|url=https://www.baltictimes.com/estonian_ex-pm__ratification_of_rail_baltic_accord_will_result_in_litigation|work=Baltic Times|date=15 June 2017|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
On 8 June 2017, Priit Humal, [[:et:Karli Lambot|Karli Lambot]], Illimar Paul and Raul Vibo, experts on logistics and engineering, published a critical analysis <ref>[http://avalikultrailbalticust.ee/PDF/RB%20EY%20errors.pdf Humal, Lambot, Paul, Vibo. Major mistakes in Rail Baltic CBA made by EY]</ref> of the Rail Baltica Cost-Benefit Analysis made by [[Ernst & Young|EY (formerly Ernst & Young)]] where they claimed that €4.1 billion of the stated socio-economic benefits are faulty and therefore the Rail Baltica project is neither feasible nor eligible for the EU financing. They asked the comments of RB RAIL AS, the Rail Baltica coordinator, who provided answers four months later.<ref>[http://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/ResponsetoARB_102017.pdf RB Rail AS Comments on MTÜ ARB’s questions]</ref> |
|||
In 2016 and 2017, three open letters were composed in Estonia which called on the Estonian government and parliament to stop the project in its planned form.<ref>[[:et:101 kiri|Open letter of 101 public people requesting the Estonian government stop Rail Baltic]] via et.wikipedia.org</ref><ref>[[:et:152 kiri|Open letter of 152 public people requesting the Estonian government stop Rail Baltic]] via et.wikipedia.org</ref><ref>[[:et:222 kiri|Open letter of 222 public people requesting the Estonian government stop Rail Baltic]] via et.wikipedia.org</ref> The main arguments in these letters were that the new track as a greenfield project will cause too much damage to nature and does not essentially improve travel possibilities. |
|||
On 18 September 2017, the meeting between Estonian pro-transparency NGO Avalikult Rail Balticust (MTÜ ARB, ''Openly About Rail Baltic'') and representatives of joint venture RB RAIL AS in Riga was cancelled as the latter did not allow the meeting to be recorded.<ref>[https://news.err.ee/619229/rb-rail-joint-venture-cancels-meeting-with-opposing-estonian-ngo RB Rail joint venture cancels meeting with opposing Estonian NGO]</ref> |
|||
On |
On 8 June 2017, Priit Humal, [[:et:Karli Lambot|Karli Lambot]], Illimar Paul, and Raul Vibo, experts on logistics and engineering, published a critical analysis of the Rail Baltica cost-benefit analysis made by [[Ernst & Young]], claiming that €4.1 billion of the stated socio-economic benefits are faulty and therefore the Rail Baltica project was neither feasible nor eligible for EU financing.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://avalikultrailbalticust.ee/PDF/RB%20EY%20errors.pdf |title=Humal, Lambot, Paul, Vibo. Major mistakes in Rail Baltic CBA made by EY |website=avalikultrailbalticust.ee}}</ref> They asked for comments from RB Rail AS, the Rail Baltica coordinator, who provided answers four months later.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/ResponsetoARB_102017.pdf|title=RB Rail AS Comments on MTÜ ARB's questions |website=www.railbaltica.org}}</ref> The authors of the first study claimed that the issues raised in their previous analysis were not adequately addressed in the official replies and that therefore Rail Baltica will be detrimental to society.<ref>[http://avalikultrailbalticust.ee/PDF/ARB_MMistakesRB_CBA_by_EY.pdf Humal, Lambot, Paul, Vibo. Major mistakes in Rail Baltica Cost-Benefit Analysis made by Ernst & Young Baltic] avalikultrailbalticust.ee</ref><ref>{{citation |url=http://www.railbaltica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/5609474-HR-to-Mr-Humal.pdf |publisher=European Commission Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport, Directorate B - Investment, Innovate & Sustainable Transport - The DIRECTOR |title=Re: Rail Baltica Project - Mr Humal Letter of 19 September 2017 |website=www.railbaltica.org |date=October 17, 2017 }}</ref> |
||
The authors of the critical analysis have been accused of having a conflict of interest, as one of the authors owns a logistics company. It has been claimed that Rail Baltica would decrease the volume of business for road transport businesses. The author has denied these claims.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.delfi.ee/news/paevauudised/eesti/tiibmanoover-valitsusparteid-kulutasid-katuseraha-rail-balticu-kohtus-takistamiseks?id=88866829 |title =Tiibmanööver: Valitsusparteid kulutasid katuseraha Rail Balticu kohtus takistamiseks |website=www.delfi.ee}}</ref> |
|||
On 10 April 2018, an open letter of 424 leading intellectuals of Estonia was published, suggesting to stop the whole plan in its current form.<ref>[https://arvamus.postimees.ee/4464987/400-avalik-kiri-valeinfo-pohjal-vastu-voetud-rail-balticu-seadus-tuleb-tuhistada?_ga=2.202947735.72904810.1520928695-495624083.1520928694 Cancel Rail Baltic in its current form.]</ref><ref>[https://news.postimees.ee/4467903/public-letter-of-the-400 English version of the public letter of the 400.]</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
* [[European route E67|Via Baltica]] (E67) |
* [[European route E67|Via Baltica]] (E67) |
||
* [[ |
* [[Helsinki–Tallinn Tunnel]] |
||
* [[Rail transport in Estonia]] |
* [[Rail transport in Estonia]] |
||
* [[Rail transport in Latvia]] |
* [[Rail transport in Latvia]] |
||
| Line 141: | Line 176: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Commons category}} |
|||
* [http://railbaltica.org/ Official website] - Global Project |
|||
* {{YouTube|3yBM_mgDkzs|Zoom in on Rail Baltica}} |
|||
* [http://rbestonia.ee/ Official website] – Estonian section |
|||
* {{YouTube|l2B85SQc0j0|The EU’s €5.8BN Railway to Secure Europe}} |
|||
* [http://edzl.lv/ Official website] – Latvian section |
|||
