Baalbek-Hermel Governorate: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Governorate of Lebanon}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
<!-- See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields and descriptions --> |
<!-- See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields and descriptions -->| name = Baalbek-Hermel |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| image_skyline = Baalbek (4594513263).jpg |
|||
| native_name_lang = <!-- ISO 639-2 code e.g. "fr" for French. If more than one, use {{lang}} instead -->ar |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| image_flag = |
||
| |
| image_seal = |
||
| |
| image_shield = |
||
| |
| image_map = Baalbek-Hermel in Lebanon 2020.svg |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| pushpin_map = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| subdivision_type = Country |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| established_title = Gazetted |
|||
| subdivision_type = Country |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| subdivision_type1 = [[Districts of Lebanon|District]] |
|||
| |
| seat = [[Baalbek]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| subdivision_type2 = [[Municipalities of Lebanon|Municipalities]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| subdivision_name2 = see [[List of municipalities of Lebanon#Baalbek-Hermel Governorate|list]] |
|||
| |
| leader_name = Bashir Khodr |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| seat_type = Capital |
|||
| |
| area_land_km2 = |
||
| |
| area_water_km2 = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| elevation_m = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| unit_pref = Metric |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| area_total_km2 = 3009 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| area_water_km2 = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| elevation_m = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| population_density_km2 = auto |
| population_density_km2 = auto |
||
| timezone1 |
| timezone1 = [[Eastern European Time|EET]] |
||
| utc_offset1 |
| utc_offset1 = +2 |
||
| timezone1_DST |
| timezone1_DST = [[Eastern European Summer Time|EEST]] |
||
| utc_offset1_DST |
| utc_offset1_DST = +3 |
||
| postal_code_type |
| postal_code_type = |
||
| postal_code |
| postal_code = |
||
| area_code_type |
| area_code_type = |
||
| area_code |
| area_code = |
||
| website |
| website = <!-- {{URL|example.com}} --> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Baalbek-Hermel |
'''Baalbek-Hermel''' ({{langx|ar|بعلبك - الهرمل}}) is a [[Governorates of Lebanon|governorate]] of [[Lebanon]] and is the largest by area in the country. It comprises the [[Districts of Lebanon|districts]] of [[Baalbek District|Baalbek]] and [[Hermel District|Hermel]],<ref name=localiban>{{cite web |url=http://www.localiban.org/rubrique894.html |title=Mohafazah de Baalbek-Hermel |publisher=Localiban |accessdate=20 February 2017 |archive-date=21 February 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170221111459/http://www.localiban.org/rubrique894.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> which in turn are subdivided into a total of 74 [[Municipalities of Lebanon|municipalities]].<ref name=profile2015/> The capital is at [[Baalbek]].<ref name=localiban/> The governorate covers an area of {{cvt|3009|km2|sqmi}}<ref name=statoids/> and is bounded by [[Akkar Governorate]] to the northwest, [[North Governorate]] to the west, [[Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate]] and [[Mount Lebanon Governorate]] to the southwest, [[Beqaa Governorate]] to the south, and the [[Syria]]n [[Governorates of Syria|governorates]] of [[Homs Governorate|Homs]] and [[Rif Dimashq Governorate|Rif Dimashq]] to the northeast and southeast. The governorate occupies the northern portion of the [[Beqaa Valley]], Lebanon's most important agricultural area.<ref name=profile2016>{{cite web |url=http://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/10052016_Bekaa%20and%20Baalbek-Hermel%20Profile.pdf |title=Bekaa and Baalbek/Hermel Governorates Profile |publisher=[[UNHCR]] |date=2016 |accessdate=20 February 2017}}</ref> |
