Ganz Works: Difference between revisions
m →History |
|||
| (112 intermediate revisions by 52 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Electrical manufacturer in Budapest, Hungary}} |
{{short description|Electrical manufacturer in Budapest, Hungary}} |
||
{{redirect|Ganz}} |
|||
{{Infobox company| |
{{Infobox company| |
||
| name = Ganz |
| name = Ganz Holdings Co. Ltd. |
||
| former_names = {{plainlist| |
|||
| type = [[Private company]] (former [[state company]]) |
|||
* Ganz–Danubius (1911–59?) |
|||
| logo = Ganz Budapest.jpg |
|||
* [[MÁVAG|Ganz-MÁVAG]] (1959–89) |
|||
}} |
|||
| type = {{plainlist| |
|||
* [[privately held company|Private]] (1845–1947) |
|||
* [[state-owned enterprise|State-owned]] (1947–59) |
|||
}} |
|||
| fate = Sold in 1989 to diverse companies that used the name 'Ganz'for their own enterprises |
|||
| image =Ganz–MÁVAG.jpg |
|||
| image_caption = The railway factory of the Ganz company (1880—1959: Ganz Wagon- and Machine Factory, 1959—1988: Ganz–MÁVAG Locomotive, Wagon- and Machine Factory)<br> / [https://www.google.com/maps/place/Budapest,+Ganz,+1087/@47.487133,19.0917537,15.17z/data=!4m6!3m5!1s0x4741dcea5d3b1dcd:0x79eebf84561bd480!8m2!3d47.487458!4d19.1006443!16s%2Fg%2F11j3s66bbj?hl=hu&entry=ttu Budapest, Kőbányai út 19-33.] / |
|||
| logo = Ganz holding logo.png |
|||
| logo_size = 200 |
|||
| slogan = |
| slogan = |
||
| foundation = |
| foundation = 1844 in [[Buda]], [[Kingdom of Hungary (1526–1867)|Kingdom of Hungary]] |
||
| defunct = {{end date and age|1989}} |
|||
| founders = [[Ábrahám Ganz]] |
| founders = [[Ábrahám Ganz]] |
||
| location = [[ |
| location = [[Buda]], Hungary |
||
| area_served = Worldwide |
| area_served = Worldwide |
||
| industry = transport |
| industry = [[transport industry|Transport]]<br>[[Metallurgy]] |
||
| gauge = |
| gauge = |
||
| products = [[ |
| products = [[Tram]]s <br>[[Train]]s <br>[[Ship]]s<br>[[Electric generator]]s |
||
| revenue = |
| revenue = |
||
| predecessors = |
| predecessors = |
||
| Line 17: | Line 30: | ||
| operating_income = |
| operating_income = |
||
| num_employees = |
| num_employees = |
||
| owner = [[Ábrahám Ganz]] and his family (1845–1947) <br>[[Hungary|State of Hungary]] ( |
| owner = [[Ábrahám Ganz]] and his family (1845–1947) <br>[[Hungary|State of Hungary]] (1947–1949) |
||
| key_people = |
| key_people = {{collapsible list| |
||
* [[Károly Zipernowsky]] |
|||
* [[Ottó Bláthy]] |
|||
* [[Miksa Déri]] |
|||
* [[András Mechwart]] |
|||
* [[Kálmán Kandó]] |
|||
* [[Donát Bánki]] |
|||
* [[János Csonka]] |
|||
* Zoltán Fitos <ref>[https://www.ganz-holding.hu/en/about-the-company About us] at Ganz Holding (19 Mar 2023)</ref> |
|||
| subsid = '''Ganz Danubius''' ([[ship yard]]) <br>'''Ganz Acélszerkezet''' (bridge steel structures) <br>'''Ganz Transelektro''' ([[power plant]] and [[power distribution]] equipment) |
|||
| homepage = http://ganzdata.hu/ |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| parent = |
|||
[[File:Ganz steam tractor 1882.jpg|thumb|Ganz steam tractor with rotary plow, (produced since the 1870s)]] |
|||
| subsid = {{plainlist| |
|||
{{redirect|Ganz}} |
|||
* Ganz Danubius ([[ship yard]]) |
|||
{{More citations needed|date=January 2014}} |
|||
* Ganz Acélszerkezet (bridge steel structures) |
|||
* Ganz Transelektro ([[power plant]] and [[power distribution]] equipment) |
|||
}} |
|||
| homepage = {{URL|https://www.ganz-holding.hu/en/|ganz-holding.hu}} |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''Ganz Machinery Works Holding''' is a [[Hungary|Hungarian]] [[holding company]]. Its products are related to rail transport, power generation, and water supply, among other industries.<ref>[https://www.ganz-holding.hu/en/ About us], Ganz-holding.hu</ref> |
|||
The original '''Ganz Works''' or '''Ganz''' ({{Langx|hu|Ganz vállalatok}} or {{lang|hu|Ganz Művek}}, ''Ganz companies'', formerly ''Ganz and Partner Iron Mill and Machine Factory'') operated between 1845 and 1949 in [[Budapest]], Hungary. It was named after [[Ábrahám Ganz]], the founder and manager of the company. Ganz is probably best known for the manufacture of [[tramcars]], but was also a pioneer in the application of [[Three-phase AC railway electrification|three-phase alternating current to electric railways]]. |
|||
Ganz also made ships (through its ''Ganz Danubius'' division), bridge steel structures (''Ganz Acélszerkezet'') and high-voltage equipment (''Ganz Transelektro''). In the early 20th century the company experienced its heyday and became the third-largest industrial enterprise in the Kingdom of Hungary after the ''[[Manfréd Weiss Steel and Metal Works]]'' and the ''[[MÁVAG]]'' company. |
|||
Since 1989, various parts of Ganz have been taken over by other companies. |
|||
The '''Ganz Works''' or '''Ganz''' ({{Lang-hu|Ganz vállalatok}} or {{lang|hu|Ganz Művek}}, ''Ganz companies'', formerly ''Ganz and Partner Iron Mill and Machine Factory'') was a group of companies operating between 1845 and 1949 in [[Budapest]], [[Hungary]]. It was named after [[Ábrahám Ganz]], the founder and the manager of the company. It is probably best known for the manufacture of [[tramcars]], but was also a pioneer in the application of [[Three-phase AC railway electrification|three-phase alternating current to electric railways]]. Ganz also made ships (''Ganz Danubius''), bridge steel structures (''Ganz Acélszerkezet'') and high-voltage equipment (''Ganz Transelektro''). In the early 20th century the company experienced its heyday, it became the third largest industrial enterprise in Kingdom of Hungary after the ''[[Manfréd Weiss Steel and Metal Works]]'' and the ''[[MÁVAG]]'' company. Since 1989, various parts of ''Ganz'' have been taken over by other companies. |
|||
== History == |
== History == |
||
[[File:%C3%81brah%C3%A1m_Ganz.jpg|thumb|left|150px|Abraham Ganz, founder]] |
|||
Before 1919, the company built [[ocean liners]], [[dreadnought]] type [[battleship]]s and [[submarine]]s, [[power plant]]s, [[automobile]]s<ref>Iván Boldizsár: NHQ; the ''New Hungarian Quarterly'', Volume 16, Issue 2; Volume 16, Issues 59–60, p. 128</ref><ref>Hungarian Technical Abstracts: Magyar Műszaki Lapszemle, Volumes 10–13, p. 41</ref> and many types of fighter aircraft.<ref>[[Iván T. Berend]]: ''Case Studies on Modern European Economy: Entrepreneurship, Inventions, and Institutions'', p. 151</ref> |
|||
The company was founded by [[Ábrahám Ganz]] in 1844. He was invited to [[Pest, Hungary]], by Count [[István Széchenyi]] and became the casting master at the ''Roller Mill Plant'' (referred to as ''Hengermalom'' in Hungarian). In 1854 he began manufacturing hard cast [[railroad wheel]]s in his own plant founded in 1844. The management of the steam mill paid a share of the profit to Ganz. This enabled him to buy, in 1844, land and a house for 4500 Forints in Víziváros, Buda castle district. Abraham Ganz built his own foundry on this site and started to work there with seven assistants. They made mostly casting products for the needs of the people of the city.[3] In 1845, he bought the neighbouring site and expanded his foundry with a cupola furnace. He gave his brother, Henrik a job as a clerk, because of the growing administration work. He made a profit in the first year, and his factory grew, even though he had not yet engaged in mass production. In 1846, at the third Hungarian Industrywork Exhibition (Magyar Iparmű Kiállítás), he introduced his stoves to the public. He won the silver medal of the exhibition committee and the bronze medaille from Archduke Joseph, Palatine of Hungary. |
|||
During the [[Hungarian Revolution of 1848]] the foundry made ten cannons and many cannonballs for the Hungarian army. Because of this, the Military Court of Austria impeached him. He got seven weeks in prison as penalty, but because of his Swiss citizenship he was acquitted of the charge.[3] |
|||
The company was founded by ''Abraham Ganz'' in 1844. He was invited to [[Pest, Hungary]], by Count [[István Széchenyi]] and became the casting master at the ''Roller Mill Plant'' (referred to as ''Hengermalom'' in Hungarian). In 1854 he began manufacturing hard cast [[railroad wheel]]s in his own plant founded in 1844. He successfully developed a [[railway wheel|railway whee]]l [[casting]] technology; it was the new method of "crust-casting" to produce cheap yet sturdy iron railway wheels, which greatly contributed to the rapid railway development in Central Europe. 86,074 pieces of hard cast wheels had been sold to 59 European railway companies until 1866. Consequently, this factory played an important role in building the infrastructure of the Hungarian Kingdom and the [[Austro-Hungarian Empire]].{{citation needed|date=October 2013}} At this time the [[agricultural machine]]s, [[steam locomotive]]s, pumps and the [[railway carriage]]s were the main products. At the beginning of the 20th century, 60 to 80% of the factory's products were sold for export. |
|||
[[File:Ganz steam tractor 1882.jpg|thumb|Ganz steam tractor with rotary plow, (produced since the 1870s)]] |
|||
At the end of the 19th century, the products of the ''Ganz and Partner Iron Mill and Machine Factory'' (hereinafter referred to as ''Ganz Works'') promoted the expansion of [[alternating-current]] [[power transmission]]s.{{citation needed|date=October 2013}} |
|||
Ganz recognized that, to develop his factory, he had to make products that were mass-produced. In 1846 the Pest-Vác railway line was built. At that time, European foundries made wrought iron rims for spoked wagon wheels by pouring the casts in shapes in sand, and leaving them to cool down. He successfully developed a [[railway wheel|railway whee]]l [[casting]] technology; it was the new method of "crust-casting" to produce cheap yet sturdy iron railway wheels, which greatly contributed to the rapid railway development in Central Europe. 86,074 pieces of hard cast wheels had been sold to 59 European railway companies until 1866. Consequently, this factory played an important role in building the infrastructure of the Hungarian Kingdom and the [[Austro-Hungarian Empire]].{{citation needed|date=October 2013}} At this time the [[agricultural machine]]s, [[steam locomotive]]s, pumps and the [[railway carriage]]s were the main products. At the beginning of the 20th century, 60 to 80% of the factory's products were sold for export. |
|||
===Prominent engineers=== |
|||