* {{YouTube|FgX1Ml2K3yc|Rail Baltica Riga/ Construction of the Central Station Riga/ Latvia/ European Mega Project Update}} |
|||
* [http://www.rail-baltica.lt/ Official website] – Lithuanian section |
|||
* {{YouTube|UIltcI7cfZ0|Rail Baltica Ülemiste ühisterminal}} |
|||
* [http://www.rail-baltica.pl/ Official website] – Polish section |
|||
* {{YouTube|GzXaFj5EOq8|Rail Baltica Central Station Project in Riga}} |
|||
* Rail Baltica Growth Corridor: [http://www.rbgc.eu/contents-2/rb-growth-strategy-wp7/rail-baltica-directory.html Rail Baltica directory] |
|||
* {{YouTube|xmJfOWFHyMU|Rail Baltica station at the Riga International Airport}} |
|||
* Rail Baltica Growth Corridor: [http://www.rbgc.eu/media/kick_off/kakulis.pdf A Feasibility Study] – kick-off presentation, 9 June 2011 |
|||
* [http://railbaltica.org/ Official website] – Rail Baltica Global Project |
|||
* [https://www.openstreetmap.org/relation/12646139#map=6/56.165/24.644 ''Planned route of Rail Baltica on Open Street Map''] |
|||
* European Commission: [http://ec.europa.eu/ten/transport/coordinators/index_en.htm Progress report on Rail Baltica compiled by the European coordinator of the project] Pavel Telička, July 2007 – July 2008 |
* European Commission: [http://ec.europa.eu/ten/transport/coordinators/index_en.htm Progress report on Rail Baltica compiled by the European coordinator of the project] Pavel Telička, July 2007 – July 2008 |
||
* [http://www.green-ten-t.eu/core-networks/corridor-1/ Information about Rail Baltica on the TEN-T website of Greens/EFA in the European Parliament] |
* [http://www.green-ten-t.eu/core-networks/corridor-1/ Information about Rail Baltica on the TEN-T website of Greens/EFA in the European Parliament] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190602141406/http://www.green-ten-t.eu/core-networks/corridor-1/ |date=2019-06-02 }} |
||
* European Commission: [http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/sources/docgener/evaluation/railbaltica/concl_en.PDF Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways – Main conclusions and recommendations] January 2007 |
* European Commission: [http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/sources/docgener/evaluation/railbaltica/concl_en.PDF Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways – Main conclusions and recommendations] January 2007 |
||
* European Commission: [http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/sources/docgener/evaluation/railbaltica/annex.PDF Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways – Annexes] January 2007 |
* European Commission: [http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/sources/docgener/evaluation/railbaltica/annex.PDF Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways – Annexes] January 2007 |
||
* |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20130211090319/http://tentea.ec.europa.eu/en/ten-t_projects/30_priority_projects/priority_project_27/priority_project_27.htm Priority Project 27] |
||
* [http://www.baltic-course.com/eng/transport/?doc=117782 Baltic countries' agreement on Rail Baltica project to be signed at the beginning of summer] |
* [http://www.baltic-course.com/eng/transport/?doc=117782 Baltic countries' agreement on Rail Baltica project to be signed at the beginning of summer] |
||
{{Trans-European Transport Networks |state=expanded}} |
{{Trans-European Transport Networks |state=expanded}} |
||
{{Higher-speed rail |state=collapsed}} |
{{Higher-speed rail |state=collapsed}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:European Union transport policy]] |
|||
[[Category:Rail transport in Estonia]] |
[[Category:Rail transport in Estonia]] |
||
[[Category:Rail transport in Latvia]] |
[[Category:Rail transport in Latvia]] |
||
| Line 167: | Line 208: | ||
[[Category:Higher-speed rail]] |
[[Category:Higher-speed rail]] |
||
[[Category:High-speed rail in Europe]] |
[[Category:High-speed rail in Europe]] |
||
[[Category:Proposed transport infrastructure in Estonia]] |
|||
[[Category:Proposed transport infrastructure in Latvia]] |
|||
[[Category:Proposed transport infrastructure in Lithuania]] |
|||
[[Category:Projects of the Three Seas Initiative]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 18:24, 6 January 2025
| Rail Baltica | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Overview | |
| Locale | Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland |
| Website | www |
| Service | |
| Type | Public high-speed railway |
| System | Rail Baltica (European gauge railway) |
| Services | Tallinn–Pärnu–Riga–Riga International Airport–Panevėžys–Kaunas/Vilnius–Lithuania/Polish Border |
| History | |
| Planned opening |
|
| Technical | |
| Number of tracks | Double track |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge (primary) |
| Electrification | 25 kV 50 Hz AC overhead line[1] |
| Operating speed |
|
| Signalling | ERTMS L2 |
Rail Baltica is an under-construction rail infrastructure project that is intended to integrate the Baltic states in the European rail network.[3] Its purpose is to provide passenger and freight service between participating countries and improve rail connections between Central and Northern Europe, specifically the area southeast of the Baltic Sea. It is also intended as a catalyst for building the economic corridor in Northeastern Europe. The project envisages a continuous rail link from Tallinn (Estonia) to Warsaw (Poland), consisting of links via Riga (Latvia), Kaunas, and Vilnius (Lithuania). Its total length in the Baltic States is 870 kilometres (540 mi), with 213 kilometres (132 mi) in Estonia, 265 kilometres (165 mi) in Latvia, and 392 kilometres (244 mi) in Lithuania.[4] Rail Baltica is one of the priority projects of the European Union (EU). It is part of the North Sea–Baltic Corridor of the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T).