||
The [[UNHCR]] estimated the population of the governorate at 416,427 in 2015, including 137,788 registered refugees of the [[Syrian Civil War]] and 8,117 [[Palestinian refugee camps|Palestinian refugees]].<ref name=profile2015/> The Lebanese |
The [[UNHCR]] estimated the population of the governorate at 416,427 in 2015, including 137,788 registered refugees of the [[Syrian Civil War]] and 8,117 [[Palestinian refugee camps|Palestinian refugees]].<ref name=profile2015/> The Lebanese citizen population is predominantly [[Shia Islam in Lebanon|Shiite]] with pockets of [[Christianity in Lebanon|Christians]] and [[Sunni Islam in Lebanon|Sunnis]], while the refugee population is predominantly Sunni Muslims.<ref name=profile2015/> |
||
Baalbek-Hermel Governorate was created by the enactment of Law 522 on 16 July 2003, in which the districts of Baalbek and Hermel were separated from Beqaa Governorate.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.localiban.org/rubrique394.html |title=Territorial administration of Lebanon |publisher=Localiban |accessdate=19 February 2017}}</ref> Implementation of the new region only began in 2014 with the appointment of the first and current governor, [[Bashir Khodr]].<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.naharnet.com/stories/en/128994 |title=Cabinet Appoints 5 New Governors, Accepts Qaloush's Resignation |date=2 May 2014 |publisher=[[Naharnet]] |accessdate=19 February 2017}}</ref> |
Baalbek-Hermel Governorate was created by the enactment of Law 522 on 16 July 2003, in which the districts of Baalbek and Hermel were separated from Beqaa Governorate.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.localiban.org/rubrique394.html |title=Territorial administration of Lebanon |publisher=Localiban |accessdate=19 February 2017 |archive-date=8 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181008101536/http://www.localiban.org/rubrique394.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> Implementation of the new region only began in 2014 with the appointment of the first and current governor, [[Bashir Khodr]].<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.naharnet.com/stories/en/128994 |title=Cabinet Appoints 5 New Governors, Accepts Qaloush's Resignation |date=2 May 2014 |publisher=[[Naharnet]] |accessdate=19 February 2017}}</ref> |
||
Already one of Lebanon's poorest regions, the recent influx of Syrian refugees has placed additional strain on the governorate's fragile infrastructure and services.<ref name=profile2016/> Violence in Syria has [[Syrian Civil War spillover in Lebanon|spilled over]] into the governorate, especially in the area around [[Arsal]] and [[Ras Baalbek]].<ref name=profile2016/> The northern Beqaa valley and Baalbek has had [[Hezbollah]] or the [[Amal Movement]] electoral victories but 46% of the electorate voted for the opposition Baalbek Madinati party in recent elections.<ref>{{cite book |last=Norton |first=Augustus |title=Hezbollah: A Short History |year=2009 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-13124-5 |page=6 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=x0MZOnnu8qcC}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=al-Solh |first=Nidal |url=https://www.pressreader.com/lebanon/the-daily-star-lebanon/20160516/281565174984202 |title=Why Hezbollah is sweating in Baalbek |date=16 May 2016 |publisher=[[The Daily Star (Lebanon)|The Daily Star]] |accessdate=20 February 2017}}</ref> |
|||
==Religion== |
|||
{{Pie chart |
|||
|thumb = middle |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|label1 = [[Islam|Sunni Islam]] |
|||
|value1 = 14 |
|||
|color1 = MediumSeaGreen |
|||
|label2 = [[Islam|Shia Islam]] |
|||
|value2 = 72 |
|||
|color2 = DarkGreen |
|||
|label3 = [[Christianity]] |
|||
|value3 = 14 |
|||
|color3 = DodgerBlue |
|||
}} |
|||
== Gallery == |
|||
<gallery mode="nolines"> |
|||
File:Baalbek-lebanon-19th Century.jpg |
|||
File:Pano Baalbek 1.jpg |
|||
File:Anna Lynker - Baalbek.jpg |
|||
File:Baalbek (detail).jpg |
|||
File:Baalbek 1.jpg |
|||
File:Baalbek ruins.jpg |
|||
File:Postcard by Sarrafian Bros. of Baalbek - Baalbek vue générale de l'acropole.png |
|||
File:Baalbek (the fallen colomn).jpg |
|||
