Russian famine of 1921–1922: Difference between revisions
Improved readability. |
m ] |
||
| (208 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Short description|Famine in the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic}} |
||
{{Use dmy dates|date=March 2022|cs1-dates=y}} |
|||
[[File:1921-Famine-map.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.5|The famine area in the fall of 1921]] |
[[File:1921-Famine-map.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.5|The famine area in the fall of 1921]] |
||
The '''Russian famine of 1921–1922''', also known as the '''Povolzhye famine''' ({{lang-rus|Голод в Поволжье}}, '[[Volga region]] famine') was a severe [[famine]] in the [[Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic]] that began early in the spring of 1921 and lasted until 1922. The famine resulted from the combined effects of severe drought,<ref name=rep2004>{{cite web|first1=Genady|last1=Golubev|author2=Nikolai Dronin|format=PDF|url=http://www2.cesr.de/component/easyfolderlistingpro/?view=download&format=raw&data=eNpFT20OwiAMvUsv4KbJ1HoYgqPbMIwSytwS492FfcRf0Nf3VY11jR_BBqFjZyjCQ_CGYHj2jrUpY2bAJBQ3gqwQQnWs-okk_cVXBKVWbLcqUq9HKmOFUJ5mQ222t1htokgu6DSU9R3hFFwiv6hNspt01tFhcs5sE3nqhyRKe6M6ZqOsV3ESsbpQLgi0pP0XTLcXoyXYSHKk1rmOTkm3w0g-s58rmtNDpLeleTsol-2Ze5ezvz-OIGHM|title=Geography of Droughts and Food Problems in Russia (1900–2000), Report No. A 0401|publisher=Center for Environmental Systems Research, University of Kassel|date=February 2004|access-date=December 17, 2016}}</ref> the continued effects of [[World War I]], economic disturbance from the [[Russian Revolution]], the [[Russian Civil War]], and failures in the government policy of [[war communism]] (especially [[prodrazvyorstka]]). It was exacerbated by rail systems that could not distribute food efficiently. |
|||
The '''Russian famine of 1921–22''', also known as '''[[Volga region|Povolzhye]] famine''', was a severe [[famine]] in [[Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic|Russia]] which began in early spring of 1921 and lasted through 1922. This famine killed an estimated 5 million, [[1921–22 famine in Tatarstan|primarily affecting]] the [[Volga region|Volga]] and [[Ural River]] regions.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://soviethistory.msu.edu/1921-2/famine-of-1921-22/|title=Famine of 1921-22|date=2015-06-17|work=Seventeen Moments in Soviet History|access-date=2018-07-20|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|url=https://archive.org/stream/TheBlackBookofCommunism10/the-black-book-of-communism-jean-louis-margolin-1999-communism#page/n71/|title=The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression|last=Courtois|first=Stéphane|last2=Werth|first2=Nicolas|last3=Panné|first3=Jean-Louis|last4=Paczkowski|first4=Andrzej|last5=Bartošek|first5=Karel|last6=Margolin|first6=Jean-Louis|publisher=Harvard University Press|year=1999|isbn=9780674076082|location=|pages=123}}</ref> |
|||
The famine killed an estimated five million people and [[1921–1922 famine in Tatarstan|primarily affected]] the [[Volga region|Volga]] and [[Ural River]] regions.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://soviethistory.msu.edu/1921-2/famine-of-1921-22/|title=Famine of 1921–1922|date=2015-06-17|work=Seventeen Moments in Soviet History|access-date=2018-07-20|language=en-US}}</ref> Many of the starving resorted to [[human cannibalism|cannibalism]].<ref name="Figes_Tragedy">{{cite book |last1=Figes |first1=Orlando |title=A People's Tragedy: The Russian Revolution 1891–1924 |title-link=A People's Tragedy |date=1997 |publisher=Pimlico |location=London |pages=777–778}}</ref><ref>{{citation |url=https://www.icrc.org/en/doc/resources/documents/article/other/5rfhjy.htm |title=Famine in Russia: the hidden horrors of 1921 - ICRC (translation) |author=Francis Haller |date=12 August 2003 |work=[[Le Temps]] |publisher=published by [[ICRC]] |access-date=14 March 2019 }}</ref><ref>{{citation |url=https://www.icrc.org/fr/doc/resources/documents/misc/5qkjlh.htm |title=Secours en temps de paix - la famine en Russie - CICR |language= fr |author=Francis Haller |date=12 August 2003 |work=[[Le Temps]] |publisher=published by [[ICRC]] | access-date=14 March 2019 }}</ref> The outbreaks of diseases such as [[cholera]] and [[typhus]] were also contributing factors to famine casualties.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Heinzen |first1=James W. |title=Inventing a Soviet Countryside: State Power and the Transformation of Rural Russia, 1917-1929 |date=1 February 2004 |publisher=University of Pittsburgh Pre |isbn=978-0-8229-7078-1 |page=52 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qICRs_f68KQC&dq=cholera+russian+famine+1921&pg=PA52 |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Raleigh |first1=Donald J. |title=Experiencing Russia's Civil War: Politics, Society, and Revolutionary Culture in Saratov, 1917-1922 |date=11 May 2021 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-1-4008-4374-9 |page=202 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=U00gEAAAQBAJ&dq=cholera+russian+famine+1921&pg=PA202 |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
The famine resulted from combined effects of economic disturbance through the disturbances of the [[Russian Revolution]]—and [[Russian Civil War]] with its policy of [[War communism|War Communism]], especially [[prodrazvyorstka]], exacerbated by rail systems that could not distribute food efficiently. |
|||
== Origins == |
|||
[[Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union|One of Russia's intermittent droughts]] in 1921 aggravated the situation to a national catastrophe. <!-- In many cases recklessness of local administration, which recognized the problems too late, contributed to the problem.{{Citation needed|date=April 2011}} (I will place it somewhere into article body later; but it should be sourced first.) For example, in summer 1921, half of the arable area of [[Crimea]] was destroyed by drought, but the local bosses asked for help as late as in May 1922 --> Hunger was so severe that it was likely seed-grain would be eaten rather than sown. At one point relief agencies had to give [[cereal|grain]] to railroad staff to get their supplies moved. |
|||
{{see also|War communism}} |
|||
[[File:Russian civil war west.svg|thumb|190px|European Theatre of the [[Russian Civil War]] in 1918–1919]] |
|||
Before the famine began, Russia had suffered three-and-a-half years of [[World War I]] and additionally the [[Russian Civil War]] of 1918–1920, many of the conflicts being fought inside Russia.{{Sfn |Kennan | 1961}} There were 7–12 million casualties during the [[Russian Civil War]], mostly civilians.<ref>{{cite book|last=Mawdsley|first=Evan|title=The Russian Civil War|location=New York|publisher=Pegasus Books|year=2007|isbn=9781681770093|url=https://archive.org/details/russiancivilwar00evan|url-access=registration|page=[https://archive.org/details/russiancivilwar00evan/page/287 287]}}</ref> Historians have noted that both [[Russian Empire|Tsarist Russia]] government councils and other opposition parties had advocated for food requisitioning prior to the ascent of the Bolsheviks.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Lih |first1=Lars T. |title=What Was Bolshevism? |date=20 October 2023 |publisher=BRILL |isbn=978-90-04-68479-9 |pages=149 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JNT7EAAAQBAJ&dq=grain+razverstka+bolsheviks&pg=PA149 |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Baykov |first1=Alexander |title=the development of the soviet economic system |date=1946 |publisher=CUP Archive |page=16 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8RY9AAAAIAAJ&dq=grain+razverstka+bolsheviks&pg=PA16 |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Sanborn |first1=Joshua A. |title=Imperial Apocalypse: The Great War and the Destruction of the Russian Empire |date=2014 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-964205-2 |page=256 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UBENBAAAQBAJ&dq=grain+requisitioning+tsarist+russia&pg=PA256 |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
Before the famine, all sides in the Russian Civil Wars of 1918–1921 (the [[Bolsheviks]], the [[White movement|Whites]], the [[Anarchism|Anarchists]], and the seceding nationalities) had provisioned themselves by seizing food from those who grew it, giving it to their armies and supporters, and denying it to their enemies. The Bolshevik government had requisitioned supplies from the peasantry for little or nothing in exchange, which led peasants to drastically reduce their crop production.<ref>Carr, EH, 1966, ''The Bolshevik Revolution 1917–1923'', Part 2, p. 233.</ref><ref>Chase, WJ, 1987, ''Workers, Society and the Soviet State: Labour and Life in Moscow 1918–1929'' pp. 26–27.</ref><ref>Nove, A, 1982, ''An Economic History of the USSR'', p. 62, cited in {{cite web |last= Flewers |first= Paul |title= War Communism in Retrospect | url= http://www.whatnextjournal.co.uk/Pages/Back/Wnext5/Warcomm.html}}</ref> |
|||
==Origins== |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: [[File:Pomogi.jpg|thumb|210px|''Help!'', a 1921 poster.]] --> |
|||
[[File:No-nb bldsa 6a027.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Fridtjof Nansen]]'s journey to the famine regions of Russia, 1921]] |
|||
[[File:No-nb bldsa 6a057.jpg|thumb|Children's corpses collected on a wagon in [[Samara]], 1921]] |
|||
Before the famine began, Russia had suffered six and a half years of [[World War I]] and the Civil Wars of 1918–20, many of the conflicts fought inside Russia.{{Sfn |Kennan | 1961}} |
|||
Aid from outside [[Soviet Russia]] was initially rejected. The [[American Relief Administration]] (ARA), which [[Herbert Hoover]] formed to help the victims of starvation of World War I, offered assistance to [[Vladimir Lenin|Lenin]] in 1919 if it had full say over the Russian railway network and handed out food impartially to all. Lenin refused that as interference in Russian internal affairs.{{Sfn |Kennan | 1961}} |
|||