Rail Baltica will add the first large-scale mainline standard gauge railway in the area. Legacy rail networks in Finland, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania are mainly in Russian gauge (1,520 mm). These countries' first railways were built in the second half of the 19th century while part of the Russian Empire. While some railways were built or converted to narrow or standard gauge between World War I and World War II in the independent or German-occupied Baltic states, these were later converted back to Russian gauge under Soviet occupation rule after 1945.
According to a study produced by Ernst & Young, the measurable socio-economic benefits are estimated at €16.2 billion.[5]: 186 The assessed GDP multiplier effect the Rail Baltica Global Project would create is an additional €2 billion.[5]: 203 As of January 2020[update], the high-speed railway connection from Tallinn to the Lithuanian-Polish border was expected to be completed by 2026.[6] In 2020, a private consortium claimed that it could open an undersea railway tunnel between Tallinn and Helsinki by mid-2026,[7] but this project has been put on hold indefinitely.[8]
Overview
[edit]Proposed environmental impact
[edit]Rail Baltica will be an electric railway, motivated by a desire to reduce carbon emissions. The railway has been planned to avoid Natura 2000 protected areas, in addition to minimising impacts on other environmentally sensitive protected areas and existing 1,520 mm gauge railway networking areas. Wherever necessary, noise protection barriers will be installed. Special animal passages will be built through the embankment.[9]
Stations
[edit]The railway project will enable intermodality and multimodality, i.e. transportation of freight through two or more methods of transportation. Rail Baltica includes plans for three multimodal freight terminals located in Muuga Harbour (Estonia), Salaspils (Latvia), and Kaunas (Lithuania). This is intended to create synergies with the existing 1,520 mm railway system infrastructure. There will be seven international passenger stations—in Tallinn, Pärnu, Riga, Riga Airport, Panevežys, Kaunas, and Vilnius—with potential regional stations and connections to airports and seaports.[9]
The section from Helsinki to Tallinn will be operated by existing commercial ferries. A proposed Helsinki to Tallinn Tunnel was considered to provide a rail link between the two cities.[10] At the end of April 2021, governments of Estonia and Finland signed a memorandum of understanding committing themselves to cooperation in the area of transport. In February 2024, the tunnel was judged by Finnish Minister of Transport and Communications, Lulu Ranne to be unrealistic and that it was not on the agenda of the government.[8]
Parameters
[edit]
Rail Baltica will be built as a new, publicly owned, fast conventional double-track railway. If the railway runs freight trains, it will be quadruple-track. It will be electrified and equipped with the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS) for signalling and communications. The maximum design speed is 249 km/h (155 mph) for passenger trains, while the maximum operational speed will be 234 km/h (145 mph).[11] For freight trains, the maximum design speed is 120 km/h (75 mph). The new railway line will be designed with a 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) gauge. Other key technical parameters include:[12]
- The maximum freight train length will be 1,050 m (3,440 ft).
- The maximum axle load will be 25 tonnes (25 long tons; 28 short tons).
- No level crossings with roads.
- No flat crossings with the 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) (Russian gauge) rail network.
- For maintenance and emergency services, access to the main line should be every 2–3 km (1.2–1.9 mi) and in specific areas.
- The railway will have ballasted track.
- Its energy system should be 25 kV.
- Its double track side should be right-hand running.
- It is ERTMS Level 2, Baseline 3.
