Mali: Difference between revisions
Jolielover (talk | contribs) m Reverted edit by 2400:C600:452E:BC8B:1:0:30ED:88AB (talk) to last version by 12.185.211.194 |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Landlocked country in West Africa}} |
|||
{{other uses}} |
|||
{{Other uses}} |
|||
{{pp-move|small=yes}} |
{{pp-move|small=yes}} |
||
{{Use dmy dates|date=May 2023}} |
|||
{{Coord|17|N|4|W|display=title}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=December 2018}} |
|||
{{Infobox country |
{{Infobox country |
||
| conventional_long_name = Republic of Mali |
| conventional_long_name = Republic of Mali |
||
| native_name = {{collapsible list |
|||
| linking_name = |
|||
|titlestyle = background:transparent;text-align:center;line-height:normal;font-size:85%; |
|||
| native_name = {{unbulleted list|item_style=font-size:88%; |{{native name|fr|République du Mali}} |{{native name|bm|Mali ka Fasojamana}}}} |
|||
|title = {{resize|1.0 em|Official names}} |
|||
| common_name = Mali |
|||
| {{Infobox |
|||
| image_flag = Flag of Mali.svg |
|||
| subbox=yes |
|||
| image_coat = Seal of Mali.svg |
|||
| bodystyle=font-size:77%;font-weight:normal; |
|||
| symbol_type = Coat of arms |
|||
| rowclass1 = mergedrow |
|||
| image_map = Mali_(orthographic_projection).svg |
|||
| label1 = [[Bambara language|Bambara]]: |
|||
| map_caption = {{map caption |countryprefix= |location_color=green}} |
|||
| data1 = {{lang|bm|Mali ka Fasojamana / ߡߊ߬ߟߌ ߞߊ ߝߊߛߏߖߊߡߊߣߊ<ref>[https://twitter.com/NkoOfficiel ''Académie N’Ko Mali ߡߊ߰ߟߌ ߒߞߏ ߟߏ߲ߞߏ߫ ߘߎ߲ߓߎ |
|||
| image_map2 = Mali - Location Map (2013) - MLI - UNOCHA.svg |
|||
''] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220514112858/https://twitter.com/NkoOfficiel|date=14 May 2022}}. Retrieved 14 May 2024</ref>}} |
|||
| national_motto = {{native phrase|fr|"Un peuple, un but, une foi"|italics=off|nolink=on}}<br />{{small|"One people, one goal, one faith"}} |
|||
| rowclass2 = mergedrow |
|||
| national_anthem = {{native phrase|fr|"[[Le Mali]]"|italic=no|nolink=on}}<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20081220122918/http://www.koulouba.pr.ml/spip.php?article93&calendrier_mois=9&calendrier_annee=2008 Presidency of Mali: Symboles de la République, L'Hymne National du Mali]. Koulouba.pr.ml. Retrieved 4 May 2012.</ref><br /><center>[[File:Malian national anthem, performed by the United States Navy Band.oga]]</center> |
|||
| label3 = [[Arabic]]: |
|||
| official_languages = [[French language|French]] |
|||
| data3 = {{lang|mey|جُمْهُورِيَّةْ مَالِي ({{lang|mey-Latn|Jumhūriyyet Māli}})}} |
|||
| languages_type = [[Lingua franca]] |
|||
| |
| label2 = [[Fula language|Fula]]: |
||
| data2 = {{lang|ff|Republik bu Maali / 𞤈𞤫𞤨𞤵𞤦𞤤𞤭𞤳 𞤦𞤵 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭}} |
|||
| languages2_type = [[National language]]s |
|||
| rowclass3 = mergedrow |
|||
| languages2 = {{hlist |[[Bambara language|Bambara]] |[[Bomu language|Bomu]] |[[Bozo language|Tieyaxo Bozo]]}} {{hlist |[[Escarpment Dogon|Toro So Dogon]]}} {{hlist |[[Maasina Fulfulde]] |[[Hassaniya Arabic|Arabic]] |[[Minyanka language|Mamara Senoufo]] |[[Kita Maninka language|Kita Maninkakan]] |[[Soninke language|Soninke]]}} {{hlist |[[Koyraboro Senni]] |[[Senara language|Syenara Senoufo]] |[[Tamasheq language|Tamasheq]] |[[Kassonke language|Xaasongaxango]]}} |
|||
| rowclass4 = mergedrow |
|||
| demonym = [[Demographics of Mali|Malian]] |
|||
| label4 = [[Soninke language|Soninke]]: |
|||
| ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list |
|||
| data4 = {{lang|snk|Mali Tɔgɔbadugu}} |
|||
| 50% [[Mandé peoples|Mande]] |
|||
| rowclass5 = mergedrow |
|||
| 16% [[Fula people|Fula]] |
|||
| label5 = [[Tamasheq languages|Tamasheq]]: |
|||
| 13% Voltaic ([[Senufo people|Senufo]] / [[Bwa people|Bwa]]) |
|||
| data5 = {{lang|taq-Latn|Tagduda n Mali}} / {{lang|taq|ⵜⴰⴳⴷⵓⴷⴰ ⵏ ⵎⴰⵍⵉ}} |
|||
| {{nowrap|10% [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] / [[Moors#Modern age|Moor]]}} |
|||
| label6 = [[Songhai language|Songhai]]: |
|||
| data6 = {{lang|ses-Latn|Mali Laamaa}}}}}} |
|||
| 4% other |
|||
| common_name = Mali |
|||
| image_flag = Flag of Mali.svg |
|||
| image_coat = Coat of arms of Mali.svg |
|||
| image_map = Mali (orthographic projection).svg |
|||
| map_caption = {{map caption |countryprefix= |location_color=green}} |
|||
| image_map2 = |
|||
| national_motto = {{native phrase|fr|"Un peuple, un but, une foi"|italics=off|nolink=on}}<br />{{native phrase|bm|"Mɔgɔ kelen, laɲini kelen, dannaya kelen"}}<br/>"One people, one goal, one faith" |
|||
| national_anthem = {{native name|fr|"[[Le Mali]]"|italic=no|nolink=on}}{{parabr}}{{center|[[File:Malian national anthem, performed by the United States Navy Band.oga]]}} |
|||
| official_languages = {{nowrap|'''[[Languages of Mali|13 national languages]]'''<ref name="Lingua 2023">{{cite web |url=https://sgg-mali.ml/JO/2023/mali-jo-2023-13-sp-2.pdf |title=JOURNAL OFFICIEL DE LA REPUBLIQUE DU MALI SECRETARIAT GENERAL DU GOUVERNEMENT - DECRET N°2023-0401/PT-RM DU 22 JUILLET 2023 PORTANT PROMULGATION DE LA CONSTITUTION |date=22 July 2023 |website=sgg-mali.ml |access-date=26 July 2023 |quote=Article 31 : Les langues nationales sont les langues officielles du Mali. |trans-quote=Article 31: The national languages are the official languages of Mali. |lang=fr |archive-date=8 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230808203503/https://sgg-mali.ml/JO/2023/mali-jo-2023-13-sp-2.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="LangNat">{{cite web |url=https://sgg-mali.ml/JO/2017/mali-jo-2017-39.pdf |title=JOURNAL OFFICIEL DE LA REPUBLIQUE DU MALI SECRETARIAT GENERAL DU GOUVERNEMENT - DECRET N°2017-0735/P-RM DU 21 AOUT 2017 FIXANT L'ORGANISATION ET LES MODALITES DE FONCTIONNEMENT DES STRUCTURES DE L'EDUCATION NON FORMELLE |date=21 August 2017 |website=sgg-mali.ml |access-date=21 October 2023 |quote=Selon la Loi n°96- 049 du 23 août 1996, les langues nationales du Mali sont : (...) |trans-quote=According to Law No. 96-049 of 23 August 1996, the national languages of Mali are: (...) |lang=fr |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803235822/https://sgg-mali.ml/JO/2017/mali-jo-2017-39.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref>}} |
|||
{{plainlist| |
|||
* [[Bambara language|Bambara]] |
|||
* [[Bobo language|Bobo]] |
|||
* [[Arabic]] |
|||
* [[Bozo language|Bozo]] |
|||
* [[Escarpment Dogon|Dogon, Toro So]] |
|||
* [[Fula language|Fula]] |
|||
* [[Kassonke language|Kassonke]] |
|||
* [[Maninka language|Maninke]] |
|||
* [[Minyanka language|Minyanka]] |
|||
* [[Senara language|Senufo, Senara]] |
|||
* [[Koyraboro Senni|Songhay, Koyraboro Senni]] |
|||
* [[Soninke language|Soninke]] |
|||
* [[Tamasheq language|Tamasheq]] |
|||
}} |
|||
| languages_type = [[Working language]] |
|||
| languages = {{unbulleted list|[[French language|French]] (de facto)<ref name="French">{{cite web |url=https://sgg-mali.ml/JO/2023/mali-jo-2023-13-sp-2.pdf |title=JOURNAL OFFICIEL DE LA REPUBLIQUE DU MALI SECRETARIAT GENERAL DU GOUVERNEMENT - DECRET N°2023-0401/PT-RM DU 22 JUILLET 2023 PORTANT PROMULGATION DE LA CONSTITUTION |date=22 July 2023 |website=sgg-mali.ml |access-date=26 July 2023 |quote=Article 31 : Le français est la langue de travail. L’Etat peut adopter toute autre langue comme langue de travail. |trans-quote=Article 31: French is the working language. The State may adopt any other language as its working language. |lang=fr |archive-date=8 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230808203503/https://sgg-mali.ml/JO/2023/mali-jo-2023-13-sp-2.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref>}} |
|||
| languages2_type = [[Spoken language]]s |
|||
| languages2 = {{hlist|[[Bambara language|Bambara]]{{efn|Bambara serves as a ''[[lingua franca]]'' spoken by around 80% of the population.<ref name=p6/>}}|[[Fula language|Fula]]|[[Arabic]]|[[Soninke language|Soninke]]|[[Songhay languages|Songhay]]|[[Mandinka language|Mandinka]]|[[Minyanka language|Minyanka]]|[[Tamasheq language|Tamasheq]]|[[Senufo languages|Senufo]]|[[Bobo language|Bobo]]|[[Bozo language|Bozo]]|[[Kassonke language|Kassonke]]|[[Samogo languages|Samogo]]|[[Marka language|Dafing]]|[[Dogon languages|Dogon]]}} |
|||
| religion = {{ubl |
|||
| | 95% [[Islam in Mali|Islam]] |
|||
| 5% [[Religion in Mali|other]]{{efn| Includes [[Christianity]], [[Irreligion|no religion]], and [[traditional African religions]].}} |
|||
}} |
|||
| religion_year = 2021 |
|||
| religion_ref = <ref>{{Cite web |title=Mali |url=https://www.state.gov/reports/2021-report-on-international-religious-freedom/mali/ |access-date=8 October 2022 |website=United States Department of State |archive-date=13 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220813150444/https://www.state.gov/reports/2021-report-on-international-religious-freedom/mali/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| demonym = [[Demographics of Mali|Malian]] |
|||
| ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list |
|||
| 33.3% [[Bambara people|Bambara]] |
|||
| 13.3% [[Fula people|Fula]] |
|||
| 9.6% [[Soninke people|Soninke]] |
|||
| 9.6% [[Senufo people|Senufo]] / [[Bwa people|Bwa]] |
|||
| 8.8% [[Mandinka people|Malinke]] |
|||
| 8.7% [[Dogon people|Dogon]] |
|||
| 5.9% [[Songhai people|Songhai]] |
|||
| 3.5% [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] |
|||
| 2.1% [[Bobo people|Bobo]] |
|||
| 4.5% [[Demographics of Mali#Ethnic groups|other]]<ref name="CIA-2021-Mali">{{cite web |title=Africa: Mali – The World Factbook – Central Intelligence Agency |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/ |website=CIA.gov |access-date=1 May 2021 |date=27 April 2021 |archive-date=30 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210330032030/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| capital = [[Bamako]] |
| capital = [[Bamako]] |
||
| coordinates = {{Coord|12|39|N|8|0|W|type:city}} |
| coordinates = {{Coord|12|39|N|8|0|W|type:city}} |
||
| largest_city = Bamako |
| largest_city = Bamako |
||
| government_type = [[Unitary state|Unitary]] [[presidential republic]] under a [[military junta]]<ref>{{cite news |last1=Booty |first1=Natasha |last2=Pivac |first2=Mark |title=Assimi Goïta: President gets sweeping powers in new Mali constitution |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-66282417 |access-date=4 August 2023 |work=[[BBC News]] |date=23 July 2023 |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802043804/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-66282417 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| government_type = [[Unitary state|Unitary]] [[semi-presidential]] [[republic]] |
|||
| leader_title1 = [[List of heads of state of Mali|President]] |
| leader_title1 = [[List of heads of state of Mali|President]] |
||
| leader_name1 = [[ |
| leader_name1 = [[Assimi Goïta]] (interim) |
||
| leader_title2 = [[List of heads of government of Mali|Prime Minister]] |
| leader_title2 = [[List of heads of government of Mali|Prime Minister]] |
||
| leader_name2 = [[ |
| leader_name2 = [[Abdoulaye Maïga (officer)|Abdoulaye Maïga]] (interim) |
||
| legislature = [[National Assembly (Mali)|National Assembly]] |
| legislature = [[National Assembly (Mali)|National Assembly]] |
||
| area_rank = 23rd |
| area_rank = 23rd |
||
| area_km2 = 1,240,192 |
| area_km2 = 1,240,192 |
||
| area_footnote = <ref name="bbc_com">{{cite web |title=Mali country profile |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-13881370 |website=BBC News |access-date=17 October 2023 |date=19 October 2023 |archive-date=11 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230911075500/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-13881370 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| area_sq_mi = 478,839 <!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]]--> |
|||
| area_sq_mi = 478,839 <!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]].--> |
|||
| percent_water = 1.6 |
|||
| percent_water = 1.6 |
|||
| population_estimate = |
|||
| population_estimate = 21,990,607<ref>{{Cite CIA World Factbook|country=Mali|access-date=22 June 2023|year=2023}}</ref> |
|||
| population_estimate_rank = |
|||
| population_estimate_year = |
| population_estimate_year = 2024 |
||
| population_estimate_rank = 61st |
|||
| population_census = 19,329,841<ref name=census>{{cite web|url=http://instat.gov.ml/voir_actu.aspx?lactu=44 |title=Mali preliminary 2018 census |publisher=Institut National de la Statistique |accessdate=29 November 2018 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20100418055748/http://instat.gov.ml/voir_actu.aspx?lactu=44 |archivedate=18 April 2010 |df= }}</ref> |
|||
| population_census_rank = 67th |
|||
| population_census_year = November 2018 |
|||
| population_density_km2 = 11.7 |
| population_density_km2 = 11.7 |
||
| population_density_sq_mi = 30.3 <!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]]--> |
| population_density_sq_mi = 30.3 <!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]].--> |
||
| population_density_rank = 215th |
| population_density_rank = 215th |
||
| GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $61.625 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.ML">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/October/weo-report?c=678,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2020&ey=2028&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2023 Edition. (Mali) |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |website=IMF.org |date=10 October 2023 |access-date=16 October 2023 |archive-date=17 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231017204907/https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/October/weo-report?c=678,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2020&ey=2028&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| GDP_PPP = $44.329 billion<ref name=imf2>{{cite web |url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2018/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=97&pr.y=10&sy=2018&ey=2021&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=678&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC&grp=0&a=|title=Mali |publisher=International Monetary Fund }}</ref> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_rank = |
| GDP_PPP_rank = 115th |
||
| GDP_PPP_year = |
| GDP_PPP_year = 2023 |
||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = $2, |
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $2,639<ref name="IMFWEO.ML" /> |
||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = |
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 174th |
||
| GDP_nominal = $ |
| GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $21.309 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.ML" /> |
||
| GDP_nominal_rank = 123rd |
|||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2018 |
|||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2023 |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = $891<ref name=imf2/> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $912<ref name="IMFWEO.ML" /> |
|||
| sovereignty_type = [[History of Mali|Independence]] |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 175th |
|||
| established_event1 = from France<sup>a</sup> |
|||
| sovereignty_type = [[History of Mali|Formation]] |
|||
| established_date1 = 20 June 1960 |
|||
| established_event1 = Establishment of the [[French Sudan|Sudanese Republic]] |
|||
| established_event2 = as Mali |
|||
| established_date1 = 24 November 1958 |
|||
| established_date2 = 22 September 1960 |
|||
| established_event2 = Merger with [[Senegal]] to create the [[Mali Federation]] |
|||
| Gini_year = 2010 |
|||
| established_date2 = 4 April 1959 |
|||
| Gini_change = <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| established_event3 = Independence from France |
|||
| Gini = 33.0 <!--number only--> |
|||
| established_date3 = 20 June 1960 |
|||
| Gini_ref = <ref name="wb-gini">{{cite web |url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI/ |title=Gini Index |publisher=[[World Bank]] |accessdate=2 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
| established_event4 = Dissolution of the Mali Federation |
|||
| Gini_rank = |
|||
| established_date4 = 20 August 1960 |
|||
| HDI_year = 2017<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> |
|||
| established_event5 = Declaration of the Republic of Mali |
|||
| HDI_change = decrease <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| established_date5 = 22 September 1960 |
|||
| HDI = 0.427 <!--number only--> |
|||
| Gini_year = 2010 |
|||
| HDI_ref = <ref>{{cite web|url=http://hdr.undp.org/en/2018-update|title=Human Development Reports|website=hdr.undp.org}}</ref> |
|||
| Gini_change = <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| HDI_rank = 182th |
|||
| Gini = 33.0 <!--number only--> |
|||
| currency = [[West African CFA franc]] |
|||
| Gini_ref = <ref name="wb-gini">{{cite web |url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI/ |title=Gini Index |publisher=[[World Bank]] |access-date=2 March 2011 |archive-date=8 December 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208203439/http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| currency_code = XOF |
|||
| Gini_rank = |
|||
| time_zone = [[Greenwich Mean Time|GMT]] |
|||
| HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> |
|||
| utc_offset = +0 |
|||
| HDI_change = decrease <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| time_zone_DST = |
|||
| HDI = 0.410 <!--number only--> |
|||
| utc_offset_DST = |
|||
| HDI_ref = <ref>{{Cite web |date=13 March 2024 |title=HUMAN DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2023-24 |url=http://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf |website=[[United Nations Development Programme]] |publisher=United Nations Development Programme |pages=274–277 |language=en |access-date=3 May 2024 |archive-date=1 May 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240501075007/https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| drives_on = right<ref>[http://www.brianlucas.ca/roadside/ Which side of the road do they drive on?] Brian Lucas. August 2005. Retrieved 28 January 2009.</ref> |
|||
| HDI_rank = 188th |
|||
| calling_code = [[+223]] |
|||
| currency = [[West African CFA franc]] |
|||
| cctld = [[.ml]] |
|||
| currency_code = XOF |
|||
| footnote_a = As the [[Sudanese Republic]], with [[Senegal]] as the [[Mali Federation]]. |
|||
| utc_offset = {{sp}} |
|||
| time_zone = [[Greenwich Mean Time|GMT]] |
|||
| date_format = dd/mm/yyyy |
|||
| drives_on = right<ref>[http://www.brianlucas.ca/roadside/ Which side of the road do they drive on?] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120414073422/http://brianlucas.ca/roadside/ |date=14 April 2012 }} Brian Lucas. August 2005. Retrieved 28 January 2009.</ref> |
|||
| calling_code = [[+223]] |
|||
| cctld = [[.ml]] |
|||
| today = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Mali''' ({{IPAc-en|audio=En-us-Mali.ogg|ˈ|m|ɑː|l|i}}; {{IPA-fr|mali}}), officially the '''Republic of Mali''' ({{lang-fr|link=no|République du Mali}}), is a [[landlocked country]] in [[West Africa]], a region geologically identified with the [[West African Craton]]. Mali is the eighth-largest country in [[Africa]], with an area of just over {{convert|1240000|sqkm|sqmi}}. The population of Mali is {{#expr:{{replace|{{UN_Population|Mali}}|,||}}/1e6 round 1}} million.{{UN_Population|ref}} Its capital is [[Bamako]]. The [[sovereign state]] of Mali consists of eight regions and its borders on the north reach deep into the middle of the [[Sahara|Sahara Desert]], while the country's southern part, where the majority of inhabitants live, features the [[Niger River|Niger]] and [[Senegal River|Senegal]] rivers. The country's economy centers on agriculture and mining. Some of Mali's prominent natural resources include gold, being the third largest producer of gold in the African continent,<ref>[http://www.sabc.co.za/news/a/65656d0049a2edb0a589ef9f13675c4c/Mali-gold-reserves-rise-in-2011-alongside-price-20120101 ''Mali gold reserves rise in 2011 alongside price''] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151121041039/http://www.sabc.co.za/news/a/65656d0049a2edb0a589ef9f13675c4c/Mali-gold-reserves-rise-in-2011-alongside-price-20120101 |date=21 November 2015 }}. Retrieved 17 January 2013</ref> and salt.<ref>[http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDI_2008_EN_Tables.pdf ''Human Development Indices''] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120112083827/http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDI_2008_EN_Tables.pdf |date=12 January 2012 }}, Table 3: Human and income poverty, p. 6. Retrieved 1 June 2009</ref> |
|||
'''Mali''',{{efn|{{IPAc-en|audio=En-us-Mali.ogg|ˈ|m|ɑː|l|i}}; {{IPA|bm|ma.li}}<br/>{{bulleted list|[[N'Ko script]]: {{lang|bm-nkoo|ߡߊߟߌ}}|{{langx|ff|𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭|italics=no}}|{{langx|ar|مالي}}}}}} officially the '''Republic of Mali''',{{efn|{{bulleted list|{{langx|bm|Mali ka Fasojamana}}, {{small|[[N'Ko script]]:}} {{lang|bm-nkoo|ߡߊߟߌ ߞߊ ߝߊߛߏߖߊߡߊߣߊ}}|{{langx|ff|𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭|Renndaandi Maali|italics=no}}|{{langx|ar|جمهورية مالي|Jumhūriyyāt Mālī}}}}}} is a [[landlocked country]] in [[West Africa]]. It is the [[List of African countries by area|eighth-largest country in Africa]], with an area of over {{convert|1240192|km2|sqmi}}.<ref name="bbc_com" /> The country is bordered to the north by [[Algeria]], to the east by [[Niger]], to the northwest by [[Mauritania]], to the south by [[Burkina Faso]] and [[Ivory Coast]], and to the west by [[Guinea]] and [[Senegal]]. The population of Mali is 24,478,595,{{UN_Population|ref}} 47.19% of which are estimated to be under the age of 15 in 2024.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.indexmundi.com/mali/age_structure.html |title=Index Mundi using CIA World Factbook statistics, January 20, 2018, retrieved April 13, 2019 |access-date=14 April 2019 |archive-date=21 December 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201221011240/https://www.indexmundi.com/mali/age_structure.html |url-status=live}}</ref> Its [[Capital city|capital]] and largest city is [[Bamako]]. The country has 13 official languages, of which [[Bambara language|Bambara]] is the most commonly spoken. |
|||
Present-day Mali was once part of three West [[African empires]] that controlled [[trans-Saharan trade]]: the [[Ghana Empire]], the [[Mali Empire]] (for which Mali is named), and the [[Songhai Empire]]. During its golden age, there was a flourishing of mathematics, [[astronomy]], literature, and art.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20131214115452/http://muslimheritage.com/topics/default.cfm?ArticleID=371 Topics]. MuslimHeritage.com (5 June 2003). Retrieved 8 October 2012.</ref><ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20110822200824/http://muslimmuseum.org/1005/sankore-university Sankore University]. Muslimmuseum.org. Retrieved 8 October 2012.</ref> At its peak in 1300, the Mali Empire covered an area about twice the size of modern-day [[France]] and stretched to the west coast of Africa.<ref>[http://www.blackpast.org/gah/mali-empire-ca-1200 Mali Empire (ca. 1200- ) | The Black Past: Remembered and Reclaimed]. The Black Past. Retrieved 8 October 2012.</ref> In the late 19th century, during the [[Scramble for Africa]], France seized control of Mali, making it a part of [[French Sudan]]. French Sudan (then known as the Sudanese Republic) joined with [[Senegal]] in 1959, achieving independence in 1960 as the [[Mali Federation]]. Shortly thereafter, following Senegal's withdrawal from the federation, the Sudanese Republic declared itself the independent Republic of Mali. After a long period of one-party rule, a coup in 1991 led to the writing of a new constitution and the establishment of Mali as a democratic, multi-party state. |
|||
The [[sovereign state]]'s northern borders reach deep into the middle of the [[Sahara|Sahara Desert]]. The country's southern part, where the majority of inhabitants live, is in the [[Sudanian savanna]] and has the [[Niger River|Niger]] and [[Senegal River|Senegal]] rivers running through it. The country's economy centres on agriculture and mining with its most prominent natural resources including [[gold]] (of which it is the third largest producer in Africa)<ref>[http://www.sabc.co.za/news/a/65656d0049a2edb0a589ef9f13675c4c/Mali-gold-reserves-rise-in-2011-alongside-price-20120101 ''Mali gold reserves rise in 2011 alongside price''] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151121041039/http://www.sabc.co.za/news/a/65656d0049a2edb0a589ef9f13675c4c/Mali-gold-reserves-rise-in-2011-alongside-price-20120101|date=21 November 2015}}. Retrieved 17 January 2013</ref> and [[salt]].<ref>[http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDI_2008_EN_Tables.pdf ''Human Development Indices''] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120112083827/http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDI_2008_EN_Tables.pdf|date=12 January 2012}}, Table 3: Human and income poverty, p. 6. Retrieved 1 June 2009</ref> |
|||
In January 2012, an [[Northern Mali conflict (2012–present)|armed conflict broke out in northern Mali]], in which [[National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad|Tuareg rebels]] took control of a territory in the north, and in April declared the [[secession]] of a new state, [[Azawad]].<ref>Polgreen, Lydia and Cowell, Alan (6 April 2012) [https://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/07/world/africa/mali-rebels-proclaim-independent-state-in-north.html?_r=1&adxnnl=1&adxnnlx=1333728086-ZXpwSz3KFqUnA4lteq4j4w "Mali Rebels Proclaim Independent State in North"], ''The New York Times''</ref> The conflict was complicated by a [[2012 Malian coup d'état|military coup]] that took place in March<ref name="telegraph.co.uk">[https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/africaandindianocean/mali/9161930/UN-Security-council-condemns-Mali-coup.html UN Security Council condemns Mali coup]. Telegraph (23 March 2012). Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> and later fighting between Tuareg and rebels. In response to territorial gains, the French military launched [[Opération Serval]] in January 2013.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.lemonde.fr/afrique/article/2013/01/12/la-france-demande-une-acceleration-de-la-mise-en-place-de-la-force-internationale-au-mali_1816033_3212.html |title=Mali – la France a mené une série de raids contre les islamistes |date=12 January 2013 |work=Le Monde |accessdate=13 January 2013}}</ref> A month later, Malian and French forces recaptured most of the north. [[Malian presidential election, 2013|Presidential elections]] were held on 28 July 2013, with a second-round run-off held on 11 August, and [[Malian parliamentary election, 2013|legislative elections]] were held on 24 November and 15 December 2013. |
|||
Mali was part of three successive powerful and wealthy West [[African empires]] that controlled [[trans-Saharan trade]]: the [[Ghana Empire]] (for which [[Ghana]] is named), the [[Mali Empire]] (for which Mali is named), and the [[Songhai Empire]]. At its peak in 1300, the Mali Empire was the wealthiest country in Africa<ref>{{Cite web |date=14 April 2020 |title=Mansa Musa (Musa I of Mali) |url=https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/mansa-musa-musa-i-mali/ |access-date=16 March 2022 |website=National Geographic Society |archive-date=2 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220702005708/https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/mansa-musa-musa-i-mali/ |url-status=live }}</ref> with its 14th-century emperor [[Mansa Musa]] believed to be one of the wealthiest individuals in history.<ref>[http://www.blackpast.org/gah/mali-empire-ca-1200 Mali Empire (ca. 1200-) | The Black Past: Remembered and Reclaimed] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190105194944/https://blackpast.org/gah/mali-empire-ca-1200 |date=5 January 2019 }}. The Black Past. Retrieved 8 October 2012.</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=10 March 2019 |title=Is Mansa Musa the richest man who ever lived? |work=BBC News |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-47379458 |access-date=16 March 2022 |archive-date=10 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190310072937/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-47379458 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Who is the richest person of all time? |url=https://www.theweek.co.uk/news/people/954992/who-is-the-richest-person-of-all-time |access-date=16 March 2022 |website=The Week UK |date=December 2021 |archive-date=16 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220316215840/https://www.theweek.co.uk/news/people/954992/who-is-the-richest-person-of-all-time |url-status=live }}</ref> Besides being a hub of trade and mining, medieval Mali was a centre of [[Islam]], culture and knowledge, with [[Timbuktu]] becoming a renowned place of learning with its [[University of Timbuktu|university]], one of the oldest in the world and still active. The expanding [[Songhai Empire]] absorbed the empire in 1468,{{Not verified in body|date=January 2024}} followed by a [[Saadi Sultanate|Saadian]] army [[Moroccan invasion of the Songhai Empire|which defeated the Songhai in 1591]]. In the late 19th century, during the [[Scramble for Africa]], France seized control of Mali, making it a part of [[French Sudan]]; as the Sudanese Republic, [[Mali Federation|a brief federation with Senegal]] was formed, achieving independence in 1960. After Senegal's withdrawal, the Republic of Mali was established. After a long period of one-party rule, a coup in 1991 led to a new constitution and the establishment of Mali as a democratic, multi-party state. |
|||
In January 2012, an [[Northern Mali conflict (2012–present)|armed conflict broke out in northern Mali]], in which [[National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad|Tuareg rebels]] took control of a territory in the north, and in April declared the [[secession]] of a new state, [[Azawad]].<ref>Polgreen, Lydia and Cowell, Alan (6 April 2012) [https://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/07/world/africa/mali-rebels-proclaim-independent-state-in-north.html?_r=1&adxnnl=1&adxnnlx=1333728086-ZXpwSz3KFqUnA4lteq4j4w "Mali Rebels Proclaim Independent State in North"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200728182302/https://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/07/world/africa/mali-rebels-proclaim-independent-state-in-north.html?_r=1&adxnnl=1&adxnnlx=1333728086-ZXpwSz3KFqUnA4lteq4j4w |date=28 July 2020 }}, ''The New York Times''</ref> The conflict was complicated by [[2012 Malian coup d'état|a military coup]] in March 2012<ref name="telegraph.co.uk">[https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/africaandindianocean/mali/9161930/UN-Security-council-condemns-Mali-coup.html UN Security Council condemns Mali coup] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201128100600/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/africaandindianocean/mali/9161930/UN-Security-council-condemns-Mali-coup.html |date=28 November 2020 }}. Telegraph (23 March 2012). Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> and later fighting between Tuareg and other rebel factions. In response to territorial gains, the French military launched [[Operation Serval]] in January 2013.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.lemonde.fr/afrique/article/2013/01/12/la-france-demande-une-acceleration-de-la-mise-en-place-de-la-force-internationale-au-mali_1816033_3212.html |title=Mali – la France a mené une série de raids contre les islamistes |date=12 January 2013 |work=Le Monde |access-date=13 January 2013 |archive-date=20 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171020023450/http://www.lemonde.fr/afrique/article/2013/01/12/la-france-demande-une-acceleration-de-la-mise-en-place-de-la-force-internationale-au-mali_1816033_3212.html |url-status=live }}</ref> A month later, Malian and French forces recaptured most of the north, although the conflict continued. [[Malian presidential election, 2013|Presidential elections]] were held on 28 July 2013, with a second-round run-off held on 11 August, and [[Malian parliamentary election, 2013|legislative elections]] were held on 24 November and 15 December 2013. In the early 2020s, Mali experienced two military takeovers by [[Assimi Goïta]]. |
|||
== Etymology == |
== Etymology == |
||
The name ''Mali'' is taken from the |
The name ''Mali'' is taken from the name of the [[Mali Empire]]. It means "the place where the king lives"<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=u5HnAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA7|title=Discovering the Empire of Mali|last=Wolny|first=Philip|date=15 December 2013|publisher=The Rosen Publishing Group|isbn=9781477718896|page=7|access-date=24 August 2020|archive-date=16 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210416180418/https://books.google.com/books?id=u5HnAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA7|url-status=live}}</ref> and carries a connotation of strength.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://archive.org/details/educationalsyste0000sasn|url-access=registration|title=Educational Systems of Africa: Interpretations for Use in the Evaluation of Academic Credentials|last1=Sasnett|first1=Martena Tenney|last2=Sepmeyer|first2=Inez Hopkins|date=1 January 1967|publisher=University of California Press|pages=[https://archive.org/details/educationalsyste0000sasn/page/673 673]}}</ref> |
||
Fourteenth-century Maghrebi traveller [[Ibn Battuta]] reported that the capital of the empire was called Mali.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zf6xAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA231|title=Historical Dictionary of Mali|last1=Imperato|first1=Pascal James|last2=Imperato|first2=Gavin H.|date=25 April 2008|publisher=Scarecrow Press|isbn=9780810864023|page=231|access-date=24 August 2020|archive-date=27 August 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210827043448/https://books.google.com/books?id=zf6xAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA231|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>[[Djibril Tamsir Niane|Niane, Djibril]] (1965). ''Sundiata: An Epic of Old Mali''.</ref> One [[Mandinka people|Mandinka]] tradition tells that the legendary first emperor [[Sundiata Keita]] changed himself into a hippopotamus upon his death in the [[Sankarani River]] and that it was possible to find villages in the area of this river called "old Mali". A study of Malian proverbs noted that in old Mali, there is a village called Malikoma, which means "New Mali", and that ''Mali'' could have formerly been the name of a city.<ref name=":0">{{cite web|url=http://ugspace.ug.edu.gh/bitstream/123456789/8845/1/A%20Study%20of%20Proverbs%20in%20Things%20Fall%20Apart%20and%20Sundiata%3B%20An%20Epic%20of%20Old%20Mali%20(Sundiata)%20-%202014.pdf|title=A STUDY OF PROVERBS IN THINGS FALL APART AND SUNDIATA: AN EPIC OF OLD MALI (SUNDIATA)|last=Aku Adjandeh|first=Evelyn|date=July 2014|publisher=University of Ghana, Legon – Institute of African Studies |page=100|access-date=19 March 2017|archive-date=20 March 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170320054429/http://ugspace.ug.edu.gh/bitstream/123456789/8845/1/A%20Study%20of%20Proverbs%20in%20Things%20Fall%20Apart%20and%20Sundiata%3B%20An%20Epic%20of%20Old%20Mali%20(Sundiata)%20-%202014.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Another theory suggests that ''Mali'' is a [[Fula language|Fulani]] pronunciation of the name of the [[Mandé peoples|Mande peoples]].<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/?id=LY5Lmc-To7cC&pg=PA92|title=African Glory: The Story of Vanished Negro Civilizations|last=Graft-Johnson|first=John Coleman De|date=1 January 1986|publisher=Black Classic Press|isbn=9780933121034| |
Another theory suggests that ''Mali'' is a [[Fula language|Fulani]] pronunciation of the name of the [[Mandé peoples|Mande peoples]].<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LY5Lmc-To7cC&pg=PA92|title=African Glory: The Story of Vanished Negro Civilizations|last=Graft-Johnson|first=John Coleman De|date=1 January 1986|publisher=Black Classic Press|isbn=9780933121034|page=92|access-date=24 August 2020|archive-date=16 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210416180445/https://books.google.com/books?id=LY5Lmc-To7cC&pg=PA92|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|url=https://archive.org/details/introductiontohi0001fyle|url-access=registration|title=Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa|last=Fyle|first=C. Magbaily|date=1999|publisher=University Press of America|isbn=9780761814566|pages=[https://archive.org/details/introductiontohi0001fyle/page/11 11]}}</ref> It is suggested that a sound shift led to the change, whereby in Fulani the alveolar segment {{IPA|/nd/}} shifts to {{IPA|/l/}} and the terminal vowel denasalizes and raises, leading "Manden" to shift to {{IPA|/mali/}}.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
==History== |
==History== |
||
[[File:MALI empire map.PNG|The extent of the [[Mali Empire]]'s peak|thumb|left]] |
|||
[[File:Timbuktu-manuscripts-astronomy-mathematics.jpg| The pages above are from [[Timbuktu Manuscripts]] written in Sudani script (a form of [[Arabic]]) from the [[Mali Empire]] showing established knowledge of astronomy and mathematics. Today there are close to a million of these manuscripts found in [[Timbuktu]] alone.|thumb|left]] |
|||
[[File:GriotsSambala.jpg|thumb|left|[[Griot]]s of [[Sambala]], king of Médina ([[Fula people]], Mali), 1890]] |
|||
{{main|History of Mali}} |
{{main|History of Mali}} |
||
===Before colonization=== |
|||
Mali was once part of three famed West African empires which controlled [[trans-Saharan trade]] in gold, salt, [[slaves]], and other precious commodities.<ref name=p1>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 1.</ref> These [[Sahelian kingdom]]s had neither rigid geopolitical boundaries nor rigid ethnic identities.<ref name=p1/> The earliest of these empires was the [[Ghana Empire]], which was dominated by the [[Soninke people|Soninke]], a [[Mande languages|Mande]]-speaking people.<ref name=p1/> The empire expanded throughout West Africa from the 8th century until 1078, when it was conquered by the [[Almoravids]].<ref name=p2>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]]. Mali was later responsible for the collapse of Islamic Slave Army from the North. The defeat of Tukuror Slave Army, was repeated by Mali against the France and Spanish Expeditionary Army in the 1800s ("Blanc et memoires"). . p. 2.</ref> |