Before the famine, all sides in the [[Russian Civil War]]s of 1918–21—the [[Bolsheviks]], the [[White movement|Whites]], the [[Anarchism|Anarchists]], the seceding nationalities—had provisioned themselves by seizing food from those who grew it, giving it to their armies and supporters, and denying it to their enemies. The Bolshevik government had requisitioned supplies from the peasantry for little or nothing in exchange. This led peasants to drastically reduce their crop production. According to the official Bolshevik position, which is still maintained by some modern Marxists, the rich peasants ([[kulak]]s) withheld their surplus grain to preserve their lives;<ref>{{Citation | url = http://www.wsws.org/correspo/1998/mar1998/leni-m06.shtml | contribution = An exchange of letters | publisher = BBC | type = documentary | title = Lenin's Secret Files | deadurl = yes | archiveurl = https://archive.li/20070213155724/http://www.wsws.org/correspo/1998/mar1998/leni-m06.shtml | archivedate = 2007-02-13 | df = }}.</ref> statistics indicate that most of the grain and the other food supplies passed through the [[black market]].<ref>Carr, EH, 1966, ''The Bolshevik Revolution 1917–1923'', Part 2, p. 233.</ref><ref>Chase, WJ, 1987, ''Workers, Society and the Soviet State: Labour and Life in Moscow 1918–1929'' pp. 26–27.</ref><ref>Nove, A, 1982, ''An Economic History of the USSR'', p. 62, cited in {{cite web |last= Flewers |first= Paul |title= War Communism in Retrospect | url= http://www.whatnextjournal.co.uk/Pages/Back/Wnext5/Warcomm.html}}</ref> The Bolsheviks believed peasants were actively trying to undermine the war effort. ''[[The Black Book of Communism]]'' asserts that Lenin ordered the seizure of the food peasants had grown for their own subsistence and their seed grain in retaliation for this "sabotage", leading to widespread peasant revolts.{{Sfn | Werth | Panné | Paczkowski | Bartosek | Margolin | 1999}} In 1920, Lenin ordered increased emphasis on food requisitioning from the peasantry. |
|||
Lenin was eventually convinced by the famine, the [[Kronstadt rebellion]], large-scale peasant uprisings such as the [[Tambov Rebellion]], and the failure of a German [[general strike]] to reverse his policy at home and abroad. He decreed the [[New Economic Policy]] on 15 March 1921. |
|||
Aid from outside Russia was initially rejected. The [[American Relief Administration]] (ARA), which [[Herbert Hoover]] formed to help the victims of starvation of [[World War I]], offered assistance to Lenin in 1919, on condition that they have full say over the Russian railway network and hand out food impartially to all. Lenin refused this as interference in Russian internal affairs.{{Sfn |Kennan | 1961}} |
|||
The famine also helped produce an opening to the West. Lenin now allowed relief organizations to bring aid. War relief was no longer required in [[Western Europe]], and the ARA had an organization set up in [[Second Polish Republic|Poland]] that relieved the Polish famine, which had begun in the winter of 1919–1920.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://query.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=9806E2D9123FE432A2575AC2A9679C946195D6CF|title= WILSON RENEWS HUNGER LOAN PLEA|work=[[The New York Times]]|date=28 January 1920|access-date=17 January 2016}}</ref> |
|||
{{ |
|||
cite web| |
|||
}} |
|||
</ref> |
|||
== Cannibalism == |
|||
==International relief effort== |
|||
[[File:Cannibalism_during_Russian_famine_1921.jpg|thumb|[[Human cannibalism|Cannibalism]] in [[Samara]] during the famine]] |
|||
[[File:No-nb bldsa 6a043.jpg|thumb|right|Victims of the famine in [[Buzuluk River (Volgograd Oblast)|Buzuluk]], [[Volga region]], next to [[Saratov]]]] |
|||
The situation became so desperate that a considerable minority of the starving resorted to cannibalism. According to the historian [[Orlando Figes]], "thousands of cases" were reported, with the number of cases that were never reported certainly even higher.{{sfn|Figes|1997|p=777}} In [[Samara]], "ten butcher shops were closed for selling human flesh."<ref>{{cite book |last1=Patenaude |first1=Bertrand M. |title=The Big Show in Bololand: The American Relief Expedition to Soviet Russia in the Famine of 1921 |date=2002 |publisher=Stanford University Press |location=Stanford, CA |page=268}}</ref> In [[Pugachyov]], "it was dangerous for children to go out after dark since there were known to be bands of cannibals and traders who killed them to eat or sell their tender flesh." An inhabitant of a nearby village stated: "There are several cafeterias in the village — and all of them serve up young children."<ref name="Figes_Tragedy" /> |
|||
[[File:1922SovietFaminevictim.jpg|thumb|Victims of the famine, 1922]] |
|||
[[File:Girl affected by famine in Buguruslan, Russia - 1921.jpg|thumb|upright|Starving Russian girl in [[Buguruslan]], 1921]] |
|||
[[File:Brothers in misfortune.jpg|thumb|upright|Starving Russian children during the famine, c. 1922]] |
|||
[[File:A starving child during the Famine of 1921-22 in Ukraine.jpg|thumb|upright|A boy from village Blahovishchenka (gubernia or province of Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine)—Ilarion Nyshchenko—from starvation killed his 3-year-old brother and ate him (1921–22)]] |
|||
Although no official request for aid was issued, a committee of well-known people without obvious party affiliations was allowed to set up an appeal for assistance. In July 1921, the writer [[Maxim Gorky]] published an appeal to the outside world, saying that millions of lives were menaced by crop failure. At a conference in [[Geneva]] on 15 August organised by the [[International Committee of the Red Cross]] and the [[International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies|League of Red Cross Societies]], the International Committee for Russian Relief (ICRR) was set up with Dr. [[Fridtjof Nansen]] as its High Commissioner. Nansen headed to Moscow, where he signed an agreement with Soviet Foreign Minister [[Georgy Chicherin]] that left the ICRR in full control of its operations. At the same time, fundraising for the famine relief operation began in earnest in Britain, with all the elements of a modern emergency relief operation — full-page newspaper advertisements, local collections, and a fundraising film shot in the famine area. By September, a ship had been despatched from London carrying 600 tons of supplies. The first feeding centre was opened in October in Saratov. |
|||
[[File:Cannibalism russian famine1921 6 peasants bouzuluk district and remains of humans they eatten.jpg|thumb|left|Six peasants of [[Buzuluk, Orenburg Oblast|Buzuluk]] and the remains of humans they had eaten during the famine]] |
|||
The main participants in the international relief effort were Hoover's [[American Relief Administration]],<ref>{{Citation | url = https://archive.org/details/gov.archives.arc.88967 | publisher = Newsreel | title= International news | volume = 442 | year = 1921}}</ref> along with other bodies such as the [[American Friends Service Committee]] and the [[International Save the Children Union]], which had the British [[Save the Children| Save the Children Fund]] as the major contributor.<ref>{{Citation | url = http://www.icrc.org/Web/Eng/siteeng0.nsf/html/5RFHJY | title = Famine in Russia: the hidden horrors of 1921 | publisher = ICRC| date = 2013-10-03 }}.</ref> Around ten million people were fed, with the bulk coming from the ARA, funded by the [[United States Congress]]; the European agencies co-ordinated by the ICRR fed two million people a day: the International Save the Children Union were feeding 375,000 in its centres at [[Saratov]] at the height of the operation.<ref name="Iconic">{{cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rRPHAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA68 | title=The Making of Humanitarian Visual Icons: On the 1921-1923 Russian Famine as Foundational Event | publisher=Palgrave Macmillan | work=Iconic Power: Materiality and Meaning in Social Life | date=3 January 2012 | accessdate=19 July 2014 | author=Kurusawa, Fuyuki | pages=68| isbn=9781137012869 }}</ref> <ref>{{Citation|chapter=FAMINE AND RELIEF 1921|date=2013-04-03|pages=102–102A|publisher=Routledge|isbn=9780203074473|doi=10.4324/9780203074473-102|title=The Routledge Atlas of Russian History}}</ref>The operation was hazardous — several workers died of cholera — and was not without its critics, including the London [[Daily Express]], which first denied the severity of the famine, and then argued that the money would better be spent in the United Kingdom.{{Sfn |Breen | 1994}} |
|||
This was no exception – Figes estimates "that a considerable proportion of the meat in Soviet factories in the Volga area ... was human flesh." Various gangs specialized in "capturing children, murdering them and selling the human flesh as horse meat or beef", with the buyers happy to have found a source of meat in a situation of extreme shortage and often willing not to "ask too many questions".<ref>Figes quoted in {{cite book |last1=Korn |first1=Daniel |last2=Radice |first2=Mark |last3=Hawes |first3=Charlie |title=Cannibal: The History of the People-Eaters |date=2001 |publisher=Channel 4 Books |location=London |page=81}}</ref> |
|||
== Relief effort == |
|||
Throughout 1922 and 1923, as famine was still widespread and the ARA was still providing relief supplies, grain was exported by the Soviet government to raise funds for the revival of industry; this seriously endangered Western support for relief, and was one instance of a long-standing Soviet policy of valuing development above the lives of the peasantry. The new Soviet government insisted that if the AYA suspended relief, the ARA arrange a foreign loan for them of about $10,000,000 1923 dollars; the ARA was unable to do this, and continued to ship in food past the grain being sold abroad.<ref name="Ellman">{{Citation | author-link = | first = Michael | last = Ellman | url = |
|||
[[File:No-nb bldsa 2a151.jpg|thumb|190px|The Norwegian explorer and diplomat [[Fridtjof Nansen]] was honored with the 1922 [[Nobel Peace Prize]], in part for his work as High Commissioner for Relief In Russia.]] |
|||
http://www.paulbogdanor.com/left/soviet/famine/ellman1933.pdf | title = Stalin and the Soviet Famine of 1932–33 Revisited | journal = Europe-Asia Studies | volume = 59 | issue = 4 |date=June 2007 | pages = 663–93 | format = [[PDF]] | doi=10.1080/09668130701291899}}.</ref><ref>{{Citation | first = Roman | last = Serbyn | contribution = The Famine of 1921–22 | title = Famine in the Ukraine, 1932–33 | place = Edmonton | year = 1986 | pages = 174–78}}.</ref> |
|||
In the summer of 1921, during one of the worst famines in history, Vladimir Lenin, the head of the new Soviet government, along with [[Maxim Gorky]], appealed in an open letter to "all honest European and American people" to "give bread and medicine".<ref name=economist/> In an open letter to all nations, dated 13 July 1921, Gorky described the crop failure which had brought his country to the brink of starvation.<ref name=bartlett>Bartlett, Charles. "U.S. Food Relief for Communists?", ''Enquirer and News'', Battle Creek, MI, 2 August 1962</ref> [[Herbert Hoover]], who would later become the [[U.S. President]], responded immediately, and negotiations with Russia took place at the Latvian capital, [[Riga]].<ref name=bartlett/> A European effort was led by the famous Arctic explorer [[Fridtjof Nansen]] through the International Committee for Russian Relief (ICRR).<ref>{{Citation | url = https://www.cairn-int.info/article-E_MATE_095_0002--fridtjof-nansen-and-european-food-aid.htm | title = Fridtjof Nansen and European Food Aid in Bolshevik Russia and Ukraine in 1921–1923 | journal = Matériaux pour l'Histoire de Notre Temps | publisher = Cairn| date = 2009 | volume = 95 | issue = 3 | last1 = Vogt | first1 = Carl-Emil }}</ref> |