The network's parameters are in accordance with the EU Technical Specifications for Interoperability (TSI – P2, F1).[13][14]
The design phase began in 2016, with design activities at the Riga Central Passenger Station and the Riga International Airport passenger station in Latvia to be continued until 2023. Meanwhile, the construction of the Rail Baltica infrastructure started in 2019, the first operations should start on some of the sections by 2028 and the overall corridor should be completed by 2030.[3][15][16]
The overall length of the railway between Tallinn and Warsaw will be at least 950 km (590 mi), while the length within the Baltic States proper will be 870 km (540 mi).[4]
Status
[edit]In 2017, all three Baltic parliaments ratified the Inter-Governmental Agreement for the Rail Baltica project, thereby confirming their long-term commitment to the project.[16] In addition, Rail Baltica Global Project's cost-benefit analysis was delivered by Ernst & Young and Atkins International experts, based on the European Union's CBA guidelines. The analysis showed that the project was financially feasible and viable, and its measurable benefits would outweigh the costs.[5]
In August 2016, the spatial planning for the entire Rail Baltica railway line was approved in Latvia by the decision of the Latvian Government. This was followed by the approval of the Lithuanian Government in January 2017 for their respective section from Kaunas to the border with Latvia. The route for the section from Kaunas to the border with Poland, known as Rail Baltica I, is subject to the results of an Upgrade Feasibility Study. On 14 February 2018, the Ministry of Public Administration of the Republic of Estonia approved the spatial plan for the line in Estonia, leading to the setting of the final route and preliminary design of the railway in the country. With Estonia's decision, the spatial territorial planning and preliminary technical design of the Rail Baltica railway in the Baltic states was finalised.[17]
The Rail Baltica project entered the design phase in all three Baltic States with the approval of detailed design guidelines. Certain sections have finished consolidating preliminary technical design, tendering the detailed technical design services, and preparing a BIM strategy. On 20 March 2018, the first Rail Baltica construction design and supervision contract—for Rail Baltica's Riga International Airport railway station, related infrastructure, and viaduct—was signed by Eiropas Dzelzceļa līnijas SIA and PROSIV, the winner of the open international tender and a partnership of suppliers from three countries: Prodex (Slovakia), Sintagma (Italy), and Vektors T (Latvia).[18]
In 2018, studies related to commercialisation and supply materials were finalised, including a long-term business plan, an operational plan, an infrastructure management study, and an upgraded feasibility study of the European gauge railway line from Kaunas to the Lithuanian–Polish border.[19] In 2019, the first cornerstone of Rail Baltica was laid in Estonia to mark the beginning of construction of the Saustinõmme viaduct. Also, detailed technical design contracts were signed for the following sections: Tallinn–Rapla and Pärnu–Rapla in Estonia, Kaunas–Ramygala and Ramygala–Latvian/Lithuanian border in Lithuania, and Vangaži–Salaspils–Misa and the main line through Riga in Latvia.[20] With the contracts signed, geotechnical research was started in different sections of the railway in order to gather information about the soil.
In 2020, the development of detailed technical design had progressed to cover 643 km (400 mi) of the main track, which included all railway sections in Estonia and Latvia as well as sections from Kaunas to the Latvian/Lithuanian border in Lithuania.[20]
In Estonia, discussions about environmental impact assessment were started and meetings were planned until the end of 2020. During the discussions, people were invited to ask questions regarding the project's environmental impact, while various technical solutions were presented.[21]
In Latvia, the Riga Central Station construction was officially started with ceremonies on 23 November 2020.[22] On the 3rd of February 2021, the project implementer of Riga Airport Station was also chosen; construction began in May 2021 and is ongoing as of July 2023[update].[23] Talks with NGOs in Riga were started to discuss technical solutions within the city, especially for infrastructure elements such as crossings and overpasses.[24]
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has raised the importance of this European project, because of the connectivity across Europe that it will create, for civilian and military travel. Lithuania has a new commission to speed construction within the cities (freight terminal facilities and passenger depot). Estonia faces cost increases and construction delays.[25]
As of 2023[update], the project completion is scheduled for 2030, with services starting in 2028 on some sections.[26]
Project implementers
[edit]The Rail Baltica project is being implemented by the three Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. Finland announced in February 2019 that it will also join the project.[27][28][29][30]
The beneficiaries of the Rail Baltica project are ministries of the three Baltic States: Estonia's Ministry of Economic Affairs and Communications, Latvia's Ministry of Transport, and Lithuania's Ministry of Transport and Communications. In 2014, they established RB Rail AS, a joint venture that acts as the main coordinator and project implementer for the project. Its main business is the design, construction, and marketing of the railway. RB Rail AS also submits EU financing proposals for the Rail Baltica purchasing body for all parties for the procurement of studies, plans, designs for the Global Project, sub-systems (control, command, and signalling and energy/electrification), raw materials, key components, and cross-border track sections.[31]
Rail Baltic Estonia OU in Estonia, Eiropas Dzelzceļa līnijas SIA in Latvia, and Rail Baltica statyba UAB and LtgInfra in Lithuania are the national implementing bodies.[28] All construction carried out by the implementing bodies is done under the supervision of RB Rail AS and is based on common procurement principles, rules, and contract templates.[32]
Financing
[edit]
A feasibility study of Rail Baltica in the three Baltic States carried out by AECOM in May 2011 estimated a cost of €3.6 billion for the railway and proved that Rail Baltica is economically viable. Based on that study, key political and practical decisions—both on the national and EU level—were made to implement Rail Baltica.[33]
Since the AECOM study, the project has grown to include additional elements to the Rail Baltica Global Project for better connectivity, passenger mobility, and inter-modality. These additions include routing the Rail Baltica passenger mainline through the Riga International Airport and the construction of the airport passenger station (Latvia), the Kaunas–Vilnius connection (Lithuania), an improved connection in Kaunas (Lithuania), and the construction of the Ülemiste–Tallinn airport tram line (Estonia). Moreover, the preparation of environmental impact assessments, spatial planning, and some preliminary designs has provided better investment estimations for the project.[5]
Thus, in April 2017, the overall cost of the Rail Baltica Global Project implementation in all three countries—including the construction of the Kaunas–Vilnius section—was estimated to be €5.8 billion, according to a cost-benefit study carried out by Ernst & Young.[34] According to the analysis, the project's economic feasibility and social benefits were still proved, providing the necessary updated parameters for continued EU and national co-financing of the project.[5]
The project's profitability lies in its wider socio-economic benefits, which Ernst & Young estimated to be around €16.22 billion.[35] In addition, several immeasurable (mostly catalytic) benefits would be created through regional integration, such as tourism development, new business creation, increased attractiveness to FDI, access to new export markets, technological transfer, and innovation.