|||
[[File:MALI empire map.PNG|thumb|left|The extent of the [[Mali Empire]]'s peak]] |
|||
[[File:Timbuktu-manuscripts-astronomy-mathematics.jpg|thumb|left|The pages above are from [[Timbuktu Manuscripts]] written in Sudani script (a form of [[Arabic]]) from the [[Mali Empire]] showing established knowledge of astronomy and mathematics. Today there are close to a million of these manuscripts found in [[Timbuktu]] alone.]] |
|||
The rock art in the [[Sahara]] suggests that northern Mali has been inhabited since 10,000 BC, when the Sahara was fertile and rich in wildlife. Early ceramics have been discovered at the central Malian site of Ounjougou dating to about 9,400 BC, and are believed to represent an instance of the independent invention of pottery in the region.<ref>Eric Huysecom, M. Rasse, L. Lespez, K. Neumann, A. Fahmy, A. Ballouche, S. Ozainne, M. Maggetti, Ch. Tribolo, S. Sorian: The emergence of pottery in Africa during the tenth millennium cal BC: new evidence from Ounjougou (Mali), in: Antiquity (2009), p. 906.</ref> Farming took place by 5000 BC and iron was used by around 500 BC. |
|||
The [[Mali Empire]] later formed on the upper [[Niger River]], and reached the height of power in the 14th century.<ref name=p2/> Under the Mali Empire, the ancient cities of [[Djenné]] and [[Timbuktu]] were centers of both trade and Islamic learning.<ref name=p2/> The empire later declined as a result of internal intrigue, ultimately being supplanted by the [[Songhai Empire]].<ref name=p2/> The Songhai people originated in current northwestern [[Nigeria]]. The Songhai had long been a major power in West Africa subject to the Mali Empire's rule.<ref name=p2/> |
|||
In the first millennium BC, early cities and towns were created by Mande peoples related to the [[Soninke people]], along the middle Niger River in central Mali, including [[Dia, Mali|Dia]] which began from around 900 BC, and reached its peak around 600 BC,<ref name="Arazi">{{cite web |last1=Arazi |first1=Noemie |title=Tracing History in Dia, in the Inland Niger Delta of Mali -Archaeology, Oral Traditions and Written Sources |url=http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1444342/1/U591645.pdf |website=University College London |publisher=Institute of Archaeology |access-date=4 November 2021 |archive-date=13 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220213144217/http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1444342/1/U591645.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> and [[Djenne-Djenno]], which lasted from around 300 BC to 900 AD. By the sixth century AD, the lucrative trans-Saharan trade in gold, salt and slaves had begun, facilitating the rise of West Africa's great empires. |
|||
There are a few references to Mali in early Islamic literature. Among these are references to "Pene" and "Malal" in the work of [[al-Bakri]] in 1068,<ref>al-Bakri in Nehemiah Levtzion and J. F. Pl Hopkins, eds and trans., ''Corpus of Early Arabic Sources for West African History'' (New York and London: Cambridge University Press, 1981, reprint edn Princeton, New Jersey,: Marcus Wiener, 2000), pp. 82–83.</ref> the story of the conversion of an early ruler, known to [[Ibn Khaldun]] (by 1397) as Barmandana,<ref>ibn Khaldun in Levtzion and Hopkins, eds, and transl. ''Corpus'', p. 333.</ref> and a few geographical details in the work of [[al-Idrisi]].<ref>al-Idrisi in Levtzion and Hopkins, eds. and transl, ''Corpus'', p. 108.</ref> |
|||
In the late 14th century, the Songhai gradually gained independence from the Mali Empire and expanded, ultimately subsuming the entire eastern portion of the Mali Empire.<ref name=p2/> The Songhai Empire's eventual collapse was largely the result of a [[Saadi dynasty|Moroccan]] invasion in 1591, under the command of [[Judar Pasha]].<ref name=p2/> The fall of the Songhai Empire marked the end of the region's role as a trading crossroads.<ref name=p2/> Following the [[European exploration of Africa|establishment of sea routes by the European powers]], the trans-Saharan trade routes lost significance.<ref name=p2/> |
|||
Mali was once part of three famed West African empires which controlled [[trans-Saharan trade]] in gold, salt, other precious commodities, and [[slaves]] majorly during the reign of [[Mansa Musa]] from c. 1312 – c. 1337.<ref name=p1>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 1.</ref> These [[Sahelian kingdom]]s had neither rigid geopolitical boundaries nor rigid ethnic identities.<ref name=p1/> The earliest of these empires was the [[Ghana Empire]], which was dominated by the [[Soninke people|Soninke]], a [[Mande languages|Mande]]-speaking people.<ref name=p1/> The empire expanded throughout West Africa from the eighth century until 1078, when it was conquered by the [[Almoravids]].<ref name=p2>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]]. Mali was later responsible for the collapse of Islamic Slave Army from the North. The defeat of Tukuror Slave Army, was repeated by Mali against the France and Spanish Expeditionary Army in the 1800s ("Blanc et memoires"). p. 2.</ref> |
|||
One of the worst [[famine]]s in the region's recorded history occurred in the 18th century. According to [[John Iliffe (historian)|John Iliffe]], "The worst crises were in the 1680s, when famine extended from the Senegambian coast to the Upper Nile and 'many sold themselves for slaves, only to get a sustenance', and especially in 1738–1756, when West Africa's greatest recorded subsistence crisis, due to drought and locusts, reportedly killed half the population of [[Timbuktu]]."<ref>[[John Iliffe (historian)|John Iliffe]] (2007) [https://books.google.com/books?id=bNGN2URP_rUC&pg=&dq&hl=en#v=onepage&q=&f=false ''Africans: the history of a continent'']. Cambridge University Press. p. 69. {{ISBN|0-521-68297-5}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Battle of Kirina]] in 1235, culminated in a victory for the [[Mandinka people|Mandinka]] under the command of the exiled prince [[Sundiata Keita]], which led to the downfall of the [[Sosso Empire]]. |
|||
[[File:TombouctouPachalik 4.png|thumb|210px|Map of the [[Pashalik of Timbuktu]] (yellow-striped) as part of the [[Saadi dynasty|Saadi dynasty of Morocco]] (outlined black) within the [[Songhai Empire]] (outlined red), {{Circa|1591}}]] |
|||
[[File:GriotsSambala.jpg|thumb|left|[[Griot]]s of [[Sambala]], king of Médina ([[Fula people]], Mali), 1890. Photo by [[Joannès Barbier]].]] |
|||
The [[Mali Empire]] later formed on the upper [[Niger River]], and reached the height of power in the 14th century.<ref name=p2/> Under the Mali Empire, the ancient cities of [[Djenné]] and [[Timbuktu]] were centers of both trade and Islamic learning.<ref name=p2/> The empire later declined as a result of internal intrigue, ultimately being supplanted by the [[Songhai Empire]].<ref name=p2/> The Songhai had long been a major power in West Africa subject to the Mali Empire's rule.<ref name=p2/> |
|||
In the late 14th century, the Songhai gradually gained independence from the Mali Empire and expanded, ultimately subsuming the entire eastern portion of the Mali Empire.<ref name=p2/> The Songhai Empire's eventual collapse was largely the result of the [[Saadian invasion of the Songhai Empire|Moroccan invasion]] of 1591 under the command of [[Judar Pasha]].<ref name=p2/> The fall of the Songhai Empire marked the end of the region's role as a trading crossroads.<ref name=p2/> Following the [[European exploration of Africa|establishment of sea routes by the European powers]], the trans-Saharan trade routes lost significance.<ref name="p2" /> At that time, the Mali Empire's abundance in wealth expanded its commercial assets of [[salt]] and [[gold]]. |
|||
One of the worst [[famine]]s in the region's recorded history occurred in the 18th century. According to [[John Iliffe (historian)|John Iliffe]], "The worst crises were in the 1680s, when famine extended from the Senegambian coast to the Upper Nile and 'many sold themselves for slaves, only to get a sustenance', and especially in 1738–1756, when West Africa's greatest recorded subsistence crisis, due to drought and locusts, reportedly killed half the population of [[Timbuktu]]."<ref>[[John Iliffe (historian)|John Iliffe]] (2007) [https://books.google.com/books?id=bNGN2URP_rUC ''Africans: the history of a continent''] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150906225011/https://books.google.com/books?id=bNGN2URP_rUC&pg=&dq&hl=en |date=6 September 2015 }}. Cambridge University Press. p. 69. {{ISBN|0-521-68297-5}}</ref> |
|||
===French colonial rule=== |
===French colonial rule=== |
||
{{Seealso|French West Africa}} |
|||
[[File:Africa. French West Africa. Currently the most important efforts of the Office du Niger are directed toward the... - NARA - 541637.tif|thumb|Cotton being processed in [[Niono]] into {{convert|400|lb|kg|abbr=on|order=flip}} bales for export to other parts of Africa and to France, {{Circa|1950}}]] |
|||
[[File:Africa. French West Africa. Currently the most important efforts of the Office du Niger are directed toward the... - NARA - 541637.jpg|thumb|upright|Cotton being processed in [[Niono]] into {{convert|400|lb|kg|abbr=on|order=flip}} bales for export to other parts of Africa and to France, c. 1950]] |
|||
Mali fell under the control of France during the late 19th century.<ref name=p2/> By 1905, most of the area was under firm French control as a part of [[French Sudan]].<ref name=p2/> In early 1959, French Sudan (which changed its name to the Sudanese Republic) and [[Senegal]] united to become the [[Mali Federation]]. The Mali Federation gained independence from France on 20 June 1960.<ref name=p2/> |
|||
Mali fell under the control of France during the [[Scramble for Africa]] in the late 19th century.<ref name=p2/> By 1905, most of the area was under firm French control as a part of [[French Sudan]].<ref name=p2/> |
|||
In November 1915, a large [[Volta-Bani War|anti-French uprising]] broke out among the tribes in the regions of present-day Mali and Burkina Faso.<ref>[http://www.cairn.info/revue-autrepart-2003-2-page-35.htm#no3 La guerre coloniale du Bani-Volta, 1915-1916 (Burkina Faso, Mali)] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171029121219/http://www.cairn.info/revue-autrepart-2003-2-page-35.htm#no3 |date=29 October 2017 }}, Autrepart, 2003.</ref> The last resistance was suppressed only in September 1916. During the suppression of the uprising, over 100 villages were destroyed by French colonial troops.<ref>''14-18 Étions-nous bien défendus ?'', Jean-Claude Flament, Société des écrivains, 2014.</ref> |
|||
On 24 November 1958, French Sudan (which changed its name to the Sudanese Republic) became an autonomous republic within the [[French Community]].<ref name="Independent Mali">{{cite web|url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Mali/Independent-Mali|title=Independent Mali|publisher=Britannica |date=1946|access-date=21 January 2021|archive-date=19 November 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201119042637/https://www.britannica.com/place/Mali/Independent-Mali|url-status=live}}</ref> In January 1959, Mali and [[Senegal]] united to become the [[Mali Federation]].<ref name="Independent Mali"/> |
|||
===Independence=== |
|||
The Mali Federation gained independence from France on 20 June 1960.<ref name=p2/> Senegal withdrew from the federation in August 1960, which allowed the Sudanese Republic to become the independent Republic of Mali on 22 September 1960, and that date is now the country's [[List of national independence days|Independence Day]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://maliembassy.us/index.php/2012-02-27-16-59-35/public-holidays |title=Public Holidays |website=Embassy of the Republic of Mali to the United States |access-date=20 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180920234345/http://maliembassy.us/index.php/2012-02-27-16-59-35/public-holidays |archive-date=20 September 2018 }}</ref> |
|||
[[Modibo Keïta]] was elected the first president.<ref name=p2/> He quickly established a one-party state, adopted an independent African and socialist orientation with close ties to the East, and implemented extensive nationalization of economic resources.<ref name=p2/> In 1960, the population of Mali was reported to be about 4.1 million.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20130530011412/http://www.unhchr.ch/tbs/doc.nsf/0/897ce24a48d43c82802565f700407640 Core document forming part of the reports of states parties: Mali]. United Nations Human Rights Website.</ref> On 19 November 1968, following progressive economic decline, the Keïta regime was overthrown in a bloodless military coup led by [[Moussa Traoré]],<ref name=p3>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 3.</ref> a day which is now commemorated as [[Liberation Day]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://aglobalworld.com/holidays-around-the-world/mali-liberation/|title=Liberation Day Commemorated in Mali|access-date=1 February 2019|archive-date=2 February 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190202042457/http://aglobalworld.com/holidays-around-the-world/mali-liberation/|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Moussa Traoré=== |
===Moussa Traoré regime=== |
||
The subsequent military-led regime, with Traoré as president, attempted to reform the economy. His efforts were frustrated by political turmoil and a devastating [[Sahel drought|drought]] from 1968 to 1974,<ref name=p3/> in which famine killed thousands of people.<ref>"[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/4132326.stm Mali's nomads face famine] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210224054313/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/4132326.stm |date=24 February 2021 }}". BBC News. 9 August 2005.</ref> The Traoré regime faced student unrest beginning in the late 1970s and three coup attempts. The Traoré regime repressed all dissenters until the late 1980s.<ref name=p3/> |
|||
The government continued to attempt economic reforms, and the populace became increasingly dissatisfied.<ref name=p3/> In response to growing demands for multi-party democracy, the Traoré regime allowed some limited political liberalization. They refused to usher in a full-fledged democratic system.<ref name=p3/> In 1990, cohesive opposition movements began to emerge, and was complicated by the turbulent rise of ethnic violence in the north following the return of many [[Tuareg people|Tuaregs]] to Mali.<ref name=p3/> |
|||
[[File:Place de la liberté - Bamako.jpg|thumb|WWI Commemorative Monument to the "Armée Noire"]] |
[[File:Place de la liberté - Bamako.jpg|thumb|WWI Commemorative Monument to the "Armée Noire"]] |
||
Opposition to the corrupt and dictatorial regime of General Moussa Traoré grew during the 1980s. During this time strict programs, imposed to satisfy demands of the International Monetary Fund, brought increased hardship upon the country's population, while elites close to the government supposedly lived in growing wealth. The government continued to attempt economic reforms, and the populace became increasingly dissatisfied.<ref name=p3/> In response to growing demands for multi-party democracy, the Traoré regime allowed some limited political liberalization in the late 1980s, but refused to usher in a full-fledged democratic system.<ref name=p3/> |
|||
In 1990, cohesive opposition movements began to emerge, and was complicated by the turbulent rise of ethnic violence in the north following the return of many [[Tuareg people|Tuaregs]] who had migrated to [[Algeria]] and [[Libya]] during the drought.<ref name=p3/> Peaceful student protests in January 1991 were brutally suppressed, with mass arrests and torture of leaders and participants.<ref name="nonviolent">{{cite web|url=http://www.nonviolent-conflict.org/index.php/movements-and-campaigns/movements-and-campaigns-summaries?sobi2Task%3Dsobi2Details%26catid%3D34%26sobi2Id%3D10 |title=Nonviolent Conflict Summaries |access-date=1 March 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110616222251/http://www.nonviolent-conflict.org/index.php/movements-and-campaigns/movements-and-campaigns-summaries?sobi2Task=sobi2Details&catid=34&sobi2Id=10 |archive-date=16 June 2011}} Mali March 1991 Revolution</ref> Scattered acts of rioting and vandalism of public buildings followed, but most actions by the dissidents remained nonviolent.<ref name="nonviolent" /> |
|||
====March Revolution==== |
|||
From 22 March through 26 March 1991, mass pro-democracy rallies and a nationwide strike was held in both urban and rural communities, which became known as ''les évenements'' ("the events") or the March Revolution. In Bamako, in response to mass demonstrations organized by university students and later joined by trade unionists and others, soldiers opened fire indiscriminately on the nonviolent demonstrators. Riots broke out briefly following the shootings. Barricades as well as roadblocks were erected and Traoré declared a state of emergency and imposed a nightly curfew. Despite an estimated loss of 300 lives over the course of four days, nonviolent protesters continued to return to Bamako each day demanding the resignation of the dictatorial president and the implementation of democratic policies.<ref name="nesbitt">{{cite web|last=Nesbitt |first=Katherine |title=Mali's March Revolution (1991) |url=http://www.nonviolent-conflict.org/index.php/movements-and-campaigns/movements-and-campaigns-summaries?sobi2Task=sobi2Details&catid=34&sobi2Id=10 |publisher=International Center on Nonviolent Conflict |accessdate=1 March 2012 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110616222251/http://www.nonviolent-conflict.org/index.php/movements-and-campaigns/movements-and-campaigns-summaries?sobi2Task=sobi2Details&catid=34&sobi2Id=10 |archivedate=16 June 2011 }}</ref> |
|||
From 22 March through 26 March 1991, mass pro-democracy rallies and a nationwide strike was held in both urban and rural communities, which became known as ''les évenements'' ("the events") or the March Revolution. In Bamako, in response to mass demonstrations organized by university students and later joined by trade unionists and others, soldiers opened fire indiscriminately on the nonviolent demonstrators. Riots broke out briefly following the shootings. Barricades as well as roadblocks were erected and Traoré declared a state of emergency and imposed a nightly curfew. Despite an estimated loss of 300 lives over the course of four days, nonviolent protesters continued to return to Bamako each day demanding the resignation of the dictatorial president and the implementation of democratic policies.<ref name="nesbitt">{{cite web|last=Nesbitt |first=Katherine |title=Mali's March Revolution (1991) |url=http://www.nonviolent-conflict.org/index.php/movements-and-campaigns/movements-and-campaigns-summaries?sobi2Task=sobi2Details&catid=34&sobi2Id=10 |publisher=International Center on Nonviolent Conflict |access-date=1 March 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110616222251/http://www.nonviolent-conflict.org/index.php/movements-and-campaigns/movements-and-campaigns-summaries?sobi2Task=sobi2Details&catid=34&sobi2Id=10 |archive-date=16 June 2011}}</ref> |
|||
26 March 1991 is the day that marks the clash between military soldiers and peaceful demonstrating students which climaxed in the massacre of dozens under the orders of then President Moussa Traoré. He and three associates were later tried and convicted and received the death sentence for their part in the decision-making of that day. Nowadays, the day is a national holiday in order to remember the tragic events and the people that were killed.<ref>{{cite web|last=Bussa|first=Edward|title=Mali's March to Democracy|url=http://www.threadster.com/2009/03/mali-march-to-democracy/|publisher=threadster.com|accessdate=1 March 2012|deadurl=yes|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120324235624/http://www.threadster.com/2009/03/mali-march-to-democracy/|archivedate=24 March 2012|date=26 March 2009}}</ref>{{unreliable source?|date=July 2013}} The coup is remembered as Mali's March Revolution of 1991. |
|||
26 March 1991 is the day that marks the clash between military soldiers and peaceful demonstrating students which climaxed in the massacre of dozens under the orders of Traoré. He and three associates were later tried and convicted and received the death sentence for their part in the decision-making of that day. Nowadays, the day is a national holiday in order to remember the tragic events and the people who were killed.<ref>{{cite web |last=Bussa |first=Edward |title=Mali's March to Democracy |url=http://www.threadster.com/2009/03/mali-march-to-democracy/ |website=Threadster.com |access-date=1 March 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120324235624/http://www.threadster.com/2009/03/mali-march-to-democracy/ |archive-date=24 March 2012 |date=26 March 2009 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Mohsin |first=Haroon |date=2022-08-18 |title=Martyr's Day in Mali |url=https://nationaltoday.com/martyrs-day-in-mali/ |access-date=2023-09-16 |website=National Today |language=en-US |archive-date=17 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231017204906/https://nationaltoday.com/martyrs-day-in-mali/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The coup is remembered as Mali's [[1991 Malian coup d'état|March Revolution of 1991]].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Turrittin |first=Jane |date=1991 |title=Mali: People Topple Traoré |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/4005962 |journal=Review of African Political Economy |volume=18 |issue=52 |pages=97–103 |doi=10.1080/03056249108703927 |jstor=4005962 |issn=0305-6244 |access-date=9 February 2023 |archive-date=9 February 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230209170251/https://www.jstor.org/stable/4005962 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
By 26 March, the growing refusal of soldiers to fire into the largely nonviolent protesting crowds turned into a full-scale tumult, and resulted in thousands of soldiers putting down their arms and joining the pro-democracy movement. That afternoon, Lieutenant Colonel [[Amadou Toumani Touré]] announced on the radio that he had arrested the dictatorial president, Moussa Traoré. As a consequence, opposition parties were legalized and a national congress of civil and political groups met to draft a new democratic constitution to be approved by a national referendum.<ref name="nesbitt"/> |
|||
By 26 March, the growing refusal of soldiers to fire into the largely nonviolent protesting crowds turned into a full-scale tumult, and resulted in thousands of soldiers putting down their arms and joining the pro-democracy movement. That afternoon, Lieutenant Colonel [[Amadou Toumani Touré]] announced on the radio that he had arrested the dictatorial president, Moussa Traoré. |
|||
===Amadou Toumani Touré presidency=== |
|||
In 1992, [[Alpha Oumar Konaré]] won Mali's first democratic, multi-party presidential election, before being re-elected for a second term in 1997, which was the last allowed under the constitution. In 2002 [[Amadou Toumani Touré]], a retired general who had been the leader of the military aspect of the 1991 democratic uprising, was elected.<ref name=p4>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 4.</ref> During this democratic period Mali was regarded as one of the most politically and socially stable countries in Africa.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20101111133055/http://www.usaid.gov/locations/sub-saharan_africa/countries/mali/ USAID Africa: Mali]. USAID. Retrieved 15 May 2008. Retrieved 3 June 2008.</ref> |
|||
===Multi-party democracy=== |
|||
[[Slavery in modern Africa|Slavery]] persists in Mali today with as many as 200,000 people held in direct servitude to a master.<ref name=slaves/> In the [[Tuareg Rebellion (2012)|Tuareg Rebellion of 2012]], ex-slaves were a vulnerable population with reports of some slaves being recaptured by their former masters.<ref>{{cite news|last=York|first=Geoffrey|title=Mali chaos gives rise to slavery, persecution |newspaper=The Globe and Mail|date=11 November 2012|url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/world/mali-chaos-gives-rise-to-slavery-persecution/article5186368/|location=Toronto}}</ref> |
|||
Opposition parties were legalized, a transitional government was formed and a national congress of civil and political groups met to draft a [[Constitution of Mali|new democratic constitution]] to be approved by a national referendum.<ref name="nesbitt"/><ref name=p3/> In 1992, [[Alpha Oumar Konaré]] won Mali's first democratic, multi-party presidential election, before being re-elected for a second term in 1997, which was the last allowed under the constitution. [[Amadou Toumani Touré]], a retired general who had been the leader of the military aspect of the 1991 democratic uprising, was elected in 2002.<ref name=p4>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 4.</ref> During this democratic period Mali was regarded as one of the most politically and socially stable countries in Africa.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20101111133055/http://www.usaid.gov/locations/sub-saharan_africa/countries/mali/ USAID Africa: Mali]. USAID. Retrieved 15 May 2008. Retrieved 3 June 2008.</ref> |
|||
[[Slavery in modern Africa|Slavery]] persists in Mali today with as many as 200,000 people held in direct servitude to a master.<ref name=slaves/> In the [[Tuareg Rebellion (2012)|Tuareg Rebellion of 2012]], ex-slaves were a vulnerable population with reports of some slaves being recaptured by their former masters.<ref>{{cite news|last=York|first=Geoffrey|title=Mali chaos gives rise to slavery, persecution|newspaper=The Globe and Mail|date=11 November 2012|url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/world/mali-chaos-gives-rise-to-slavery-persecution/article5186368/|location=Toronto|access-date=4 September 2017|archive-date=29 November 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161129023715/http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/world/mali-chaos-gives-rise-to-slavery-persecution/article5186368/|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===Northern Mali conflict=== |
===Northern Mali conflict=== |
||
{{main| |
{{main|Mali War}} |
||
{{Seealso|International Criminal Court investigation in Mali}} |
|||
[[File:Le Mali confronté aux sanctions et à lavancée des rebelles islamistes (6904946068).jpg|thumb|Tuareg separatist rebels in Mali, January 2012]] |
[[File:Le Mali confronté aux sanctions et à lavancée des rebelles islamistes (6904946068).jpg|thumb|Tuareg separatist rebels in Mali, January 2012]] |
||
In January 2012 [[Tuareg rebellion (2012)|a Tuareg rebellion]] began in Northern Mali, led by the [[National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad]] (MNLA).<ref>[http://www.news24.com/Africa/News/Mali-clashes-force-120-000-from-homes-20120222 Mali clashes force 120 000 from homes]. News24 (22 February 2012). Retrieved 23 February 2012.</ref> In March, military officer [[Amadou Sanogo]] seized power in [[2012 Malian coup d'état|a coup d'état]], citing Touré's failures in quelling the rebellion, and leading to sanctions and an embargo by the [[Economic Community of West African States]].<ref>Callimachi, Rukmini (3 April 2012) [https://web.archive.org/web/20120404171138/http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/world/post-coup-mali-hit-with-sanctions-by-african-neighbours/article2390504/ "Post-coup Mali hit with sanctions by African neighbours"]. ''Globe and Mail''. Retrieved 4 May 2012.</ref> The MNLA quickly took control of the north, declaring independence as [[Azawad]].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.france24.com/en/20120406-france-24-exclusive-tuareg-rebels-declare-independence-mlna-mali-ansar-dine-azawad |title=Tuareg rebels declare independence in north Mali |publisher=France 24 |date=6 April 2012 |accessdate=28 July 2012}}</ref> However, Islamist groups including [[Ansar Dine]] and [[Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb|Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM)]], who had helped the MNLA defeat the government, turned on the Tuareg and took control of the North<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/2012/06/28/us-mali-crisis-idUSBRE85R15720120628 |title=Islamists declare full control of Mali's north |author=Tiemoko Diallo |author2=Adama Diarra |agency=Reuters |date=28 June 2012 |accessdate=28 July 2012}}</ref> with the goal of implementing [[sharia]] in Mali.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5h7XMRIbuZL6BjKF-U-RbRw5W30GA?docId=CNG.03a07b9823792a080c03447fb210148d.121 |archive-url=https://archive.is/20121216092840/http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5h7XMRIbuZL6BjKF-U-RbRw5W30GA?docId=CNG.03a07b9823792a080c03447fb210148d.121 |dead-url=yes |archive-date=16 December 2012 |title=Mali Islamists want sharia not independence |agency=Agence France-Presse |publisher=Google News |date=20 June 2012 |accessdate=28 July 2012 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.ictj.org/publication/possibilities-and-challenges-transitional-justice-mali |title=Mali Possibilities and Challenges for Transitional Justice in Mali |agency=International Center for Transitional Justice |date=9 January 2014 |accessdate=25 August 2016 }}</ref> |
|||
In January 2012 [[Tuareg rebellion (2012)|a Tuareg rebellion]] began in northern Mali, led by the [[National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad]] (MNLA).<ref>[http://www.news24.com/Africa/News/Mali-clashes-force-120-000-from-homes-20120222 Mali clashes force 120 000 from homes] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010190149/http://www.news24.com/Africa/News/Mali-clashes-force-120-000-from-homes-20120222 |date=10 October 2017 }}. News24 (22 February 2012). Retrieved 23 February 2012.</ref> In March, military officer [[Amadou Sanogo]] seized power in [[2012 Malian coup d'état|a coup d'état]], citing Touré's failures in quelling the rebellion, and leading to sanctions and an embargo by the [[Economic Community of West African States]].<ref>Callimachi, Rukmini (3 April 2012) [https://web.archive.org/web/20120404171138/http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/world/post-coup-mali-hit-with-sanctions-by-african-neighbours/article2390504/ "Post-coup Mali hit with sanctions by African neighbours"]. ''Globe and Mail''. Retrieved 4 May 2012.</ref> The MNLA quickly took control of the north, declaring its independence as [[Azawad]].<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.france24.com/en/20120406-france-24-exclusive-tuareg-rebels-declare-independence-mlna-mali-ansar-dine-azawad |title=Tuareg rebels declare independence in north Mali |publisher=France 24 |date=6 April 2012 |access-date=28 July 2012 |archive-date=8 April 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120408061146/http://www.france24.com/en/20120406-france-24-exclusive-tuareg-rebels-declare-independence-mlna-mali-ansar-dine-azawad |url-status=live }}</ref> However, Islamist groups, including [[Ansar Dine]] and [[Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb|Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM)]], who had helped the MNLA defeat the government, turned on the Tuareg and took control of the north<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-mali-crisis-idUSBRE85R15720120628 |title=Islamists declare full control of Mali's north |author=Tiemoko Diallo |author2=Adama Diarra |work=Reuters |date=28 June 2012 |access-date=28 July 2012 |archive-date=15 August 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200815183330/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-mali-crisis/islamists-declare-full-control-of-malis-north-idUSBRE85R15720120628 |url-status=live }}</ref> with the goal of implementing [[sharia]] in Mali.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5h7XMRIbuZL6BjKF-U-RbRw5W30GA?docId=CNG.03a07b9823792a080c03447fb210148d.121 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20121216092840/http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5h7XMRIbuZL6BjKF-U-RbRw5W30GA?docId=CNG.03a07b9823792a080c03447fb210148d.121 |archive-date=16 December 2012 |title=Mali Islamists want sharia not independence |agency=Agence France-Presse |date=20 June 2012 |access-date=28 July 2012 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.ictj.org/publication/possibilities-and-challenges-transitional-justice-mali |title=Mali Possibilities and Challenges for Transitional Justice in Mali |agency=International Center for Transitional Justice |date=9 January 2014 |access-date=25 August 2016 |archive-date=18 September 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160918152945/https://www.ictj.org/publication/possibilities-and-challenges-transitional-justice-mali |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
On 11 January 2013, the [[French Armed Forces]] [[Operation Serval|intervened]] at the request of the interim government. |
|||
On 30 January, the coordinated advance of the French and Malian troops claimed to have retaken the last remaining Islamist stronghold of Kidal, which was also the last of three northern provincial capitals.<ref name = "kidal retaken">{{cite news |
|||
On 11 January 2013, the [[French Armed Forces]] [[Operation Serval|intervened]] at the request of the interim government of president [[Dioncounda Traoré]]. On 30 January, the coordinated advance of the French and Malian troops claimed to have retaken the last remaining Islamist stronghold of Kidal, which was also the last of three northern provincial capitals.<ref name="kidal retaken">{{cite news |
|||
| url = https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2013/01/30/french-troops-control-key-airport-in-north-mali/1876543/ |
| url = https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2013/01/30/french-troops-control-key-airport-in-north-mali/1876543/ |
||
| title= French Troops Retake Kidal Airport, Move into City |
| title = French Troops Retake Kidal Airport, Move into City |
||
| |
| access-date = 30 January 2013 |
||
| work=USA Today |
| work = USA Today |
||
| date=30 January 2013 |
| date = 30 January 2013 |
||
| archive-date = 30 January 2013 |
|||
</ref> On 2 February, the French President, [[François Hollande]], joined Mali's interim President, [[Dioncounda Traoré]], in a public appearance in recently recaptured Timbuktu.<ref name="BBC-Hollande Timbuktu">{{cite news|title=Mali conflict: Timbuktu hails French President Hollande |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-21304079 |accessdate=4 February 2013 |publisher=BBC News |date=2 February 2013 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130202191543/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-21304079 |archivedate=2 February 2013 }}</ref> |
|||
| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20130130111918/http://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2013/01/30/french-troops-control-key-airport-in-north-mali/1876543/ |
|||
| url-status = live |
|||
}} French troops retake the last remaining Islamist urban stronghold in Mali.</ref> On 2 February, French president [[François Hollande]] joined Dioncounda Traoré in a public appearance in recently recaptured Timbuktu.<ref name="BBC-Hollande Timbuktu">{{cite news |title=Mali conflict: Timbuktu hails French President Hollande |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-21304079 |access-date=4 February 2013 |work=BBC News |date=2 February 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130202191543/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-21304079 |archive-date=2 February 2013 }}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Northern Mali conflict.svg|thumb|Map showing the fullest extent of rebel-held territory in January 2013]] |
|||
In August 2013, [[Ibrahim Boubacar Keita]] was elected as the new [[president of Mali]] in the second round of [[2013 Malian presidential election|the election]].<ref>{{cite news |title=Ibrahim Boubacar Keita wins Mali presidential election |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-23677124 |work=BBC News |date=13 August 2013 |access-date=15 October 2022 |archive-date=20 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220120142538/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-23677124 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
=== Conflict in Central Mali === |
=== Conflict in Central Mali === |
||
In the central Mali province of [[Mopti Region|Mopti]], conflict has escalated since 2015 between agricultural communities like the [[Dogon people|Dogon]] and the [[Bambara people|Bambara]], and the [[Pastoralism|pastoral]] [[Fula people|Fula (or Fulani) people]].<ref name=":4">{{Cite |
In the central Mali province of [[Mopti Region|Mopti]], conflict has escalated since 2015 between agricultural communities like the [[Dogon people|Dogon]] and the [[Bambara people|Bambara]], and the [[Pastoralism|pastoral]] [[Fula people|Fula (or Fulani) people]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.thenewhumanitarian.org/in-depth/sahel-flames-Burkina-Faso-Mali-Niger-militancy-conflict|title=The Sahel in flames|date=31 May 2019|website=The New Humanitarian |access-date=23 June 2019|archive-date=13 November 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211113161848/https://www.thenewhumanitarian.org/in-depth/sahel-flames-Burkina-Faso-Mali-Niger-militancy-conflict|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=":4">{{Cite journal|url=https://www.hrw.org/report/2018/12/07/we-used-be-brothers/self-defense-group-abuses-central-mali|title="We Used to Be Brothers" {{!}} Self-Defense Group Abuses in Central Mali|date=7 December 2018|website=Human Rights Watch |access-date=30 March 2019|last3=t 1.212.290.4700|first3=NY 10118-3299 USA {{!}}|archive-date=2 April 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190402024327/https://www.hrw.org/report/2018/12/07/we-used-be-brothers/self-defense-group-abuses-central-mali|url-status=live}}</ref> Historically, the two sides have fought over access to land and water, factors which have been exacerbated by [[climate change]] as the Fula move into new areas.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://foreignpolicy.com/2019/03/29/radical-islamists-have-opened-a-new-front-in-mali/|title=Radical Islamists Have Opened a New Front in Mali|last=Blake|first=James|website=Foreign Policy |date=29 March 2019 |access-date=30 March 2019|archive-date=30 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190330032447/https://foreignpolicy.com/2019/03/29/radical-islamists-have-opened-a-new-front-in-mali/|url-status=live}}</ref> The Dogon and the Bambara communities have formed "self-defense groups"<ref name=":4" /> to fight the Fula. They accuse the Fula of working with armed [[Islamic terrorism|Islamists]] linked to [[al-Qaeda]].<ref name=":4" /> While some Fula have joined Islamist groups, [[Human Rights Watch]] reports that the links have been "exaggerated and instrumentalized by different actors for opportunistic ends".<ref name=":4" /> |
