Ben Gurion Airport: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 883523762 by 79.176.49.10 (talk) |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Added date. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Dominic3203 | Linked from User:Mako001/sandbox | #UCB_webform_linked 910/3639 |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Short description|Main international airport of Israel}} |
||
{{Redirect| |
{{Redirect|Lod airport|the airport in Vanuatu with IATA code LOD|Longana Airport|first suicide attack on Israel|Lod Airport massacre}} |
||
{{Redirect| |
{{Redirect|Tel Aviv Airport|the closed airport that also served Tel Aviv|Sde Dov Airport}} |
||
{{Use dmy dates|date= |
{{Use dmy dates|date=June 2022}} |
||
{{Infobox airport |
{{Infobox airport |
||
| name = Ben Gurion Airport |
| name = Ben Gurion International Airport |
||
| nativename = {{ |
| nativename-a = {{nobold|{{lang|he|{{Script/Hebrew|נמל התעופה בן-גוריון}}}}<br />}} |
||
| image = IAA-Logo-Transparent.png |
|||
| image = <!--airport logo--> |
|||
| image-width = |
| image-width = 250 |
||
| image2 = File:Ben-gurion-airport-terminal--september-2012 |
| image2 = File:Ben-gurion-airport-terminal--september-2012.jpg |
||
| image2-width = 250 |
| image2-width = 250 |
||
| IATA = TLV |
| IATA = TLV |
||
| ICAO = LLBG |
| ICAO = LLBG |
||
| type = Public |
| type = Public |
||
| owner = [[Ministry of Transport and Road Safety]] |
|||
| owner = |
|||
| operator = [[Israel Airports Authority]] |
| operator = [[Israel Airports Authority]] |
||
| location = [[Central District (Israel)|Central District]], |
| location = [[Central District (Israel)|Central District]], Israel |
||
| city-served = [[Gush Dan]] and [[Greater Jerusalem]]<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.timesofisrael.com/jerusalems-new-high-speed-train-starts-regular-trips-to-ben-gurion-airport/ |title=Jerusalem's new high-speed train starts regular trips to Ben Gurion Airport |date=25 September 2018 |newspaper=[[The Times of Israel]] |location=[[Jerusalem]]|access-date=1 June 2019}}</ref> |
|||
| hub = |
|||
| hub = {{Plainlist| |
|||
*[[Arkia]] |
*[[Arkia]] |
||
*[[CAL Cargo |
*[[CAL Cargo Airlines]] |
||
*[[El Al]] |
*[[El Al]] |
||
*[[Israir Airlines]] |
*[[Israir Airlines]] |
||
*[[Sun |
*[[Sun d'Or]] |
||
| elevation-f = 134 |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|32|00|34|N|034|52|58|E|region:IL|display=inline,title}} |
|||
| pushpin_map = Israel |
|||
| pushpin_label = TLV |
|||
| pushpin_map_caption = Location within Israel |
|||
| website = [http://www.iaa.gov.il/en-US/airports/bengurion/Pages/default.aspx iaa.gov.il] |
|||
| metric-rwy = yes |
|||
| r1-number = 03/21 |
|||
| r1-length-m = 2772 |
|||
| r1-surface = [[Asphalt]] |
|||
| r2-number = 08/26 |
|||
| r2-length-m = 4062 |
|||
| r2-surface = [[Asphalt]] |
|||
| r3-number = 12/30 |
|||
| r3-length-m = 3112 |
|||
| r3-surface = [[Asphalt]] |
|||
| stat-year = 2018<ref name="IAAreports">{{cite web|title=IAA Periodic Activity Reports for Ben Gurion Airport|url=http://brin.iaa.gov.il/monthlyreport|website=IAA Website|publisher=[[Israel Airports Authority]]|accessdate=15 January 2017}}</ref><ref name="IAAstats">{{cite web|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/en-US/airports/bengurion/Pages/statistics.aspx |title=Official airport statistics for Ben Gurion Airport |publisher=IAA |date= |accessdate=2019-01-10|language=English}}</ref> |
|||
| stat1-header = Total passengers |
|||
| stat1-data = 22,949,676 |
|||
| stat2-header = International passengers |
|||
| stat2-data = 22,357,736 |
|||
| stat3-header = Domestic passengers |
|||
| stat3-data = 591,940 |
|||
| stat4-header = Aircraft movements |
|||
| stat4-data = 157,312 |
|||
| footnotes = Sources: [[Civil Aviation Authority of Israel]]<ref name="AIP"/> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| focus_city = [[Bluebird Airways]], [[TUS Airways]], [[Wizz Air]] |
|||
| elevation-f = 135 |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|32|00|34|N|034|52|58|E|region:IL|display=inline,title}} |
|||
| pushpin_map = Israel#Middle East2 |
|||
| pushpin_label = '''TLV''' |
|||
| pushpin_map_caption = Location within Israel##Location within the [[Middle East]] |
|||
| website = [http://www.iaa.gov.il/en-US/airports/bengurion/Pages/default.aspx iaa.gov.il] |
|||
| metric-rwy = yes |
|||
| r1-number = 03/21 |
|||
| r1-length-m = 2772 |
|||
| r1-surface = Asphalt |
|||
| r2-number = 08/26 |
|||
| r2-length-m = 4062 |
|||
| r2-surface = Asphalt |
|||
| r3-number = 12/30 |
|||
| r3-length-m = 3112 |
|||
| r3-surface = Asphalt |
|||
| stat-year = 2023 |
|||
| stat1-header = Total passengers |
|||
| stat1-data = 21,882,716 |
|||
| stat2-header = International passengers |
|||
| stat2-data = 21,088,237 |
|||
| stat3-header = Domestic passengers |
|||
| stat3-data = 794,479 |
|||
| stat4-header = Aircraft movements |
|||
| stat4-data = 152,411 |
|||
| footnotes = Source: [[Civil Aviation Authority of Israel]]<ref name="AIP"/><ref name="IAAreports"/> |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Ben Gurion International Airport'''{{efn|{{langx|he|נמל התעופה בן-גוריון|Nēmāl ha-tē‘ufā Bēn-Guriyôn}}; {{langx|ar|مطار بن غوريون الدولي|Maṭār Bin Ġūriyūn ad-duwalī}}.<!--This article should include the Arabic-language name because: |
|||
* Arabic was an official language of Israel for many years, and it still has special status |
|||
* This is an Israeli governmental institution-->}} {{Airport codes|TLV|LLBG}}, commonly known by the [[Hebrew language|Hebrew]]-language acronym '''{{Transliteration|he|Natbag}}''' ({{lang|he|{{Script/Hebrew|נתב״ג}}|rtl=yes}}), is the main international airport of [[Israel]]. Situated on outskirts north of the city of [[Lod]] and directly south of the city of [[Or Yehuda]], it is the busiest airport in the country. It is located {{Convert|45|km|mi}} to the northwest of [[Jerusalem]] and {{Convert|20|km|mi}} to the southeast of [[Tel Aviv]].<ref name="AIP">{{cite web |url=http://en.caa.gov.il/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_download&gid=1359&Itemid= |title=AD 2.5 TEL-AVIV / BEN-GURION – LLBG |access-date=18 July 2014 |archive-date=12 October 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131012085055/http://en.caa.gov.il/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_download&gid=1359&Itemid= |url-status=dead }}</ref> It was known as '''Lod Airport''' until 1973, when it was renamed in honour of [[David Ben-Gurion]] (1886–1973), the first prime minister of Israel. The airport serves as a hub for [[El Al]], [[Israir Airlines]], [[Arkia]], and [[Sun d'Or]], and is managed by the [[Israel Airports Authority]]. |
|||
In 2023, Ben Gurion Airport handled 21.1 million passengers,<ref name=":12">{{cite web |title=Monthly Report |url=https://monthlyreport.iaa.gov.il/OpenPdf.aspx?lang=eng&val=202312 |access-date=22 January 2024 |website=Israel Airport Authority |publisher=Ben Gurion Int'l Airport - Managing Director Office}}</ref> making it one of [[List of the busiest airports in the Middle East|the busiest airports in the Middle East]]. It is considered to be among the five best airports in the [[Middle East]] due to its passenger experience and its high level of security;<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/2013-Winners/Best-Airport-By-Region/Middle-East|title=ASQ Awards|access-date=3 June 2015}}</ref> while it has been the target of several terrorist attacks, no attempt to hijack a plane departing from Ben Gurion Airport has ever succeeded.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=S3rFr5gWKQUC&pg=PA131|title=Introduction to Private Security|last=Dempsey|first=John S.|date=23 March 2010|publisher=Cengage Learning|isbn=978-0495809852|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
'''Ben Gurion Airport''' ({{lang-he|נמל התעופה בן-גוריון}}) {{Airport codes|TLV|LLBG}}, commonly known as '''Natbag''' ({{lang|he|נתב״ג}}), is the main international airport of [[Israel]] and the busiest airport in the country, located on the northern outskirts of the city of [[Lod]], which is about {{convert|45|km|abbr=on}} northwest of [[Jerusalem]] and {{convert|20|km|abbr=on}} to the southeast of [[Tel Aviv]].<ref name="AIP">{{cite web|url=http://en.caa.gov.il/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_download&gid=1359&Itemid= |title=AD 2.5 TEL-AVIV / BEN-GURION – LLBG |date= |accessdate=2014-07-18}}</ref> Named after Israel's first Prime Minister [[David Ben-Gurion]], the airport serves as a hub for [[El Al]], [[Israir Airlines]], [[Arkia]], and [[Sun D'Or]]. It is operated by the [[Israel Airports Authority]], a [[government-owned corporation]] that manages all public airports and [[Border control|border crossing]]s in Israel. |
|||
The airport is of great importance to Israel as it is one of the few convenient entry points into the country for most travellers.<ref name="The Christian Science Monitor 2014">{{cite web | author=The Christian Science Monitor | title=The importance of Ben Gurion airport to Israel | website=The Christian Science Monitor | date=22 July 2014 | url=https://www.csmonitor.com/World/Security-Watch/Backchannels/2014/0722/The-importance-of-Ben-Gurion-airport-to-Israel | access-date=25 January 2021}}</ref> As it was Israel's only international airport, it was regarded as a [[single point of failure]], which led to the opening of [[Ramon Airport]] in 2019.<ref name="Lewis 2019">{{cite web | last=Lewis | first=Ori | title=Israel opens new international airport, named for astronaut Ramon, near Red Sea | website=The Times of Israel | date=21 January 2019 | url=https://www.timesofisrael.com/israel-opens-new-international-airport-near-red-sea/ | access-date=25 January 2021}}</ref> |
|||
In 2018, Ben Gurion handled 23 million passengers.<ref name="IAAreports"/> The airport is considered to be among the five best airports in the [[Middle East]] due to its passenger experience and its high level of security.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/2013-Winners/Best-Airport-By-Region/Middle-East|title=ASQ Awards|publisher=|accessdate=3 June 2015}}</ref> [[Israeli security forces|Security forces]] such as [[Israel Police]] officers, [[Israel Defense Forces|IDF]] and [[Israel Border Police]] soldiers are complemented by airport security guards who operate both in uniform and [[undercover]]. The airport has been the target of several terrorist attacks, but no attempt to hijack a plane departing from Ben Gurion airport has ever succeeded.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=S3rFr5gWKQUC&pg=PA131|title=Introduction to Private Security|last=Dempsey|first=John S.|date=2010-03-23|publisher=Cengage Learning|isbn=0495809853|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
===British Mandatory period (1934–1948)=== |
|||
[[File:Lod Airport 1958.jpg|thumb|Lod Airport, 1958. The building is currently the Terminal 1 building.]] |
|||
[[File:BGsculptureS.jpg|thumb|Bust of [[David Ben-Gurion]] at Ben Gurion Airport, named in his honour]] |
|||
The airport began during the [[Mandatory Palestine|British Mandate for Palestine]] as an airstrip of two unpaved runways on the outskirts of the town of Lydda (now [[Lod]]), near the [[Templers (religious believers)|Templer]] colony of [[Wilhelma, Palestine|Wilhelma]]. It was built in 1934, largely at the urging of [[Airwork Services]].<ref name="iam">{{cite web|url=https://www.israelairlinemuseum.org/el-al-israels-flying-star/chapter-1-from-flying-camels-to-flying-stars-israel-reborn/|title = Chapter 1 – from Flying Camels to Flying Stars: Israel Reborn (1917–1948) | Israel Airline Museum| date=5 August 2016 }}</ref> The first passenger service at the new airport was the [[EgyptAir#Early years: Misr Airwork (1932–1949)|Misr Airwork]] route [[Cairo]]—Lydda—[[Nicosia]], inaugurated on 3 August 1935. Subsequently, Misr flew via Lydda to [[Haifa Airport|Haifa]] and [[Baghdad]]. The first continental European airline with a regular service to Lydda was [[LOT Polish Airlines]] since 4 April 1937. By that time, Lydda Airport boasted four fully operational concrete runways. Holland's [[KLM]], which had since 1933 stopped at [[RAF Gaza|Gaza]] en route to [[Batavia, Dutch East Indies]] (now [[Jakarta]], Indonesia), moved the service to Lydda in 1937. [[Imperial Airways]], too, used Lydda as a refueling stop en route to India. |
|||
During [[World War II]], Imperial Airways and later [[British Overseas Airways Corporation]] continued the service to Lydda until the [[fall of France]] in June 1940. When the Japanese military advanced into [[Japanese invasion of Burma|Burma]] and [[Japanese invasion of Malaya|Malaya]] in February 1942, KLM curtailed its route to Batavia and made Lydda the eastern terminus of the route. Misr Airwork, which had suspended flights upon the British declaration of war, resumed the weekly Cairo—Lydda—Nicosia service in May 1940.<ref name="iam"/> |
|||
===Early history=== |
|||
[[File:Lod Airport 1958.jpg|thumb|left|Lod Airport, 1958. The building is currently the Terminal 1 building.]] |
|||
[[File:BGsculptureS.jpg|thumb|left|Sculpture of [[David Ben-Gurion]] at Ben Gurion Airport, named in his honour]] |
|||
The airport began as an airstrip of four concrete runways on the outskirts of the town of Lydda (now [[Lod]]). It was built in 1936, during the [[Mandatory Palestine|British Mandate for Palestine]], chiefly for military purposes.<ref name="30's">{{cite web |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/AbouttheAirport/History/30/ |title=Ben Gurion Airport- The 30's |accessdate=27 April 2007|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> First known as [[Wilhelma, Palestine|Wilhelma]] airport, it was renamed [[Royal Air Force station|RAF Station]] Lydda in 1943. During [[World War II]] it served as a major airfield for military air transport and aircraft ferry operations between military bases in Europe, Africa, the Middle East (mainly Iraq and Persia) and South/Southeast Asia. |
|||
In 1943, the airport was renamed "[[RAF Station Lydda]]" and continued to serve as a major airfield for military air transport and aircraft ferry operations between military bases in [[Europe]], [[Africa]], the [[Middle East]] (mainly [[Iraq]] and [[Iran|Persia]]) and South/[[Southeast Asia]]. In 1944, as the German threat in the Middle East subsided, [[Aviron Aviation Company]] initiated service four times a week between Lydda and Haifa.<ref name="iam"/> |
|||
The first civilian transatlantic route, New York City to Tel Aviv, was inaugurated by [[Trans World Airlines|TWA]] in 1946. The British gave up Lydda airport at the end of April 1948. Soldiers of the [[Israel Defense Forces]] captured the airport on 10 July 1948, in [[Operation Danny]], transferring control to the newly [[Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel|declared State of Israel]]. In 1948 the Israelis changed the name of the airport from Lydda to Lod.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://aviation-safety.net/database/airport/airport.php?id=TLV1|title=Lydda Airport profile - Aviation Safety Network|author=Harro Ranter|publisher=|accessdate=3 June 2015}}</ref> Flights resumed on 24 November 1948.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/AbouttheAirport/History/40/ |title=Ben Gurion Airport- The 40's|accessdate=29 April 2007|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> That year, 40,000 passengers passed through the terminal. By 1952, the number had risen to 100,000 a month. Within a decade, air traffic increased to the point where local flights had to be redirected to Tel Aviv's other airport, the [[Sde Dov Airport|Sde Dov]] airfield (SDV) on the city's northern coast. By the mid-1960s, 14 international airlines were landing at the airport. |
|||
The first civilian transatlantic route, [[New York City]] to Lydda Airport, was inaugurated by [[Trans World Airlines|TWA]] in 1946. The British gave up the airport at the end of April 1948. |
|||
The airport's name was changed from Lod to Ben Gurion International Airport in 1973 to honour Israel's first Prime Minister, [[David Ben-Gurion]]. |
|||
===Israel's first decades (1948–1973)=== |
|||
Although the airport was previously known as "Lod Airport" and is sometimes referred to as "Tel Aviv Airport", it doesn't actually lie within the boundaries of any particular municipality. Rather, it is located in an [[unincorporated area]] within the [[Central District (Israel)|Central District]] of Israel. |
|||
[[File:Moroccan Children in Lod Airport 1949.jpg|thumb|219x219px|[[Moroccan Jewish]] children arrive at the airport in 1949; transported via Norway.]] |
|||
Soldiers of the [[Israel Defense Forces]] captured the airport on 10 July 1948, in [[Operation Danny]], transferring control to the newly [[Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel|declared State of Israel]].{{citation needed|date=April 2019}} In 1948 the Israelis changed the official name of the airport from Lydda to Lod (the nearby town's name in Hebrew), the airport's name becoming '''Lod Airport'''.<ref name="Safety">{{cite web |url= http://aviation-safety.net/database/airport/airport.php?id=TLV1 |title= Lydda Airport profile – Aviation Safety Network |author= Harro Ranter |access-date=3 June 2015}}</ref> Flights resumed on 24 November 1948.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/AbouttheAirport/History/40/ |title=Ben Gurion Airport- The 40s|access-date=29 April 2007|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> That year, 40,000 passengers passed through the terminal. By 1952, the number had risen to 100,000 a month. Within a decade, air traffic increased to the point where local flights had to be redirected to Tel Aviv's other airport, the [[Sde Dov Airport|Sde Dov]] airfield (SDV) on the city's northern coast. By the mid-1960s, 14 international airlines were landing at the airport. |
|||
The airport's name was changed from Lod to '''Ben Gurion International Airport''' in 1973 to honour Israel's first Prime Minister, [[David Ben-Gurion]], who died that year. |
|||
===Modern history=== |
|||
====Terrorist incidents (1972)==== |
|||
More buildings and runways were added over the years, but with the onset of mass [[aliyah|immigration]] from [[Ethiopian Jews#Israel intervenes|Ethiopia]] and the former [[Russian aliya|Soviet Union]] in the 1980s and 90s, as well as the global increase of international business travel, the existing facilities became painfully inadequate, prompting the design of a new state-of-the-art terminal that could also accommodate the expected tourism influx for the 2000 millennium celebrations. The decision to go ahead with the project was reached in January 1994, but the new terminal, known as Terminal 3, only opened its doors a decade later, on 2 November 2004.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.historycentral.com/Aviation/airports/Bengurion.html | title=Ben Gurion | accessdate=29 April 2007| publisher=History Central| archiveurl= https://web.archive.org/web/20070330173158/http://www.historycentral.com/Aviation/airports/Bengurion.html| archivedate= 30 March 2007| deadurl= no}}</ref> During a [[2014 Israel–Gaza conflict|conflict with Gaza]] in July 2014, several airlines [[2014 Ben Gurion Airport flight bans|banned their flights]] to the airport for a couple of days.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://news.yahoo.com/faa-lifts-ban-us-flights-tel-aviv-airport-041535461--politics.html|title=FAA lifts ban on US flights to Tel Aviv airport|date=24 July 2014|work=Yahoo News|accessdate=3 June 2015}}</ref> [[Ramon Airport]], an international airport under construction in the [[Timna Valley]] in southern Israel, will serve as a [[diversion airport]] for Ben Gurion when it opens in 2019. The longest flight from the airport was across Europe, the Arctic Ocean, Alaska, and to Honolulu, Hawaii on January 2, 2017 by the private [[Airbus A340-500]] of billionaire casino mogul, Sheldon Adelson.<ref>Melnitcki, Gili. (4 January 2017). "Next Stop Hawaii: Sheldon Adelson sets Record With 18-hour Flight From Israel" Retrieved January 15, 2017 [http://www.haaretz.com/israel-news/1.762882 Haaretz website]</ref> |
|||
While Ben Gurion Airport has been a target of Palestinian attacks, the adoption of [[airport security|strict security precaution]]s has ensured that no aircraft departing from Ben Gurion airport has ever been [[Aircraft hijacking|hijacked]]. On the other hand, airliners hijacked from other countries have landed at Ben Gurion, contributing to two major incidents in the airport's history. |
|||
In the first incident, on 8 May 1972, four Palestinian [[Black September (group)|Black September]] terrorists [[Hijacking of Sabena Flight 572|hijacked a Sabena flight]] en route from Vienna and forced it to land at Ben Gurion airport. [[Sayeret Matkal]] commandos, including [[Benjamin Netanyahu]], led by [[Ehud Barak]] (both future Israeli Prime Ministers) stormed the plane, killing two of the hijackers and capturing the other two. One passenger was killed.<ref>{{cite news |last= Sontag |first= Deborah |title= 2 Who Share a Past Are Rivals for Israel's Future |newspaper= [[The New York Times]] |pages= Section A, Page 3, Column 1 |url= https://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=F30917FD3D5E0C738EDDAD0894D1494D81&n=Top%2fReference%2fTimes%20Topics%2fPeople%2fB%2fBarak%2c%20Ehud |date= 20 April 1999}}</ref> |
|||
===Hijack incidents=== |
|||
While Ben Gurion Airport has been a target of Palestinian attacks, the adoption of [[airport security|strict security precaution]]s has ensured that no aircraft departing from Ben Gurion airport has ever been [[Aircraft hijacking|hijacked]]. On the other hand, airliners hijacked from other countries have landed at Ben Gurion, contributing to two major incidents in the airport's history. In the first, on 8 May 1972, four Palestinian [[Black September (group)|Black September]] terrorists [[Hijacking of Sabena Flight 572|hijacked a Sabena flight]] en route from Vienna and forced it to land at Ben Gurion airport. [[Sayeret Matkal]] commandos led by [[Ehud Barak]] stormed the plane, killing two of the hijackers and capturing the other two. One passenger was killed.<ref>{{Cite news | last =Sontag | first =Deborah | title =2 Who Share a Past Are Rivals for Israel's Future | publisher = The New York Times | pages =Section A, Page 3, Column 1 | url =https://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=F30917FD3D5E0C738EDDAD0894D1494D81&n=Top%2fReference%2fTimes%20Topics%2fPeople%2fB%2fBarak%2c%20Ehud| date =20 April 1999}}</ref> Later that month, on 30 May 1972, in an attack known as the [[Lod Airport massacre]], 24 people were killed and 80 injured when three members of the [[Japanese Red Army]] sprayed machine gun fire into the passenger arrival area. The victims included [[Aharon Katzir]], a prominent [[protein]] [[biophysics|biophysicist]] and brother of Israel's 4th president. Those injured included [[Efraim Katzir]] and a group of twenty [[Puerto Rico|Puerto Rican]] tourists who had just arrived in Israel.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/may/29/newsid_2542000/2542263.stm |title=1972: Japanese kill 26 at Tel Aviv airport |publisher=BBC.co.uk|accessdate=28 April 2007| date=29 May 1972}}</ref> The only terrorist who survived was [[Kozo Okamoto]], who received a life sentence but was set free in a prisoner exchange with the [[Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine - General Command|PFLP-GC]].<ref>{{cite news|title=Israel frees 1,150 to obtain release of last 3 soldiers |
|||
Later that month, on 30 May 1972, in an attack known as the [[Lod Airport massacre]], 24 people were killed and 80 injured when three members of the [[Japanese Red Army]] sprayed machine gun fire into the passenger arrival area. The victims included [[Aharon Katzir]], a prominent [[protein]] [[biophysics|biophysicist]] and brother of Israel's 4th president. Those injured included a group of twenty [[Puerto Rico|Puerto Rican]] tourists who had just arrived in Israel.<ref>{{cite news |url= http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/may/29/newsid_2542000/2542263.stm |title= 1972: Japanese kill 26 at Tel Aviv airport |publisher= BBC.co.uk |access-date=28 April 2007 |date= 29 May 1972}}</ref> The only terrorist who survived was [[Kozo Okamoto]], who received a life sentence but was released in 1985 as part of a prisoner exchange with the [[Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine - General Command|PFLP-GC]].<ref>{{cite news |title= Israel frees 1,150 to obtain release of last 3 soldiers |url= https://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=F40F14FB385F0C728EDDAC0894DD484D81 |last= Lewis |first= Paul |work= The New York Times |date=21 May 1985 |access-date=29 April 2007}}</ref> |
|||
| url=https://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=F40F14FB385F0C728EDDAC0894DD484D81|last=Lewis|first=Paul |
|||
|work=The New York Times|date=21 May 1985|accessdate=29 April 2007}}</ref> |
|||
===Since the 1980s=== |
|||
More buildings and runways were added over the years, but with the onset of mass [[aliyah|immigration]] from [[Ethiopian Jews#Israel intervenes|Ethiopia]] and the former [[Russian aliya|Soviet Union]] in the 1980s and 90s, as well as the global increase of international business travel, the existing facilities became painfully inadequate, prompting the design of a new state-of-the-art terminal that could also accommodate the expected tourism influx for the 2000 millennium celebrations. The decision to go ahead with the project was reached in January 1994, but the new terminal, known as Terminal 3, only opened its doors a decade later, on 2 November 2004.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.historycentral.com/Aviation/airports/Bengurion.html |title= Ben Gurion |access-date=29 April 2007 |publisher= History Central |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070330173158/http://www.historycentral.com/Aviation/airports/Bengurion.html |archive-date= 30 March 2007 |url-status= live}}</ref> |
|||
During the [[2014 Israel–Gaza conflict|2014 conflict with Gaza]], several airlines [[2014 Ben Gurion Airport flight bans|banned their flights]] to the airport for a couple of days.<ref>{{cite web |url= https://news.yahoo.com/faa-lifts-ban-us-flights-tel-aviv-airport-041535461--politics.html |title= FAA lifts ban on US flights to Tel Aviv airport |date=24 July 2014 |work= Yahoo News |access-date=3 June 2015}}</ref> In October 2023, with the outbreak of the [[Israel–Hamas war]], the number of airlines that flew into the airport dropped to just 7. By February 2024, only 45 airlines flew into the airport.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/2/28/are-airlines-returning-to-israel-despite-the-war-on-gaza|title=Are airlines returning to Israel, despite the war on Gaza?|date=February 28, 2024|publisher=[[Al Jazeera]]}}</ref> |
|||
The furthest nonstop flight to have departed the airport was a private [[Airbus A340-500]] owned by billionaire casino mogul [[Sheldon Adelson]] who flew on 2 January 2017 to [[Honolulu]] on a route over the [[Arctic Ocean]]. The flight was projected to last 17 hours and 40 minutes.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.haaretz.com/israel-news/1.762882 |title= "Next Stop Hawaii: Sheldon Adelson sets record with 18-hour flight from Israel"| author=Melnitcki, Gili |date=4 January 2017|access-date= 15 January 2017 |website=Haaretz}}</ref> |
|||
[[Ramon Airport]], an international airport near the southern Israeli city of [[Eilat]], serves as a [[diversion airport]] for Ben Gurion Airport.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.garda.com/crisis24/news-alerts/191081/israel-ramon-airport-etm-in-eilat-set-to-open-gradually-from-january-22|title=Israel: Ramon Airport (ETM) in Eilat set to open gradually from January 22|website=GardaWorld}}</ref> |
|||
==Passenger terminals== |
==Passenger terminals== |
||
| Line 82: | Line 101: | ||
====History==== |
====History==== |
||
Prior to the opening of Terminal 3, Terminal 1 was the main terminal building at Ben Gurion Airport. At that time, the departures [[Airport |
Prior to the opening of Terminal 3, Terminal 1 was the main terminal building at Ben Gurion Airport. At that time, the departures [[Airport check-in|check-in area]] was located on the ground floor. From there, passengers proceeded upstairs to the main departures hall, which contained [[Border control|passport control]], [[duty-free shop]]s, [[Airport lounge|VIP lounge]]s, one synagogue and boarding gates. At the gates, travelers would be required to descend a flight of stairs to return to the ground floor where waiting shuttle buses transported them to airplanes on the [[Airport ramp|tarmac]]. The arrivals hall with passport control, luggage carousels, duty-free pick-up and customs was located at the south end of the building. The [[Airport bus#On airport transfer|apron buses]] transferred passengers and crews to and from the terminal to airplanes which were parked on the tarmac over {{convert|500|m|abbr=on}} away. After Terminal 3 opened, Terminal 1 was closed except for domestic flights to the airport in [[Eilat]] and government flights such as special immigrant flights from North America and Africa. Chartered flights organised by [[Nefesh B'Nefesh]] carrying immigrants from North America and England use this terminal for their landing ceremonies several times a year.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.historycentral.com/Aviation/airports/Bengurion.html |title=Ben Gurion Airport|access-date=28 April 2007|publisher=HistoryCentral| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070330173158/http://www.historycentral.com/Aviation/airports/Bengurion.html| archive-date= 30 March 2007| url-status= live}}</ref> |
||
Although Terminal 1 was closed between 2003 and 2007, the building served as a venue for various events and large-scale exhibitions including the "[[Bezalel Academy of Art and Design|Bezalel Academy of Arts]] Centennial Exhibition" which was held there in 2006. |
Although Terminal 1 was closed between 2003 and 2007, the building served as a venue for various events and large-scale exhibitions including the "[[Bezalel Academy of Art and Design|Bezalel Academy of Arts]] Centennial Exhibition" which was held there in 2006. |
||
The renovations for the terminal were designed by Yosef Assa with three individual atmospheric themes. Firstly, the public halls have a ''Land-of-Israel character'' with walls painted in the colors of Israel's [[Judean Hills|Judean]], [[Jerusalem]] and [[Galilee]] mountains. The |
The renovations for the terminal were designed by Yosef Assa with three individual atmospheric themes. Firstly, the public halls have a ''Land-of-Israel character'' with walls painted in the colors of Israel's [[Judean Hills|Judean]], [[Jerusalem]] and [[Galilee]] mountains. The departure hall is given an atmosphere of vacation and leisure, whilst the arrivals hall is given a more urban theme as passengers return to the city.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/Terminal+1/PrinciplesofArchitecturalPlanning_en.htm |title=Principles of Architectural Planning |access-date=12 April 2008 |publisher=IAA |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080412034555/http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/Terminal%2B1/PrinciplesofArchitecturalPlanning_en.htm |archive-date=12 April 2008 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
[[File:Terminal 1 TLV 19645.jpg|thumb|Private jets on the apron at Terminal 1]] |
[[File:Terminal 1 TLV 19645.jpg|thumb|Private jets on the apron at Terminal 1]] |
||
In February 2006, the [[Israel Airports Authority]] announced plans to invest 4.3 million [[Israeli new sheqel|NIS]] in a new VIP wing for [[Business jet|private jet]] passengers and crews, as well as others interested in avoiding the main terminal. VIP ground services already exist, but a substantial increase in users has justified expanding the facilities, which will also boost airport revenues. The IAA released figures showing significant growth in private jet flights (4,059, a 36.5% increase from 2004) as well as private jet users (14,613, a 46.2% increase from 2004). The new VIP wing, operated by an outside licensee, will be located in an upgraded and expanded section of Terminal 1. All flight procedures (security check, [[Border control|passport control]] and [[customs]]) will be handled here. This wing will include a hall equipped for press conferences, a deluxe lounge, special meeting rooms equipped with state-of-the-art business facilities and a designated lounge for flight crews who spend time at the airport between flights.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Rashot/MessagesArchive/SpokesMan/Spokesman_En_210206.htm |title=Israel Airports Authority to Build a Special Terminal for Executive and Private Flights at Ben Gurion Airport | |