The project is financed by the member states, the European Union TEN-T budget, and the Structural and Cohesion Funds provided to the EU New Member States.[36] By the start of 2018, the three Baltic States and RB Rail AS had received two grants totaling €765 million designed under the CEF for the construction of the Rail Baltica railway. On 13 July 2018, a third grant agreement was signed for an additional €130 million, of which €110 million was CEF contribution.[37] In July 2020, another CEF funding was received, amounting to €216 million for construction, technical design, and planning works.[38] In total, the project has received around €1.2 billion from the EU and national funds.
In October 2023 Rail Baltica joint venture of the Baltic States, RB Rail AS, announced the signing of an additional cross-border Grant Agreement for Connecting Europe Facility (CEF) funding, which amounted to 928 million euros CEF support. This substantial funding, combined with national co-financing from the three Baltic States, will exceed 1.1 billion euros, enabling necessary activities for further high-speed infrastructure development.[39]
Route and standard
[edit]
The planning phase of Rail Baltica took place from 2010 to 2017.[citation needed] In 2011, the three Baltic States agreed on a route connecting Tallinn, Pärnu, Riga, Panevėžys, and Kaunas.[40] A feasibility study for this option estimated the line would cost about €3.68 billion in total.[41]
During the planning of the location of the project route in the Baltic States, a conceptual agreement among the three countries was reached that the railway should be as straight as possible, as this provides the highest benefits at the lowest cost. The shorter and more direct the route is, the faster traffic it can ensure, which economically has the highest advantage compared to its alternatives. This was confirmed by an AECOM study in 2013.[citation needed]
Initially, two options were considered. Both options included upgrading the existing standard gauge railway to enable travel speeds of up to 160 km/h (99 mph) along the stretch in Poland from Warsaw via Białystok and Ełk to Trakiszki,[42] followed by a new railway with standard gauge from Trakiszki to Kaunas. For the remainder of the route to Tallinn, two different options were considered:
- The first option was to upgrade the existing state-owned Tallinn–Tartu–Riga–Joniškis railway to 160 km/h (maintaining its Russian gauge) and build a new state-owned railway from Joniškis–Kaunas with 160 km/h, also at Russian gauge. However, because of the break of gauge at Kaunas, passengers would have to change trains there. For freight, a reloading facility or a bogie exchange station would be placed near Kaunas. This option was already completed as Rail Baltica I.[citation needed]
- The second option was a new standard gauge railway with 200 km/h (120 mph) speed and 3 kV DC power (the same voltage as in Poland) from Kaunas via Joniškis to Riga, as above, but then continuing in a shorter, straighter line via Pärnu to Tallinn.[42] This option was chosen as the preferred route. The existing Lelle–Pärnu line in Estonia was permanently closed for passenger operations on 9 December 2018,[43] as it required a €17 million refurbishment.[44]
The Šiauliai–Latvian border rail section (using broad gauge) was newly built and scheduled to be finished in 2015[needs update] with an estimated cost of €270 million. In Latvia, the existing railway upgrade between Riga and Valka was finished in 2016 at a cost of €97 million. The EU contributed about 25% of the cost for the three parts.[citation needed]
Construction (2017–present)
[edit]


In 2017, the parliaments of the three Baltic States ratified the intergovernmental agreement on Rail Baltica, stating that the "route shall be from Tallinn through Pärnu–Riga–Panevėžys–Kaunas to the Lithuanian/Polish state border with a connection of Vilnius–Kaunas as a part of the railway"[16] and defining a design speed of 240 km/h for passenger travel. Thus, the Rail Baltica Global Project route was aligned from Tallinn until Kaunas, with the pre-existing European gauge railway line section from Kaunas to the Lithuanian/Polish border being subject to the results of the Upgrade Feasibility Study.[45] Nevertheless, in April 2018, the Ministries of the three Baltic States approved the design guidelines of Rail Baltica, which state that the maximum design speed will be 249 km/h and maximum operational speed should be 234 km/h.[46]
For the Kaunas (Jiesia)–Lithuanian/Polish border section, a 78.1 km route named "alternative 6A" was approved in May 2022 by the Lithuanian Ministry of Transport and Communications, taking into account the opinion of the majority of the local residents.[4][47] This optimal route is the shortest among the alternatives which were proposed and the most remote from the urban areas.