After the death of Abraham Ganz, the heirs entrusted the management of the factory to his direct colleagues at Ganz Művek: Antal Eichleter, Ulrik Keller and Andreas Mechwart, which then took the name Ganz & Co. The Ganz family sold the company, which consisted of five departments, and in April 1869 it was transformed into a joint-stock company, and continued its operations under the name of "Ganz és Társa vasontöde és Gépgyár Rt." (Ganz & Partners Iron Foundry and Machine Factory Co.) The technical director was András Mechwart, under whose direction Ganz became one of the most important groups of machine building companies in the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy after 1869. |
|||
Prominent engineers at ''Ganz works'' included [[András Mechwart]], [[Károly Zipernowsky]], [[Miksa Déri]], [[Ottó Titusz Bláthy]], [[Kálmán Kandó]] and [[Ernő Wilczek]]. |
|||
At the end of the 19th century, the products of the ''Ganz and Partner Iron Mill and Machine Factory'' (hereinafter referred to as ''Ganz Works'') promoted the expansion of [[alternating-current]] [[power transmission]]s. |
|||
=== Prominent engineers === |
|||
[[File:Józsefvárosi madártávlat.jpg|thumb|The Ganz wagon factory (aerial view)]] |
|||
[[File:Hajógyári favázas ipari csarnoképület (1186. számú műemlék) 2.jpg|thumb|Ganz Shipyard hall building (The Shipyard was demolished in the early 2000s. This old, fachwerk-style hall was originally intended to be preserved, but it was also destroyed in 2015.) — [https://www.google.com/maps/@47.5505905,19.0691549,16.71z?hl=hu&entry=ttu Budapest, Meder utca] ]] |
|||
[[File:Foundry_Museum,_Budapest-2.jpg|thumb|Ganz Trunk Factory Bark Foundry (now: Foundry Museum) — [https://www.google.com/maps/place/Muzeum/@47.5115514,19.0353033,19z/data=!4m6!3m5!1s0x4741dc1ccc1f6c2d:0x10ae5c4a6b053b5a!8m2!3d47.5116798!4d19.035453!16s%2Fg%2F11pz716n8v?hl=hu&entry=ttu Budapest, Bem József u. 20.] ]] |
|||
[[File:Budapest_-_Millipop_Mosolygyár.jpg|thumb|Ganz Electric Works (now: Millennium Park) — [https://www.google.com/maps/place/Millen%C3%A1ris+B+%C3%A9p%C3%BClet+(Nagycsarnok)/@47.5122431,19.0241549,18.75z/data=!4m6!3m5!1s0x4741df5883c85a5d:0xa3d38b08b6271294!8m2!3d47.5124869!4d19.02393!16s%2Fg%2F11k4vj4hrb?hl=hu&entry=ttu Budapest, Lövőház utca 39.] ]] |
|||
[[File:Ganz_Kapcsoló-_és_Készülékgyártó_Kft.4.jpg|thumb|Ganz Switches and Devices Factory (it works) — [https://www.google.com/maps/place/Ganz+Kapcsol%C3%B3-+%C3%A9s+K%C3%A9sz%C3%BCl%C3%A9kgy%C3%A1rt%C3%B3+Kft./@47.4854003,19.1106485,15.54z/data=!4m6!3m5!1s0x4741dcc63f68c949:0xd892b5a894e97e25!8m2!3d47.485355!4d19.1114436!16s%2Fg%2F1tgr_qf6?hl=hu&entry=ttu Budapest, Kőbányai út 41/c.] ]] |
|||
Prominent engineers at ''Ganz works'' included [[András Mechwart]], [[Károly Zipernowsky]], [[Miksa Déri]], [[Ottó Titusz Bláthy]], [[Kálmán Kandó]], [[György Jendrassik]] and [[Ernő Wilczek]]. |
|||
===Revolution in the milling industry=== |
|||
The invention of the modern industrial mill (the [[roller mill]] ) – by [[András Mechwart]] in 1874 – guaranteed a solid technological superiority and revolutionized the world's milling industry. Budapest's milling industry grow the second largest in the world, behind the American Minneapolis. The Hungarian grain export increased by 66% within some years.<ref>{{cite book|author1=Mikulas Teich|author2=Roy Porter|author3=Bo Gustafsson|title=The Industrial Revolution in National Context: Europe and the USA|publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]]|year=1996|page=280|isbn=9780521409407|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=z7GVCC0hlBsC&q=ganz+milling+minneapolis&pg=PA280}}</ref> |
|||
===Power plants, generators turbines and transformers=== |
===Power plants, generators turbines and transformers=== |
||
[[File:ZBD team.jpg|thumb|The Hungarian ''"ZBD" Team'': [[ |
[[File:ZBD team.jpg|thumb|The Hungarian ''"ZBD" Team'': [[Miksa Déri]], [[Ottó Bláthy]], [[Károly Zipernowsky]]]] |
||
[[File:DBZ trafo.jpg|thumb|first high efficiency transformer prototypes (1885; Széchenyi István Memorial Exhibition, [[Nagycenk]], [[Hungary]])]] |
|||
In 1878, the company's general manager [[András Mechwart]] founded the Department of Electrical Engineering headed by [[Károly Zipernowsky]]. Engineers [[Miksa Déri]] and [[Ottó Bláthy]] also worked at the department producing [[Dynamo|direct-current machines]] and [[arc lamp]]s. |
In 1878, the company's general manager [[András Mechwart]] founded the Department of Electrical Engineering headed by [[Károly Zipernowsky]]. Engineers [[Miksa Déri]] and [[Ottó Bláthy]] also worked at the department producing [[Dynamo|direct-current machines]] and [[arc lamp]]s. |
||
In 1878, the company began producing equipment for electric lighting and, by 1883, had installed over fifty systems in Austria-Hungary. Their AC systems used arc and incandescent lamps, generators, and other equipment.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Guarnieri|first=M.|year=2013|title=Who Invented the Transformer?|journal=IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine|volume=7|issue=4|pages=56–59|doi= 10.1109/MIE.2013.2283834|s2cid=27936000}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=g07Q9M4agp4C&pg=PA96| last = Hughes | first = Thomas P.| title = Networks of Power: Electrification in Western Society, 1880-1930| publisher = The Johns Hopkins University Press| location = Baltimore| year = 1993| pages = 95-96| access-date = Sep 9, 2009| isbn = 978-0-8018-2873-7}}</ref> |
|||
==== Generators ==== |
==== Generators ==== |
||
The first turbo generators were [[water turbines]] which drove [[electric generator]]s. The first Hungarian water turbine was designed by engineers of the Ganz Works in 1866. Mass production of dynamo generators started in 1883.<ref>http://www.sze.hu/~mgergo/EnergiatudatosEpulettervezes/2013_1_feladat/ErosErika/V%EDzenergia%20hasznos%EDt%E1s%20szigetk%F6zi%20szemmel%20EL%D5AD%C1SANYAG.pdf{{dead link|date=September 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> |
The first turbo generators were [[water turbines]] which drove [[electric generator]]s. The first Hungarian water turbine was designed by engineers of the Ganz Works in 1866. Mass production of dynamo generators started in 1883.<ref>http://www.sze.hu/~mgergo/EnergiatudatosEpulettervezes/2013_1_feladat/ErosErika/V%EDzenergia%20hasznos%EDt%E1s%20szigetk%F6zi%20szemmel%20EL%D5AD%C1SANYAG.pdf{{dead link|date=September 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> |
||
The missing link of a full Voltage Sensitive/Voltage Intensive (VSVI) system was the reliable [[alternating current]] constant voltage generator. Therefore the invention of the constant voltage generator by the Ganz Works in 1883<ref>{{cite book|author= |
The missing link of a full Voltage Sensitive/Voltage Intensive (VSVI) system was the reliable [[alternating current]] constant voltage generator. Therefore, the invention of the constant voltage generator by the Ganz Works in 1883<ref>{{cite book|author=American Society for Engineering Education|title=Proceedings, Part 2|year=1995|page=1848|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EZVRAAAAMAAJ&q=ganz+%22constant+voltage+generator%22|author-link=American Society for Engineering Education}}</ref> had a crucial role in the beginnings of industrial scale AC power generation, because only these type of generators can produce a stable output voltage, regardless of the actual load.<ref>{{cite book|author=Robert L. Libbey|title=A Handbook of Circuit Math for Technical Engineers|publisher=CRC Press|year=1991|page=22|isbn=9780849374005|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=b6dD_bqZNyoC&q=%22constant+voltage+generator%22&pg=PA22}}</ref> |
||
==== Transformers ==== |
==== Transformers ==== |
||
[[File:DBZ trafo.jpg|thumb|first high efficiency transformer prototypes (1885; Széchenyi István Memorial Exhibition, [[Nagycenk]], [[Hungary]])]] |
|||
In cooperation, Zipernovsky, Bláthy and Déri (known as the ZBD team) constructed and patented the [[transformer]]. The "transformer" was named by Ottó Titusz Bláthy. The three invented the first high efficiency, closed core shunt connection transformer. They also invented the modern [[electric distribution systems|power distribution system]]: Instead of a series of connections they connected supply transformers in parallel to the main line.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.omikk.bme.hu/archivum/angol/htm/blathy_o.htm|title=Bláthy, Ottó Titusz|publisher=|accessdate=20 December 2016}}</ref> |
|||
In cooperation, Zipernovsky, Bláthy and Déri (known as the ZBD team) constructed and patented the [[transformer]]. The "transformer" was named by Ottó Titusz Bláthy. The three invented the first high efficiency, closed core shunt connection transformer. They also invented the modern [[electric distribution systems|power distribution system]]: Instead of a series of connections they connected supply transformers in parallel to the main line.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.omikk.bme.hu/archivum/angol/htm/blathy_o.htm|title=Bláthy, Ottó Titusz|access-date=20 December 2016}}</ref> |
|||
The transformer patents described two basic principles. Loads were to be connected in parallel, not in series as had been the general practice until 1885. Additionally, the inventors described the closed armature as an essential part of the transformer. Both factors assisted the stabilisation of voltage under varying load, and allowed definition of standard voltages for distribution and loads. The parallel connection and efficient closed core made construction of electrical distribution systems technically and economically feasible. |
The transformer patents described two basic principles. Loads were to be connected in parallel, not in series as had been the general practice until 1885. Additionally, the inventors described the closed armature as an essential part of the transformer. Both factors assisted the stabilisation of voltage under varying load, and allowed definition of standard voltages for distribution and loads. The parallel connection and efficient closed core made construction of electrical distribution systems technically and economically feasible. |
||
The Ganz Works built the first transformers using iron plating of enamelled mild iron wire, and started to use laminated |
The Ganz Works built the first transformers using iron plating of enamelled mild iron wire, and started to use laminated cores to eliminate [[eddy currents]]<ref>{{cite book|author=Electrical Society of Cornell University|title=Proceedings of the Electrical Society of Cornell University|publisher=Andrus & Church|year=1896|page=39}}</ref> |
||
==== Power stations ==== |
==== AC Power stations ==== |
||