|||
Hoover's ARA had already been distributing food aid throughout Europe since 1914. After the Germans invaded Belgium in 1914, Hoover set up the Belgian Relief Committee to alleviate the devastation and starvation that followed. As World War I expanded, the ARA grew, and it next entered northern France and assisted France and Germany from 1914 to 1919.<ref name=masters>Masters, Ann V. "Herbert Hoover's Humanitarian Corp Plans 32nd Reunion", ''[[Bridgeport Sunday Post]]'' (Bridgeport, Connecticut), 18 April 1965 p. 5</ref> In 1920 and 1921, it provided one meal a day to 3.2 million children in Finland, Estonia, various Russian regions, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Ukraine, Czechoslovakia, Austria, Hungary, and Armenia. When it began its emergency feeding operation in Russia, it planned to feed about one million Russian children for a full year.<ref name=indiana>"American Relief Administrating", ''Indiana Evening Gazette'', 25 October 1921</ref> Other bodies such as the [[American Friends Service Committee]], the British Friends' War Victims Relief Committee and the [[International Save the Children Union]], with the British [[Save the Children|Save the Children Fund]] as the major contributor, also later took part.<ref>{{Citation | url = http://www.icrc.org/Web/Eng/siteeng0.nsf/html/5RFHJY | title = Famine in Russia: the hidden horrors of 1921 | publisher = ICRC| date = 2013-10-03}}; Luke Kelly, British Humanitarian Activity and Russia, 1890-1923 (Palgrave Macmillan, 2017), pp. 159-211.</ref> As the historian [[Douglas Smith (writer)|Douglas Smith]] writes, the food relief would probably help "save communist Russia from ruin."<ref name=amazon>[https://www.amazon.com/Russian-Job-Forgotten-America-Soviet/dp/0374252963/ref=sr_1_1?keywords=the+russian+job+smith&qid=1574401021&sr=8-1 "The Russian Job: The Forgotten Story of How America Saved the Soviet Union from Ruin"], Amazon review</ref> |
|||
==Death toll== |
|||
As with other large-scale famines, the range of estimates is considerable. An official Soviet publication of the early 1920s concluded that about five million deaths occurred in 1921 from famine and related disease: this number is usually quoted in textbooks.<ref>Norman Lowe. Mastering Twentieth-Century Russian History. Palgrave, 2002. P. 155.</ref> More conservative figures counted not more than a million, while another assessment, based on the ARA's medical division, spoke of two million.<ref>Betrand M. Patenaude. The Big Show in Bololand. The American Relief Expedition to Soviet Russia in the Famine of 1921. Stanford University Press, 2002. P. 197.</ref> On the other side of the scale, some sources spoke of ten million dead.<ref>[http://news.stanford.edu/news/2011/april/famine-040411.html How the U.S. saved a starving Soviet Russia: PBS film highlights Stanford scholar's research on the 1921-23 famine] Stanford News</ref> According to Betrand M. Patenaude, "such a number hardly seems extravagant after the many tens of millions of victims of war, famine, and terror in the twentieth century".<ref>Patenaude, op. cit. p. 197-8.</ref> |
|||
The United States was the first country to respond, with Hoover appointing Colonel [[William N. Haskell]] to direct the [[American Relief Administration]] (ARA) in Russia. Within a month, ships loaded with food were headed for Russia. The main contributor to the international relief effort would be the ARA, which was founded and directed by Hoover.<ref name=Smith>Smith, Douglas. ''The Russian Job'', Farrar, Straus and Giroux (2019)</ref><ref name=economist>[https://www.economist.com/books-and-arts/2019/11/09/a-century-ago-america-saved-millions-of-russians-from-starvation "A century ago America saved millions of Russians from starvation"], ''The Economist'', 11 November 2019</ref><ref>{{Citation | url = https://archive.org/details/gov.archives.arc.88967 | publisher = Newsreel | title= International news | volume = 442 | year = 1921}}</ref> It had agreed to provide food for a million people, mostly children, but within a year it was feeding more than 10 times that number daily.<ref name=ramsey>Ramsey, W. Howard. "Two Hundred Americans Return Victorious From War On Russian Famine and Pestilence", ''News-Journal'', (Mansfield, Ohio), 11 August 1923 p. 7</ref> |
|||
==Political uses== |
|||
The famine came at the end of six and a half years of unrest and violence (first World War I, then the two Russian revolutions of 1917, then the Russian Civil War). Many different political and military factions were involved in those events, and most of them have been accused by their enemies of having contributed to, or even bearing sole responsibility for, the famine.<ref>[https://www.academia.edu/7079495/Aftermath_of_the_Famine_1922-1923_in_Hunger_and_Scarcity_under_State-Socialism_eds._M._Middell_and_F._Wemheuer_Leipziger_Universitatsverlag_2012 Academia.edu]</ref> |
|||
The ARA insisted on autonomy as to how the food would be distributed and stated its requirement that food would be given without regard to "race, creed or social status", a condition that was stated in Section 25 of the Riga agreement.<ref name=economist/> U.S. spokesmen said that it would also want to have storage facilities built in Russia, wrote the journalist [[Charles L. Bartlett (journalist)|Charles Bartlett]], and would expect to have full access to those to assure that food was distributed properly.<ref name=bartlett/>{{efn|At a conference in [[Geneva]] on 15 August organised by the [[International Committee of the Red Cross]] and the [[International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies|League of Red Cross Societies]], the International Committee for Russian Relief (ICRR) was set up with Dr. [[Fridtjof Nansen]] as its High Commissioner. Nansen headed to Moscow, where he signed an agreement with Soviet Foreign Minister [[Georgy Chicherin]] that left the ICRR in full control of its operations. At the same time, fundraising for the famine relief operation began in earnest in Britain, with all the elements of a modern emergency relief operation—full-page newspaper advertisements, local collections, and a fundraising film shot in the famine area. By September, a ship had been despatched from London carrying 600 tons of supplies. The first feeding centre was opened in October in Saratov.{{citation needed|date=November 2019}}}} |
|||
Since 1922, Bolsheviks started a campaign [[1922 confiscation of Russian Orthodox Church property|of seizing church property]]. In 1922, over 4.5 million [[Chervonets|golden rouble]]s of property were seized. Out of these, one million gold roubles were spent for famine relief.<ref>А. Г. Латышев. Рассекреченный Ленин. — 1-е изд. — М.: Март, 1996. — Pages 145—172. — 336 с. — 15 000 экз. — {{ISBN|5-88505-011-2}}.</ref> In a secret March 19, 1922 letter to the Politburo, Lenin expressed an intention to seize several hundred million golden roubles for famine relief.<ref name=kri>[https://web.archive.org/web/20150225230446/http://elib.spbstu.ru/dl/327/Theme_10/Literature/Krivova.htm Н.А. Кривова, "Власть и церковь в 1922-1925гг"]</ref> |
|||
Hoover also demanded for Russia to use some of its gold holdings to defray the cost of the relief effort. He secured $18 million from the Russian leadership, $20 million from the U.S. Congress, $8 million from the U.S. military, and additional money from U.S. charities to arrive at a total of approximately $78 million from all those sources.<ref name=bartlett/> After an agreement was finally signed at Riga, the U.S. set up its first kitchen in [[Petrograd]], where 1.6 million people had already starved to death.<ref name=bartlett/> |
|||
In Lenin's secret letter to the Politburo, Lenin explains that the famine provides an opportunity against the church.<ref name=kri/> [[Richard Pipes]] argued that the famine was used politically as an excuse for the Bolshevik leadership to persecute the Orthodox Church, which held significant sway over much of the peasant populace.{{Sfn | Pipes | 1995, pg. 415}} |
|||
{{quote box| align = right| width = 25em| bgcolor = Bisque |
|||
Russian anti-Bolshevik exiles in London, Paris, and elsewhere also used the famine as a media opportunity to highlight the iniquities of the Soviet regime in an effort to prevent trade with and official recognition of the Bolshevik Government.<ref>{{Cite book|title=After October: Russian Liberalism as a Work-in-Progress, 1917-1945|last=Jansen|first=Dinah|publisher=Queen's University|year=2015|isbn=|location=Kingston|pages=}}</ref> |
|||
| quote =For almost two years now a scant two hundred Americans, on a battle line far longer than the western front, have been fighting a foe more pitiless than any the allied armies faced. From the Baltic to the Caspian Sea, from the Crimea to the Urals, they have conquered the famine, saved more lives than were lost in the World War, healed a sorely-suffering people of the diseases which threatened to sweep the whole of Europe, won the benedictions of a great, but stricken, nation, achieved the world's greatest adventure in humanity! |
|||
| source = W. Howard Ramsey, newspaper editor<ref name=ramsey/>}} |
|||
Over 10 million people were fed daily, with the bulk of food coming from the ARA, which had provided more than 768 million tons of flour, grain, rice, beans, pork, milk, and sugar, with a value of over $98 million.<ref name=bartlett/> To transport and distribute the food after it was collected in the U.S., the ARA used 237 ships, under the direction of 200 Americans and with the help of 125,000 Russians on location for unloading, warehousing, hauling, weighing, cooking and serving the food in more than 21,000 new kitchens.<ref name=ramsey/> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
*[[1921 Mari wildfires]] |
|||
*[[1921–22 famine in Tatarstan]] |
|||
*[[Kazakh famine of 1919–1922]] |
|||
*[[Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union|Famines in Russia and the USSR]] |
|||
*[[Fram (play)]] |
|||
*[[List of famines]] |
|||
*[[Pomgol]] |
|||
*[[Soviet famine of 1932–33]] |
|||
*[[Soviet famine of 1946–47]] |
|||
*[[American Relief Administration]] |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
Even after the food had reached the people in need, Colonel Haskell informed Hoover of an unexpected new danger. He explained that fuel was unavailable for heating or cooking and millions of Russian peasants had clothing consisting mostly of rags, which would lead to certain death from cold exposure during the approaching winter.<ref name=spokesman>"Banks in State to Aid Relief. American Relief Administration Organizes to Send Clothing to Russian Children", ''The Spokesman Review'', (Spokane, WA) 19 November 1922</ref> |
|||
==References== |
|||