The Polish section of Rail Baltica is being upgraded to allow passenger trains to run at 200 km/h.[48] The Ełk–state border section may be built to allow 250 km/h and may be electrified using the 25 kV AC system.[49]
On 29 February 2024, construction on the Rail Baltica Riga Central Railway Station reached the rooftop, which was celebrated with a ceremony according to Latvian tradition. This train station is expected to become the busiest in the Baltics once Rail Baltica is fully operational.[50]
Rail Baltica I
[edit]The name "Rail Baltica" is also sometimes used to mean the first phase of European gauge railway construction from the Poland/Lithuania border to Kaunas in Lithuania. It was inaugurated on 16 October 2015. The project, which built one track at European standard-gauge alongside the existing Russian gauge tracks, cost €380 million. The 119 km line accommodates diesel trains, with passenger trains running at up to 120 km/h and freight trains at up to 80 km/h. Higher speeds will depend on future electrification, a new signal system, and more level crossing gates. In June 2016, Lithuanian Railways and Polregio started weekend passenger train service between Kaunas and Białystok.[51]
In Estonia and Latvia, implementation of the Rail Baltica I project included upgrades of the existing rail lines in the region.[52] The 66-kilometre-long (41 mi) Russian gauge line from Tartu to Valga (on the Latvian border) in Estonia was renovated between 2008 and 2010. The work was done by the Finnish VR Group for a cost of €40 million.[53][54]
Benefits
[edit]The Baltic railway infrastructure will be connected to the European railway corridor, ensuring high-speed passenger travel and freight movement. Rail Baltica creates the possibility to shift the major freight transport in the regions from road to rail, which is currently being transported towards Russia and then north by heavy trucks. In the case of Poland, trucks follow local roads and directly cross the villages of Podlaskie Voivodeship.[citation needed]

According to the 2017 cost-benefit study by Ernst & Young, the benefits from Rail Baltica are calculated to be:
- €7.1 billion saved in climate change and noise reduction
- 30–40% relevant truck traffic flow shifted to railways
- 13,000 jobs created during the construction phase
- €5.3 billion saved for passenger and freight travel
- 5.3 million passenger hours saved
- 400 human lives saved in 29 years
All in total, measurable socio-economic benefits are estimated at €16.2 billion. The assessed GDP multiplier effect the Rail Baltica Global Project would create is an additional €2 billion. It is also claimed there will be "substantial unmeasurable benefits".[5]
In late April 2022, implementers of the Rail Baltica project presented the progress at the European Parliament where the strategic and geopolitical security importance of the project was stressed repeatedly in reference to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[55]
Criticism
[edit]Criticism started after the feasibility study published by AECOM in 2011, with the government of Lithuania keen to include a link to Vilnius.[56] The mayor of Tartu, Estonia's second-largest city, called for the city to be included in the route.[57][58]
In 2013, the Estonian Association for the Club of Rome advised the government to abandon the Rail Baltica route.[59] Problems in the environmental assessment programme have also been claimed.[60]
In 2017, two Estonian environmental groups claimed that the lack of public participation on the decision made by Baltic governments and building of a new line, rather than upgrading the existing network, is in conflict with the Aarhus Convention.[61]
In 2016 and 2017, three open letters were composed in Estonia which called on the Estonian government and parliament to stop the project in its planned form.[62][63][64] The main arguments in these letters were that the new track as a greenfield project will cause too much damage to nature and does not essentially improve travel possibilities.
On 8 June 2017, Priit Humal, Karli Lambot, Illimar Paul, and Raul Vibo, experts on logistics and engineering, published a critical analysis of the Rail Baltica cost-benefit analysis made by Ernst & Young, claiming that €4.1 billion of the stated socio-economic benefits are faulty and therefore the Rail Baltica project was neither feasible nor eligible for EU financing.[65] They asked for comments from RB Rail AS, the Rail Baltica coordinator, who provided answers four months later.[66] The authors of the first study claimed that the issues raised in their previous analysis were not adequately addressed in the official replies and that therefore Rail Baltica will be detrimental to society.[67][68]
The authors of the critical analysis have been accused of having a conflict of interest, as one of the authors owns a logistics company. It has been claimed that Rail Baltica would decrease the volume of business for road transport businesses. The author has denied these claims.[69]
See also
[edit]- Via Baltica (E67)
- Helsinki–Tallinn Tunnel
- Rail transport in Estonia
- Rail transport in Latvia
- Rail transport in Lithuania
- Rail transport in Poland
- Rail transport in the European Union
- Pan-European Corridor I
References
[edit]- ^ "Technical Parameters". RB Rail AS. Retrieved 2017-10-11.
- ^ "Technical Parameters". Rail Baltica Global Project.
- ^ a b "Rail Baltica – Project of the Century". www.railbaltica.org.
- ^ a b c Route alternative approved for the future construction of the Rail Baltica railway from Kaunas to the border with Poland, railbaltica.org, 12 May 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f EY. "Rail Baltica Global Project Cost-Benefit Analysis Final Report" (PDF). www.railbaltica.org.