||
Added a top Mali military commander:<blockquote> |
Added a top Mali military commander:<blockquote>I’ve discussed the growing violence with my commanders and with village chiefs from all sides. Yes, sure, there are jihadists in this zone, but the real problem is banditry, animal theft, score settling – people are enriching themselves using the fight against terrorists as a cover.<ref name=":4" /></blockquote> |
||
The conflict has seen the creation and growth of Dogon and Bambara militias. The government of Mali is suspected of supporting some of these groups under the guise of being proxies in the war against Islamists in the [[Northern Mali conflict]].<ref name=":5">{{Cite news|url=https://www.lemonde.fr/afrique/article/2018/07/24/au-mali-les-liaisons-dangereuses-entre-l-etat-et-les-milices_5335256_3212.html|title=Au Mali, les liaisons dangereuses entre l'Etat et les milices|date=24 July 2018|access-date=30 March 2019|language=fr|archive-date=30 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190330013608/https://www.lemonde.fr/afrique/article/2018/07/24/au-mali-les-liaisons-dangereuses-entre-l-etat-et-les-milices_5335256_3212.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The government denies this.<ref name=":5" /> One such militia is the Dogon group [[Dan Na Ambassagou]], created in 2016.<ref name=":4" /> |
|||
In September 2018, the [[Centre for Humanitarian Dialogue]] negotiated a unilateral ceasefire with Dan Na Ambassagou "in the context of the conflict which opposes the group to other community armed groups in central Mali."<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.hdcentre.org/updates/youssouf-toloba-and-his-dan-nan-ambassagou-armed-group-sign-a-commitment-towards-a-ceasefire-in-central-mali/|title=Youssouf Toloba and his Dan Nan Ambassagou armed group sign a commitment towards a ceasefire in central Mali {{!}} HD Centre|access-date=2019-03-30}}</ref> However, the group has been blamed for the [[March 2019 attacks against Fulani herders|March 24, 2019 massacre of 160 Fula villagers]].<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2019/03/united-nations-investigate-horrific-massacre-mali-190326135707656.html|title=UN to probe 'horrific' Mali attacks as death toll jumps to 160|date=26 March 2019|publisher=Al-Jazeera}}</ref> The group denied the attack, but afterwards Malian President Keita ordered the group to disband.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://africanarguments.org/2019/03/26/insiders-insight-explaining-the-mali-massacre/|title=Insiders Insight: Explaining the Mali massacre|date=2019-03-26|website=African Arguments|language=en-GB|access-date=2019-03-30}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Modibo Sidibe voting in Bamako, 2018 Malian presidential election.jpg|thumb|[[Modibo Sidibe]] voting in Bamako, 2018 Malian presidential election]] |
|||
The UN Special Adviser on the Prevention of Genocide, [[Adama Dieng]], warned of a growing [[ethnicization]] of the conflict.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://news.un.org/en/story/2019/03/1035661|title=Central Mali: Top UN genocide prevention official sounds alarm over recent ethnically-targeted killings|date=2019-03-28|website=UN News|language=en|access-date=2019-03-30}}</ref> |
|||
In the [[2018 Malian presidential election]] held on 29 July 2018,<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.africanews.com/2018/07/10/mali-2018-presidential-election-background-to-a-critical-election-in-an/ |title=Everything you need to know about Mali 2018 presidential election|last=Mumbere|first=Daniel|date=10 July 2018 |work=Africanews.com|access-date=28 July 2018 |archive-date=24 July 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180724062858/http://www.africanews.com/2018/07/10/mali-2018-presidential-election-background-to-a-critical-election-in-an/ |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://maliactu.net/mali-election-presidentielle-2018-le-premier-tour-aura-lieu-le-dimanche-29-juillet/ |title=Mali: Élection présidentielle 2018 : Le premier tour aura lieu le dimanche 29 juillet|date=12 February 2018|website=maliactu.net|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180212142217/http://maliactu.net/mali-election-presidentielle-2018-le-premier-tour-aura-lieu-le-dimanche-29-juillet/ |archive-date=12 February 2018|access-date=17 April 2018}}</ref> no candidate received more than 50% of the vote in the first round. A runoff was held on 12 August 2018 between the top two candidates, incumbent president [[Ibrahim Boubacar Keïta]] of the [[Rally for Mali]] and [[Soumaïla Cissé]] of the [[Union for the Republic and Democracy]], and Keïta was re-elected with 67% of the vote.<ref>{{cite news |title=Incumbent President Keita wins re-election in Mali |url=https://www.france24.com/en/20180816-mali-incumbent-president-ibraham-boubacar-keita-wins-election |work=France 24 |date=16 August 2018 |access-date=15 October 2022 |archive-date=16 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240116002945/https://www.france24.com/en/20180816-mali-incumbent-president-ibraham-boubacar-keita-wins-election |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
In September 2018, the [[Centre for Humanitarian Dialogue]] negotiated a unilateral ceasefire with Dan Na Ambassagou "in the context of the conflict which opposes the group to other community armed groups in central Mali".<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.hdcentre.org/updates/youssouf-toloba-and-his-dan-nan-ambassagou-armed-group-sign-a-commitment-towards-a-ceasefire-in-central-mali/|title=Youssouf Toloba and his Dan Nan Ambassagou armed group sign a commitment towards a ceasefire in central Mali {{!}} HD Centre|access-date=30 March 2019|archive-date=29 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190329224050/https://www.hdcentre.org/updates/youssouf-toloba-and-his-dan-nan-ambassagou-armed-group-sign-a-commitment-towards-a-ceasefire-in-central-mali/|url-status=live}}</ref> However, the group has been blamed for the [[March 2019 attacks against Fulani herders|24 March 2019 massacre of 160 Fula villagers]].<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2019/03/united-nations-investigate-horrific-massacre-mali-190326135707656.html|title=UN to probe 'horrific' Mali attacks as death toll jumps to 160|date=26 March 2019|publisher=Al-Jazeera|access-date=29 March 2019|archive-date=29 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190329130105/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2019/03/united-nations-investigate-horrific-massacre-mali-190326135707656.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The group denied the attack, but afterwards Malian president Keita ordered the group to disband.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://africanarguments.org/2019/03/26/insiders-insight-explaining-the-mali-massacre/|title=Insiders Insight: Explaining the Mali massacre|date=26 March 2019|website=African Arguments |access-date=30 March 2019|archive-date=18 September 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200918134833/https://africanarguments.org/2019/03/26/insiders-insight-explaining-the-mali-massacre/ |url-status=live}}</ref> The UN Special Adviser on the Prevention of Genocide, [[Adama Dieng]], warned of a growing [[ethnicization]] of the conflict.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://news.un.org/en/story/2019/03/1035661|title=Central Mali: Top UN genocide prevention official sounds alarm over recent ethnically-targeted killings |date=28 March 2019|website=UN News |access-date=30 March 2019|archive-date=29 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190329172541/https://news.un.org/en/story/2019/03/1035661 |url-status=live}}</ref> By 2020, more than 600,000 people had been [[Refugee|displaced]] by the conflict in Mali.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Giannangeli |first1=Marco |title=Britain 'sleepwalking' into deadly conflict in war-torn West Africa |url=https://www.express.co.uk/news/uk/1354747/british-army-mali-west-africa-troops-war-terrorism-royal-anglian-light-dragoons-al-qaeda |access-date=30 November 2020 |publisher=express.co.uk |date=1 November 2020 |archive-date=26 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201126044622/https://www.express.co.uk/news/uk/1354747/british-army-mali-west-africa-troops-war-terrorism-royal-anglian-light-dragoons-al-qaeda |url-status=live }}</ref> The United Nations reported that the number of children killed in the conflict in the first six months of 2019 was twice as many for the entire year of 2018. Many of the children have been killed in intercommunal attacks attributed to ethnic militias, with the majority of attacks occurring around [[Mopti]]. It is reported that around 900 schools have closed down and that armed militias are recruiting children.<ref>{{cite news |title=Sharp rise in number of children killed in Mali's deadly attacks |url=https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2019/aug/13/sharp-rise-number-children-killed-mali |access-date=1 September 2019 |work=The Guardian |date=13 August 2019 |archive-date=31 August 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190831235440/https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2019/aug/13/sharp-rise-number-children-killed-mali |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
During the first week of October 2019, two jihadist attacks in the towns of Boulikessi and [[Mondoro]] killed more than 25 Mali soldiers near the border with [[Burkina Faso]].<ref>{{cite web | url = http://en.puic.org/news/10181 | title = PUIC Secretary General condemns terrorist attacks in Mali | date = 8 October 2019 | publisher = [[Parliamentary Union of the OIC Member States]] | archive-url = https://archive.today/20191022180105/http://en.puic.org/news/10181 | archive-date = 22 October 2019 | url-status = live | access-date = 22 October 2019 }}</ref> President Keïta declared that "no military coup will prevail in Mali", continuing by saying that he does not think it "is on the agenda at all and cannot worry us".<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2019/10/07/world/mali-president-dismisses-coup-speculation-jihadi-attacks-kill-dozens-troops-near-burkina-faso-border/#.Xa8-j5IzbIU |title=Mali president dismisses coup speculation after jihadi attacks kill dozens of troops near Burkina Faso border |date=7 October 2019 |website=[[Japantimes.co.jp]] |archive-url=https://archive.today/20191022175954/https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2019/10/07/world/mali-president-dismisses-coup-speculation-jihadi-attacks-kill-dozens-troops-near-burkina-faso-border/%23.Xa9DXtLLfK5#.Xa8-j5IzbIU |archive-date=22 October 2019 |url-status=live |access-date=22 October 2019 }}</ref> On 1 November 2019, the [[Islamic State in the Greater Sahara|IS-GS]] militants killed at least 50 soldiers in the [[2019 Indelimane attack]] in the [[Ménaka Region]] of Mali.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nbcnews.com/news/world/militants-kill-54-attack-mali-army-post-claims-responsibility-n1075721|title=Militants kill 54 in attack on Mali army post, ISIS claims responsibility|website=[[NBC News]]|date=3 November 2019 |accessdate=12 December 2019}}</ref> In February 2020, Human Rights Watch documented atrocities against civilians in Central Mali and said that at least 456 civilians were killed, while hundreds were injured from January 2019 until November.<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://www.hrw.org/report/2020/02/10/how-much-more-blood-must-be-spilled/atrocities-against-civilians-central-mali|title=How Much More Blood Must Be Spilled?|website=HRW|date=10 February 2020|access-date=31 May 2023|archive-date=31 May 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230531102933/https://www.hrw.org/report/2020/02/10/how-much-more-blood-must-be-spilled/atrocities-against-civilians-central-mali |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
===2020s coups and Assimi Goïta junta=== |
|||
{{Main|2020 Malian coup d'état|2021 Malian coup d'état}} |
|||
{{Seealso|List of terrorist attacks in Mali}} |
|||
[[File:Comité national pour le salut du Peuple - 2020 Malian coup d'Etat 2.jpg|thumb|Members of the [[National Committee for the Salvation of the People]], September 2020]] |
|||
Popular unrest began on 5 June 2020 following irregularities in the March and April parliamentary elections, including outrage against the kidnapping of opposition leader [[Soumaïla Cissé]].<ref>{{cite news|website=ABC News|date=5 June 2020|access-date=21 August 2020|agency=Associated Press|first=Baba |last=Ahmed |title=Thousands in Mali's capital demand that president step down |url=https://abcnews.go.com/International/wireStory/thousands-malis-capital-demand-president-step-71093627 |archive-date=13 September 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200913072323/https://abcnews.go.com/International/wireStory/thousands-malis-capital-demand-president-step-71093627|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|date=6 October 2020|title=Kidnapped Mali politician and French aid worker freed |url=http://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/oct/06/kidnapped-mali-politician-and-french-aid-worker-freed |access-date=30 May 2021|website=the Guardian |archive-date=3 June 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210603113914/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/oct/06/kidnapped-mali-politician-and-french-aid-worker-freed|url-status=live}}</ref> Between 11 and 23 deaths followed protests that took place from 10 to 13 June.<ref name="cnews" /> In July, President Keïta dissolved the constitutional court. |
|||
Members of the military led by Colonel [[Assimi Goïta]] and Colonel-Major [[Ismaël Wagué]] in [[Kati, Mali|Kati]], [[Koulikoro Region]], began a mutiny on 18 August 2020.<ref name=cnews>{{cite web|url=https://www.cnews.fr/monde/2020-08-19/tout-comprendre-sur-la-situation-au-mali-990104|title=TOUT COMPRENDRE SUR LA SITUATION AU MALI|date=19 August 2020|access-date=21 August 2020|language=fr|trans-title=Understanding everything about the situation in Mali |website=CNews |archive-date=26 August 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200826193119/https://www.cnews.fr/monde/2020-08-19/tout-comprendre-sur-la-situation-au-mali-990104|url-status=live}}</ref> President Ibrahim Boubacar Keïta and Prime Minister [[Boubou Cissé]] were arrested, and shortly after midnight Keïta announced his resignation, saying he did not want to see any bloodshed.<ref name=cnews /> Wagué announced the formation of the [[National Committee for the Salvation of the People]] (CNSP) and promised elections in the future. A curfew was begun and the streets of Bamako were quiet.<ref name=cnews /> The [[Economic Community of West African States]] (ECOWAS) condemned the coup and demanded that Keïta be reinstated as president.<ref name="neighbours">{{cite web |website=BBC |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-53848223|date=21 August 2020|access-date=21 August 2020|title=Mali's coup is cheered at home but upsets neighbours |archive-date=21 August 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200821112314/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-53848223|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
On 12 September 2020, the CNSP agreed to an 18-month political transition to civilian rule. Shortly after, [[Bah Ndaw|Bah N'daw]] was named interim president by a group of 17 electors, with Goïta being appointed vice president. The government was inaugurated on 25 September 2020. On 18 January 2021, the transitional government announced that the CNSP had been disbanded, almost four months after had been promised under the initial agreement.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Mali: President Bah N'Daw decrees the dissolution of the CNSP |url=https://www.theafricareport.com/62102/mali-president-bah-ndaw-decrees-the-dissolution-of-the-cnsp/ |access-date=2023-09-16 |website=The Africa Report.com |language=en |archive-date=26 May 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210526041635/https://www.theafricareport.com/62102/mali-president-bah-ndaw-decrees-the-dissolution-of-the-cnsp/ |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Tensions between the civilian transitional government and the military ran high after the handover of power in September 2020. The tensions came to a head on 24 May 2021 after a cabinet reshuffle, where two leaders of the 2020 military coup – [[Sadio Camara]] and [[Modibo Kone]] – were replaced by N'daw's administration.<ref>{{cite web|date=25 May 2021|title=EU condemns 'grave and serious' kidnapping of Mali's leaders|url=http://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/may/24/mali-president-prime-minister-and-defence-minister-arrested-sources-say|access-date=25 May 2021|website=the Guardian |archive-date=25 May 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210525203413/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/may/24/mali-president-prime-minister-and-defence-minister-arrested-sources-say|url-status=live}}</ref> Later that day, journalists reported that three key civilian leaders – President N'daw, Prime Minister [[Moctar Ouane]] and Defence Minister [[Souleymane Doucouré]], were being detained in a military base in [[Kati, Mali|Kati]], outside Bamako.<ref>{{cite web|title=Mali's military detains president, prime minister|url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2021/5/24/military-arrest-malis-president-pm-following-govt-reshuffle|access-date=25 May 2021|website=AlJazeera.com |archive-date=25 May 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210525105349/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2021/5/24/military-arrest-malis-president-pm-following-govt-reshuffle|url-status=live}}</ref> On 7 June 2021, Mali's military commander Assimi Goïta was sworn into office as the new interim president.<ref>{{cite news |title=Mali's military leader Goita sworn in as transitional president |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2021/6/7/assimi-goita-mali-military-leader-sworn-in-as-interim-president |website=AlJazeera.com |access-date=6 April 2022 |archive-date=25 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230525194705/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2021/6/7/assimi-goita-mali-military-leader-sworn-in-as-interim-president |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:MaliWar.svg|thumb|Military situation in Mali. For a detailed map, see [[Template:Mali War detailed map|here]].]] |
|||
In 2022 and 2023, the [[Islamic State in the Greater Sahara]] saw major gains in the [[Mali War]], occupying large swathes of territory in southeastern Mali. [[Ansongo]] and [[Tidermène]] were also captured by the group.<ref name=bbc_africatoday>{{citation | url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/p0fgbb9g | publisher=BBC | year=2023 | language=English | title=BBC Africa Today: Islamic State Sahel Province fighters seize commune in Mali | access-date=31 May 2023 | archive-date=11 May 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230511065705/https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/p0fgbb9g | url-status=live}}</ref> By mid-2023, the militant group had doubled the amount of territory it controlled since the overthrow of the previous government and establishment of the junta.<ref name=npr>{{citation | url=https://www.npr.org/2023/08/26/1196189708/islamic-state-mali-al-qaida-west-africa-extremist | publisher=NPR | year=2023 | language=English | title=NPR: Islamic State group almost doubled its territory in Mali in under a year, U.N. says | access-date=27 August 2023 | archive-date=27 August 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230827063702/https://www.npr.org/2023/08/26/1196189708/islamic-state-mali-al-qaida-west-africa-extremist | url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
On 10 January 2022, Mali announced the closure of its borders and recalled several ambassadors to ECOWAS countries in response to sanctions placed on Mali for deferring elections for four years.<ref>{{cite web|last=Ahmed |first=Baba |date=10 January 2022|title=Mali's junta deplores new sanctions imposed by regional bloc|url=https://www.sfgate.com/news/article/Mali-s-junta-deplores-new-sanctions-imposed-by-16763433.php|access-date=10 January 2022|website=SFGate |archive-date=10 January 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220110161440/https://www.sfgate.com/news/article/Mali-s-junta-deplores-new-sanctions-imposed-by-16763433.php|url-status=live}}</ref> On 4 February, France's ambassador was expelled.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/2/5/thousands-in-mali-celebrate-expulsion-of-french-ambassador |title=Thousands in Mali celebrate expulsion of French ambassador | Armed Groups News |publisher=Al Jazeera |date=5 February 2022 |access-date=13 February 2022 |archive-date=7 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220207034714/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/2/5/thousands-in-mali-celebrate-expulsion-of-french-ambassador |url-status=live}}</ref> According to [[Human Rights Watch]], Malian troops and suspected Russian mercenaries from the [[Wagner Group]] executed around 300 civilian men in central Mali in March 2022. France had started withdrawing French troops from Mali in February 2022, commencing the end of [[Operation Barkhane]].<ref>{{cite news |title=Mali troops and suspected Russian fighters accused of massacre |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-60997602 |work=BBC News |date=5 April 2022 |access-date=6 April 2022 |archive-date=6 April 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220406192814/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-60997602 |url-status=live}}</ref> On 2 May, the military government announced breaking its defence accords concluded in 2013 with France, constituting an additional step in the deterioration of Malian–French relations.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Mali: Military government breaks defence accords with France |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/5/3/malis-junta-breaks-off-from-defence-accords-with-france |access-date=10 May 2022 |website=AlJazeera.com |archive-date=9 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220509235754/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/5/3/malis-junta-breaks-off-from-defence-accords-with-france |url-status=live}}</ref> This latest announcement has been criticized by French authorities and considered as "illegitimate".<ref>{{Cite web |date=9 May 2022 |title=Mali: France opposed to Assimi Goïta's junta demanding an end to defence agreements |url=https://www.theafricareport.com/201855/mali-france-opposed-to-assimi-goitas-junta-demanding-an-end-to-defence-agreements/ |access-date=10 May 2022 |website=The Africa Report.com |archive-date=9 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220509155505/https://www.theafricareport.com/201855/mali-france-opposed-to-assimi-goitas-junta-demanding-an-end-to-defence-agreements/ |url-status=live}}</ref> A UN panel reported that in the first three months of 2022, 543 civilians were killed and 269 wounded, warning the 2015 peace agreement between the government and pro-independence groups was threatened by a potential risk of confrontation for the first time in five years. The report also noted a sharp increase in the number of people needing humanitarian assistance over the previous year.<ref>{{Cite web |date=5 August 2022 |title=UN experts: Malian military and 'white' soldiers killed 33 |url=https://news.yahoo.com/un-experts-malian-military-white-015227805.html |access-date=6 August 2022 |website=Yahoo News |archive-date=6 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220806021317/https://news.yahoo.com/un-experts-malian-military-white-015227805.html |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
[[Sergey Lavrov]], the Russian foreign minister, visited Bamako on 7 February 2023 and said that Moscow would continue to help Mali improve its military capabilities.<ref>{{Cite web |date=8 February 2023 |title=Russian Foreign Minister visits Mali in sign of deepening ties |url=https://www.euronews.com/2023/02/08/russian-foreign-minister-sergei-lavrov-visits-mali-in-sign-of-deepening-ties |access-date=9 February 2023 |website=EuroNews |archive-date=8 February 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230208210854/http://www.euronews.com/2023/02/08/russian-foreign-minister-sergei-lavrov-visits-mali-in-sign-of-deepening-ties |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
In June 2023, Mali removed French, the language of its former colonizer, as an official language with the approval of a new constitution by 97% of voters in [[2023 Malian constitutional referendum|a referendum]] conducted by the junta.<ref>{{Cite news |date=4 August 2023 |title=Mali demotes French, language of its former colonizer, in symbolic move |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2023/08/03/mali-french-new-constitution/ |access-date=9 February 2023 |newspaper=Washington Post |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803234614/https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2023/08/03/mali-french-new-constitution/ |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
On 7 September 2023, al-Qaeda linked [[Jama'at Nasr al-Islam wal-Muslimin|JNIM]] militants [[Tombouctou and Bamba attacks|attacked]] a vessel on the [[Niger River]], killing at least 154 civilians.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-11-01 |title=Mali : Les groupes islamistes armés et l'armée prennent les civils pour cible |url=https://www.hrw.org/fr/news/2023/11/01/mali-les-groupes-islamistes-armes-et-larmee-prennent-les-civils-pour-cible |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231214185052/https://www.hrw.org/fr/news/2023/11/01/mali-les-groupes-islamistes-armes-et-larmee-prennent-les-civils-pour-cible |archive-date=14 December 2023 |access-date=2024-01-01 |publisher=[[Human Rights Watch]] |language=fr}}</ref> |
|||
In July 2024, [[Strategic Framework for the Defense of the People of Azawad|CSP-DPA]] rebels and JNIM militants killed dozens of Russian mercenaries and Malian government forces during the [[Battle of Tinzaouaten (2024)|Battle of Tinzaouaten]].<ref>{{Cite web |author1=Darya Tarasova |author2=Tim Lister |author3=Avery Schmitz |date=2024-07-29 |title=Dozens of Russian mercenaries killed in rebel ambush in Mali, in their worst known loss in Africa |url=https://www.cnn.com/2024/07/29/africa/russian-mercenaries-wagner-killed-mali-intl-latam/index.html |access-date=2024-07-30 |website=CNN |language=en}}</ref> On 5 August 2024 the Republic of Mali announced that it was severing diplomatic relations with [[Ukraine]].<ref>{{cite news|url=https://newsukraine.rbc.ua/news/mali-announces-severance-of-diplomatic-relations-1722838542.html|title=Mali announces severance of diplomatic relations with Ukraine|publisher=[[RBC-Ukraine|РБК]]|date=5 August 2024|accessdate=5 August 2024|archive-date=5 August 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240805181211/https://newsukraine.rbc.ua/news/mali-announces-severance-of-diplomatic-relations-1722838542.html}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Was Ukraine's role in big Wagner defeat an own goal in Africa? |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c78ld18lgr9o |work=BBC News |date=12 August 2024}}</ref> |
|||
On 17 September 2024, al-Qaeda linked JNIM militants [[2024 Bamako attacks|attacked several locations]] across [[Bamako]], killing at least 77 people and injuring 255 others.<ref>{{Cite web |date=September 17, 2024 |title=Attack by al-Qaeda linked group in Mali killed more than 70 people |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/9/20/attack-by-al-qaeda-linked-group-in-mali-killed-more-than-70-people |access-date=September 20, 2024 |publisher=[[Al Jazeera English]] |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
{{Main|Geography of Mali}} |
|||
[[File:Mali sat.png|Satellite image of Mali|thumb]] |
[[File:Mali sat.png|Satellite image of Mali|thumb]] |
||
[[File:Mali map of Köppen climate classification.svg|thumb|Mali map of Köppen climate classification]] |
|||
Mali is a landlocked country in West Africa, located southwest of [[Algeria]]. It lies between latitudes [[10th parallel north|10°]] and [[25th parallel north|25°N]], and longitudes [[13th meridian west|13°W]] and [[5th meridian east|5°E]]. Mali borders Algeria to [[Algeria–Mali border|the north-northeast]], [[Niger]] to [[Mali–Niger border|the east]], [[Burkina Faso]] to [[Burkina Faso–Mali border|the south-east]], [[Ivory Coast]] to [[Ivory Coast–Mali border|the south]], [[Guinea]] to [[Guinea–Mali border|the south-west]], and [[Senegal]] to [[Mali–Senegal border|the west]] and [[Mauritania]] to [[Mali–Mauritania border|the north-west]].<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Griffiths|first=Ieuan|date=July 1986|title=The Scramble for Africa: Inherited Political Boundaries|journal=The Geographical Journal|volume=152|issue=2|pages=204–216|doi=10.2307/634762|jstor=634762|bibcode=1986GeogJ.152..204G |issn=0016-7398}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Hand der Fatima.jpg|left|Landscape in [[Hombori]]|thumb]] |
[[File:Hand der Fatima.jpg|left|Landscape in [[Hombori]]|thumb]] |
||
[[File:Koppen-Geiger Map MLI present.svg|thumb|Mali map of Köppen climate classification]] |
|||
{{Main|Geography of Mali}} |
|||
Mali is a landlocked country in West Africa, located southwest of [[Algeria]]. It lies between latitudes [[10th parallel north|10°]] and [[25th parallel north|25°N]], and longitudes [[13th meridian west|13°W]] and [[5th meridian east|5°E]]. Mali borders [[Algeria]] to the north-northeast, [[Niger]] to the east, [[Burkina Faso]] and [[Ivory Coast]] to the south, [[Guinea]] to the southwest, and [[Senegal]] and [[Mauritania]] to the west. |
|||
At {{convert| |
At {{convert|1240192|km2|sqmi|0|sigfig=3}},<ref name="CIA-2021-Mali"/> Mali is the [[List of countries and outlying territories by total area|24th-largest country]] in the world and the [[List of African countries by area|eighth-largest country in Africa]].<ref>{{cite web |title=List of African countries by area |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/list-of-African-countries-by-area |website=www.britannica.com |language=en |date=27 September 2024}}</ref> It is comparable in size to South Africa or [[Angola]]. Most of the country lies in the southern [[Sahara Desert]], which produces an extremely hot, dust-laden [[Sudan (region)|Sudanian savanna]] zone.<ref name=geography>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 5.</ref> Mali is mostly flat, rising to rolling northern plains covered by [[sand]]. The [[Adrar des Ifoghas]] massif lies in the northeast. |
||
Mali lies in the [[Geographical zone#Torrid Zone|torrid zone]] and is among the hottest countries in the world. The [[thermal equator]], which matches the hottest spots year-round on the planet based on the mean daily annual temperature, crosses the country.<ref name=geography/> Most of Mali receives negligible rainfall and droughts are very frequent.<ref name=geography/> Late |
Mali lies in the [[Geographical zone#Torrid Zone|torrid zone]] and is among the hottest countries in the world. The [[thermal equator]], which matches the hottest spots year-round on the planet based on the mean daily annual temperature, crosses the country.<ref name=geography/> Most of Mali receives negligible rainfall and droughts are very frequent.<ref name=geography/> Late April to early October is the rainy season in the southernmost area. During this time, flooding of the Niger River is common, creating the [[Inner Niger Delta]].<ref name=geography/> The vast northern desert part of Mali has a [[hot desert climate]] ([[Köppen climate classification]] ''BWh'') with long, extremely hot summers and scarce rainfall which decreases northwards. The central area has a [[hot semi-arid climate]] (Köppen climate classification ''BSh'') with very high temperatures year-round, a long, intense dry season and a brief, irregular rainy season. The southern areas have a [[tropical wet and dry climate]]. (Köppen climate classification ''Aw'') In review, Mali's climate is tropical, with March to May being the hot, dry season. June to October is rainy, humid and mild. November to February is the cool, dry season. |
||
Mali has considerable natural resources, with gold, uranium, [[phosphates]], [[kaolinite]], salt and [[limestone]] being most widely exploited. Mali is estimated to have in excess of 17,400 tonnes of uranium (measured + indicated + inferred).<ref>[http://www.wise-uranium.org/uoafr.html#ML Uranium Mine Ownership – Africa]. Wise-uranium.org. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref><ref>Muller, CJ and Umpire, A (22 November 2012) [http://www.sedar.com/GetFile.do?lang=EN&docClass=24&issuerNo=00022459&fileName=/csfsprod/data138/filings/02005552/00000001/y%3A\Web_Documents\RADAR\E3\RCGQ\14JA13046\121122TR_Falea_cn.pdf An Independent Technical Report on the Mineral Resources of Falea Uranium, Copper and Silver Deposit, Mali, West Africa]. Minxcon.</ref> In 2012, a further uranium mineralized north zone was identified.<ref>[http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/Country-Profiles/Others/Uranium-in-Africa/ Uranium in Africa]. World-nuclear.org. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> Mali faces numerous environmental challenges, including [[desertification]], [[deforestation]], [[soil erosion]], and inadequate [[Water supply|supplies]] of [[potable water]].<ref name=geography/> |
Mali has considerable natural resources, with gold, uranium, [[phosphates]], [[kaolinite]], salt and [[limestone]] being most widely exploited. Mali is estimated to have in excess of 17,400 tonnes of uranium (measured + indicated + inferred).<ref>[http://www.wise-uranium.org/uoafr.html#ML Uranium Mine Ownership – Africa] {{Webarchive|url=https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20200415020226/http://www.wise%2Duranium.org/uoafr.html#ML |date=15 April 2020 }}. Wise-uranium.org. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref><ref>Muller, CJ and Umpire, A (22 November 2012) [http://www.sedar.com/GetFile.do?lang=EN&docClass=24&issuerNo=00022459&fileName=/csfsprod/data138/filings/02005552/00000001/y%3A\Web_Documents\RADAR\E3\RCGQ\14JA13046\121122TR_Falea_cn.pdf An Independent Technical Report on the Mineral Resources of Falea Uranium, Copper and Silver Deposit, Mali, West Africa] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210824024212/https://www.sedar.com/GetFile.do?lang=EN&docClass=24&issuerNo=00022459&fileName=%2Fcsfsprod%2Fdata138%2Ffilings%2F02005552%2F00000001%2Fy%3A%5CWeb_Documents%5CRADAR%5CE3%5CRCGQ%5C14JA13046%5C121122TR_Falea_cn.pdf |date=24 August 2021 }}. Minxcon.</ref> In 2012, a further uranium mineralized north zone was identified.<ref>[http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/Country-Profiles/Others/Uranium-in-Africa/ Uranium in Africa] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140417025834/http://world-nuclear.org/info/Country-Profiles/Others/Uranium-in-Africa/ |date=17 April 2014 }}. World-nuclear.org. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> Mali faces numerous environmental challenges, including [[desertification]], [[deforestation]], [[soil erosion]], and inadequate [[Water supply|supplies]] of [[potable water]].<ref name=geography/> |
||
===Biodiversity=== |
|||
{{See also|Wildlife of Mali}} |
|||