In February 2006, the [[Israel Airports Authority]] announced plans to invest 4.3 million [[Israeli new sheqel|NIS]] in a new VIP wing for [[Business jet|private jet]] passengers and crews, as well as others interested in avoiding the main terminal. VIP ground services already exist, but a substantial increase in users has justified expanding the facilities, which will also boost airport revenues. The IAA released figures showing significant growth in private jet flights (4,059, a 36.5% increase from 2004) as well as private jet users (14,613, a 46.2% increase from 2004). The new VIP wing, operated by an outside licensee, will be located in an upgraded and expanded section of Terminal 1. All flight procedures (security check, [[Border control|passport control]] and [[customs]]) will be handled here. This wing will include a hall equipped for press conferences, a deluxe lounge, special meeting rooms equipped with state-of-the-art business facilities and a designated lounge for flight crews who spend time at the airport between flights.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Rashot/MessagesArchive/SpokesMan/Spokesman_En_210206.htm |title=Israel Airports Authority to Build a Special Terminal for Executive and Private Flights at Ben Gurion Airport |access-date=28 April 2007|date=21 February 2006|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> It was announced in January 2008, however, that the IAA planned to construct a new {{Convert|1000|m2|adj=on}} VIP terminal next to Terminal 3.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://fr.jpost.com/servlet/Satellite?cid=1200572515252&pagename=JPost/JPArticle/ShowFull| title=Terminal for private flights to be built at airport| date=22 January 2008| access-date=22 January 2008| work=[[The Jerusalem Post]]}} {{dead link|date=December 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> |
||
====International low-cost and domestic terminal==== |
====International low-cost and domestic terminal==== |
||
[[File:Ben Gurion International Airport terminal 3 EASY JET.JPG|thumb|An [[ |
[[File:Ben Gurion International Airport terminal 3 EASY JET.JPG|thumb|An [[easyJet Switzerland]] [[Airbus A320]] on stand at Terminal 3. Previously passengers on some low-cost international carriers such as [[easyJet]] checked-in at Terminal 1 and were bussed to Terminal 3 departures for boarding.]] |
||
Terminal 1 was closed in 2003 and re-opened in 2007 as the domestic terminal following extensive renovations,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Rashot/MessagesArchive/SpokesMan/Spokesman_En_200207.htm |title=End of an Era – The Historic Terminal 1 has Re-opened, Serving Passengers on Domestic Flights |accessdate=28 April 2007|date=20 February 2007|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> and in July 2008, to cater for summer charter and low-cost flights.<ref name="reopen">{{cite news | url=http://fr.jpost.com/servlet/Satellite?cid=1214726184832&pagename=JPost/JPArticle/ShowFull | title=Ben-Gurion's old terminal reopens for summer charters | accessdate=12 July 2008 | publisher=Jerusalem Post | date=2 July 2008 }}{{dead link|date=December 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> It remained open for these charter and low-cost flights for the 2008 summer season then temporarily closed in October 2008, when it underwent further renovation and reopened again in Summer 2009, when it was expected to reach a three-month capacity of 600,000 passengers on international flights.<ref name="reopen" /> As of 2010, several [[low-cost carriers]]' international flights were operating out of Terminal 1 year-round including [[Vueling]] flights to [[Barcelona El Prat Airport|Barcelona]] and [[easyJet]] flights to [[London Luton Airport|London]] (Luton), [[Manchester Airport|Manchester]], [[Geneva International Airport|Geneva]], and [[EuroAirport Basel-Mulhouse-Freiburg|Basel]]. In 2015, due to increased demand and following another expansion of the terminal, the Israel Airports Authority made Terminal 1 available to all low-cost carriers under certain conditions.<ref>{{cite web|title=Operating International Flights from Terminal 1 at Ben Gurion Int'l Airport|publisher=[[Israel Airports Authority]]|accessdate=18 April 2015|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/en-US/rashot/Documents/operating%20flights%20terminal%201.pdf|date=10 February 2015}}</ref> Flights operating out of Terminal 1 are charged lower airport fees than those operating out of Terminal 3. |
|||
Terminal 1 was closed in 2003 and reopened in 2007 as the domestic terminal following extensive renovations,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Rashot/MessagesArchive/SpokesMan/Spokesman_En_200207.htm |title=End of an Era – The Historic Terminal 1 has Re-opened, Serving Passengers on Domestic Flights |access-date=28 April 2007|date=20 February 2007|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> and in July 2008, to cater for summer charter and low-cost flights.<ref name="reopen">{{cite news | url=http://fr.jpost.com/servlet/Satellite?cid=1214726184832&pagename=JPost/JPArticle/ShowFull | title=Ben-Gurion's old terminal reopens for summer charters | access-date=12 July 2008 | newspaper=The Jerusalem Post | date=2 July 2008 }} {{dead link|date=December 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> It remained open for these charter and low-cost flights for the 2008 summer season then temporarily closed in October 2008, when it underwent further renovation and reopened again in the summer of 2009, when it was expected to reach a three-month capacity of 600,000 passengers on international flights.<ref name="reopen" /> As of 2010, several [[low-cost carriers]]' international flights were operating out of Terminal 1 year-round including [[Vueling]] flights to [[Barcelona El Prat Airport|Barcelona]] and [[easyJet]] flights to [[London Luton Airport|London]] (Luton), [[Manchester Airport|Manchester]], [[Geneva International Airport|Geneva]], and [[EuroAirport Basel-Mulhouse-Freiburg|Basel]]. In 2015, due to increased demand and following another expansion of the terminal, the Israel Airports Authority made Terminal 1 available to all low-cost carriers under certain conditions.<ref>{{cite web|title=Operating International Flights from Terminal 1 at Ben Gurion Int'l Airport|publisher=[[Israel Airports Authority]]|access-date=18 April 2015|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/en-US/rashot/Documents/operating%20flights%20terminal%201.pdf|date=10 February 2015}}</ref> Flights operating out of Terminal 1 are charged lower airport fees than those operating out of Terminal 3.<ref name="themarker-expansion">{{cite news|url=https://www.themarker.com/consumer/tourism/1.8188336|title=6 מיליארד שקל לתוכנית הפיתוח של נתב"ג לשלוש השנים הקרובות|trans-title=ILS Six Billion for the Ben Gurion Airport Expansion Plan in the Next Three Years|author=Rosenberg-Kandel, Rina|date=27 November 2019|access-date=27 November 2019|language=he}}</ref> |
|||
Until the summer of 2017 Terminal 1 was used for flight check-in, security screening and passport-control for international flights for passengers of certain low-cost airlines, but following passport control passengers were bussed to the departures concourse of Terminal 3 from which they boarded their flights. All incoming flights for airlines operating out of Terminal 1 were handled in Terminal 3. However, beginning on 19 June 2017 and following several months of renovations, Terminal 1 passengers began being bussed directly to their flights from Terminal 1, although incoming passengers continue to be handled in Terminal 3. The renovations to Terminal 1's boarding area included adding duty-free shops, restaurants and cafes. The terminal was also equipped with advanced checked-baggage handling and screening systems, similar to those in Terminal 3. |
Until the summer of 2017 Terminal 1 was used for flight check-in, security screening and passport-control for international flights for passengers of certain low-cost airlines, but following passport control passengers were bussed to the departures concourse of Terminal 3 from which they boarded their flights. All incoming flights for airlines operating out of Terminal 1 were handled in Terminal 3. However, beginning on 19 June 2017 and following several months of renovations, Terminal 1 passengers began being bussed directly to their flights from Terminal 1, although incoming passengers continue to be handled in Terminal 3. The renovations to Terminal 1's boarding area included adding duty-free shops, restaurants and cafes. The terminal was also equipped with advanced checked-baggage handling and screening systems, similar to those in Terminal 3. |
||
| Line 99: | Line 119: | ||
===Terminal 3=== |
===Terminal 3=== |
||
[[File:Ben |
[[File:Ben-gurion-airport-terminal--september-2012 (cropped).jpg|thumb|Aerial view of Terminal 3]] |
||
[[File:16-03-30-Ben Gurion International Airport-RalfR-DSCF7550.jpg|thumb|Terminal 3 arrivals hall]] |
|||
Terminal 3, which opened on 28 October 2004,<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/Government/Speeches+by+Israeli+leaders/2004/Address%20by%20PM%20Sharon%20at%20inauguration%20of%20Ben%20Gurion%20Airport%202000%2028-Oct-2004|title= Address by PM Sharon at inauguration of Ben Gurion Airport 2000 |
Terminal 3, which opened on 28 October 2004,<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/Government/Speeches+by+Israeli+leaders/2004/Address%20by%20PM%20Sharon%20at%20inauguration%20of%20Ben%20Gurion%20Airport%202000%2028-Oct-2004|title= Address by PM Sharon at inauguration of Ben Gurion Airport 2000 |
||
| |
|access-date=27 April 2007| publisher=[[Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs]]}}</ref> replaced Terminal 1 as the main international gateway to and from Israel. The building was designed by [[Skidmore, Owings & Merrill]] (SOM).<ref name="archrecord">{{cite magazine|url=http://archrecord.construction.com/projects/bts/archives/transportation/05_benGurion/overview.asp|title=Ben Gurion International Airport, Terminal 3 |magazine=[[Architectural Record]]|date=October 2005}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.som.com/content.cfm/ben_gurion_international_airport|title=Ben Gurion International Airport International Terminal|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100516093025/http://www.som.com/content.cfm/ben_gurion_international_airport|archive-date=16 May 2010}} SOM.com Project Page</ref> [[Moshe Safdie]] & Associates<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.msafdie.com/php/print_project.php?id=59|title=Ben Gurion International Airport International Terminal}} {{dead link|date=December 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} Moshe Safdie & Associates Project Page</ref> and TRA (now [[Black & Veatch Corporation|Black and Veatch]])<ref name="archrecord" /> designed a linking structure and the airside departure areas and gates. [[Ram Karmi]]<ref name="archrecord" /> and other Israeli architects were the local architects of record. The inaugural flight was an [[El Al]] flight to [[John F. Kennedy International Airport]] in New York City. |
||
Work on ''Natbag 2000'', as the Terminal 3 project was known, was scheduled for completion prior to 2000 in order to handle a massive influx of [[pilgrim]]s expected for the [[Great Jubilee|Millennium celebrations]]. This deadline was not met due to higher than anticipated costs and a series of work stoppages in the wake of the bankruptcy of the main Turkish contractor. The project eventually cost an estimated one billion US dollars. Due to the proximity of the airport to the country's largest population centres and the problem of [[noise pollution]], another international airport is being considered to be built elsewhere in the country,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/AbouttheAirport/Statistics/ |title=Facts and Figures | |
Work on ''Natbag 2000'', as the Terminal 3 project was known, was scheduled for completion prior to 2000 in order to handle a massive influx of [[pilgrim]]s expected for the [[Great Jubilee|Millennium celebrations]]. This deadline was not met due to higher than anticipated costs and a series of work stoppages in the wake of the bankruptcy of the main Turkish contractor. The project eventually cost an estimated one billion US dollars. Due to the proximity of the airport to the country's largest population centres and the problem of [[noise pollution]], another international airport is being considered to be built elsewhere in the country,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/AbouttheAirport/Statistics/ |title=Facts and Figures |access-date=4 May 2007|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> such as the new [[Ramon Airport|Ilan and Assaf Ramon Airport]] in Southern Israel. |
||
The overall layout of Terminal 3 is similar to that of airports in Europe and North America, with multiple levels and considerable distances to walk after disembarking from the aircraft. The walk is assisted by [[escalators]] and [[Escalators#Moving walkways|moving walkways]]. The upper level departures hall, with an area of over {{convert|10000|m2|abbr=on}}, is equipped with 110 [[Airport Check-in|check-in counters]] and as well as [[flight information display system]]s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/AbouttheAirport/PassengersHalls/CheckInHall/ |title=Check-In Hall |access-date=28 April 2007|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> A small shopping mall, known as Buy & Bye, is open to both travellers and the general public. The mall, which includes shops, restaurants and a post office, was planned to be a draw for non-flyers too. On the same level as the mall, passengers enter passport control and the security check. Planes taking off and landing can be viewed from a distinctive tilted glass wall. The arrivals hall is located on the ground floor where there are also 20 additional check-in counters (serving [[Star Alliance]] airlines). [[Car rental]] counters are located in an intermediate level situated between the departing and arriving passenger halls. Terminal 3 has two [[synagogues]].<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3342862,00.html | title=Muslim prayer room set up at Ben-Gurion Airport | newspaper=Ynetnews | publisher=Ynet | access-date=5 May 2007| date=21 December 2006 | last1=Senyor | first1=Eli }}</ref> |
|||
[[File:012 2010-09-04 13-44-43 Ben Gurion Airport.JPG|thumb|Airside duty-free rotunda, Terminal 3 departures]] |
[[File:012 2010-09-04 13-44-43 Ben Gurion Airport.JPG|thumb|Airside duty-free rotunda, Terminal 3 departures]] |
||
After the main security check, passengers wait for their flights in the star-shaped duty-free rotunda. A variety of cafes, restaurants and duty-free shops are located there, open 24 hours a day, as well as a synagogue, banking facilities, a transit hall for connecting passengers and a desk for [[value added tax|VAT]] refunds.<ref>{{cite web| url= http://parking.essentialtravel.co.uk/worldairport/israel/tel_aviv_-_ben_gurion.htm| title= Tel Aviv – Ben Gurion Airport (TLV) Information| publisher= Essential Travel| accessdate= 29 April 2007| archiveurl= https://web.archive.org/web/20070421224455/http://parking.essentialtravel.co.uk/worldairport/israel/tel_aviv_-_ben_gurion.htm| archivedate= 21 April 2007| deadurl= yes| df= dmy-all}}</ref> |
|||
After the main security check, passengers wait for their flights in the star-shaped duty-free rotunda. A variety of cafes, restaurants and duty-free shops are located there, open 24 hours a day, as well as a synagogue, banking facilities, a transit hall for connecting passengers and a desk for [[value added tax|VAT]] refunds.<ref>{{cite web| url= http://parking.essentialtravel.co.uk/worldairport/israel/tel_aviv_-_ben_gurion.htm| title= Tel Aviv – Ben Gurion Airport (TLV) Information| publisher= Essential Travel| access-date= 29 April 2007| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070421224455/http://parking.essentialtravel.co.uk/worldairport/israel/tel_aviv_-_ben_gurion.htm| archive-date= 21 April 2007| url-status= dead| df= dmy-all}}</ref> |
|||
Terminal 3 has a total of 40 gates divided among four concourses (B, C, D, and E), each with 8 jetway-equipped gates (numbered 2 through 9), as well as two stand gates (bus bays 1 and 1A) from which passengers are ferried to aircraft. Concourses B, C, and D were opened when terminal 3 opened in 2004, while concourse E was completed in 2018.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Blumenthal|first1=Itay|title=נתב"ג מתרחב: נחנכה הזרוע הרביעית|trans-title=Ben Gurion Airport Expands: Fourth Concourse Inaugurated|url=https://www.ynet.co.il/articles/0,7340,L-5115293,00.html|accessdate=17 February 2018|publisher=[[Ynet]]|date=15 February 2018}}</ref> Space exists for one additional concourse (A) at Terminal 3. |
|||
Terminal 3 has a total of 40 gates divided among four concourses (B, C, D, and E), each with 8 [[jet bridge]]-equipped gates (numbered 2 through 9), as well as two stand gates (bus bays 1 and 1A) from which passengers are ferried to aircraft. Two gates in concourse E utilize dual jet bridges for more efficient processing of very large widebody aircraft. Concourses B, C, and D were opened when terminal 3 opened in 2004, while concourse E was completed in 2018.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Blumenthal|first1=Itay|title=נתב"ג מתרחב: נחנכה הזרוע הרביעית|trans-title=Ben Gurion Airport Expands: Fourth Concourse Inaugurated|url=https://www.ynet.co.il/articles/0,7340,L-5115293,00.html|access-date=17 February 2018|publisher=[[Ynet]]|date=15 February 2018}}</ref> Space exists for one additional concourse (A) at Terminal 3. |
|||
Free [[Wi-Fi|wireless internet]] is provided throughout the terminal.<ref>[http://www.iaa.gov.il/NR/rdonlyres/DA3B095B-2E92-4862-B199-D3FFC56A2149/0/ntbg.pdf IAA TLV Free Airport WiFi Flyer] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120314060040/http://www.iaa.gov.il/NR/rdonlyres/DA3B095B-2E92-4862-B199-D3FFC56A2149/0/ntbg.pdf |date=14 March 2012 }} (PDF)</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Free Wi-Fi in Airports|url=http://www.wififreespot.com/airport.html|accessdate=4 May 2007| archiveurl= https://web.archive.org/web/20070429171530/http://www.wififreespot.com/airport.html| archivedate= 29 April 2007| deadurl= no}}</ref> |
|||
The terminal has three business lounges—the exclusive [[El Al]] [[King David Lounge]] for frequent flyers and two ''Dan'' lounges for either privileged or paying flyers. |
|||
Free [[Wi-Fi|wireless internet]] is provided throughout the terminal.<ref>{{Cite web |date=14 Mar 2012 |title=012 wireless Ben Guiron |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/NR/rdonlyres/DA3B095B-2E92-4862-B199-D3FFC56A2149/0/ntbg.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071026012732/http://www.iaa.gov.il/NR/rdonlyres/DA3B095B-2E92-4862-B199-D3FFC56A2149/0/ntbg.pdf |archive-date=26 Oct 2007 |access-date=17 Aug 2024 |website=iaa.gov.il |ref={{sfnref|iaa.gov.il|2012}}}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Free Wi-Fi in Airports|url=http://www.wififreespot.com/airport.html|access-date=4 May 2007| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070429171530/http://www.wififreespot.com/airport.html| archive-date= 29 April 2007| url-status= live}}</ref> |
|||
In January 2007, the IAA announced plans for a 120-bed hotel to be located about 300m west of Terminal 3.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.port2port.com/Index.asp?CategoryID=46&ArticleID=1210|title=A BOT tender to be published for Ben Gurion hotel|accessdate=28 April 2007|date=15 January 2007|publisher=PORT2PORT- Israel's Trade Portal|deadurl=yes|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070927190547/http://www.port2port.com/Index.asp?CategoryID=46&ArticleID=1210|archivedate=27 September 2007|df=dmy-all}}</ref> The tender for the hotel was published by the IAA in late 2017. The winning bidder will construct and operate the hotel for a period of 25 years. |
|||
The terminal has three business lounges—the exclusive [[El Al]] [[King David Lounge]] for frequent flyers and three ''Dan'' lounges for either privileged or paying flyers. |
|||
In January 2007, the IAA announced plans for a 120-bed hotel to be located about {{Cvt|300|m}} west of Terminal 3.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.port2port.com/Index.asp?CategoryID=46&ArticleID=1210|title=A BOT tender to be published for Ben Gurion hotel|access-date=28 April 2007|date=15 January 2007|publisher=PORT2PORT- Israel's Trade Portal|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070927190547/http://www.port2port.com/Index.asp?CategoryID=46&ArticleID=1210|archive-date=27 September 2007}}</ref> The tender for the hotel was published by the IAA in late 2017. |
|||
When the terminal was built, it was said to have a capacity for up to 12 million passengers a year. In 2023, 25 million passengers are expected to pass through Ben Gurion Airport.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Gilad |first=Moshe |date=4 Jul 2023 |title=Read Before You Land: Everything to Know About Israel's Ben-Gurion Airport |url=https://www.haaretz.com/israel-news/travel/2023-07-04/ty-article-magazine/.premium/read-before-you-land-everything-to-know-about-israels-ben-gurion-airport/00000189-208d-d8d6-a18f-26afaf750000 |access-date=17 Aug 2024 |website=Haaretz.com}}</ref> |
|||
===Former and unopened terminals=== |
===Former and unopened terminals=== |
||
====Terminal 2==== |
====Terminal 2==== |
||
Terminal 2 was inaugurated in 1969 when [[Arkia]] resumed operations at the airport after the [[Six-Day War]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/AbouttheAirport/History/60/|title=Ben Gurion Airoport – The |
Terminal 2 was inaugurated in 1969 when [[Arkia]] resumed operations at the airport after the [[Six-Day War]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/AbouttheAirport/History/60/|title=Ben Gurion Airoport – The 60s (IE browser required)|access-date=12 June 2008|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> Terminal 2 served domestic flights until 20 February 2007 when these services moved into the refurbished Terminal 1. Due to increased traffic in the late 1990s and [[over-capacity]] reached at Terminal 1, an international section was added until Terminal 3 was opened. After the transfer of domestic services to Terminal 1, Terminal 2 was demolished in order to make room for additional air freight handling areas. |
||
====Terminal 4==== |
====Terminal 4==== |
||
This terminal, built in 1999, was meant to handle the crowds expected in 2000, but never officially opened. To date, it has only been used as a terminal for passengers arriving from Asia during the [[SARS]] epidemic.<ref>{{cite news |first=Michael |last=Strongin |title=Ministry begins checking for SARS at Ben-Gurion |url=https://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/jpost/access/330779551.html?dids=330779551:330779551&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:FT&date=Apr+30%2C+2003&author=MICHAEL+STRONGIN&pub=Jerusalem+Post&edition=&startpage=03&desc=Ministry+begins+checking+for+SARS+at+Ben-Gurion | |
This terminal, built in 1999, was meant to handle the crowds expected in 2000, but never officially opened. To date, it has only been used as a terminal for passengers arriving from Asia during the [[SARS]] epidemic.<ref>{{cite news |first=Michael |last=Strongin |title=Ministry begins checking for SARS at Ben-Gurion |url=https://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/jpost/access/330779551.html?dids=330779551:330779551&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:FT&date=Apr+30%2C+2003&author=MICHAEL+STRONGIN&pub=Jerusalem+Post&edition=&startpage=03&desc=Ministry+begins+checking+for+SARS+at+Ben-Gurion |newspaper=[[The Jerusalem Post]] |page=3 |date=30 April 2003 |access-date=5 July 2017 |archive-date=7 November 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121107160234/http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/jpost/access/330779551.html?dids=330779551:330779551&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:FT&date=Apr+30%2C+2003&author=MICHAEL+STRONGIN&pub=Jerusalem+Post&edition=&startpage=03&desc=Ministry+begins+checking+for+SARS+at+Ben-Gurion |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
Another use for the terminal was for the memorial ceremonies upon the arrival of the [[casket]] of Col. [[Ilan Ramon]] after the [[Space Shuttle Columbia disaster]] in February 2003 and the arrival of [[Elhanan Tannenbaum]] and the caskets of |
Another use for the terminal was for the memorial ceremonies upon the arrival of the [[Coffin|casket]] of Col. [[Ilan Ramon]] after the [[Space Shuttle Columbia disaster|Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster]] in February 2003 and the arrival of [[Elhanan Tannenbaum]] and the caskets of three Israeli soldiers from Lebanon in January 2004. |
||
==Development plans== |
|||
In December 2017, the IAA announced a long-term expansion plan for Ben Gurion Airport estimated to cost approximately NIS 9 billion. Plans include further expansion of Terminal 1, a new dedicated domestic flights terminal, a major expansion of Terminal 3's landside terminal which would add approximately 90 additional check-in counters, construction of Concourse A, and additional aircraft parking spaces and ramps. In addition, air cargo facilities would be relocated to a large, currently-unused tract of land in the northern part of the airport's property (north of runway 08/26) where additional aircraft maintenance facilities would also be built. |
|||
In the meantime, to ease immediate overcrowding problems at Terminal 3's landside terminal, in the spring of 2018 a temporary large, air-conditioned tent was erected adjacent to Terminal 3 housing 25 check-in counters and security screening facilities. This tent was used for compulsory COVID-19 testing for all arriving passengers between 2020 and 2022. |
|||
==Future development== |
|||
In December 2017, the IAA announced a long-term expansion plan for Ben Gurion Airport estimated to cost approximately NIS 9 billion. Plans include further expansion of Terminal 1, a new dedicated domestic flights terminal, a major expansion of Terminal 3’s landside terminal which would add approximately 90 additional check-in counters, construction of Concourse A, and additional aircraft parking spaces and ramps. In addition, air cargo facilities would be relocated to a large, currently-unused tract of land in the northern part of the airport’s property (north of runway 08/26) where additional aircraft maintenance facilities would also be built. |
|||
In August 2018, the IAA published a tender for the construction and operation of a new terminal, dedicated to handling private and executive aircraft traffic.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.port2port.com/article/Air-Transport/Airports/Israel-Airports-Authority-to-build-private-plane-terminal-at-Ben-Gurion-Airport|title=Israel Airports Authority to build private plane terminal at Ben Gurion Airport|publisher=port2port.co.il|access-date=28 August 2018|archive-date=28 August 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180828001813/http://www.port2port.com/article/Air-Transport/Airports/Israel-Airports-Authority-to-build-private-plane-terminal-at-Ben-Gurion-Airport/|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
In the meantime, to ease immediate overcrowding problems at Terminal 3’s landside terminal, in the Spring of 2018 a temporary large, air-conditioned tent was erected adjacent to Terminal 3 housing 25 check-in counters and security screening facilities. |
|||
In late 2021 construction began on a new interchange that will provide additional access to the airport from Highway 1. The new interchange significantly reduced the distance vehicles must travel to access the airport's main terminal from the direction of Tel Aviv and other points north and west of the airport. |
|||
In August 2018, the IAA published a tender for the construction and operation of a new terminal, dedicated to handling private and executive aircraft traffic.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.port2port.com/article/Air-Transport/Airports/Israel-Airports-Authority-to-build-private-plane-terminal-at-Ben-Gurion-Airport|title=Israel Airports Authority to build private plane terminal at Ben Gurion Airport|publisher=port2port.co.il|accessdate=28 August 2018}}</ref> |
|||
==Office buildings== |
==Office buildings== |
||
The Airport City development, a large office park, is located east of the main airport property. It is at the junction of the [[Jerusalem]] |
The Airport City development, a large office park, is located east of the main airport property. It is at the junction of the [[Jerusalem]] and [[Tel Aviv]] metropolitan areas.<ref>{{Cite web |date=30 Aug 2012 |title=Airport City – business park, offices, storage, industry, logistics |url=http://www.airport-city.co.il/en/location.php |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130103122626/http://www.airport-city.co.il/en/location.php |archive-date=3 Jan 2013 |access-date=17 Aug 2024 |website=airport-city.co.il}}</ref> |
||
The head office of [[El Al]] is located at Ben Gurion Airport,<ref name="nytimes.com">Orme, William A. Jr. "El Al at a Turning Point; A Mirror of Israel's Divisions Prepares to Go 49% Public. |
The head office of [[El Al]] is located at Ben Gurion Airport,<ref name="nytimes.com">Orme, William A. Jr. "El Al at a Turning Point; A Mirror of Israel's Divisions Prepares to Go 49% Public". ''The New York Times''. 5 March 1999. C1, New York Edition. [https://www.nytimes.com/1999/03/05/business/el-al-at-a-turning-point-a-mirror-of-israel-s-divisions-prepares-to-go-49-public.html?pagewanted=1 1]. Retrieved 15 February 2010.</ref> as is the head office of the [[Israel Airports Authority]].<ref>[http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Rashot/TelephoneNumbersandAddresses/IaaPhones.htm "IAA Head Office"]. [[Israel Airports Authority]]. Retrieved 6 March 2010.{{dead link|date=August 2024}}</ref> |
||
The head offices of the [[Civil Aviation Authority (Israel)|Civil Aviation Authority]] and [[ |
The head offices of the [[Civil Aviation Authority (Israel)|Civil Aviation Authority]] and [[Challenge Airlines IL]] are located in the Airport City office park nearby the airport.<ref>{{cite web|title=CAA Relocates to Airport City office park|url=http://en.caa.gov.il/index.php?option=com_content&iotype=w&view=article&id=403|publisher=[[Civil Aviation Authority (Israel)|Civil Aviation Authority]]|access-date=14 December 2015|date=2 August 2010|archive-date=22 December 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151222095535/http://en.caa.gov.il/index.php?option=com_content&iotype=w&view=article&id=403|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>[http://www.cal.co.il/ContactUs/ "Contact Information"]. [[CAL Cargo Air Lines]]. Retrieved on 1 January 2012. "Contact Information Headquarters C.A.L. Cargo Airlines 1 Hayarden Street, Airport City P.O.B. 271 Ben Gurion Airport 70100, Israel"{{Dead link|date=August 2024}}</ref> |
||
[[Israel Aerospace Industries]] maintains its head office on airport grounds as well as extensive aviation construction and repair facilities.<ref name="Israel Aerospace Industries">{{cite web|title=IAI Head Office|url=http://www.iai.co.il/23286-en/IAI.aspx|publisher=Israel Aerospace Industries}}</ref> |
|||
==Runways== |
==Runways== |
||
[[File:BenGurionAerodromeChart-2004.jpg|thumb|Runway and taxiway layout as it existed from the 1970s until the mid-2010s. The runway depicted on the right was seldom used by commercial traffic due to being only 1, |
[[File:BenGurionAerodromeChart-2004.jpg|thumb|Runway and taxiway layout as it existed from the 1970s until the mid-2010s. The runway depicted on the right was seldom used by commercial traffic due to being only 1,780 m long.]] |
||
[[File:TLV-LLBG Aerodome Chart 2014.pdf|thumb|Airport layout following the runway and taxiway reconstruction and reconfiguration completed in 2014 |
[[File:TLV-LLBG Aerodome Chart 2014.pdf|thumb|Airport layout following the runway and taxiway reconstruction and reconfiguration completed in 2014]] |
||
===Main runway=== |
===Main runway=== |
||
The closest [[runway]] to terminals 1 and 3 is '''12/30''', {{convert|3112|m|abbr=on}} in length, and is followed by a [[taxiway]]. Most [[landing]]s take place on this runway from West to East, approaching from the [[Mediterranean Sea]] over southern Tel Aviv.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.airports-worldwide.com/israel/ben_gurion_israel.htm |title=Ben Gurion Airport | |
The closest [[runway]] to terminals 1 and 3 is '''12/30''', {{convert|3112|m|abbr=on}} in length, and is followed by a [[taxiway]]. Most [[landing]]s take place on this runway from West to East, approaching from the [[Mediterranean Sea]] over southern Tel Aviv.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.airports-worldwide.com/israel/ben_gurion_israel.htm |title=Ben Gurion Airport |access-date=27 April 2007|publisher=World Aero Data}}</ref> During inclement weather, it may also be used for [[takeoff]]s (Direction 12). A 17 million NIS renovation project was completed in November 2007 which reinforced the runway and made it suitable for future [[wide-body aircraft]]. In September 2008, a new [[Instrument landing system|ILS]] serving the runway was activated. The main runway was closed from 2011 until early 2014 in order to accommodate the extension of runway 03/21 and other construction activity in the vicinity of the runway. |
||
===Short runway=== |
===Short runway=== |
||
| Line 153: | Line 180: | ||
===Quiet runway=== |
===Quiet runway=== |
||
The longest runway at the airfield, {{convert|4062|m|abbr=on}}, and the main take off runway from east to west (direction '''08/26'''), is referred to as "the quiet runway" since jets taking off in this direction produce less [[noise pollution]] for surrounding residents{{vague|date=November 2014}} |