- ^ "Implementation of Rail Baltic by 2026 remaining target for RB Rail". The Baltic Times. 7 January 2020. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ David Burroughs (18 June 2020). "Finnish regional council delays Finland – Estonia undersea rail tunnel". International Railway Journal. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ a b Kapper, Külli (8 February 2024). "INTERVJUU > Soome minister: Tallinna ja Helsingi vaheline tunnel on ebarealistlik" [INTERVIEW > Minister of Finland: The tunnel between Tallinn and Helsinki is unrealistic]. Postimees (in Estonian). Retrieved 12 February 2024.
- ^ a b "Rail Baltica – Project of the Century". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ "Helsinki-Tallinn Rail Tunnel Link?". YLE News. 31 October 2008. Archived from the original on 4 April 2008. Retrieved 11 May 2008.
- ^ "Technical Parameters". Rail Baltica Global Project.
- ^ "Rail Baltica - Design Guidelines" (PDF). www.railbaltica.org. 2018-04-11. Retrieved 2022-01-28.
- ^ "Rail Baltica Design Guidelines Approved | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. 2018-05-03. Retrieved 2022-01-28.
- ^ "Technical Specifications for Interoperability". European Union Agency for Railways. October 2018. Retrieved 2022-01-28.
- ^ "Rail Baltica is your future | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ a b c "AGREEMENT OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE RAIL BALTIC/RAIL BALTICA RAILWAY CONNECTION" (PDF).
- ^ "Route setting and spatial territorial planning for Rail Baltica railway finalised in all three Baltic states | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ "The first Rail Baltica construction design and supervision contract signed in the Baltics - Edzl". edzl.lv (in Latvian). Archived from the original on 2018-08-06. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ "Annual Press Conference of the Rail Baltica implementers | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ a b "Interactive map". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2020-09-21.
- ^ "Kõrvek: Conducting Rail Baltica's environmental impact assessment discussions electronically has proven itself useful | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2020-09-21.
- ^ "The Start of Construction of Rail Baltica Central Hub in Riga | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- ^ "At Riga International Airport, the construction of the Rail Baltica passenger terminal's reinforced concrete structures and railway platforms is underway | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. 2023-07-05. Retrieved 2023-12-06.
- ^ "Publiskā diskusija "Rail Baltica kā projekts Rīgas attīstībai" | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org (in Latvian). Retrieved 2020-09-21.
- ^ Tunnicliffe, Andrew (March 7, 2023). "How Rail Baltica is making progress". Railway Technology. Retrieved June 30, 2023.
In addition, projected costs for the multi-billion-Euro project continue to rise above initial estimates. At the end of 2022, it was reported costs for the Estonia section alone were expected to be €1.8bn, almost double what had originally been projected. Speaking to Estonia's daily newspaper, Postimees, Anvar Salomets, Chair of the board at RB Eesti, acknowledged the difficulties this section had faced, saying: "It is indeed the case that the design of the main route of the railway has proved difficult."
- ^ Rail Baltica – Project of the Century" on the Rail Baltica official website, accessed on 26 April 2023.
- ^ Estonian Public Broadcasting, BNS | (2019-02-03). "Finland to formally join Rail Baltica joint venture". ERR. Retrieved 2019-02-15.
- ^ a b "Finland to join the Rail Baltica Joint Ventures as a shareholder | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. 2019-02-05. Retrieved 2019-02-15.
- ^ "Finland will take part in Rail Baltica". RailTech.com. 2019-02-04. Retrieved 2019-02-15.
- ^ Shah, Shakhil (2019-02-05). "Finland hops on board Rail Baltica". Emerging Europe. Retrieved 2019-02-15.
- ^ "Main Coordinator". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ "Project Implementers". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ "Rail Baltica Final Report" (PDF).
- ^ ERR (3 April 2017). "Rail Baltic to cost €5.8 billion". ERR.
- ^ ERR (25 April 2017). "Analysis: Rail Baltic project to have €3.96 billion gap". ERR.
- ^ "Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T): selection of projects for the TEN-T multi-annual programme 2007–2013 and the annual TEN-T programme 2007" (Press release). European Union. 21 November 2007.
- ^ "Third CEF Grant Agreement for Rail Baltica Global project signed". Rail Baltica. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- ^ "Rail Baltica receives next round of funding | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2020-09-21.
- ^ "Rail Baltica cleared to receive another billion euros". Public broadcasting of Latvia. 18 October 2023.
- ^ "Rail Baltica's fate to become clearer by the end of May" (PDF). March 2011.
- ^ "Project Rail Baltica would cost EUR 3.68 bln". June 2011.
- ^ a b "Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways" (PDF). European Commission, Directorate-General for Regional Policy. January 2007.
- ^ "Estonia to close railway line and wait for Rail Baltica". Baltic News Network. 6 November 2018.