In 1886, the ZBD engineers designed, and the company supplied, electrical equipment for the world's first [[power station]] to use AC generators to power a parallel connected common electrical network. This was the Italian steam-powered Rome-Cerchi power plant.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iec.ch/cgi-bin/tl_to_htm.pl?section=technology&item=144 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070930171011/http://www.iec.ch/cgi-bin/tl_to_htm.pl?section=technology&item=144 |url-status=dead |archive-date=September 30, 2007 |title=Ottó Bláthy, Miksa Déri, Károly Zipernowsky |publisher=IEC Techline | |
In 1886, the ZBD engineers designed, and the company supplied, electrical equipment for the world's first [[power station]] to use AC generators to power a parallel connected common electrical network. This was the Italian steam-powered Rome-Cerchi power plant.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iec.ch/cgi-bin/tl_to_htm.pl?section=technology&item=144 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070930171011/http://www.iec.ch/cgi-bin/tl_to_htm.pl?section=technology&item=144 |url-status=dead |archive-date=September 30, 2007 |title=Ottó Bláthy, Miksa Déri, Károly Zipernowsky |publisher=IEC Techline |access-date=Apr 16, 2010 }}</ref> |
||
Following the introduction of the transformer, the Ganz Works changed over to production of alternating-current equipment. For instance, Rome's electricity was supplied by hydroelectric plant and long-distance energy transfer.<ref>[http://www.institutoideal.org/conteudo_eng.php?&sys=biblioteca_eng&arquivo=1&artigo=94&ano=2008 Hungarian Inventors and their Inventions] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120322223457/http://www.institutoideal.org/conteudo_eng.php?&sys=biblioteca_eng&arquivo=1&artigo=94&ano=2008 |date=2012-03-22 }}</ref> |
Following the introduction of the transformer, the Ganz Works changed over to production of alternating-current equipment. For instance, Rome's electricity was supplied by hydroelectric plant and long-distance energy transfer.<ref>[http://www.institutoideal.org/conteudo_eng.php?&sys=biblioteca_eng&arquivo=1&artigo=94&ano=2008 Hungarian Inventors and their Inventions] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120322223457/http://www.institutoideal.org/conteudo_eng.php?&sys=biblioteca_eng&arquivo=1&artigo=94&ano=2008 |date=2012-03-22 }}</ref> |
||
{{clear}} <gallery mode="packed" class="center centered" perrow="4" widths=220 heights=140 style="font-size:90%; line-height:120%" caption="''Ganz Transelektro'' power plant and power distribution products"> |
{{clear}} <gallery mode="packed" class="center centered" perrow="4" widths=220 heights=140 style="font-size:90%; line-height:120%" caption="''Ganz Transelektro'' power plant and power distribution products"> |
||
File:Ganz Transformers december 1886.jpg|Ganz Transformers in december 1886 |
|||
File:Turbinaszerelés.jpg|construction of a ''Ganz'' water [[turbo generator]] (1886) |
File:Turbinaszerelés.jpg|construction of a ''Ganz'' water [[turbo generator]] (1886) |
||
File:PSM V56 D0433 Direct connected electric railway generator.png|PSM V56 D0433 direct connected [[electric railway]] [[Electric generator|generator]] (1899) |
File:PSM V56 D0433 Direct connected electric railway generator.png|PSM V56 D0433 direct connected [[electric railway]] [[Electric generator|generator]] (1899) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 120: | ||
==== Electricity meters ==== |
==== Electricity meters ==== |
||
The first mass-produced kilowatt-hour meter ([[electricity meter]]), based on Hungarian [[Ottó Bláthy]]'s patent and named after him, was presented by the Ganz Works at the Frankfurt Fair in the autumn of 1889, and the company was marketing the first induction kilowatt-hour meter by the end of the year. These were the first alternating-current wattmeters, known by the name of Bláthy-meters.<ref>{{cite web|author=Eugenii Katz |url=http://people.clarkson.edu/~ekatz/scientists/blathy.html |title=Blathy |publisher=Clarkson University | |
The first mass-produced kilowatt-hour meter ([[electricity meter]]), based on Hungarian [[Ottó Bláthy]]'s patent and named after him, was presented by the Ganz Works at the Frankfurt Fair in the autumn of 1889, and the company was marketing the first induction kilowatt-hour meter by the end of the year. These were the first alternating-current wattmeters, known by the name of Bláthy-meters.<ref>{{cite web|author=Eugenii Katz |url=http://people.clarkson.edu/~ekatz/scientists/blathy.html |title=Blathy |publisher=Clarkson University |access-date=2009-08-04 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080625015707/http://people.clarkson.edu/~ekatz/scientists/blathy.html |archive-date=June 25, 2008 }}</ref> |
||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
[[File:Csonka János autó.jpg|thumb|[[Csonka (automobile)|Csonka]] automobile of 1905]] |
|||
==== Industrial refrigerators and air conditioners==== |
|||
[[File:Ganz autobus from 1914.jpg|thumb|Ganz bus (1914; published in ''Vasárnapi Újság'' in 1916)]] |
|||
In 1894, Hungarian inventor and industrialist [[István Röck]] started to manufacture a large industrial ammonia refrigerator (together with the Esslingen Machine Works) which was powered by Ganz electric compressors. At the 1896 Millennium Exhibition, Röck and the Esslingen Machine Works presented a 6-tonne capacity artificial ice producing plant. In 1906, the first large Hungarian cold store (with a capacity of 3,000 tonnes, the largest in Europe) opened in Tóth Kálmán Street, Budapest, the machine was manufactured by the Ganz Works. Until nationalisation after the Second World War, large-scale industrial refrigerator production in Hungary was in the hands of Röck and Ganz Works.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20220506202421/https://mek.oszk.hu/02100/02185/html/703.html The development and heyday of mechanical science (Hungarian) Link]</ref> |
|||
=== Combustion engines and vehicles === |
|||
The contract between Ganz and Egypt in the 1930s played a key role in the development of cooling equipment: railcars delivered to Egypt were equipped with air-conditioning cooling systems. The collective of the Ganz factory (machine designers: Gábor Hollerung, Rezső Oláh, István Pfeifer, Prónai) designed and built the 3-cylinder, 20 kW compressors with freon refrigerant, air condenser and evaporator. The machine could also be converted to heat pump operation.<ref>[https://mek.oszk.hu/02100/02185/html/703.html The development and heyday of mechanical science (Hungarian) Link]</ref> |
|||
=== ICE engines and vehicles === |
|||
The beginning of [[gas engine]] manufacturing in Hungary is linked to [[Donát Bánki]] and [[János Csonka]] but it is not clear that they ever worked for Ganz. |
The beginning of [[gas engine]] manufacturing in Hungary is linked to [[Donát Bánki]] and [[János Csonka]] but it is not clear that they ever worked for Ganz. |
||
Ganz produced engines whose designs were licensed to Western European partners, notably in the United Kingdom and Italy. |
Ganz produced engines whose designs were licensed to Western European partners, notably in the United Kingdom and Italy. |
||
[[File:Csonka János autó.jpg|thumb|[[Csonka (automobile)|Csonka]] automobile of 1905]] |
|||
[[File:Ganz autobus from 1914.jpg|thumb|Ganz bus (1914; published in ''Vasárnapi Újság'' in 1916)]] |
|||
;Timeline |
;Timeline |
||
*1889 the first [[four-stroke]] gas engine was built by the Ganz factory |
*1889 the first [[four-stroke]] gas engine was built by the Ganz factory |
||
| Line 94: | Line 147: | ||
*1929 the first export delivery of a railway engine using the system of Ganz-Jendrassik |
*1929 the first export delivery of a railway engine using the system of Ganz-Jendrassik |
||
*1934 there was an engine reliability World Competition in the USSR where the Ganz engine achieved the best fuel consumption in its category |
*1934 there was an engine reliability World Competition in the USSR where the Ganz engine achieved the best fuel consumption in its category |
||
*1939 Scale model of Ganz Ac Electric locomotive exhibited at the Italy Pavilion of the New York World's Fair |
|||
*1939–42 construction of the [[Jendrassik Cs-1]] [[turboprop]] engine |
*1939–42 construction of the [[Jendrassik Cs-1]] [[turboprop]] engine |
||
*1944 the first application of the engine type XII JV 170/240 in a motor-train set |
*1944 the first application of the engine type XII JV 170/240 in a motor-train set |
||
| Line 100: | Line 154: | ||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
===Railways=== |
===Railways=== |
||
[[File:Foldalatti Andrassy.png|thumb|Cutaway Drawing of [[Millennium Underground]] in Budapest (1894–1896) which was the first underground in [[Continental Europe]] ]] |
|||
====Steam motors==== |
|||
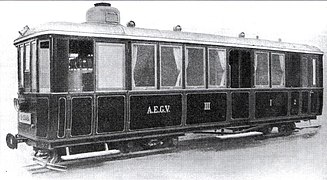
[[File:AEGV gőzmotorkocsi.JPG|thumb|The first steam railcar built by Ganz and de Dion-Bouton]] |
|||
[[File:Foldalatti Andrassy.png|thumb|Cutaway Drawing of [[Millennium Underground]] in Budapest (1894–1896) which was the first underground in [[Continental Europe]]]] |
|||
The Ganz Company started to construct [[steam locomotive]]s and [[steam railcar]]s from the 1860s. |
The Ganz Company started to construct [[steam locomotive]]s and [[steam railcar]]s from the 1860s. |
||
Between 1901 and 1908, Ganz Works of Budapest and [[de Dion-Bouton]] of Paris collaborated to build a number of railcars for the Hungarian State Railways together with units with de Dion-Bouton boilers, Ganz steam motors and equipments, and Raba carriages built by the [[Rába (company)|Raba Hungarian Wagon and Machine Factory]] in [[Győr]]. In 1908, the Borzsavölgyi Gazdasági Vasút (BGV), a [[narrow-gauge railway]] in Carpathian Ruthenia (today's Ukraine), purchased five railcars from Ganz and four railcars from the Hungarian Royal State Railway Machine Factory with de Dion-Bouton boilers. The Ganz company started to export [[steam motor]] railcars to the United Kingdom, Italy, Canada, Japan, Russia and Bulgaria.<ref>Railroad Gazette – Volume 37 – Page 296 (printed in 1904)</ref><ref>Modern Machinery – Volumes 19–20 – Page 206 (Printed in 1906)</ref><ref>[[John Robertson Dunlap]], [[Arthur Van Vlissingen]], [[John Michael Carmody]]: Factory and Industrial Management – Volume 33 – Page 1003 (printed in 1907</ref> |
Between 1901 and 1908, Ganz Works of Budapest and [[de Dion-Bouton]] of Paris collaborated to build a number of railcars for the Hungarian State Railways together with units with de Dion-Bouton boilers, Ganz steam motors and equipments, and Raba carriages built by the [[Rába (company)|Raba Hungarian Wagon and Machine Factory]] in [[Győr]]. In 1908, the Borzsavölgyi Gazdasági Vasút (BGV), a [[narrow-gauge railway]] in [[Carpathian Ruthenia]] (today's Ukraine), purchased five railcars from Ganz and four railcars from the Hungarian Royal State Railway Machine Factory with de Dion-Bouton boilers. The Ganz company started to export [[steam motor]] railcars to the United Kingdom, Italy, Canada, Japan, Russia and Bulgaria.<ref>Railroad Gazette – Volume 37 – Page 296 (printed in 1904)</ref><ref>Modern Machinery – Volumes 19–20 – Page 206 (Printed in 1906)</ref><ref>[[John Robertson Dunlap]], [[Arthur Van Vlissingen]], [[John Michael Carmody]]: Factory and Industrial Management – Volume 33 – Page 1003 (printed in 1907</ref> |