Five terrestrial ecoregions lie within Mali's borders: [[Sahelian Acacia savanna]], [[West Sudanian savanna]], [[Inner Niger Delta flooded savanna]], [[South Saharan steppe and woodlands]], and [[West Saharan montane xeric woodlands]].<ref name="DinersteinOlson2017">{{cite journal|last1=Dinerstein|first1=Eric|last2=Olson|first2=David|last3=Joshi|first3=Anup|last4=Vynne|first4=Carly|last5=Burgess|first5=Neil D.|last6=Wikramanayake|first6=Eric|last7=Hahn|first7=Nathan|last8=Palminteri|first8=Suzanne|last9=Hedao|first9=Prashant|last10=Noss|first10=Reed|last11=Hansen|first11=Matt|last12=Locke|first12=Harvey|last13=Ellis|first13=Erle C|last14=Jones|first14=Benjamin|last15=Barber|first15=Charles Victor|last16=Hayes|first16=Randy|last17=Kormos|first17=Cyril|last18=Martin|first18=Vance|last19=Crist|first19=Eileen|last20=Sechrest|first20=Wes|last21=Price|first21=Lori|last22=Baillie|first22=Jonathan E. M.|last23=Weeden|first23=Don|last24=Suckling|first24=Kierán|last25=Davis|first25=Crystal|last26=Sizer|first26=Nigel|last27=Moore|first27=Rebecca|last28=Thau|first28=David|last29=Birch|first29=Tanya|last30=Potapov|first30=Peter|last31=Turubanova|first31=Svetlana|last32=Tyukavina|first32=Alexandra|last33=de Souza|first33=Nadia|last34=Pintea|first34=Lilian|last35=Brito|first35=José C.|last36=Llewellyn|first36=Othman A.|last37=Miller|first37=Anthony G.|last38=Patzelt|first38=Annette|last39=Ghazanfar|first39=Shahina A.|last40=Timberlake|first40=Jonathan|last41=Klöser|first41=Heinz|last42=Shennan-Farpón|first42=Yara|last43=Kindt|first43=Roeland|last44=Lillesø|first44=Jens-Peter Barnekow|last45=van Breugel|first45=Paulo|last46=Graudal|first46=Lars|last47=Voge|first47=Maianna|last48=Al-Shammari|first48=Khalaf F.|last49=Saleem|first49=Muhammad|display-authors=1|title=An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm|journal=BioScience|volume=67|issue=6|year=2017|pages=534–545|issn=0006-3568|doi=10.1093/biosci/bix014|pmid=28608869|pmc=5451287|doi-access=free}}</ref> The country had a 2019 [[Forest Landscape Integrity Index]] mean score of 7.16/10, ranking it 51st globally out of 172 countries.<ref name="FLII-Supplementary">{{cite journal|last1=Grantham|first1=H. S.|last2=Duncan|first2=A.|last3=Evans|first3=T. D.|last4=Jones|first4=K. R.|last5=Beyer|first5=H. L.|last6=Schuster|first6=R.|last7=Walston|first7=J.|last8=Ray|first8=J. C.|last9=Robinson|first9=J. G.|last10=Callow|first10=M.|last11=Clements|first11=T.|last12=Costa|first12=H. M.|last13=DeGemmis|first13=A.|last14=Elsen|first14=P. R.|last15=Ervin|first15=J.|last16=Franco|first16=P.|last17=Goldman|first17=E.|last18=Goetz|first18=S.|last19=Hansen|first19=A.|last20=Hofsvang|first20=E.|last21=Jantz|first21=P.|last22=Jupiter|first22=S.|last23=Kang|first23=A.|last24=Langhammer|first24=P.|last25=Laurance|first25=W. F.|last26=Lieberman|first26=S.|last27=Linkie|first27=M.|last28=Malhi|first28=Y.|last29=Maxwell|first29=S.|last30=Mendez|first30=M.|last31=Mittermeier|first31=R.|last32=Murray|first32=N. J.|last33=Possingham|first33=H.|last34=Radachowsky|first34=J.|last35=Saatchi|first35=S.|last36=Samper|first36=C.|last37=Silverman|first37=J.|last38=Shapiro|first38=A.|last39=Strassburg|first39=B.|last40=Stevens|first40=T.|last41=Stokes|first41=E.|last42=Taylor|first42=R.|last43=Tear|first43=T.|last44=Tizard|first44=R.|last45=Venter|first45=O.|last46=Visconti|first46=P.|last47=Wang|first47=S.|last48=Watson|first48=J. E. M.|display-authors=1|title=Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material|journal=Nature Communications|volume=11|issue=1|year=2020|page=5978|issn=2041-1723|doi=10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3|pmid=33293507|pmc=7723057|bibcode=2020NatCo..11.5978G |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
{{clear right}} |
{{clear right}} |
||
==Politics and government== |
|||
{{main|Politics of Mali}} |
|||
===Government=== |
|||
[[File:Assimi Goita, August 2021.png|thumb|[[Assimi Goita]], interim president of Mali since [[2021 Malian coup d'état]]]] |
|||
Until the military coup of 22 March 2012,<ref name="telegraph.co.uk"/><ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20120323134828/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/africaandindianocean/mali/9161659/US-condemns-Mali-coup-amid-reports-of-looting.html Video: US condemns Mali coup amid reports of looting]. Telegraph (22 March 2012). Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> Mali was a [[constitutional democracy]] governed by the Constitution of 12 January 1992, which was amended in 1999.<ref name=p14/> The constitution provides for a separation of powers among the executive, [[legislative]], and [[judicial]] branches of government.<ref name=p14>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 14.</ref> The system of government can be described as "[[semi-presidential]]".<ref name=p14/> Executive power is vested in a president, who is elected to a five-year term by [[universal suffrage]] and is limited to two terms.<ref name=p14/><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 30.</ref> |
|||
The president serves as a [[chief of state]] and [[commander in chief]] of the armed forces.<ref name="p14" /><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 29 & 46.</ref> A prime minister appointed by the president serves as head of government and in turn appoints the Council of Ministers.<ref name="p14" /><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 38.</ref> The unicameral [[National Assembly (Mali)|National Assembly]] is Mali's sole legislative body, consisting of deputies elected to five-year terms.<ref name="p15">[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 15.</ref><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 59 & 61.</ref> Following the 2007 elections, the [[Alliance for Democracy and Progress (Mali)|Alliance for Democracy and Progress]] held 113 of 160 seats in the assembly.<ref>{{in lang|fr}} Koné, Denis. [http://fr.allafrica.com/stories/200708131307.html Mali: "Résultats définitifs des Législatives"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121229150933/http://fr.allafrica.com/stories/200708131307.html |date=29 December 2012 }}. ''[[Les Échos (Mali)|Les Echos]]'' ([[Bamako]]) (13 August 2007). Retrieved 24 June 2008.</ref> The assembly holds two regular sessions each year, during which it debates and votes on legislation that has been submitted by a member or by the government.<ref name=p15/><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 65.</ref> |
|||
Mali's constitution provides for an independent judiciary,<ref name="p15" /><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 81.</ref> but the executive continues to exercise influence over the judiciary by virtue of power to appoint judges and oversee both judicial functions and law enforcement.<ref name="p15" /> Mali's highest courts are the Supreme Court, which has both judicial and administrative powers, and a separate Constitutional Court that provides judicial review of legislative acts and serves as an election arbiter.<ref name="p15" /><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 83–94.</ref> Various lower courts exist, though village chiefs and elders resolve most local disputes in rural areas.<ref name="p15" /> |
|||
The transition government pushed back the timetable for a new election, initially to be held in February 2022, to February 2024.<ref name="New Election">{{cite web |title=Mali's transition govt sets February 2024 for presidential election |url=https://www.africanews.com/2022/07/01/malis-transition-govt-sets-february-2024-for-presidential-election// |website=AfricaNews |access-date=18 August 2023 |date=1 July 2022 |archive-date=18 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230818190836/https://www.africanews.com/2022/07/01/malis-transition-govt-sets-february-2024-for-presidential-election// |url-status=live }}</ref> In exchange for the government's commitment to a 2024 election, [[Economic Community of West African States|ECOWAS]] agreed to lift sanctions on the country.<ref name="ECOWAS sanctions lifted">{{cite web |last1=Melly |first1=Paul |title=Mali coup: How junta got Ecowas economic sanctions lifted |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-62037317 |website=BBC |access-date=18 August 2023 |date=6 July 2022 |archive-date=5 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230805123950/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-62037317 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
=== Foreign relations === |
|||
{{Main|Foreign relations of Mali|France–Mali relations}} |
|||
[[File:Rutte and Touré.jpg|thumb|Former President of Mali [[Amadou Toumani Touré]] and Minister-president of the Netherlands [[Mark Rutte]]]] |
|||
[[File:Malick Diaw and Vyacheslav Volodin (2023-03-19).jpg|thumb|Representatives of Mali and [[Russia]] at the 2nd International Parliamentary Conference “Russia-Africa” in Moscow, 19 March 2023]] |
|||
Until 2012, Mali's foreign policy orientation had become increasingly pragmatic and pro-Western over time.<ref name=p17>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 17.</ref> Since the institution of a democratic form of government in 2002, Mali's relations with the West in general and [[Mali-United States relations|with the United States]] in particular have improved significantly.<ref name=p17/> Mali has a longstanding yet ambivalent relationship with France, a [[French Sudan|former colonial ruler]].<ref name=p17/> Mali was active in regional organizations such as the [[African Union]] until its suspension over the [[2012 Malian coup d'état]].<ref name="p17" /><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.aljazeera.com/news/africa/2012/03/2012323134643629717.html|title=ion suspends Mali over coup|date=23 March 2012|access-date=23 March 2012|publisher=Al Jazeera|archive-date=25 March 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120325235036/http://www.aljazeera.com/news/africa/2012/03/2012323134643629717.html|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Working to control and resolve regional conflicts, such as in [[Ivory Coast]], [[Liberia]], and [[Sierra Leone]], is one of Mali's major foreign policy goals.<ref name="p17" /> Mali feels threatened by the potential for the spillover of conflicts in neighboring states, and relations with those neighbors are often uneasy.<ref name=p17/> General insecurity along borders in the north, including cross-border [[banditry]] and terrorism, remain troubling issues in regional relations.<ref name="p17" /> |
|||
In early 2019, [[Al Qaeda]] claimed responsibility for an attack on a [[United Nations]] base in Mali that killed 10 peacekeepers from [[Chad]]. 25 people were reported to have been injured in the attack. Al Qaeda's stated reason for the attack was Chad's re-establishing diplomatic ties with Israel. The base was attacked in [[Anguelhok]], a village located in an especially unstable region of the country.<ref name=p17/><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2019/01/20/world/africa/united-nations-peacekeepers-killed-mali.html |title=Al Qaeda Claims U.N. Peacekeeper Attack That Killed 10 in Mali |date=20 January 2019 |access-date=21 January 2019 |newspaper=NY Times |archive-date=21 January 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190121175200/https://www.nytimes.com/2019/01/20/world/africa/united-nations-peacekeepers-killed-mali.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
=== Military === |
|||
{{Further|Military of Mali}} |
|||
[[Military of Mali|Mali's military forces]] consist of an army, which includes land forces and air force,<ref name=factbook/> as well as the paramilitary Gendarmerie and Republican Guard, all of which are under the control of Mali's Ministry of Defense and Veterans, [[civilian control of the military|headed by a civilian]]. |
|||
===Regions and cercles=== |
===Regions and cercles=== |
||
{{main|Regions of Mali|Cercles of Mali|Communes of Mali}} |
{{main|Regions of Mali|Cercles of Mali|Communes of Mali}} |
||
[[File:Cartes des régions du Mali,depuis 2023.png|alt=A map of former regions of Mali|thumb|Regions of Mali since 2023]] |
|||
{{Regions of Mali Image Map}} |
{{Regions of Mali Image Map}} |
||
Since 2016, Mali has been divided into ten regions and the District of Bamako.<ref>{{cite book | last = Martin | first = Phillip L. | title = Managing Migration: The Promise of Cooperation | publisher=Lexington Books | |
Since 2016, Mali has been divided into ten regions and the District of Bamako.<ref>{{cite book | last = Martin | first = Phillip L. | title = Managing Migration: The Promise of Cooperation | publisher=Lexington Books |date= 2006 | location = Lanham, Maryland | isbn = 978-0-7391-1341-7 |page=134}}</ref> Each region has a governor.<ref name=pictures>[[#DiPiazza|DiPiazza]], p. 37.</ref> The implementation of the two newest regions, Taoudénit (formerly part of Tombouctou Region) and Ménaka (formerly [[Ménaka Cercle]] in Gao Region), has been ongoing since January 2016;<ref>{{cite web |url=https://minusma.unmissions.org/sites/default/files/160328_sg_report_mali_english.pdf |title=Report of the Secretary-General on the situation in Mali |date=28 March 2016 |publisher=[[MINUSMA]] |access-date=21 February 2017 |archive-date=22 February 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222055230/https://minusma.unmissions.org/sites/default/files/160328_sg_report_mali_english.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=malijet>{{cite web |url=http://malijet.com/la_societe_malienne_aujourdhui/144815-regionalisation-deux-nouvelles-regions-creees-au-mali.html |title=Régionalisation: Deux Nouvelles régions créées au Mali |date=21 January 2016 |publisher=Malijet |access-date=21 February 2017 |archive-date=22 February 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222105836/http://malijet.com/la_societe_malienne_aujourdhui/144815-regionalisation-deux-nouvelles-regions-creees-au-mali.html |url-status=live }}</ref> a governor and transitional council has been appointed for both regions.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://minusma.unmissions.org/sites/default/files/sg_report_on_the_situation_in_mali_december_2016.pdf |title=Report of the Secretary-General on the situation in Mali |date=30 December 2016 |publisher=MINUSMA |access-date=21 February 2017 |archive-date=29 January 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170129153531/http://minusma.unmissions.org/sites/default/files/sg_report_on_the_situation_in_mali_december_2016.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
Since 2023, Mali has added nine new regions to its administrative structure, bringing the total to 19 regions plus the district of Bamako. This reorganization aims to improve governance and bring public services closer to local populations. This initiative continues the decentralization efforts that began with the creation of the Taoudénit and Ménaka regions in 2016. The nineteen regions in turn are subdivided into 159 [[Cercle (Mali)|''cercle''s]] and [[Cercle (Mali)|815]] [[Communes of Mali|''communes'']].<ref>{{cite web |date=1999 |title=Loi N°99-035/ Du 10 Aout 1999 Portant Creation des Collectivites Territoriales de Cercles et de Regions |url=http://www.matcl.gov.ml/PDF/LoiCreationCercleReg.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120309073942/http://www.matcl.gov.ml/PDF/LoiCreationCercleReg.pdf |archive-date=9 March 2012 |publisher=Ministère de l'Administration Territoriales et des Collectivités Locales, République du Mali |language=fr}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Djiguiba |first=Issa |date=21 September 2024 |title=Administrative and territorial division: the new administrative map of Mali is operational |url=https://www.ortm.ml/decoupage-administratif-et-territorial-la-nouvelle-carte-administrative-du-mali-operationnelle |access-date=6 November 2024 |website=www.ortm.ml}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Regions of Mali|''régions'']] and Capital District are: |
|||
The [[Regions of Mali|''régions'']] and Capital District are:<ref>{{Cite web |last=Coulibaly |first=Bassidi |date=October 2013 |title=Etats Generaux De La Decentralisation (in French) |url=https://arpdeveloppement.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/A_14_Theme_9_DGAT.pdf |access-date=6 November 2024 |website=arpdeveloppement.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=November 2023 |title=CINQUIEME RECENSEMENT GENERAL DE LA POPULATION ET DE L'HABITAT (in French) |url=https://www.instat-mali.org/laravel-filemanager/files/shares/rgph/rapport-resultats-globaux-rgph5_rgph.pdf |access-date=6 November 2024 |website=www.instat-mali.org}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="sortable wikitable" |
{| class="sortable wikitable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
!No |
|||
! Region name || Area (km<sup>2</sup>) || Population<br />Census 1998 || Population<br />Census 2009 |
|||
! Region name || Area (km<sup>2</sup>) |
|||
!Population<br />Census 2023 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|00 |
|||
| [[Kayes Region|Kayes]]||align="right"|119,743||align="right"|1,374,316||align="right"|1,996,812 |
|||
| [[Bamako Capital District|Bamako<br />Capital District]]|| align="right" |252 |
|||
|4 227 569 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|01 |
|||
| [[Koulikoro Region|Koulikoro]]||align="right"|95,848||align="right"|1,570,507||align="right"|2,418,305 |
|||
| [[Kayes Region|Kayes]]|| align="right" |62,914 |
|||
|1 840 329 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|02 |
|||
| [[Bamako Capital District|Bamako<br />Capital District]]||align="right"|252||align="right"|1,016,296||align="right"|1,809,106 |
|||
| [[Koulikoro Region|Koulikoro]]|| align="right" |71,178 |
|||
|2 255 157 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|03 |
|||
| [[Sikasso Region|Sikasso]]||align="right"|70,280||align="right"|1,782,157||align="right"|2,625,919 |
|||
| [[Sikasso Region|Sikasso]]|| align="right" |21,378 |
|||
|1 533 123 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|04 |
|||
| [[Ségou Region|Ségou]]||align="right"|64,821||align="right"|1,675,357||align="right"|2,336,255 |
|||
| [[Ségou Region|Ségou]]|| align="right" |31,996 |
|||
|2 455 263 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|05 |
|||
| [[Mopti Region|Mopti]]||align="right"|79,017||align="right"|1,484,601||align="right"|2,037,330 |
|||
| [[Mopti Region|Mopti]]|| align="right" |49,077 |
|||
|935 579 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|06 |
|||
| [[Tombouctou Region|Tombouctou<br />(Timbuktu)]]||align="right"|496,611||align="right"|442,619||align="right"|681,691 |
|||
| [[Tombouctou Region|Tombouctou]]|| align="right" |180,781 |
|||
|974 278 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|07 |
|||
| [[Gao Region|Gao]]||align="right"|89,532||align="right"|341,542||align="right"|544,120 |
|||
| [[Gao Region|Gao]]|| align="right" |89,532 |
|||
|727 517 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|08 |
|||
| [[Kidal Region|Kidal]]||align="right"|151,430||align="right"|38,774||align="right"|67,638 |
|||
| [[Kidal Region|Kidal]]|| align="right" |151,430 |
|||
|83 192 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|09 |
|||
| ''[[Taoudénit Region|Taoudénit]]'' ||align="right"| – ||align="right"| – ||align="right"| – |
|||
| [[Taoudénit Region|Taoudénit]] || align="right" | 323,326 |
|||
|100 358 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|10 |
|||
| ''[[Ménaka Region|Ménaka]]'' ||align="right"| 81,040 ||align="right"| – ||align="right"| – |
|||
| [[Ménaka Region|Ménaka]] || align="right" | 81,040 |
|||
|318 876 |
|||
|- |
|||
|11 |
|||
|Bougouni |
|||
| align="right" | 41,052 |
|||
|1 570 979 |
|||
|- |
|||
|12 |
|||
|Dioila |
|||
| align="right" | 12,984 |
|||
|675 965 |
|||
|- |
|||
|13 |
|||
|Nioro |
|||
| align="right" | 24,179 |
|||
|678 061 |
|||
|- |
|||
|14 |
|||
|Koutiala |
|||
| align="right" |14,739 |
|||
|1 169 882 |
|||
|- |
|||
|15 |
|||
|Kita |
|||
| align="right" |44,175 |
|||
|681 671 |
|||
|- |
|||
|16 |
|||
|Nara |
|||
| align="right" |26,213 |
|||
|307 777 |
|||
|- |
|||
|17 |
|||
|Bandiagara |
|||
| align="right" |25,709 |
|||
|868 916 |
|||
|- |
|||
|18 |
|||
|San |
|||
| align="right" |15,516 |
|||
|820 807 |
|||
|- |
|||
|19 |
|||
|Douentza |
|||
| align="right" |63,515 |
|||
|170 189 |
|||
|- |
|||
| colspan="2" |Total |
|||
| align="right" |1,240,192 |
|||
|22 395 489 |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
=== Extent of central government control === |
|||
In March 2012, the Malian government lost control over Tombouctou, Gao and Kidal Regions and the north-eastern portion of Mopti Region. On 6 April 2012, the [[National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad]] unilaterally declared their secession from Mali as [[Azawad]], an act that neither Mali nor the international community [[diplomatic recognition|recognised]].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://english.alarabiya.net/articles/2012/04/06/205763.html|publisher=Al Arabiya|title=Tuareg rebels declare the independence of Azawad, north of Mali|date=6 April 2012|accessdate=6 April 2012}}</ref> The government later regained control over these areas. |
|||
==Politics and government== |
|||
{{main|Politics of Mali}} |
|||
[[File:Dioncounda Traore photo officielle de campagne 3 Mali 2012.jpg|thumb|Ex-Malian Transition President [[Dioncounda Traoré]]]] |
|||
Until the military coup of 22 March 2012<ref name="telegraph.co.uk"/><ref>[https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/africaandindianocean/mali/9161659/US-condemns-Mali-coup-amid-reports-of-looting.html Video: US condemns Mali coup amid reports of looting]. Telegraph (22 March 2012). Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> and a second military coup in December 2012,<ref>Hossiter, Adam (12 December 2012) [https://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/12/world/africa/malis-prime-minister-arrested-by-military.html?_r=0 Mali’s Prime Minister Resigns After Arrest, Muddling Plans to Retake North]. The New York Times</ref> Mali was a [[constitutional democracy]] governed by the Constitution of 12 January 1992, which was amended in 1999.<ref name=p14/> The constitution provides for a separation of powers among the executive, [[legislative]], and [[judicial]] branches of government.<ref name=p14>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 14.</ref> The system of government can be described as "semi-presidential".<ref name=p14/> Executive power is vested in a president, who is elected to a five-year term by [[universal suffrage]] and is limited to two terms.<ref name=p14/><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 30.</ref> |
|||
The president serves as a [[chief of state]] and [[commander in chief]] of the armed forces.<ref name=p14/><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 29 & 46.</ref> A prime minister appointed by the president serves as head of government and in turn appoints the Council of Ministers.<ref name=p14/><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 38.</ref> The unicameral National Assembly is Mali's sole legislative body, consisting of deputies elected to five-year terms.<ref name=p15>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 15.</ref><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 59 & 61.</ref> Following the 2007 elections, the [[Alliance for Democracy and Progress (Mali)|Alliance for Democracy and Progress]] held 113 of 160 seats in the assembly.<ref>{{fr icon}} Koné, Denis. [http://fr.allafrica.com/stories/200708131307.html Mali: "Résultats définitifs des Législatives"]. ''[[Les Échos (Mali)|Les Echos]]'' ([[Bamako]]) (13 August 2007). Retrieved 24 June 2008.</ref> The assembly holds two regular sessions each year, during which it debates and votes on legislation that has been submitted by a member or by the government.<ref name=p15/><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 65.</ref> |
|||
Mali's constitution provides for an independent judiciary,<ref name=p15/><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 81.</ref> but the executive continues to exercise influence over the judiciary by virtue of power to appoint judges and oversee both judicial functions and law enforcement.<ref name=p15/> Mali's highest courts are the Supreme Court, which has both judicial and administrative powers, and a separate Constitutional Court that provides judicial review of legislative acts and serves as an election arbiter.<ref name=p15/><ref>[[#Const|Constitution of Mali]], Art. 83–94.</ref> Various lower courts exist, though village chiefs and elders resolve most local disputes in rural areas.<ref name=p15/> |
|||
=== Foreign relations === |
|||
{{Main|Foreign relations of Mali}} |
|||
[[File:Rutte and Touré.jpg|Former President of Mali [[Amadou Toumani Touré]] and Minister-president of the Netherlands [[Mark Rutte]]|thumb]] |
|||
Mali's foreign policy orientation has become increasingly pragmatic and pro-Western over time.<ref name=p17>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 17.</ref> Since the institution of a democratic form of government in 2002, Mali's relations with the West in general and [[Mali-United States relations|with the United States]] in particular have improved significantly.<ref name=p17/> Mali has a longstanding yet ambivalent relationship with France, a [[French Sudan|former colonial ruler]].<ref name=p17/> Mali was active in regional organizations such as the [[African Union]] until its suspension over the [[2012 Malian coup d'état]].<ref name=p17/><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.aljazeera.com/news/africa/2012/03/2012323134643629717.html|title=ion suspends Mali over coup|date=23 March 2012|accessdate=23 March 2012|publisher=Al Jazeera}}</ref> |
|||
Working to control and resolve regional conflicts, such as in [[Ivory Coast]], [[Liberia]], and [[Sierra Leone]], is one of Mali's major foreign policy goals.<ref name=p17/> Mali feels threatened by the potential for the spillover of conflicts in neighboring states, and relations with those neighbors are often uneasy.<ref name=p17/> General insecurity along borders in the north, including cross-border [[banditry]] and terrorism, remain troubling issues in regional relations.<ref name=p17/> |
|||
In early 2019, [[Al Qaeda]] claimed responsibility for an attack on a [[United Nations]] base in Mali that killed 10 peacekeepers from [[Chad]]. 25 people were reported to have been injured in the attack. Al Qaeda's stated reason for the attack was Chad's re-establishing diplomatic ties with [[Israel]]. The base was attacked in [[Anguelhok]], a village located in an especially unstable region of the country.<ref name=p17/><ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2019/01/20/world/africa/united-nations-peacekeepers-killed-mali.html| title=Al Qaeda Claims U.N. Peacekeeper Attack That Killed 10 in Mali |date=20 January 2019|accessdate=21 January 2019|publisher=NY Times}}</ref> |
|||
=== Military === |
|||
{{Further|Military of Mali}} |
|||
[[Military of Mali|Mali's military forces]] consist of an army, which includes land forces and air force,<ref name=factbook/> as well as the paramilitary Gendarmerie and Republican Guard, all of which are under the control of Mali's Ministry of Defense and Veterans, [[civilian control of the military|headed by a civilian]].<ref name=ns>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 18.</ref> The military is underpaid, poorly equipped, and in need of rationalization.<ref name=ns/> |
|||
==Economy== |
==Economy== |
||
{{main|Economy of Mali}} |
{{main|Economy of Mali}} |
||
{{confusing|section|date=July 2021}} |
|||
[[File:Djenne market.jpg|thumb|A market scene in [[Djenné]]]] |
[[File:Djenne market.jpg|thumb|A market scene in [[Djenné]]]] |
||
[[File:Mali Product Exports (2019).svg|thumb|A proportional representation of Mali exports, 2019]] |
|||
[[File:Kalabougou potters (6392346).jpg|thumb|[[Kalabougou]] potters]] |
|||
[[File:Kalabougou potters (6392346).jpg|thumb|upright|[[Kalabougou]] potters]] |
|||
[[File:Usine de coton CMDT.png|thumb|Cotton processing at CMDT]] |
[[File:Usine de coton CMDT.png|thumb|Cotton processing at CMDT]] |
||
The [[Central Bank of West African States]] handles the financial affairs of Mali and additional members of the [[Economic Community of West African States]]. Mali is one of the poorest countries in the world.<ref name=factbook>{{cite web |author=Central Intelligence Agency | |
The [[Central Bank of West African States]] handles the financial affairs of Mali and additional members of the [[Economic Community of West African States]]. Mali is considered one of the poorest countries in the world.<ref name=factbook>{{cite web |author=Central Intelligence Agency |author-link=CIA |work=[[The World Factbook]] |title=Mali |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/ |year=2009 |access-date=12 January 2010 |archive-date=30 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210330032030/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The average worker's annual salary is approximately US$1,500.<ref name="state" /> |
||
[[File:GDP per capita development of Mali.svg|thumb|GDP per capita development of Mali]] |
|||
Mali underwent economic reform, beginning in 1988 by signing agreements with the [[World Bank]] and the [[International Monetary Fund]].<ref name="state"/> During 1988 to 1996, Mali's government largely reformed public enterprises. Since the agreement, sixteen enterprises were privatized, 12 partially privatized, and 20 liquidated.<ref name="state"/> In 2005, the Malian government conceded a railroad company to the Savage Corporation.<ref name="state"/> Two major companies, Societé de Telecommunications du Mali ([[SOTELMA]]) and the Cotton Ginning Company ([[Compagnie malienne pour le développement du textile|CMDT]]), were expected to be privatized in 2008.<ref name="state"/> |
Mali underwent economic reform, beginning in 1988 by signing agreements with the [[World Bank]] and the [[International Monetary Fund]].<ref name="state"/> During 1988 to 1996, Mali's government largely reformed public enterprises. Since the agreement, sixteen enterprises were privatized, 12 partially privatized, and 20 liquidated.<ref name="state"/> In 2005, the Malian government conceded a railroad company to the Savage Corporation.<ref name="state"/> Two major companies, Societé de Telecommunications du Mali ([[SOTELMA]]) and the Cotton Ginning Company ([[Compagnie malienne pour le développement du textile|CMDT]]), were expected to be privatized in 2008.<ref name="state"/> |
||
Between 1992 and 1995, Mali implemented an economic adjustment programme that resulted in economic growth and a reduction in financial imbalances. The programme increased social and economic conditions, and led to Mali joining the [[World Trade Organization]] on 31 May 1995.<ref>[http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/countries_e/mali_e.htm Mali and the WTO]. World Trade Organization. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> |
Between 1992 and 1995, Mali implemented an economic adjustment programme that resulted in economic growth and a reduction in financial imbalances{{vague|date=July 2021}}. The programme increased social and economic conditions{{vague|date=July 2021}}, and led to Mali joining the [[World Trade Organization]] on 31 May 1995.<ref>[http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/countries_e/mali_e.htm Mali and the WTO] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130211173417/http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/countries_e/mali_e.htm |date=11 February 2013 }}. World Trade Organization. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> |
||
Mali is also a member of the [[Organization for the Harmonization of Business Law in Africa]] ([[OHADA]]).<ref name="ohada.com">{{cite web | title=OHADA.com: The business law portal in Africa | url=http://www.ohada.com/index.php | access-date=22 March 2009 | archive-date=26 March 2009 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090326033744/http://www.ohada.com/index.php | url-status=live }}</ref> The gross domestic product (GDP) has risen since. In 2002, the GDP amounted to US$3.4 billion,<ref name="p9">[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 9.</ref> and increased to US$5.8 billion in 2005,<ref name="state">{{cite web |title=Mali |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/2828.htm |access-date=4 June 2008 |date=May 2008 |publisher=[[U.S. State Department]] |archive-date=22 January 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170122194505/https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/2828.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> which amounts to an approximately 17.6% annual growth rate. |
|||
Mali is a part of the "Franc Zone" (''Zone Franc''), which means that it uses the [[CFA franc]]. Mali is connected with the French government by agreement since 1962 (creation of [[BCEAO]]). Today all seven countries of BCEAO (including Mali) are connected to French Central Bank.<ref>[http://www.banque-france.fr/eurosysteme-et-international/zone-franc.html Zone franc sur le site de la Banque de France] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130120074029/http://www.banque-france.fr/eurosysteme-et-international/zone-franc.html |date=20 January 2013 }}. Banque-france.fr. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> |
|||
Mali is also a member of the [[Organization for the Harmonization of Business Law in Africa]] ([[OHADA]]).<ref name="ohada.com">{{cite web | title = OHADA.com: The business law portal in Africa | url = http://www.ohada.com/index.php | accessdate =22 March 2009}}</ref> The gross domestic product (GDP) has risen since. In 2002, the GDP amounted to US$3.4 billion,<ref name=p9>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 9.</ref> and increased to US$5.8 billion in 2005,<ref name="state">{{cite web|title=Mali|url=https://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/2828.htm |accessdate=4 June 2008 |date=May 2008|publisher=[[U.S. State Department]] }}</ref> which amounts to an approximately 17.6 percent annual growth rate. |
|||
Mali was ranked 136th out of 139 in the [[Global Innovation Index]] in 2024.<ref>{{cite book|url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/|title=Global Innovation Index 2024. Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship|access-date=2024-10-22|author=[[World Intellectual Property Organization]]|year=2024|isbn=978-92-805-3681-2|doi= 10.34667/tind.50062|website=www.wipo.int|location=Geneva|page=18}}</ref> |
|||
Mali is a part of the "Franc Zone" (''Zone Franc''), which means that it uses the [[CFA franc]]. Mali is connected with the French government by agreement since 1962 (creation of [[BCEAO]]). Today all seven countries of BCEAO (including Mali) are connected to French Central Bank.<ref>[http://www.banque-france.fr/eurosysteme-et-international/zone-franc.html Zone franc sur le site de la Banque de France]. Banque-france.fr. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> |
|||
=== Agriculture === |
=== Agriculture === |
||
Mali's key industry is agriculture. Cotton is the country's largest crop export and is exported west throughout Senegal and Ivory Coast.<ref name=Goldenhope>{{cite news | first=Briony | last=Hale | title=Mali's Golden Hope | date=13 May 1998 | |
Mali's key industry is agriculture. Cotton is the country's largest crop export and is exported west throughout Senegal and Ivory Coast.<ref name=Goldenhope>{{cite news | first=Briony | last=Hale | title=Mali's Golden Hope | date=13 May 1998 | work=BBC News | url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/1945588.stm | access-date=4 June 2008 | archive-date=11 July 2018 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180711170446/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/1945588.stm | url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=marshall>{{cite book | last = Cavendish | first = Marshall | title = World and Its Peoples: Middle East, Western Asia, and Northern Africa | publisher = Marshall Cavendish | year = 2007 | location = Tarrytown, New York | isbn = 978-0-7614-7571-2 | page = 1367 | url = https://archive.org/details/worlditspeoplesm0000unse | url-access = registration }}</ref> During 2002, 620,000 tons of cotton were produced in Mali but cotton prices declined significantly in 2003.<ref name=Goldenhope/><ref name=marshall/> In addition to cotton, Mali produces rice, [[millet]], [[Maize|corn]], vegetables, tobacco, and tree crops. Gold, livestock, and agriculture amount to 80% of Mali's exports.<ref name="state"/> |
||
Eighty percent of Malian workers are employed in agriculture. 15 |
Eighty percent of Malian workers are employed in agriculture. 15% of Malian workers are employed in the service sector.<ref name=marshall/> Seasonal variations lead to regular [[temporary employment|temporary unemployment]] of agricultural workers.<ref>{{cite book |ref=May| last = May | first = Jacques Meyer | title = The Ecology of Malnutrition in the French Speaking Countries of West Africa and Madagascar | publisher=Macmillan Publishing Company |date= 1968 | location = New York | isbn = 978-0-02-848960-5 |page=291}}</ref> |
||
=== Mining === |
=== Mining === |
||
In 1991, with the assistance of the [[International Development Association]], Mali relaxed the enforcement of mining codes which led to renewed foreign interest and investment in the mining industry.<ref>{{cite book | |
In 1991, with the assistance of the [[International Development Association]], Mali relaxed the enforcement of mining codes which led to renewed foreign interest and investment in the mining industry.<ref>{{cite book |last=Campbell |first=Bonnie |title=Regulating Mining in Africa: For Whose Benefit? |publisher=Nordic African Institute |date=2004 |location=Uppsala, Sweden |isbn=978-0-7614-7571-2 |page=43 |url=https://archive.org/details/worlditspeoplesm0000unse |url-access=registration }}</ref> Gold is mined in the southern region and Mali has the third highest gold production in Africa (after South Africa and [[Ghana]]).<ref name="Goldenhope" /> In 2015, the country has produced 41 metric tonnes of gold.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Gold production |url=https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/gold-production?tab=table |archive-url=http://web.archive.org/web/20231129233804/https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/gold-production?tab=table |archive-date=2023-11-29 |access-date=2024-12-17 |website=Our World in Data}}</ref> |
||
The emergence of gold as Mali's leading export product since 1999 has helped mitigate some of the negative impact of the cotton and Ivory Coast crises.<ref>African Development Bank, p. 186.</ref> Other natural resources include [[kaolin]], salt, [[phosphate]], and [[limestone]].<ref name="state"/> |
The emergence of gold as Mali's leading export product since 1999 has helped mitigate some of the negative impact of the cotton and Ivory Coast crises.<ref>African Development Bank, p. 186.</ref> Other natural resources include [[kaolin]], salt, [[phosphate]], and [[limestone]].<ref name="state" /> |
||
=== Energy === |
=== Energy === |
||
{{See also|List of power stations in Mali}} |
{{See also|List of power stations in Mali}} |
||
Electricity and water are maintained by the Energie du Mali, or EDM, and textiles are generated by Industry Textile du Mali, or ITEMA.<ref name="state"/> Mali has made efficient use of [[hydroelectricity]], consisting of over half of Mali's electrical power. In 2002, 700 [[KWh#Multiples|GWh]] of hydroelectric power were produced in Mali.<ref name=marshall/> |
Electricity and water are maintained by the Energie du Mali, or EDM, and textiles are generated by Industry Textile du Mali, or ITEMA.<ref name="state"/> Mali has made efficient use of [[hydroelectricity]], consisting of over half of Mali's electrical power. In 2002, 700 [[KWh#Multiples|GWh]] of hydroelectric power were produced in Mali.<ref name=marshall/> |
||
Energie du Mali is an electric company that provides electricity to Mali citizens. Only 55 |