- ^ ERR News. Tallinn-Pärnu railway line to be closed permanently in December. news.err.ee accessed 7 June 2019
- ^ "Rail Baltica Route Setting in the Baltics | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ "Rail Baltica Design Guidelines Approved | Rail Baltica". www.railbaltica.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- ^ "Tekstiniai Priedai (Text Attachments) (planning document comparing several alternative routes for the Kaunas (Jiesia) - Lithuanian-Polish border section)" (PDF). February 2022. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-03-31. Retrieved 2022-05-18 – via Government of Lithuania.
- ^ Madrjas, Jakub (24 January 2020). "Zmieniona koncepcja Rail Baltiki w Polsce. Nowy przebieg i obwodnica Białegostoku" [Amended concept of Rail Baltica in Poland. New route and Białystok bypass]. Rynek Kolejowy (in Polish).
- ^ Madrjas, Jakub (25 July 2019). "Adamczyk: Zmieniamy projekt Rail Baltica na prośbę Komisji Europejskiej. Będzie 250 km/h?" [Adamczyk: following European Commission request, we amend Rail Baltica project. Will there be 250 km/h?]. Rynek Kolejowy (in Polish).
- ^ "The rooftop ceremony of Rail Baltica at Riga Central Station was celebrated". baltictimes.com. 1 March 2024. Retrieved 19 April 2024.
- ^ "Lithuanian, Polish railways to launch Kaunas-Bialystok passenger route in June". The Baltic Course. 31 May 2016.
- ^ "Priority Project 27". Innovation and Networks Executive Agency - European Commission.
- ^ "Mid-Term Review" (PDF). Detailed report from 2010. 2010. pp. 161–172 (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF, 65 MB) on 2012-11-03.
- ^ VR Group (28 April 2008). "VR-Track wins superstructure renovation contract for Tartu-Valga track" (Press release). Finland.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Rail Baltica global project progress presented at the European Parliament: necessity of swift implementation of Rail Baltica and EU added value clearer than ever (26 April 2022)
- ^ Barrow, Keith (11 March 2014). "Governments edge towards consensus on Rail Baltica". International Rail Journal.
- ^ "Current Rail Baltic route through Latvia publicly approved". ERR. 30 November 2016.
- ^ "Tartu-Valga Rail Baltic Route Should Be Considered, Says Tartu Mayor". ERR. 17 January 2014.
- ^ "Eesti Rooma Klubi soovitab Rail Balticust loobuda". ERR (in Estonian). 15 November 2013.
- ^ Arumäe, Liisu (7 November 2013). "Expert says Rail Baltica endangers Tallinn drinking water". Postimees.
- ^ "Estonian ex-PM: Ratification of Rail Baltic accord will result in litigation". Baltic Times. 15 June 2017.
- ^ Open letter of 101 public people requesting the Estonian government stop Rail Baltic via et.wikipedia.org
- ^ Open letter of 152 public people requesting the Estonian government stop Rail Baltic via et.wikipedia.org
- ^ Open letter of 222 public people requesting the Estonian government stop Rail Baltic via et.wikipedia.org
- ^ "Humal, Lambot, Paul, Vibo. Major mistakes in Rail Baltic CBA made by EY" (PDF). avalikultrailbalticust.ee.
- ^ "RB Rail AS Comments on MTÜ ARB's questions" (PDF). www.railbaltica.org.
- ^ Humal, Lambot, Paul, Vibo. Major mistakes in Rail Baltica Cost-Benefit Analysis made by Ernst & Young Baltic avalikultrailbalticust.ee
- ^ "Re: Rail Baltica Project - Mr Humal Letter of 19 September 2017" (PDF), www.railbaltica.org, European Commission Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport, Directorate B - Investment, Innovate & Sustainable Transport - The DIRECTOR, October 17, 2017
- ^ "Tiibmanööver: Valitsusparteid kulutasid katuseraha Rail Balticu kohtus takistamiseks". www.delfi.ee.
External links
[edit]- Zoom in on Rail Baltica on YouTube
- The EU’s €5.8BN Railway to Secure Europe on YouTube
- Rail Baltica Riga/ Construction of the Central Station Riga/ Latvia/ European Mega Project Update on YouTube
- Rail Baltica Ülemiste ühisterminal on YouTube
- Rail Baltica Central Station Project in Riga on YouTube
- Rail Baltica station at the Riga International Airport on YouTube
- Official website – Rail Baltica Global Project
- Planned route of Rail Baltica on Open Street Map
- European Commission: Progress report on Rail Baltica compiled by the European coordinator of the project Pavel Telička, July 2007 – July 2008
- Information about Rail Baltica on the TEN-T website of Greens/EFA in the European Parliament Archived 2019-06-02 at the Wayback Machine
- European Commission: Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways – Main conclusions and recommendations January 2007
- European Commission: Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways – Annexes January 2007
- Priority Project 27
- Baltic countries' agreement on Rail Baltica project to be signed at the beginning of summer
- European Union transport policy
- Rail transport in Estonia
- Rail transport in Latvia
- Rail transport in Lithuania
- Rail infrastructure in Poland
- Proposed rail infrastructure in Europe
- Higher-speed rail
- High-speed rail in Europe
- Proposed transport infrastructure in Estonia
- Proposed transport infrastructure in Latvia
- Proposed transport infrastructure in Lithuania
- Projects of the Three Seas Initiative