||
===== The World's first electrified main railway line in Italy ===== |
|||
The Ganz Works, having identified the significance of [[induction motor]]s and [[synchronous motor]]s, commissioned [[Kálmán Kandó]] to develop them. In 1894, Hungarian engineer Kálmán Kandó developed high-voltage [[Three-phase AC railway electrification|three-phase AC motors and generators]] for [[electric locomotive]]s. The first-ever electric rail vehicle manufactured by Ganz Works was a 6 HP pit locomotive with direct current traction system. The first Ganz made [[Induction motor|asynchronous]] rail vehicles (altogether 2 pieces) were supplied in 1898 to [[Évian-les-Bains]] (France) with a 37 HP asynchronous traction system. The Ganz Works won the tender for electrification of the [[Valtellina]] Railway in Italy in 1897. Under the management, and on the basis of plans from Kálmán Kandó, three phase electric power at 3 kV and 15 Hz was fed through two upper wires and the rails. The electricity was produced in a dedicated power station and the system operated for thirty years from 1902. Italian railways were the first in the world to introduce electric traction for the entire length of a main line rather than just a short stretch. The 106 km Valtellina line was opened on 4 September 1902, designed by Kandó and a team from the Ganz works.{{sfnp|Duffy|2003|p=120-121}}<ref name="Patent Office" /> The voltage was significantly higher than used earlier and it required new designs for electric motors and switching devices.<ref name="Kalman Kando2">{{cite web|url=http://www.omikk.bme.hu/archivum/angol/htm/kando_k.htm|title=Kalman Kando|accessdate=2011-10-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://profiles.incredible-people.com/kalman-kando/ |archive-url=https://archive.is/20120712234334/http://profiles.incredible-people.com/kalman-kando/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=2012-07-12 |title=Kalman Kando |accessdate=2009-12-05 }}</ref> The three-phase two-wire system was used on several railways in Northern Italy and became known as "the Italian system". Kandó was invited in 1905 to undertake the management of Società Italiana Westinghouse and led the development of several Italian electric locomotives.<ref name="Kalman Kando2" /> In 1918,<ref>{{cite book|author=Michael C. Duffy|title=Electric Railways 1880–1990|publisher=[[Institution of Engineering and Technology (professional society)|IET]]|year=2003|page=137|isbn=9780852968055|url=https://books.google.com/?id=cpFEm3aqz_MC&pg=PA137&dq=close+links+between+ganz#v=onepage&q=close%20links%20between%20ganz&f=false}}</ref> Kandó invented and developed the [[rotary phase converter]], enabling electric locomotives to use three-phase motors whilst supplied via a single overhead wire, carrying the simple industrial frequency (50 Hz) single phase AC of the high-voltage national networks.<ref name="Patent Office">{{cite web |
|||
{{Main|FS Class E.430|FS Class E.360}} |
|||
The Ganz Works, having identified the significance of [[induction motor]]s and [[synchronous motor]]s, commissioned [[Kálmán Kandó]] to develop them. In 1894, Hungarian engineer Kálmán Kandó developed high-voltage [[Three-phase AC railway electrification|three-phase AC motors and generators]] for [[electric locomotive]]s. The first-ever electric rail vehicle manufactured by Ganz Works was a 6 HP pit locomotive with direct current traction system. The first Ganz made [[Induction motor|asynchronous]] rail vehicles (altogether 2 pieces) were supplied in 1898 to [[Évian-les-Bains]] (France) with a 37 HP asynchronous traction system. The Ganz Works won the tender for electrification of the [[Valtellina]] Railway in Italy in 1897. Under the management, and on the basis of plans from Kálmán Kandó, three phase electric power at 3 kV and 15 Hz was fed through two upper wires and the rails. |
|||
[[file:Ganz Works Text Logo.svg|thumb|left|200px|Former logo of the Ganz Works]] |
|||
The electricity was produced in a dedicated power station and the system operated for thirty years from 1902. Italian railways were the first in the world to introduce electric traction for the entire length of a main line rather than just a short stretch. The 106 km Valtellina line was opened on 4 September 1902, designed by Kandó and a team from the Ganz works.{{sfnp|Duffy|2003|p=120-121}}<ref name="Patent Office" /> The voltage was significantly higher than used earlier and it required new designs for electric motors and switching devices.<ref name="Kalman Kando2">{{cite web|url=http://www.omikk.bme.hu/archivum/angol/htm/kando_k.htm|title=Kalman Kando|access-date=2011-10-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://profiles.incredible-people.com/kalman-kando/ |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120712234334/http://profiles.incredible-people.com/kalman-kando/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=2012-07-12 |title=Kalman Kando |access-date=2009-12-05 }}</ref> The three-phase two-wire system was used on several railways in Northern Italy and became known as "the Italian system". Kandó was invited in 1905 to undertake the management of Società Italiana Westinghouse and led the development of several Italian electric locomotives.<ref name="Kalman Kando2" /> |
|||
=====Invention of the Phase Converter===== |
|||
In 1918,<ref>{{cite book|last=Duffy | first=Michael C.|title=Electric Railways 1880–1990|publisher=[[Institution of Engineering and Technology (professional society)|IET]]|year=2003|page=137|isbn=9780852968055|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cpFEm3aqz_MC&q=close+links+between+ganz&pg=PA137}}</ref> Kandó invented and developed the [[rotary phase converter]], enabling electric locomotives to use three-phase motors whilst supplied via a single overhead wire, carrying the simple industrial frequency (50 Hz) single phase AC of the high-voltage national networks.<ref name="Patent Office">{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.mszh.hu/English/feltalalok/kando.html |
|url=http://www.mszh.hu/English/feltalalok/kando.html |
||
|title=Kálmán Kandó (1869–1931) |
|title=Kálmán Kandó (1869–1931) |
||
|author=Hungarian Patent Office |
|author=Hungarian Patent Office |
||
|publisher=www.mszh.hu |
|publisher=www.mszh.hu |
||
| |
|access-date=2008-08-10 |
||
|archive-date=2010-10-08 |
|||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101008073106/http://www.mszh.hu/English/feltalalok/kando.html |
|||
After [[World War I]], at the Ganz Works, Kálmán Kandó constructed a single-phase electric railway system using 16 kV at 50 Hz. A similar system, but using [[15 kV AC railway electrification|15 kV at 16.7 Hz]], later became widely used in Europe. The main attribute of Kandó's 50 Hz system was that it was fed by the normal power network, so dedicated railway power stations became unnecessary. Because of the early death of Kálmán Kandó, [[László Verebélÿ]] continued the work for the [[Hungarian State Railways]] (MÁV).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://energyhistory.energosolar.com/en_20th_century_electric_history.htm|title=Ganz and Tungsram – the 20th century|date=2007|website=Electric History|publisher=EnergoSolar.com|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20090106115646/http://energyhistory.energosolar.com/en_20th_century_electric_history.htm|archivedate=6 January 2009|url-status=dead|accessdate=20 December 2016}}</ref> |
|||
|url-status=dead |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
After [[World War I]], at the Ganz Works, Kálmán Kandó constructed a single-phase electric railway system using 16 kV at 50 Hz. A similar system, but using [[15 kV AC railway electrification|15 kV at 16.7 Hz]], later became widely used in Europe. The main attribute of Kandó's 50 Hz system was that it was fed by the normal power network, so dedicated railway power stations became unnecessary. Because of the early death of Kálmán Kandó, [[László Verebélÿ]] continued the work for the [[Hungarian State Railways]] (MÁV).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://energyhistory.energosolar.com/en_20th_century_electric_history.htm|title=Ganz and Tungsram – the 20th century|date=2007|website=Electric History|publisher=EnergoSolar.com|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090106115646/http://energyhistory.energosolar.com/en_20th_century_electric_history.htm|archive-date=6 January 2009|url-status=dead|access-date=20 December 2016}}</ref> |
|||
<gallery class=center mode=packed perrow=4 widths= heights=100 style="font-size:90%; line-height:120%" caption="Ganz Rail rolling stock"> |
|||
File:AEGV gőzmotorkocsi.JPG|The first steam railcar built by Ganz and de Dion-Bouton |
|||
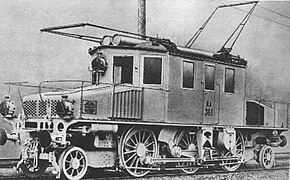
File:Ganz engine Valtellina.jpg|Ganz AC electric locomotive prototype (1901 [[Valtellina]], Italy) |
File:Ganz engine Valtellina.jpg|Ganz AC electric locomotive prototype (1901 [[Valtellina]], Italy) |
||
File:RA 361 Ganz Valtellina.jpg|Electric locomotive RA 361 (later [[FS Class E.360]]) by Ganz for the Valtellina line, 1904 |
|||
File:V50.jpg|The first locomotive with a phase converter was Kando's V50 locomotive (only for demonstration and testing purposes) |
|||
File:Vasútállomás, Ganz gyártmányú Árpád sorozatú (TAS) sínautóbusz. Fortepan 23230.jpg|Árpád Diesel railbus in 1937 |
|||
File:Provincia del Chubut - Bariloche - Ganz 2.jpg|Ganz train on the [[Ferrocarriles Patagónicos]] railway in Argentina (1945) |
File:Provincia del Chubut - Bariloche - Ganz 2.jpg|Ganz train on the [[Ferrocarriles Patagónicos]] railway in Argentina (1945) |
||
File:BASA-PZ-643-8-6-16- |
File:BASA-PZ-643-8-6-16-Diesel railcar, Avramovo-Saint Petka Station.jpg|Ganz [[diesel railcar]] on [[Septemvri-Dobrinishte narrow gauge line]], [[Bulgaria]], 1950-1963 |
||
File:V63.jpg|A series [[MÁV Class V63|V63]] [[Ganz-MÁVAG]] electric locomotive of Hungarian State Railways |
File:V63.jpg|A series [[MÁV Class V63|V63]] [[Ganz-MÁVAG]] electric locomotive of Hungarian State Railways |
||
File:EM_1367_leading_a_southbound_4_car_set_as_the_morning_sun_breaks_through_the_clouds,_near_Epuni_-_17_May_2003.jpg|[[Tranz Metro]] [[New Zealand EM class electric multiple unit|EM class]] [[Ganz-MÁVAG]] unit in service in the Hutt Valley, New Zealand |