The longest runway at the airfield, {{convert|4062|m|abbr=on}}, and the main take off runway from east to west (direction '''08/26'''), is referred to as "the quiet runway" since jets taking off in this direction produce less [[noise pollution]] for surrounding residents.{{vague|date=November 2014}} A 24 million NIS renovation project completed in February 2006 reinforced the runway and made it suitable for [[wide-body aircraft]] such as [[Airbus A380]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Rashot/MessagesArchive/SpokesMan/Spokesman_En_070306.htm |title=Renovation of Runway 26-08 Completed; Became Operative on Sunday, February 26 |access-date=28 April 2007|date=7 March 2006|publisher=Israel Airports Authority}}</ref> |
||
===History and development=== |
===History and development=== |
||
The original layout of the airfield as designed by the British in the 1930s included four intersecting 800 m runways suitable for the piston |
The original layout of the airfield as designed by the British in the 1930s included four intersecting 800 m runways suitable for the [[Reciprocating engine|piston engined]] aircraft of the day. However, none of this original layout is visible nowadays since as usage increased and aircraft types and needs changed over the years various runways on the airport's premises were built and removed. |
||
The main runway (12/30) is the oldest surviving runway in the airport, with the quiet (08/26) and short (03/21) runways having been built in the late 1960s and 1970s. Since very little commercial traffic could operate on the short runway, |
The main runway (12/30) is the oldest surviving runway in the airport, with the quiet (08/26) and short (03/21) runways having been built in the late 1960s and 1970s. Since very little commercial traffic could operate on the short runway, for approximately forty years, the airport mostly relied on runways 12/30 and 08/26. This presented a problem, however: the fact that these two runways intersect near their western end creates a crisscross pattern between aircraft landing and taking off. This pattern reduces the number of aircraft which can arrive to and depart from the airport and has detrimental safety implications as well. |
||
With passenger traffic projected to increase, plans were drawn in the 1980s and 90s for the extension of runways 03/21 and 08/26 as a means of alleviating some of Ben Gurion's safety and capacity concerns. These plans were approved in 1997 and construction began in 2010. The extension of runway 03/21 allows the airport to operate in an "open V" configuration, allowing for simultaneous landings and take offs on runways 08/26 and 03/21 and thus more than double the number of aircraft movements which can be handled at peak times, while increasing the overall level of air safety in and around the airport. Construction took four years and cost 1 billion NIS (financed from the Israeli Airports Authority budget) and was completed 29 May 2014. It included paving 22 |
With passenger traffic projected to increase, plans were drawn in the 1980s and 90s for the extension of runways 03/21 and 08/26 as a means of alleviating some of Ben Gurion's safety and capacity concerns. These plans were approved in 1997 and construction began in 2010. The extension of runway 03/21 allows the airport to operate in an "open V" configuration, allowing for simultaneous landings and take offs on runways 08/26 and 03/21 and thus more than double the number of aircraft movements which can be handled at peak times, while increasing the overall level of air safety in and around the airport. Construction took four years and cost 1 billion NIS (financed from the Israeli Airports Authority budget) and was completed 29 May 2014. It included paving {{Convert|22|km}} of runways and taxiways, using more than 1.5 million tons of asphalt, laying one million meters of runway lighting cables, {{Convert|50000|m}} of high-voltage power lines and 10,000 light fixtures.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.globes.co.il/en/article-New-Ben-Gurion-airport-runways-inaugurated-1000942781 |title=New Ben Gurion airport runways inaugurated |access-date=29 May 2014|last=Peretz-Zilberman |first=Sapir |date=29 May 2014|publisher=Globes English }}</ref> The construction of several new taxiways between the existing runways and terminals also significantly reduced [[taxiing|taxi]] times at the airport. |
||
=== |
===Israel-Hamas War (2023- )=== |
||
Due to the threat of missiles, the runway directions are restricted to avoid flying over the [[Israel–Hamas war|war zone in Gaza]]. 08/26 is restricted to departing flights, and 03/21 is restricted to arriving flights.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.flightradar24.com/airport/tlv | title=Live Flight Tracker - Real-Time Flight Tracker Map }}</ref> |
|||
While Ben Gurion Airport is conveniently located in the very center of the country, this fact also means that the airport is surrounded by various residential communities who often complain of noise pollution caused by the airport. Following the completion of the extension of runway 03/21, residents north of the airport sued the Israeli aviation authorities claiming that the authorities intend to use the runway to a greater degree than was originally agreed with them during the approval process for the airport runways' reconfiguration project. |
|||
==Security procedures== |
==Security procedures== |
||
===Overview=== |
===Overview=== |
||
Ben Gurion International Airport |
Security at Ben Gurion International Airport operates on several levels.<ref>{{cite magazine |url=http://www.time.com/time/covers/1101010924/belal.html |title=Is This What We Really Want? |access-date=27 April 2007|last=Beyer |first=Lisa |magazine=[[Time (magazine)|Time]] | date=24 September 2001|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070312052712/http://www.time.com/time/covers/1101010924/belal.html|archive-date=12 March 2007}}</ref> |
||
All cars, taxis, buses and trucks go through a preliminary security [[Border checkpoint|checkpoint]] before entering the airport compound. Armed [[security guard|guards]] spot-check the vehicles by looking into cars, taxis and boarding buses, exchanging a few words with the driver and passengers. Armed security personnel stationed at the terminal entrances keep a close watch on those who enter the buildings. If someone arouses their suspicion or looks nervous, they may strike up a conversation to further assess the person's intent. [[Undercover|Plainclothes]] armed personnel patrol the area outside the building, and hidden [[surveillance camera]]s operate at all times.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://securitysolutions.com/news/security_exposing_hostile_intent|title=What can we learn from Ben Gurion Airport in Israel to help push aviation security in the U.S. to the next level?|publisher=Access Control & Security Systems| |
All cars, taxis, buses and trucks go through a preliminary security [[Border checkpoint|checkpoint]] before entering the airport compound. Armed [[security guard|guards]] spot-check the vehicles by looking into cars, taxis and boarding buses, exchanging a few words with the driver and passengers. Armed security personnel stationed at the terminal entrances keep a close watch on those who enter the buildings. If someone arouses their suspicion or looks nervous, they may strike up a conversation to further assess the person's intent. [[Undercover|Plainclothes]] armed personnel patrol the area outside the building, and hidden [[surveillance camera]]s operate at all times.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://securitysolutions.com/news/security_exposing_hostile_intent|title=What can we learn from Ben Gurion Airport in Israel to help push aviation security in the U.S. to the next level?|publisher=Access Control & Security Systems|access-date=4 May 2007}}</ref> Inside the building, both uniformed and plainclothes security officers are on constant patrol. Departing passengers are personally questioned by security agents even before arriving at the check-in desk. This interview can last as little as a minute, or as long as an hour if a passenger is selected for additional screening. Luggage and [[Strip search|body search]]es may be conducted. |
||
Until August 2007 there was a system of color codes on [[checked baggage]] but the practice was discontinued after complaints of discrimination.<ref>{{cite web|last=Blumenkrantz |first=Zohar |url=http://www.haaretz.com/news/colored-tags-for-arabs-luggage-at-ben-gurion-airport-discontinued-1.227007 |title=Color tags discontinued |publisher=Haaretz.com |date=2007 |
Until August 2007, there was a system of color codes on [[checked baggage]] but the practice was discontinued after complaints of discrimination.<ref>{{cite web|last=Blumenkrantz |first=Zohar |url=http://www.haaretz.com/news/colored-tags-for-arabs-luggage-at-ben-gurion-airport-discontinued-1.227007 |title=Color tags discontinued |publisher=Haaretz.com |date=7 August 2007 |access-date=18 July 2014}}</ref> In the past, checked bags were screened following the personal interview and before passengers arrived at the check-in desks. Occasionally, if security assessed a person as a low risk, they were passed straight through to the check-in desks, bypassing the main [[X-ray]] machines, a practice which also drew some discrimination complaints. This process ceased in April 2014 when the main X-ray machines were removed from the passenger queuing area in Terminal 3 and baggage screening began being performed after the baggage was checked-in by airline representatives (as is common in most airports around the world). Terminal 1 began using the same procedure in the summer of 2017. |
||
===Baggage screening=== |
===Baggage screening=== |
||
After check-in, all checked baggage |
After check-in, all checked baggage are screened using sophisticated X-ray and [[Industrial computed tomography|CT]] scanners and put in a [[pressure chamber]] to trigger any possible explosive devices which have a trigger dependent on air pressure. Following the check-in process, passengers continue to personal security and passport control. Before passing through the [[metal detector]]s and putting carry-on baggage through the X-ray machine at the security checkpoint, passports and boarding passes are re-inspected and additional questions may be asked. Before boarding the aircraft, passports and boarding passes are verified once again. Security procedures for incoming flights are not as stringent, but passengers may be questioned by passport control depending on [[country of origin]], or countries visited prior to arrival in Israel. Passengers who have recently visited Arab countries are subject to further questioning.<ref name="CAv.org">{{cite news|title=Israel airport is safe but hard to emulate|url=http://archives.californiaaviation.org/airport/msg17059.html|work=The Wall Street Journal|date=17 September 2001|first1=Paulo|last1=Prada|first2=Daniel|last2=Michaels|access-date=4 May 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071031045808/http://archives.californiaaviation.org/airport/msg17059.html|archive-date=31 October 2007|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
||
==Airlines and destinations== |
==Airlines and destinations== |
||
===Passenger=== |
===Passenger=== |
||
The following airlines serve regular scheduled and charter destinations at Ben Gurion Airport.<ref>{{cite web |title=Full List of Flights to Ben Gurion Airport, Tel Aviv, Israel |url=https://www.touristisrael.com/full-list-flights-tel-aviv-israel/12331/ |access-date=22 February 2020|date=27 July 2015 }}</ref> Most of the airlines have been suspended or have delayed their resumption due to the Israel-Hamas War since October 7th, 2023 and the ongoing situation in the Middle East.<ref>{{cite news |title=Full list of Flight cancellations to Ben Gurion Airport amid the October 7th War with Hamas |access-date=June 15, 2024 |url=https://www.israelhayom.com/2024/11/13/the-complete-guide-to-all-airline-flight-cancellations-to-israel-2/ |newspaper=[[Israel Hayom]] }}</ref> Some Airports have even taken out flights to Tel Aviv from their list of destinations. |
|||
<!--DO NOT ADD OR REMOVE ROUTES WITHOUT GIVING A VALID INDEPENDENT SOURCE. EXACT DATES ARE MANDATORY FOR NEW ROUTES TO BE ADDED HERE. ALSO ADD INLINE CITATIONS IF POSSIBLE.--> |
|||
{{Airport-dest-list |
{{Airport-dest-list |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Aegean Airlines]] | [[Athens International Airport|Athens]] (resumes {{date|2024-12-10}}),<ref name="A3_TLV_12-24">{{cite news |last1=אזולאי |first1=עדי |title=חברת Aegean Airlines חוזרת לישראל |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/193581 |access-date=27 November 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=27 November 2024 |language=he}}</ref> [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]] (resumes {{date|2024-12-10}}),<ref name="A3_TLV_12-24" /> [[Thessaloniki Airport|Thessaloniki]] (suspended until {{date|2025-1-14}})<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
| [[Adria Airways]] | '''Seasonal:''' [[Ljubljana Jože Pučnik Airport|Ljubljana]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Air Canada]] | [[Toronto Pearson International Airport|Toronto–Pearson]] (suspended)<br />'''Seasonal:''' [[Montréal–Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport|Montréal–Trudeau]] (suspended)<ref name="AirCanadaIL_24-25">{{cite web |title=Travel to or from Israel |url=https://www.aircanada.com/ca/en/aco/home/book/travel-news-and-updates/2024/travel-to-from-israel.html#/ |website=www.aircanada.com |publisher=Air Canada |access-date=14 July 2024 |language=en-ca}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Aegean Airlines]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Flight Schedules |url=https://en.aegeanair.com/plan/flight-schedules/ |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Athens International Airport|Athens]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[Thessaloniki International Airport|Thessaloniki]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Mykonos Airport|Mykonos]]<br>'''Seasonal charter:''' [[Kos International Airport|Kos]], [[Rhodes International Airport|Rhodes]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Air Europa]] | [[Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport|Madrid]] (resumes {{date|2024-12-18}}) |
|||
| [[Aeroflot]] | [[Moscow–Sheremetyevo]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Air France]] | [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]] (suspended until {{date|2024-12-31}})<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
| [[airBaltic]] | [[Riga International Airport|Riga]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Air India]] | [[Indira Gandhi International Airport|Delhi]] (suspended until {{date|2025-2-27}})<ref>{{cite news |title=אייר אינדיה: הטיסות לישראל מבוטלות עד למועד זה |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/193611 |access-date=29 November 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=29 November 2024 |language=he}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Air Bucharest]] |'''Seasonal:''' [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Air Seychelles]] | [[Seychelles International Airport|Mahé]] (resumes {{date|2025-1-8}})<ref>{{cite news |title=המגמה נמשכת: גם אייר סיישל חוזרת לישראל |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/193594 |access-date=28 November 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=28 November 2024 |language=he}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Air Canada]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Air Canada flight schedules |url=https://www.aircanada.com/ca/en/aco/home/book/routes-and-partners/flight-schedules.html |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Toronto Pearson International Airport|Toronto–Pearson]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Montréal-Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport|Montréal–Trudeau]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[airBaltic]] | [[Riga International Airport|Riga]] (suspended until {{date|2024-12-21}}),<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> [[Vilnius Airport|Vilnius]] (begins {{date|2025-3-31}})<ref>{{cite news |last1=Reinstein |first1=Ziv |title=New direct flights from Israel to Lithuania by Air Baltic, begin March 31 |url=https://www.jpost.com/israel-news/article-818772 |access-date=22 October 2024 |work=JPost.com |publisher=The Jerusalem Post |date=4 September 2024 |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[airHaifa]] | [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]]<ref>{{cite news |last1=COHEN |first1=MOSHE |title=Joining the line: The new Israeli company will start flying to Cyprus |url=https://www.jpost.com/brandblend/joining-the-line-the-new-israeli-company-will-start-flying-to-cyprus-823897 |access-date=10 October 2024 |work=JPost.com |publisher=The Jerusalem Post |date=9 October 2024 |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Air Europa]] | [[Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport|Madrid]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]], [[Palma de Mallorca Airport|Palma de Mallorca]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[American Airlines]] | [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]] (suspended)<ref>{{Cite web |title=American Airlines won't fly to Israel again until at least September 2025|url=https://www.jta.org/2024/11/04/israel/american-airlines-wont-fly-to-israel-again-until-at-least-september-2025|website=Jewish Telegraphic Agency |date=November 4, 2024|access-date=November 5, 2024}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Air France]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Air France flight schedule |url=https://www.airfrance.us/US/en/local/resainfovol/horaires/horaires.do |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Nice Côte d'Azur Airport|Nice]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[arkia]] | [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]], [[Athens International Airport|Athens]], [[Josep Tarradellas Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]],<ref>{{cite news |title=Arkia Adds One-time Leased 737 MAX Barcelona Service in mid-August 2023 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/230808-izaug23bcn |access-date=9 August 2023 |work=AeroRoutes |date=8 August 2023 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport|Belgrade]], [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest–Otopeni]], [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]],<ref name="IZ_BUD_MXP">{{cite news |last1=קוטלר |first1=עמית |title=החל מ-169 דולר: מילאנו, בודפשט, דובאי וגם יוון וקפריסין. לוח הטיסות החדש של ארקיע |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/192863 |access-date=22 October 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=22 October 2024 |language=he}}</ref> [[Dubai International Airport|Dubai–International]], [[Ramon Airport|Eilat]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[Manchester Airport|Manchester]],<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Arkia Schedules Tel Aviv – Manchester Service in Oct 2024 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240718-izoct24man |access-date=19 July 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=18 July 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Milan Malpensa Airport|Milan–Malpensa]],<ref name="IZ_BUD_MXP" /> [[Paphos International Airport|Paphos]], [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]],<ref>{{cite news |title=מרחיבה פעילותה: ארקיע תפעיל טיסות לפריז |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/193073 |access-date=4 November 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |date=4 November 2024 |language=he}}</ref> [[Václav Havel Airport Prague|Prague]],<ref name="IZ_BUD_MXP" /> [[Leonardo da Vinci-Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]], [[Shota Rustaveli Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]], [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]]<br /> '''Seasonal:''' [[Batumi International Airport|Batumi]], [[Corfu International Airport|Corfu]], [[Heraklion International Airport|Heraklion]], [[Mykonos Airport|Mykonos]], [[Plovdiv Airport|Plovdiv]], [[Rhodes International Airport|Rhodes]] |
|||
| [[Air India]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Air India timetable |url=http://www.airindia.in/time-table.htm |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Indira Gandhi International Airport|Delhi]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ |
| [[Austrian Airlines]] | [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]] (suspended until {{date|2025-1-31}})<ref name="LH_G_TLV_Jan25" /> |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Azerbaijan Airlines]] | [[Heydar Aliyev International Airport|Baku]]<ref>{{cite news |last1=אזולאי |first1=רואי |title=הראשונה לחזור: אזרבייג׳ן איירליינס תשוב להפעיל טיסות בקו ת״א - באקו |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/193576 |access-date=27 November 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=27 November 2024 |language=he}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Air Moldova]] | [[Chișinău International Airport|Chișinău]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ |
| [[Azimuth (airline)|azimuth]] | [[Adler-Sochi International Airport|Sochi]] |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Bees Airlines]] | [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest–Otopeni]],<ref name="E8_TLV">{{cite news |last1=Sipinski |first1=Dominik |title=Romania's Bees Airlines to launch scheduled ops in 3Q24 |url=https://www.ch-aviation.com/news/143081-romanias-bees-airlines-to-launch-scheduled-ops-in-3q24 |access-date=1 August 2024 |publisher=ch-aviation GmbH |date=30 July 2024}}</ref> [[Suceava Ștefan cel Mare International Airport|Suceava]] (both suspended until {{date|2024-12-15}})<ref name="E8_TLV" /><ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
| [[Air Sinai]] | [[Cairo International Airport|Cairo]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Bluebird Airways]]<ref name=BB_TLV_NOV_24>{{cite news |last1=קוטלר |first1=עמית |title=החל מ-59$ לכיוון, 198$ לטיסת הלוך ושוב: מבצעי החזרה לישראל של Blue Bird |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/192867 |access-date=22 October 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=22 October 2024 |language=he}}</ref> | [[Athens International Airport|Athens]], [[Josep Tarradellas Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]], [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[Václav Havel Airport Prague|Prague]], [[Sofia International Airport|Sofia]], [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]] |
|||
| [[AlbaStar]] | '''Seasonal charter:''' [[Palma de Mallorca Airport|Palma de Mallorca]],<ref name="iaa">{{cite web|url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/en-US/airports/bengurion/Pages/OnlineFlights.aspx?mode=in#|title=Online Flights|publisher=iaa.gov.il|accessdate=1 April 2018}}</ref> [[Verona Villafranca Airport|Verona]]<ref name="iaa"/> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[British Airways]] | [[Heathrow Airport|London–Heathrow]] (suspended until {{date|2025-3-30}})<ref>{{cite news |title=British Airways to cancel all flights to Israel until end of March next year |url=https://www.jpost.com/breaking-news/article-825501 |access-date=21 October 2024 |work=The Jerusalem Post |publisher=JPost.com |date=21 October 2024 |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Albawings]] | '''Seasonal charter:''' [[Tirana International Airport Nënë Tereza|Tirana]]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.tirana-airport.com/d/7/46/156/tirana-international-airport-welcomes-first-israeli-tourists-on-board-albawings/|title=Tirana International Airport: New flight Tirana–Dortmund begins, operated by Wizz Air - Tirana International Airport|website=www.tirana-airport.com}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Brussels Airlines]] | [[Brussels Airport|Brussels]] (suspended until {{date|2025-1-31}})<ref name="LH_G_TLV_Jan25" /> |
|||
| [[Alitalia]] | [[Athens International Airport|Athens]], [[Milan Malpensa Airport|Milan–Malpensa]] (resumes 29 July 2019),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/282946/alitalia-resumes-milan-tel-aviv-route-from-late-july-2019/|title=Alitalia resumes Milan – Tel Aviv service from late-July 2019|date=14 February 2019|website=routesonline.com}}</ref> [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Bulgaria Air]] | [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]] (resumes {{date|2024-12-26}})<ref>{{cite news |title=השמיים נפתחים: בולגריה אייר חוזרת לישראל |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/193598 |access-date=28 November 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=28 November 2024 |language=he}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Arkia]] | [[Suvarnabhumi Airport|Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi]], [[Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]], [[Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport|Belgrade]], [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest]], [[Chișinău International Airport|Chișinău]], [[Eilat Airport|Eilat–Hozman]] (ends 18 March 2019),<ref name=eilat_closedown>{{Cite news|url=https://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-5449527,00.html|title=Eilat Airport to close down after 70 years}}</ref> [[Ramon Airport|Eilat–Ramon]],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://en.globes.co.il/en/article-can-ramon-airport-breathe-new-life-into-eilat-1001269663/|title=Can Ramon Airport breathe new life into Eilat?|publisher=en.globes.co.il|date=20 January 2019}}</ref> [[Cochin International Airport|Kochi]] (begins 27 September 2019),<ref name=India>{{Cite news|url=https://en.globes.co.il/en/article-arkia- to-launch-2-israel-india-routes-1001272773?fbclid=IwAR2Jya6Udpv2OYCq8exnUvk5m-sXNQCcAY5iyvSnVsUUMovOk47n8IgkReI|title=Arkia to launch 2 Israel - India routes|publisher=[[Globes]]|accessdate=12 Feb 2019}}</ref> [[London Stansted Airport|London–Stansted]] <br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]], [[Heydar Aliyev International Airport|Baku]], [[EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg|Basel/Mulhouse]], [[Batumi International Airport|Batumi]], [[Orio al Serio International Airport|Bergamo]], [[Bergen Airport, Flesland|Bergen]] (begins 10 July 2019),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/281508/arkia-s19-norway-service-changes/|title=Arkia S19 Norway service changes|publisher=routesonline.com|date=14 November 2018}}</ref> [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]], [[Catania–Fontanarossa Airport|Catania]], [[Dublin Airport|Dublin]], [[Heraklion International Airport|Heraklion]], [[Kos International Airport|Kos]], [[Ljubljana Jože Pučnik Airport|Ljubljana]], [[Seychelles International Airport|Mahé]], [[Munich Airport|Munich]], [[Mykonos Airport|Mykonos]], [[Ohrid St. Paul the Apostle Airport|Ohrid]], [[Gardermoen Airport|Oslo–Gardermoen]], [[Paphos International Airport|Paphos]] (resumes {{date|2019-6-7}}),<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Arkia adds Paphos service from June 2019 |url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/282780/arkia-adds-paphos-service-from-june-2019/ |accessdate=5 February 2019 |work=Routesonline |date=5 February 2019}}</ref> [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]], [[Rhodes International Airport|Rhodes]], [[Rijeka Airport|Rijeka]], [[Rovaniemi Airport|Rovaniemi]], [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]],<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Arkia adds Sofia service in 1Q19 |url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/281865/arkia-adds-sofia-service-in-1q19/ |accessdate=6 December 2018 |work=Routesonline |date=6 December 2018}}</ref> [[Strasbourg Airport|Strasbourg]] (begins 2 July 2019),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/281444/arkia-plans-strasbourg-seasonal-service-in-3q19/|title=Arkia plans Strasbourg seasonal service in 3Q19|publisher=routesonline.com|date=9 November 2018}}</ref> [[Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]], [[Thessaloniki International Airport|Thessaloniki]], [[Zvartnots International Airport|Yerevan]], [[Zanzibar International Airport|Zanzibar]]<br>'''Seasonal charter:''' [[Berlin Schönefeld Airport|Berlin–Schönefeld]],<ref name="iaa"/> [[Burgas Airport|Burgas]],<ref name="iaa"/> [[Geneva Airport|Geneva]],<ref name="iaa"/> [[Alpes–Isère Airport|Grenoble]],<ref name="iaa"/> [[Karpathos Island National Airport|Karpathos]],<ref name="iaa"/> [[Plovdiv Airport|Plovdiv]],<ref name="iaa"/> [[Verona Villafranca Airport|Verona]]<ref name="iaa"/> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Cathay Pacific]] | [[Hong Kong International Airport|Hong Kong]] (suspended)<ref>{{cite news |last1=Wrobel |first1=Sharon |title=Cathay Pacific extends suspension of flights between Hong Kong and Israel until March 2025 |url=https://www.timesofisrael.com/liveblog_entry/cathay-pacific-extends-suspension-of-flights-between-hong-kong-and-israel-until-march-2025/ |access-date=21 July 2024 |publisher=The Times of Israel |date=17 July 2024}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Armenia Aircompany]] | [[Zvartnots International Airport|Yerevan]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Corendon Airlines]] | '''Seasonal charter:''' [[Rovaniemi Airport|Rovaniemi]] (begins {{date|2025-1-31}})<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Corendon Airlines 1Q25 Tel Aviv – Rovaniemi Charters |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/241118-xr1q25tlvrvn |access-date=19 November 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=19 November 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> |
|||
| [[ASL Airlines France]] | '''Seasonal:''' [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ |
| [[Cyprus Airways]] | [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]]<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Delta Air Lines]]| [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]] (suspended until {{date|2025-3-31}})<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24">{{cite news |title=כל העדכונים השוטפים של חברות התעופה: פספורטניוז עושה לכם סדר |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/191420 |access-date=6 August 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=6 August 2024 |language=he}}</ref> |
|||
|[[AtlasGlobal]] | [[Istanbul Atatürk Airport|Istanbul–Atatürk]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[easyJet]]<ref>{{cite news |title=easyJet suspends Israel flights until March 2025 |url=https://en.globes.co.il/en/article-easyjet-suspends-israel-flights-until-march-2025-1001486182 |access-date=25 August 2024 |work=Globes |publisher=Globes, Israel business news |date=8 July 2024 |language=en}}</ref> | [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]] (resumes 1 April 2025), [[EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg|Basel/Mulhouse]] (resumes 30 March 2025), [[Berlin Brandenburg Airport|Berlin]] (resumes 30 March 2025), [[Geneva Airport|Geneva]] (resumes 30 March 2025), [[Luton Airport|London–Luton]] (resumes 30 March 2025), [[Milan Malpensa Airport|Milan–Malpensa]] (resumes 1 April 2025), [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]] (resumes 1 April 2025) |
|||