Energie du Mali is an electric company that provides electricity to Mali citizens. Only 55 percent of the population in cities have access to EDM.<ref>Farvacque-Vitkovic, Catherine ''et al.'' (September 2007) [http://www.worldbank.org/afr/wps/wp104_english.pdf DEVELOPMENT OF THE CITIES OF MALI — Challenges and Priorities] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120916110947/http://www.worldbank.org/afr/wps/wp104_english.pdf |date=16 September 2012 }}. Africa Region Working Paper Series No. 104/a. World Bank</ref> |
||
=== Transport infrastructure === |
=== Transport infrastructure === |
||
{{Main|Transport in Mali}} |
{{Main|Transport in Mali}} |
||
In Mali, there is a railway that connects to bordering countries. There are also approximately 29 airports of which 8 have paved runways. Urban areas are known for their large quantity of green and white [[taxicab]]s. A significant sum of the population is dependent on [[public transportation]]. |
|||
In Mali, there is a railway that connects to bordering countries. There are also approximately 29 airports, of which 8 have paved runways.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Mali transportation, roads, railways and airports {{!}} - CountryReports |url=https://www.countryreports.org/country/Mali/transportation.htm |access-date=2023-09-16 |website=www.countryreports.org |archive-date=14 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231014085131/https://www.countryreports.org/country/Mali/transportation.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Urban areas are known for their large quantity of green and white [[taxicab]]s. A significant sum of the population is dependent on [[public transportation]]. |
|||
== Society == |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
[[File:Mali - Bozo girl in Bamako.jpg|thumb|upright|A [[Bozo people|Bozo]] girl in Bamako]] |
|||
{{main|Demographics of Mali}} |
{{main|Demographics of Mali}} |
||
[[File:Mali - Bozo girl in Bamako.jpg|thumb|upright|A [[Bozo people|Bozo]] girl in Bamako]] |
|||
{|class="wikitable" style="float: right; margin-left: 10px" |
|||
! colspan="4" style="text-align:center; background:#cfb;"|Population in Mali{{UN_Population|ref}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable floatleft" |
|||
|+ Population in Mali{{UN Population|ref}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! style="background:#cfb;"|Year |
! style="background:#cfb;"| Year |
||
! style="background:#cfb;"|Million |
! style="background:#cfb;"| Million |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|style="text-align:left;"|1950 ||style="text-align:right;"|4.7 |
|style="text-align:left;"| 1950 ||style="text-align:right;"| 4.7 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|style="text-align:left;"|2000 ||style="text-align:right;"|11 |
|style="text-align:left;"| 2000 ||style="text-align:right;"| 11 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|style="text-align:left;"|{{ |
|style="text-align:left;"| {{UN Population|Year}} ||style="text-align:right;"| {{#expr:{{formatnum:{{UN Population|Mali}}|R}}/1e6 round 1}} |
||
|} |
|} |
||
In {{UN_Population|Year}}, Mali's population was an estimated {{#expr:{{replace|{{UN_Population|Mali}}|,||}}/1e6 round 1}} million{{UN_Population|ref}}. The population is predominantly rural (68 percent in 2002), and 5–10 percent of Malians are [[nomad]]ic.<ref name=p6>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 6.</ref> More than 90 percent of the population lives in the southern part of the country, especially in [[Bamako]], which has over 1 million residents.<ref name=p6/> |
|||
In {{UN Population|Year}}, Mali's population was an estimated {{#expr:{{replace|{{UN Population|Mali}}|,||}}/1e6 round 1}} million{{UN Population|ref}}. Mali's population grew from 7.7 million in 1982 to 19.9 million in 2018.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL?end=2018&locations=ML&name_desc=true&start=1982|title=Population, total {{!}} Data|website=data.worldbank.org|date=2022|access-date=31 May 2023|archive-date=18 May 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240518181332/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL?end=2018&locations=ML&name_desc=true&start=1982|url-status=live}}</ref> The population is predominantly rural (68% in 2002), and 5%–10% of Malians are [[nomad]]ic.<ref name="p6">[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 6.</ref> More than 90% of the population lives in the southern part of the country, especially in [[Bamako]], which has over 2 million residents.<ref name="p6" /> |
|||
In 2007, about 48 percent of Malians were younger than 12 years old, 49 percent were 15–64 years old, and 3 percent were 65 and older.<ref name=factbook/> The median age was 15.9 years.<ref name=factbook/> The [[birth rate]] in 2014 is 45.53 births per 1,000, and the [[total fertility rate]] (in 2012) was 6.4 children per woman.<ref name=factbook/><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.indexmundi.com/mali/demographics_profile.html|title=Mali Demographics Profile 2014}}</ref> The [[death rate]] in 2007 was 16.5 deaths per 1,000.<ref name=factbook/> [[Life expectancy]] at birth was 53.06 years total (51.43 for males and 54.73 for females).<ref name=factbook/> Mali has one of the [[List of countries by infant mortality rate|world's highest rates]] of [[infant mortality]],<ref name=p6/> with 106 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2007.<ref name=factbook/> |
|||
In 2007, about 48% of Malians were younger than 12 years old, 49% were 15–64 years old, and 3% were 65 and older.<ref name="factbook" /> The median age was 15.9 years.<ref name="factbook" /> The [[birth rate]] in 2014 was 45.53 births per 1,000, and the [[total fertility rate]] (in 2012) was 6.4 children per woman.<ref name="factbook" /><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.indexmundi.com/mali/demographics_profile.html|title=Mali Demographics Profile 2014|access-date=14 December 2014|archive-date=7 January 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150107120928/http://www.indexmundi.com/mali/demographics_profile.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The [[death rate]] in 2007 was 16.5 deaths per 1,000.<ref name=factbook/> [[Life expectancy]] at birth was 53.06 years total (51.43 for males and 54.73 for females).<ref name="factbook" /> Mali has one of the [[List of countries by infant mortality rate|world's highest rates]] of [[infant mortality]],<ref name=p6/> with 106 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2007.<ref name="factbook" /> |
|||
{{Largest cities of Mali}} |
|||
=== |
===Largest cities in Mali=== |
||
{{main list|List of cities in Mali}} |
|||
[[File:Mali1974-151 hg.jpg|thumb|left|The [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] are historic, nomadic inhabitants of northern Mali.]] |
|||
{{Largest cities of Mali}} |
|||
Mali's population encompasses a number of [[sub-Saharan]] ethnic groups. |
|||
The [[Bambara people|Bambara]] ({{lang-bm|Bamanankaw}}) are by far the largest single ethnic group, making up 36.5 percent of the population.<ref name=p6/> |
|||
Collectively, the Bambara, [[Soninke people|Soninké]], [[Khassonké]], and [[Mandinka people|Malinké]] (also called [[Mandinka language|Mandinka]]), all part of the broader [[Mandé]] group, constitute 50 percent of Mali's population.<ref name=factbook/> Other significant groups are the [[Fula people|Fula]] ({{lang-fr|link=no|Peul}}; {{lang-ff|Fulɓe}}) (17 percent), [[Gur languages|Voltaic]] (12 percent), [[Songhai people|Songhai]] (6 percent), and [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] and [[Moors|Moor]] (10 percent).<ref name=factbook/> In Mali as well as [[Niger]], the Moors are also known as [[Azawagh Arabs]], named after the [[Azawagh]] region of the [[Sahara]]. They speak mainly [[Hassaniya Arabic]] which is one of the regional [[varieties of Arabic]].<ref>Popenoe, Rebecca (2003) ''Feeding Desire — Fatness, Beauty and Sexuality among a Saharan People''. Routledge, London. pp. 16–17. {{ISBN|0-415-28096-6}}</ref> Personal names reflect Mali's complex regional identities.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://blog.namsor.com/2017/11/24/popular-baby-names-of-mali-west-africa/|title=Popular baby names of MALI, West Africa|date=24 November 2017|work=NamSor Blog|access-date=24 November 2017}}</ref> |
|||
===Ethnic groups=== |
|||
In the far north, there is a division between [[Berber people|Berber]]-descendent [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] nomad populations and the darker-skinned Bella or [[Tamasheq]] people, due to the historical spread of [[Slavery in Mali|slavery]] in the region. |
|||
[[File:Traveller_at_Bambara_wedding,_Mali,_West_Africa.tiff|thumb|left|A [[Bambara people|Bambara]] wedding in Mali, observed by a tourist.]] |
|||
[[File:Mali_family.jpg|thumb|left|[[Fulani]] children in Mali.]] |
|||
[[File:Mali1974-151 hg.jpg|thumb|left|The [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] are nomadic inhabitants of northern Mali.]] |
|||
Mali's population encompasses a number of [[sub-Saharan]] ethnic groups. The [[Bambara people|Bambara]] are by far the largest single ethnic group, making up a third of the population.<ref>https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/#people-and-society</ref> The largest ethnic groups are Bambara (33.3%), Fulani (Peuhl) (13.3%), Sarakole/Soninke/Marka (9.8%), Senufo/Manianka (9.6%), Malinke (8.8%), Dogon (8.7%), Sonrai (5.9%), Bobo (2.1%), Tuareg/Bella (1.7%), other Malian (6%), from members of Economic Community of West Africa (0.4%), other (0.3%) (2018 est.).<ref>https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/#people-and-society</ref> In Mali and in [[Niger]], the Moors are also known as [[Azawagh Arabs]], named after the [[Azawagh]] region of the [[Sahara]]. They speak mainly [[Hassaniya Arabic]], one of the regional [[varieties of Arabic]].<ref>Popenoe, Rebecca (2003) ''Feeding Desire – Fatness, Beauty and Sexuality among a Saharan People''. Routledge, London. pp. 16–17. {{ISBN|0-415-28096-6}}</ref> |
|||
An estimated 800,000 people in Mali are descended from [[slavery|slaves]].<ref name=slaves>{{cite news|last=Tran|first=Mark|title=Mali conflict puts freedom of 'slave descendants' in peril|newspaper=The Guardian|date=23 October 2012|url=https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2012/oct/23/mali-conflict-freedom-slave-descendants-peril|accessdate=24 November 2012|ref=harv|location=London}}</ref> Slavery in Mali has persisted for centuries.<ref>{{cite news|last=Fortin|first=Jacey|title=Mali's Other Crisis: Slavery Still Plagues Mali, And Insurgency Could Make It Worse |newspaper=International Business Times|date=16 January 2013|url=http://www.ibtimes.com/malis-other-crisis-slavery-still-plagues-mali-insurgency-could-make-it-worse-1017280}}</ref> |
|||
The Arabic population kept slaves well into the 20th century, until slavery was suppressed by [[French Sudan|French authorities]] around the mid-20th century. There still persist certain hereditary servitude relationships,<ref>"[http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2002/12/1206_021205_salakkayak.html Kayaking to Timbuktu, Writer Sees Slave Trade]". National Geographic News. 5 December 2002.</ref><ref>"[http://www.kirasalak.com/Mali.html Kayaking to Timbuktu, Original National Geographic Adventure Article discussing Slavery in Mali]". National Geographic Adventure. December 2002/January 2003.</ref> and according to some estimates, even today approximately 200,000 Malians are still enslaved.<ref>{{cite news|last=MacInnes-Rae|first=Rick| |
In the far north, there is a division between [[Berber people|Berber]]-descended [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] nomad populations and the darker-skinned Bella or [[Tamasheq]] people, due to the historical spread of [[Slavery in Mali|slavery]] in the region. An estimated 800,000 people in Mali are descended from slaves.<ref name=slaves>{{cite news|last=Tran|first=Mark|title=Mali conflict puts freedom of 'slave descendants' in peril|newspaper=The Guardian |date=23 October 2012 |url=https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2012/oct/23/mali-conflict-freedom-slave-descendants-peril|access-date=24 November 2012 |location=London |archive-date=5 October 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131005100538/http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2012/oct/23/mali-conflict-freedom-slave-descendants-peril |url-status=live}}</ref> [[Slavery]] has persisted in Mali for centuries.<ref>{{cite news |last=Fortin|first=Jacey|title=Mali's Other Crisis: Slavery Still Plagues Mali, And Insurgency Could Make It Worse|newspaper=International Business Times|date=16 January 2013 |url=http://www.ibtimes.com/malis-other-crisis-slavery-still-plagues-mali-insurgency-could-make-it-worse-1017280 |access-date=16 January 2013|archive-date=8 December 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141208102058/http://www.ibtimes.com/malis-other-crisis-slavery-still-plagues-mali-insurgency-could-make-it-worse-1017280|url-status=live}}</ref> The Arabic population kept slaves well into the 20th century, until slavery was suppressed by [[French Sudan|French authorities]] around the mid-20th century. There still persist certain hereditary servitude relationships,<ref>"[http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2002/12/1206_021205_salakkayak.html Kayaking to Timbuktu, Writer Sees Slave Trade] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010190141/http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2002/12/1206_021205_salakkayak.html |date=10 October 2017 }}". National Geographic News. 5 December 2002.</ref><ref>"[http://www.kirasalak.com/Mali.html Kayaking to Timbuktu, Original National Geographic Adventure Article discussing Slavery in Mali] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100922151608/http://www.kirasalak.com/Mali.html |date=22 September 2010 }}". National Geographic Adventure. December 2002/January 2003.</ref> and according to some estimates, even today approximately 200,000 Malians are still enslaved.<ref>{{cite news|last=MacInnes-Rae|first=Rick|author-link=Rick MacInnes-Rae|title=Al-Qaeda complicating anti-slavery drive in Mali|publisher=CBC News |url=http://www.cbc.ca/news/world/al-qaeda-complicating-anti-slavery-drive-in-mali-1.1150057 |date=26 November 2012|access-date=25 April 2014|archive-date=5 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140305175918/http://www.cbc.ca/news/world/al-qaeda-complicating-anti-slavery-drive-in-mali-1.1150057|url-status=live}}</ref> |
||
Some mixed European/African descendants of Muslims of [[Spanish people|Spanish]], as well as French, Irish, Italian and Portuguese origin, live in Mali, where they are known as the [[Arma people]] (1% of the nation's population).<ref>{{cite book|url=https://archive.org/details/cambridgehistory05fage|url-access=registration|title=The Cambridge History of Africa|first1=J. D.|last1=Fage|first2=Richard|last2=Gray|first3=Roland|last3=Oliver|date=1975|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=9780521204132}}</ref> |
|||
Although Mali has enjoyed |
Although Mali has enjoyed reasonably good inter-ethnic relationships based on a long history of coexistence, some hereditary servitude and bondage relationship exist, as well as ethnic tension between settled Songhai and nomadic Tuaregs of the north.<ref name=p6/> Due to a backlash against the northern population after independence, Mali is now in a situation where both groups complain about discrimination on the part of the other group.<ref>Hall, Bruce S. (2011) ''A History of Race in Muslim West Africa'', 1600–1960. Cambridge University Press. {{ISBN|9781107002876}}: "The mobilization of local ideas about racial difference has been important in generating, and intensifying, civil wars that have occurred since the end of colonial rule in all of the countries that straddle the southern edge of the Sahara Desert.{{nbsp}}... contemporary conflicts often hearken back to an older history in which blackness could be equated with slavery and non-blackness with predatory and uncivilized banditry." (cover text)</ref> This conflict also plays a role in the continuing [[Northern Mali conflict (2012–present)|Northern Mali conflict]] where there is a tension between both Tuaregs and the Malian government, and the Tuaregs and radical [[Islamist]]s who are trying to establish [[sharia law]].<ref>Hirsch, Afua (6 July 2012) [https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2012/jul/06/mali-war-over-skin-colour Mali's conflict and a 'war over skin colour'] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170211081540/https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2012/jul/06/mali-war-over-skin-colour |date=11 February 2017 }}, ''The Guardian''.</ref> |
||
=== Languages === |
=== Languages === |
||
{{bar box |
|||
|title=Spoken Languages in Mali (2009 Census)<ref name="instat-mali.org">{{cite web |url=http://www.instat-mali.org/contenu/rgph/tdemo09_rgph.pdf |title=4ème Recensement General de la Population et de L'Habitat du Mali (RGPH) |language=French |publisher=Institut National de la Statistique |access-date=25 January 2020 |archive-date=11 January 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200111002517/http://www.instat-mali.org/contenu/rgph/tdemo09_rgph.pdf }}</ref> |
|||
|titlebar=#ddd |
|||
|left1=Spoken Languages |
|||
|right1=percent |
|||
|float=right |
|||
|bars= |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Bambara language|Bambara]]|darkgreen|51.82}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Fula language|Fula]]|purple|8.29}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Dogon language|Dogon]]|red|6.48}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Soninké language|Maraka / Soninké]]|black|5.69}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Songhai language|Songhai]] / [[Zarma language|Zarma]]|orange|5.27}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Mandinka language|Mandinka]]|green|5.12}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Minyanka language|Minyanka]]|darkblue|3.77}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Tamasheq language|Tamasheq]]|pink|3.18}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Senufo language|Senufo]]|darkred|2.03}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Bobo language|Bobo]]|gray|1.89}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Bozo language|Bozo]]|red|1.58}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Kassonke language|Kassonké]]|lime|1.07}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Maure language|Maure]]|violet|1}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Samogo languages|Samogo]]|purple|0.43}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Marka language|Dafing]]|yellow|0.41}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Arabic]]|brown|0.33}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Hausa language|Hausa]]|black|0.03}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Languages of Mali|Other Malian]]|green|0.49}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Languages of Africa|Other African]]|orange|0.18}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Other foreign|red|0.18}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Not Stated|pink|0.75}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{bar box |
|||
|title=Mother Tongues in Mali (2009 Census)<ref name="instat-mali.org" /> |
|||
|titlebar=#ddd |
|||
|left1=Mother Tongues |
|||
|right1=percent |
|||
|float=right |
|||
|bars= |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Bambara language|Bambara]]|darkgreen|46.5}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Fula language|Fula]]|purple|9.39}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Dogon language|Dogon]]|red|7.12}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Soninké language|Maraka / Soninké]]|black|6.33}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Mandinka language|Mandinka]]|green|5.6}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Songhai language|Songhai]] / [[Zarma language|Zarma]]|orange|5.58}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Minianka language|Minianka]]|darkblue|4.29}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Tamasheq language|Tamasheq]]|pink|3.4}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Senufo language|Senufo]]|darkred|2.56}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Bobo language|Bobo]]|gray|2.15}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Bozo language|Bozo]]|red|1.85}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Kassonke language|Kassonké]]|lime|1.17}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Maure language|Maure]]|violet|1.1}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Samogo languages|Samogo]]|yellow|0.5}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Marka language|Dafing]]|purple|0.46}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Arabic]]|brown|0.34}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Hausa language|Hausa]]|black|0.04}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Languages of Mali|Other Malian]]|green|0.55}} |
|||
{{bar percent|[[Languages of Africa|Other African]]|orange|0.31}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Other Foreign|red|0.08}} |
|||
{{bar percent|Not Stated|pink|0.69}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Main| Languages of Mali}} |
{{Main| Languages of Mali}} |
||
In January 2022, due to deteriorating relations between Mali and the French government, the Mali government announced making Bambara the official language.<ref name=2022endfrench>{{cite web |url=https://edition.cnn.com/2022/01/31/africa/mali-french-ambassador-expelled-intl/index.html |title=Mali's military rulers say French ambassador has 72 hours to leave the country |publisher=CNN |date=31 January 2022 |access-date=14 February 2022 |archive-date=13 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220213181820/https://edition.cnn.com/2022/01/31/africa/mali-french-ambassador-expelled-intl/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref> In July 2023, [[French language|French]] was dropped as an official language, becoming instead a [[working language]].<ref name="Lingua 2023"/> At the same time, the 13 national languages,<ref name="LangNat"/> namely [[Bambara language|Bambara]], [[Bobo language|Bobo]], [[Bozo language|Bozo]], [[Dogon languages|Dogon]], [[Fula language|Fula]], [[Hassaniya Arabic]], [[Kassonke language|Kassonke]], [[Maninka language|Maninke]], [[Minyanka language|Minyanka]], [[Senufo languages|Senufo]], the [[Songhay languages]], [[Soninke language|Soninke]] and [[Tamasheq language|Tamasheq]], became official languages.<ref name="Lingua 2023"/> The ''[[lingua franca]]'' in Mali is mainly [[Bambara language|Bambara]], which about 80 percent of the population can communicate in.<ref name=p6/> Over 40 other [[African languages]] are spoken by the various ethnic groups of Mali.<ref name=p6/> |
|||
Mali's official language is [[French language|French]] and over 40 [[African languages]] also are spoken by the various ethnic groups.<ref name=p6/> About 80 percent of Mali's population can communicate in [[Bambara language|Bambara]], which serves as an important [[lingua franca]].<ref name=p6/> |
|||
According to the 2009 census, the languages spoken natively in Mali were [[Bambara language|Bambara]] by 51.5%, [[Fula language|Fula]] (8.3%), [[Dogon language|Dogon]] (6.6%) [[Soninké language|Soninké]] (5.7%), [[Songhai language|Songhai]] (5.3%), [[Mandinka language|Mandinka]] (5.2%), [[Minianka language|Minianka]] (3.8%), [[Tamasheq language|Tamasheq]] (3.2%), [[Sénoufo language|Sénoufo]] (2%), [[Bobo language|Bobo]] (1.9%), [[Bozo language|Tieyaxo Bozo]] (1.6%), [[Kassonke language|Kassonké]] (1.1%), [[Maure language|Maure]] (1%), [[Marka language|Dafing]] (0.4%), [[Samogo languages|Samogo]] (0.4%), [[Arabic]] ([[Hassaniya Arabic|Hassaniya]]) (0.3%), other [[Languages of Mali|Malian languages]] (0.5%), other African languages (0.2%), and other non-African languages (0.2%); 0.7% did not declare their first language.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.instat-mali.org/contenu/rgph/rastr09_rgph.pdf |title=4ème RECENSEMENT GENERAL DE LA POPULATION ET DE L'HABITAT DU MALI (RGPH-2009) |publisher=Mali National Institute of Statistics |language=fr |trans-title=4th GENERAL POPULATION CENSUS AND HABITAT OF MALI (RGPH-2009) |access-date=14 December 2019 |archive-date=19 August 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190819064921/http://www.instat-mali.org/contenu/rgph/rastr09_rgph.pdf }}</ref> |
|||
Mali has 12 [[national language]]s beside [[French language|French]] and [[Bambara language|Bambara]], namely [[Bomu language|Bomu]], [[Bozo language|Tieyaxo Bozo]], [[Escarpment Dogon|Toro So Dogon]], [[Maasina Fulfulde]], [[Hassaniya Arabic]], [[Minyanka language|Mamara Senoufo]], [[Kita Maninka language|Kita Maninkakan]], [[Soninke language|Soninke]], [[Koyraboro Senni]], [[Senara language|Syenara Senoufo]], [[Tamasheq language|Tamasheq]] and [[Kassonke language|Xaasongaxango]]. Each is spoken as a first language primarily by the ethnic group with which it is associated. |
|||
===Religion=== |
===Religion=== |
||
| Line 328: | Line 590: | ||
|float=right |
|float=right |
||
|bars= |
|bars= |
||
{{bar percent|[[Islam |
{{bar percent|[[Islam in Mali|Islam]]|green|90}} |
||
{{bar percent|Christianity|blue|5}} |
{{bar percent|Christianity|blue|5}} |
||
{{bar percent|[[Indigenous religion|Indigenous]]|red|5}} |
{{bar percent|[[Indigenous religion|Indigenous]]|red|5}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File:Mosque entrance (6862566).jpg|thumb| |
[[File:Mosque entrance (6862566).jpg|thumb|upright|An entrance to the Djinguereber mosque]] |
||
Islam was introduced to West Africa in the 11th century and remains the predominant religion in much of the region. An estimated 90 percent of Malians are [[Islam in Mali|Muslim]] (mostly [[Sunni]],<ref name="pew">{{cite web | url=http://www.pewforum.org/uploadedFiles/Topics/Religious_Affiliation/Muslim/the-worlds-muslims-full-report.pdf | title=The World's Muslims: Unity and Diversity | accessdate=2 June 2014 | date=9 August 2012 | publisher=Pew Forum on Religious & Public life | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121024125551/http://www.pewforum.org/uploadedFiles/Topics/Religious_Affiliation/Muslim/the-worlds-muslims-full-report.pdf | archive-date=24 October 2012 | dead-url=yes | df=dmy-all }}</ref>), approximately 5 percent are Christian (about two-thirds [[Roman Catholicism in Mali|Roman Catholic]] and one-third [[Protestantism|Protestant]]) and the remaining 5 percent adhere to [[African traditional religion|indigenous or traditional animist beliefs]].<ref name = IRFR>[https://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/2008/108379.htm International Religious Freedom Report 2008: Mali]. State.gov (19 September 2008). Retrieved 4 May 2012.</ref> [[Atheism]] and [[agnosticism]] are believed to be rare among Malians, most of whom practice their religion on a daily basis.<ref name=p7/> |
|||
Islam was introduced to West Africa in the 11th century and remains the predominant religion in much of the region. An estimated 90% of Malians are [[Islam in Mali|Muslim]] (mostly [[Sunni]]<ref name="pew">{{cite web | url=http://www.pewforum.org/uploadedFiles/Topics/Religious_Affiliation/Muslim/the-worlds-muslims-full-report.pdf | title=The World's Muslims: Unity and Diversity | access-date=2 June 2014 | date=9 August 2012 | publisher=Pew Forum on Religious & Public life | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121024125551/http://www.pewforum.org/uploadedFiles/Topics/Religious_Affiliation/Muslim/the-worlds-muslims-full-report.pdf | archive-date=24 October 2012 | df=dmy-all }}</ref>), approximately 5% are Christian (about two-thirds [[Roman Catholicism in Mali|Roman Catholic]] and one-third [[Protestantism|Protestant]]) and the remaining 5% adhere to [[traditional African religions]] such as the [[Dogon religion]].<ref name = IRFR>[https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/2008/108379.htm International Religious Freedom Report 2008: Mali] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200118035332/https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/2008/108379.htm |date=18 January 2020 }}. State.gov (19 September 2008). Retrieved 4 May 2012.</ref> [[Atheism]] and [[agnosticism]] are believed to be rare among Malians, most of whom practice their religion daily.<ref name=p7/> |
|||
The constitution establishes a [[secular state]] and provides for [[freedom of religion]], and the government largely respects this right.<ref name=p7/> |
The constitution establishes a [[secular state]] and provides for [[freedom of religion]], and the government largely respects this right.<ref name=p7/> |
||
Islam as historically practiced in Mali has been malleable and adapted to local conditions; relations between Muslims and practitioners of minority religious faiths have generally been amicable.<ref name=p7/> |
Islam as historically practiced in Mali has been malleable and adapted to local conditions; relations between Muslims and practitioners of minority religious faiths have generally been amicable.<ref name=p7/> |
||
After the 2012 imposition of [[sharia]] rule in northern parts of the country, however, Mali came to be listed high (number 7) in the Christian persecution index published by [[Open Doors]], which described the persecution in the north as severe.<ref name = DeutscheWelle>[http://www.dw.de/report-points-to-100-million-persecuted-christians/a-16507067 Report points to 100 million persecuted Christians.]. Retrieved 10 January 2013.</ref><ref name = OpenDoor>[http://www.worldwatchlist.us/ OPEN DOORS World Watch list 2012]. Worldwatchlist.us. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> |
After the 2012 imposition of [[sharia]] rule in northern parts of the country, however, Mali came to be listed high (number 7) in the Christian persecution index published by [[Open Doors]], which described the persecution in the north as severe.<ref name = DeutscheWelle>[http://www.dw.de/report-points-to-100-million-persecuted-christians/a-16507067 Report points to 100 million persecuted Christians.] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150406223430/http://www.dw.de/report-points-to-100-million-persecuted-christians/a-16507067 |date=6 April 2015 }}. Retrieved 10 January 2013.</ref><ref name = OpenDoor>[http://www.worldwatchlist.us/ OPEN DOORS World Watch list 2012] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191210101952/https://worldwatchlist.us/ |date=10 December 2019 }}. Worldwatchlist.us. Retrieved 24 March 2013.</ref> |
||
=== Education === |
=== Education === |
||
| Line 345: | Line 608: | ||
[[File:Lycéens kati.jpg|thumb|left|High school students in [[Kati]]]] |
[[File:Lycéens kati.jpg|thumb|left|High school students in [[Kati]]]] |
||
Public education in Mali is in principle provided free of charge and is compulsory for nine years between the ages of seven and sixteen.<ref name=p7/> The system encompasses six years of primary education beginning at age 7, followed by six years of secondary education.<ref name=p7/> Mali's actual primary school |
Public education in Mali is in principle provided free of charge and is compulsory for nine years between the ages of seven and sixteen.<ref name=p7/> The system encompasses six years of primary education beginning at age 7, followed by six years of secondary education.<ref name=p7/> Mali's actual primary school enrolment rate is low, in large part because families are unable to cover the cost of uniforms, books, supplies, and other fees required to attend.<ref name=p7/> |
||
In |
In 2017, the primary school enrolment rate was 61% (65% of males and 58% of females).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://datatopics.worldbank.org/education/country/mali|title=Education Statistics|website=datatopics.worldbank.org|access-date=19 November 2019|archive-date=7 May 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210507101442/https://datatopics.worldbank.org/education/country/mali|url-status=live}}</ref> In the late 1990s, the secondary school enrolment rate was 15% (20% of males and 10% of females).<ref name=p7/> The education system is plagued by a lack of schools in rural areas, as well as shortages of teachers and materials.<ref name=p7/> |
||
Estimates of literacy rates in Mali range from 27–30 to 46.4 |
Estimates of literacy rates in Mali range from 27–30 to 46.4%, with literacy rates significantly lower among women than men.<ref name=p7/> The [[University of Bamako]], which includes four constituent universities, is the largest university in the country and enrols approximately 60,000 undergraduate and graduate students.<ref>{{cite web|title=Université de Bamako – Bamako, Mali|url=http://globalhealth.northwestern.edu/meded/current-affiliations/Bamako_Mali.html|publisher=Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine|access-date=8 July 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130513192022/http://globalhealth.northwestern.edu/MedEd/current-affiliations/Bamako_Mali.html|archive-date=13 May 2013}}</ref> |
||
=== Health === |
=== Health === |
||
{{main|Health in Mali}} |
{{main|Health in Mali}} |
||
Mali faces numerous health challenges related to poverty, [[malnutrition]], and inadequate [[hygiene]] and [[sanitation]].<ref name=p7>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 7.</ref> Mali's health and development indicators rank among the worst in the world.<ref name=p7/> Life expectancy at birth is estimated to be 53.06 years in 2012.<ref>[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2102rank.html?countryName=Mali&countryCode=ml®ionCode=afr&rank=206#ml Life Expectancy ranks]. CIA World Factbook</ref> In 2000, 62–65 percent of the population was estimated to have access to safe drinking water and only 69 percent to sanitation services of some kind.<ref name=p7/> In 2001, the general government expenditures on health totalled about US$4 per capita at an average exchange rate.<ref name=p8>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 8.</ref> |
|||
Mali faces numerous health challenges related to poverty, [[malnutrition]], and inadequate [[hygiene]] and [[sanitation]].<ref name=p7>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 7.</ref> Mali's health and development indicators rank among the worst in the world.<ref name=p7/> Life expectancy at birth is estimated to be 53.06 years in 2012.<ref>[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2102rank.html?countryName=Mali&countryCode=ml®ionCode=afr&rank=206#ml Life Expectancy ranks] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181206001558/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2102rank.html?countryName=Mali&countryCode=ml®ionCode=afr&rank=206#ml |date=6 December 2018 }}. CIA World Factbook</ref> In 2000, 62–65% of the population was estimated to have access to safe drinking water and only 69% to sanitation services of some kind.<ref name=p7/> In 2001, the general government expenditures on health totaled about US$4 per capita at an average exchange rate.<ref name=p8>[[#Prof|Mali country profile]], p. 8.</ref> |
|||
Efforts have been made to improve nutrition, and reduce associated health problems, by encouraging women to make nutritious versions of local recipes. For example, the [[International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics]] ([[ICRISAT]]) and the [[Aga Khan Foundation]], trained women's groups to make ''equinut'', a healthy and nutritional version of the traditional recipe ''di-dèguè'' (comprising peanut paste, honey and millet or rice flour). The aim was to boost nutrition and livelihoods by producing a product that women could make and sell, and which would be accepted by the local community because of its local heritage.<ref>[http://www.impatientoptimists.org/Posts/2013/04/Nourishing-Communities-Through-Holistic-Farming ''Nourishing communities through holistic farming''], Impatient optimists, [[Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation]]. 30 April 2013.</ref> |
|||
Efforts have been made to improve nutrition, and reduce associated health problems, by encouraging women to make nutritious versions of local recipes. For example, the [[International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics]] (ICRISAT) and the [[Aga Khan Foundation]], trained women's groups to make ''equinut'', a healthy and nutritional version of the traditional recipe ''di-dèguè'' (comprising peanut paste, honey and millet or rice flour). The aim was to boost nutrition and livelihoods by producing a product that women could make and sell, and which would be accepted by the local community because of its local heritage.<ref>[http://www.impatientoptimists.org/Posts/2013/04/Nourishing-Communities-Through-Holistic-Farming ''Nourishing communities through holistic farming''] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181006235945/https://www.impatientoptimists.org/Posts/2013/04/Nourishing-Communities-Through-Holistic-Farming |date=6 October 2018 }}, Impatient optimists, [[Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation]]. 30 April 2013.</ref> |
|||
[[File:Village Telly in Mali.jpg|thumb|Village in the [[Sahel]] region]] |
[[File:Village Telly in Mali.jpg|thumb|Village in the [[Sahel]] region]] |
||
Medical facilities in Mali are very limited, and medicines are in short supply.<ref name=p8/> [[Malaria]] and other [[arthropod]]-borne diseases are prevalent in Mali, as are a number of [[infectious disease]]s such as [[cholera]] and [[tuberculosis]].<ref name=p8/> Mali's population also suffers from a high rate of child malnutrition and a low rate of [[immunization]].<ref name=p8/> An estimated 1.9 percent of the adult and children population was afflicted with HIV/AIDS that year,{{clarify|date=January 2019}} among the lowest rates in [[Sub-Saharan Africa]].<ref name=p8/>{{dead link|date=January 2019}} An estimated 85–91 percent of Mali's girls and women have had [[female genital mutilation]] (2006 and 2001 data).<ref>[http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/topics/fgm/prevalence/en/index.html WHO | Female genital mutilation and other harmful practices]. Who.int (6 May 2011). Retrieved 4 May 2012.</ref><ref>[http://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/CR7/CR7.pdf Female genital cutting in the Demographic Health Surveys: a critical and comparative analysis. Calverton, MD: ORC Marco; 2004 (DHS Comparative Reports No. 7)]. (PDF). Retrieved 18 January 2013.</ref> |