File:EM_1367_leading_a_southbound_4_car_set_as_the_morning_sun_breaks_through_the_clouds,_near_Epuni_-_17_May_2003.jpg|[[Tranz Metro]] [[New Zealand EM class electric multiple unit|EM class]] [[Ganz-MÁVAG]] unit in service in the Hutt Valley, New Zealand |
||
| Line 127: | Line 198: | ||
==== Ganz-MÁVAG rail rolling stock ==== |
==== Ganz-MÁVAG rail rolling stock ==== |
||
{{Main|Ganz-MÁVAG}} |
{{Main|Ganz-MÁVAG}} |
||
[[file:Ganz mavag logo.png|thumb|150px|Logo of Ganz-Mavag, formed in 1959]] |
|||
In 1959 Ganz merged with the [[MÁVAG]] company and was renamed [[Ganz-MÁVAG]]. |
In 1959 Ganz merged with the [[MÁVAG]] company and was renamed [[Ganz-MÁVAG]]. |
||
In 1976 Ganz-Mávag supplied ten [[standard gauge]] 3-car diesel trainset to the [[Hellenic Railways Organisation]] (OSE), designated as Class AA-91 and four [[metre gauge]] 4-car trainsets, designated as Class A-6451. In 1981/82 Ganz-Mávag supplied to OSE 11 B-B diesel-hydraulic DHM7-9 locomotives, designated as class A-251. Finally, in 1983, OSE bought eleven 3-car metre gauge trainsets, designated as Class A-6461. All these locomotives and trainsets have been withdrawn with the exception of one standard and one metre gauge trainset.{{citation needed|date=January 2014}} |
In 1976 Ganz-Mávag supplied ten [[standard gauge]] 3-car diesel trainset to the [[Hellenic Railways Organisation]] (OSE), designated as Class AA-91 and four [[metre gauge]] 4-car trainsets, designated as Class A-6451. In 1981/82 Ganz-Mávag supplied to OSE 11 B-B diesel-hydraulic DHM7-9 locomotives, designated as class A-251. Finally, in 1983, OSE bought eleven 3-car metre gauge trainsets, designated as Class A-6461. All these locomotives and trainsets have been withdrawn with the exception of one standard and one metre gauge trainset.{{citation needed|date=January 2014}} |
||
| Line 138: | Line 210: | ||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
===Shipbuilding=== |
===Shipbuilding, Ganz - Danubius=== |
||
In 1911, |
In 1911, the Ganz Company merged with the [[3. Maj|Danubius shipbuilding company]], which was the largest shipbuilding company in Hungary. From 1911, the unified company adopted the ''"Ganz–Danubius''" brand name. In the beginning of the 20th century the company had 19 shipyards on the Danube and the Adriatic Sea in the city of Rijeka and Pula.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20200322132134/http://ganz-danubius.com/index.php/en/history History of Ganz Danubius]</ref> |
||
As Ganz Danubius, the company became involved in shipbuilding before, and during, [[World War I]]. Ganz was responsible for building the dreadnought {{SMS|Szent István}}, all of the [[Novara-class cruiser|''Novara''-class cruiser]]s, and built diesel-electric [[U-boat]]s at its shipyard in Budapest, for final assembly at [[Fiume]]. Several U-boats of the [[Austro-Hungarian submarine U-XXIX|U-XXIX class]], [[Austro-Hungarian submarine U-XXX|U-XXX class]], [[Austro-Hungarian submarine U-XXXI|U-XXXI class]] and [[Austro-Hungarian submarine U-XXXII|U-XXXII class]] were completed,<ref>{{cite book|author=R.H. Gibson, Maurice Prendergast|title=The German Submarine War 1914–1918|publisher=Periscope Publishing Ltd|year=2002|page=386|isbn=9781904381082|url=https://books.google.com/?id=uqj0bZR_EggC& |
As Ganz Danubius, the company became involved in shipbuilding before, and during, [[World War I]]. Ganz was responsible for building the dreadnought {{SMS|Szent István}}, all of the [[Novara-class cruiser|''Novara''-class cruiser]]s, and built diesel-electric [[U-boat]]s at its shipyard in Budapest, for final assembly at [[Fiume]]. Several U-boats of the [[Austro-Hungarian submarine U-XXIX|U-XXIX class]], [[Austro-Hungarian submarine U-XXX|U-XXX class]], [[Austro-Hungarian submarine U-XXXI|U-XXXI class]] and [[Austro-Hungarian submarine U-XXXII|U-XXXII class]] were completed,<ref>{{cite book|author=R.H. Gibson, Maurice Prendergast|title=The German Submarine War 1914–1918|publisher=Periscope Publishing Ltd|year=2002|page=386|isbn=9781904381082|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uqj0bZR_EggC&q=ganz+danubius+submarine&pg=PA386}}</ref> A number of other types were laid down, but remained incomplete at the war's end.<ref>http://www.gwpda.org/naval/ahsubs.htm Sieche article on KuK U-Boats</ref> By the end of the First World War, 116 naval vessels had been built by The Ganz-Danubius company. The company also produces transatlantic ocean liners for passenger lines Trieste - New York, Trieste - Montevideo, as a reflection of already formed wave of mass migration from Central Europe to America. |
||
<gallery mode="packed" class="center centered" perrow="widths=" heights="90" style="font-size:90%; line-height:120%" caption="''Ganz–Danubius'' ships and submarines"> |
|||
File:The assembly of a SM U-31 submarine in the Ganz-Danubius company.jpg|The back of [[SM U-29]] [[submarine]] during assembly (24 April 1916) |
File:The assembly of a SM U-31 submarine in the Ganz-Danubius company.jpg|The back of the [[SM U-29 (Austria-Hungary)|SM U-29]] [[submarine]] during assembly (24 April 1916) |
||
File:SM U29 Ganz-Danubius.jpg|[[SM U-29]] [[submarine]] of the [[Austro-Hungarian Navy]], built by Ganz-Danubius |
|||
File:Novaral.jpg|The battle-damaged {{SMS|Novara|1913}} after a victorious [[naval battle]] |
File:Novaral.jpg|The battle-damaged {{SMS|Novara|1913}} after a victorious [[naval battle]] |
||
File:Szent Istvan.jpg|Austro-Hungarian built [[dreadnought]] class [[battleship]] {{SMS|Szent István}} at [[Pula]] (military dock) |
File:Szent Istvan.jpg|Austro-Hungarian built [[dreadnought]] class [[battleship]] {{SMS|Szent István}} at [[Pula]] (military dock) |
||
| Line 151: | Line 222: | ||
===Aircraft=== |
===Aircraft=== |
||
{{Main|UFAG}} |
|||
The first Hungarian "aeroplane factory" was founded by the Ganz Company and [[Weiss-Manfréd]] Works in 1912. During World War I, the company made many types of [[Albatros Flugzeugwerke|Albatros]] and [[Fokker]] fighter planes. |
|||
The first Hungarian "aeroplane factory" ( [[UFAG]] ) was founded by the Ganz Company and [[Weiss-Manfréd]] Works in 1912. During World War I, the company made many types of [[Albatros Flugzeugwerke|Albatros]] and [[Fokker]] fighter planes. |
|||
Before 1919, the company built [[ocean liners]], [[dreadnought]] type [[battleship]]s and [[submarine]]s, [[power plant]]s, [[automobile]]s<ref>Iván Boldizsár: NHQ; the ''New Hungarian Quarterly'', Volume 16, Issue 2; Volume 16, Issues 59–60, p. 128</ref><ref>Hungarian Technical Abstracts: Magyar Műszaki Lapszemle, Volumes 10–13, p. 41</ref> and many types of fighter aircraft.<ref>[[Iván T. Berend]]: ''Case Studies on Modern European Economy: Entrepreneurship, Inventions, and Institutions'', p. 151</ref> |
|||
The world's first [[turboprop]] engine was the [[Jendrassik Cs-1]] designed by the Hungarian mechanical engineer [[György Jendrassik]]. It was built and tested in the Ganz factory in Budapest between 1939 and 1942. It was planned to be fitted to the Varga RMI-1 X/H twin-engined reconnaissance bomber designed by László Varga in 1940, but the program was cancelled. Jendrassik had also designed a small-scale 75 kW turboprop in 1937.{{citation needed|date=January 2014}} |
The world's first [[turboprop]] engine was the [[Jendrassik Cs-1]] designed by the Hungarian mechanical engineer [[György Jendrassik]]. It was built and tested in the Ganz factory in Budapest between 1939 and 1942. It was planned to be fitted to the Varga RMI-1 X/H twin-engined reconnaissance bomber designed by László Varga in 1940, but the program was cancelled. Jendrassik had also designed a small-scale 75 kW turboprop in 1937.{{citation needed|date=January 2014}} |
||
| Line 165: | Line 239: | ||
In 1989, the British company Telfos Holdings gained a majority of the shares in Ganz Railway Vehicle Factory Co. Ltd. and the name of the company was changed to Ganz-Hunslet Co. Ltd. In the course of 1991 and 1992, the Austrian company [[Jenbacher Werke]] obtained 100% of the company's shares and consequently the railway vehicle factory is now a member of the international railway vehicle manufacturing group, Jenbacher Transport Systeme. At present, the Ganz Electric Works, under the name of Ganz-Ansaldo is a member of the Italian industrial giant, [[AnsaldoBreda]]. The Ganz Works were transformed into holdings. Ganz-Danubius was wound up in 1994. The Ganz Electric Meter Factory in Gödöllő became the member of the international Schlumberger group. |
In 1989, the British company Telfos Holdings gained a majority of the shares in Ganz Railway Vehicle Factory Co. Ltd. and the name of the company was changed to Ganz-Hunslet Co. Ltd. In the course of 1991 and 1992, the Austrian company [[Jenbacher Werke]] obtained 100% of the company's shares and consequently the railway vehicle factory is now a member of the international railway vehicle manufacturing group, Jenbacher Transport Systeme. At present, the Ganz Electric Works, under the name of Ganz-Ansaldo is a member of the Italian industrial giant, [[AnsaldoBreda]]. The Ganz Works were transformed into holdings. Ganz-Danubius was wound up in 1994. The Ganz Electric Meter Factory in Gödöllő became the member of the international Schlumberger group. |
||
In 2006, the power transmission and distribution sectors of Ganz Transelektro were acquired by [[Crompton Greaves]],<ref>[http://www.ganztrans.hu/index.php?fooldal=1 Ganz is now CG] Retrieved 2009-11-28.</ref> but still doing business under the Ganz brand name, while the unit dealing with electric traction (propulsion and control systems for electric vehicles) was acquired by [[Škoda Transportation]] and is now a part of [[Škoda Electric]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.skoda.cz/ganz-skoda|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080413005712/http://www.skoda.cz/ganz-skoda|url-status=dead|archive-date=13 April 2008|title=Česká verze – ŠKODA TRANSPORTATION a.s.|first=Lundegaard – e-business solutions provider, www.lundegaard.cz |
In 2006, the power transmission and distribution sectors of Ganz Transelektro were acquired by [[Crompton Greaves]],<ref>[http://www.ganztrans.hu/index.php?fooldal=1 Ganz is now CG] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110310150846/http://www.ganztrans.hu/index.php?fooldal=1 |date=2011-03-10 }} Retrieved 2009-11-28.</ref> but still doing business under the Ganz brand name, while the unit dealing with electric traction (propulsion and control systems for electric vehicles) was acquired by [[Škoda Transportation]] and is now a part of [[Škoda Electric]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.skoda.cz/ganz-skoda|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080413005712/http://www.skoda.cz/ganz-skoda|url-status=dead|archive-date=13 April 2008|title=Česká verze – ŠKODA TRANSPORTATION a.s.|first=Lundegaard – e-business solutions provider, www.lundegaard.cz|last=info@lundegaard.cz|access-date=20 December 2016}}</ref> |