The children at risk included those in orphanages and other institutions, as they usually had only one garment, often made of flour sacks, and they lacked shoes, stockings, underclothing, or any other clothing to keep warm. Also at risk were children living at home with their parents, who also lacked enough clothing, which made them unable to reach the American relief kitchens. Haskell cabled Hoover that at least one million children were in extreme need of clothes. Hoover quickly initiated a plan for collecting and sending clothing packages to Russia, which would come from donations by individuals, businesses and banks.<ref name=spokesman/> |
|||
[[File:Children during famine in Russia.png|thumb|Starving children in 1922]] |
|||
Medical needs were also paramount. As noted by Dr. Henry Beeuwkes, the chief of the Medical Division in Russia, American relief was supplying over 16,000 hospitals, which were treating more than a million persons daily.<ref name=ramsey/> Because those institutions were scattered over areas with few railroads and often poor roads, with some hospitals over a thousand miles from the main supply base in Moscow, the task was monumental. Dr. Louis L. Shapiro, an army colonel who was one of the ARA's medical directors in Russia, recalled that [[southern Russia]] had little more than "mud ruts for roads, with limitless prairies."<ref name=masters/> On one trip, with few car necessities or regular gas, he drove 150 miles on tires without inner tubes, instead stuffed with straw.<ref name=masters/> "After our kitchens were established and our clinics able to distribute medical supplies" said Shapiro, "children who had been eating a diet of clay and leather scrapings, responded quite rapidly."<ref name=masters/> |
|||
According to Dr. Beeuwkes, everything was in short supply, including beds, blankets, sheets, and most medical tools and medicines. Operations were performed in unheated operating rooms without anesthetics and often with bare hands. Wounds were dressed with newspapers or rags. Water supplies were polluted, with much of the plumbing unusable. |
|||
To help the widespread medical emergency, the ARA distributed medical supplies, which included over 2,000 necessities, from medicines to surgical instruments. There were 125,000 medical packages, weighing 15 million pounds, sent on 69 ships.<ref name=ramsey/> According to Dr. Shapiro, when the ARA left Russia in 1923, after two years of relief efforts, "the Russians had been pulled out of the slough of famine and death. I can say without boasting that no relief organization ever worked so hard to complete its task."<ref name=masters/> |
|||
In May 1922, [[Lev Kamenev]], President of the Moscow Soviet and deputy chairman of all Russian famine relief committees, wrote a letter to Haskell that thanked him and the ARA for its help and also paid tribute to the American people |
|||
{{blockquote|The government of the Russian nation will never forget the generous help that was afforded them in the terrible calamity and dangers visited upon them.... I wish to express, on behalf of the Soviet government, my satisfaction and thanks to the American Relief Administration, through your person, for the substantial support which they are offering to the calamity stricken population of the Volga area.<ref name=indiana/><ref>"Admit America Saved Russia", AP, ''Los Angeles Times'', 6 May 1922 p. 6</ref>}} |
|||
By the summer of 1923, it was estimated that the U.S. relief that was given to Russia amounted to over twice the total of relief given it by all other foreign organizations combined.<ref name=kenosha>"Russian Relief Still Continues", ''Kenosha Evening News'', (Kenosha, Wisconsin,) 28 August 1923 p. 4</ref> European agencies co-ordinated by the ICRR also fed two million people a day, while the International Save the Children Union fed up to 375,000.<ref name="Iconic">{{cite book |author=Kurasawa, Fuyuki |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rRPHAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA68 |title=The Making of Humanitarian Visual Icons: On the 1921-1923 Russian Famine as Foundational Event |date=3 January 2012 |work=Iconic Power: Materiality and Meaning in Social Life |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |isbn=9781137012869 |pages=68 |access-date=19 July 2014}}</ref><ref>{{Citation|chapter=FAMINE AND RELIEF 1921|date=2013-04-03|pages=102–102A|publisher=Routledge|isbn=9780203074473|doi=10.4324/9780203074473-102|title=The Routledge Atlas of Russian History}}</ref> The operation was hazardous since several workers died of cholera, and it was not without its critics, including the London ''[[Daily Express]]'', which first denied the severity of the famine and then argued that the money would better be spent in the United Kingdom.{{Sfn |Breen | 1994}} |
|||
[[File:Fridtjof Nansen, Les deux étapes de la faim (1922).jpg|thumb|190px|Nansen's photos on postcards were meant to raise awareness about the famine.]] |
|||
Throughout 1922 and 1923, as famine was still widespread and the ARA was still providing relief supplies, grain was exported by the Soviet government to raise funds for the revival of industry, which seriously endangered Western support for relief. The new Soviet government insisted that if the AYA suspended relief, the ARA was to arrange a foreign loan for them of about $10,000,000 1923 dollars; the ARA was unable to do so and continued to ship in food past the grain being sold abroad.<ref name="Ellman">{{Citation | first = Michael | last = Ellman | url =http://www.paulbogdanor.com/left/soviet/famine/ellman1933.pdf | title = Stalin and the Soviet Famine of 1932–33 Revisited | journal = Europe-Asia Studies | volume = 59 | issue = 4 |date=June 2007 | pages = 663–693 | doi=10.1080/09668130701291899| s2cid = 53655536}}.</ref><ref>{{Citation | first = Roman | last = Serbyn | contribution = The Famine of 1921–22 | title = Famine in the Ukraine, 1932–33 | place = Edmonton | year = 1986 | pages = 174–178}}.</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" |
|||
! America's Contribution to the Russian Famine Relief Effort<ref name=ramsey/> !! |
|||
|- |
|||
| Children fed daily || 4,173,339 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Adults fed daily || 6,317,958 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Maximum number fed daily || 10,491,297 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Number of meals served || 1,750,000,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Number of separate kitchens opened || 21,435 |
|||
|- |
|||
| People clothed || 333,125 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Medical supplies value || $7,685,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Hospitals provided with supplies || 16,400 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Number of inoculations given || 6,396,598 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Number of vaccinations given || 1,304,401 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Tons of food provided || 912,121 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Tons of medical supplies provided || 7,500 |
|||
|- |
|||
| Number of U.S. ships used || 237 |
|||
|} |
|||
== Death toll == |
|||
As with other large-scale famines, the range of estimates is considerable. An official Soviet publication of the early 1920s concluded that about five million deaths occurred in 1921 from famine and related disease, the number that is usually quoted in textbooks.<ref>Norman Lowe. Mastering Twentieth-Century Russian History. Palgrave, 2002. p. 155.</ref> More conservative figures counted not more than a million, and another assessment, based on the ARA's medical division, spoke of two million.<ref>Bertrand M. Patenaude. The Big Show in Bololand. The American Relief Expedition to Soviet Russia in the Famine of 1921. Stanford University Press, 2002. p. 197.</ref> On the other side of the scale, some sources spoke of ten million dead.<ref>[http://news.stanford.edu/news/2011/april/famine-040411.html How the U.S. saved a starving Soviet Russia: PBS film highlights Stanford scholar's research on the 1921-23 famine] Stanford News</ref> According to Bertrand M. Patenaude, "such a number hardly seems extravagant after the many tens of millions of victims of war, famine, and terror in the twentieth century."{{sfn|Patenaude|2002|pp=197–198}} |
|||
<gallery widths="180px" heights="180px"> |
|||
File:No-nb bldsa 6a027.jpg|[[Fridtjof Nansen]]'s journey to the famine regions of Russia, 1921 |
|||
File:No-nb bldsa 6a057.jpg|Children's corpses collected on a wagon in [[Samara]], 1921 |
|||
File:No-nb bldsa 6a043.jpg|Victims of the famine in [[Buzuluk, Orenburg Oblast|Buzuluk]], next to [[Samara]] |
|||
File:1922SovietFaminevictim.jpg|Victims of the Russian famine, 1922 |
|||
File:Girl affected by famine in Buguruslan, Russia - 1921.jpg|Starving Russian girl in [[Buguruslan]], 1921 |
|||
File:A starving child during the Famine of 1921-22 in Ukraine.jpg|A starving boy from the village of Blagoveshchenka ([[Zaporizhzhia Oblast|Zaporizhzhia]], Ukraine), who during the famine of 1921–1922 killed his three-year-old brother and ate him |
|||
File:Victims of the 1921 famine in Russia.jpg|Victims of the 1921 famine during the [[Russian Civil War]] |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== Political uses == |
|||
The famine came at the end of six-and-a-half years of unrest and violence (World War I, the two Russian Revolutions of 1917, and the Russian Civil War). Many political and military factions were involved in the events, and most of them have been accused by their enemies of having contributed to or even bearing sole responsibility for the famine.<ref>[https://www.academia.edu/7079495/Aftermath_of_the_Famine_1922-1923_in_Hunger_and_Scarcity_under_State-Socialism_eds._M._Middell_and_F._Wemheuer_Leipziger_Universitatsverlag_2012 Academia.edu]</ref> |
|||
The Bolsheviks started a campaign of [[1922 confiscation of Russian Orthodox Church property|seizing church property]] in 1922. That year, over 4.5 million [[Chervonets|golden roubles]] of property were seized. Of those, one million gold roubles were spent for famine relief.<ref>А. Г. Латышев. Рассекреченный Ленин. — 1-е изд. — М.: Март, 1996. — Pages 145—172. — 336 с. — 15 000 экз. — {{ISBN|5-88505-011-2}}.</ref> In a secret March 19, 1922 letter to the Politburo, Lenin expressed an intention to seize several hundred million golden roubles for famine relief.<ref name=kri>[https://web.archive.org/web/20150225230446/http://elib.spbstu.ru/dl/327/Theme_10/Literature/Krivova.htm Н.А. Кривова, "Власть и церковь в 1922-1925гг"]</ref> |
|||
In Lenin's secret letter to the Politburo, he explains that the famine provides an opportunity against the church.<ref name=kri/> [[Richard Pipes]] argued that the famine was used politically as an excuse for the Bolshevik leadership to persecute the Orthodox Church, which held significant sway over much of the peasantry.{{Sfn | Pipes | 1995|p=415}} |
|||