|||
Medical facilities in Mali are very limited, and medicines are in short supply.<ref name=p8/> [[Malaria]] and other [[arthropod]]-borne diseases are prevalent in Mali, as are a number of [[infectious disease]]s such as [[cholera]] and [[tuberculosis]].<ref name=p8/> Mali's population also suffers from a high rate of child malnutrition and a low rate of [[immunization]].<ref name=p8/> An estimated 1.9% of the adult and children population was afflicted with HIV/AIDS that year,{{clarify|date=January 2019}} among the lowest rates in [[Sub-Saharan Africa]].<ref name=p8/>{{dead link|date=January 2019}} An estimated 85%–91% of Mali's girls and women have had [[female genital mutilation]] (2006 and 2001 data).<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20090716094114/http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/topics/fgm/prevalence/en/index.html WHO | Female genital mutilation and other harmful practices]. Who.int (6 May 2011). Retrieved 4 May 2012.</ref><ref>[http://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/CR7/CR7.pdf Female genital cutting in the Demographic Health Surveys: a critical and comparative analysis. Calverton, MD: ORC Marco; 2004 (DHS Comparative Reports No. 7)] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140426233743/http://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/CR7/CR7.pdf |date=26 April 2014 }}. (PDF). Retrieved 18 January 2013.</ref> |
|||
=== Gender equality === |
=== Gender equality === |
||
In 2017, Mali ranked 157th out of 160 countries in the gender inequality index as reported by the [[United Nations Development |
In 2017, Mali ranked 157th out of 160 countries in the gender inequality index as reported by the [[United Nations Development Programme]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://hdr.undp.org/sites/all/themes/hdr_theme/country-notes/MLI.pdf|title=Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update: Mali|website=United Nations Development Programme|access-date=24 November 2018|archive-date=25 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190325093238/http://hdr.undp.org/sites/all/themes/hdr_theme/country-notes/MLI.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> The Malian Constitution states that it protects women's rights, however many laws exist that discriminate against women.<ref name=":02">{{cite web|url=http://www.omct.org/files/2004/07/2409/eng_2003_07_mali.pdf|title=Violence against Women in Mali|date=7 July 2004|website=World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT)|access-date=24 November 2018|archive-date=8 August 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190808040337/http://www.omct.org/files/2004/07/2409/eng_2003_07_mali.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> Provisions in the laws limit women's decision-making power after marriage, in which the husband becomes superior to his wife.<ref name=":02" /> Women are blamed for not maintaining the appearance of their husbands and are also blamed for the actions of their children if they misbehave, which encourages the cultural attitude that women are inferior to men.<ref name=":02" /> The lack of participation of women in politics is due to the idea that politics is associated with men and that women should avoid this sector.<ref name=":02" /> Education is also an area in which boys dominate, since it is a better investment for the parents.<ref name=":02" /> As traditional values and practices have contributed to gender inequality in Mali, conflict and lawlessness have also influenced the growing gap in gender through gender-based violence.<ref name=":2">{{cite web|url=https://www.usaid.gov/sites/default/files/documents/1860/Mali%20Gender%20Assessment%20Addendum%20Final.pdf|title=USAID MALI:ADDENDUM TO THE 2012 GENDER ASSESSMENT|date=May 2015|website=United States Agency of International Development|access-date=24 November 2018|archive-date=5 September 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180905122408/https://www.usaid.gov/sites/default/files/documents/1860/Mali%20Gender%20Assessment%20Addendum%20Final.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> The unstable government of Mali has led to organizations like USAID attempting to improve the lives of the people, mainly women and girls' rights in order to re-engage the development of the country.<ref name=":2" /> |
||
==== |
==== Gender relations ==== |
||
Religion, the patriarchal |
Religion, the patriarchal norms, and [[gender-based violence]] are major negative factors shaping the life of women in Mali.<ref name=":1">{{cite web|url=http://www.undp.org/content/dam/undp/library/Democratic%20Governance/Women-s%20Empowerment/MaliFinal%20-%20HiRes.pdf|title=GENDER EQUALITY AND WOMEN'S EMPOWERMENT IN PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION: MALI CASE STUDY|date=2012|website=United Nations Development Programme|access-date=24 November 2018|archive-date=18 December 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181218054809/http://www.undp.org/content/dam/undp/library/Democratic%20Governance/Women-s%20Empowerment/MaliFinal%20-%20HiRes.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> Patriarchal norms cause major gender inequalities and lead to male domination within the household.<ref name=":1" /> Girls learn household activities like chores, cooking, childcare, etc. at a young age and are expected to take the main responsibility of household chores throughout their life. This hampers women's ability to enter the formal workforce and leads to a lack of education of girls.<ref name=":1" /> Gender-based violence in Mali happens both on a national and a family level. At the national level, in 2012 the conflict in the Northern part of the country increased cases of kidnappings and rapes.<ref name=":2" /> The conflict also reduced women's access to resources, economy, and opportunities.<ref name=":2" /> At the household level, Malian women face gender-based violence through domestic violence, forced marriages, and marital rape.<ref name=":02" /> The Demographic Health Survey for Mali in 2013 stated that 76% of women and 54% of men believed physical harm towards women was acceptable if the women burnt food, argued back, went out without notifying her husband, or refused sexual relations with her husband.<ref name=":2" /> In 2024, Mali officials pushed a bill that would criminalise [[LGBTQ rights in Mali|homosexual relations]] between men.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Billson |first=Chantelle |date=2024-11-05 |title=Mali moves to criminalise homosexuality for the first time with new anti-gay law |url=https://www.thepinknews.com/2024/11/05/mali-moves-to-criminalise-homosexuality-with-new-anti-gay-law/ |access-date=2024-11-20 |website=PinkNews {{!}} Latest lesbian, gay, bi and trans news {{!}} LGBTQ+ news |language=en-US}}</ref> |
||
==== Area of opportunity ==== |
==== Area of opportunity ==== |
||
The lack of education has increased gender inequality in Mali because not many women are working outside the household are even participating in the Public Administration sector.<ref name=":1" /> After adjusting the entrance requirements and access to education, girls still have lower enrollment rates and less access to formal education.<ref name=":1" /> Drop-out rates for girls are 15% higher than that of boys because they have a higher responsibility at home and most parents refuse to allow all their children to go to school, so boys tend to become educated.<ref name=":1" /> Similarly, technical and vocational education has a lower numbers of girls participating and are inadequately distributed in the country because the training centers are focused in the urban cities.<ref name=":1" /> Finally, higher education for girls consist of short programs because early marriages prevent most girls from pursuing a longer term education program like those in science.<ref name=":1" /> Although women do not have the same access of education, in recent decades women have been entering and representing in decision-making positions in the Public Administration sector.<ref name=":1" /> |
The lack of education has increased gender inequality in Mali because not many women are working outside the household are even participating in the Public Administration sector.<ref name=":1" /> After adjusting the entrance requirements and access to education, girls still have lower enrollment rates and less access to formal education.<ref name=":1" /> Drop-out rates for girls are 15% higher than that of boys because they have a higher responsibility at home and most parents refuse to allow all their children to go to school, so boys tend to become educated.<ref name=":1" /> Similarly, technical and vocational education has a lower numbers of girls participating and are inadequately distributed in the country because the training centers are focused in the urban cities.<ref name=":1" /> Finally, higher education for girls consist of short programs because early marriages prevent most girls from pursuing a longer term education program like those in science.<ref name=":1" /> Although women do not have the same access of education, in recent decades women have been entering and representing in decision-making positions in the Public Administration sector.<ref name=":1" /> Out of 147 members of Parliament, 15 were women in 2010.<ref name=":1" /> Recent decades show that women are slowly joining important decision-making positions which is changing the attitude and status of women in Mali, which has led to the promotion of women's rights in the political sphere.<ref name=":1" /> |
||
==== Efforts ==== |
==== Efforts ==== |
||
Legislation at the international and national levels have been implemented over the decades to help promote women's rights in Mali.<ref name=":1" /> At the international, Mali signed the [[Beijing Platform for Action]] which suggest that women should participate in decision-making and the |
Legislation at the international and national levels have been implemented over the decades to help promote women's rights in Mali.<ref name=":1" /> At the international, Mali signed the [[Beijing Platform for Action]] which suggest that women should participate in decision-making and the convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women which is the foundation to women's rights promotion.<ref name=":1" /> At the national level, Mali's Constitution has the Decree No. 092-073P-CTSP that claims equality to all Malian citizens and discrimination is prohibited, which has not been followed.<ref name=":1" /> The Poverty Reduction Strategy Programme (PRSP) and the Growth and Poverty Reduction Strategy Programme under the Malian Government seek to improve the well-being of the citizens, and changes to governance and gender in the country.<ref name=":1" /> The Ministry for Advancement of Women, Children and the Family was created specifically for women and children so that their basics rights and needs get met under the law.<ref name=":1" /> Although there exists legislation and policy for gender equality the institutionalization of the National Gender Policy of Mali is necessary to support the importance of women's rights.<ref name=":1" /> Strengthening and the support of girls' and women's access to education and training is recommended to improve gender equality in Mali.<ref name=":1" /> The involvement of international organizations like USAID assist Mali financially to enhance their development through the efforts of the improvement of women's rights.<ref name=":2" /> |
||
==Culture== |
==Culture== |
||
{{main|Culture of Mali}} |
{{main|Culture of Mali}} |
||
[[File:Konoguel Mosque tower (6439210).jpg|thumb|[[Konoguel Mosque]] tower]] |
[[File:Konoguel Mosque tower (6439210).jpg|thumb|upright|[[Konoguel Mosque]] tower]] |
||
The varied everyday culture of Malians reflects the country's ethnic and geographic diversity.<ref name=p13>Pye-Smith, Charlie & Rhéal Drisdelle. ''Mali: A Prospect of Peace?'' Oxfam (1997). {{ISBN|0-85598-334-5}}, p. 13.</ref> Most Malians wear flowing, colorful robes called [[boubou (clothing)|boubous]] that are typical of West Africa. Malians frequently participate in traditional festivals, dances, and ceremonies.<ref name=p13/> |
The varied everyday culture of Malians reflects the country's ethnic and geographic diversity.<ref name=p13>Pye-Smith, Charlie & Rhéal Drisdelle. ''Mali: A Prospect of Peace?'' Oxfam (1997). {{ISBN|0-85598-334-5}}, p. 13.</ref> Most Malians wear flowing, colorful robes called [[boubou (clothing)|boubous]] that are typical of West Africa. Malians frequently participate in traditional festivals, dances, and ceremonies.<ref name=p13/> |
||
=== Music === |
=== Music === |
||
{{Main|Music of Mali}} |
|||
[[Music of Mali|Malian musical traditions]] are derived from the [[griot]]s, who are known as "Keepers of Memories".<ref>Crabill, Michelle and Tiso, Bruce (January 2003). [https://web.archive.org/web/20030625150509/http://www.fcps.edu/KingsParkES/technology/mali/malihis.htm Mali Resource Website]. Fairfax County Public Schools. Retrieved 4 June 2008.</ref> Malian music is diverse and has several different genres. Some famous Malian influences in music are [[kora (instrument)|kora]] virtuoso musician [[Toumani Diabaté]], the [[Ngoni (instrument)|ngoni]] with [[Bassekou Kouyate]] the virtuoso of the electric [[Ngoni (instrument)|jeli ngoni]], the late roots and blues guitarist [[Ali Farka Touré]], the [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] band [[Tinariwen]], and several [[Afro pop music|Afro-pop]] artists such as [[Salif Keita]], the duo [[Amadou et Mariam]], [[Oumou Sangare]], [[Rokia Traore]], and [[Habib Koité]]. Dance also plays a large role in Malian culture.<ref name=embassy>{{cite web|title=Music|url=http://ambamali-jp.org/en/e04-05.html|publisher=Embassy of the Republic of Mali in Japan|accessdate=8 July 2013|deadurl=yes|archiveurl=https://archive.is/20130708063354/http://ambamali-jp.org/en/e04-05.html|archivedate=8 July 2013}}</ref> Dance parties are common events among friends, and traditional mask dances are performed at ceremonial events.<ref name=embassy/> |
|||
[[File:Mali Dogon Dance.jpg|thumb|left|Mali Dogon Dance]] |
|||
[[Music of Mali|Malian musical traditions]] are derived from the [[griot]]s, who are known as "Keepers of Memories".<ref>Crabill, Michelle and Tiso, Bruce (January 2003). [https://web.archive.org/web/20030625150509/http://www.fcps.edu/KingsParkES/technology/mali/malihis.htm Mali Resource Website]. Fairfax County Public Schools. Retrieved 4 June 2008.</ref> Malian music is diverse and has several different genres. Some famous Malian influences in music are [[Kora (instrument)|kora]] virtuoso musician [[Toumani Diabaté]], the [[Ngoni (instrument)|ngoni]] with [[Bassekou Kouyate]] the virtuoso of the electric [[Ngoni (instrument)|jeli ngoni]], the late roots and blues guitarist [[Ali Farka Touré]], the [[Tuareg people|Tuareg]] band [[Tinariwen]], [[Khaira Arby]], and several [[Afro pop music|Afro-pop]] artists such as [[Salif Keita]], the duo [[Amadou et Mariam]], [[Oumou Sangare]], [[Fatoumata Diawara]], [[Rokia Traore]], and [[Habib Koité]]. Dance also plays a large role in Malian culture.<ref name="embassy">{{cite web|title=Music|url=http://ambamali-jp.org/en/e04-05.html|publisher=Embassy of the Republic of Mali in Japan|access-date=8 July 2013 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130708063354/http://ambamali-jp.org/en/e04-05.html|archive-date=8 July 2013}}</ref> Dance parties are common events among friends, and traditional mask dances are performed at ceremonial events.<ref name="embassy" /> |
|||
=== Literature === |
=== Literature === |
||
Though Mali's literature is less famous than its music,<ref name=p29>[[#Velton|Velton]], p. 29.</ref> Mali has always been one of Africa's liveliest intellectual centers.<ref name=p128/> Mali's literary tradition is passed mainly by word of mouth, with ''jalis'' reciting or singing histories and stories known by heart.<ref name=p128 |
Though Mali's literature is less famous than its music,<ref name=p29>[[#Velton|Velton]], p. 29.</ref> Mali has always been one of Africa's liveliest intellectual centers.<ref name="p128">[[#Milet|Milet]], p. 128.</ref> Mali's literary tradition is passed mainly by word of mouth, with ''jalis'' reciting or singing histories and stories known by heart.<ref name="p128" /><ref name="p28">[[#Velton|Velton]], p. 28.</ref> [[Amadou Hampâté Bâ]], Mali's best-known historian, spent much of his life writing these oral traditions down for the world to remember.<ref name="p28" /> |
||
The best-known novel by a Malian writer is [[Yambo Ouologuem]]'s ''Le devoir de violence'', which won the 1968 [[Prix Renaudot]] but whose legacy was marred by accusations of plagiarism.<ref name=p128/><ref name=p28/> Other well-known Malian writers include Baba Traoré, Modibo Sounkalo Keita, [[Massa Makan Diabaté]], [[Moussa Konaté]], and [[Fily Dabo Sissoko]].<ref name=p128/><ref name=p28/> |
The best-known novel by a Malian writer is [[Yambo Ouologuem]]'s ''Le devoir de violence'', which won the 1968 {{Lang|fr|[[Prix Renaudot]]|italic=no}} but whose legacy was marred by accusations of plagiarism.<ref name=p128/><ref name="p28" /> Other well-known Malian writers include Baba Traoré, Modibo Sounkalo Keita, [[Massa Makan Diabaté]], [[Moussa Konaté (writer)|Moussa Konaté]], and [[Fily Dabo Sissoko]].<ref name=p128/><ref name=p28/> |
||
=== Sport === |
=== Sport === |
||
[[File:Mali football.jpg|thumb|Malian children playing football in a [[Dogon people|Dogon]] village]] |
[[File:Mali football.jpg|thumb|Malian children playing football in a [[Dogon people|Dogon]] village]] |
||
The [[Football in Mali|most popular sport in Mali]] is [[ |
The [[Football in Mali|most popular sport in Mali]] is [[association football]],<ref name=p151>[[#Milet|Milet]], p. 151.</ref><ref name=p55>[[#DiPiazza|DiPiazza]], p. 55.</ref> which became more prominent after Mali hosted the [[2002 African Cup of Nations]].<ref name="p151" /><ref name="p320">Hudgens, Jim, Richard Trillo, and Nathalie Calonnec. ''The Rough Guide to West Africa''. [[Rough Guides]] (2003). {{ISBN|1-84353-118-6}}, p. 320.</ref> Most towns and cities have regular games;<ref name="p320" /> the most popular teams nationally are [[Djoliba AC]], [[Stade Malien]], and [[Real Bamako]], all based in the capital.<ref name=p55/> Informal games are often played by youths using a bundle of rags as a ball.<ref name="p55" /> |
||
Basketball is another major sport;<ref name="p55" /><ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20080101165700/http://www.africabasket.com/mli/mli.asp "Malian Men Basketball"]. [[Africabasket.com]]. Retrieved 3 June 2008.</ref> the [[Mali women's national basketball team]], led by [[Hamchetou Maiga]], competed at the 2008 [[2008 Summer Olympics|Beijing Olympics]].<ref>Chitunda, Julio. [http://www.fiba.com/pages/eng/fc/news/lateNews/arti.asp?newsid=23726 "Ruiz looks to strengthen Mali roster ahead of Beijing"]. [[FIBA]].com (13 March 2008). Retrieved 24 June 2008.</ref> [[Lutte Traditionnelle|Traditional wrestling]] (''la lutte'') is also somewhat common, though popularity has declined in recent years.<ref name="p320" /> The game [[Oware|wari]], a [[mancala]] variant, is a common pastime.<ref name="p55" /> |
Basketball is another major sport;<ref name="p55" /><ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20080101165700/http://www.africabasket.com/mli/mli.asp "Malian Men Basketball"]. [[Africabasket.com]]. Retrieved 3 June 2008.</ref> the [[Mali women's national basketball team]], led by [[Hamchetou Maiga]], competed at the 2008 [[2008 Summer Olympics|Beijing Olympics]].<ref>Chitunda, Julio. [http://www.fiba.com/pages/eng/fc/news/lateNews/arti.asp?newsid=23726 "Ruiz looks to strengthen Mali roster ahead of Beijing"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303184921/http://www.fiba.com/pages/eng/fc/news/latenews/arti.asp?newsid=23726 |date=3 March 2016 }}. [[FIBA]].com (13 March 2008). Retrieved 24 June 2008.</ref> [[Lutte Traditionnelle|Traditional wrestling]] (''la lutte'') is also somewhat common, though popularity has declined in recent years.<ref name="p320" /> The game [[Oware|wari]], a [[mancala]] variant, is a common pastime.<ref name="p55" /> |
||
Mali featured a men's national team in [[beach volleyball]] that competed at the [[2018–2020 CAVB Beach Volleyball Continental Cup]].<ref>{{cite news |title=Continental Cup Finals start in Africa |url=https://www.fivb.com/en/about/news/continental-cup-finals-start-in-africa?id=94414 |access-date=7 August 2021 |work=[[FIVB]] |date=22 June 2021 |archive-date=7 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210807141038/https://www.fivb.com/en/about/news/continental-cup-finals-start-in-africa?id=94414 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
===Cuisine=== |
===Cuisine=== |
||
| Line 396: | Line 667: | ||
[[File:Malian Tea2.JPG|thumb|Malian tea]] |
[[File:Malian Tea2.JPG|thumb|Malian tea]] |
||
Rice and [[millet]] are the staples of [[Malian cuisine]], which is heavily based on cereal grains.<ref name=p30>[[#Velton|Velton]], p. 30.</ref><ref name=p146/> Grains are generally prepared with sauces made from edible leaves, such as [[spinach]] or [[Adansonia digitata|baobab]], with tomato peanut sauce, and may be accompanied by pieces of grilled meat (typically chicken, [[mutton]], beef, or goat).<ref name=p30/><ref name=p146 |
Rice and [[millet]] are the staples of [[Malian cuisine]], which is heavily based on cereal grains.<ref name="p30">[[#Velton|Velton]], p. 30.</ref><ref name="p146">[[#Milet|Milet]], p. 146.</ref> Grains are generally prepared with sauces made from edible leaves, such as [[spinach]] or [[Adansonia digitata|baobab]], with tomato peanut sauce, and may be accompanied by pieces of grilled meat (typically chicken, [[mutton]], beef, or goat).<ref name="p30" /><ref name="p146" /> Malian cuisine varies regionally.<ref name="p30" /><ref name="p146" /> Other popular dishes include [[fufu]], [[jollof rice]], and [[maafe]]. |
||
===Media=== |
===Media=== |
||
{{main|Media of Mali}} |
{{main|Media of Mali}} |
||
In Mali, there are several newspapers such as ''Les Echos'', ''L'Essor'', ''Info Matin'', ''Nouvel Horizon'', and ''Le Républicain''.<ref>{{cite book|editor=Murison, Katharine |title=Africa South of the Sahara 2003|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1KBP7QbalX0C&pg=PA652|year=2002|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-1-85743-131-5|pages=652–53}}</ref> The [[Telecommunications in Mali]] include 869,600 mobile phones, 45,000 televisions and 414,985 Internet users.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.best-country.com/africa/mali/traditions|title=Culture of Mali|last=Batvina|first=Iryna|website=www.best-country.com|access-date=18 September 2016}}</ref> |
|||
In Mali, there are several newspapers such as ''[[Les Échos (Mali)|Les Echos]]'', ''[[L'Essor]]'', ''[[Info Matin]]'', ''[[Nouvel Horizon (Mali)|Nouvel Horizon]]'', and ''{{ill|Le Républicain (Mali)|lt=Le Républicain|fr|Le Républicain (Mali)}}''.<ref>{{cite book|editor-last=Murison |editor-first=Katharine|title=Africa South of the Sahara 2003|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1KBP7QbalX0C&pg=PA652|year=2002|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-1-85743-131-5|pages=652–53|access-date=20 June 2015|archive-date=6 September 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150906191638/https://books.google.com/books?id=1KBP7QbalX0C&pg=PA652|url-status=live}}</ref> [[Office de Radiodiffusion-Télévision du Mali]] is the state-owned service. [[Telecommunications in Mali]] include 869,600 mobile phones, 45,000 televisions and 414,985 Internet users.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.best-country.com/africa/mali/traditions|title=Culture of Mali|last=Batvina|first=Iryna|website=Best-Country.com|access-date=18 September 2016|archive-date=5 November 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161105173621/http://www.best-country.com/africa/mali/traditions|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{ |
{{Portal|Mali|Africa}} |
||
* [[Index of Mali-related articles]] |
* [[Index of Mali-related articles]] |
||
* [[Outline of Mali]] |
* [[Outline of Mali]] |
||
{{clear}} |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
{{Notelist}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist |
{{Reflist}} |
||
==Bibliography== |
==Bibliography== |
||
{{Refbegin}} |
{{Refbegin}} |
||
* {{cite web|ref=Const|url=http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/CAFRAD/UNPAN002746.pdf |title=Constitution of Mali|language= |
* {{cite web |ref=Const |url=http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/CAFRAD/UNPAN002746.pdf |title=Constitution of Mali |language=fr |access-date=2 April 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180920144209/http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/CAFRAD/UNPAN002746.pdf |archive-date=20 September 2018 }} A student-translated [http://confinder.richmond.edu/admin/docs/Mali.pdf English version] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120912141413/http://confinder.richmond.edu/admin/docs/Mali.pdf |date=12 September 2012 }} is also available. |
||
* {{cite web |ref=Prof|url=https://tile.loc.gov/storage-services/master/frd/copr/Mali.pdf|title=Country profile: Mali|publisher=[[Library of Congress]] – [[Federal Research Division]]|date=January 2005|access-date=30 July 2024}} ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the [[public domain]].'' |
|||
* {{cite book|ref=DiPiazza | last = DiPiazza | first = Francesca Davis | title = Mali in Pictures | publisher=Learner Publishing Group | year = 2006 | location = Minneapolis, Minnesota | isbn = 978-0-8225-6591-8 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OR4Ovt7U_2IC&pg=PA55 }} |
|||
* {{cite book |ref=DiPiazza |last=DiPiazza |first=Francesca Davis |title=Mali in Pictures |publisher=Learner Publishing Group |date=2006 |location=Minneapolis, Minnesota |isbn=978-0-8225-6591-8 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OR4Ovt7U_2IC&pg=PA55 |access-date=20 June 2015 |archive-date=7 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150907193017/https://books.google.com/books?id=OR4Ovt7U_2IC&pg=PA55 |url-status=live }} |
|||
* {{cite web|ref=Prof|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/profiles/Mali.pdf |title=Mali country profile|publisher=[[Library of Congress]] [[Federal Research Division]] |date=January 2005}} ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the [[public domain]].'' |
|||
* {{cite book|ref=Milet|author1=Milet, Eric |
* {{cite book |ref=Milet|author1=Milet, Eric|author2=Manaud, Jean-Luc|name-list-style=amp|title=Mali|url=https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_DC0Dj2if8DwC_2|publisher=Editions Olizane |date=2007|isbn=978-2-88086-351-7|language=fr}} |
||
* {{cite book|ref=Velton| |
* {{cite book |ref=Velton|last=Velton |first=Ross|title=Mali|publisher=Bradt Travel Guides |date=2004 |isbn=978-1-84162-077-0 }} |
||
{{Refend}} |
{{Refend}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{ |
{{Sisterlinks|Mali|voy=Mali}} |
||
* |
* [http://primature.ml/ Official website] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200609221350/http://primature.ml/ |date=9 June 2020 }} |
||
* {{ |
* {{Wikiatlas|Mali}} |
||
* {{Osmrelation-inline|192785}} |
|||
* {{CIA World Factbook link|ml|Mali}} |
|||
* [https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/ Mali] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210330032030/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/ |date=30 March 2021 }}. ''[[The World Factbook]]''. [[Central Intelligence Agency]]. |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080607085209/http://ucblibraries.colorado.edu/govpubs/for/mali.htm Mali] from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' |
|||
* [https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-13881370 Mali profile] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180624085511/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-13881370 |date=24 June 2018 }} from the [[BBC News]] |
|||
* {{dmoz|Regional/Africa/Mali}} |
|||
* [https://www.ictj.org/publication/possibilities-and-challenges-transitional-justice-mali Possibilities and Challenges for Transitional Justice in Mali] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160918152945/https://www.ictj.org/publication/possibilities-and-challenges-transitional-justice-mali |date=18 September 2016 }} from the [[ICTJ]] |
|||
* [https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-13881370 Mali profile] from the [[BBC News]] |
|||
* [https://www.facebook.com/Ngonifamily Facebook group about Ngoni] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220219035049/https://www.facebook.com/Ngonifamily |date=19 February 2022 }}, considered a traditional instrument of Mali; also known as Xalam, Jeli N'goni, Hoddu, Khalam, Tehardent, or Gambare |
|||
* [https://www.ictj.org/publication/possibilities-and-challenges-transitional-justice-mali Possibilities and Challenges for Transitional Justice in Mali] from the [[ICTJ]] |
|||
* [http://wits.worldbank.org/CountryProfile/Country/MLI/Year/2012/Summary Mali 2012 Trade Summary Statistics] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407084716/http://wits.worldbank.org/CountryProfile/Country/MLI/Year/2012/Summary |date=7 April 2014 }} |
|||
* [https://www.facebook.com/Ngonifamily Community about Ngoni ( Xalam, Jeli N'goni, Hoddu, Khalam, Tehardent, Gambare...)] |
|||
* [https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/mali-population/ - Mali Population-Worldometer] |
|||
; Trade |
|||
* [http://wits.worldbank.org/CountryProfile/Country/MLI/Year/2012/Summary Mali 2012 Trade Summary Statistics] |
|||
{{Mali topics|state=collapsed}} |
{{Mali topics|state=collapsed}} |
||
| Line 439: | Line 713: | ||
{{Countries of Africa}} |
{{Countries of Africa}} |
||
{{African Union}} |
{{African Union}} |
||
{{Community of |
{{Community of Sahel–Saharan States}} |
||
{{La Francophonie}} |
{{La Francophonie}} |
||
{{Organisation of the Islamic Conference}} |
{{Organisation of the Islamic Conference}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
{{Coord|17|N|4|W|type:country|display=title}} |
|||
[[Category:Mali| ]] |
[[Category:Mali| ]] |
||
[[Category:1960 establishments in Africa]] |
[[Category:1960 establishments in Africa]] |
||
[[Category:Countries and territories where Arabic is an official language]] |
|||
[[Category:Countries in Africa]] |
[[Category:Countries in Africa]] |
||
[[Category:Former French colonies]] |
[[Category:Former French colonies]] |
||
[[Category:French-speaking countries and territories]] |
|||
[[Category:Landlocked countries]] |
[[Category:Landlocked countries]] |
||
[[Category:Least developed countries]] |
[[Category:Least developed countries]] |
||
Latest revision as of 16:23, 26 December 2024
Republic of Mali | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Un peuple, un but, une foi" (French) "Mɔgɔ kelen, laɲini kelen, dannaya kelen" (Bambara) "One people, one goal, one faith" | |
| Anthem: "Le Mali" (French) | |
 Location of Mali (green) | |
| Capital and largest city | Bamako 12°39′N 8°0′W / 12.650°N 8.000°W |
| Official languages | 13 national languages[2][3] |
| Working language | |
| Spoken languages | |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Religion (2021)[7] | |
| Demonym(s) | Malian |
| Government | Unitary presidential republic under a military junta[8] |
| Assimi Goïta (interim) | |
| Abdoulaye Maïga (interim) | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Formation | |
• Establishment of the Sudanese Republic | 24 November 1958 |
• Merger with Senegal to create the Mali Federation | 4 April 1959 |
• Independence from France | 20 June 1960 |
• Dissolution of the Mali Federation | 20 August 1960 |
• Declaration of the Republic of Mali | 22 September 1960 |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,240,192 km2 (478,841 sq mi)[9] (23rd) |
• Water (%) | 1.6 |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | 21,990,607[10] (61st) |
• Density | 11.7/km2 (30.3/sq mi) (215th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2010) | 33.0[12] medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | low (188th) |
| Currency | West African CFA franc (XOF) |
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Drives on | Right[14] |
| Calling code | +223 |
| ISO 3166 code | ML |
| Internet TLD | .ml |
Mali,[c] officially the Republic of Mali,[d] is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over 1,240,192 square kilometres (478,841 sq mi).[9] The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east by Niger, to the northwest by Mauritania, to the south by Burkina Faso and Ivory Coast, and to the west by Guinea and Senegal. The population of Mali is 24,478,595,[15][16] 47.19% of which are estimated to be under the age of 15 in 2024.[17] Its capital and largest city is Bamako. The country has 13 official languages, of which Bambara is the most commonly spoken.
The sovereign state's northern borders reach deep into the middle of the Sahara Desert. The country's southern part, where the majority of inhabitants live, is in the Sudanian savanna and has the Niger and Senegal rivers running through it. The country's economy centres on agriculture and mining with its most prominent natural resources including gold (of which it is the third largest producer in Africa)[18] and salt.[19]
Mali was part of three successive powerful and wealthy West African empires that controlled trans-Saharan trade: the Ghana Empire (for which Ghana is named), the Mali Empire (for which Mali is named), and the Songhai Empire. At its peak in 1300, the Mali Empire was the wealthiest country in Africa[20] with its 14th-century emperor Mansa Musa believed to be one of the wealthiest individuals in history.[21][22][23] Besides being a hub of trade and mining, medieval Mali was a centre of Islam, culture and knowledge, with Timbuktu becoming a renowned place of learning with its university, one of the oldest in the world and still active. The expanding Songhai Empire absorbed the empire in 1468,[not verified in body] followed by a Saadian army which defeated the Songhai in 1591. In the late 19th century, during the Scramble for Africa, France seized control of Mali, making it a part of French Sudan; as the Sudanese Republic, a brief federation with Senegal was formed, achieving independence in 1960. After Senegal's withdrawal, the Republic of Mali was established. After a long period of one-party rule, a coup in 1991 led to a new constitution and the establishment of Mali as a democratic, multi-party state.
In January 2012, an armed conflict broke out in northern Mali, in which Tuareg rebels took control of a territory in the north, and in April declared the secession of a new state, Azawad.[24] The conflict was complicated by a military coup in March 2012[25] and later fighting between Tuareg and other rebel factions. In response to territorial gains, the French military launched Operation Serval in January 2013.[26] A month later, Malian and French forces recaptured most of the north, although the conflict continued. Presidential elections were held on 28 July 2013, with a second-round run-off held on 11 August, and legislative elections were held on 24 November and 15 December 2013. In the early 2020s, Mali experienced two military takeovers by Assimi Goïta.
Etymology
[edit]The name Mali is taken from the name of the Mali Empire. It means "the place where the king lives"[27] and carries a connotation of strength.[28]
Fourteenth-century Maghrebi traveller Ibn Battuta reported that the capital of the empire was called Mali.[29][30] One Mandinka tradition tells that the legendary first emperor Sundiata Keita changed himself into a hippopotamus upon his death in the Sankarani River and that it was possible to find villages in the area of this river called "old Mali". A study of Malian proverbs noted that in old Mali, there is a village called Malikoma, which means "New Mali", and that Mali could have formerly been the name of a city.[31]
Another theory suggests that Mali is a Fulani pronunciation of the name of the Mande peoples.[32][33] It is suggested that a sound shift led to the change, whereby in Fulani the alveolar segment /nd/ shifts to /l/ and the terminal vowel denasalizes and raises, leading "Manden" to shift to /mali/.[31]
History
[edit]Before colonization
[edit]

The rock art in the Sahara suggests that northern Mali has been inhabited since 10,000 BC, when the Sahara was fertile and rich in wildlife. Early ceramics have been discovered at the central Malian site of Ounjougou dating to about 9,400 BC, and are believed to represent an instance of the independent invention of pottery in the region.[34] Farming took place by 5000 BC and iron was used by around 500 BC. In the first millennium BC, early cities and towns were created by Mande peoples related to the Soninke people, along the middle Niger River in central Mali, including Dia which began from around 900 BC, and reached its peak around 600 BC,[35] and Djenne-Djenno, which lasted from around 300 BC to 900 AD. By the sixth century AD, the lucrative trans-Saharan trade in gold, salt and slaves had begun, facilitating the rise of West Africa's great empires.
There are a few references to Mali in early Islamic literature. Among these are references to "Pene" and "Malal" in the work of al-Bakri in 1068,[36] the story of the conversion of an early ruler, known to Ibn Khaldun (by 1397) as Barmandana,[37] and a few geographical details in the work of al-Idrisi.[38]
Mali was once part of three famed West African empires which controlled trans-Saharan trade in gold, salt, other precious commodities, and slaves majorly during the reign of Mansa Musa from c. 1312 – c. 1337.[39] These Sahelian kingdoms had neither rigid geopolitical boundaries nor rigid ethnic identities.[39] The earliest of these empires was the Ghana Empire, which was dominated by the Soninke, a Mande-speaking people.[39] The empire expanded throughout West Africa from the eighth century until 1078, when it was conquered by the Almoravids.[40]
The Battle of Kirina in 1235, culminated in a victory for the Mandinka under the command of the exiled prince Sundiata Keita, which led to the downfall of the Sosso Empire.