| [[Austrian Airlines]] | [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[El Al]]<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/230322-ly777 | title=El al NS23 Boeing 777 European Network – 21MAR23 }}</ref> | [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]],<ref name="auto">{{Cite web|url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240805-ly1h25787|title=El Al Outlines 293-seater 787-9 Network in 2025|website=AeroRoutes|accessdate=17 August 2024}}</ref> [[Athens International Airport|Athens]],<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/230222-ly772 | title=El al NS23 Boeing 777 European Operations – 20FEB23 }}</ref> [[Suvarnabhumi Airport|Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi]],<ref name="auto"/><ref name="seat1">{{cite web | url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240805-ly1h25787 | title=El al Outlines 293-seater 787-9 Network in 2025 }}</ref> [[Josep Tarradellas Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]],<ref name="aeroroutes_240315-lyns24eu">{{Cite web|url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240315-lyns24eu|title=El Al NS24 Europe Service Changes – 14MAR24|website=Aeroroutes}}</ref> [[Berlin Brandenburg Airport|Berlin]],<ref name="aeroroutes_240315-lyns24eu"/> [[Boston Logan International Airport|Boston]],<ref name="aeroroutes_231218-dllycodeshare">{{Cite web|url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/231218-dllycodeshare|title=Delta / El Al Begins Codeshare Partnership From Jan 2024|website=Aeroroutes}}</ref> [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest–Otopeni]],<ref name="aeroroutes_240315-lyns24eu"/> [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]], [[Dubai International Airport|Dubai–International]],<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240315-lyjun24dxb | title=El al June – September 2024 Dubai Service Changes }}</ref> [[Fort Lauderdale–Hollywood International Airport|Fort Lauderdale]],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.local10.com/news/local/2023/02/15/fort-lauderdale-airport-getting-first-ever-flights-to-israel-heres-when-they-start/|title=Fort Lauderdale airport getting first-ever flights to Israel; here's when they start|website=Local10News|date=15 February 2023|access-date=15 February 2023}}</ref> [[Frankfurt Airport|Frankfurt]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[Lisbon Airport|Lisbon]],<ref name="aeroroutes_240315-lyns24eu"/> [[Heathrow Airport|London–Heathrow]],<ref name="part1">{{Cite web|url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240129-sklycodeshare|title=El Al / SAS Begins Codeshare Partnership From Feb 2024|website=Aeroroutes}}</ref> [[Luton Airport|London–Luton]], [[Los Angeles International Airport|Los Angeles]],<ref name="aeroroutes_231218-dllycodeshare"/> [[Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport|Madrid]],<ref name="part1"/> [[Marseille Provence Airport|Marseille]],<ref name="aeroroutes.com">{{cite web | url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240311-aflycodeshare | title=Air France / El al Begins Reciprocal Codeshare Partnership in NS24 }}</ref> [[Miami International Airport|Miami]],<ref name="aeroroutes_231218-dllycodeshare"/> [[Milan Malpensa Airport|Milan–Malpensa]],<ref name="aeroroutes_240315-lyns24eu"/> [[Moscow Domodedovo Airport|Moscow–Domodedovo]], [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark]],<ref name="aeroroutes_231214-lynw23nyc">{{cite web | url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/231214-lynw23nyc | title=El al Israel Airlines New York JFK Nov 2023 – Jan 2024 Service Increases }}</ref> [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]],<ref name="aeroroutes_231214-lynw23nyc"/> [[Nice Côte d'Azur Airport|Nice]],<ref name="aeroroutes.com"/> [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]],<ref name="aeroroutes_240315-lyns24eu"/> [[Phuket International Airport|Phuket]],<ref name="auto"/><ref name="seat1"/> [[Václav Havel Airport Prague|Prague]], [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]],<ref name="aeroroutes_240315-lyns24eu"/> [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]],<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/220817-lynw22sof | title=El al NW22 Sofia Aircraft Changes }}</ref> [[Thessaloniki Airport|Thessaloniki]],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://money-tourism.gr/el-al-nees-syndeseis-pros-thessaloniki-ptiseis-koinoy-kodikoy-aegean-eurowings/ |title=El Al: Νέες συνδέσεις προς Θεσσαλονίκη |date=15 March 2024}}</ref> [[Narita International Airport|Tokyo–Narita]],<ref>{{cite news |title=El Al Maintains Tokyo March 2024 Service Resumption |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240108-lymar24nrt |access-date=9 January 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=8 January 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]], [[Zurich Airport|Zürich]]<ref name="aeroroutes_240315-lyns24eu"/> <br /> '''Seasonal:''' [[Venice Marco Polo Airport|Venice]] |
|||
| [[Azerbaijan Airlines]] | [[Heydar Aliyev International Airport|Baku]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ |
| [[Ethiopian Airlines]] | [[Addis Ababa Bole International Airport|Addis Ababa]]<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Blue Air]] | [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest]], [[Cluj International Airport|Cluj-Napoca]] (ends 30 June 2019) |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Etihad Airways]] | [[Abu Dhabi International Airport|Abu Dhabi]] |
|||
| [[Bluebird Airways]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Bluebird Airways Flight Status |url=https://www.airportia.com/airlines/bluebird-airways |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | '''Seasonal:''' [[Berlin Schönefeld Airport|Berlin–Schönefeld]], [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest]], [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]], [[Heraklion International Airport|Heraklion]], [[Kos International Airport|Kos]], [[Rhodes International Airport|Rhodes]], [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]], [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Eurowings]] | [[Düsseldorf Airport|Düsseldorf]] (suspended until {{date|2025-1-31}})<ref name="LH_G_TLV_Jan25" /> |
|||
| [[British Airways]]<ref>{{cite web |title=British Airways - Timetables |url=https://www.britishairways.com/travel/schedules/public/en_us |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Heathrow Airport|London–Heathrow]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ |
| [[flydubai]] | [[Dubai International Airport|Dubai–International]] |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[FlyOne]] | [[Chișinău International Airport|Chișinău]]<ref name="5F_Res_TLV_24">{{cite news |last1=אזולאי |first1=איתי |title=FLYONE מולדובה חוזרת לטוס לישראל |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/188836 |access-date=20 February 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |date=20 February 2024 |language=he}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Bulgaria Air]] | [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Burgas Airport|Burgas]], [[Varna Airport|Varna]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[FlyOne Armenia]] | [[Zvartnots International Airport|Yerevan]]<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://flyone.eu/en/About-FLYONE/News/2021/10/28/FLYONE-Armenia-received-the-Air-Operator-Certificate |title=FLYONE Armenia received the Air Operator Certificate!|date=28 October 2021 |website=flyone.eu}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Bulgarian Air Charter]] | '''Seasonal charter:''' [[Burgas Airport|Burgas]],<ref name="iaa"/> [[Varna Airport|Varna]]<ref name="iaa"/> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Georgian Airways]] | [[Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Daily Direct Flights To Tel Aviv |url=https://georgian-airways.com/en/news/daily-direct-flights-to-tel-aviv |website=georgian-airways.com |publisher=Georgian Airways |access-date=4 May 2024}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Cathay Pacific]] | [[Hong Kong International Airport|Hong Kong]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ |
| [[Hainan Airlines]] | [[Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport|Shenzhen]] |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[HiSky]] | [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest–Otopeni]],<ref name="aeroroutes_230307-h4tlv">{{Cite web|url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/230307-h4tlv|title=HiSky Adds Cluj – Tel Aviv Service in NS23|website=Aeroroutes.com|accessdate=2 November 2024}}</ref> [[Chișinău International Airport|Chișinău]]<ref name="aeroroutes_230307-h4tlv"/> |
|||
| [[Croatia Airlines]] | '''Seasonal:''' [[Dubrovnik Airport|Dubrovnik]], [[Zagreb Airport|Zagreb]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Iberia Express]] | [[Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport|Madrid]] (suspended until {{date|2025-3-31}})<ref>{{cite news |title=לא בקרוב: Iberia Express משעה טיסותיה לישראל עד למועד זה |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/193625 |access-date=30 November 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=30 November 2024 |language=he}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Charlie Airlines|Cyprus Airways]] | [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Israir Airlines]] | [[Athens International Airport|Athens]], [[Heydar Aliyev International Airport|Baku]], [[Batumi International Airport|Batumi]], [[Orio al Serio International Airport|Bergamo]] (resumes {{date|2025-1-11}}),<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Israir Adds Milan Bergamo in 1Q25 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/241125-6h1q25bgy |access-date=25 November 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=25 November 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Berlin Brandenburg Airport|Berlin]], [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest–Otopeni]], [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]], [[Chișinău International Airport|Chișinău]],<ref>{{cite news |title=Israir Schedules Chisinau Service in NW23 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/230808-6hnw23kiv |access-date=9 August 2023 |work=AeroRoutes |date=8 August 2023 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Dubai International Airport|Dubai–International]], [[Ramon Airport|Eilat]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[Lisbon Airport|Lisbon]],<ref name="IsrairAdditions"/> [[Luton Airport|London–Luton]],<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Israir Adds Tel Aviv – London Luton From mid-Nov 2024 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/241104-6hnov24ltn |access-date=4 November 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=4 November 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Václav Havel Airport Prague|Prague]], [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]],<ref name="Israir_NS24">{{cite news |title=Israir NS24 Leased Smartwings Boeing 737 Operations |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240321-6hns24qs |access-date=21 March 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=21 March 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]], [[Varna Airport|Varna]] <br /> '''Seasonal:''' [[Catania–Fontanarossa Airport|Catania]],<ref name="6H">{{cite web |title=Israir NS22 Network Additions Update - 03Apr22 |url=https://aeroroutes.com/eng/220404-6hns22 |website=Aeroroutes |access-date=4 April 2022}}</ref> [[Chania International Airport|Chania]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.israirairlines.com|title=Israir|website=www.israirairlines.com}}</ref> [[Corfu International Airport|Corfu]], [[Heraklion International Airport|Heraklion]], [[Ljubljana Jože Pučnik Airport|Ljubljana]], [[Málaga Airport|Málaga]],<ref name="IsrairAdditions">{{cite web|url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/221107-6hns23eu|title=ISRAIR NS23 EUROPEAN NETWORK ADDITIONS – 06NOV22|website=Aeroroutes|date=7 November 2022|access-date=12 December 2022}}</ref> [[Naples International Airport|Naples]], [[Paphos International Airport|Paphos]],<ref name="Israir_NS24"/> [[Rhodes International Airport|Rhodes]], [[Salzburg Airport|Salzburg]],<ref name="Israir_NS24" /> [[Tirana Airport|Tirana]],<ref name="Israir_NS24" /> [[Tivat Airport|Tivat]],<ref name="Israir_NS24" /> [[Verona Villafranca Airport|Verona]], [[Abeid Amani Karume International Airport|Zanzibar]] |
|||
| [[Delta Air Lines]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Delta Routes |url=https://www.delta.com/us/en/flight-deals/overview |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ITA - Italia Trasporto Aereo|ITA Airways]] | [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]] (suspended until {{date|2025-1-12}})<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
| [[easyJet]]<ref name="auto">{{cite web |title= easyJet.com {{!}} Flight Timetables |url= http://www.easyjet.com/en/cheap-flights/timetables |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]], [[Berlin Schönefeld Airport|Berlin–Schönefeld]], [[Berlin Tegel Airport|Berlin–Tegel]], [[Bordeaux–Mérignac Airport|Bordeaux]], [[Luton Airport|London–Luton]], [[Lyon–Saint-Exupéry Airport|Lyon]], [[Manchester Airport|Manchester]], [[Malpensa Airport|Milan–Malpensa]], [[Nantes Atlantique Airport|Nantes]] (begins 1 April 2019), [[Naples International Airport|Naples]], [[Nice Côte d'Azur Airport|Nice]], [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]], [[Venice Marco Polo Airport|Venice]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Gatwick Airport|London–Gatwick]], [[London Stansted Airport|London–Stansted]]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.easyjet.com/en/cheap-flights/london-stansted/tel-aviv|title=London Stansted to Tel Aviv - Cheap Flights £99.27 or less|website=www.easyjet.com}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[KLM]] | [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]] (suspended until {{date|2025-3-25}}))<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
| [[easyJet Switzerland]]<ref name="auto"/> | [[EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg|Basel/Mulhouse]], [[Geneva Airport|Geneva]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[LOT Polish Airlines]]| [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw–Chopin]] (suspended until {{date|2024-12-17}})<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
| [[El Al]]<ref name="elalofficial">[https://www.elal.com/en/PassengersInfo/Useful-Info/Flight-Schedule/Pages/Flights-Schedule.aspx elal.com - Flight Schedule] retrieved 16 October 2018</ref> | [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]], [[Athens International Airport|Athens]], [[Suvarnabhumi Airport|Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi]], [[Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]], [[Beijing Capital International Airport|Beijing–Capital]], [[Berlin Schönefeld Airport|Berlin–Schönefeld]], [[Logan International Airport|Boston]], [[Brussels Airport|Brussels]], [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest]], [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]], [[Frankfurt Airport|Frankfurt]], [[Geneva Airport|Geneva]], [[Hong Kong International Airport|Hong Kong]], [[O. R. Tambo International Airport|Johannesburg–O. R. Tambo]], [[Boryspil International Airport|Kiev–Boryspil]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[McCarran International Airport|Las Vegas]] (begins 14 June 2019),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://en.globes.co.il/en/article-el-al-to-launch-tel-aviv-las-vegas-flights-1001264150|title=El Al to launch Tel Aviv - Las Vegas flights|last=Raz-Chaimovich|first=Michal|website=Globes: Israel's Business Arena|publisher=Globes|date=10 December 2018 |accessdate=10 December 2018}}</ref> [[Lisbon Airport|Lisbon]], [[Heathrow Airport|London–Heathrow]], [[Luton Airport|London–Luton]], [[Los Angeles International Airport|Los Angeles]], [[Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport|Madrid]], [[Manchester Airport|Manchester]] (resumes 26 May 2019),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/281350/el-al-proposes-manchester-service-resumption-from-late-may-2019/|title=El Al proposes Manchester service resumption from late-May 2019|publisher=Routesonline|date=5 November 2018}}</ref> [[Marseille Provence Airport|Marseille]], [[Miami International Airport|Miami]], [[Milan Malpensa Airport|Milan–Malpensa]], [[Domodedovo International Airport|Moscow–Domodedovo]], [[Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport|Mumbai]], [[Munich Airport|Munich]], [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]], [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark]], [[Nice Côte d'Azur Airport|Nice]] (begins 7 April 2019),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ias.co.il/%D7%AA%D7%99%D7%99%D7%A8%D7%95%D7%AA/%D7%90%D7%9C-%D7%A2%D7%9C-%D7%AA%D7%97%D7%9C-%D7%9C%D7%98%D7%95%D7%A1-%D7%9C%D7%A0%D7%99%D7%A1-%D7%A9%D7%91%D7%A8%D7%99%D7%91%D7%99%D7%99%D7%A8%D7%94-%D7%94%D7%A6%D7%A8%D7%A4%D7%AA%D7%99%D7%AA-%D7%91%D7%90%D7%91%D7%99%D7%91/|title=אל על תחל לטוס לניס שבריביירה הצרפתית באביב - IAS|date=25 October 2018|publisher=}}</ref> [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]], [[Václav Havel Airport Prague|Prague]], [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]], [[San Francisco International Airport|San Francisco]] (begins 13 May 2019),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/278831/el-al-delays-san-francisco-launch-to-may-2019/|title=El Al delays San Francisco launch to May 2019|last=Liu|first=Jim|publisher=UBM (UK) Ltd.|website=routesonline|accessdate=27 May 2018}}</ref> [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]], [[Toronto Pearson International Airport|Toronto–Pearson]], [[Venice Marco Polo Airport|Venice]], [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]], [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw–Chopin]], [[Zurich Airport|Zürich]]<br>'''Seasonal''': [[Orlando International Airport|Orlando]] (begins 2 July 2019)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/282927/el-al-adds-seasonal-orlando-service-in-3q19/|title=El Al adds seasonal Orlando service in 3Q19|publisher=Airlineroute|date=13 February 2019|accessdate=13 February 2019}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Lufthansa]] | [[Frankfurt Airport|Frankfurt]], [[Munich Airport|Munich]] (both suspended until {{date|2025-1-31}})<ref name="LH_G_TLV_Jan25">{{cite news |last1=Wrobel |first1=Sharon |title=Lufthansa extends suspension of Tel Aviv flights until Jan. 31 |url=https://www.timesofisrael.com/liveblog_entry/lufthansa-extends-suspension-of-tel-aviv-flights-until-jan-31/ |access-date=2 December 2024 |publisher=The Times of Israel |date=2 December 2024}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Enter Air]] | '''Seasonal charter:''' [[Katowice International Airport|Katowice]], [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw–Chopin]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Qanot Sharq]] | [[Samarkand International Airport|Samarqand]],<ref name="HHtoTLV" /> [[Islam Karimov Tashkent International Airport|Tashkent]]<ref name="HHtoTLV">{{cite news |title=Qanot Sharq Adds Tel Aviv Schedule in NS23 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/230316-hhtlv |access-date=13 July 2023 |work=AeroRoutes |date=16 March 2023 |language=en-CA}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Ethiopian Airlines]] | [[Addis Ababa Bole International Airport|Addis Ababa]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Red Wings Airlines]] | [[Moscow Domodedovo Airport|Moscow–Domodedovo]],<ref name="WZ_TLV_MOW_24">{{cite news |title=Red Wings Resumes Moscow – Tel Aviv Service From late-Jan 2024 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240105-wzjan24tlv |access-date=7 January 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=5 January 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Zhukovsky International Airport|Moscow–Zhukovsky]], [[Adler-Sochi International Airport|Sochi]] |
|||
| [[Finnair]] | [[Helsinki Airport|Helsinki]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Ryanair]]<ref name='FR_TLV_J24'>{{cite news |last1=Lifshitz-Klieger |first1=Iris |title=Irish low-cost carrier Ryanair to resume Israel operations |url=https://www.ynetnews.com/travel/article/rkpf7b3kr |access-date=6 April 2024 |work=Ynetnews |date=4 April 2024 |language=en}}</ref><ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> | [[Athens International Airport|Athens]] (resumes {{date|2025-04-01}}), [[Bari Karol Wojtyła Airport|Bari]] (resumes {{date|2025-04-01}}), [[Orio al Serio International Airport|Bergamo]] (resumes {{date|2025-02-01}}),<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/230516-frns23it|title=Ryanair May – Oct 2023 Italy Frequency Variations – 14MAY23|website=Aeroroutes}}</ref> [[Berlin Brandenburg Airport|Berlin]] (resumes {{date|2025-02-02}}), [[Bologna Airport|Bologna]] (resumes {{date|2025-03-30}}), [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest–Otopeni]] (resumes {{date|2025-04-02}}), [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]] (resumes {{date|2025-02-01}}), [[Chania Airport|Chania]] (begins 1 June 2025), [[Charleroi Airport|Charleroi]] (resumes {{date|2025-02-02}}),<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.aviation24.be/airlines/ryanair/ryanair-expands-brussels-south-charleroi-network-with-9-new-or-resumed-winter-routes-in-2024/ | title=Ryanair expands Brussels South Charleroi network with 9 new or resumed winter routes in 2024 | date=27 August 2024 }}</ref> [[Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden Airport|Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden]] (resumes {{date|2025-03-30}}), [[Kraków John Paul II International Airport|Kraków]] (resumes {{date|2025-02-03}}), [[Malta International Airport|Malta]] (suspended until {{date|2025-04-01}}), [[Naples Airport|Naples]] (resumes {{date|2025-03-31}}), [[Paphos International Airport|Paphos]] (resumes {{date|2025-02-01}}), [[Poznań–Ławica Airport|Poznań]] (resumes {{date|2025-03-30}}), [[Rome Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]] (resumes {{date|2025-02-04}}), [[Sofia International Airport|Sofia]] (resumes {{date|2025-03-31}}), [[Macedonia International Airport|Thessaloniki]] (begins {{date|2025-03-30}}), [[Treviso Airport|Treviso]] (resumes {{date|2025-04-05}}), [[Turin Airport|Turin]] (resumes {{date|2025-03-30}}), [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]] (resumes {{date|2025-02-01}}), [[Vilnius International Airport|Vilnius]] (resumes {{date|2025-04-02}}) |
|||
| [[Georgian Airways]] | [[Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Batumi International Airport|Batumi]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Smartwings]] | [[Václav Havel Airport Prague|Prague]]<ref name="QS_res_TLV_24">{{cite news |last1=אביטן |first1=יותם |title=חברת תעופה אירופאית נוספת חוזרת לישראל |url=https://aviationews.co.il/2024/01/16/%d7%97%d7%91%d7%a8%d7%aa-%d7%aa%d7%a2%d7%95%d7%a4%d7%94-%d7%90%d7%99%d7%a8%d7%95%d7%a4%d7%90%d7%99%d7%aa-%d7%a0%d7%95%d7%a1%d7%a4%d7%aa-%d7%97%d7%95%d7%96%d7%a8%d7%aa-%d7%9c%d7%99%d7%a9%d7%a8%d7%90-2/ |access-date=17 January 2024 |work=חדשות תעופה |date=16 January 2024 |language=he-IL}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Hainan Airlines]] | [[Beijing Capital International Airport|Beijing–Capital]], [[Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport|Guangzhou]] (ends {{date|2019-2-20}}),<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Hainan Airlines ends Guangzhou – Tel Aviv service in Feb 2019 |url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/282431/hainan-airlines-ends-guangzhou-tel-aviv-service-in-feb-2019/ |accessdate=15 January 2019 |work=Routesonline |date=15 January 2019}}</ref> [[Shanghai Pudong International Airport|Shanghai–Pudong]], [[Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport|Shenzhen]] (begins 22 February 2019)<ref>https://www.ynet.co.il/articles/0,7340,L-5443666,00.html</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Sun d'Or]]<ref name="Sun_dOr_NS24">{{cite news |title=Sun d'Or NS24 A320 Operations – 14JAN24 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240116-lyns24320 |access-date=16 January 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=16 January 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref><ref name='Sundor_NW24'>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Sun d'Or NW24 Preliminary Network Additions |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240819-lynw24 |access-date=19 August 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=19 August 2024 |ref=Sun d'Or NW24 |language=en-CA}}</ref> | [[Belgrade Airport|Belgrade]],<ref name="BEG-TLV">{{cite news |title=El Al's Sun d'Or to launch scheduled Belgrade flights |url=https://www.exyuaviation.com/2024/06/el-als-sun-dor-to-launch-scheduled.html |access-date=13 June 2024 |publisher=EX-YU Aviation News |date=11 June 2024}}</ref> [[Chișinău International Airport|Chișinău]], [[Kraków John Paul II International Airport|Kraków]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[Porto Airport|Porto]],<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Sun d'Or Resumes Tel Aviv – Porto Service in NS24 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240711-lyns24opo |access-date=11 July 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=11 July 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]], [[Macedonia International Airport|Thessaloniki]], [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw–Chopin]]<br />'''Seasonal:''' [[Batumi International Airport|Batumi]], [[Kefalonia International Airport|Kefalonia]],<ref name="SunD'Or_GRE_NS24">{{cite news |title=Sun d'Or NS24 Greece Network Additions |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240513-lyjun24gr |access-date=13 May 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=13 May 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Paphos International Airport|Paphos]], [[Podgorica Airport|Podgorica]], [[Rhodes Airport|Rhodes]], [[Sitia Public Airport|Sitia]],<ref name="SunD'Or_GRE_NS24" /> [[Tivat Airport|Tivat]] |
|||
| [[Iberia (airline)|Iberia]] | [[Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport|Madrid]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| {{nowrap|[[Swiss International Air Lines]]}} | [[Zurich Airport|Zürich]] (suspended until {{date|2025-1-31}})<ref name="LH_G_TLV_Jan25" /> |
|||
| [[Israir Airlines]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Israir Airlines - Information |url=https://flights.idealo.com/airline/Israir-Airlines-6H/ |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Eilat Airport|Eilat–Hozman]] (ends 18 March 2019),<ref name="ynetnews">[https://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-5449527,00.html ynetnews.com - Eilat Airport to close down after 70 years] 19 January 2019</ref> [[Ramon Airport|Eilat-Ramon]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]] <br>'''Seasonal charter:''' [[Heydar Aliyev International Airport|Baku]], [[Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport|Belgrade]], [[Bergen Airport, Flesland|Bergen]], [[Berlin Schönefeld Airport|Berlin–Schönefeld]], [[Burgas Airport|Burgas]], [[Corfu International Airport|Corfu]], [[Genoa Cristoforo Colombo Airport|Genoa]], [[Heraklion International Airport|Heraklion]], [[Innsbruck Airport|Innsbruck]], [[Ljubljana Jože Pučnik Airport|Ljubljana]], [[Munich Airport|Munich]], [[Oslo Airport, Gardermoen|Oslo–Gardermoen]], [[Poprad–Tatry Airport|Poprad]] (begins {{date|2019-7-3}}),<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Israir adds Poprad/Tatry scheduled charter in 3Q19 |url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/282576/israir-adds-popradtatry-scheduled-charter-in-3q19/ |accessdate=23 January 2019 |work=Routesonline}}</ref> [[Rhodes International Airport|Rhodes]], [[Rovaniemi Airport|Rovaniemi]], [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]], [[Salzburg Airport|Salzburg]], [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]], [[Stuttgart Airport|Stuttgart]], [[Tbilisi Airport|Tbilisi]], [[Thessaloniki International Airport|Thessaloniki]], [[Tirana International Airport Nënë Tereza|Tirana]], [[Tivat Airport|Tivat]], [[Varna Airport|Varna]], [[Zvartnots International Airport|Yerevan]], [[Zakynthos International Airport|Zakynthos]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[TAROM]] | [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest–Otopeni]]<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
| [[KLM]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Timetable - KLM.com |url=https://www.klm.com/travel/ie_en/prepare_for_travel/up_to_date/timetable/timetable_result.htm |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Transavia]] | [[Amsterdam Airport Schiphol|Amsterdam]]{{cn|date=November 2024}}<!-- AMSTERDAM - TEL AVIV NO LONGER ON SALE ON TRANSAVIA WEBSITE -->, [[Orly Airport|Paris–Orly]] (both suspended until {{date|2025-3-31}})<ref name="IsrHY_Susp_24">{{cite news |last1=Yaish |first1=Shimon |title=The complete guide to all airline flight cancellations to Israel |url=https://www.israelhayom.com/2024/10/11/the-complete-guide-to-all-airline-flight-cancellations-to-israel-2/ |access-date=12 October 2024 |work=www.israelhayom.com |date=10 October 2024}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Korean Air]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Flight Status & Schedules |url=https://www.koreanair.com/global/en/booking/schedule-flight.html#flight |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Incheon International Airport|Seoul–Incheon]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Tus Airways]]| [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]],<ref name='TUS_ISR_24'>{{cite news |title=פרסום ראשון: TUS Airways חוזרת לנתב"ג |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/188163 |access-date=14 January 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |date=14 January 2024 |language=he}}</ref> [[Sofia International Airport|Sofia]],<ref name="U8_TLV-EU_NS24">{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Tus Airways Sep 2024 Tel Aviv Network Additions |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240726-u8sep24tlv |access-date=26 July 2024 |work=AeroRoutes |date=26 July 2024 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]]<ref name="U8_TLV-EU_NS24" /> |
|||
| [[LATAM Chile]] | [[Comodoro Arturo Merino Benitez International Airport|Santiago]], [[São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport|São Paulo–Guarulhos]]<ref>{{cite web|url=https://passportnews.co.il/latam-will-operate-a-direct-line-from-brazil-to-israel/|title=Hola ברזיל: חברת התעופה LATAM תפעיל קו ישיר לישראל - Passportnews|date=4 April 2018|publisher=}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/277994/latam-airlines-chile-plans-tel-aviv-launch-in-december-2018/|title=LATAM Airlines Chile plans Tel Aviv launch in December 2018|first=UBM (UK) Ltd.|last=2018|publisher=}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[United Airlines]] | [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark]] (suspended)<ref>{{cite news |title=United, Delta Airlines set to halt flights to Israel starting Thursday |url=https://www.jpost.com/breaking-news/article-812784 |access-date=2 Aug 2024 |publisher=The Jerusalem Post |date=31 July 2024 |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
| [[LOT Polish Airlines]] | [[Gdańsk Lech Wałęsa Airport|Gdańsk]], [[Kraków John Paul II International Airport|Kraków]] (begins 25 February 2019),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/279568/lot-polish-airlines-plans-krakow-tel-aviv-launch-from-feb-2019/|title=LOT Polish Airlines plans Krakow – Tel Aviv launch from Feb 2019|publisher=Routesonline|accessdate=13 July 2018}}</ref> [[Lublin Airport|Lublin]], [[Poznań–Ławica Airport|Poznań]] (ends 20 February 2019), [[Rzeszów-Jasionka Airport|Rzeszów]], [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw–Chopin]], [[Copernicus Airport Wrocław|Wrocław]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ |
| [[Uzbekistan Airways]] | [[Samarqand International Airport|Samarqand]],<ref>{{cite news |title=Uzbekistan Airways Adds Tel Aviv – Samarkand One-Way Service in NW23 |url=https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/230913-hynw23tlvskd |access-date=14 September 2023 |work=AeroRoutes |date=13 September 2023 |language=en-CA}}</ref> [[Tashkent International Airport|Tashkent]] |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Virgin Atlantic]] | [[Heathrow Airport|London–Heathrow]]<ref>{{cite news |last1=אזולאי |first1=איתי |title=עד אוקטובר 2025: וירג׳ין אטלנטיק דוחה שוב את חזרתה לישראל |url=https://passportnews.co.il/article/193252 |access-date=11 November 2024 |work=פספורטניוז |publisher=PassportNews |date=11 November 2024 |language=he}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Montenegro Airlines]] | '''Seasonal charter:''' [[Podgorica Airport|Podgorica]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Vueling]] | [[Josep Tarradellas Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]] (suspended)<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
| [[MyWay Airlines]] | [[Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Neos (airline)|Neos]] | '''Seasonal:''' [[Verona Airport|Verona]]<br>'''Seasonal charter:''' [[Zadar Airport|Zadar]]<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/278257/neos-adds-zadar-tel-aviv-service-in-s18//|title=Neos adds Zadar – Tel Aviv service in S18 |publisher=Routesonline |date= |accessdate=2018-04-22}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Norwegian Air Shuttle]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Norwegian Route Map |url=https://www.norwegian.com/us/route-map/ |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Barcelona-El Prat Airport|Barcelona]], [[Copenhagen Airport|Copenhagen]], [[Helsinki Airport|Helsinki]],<ref>[http://lentoposti.fi/uutiset/norwegian_avaa_reitit_helsinki_vantaalta_tel_aviviin_ja_gdanskiin Norwegian avaa reitit Helsinki-Vantaalta Tel Aviviin ja Gdanskiin] ''Lentoposti.fi'' (in Finnish) 27 June 2018. Retrieved 27 June 2018</ref> [[Oslo Airport, Gardermoen|Oslo–Gardermoen]], [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]] (ends 30 March 2019),<ref>http://www.iaa.gov.il/he-IL/airports/BenGurion/Pages/OnlineFlights.aspx#</ref> [[Stockholm Arlanda Airport|Stockholm–Arlanda]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Pegas Fly]] | [[Zhukovsky International Airport|Moscow–Zhukovsky]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Pegasus Airlines]] | [[Sabiha Gökçen International Airport|Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Antalya Airport|Antalya]], [[Dalaman Airport|Dalaman]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Rossiya Airlines]] | [[Platov International Airport|Rostov-on-Don]], [[Pulkovo Airport|Saint Petersburg]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Royal Jordanian]] | [[Queen Alia International Airport|Amman–Queen Alia]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Ryanair]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Ryanair Timetable |url=https://www.ryanair.com/us/en/timetable |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Athens International Airport|Athens]] (begins 10 May 2019), [[Orio al Serio International Airport|Bergamo]], [[Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden Airport|Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden]], [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest]] (begins 11 May 2019), [[Kaunas Airport|Kaunas]], [[John Paul II International Airport Kraków–Balice|Kraków]], [[Memmingen Airport|Memmingen]], [[Paphos International Airport|Paphos]], [[Poznań–Ławica Henryk Wieniawski Airport|Poznań]], [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]], [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]] (begins 8 May 2019), [[Copernicus Airport Wrocław|Wrocław]]<br> '''Seasonal:''' [[Burgas Airport|Burgas]], [[Thessaloniki Airport|Thessaloniki]] (begins 1 April 2019)<ref>https://corporate.ryanair.com/news/%CE%B7-ryanair-%CE%B1%CE%BD%CE%B1%CE%BA%CE%BF%CE%B9%CE%BD%CF%89%CE%BD%CE%B5%CE%B9-%CE%BD%CE%B5%CE%BF-%CE%B4%CF%81%CE%BF%CE%BC%CE%BF%CE%BB%CE%BF%CE%B3%CE%B9%CE%BF-%CE%B1%CF%80%CE%BF-%CF%84%CE%B7-6/</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Sichuan Airlines]] | [[Chengdu Shuangliu International Airport|Chengdu]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[SkyUp]] |[[Kharkiv International Airport|Kharkiv]] (begins 31 March 2019)<ref name="skyup">{{cite web|url=https://economics.unian.info/10395456-ukraine-s-skyup-licensed-to-fly-to-montenegro-czech-republic-israel.html/|title=Ukraine's SkyUp licensed to fly to Montenegro, Czech Republic, Israel |