Russian anti-Bolshevik [[white émigrés]] in London, Paris, and elsewhere also used the famine as a media opportunity to highlight the iniquities of the Soviet regime to prevent trade with and official recognition of the Bolshevik government.<ref>{{Cite book|title=After October: Russian Liberalism as a Work-in-Progress, 1917–1945|last=Jansen|first=Dinah|publisher=Queen's University|year=2015|location=Kingston}}</ref> |
|||
==2022 Russian documentary film== |
|||
On September 24, 2022, at the [[:ru:Октябрь (кинотеатр, Москва)|Oktyabr cinema]] in Moscow, the Russian documentary film [[:ru:Голод (фильм, 2022)|''Hunger'']] or ''Famine'' ({{langx|ru|Голод}}) premiered which depicts the mass famine in the Volga region, Ukraine, the Urals, Bashkiria, Samara and Chelyabinsk regions, Kazakhstan and Western Siberia affecting over 35 oblasts of Soviet Russia in the early 1920s and a total population of approximately 90 million people.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.imdb.com/title/tt25273434/ |title=Famine |work=[[IMDb]] |date= |access-date=September 11, 2024}}</ref> The film was directed by [[:ru:Сорокина, Татьяна Александровна|Tatyana Sorokina]] with [[:ru:Архангельский, Александр Николаевич|Aleksandr Arkhangelsky]] writing the script and [[:ru:Курников, Максим Владимирович|Maxim Kournikov]] providing the inspiration behind the creation of the film.<ref name=Svoboda23122022>{{cite news |last=Легалов |first=Евгений (Legalov, Evgeniy) |url=https://www.svoboda.org/a/sama-rodila-sama-i-syem-v-prage-proshel-pokaz-filma-golod/32190900.html |title="Сама родила – сама и съем". В Праге прошёл показ фильма "Голод" |trans-title="I gave birth to her myself - I'll eat her myself." The film "Hunger" was screened in Prague |language=ru |work=[[Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty|«Радио Свобода»]] |date=December 23, 2022 |access-date=September 11, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240911220759/https://www.svoboda.org/a/sama-rodila-sama-i-syem-v-prage-proshel-pokaz-filma-golod/32190900.html |archive-date=September 11, 2024}}</ref> On October 30, 2022, ''Famine'' was first shown at a public theater in [[Yekaterinburg]].<ref name=Kommersant>{{Cite news |last=Воронов |first=Александр (Voronov, Alexander) |url=https://www.kommersant.ru/doc/5667741 |title=«Голод» отменяют по просьбам трудящихся |trans-title="Famine" canceled at the request of workers |language=ru |work=[[Kommersant|Коммерсантъ]] |date=November 14, 2022 |access-date=September 11, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221115150529/https://www.kommersant.ru/doc/5667741 |archive-date=November 15, 2022}}</ref> In November 2022, the [[Ministry of Culture (Russia)|Russian Ministry of Culture]] banned the distribution of ''Голод'' in Russia.<ref name=Kommersant/><ref name=Svoboda14112022>{{cite news |url=https://www.svoboda.org/a/minkuljt-otozval-prokatnoe-udostoverenie-u-filjma-golod-/32130023.html |title=Минкульт отозвал прокатное удостоверение у фильма "Голод" |trans-title=The Ministry of Culture revoked the distribution certificate for the film "Hunger" |language=ru |work=[[Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty|«Радио Свобода»]] |date=November 14, 2022 |access-date=September 11, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240911220759/https://www.svoboda.org/a/sama-rodila-sama-i-syem-v-prage-proshel-pokaz-filma-golod/32190900.html |archive-date=September 11, 2024}}</ref> In December 2022, ''Famine'' received the monthly journalistic award from [[Redkollegia]] and, in April 2023, it received the Audience Prize and a special mention jury diploma at the 2023 [[Artdocfest]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://redkollegia.org/archives/text/golod |title=Голод |trans-title=Famine |website=[[Redkollegia|Редколлегия]] |date=December 31, 2022 |access-date=September 11, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230207214905/https://redkollegia.org/archives/text/golod |archive-date=February 7, 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://artdocfest.com/ru/news/artdocnet-2023-winners/ |title=Объявлены итоги конкурса АртдокСеть-2023 |trans-title=Results of the 2023 Artdocfest |language=ru |work=[[Artdocfest|Артдокфест]] |date=April 15, 2023 |accessdate=September 11, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230923094955/https://artdocfest.com/ru/news/artdocnet-2023-winners/ |archive-date=September 23, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
== See also == |
|||
* [[1921 Mari wildfires]] |
|||
* [[1921–1922 famine in Tatarstan]] |
|||
* [[American Relief Administration]] |
|||
* [[Cannibalism in Europe]] |
|||
* [[Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union|Famines in Russia and the USSR]] |
|||
* [[Fram (play)]] |
|||
* [[Kazakh famine of 1919–1922]] |
|||
* [[List of famines]] |
|||
* [[Pomgol]] |
|||
* [[Soviet famine of 1930–1933]] |
|||
** [[Holodomor]] (Ukrainian famine 1932–1933) |
|||
* [[Soviet famine of 1946–1947]] |
|||
== Notes == |
|||
{{notelist}} |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{Reflist|30em}} |
{{Reflist|30em}} |
||
== |
== Sources == |
||
* {{Citation | author-link = George F. Kennan| last = Kennan | first = George Frost | title = Russia and the West under Lenin and Stalin | place = Boston | year = 1961 | pages = 141–50, 168, 179–85}}. Default reference for the historical and aftermath sections. |
|||
* {{Citation | last = Kennan | author-mask = 8 | title = The Decline of Bismarck's European Order: Franco-Russian Relations, 1875–1890 | place = Princeton | year = 1979 | page = 387}}. |
|||
*[[David Fromkin|Fromkin, David]]: ''Peace to End All Peace'' (1989 hc) p. 360 (on Tsarist corruption and the closure of the Dardanelles). |
|||
* {{Citation | author-link = François Furet | first = François | last = Furet | title = Passing of an Illusion | year = 1999 | origyear = 1995}}. |
|||
* {{Citation | last = Breen | first = Rodney | year = 1994 | title = Saving Enemy Children: Save the Children's Russian Relief Organisation, 1921–1923 | journal = Disasters | volume = 18 | issue = 3 | pages = 221–37 | doi=10.1111/j.1467-7717.1994.tb00309.x| pmid = 7953492 }}. |
|||
* {{Citation | editor-link = Stéphane Courtois | editor-first = Stéphane | editor-last = Courtois | author1-link = Nicolas Werth | first1 = Nicolas | last1 = Werth | author2-link = Jean-Louis Panné | first2 = Jean-Louis | last2 = Panné | author3-link = Andrzej Paczkowski | first3 = Andrzej | last3 = Paczkowski | author4-link = Karel Bartosek | first4 = Karel | last4 = Bartosek | author5-link = Jean-Louis Margolin | first5 = Jean-Louis | last5 = Margolin | title = The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression | pages = 92–97; 116–21 | isbn = 978-0-674-07608-2 |date=October 1999 | publisher = [[Harvard University Press]] | url = https://books.google.com/?id=H1jsgYCoRioC}}. |
|||
*Trotsky, Leon ''My Life'' (1930) [http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1930-lif/ch38.htm Chapter 38] His advice to Lenin. |
|||
*[[Alexander Nikolaevich Yakovlev|Alexander N. Yakovlev]]. ''A Century of Violence in Soviet Russia''. [[Yale University Press]], 2002 {{ISBN|0-300-08760-8}} [https://books.google.com/books?id=ChRk43tVxTwC&pg=PA155 pp 155–56]. |
|||
* {{Citation | author-link = Richard Pipes | first = Richard | last = Pipes | title = Russia under the Bolshevik regime 1919–1924 | place = London | origyear = 1994 | publisher = [[Vintage (publisher)|Vintage]] | year = 1995 | isbn = 978-0-679-76184-6}}. |
|||
* Jansen, Dinah (2015), "After October: Russian Liberalism as a Work-in Progress, 1917-1945" Kingston, Queen's University. PhD Dissertation. |
|||
Journal of British Studies 55 (July 2016): 519–537. doi:10.1017/jbr.2016.57 © The North American Conference on British Studies, 2016 |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
* {{Citation | last = Breen | first = Rodney | year = 1994 | title = Saving Enemy Children: Save the Children's Russian Relief Organisation, 1921–1923 | journal = Disasters | volume = 18 | issue = 3 | pages = 221–237 | doi=10.1111/j.1467-7717.1994.tb00309.x| pmid = 7953492 }}. |
|||
{{wikisource|ru:Письмо членам Политбюро от 19 марта 1922 (Ленин)|March 19, 1922 Vladimir Lenin's secret letter to Politburo about the confiscation}} |
|||
* Cameron, Sarah Isabel. ''The Hungry Steppe: Soviet Kazakhstan and the Kazakh Famine, 1921–1934'' (PhD. Diss. Yale University, 2011). |
|||
* [http://news.stanford.edu/news/2011/april/famine-040411.html How the U.S. saved a starving Soviet Russia: PBS film highlights Stanford scholar's research on the 1921-23 famine] - A PBS Documentary |
|||
* Edmondson, Charles M. "The politics of hunger: The Soviet response to famine, 1921". ''Soviet Studies'' 29.4 (October 1977): 506–518. {{JSTOR|150533}}. |
|||
* [https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/americanexperience/films/famine/player/ The Great Famine] — An [[American Experience]] Documentary |
|||
* Fisher, Harold Henry. ''The Famine in Soviet Russia, 1919–1923: The Operations of the American Relief Administration'' (Macmillan, 1927). [https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.189554 online] |
|||
* [http://www.dissercat.com/content/golod-v-povolzhe-1919-1925-gg V.A. Polyakov, ''Hunger in Volga region 1919-25''] |
|||
* [[David Fromkin|Fromkin, David]]: ''Peace to End All Peace'' (1989 hc) p. 360 (on Tsarist corruption and the closure of the Dardanelles). |
|||
* [https://www2.warwick.ac.uk/services/library/mrc/explorefurther/digital/russia/famine/ University of Warwick] |
|||
* {{Citation | author-link = François Furet | first = François | last = Furet | title = Passing of an Illusion | date = 1999 | orig-date = 1995}}. |
|||
* Jansen, Dinah (2015), "After October: Russian Liberalism as a Work-in Progress, 1917–1945" Kingston, Queen's University. PhD Dissertation. |
|||
* {{Citation | author-link = George F. Kennan| last = Kennan | first = George Frost | title = Russia and the West under Lenin and Stalin | place = Boston | year = 1961 | pages = 141–150, 168, 179–185}}. Default reference for the historical and aftermath sections. |
|||
* {{Citation | last = Kennan | author-mask = 2 | title = The Decline of Bismarck's European Order: Franco-Russian Relations, 1875–1890 | place = Princeton | year = 1979 | page = 387}}. |
|||
* Patenaude, Bertrand M. ''The big show in Bololand: The American relief expedition to Soviet Russia in the famine of 1921'' (Stanford University Press, 2002). |
|||
* {{Cite book | author-link = Richard Pipes | first = Richard | last = Pipes | title = Russia under the Bolshevik regime 1919–1924 | place = London | orig-year = 1994 | publisher =Vintage | year = 1995 | isbn = 978-0-679-76184-6}} |
|||
* {{Cite journal |last=Sasson |first=Tehila |date=July 2016 |title=From Empire to Humanity: The Russian Famine and the Imperial Origins of International Humanitarianism |journal=Journal of British Studies |volume=55 |issue=3 |pages=519–537 |doi=10.1017/jbr.2016.57|doi-access=free }} |