||
Now the plant is operated by a new investor as a tenant, Ganz Transformer Motor and Manufacturing Ltd., after the previous owner was unable to finance the production.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Production resumes at the Ganz factory – Ganz Group|date=8 September 2020 |url=https://ganzelectric.com/en/production-resumes-at-the-ganz-factory/|access-date=2021-03-23|language=en-GB}}</ref> |
|||
'''Timeline'''<ref>{{Cite web|title=About us – Ganz Group|url=https://ganzelectric.com/en/about-us/|access-date=2021-03-23|language=en-GB}}</ref> |
|||
1991: Joint Venture with Italian Ansaldo named Ganz Ansaldo Ltd. |
|||
1994: Air-cooled turbogenerator from 20 up to 70MVA |
|||
1998: Development of double-cage induction motor for twin-drives first on the world |
|||
2000: Acquisition by Tranelektro Group under name of Ganz-Transelektro |
|||
2001: Developed 1MW ExN Non-sparking gasturbine starter motors for GE |
|||
2002: First transformer in the world for 123 kV with ester liquid |
|||
2006: Became a Part of Crompton Greaves Ltd as CG Electric Systerms Hungary |
|||
2010: Start of manufacturing Safety Class 3&4 motors for Nuclear Power Plants |
|||
2018: Developing VFD-driven Increased Safety LVAC motors for driving OEM pumps used in Oil&gas fields |
|||
2020: Establishment of Ganz Transformer Motor and Generator Ltd., Ganz brand back in Hungarian ownership |
|||
== Divisions == |
|||
Source:<ref>{{Cite web|title=Ganz Group|url=https://ganzelectric.com/en/home/|access-date=2021-03-23|language=en-GB}}</ref> |
|||
'''Transformer division'''<ref>{{Cite web|title=Transformer Division – Ganz Group|url=https://ganzelectric.com/en/transformer/|access-date=2021-03-23|language=en-GB}}</ref> |
|||
The Transformer division specializes in the design, manufacture and testing of substation transformers, generation transformers, auxiliary transformers, mobile transformers and traction transformers from 20 to 600 MVA (1000 MVA for autotransformers) from 52 to 800 kV. |
|||
'''Rotating machines division'''<ref>{{Cite web|title=Rotating Machines Division – Ganz Group|url=https://ganzelectric.com/en/rotating-machines/|access-date=2021-03-23|language=en-GB}}</ref> |
|||
The production of three-phase, alternating current induction motors began in the factory in 1894. Through the 90's Ganz has developed more advanced motors with decreased total weight, increased efficiency and low noise levels in order to satisfy the actual needs of the market and all conditions of the industrial application and to conform to IEC, NEMA, ATEX and EAC standards. |
|||
'''GIS Service Division'''<ref>{{Cite web|title=GIS Service Division – Ganz Group|url=https://ganzelectric.com/en/gis-service-division/|access-date=2021-03-23|language=en-GB}}</ref> |
|||
GIS Service division performs onsite works like maintenance, inspection, modification, overhaul, extensions on former GANZ and other brands of switchgears. The activity is mainly focused on the existing substations and equipment. |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
| Line 171: | Line 285: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{Commons category |
{{Commons category}} |
||
* {{official website}} – Ganz Machinery Works Holding, current company |
|||
*[http://www.nzetc.org/tm/scholarly/Gov11_01Rail-fig-Gov11_01Rail038a.html A photo of a Ganz railcar of Hungarian State Railways c1936] |
|||
* [https://nzetc.victoria.ac.nz/tm/scholarly/Gov11_01Rail-fig-Gov11_01Rail038a.html A photo of a Ganz railcar of Hungarian State Railways c1936] |
|||
*[http://vaunut.org/kuvasivu.php/30033 A withdrawn Ganz-Mavag DMU at Mendoza, Argentina] |
|||
*[http:// |
* [http://vaunut.org/kuvasivu.php/30033 A withdrawn Ganz-Mavag DMU at Mendoza, Argentina] |
||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/ |
* [http://www.ganztrans.hu/index.php?fooldal=1 Ganz Transelektro Ltd's page in English] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110310150846/http://www.ganztrans.hu/index.php?fooldal=1 |date=2011-03-10 }} |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20090322023622/http://www.gdvitla.hu/english.php Ganz Danubius homepage] |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ganz Company}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ganz Company}} |
||
[[Category:Ganz Works| ]] |
[[Category:Ganz Works| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Rolling stock manufacturers of Hungary]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Hungarian brands]] |
||
[[Category:Tram manufacturers]] |
[[Category:Tram manufacturers]] |
||
[[Category:Companies of Austria-Hungary]] |
[[Category:Companies of Austria-Hungary]] |
||
| Line 188: | Line 303: | ||
[[Category:1844 establishments in the Austrian Empire]] |
[[Category:1844 establishments in the Austrian Empire]] |
||
[[Category:Electrical engineering companies]] |
[[Category:Electrical engineering companies]] |
||
[[Category:Avantha Group]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 22:18, 2 November 2024
 | |
 The railway factory of the Ganz company (1880—1959: Ganz Wagon- and Machine Factory, 1959—1988: Ganz–MÁVAG Locomotive, Wagon- and Machine Factory) / Budapest, Kőbányai út 19-33. / | |
| Formerly |
|
|---|---|
| Company type |
|
| Industry | Transport Metallurgy |
| Founded | 1844 in Buda, Kingdom of Hungary |
| Founders | Ábrahám Ganz |
| Defunct | 1989 |
| Fate | Sold in 1989 to diverse companies that used the name 'Ganz'for their own enterprises |
| Headquarters | Buda, Hungary |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people | List |
| Products | Trams Trains Ships Electric generators |
| Owner | Ábrahám Ganz and his family (1845–1947) State of Hungary (1947–1949) |
| Subsidiaries |
|
| Website | ganz-holding.hu |
The Ganz Machinery Works Holding is a Hungarian holding company. Its products are related to rail transport, power generation, and water supply, among other industries.[2]
The original Ganz Works or Ganz (Hungarian: Ganz vállalatok or Ganz Művek, Ganz companies, formerly Ganz and Partner Iron Mill and Machine Factory) operated between 1845 and 1949 in Budapest, Hungary. It was named after Ábrahám Ganz, the founder and manager of the company. Ganz is probably best known for the manufacture of tramcars, but was also a pioneer in the application of three-phase alternating current to electric railways.
Ganz also made ships (through its Ganz Danubius division), bridge steel structures (Ganz Acélszerkezet) and high-voltage equipment (Ganz Transelektro). In the early 20th century the company experienced its heyday and became the third-largest industrial enterprise in the Kingdom of Hungary after the Manfréd Weiss Steel and Metal Works and the MÁVAG company.
Since 1989, various parts of Ganz have been taken over by other companies.
History
[edit]
The company was founded by Ábrahám Ganz in 1844. He was invited to Pest, Hungary, by Count István Széchenyi and became the casting master at the Roller Mill Plant (referred to as Hengermalom in Hungarian). In 1854 he began manufacturing hard cast railroad wheels in his own plant founded in 1844. The management of the steam mill paid a share of the profit to Ganz. This enabled him to buy, in 1844, land and a house for 4500 Forints in Víziváros, Buda castle district. Abraham Ganz built his own foundry on this site and started to work there with seven assistants. They made mostly casting products for the needs of the people of the city.[3] In 1845, he bought the neighbouring site and expanded his foundry with a cupola furnace. He gave his brother, Henrik a job as a clerk, because of the growing administration work. He made a profit in the first year, and his factory grew, even though he had not yet engaged in mass production. In 1846, at the third Hungarian Industrywork Exhibition (Magyar Iparmű Kiállítás), he introduced his stoves to the public. He won the silver medal of the exhibition committee and the bronze medaille from Archduke Joseph, Palatine of Hungary.
During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 the foundry made ten cannons and many cannonballs for the Hungarian army. Because of this, the Military Court of Austria impeached him. He got seven weeks in prison as penalty, but because of his Swiss citizenship he was acquitted of the charge.[3]

Ganz recognized that, to develop his factory, he had to make products that were mass-produced. In 1846 the Pest-Vác railway line was built. At that time, European foundries made wrought iron rims for spoked wagon wheels by pouring the casts in shapes in sand, and leaving them to cool down. He successfully developed a railway wheel casting technology; it was the new method of "crust-casting" to produce cheap yet sturdy iron railway wheels, which greatly contributed to the rapid railway development in Central Europe. 86,074 pieces of hard cast wheels had been sold to 59 European railway companies until 1866. Consequently, this factory played an important role in building the infrastructure of the Hungarian Kingdom and the Austro-Hungarian Empire.[citation needed] At this time the agricultural machines, steam locomotives, pumps and the railway carriages were the main products. At the beginning of the 20th century, 60 to 80% of the factory's products were sold for export.
After the death of Abraham Ganz, the heirs entrusted the management of the factory to his direct colleagues at Ganz Művek: Antal Eichleter, Ulrik Keller and Andreas Mechwart, which then took the name Ganz & Co. The Ganz family sold the company, which consisted of five departments, and in April 1869 it was transformed into a joint-stock company, and continued its operations under the name of "Ganz és Társa vasontöde és Gépgyár Rt." (Ganz & Partners Iron Foundry and Machine Factory Co.) The technical director was András Mechwart, under whose direction Ganz became one of the most important groups of machine building companies in the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy after 1869.
At the end of the 19th century, the products of the Ganz and Partner Iron Mill and Machine Factory (hereinafter referred to as Ganz Works) promoted the expansion of alternating-current power transmissions.
Prominent engineers
[edit]




Prominent engineers at Ganz works included András Mechwart, Károly Zipernowsky, Miksa Déri, Ottó Titusz Bláthy, Kálmán Kandó, György Jendrassik and Ernő Wilczek.