|||
|first=|last=|publisher=}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Smartwings]] |[[Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport|Madrid]], [[Václav Havel Airport Prague|Prague]], [[Tenerife South Airport|Tenerife–South]] <br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Bratislava Airport|Bratislava]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Sun d'Or]] | [[Kraków John Paul II International Airport|Krakow]], [[Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]], [[Zagreb Airport|Zagreb]] <br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Amsterdam Schiphol Airport|Amsterdam]], [[Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]], [[Batumi International Airport|Batumi]], [[Dubrovnik Airport|Dubrovnik]] (begins {{date|2019-6-4}}),<ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=Sun d'Or adds Tel Aviv – Dubrovnik seasonal route in S19 |url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/281387/sun-dor-adds-tel-aviv-dubrovnik-seasonal-route-in-s19/ |accessdate=7 November 2018 |work=Routesonline |date=7 November 2018}}</ref> [[Ljubljana Jože Pučnik Airport|Ljubljana]], [[Málaga Airport|Málaga]], [[Naples International Airport|Naples]], [[Nice Côte d'Azur Airport|Nice]] (ends 6 January 2019), [[Odessa International Airport|Odessa]], [[Porto Airport|Porto]], [[Salzburg Airport|Salzburg]] (begins 8 April 2019),<ref name="auto1">{{cite web|url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/280498/el-al-sun-dor-schedules-new-seasonal-routes-in-s19/|title=El Al / Sun d'Or schedules new seasonal routes in S19|first=UBM (UK) Ltd.|last=2018|publisher=}}</ref> [[Thessaloniki Airport|Thessaloniki]] (begins 14 April 2019)<ref name="auto1"/> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| {{nowrap|[[Swiss International Air Lines]]}} | [[Zürich Airport|Zürich]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Tandem Aero]] | [[Chișinău International Airport|Chișinău]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[TAP Air Portugal]] | [[Lisbon Airport|Lisbon]] (resumes 1 April 2019)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://nit.pt/out-of-town/viagens/tap-vai-voar-telavive-dublin-basileia |title=TAP lança rotas para Telavive, Dublin e Basileia — e há voos para Israel a 120€ |language=Portuguese |publisher=NiT |date=10 September 2018 |accessdate=10 September 2018}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[TAROM]] | [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest]], [[Iași International Airport|Iași]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Transavia]] | [[Amsterdam Schiphol Airport|Amsterdam]], [[Eindhoven Airport|Eindhoven]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Transavia France]] | [[Lyon–Saint-Exupéry Airport|Lyon]], [[Nantes Atlantique Airport|Nantes]],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.transavia.com/en-EU/home/|title=Transavia is the airline of choice for affordable flights!|website=www.transavia.com}}</ref> [[Paris–Orly]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Travel Service (airline)|Travel Service]] | '''Seasonal charter:''' [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]], [[Katowice International Airport|Katowice]], [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw–Chopin]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Turkish Airlines]] | [[Istanbul Airport|Istanbul]], [[Sabiha Gökçen International Airport|Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Antalya Airport|Antalya]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Tus Airways]] | [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]]<br>'''Seasonal charter:''' [[Paphos International Airport|Paphos]]<ref name="iaa"/> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| {{nowrap|[[Ukraine International Airlines]]}} | [[Dnipropetrovsk International Airport|Dnipropetrovsk]], [[Kharkiv International Airport|Kharkiv]], [[Boryspil International Airport|Kiev–Boryspil]], [[Lviv Danylo Halytskyi International Airport|Lviv]], [[Odessa International Airport|Odessa]], [[Havryshivka Vinnytsia International Airport|Vinnytsia]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[United Airlines]]<ref>{{cite web |title=United Flight Schedules |url=https://www.united.com/web/en-US/apps/travel/timetable/default.aspx |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark]], [[San Francisco International Airport|San Francisco]], [[Washington Dulles International Airport|Washington–Dulles]] (begins 22 May 2019)<ref>{{cite web|title=United Airlines Announces New Nonstop Service Between Washington, D.C. and Tel Aviv| url=https://hub.united.com/-new-nonstopd--and-tel-aviv-2592103601.html|access-date=2 August 2018}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Ural Airlines]] | [[Pashkovsky Airport|Krasnodar]], [[Mineralnye Vody Airport|Mineralnye Vody]], [[Zhukovsky International Airport|Moscow–Zhukovsky]], [[Pulkovo Airport|Saint Petersburg]], [[Kurumoch International Airport|Samara]], [[Sochi International Airport|Sochi]], [[Koltsovo Airport|Yekaterinburg]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Utair]] | [[Mineralnye Vody Airport|Mineralnye Vody]] <ref>{{cite news |last1=Liu |first1=Jim |title=UTair adds Mineralnye Vody – Tel Aviv service from late-Nov 2018 |url=https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/281512/utair-adds-mineralnye-vody-tel-aviv-service-from-late-nov-2018/ |accessdate=14 November 2018 |work=Routesonline |date=14 November 2018}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Uzbekistan Airways]] | [[Tashkent International Airport|Tashkent]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Virgin Atlantic]] | [[London-Heathrow]] (begins 26 September 2019)<ref>https://www.ynet.co.il/articles/0,7340,L-5460012,00.html#autoplay</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Vueling]] | [[Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]], [[Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Florence Airport, Peretola|Florence]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Wizz Air]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Wizz Air Timetable |url=https://wizzair.com/en-gb/flights/timetable |accessdate=27 October 2018}}</ref> | [[Henri Coanda International Airport|Bucharest]], [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]], [[Cluj-Napoca International Airport|Cluj-Napoca]], [[Craiova International Airport|Craiova]], [[Debrecen International Airport|Debrecen]], [[Iași International Airport|Iași]], [[Katowice International Airport|Katowice]], [[Luton Airport|London–Luton]], [[Riga International Airport|Riga]], [[Sibiu International Airport|Sibiu]], [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]], [[Timișoara Traian Vuia International Airport|Timișoara]], [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]], [[Vilnius Airport|Vilnius]], [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw–Chopin]]<br>'''Seasonal:''' [[Varna International Airport|Varna]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[WOW air]] | '''Seasonal:''' [[Keflavík International Airport|Reykjavík–Keflavík]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[XL Airways France]] | '''Seasonal:''' [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
| [[Yanair]] | '''Seasonal:''' [[Kyiv International Airport (Zhuliany)|Kiev–Zhuliany]], [[Odessa International Airport|Odessa]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Wizz Air]]<ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> | [[Zayed International Airport|Abu Dhabi]], [[Athens International Airport|Athens]],<ref name="Wizz_Res_Isr">{{cite news |last1=יעיש |first1=שמעון |title=צפו לירידה במחירי הטיסות - אלו היעדים החדשים של וויז אייר מישראל |url=https://www.israelhayom.co.il/travel/aviation/article/15301140?amp=1 |access-date=11 March 2024 |work=www.israelhayom.co.il |date=11 March 2024}}</ref> [[Henri Coandă International Airport|Bucharest–Otopeni]],<ref name="Wizz_res_TLV_24" /> [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]],<ref name="Wizz_res_TLV_24">{{cite news |title=Wizz Air Flights to Operate Again between Budapest and Tel Aviv |url=https://hungarytoday.hu/wizz-air-flights-to-operate-again-between-budapest-and-tel-aviv/ |access-date=17 January 2024 |work=Hungary Today |date=17 January 2024 |language=en}}</ref> [[Cluj International Airport|Cluj-Napoca]], [[Debrecen International Airport|Debrecen]], [[Iași International Airport|Iași]], [[Katowice Airport|Katowice]], [[Kraków John Paul II International Airport|Kraków]],<ref name="Wizz_res_TLV_24" /> [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]] (resumes {{date|2024-12-20}}),<ref>{{cite news |last1=Livne |first1=Stav |title=Wizz Air brings forward return to Israel |url=https://en.globes.co.il/en/article-wizz-air-restoring-israel-flights-1001495368 |access-date=27 November 2024 |publisher=Globes - Israel Business News |date=27 November 2024 |language=en}}</ref> [[Gatwick Airport|London–Gatwick]], [[Luton Airport|London–Luton]],<ref name="Wizz_res_TLV_24" /> [[Milan Malpensa Airport|Milan–Malpensa]],<ref name="Wizz_Res_Isr" /> [[Rome Fiumicino Airport|Rome–Fiumicino]],<ref name="Wizz_res_TLV_24" /> [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]],<ref name="Wizz_res_TLV_24" /> [[Varna Airport|Varna]], [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]],<ref name="Wizz_Res_Isr" /> [[Vilnius Airport|Vilnius]],<ref>{{cite news |title=Wizz Air, Ryanair to resume flights from Vilnius to Tel Aviv in spring |url=https://www.baltictimes.com/wizz_air__ryanair_to_resume_flights_from_vilnius_to_tel_aviv_in_spring/ |access-date=11 March 2024 |work=www.baltictimes.com |publisher=The Baltic Times |date=26 February 2024}}</ref> [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw–Chopin]] (all suspended until {{date|2025-1-14}})<ref name="Wizz_Res_Isr" /><ref name="TLV_Susp_Aug_24" /> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 353: | Line 321: | ||
{{Airport-dest-list |
{{Airport-dest-list |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[ASL Airlines]] | [[Liège Airport|Liège]] |
|||
|[[CAL Cargo Air Lines]] | [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[Liège Airport|Liège]], [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]], [[Oslo Gardermoen Airport|Oslo-Gardermoen]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://oslomedia.avinor.no/news/cal-cargo-airlines-til-oslo-lufthavn-240489|title=CAL Cargo Airlines til Oslo lufthavn|author=|date=|website=Avinor.no|access-date=30 September 2017}}</ref> [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
|[[CargoLogicAir]] | [[Frankfurt International Airport|Frankfurt]], [[London Stansted Airport|London-Stansted]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Astral Aviation]]<ref>{{cite press release|title=ASTRAL AVIATION LAUNCHES SCHEDULED FLIGHT TO TEL AVIV|url=https://astral-aviation.com/astral-aviation-launches-scheduled-flight-to-tel-aviv/|work=[[Astral Aviation]]|date=8 June 2023|access-date=2 August 2023|language=en}}</ref> | [[Jomo Kenyatta International Airport|Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta]] |
|||
|[[DHL Aviation]] | [[Il Caravaggio International Airport|Bergamo]], [[Leipzig/Halle Airport|Leipzig/Halle]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[CAL Cargo Air Lines]]<ref>{{Cite web |date=21 Apr 2019 |title=CAL Cargo |url=https://www.cal-cargo.com/network/overview/ |url-status=unfit |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320221042/https://www.cal-cargo.com/network/overview/ |archive-date=20 Mar 2023 |access-date=17 Aug 2024 |website=CAL Cargo |ref={{sfnref|CAL Cargo|2019}}}}</ref> | [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]], [[Liège Airport|Liège]], [[Hong Kong International Airport|Hong Kong]], [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York]] |
|||
|[[El Al Cargo]] | [[Liège Airport|Liège]], [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[DHL Aviation]]<ref>[https://aviationcargo.dhl.com/destinations-served aviationcargo.dhl.com – Destinations served] retrieved 29 May 2021 {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220505063723/https://aviationcargo.dhl.com/destinations-served |date=5 May 2022 }}</ref> | [[Leipzig/Halle Airport|Leipzig/Halle]] |
|||
| [[Ethiopian Airlines Cargo]] | [[Bole International Airport|Addis Ababa]], [[Istanbul Atatürk Airport|Istanbul-Atatürk]]<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ethiopianairlines.com/corporate/group/cargo/network-and-schedule/schedule|title=Cargo Schedule - Ethiopian Airlines|first=|last=KirubelS|date=|website=www.EthiopianAirlines.com|access-date=30 September 2017}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Easy Charter]] | [[Liège Airport|Liège]] |
|||
|[[FedEx Express]] | [[Athens International Airport|Athens]], [[Cologne/Bonn Airport|Cologne/Bonn]], [[Munich Airport|Munich]], [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris–Charles de Gaulle]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
|[[ |
| [[El Al|El Al Cargo]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.aircargonews.net/airlines/el-al-provides-update-on-cargo-operations/|title=EL AL provides update on cargo operations|date=7 March 2020|website=www.aircargonews.net}}</ref> | [[Liège Airport|Liège]], [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York-JFK]], [[Incheon International Airport|Seoul–Incheon]] |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
|[[Lufthansa Cargo]] | [[Frankfurt Airport|Frankfurt]] |
| [[Lufthansa Cargo]]<ref>[https://lufthansa-cargo.com/de/network/schedule-routings lufthansa-cargo.com – Routes & Schedules] retrieved 29 May 2021</ref> | [[Frankfurt Airport|Frankfurt]] |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
|[[ |
| [[My Freighter Airlines]] | [[Islam Karimov Tashkent International Airport|Tashkent]] |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
|[[ |
| [[MyWay Airlines]] | [[Shota Rustaveli Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]] |
||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[Silk Way West Airlines]]<ref>[http://www.silkwayairlines.com/our-network silkwayairlines.com – Our Network] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191103090613/http://www.silkwayairlines.com/our-network |date=3 November 2019 }} retrieved 29 May 2021</ref> | [[Heydar Aliyev International Airport|Baku]] |
|||
|[[Silk Way West Airlines]] | [[Baku International Airport|Baku]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
| [[UPS Airlines]]<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.aircargonews.net/airlines/freighter-operator/ups-adds-cologne-tel-aviv-flight/ | title=UPS adds Cologne-Tel Aviv flight | date=23 November 2021 }}</ref> | [[Cologne Bonn Airport|Cologne/Bonn]], [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]] |
|||
|[[Turkish Airlines Cargo]] | [[Istanbul Atatürk Airport|Istanbul-Atatürk]] |
|||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
==Statistics== |
==Statistics== |
||
The airport's busiest year so far was 2018, with 22,949,676 passengers passing through the airport. The ten busiest airlines on international routes were: [[El Al]] (5,634,892 million passengers), [[Turkish Airlines]] (1,086,366), [[Wizz Air]] (1,055,266), [[easyJet]] (1,014,987), [[Aeroflot]] (761,352), [[Ukraine International Airlines]] (705,742), [[Arkia]] (686,213), [[Israir Airlines|Israir]] (656,798), [[United Airlines]] (603,532) and [[Lufthansa]] (602,062).<ref name="IAAreports"/> |
|||
Commercial flights from [[Sde Dov Airport]] which, until its closure in July 2019, handled more domestic passengers annually than TLV have been moved to Ben Gurion.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3420369,00.html |title=Tel Aviv airport to make way for luxury project |newspaper=Ynetnews |date=3 July 2007 |access-date=3 July 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070705190018/http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0%2C7340%2CL-3420369%2C00.html |archive-date= 5 July 2007 |url-status=live |last1=Petersburg |first1=Ofer }}</ref> |
|||
{{Airport-Statistics|iata=TLV}} |
|||
<center> |
|||
{| class="sortable wikitable" style="margin:0 0 0.5em 1em;" |
|||
{| class="sortable wikitable" style="margin:1em auto;" |
|||
|+ Usage statistics for commercial operations<ref name="IAAreports"/><ref name="IAAstats"/> |
|||
|+ Usage statistics for commercial operations<ref name="IAAreports">{{cite web |title=IAA Periodic Activity Reports for Ben Gurion Airport |url=http://brin.iaa.gov.il/monthlyreport |access-date=9 January 2023 |website=IAA Website |publisher=[[Israel Airports Authority]] |format=PDF |archive-date=12 January 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190112044317/http://brin.iaa.gov.il/monthlyreport/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
! Year !! Total passengers !! Percentage change !! Total operations !! Percentage change |
! Year !! Total passengers !! Percentage change !! Total operations !! Percentage change |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 1999 |
! 1999 |
||
| 8,916,436|| || || |
| {{0}}8,916,436|| || || |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2000 |
! 2000 |
||
| 9,879,470|| {{increase}}10.8%|| 80,187|| |
| {{0}}9,879,470|| {{increase}}{{0}}10.8%|| {{0}}80,187|| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2001 |
! 2001 |
||
| 8,349,657|| {{decrease}}15.5%|| 69,226|| {{decrease}}13.7% |
| {{0}}8,349,657|| {{decrease}}{{0}}15.5%|| {{0}}69,226|| {{decrease}}13.7% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2002 |
! 2002 |
||
| 7,308,977|| {{decrease}}12.5%|| 63,206|| {{decrease}}8.7% |
| {{0}}7,308,977|| {{decrease}}{{0}}12.5%|| {{0}}63,206|| {{decrease}}{{0}}8.7% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2003 |
! 2003 |
||
| 7,392,026|| {{increase}}1.1%|| 61,202|| {{decrease}}3.2% |
| {{0}}7,392,026|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}1.1%|| {{0}}61,202|| {{decrease}}{{0}}3.2% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2004 |
! 2004 |
||
| 8,051,895|| {{increase}}8.9%|| 66,638|| {{increase}}8.9% |
| {{0}}8,051,895|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}8.9%|| {{0}}66,638|| {{increase}}{{0}}8.9% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2005 |
! 2005 |
||
| 8,917,421|| {{increase}}10.7%|| 70,139|| {{increase}}5.3% |
| {{0}}8,917,421|| {{increase}}{{0}}10.7%|| {{0}}70,139|| {{increase}}{{0}}5.3% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2006 |
! 2006 |
||
| 9,221,558|| {{increase}}3.4%|| 76,735|| {{increase}}9.4% |
| {{0}}9,221,558|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}3.4%|| {{0}}76,735|| {{increase}}{{0}}9.4% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2007 |
! 2007 |
||
|10,526,562|| {{increase}}14.2%|| 84,568|| {{increase}}10.3% |
|10,526,562|| {{increase}}{{0}}14.2%|| {{0}}84,568|| {{increase}}10.3% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2008 |
! 2008 |
||
|11,550,433|| {{increase}}9.7%|| 94,644|| {{increase}}11.9% |
|11,550,433|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}9.7%|| {{0}}94,644|| {{increase}}11.9% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2009 |
! 2009 |
||
|10,925,970|| {{decrease}}5.4%|| 89,442|| {{decrease}}5.5% |
|10,925,970|| {{decrease}}{{0}}{{0}}5.4%|| {{0}}89,442|| {{decrease}}{{0}}5.5% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2010 |
! 2010 |
||
|12,160,339|| {{increase}}11.3%|| 95,171|| {{increase}}6.4% |
|12,160,339|| {{increase}}{{0}}11.3%|| {{0}}95,171|| {{increase}}{{0}}6.4% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2011 |
! 2011 |
||
|12,978,605|| {{increase}}6.7%|| 99,527|| {{increase}}4.6% |
|12,978,605|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}6.7%|| {{0}}99,527|| {{increase}}{{0}}4.6% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2012 |
! 2012 |
||
|13,133,992|| {{increase}}1.2%|| 97,824|| {{decrease}}1.7% |
|13,133,992|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}1.2%|| {{0}}97,824|| {{decrease}}{{0}}1.7% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2013 |
! 2013 |
||
|14,227,612|| {{increase}}8.3%|| 104,850|| {{increase}}7.2% |
|14,227,612|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}8.3%|| 104,850|| {{increase}}{{0}}7.2% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2014 |
! 2014 |
||
|14,925,369|| {{increase}}4.9%|| 112,653|| {{increase}}6.9% |
|14,925,369|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}4.9%|| 112,653|| {{increase}}{{0}}6.9% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2015 |
! 2015 |
||
|16,299,406|| {{increase}}9.2%|| 118,861|| {{increase}}5.5% |
|16,299,406|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}9.2%|| 118,861|| {{increase}}{{0}}5.5% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2016 |
! 2016 |
||
|17,936,810|| {{increase}}10%|| 127,575|| {{increase}}10.1% |
|17,936,810|| {{increase}}{{0}}10.0%|| 127,575|| {{increase}}10.1% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2017 |
! 2017 |
||
|20,781,226|| {{increase}}15. |
|20,781,226|| {{increase}}{{0}}15.8%|| 142,938|| {{increase}}12.9% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
!2018 |
! 2018 |
||
|22,949,676|| {{increase}}{{0}}10.8%|| 157,312|| {{increase}}10.1% |
|||
|22,949,676 |
|||
|{{increase}}10.75% |
|||
|157,312 |
|||
|{{increase}}10.05% |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! 2019 |
|||
|24,821,767|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}8.2%|| 167,886|| {{increase}}{{0}}6.7% |
|||
|- |
|||
! 2020 |
|||
|{{0}}4,457,439|| {{decrease}}{{0}}80.6%||{{0}}49,223|| {{decrease}}67.3% |
|||
|- |
|||
! 2021 |
|||
|{{0}}6,719,901|| {{increase}}{{0}}50.8%||{{0}}75,321|| {{increase}}53.0% |
|||
|- |
|||
! 2022 |
|||
|20,008,532|| {{increase}}197.8%|| 143,884|| {{increase}}91.0% |
|||
|- |
|||
! 2023 |
|||
|21,882,716|| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}9.4%|| 152,411|| {{increase}}{{0}}5.9% |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
</center> |
|||
===Top destinations=== |
===Top destinations by number of passengers=== |
||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin:1em auto; font-size: 95%" |
|||
<center> |
|||
|+ '''Busiest routes to and from TLV (2023)'''<ref name=":1">{{cite web |title=Monthly Report |url=https://monthlyreport.iaa.gov.il/OpenPdf.aspx?lang=eng&val=202312 |website=Israel Airport Authority |publisher=Ben Gurion Int'l Airport - Managing Director Office |access-date=22 January 2024}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size: 95%" |
|||
|+ '''Busiest International Routes to and from TLV (2018)'''<ref name="IAAreports"/> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! Rank |
! Rank |
||
! Airport |
! Airport |
||
! Passengers |
! Passengers |
||
! Annual |
! Annual change |
||
! Carriers |
! Carriers |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 1 |
| 1 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|United Arab Emirates}} [[Dubai International Airport|Dubai, United Arab Emirates]] |
||
| |
| 917,870 |
||
| {{increase}}{{0}} |
| {{increase}}{{0}}20.23% |
||
| Arkia, El Al, Emirates, flydubai, Israir |
|||
| AtlasGlobal, Turkish Airlines |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2 |
| 2 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|Turkey}} [[Istanbul Airport|Istanbul, Turkey]] |
||
| |
| 865,985 |
||
| {{ |
| {{decrease}}{{0}}10.09% |
||
| Turkish Airlines |
|||
| Air France, ASL, Arkia, Easyjet, El Al, XL Airways |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| 3 |
| 3 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|Greece}} [[Athens International Airport|Athens, Greece]] |
||
| |
| 788,920 |
||
| {{increase}}{{0}} |
| {{increase}}{{0}}31.75% |
||
| |
| Aegean, Arkia, Bluebird Airways, El Al, Israir, Ryanair |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 4 |
| 4 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|France}} [[Charles de Gaulle Airport|Paris-Charles de Gaulle, France]] |
||
| |
| 774,386 |
||
| {{ |
| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}1.49% |
||
| Air France, Arkia, easyJet, El Al |
|||
| Aeroflot |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| 5 |
| 5 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|UK}} [[Heathrow Airport|London–Heathrow, United Kingdom]] |
||
| |
| 688,755 |
||
| {{increase}}{{0}} |
| {{increase}}{{0}}18.46% |
||
| El Al, |
| British Airways, El Al, Virgin Atlantic |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 6 |
| 6 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|Cyprus}} [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca, Cyprus]] |
||
| |
| 676,208 |
||
| {{increase}}{{0}} |
| {{increase}}{{0}}54.64% |
||
| |
| Arkia, Bluebird Airways, Cyprus Airways, El Al, Israir, Sun d'Or, Tus Airways |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 7 |
| 7 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|Turkey}} [[Istanbul Sabiha Gökçen International Airport|Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen, Turkey]] |
||
| |
| 672,977 |
||
| {{ |
| {{decrease}}{{0}}16.51% |
||
| AnadoluJet, Pegasus Airlines |
|||
| El Al, United |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| 8 |
| 8 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|Turkey}} [[Antalya Airport|Antalya, Turkey]] |
||
| |
| 662,054 |
||
| {{ |
| {{increase}}{{0}}{{0}}2.93% |
||
| AnadoluJet, Corendon, Pegasus Airlines, Turkish Airlines |
|||
| Delta, El Al |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| 9 |
| 9 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|United States}} [[John F. Kennedy International Airport|New York–JFK, United States]] |
||
| |
| 640,004 |
||
| {{ |
| {{decrease}}{{0}}{{0}}5.24% |
||
| |
| American, Delta, El Al |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 10 |
| 10 |
||
| |
|{{flagicon|United States}} [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark, United States]] |
||
| |
| 606,971 |
||
| {{ |
| {{decrease}}{{0}}{{0}}0.25% |
||
| |
| El Al, United |
||
|} |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin:1em auto; font-size: 95%" |
|||
|+ '''Busiest countries served to and from TLV (2023)'''<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! Rank |
|||
| 11 |
|||
! Country |
|||
| {{flagicon|Spain}} [[Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport|Madrid]] |
|||
! Passengers |
|||
| 517,492 |
|||
! Rate of total |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}17.38% |
|||
! Annual change |
|||
| Air Europa, El Al, Iberia, Smartwings |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 1 |
||
|{{TUR}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Germany}} [[Frankfurt Airport|Frankfurt]] |
|||
| |
| 2,305,977 |
||
| {{decrease}}{{0}} |
| 10.93% |
||
| {{decrease}}{{0}}8.46% |
|||
| El Al, Lufthansa |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 2 |
||
| {{USA}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Turkey}} [[Antalya Airport|Antalya]] |
|||
| |
| 2,009,244 |
||
| |
| {{0}}9.52% |
||
| {{increase}}{{0}}4.73% |
|||
| Pegasus, Tailwind, Turkish Airlines |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 3 |
||
| {{GRE}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|UK}} [[London Luton Airport|London (Luton)]] |
|||
| |
| 1,753,248 |
||
| |
| {{0}}8.31% |
||
| {{increase}}19.03% |
|||
| easyJet, El Al, Wizz Air |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 4 |
||
| {{ITA}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Turkey}} [[Sabiha Gökçen International Airport|Istanbul (Sabiha Gökçen)]] |
|||
| |
| 1,466,320 |
||
| |
| {{0}}6.95% |
||
| {{increase}}12.81% |
|||
| Pegasus, Turkish Airlines |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 5 |
||
| {{UK}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Poland}} [[Warsaw Chopin Airport|Warsaw (Chopin)]] |
|||
| |
| 1,214,291 |
||
| |
| {{0}}5.75% |
||
| {{increase}}{{0}}9.28% |
|||
| El Al, Enter Air, LOT, Wizz Air |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 6 |
||
| {{FRA}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Switzerland}} [[Zurich Airport|Zurich]] |
|||
| |
| 1,198,962 |
||
| |
| {{0}}5.68% |
||
| {{decrease}}{{0}}1.95% |
|||
| El Al, Swiss |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 7 |
||
| {{UAE}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Greece}} [[Athens International Airport|Athens]] |
|||
| |
| 1,148,542 |
||
| |
| {{0}}5.44% |
||
| {{increase}}17.30% |
|||
| Aegean, Alitalia, El Al |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 8 |
||
| {{GER}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Hungary}} [[Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport|Budapest]] |
|||
| |
| {{0}}999,904 |
||
| |
| {{0}}4.74% |
||
| {{decrease}}{{0}}6.44% |
|||
| El Al, Israir, Wizz Air |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 9 |
||
| {{CYP}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Cyprus}} [[Larnaca International Airport|Larnaca]] |
|||
| |
| {{0}}981,105 |
||
| |
| {{0}}4.65% |
||
| {{increase}}45.75% |
|||
| Aegean, Arkia, Cobalt Air, Cyprus Airways, El Al, Israir, Tus Air |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 10 |
||
| {{ESP}} |
|||
| {{flagicon|Spain}} [[Barcelona–El Prat Airport|Barcelona]] |
|||
| |
| {{0}}883,249 |
||
| |
| {{0}}4.18% |
||
| {{increase}}31.51% |
|||
| Air Europa, Arkia, El Al, Israir, Norwegian, Sun d'Or, Vueling |
|||
|} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+Top 10 busiest airlines serving to and from Ben Gurion Airport (2023)<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
!Rank |
|||
!Airline |
|||
!Passengers |
|||
!Percentage of total passengers |
|||
!Headquarters |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|1 |
||
|[[El Al|El Al Israel Airlines]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Austria}} [[Vienna International Airport|Vienna]] |
|||
|5,539,127 |
|||
| 412,095 |
|||
|26.26% |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}18.57% |
|||
|Ben Gurion Airport, Israel |
|||
| Austrian, El Al, Wizz Air |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|2 |
||
|[[Wizz Air]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Czech Republic}} [[Václav Havel Airport Prague|Prague]] |
|||
|1,998,168 |
|||
| 388,367 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}9.47% |
||
|[[Budapest|Budapest, Hungary]] |
|||
| El Al, Smartwings |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|3 |
||
|[[Ryanair]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Germany}} [[Munich Airport|Munich]] |
|||
|1,147,880 |
|||
| 356,948 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}5.44% |
||
|[[Swords, Dublin|Swords, Ireland]] |
|||
| Arkia, El Al, Israir, Lufthansa |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|4 |
||
|[[Turkish Airlines]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Belgium}} [[Brussels Airport|Brussels]] |
|||
|1,107,125 |
|||
| 287,614 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}5.24% |
||
|[[Istanbul|Istanbul, Turkey]] |
|||
| Brussels Airlines, El Al |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|5 |
||
|[[Israir Airlines]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Germany}} [[Berlin Schonefeld Airport|Berlin (Schonefeld)]] |
|||
|{{0}}1,003,654 |
|||
| 286,524 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}4.75% |
||
|[[Tel Aviv|Tel Aviv, Israel]] |
|||
| easyjet, El Al, Israir |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|6 |
||
|[[Arkia]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Greece}} [[Rhodes International Airport|Rhodes]] |
|||
|{{0}}723,989 |
|||
| 286,291 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}3.43% |
||
|[[Tel Aviv|Tel Aviv, Israel]] |
|||
| Aegean, Arkia, Bluebird, Israir, Sun d'Or |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|7 |
||
|[[Pegasus Airlines]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Italy}} [[Milan Malpensa Airport|Milan (Malpensa)]] |
