GV (nerve agent): Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
removed Category:Amines; added Category:Dimethylamino compounds using HotCat |
added Category:Phosphorus-nitrogen compounds using HotCat |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| Verifiedfields = changed |
| Verifiedfields = changed |
||
| verifiedrevid = 470455587 |
| verifiedrevid = 470455587 |
||
| Name = GV |
| Name = GV |
||
| OtherNames = EA-5365 |
|||
| ImageFile1 = GV-2D-skeletal.png |
| ImageFile1 = GV-2D-skeletal.png |
||
| ImageName1 = Skeletal formula of GV |
| ImageName1 = Skeletal formula of GV |
||
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
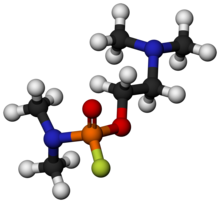
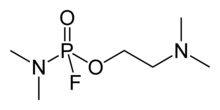
'''GV''' ([[IUPAC]] name: '''2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl ''N'',''N''-dimethylphosphoramidofluoridate''') is an [[organophosphate]] [[nerve agent]]. GV is a part of a new series of nerve agents with properties similar to |
'''GV''' ([[IUPAC]] name: '''2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl ''N'',''N''-dimethylphosphoramidofluoridate'''), also known as '''EA-5365''', is an [[organophosphate]] [[nerve agent]]. GV is a part of a new series of nerve agents with properties similar to the "G-series" and "V-series". It is a potent [[acetylcholinesterase]] inhibitor with properties similar to other nerve agents, being a highly poisonous vapour. Treatment for poisoning with GV involves drugs such as [[atropine]], [[benactyzine]], [[obidoxime]], and [[HI-6]].<ref>{{ cite journal | vauthors = Fusek J, Bajgar J | title = Treatment of intoxication with GV compound in laboratory rats | journal = Sb Ved Pr Lek Fak Karlovy Univerzity Hradci Kralove | year = 1994 | volume = 37 | issue = 2 | pages = 57–62 | pmid = 7784799 }}</ref><ref>{{ cite journal | vauthors = Kassa J, Bajgar J | title = Therapeutic efficacy of obidoxime or HI-6 with atropine against intoxication with some nerve agents in mice | journal = Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) | year = 1996 | volume = 39 | issue = 1 | pages = 27–30 | pmid = 9106387 }}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Commons category|GV nerve agent}} |
{{Commons category|GV nerve agent}} |
||
*{{ |
*{{cite web | vauthors = Harvey SP, Cheng TC | title = Identification, Purification, and Partial Characterization of the GV-Degrading Enzyme from ATCC # 29660 ''Alteromonas undina'' | publisher = Edgewood | location = Aberdeen Proving Ground | year = 2002 | id = Report ECBC-TR-229 | oclc = 74239874 | url = http://www.dtic.mil/cgi-bin/GetTRDoc?Location=U2&doc=GetTRDoc.pdf&AD=ADA411415 | format = pdf | access-date = 2013-09-09 | archive-date = 2013-09-09 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20130909103146/http://www.dtic.mil/cgi-bin/GetTRDoc?Location=U2&doc=GetTRDoc.pdf&AD=ADA411415 | url-status = dead }} |
||
*{{ cite journal | author = Bajgar J | title = Some Toxic Chemicals as Potential Chemical Warfare Agents - The Threat for the Future? | journal = ASA |
*{{ cite journal | author = Bajgar J | title = Some Toxic Chemicals as Potential Chemical Warfare Agents - The Threat for the Future? | journal = ASA Newsletter | year = 1998 | volume = 1998 | issue = 6 | url = http://www.asanltr.com/ASANews-98/chemistry.html }} |
||
{{Chemical warfare}} |
{{Chemical warfare}} |
||
| Line 54: | Line 55: | ||
[[Category:Phosphorofluoridates]] |
[[Category:Phosphorofluoridates]] |
||
[[Category:G-series nerve agents]] |
[[Category:G-series nerve agents]] |
||
[[Category:Phosphorus-nitrogen compounds]] |
|||
{{Organic-compound-stub}} |
{{Organic-compound-stub}} |
||
Latest revision as of 11:57, 14 November 2024
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl N,N-dimethylphosphoramidofluoridate
| |
| Other names
EA-5365
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H16FN2O2P | |
| Molar mass | 198.176 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
GV (IUPAC name: 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl N,N-dimethylphosphoramidofluoridate), also known as EA-5365, is an organophosphate nerve agent. GV is a part of a new series of nerve agents with properties similar to the "G-series" and "V-series". It is a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor with properties similar to other nerve agents, being a highly poisonous vapour. Treatment for poisoning with GV involves drugs such as atropine, benactyzine, obidoxime, and HI-6.[1][2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Fusek J, Bajgar J (1994). "Treatment of intoxication with GV compound in laboratory rats". Sb Ved Pr Lek Fak Karlovy Univerzity Hradci Kralove. 37 (2): 57–62. PMID 7784799.
- ^ Kassa J, Bajgar J (1996). "Therapeutic efficacy of obidoxime or HI-6 with atropine against intoxication with some nerve agents in mice". Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 39 (1): 27–30. PMID 9106387.
External links
[edit]Wikimedia Commons has media related to GV nerve agent.
- Harvey SP, Cheng TC (2002). "Identification, Purification, and Partial Characterization of the GV-Degrading Enzyme from ATCC # 29660 Alteromonas undina". Aberdeen Proving Ground: Edgewood. OCLC 74239874. Report ECBC-TR-229. Archived from the original (pdf) on 2013-09-09. Retrieved 2013-09-09.
- Bajgar J (1998). "Some Toxic Chemicals as Potential Chemical Warfare Agents - The Threat for the Future?". ASA Newsletter. 1998 (6).