File:Baalbek-stoneofpregnantwoman.jpg |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 77: | Line 68: | ||
{{Governorates of Lebanon}} |
{{Governorates of Lebanon}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Baalbek-Hermel Governorate]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Hermel District}} |
|||
{{Baalbek District}} |
|||
[[Category:Governorates of Lebanon]] |
[[Category:Governorates of Lebanon]] |
||
[[Category:States and territories established in |
[[Category:States and territories established in 2003]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:2003 establishments in Lebanon]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 11:59, 5 December 2024
Baalbek-Hermel
Arabic: بعلبك - الهرمل | |
|---|---|
 Baalbek | |
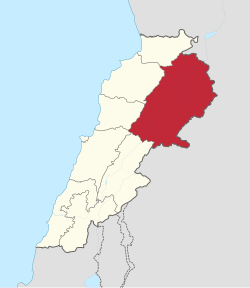 Location of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate in Lebanon | |
| Coordinates: 34°12′N 36°18′E / 34.2°N 36.3°E | |
| Country | |
| Gazetted | 16 July 2003 |
| Capital | Baalbek |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Bashir Khodr |
| Area | |
• Total | 3,009 km2 (1,162 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate (June 2015)[2] | 416,427 |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
Baalbek-Hermel (Arabic: بعلبك - الهرمل) is a governorate of Lebanon and is the largest by area in the country. It comprises the districts of Baalbek and Hermel,[3] which in turn are subdivided into a total of 74 municipalities.[2] The capital is at Baalbek.[3] The governorate covers an area of 3,009 km2 (1,162 sq mi)[1] and is bounded by Akkar Governorate to the northwest, North Governorate to the west, Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate and Mount Lebanon Governorate to the southwest, Beqaa Governorate to the south, and the Syrian governorates of Homs and Rif Dimashq to the northeast and southeast. The governorate occupies the northern portion of the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon's most important agricultural area.[4]
The UNHCR estimated the population of the governorate at 416,427 in 2015, including 137,788 registered refugees of the Syrian Civil War and 8,117 Palestinian refugees.[2] The Lebanese citizen population is predominantly Shiite with pockets of Christians and Sunnis, while the refugee population is predominantly Sunni Muslims.[2]
Baalbek-Hermel Governorate was created by the enactment of Law 522 on 16 July 2003, in which the districts of Baalbek and Hermel were separated from Beqaa Governorate.[5] Implementation of the new region only began in 2014 with the appointment of the first and current governor, Bashir Khodr.[6]
Already one of Lebanon's poorest regions, the recent influx of Syrian refugees has placed additional strain on the governorate's fragile infrastructure and services.[4] Violence in Syria has spilled over into the governorate, especially in the area around Arsal and Ras Baalbek.[4] The northern Beqaa valley and Baalbek has had Hezbollah or the Amal Movement electoral victories but 46% of the electorate voted for the opposition Baalbek Madinati party in recent elections.[7][8]
Gallery
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Law, Gwillim. "Lebanon Provinces". Statoids. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Baalbek-Hermel Governorate Profile" (PDF). UNHCR. June 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ a b "Mohafazah de Baalbek-Hermel". Localiban. Archived from the original on 21 February 2017. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ a b c "Bekaa and Baalbek/Hermel Governorates Profile" (PDF). UNHCR. 2016. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ "Territorial administration of Lebanon". Localiban. Archived from the original on 8 October 2018. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
- ^ "Cabinet Appoints 5 New Governors, Accepts Qaloush's Resignation". Naharnet. 2 May 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
- ^ Norton, Augustus (2009). Hezbollah: A Short History. Princeton University Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-691-13124-5.
- ^ al-Solh, Nidal (16 May 2016). "Why Hezbollah is sweating in Baalbek". The Daily Star. Retrieved 20 February 2017.