|||
|{{0}}692,688 |
|||
| 276,151 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}3.28% |
||
|[[Istanbul|Istanbul, Turkey]] |
|||
| easyjet, El Al, Israir, Neos |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|8 |
||
|[[EasyJet|Easyjet]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|France}} [[Orly Airport|Paris (Orly)]] |
|||
|{{0}}658,400 |
|||
| 269,901 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}3.12% |
||
|[[Luton|Luton, United Kingdom]] |
|||
| Transavia |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|9 |
||
|[[United Airlines]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Greece}} [[Heraklion International Airport|Heraklion]] |
|||
|{{0}}605,753 |
|||
| 269,068 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}2.87% |
||
|[[Chicago|Chicago, Illinois, United States]] |
|||
| Aegean, Arkia, Bluebird, Israir |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|10 |
||
|[[Lufthansa]] |
|||
| {{flagicon|Bulgaria}} [[Sofia Airport|Sofia]] |
|||
|{{0}}440,612 |
|||
| 249,960 |
|||
| |
|{{0}}2.08% |
||
|[[Cologne|Cologne, Germany]] |
|||
| Bulgaria Air, El Al, Israir, Wizz Air |
|||
|- |
|||
| 32 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Hong Kong}} [[Hong Kong International Airport|Hong Kong]] |
|||
| 244,977 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}22.74% |
|||
| Cathay Pacific, El Al |
|||
|- |
|||
| 33 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Canada}} [[Toronto Pearson International Airport|Toronto (Pearson)]] |
|||
| 244,537 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}7.46% |
|||
| Air Canada, El Al |
|||
|- |
|||
| 34 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Thailand}} [[Suvarnabhumi Airport|Bangkok (Suvarnabhumi)]] |
|||
| 222,889 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}9.82% |
|||
| Arkia, El Al |
|||
|- |
|||
| 35 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Georgia}} [[Tbilisi International Airport|Tbilisi]] |
|||
| 204,256 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}24.62% |
|||
| Arkia, Georgian, Israir, MyWay, Sun d'Or |
|||
|- |
|||
| 36 |
|||
| {{flagicon|USA}} [[San Francisco International Airport|San Francisco]] |
|||
| 178,669 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}29.15% |
|||
| United |
|||
|- |
|||
| 37 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Ethiopia}} [[Addis Ababa Bole International Airport|Addis Ababa]] |
|||
| 158,587 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}12.94% |
|||
| Ethiopian |
|||
|- |
|||
| 38 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Georgia}} [[Batumi International Airport|Batumi]] |
|||
| 158,561 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}60.07% |
|||
| Arkia, Georgian, Sun d'Or |
|||
|- |
|||
| 39 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Jordan}} [[Queen Alia International Airport|Amman (Queen Alia)]] |
|||
| 157,458 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}10.11% |
|||
| Royal Jordanian |
|||
|- |
|||
| 40 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Russia}} [[Moscow Domodedovo Airport|Moscow (Domodedovo)]] |
|||
| 153,364 |
|||
| {{decrease}}{{0}}26.87% |
|||
| El Al |
|||
|- |
|||
| 41 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Ukraine}} [[Odessa International Airport|Odessa]] |
|||
| 153,186 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}24.69% |
|||
| Sun d'Or, Ukraine International, Yanair |
|||
|- |
|||
| 42 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Cyprus}} [[Paphos International Airport|Paphos]] |
|||
| 149,446 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}57.44% |
|||
| Arkia, Ryanair |
|||
|- |
|||
| 43 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Germany}} [[Berlin Tegel Airport|Berlin (Tegel)]] |
|||
| 148,015 |
|||
| {{decrease}}{{0}}15.45% |
|||
| easyjet, Germania |
|||
|- |
|||
| 44 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Russia}} [[Pulkovo Airport|St. Petersburg]] |
|||
| 147,779 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}33.79% |
|||
| Aeroflot, Ural Airlines |
|||
|- |
|||
| 45 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Bulgaria}} [[Burgas Airport|Burgas]] |
|||
| 147,460 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}9.41% |
|||
| Arkia, Bul Air, Bulgaria Air, Bulgaria Air Charter, Israir, Ryanair |
|||
|- |
|||
| 46 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Switzerland}} [[Geneva Airport|Geneva]] |
|||
| 146,318 |
|||
| {{decrease}}{{0}}1.66% |
|||
| easyJet, El Al |
|||
|- |
|||
| 47 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Greece}} [[Thessaloniki Airport|Thessaloniki]] |
|||
| 124,897 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}122.75% |
|||
| Aegean, Astra |
|||
|- |
|||
| 48 |
|||
| {{flagicon|China}} [[Beijing Capital International Airport|Beijing (Capital)]] |
|||
| 122,795 |
|||
| {{decrease}}{{0}}8.53% |
|||
| El Al, Hainan |
|||
|- |
|||
| 49 |
|||
| {{flagicon|Bulgaria}} [[Varna Airport|Varna]] |
|||
| 111,829 |
|||
| {{increase}}{{0}}12.39% |
|||
| Bul Air, Bulgaria Air, Bulgaria Air Charter, Israir, Wizz Air |
|||
|- |
|||
| 50 |
|||
| {{flagicon|USA}} [[Los Angeles International Airport|Los Angeles]] |
|||
| 100,642 |
|||
| {{decrease}}{{0}}0.07% |
|||
| El Al |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
</center> |
|||
==Ground transportation== |
==Ground transportation== |
||
The airport is located near [[Highway 1 (Israel)|Highway 1]], the main |
The airport is located near [[Highway 1 (Israel)|Highway 1]], the main Jerusalem–Tel Aviv Highway and [[Highway 40 (Israel)|Highway 40]]. The airport is accessible by car or public bus. [[Israel Railways]] operates [[airport rail link|train service from the airport]] to several parts of the country and taxi stands are located outside the arrivals building. A popular transportation option is a [[share taxi]] van, known in Hebrew as a ''monit sherut'' (service cab), going to [[Jerusalem]], [[Haifa]], and [[Beersheba]]. |
||
===Public transport=== |
===Public transport=== |
||
Israel has an integrated nationwide [[public transport]] payment system covering multiple transit options |
Israel has an integrated nationwide [[public transport]] payment system covering multiple transit options (train, bus, and light rail) run by various operators using a single payment card: the [[Rav-Kav]]. It features flexible tariff arrangements and offers free transfers between transit methods within certain geographical zones and time periods. A public transport information office which also issues Rav-Kav cards is located in the arrivals hall of Terminal 3. With a few exceptions, most public transport options (except for taxis and service cabs) do not operate on the Sabbath (i.e., from early Friday evenings to late Saturday evenings as well as certain Jewish holidays). |
||
A new app payment system was introduced in December 2020. The apps have a different, simpler fare system and it's post pay (The Rav Kav is a pre-paid card that you need to top up). The charge is at the end of each month (so a registration and a payment method are required). The two apps supporting routing and payment are: RavPass (by HopOn), and Moovit (by Moovit and Pango).{{citation needed|date=April 2022}} |
|||
====Rail==== |
====Rail==== |
||
[[File:BenGuTra.jpg|thumb|Platform 1 of the airport train station at Terminal 3]] |
[[File:BenGuTra.jpg|thumb|Platform 1 of the airport train station at Terminal 3]] |
||
[[Israel Railways]] operates the [[Ben Gurion Airport Railway Station]], located in the lower level of Terminal 3. From this station passengers may head northwest to [[Tel Aviv]], [[Haifa]] and other destinations in the north, or southeast to [[Modi'in]] and [[Jerusalem]]. The journey to [[Tel Aviv Savidor Central railway station]] takes about 18 minutes and to Jerusalem's [[Jerusalem–Yitzhak Navon railway station|Yitzhak Navon station]] about 25 minutes. There is also late night/early morning train service to and from the airport terminating at [[Be'er Sheva Center railway station|Beersheba Center]] via [[Lod railway station|Lod]], [[Ashkelon railway station|Ashkelon]], and selected destinations in between. Almost 3.3 million passengers used the railway line to and from the airport in 2009. The service does not operate on [[Shabbat]] and [[Jewish holiday]]s but on all other days it runs day and night. The line to [[Nahariya]] through Tel Aviv and Haifa operated 24 hours a day on weekdays, but these services were suspended following the COVID-19 pandemic and put on hold until railway electrification works are completed in the mid-2020s, following which the line would run from Jerusalem and terminate at [[Karmiel]] instead of Nahariya (though it would continue to service Tel Aviv and Haifa). |
|||
{{main|Ben Gurion Airport Railway Station}} |
|||
[[Israel Railways]] operates the Ben Gurion Airport Railway Station, located in the lower level of Terminal 3. From this station passengers may head north-west to [[Tel Aviv]], [[Haifa]] and other destinations in the north or south-east to [[Modi'in]] and [[Jerusalem]]. The journey to [[Tel Aviv Savidor Central railway station]] takes about 18 minutes. Almost 3.3 million passengers used the railway line to and from the airport in 2009. The line to Jerusalem opened for a commissioning period on September 25, 2018. The service does not operate on [[Shabbat]] and [[Jewish holiday]]s but on all other days it runs day and night. The line to [[Nahariya]] through Tel Aviv and Haifa operates 24 hours a day on weekdays. |
|||
====Bus or taxi==== |
====Bus or taxi==== |
||
The airport is served by regular inter-city bus lines, limousine and private shuttle services, [[Share taxi|Sherut]] "shared" door to door taxi vans and regular taxis.<ref>{{cite web| title=Guidelines for Taxi Passengers| url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/TransportationToandFromtheAirport/Taxis/| publisher=Israel Airports Authority| |
The airport is served by regular inter-city bus lines, limousine and private shuttle services, [[Share taxi|Sherut]] "shared" door to door taxi vans and regular taxis.<ref>{{cite web| title=Guidelines for Taxi Passengers| url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/TransportationToandFromtheAirport/Taxis/| publisher=Israel Airports Authority| access-date=27 April 2007| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20061117091144/http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/TransportationToandFromtheAirport/Taxis/| archive-date=17 November 2006| url-status= live}}</ref> Afikim bus company provides 24 hours a day, on the hour, direct service to Jerusalem with line 485. the line departs from Terminal 3 on the 2nd floor and passes through Terminal 1.<ref>{{cite web | title=The resource cannot be found. | url=http://www.callkav.gov.il/WebForms/wfrmMain.aspx?width=1024&company=1&language=he&state=# | publisher=Ministry of Transport | access-date=30 September 2017 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170714023040/http://www.callkav.gov.il/WebForms/wfrmMain.aspx?width=1024&company=1&language=he&state= | archive-date=14 July 2017 | url-status=dead | df=dmy-all }}</ref> [[Egged Bus Cooperative|Egged]] bus number 5 ferries passengers between the terminals and a small bus terminal in the nearby Airport City business park near El Al junction just outside the airport where they can connect to regular Egged bus routes passing through the area. Passengers connecting at Airport City can pay for both rides on the same ticket, not having to pay an extra fare for bus No. 5. Other bus companies directly serve Terminal 3, and the airport also provides a free shuttle bus between terminals.<ref>{{cite web| title=Public Transportation| url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/TransportationToandFromtheAirport/PublicTransport/|publisher=Israel Airports Authority| access-date=27 April 2007| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070513025204/http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/TransportationToandFromtheAirport/PublicTransport/| archive-date= 13 May 2007| url-status= live}}</ref> On Shabbat, when there is no train service, a shared shuttle service is available between the airport and Tel Aviv hotels.<ref>{{cite web |title=Shuttle from Ben Gurion Airport to Tel Aviv |url=https://www.withflo.com/tel-aviv/ |url-status=dead |access-date=14 August 2016 |website=withflo.com |archive-date=21 August 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160821165951/https://www.withflo.com/tel-aviv/ }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Tel Aviv Airport Taxi & Transfer |url=https://atobtransfer.com/israel/tel-aviv-airport-taxi/ |access-date=2022-07-07 |website=Atob Transfer |language=en-US}}</ref> |
||
===Car=== |
===Car=== |
||
Located on [[Highway 1 (Israel)|Highway 1]], the Jerusalem – Tel Aviv highway, the airport has a total of |
Located on [[Highway 1 (Israel)|Highway 1]], the Jerusalem – Tel Aviv highway, the airport has a total of approximately 20,000 [[parking space]]s for short and long-term parking.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.calcalist.co.il/local/articles/0,7340,L-3776021,00.html|title = בתכנון: החניון בנתב"ג יורחב ב־30% ויכיל 26 אלף חניות|date = 18 December 2019}}</ref> The spaces for long-term parking are situated several kilometres from the terminal, and are reached by a free shuttle bus.<ref>{{cite web| title=Parking Lots| url=http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/ParkingLots/|publisher=Israel Airports Authority| access-date=27 April 2007| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070427165908/http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/InformationforTravelers/ParkingLots/| archive-date= 27 April 2007| url-status= live}}</ref> Car rental at the airport is available from Avis, Budget, Eldan, Tamir Rental,<ref>{{cite web|title=Car Rental Tel Aviv Airport|url=https://www.tamir-rental.com/car-rental-ben-gurion-airport|access-date=28 June 2020|website=Tamir Rental}}</ref> Thrifty, Hertz, and Shlomo Sixt.<ref>{{cite web|title = Car Rental in Ben Gurion Airport-up to 15% discount-Shlomo Sixt|url = https://en.shlomo.co.il/branches/16/Car-Rental-in-Ben-Gurion-Airport-Terminal-3/|website = en.shlomo.co.il|access-date = 14 December 2015|archive-date = 16 May 2023|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230516204754/https://en.shlomo.co.il/branches/16/Car-Rental-in-Ben-Gurion-Airport-Terminal-3/|url-status = dead}}</ref> |
||
==Service quality== |
==Service quality== |
||
===Passenger rankings=== |
===Passenger rankings=== |
||
In December 2006, Ben Gurion International Airport ranked first among 40 European airports and 8th out of 77 airports in the world, in a survey, conducted by [[Airports Council International]], to determine the most customer-friendly airport. [[Tel Aviv]] placed second in the grouping of airports which carry between 5 and 15 million passengers per year behind [[Japan]]'s [[Chūbu Centrair International Airport|Nagoya Airport]]. The survey consisted of 34 questions. A random sampling of 350 passengers at the departure gate were asked how satisfied they were with the service, infrastructure and facilities. Ben Gurion received a rating of 3.94 out of 5, followed by Vienna, Munich, Amsterdam, Brussels, |
In December 2006, Ben Gurion International Airport ranked first among 40 European airports and 8th out of 77 airports in the world, in a survey, conducted by [[Airports Council International]], to determine the most customer-friendly airport. [[Tel Aviv]] placed second in the grouping of airports which carry between 5 and 15 million passengers per year behind [[Japan]]'s [[Chūbu Centrair International Airport|Nagoya Airport]]. The survey consisted of 34 questions. A random sampling of 350 passengers at the departure gate were asked how satisfied they were with the service, infrastructure and facilities. Ben Gurion received a rating of 3.94 out of 5, followed by Vienna, Munich, Amsterdam, Brussels, Zürich, Copenhagen, and Helsinki. The airport retained its title as the best Middle Eastern airport in the 2007, 2008, and 2009 surveys.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://fr.jpost.com/servlet/Satellite?cid=1164881920231&pagename=JPost/JPArticle/ShowFull |title=Ben Gurion ranks first in airport survey |access-date=27 April 2007|first=Avi|last= Krawitz |date=18 December 2006|newspaper=[[The Jerusalem Post]]}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3511386,00.html |title=Ben Gurion Airport ranks best in Mideast |date=26 February 2008 |access-date=26 February 2008 |work=Ynetnews |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080227055902/http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0%2C7340%2CL-3511386%2C00.html |archive-date=27 February 2008 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
===Awards=== |
===Awards=== |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin:1em auto; text-align:center" |
|||
<center> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! Year !! style="width:200px;"|Award !! style="width:300px;"|Category !! Results !! Ref |
! Year !! style="width:200px;"|Award !! style="width:300px;"|Category !! Results !! Ref |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan=2|2007 || rowspan=11|Airport Service Quality Awards<br />by [[Airports Council International]] || Best Airport in Middle East || {{won}} ||rowspan=2|<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2007 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 28 April 2015</ref> |
| rowspan=2|2007 || rowspan=11|Airport Service Quality Awards<br />by [[Airports Council International]] || Best Airport in Middle East || {{won}} ||rowspan=2|<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2007 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151125101306/http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2007 |date=25 November 2015 }} ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 28 April 2015</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Best Airport by Size (5–15 million passengers) || 2nd |
| Best Airport by Size (5–15 million passengers) || 2nd |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan=2|2008 || Best Airport in Middle East || {{won}} || rowspan=2|<ref>[http://www.airportservicequalityawards.com/pastwinners2008 "ASQ Award for winners for 2008"] ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 13 April 2012</ref><ref>{{cite |
| rowspan=2|2008 || Best Airport in Middle East || {{won}} || rowspan=2|<ref>[http://www.airportservicequalityawards.com/pastwinners2008 "ASQ Award for winners for 2008"] ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 13 April 2012</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Tel Aviv's Ben Gurion named top Middle East airport|url=http://www.globes.co.il/serveen/globes/DocView.asp?did=1000432940&fid=1725|newspaper=Globes|access-date=10 March 2009}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Best Airport by Size (5–15 million passengers) || 2nd |
| Best Airport by Size (5–15 million passengers) || 2nd |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2009 || rowspan=7|Best Airport in Middle East || {{won}} ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2009 "ASQ Award for winners for 2009"] ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 13 April 2012</ref> |
| 2009 || rowspan=7|Best Airport in Middle East || {{won}} ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2009 "ASQ Award for winners for 2009"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151125102652/http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2009 |date=25 November 2015 }} ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 13 April 2012</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2010 || 3rd ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2010 "ASQ Award for winners for 2010"] ''Airports Council International''. 14 February 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012</ref> |
| 2010 || 3rd ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2010 "ASQ Award for winners for 2010"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151125104014/http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2010 |date=25 November 2015 }} ''Airports Council International''. 14 February 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2011 || 3rd ||<ref>[http://www.airportservicequalityawards.com/best-airport-region-middle-east "ASQ Award for Best Airport in Middle East"] ''Airports Council International''. 14 February 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012</ref> |
| 2011 || 3rd ||<ref>[http://www.airportservicequalityawards.com/best-airport-region-middle-east "ASQ Award for Best Airport in Middle East"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120902065207/http://www.airportservicequalityawards.com/best-airport-region-middle-east |date=2 September 2012 }} ''Airports Council International''. 14 February 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2012 || 4th ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2012 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 28 April 2015</ref> |
| 2012 || 4th ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2012 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160516215649/http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2012 |date=16 May 2016 }} ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 28 April 2015</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2013 || 4th ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2013 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 28 April 2015</ref> |
| 2013 || 4th ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2013 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160516215654/http://www.aci.aero/Airport-Service-Quality/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2013 |date=16 May 2016 }} ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 28 April 2015</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2014 || 3rd ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Customer-Experience-ASQ/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2014 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 11 December 2017</ref> |
| 2014 || 3rd ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Customer-Experience-ASQ/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2014 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170918154815/http://www.aci.aero/Customer-Experience-ASQ/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2014 |date=18 September 2017 }} ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 11 December 2017</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2015 || 3rd (tie) ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Customer-Experience-ASQ/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2015 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 11 December 2017</ref> |
| 2015 || 3rd (tie) ||<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/Customer-Experience-ASQ/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2015 "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170918155050/http://www.aci.aero/Customer-Experience-ASQ/ASQ-Awards/Past-Winners/2015 |date=18 September 2017 }} ''Airports Council International''. Retrieved 11 December 2017</ref> |
||
|} |
|} |
||
</center> |
|||
== Accidents and incidents == |
|||
* On 13 February 1939, a [[Fokker F.XVIII]] (VQ-PAF) of the newly founded Commercial Aviation Company Ltd. was being flown around the airport for an inaugural celebration. While landing the pilot lost control and veered off into the mud, damaging it beyond repair.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Fokker F.XVIII VQ-PAF Lydda Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19390113-2 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 5 February 1950, a [[Douglas C-54 Skymaster|Douglas C-54A-10-DC]] (4X-ACD) of El Al skidded off during takeoff, caught fire, and was damaged beyond repair. All 50 occupants survived.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Douglas C-54A-10-DC (DC-4) 4X-ACD Lydda Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19500205-1 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 15 May 1953, a [[Douglas C-47 Skytrain|Douglas C-47]] of the [[United States Air Force|USAF]] as part of a US military attaché in Israel caught fire standing at night and was burned out. Sabotage was suspected.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Douglas C-47 (DC-3) registration unknown Lydda Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19530515-2 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 26 October 1969, a [[Vickers Viscount|Vickers 833 Viscount]] (4X-AVC) of Arkia crashed during a nighttime training flight and was damaged beyond repair. All three occupants survived.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Vickers 833 Viscount 4X-AVC Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19691026-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 30 November 1970, a [[Boeing 707|Boeing 707-373C]] (N790TW) of [[Trans World Airlines|TWA]] was taking off for a cargo flight to Frankfurt at 02:00 on runway 30 when an empty, unlit [[Israeli Air Force|IAF]] [[Boeing 377 Stratocruiser|Stratocruiser]] (4X-FPS/037) was towed across the runway; the 707 hit the Stratocruiser and both aircraft caught fire. Both planes were damaged beyond repair, and all three crew on the 707 survived. However, two persons were killed on the ground.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 707-373C N790TW Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19701130-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Boeing KC-97G Stratofreighter 4X-FPS/037 Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19701130-1 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 8 May 1972, a Boeing 707-329 (OO-SJG) of [[Sabena]] was hijacked en route to Tel Aviv from Vienna and landed here (the intended destination); the four hijackers demanded prisoner releases. Two were shot and killed by military personnel in ground engineer uniforms the same day, and a passenger died eight days later from injuries sustained in the gun battle.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 707-329 OO-SJG Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19720508-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 16 August 1973, a [[Boeing 720|Boeing 720-023B]] (OD-AFR) of [[Middle East Airlines|MEA]] was hijacked en route from [[Benghazi]] to [[Beirut]] over [[Cyprus]] by a male hijacker with two guns who demanded to be flown here; he was overpowered by ground police upon arrival.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 720-023B OD-AFR Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19730816-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 31 July 1980, a Boeing 707-358C (4X-ATX) of El Al had a fire erupt in the rear lavatory prior to departure here; the aircraft was evacuated and fire services had to cut a hole in the fuselage to put out the flames. The aircraft was later repaired.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 707-358C 4X-ATX Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19800731-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 16 February 1987, a [[Convair CV-240 family|Convair CV-240-24]] (N93218) of [[Israel Aerospace Industries|IAI]] was destroyed in a hangar fire.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Convair CV-240-24 N93218 Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19870216-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 1 December 1988: [[1988 Ordzhonikidze bus hijacking]]. Five men in [[Vladikavkaz|Ordzhonikidze]] hijacked a [[school bus]], demanding 2,000,000 [[Soviet ruble|rubles]] and an airplane to fly them to Israel. The bus went to [[Mineralnye Vody Airport]] and the hijackers boarded an [[Ilyushin Il-76|Ilyushin Il-76T]] of Aeroflot in exchange for 30 hostages. The plane arrived here the following day, and the hijackers surrendered.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Ilyushin Il-76T registration unknown Tel aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19881202-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 18 June 2001, a [[ATR 42|ATR 42-320]] (4X-ATK) of Israir could not lower its starboard main undercarriage and had to land without it; none of the 42 occupants were injured. The plane was written off and converted into a training rig.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident ATR 42-320 4X-ATK Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=20010618-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 8 April 2015, a [[British Aerospace 125|British Aerospace BAe 125-800A]] (4X-CZO) of Arrow Aviation aborted a takeoff from runway 26 due to a swerve issue, and after stopping a fire broke out in the right main gear wheel area. The plane, an air ambulance, was substantially damaged.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident British Aerospace BAe 125-800A 4X-CZO Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=20150408-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
* On 28 March 2018, a [[Boeing 737|Boeing 737-76J (WL)]] (D-ABLB) on Germania Flight 4915 to Berlin collided with a [[Boeing 767|Boeing 767-300ER]] (4X-EAK) on El Al Flight 385 to Rome while both aircraft were in the pushback/towing phase at 06:22. The 737's tail fin hit the right horizontal stabilizer of the 767 after ground controllers cleared both for pushback without realizing they were blocking each other. The 737 was later repaired, but the 767 was written off.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 737-76J (WL) D-ABLB Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=20180328-0 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 767-3Q8ER 4X-EAK Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV) |url=https://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=20180328-1 |access-date=2023-07-22 |website=aviation-safety.net}}</ref> |
|||
== See also == |
|||
* [[Transportation in Israel]] |
|||
* [[Ramon Airport]] |
|||
* [[Haifa Airport]] |
|||
* [[List of the busiest airports in the Middle East]] |
|||
== Notes == |
|||
{{Notelist}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{ |
{{reflist|colwidth=30em}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Wikivoyage-inline|Ben Gurion International Airport}}<br> |
|||
{{ |
{{Wikivoyage inline|Ben Gurion International Airport}}<br /> |
||
{{Commons category-inline|Ben Gurion International Airport}} |
|||
* {{Official website|http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/BenGurion/}} |
|||
* {{ASN|TLV}} |
* {{ASN|TLV}} |
||
* [https://en.shlomo.co.il/branches/16/Car-Rental-in-Ben-Gurion-Airport-Terminal-3/ Shlomo SIXT Car rental branch in Ben Gurion Airport] |
|||
{{Portalbar|Israel|Aviation}} |
{{Portalbar|Israel|Aviation}} |
||
| Line 834: | Line 730: | ||
{{Israel Airports Authority}} |
{{Israel Airports Authority}} |
||
{{authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:1936 establishments in Mandatory Palestine]] |
|||
[[Category:Airports established in 1936]] |
|||
[[Category:1934 establishments in Mandatory Palestine]] |
|||
[[Category:Airports established in 1934]] |
|||
[[Category:Airports in Israel]] |
[[Category:Airports in Israel]] |
||
[[Category:Buildings and structures in Central District (Israel)]] |
[[Category:Buildings and structures in Central District (Israel)]] |
||
| Line 841: | Line 739: | ||
[[Category:Skidmore, Owings & Merrill buildings]] |
[[Category:Skidmore, Owings & Merrill buildings]] |
||
[[Category:Commemoration of David Ben-Gurion]] |
[[Category:Commemoration of David Ben-Gurion]] |
||
[[Category:Companies in the TA-35 Index]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 08:50, 4 December 2024
Ben Gurion International Airport נמל התעופה בן-גוריון | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | Ministry of Transport and Road Safety | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operator | Israel Airports Authority | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Gush Dan and Greater Jerusalem[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Central District, Israel | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for | |||||||||||||||||||
| Focus city for | Bluebird Airways, TUS Airways, Wizz Air | ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 135 ft / 41 m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 32°00′34″N 034°52′58″E / 32.00944°N 34.88278°E | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | iaa.gov.il | ||||||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||||||
Location within the Middle East | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2023) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Ben Gurion International Airport[a] (IATA: TLV, ICAO: LLBG), commonly known by the Hebrew-language acronym Natbag (נתב״ג), is the main international airport of Israel. Situated on outskirts north of the city of Lod and directly south of the city of Or Yehuda, it is the busiest airport in the country. It is located 45 kilometres (28 mi) to the northwest of Jerusalem and 20 kilometres (12 mi) to the southeast of Tel Aviv.[2] It was known as Lod Airport until 1973, when it was renamed in honour of David Ben-Gurion (1886–1973), the first prime minister of Israel. The airport serves as a hub for El Al, Israir Airlines, Arkia, and Sun d'Or, and is managed by the Israel Airports Authority.