|||
* Trotsky, Leon (1930). ''My Life''. [http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1930-lif/ch38.htm Chapter 38]. His advice to Lenin. |
|||
* Weissman, Benjamin M. [https://books.google.com/books?id=v_Es-_Jh2qUC ''Herbert Hoover and famine relief to Soviet Russia, 1921–1923''] (Hoover Institution Press, 1974). |
|||
* {{Citation | last1 = Werth | first1 = Nicolas | author1-link = Nicolas Werth | author2-link = Jean-Louis Panné | first2 = Jean-Louis | last2 = Panné | author3-link = Andrzej Paczkowski | first3 = Andrzej | last3 = Paczkowski | author4-link = Karel Bartosek | first4 = Karel | last4 = Bartosek | author5-link = Jean-Louis Margolin | first5 = Jean-Louis | last5 = Margolin | editor-link = Stéphane Courtois | editor-first = Stéphane | editor-last = Courtois | title = The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression | pages = 92–97; 116–121 | isbn = 978-0-674-07608-2 |date=October 1999 | publisher = Harvard University Press | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=H1jsgYCoRioC}}. |
|||
* [[Alexander Nikolaevich Yakovlev|Yakovlev, Alexander N]]. ''A Century of Violence in Soviet Russia''. [[Yale University Press]], 2002, {{ISBN|0-300-08760-8}}, [https://books.google.com/books?id=ChRk43tVxTwC&pg=PA155 pp. 155–156] • [https://books.google.com/books?id=ChRk43tVxTwC&q=famine+1921 (famine of 1921) ] |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
== External links == |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Russian Famine Of 1921}} |
|||
{{wikisource|ru:Письмо членам Политбюро от 19 марта 1922 (Ленин)|19 March 1922 Vladimir Lenin's secret letter to Politburo about the confiscation}} |
|||
[[Category:Famines in the Soviet Union]] |
|||
* [http://news.stanford.edu/news/2011/april/famine-040411.html How the U.S. saved a starving Soviet Russia: PBS film highlights Stanford scholar's research on the 1921–1923 famine]—A PBS Documentary |
|||
[[Category:Famines in Russia]] |
|||
* [https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/americanexperience/films/famine/player/ The Great Famine]—An ''[[American Experience]]'' Documentary |
|||
[[Category:Economic crises in Europe]] |
|||
* [http://www.dissercat.com/content/golod-v-povolzhe-1919-1925-gg V. A. Polyakov, ''Hunger in Volga region 1919–1925''] (dissertation) {{in lang|ru}} |
|||
[[Category:Aftermath of World War I in Russia and in the Soviet Union]] |
|||
* [https://www2.warwick.ac.uk/services/library/mrc/explorefurther/digital/russia/famine/ Famine in Russia, 1921–1922]—University of Warwick |
|||
* [https://www.histclo.com/essay/war/com/sov/cw/fam/rcwf-arm.html American food relief to Russia ] |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Russian famine Of 1921}} |
|||
[[Category:1921 in Russia]] |
[[Category:1921 in Russia]] |
||
[[Category:1922 in Russia]] |
[[Category:1922 in Russia]] |
||
[[Category:Aftermath of World War I in Russia and in the Soviet Union]] |
|||
[[Category:Economic crises in Europe]] |
|||
[[Category:Famines in Russia]] |
|||
[[Category:Famines in the Soviet Union]] |
|||
[[Category:20th-century famines]] |
|||
[[Category:Russian Civil War]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 14:45, 5 December 2024
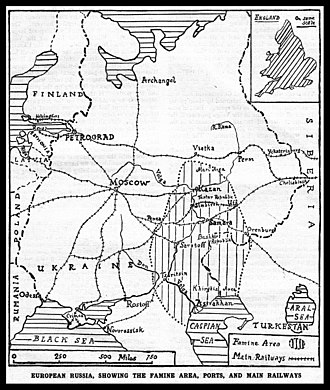
The Russian famine of 1921–1922, also known as the Povolzhye famine (Russian: Голод в Поволжье, 'Volga region famine') was a severe famine in the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic that began early in the spring of 1921 and lasted until 1922. The famine resulted from the combined effects of severe drought,[1] the continued effects of World War I, economic disturbance from the Russian Revolution, the Russian Civil War, and failures in the government policy of war communism (especially prodrazvyorstka). It was exacerbated by rail systems that could not distribute food efficiently.
The famine killed an estimated five million people and primarily affected the Volga and Ural River regions.[2] Many of the starving resorted to cannibalism.[3][4][5] The outbreaks of diseases such as cholera and typhus were also contributing factors to famine casualties.[6][7]
Origins
[edit]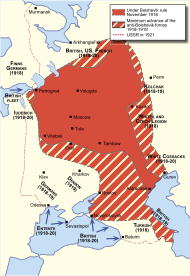
Before the famine began, Russia had suffered three-and-a-half years of World War I and additionally the Russian Civil War of 1918–1920, many of the conflicts being fought inside Russia.[8] There were 7–12 million casualties during the Russian Civil War, mostly civilians.[9] Historians have noted that both Tsarist Russia government councils and other opposition parties had advocated for food requisitioning prior to the ascent of the Bolsheviks.[10][11][12]
Before the famine, all sides in the Russian Civil Wars of 1918–1921 (the Bolsheviks, the Whites, the Anarchists, and the seceding nationalities) had provisioned themselves by seizing food from those who grew it, giving it to their armies and supporters, and denying it to their enemies. The Bolshevik government had requisitioned supplies from the peasantry for little or nothing in exchange, which led peasants to drastically reduce their crop production.[13][14][15]
Aid from outside Soviet Russia was initially rejected. The American Relief Administration (ARA), which Herbert Hoover formed to help the victims of starvation of World War I, offered assistance to Lenin in 1919 if it had full say over the Russian railway network and handed out food impartially to all. Lenin refused that as interference in Russian internal affairs.[8]
Lenin was eventually convinced by the famine, the Kronstadt rebellion, large-scale peasant uprisings such as the Tambov Rebellion, and the failure of a German general strike to reverse his policy at home and abroad. He decreed the New Economic Policy on 15 March 1921.
The famine also helped produce an opening to the West. Lenin now allowed relief organizations to bring aid. War relief was no longer required in Western Europe, and the ARA had an organization set up in Poland that relieved the Polish famine, which had begun in the winter of 1919–1920.[16]
Cannibalism
[edit]
The situation became so desperate that a considerable minority of the starving resorted to cannibalism. According to the historian Orlando Figes, "thousands of cases" were reported, with the number of cases that were never reported certainly even higher.[17] In Samara, "ten butcher shops were closed for selling human flesh."[18] In Pugachyov, "it was dangerous for children to go out after dark since there were known to be bands of cannibals and traders who killed them to eat or sell their tender flesh." An inhabitant of a nearby village stated: "There are several cafeterias in the village — and all of them serve up young children."[3]

This was no exception – Figes estimates "that a considerable proportion of the meat in Soviet factories in the Volga area ... was human flesh." Various gangs specialized in "capturing children, murdering them and selling the human flesh as horse meat or beef", with the buyers happy to have found a source of meat in a situation of extreme shortage and often willing not to "ask too many questions".[19]
Relief effort
[edit]
In the summer of 1921, during one of the worst famines in history, Vladimir Lenin, the head of the new Soviet government, along with Maxim Gorky, appealed in an open letter to "all honest European and American people" to "give bread and medicine".[20] In an open letter to all nations, dated 13 July 1921, Gorky described the crop failure which had brought his country to the brink of starvation.[21] Herbert Hoover, who would later become the U.S. President, responded immediately, and negotiations with Russia took place at the Latvian capital, Riga.[21] A European effort was led by the famous Arctic explorer Fridtjof Nansen through the International Committee for Russian Relief (ICRR).[22]
Hoover's ARA had already been distributing food aid throughout Europe since 1914. After the Germans invaded Belgium in 1914, Hoover set up the Belgian Relief Committee to alleviate the devastation and starvation that followed. As World War I expanded, the ARA grew, and it next entered northern France and assisted France and Germany from 1914 to 1919.[23] In 1920 and 1921, it provided one meal a day to 3.2 million children in Finland, Estonia, various Russian regions, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Ukraine, Czechoslovakia, Austria, Hungary, and Armenia. When it began its emergency feeding operation in Russia, it planned to feed about one million Russian children for a full year.[24] Other bodies such as the American Friends Service Committee, the British Friends' War Victims Relief Committee and the International Save the Children Union, with the British Save the Children Fund as the major contributor, also later took part.[25] As the historian Douglas Smith writes, the food relief would probably help "save communist Russia from ruin."[26]
The United States was the first country to respond, with Hoover appointing Colonel William N. Haskell to direct the American Relief Administration (ARA) in Russia. Within a month, ships loaded with food were headed for Russia. The main contributor to the international relief effort would be the ARA, which was founded and directed by Hoover.[27][20][28] It had agreed to provide food for a million people, mostly children, but within a year it was feeding more than 10 times that number daily.[29]
The ARA insisted on autonomy as to how the food would be distributed and stated its requirement that food would be given without regard to "race, creed or social status", a condition that was stated in Section 25 of the Riga agreement.[20] U.S. spokesmen said that it would also want to have storage facilities built in Russia, wrote the journalist Charles Bartlett, and would expect to have full access to those to assure that food was distributed properly.[21][a]
Hoover also demanded for Russia to use some of its gold holdings to defray the cost of the relief effort. He secured $18 million from the Russian leadership, $20 million from the U.S. Congress, $8 million from the U.S. military, and additional money from U.S. charities to arrive at a total of approximately $78 million from all those sources.[21] After an agreement was finally signed at Riga, the U.S. set up its first kitchen in Petrograd, where 1.6 million people had already starved to death.[21]
For almost two years now a scant two hundred Americans, on a battle line far longer than the western front, have been fighting a foe more pitiless than any the allied armies faced. From the Baltic to the Caspian Sea, from the Crimea to the Urals, they have conquered the famine, saved more lives than were lost in the World War, healed a sorely-suffering people of the diseases which threatened to sweep the whole of Europe, won the benedictions of a great, but stricken, nation, achieved the world's greatest adventure in humanity!