The Mali Empire later formed on the upper Niger River, and reached the height of power in the 14th century.[40] Under the Mali Empire, the ancient cities of Djenné and Timbuktu were centers of both trade and Islamic learning.[40] The empire later declined as a result of internal intrigue, ultimately being supplanted by the Songhai Empire.[40] The Songhai had long been a major power in West Africa subject to the Mali Empire's rule.[40]
In the late 14th century, the Songhai gradually gained independence from the Mali Empire and expanded, ultimately subsuming the entire eastern portion of the Mali Empire.[40] The Songhai Empire's eventual collapse was largely the result of the Moroccan invasion of 1591 under the command of Judar Pasha.[40] The fall of the Songhai Empire marked the end of the region's role as a trading crossroads.[40] Following the establishment of sea routes by the European powers, the trans-Saharan trade routes lost significance.[40] At that time, the Mali Empire's abundance in wealth expanded its commercial assets of salt and gold.
One of the worst famines in the region's recorded history occurred in the 18th century. According to John Iliffe, "The worst crises were in the 1680s, when famine extended from the Senegambian coast to the Upper Nile and 'many sold themselves for slaves, only to get a sustenance', and especially in 1738–1756, when West Africa's greatest recorded subsistence crisis, due to drought and locusts, reportedly killed half the population of Timbuktu."[41]
French colonial rule
[edit]
Mali fell under the control of France during the Scramble for Africa in the late 19th century.[40] By 1905, most of the area was under firm French control as a part of French Sudan.[40]
In November 1915, a large anti-French uprising broke out among the tribes in the regions of present-day Mali and Burkina Faso.[42] The last resistance was suppressed only in September 1916. During the suppression of the uprising, over 100 villages were destroyed by French colonial troops.[43]
On 24 November 1958, French Sudan (which changed its name to the Sudanese Republic) became an autonomous republic within the French Community.[44] In January 1959, Mali and Senegal united to become the Mali Federation.[44]
Independence
[edit]The Mali Federation gained independence from France on 20 June 1960.[40] Senegal withdrew from the federation in August 1960, which allowed the Sudanese Republic to become the independent Republic of Mali on 22 September 1960, and that date is now the country's Independence Day.[45]
Modibo Keïta was elected the first president.[40] He quickly established a one-party state, adopted an independent African and socialist orientation with close ties to the East, and implemented extensive nationalization of economic resources.[40] In 1960, the population of Mali was reported to be about 4.1 million.[46] On 19 November 1968, following progressive economic decline, the Keïta regime was overthrown in a bloodless military coup led by Moussa Traoré,[47] a day which is now commemorated as Liberation Day.[48]
Moussa Traoré regime
[edit]The subsequent military-led regime, with Traoré as president, attempted to reform the economy. His efforts were frustrated by political turmoil and a devastating drought from 1968 to 1974,[47] in which famine killed thousands of people.[49] The Traoré regime faced student unrest beginning in the late 1970s and three coup attempts. The Traoré regime repressed all dissenters until the late 1980s.[47]

Opposition to the corrupt and dictatorial regime of General Moussa Traoré grew during the 1980s. During this time strict programs, imposed to satisfy demands of the International Monetary Fund, brought increased hardship upon the country's population, while elites close to the government supposedly lived in growing wealth. The government continued to attempt economic reforms, and the populace became increasingly dissatisfied.[47] In response to growing demands for multi-party democracy, the Traoré regime allowed some limited political liberalization in the late 1980s, but refused to usher in a full-fledged democratic system.[47]
In 1990, cohesive opposition movements began to emerge, and was complicated by the turbulent rise of ethnic violence in the north following the return of many Tuaregs who had migrated to Algeria and Libya during the drought.[47] Peaceful student protests in January 1991 were brutally suppressed, with mass arrests and torture of leaders and participants.[50] Scattered acts of rioting and vandalism of public buildings followed, but most actions by the dissidents remained nonviolent.[50]
From 22 March through 26 March 1991, mass pro-democracy rallies and a nationwide strike was held in both urban and rural communities, which became known as les évenements ("the events") or the March Revolution. In Bamako, in response to mass demonstrations organized by university students and later joined by trade unionists and others, soldiers opened fire indiscriminately on the nonviolent demonstrators. Riots broke out briefly following the shootings. Barricades as well as roadblocks were erected and Traoré declared a state of emergency and imposed a nightly curfew. Despite an estimated loss of 300 lives over the course of four days, nonviolent protesters continued to return to Bamako each day demanding the resignation of the dictatorial president and the implementation of democratic policies.[51]
26 March 1991 is the day that marks the clash between military soldiers and peaceful demonstrating students which climaxed in the massacre of dozens under the orders of Traoré. He and three associates were later tried and convicted and received the death sentence for their part in the decision-making of that day. Nowadays, the day is a national holiday in order to remember the tragic events and the people who were killed.[52][53] The coup is remembered as Mali's March Revolution of 1991.[54]
By 26 March, the growing refusal of soldiers to fire into the largely nonviolent protesting crowds turned into a full-scale tumult, and resulted in thousands of soldiers putting down their arms and joining the pro-democracy movement. That afternoon, Lieutenant Colonel Amadou Toumani Touré announced on the radio that he had arrested the dictatorial president, Moussa Traoré.
Multi-party democracy
[edit]Opposition parties were legalized, a transitional government was formed and a national congress of civil and political groups met to draft a new democratic constitution to be approved by a national referendum.[51][47] In 1992, Alpha Oumar Konaré won Mali's first democratic, multi-party presidential election, before being re-elected for a second term in 1997, which was the last allowed under the constitution. Amadou Toumani Touré, a retired general who had been the leader of the military aspect of the 1991 democratic uprising, was elected in 2002.[55] During this democratic period Mali was regarded as one of the most politically and socially stable countries in Africa.[56]
Slavery persists in Mali today with as many as 200,000 people held in direct servitude to a master.[57] In the Tuareg Rebellion of 2012, ex-slaves were a vulnerable population with reports of some slaves being recaptured by their former masters.[58]
Northern Mali conflict
[edit]
In January 2012 a Tuareg rebellion began in northern Mali, led by the National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad (MNLA).[59] In March, military officer Amadou Sanogo seized power in a coup d'état, citing Touré's failures in quelling the rebellion, and leading to sanctions and an embargo by the Economic Community of West African States.[60] The MNLA quickly took control of the north, declaring its independence as Azawad.[61] However, Islamist groups, including Ansar Dine and Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM), who had helped the MNLA defeat the government, turned on the Tuareg and took control of the north[62] with the goal of implementing sharia in Mali.[63][64]
On 11 January 2013, the French Armed Forces intervened at the request of the interim government of president Dioncounda Traoré. On 30 January, the coordinated advance of the French and Malian troops claimed to have retaken the last remaining Islamist stronghold of Kidal, which was also the last of three northern provincial capitals.[65] On 2 February, French president François Hollande joined Dioncounda Traoré in a public appearance in recently recaptured Timbuktu.[66]

In August 2013, Ibrahim Boubacar Keita was elected as the new president of Mali in the second round of the election.[67]
Conflict in Central Mali
[edit]In the central Mali province of Mopti, conflict has escalated since 2015 between agricultural communities like the Dogon and the Bambara, and the pastoral Fula (or Fulani) people.[68][69] Historically, the two sides have fought over access to land and water, factors which have been exacerbated by climate change as the Fula move into new areas.[70] The Dogon and the Bambara communities have formed "self-defense groups"[69] to fight the Fula. They accuse the Fula of working with armed Islamists linked to al-Qaeda.[69] While some Fula have joined Islamist groups, Human Rights Watch reports that the links have been "exaggerated and instrumentalized by different actors for opportunistic ends".[69]
Added a top Mali military commander:
I’ve discussed the growing violence with my commanders and with village chiefs from all sides. Yes, sure, there are jihadists in this zone, but the real problem is banditry, animal theft, score settling – people are enriching themselves using the fight against terrorists as a cover.[69]
The conflict has seen the creation and growth of Dogon and Bambara militias. The government of Mali is suspected of supporting some of these groups under the guise of being proxies in the war against Islamists in the Northern Mali conflict.[71] The government denies this.[71] One such militia is the Dogon group Dan Na Ambassagou, created in 2016.[69]

In the 2018 Malian presidential election held on 29 July 2018,[72][73] no candidate received more than 50% of the vote in the first round. A runoff was held on 12 August 2018 between the top two candidates, incumbent president Ibrahim Boubacar Keïta of the Rally for Mali and Soumaïla Cissé of the Union for the Republic and Democracy, and Keïta was re-elected with 67% of the vote.[74]
In September 2018, the Centre for Humanitarian Dialogue negotiated a unilateral ceasefire with Dan Na Ambassagou "in the context of the conflict which opposes the group to other community armed groups in central Mali".[75] However, the group has been blamed for the 24 March 2019 massacre of 160 Fula villagers.[76] The group denied the attack, but afterwards Malian president Keita ordered the group to disband.[77] The UN Special Adviser on the Prevention of Genocide, Adama Dieng, warned of a growing ethnicization of the conflict.[78] By 2020, more than 600,000 people had been displaced by the conflict in Mali.[79] The United Nations reported that the number of children killed in the conflict in the first six months of 2019 was twice as many for the entire year of 2018. Many of the children have been killed in intercommunal attacks attributed to ethnic militias, with the majority of attacks occurring around Mopti. It is reported that around 900 schools have closed down and that armed militias are recruiting children.[80]
During the first week of October 2019, two jihadist attacks in the towns of Boulikessi and Mondoro killed more than 25 Mali soldiers near the border with Burkina Faso.[81] President Keïta declared that "no military coup will prevail in Mali", continuing by saying that he does not think it "is on the agenda at all and cannot worry us".[82] On 1 November 2019, the IS-GS militants killed at least 50 soldiers in the 2019 Indelimane attack in the Ménaka Region of Mali.[83] In February 2020, Human Rights Watch documented atrocities against civilians in Central Mali and said that at least 456 civilians were killed, while hundreds were injured from January 2019 until November.[84]
2020s coups and Assimi Goïta junta
[edit]
Popular unrest began on 5 June 2020 following irregularities in the March and April parliamentary elections, including outrage against the kidnapping of opposition leader Soumaïla Cissé.[85][86] Between 11 and 23 deaths followed protests that took place from 10 to 13 June.[87] In July, President Keïta dissolved the constitutional court.
Members of the military led by Colonel Assimi Goïta and Colonel-Major Ismaël Wagué in Kati, Koulikoro Region, began a mutiny on 18 August 2020.[87] President Ibrahim Boubacar Keïta and Prime Minister Boubou Cissé were arrested, and shortly after midnight Keïta announced his resignation, saying he did not want to see any bloodshed.[87] Wagué announced the formation of the National Committee for the Salvation of the People (CNSP) and promised elections in the future. A curfew was begun and the streets of Bamako were quiet.[87] The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) condemned the coup and demanded that Keïta be reinstated as president.[88]
On 12 September 2020, the CNSP agreed to an 18-month political transition to civilian rule. Shortly after, Bah N'daw was named interim president by a group of 17 electors, with Goïta being appointed vice president. The government was inaugurated on 25 September 2020. On 18 January 2021, the transitional government announced that the CNSP had been disbanded, almost four months after had been promised under the initial agreement.[89]
Tensions between the civilian transitional government and the military ran high after the handover of power in September 2020. The tensions came to a head on 24 May 2021 after a cabinet reshuffle, where two leaders of the 2020 military coup – Sadio Camara and Modibo Kone – were replaced by N'daw's administration.[90] Later that day, journalists reported that three key civilian leaders – President N'daw, Prime Minister Moctar Ouane and Defence Minister Souleymane Doucouré, were being detained in a military base in Kati, outside Bamako.[91] On 7 June 2021, Mali's military commander Assimi Goïta was sworn into office as the new interim president.[92]
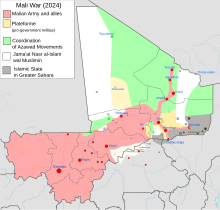
In 2022 and 2023, the Islamic State in the Greater Sahara saw major gains in the Mali War, occupying large swathes of territory in southeastern Mali. Ansongo and Tidermène were also captured by the group.[93] By mid-2023, the militant group had doubled the amount of territory it controlled since the overthrow of the previous government and establishment of the junta.[94]
On 10 January 2022, Mali announced the closure of its borders and recalled several ambassadors to ECOWAS countries in response to sanctions placed on Mali for deferring elections for four years.[95] On 4 February, France's ambassador was expelled.[96] According to Human Rights Watch, Malian troops and suspected Russian mercenaries from the Wagner Group executed around 300 civilian men in central Mali in March 2022. France had started withdrawing French troops from Mali in February 2022, commencing the end of Operation Barkhane.[97] On 2 May, the military government announced breaking its defence accords concluded in 2013 with France, constituting an additional step in the deterioration of Malian–French relations.[98] This latest announcement has been criticized by French authorities and considered as "illegitimate".[99] A UN panel reported that in the first three months of 2022, 543 civilians were killed and 269 wounded, warning the 2015 peace agreement between the government and pro-independence groups was threatened by a potential risk of confrontation for the first time in five years. The report also noted a sharp increase in the number of people needing humanitarian assistance over the previous year.[100]
Sergey Lavrov, the Russian foreign minister, visited Bamako on 7 February 2023 and said that Moscow would continue to help Mali improve its military capabilities.[101]
In June 2023, Mali removed French, the language of its former colonizer, as an official language with the approval of a new constitution by 97% of voters in a referendum conducted by the junta.[102]
On 7 September 2023, al-Qaeda linked JNIM militants attacked a vessel on the Niger River, killing at least 154 civilians.[103]
In July 2024, CSP-DPA rebels and JNIM militants killed dozens of Russian mercenaries and Malian government forces during the Battle of Tinzaouaten.[104] On 5 August 2024 the Republic of Mali announced that it was severing diplomatic relations with Ukraine.[105][106]
On 17 September 2024, al-Qaeda linked JNIM militants attacked several locations across Bamako, killing at least 77 people and injuring 255 others.[107]
Geography
[edit]
Mali is a landlocked country in West Africa, located southwest of Algeria. It lies between latitudes 10° and 25°N, and longitudes 13°W and 5°E. Mali borders Algeria to the north-northeast, Niger to the east, Burkina Faso to the south-east, Ivory Coast to the south, Guinea to the south-west, and Senegal to the west and Mauritania to the north-west.[108]


At 1,240,192 square kilometres (478,841 sq mi),[6] Mali is the 24th-largest country in the world and the eighth-largest country in Africa.[109] It is comparable in size to South Africa or Angola. Most of the country lies in the southern Sahara Desert, which produces an extremely hot, dust-laden Sudanian savanna zone.[110] Mali is mostly flat, rising to rolling northern plains covered by sand. The Adrar des Ifoghas massif lies in the northeast.
Mali lies in the torrid zone and is among the hottest countries in the world. The thermal equator, which matches the hottest spots year-round on the planet based on the mean daily annual temperature, crosses the country.[110] Most of Mali receives negligible rainfall and droughts are very frequent.[110] Late April to early October is the rainy season in the southernmost area. During this time, flooding of the Niger River is common, creating the Inner Niger Delta.[110] The vast northern desert part of Mali has a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh) with long, extremely hot summers and scarce rainfall which decreases northwards. The central area has a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification BSh) with very high temperatures year-round, a long, intense dry season and a brief, irregular rainy season. The southern areas have a tropical wet and dry climate. (Köppen climate classification Aw) In review, Mali's climate is tropical, with March to May being the hot, dry season. June to October is rainy, humid and mild. November to February is the cool, dry season.
Mali has considerable natural resources, with gold, uranium, phosphates, kaolinite, salt and limestone being most widely exploited. Mali is estimated to have in excess of 17,400 tonnes of uranium (measured + indicated + inferred).[111][112] In 2012, a further uranium mineralized north zone was identified.[113] Mali faces numerous environmental challenges, including desertification, deforestation, soil erosion, and inadequate supplies of potable water.[110]
Biodiversity
[edit]Five terrestrial ecoregions lie within Mali's borders: Sahelian Acacia savanna, West Sudanian savanna, Inner Niger Delta flooded savanna, South Saharan steppe and woodlands, and West Saharan montane xeric woodlands.[114] The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.16/10, ranking it 51st globally out of 172 countries.[115]
Politics and government
[edit]Government
[edit]
Until the military coup of 22 March 2012,[25][116] Mali was a constitutional democracy governed by the Constitution of 12 January 1992, which was amended in 1999.[117] The constitution provides for a separation of powers among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government.[117] The system of government can be described as "semi-presidential".[117] Executive power is vested in a president, who is elected to a five-year term by universal suffrage and is limited to two terms.[117][118]
The president serves as a chief of state and commander in chief of the armed forces.[117][119] A prime minister appointed by the president serves as head of government and in turn appoints the Council of Ministers.[117][120] The unicameral National Assembly is Mali's sole legislative body, consisting of deputies elected to five-year terms.[121][122] Following the 2007 elections, the Alliance for Democracy and Progress held 113 of 160 seats in the assembly.[123] The assembly holds two regular sessions each year, during which it debates and votes on legislation that has been submitted by a member or by the government.[121][124]
Mali's constitution provides for an independent judiciary,[121][125] but the executive continues to exercise influence over the judiciary by virtue of power to appoint judges and oversee both judicial functions and law enforcement.[121] Mali's highest courts are the Supreme Court, which has both judicial and administrative powers, and a separate Constitutional Court that provides judicial review of legislative acts and serves as an election arbiter.[121][126] Various lower courts exist, though village chiefs and elders resolve most local disputes in rural areas.[121]
The transition government pushed back the timetable for a new election, initially to be held in February 2022, to February 2024.[127] In exchange for the government's commitment to a 2024 election, ECOWAS agreed to lift sanctions on the country.[128]
Foreign relations
[edit]

Until 2012, Mali's foreign policy orientation had become increasingly pragmatic and pro-Western over time.[129] Since the institution of a democratic form of government in 2002, Mali's relations with the West in general and with the United States in particular have improved significantly.[129] Mali has a longstanding yet ambivalent relationship with France, a former colonial ruler.[129] Mali was active in regional organizations such as the African Union until its suspension over the 2012 Malian coup d'état.[129][130]
Working to control and resolve regional conflicts, such as in Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone, is one of Mali's major foreign policy goals.[129] Mali feels threatened by the potential for the spillover of conflicts in neighboring states, and relations with those neighbors are often uneasy.[129] General insecurity along borders in the north, including cross-border banditry and terrorism, remain troubling issues in regional relations.[129]
In early 2019, Al Qaeda claimed responsibility for an attack on a United Nations base in Mali that killed 10 peacekeepers from Chad. 25 people were reported to have been injured in the attack. Al Qaeda's stated reason for the attack was Chad's re-establishing diplomatic ties with Israel. The base was attacked in Anguelhok, a village located in an especially unstable region of the country.[129][131]
Military
[edit]Mali's military forces consist of an army, which includes land forces and air force,[132] as well as the paramilitary Gendarmerie and Republican Guard, all of which are under the control of Mali's Ministry of Defense and Veterans, headed by a civilian.
Regions and cercles
[edit]
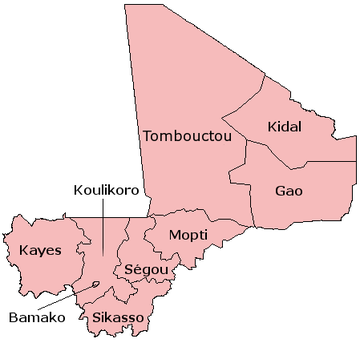
Since 2016, Mali has been divided into ten regions and the District of Bamako.[133] Each region has a governor.[134] The implementation of the two newest regions, Taoudénit (formerly part of Tombouctou Region) and Ménaka (formerly Ménaka Cercle in Gao Region), has been ongoing since January 2016;[135][136] a governor and transitional council has been appointed for both regions.[137]
Since 2023, Mali has added nine new regions to its administrative structure, bringing the total to 19 regions plus the district of Bamako. This reorganization aims to improve governance and bring public services closer to local populations. This initiative continues the decentralization efforts that began with the creation of the Taoudénit and Ménaka regions in 2016. The nineteen regions in turn are subdivided into 159 cercles and 815 communes.[138][139]
The régions and Capital District are:[140][141]
| No | Region name | Area (km2) | Population Census 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | Bamako Capital District |
252 | 4 227 569 |
| 01 | Kayes | 62,914 | 1 840 329 |
| 02 | Koulikoro | 71,178 | 2 255 157 |
| 03 | Sikasso | 21,378 | 1 533 123 |
| 04 | Ségou | 31,996 | 2 455 263 |
| 05 | Mopti | 49,077 | 935 579 |
| 06 | Tombouctou | 180,781 | 974 278 |
| 07 | Gao | 89,532 | 727 517 |
| 08 | Kidal | 151,430 | 83 192 |
| 09 | Taoudénit | 323,326 | 100 358 |
| 10 | Ménaka | 81,040 | 318 876 |
| 11 | Bougouni | 41,052 | 1 570 979 |
| 12 | Dioila | 12,984 | 675 965 |
| 13 | Nioro | 24,179 | 678 061 |
| 14 | Koutiala | 14,739 | 1 169 882 |
| 15 | Kita | 44,175 | 681 671 |
| 16 | Nara | 26,213 | 307 777 |
| 17 | Bandiagara | 25,709 | 868 916 |
| 18 | San | 15,516 | 820 807 |
| 19 | Douentza | 63,515 | 170 189 |
| Total | 1,240,192 | 22 395 489 | |
Economy
[edit]This section may be confusing or unclear to readers. (July 2021) |




The Central Bank of West African States handles the financial affairs of Mali and additional members of the Economic Community of West African States. Mali is considered one of the poorest countries in the world.[132] The average worker's annual salary is approximately US$1,500.[142]

Mali underwent economic reform, beginning in 1988 by signing agreements with the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund.[142] During 1988 to 1996, Mali's government largely reformed public enterprises. Since the agreement, sixteen enterprises were privatized, 12 partially privatized, and 20 liquidated.[142] In 2005, the Malian government conceded a railroad company to the Savage Corporation.[142] Two major companies, Societé de Telecommunications du Mali (SOTELMA) and the Cotton Ginning Company (CMDT), were expected to be privatized in 2008.[142]
Between 1992 and 1995, Mali implemented an economic adjustment programme that resulted in economic growth and a reduction in financial imbalances[vague]. The programme increased social and economic conditions[vague], and led to Mali joining the World Trade Organization on 31 May 1995.[143]
Mali is also a member of the Organization for the Harmonization of Business Law in Africa (OHADA).[144] The gross domestic product (GDP) has risen since. In 2002, the GDP amounted to US$3.4 billion,[145] and increased to US$5.8 billion in 2005,[142] which amounts to an approximately 17.6% annual growth rate.
Mali is a part of the "Franc Zone" (Zone Franc), which means that it uses the CFA franc. Mali is connected with the French government by agreement since 1962 (creation of BCEAO). Today all seven countries of BCEAO (including Mali) are connected to French Central Bank.[146]
Mali was ranked 136th out of 139 in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.[147]
Agriculture
[edit]Mali's key industry is agriculture. Cotton is the country's largest crop export and is exported west throughout Senegal and Ivory Coast.[148][149] During 2002, 620,000 tons of cotton were produced in Mali but cotton prices declined significantly in 2003.[148][149] In addition to cotton, Mali produces rice, millet, corn, vegetables, tobacco, and tree crops. Gold, livestock, and agriculture amount to 80% of Mali's exports.[142]
Eighty percent of Malian workers are employed in agriculture. 15% of Malian workers are employed in the service sector.[149] Seasonal variations lead to regular temporary unemployment of agricultural workers.[150]
Mining
[edit]In 1991, with the assistance of the International Development Association, Mali relaxed the enforcement of mining codes which led to renewed foreign interest and investment in the mining industry.[151] Gold is mined in the southern region and Mali has the third highest gold production in Africa (after South Africa and Ghana).[148] In 2015, the country has produced 41 metric tonnes of gold.[152]
The emergence of gold as Mali's leading export product since 1999 has helped mitigate some of the negative impact of the cotton and Ivory Coast crises.[153] Other natural resources include kaolin, salt, phosphate, and limestone.[142]
Energy
[edit]Electricity and water are maintained by the Energie du Mali, or EDM, and textiles are generated by Industry Textile du Mali, or ITEMA.[142] Mali has made efficient use of hydroelectricity, consisting of over half of Mali's electrical power. In 2002, 700 GWh of hydroelectric power were produced in Mali.[149]
Energie du Mali is an electric company that provides electricity to Mali citizens. Only 55 percent of the population in cities have access to EDM.[154]
Transport infrastructure
[edit]In Mali, there is a railway that connects to bordering countries. There are also approximately 29 airports, of which 8 have paved runways.[155] Urban areas are known for their large quantity of green and white taxicabs. A significant sum of the population is dependent on public transportation.
Demographics
[edit]
| Year | Million |
|---|---|
| 1950 | 4.7 |
| 2000 | 11 |
| 2021 | 21.9 |
In 2021, Mali's population was an estimated 21.9 million[15][16]. Mali's population grew from 7.7 million in 1982 to 19.9 million in 2018.[156] The population is predominantly rural (68% in 2002), and 5%–10% of Malians are nomadic.[5] More than 90% of the population lives in the southern part of the country, especially in Bamako, which has over 2 million residents.[5]
In 2007, about 48% of Malians were younger than 12 years old, 49% were 15–64 years old, and 3% were 65 and older.[132] The median age was 15.9 years.[132] The birth rate in 2014 was 45.53 births per 1,000, and the total fertility rate (in 2012) was 6.4 children per woman.[132][157] The death rate in 2007 was 16.5 deaths per 1,000.[132] Life expectancy at birth was 53.06 years total (51.43 for males and 54.73 for females).[132] Mali has one of the world's highest rates of infant mortality,[5] with 106 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2007.[132]
Largest cities in Mali
[edit]| Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Bamako  Sikasso |
1 | Bamako | Bamako | 1,810,366 | |||||
| 2 | Sikasso | Sikasso | 226,618 | ||||||
| 3 | Koutiala | Sikasso | 141,444 | ||||||
| 4 | Ségou | Ségou | 133,501 | ||||||
| 5 | Kayes | Kayes | 126,319 | ||||||
| 6 | Mopti | Mopti | 120,786 | ||||||
| 7 | Kalabancoro | Koulikoro | 96,173 | ||||||
| 8 | Gao | Gao | 86,353 | ||||||
| 9 | Kati | Koulikoro | 84,500 | ||||||
| 10 | San | Ségou | 66,967 | ||||||
Ethnic groups
[edit]


Mali's population encompasses a number of sub-Saharan ethnic groups. The Bambara are by far the largest single ethnic group, making up a third of the population.[159] The largest ethnic groups are Bambara (33.3%), Fulani (Peuhl) (13.3%), Sarakole/Soninke/Marka (9.8%), Senufo/Manianka (9.6%), Malinke (8.8%), Dogon (8.7%), Sonrai (5.9%), Bobo (2.1%), Tuareg/Bella (1.7%), other Malian (6%), from members of Economic Community of West Africa (0.4%), other (0.3%) (2018 est.).[160] In Mali and in Niger, the Moors are also known as Azawagh Arabs, named after the Azawagh region of the Sahara. They speak mainly Hassaniya Arabic, one of the regional varieties of Arabic.[161]
In the far north, there is a division between Berber-descended Tuareg nomad populations and the darker-skinned Bella or Tamasheq people, due to the historical spread of slavery in the region. An estimated 800,000 people in Mali are descended from slaves.[57] Slavery has persisted in Mali for centuries.[162] The Arabic population kept slaves well into the 20th century, until slavery was suppressed by French authorities around the mid-20th century. There still persist certain hereditary servitude relationships,[163][164] and according to some estimates, even today approximately 200,000 Malians are still enslaved.[165]
Some mixed European/African descendants of Muslims of Spanish, as well as French, Irish, Italian and Portuguese origin, live in Mali, where they are known as the Arma people (1% of the nation's population).[166]
Although Mali has enjoyed reasonably good inter-ethnic relationships based on a long history of coexistence, some hereditary servitude and bondage relationship exist, as well as ethnic tension between settled Songhai and nomadic Tuaregs of the north.[5] Due to a backlash against the northern population after independence, Mali is now in a situation where both groups complain about discrimination on the part of the other group.[167] This conflict also plays a role in the continuing Northern Mali conflict where there is a tension between both Tuaregs and the Malian government, and the Tuaregs and radical Islamists who are trying to establish sharia law.[168]
Languages
[edit]In January 2022, due to deteriorating relations between Mali and the French government, the Mali government announced making Bambara the official language.[170] In July 2023, French was dropped as an official language, becoming instead a working language.[2] At the same time, the 13 national languages,[3] namely Bambara, Bobo, Bozo, Dogon, Fula, Hassaniya Arabic, Kassonke, Maninke, Minyanka, Senufo, the Songhay languages, Soninke and Tamasheq, became official languages.[2] The lingua franca in Mali is mainly Bambara, which about 80 percent of the population can communicate in.[5] Over 40 other African languages are spoken by the various ethnic groups of Mali.[5]
According to the 2009 census, the languages spoken natively in Mali were Bambara by 51.5%, Fula (8.3%), Dogon (6.6%) Soninké (5.7%), Songhai (5.3%), Mandinka (5.2%), Minianka (3.8%), Tamasheq (3.2%), Sénoufo (2%), Bobo (1.9%), Tieyaxo Bozo (1.6%), Kassonké (1.1%), Maure (1%), Dafing (0.4%), Samogo (0.4%), Arabic (Hassaniya) (0.3%), other Malian languages (0.5%), other African languages (0.2%), and other non-African languages (0.2%); 0.7% did not declare their first language.[171]
Religion
[edit]
Islam was introduced to West Africa in the 11th century and remains the predominant religion in much of the region. An estimated 90% of Malians are Muslim (mostly Sunni[173]), approximately 5% are Christian (about two-thirds Roman Catholic and one-third Protestant) and the remaining 5% adhere to traditional African religions such as the Dogon religion.[172] Atheism and agnosticism are believed to be rare among Malians, most of whom practice their religion daily.[174]
The constitution establishes a secular state and provides for freedom of religion, and the government largely respects this right.[174]
Islam as historically practiced in Mali has been malleable and adapted to local conditions; relations between Muslims and practitioners of minority religious faiths have generally been amicable.[174] After the 2012 imposition of sharia rule in northern parts of the country, however, Mali came to be listed high (number 7) in the Christian persecution index published by Open Doors, which described the persecution in the north as severe.[175][176]
Education
[edit]
Public education in Mali is in principle provided free of charge and is compulsory for nine years between the ages of seven and sixteen.[174] The system encompasses six years of primary education beginning at age 7, followed by six years of secondary education.[174] Mali's actual primary school enrolment rate is low, in large part because families are unable to cover the cost of uniforms, books, supplies, and other fees required to attend.[174]
In 2017, the primary school enrolment rate was 61% (65% of males and 58% of females).[177] In the late 1990s, the secondary school enrolment rate was 15% (20% of males and 10% of females).[174] The education system is plagued by a lack of schools in rural areas, as well as shortages of teachers and materials.[174]
Estimates of literacy rates in Mali range from 27–30 to 46.4%, with literacy rates significantly lower among women than men.[174] The University of Bamako, which includes four constituent universities, is the largest university in the country and enrols approximately 60,000 undergraduate and graduate students.[178]
Health
[edit]Mali faces numerous health challenges related to poverty, malnutrition, and inadequate hygiene and sanitation.[174] Mali's health and development indicators rank among the worst in the world.[174] Life expectancy at birth is estimated to be 53.06 years in 2012.[179] In 2000, 62–65% of the population was estimated to have access to safe drinking water and only 69% to sanitation services of some kind.[174] In 2001, the general government expenditures on health totaled about US$4 per capita at an average exchange rate.[180]
Efforts have been made to improve nutrition, and reduce associated health problems, by encouraging women to make nutritious versions of local recipes. For example, the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) and the Aga Khan Foundation, trained women's groups to make equinut, a healthy and nutritional version of the traditional recipe di-dèguè (comprising peanut paste, honey and millet or rice flour). The aim was to boost nutrition and livelihoods by producing a product that women could make and sell, and which would be accepted by the local community because of its local heritage.[181]

Medical facilities in Mali are very limited, and medicines are in short supply.[180] Malaria and other arthropod-borne diseases are prevalent in Mali, as are a number of infectious diseases such as cholera and tuberculosis.[180] Mali's population also suffers from a high rate of child malnutrition and a low rate of immunization.[180] An estimated 1.9% of the adult and children population was afflicted with HIV/AIDS that year,[clarification needed] among the lowest rates in Sub-Saharan Africa.[180][dead link] An estimated 85%–91% of Mali's girls and women have had female genital mutilation (2006 and 2001 data).[182][183]
Gender equality
[edit]In 2017, Mali ranked 157th out of 160 countries in the gender inequality index as reported by the United Nations Development Programme.[184] The Malian Constitution states that it protects women's rights, however many laws exist that discriminate against women.[185] Provisions in the laws limit women's decision-making power after marriage, in which the husband becomes superior to his wife.[185] Women are blamed for not maintaining the appearance of their husbands and are also blamed for the actions of their children if they misbehave, which encourages the cultural attitude that women are inferior to men.[185] The lack of participation of women in politics is due to the idea that politics is associated with men and that women should avoid this sector.[185] Education is also an area in which boys dominate, since it is a better investment for the parents.[185] As traditional values and practices have contributed to gender inequality in Mali, conflict and lawlessness have also influenced the growing gap in gender through gender-based violence.[186] The unstable government of Mali has led to organizations like USAID attempting to improve the lives of the people, mainly women and girls' rights in order to re-engage the development of the country.[186]
Gender relations
[edit]Religion, the patriarchal norms, and gender-based violence are major negative factors shaping the life of women in Mali.[187] Patriarchal norms cause major gender inequalities and lead to male domination within the household.[187] Girls learn household activities like chores, cooking, childcare, etc. at a young age and are expected to take the main responsibility of household chores throughout their life. This hampers women's ability to enter the formal workforce and leads to a lack of education of girls.[187] Gender-based violence in Mali happens both on a national and a family level. At the national level, in 2012 the conflict in the Northern part of the country increased cases of kidnappings and rapes.[186] The conflict also reduced women's access to resources, economy, and opportunities.[186] At the household level, Malian women face gender-based violence through domestic violence, forced marriages, and marital rape.[185] The Demographic Health Survey for Mali in 2013 stated that 76% of women and 54% of men believed physical harm towards women was acceptable if the women burnt food, argued back, went out without notifying her husband, or refused sexual relations with her husband.[186] In 2024, Mali officials pushed a bill that would criminalise homosexual relations between men.[188]
Area of opportunity
[edit]The lack of education has increased gender inequality in Mali because not many women are working outside the household are even participating in the Public Administration sector.[187] After adjusting the entrance requirements and access to education, girls still have lower enrollment rates and less access to formal education.[187] Drop-out rates for girls are 15% higher than that of boys because they have a higher responsibility at home and most parents refuse to allow all their children to go to school, so boys tend to become educated.[187] Similarly, technical and vocational education has a lower numbers of girls participating and are inadequately distributed in the country because the training centers are focused in the urban cities.[187] Finally, higher education for girls consist of short programs because early marriages prevent most girls from pursuing a longer term education program like those in science.[187] Although women do not have the same access of education, in recent decades women have been entering and representing in decision-making positions in the Public Administration sector.[187] Out of 147 members of Parliament, 15 were women in 2010.[187] Recent decades show that women are slowly joining important decision-making positions which is changing the attitude and status of women in Mali, which has led to the promotion of women's rights in the political sphere.[187]
Efforts
[edit]Legislation at the international and national levels have been implemented over the decades to help promote women's rights in Mali.[187] At the international, Mali signed the Beijing Platform for Action which suggest that women should participate in decision-making and the convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women which is the foundation to women's rights promotion.[187] At the national level, Mali's Constitution has the Decree No. 092-073P-CTSP that claims equality to all Malian citizens and discrimination is prohibited, which has not been followed.[187] The Poverty Reduction Strategy Programme (PRSP) and the Growth and Poverty Reduction Strategy Programme under the Malian Government seek to improve the well-being of the citizens, and changes to governance and gender in the country.[187] The Ministry for Advancement of Women, Children and the Family was created specifically for women and children so that their basics rights and needs get met under the law.[187] Although there exists legislation and policy for gender equality the institutionalization of the National Gender Policy of Mali is necessary to support the importance of women's rights.[187] Strengthening and the support of girls' and women's access to education and training is recommended to improve gender equality in Mali.[187] The involvement of international organizations like USAID assist Mali financially to enhance their development through the efforts of the improvement of women's rights.[186]
Culture
[edit]
The varied everyday culture of Malians reflects the country's ethnic and geographic diversity.[189] Most Malians wear flowing, colorful robes called boubous that are typical of West Africa. Malians frequently participate in traditional festivals, dances, and ceremonies.[189]
Music
[edit]
Malian musical traditions are derived from the griots, who are known as "Keepers of Memories".[190] Malian music is diverse and has several different genres. Some famous Malian influences in music are kora virtuoso musician Toumani Diabaté, the ngoni with Bassekou Kouyate the virtuoso of the electric jeli ngoni, the late roots and blues guitarist Ali Farka Touré, the Tuareg band Tinariwen, Khaira Arby, and several Afro-pop artists such as Salif Keita, the duo Amadou et Mariam, Oumou Sangare, Fatoumata Diawara, Rokia Traore, and Habib Koité. Dance also plays a large role in Malian culture.[191] Dance parties are common events among friends, and traditional mask dances are performed at ceremonial events.[191]
Literature
[edit]Though Mali's literature is less famous than its music,[192] Mali has always been one of Africa's liveliest intellectual centers.[193] Mali's literary tradition is passed mainly by word of mouth, with jalis reciting or singing histories and stories known by heart.[193][194] Amadou Hampâté Bâ, Mali's best-known historian, spent much of his life writing these oral traditions down for the world to remember.[194]
The best-known novel by a Malian writer is Yambo Ouologuem's Le devoir de violence, which won the 1968 Prix Renaudot but whose legacy was marred by accusations of plagiarism.[193][194] Other well-known Malian writers include Baba Traoré, Modibo Sounkalo Keita, Massa Makan Diabaté, Moussa Konaté, and Fily Dabo Sissoko.[193][194]
Sport
[edit]
The most popular sport in Mali is association football,[195][196] which became more prominent after Mali hosted the 2002 African Cup of Nations.[195][197] Most towns and cities have regular games;[197] the most popular teams nationally are Djoliba AC, Stade Malien, and Real Bamako, all based in the capital.[196] Informal games are often played by youths using a bundle of rags as a ball.[196]
Basketball is another major sport;[196][198] the Mali women's national basketball team, led by Hamchetou Maiga, competed at the 2008 Beijing Olympics.[199] Traditional wrestling (la lutte) is also somewhat common, though popularity has declined in recent years.[197] The game wari, a mancala variant, is a common pastime.[196]
Mali featured a men's national team in beach volleyball that competed at the 2018–2020 CAVB Beach Volleyball Continental Cup.[200]
Cuisine
[edit]
Rice and millet are the staples of Malian cuisine, which is heavily based on cereal grains.[201][202] Grains are generally prepared with sauces made from edible leaves, such as spinach or baobab, with tomato peanut sauce, and may be accompanied by pieces of grilled meat (typically chicken, mutton, beef, or goat).[201][202] Malian cuisine varies regionally.[201][202] Other popular dishes include fufu, jollof rice, and maafe.