In 2023, Ben Gurion Airport handled 21.1 million passengers,[4] making it one of the busiest airports in the Middle East. It is considered to be among the five best airports in the Middle East due to its passenger experience and its high level of security;[5] while it has been the target of several terrorist attacks, no attempt to hijack a plane departing from Ben Gurion Airport has ever succeeded.[6]
The airport is of great importance to Israel as it is one of the few convenient entry points into the country for most travellers.[7] As it was Israel's only international airport, it was regarded as a single point of failure, which led to the opening of Ramon Airport in 2019.[8]
History
[edit]British Mandatory period (1934–1948)
[edit]

The airport began during the British Mandate for Palestine as an airstrip of two unpaved runways on the outskirts of the town of Lydda (now Lod), near the Templer colony of Wilhelma. It was built in 1934, largely at the urging of Airwork Services.[9] The first passenger service at the new airport was the Misr Airwork route Cairo—Lydda—Nicosia, inaugurated on 3 August 1935. Subsequently, Misr flew via Lydda to Haifa and Baghdad. The first continental European airline with a regular service to Lydda was LOT Polish Airlines since 4 April 1937. By that time, Lydda Airport boasted four fully operational concrete runways. Holland's KLM, which had since 1933 stopped at Gaza en route to Batavia, Dutch East Indies (now Jakarta, Indonesia), moved the service to Lydda in 1937. Imperial Airways, too, used Lydda as a refueling stop en route to India.
During World War II, Imperial Airways and later British Overseas Airways Corporation continued the service to Lydda until the fall of France in June 1940. When the Japanese military advanced into Burma and Malaya in February 1942, KLM curtailed its route to Batavia and made Lydda the eastern terminus of the route. Misr Airwork, which had suspended flights upon the British declaration of war, resumed the weekly Cairo—Lydda—Nicosia service in May 1940.[9]
In 1943, the airport was renamed "RAF Station Lydda" and continued to serve as a major airfield for military air transport and aircraft ferry operations between military bases in Europe, Africa, the Middle East (mainly Iraq and Persia) and South/Southeast Asia. In 1944, as the German threat in the Middle East subsided, Aviron Aviation Company initiated service four times a week between Lydda and Haifa.[9]
The first civilian transatlantic route, New York City to Lydda Airport, was inaugurated by TWA in 1946. The British gave up the airport at the end of April 1948.
Israel's first decades (1948–1973)
[edit]
Soldiers of the Israel Defense Forces captured the airport on 10 July 1948, in Operation Danny, transferring control to the newly declared State of Israel.[citation needed] In 1948 the Israelis changed the official name of the airport from Lydda to Lod (the nearby town's name in Hebrew), the airport's name becoming Lod Airport.[10] Flights resumed on 24 November 1948.[11] That year, 40,000 passengers passed through the terminal. By 1952, the number had risen to 100,000 a month. Within a decade, air traffic increased to the point where local flights had to be redirected to Tel Aviv's other airport, the Sde Dov airfield (SDV) on the city's northern coast. By the mid-1960s, 14 international airlines were landing at the airport.
The airport's name was changed from Lod to Ben Gurion International Airport in 1973 to honour Israel's first Prime Minister, David Ben-Gurion, who died that year.
Terrorist incidents (1972)
[edit]While Ben Gurion Airport has been a target of Palestinian attacks, the adoption of strict security precautions has ensured that no aircraft departing from Ben Gurion airport has ever been hijacked. On the other hand, airliners hijacked from other countries have landed at Ben Gurion, contributing to two major incidents in the airport's history.
In the first incident, on 8 May 1972, four Palestinian Black September terrorists hijacked a Sabena flight en route from Vienna and forced it to land at Ben Gurion airport. Sayeret Matkal commandos, including Benjamin Netanyahu, led by Ehud Barak (both future Israeli Prime Ministers) stormed the plane, killing two of the hijackers and capturing the other two. One passenger was killed.[12]
Later that month, on 30 May 1972, in an attack known as the Lod Airport massacre, 24 people were killed and 80 injured when three members of the Japanese Red Army sprayed machine gun fire into the passenger arrival area. The victims included Aharon Katzir, a prominent protein biophysicist and brother of Israel's 4th president. Those injured included a group of twenty Puerto Rican tourists who had just arrived in Israel.[13] The only terrorist who survived was Kozo Okamoto, who received a life sentence but was released in 1985 as part of a prisoner exchange with the PFLP-GC.[14]
Since the 1980s
[edit]More buildings and runways were added over the years, but with the onset of mass immigration from Ethiopia and the former Soviet Union in the 1980s and 90s, as well as the global increase of international business travel, the existing facilities became painfully inadequate, prompting the design of a new state-of-the-art terminal that could also accommodate the expected tourism influx for the 2000 millennium celebrations. The decision to go ahead with the project was reached in January 1994, but the new terminal, known as Terminal 3, only opened its doors a decade later, on 2 November 2004.[15]
During the 2014 conflict with Gaza, several airlines banned their flights to the airport for a couple of days.[16] In October 2023, with the outbreak of the Israel–Hamas war, the number of airlines that flew into the airport dropped to just 7. By February 2024, only 45 airlines flew into the airport.[17]
The furthest nonstop flight to have departed the airport was a private Airbus A340-500 owned by billionaire casino mogul Sheldon Adelson who flew on 2 January 2017 to Honolulu on a route over the Arctic Ocean. The flight was projected to last 17 hours and 40 minutes.[18]
Ramon Airport, an international airport near the southern Israeli city of Eilat, serves as a diversion airport for Ben Gurion Airport.[19]
Passenger terminals
[edit]Terminal 1
[edit]
History
[edit]Prior to the opening of Terminal 3, Terminal 1 was the main terminal building at Ben Gurion Airport. At that time, the departures check-in area was located on the ground floor. From there, passengers proceeded upstairs to the main departures hall, which contained passport control, duty-free shops, VIP lounges, one synagogue and boarding gates. At the gates, travelers would be required to descend a flight of stairs to return to the ground floor where waiting shuttle buses transported them to airplanes on the tarmac. The arrivals hall with passport control, luggage carousels, duty-free pick-up and customs was located at the south end of the building. The apron buses transferred passengers and crews to and from the terminal to airplanes which were parked on the tarmac over 500 m (1,600 ft) away. After Terminal 3 opened, Terminal 1 was closed except for domestic flights to the airport in Eilat and government flights such as special immigrant flights from North America and Africa. Chartered flights organised by Nefesh B'Nefesh carrying immigrants from North America and England use this terminal for their landing ceremonies several times a year.[20]
Although Terminal 1 was closed between 2003 and 2007, the building served as a venue for various events and large-scale exhibitions including the "Bezalel Academy of Arts Centennial Exhibition" which was held there in 2006. The renovations for the terminal were designed by Yosef Assa with three individual atmospheric themes. Firstly, the public halls have a Land-of-Israel character with walls painted in the colors of Israel's Judean, Jerusalem and Galilee mountains. The departure hall is given an atmosphere of vacation and leisure, whilst the arrivals hall is given a more urban theme as passengers return to the city.[21]

In February 2006, the Israel Airports Authority announced plans to invest 4.3 million NIS in a new VIP wing for private jet passengers and crews, as well as others interested in avoiding the main terminal. VIP ground services already exist, but a substantial increase in users has justified expanding the facilities, which will also boost airport revenues. The IAA released figures showing significant growth in private jet flights (4,059, a 36.5% increase from 2004) as well as private jet users (14,613, a 46.2% increase from 2004). The new VIP wing, operated by an outside licensee, will be located in an upgraded and expanded section of Terminal 1. All flight procedures (security check, passport control and customs) will be handled here. This wing will include a hall equipped for press conferences, a deluxe lounge, special meeting rooms equipped with state-of-the-art business facilities and a designated lounge for flight crews who spend time at the airport between flights.[22] It was announced in January 2008, however, that the IAA planned to construct a new 1,000-square-metre (11,000 sq ft) VIP terminal next to Terminal 3.[23]
International low-cost and domestic terminal
[edit]
Terminal 1 was closed in 2003 and reopened in 2007 as the domestic terminal following extensive renovations,[24] and in July 2008, to cater for summer charter and low-cost flights.[25] It remained open for these charter and low-cost flights for the 2008 summer season then temporarily closed in October 2008, when it underwent further renovation and reopened again in the summer of 2009, when it was expected to reach a three-month capacity of 600,000 passengers on international flights.[25] As of 2010, several low-cost carriers' international flights were operating out of Terminal 1 year-round including Vueling flights to Barcelona and easyJet flights to London (Luton), Manchester, Geneva, and Basel. In 2015, due to increased demand and following another expansion of the terminal, the Israel Airports Authority made Terminal 1 available to all low-cost carriers under certain conditions.[26] Flights operating out of Terminal 1 are charged lower airport fees than those operating out of Terminal 3.[27]
Until the summer of 2017 Terminal 1 was used for flight check-in, security screening and passport-control for international flights for passengers of certain low-cost airlines, but following passport control passengers were bussed to the departures concourse of Terminal 3 from which they boarded their flights. All incoming flights for airlines operating out of Terminal 1 were handled in Terminal 3. However, beginning on 19 June 2017 and following several months of renovations, Terminal 1 passengers began being bussed directly to their flights from Terminal 1, although incoming passengers continue to be handled in Terminal 3. The renovations to Terminal 1's boarding area included adding duty-free shops, restaurants and cafes. The terminal was also equipped with advanced checked-baggage handling and screening systems, similar to those in Terminal 3.
A free public shuttle from Terminal 3 and the railway station to and from Terminal 1 operates approximately every 15 to 30 minutes (depending on the time of day).
Terminal 3
[edit]

Terminal 3, which opened on 28 October 2004,[28] replaced Terminal 1 as the main international gateway to and from Israel. The building was designed by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM).[29][30] Moshe Safdie & Associates[31] and TRA (now Black and Veatch)[29] designed a linking structure and the airside departure areas and gates. Ram Karmi[29] and other Israeli architects were the local architects of record. The inaugural flight was an El Al flight to John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York City.
Work on Natbag 2000, as the Terminal 3 project was known, was scheduled for completion prior to 2000 in order to handle a massive influx of pilgrims expected for the Millennium celebrations. This deadline was not met due to higher than anticipated costs and a series of work stoppages in the wake of the bankruptcy of the main Turkish contractor. The project eventually cost an estimated one billion US dollars. Due to the proximity of the airport to the country's largest population centres and the problem of noise pollution, another international airport is being considered to be built elsewhere in the country,[32] such as the new Ilan and Assaf Ramon Airport in Southern Israel.
The overall layout of Terminal 3 is similar to that of airports in Europe and North America, with multiple levels and considerable distances to walk after disembarking from the aircraft. The walk is assisted by escalators and moving walkways. The upper level departures hall, with an area of over 10,000 m2 (110,000 sq ft), is equipped with 110 check-in counters and as well as flight information display systems.[33] A small shopping mall, known as Buy & Bye, is open to both travellers and the general public. The mall, which includes shops, restaurants and a post office, was planned to be a draw for non-flyers too. On the same level as the mall, passengers enter passport control and the security check. Planes taking off and landing can be viewed from a distinctive tilted glass wall. The arrivals hall is located on the ground floor where there are also 20 additional check-in counters (serving Star Alliance airlines). Car rental counters are located in an intermediate level situated between the departing and arriving passenger halls. Terminal 3 has two synagogues.[34]

After the main security check, passengers wait for their flights in the star-shaped duty-free rotunda. A variety of cafes, restaurants and duty-free shops are located there, open 24 hours a day, as well as a synagogue, banking facilities, a transit hall for connecting passengers and a desk for VAT refunds.[35]
Terminal 3 has a total of 40 gates divided among four concourses (B, C, D, and E), each with 8 jet bridge-equipped gates (numbered 2 through 9), as well as two stand gates (bus bays 1 and 1A) from which passengers are ferried to aircraft. Two gates in concourse E utilize dual jet bridges for more efficient processing of very large widebody aircraft. Concourses B, C, and D were opened when terminal 3 opened in 2004, while concourse E was completed in 2018.[36] Space exists for one additional concourse (A) at Terminal 3.
Free wireless internet is provided throughout the terminal.[37][38] The terminal has three business lounges—the exclusive El Al King David Lounge for frequent flyers and three Dan lounges for either privileged or paying flyers.
In January 2007, the IAA announced plans for a 120-bed hotel to be located about 300 m (980 ft) west of Terminal 3.[39] The tender for the hotel was published by the IAA in late 2017.
When the terminal was built, it was said to have a capacity for up to 12 million passengers a year. In 2023, 25 million passengers are expected to pass through Ben Gurion Airport.[40]
Former and unopened terminals
[edit]Terminal 2
[edit]Terminal 2 was inaugurated in 1969 when Arkia resumed operations at the airport after the Six-Day War.[41] Terminal 2 served domestic flights until 20 February 2007 when these services moved into the refurbished Terminal 1. Due to increased traffic in the late 1990s and over-capacity reached at Terminal 1, an international section was added until Terminal 3 was opened. After the transfer of domestic services to Terminal 1, Terminal 2 was demolished in order to make room for additional air freight handling areas.
Terminal 4
[edit]This terminal, built in 1999, was meant to handle the crowds expected in 2000, but never officially opened. To date, it has only been used as a terminal for passengers arriving from Asia during the SARS epidemic.[42] Another use for the terminal was for the memorial ceremonies upon the arrival of the casket of Col. Ilan Ramon after the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster in February 2003 and the arrival of Elhanan Tannenbaum and the caskets of three Israeli soldiers from Lebanon in January 2004.
Development plans
[edit]In December 2017, the IAA announced a long-term expansion plan for Ben Gurion Airport estimated to cost approximately NIS 9 billion. Plans include further expansion of Terminal 1, a new dedicated domestic flights terminal, a major expansion of Terminal 3's landside terminal which would add approximately 90 additional check-in counters, construction of Concourse A, and additional aircraft parking spaces and ramps. In addition, air cargo facilities would be relocated to a large, currently-unused tract of land in the northern part of the airport's property (north of runway 08/26) where additional aircraft maintenance facilities would also be built.
In the meantime, to ease immediate overcrowding problems at Terminal 3's landside terminal, in the spring of 2018 a temporary large, air-conditioned tent was erected adjacent to Terminal 3 housing 25 check-in counters and security screening facilities. This tent was used for compulsory COVID-19 testing for all arriving passengers between 2020 and 2022.
In August 2018, the IAA published a tender for the construction and operation of a new terminal, dedicated to handling private and executive aircraft traffic.[43]
In late 2021 construction began on a new interchange that will provide additional access to the airport from Highway 1. The new interchange significantly reduced the distance vehicles must travel to access the airport's main terminal from the direction of Tel Aviv and other points north and west of the airport.
Office buildings
[edit]The Airport City development, a large office park, is located east of the main airport property. It is at the junction of the Jerusalem and Tel Aviv metropolitan areas.[44]
The head office of El Al is located at Ben Gurion Airport,[45] as is the head office of the Israel Airports Authority.[46]
The head offices of the Civil Aviation Authority and Challenge Airlines IL are located in the Airport City office park nearby the airport.[47][48]
Israel Aerospace Industries maintains its head office on airport grounds as well as extensive aviation construction and repair facilities.[49]
Runways
[edit]
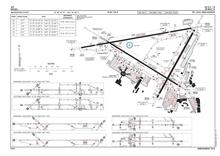
Main runway
[edit]The closest runway to terminals 1 and 3 is 12/30, 3,112 m (10,210 ft) in length, and is followed by a taxiway. Most landings take place on this runway from West to East, approaching from the Mediterranean Sea over southern Tel Aviv.[50] During inclement weather, it may also be used for takeoffs (Direction 12). A 17 million NIS renovation project was completed in November 2007 which reinforced the runway and made it suitable for future wide-body aircraft. In September 2008, a new ILS serving the runway was activated. The main runway was closed from 2011 until early 2014 in order to accommodate the extension of runway 03/21 and other construction activity in the vicinity of the runway.
Short runway
[edit]When it was originally built, the short runway (direction 03/21) was 1,780 m (5,840 ft) long, making it too short to accommodate most mainline passenger jets. At the time it mainly served cargo aircraft of the Israeli Air Force and as a taxiway for runway 26. However, by late 2011, the runway was closed and most of the activity in the military apron to the east of the runway was permanently relocated to the Nevatim Airbase in southern Israel. In late May 2014 the runway was reopened after having been rebuilt and lengthened to 2,772 m (9,094 ft), allowing it to handle most types of aircraft. It is equipped with an ILS and mostly handles landings from north to south.
Quiet runway
[edit]The longest runway at the airfield, 4,062 m (13,327 ft), and the main take off runway from east to west (direction 08/26), is referred to as "the quiet runway" since jets taking off in this direction produce less noise pollution for surrounding residents.[vague] A 24 million NIS renovation project completed in February 2006 reinforced the runway and made it suitable for wide-body aircraft such as Airbus A380.[51]
History and development
[edit]The original layout of the airfield as designed by the British in the 1930s included four intersecting 800 m runways suitable for the piston engined aircraft of the day. However, none of this original layout is visible nowadays since as usage increased and aircraft types and needs changed over the years various runways on the airport's premises were built and removed.
The main runway (12/30) is the oldest surviving runway in the airport, with the quiet (08/26) and short (03/21) runways having been built in the late 1960s and 1970s. Since very little commercial traffic could operate on the short runway, for approximately forty years, the airport mostly relied on runways 12/30 and 08/26. This presented a problem, however: the fact that these two runways intersect near their western end creates a crisscross pattern between aircraft landing and taking off. This pattern reduces the number of aircraft which can arrive to and depart from the airport and has detrimental safety implications as well.
With passenger traffic projected to increase, plans were drawn in the 1980s and 90s for the extension of runways 03/21 and 08/26 as a means of alleviating some of Ben Gurion's safety and capacity concerns. These plans were approved in 1997 and construction began in 2010. The extension of runway 03/21 allows the airport to operate in an "open V" configuration, allowing for simultaneous landings and take offs on runways 08/26 and 03/21 and thus more than double the number of aircraft movements which can be handled at peak times, while increasing the overall level of air safety in and around the airport. Construction took four years and cost 1 billion NIS (financed from the Israeli Airports Authority budget) and was completed 29 May 2014. It included paving 22 kilometres (14 mi) of runways and taxiways, using more than 1.5 million tons of asphalt, laying one million meters of runway lighting cables, 50,000 metres (160,000 ft) of high-voltage power lines and 10,000 light fixtures.[52] The construction of several new taxiways between the existing runways and terminals also significantly reduced taxi times at the airport.
Israel-Hamas War (2023- )
[edit]Due to the threat of missiles, the runway directions are restricted to avoid flying over the war zone in Gaza. 08/26 is restricted to departing flights, and 03/21 is restricted to arriving flights.[53]
Security procedures
[edit]Overview
[edit]Security at Ben Gurion International Airport operates on several levels.[54]
All cars, taxis, buses and trucks go through a preliminary security checkpoint before entering the airport compound. Armed guards spot-check the vehicles by looking into cars, taxis and boarding buses, exchanging a few words with the driver and passengers. Armed security personnel stationed at the terminal entrances keep a close watch on those who enter the buildings. If someone arouses their suspicion or looks nervous, they may strike up a conversation to further assess the person's intent. Plainclothes armed personnel patrol the area outside the building, and hidden surveillance cameras operate at all times.[55] Inside the building, both uniformed and plainclothes security officers are on constant patrol. Departing passengers are personally questioned by security agents even before arriving at the check-in desk. This interview can last as little as a minute, or as long as an hour if a passenger is selected for additional screening. Luggage and body searches may be conducted.
Until August 2007, there was a system of color codes on checked baggage but the practice was discontinued after complaints of discrimination.[56] In the past, checked bags were screened following the personal interview and before passengers arrived at the check-in desks. Occasionally, if security assessed a person as a low risk, they were passed straight through to the check-in desks, bypassing the main X-ray machines, a practice which also drew some discrimination complaints. This process ceased in April 2014 when the main X-ray machines were removed from the passenger queuing area in Terminal 3 and baggage screening began being performed after the baggage was checked-in by airline representatives (as is common in most airports around the world). Terminal 1 began using the same procedure in the summer of 2017.
Baggage screening
[edit]After check-in, all checked baggage are screened using sophisticated X-ray and CT scanners and put in a pressure chamber to trigger any possible explosive devices which have a trigger dependent on air pressure. Following the check-in process, passengers continue to personal security and passport control. Before passing through the metal detectors and putting carry-on baggage through the X-ray machine at the security checkpoint, passports and boarding passes are re-inspected and additional questions may be asked. Before boarding the aircraft, passports and boarding passes are verified once again. Security procedures for incoming flights are not as stringent, but passengers may be questioned by passport control depending on country of origin, or countries visited prior to arrival in Israel. Passengers who have recently visited Arab countries are subject to further questioning.[57]
Airlines and destinations
[edit]Passenger
[edit]The following airlines serve regular scheduled and charter destinations at Ben Gurion Airport.[58] Most of the airlines have been suspended or have delayed their resumption due to the Israel-Hamas War since October 7th, 2023 and the ongoing situation in the Middle East.[59] Some Airports have even taken out flights to Tel Aviv from their list of destinations.
Cargo
[edit]Statistics
[edit]Commercial flights from Sde Dov Airport which, until its closure in July 2019, handled more domestic passengers annually than TLV have been moved to Ben Gurion.[135]
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
| Year | Total passengers | Percentage change | Total operations | Percentage change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 | 8,916,436 | |||
| 2000 | 9,879,470 | 80,187 | ||
| 2001 | 8,349,657 | 69,226 | ||
| 2002 | 7,308,977 | 63,206 | ||
| 2003 | 7,392,026 | 61,202 | ||
| 2004 | 8,051,895 | 66,638 | ||
| 2005 | 8,917,421 | 70,139 | ||
| 2006 | 9,221,558 | 76,735 | ||
| 2007 | 10,526,562 | 84,568 | ||
| 2008 | 11,550,433 | 94,644 | ||
| 2009 | 10,925,970 | 89,442 | ||
| 2010 | 12,160,339 | 95,171 | ||
| 2011 | 12,978,605 | 99,527 | ||
| 2012 | 13,133,992 | 97,824 | ||
| 2013 | 14,227,612 | 104,850 | ||
| 2014 | 14,925,369 | 112,653 | ||
| 2015 | 16,299,406 | 118,861 | ||
| 2016 | 17,936,810 | 127,575 | ||
| 2017 | 20,781,226 | 142,938 | ||
| 2018 | 22,949,676 | 157,312 | ||
| 2019 | 24,821,767 | 167,886 | ||
| 2020 | 4,457,439 | 49,223 | ||
| 2021 | 6,719,901 | 75,321 | ||
| 2022 | 20,008,532 | 143,884 | ||
| 2023 | 21,882,716 | 152,411 |
Top destinations by number of passengers
[edit]| Rank | Airport | Passengers | Annual change | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 917,870 | Arkia, El Al, Emirates, flydubai, Israir | ||
| 2 | 865,985 | Turkish Airlines | ||
| 3 | 788,920 | Aegean, Arkia, Bluebird Airways, El Al, Israir, Ryanair | ||
| 4 | 774,386 | Air France, Arkia, easyJet, El Al | ||
| 5 | 688,755 | British Airways, El Al, Virgin Atlantic | ||
| 6 | 676,208 | Arkia, Bluebird Airways, Cyprus Airways, El Al, Israir, Sun d'Or, Tus Airways | ||
| 7 | 672,977 | AnadoluJet, Pegasus Airlines | ||
| 8 | 662,054 | AnadoluJet, Corendon, Pegasus Airlines, Turkish Airlines | ||
| 9 | 640,004 | American, Delta, El Al | ||
| 10 | 606,971 | El Al, United |
| Rank | Country | Passengers | Rate of total | Annual change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2,305,977 | 10.93% | ||
| 2 | 2,009,244 | 9.52% | ||
| 3 | 1,753,248 | 8.31% | ||
| 4 | 1,466,320 | 6.95% | ||
| 5 | 1,214,291 | 5.75% | ||
| 6 | 1,198,962 | 5.68% | ||
| 7 | 1,148,542 | 5.44% | ||
| 8 | 999,904 | 4.74% | ||
| 9 | 981,105 | 4.65% | ||
| 10 | 883,249 | 4.18% |
| Rank | Airline | Passengers | Percentage of total passengers | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | El Al Israel Airlines | 5,539,127 | 26.26% | Ben Gurion Airport, Israel |
| 2 | Wizz Air | 1,998,168 | 9.47% | Budapest, Hungary |
| 3 | Ryanair | 1,147,880 | 5.44% | Swords, Ireland |
| 4 | Turkish Airlines | 1,107,125 | 5.24% | Istanbul, Turkey |
| 5 | Israir Airlines | 1,003,654 | 4.75% | Tel Aviv, Israel |
| 6 | Arkia | 723,989 | 3.43% | Tel Aviv, Israel |
| 7 | Pegasus Airlines | 692,688 | 3.28% | Istanbul, Turkey |
| 8 | Easyjet | 658,400 | 3.12% | Luton, United Kingdom |
| 9 | United Airlines | 605,753 | 2.87% | Chicago, Illinois, United States |
| 10 | Lufthansa | 440,612 | 2.08% | Cologne, Germany |
Ground transportation
[edit]The airport is located near Highway 1, the main Jerusalem–Tel Aviv Highway and Highway 40. The airport is accessible by car or public bus. Israel Railways operates train service from the airport to several parts of the country and taxi stands are located outside the arrivals building. A popular transportation option is a share taxi van, known in Hebrew as a monit sherut (service cab), going to Jerusalem, Haifa, and Beersheba.