Over 10 million people were fed daily, with the bulk of food coming from the ARA, which had provided more than 768 million tons of flour, grain, rice, beans, pork, milk, and sugar, with a value of over $98 million.[21] To transport and distribute the food after it was collected in the U.S., the ARA used 237 ships, under the direction of 200 Americans and with the help of 125,000 Russians on location for unloading, warehousing, hauling, weighing, cooking and serving the food in more than 21,000 new kitchens.[29]
Even after the food had reached the people in need, Colonel Haskell informed Hoover of an unexpected new danger. He explained that fuel was unavailable for heating or cooking and millions of Russian peasants had clothing consisting mostly of rags, which would lead to certain death from cold exposure during the approaching winter.[30]
The children at risk included those in orphanages and other institutions, as they usually had only one garment, often made of flour sacks, and they lacked shoes, stockings, underclothing, or any other clothing to keep warm. Also at risk were children living at home with their parents, who also lacked enough clothing, which made them unable to reach the American relief kitchens. Haskell cabled Hoover that at least one million children were in extreme need of clothes. Hoover quickly initiated a plan for collecting and sending clothing packages to Russia, which would come from donations by individuals, businesses and banks.[30]

Medical needs were also paramount. As noted by Dr. Henry Beeuwkes, the chief of the Medical Division in Russia, American relief was supplying over 16,000 hospitals, which were treating more than a million persons daily.[29] Because those institutions were scattered over areas with few railroads and often poor roads, with some hospitals over a thousand miles from the main supply base in Moscow, the task was monumental. Dr. Louis L. Shapiro, an army colonel who was one of the ARA's medical directors in Russia, recalled that southern Russia had little more than "mud ruts for roads, with limitless prairies."[23] On one trip, with few car necessities or regular gas, he drove 150 miles on tires without inner tubes, instead stuffed with straw.[23] "After our kitchens were established and our clinics able to distribute medical supplies" said Shapiro, "children who had been eating a diet of clay and leather scrapings, responded quite rapidly."[23]
According to Dr. Beeuwkes, everything was in short supply, including beds, blankets, sheets, and most medical tools and medicines. Operations were performed in unheated operating rooms without anesthetics and often with bare hands. Wounds were dressed with newspapers or rags. Water supplies were polluted, with much of the plumbing unusable.
To help the widespread medical emergency, the ARA distributed medical supplies, which included over 2,000 necessities, from medicines to surgical instruments. There were 125,000 medical packages, weighing 15 million pounds, sent on 69 ships.[29] According to Dr. Shapiro, when the ARA left Russia in 1923, after two years of relief efforts, "the Russians had been pulled out of the slough of famine and death. I can say without boasting that no relief organization ever worked so hard to complete its task."[23]
In May 1922, Lev Kamenev, President of the Moscow Soviet and deputy chairman of all Russian famine relief committees, wrote a letter to Haskell that thanked him and the ARA for its help and also paid tribute to the American people
The government of the Russian nation will never forget the generous help that was afforded them in the terrible calamity and dangers visited upon them.... I wish to express, on behalf of the Soviet government, my satisfaction and thanks to the American Relief Administration, through your person, for the substantial support which they are offering to the calamity stricken population of the Volga area.[24][31]
By the summer of 1923, it was estimated that the U.S. relief that was given to Russia amounted to over twice the total of relief given it by all other foreign organizations combined.[32] European agencies co-ordinated by the ICRR also fed two million people a day, while the International Save the Children Union fed up to 375,000.[33][34] The operation was hazardous since several workers died of cholera, and it was not without its critics, including the London Daily Express, which first denied the severity of the famine and then argued that the money would better be spent in the United Kingdom.[35]

Throughout 1922 and 1923, as famine was still widespread and the ARA was still providing relief supplies, grain was exported by the Soviet government to raise funds for the revival of industry, which seriously endangered Western support for relief. The new Soviet government insisted that if the AYA suspended relief, the ARA was to arrange a foreign loan for them of about $10,000,000 1923 dollars; the ARA was unable to do so and continued to ship in food past the grain being sold abroad.[36][37]
| America's Contribution to the Russian Famine Relief Effort[29] | |
|---|---|
| Children fed daily | 4,173,339 |
| Adults fed daily | 6,317,958 |
| Maximum number fed daily | 10,491,297 |
| Number of meals served | 1,750,000,000 |
| Number of separate kitchens opened | 21,435 |
| People clothed | 333,125 |
| Medical supplies value | $7,685,000 |
| Hospitals provided with supplies | 16,400 |
| Number of inoculations given | 6,396,598 |
| Number of vaccinations given | 1,304,401 |
| Tons of food provided | 912,121 |
| Tons of medical supplies provided | 7,500 |
| Number of U.S. ships used | 237 |
Death toll
[edit]As with other large-scale famines, the range of estimates is considerable. An official Soviet publication of the early 1920s concluded that about five million deaths occurred in 1921 from famine and related disease, the number that is usually quoted in textbooks.[38] More conservative figures counted not more than a million, and another assessment, based on the ARA's medical division, spoke of two million.[39] On the other side of the scale, some sources spoke of ten million dead.[40] According to Bertrand M. Patenaude, "such a number hardly seems extravagant after the many tens of millions of victims of war, famine, and terror in the twentieth century."[41]
-
Fridtjof Nansen's journey to the famine regions of Russia, 1921
-
Children's corpses collected on a wagon in Samara, 1921
-
Victims of the Russian famine, 1922
-
Starving Russian girl in Buguruslan, 1921
-
A starving boy from the village of Blagoveshchenka (Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine), who during the famine of 1921–1922 killed his three-year-old brother and ate him
-
Victims of the 1921 famine during the Russian Civil War
Political uses
[edit]The famine came at the end of six-and-a-half years of unrest and violence (World War I, the two Russian Revolutions of 1917, and the Russian Civil War). Many political and military factions were involved in the events, and most of them have been accused by their enemies of having contributed to or even bearing sole responsibility for the famine.[42]
The Bolsheviks started a campaign of seizing church property in 1922. That year, over 4.5 million golden roubles of property were seized. Of those, one million gold roubles were spent for famine relief.[43] In a secret March 19, 1922 letter to the Politburo, Lenin expressed an intention to seize several hundred million golden roubles for famine relief.[44]
In Lenin's secret letter to the Politburo, he explains that the famine provides an opportunity against the church.[44] Richard Pipes argued that the famine was used politically as an excuse for the Bolshevik leadership to persecute the Orthodox Church, which held significant sway over much of the peasantry.[45]
Russian anti-Bolshevik white émigrés in London, Paris, and elsewhere also used the famine as a media opportunity to highlight the iniquities of the Soviet regime to prevent trade with and official recognition of the Bolshevik government.[46]
2022 Russian documentary film
[edit]On September 24, 2022, at the Oktyabr cinema in Moscow, the Russian documentary film Hunger or Famine (Russian: Голод) premiered which depicts the mass famine in the Volga region, Ukraine, the Urals, Bashkiria, Samara and Chelyabinsk regions, Kazakhstan and Western Siberia affecting over 35 oblasts of Soviet Russia in the early 1920s and a total population of approximately 90 million people.[47] The film was directed by Tatyana Sorokina with Aleksandr Arkhangelsky writing the script and Maxim Kournikov providing the inspiration behind the creation of the film.[48] On October 30, 2022, Famine was first shown at a public theater in Yekaterinburg.[49] In November 2022, the Russian Ministry of Culture banned the distribution of Голод in Russia.[49][50] In December 2022, Famine received the monthly journalistic award from Redkollegia and, in April 2023, it received the Audience Prize and a special mention jury diploma at the 2023 Artdocfest.[51][52]
See also
[edit]- 1921 Mari wildfires
- 1921–1922 famine in Tatarstan
- American Relief Administration
- Cannibalism in Europe
- Famines in Russia and the USSR
- Fram (play)
- Kazakh famine of 1919–1922
- List of famines
- Pomgol
- Soviet famine of 1930–1933
- Holodomor (Ukrainian famine 1932–1933)
- Soviet famine of 1946–1947
Notes
[edit]- ^ At a conference in Geneva on 15 August organised by the International Committee of the Red Cross and the League of Red Cross Societies, the International Committee for Russian Relief (ICRR) was set up with Dr. Fridtjof Nansen as its High Commissioner. Nansen headed to Moscow, where he signed an agreement with Soviet Foreign Minister Georgy Chicherin that left the ICRR in full control of its operations. At the same time, fundraising for the famine relief operation began in earnest in Britain, with all the elements of a modern emergency relief operation—full-page newspaper advertisements, local collections, and a fundraising film shot in the famine area. By September, a ship had been despatched from London carrying 600 tons of supplies. The first feeding centre was opened in October in Saratov.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ Golubev, Genady; Nikolai Dronin (February 2004). "Geography of Droughts and Food Problems in Russia (1900–2000), Report No. A 0401" (PDF). Center for Environmental Systems Research, University of Kassel. Retrieved 2016-12-17.
- ^ "Famine of 1921–1922". Seventeen Moments in Soviet History. 2015-06-17. Retrieved 2018-07-20.
- ^ a b Figes, Orlando (1997). A People's Tragedy: The Russian Revolution 1891–1924. London: Pimlico. pp. 777–778.