Revolution in the milling industry
[edit]The invention of the modern industrial mill (the roller mill ) – by András Mechwart in 1874 – guaranteed a solid technological superiority and revolutionized the world's milling industry. Budapest's milling industry grow the second largest in the world, behind the American Minneapolis. The Hungarian grain export increased by 66% within some years.[3]
Power plants, generators turbines and transformers
[edit]
In 1878, the company's general manager András Mechwart founded the Department of Electrical Engineering headed by Károly Zipernowsky. Engineers Miksa Déri and Ottó Bláthy also worked at the department producing direct-current machines and arc lamps.
In 1878, the company began producing equipment for electric lighting and, by 1883, had installed over fifty systems in Austria-Hungary. Their AC systems used arc and incandescent lamps, generators, and other equipment.[4][5]
Generators
[edit]The first turbo generators were water turbines which drove electric generators. The first Hungarian water turbine was designed by engineers of the Ganz Works in 1866. Mass production of dynamo generators started in 1883.[6]
The missing link of a full Voltage Sensitive/Voltage Intensive (VSVI) system was the reliable alternating current constant voltage generator. Therefore, the invention of the constant voltage generator by the Ganz Works in 1883[7] had a crucial role in the beginnings of industrial scale AC power generation, because only these type of generators can produce a stable output voltage, regardless of the actual load.[8]
Transformers
[edit]
In cooperation, Zipernovsky, Bláthy and Déri (known as the ZBD team) constructed and patented the transformer. The "transformer" was named by Ottó Titusz Bláthy. The three invented the first high efficiency, closed core shunt connection transformer. They also invented the modern power distribution system: Instead of a series of connections they connected supply transformers in parallel to the main line.[9]
The transformer patents described two basic principles. Loads were to be connected in parallel, not in series as had been the general practice until 1885. Additionally, the inventors described the closed armature as an essential part of the transformer. Both factors assisted the stabilisation of voltage under varying load, and allowed definition of standard voltages for distribution and loads. The parallel connection and efficient closed core made construction of electrical distribution systems technically and economically feasible.
The Ganz Works built the first transformers using iron plating of enamelled mild iron wire, and started to use laminated cores to eliminate eddy currents[10]
AC Power stations
[edit]In 1886, the ZBD engineers designed, and the company supplied, electrical equipment for the world's first power station to use AC generators to power a parallel connected common electrical network. This was the Italian steam-powered Rome-Cerchi power plant.[11]
Following the introduction of the transformer, the Ganz Works changed over to production of alternating-current equipment. For instance, Rome's electricity was supplied by hydroelectric plant and long-distance energy transfer.[12]
- Ganz Transelektro power plant and power distribution products
-
Ganz Transformers in december 1886
-
construction of a Ganz water turbo generator (1886)
-
PSM V56 D0433 direct connected electric railway generator (1899)
-
Ganz 21.000 kW Transformer (1911, weight: 38t)
-
A generator assembly hall of the Ganz Works (1922)
Electricity meters
[edit]The first mass-produced kilowatt-hour meter (electricity meter), based on Hungarian Ottó Bláthy's patent and named after him, was presented by the Ganz Works at the Frankfurt Fair in the autumn of 1889, and the company was marketing the first induction kilowatt-hour meter by the end of the year. These were the first alternating-current wattmeters, known by the name of Bláthy-meters.[13]
Industrial refrigerators and air conditioners
[edit]In 1894, Hungarian inventor and industrialist István Röck started to manufacture a large industrial ammonia refrigerator (together with the Esslingen Machine Works) which was powered by Ganz electric compressors. At the 1896 Millennium Exhibition, Röck and the Esslingen Machine Works presented a 6-tonne capacity artificial ice producing plant. In 1906, the first large Hungarian cold store (with a capacity of 3,000 tonnes, the largest in Europe) opened in Tóth Kálmán Street, Budapest, the machine was manufactured by the Ganz Works. Until nationalisation after the Second World War, large-scale industrial refrigerator production in Hungary was in the hands of Röck and Ganz Works.[14]
The contract between Ganz and Egypt in the 1930s played a key role in the development of cooling equipment: railcars delivered to Egypt were equipped with air-conditioning cooling systems. The collective of the Ganz factory (machine designers: Gábor Hollerung, Rezső Oláh, István Pfeifer, Prónai) designed and built the 3-cylinder, 20 kW compressors with freon refrigerant, air condenser and evaporator. The machine could also be converted to heat pump operation.[15]
ICE engines and vehicles
[edit]The beginning of gas engine manufacturing in Hungary is linked to Donát Bánki and János Csonka but it is not clear that they ever worked for Ganz.
Ganz produced engines whose designs were licensed to Western European partners, notably in the United Kingdom and Italy.


- Timeline
- 1889 the first four-stroke gas engine was built by the Ganz factory
- 1893 the manufacture of paraffin and petrol fuelled engine with carburetor
- 1898 the manufacture of engines with the Bánki water injection system
- 1908 the introduction of a new petrol engine type, the series Am
- 1913 the manufacture of Büssing petrol engines for trucks
- 1914–18 the manufacture of fighter plane engines
- 1916 the manufacture of petrol engines, type Fiat
- 1920 the modification of petrol engines for suction gas operation
- 1924 György Jendrassik started his engine development activity
- 1928 the first railway diesel engine was completed, according to the plans of Ganz-Jendrassik
- 1929 the first export delivery of a railway engine using the system of Ganz-Jendrassik
- 1934 there was an engine reliability World Competition in the USSR where the Ganz engine achieved the best fuel consumption in its category
- 1939 Scale model of Ganz Ac Electric locomotive exhibited at the Italy Pavilion of the New York World's Fair
- 1939–42 construction of the Jendrassik Cs-1 turboprop engine
- 1944 the first application of the engine type XII JV 170/240 in a motor-train set
- 1953 modernisationon of the diesel engine system Ganz-Jendrassik
- 1959 the union of the Ganz factory and the MÁVAG company, establishing Ganz-MÁVAG
Railways
[edit]Steam motors
[edit]
The Ganz Company started to construct steam locomotives and steam railcars from the 1860s. Between 1901 and 1908, Ganz Works of Budapest and de Dion-Bouton of Paris collaborated to build a number of railcars for the Hungarian State Railways together with units with de Dion-Bouton boilers, Ganz steam motors and equipments, and Raba carriages built by the Raba Hungarian Wagon and Machine Factory in Győr. In 1908, the Borzsavölgyi Gazdasági Vasút (BGV), a narrow-gauge railway in Carpathian Ruthenia (today's Ukraine), purchased five railcars from Ganz and four railcars from the Hungarian Royal State Railway Machine Factory with de Dion-Bouton boilers. The Ganz company started to export steam motor railcars to the United Kingdom, Italy, Canada, Japan, Russia and Bulgaria.[16][17][18]
The World's first electrified main railway line in Italy
[edit]The Ganz Works, having identified the significance of induction motors and synchronous motors, commissioned Kálmán Kandó to develop them. In 1894, Hungarian engineer Kálmán Kandó developed high-voltage three-phase AC motors and generators for electric locomotives. The first-ever electric rail vehicle manufactured by Ganz Works was a 6 HP pit locomotive with direct current traction system. The first Ganz made asynchronous rail vehicles (altogether 2 pieces) were supplied in 1898 to Évian-les-Bains (France) with a 37 HP asynchronous traction system. The Ganz Works won the tender for electrification of the Valtellina Railway in Italy in 1897. Under the management, and on the basis of plans from Kálmán Kandó, three phase electric power at 3 kV and 15 Hz was fed through two upper wires and the rails.

The electricity was produced in a dedicated power station and the system operated for thirty years from 1902. Italian railways were the first in the world to introduce electric traction for the entire length of a main line rather than just a short stretch. The 106 km Valtellina line was opened on 4 September 1902, designed by Kandó and a team from the Ganz works.[19][20] The voltage was significantly higher than used earlier and it required new designs for electric motors and switching devices.[21][22] The three-phase two-wire system was used on several railways in Northern Italy and became known as "the Italian system". Kandó was invited in 1905 to undertake the management of Società Italiana Westinghouse and led the development of several Italian electric locomotives.[21]
Invention of the Phase Converter
[edit]In 1918,[23] Kandó invented and developed the rotary phase converter, enabling electric locomotives to use three-phase motors whilst supplied via a single overhead wire, carrying the simple industrial frequency (50 Hz) single phase AC of the high-voltage national networks.[20] After World War I, at the Ganz Works, Kálmán Kandó constructed a single-phase electric railway system using 16 kV at 50 Hz. A similar system, but using 15 kV at 16.7 Hz, later became widely used in Europe. The main attribute of Kandó's 50 Hz system was that it was fed by the normal power network, so dedicated railway power stations became unnecessary. Because of the early death of Kálmán Kandó, László Verebélÿ continued the work for the Hungarian State Railways (MÁV).[24]
- Ganz Rail rolling stock
-
The first steam railcar built by Ganz and de Dion-Bouton
-
Ganz AC electric locomotive prototype (1901 Valtellina, Italy)
-
Electric locomotive RA 361 (later FS Class E.360) by Ganz for the Valtellina line, 1904
-
The first locomotive with a phase converter was Kando's V50 locomotive (only for demonstration and testing purposes)
-
Árpád Diesel railbus in 1937
-
Ganz train on the Ferrocarriles Patagónicos railway in Argentina (1945)
-
A series V63 Ganz-MÁVAG electric locomotive of Hungarian State Railways
Ganz-MÁVAG rail rolling stock
[edit]
In 1959 Ganz merged with the MÁVAG company and was renamed Ganz-MÁVAG. In 1976 Ganz-Mávag supplied ten standard gauge 3-car diesel trainset to the Hellenic Railways Organisation (OSE), designated as Class AA-91 and four metre gauge 4-car trainsets, designated as Class A-6451. In 1981/82 Ganz-Mávag supplied to OSE 11 B-B diesel-hydraulic DHM7-9 locomotives, designated as class A-251. Finally, in 1983, OSE bought eleven 3-car metre gauge trainsets, designated as Class A-6461. All these locomotives and trainsets have been withdrawn with the exception of one standard and one metre gauge trainset.[citation needed]
In 1982/83 Ganz-Mávag supplied an order for electric multiple units to New Zealand Railways Corporation for Wellington suburban services. The order was made in 1979, and was for 44 powered units and 44 trailer units, see New Zealand EM class electric multiple unit.[citation needed]
Ganz-MÁVAG Trams
[edit]Ganz-MÁVAG delivered 29 trams (2 car sets) to Alexandria, Egypt from 1985 to 1986.[25]
Shipbuilding, Ganz - Danubius
[edit]In 1911, the Ganz Company merged with the Danubius shipbuilding company, which was the largest shipbuilding company in Hungary. From 1911, the unified company adopted the "Ganz–Danubius" brand name. In the beginning of the 20th century the company had 19 shipyards on the Danube and the Adriatic Sea in the city of Rijeka and Pula.[26] As Ganz Danubius, the company became involved in shipbuilding before, and during, World War I. Ganz was responsible for building the dreadnought SMS Szent István, all of the Novara-class cruisers, and built diesel-electric U-boats at its shipyard in Budapest, for final assembly at Fiume. Several U-boats of the U-XXIX class, U-XXX class, U-XXXI class and U-XXXII class were completed,[27] A number of other types were laid down, but remained incomplete at the war's end.[28] By the end of the First World War, 116 naval vessels had been built by The Ganz-Danubius company. The company also produces transatlantic ocean liners for passenger lines Trieste - New York, Trieste - Montevideo, as a reflection of already formed wave of mass migration from Central Europe to America.