Public transport
[edit]Israel has an integrated nationwide public transport payment system covering multiple transit options (train, bus, and light rail) run by various operators using a single payment card: the Rav-Kav. It features flexible tariff arrangements and offers free transfers between transit methods within certain geographical zones and time periods. A public transport information office which also issues Rav-Kav cards is located in the arrivals hall of Terminal 3. With a few exceptions, most public transport options (except for taxis and service cabs) do not operate on the Sabbath (i.e., from early Friday evenings to late Saturday evenings as well as certain Jewish holidays).
A new app payment system was introduced in December 2020. The apps have a different, simpler fare system and it's post pay (The Rav Kav is a pre-paid card that you need to top up). The charge is at the end of each month (so a registration and a payment method are required). The two apps supporting routing and payment are: RavPass (by HopOn), and Moovit (by Moovit and Pango).[citation needed]
Rail
[edit]
Israel Railways operates the Ben Gurion Airport Railway Station, located in the lower level of Terminal 3. From this station passengers may head northwest to Tel Aviv, Haifa and other destinations in the north, or southeast to Modi'in and Jerusalem. The journey to Tel Aviv Savidor Central railway station takes about 18 minutes and to Jerusalem's Yitzhak Navon station about 25 minutes. There is also late night/early morning train service to and from the airport terminating at Beersheba Center via Lod, Ashkelon, and selected destinations in between. Almost 3.3 million passengers used the railway line to and from the airport in 2009. The service does not operate on Shabbat and Jewish holidays but on all other days it runs day and night. The line to Nahariya through Tel Aviv and Haifa operated 24 hours a day on weekdays, but these services were suspended following the COVID-19 pandemic and put on hold until railway electrification works are completed in the mid-2020s, following which the line would run from Jerusalem and terminate at Karmiel instead of Nahariya (though it would continue to service Tel Aviv and Haifa).
Bus or taxi
[edit]The airport is served by regular inter-city bus lines, limousine and private shuttle services, Sherut "shared" door to door taxi vans and regular taxis.[137] Afikim bus company provides 24 hours a day, on the hour, direct service to Jerusalem with line 485. the line departs from Terminal 3 on the 2nd floor and passes through Terminal 1.[138] Egged bus number 5 ferries passengers between the terminals and a small bus terminal in the nearby Airport City business park near El Al junction just outside the airport where they can connect to regular Egged bus routes passing through the area. Passengers connecting at Airport City can pay for both rides on the same ticket, not having to pay an extra fare for bus No. 5. Other bus companies directly serve Terminal 3, and the airport also provides a free shuttle bus between terminals.[139] On Shabbat, when there is no train service, a shared shuttle service is available between the airport and Tel Aviv hotels.[140][141]
Car
[edit]Located on Highway 1, the Jerusalem – Tel Aviv highway, the airport has a total of approximately 20,000 parking spaces for short and long-term parking.[142] The spaces for long-term parking are situated several kilometres from the terminal, and are reached by a free shuttle bus.[143] Car rental at the airport is available from Avis, Budget, Eldan, Tamir Rental,[144] Thrifty, Hertz, and Shlomo Sixt.[145]
Service quality
[edit]Passenger rankings
[edit]In December 2006, Ben Gurion International Airport ranked first among 40 European airports and 8th out of 77 airports in the world, in a survey, conducted by Airports Council International, to determine the most customer-friendly airport. Tel Aviv placed second in the grouping of airports which carry between 5 and 15 million passengers per year behind Japan's Nagoya Airport. The survey consisted of 34 questions. A random sampling of 350 passengers at the departure gate were asked how satisfied they were with the service, infrastructure and facilities. Ben Gurion received a rating of 3.94 out of 5, followed by Vienna, Munich, Amsterdam, Brussels, Zürich, Copenhagen, and Helsinki. The airport retained its title as the best Middle Eastern airport in the 2007, 2008, and 2009 surveys.[146][147]
Awards
[edit]| Year | Award | Category | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | Airport Service Quality Awards by Airports Council International |
Best Airport in Middle East | Won | [148] |
| Best Airport by Size (5–15 million passengers) | 2nd | |||
| 2008 | Best Airport in Middle East | Won | [149][150] | |
| Best Airport by Size (5–15 million passengers) | 2nd | |||
| 2009 | Best Airport in Middle East | Won | [151] | |
| 2010 | 3rd | [152] | ||
| 2011 | 3rd | [153] | ||
| 2012 | 4th | [154] | ||
| 2013 | 4th | [155] | ||
| 2014 | 3rd | [156] | ||
| 2015 | 3rd (tie) | [157] |
Accidents and incidents
[edit]- On 13 February 1939, a Fokker F.XVIII (VQ-PAF) of the newly founded Commercial Aviation Company Ltd. was being flown around the airport for an inaugural celebration. While landing the pilot lost control and veered off into the mud, damaging it beyond repair.[158]
- On 5 February 1950, a Douglas C-54A-10-DC (4X-ACD) of El Al skidded off during takeoff, caught fire, and was damaged beyond repair. All 50 occupants survived.[159]
- On 15 May 1953, a Douglas C-47 of the USAF as part of a US military attaché in Israel caught fire standing at night and was burned out. Sabotage was suspected.[160]
- On 26 October 1969, a Vickers 833 Viscount (4X-AVC) of Arkia crashed during a nighttime training flight and was damaged beyond repair. All three occupants survived.[161]
- On 30 November 1970, a Boeing 707-373C (N790TW) of TWA was taking off for a cargo flight to Frankfurt at 02:00 on runway 30 when an empty, unlit IAF Stratocruiser (4X-FPS/037) was towed across the runway; the 707 hit the Stratocruiser and both aircraft caught fire. Both planes were damaged beyond repair, and all three crew on the 707 survived. However, two persons were killed on the ground.[162][163]
- On 8 May 1972, a Boeing 707-329 (OO-SJG) of Sabena was hijacked en route to Tel Aviv from Vienna and landed here (the intended destination); the four hijackers demanded prisoner releases. Two were shot and killed by military personnel in ground engineer uniforms the same day, and a passenger died eight days later from injuries sustained in the gun battle.[164]
- On 16 August 1973, a Boeing 720-023B (OD-AFR) of MEA was hijacked en route from Benghazi to Beirut over Cyprus by a male hijacker with two guns who demanded to be flown here; he was overpowered by ground police upon arrival.[165]
- On 31 July 1980, a Boeing 707-358C (4X-ATX) of El Al had a fire erupt in the rear lavatory prior to departure here; the aircraft was evacuated and fire services had to cut a hole in the fuselage to put out the flames. The aircraft was later repaired.[166]
- On 16 February 1987, a Convair CV-240-24 (N93218) of IAI was destroyed in a hangar fire.[167]
- On 1 December 1988: 1988 Ordzhonikidze bus hijacking. Five men in Ordzhonikidze hijacked a school bus, demanding 2,000,000 rubles and an airplane to fly them to Israel. The bus went to Mineralnye Vody Airport and the hijackers boarded an Ilyushin Il-76T of Aeroflot in exchange for 30 hostages. The plane arrived here the following day, and the hijackers surrendered.[168]
- On 18 June 2001, a ATR 42-320 (4X-ATK) of Israir could not lower its starboard main undercarriage and had to land without it; none of the 42 occupants were injured. The plane was written off and converted into a training rig.[169]
- On 8 April 2015, a British Aerospace BAe 125-800A (4X-CZO) of Arrow Aviation aborted a takeoff from runway 26 due to a swerve issue, and after stopping a fire broke out in the right main gear wheel area. The plane, an air ambulance, was substantially damaged.[170]
- On 28 March 2018, a Boeing 737-76J (WL) (D-ABLB) on Germania Flight 4915 to Berlin collided with a Boeing 767-300ER (4X-EAK) on El Al Flight 385 to Rome while both aircraft were in the pushback/towing phase at 06:22. The 737's tail fin hit the right horizontal stabilizer of the 767 after ground controllers cleared both for pushback without realizing they were blocking each other. The 737 was later repaired, but the 767 was written off.[171][172]
See also
[edit]- Transportation in Israel
- Ramon Airport
- Haifa Airport
- List of the busiest airports in the Middle East
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Jerusalem's new high-speed train starts regular trips to Ben Gurion Airport". The Times of Israel. Jerusalem. 25 September 2018. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ^ a b "AD 2.5 TEL-AVIV / BEN-GURION – LLBG". Archived from the original on 12 October 2013. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ a b "IAA Periodic Activity Reports for Ben Gurion Airport". IAA Website. Israel Airports Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 January 2019. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ "Monthly Report". Israel Airport Authority. Ben Gurion Int'l Airport - Managing Director Office. Retrieved 22 January 2024.
- ^ "ASQ Awards". Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ Dempsey, John S. (23 March 2010). Introduction to Private Security. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0495809852.
- ^ The Christian Science Monitor (22 July 2014). "The importance of Ben Gurion airport to Israel". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ Lewis, Ori (21 January 2019). "Israel opens new international airport, named for astronaut Ramon, near Red Sea". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ a b c "Chapter 1 – from Flying Camels to Flying Stars: Israel Reborn (1917–1948) | Israel Airline Museum". 5 August 2016.
- ^ Harro Ranter. "Lydda Airport profile – Aviation Safety Network". Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "Ben Gurion Airport- The 40s". Israel Airports Authority. Retrieved 29 April 2007.
- ^ Sontag, Deborah (20 April 1999). "2 Who Share a Past Are Rivals for Israel's Future". The New York Times. pp. Section A, Page 3, Column 1.
- ^ "1972: Japanese kill 26 at Tel Aviv airport". BBC.co.uk. 29 May 1972. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ Lewis, Paul (21 May 1985). "Israel frees 1,150 to obtain release of last 3 soldiers". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 April 2007.
- ^ "Ben Gurion". History Central. Archived from the original on 30 March 2007. Retrieved 29 April 2007.
- ^ "FAA lifts ban on US flights to Tel Aviv airport". Yahoo News. 24 July 2014. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "Are airlines returning to Israel, despite the war on Gaza?". Al Jazeera. 28 February 2024.
- ^ Melnitcki, Gili (4 January 2017). ""Next Stop Hawaii: Sheldon Adelson sets record with 18-hour flight from Israel"". Haaretz. Retrieved 15 January 2017.
- ^ "Israel: Ramon Airport (ETM) in Eilat set to open gradually from January 22". GardaWorld.
- ^ "Ben Gurion Airport". HistoryCentral. Archived from the original on 30 March 2007. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ "Principles of Architectural Planning". IAA. Archived from the original on 12 April 2008. Retrieved 12 April 2008.
- ^ "Israel Airports Authority to Build a Special Terminal for Executive and Private Flights at Ben Gurion Airport". Israel Airports Authority. 21 February 2006. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ "Terminal for private flights to be built at airport". The Jerusalem Post. 22 January 2008. Retrieved 22 January 2008. [permanent dead link]
- ^ "End of an Era – The Historic Terminal 1 has Re-opened, Serving Passengers on Domestic Flights". Israel Airports Authority. 20 February 2007. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ a b "Ben-Gurion's old terminal reopens for summer charters". The Jerusalem Post. 2 July 2008. Retrieved 12 July 2008. [permanent dead link]
- ^ "Operating International Flights from Terminal 1 at Ben Gurion Int'l Airport" (PDF). Israel Airports Authority. 10 February 2015. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ^ Rosenberg-Kandel, Rina (27 November 2019). "6 מיליארד שקל לתוכנית הפיתוח של נתב"ג לשלוש השנים הקרובות" [ILS Six Billion for the Ben Gurion Airport Expansion Plan in the Next Three Years] (in Hebrew). Retrieved 27 November 2019.
- ^ "Address by PM Sharon at inauguration of Ben Gurion Airport 2000". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ^ a b c "Ben Gurion International Airport, Terminal 3". Architectural Record. October 2005.
- ^ "Ben Gurion International Airport International Terminal". Archived from the original on 16 May 2010. SOM.com Project Page
- ^ "Ben Gurion International Airport International Terminal". [permanent dead link] Moshe Safdie & Associates Project Page
- ^ "Facts and Figures". Israel Airports Authority. Retrieved 4 May 2007.
- ^ "Check-In Hall". Israel Airports Authority. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ Senyor, Eli (21 December 2006). "Muslim prayer room set up at Ben-Gurion Airport". Ynetnews. Ynet. Retrieved 5 May 2007.
- ^ "Tel Aviv – Ben Gurion Airport (TLV) Information". Essential Travel. Archived from the original on 21 April 2007. Retrieved 29 April 2007.
- ^ Blumenthal, Itay (15 February 2018). "נתב"ג מתרחב: נחנכה הזרוע הרביעית" [Ben Gurion Airport Expands: Fourth Concourse Inaugurated]. Ynet. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ^ "012 wireless Ben Guiron" (PDF). iaa.gov.il. 14 March 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 October 2007. Retrieved 17 August 2024.
- ^ "Free Wi-Fi in Airports". Archived from the original on 29 April 2007. Retrieved 4 May 2007.
- ^ "A BOT tender to be published for Ben Gurion hotel". PORT2PORT- Israel's Trade Portal. 15 January 2007. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ Gilad, Moshe (4 July 2023). "Read Before You Land: Everything to Know About Israel's Ben-Gurion Airport". Haaretz.com. Retrieved 17 August 2024.
- ^ "Ben Gurion Airoport – The 60s (IE browser required)". Israel Airports Authority. Retrieved 12 June 2008.
- ^ Strongin, Michael (30 April 2003). "Ministry begins checking for SARS at Ben-Gurion". The Jerusalem Post. p. 3. Archived from the original on 7 November 2012. Retrieved 5 July 2017.
- ^ "Israel Airports Authority to build private plane terminal at Ben Gurion Airport". port2port.co.il. Archived from the original on 28 August 2018. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
- ^ "Airport City – business park, offices, storage, industry, logistics". airport-city.co.il. 30 August 2012. Archived from the original on 3 January 2013. Retrieved 17 August 2024.
- ^ Orme, William A. Jr. "El Al at a Turning Point; A Mirror of Israel's Divisions Prepares to Go 49% Public". The New York Times. 5 March 1999. C1, New York Edition. 1. Retrieved 15 February 2010.
- ^ "IAA Head Office". Israel Airports Authority. Retrieved 6 March 2010.[dead link]
- ^ "CAA Relocates to Airport City office park". Civil Aviation Authority. 2 August 2010. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 14 December 2015.
- ^ "Contact Information". CAL Cargo Air Lines. Retrieved on 1 January 2012. "Contact Information Headquarters C.A.L. Cargo Airlines 1 Hayarden Street, Airport City P.O.B. 271 Ben Gurion Airport 70100, Israel"[dead link]
- ^ "IAI Head Office". Israel Aerospace Industries.
- ^ "Ben Gurion Airport". World Aero Data. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ^ "Renovation of Runway 26-08 Completed; Became Operative on Sunday, February 26". Israel Airports Authority. 7 March 2006. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ Peretz-Zilberman, Sapir (29 May 2014). "New Ben Gurion airport runways inaugurated". Globes English. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
- ^ "Live Flight Tracker - Real-Time Flight Tracker Map".
- ^ Beyer, Lisa (24 September 2001). "Is This What We Really Want?". Time. Archived from the original on 12 March 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ^ "What can we learn from Ben Gurion Airport in Israel to help push aviation security in the U.S. to the next level?". Access Control & Security Systems. Retrieved 4 May 2007.
- ^ Blumenkrantz, Zohar (7 August 2007). "Color tags discontinued". Haaretz.com. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Prada, Paulo; Michaels, Daniel (17 September 2001). "Israel airport is safe but hard to emulate". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 31 October 2007. Retrieved 4 May 2007.
- ^ "Full List of Flights to Ben Gurion Airport, Tel Aviv, Israel". 27 July 2015. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- ^ "Full list of Flight cancellations to Ben Gurion Airport amid the October 7th War with Hamas". Israel Hayom. Retrieved 15 June 2024.
- ^ a b אזולאי, עדי (27 November 2024). "חברת Aegean Airlines חוזרת לישראל". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. Retrieved 27 November 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "כל העדכונים השוטפים של חברות התעופה: פספורטניוז עושה לכם סדר". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. 6 August 2024. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "Travel to or from Israel". www.aircanada.com. Air Canada. Retrieved 14 July 2024.
- ^ "אייר אינדיה: הטיסות לישראל מבוטלות עד למועד זה". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. 29 November 2024. Retrieved 29 November 2024.
- ^ "המגמה נמשכת: גם אייר סיישל חוזרת לישראל". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. 28 November 2024. Retrieved 28 November 2024.
- ^ Reinstein, Ziv (4 September 2024). "New direct flights from Israel to Lithuania by Air Baltic, begin March 31". JPost.com. The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ COHEN, MOSHE (9 October 2024). "Joining the line: The new Israeli company will start flying to Cyprus". JPost.com. The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 10 October 2024.
- ^ "American Airlines won't fly to Israel again until at least September 2025". Jewish Telegraphic Agency. 4 November 2024. Retrieved 5 November 2024.
- ^ "Arkia Adds One-time Leased 737 MAX Barcelona Service in mid-August 2023". AeroRoutes. 8 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ a b c קוטלר, עמית (22 October 2024). "החל מ-169 דולר: מילאנו, בודפשט, דובאי וגם יוון וקפריסין. לוח הטיסות החדש של ארקיע". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ Liu, Jim (18 July 2024). "Arkia Schedules Tel Aviv – Manchester Service in Oct 2024". AeroRoutes. Retrieved 19 July 2024.
- ^ "מרחיבה פעילותה: ארקיע תפעיל טיסות לפריז". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). 4 November 2024. Retrieved 4 November 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Wrobel, Sharon (2 December 2024). "Lufthansa extends suspension of Tel Aviv flights until Jan. 31". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ^ אזולאי, רואי (27 November 2024). "הראשונה לחזור: אזרבייג׳ן איירליינס תשוב להפעיל טיסות בקו ת״א - באקו". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. Retrieved 27 November 2024.
- ^ a b Sipinski, Dominik (30 July 2024). "Romania's Bees Airlines to launch scheduled ops in 3Q24". ch-aviation GmbH. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ^ קוטלר, עמית (22 October 2024). "החל מ-59$ לכיוון, 198$ לטיסת הלוך ושוב: מבצעי החזרה לישראל של Blue Bird". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ "British Airways to cancel all flights to Israel until end of March next year". The Jerusalem Post. JPost.com. 21 October 2024. Retrieved 21 October 2024.
- ^ "השמיים נפתחים: בולגריה אייר חוזרת לישראל". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. 28 November 2024. Retrieved 28 November 2024.
- ^ Wrobel, Sharon (17 July 2024). "Cathay Pacific extends suspension of flights between Hong Kong and Israel until March 2025". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 21 July 2024.
- ^ Liu, Jim (19 November 2024). "Corendon Airlines 1Q25 Tel Aviv – Rovaniemi Charters". AeroRoutes. Retrieved 19 November 2024.
- ^ "easyJet suspends Israel flights until March 2025". Globes. Globes, Israel business news. 8 July 2024. Retrieved 25 August 2024.
- ^ "El al NS23 Boeing 777 European Network – 21MAR23".
- ^ a b c "El Al Outlines 293-seater 787-9 Network in 2025". AeroRoutes. Retrieved 17 August 2024.
- ^ "El al NS23 Boeing 777 European Operations – 20FEB23".
- ^ a b "El al Outlines 293-seater 787-9 Network in 2025".
- ^ a b c d e f g h "El Al NS24 Europe Service Changes – 14MAR24". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "El al June – September 2024 Dubai Service Changes".
- ^ "Fort Lauderdale airport getting first-ever flights to Israel; here's when they start". Local10News. 15 February 2023. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ^ a b "El Al / SAS Begins Codeshare Partnership From Feb 2024". Aeroroutes.
- ^ a b "Air France / El al Begins Reciprocal Codeshare Partnership in NS24".
- ^ a b "El al Israel Airlines New York JFK Nov 2023 – Jan 2024 Service Increases".
- ^ "El al NW22 Sofia Aircraft Changes".
- ^ "El Al: Νέες συνδέσεις προς Θεσσαλονίκη". 15 March 2024.
- ^ "El Al Maintains Tokyo March 2024 Service Resumption". AeroRoutes. 8 January 2024. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ^ אזולאי, איתי (20 February 2024). "FLYONE מולדובה חוזרת לטוס לישראל". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). Retrieved 20 February 2024.
- ^ "FLYONE Armenia received the Air Operator Certificate!". flyone.eu. 28 October 2021.
- ^ "Daily Direct Flights To Tel Aviv". georgian-airways.com. Georgian Airways. Retrieved 4 May 2024.
- ^ a b "HiSky Adds Cluj – Tel Aviv Service in NS23". Aeroroutes.com. Retrieved 2 November 2024.
- ^ "לא בקרוב: Iberia Express משעה טיסותיה לישראל עד למועד זה". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. 30 November 2024. Retrieved 30 November 2024.
- ^ Liu, Jim (25 November 2024). "Israir Adds Milan Bergamo in 1Q25". AeroRoutes. Retrieved 25 November 2024.
- ^ "Israir Schedules Chisinau Service in NW23". AeroRoutes. 8 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ a b "ISRAIR NS23 EUROPEAN NETWORK ADDITIONS – 06NOV22". Aeroroutes. 7 November 2022. Retrieved 12 December 2022.
- ^ Liu, Jim (4 November 2024). "Israir Adds Tel Aviv – London Luton From mid-Nov 2024". AeroRoutes. Retrieved 4 November 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "Israir NS24 Leased Smartwings Boeing 737 Operations". AeroRoutes. 21 March 2024. Retrieved 21 March 2024.
- ^ "Israir NS22 Network Additions Update - 03Apr22". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 4 April 2022.
- ^ "Israir". www.israirairlines.com.
- ^ a b "Qanot Sharq Adds Tel Aviv Schedule in NS23". AeroRoutes. 16 March 2023. Retrieved 13 July 2023.
- ^ "Red Wings Resumes Moscow – Tel Aviv Service From late-Jan 2024". AeroRoutes. 5 January 2024. Retrieved 7 January 2024.
- ^ Lifshitz-Klieger, Iris (4 April 2024). "Irish low-cost carrier Ryanair to resume Israel operations". Ynetnews. Retrieved 6 April 2024.
- ^ "Ryanair May – Oct 2023 Italy Frequency Variations – 14MAY23". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "Ryanair expands Brussels South Charleroi network with 9 new or resumed winter routes in 2024". 27 August 2024.
- ^ אביטן, יותם (16 January 2024). "חברת תעופה אירופאית נוספת חוזרת לישראל". חדשות תעופה (in Hebrew). Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- ^ "Sun d'Or NS24 A320 Operations – 14JAN24". AeroRoutes. 16 January 2024. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ Liu, Jim (19 August 2024). "Sun d'Or NW24 Preliminary Network Additions". AeroRoutes. Retrieved 19 August 2024.
- ^ "El Al's Sun d'Or to launch scheduled Belgrade flights". EX-YU Aviation News. 11 June 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ Liu, Jim (11 July 2024). "Sun d'Or Resumes Tel Aviv – Porto Service in NS24". AeroRoutes. Retrieved 11 July 2024.
- ^ a b "Sun d'Or NS24 Greece Network Additions". AeroRoutes. 13 May 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Yaish, Shimon (10 October 2024). "The complete guide to all airline flight cancellations to Israel". www.israelhayom.com. Retrieved 12 October 2024.
- ^ "פרסום ראשון: TUS Airways חוזרת לנתב"ג". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). 14 January 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ a b Liu, Jim (26 July 2024). "Tus Airways Sep 2024 Tel Aviv Network Additions". AeroRoutes. Retrieved 26 July 2024.
- ^ "United, Delta Airlines set to halt flights to Israel starting Thursday". The Jerusalem Post. 31 July 2024. Retrieved 2 August 2024.
- ^ "Uzbekistan Airways Adds Tel Aviv – Samarkand One-Way Service in NW23". AeroRoutes. 13 September 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- ^ אזולאי, איתי (11 November 2024). "עד אוקטובר 2025: וירג׳ין אטלנטיק דוחה שוב את חזרתה לישראל". פספורטניוז (in Hebrew). PassportNews. Retrieved 11 November 2024.
- ^ a b c d יעיש, שמעון (11 March 2024). "צפו לירידה במחירי הטיסות - אלו היעדים החדשים של וויז אייר מישראל". www.israelhayom.co.il. Retrieved 11 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f "Wizz Air Flights to Operate Again between Budapest and Tel Aviv". Hungary Today. 17 January 2024. Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- ^ Livne, Stav (27 November 2024). "Wizz Air brings forward return to Israel". Globes - Israel Business News. Retrieved 27 November 2024.
- ^ "Wizz Air, Ryanair to resume flights from Vilnius to Tel Aviv in spring". www.baltictimes.com. The Baltic Times. 26 February 2024. Retrieved 11 March 2024.
- ^ "ASTRAL AVIATION LAUNCHES SCHEDULED FLIGHT TO TEL AVIV". Astral Aviation (Press release). 8 June 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "CAL Cargo". CAL Cargo. 21 April 2019. Archived from the original on 20 March 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ aviationcargo.dhl.com – Destinations served retrieved 29 May 2021 Archived 5 May 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "EL AL provides update on cargo operations". www.aircargonews.net. 7 March 2020.
- ^ lufthansa-cargo.com – Routes & Schedules retrieved 29 May 2021
- ^ silkwayairlines.com – Our Network Archived 3 November 2019 at the Wayback Machine retrieved 29 May 2021
- ^ "UPS adds Cologne-Tel Aviv flight". 23 November 2021.
- ^ Petersburg, Ofer (3 July 2007). "Tel Aviv airport to make way for luxury project". Ynetnews. Archived from the original on 5 July 2007. Retrieved 3 July 2007.
- ^ a b c "Monthly Report". Israel Airport Authority. Ben Gurion Int'l Airport - Managing Director Office. Retrieved 22 January 2024.
- ^ "Guidelines for Taxi Passengers". Israel Airports Authority. Archived from the original on 17 November 2006. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ^ "The resource cannot be found". Ministry of Transport. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 30 September 2017.
- ^ "Public Transportation". Israel Airports Authority. Archived from the original on 13 May 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ^ "Shuttle from Ben Gurion Airport to Tel Aviv". withflo.com. Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 14 August 2016.
- ^ "Tel Aviv Airport Taxi & Transfer". Atob Transfer. Retrieved 7 July 2022.
- ^ "בתכנון: החניון בנתב"ג יורחב ב־30% ויכיל 26 אלף חניות". 18 December 2019.
- ^ "Parking Lots". Israel Airports Authority. Archived from the original on 27 April 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ^ "Car Rental Tel Aviv Airport". Tamir Rental. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ "Car Rental in Ben Gurion Airport-up to 15% discount-Shlomo Sixt". en.shlomo.co.il. Archived from the original on 16 May 2023. Retrieved 14 December 2015.
- ^ Krawitz, Avi (18 December 2006). "Ben Gurion ranks first in airport survey". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ^ "Ben Gurion Airport ranks best in Mideast". Ynetnews. 26 February 2008. Archived from the original on 27 February 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2008.
- ^ "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)" Archived 25 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine Airports Council International. Retrieved 28 April 2015
- ^ "ASQ Award for winners for 2008" Airports Council International. Retrieved 13 April 2012
- ^ "Tel Aviv's Ben Gurion named top Middle East airport". Globes. Retrieved 10 March 2009.
- ^ "ASQ Award for winners for 2009" Archived 25 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine Airports Council International. Retrieved 13 April 2012
- ^ "ASQ Award for winners for 2010" Archived 25 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine Airports Council International. 14 February 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012
- ^ "ASQ Award for Best Airport in Middle East" Archived 2 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine Airports Council International. 14 February 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012
- ^ "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)" Archived 16 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine Airports Council International. Retrieved 28 April 2015
- ^ "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)" Archived 16 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine Airports Council International. Retrieved 28 April 2015
- ^ "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)" Archived 18 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine Airports Council International. Retrieved 11 December 2017
- ^ "Airport Service Quality (ASQ)" Archived 18 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine Airports Council International. Retrieved 11 December 2017
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Fokker F.XVIII VQ-PAF Lydda Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Douglas C-54A-10-DC (DC-4) 4X-ACD Lydda Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Douglas C-47 (DC-3) registration unknown Lydda Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Vickers 833 Viscount 4X-AVC Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 707-373C N790TW Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing KC-97G Stratofreighter 4X-FPS/037 Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 707-329 OO-SJG Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 720-023B OD-AFR Tel Aviv-Lod International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 707-358C 4X-ATX Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Convair CV-240-24 N93218 Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Ilyushin Il-76T registration unknown Tel aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident ATR 42-320 4X-ATK Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident British Aerospace BAe 125-800A 4X-CZO Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 737-76J (WL) D-ABLB Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 767-3Q8ER 4X-EAK Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion International Airport (TLV)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
External links
[edit]![]() Ben Gurion International Airport travel guide from Wikivoyage
Ben Gurion International Airport travel guide from Wikivoyage
![]() Media related to Ben Gurion International Airport at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ben Gurion International Airport at Wikimedia Commons