- ^ Francis Haller (2003-08-12), "Famine in Russia: the hidden horrors of 1921 - ICRC (translation)", Le Temps, published by ICRC, retrieved 2019-03-14
- ^ Francis Haller (2003-08-12), "Secours en temps de paix - la famine en Russie - CICR", Le Temps (in French), published by ICRC, retrieved 2019-03-14
- ^ Heinzen, James W. (2004-02-01). Inventing a Soviet Countryside: State Power and the Transformation of Rural Russia, 1917-1929. University of Pittsburgh Pre. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-8229-7078-1.
- ^ Raleigh, Donald J. (2021-05-11). Experiencing Russia's Civil War: Politics, Society, and Revolutionary Culture in Saratov, 1917-1922. Princeton University Press. p. 202. ISBN 978-1-4008-4374-9.
- ^ a b Kennan 1961.
- ^ Mawdsley, Evan (2007). The Russian Civil War. New York: Pegasus Books. p. 287. ISBN 9781681770093.
- ^ Lih, Lars T. (2023-10-20). What Was Bolshevism?. BRILL. p. 149. ISBN 978-90-04-68479-9.
- ^ Baykov, Alexander (1946). the development of the soviet economic system. CUP Archive. p. 16.
- ^ Sanborn, Joshua A. (2014). Imperial Apocalypse: The Great War and the Destruction of the Russian Empire. Oxford University Press. p. 256. ISBN 978-0-19-964205-2.
- ^ Carr, EH, 1966, The Bolshevik Revolution 1917–1923, Part 2, p. 233.
- ^ Chase, WJ, 1987, Workers, Society and the Soviet State: Labour and Life in Moscow 1918–1929 pp. 26–27.
- ^ Nove, A, 1982, An Economic History of the USSR, p. 62, cited in Flewers, Paul. "War Communism in Retrospect".
- ^ "WILSON RENEWS HUNGER LOAN PLEA". The New York Times. 1920-01-28. Retrieved 2016-01-17.
- ^ Figes 1997, p. 777.
- ^ Patenaude, Bertrand M. (2002). The Big Show in Bololand: The American Relief Expedition to Soviet Russia in the Famine of 1921. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. p. 268.
- ^ Figes quoted in Korn, Daniel; Radice, Mark; Hawes, Charlie (2001). Cannibal: The History of the People-Eaters. London: Channel 4 Books. p. 81.
- ^ a b c "A century ago America saved millions of Russians from starvation", The Economist, 11 November 2019
- ^ a b c d e f Bartlett, Charles. "U.S. Food Relief for Communists?", Enquirer and News, Battle Creek, MI, 2 August 1962
- ^ Vogt, Carl-Emil (2009), "Fridtjof Nansen and European Food Aid in Bolshevik Russia and Ukraine in 1921–1923", Matériaux pour l'Histoire de Notre Temps, 95 (3), Cairn
- ^ a b c d e Masters, Ann V. "Herbert Hoover's Humanitarian Corp Plans 32nd Reunion", Bridgeport Sunday Post (Bridgeport, Connecticut), 18 April 1965 p. 5
- ^ a b "American Relief Administrating", Indiana Evening Gazette, 25 October 1921
- ^ Famine in Russia: the hidden horrors of 1921, ICRC, 2013-10-03; Luke Kelly, British Humanitarian Activity and Russia, 1890-1923 (Palgrave Macmillan, 2017), pp. 159-211.
- ^ "The Russian Job: The Forgotten Story of How America Saved the Soviet Union from Ruin", Amazon review
- ^ Smith, Douglas. The Russian Job, Farrar, Straus and Giroux (2019)
- ^ International news, vol. 442, Newsreel, 1921
- ^ a b c d e f Ramsey, W. Howard. "Two Hundred Americans Return Victorious From War On Russian Famine and Pestilence", News-Journal, (Mansfield, Ohio), 11 August 1923 p. 7
- ^ a b "Banks in State to Aid Relief. American Relief Administration Organizes to Send Clothing to Russian Children", The Spokesman Review, (Spokane, WA) 19 November 1922
- ^ "Admit America Saved Russia", AP, Los Angeles Times, 6 May 1922 p. 6
- ^ "Russian Relief Still Continues", Kenosha Evening News, (Kenosha, Wisconsin,) 28 August 1923 p. 4
- ^ Kurasawa, Fuyuki (2012-01-03). The Making of Humanitarian Visual Icons: On the 1921-1923 Russian Famine as Foundational Event. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 68. ISBN 9781137012869. Retrieved 2014-07-19.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ "FAMINE AND RELIEF 1921", The Routledge Atlas of Russian History, Routledge, 2013-04-03, pp. 102–102A, doi:10.4324/9780203074473-102, ISBN 9780203074473
- ^ Breen 1994.
- ^ Ellman, Michael (June 2007), "Stalin and the Soviet Famine of 1932–33 Revisited" (PDF), Europe-Asia Studies, 59 (4): 663–693, doi:10.1080/09668130701291899, S2CID 53655536.
- ^ Serbyn, Roman (1986), "The Famine of 1921–22", Famine in the Ukraine, 1932–33, Edmonton, pp. 174–178
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link). - ^ Norman Lowe. Mastering Twentieth-Century Russian History. Palgrave, 2002. p. 155.
- ^ Bertrand M. Patenaude. The Big Show in Bololand. The American Relief Expedition to Soviet Russia in the Famine of 1921. Stanford University Press, 2002. p. 197.
- ^ How the U.S. saved a starving Soviet Russia: PBS film highlights Stanford scholar's research on the 1921-23 famine Stanford News
- ^ Patenaude 2002, pp. 197–198.
- ^ Academia.edu
- ^ А. Г. Латышев. Рассекреченный Ленин. — 1-е изд. — М.: Март, 1996. — Pages 145—172. — 336 с. — 15 000 экз. — ISBN 5-88505-011-2.
- ^ a b Н.А. Кривова, "Власть и церковь в 1922-1925гг"
- ^ Pipes 1995, p. 415.
- ^ Jansen, Dinah (2015). After October: Russian Liberalism as a Work-in-Progress, 1917–1945. Kingston: Queen's University.
- ^ "Famine". IMDb. Retrieved 2024-09-11.
- ^ Легалов, Евгений (Legalov, Evgeniy) (2022-12-23). ""Сама родила – сама и съем". В Праге прошёл показ фильма "Голод"" ["I gave birth to her myself - I'll eat her myself." The film "Hunger" was screened in Prague]. «Радио Свобода» (in Russian). Archived from the original on 2024-09-11. Retrieved 2024-09-11.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Воронов, Александр (Voronov, Alexander) (2022-11-14). "«Голод» отменяют по просьбам трудящихся" ["Famine" canceled at the request of workers]. Коммерсантъ (in Russian). Archived from the original on 2022-11-15. Retrieved 2024-09-11.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Минкульт отозвал прокатное удостоверение у фильма "Голод"" [The Ministry of Culture revoked the distribution certificate for the film "Hunger"]. «Радио Свобода» (in Russian). 2022-11-14. Archived from the original on 2024-09-11. Retrieved 2024-09-11.
- ^ "Голод" [Famine]. Редколлегия. 2022-12-31. Archived from the original on 2023-02-07. Retrieved 2024-09-11.
- ^ "Объявлены итоги конкурса АртдокСеть-2023" [Results of the 2023 Artdocfest]. Артдокфест (in Russian). 2023-04-15. Archived from the original on 2023-09-23. Retrieved 2024-09-11.
Sources
[edit]- Breen, Rodney (1994), "Saving Enemy Children: Save the Children's Russian Relief Organisation, 1921–1923", Disasters, 18 (3): 221–237, doi:10.1111/j.1467-7717.1994.tb00309.x, PMID 7953492.
- Cameron, Sarah Isabel. The Hungry Steppe: Soviet Kazakhstan and the Kazakh Famine, 1921–1934 (PhD. Diss. Yale University, 2011).
- Edmondson, Charles M. "The politics of hunger: The Soviet response to famine, 1921". Soviet Studies 29.4 (October 1977): 506–518. JSTOR 150533.
- Fisher, Harold Henry. The Famine in Soviet Russia, 1919–1923: The Operations of the American Relief Administration (Macmillan, 1927). online
- Fromkin, David: Peace to End All Peace (1989 hc) p. 360 (on Tsarist corruption and the closure of the Dardanelles).
- Furet, François (1999) [1995], Passing of an Illusion.
- Jansen, Dinah (2015), "After October: Russian Liberalism as a Work-in Progress, 1917–1945" Kingston, Queen's University. PhD Dissertation.
- Kennan, George Frost (1961), Russia and the West under Lenin and Stalin, Boston, pp. 141–150, 168, 179–185
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link). Default reference for the historical and aftermath sections. - —— (1979), The Decline of Bismarck's European Order: Franco-Russian Relations, 1875–1890, Princeton, p. 387
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link). - Patenaude, Bertrand M. The big show in Bololand: The American relief expedition to Soviet Russia in the famine of 1921 (Stanford University Press, 2002).
- Pipes, Richard (1995) [1994]. Russia under the Bolshevik regime 1919–1924. London: Vintage. ISBN 978-0-679-76184-6.
- Sasson, Tehila (July 2016). "From Empire to Humanity: The Russian Famine and the Imperial Origins of International Humanitarianism". Journal of British Studies. 55 (3): 519–537. doi:10.1017/jbr.2016.57.
- Trotsky, Leon (1930). My Life. Chapter 38. His advice to Lenin.
- Weissman, Benjamin M. Herbert Hoover and famine relief to Soviet Russia, 1921–1923 (Hoover Institution Press, 1974).
- Werth, Nicolas; Panné, Jean-Louis; Paczkowski, Andrzej; Bartosek, Karel; Margolin, Jean-Louis (October 1999), Courtois, Stéphane (ed.), The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression, Harvard University Press, pp. 92–97, 116–121, ISBN 978-0-674-07608-2.
- Yakovlev, Alexander N. A Century of Violence in Soviet Russia. Yale University Press, 2002, ISBN 0-300-08760-8, pp. 155–156 • (famine of 1921)
External links
[edit]- How the U.S. saved a starving Soviet Russia: PBS film highlights Stanford scholar's research on the 1921–1923 famine—A PBS Documentary
- The Great Famine—An American Experience Documentary
- V. A. Polyakov, Hunger in Volga region 1919–1925 (dissertation) (in Russian)
- Famine in Russia, 1921–1922—University of Warwick
- American food relief to Russia