- Ganz–Danubius ships and submarines
-
The battle-damaged SMS Novara (1913) after a victorious naval battle
-
Aircraft
[edit]The first Hungarian "aeroplane factory" ( UFAG ) was founded by the Ganz Company and Weiss-Manfréd Works in 1912. During World War I, the company made many types of Albatros and Fokker fighter planes.
Before 1919, the company built ocean liners, dreadnought type battleships and submarines, power plants, automobiles[29][30] and many types of fighter aircraft.[31]
The world's first turboprop engine was the Jendrassik Cs-1 designed by the Hungarian mechanical engineer György Jendrassik. It was built and tested in the Ganz factory in Budapest between 1939 and 1942. It was planned to be fitted to the Varga RMI-1 X/H twin-engined reconnaissance bomber designed by László Varga in 1940, but the program was cancelled. Jendrassik had also designed a small-scale 75 kW turboprop in 1937.[citation needed]
After World War II
[edit]In 1947, the Ganz Works was nationalised and in 1949 it became independent and six big companies came into existence, including the Ganz Transformer Factory. In 1959, Ganz Wagon and Machine Factory merged with the MÁVAG Locomotive and Machine Factory under the name of Ganz-MÁVAG Locomotive, Wagon and Machine Works. Of the products of the Works, outstanding results were shown in the field of the manufacture of diesel railcars and multiple units. Traditional products included tramcars as well, and customers included the tramway network of Budapest. In the meantime the Foundry workshop was closed down.
In 1974, the locomotive and wagon Works were merged under the name of Railway Vehicle Factory and then the machine construction branch went through significant development. The production of industrial and apartment house lifts became a new branch. Ganz-MÁVAG took over a lot of smaller plants in the 1960s and 1970s and their product range was extended. Among other things, they increased their bridge-building capacity. They made iron structures for several Tisza bridges, for the Erzsébet Bridge in Budapest, for public road bridges in Yugoslavia and for several industrial halls.
The Ganz Shipyard experienced its most productive times during the four decades following nationalisation. In the course of this period 1100 ship units were produced, the number of completed seagoing ships was 240 and that of floating cranes was 663. As a result of the great economic and social crises of the 1980s, Ganz-MÁVAG had to be reorganised. The company was transformed into seven independent Works and three joint ventures.
Ganz since 1989
[edit]In 1989, the British company Telfos Holdings gained a majority of the shares in Ganz Railway Vehicle Factory Co. Ltd. and the name of the company was changed to Ganz-Hunslet Co. Ltd. In the course of 1991 and 1992, the Austrian company Jenbacher Werke obtained 100% of the company's shares and consequently the railway vehicle factory is now a member of the international railway vehicle manufacturing group, Jenbacher Transport Systeme. At present, the Ganz Electric Works, under the name of Ganz-Ansaldo is a member of the Italian industrial giant, AnsaldoBreda. The Ganz Works were transformed into holdings. Ganz-Danubius was wound up in 1994. The Ganz Electric Meter Factory in Gödöllő became the member of the international Schlumberger group.
In 2006, the power transmission and distribution sectors of Ganz Transelektro were acquired by Crompton Greaves,[32] but still doing business under the Ganz brand name, while the unit dealing with electric traction (propulsion and control systems for electric vehicles) was acquired by Škoda Transportation and is now a part of Škoda Electric.[33]
Now the plant is operated by a new investor as a tenant, Ganz Transformer Motor and Manufacturing Ltd., after the previous owner was unable to finance the production.[34]
Timeline[35]
1991: Joint Venture with Italian Ansaldo named Ganz Ansaldo Ltd.
1994: Air-cooled turbogenerator from 20 up to 70MVA
1998: Development of double-cage induction motor for twin-drives first on the world
2000: Acquisition by Tranelektro Group under name of Ganz-Transelektro
2001: Developed 1MW ExN Non-sparking gasturbine starter motors for GE
2002: First transformer in the world for 123 kV with ester liquid
2006: Became a Part of Crompton Greaves Ltd as CG Electric Systerms Hungary
2010: Start of manufacturing Safety Class 3&4 motors for Nuclear Power Plants
2018: Developing VFD-driven Increased Safety LVAC motors for driving OEM pumps used in Oil&gas fields
2020: Establishment of Ganz Transformer Motor and Generator Ltd., Ganz brand back in Hungarian ownership
Divisions
[edit]Source:[36]
Transformer division[37]
The Transformer division specializes in the design, manufacture and testing of substation transformers, generation transformers, auxiliary transformers, mobile transformers and traction transformers from 20 to 600 MVA (1000 MVA for autotransformers) from 52 to 800 kV.
Rotating machines division[38]
The production of three-phase, alternating current induction motors began in the factory in 1894. Through the 90's Ganz has developed more advanced motors with decreased total weight, increased efficiency and low noise levels in order to satisfy the actual needs of the market and all conditions of the industrial application and to conform to IEC, NEMA, ATEX and EAC standards.
GIS Service Division[39]
GIS Service division performs onsite works like maintenance, inspection, modification, overhaul, extensions on former GANZ and other brands of switchgears. The activity is mainly focused on the existing substations and equipment.
References
[edit]- ^ About us at Ganz Holding (19 Mar 2023)
- ^ About us, Ganz-holding.hu
- ^ Mikulas Teich; Roy Porter; Bo Gustafsson (1996). The Industrial Revolution in National Context: Europe and the USA. Cambridge University Press. p. 280. ISBN 9780521409407.
- ^ Guarnieri, M. (2013). "Who Invented the Transformer?". IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine. 7 (4): 56–59. doi:10.1109/MIE.2013.2283834. S2CID 27936000.
- ^ Hughes, Thomas P. (1993). Networks of Power: Electrification in Western Society, 1880-1930. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 95–96. ISBN 978-0-8018-2873-7. Retrieved Sep 9, 2009.
- ^ http://www.sze.hu/~mgergo/EnergiatudatosEpulettervezes/2013_1_feladat/ErosErika/V%EDzenergia%20hasznos%EDt%E1s%20szigetk%F6zi%20szemmel%20EL%D5AD%C1SANYAG.pdf[permanent dead link]
- ^ American Society for Engineering Education (1995). Proceedings, Part 2. p. 1848.
- ^ Robert L. Libbey (1991). A Handbook of Circuit Math for Technical Engineers. CRC Press. p. 22. ISBN 9780849374005.
- ^ "Bláthy, Ottó Titusz". Retrieved 20 December 2016.
- ^ Electrical Society of Cornell University (1896). Proceedings of the Electrical Society of Cornell University. Andrus & Church. p. 39.
- ^ "Ottó Bláthy, Miksa Déri, Károly Zipernowsky". IEC Techline. Archived from the original on September 30, 2007. Retrieved Apr 16, 2010.
- ^ Hungarian Inventors and their Inventions Archived 2012-03-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Eugenii Katz. "Blathy". Clarkson University. Archived from the original on June 25, 2008. Retrieved 2009-08-04.
- ^ The development and heyday of mechanical science (Hungarian) Link
- ^ The development and heyday of mechanical science (Hungarian) Link
- ^ Railroad Gazette – Volume 37 – Page 296 (printed in 1904)
- ^ Modern Machinery – Volumes 19–20 – Page 206 (Printed in 1906)
- ^ John Robertson Dunlap, Arthur Van Vlissingen, John Michael Carmody: Factory and Industrial Management – Volume 33 – Page 1003 (printed in 1907
- ^ Duffy (2003), p. 120-121.
- ^ a b Hungarian Patent Office. "Kálmán Kandó (1869–1931)". www.mszh.hu. Archived from the original on 2010-10-08. Retrieved 2008-08-10.
- ^ a b "Kalman Kando". Retrieved 2011-10-26.
- ^ "Kalman Kando". Archived from the original on 2012-07-12. Retrieved 2009-12-05.
- ^ Duffy, Michael C. (2003). Electric Railways 1880–1990. IET. p. 137. ISBN 9780852968055.
- ^ "Ganz and Tungsram – the 20th century". Electric History. EnergoSolar.com. 2007. Archived from the original on 6 January 2009. Retrieved 20 December 2016.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-01-10. Retrieved 2015-01-10.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ History of Ganz Danubius
- ^ R.H. Gibson, Maurice Prendergast (2002). The German Submarine War 1914–1918. Periscope Publishing Ltd. p. 386. ISBN 9781904381082.
- ^ http://www.gwpda.org/naval/ahsubs.htm Sieche article on KuK U-Boats
- ^ Iván Boldizsár: NHQ; the New Hungarian Quarterly, Volume 16, Issue 2; Volume 16, Issues 59–60, p. 128
- ^ Hungarian Technical Abstracts: Magyar Műszaki Lapszemle, Volumes 10–13, p. 41
- ^ Iván T. Berend: Case Studies on Modern European Economy: Entrepreneurship, Inventions, and Institutions, p. 151
- ^ Ganz is now CG Archived 2011-03-10 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2009-11-28.
- ^ info@lundegaard.cz, Lundegaard – e-business solutions provider, www.lundegaard.cz. "Česká verze – ŠKODA TRANSPORTATION a.s." Archived from the original on 13 April 2008. Retrieved 20 December 2016.
{{cite web}}:|first=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Production resumes at the Ganz factory – Ganz Group". 8 September 2020. Retrieved 2021-03-23.
- ^ "About us – Ganz Group". Retrieved 2021-03-23.
- ^ "Ganz Group". Retrieved 2021-03-23.
- ^ "Transformer Division – Ganz Group". Retrieved 2021-03-23.
- ^ "Rotating Machines Division – Ganz Group". Retrieved 2021-03-23.
- ^ "GIS Service Division – Ganz Group". Retrieved 2021-03-23.
External links
[edit]- Official website
 – Ganz Machinery Works Holding, current company
– Ganz Machinery Works Holding, current company - A photo of a Ganz railcar of Hungarian State Railways c1936
- A withdrawn Ganz-Mavag DMU at Mendoza, Argentina
- Ganz Transelektro Ltd's page in English Archived 2011-03-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Ganz Danubius homepage
- Ganz Works
- Rolling stock manufacturers of Hungary
- Hungarian brands
- Tram manufacturers
- Companies of Austria-Hungary
- Motor vehicle manufacturers of Austria-Hungary
- Shipbuilding companies of Austria-Hungary
- Manufacturing companies established in 1844
- 1844 establishments in the Austrian Empire
- Electrical engineering companies
- Avantha Group