Media
[edit]In Mali, there are several newspapers such as Les Echos, L'Essor, Info Matin, Nouvel Horizon, and Le Républicain.[203] Office de Radiodiffusion-Télévision du Mali is the state-owned service. Telecommunications in Mali include 869,600 mobile phones, 45,000 televisions and 414,985 Internet users.[204]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Bambara serves as a lingua franca spoken by around 80% of the population.[5]
- ^ Includes Christianity, no religion, and traditional African religions.
- ^ /ˈmɑːli/ ⓘ; Bambara pronunciation: [ma.li]
- N'Ko script: ߡߊߟߌ
- Fula: 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭
- Arabic: مالي
- ^
- Bambara: Mali ka Fasojamana, N'Ko script: ߡߊߟߌ ߞߊ ߝߊߛߏߖߊߡߊߣߊ
- Fula: 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, romanized: Renndaandi Maali
- Arabic: جمهورية مالي, romanized: Jumhūriyyāt Mālī
References
[edit]- ^ [https://twitter.com/NkoOfficiel Académie N’Ko Mali ߡߊ߰ߟߌ ߒߞߏ ߟߏ߲ߞߏ߫ ߘߎ߲ߓߎ ] Archived 14 May 2022 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 14 May 2024
- ^ a b c "JOURNAL OFFICIEL DE LA REPUBLIQUE DU MALI SECRETARIAT GENERAL DU GOUVERNEMENT - DECRET N°2023-0401/PT-RM DU 22 JUILLET 2023 PORTANT PROMULGATION DE LA CONSTITUTION" (PDF). sgg-mali.ml (in French). 22 July 2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 26 July 2023.
Article 31 : Les langues nationales sont les langues officielles du Mali.
[Article 31: The national languages are the official languages of Mali.] - ^ a b "JOURNAL OFFICIEL DE LA REPUBLIQUE DU MALI SECRETARIAT GENERAL DU GOUVERNEMENT - DECRET N°2017-0735/P-RM DU 21 AOUT 2017 FIXANT L'ORGANISATION ET LES MODALITES DE FONCTIONNEMENT DES STRUCTURES DE L'EDUCATION NON FORMELLE" (PDF). sgg-mali.ml (in French). 21 August 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
Selon la Loi n°96- 049 du 23 août 1996, les langues nationales du Mali sont : (...)
[According to Law No. 96-049 of 23 August 1996, the national languages of Mali are: (...)] - ^ "JOURNAL OFFICIEL DE LA REPUBLIQUE DU MALI SECRETARIAT GENERAL DU GOUVERNEMENT - DECRET N°2023-0401/PT-RM DU 22 JUILLET 2023 PORTANT PROMULGATION DE LA CONSTITUTION" (PDF). sgg-mali.ml (in French). 22 July 2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 26 July 2023.
Article 31 : Le français est la langue de travail. L'Etat peut adopter toute autre langue comme langue de travail.
[Article 31: French is the working language. The State may adopt any other language as its working language.] - ^ a b c d e f g Mali country profile, p. 6.
- ^ a b "Africa: Mali – The World Factbook – Central Intelligence Agency". CIA.gov. 27 April 2021. Archived from the original on 30 March 2021. Retrieved 1 May 2021.
- ^ "Mali". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 13 August 2022. Retrieved 8 October 2022.
- ^ Booty, Natasha; Pivac, Mark (23 July 2023). "Assimi Goïta: President gets sweeping powers in new Mali constitution". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Mali country profile". BBC News. 19 October 2023. Archived from the original on 11 September 2023. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ^ "Mali". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 22 June 2023.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2023 Edition. (Mali)". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. 10 October 2023. Archived from the original on 17 October 2023. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ "Gini Index". World Bank. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
- ^ "HUMAN DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2023-24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. pp. 274–277. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 May 2024. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ^ Which side of the road do they drive on? Archived 14 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine Brian Lucas. August 2005. Retrieved 28 January 2009.
- ^ a b c "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ a b c "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ "Index Mundi using CIA World Factbook statistics, January 20, 2018, retrieved April 13, 2019". Archived from the original on 21 December 2020. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- ^ Mali gold reserves rise in 2011 alongside price Archived 21 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 17 January 2013
- ^ Human Development Indices Archived 12 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Table 3: Human and income poverty, p. 6. Retrieved 1 June 2009
- ^ "Mansa Musa (Musa I of Mali)". National Geographic Society. 14 April 2020. Archived from the original on 2 July 2022. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ^ Mali Empire (ca. 1200-) | The Black Past: Remembered and Reclaimed Archived 5 January 2019 at the Wayback Machine. The Black Past. Retrieved 8 October 2012.
- ^ "Is Mansa Musa the richest man who ever lived?". BBC News. 10 March 2019. Archived from the original on 10 March 2019. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ^ "Who is the richest person of all time?". The Week UK. December 2021. Archived from the original on 16 March 2022. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ^ Polgreen, Lydia and Cowell, Alan (6 April 2012) "Mali Rebels Proclaim Independent State in North" Archived 28 July 2020 at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times
- ^ a b UN Security Council condemns Mali coup Archived 28 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine. Telegraph (23 March 2012). Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ "Mali – la France a mené une série de raids contre les islamistes". Le Monde. 12 January 2013. Archived from the original on 20 October 2017. Retrieved 13 January 2013.
- ^ Wolny, Philip (15 December 2013). Discovering the Empire of Mali. The Rosen Publishing Group. p. 7. ISBN 9781477718896. Archived from the original on 16 April 2021. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- ^ Sasnett, Martena Tenney; Sepmeyer, Inez Hopkins (1 January 1967). Educational Systems of Africa: Interpretations for Use in the Evaluation of Academic Credentials. University of California Press. pp. 673.
- ^ Imperato, Pascal James; Imperato, Gavin H. (25 April 2008). Historical Dictionary of Mali. Scarecrow Press. p. 231. ISBN 9780810864023. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- ^ Niane, Djibril (1965). Sundiata: An Epic of Old Mali.
- ^ a b Aku Adjandeh, Evelyn (July 2014). "A STUDY OF PROVERBS IN THINGS FALL APART AND SUNDIATA: AN EPIC OF OLD MALI (SUNDIATA)" (PDF). University of Ghana, Legon – Institute of African Studies. p. 100. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 19 March 2017.
- ^ Graft-Johnson, John Coleman De (1 January 1986). African Glory: The Story of Vanished Negro Civilizations. Black Classic Press. p. 92. ISBN 9780933121034. Archived from the original on 16 April 2021. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- ^ Fyle, C. Magbaily (1999). Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa. University Press of America. pp. 11. ISBN 9780761814566.
- ^ Eric Huysecom, M. Rasse, L. Lespez, K. Neumann, A. Fahmy, A. Ballouche, S. Ozainne, M. Maggetti, Ch. Tribolo, S. Sorian: The emergence of pottery in Africa during the tenth millennium cal BC: new evidence from Ounjougou (Mali), in: Antiquity (2009), p. 906.
- ^ Arazi, Noemie. "Tracing History in Dia, in the Inland Niger Delta of Mali -Archaeology, Oral Traditions and Written Sources" (PDF). University College London. Institute of Archaeology. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 February 2022. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ al-Bakri in Nehemiah Levtzion and J. F. Pl Hopkins, eds and trans., Corpus of Early Arabic Sources for West African History (New York and London: Cambridge University Press, 1981, reprint edn Princeton, New Jersey,: Marcus Wiener, 2000), pp. 82–83.
- ^ ibn Khaldun in Levtzion and Hopkins, eds, and transl. Corpus, p. 333.
- ^ al-Idrisi in Levtzion and Hopkins, eds. and transl, Corpus, p. 108.
- ^ a b c Mali country profile, p. 1.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Mali country profile. Mali was later responsible for the collapse of Islamic Slave Army from the North. The defeat of Tukuror Slave Army, was repeated by Mali against the France and Spanish Expeditionary Army in the 1800s ("Blanc et memoires"). p. 2.
- ^ John Iliffe (2007) Africans: the history of a continent Archived 6 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Cambridge University Press. p. 69. ISBN 0-521-68297-5
- ^ La guerre coloniale du Bani-Volta, 1915-1916 (Burkina Faso, Mali) Archived 29 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Autrepart, 2003.
- ^ 14-18 Étions-nous bien défendus ?, Jean-Claude Flament, Société des écrivains, 2014.
- ^ a b "Independent Mali". Britannica. 1946. Archived from the original on 19 November 2020. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ "Public Holidays". Embassy of the Republic of Mali to the United States. Archived from the original on 20 September 2018. Retrieved 20 September 2018.
- ^ Core document forming part of the reports of states parties: Mali. United Nations Human Rights Website.
- ^ a b c d e f g Mali country profile, p. 3.
- ^ "Liberation Day Commemorated in Mali". Archived from the original on 2 February 2019. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- ^ "Mali's nomads face famine Archived 24 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine". BBC News. 9 August 2005.
- ^ a b "Nonviolent Conflict Summaries". Archived from the original on 16 June 2011. Retrieved 1 March 2012. Mali March 1991 Revolution
- ^ a b Nesbitt, Katherine. "Mali's March Revolution (1991)". International Center on Nonviolent Conflict. Archived from the original on 16 June 2011. Retrieved 1 March 2012.
- ^ Bussa, Edward (26 March 2009). "Mali's March to Democracy". Threadster.com. Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 1 March 2012.
- ^ Mohsin, Haroon (18 August 2022). "Martyr's Day in Mali". National Today. Archived from the original on 17 October 2023. Retrieved 16 September 2023.
- ^ Turrittin, Jane (1991). "Mali: People Topple Traoré". Review of African Political Economy. 18 (52): 97–103. doi:10.1080/03056249108703927. ISSN 0305-6244. JSTOR 4005962. Archived from the original on 9 February 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ^ Mali country profile, p. 4.
- ^ USAID Africa: Mali. USAID. Retrieved 15 May 2008. Retrieved 3 June 2008.
- ^ a b Tran, Mark (23 October 2012). "Mali conflict puts freedom of 'slave descendants' in peril". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- ^ York, Geoffrey (11 November 2012). "Mali chaos gives rise to slavery, persecution". The Globe and Mail. Toronto. Archived from the original on 29 November 2016. Retrieved 4 September 2017.
- ^ Mali clashes force 120 000 from homes Archived 10 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine. News24 (22 February 2012). Retrieved 23 February 2012.
- ^ Callimachi, Rukmini (3 April 2012) "Post-coup Mali hit with sanctions by African neighbours". Globe and Mail. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ^ "Tuareg rebels declare independence in north Mali". France 24. 6 April 2012. Archived from the original on 8 April 2012. Retrieved 28 July 2012.
- ^ Tiemoko Diallo; Adama Diarra (28 June 2012). "Islamists declare full control of Mali's north". Reuters. Archived from the original on 15 August 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2012.
- ^ "Mali Islamists want sharia not independence". Agence France-Presse. 20 June 2012. Archived from the original on 16 December 2012. Retrieved 28 July 2012.
- ^ "Mali Possibilities and Challenges for Transitional Justice in Mali". International Center for Transitional Justice. 9 January 2014. Archived from the original on 18 September 2016. Retrieved 25 August 2016.
- ^ "French Troops Retake Kidal Airport, Move into City". USA Today. 30 January 2013. Archived from the original on 30 January 2013. Retrieved 30 January 2013. French troops retake the last remaining Islamist urban stronghold in Mali.
- ^ "Mali conflict: Timbuktu hails French President Hollande". BBC News. 2 February 2013. Archived from the original on 2 February 2013. Retrieved 4 February 2013.
- ^ "Ibrahim Boubacar Keita wins Mali presidential election". BBC News. 13 August 2013. Archived from the original on 20 January 2022. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- ^ "The Sahel in flames". The New Humanitarian. 31 May 2019. Archived from the original on 13 November 2021. Retrieved 23 June 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f ""We Used to Be Brothers" | Self-Defense Group Abuses in Central Mali". Human Rights Watch. 7 December 2018. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ Blake, James (29 March 2019). "Radical Islamists Have Opened a New Front in Mali". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ a b "Au Mali, les liaisons dangereuses entre l'Etat et les milices" (in French). 24 July 2018. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ Mumbere, Daniel (10 July 2018). "Everything you need to know about Mali 2018 presidential election". Africanews.com. Archived from the original on 24 July 2018. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ^ "Mali: Élection présidentielle 2018 : Le premier tour aura lieu le dimanche 29 juillet". maliactu.net. 12 February 2018. Archived from the original on 12 February 2018. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- ^ "Incumbent President Keita wins re-election in Mali". France 24. 16 August 2018. Archived from the original on 16 January 2024. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- ^ "Youssouf Toloba and his Dan Nan Ambassagou armed group sign a commitment towards a ceasefire in central Mali | HD Centre". Archived from the original on 29 March 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ "UN to probe 'horrific' Mali attacks as death toll jumps to 160". Al-Jazeera. 26 March 2019. Archived from the original on 29 March 2019. Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- ^ "Insiders Insight: Explaining the Mali massacre". African Arguments. 26 March 2019. Archived from the original on 18 September 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ "Central Mali: Top UN genocide prevention official sounds alarm over recent ethnically-targeted killings". UN News. 28 March 2019. Archived from the original on 29 March 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ Giannangeli, Marco (1 November 2020). "Britain 'sleepwalking' into deadly conflict in war-torn West Africa". express.co.uk. Archived from the original on 26 November 2020. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ "Sharp rise in number of children killed in Mali's deadly attacks". The Guardian. 13 August 2019. Archived from the original on 31 August 2019. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- ^ "PUIC Secretary General condemns terrorist attacks in Mali". Parliamentary Union of the OIC Member States. 8 October 2019. Archived from the original on 22 October 2019. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- ^ "Mali president dismisses coup speculation after jihadi attacks kill dozens of troops near Burkina Faso border". Japantimes.co.jp. 7 October 2019. Archived from the original on 22 October 2019. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- ^ "Militants kill 54 in attack on Mali army post, ISIS claims responsibility". NBC News. 3 November 2019. Retrieved 12 December 2019.
- ^ "How Much More Blood Must Be Spilled?". HRW. 10 February 2020. Archived from the original on 31 May 2023. Retrieved 31 May 2023.
- ^ Ahmed, Baba (5 June 2020). "Thousands in Mali's capital demand that president step down". ABC News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 13 September 2020. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ "Kidnapped Mali politician and French aid worker freed". the Guardian. 6 October 2020. Archived from the original on 3 June 2021. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- ^ a b c d "TOUT COMPRENDRE SUR LA SITUATION AU MALI" [Understanding everything about the situation in Mali]. CNews (in French). 19 August 2020. Archived from the original on 26 August 2020. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ "Mali's coup is cheered at home but upsets neighbours". BBC. 21 August 2020. Archived from the original on 21 August 2020. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ "Mali: President Bah N'Daw decrees the dissolution of the CNSP". The Africa Report.com. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 16 September 2023.
- ^ "EU condemns 'grave and serious' kidnapping of Mali's leaders". the Guardian. 25 May 2021. Archived from the original on 25 May 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2021.
- ^ "Mali's military detains president, prime minister". AlJazeera.com. Archived from the original on 25 May 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2021.
- ^ "Mali's military leader Goita sworn in as transitional president". AlJazeera.com. Archived from the original on 25 May 2023. Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- ^ BBC Africa Today: Islamic State Sahel Province fighters seize commune in Mali, BBC, 2023, archived from the original on 11 May 2023, retrieved 31 May 2023
- ^ NPR: Islamic State group almost doubled its territory in Mali in under a year, U.N. says, NPR, 2023, archived from the original on 27 August 2023, retrieved 27 August 2023
- ^ Ahmed, Baba (10 January 2022). "Mali's junta deplores new sanctions imposed by regional bloc". SFGate. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ^ "Thousands in Mali celebrate expulsion of French ambassador | Armed Groups News". Al Jazeera. 5 February 2022. Archived from the original on 7 February 2022. Retrieved 13 February 2022.
- ^ "Mali troops and suspected Russian fighters accused of massacre". BBC News. 5 April 2022. Archived from the original on 6 April 2022. Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- ^ "Mali: Military government breaks defence accords with France". AlJazeera.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2022. Retrieved 10 May 2022.
- ^ "Mali: France opposed to Assimi Goïta's junta demanding an end to defence agreements". The Africa Report.com. 9 May 2022. Archived from the original on 9 May 2022. Retrieved 10 May 2022.
- ^ "UN experts: Malian military and 'white' soldiers killed 33". Yahoo News. 5 August 2022. Archived from the original on 6 August 2022. Retrieved 6 August 2022.
- ^ "Russian Foreign Minister visits Mali in sign of deepening ties". EuroNews. 8 February 2023. Archived from the original on 8 February 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ^ "Mali demotes French, language of its former colonizer, in symbolic move". Washington Post. 4 August 2023. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ^ "Mali : Les groupes islamistes armés et l'armée prennent les civils pour cible" (in French). Human Rights Watch. 1 November 2023. Archived from the original on 14 December 2023. Retrieved 1 January 2024.
- ^ Darya Tarasova; Tim Lister; Avery Schmitz (29 July 2024). "Dozens of Russian mercenaries killed in rebel ambush in Mali, in their worst known loss in Africa". CNN. Retrieved 30 July 2024.
- ^ "Mali announces severance of diplomatic relations with Ukraine". РБК. 5 August 2024. Archived from the original on 5 August 2024. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ "Was Ukraine's role in big Wagner defeat an own goal in Africa?". BBC News. 12 August 2024.
- ^ "Attack by al-Qaeda linked group in Mali killed more than 70 people". Al Jazeera English. 17 September 2024. Retrieved 20 September 2024.
- ^ Griffiths, Ieuan (July 1986). "The Scramble for Africa: Inherited Political Boundaries". The Geographical Journal. 152 (2): 204–216. Bibcode:1986GeogJ.152..204G. doi:10.2307/634762. ISSN 0016-7398. JSTOR 634762.
- ^ "List of African countries by area". www.britannica.com. 27 September 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Mali country profile, p. 5.
- ^ Uranium Mine Ownership – Africa Archived 15 April 2020 at Archive-It. Wise-uranium.org. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ Muller, CJ and Umpire, A (22 November 2012) An Independent Technical Report on the Mineral Resources of Falea Uranium, Copper and Silver Deposit, Mali, West Africa Archived 24 August 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Minxcon.
- ^ Uranium in Africa Archived 17 April 2014 at the Wayback Machine. World-nuclear.org. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ Video: US condemns Mali coup amid reports of looting. Telegraph (22 March 2012). Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f Mali country profile, p. 14.
- ^ Constitution of Mali, Art. 30.
- ^ Constitution of Mali, Art. 29 & 46.
- ^ Constitution of Mali, Art. 38.
- ^ a b c d e f Mali country profile, p. 15.
- ^ Constitution of Mali, Art. 59 & 61.
- ^ (in French) Koné, Denis. Mali: "Résultats définitifs des Législatives" Archived 29 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Les Echos (Bamako) (13 August 2007). Retrieved 24 June 2008.
- ^ Constitution of Mali, Art. 65.
- ^ Constitution of Mali, Art. 81.
- ^ Constitution of Mali, Art. 83–94.
- ^ "Mali's transition govt sets February 2024 for presidential election". AfricaNews. 1 July 2022. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ Melly, Paul (6 July 2022). "Mali coup: How junta got Ecowas economic sanctions lifted". BBC. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Mali country profile, p. 17.
- ^ "ion suspends Mali over coup". Al Jazeera. 23 March 2012. Archived from the original on 25 March 2012. Retrieved 23 March 2012.
- ^ "Al Qaeda Claims U.N. Peacekeeper Attack That Killed 10 in Mali". NY Times. 20 January 2019. Archived from the original on 21 January 2019. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Central Intelligence Agency (2009). "Mali". The World Factbook. Archived from the original on 30 March 2021. Retrieved 12 January 2010.
- ^ Martin, Phillip L. (2006). Managing Migration: The Promise of Cooperation. Lanham, Maryland: Lexington Books. p. 134. ISBN 978-0-7391-1341-7.
- ^ DiPiazza, p. 37.
- ^ "Report of the Secretary-General on the situation in Mali" (PDF). MINUSMA. 28 March 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ^ "Régionalisation: Deux Nouvelles régions créées au Mali". Malijet. 21 January 2016. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ^ "Report of the Secretary-General on the situation in Mali" (PDF). MINUSMA. 30 December 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 January 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ^ "Loi N°99-035/ Du 10 Aout 1999 Portant Creation des Collectivites Territoriales de Cercles et de Regions" (PDF) (in French). Ministère de l'Administration Territoriales et des Collectivités Locales, République du Mali. 1999. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 March 2012.
- ^ Djiguiba, Issa (21 September 2024). "Administrative and territorial division: the new administrative map of Mali is operational". www.ortm.ml. Retrieved 6 November 2024.
- ^ Coulibaly, Bassidi (October 2013). "Etats Generaux De La Decentralisation (in French)" (PDF). arpdeveloppement.com. Retrieved 6 November 2024.
- ^ "CINQUIEME RECENSEMENT GENERAL DE LA POPULATION ET DE L'HABITAT (in French)" (PDF). www.instat-mali.org. November 2023. Retrieved 6 November 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Mali". U.S. State Department. May 2008. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
- ^ Mali and the WTO Archived 11 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine. World Trade Organization. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ "OHADA.com: The business law portal in Africa". Archived from the original on 26 March 2009. Retrieved 22 March 2009.
- ^ Mali country profile, p. 9.
- ^ Zone franc sur le site de la Banque de France Archived 20 January 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Banque-france.fr. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ World Intellectual Property Organization (2024). Global Innovation Index 2024. Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship. Geneva. p. 18. doi:10.34667/tind.50062. ISBN 978-92-805-3681-2. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b c Hale, Briony (13 May 1998). "Mali's Golden Hope". BBC News. Archived from the original on 11 July 2018. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
- ^ a b c d Cavendish, Marshall (2007). World and Its Peoples: Middle East, Western Asia, and Northern Africa. Tarrytown, New York: Marshall Cavendish. p. 1367. ISBN 978-0-7614-7571-2.
- ^ May, Jacques Meyer (1968). The Ecology of Malnutrition in the French Speaking Countries of West Africa and Madagascar. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company. p. 291. ISBN 978-0-02-848960-5.
- ^ Campbell, Bonnie (2004). Regulating Mining in Africa: For Whose Benefit?. Uppsala, Sweden: Nordic African Institute. p. 43. ISBN 978-0-7614-7571-2.
- ^ "Gold production". Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ African Development Bank, p. 186.
- ^ Farvacque-Vitkovic, Catherine et al. (September 2007) DEVELOPMENT OF THE CITIES OF MALI — Challenges and Priorities Archived 16 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Africa Region Working Paper Series No. 104/a. World Bank
- ^ "Mali transportation, roads, railways and airports | - CountryReports". www.countryreports.org. Archived from the original on 14 October 2023. Retrieved 16 September 2023.
- ^ "Population, total | Data". data.worldbank.org. 2022. Archived from the original on 18 May 2024. Retrieved 31 May 2023.
- ^ "Mali Demographics Profile 2014". Archived from the original on 7 January 2015. Retrieved 14 December 2014.
- ^ "Mali: Regions, Major Cities & Localities". Population Statistics in Maps and Charts. Retrieved 5 September 2019.
- ^ https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/#people-and-society
- ^ https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/mali/#people-and-society
- ^ Popenoe, Rebecca (2003) Feeding Desire – Fatness, Beauty and Sexuality among a Saharan People. Routledge, London. pp. 16–17. ISBN 0-415-28096-6
- ^ Fortin, Jacey (16 January 2013). "Mali's Other Crisis: Slavery Still Plagues Mali, And Insurgency Could Make It Worse". International Business Times. Archived from the original on 8 December 2014. Retrieved 16 January 2013.
- ^ "Kayaking to Timbuktu, Writer Sees Slave Trade Archived 10 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine". National Geographic News. 5 December 2002.
- ^ "Kayaking to Timbuktu, Original National Geographic Adventure Article discussing Slavery in Mali Archived 22 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine". National Geographic Adventure. December 2002/January 2003.
- ^ MacInnes-Rae, Rick (26 November 2012). "Al-Qaeda complicating anti-slavery drive in Mali". CBC News. Archived from the original on 5 March 2014. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ^ Fage, J. D.; Gray, Richard; Oliver, Roland (1975). The Cambridge History of Africa. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521204132.
- ^ Hall, Bruce S. (2011) A History of Race in Muslim West Africa, 1600–1960. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107002876: "The mobilization of local ideas about racial difference has been important in generating, and intensifying, civil wars that have occurred since the end of colonial rule in all of the countries that straddle the southern edge of the Sahara Desert. ... contemporary conflicts often hearken back to an older history in which blackness could be equated with slavery and non-blackness with predatory and uncivilized banditry." (cover text)
- ^ Hirsch, Afua (6 July 2012) Mali's conflict and a 'war over skin colour' Archived 11 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine, The Guardian.
- ^ a b "4ème Recensement General de la Population et de L'Habitat du Mali (RGPH)" (PDF) (in French). Institut National de la Statistique. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 January 2020. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ^ "Mali's military rulers say French ambassador has 72 hours to leave the country". CNN. 31 January 2022. Archived from the original on 13 February 2022. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "4ème RECENSEMENT GENERAL DE LA POPULATION ET DE L'HABITAT DU MALI (RGPH-2009)" [4th GENERAL POPULATION CENSUS AND HABITAT OF MALI (RGPH-2009)] (PDF) (in French). Mali National Institute of Statistics. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2019. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ^ a b International Religious Freedom Report 2008: Mali Archived 18 January 2020 at the Wayback Machine. State.gov (19 September 2008). Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ^ "The World's Muslims: Unity and Diversity" (PDF). Pew Forum on Religious & Public life. 9 August 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Mali country profile, p. 7.
- ^ Report points to 100 million persecuted Christians. Archived 6 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- ^ OPEN DOORS World Watch list 2012 Archived 10 December 2019 at the Wayback Machine. Worldwatchlist.us. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ "Education Statistics". datatopics.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 7 May 2021. Retrieved 19 November 2019.
- ^ "Université de Bamako – Bamako, Mali". Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 13 May 2013. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ^ Life Expectancy ranks Archived 6 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine. CIA World Factbook
- ^ a b c d e Mali country profile, p. 8.
- ^ Nourishing communities through holistic farming Archived 6 October 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Impatient optimists, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. 30 April 2013.
- ^ WHO | Female genital mutilation and other harmful practices. Who.int (6 May 2011). Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ^ Female genital cutting in the Demographic Health Surveys: a critical and comparative analysis. Calverton, MD: ORC Marco; 2004 (DHS Comparative Reports No. 7) Archived 26 April 2014 at the Wayback Machine. (PDF). Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- ^ "Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update: Mali" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 March 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f "Violence against Women in Mali" (PDF). World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT). 7 July 2004. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 August 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f "USAID MALI:ADDENDUM TO THE 2012 GENDER ASSESSMENT" (PDF). United States Agency of International Development. May 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 September 2018. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r "GENDER EQUALITY AND WOMEN'S EMPOWERMENT IN PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION: MALI CASE STUDY" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2012. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 December 2018. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
- ^ Billson, Chantelle (5 November 2024). "Mali moves to criminalise homosexuality for the first time with new anti-gay law". PinkNews | Latest lesbian, gay, bi and trans news | LGBTQ+ news. Retrieved 20 November 2024.
- ^ a b Pye-Smith, Charlie & Rhéal Drisdelle. Mali: A Prospect of Peace? Oxfam (1997). ISBN 0-85598-334-5, p. 13.
- ^ Crabill, Michelle and Tiso, Bruce (January 2003). Mali Resource Website. Fairfax County Public Schools. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
- ^ a b "Music". Embassy of the Republic of Mali in Japan. Archived from the original on 8 July 2013. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ^ Velton, p. 29.
- ^ a b c d Milet, p. 128.
- ^ a b c d Velton, p. 28.
- ^ a b Milet, p. 151.
- ^ a b c d e DiPiazza, p. 55.
- ^ a b c Hudgens, Jim, Richard Trillo, and Nathalie Calonnec. The Rough Guide to West Africa. Rough Guides (2003). ISBN 1-84353-118-6, p. 320.
- ^ "Malian Men Basketball". Africabasket.com. Retrieved 3 June 2008.
- ^ Chitunda, Julio. "Ruiz looks to strengthen Mali roster ahead of Beijing" Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. FIBA.com (13 March 2008). Retrieved 24 June 2008.
- ^ "Continental Cup Finals start in Africa". FIVB. 22 June 2021. Archived from the original on 7 August 2021. Retrieved 7 August 2021.
- ^ a b c Velton, p. 30.
- ^ a b c Milet, p. 146.
- ^ Murison, Katharine, ed. (2002). Africa South of the Sahara 2003. Taylor & Francis. pp. 652–53. ISBN 978-1-85743-131-5. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ Batvina, Iryna. "Culture of Mali". Best-Country.com. Archived from the original on 5 November 2016. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
Bibliography
[edit]- "Constitution of Mali" (PDF) (in French). Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2018. Retrieved 2 April 2008. A student-translated English version Archived 12 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine is also available.
- "Country profile: Mali" (PDF). Library of Congress – Federal Research Division. January 2005. Retrieved 30 July 2024. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- DiPiazza, Francesca Davis (2006). Mali in Pictures. Minneapolis, Minnesota: Learner Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-8225-6591-8. Archived from the original on 7 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Milet, Eric & Manaud, Jean-Luc (2007). Mali (in French). Editions Olizane. ISBN 978-2-88086-351-7.
- Velton, Ross (2004). Mali. Bradt Travel Guides. ISBN 978-1-84162-077-0.
External links
[edit]- Official website Archived 9 June 2020 at the Wayback Machine
 Wikimedia Atlas of Mali
Wikimedia Atlas of Mali Geographic data related to Mali at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Mali at OpenStreetMap- Mali Archived 30 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Mali profile Archived 24 June 2018 at the Wayback Machine from the BBC News
- Possibilities and Challenges for Transitional Justice in Mali Archived 18 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine from the ICTJ
- Facebook group about Ngoni Archived 19 February 2022 at the Wayback Machine, considered a traditional instrument of Mali; also known as Xalam, Jeli N'goni, Hoddu, Khalam, Tehardent, or Gambare
- Mali 2012 Trade Summary Statistics Archived 7 April 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- - Mali Population-Worldometer
- Mali
- 1960 establishments in Africa
- Countries and territories where Arabic is an official language
- Countries in Africa
- Former French colonies
- Landlocked countries
- Least developed countries
- Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
- Member states of the African Union
- Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- Member states of the United Nations
- Republics
- Saharan countries
- States and territories established in 1960
- West African countries


