Ear canal: Difference between revisions
m Reverted 1 edit by 27.60.82.1 (talk) to last revision by GreenC bot (TW) |
removed period Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear}} |
|||
{{Infobox anatomy |
{{Infobox anatomy |
||
| Name = Ear canal |
| Name = Ear canal |
||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
| Image2 = |
| Image2 = |
||
| Caption2 = |
| Caption2 = |
||
| Precursor = |
| Precursor = Groove (cleft) of the [[first branchial arch]]<ref>{{EmbryologyUNC|hednk|022}}</ref> |
||
| System = |
| System = |
||
| Artery = |
| Artery = Anterior part: [[Anterior auricular branches of superficial temporal artery|superficial temporal artery]]<br />posterior part: [[posterior auricular artery]] |
||
| Vein = [[ |
| Vein = [[Superficial temporal vein]]s, [[external jugular vein]], [[pterygoid plexus]] |
||
| Nerve = [[ |
| Nerve = [[Auriculotemporal nerve]], [[great auricular nerve]], [[auricular branch of vagus nerve]] |
||
| Lymph = [[ |
| Lymph = [[Superficial cervical lymph nodes]], [[deep cervical lymph nodes]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''ear canal''' ('''external acoustic meatus''', '''external auditory meatus''', '''EAM''') is a pathway running from the [[outer ear]] to the [[middle ear]]. The adult human ear canal extends from the [[ |
The '''ear canal''' ('''external acoustic meatus''', '''external auditory meatus''', '''EAM''') is a pathway running from the [[outer ear]] to the [[middle ear]]. The adult human ear canal extends from the [[Auricle (anatomy)|auricle]] to the [[eardrum]] and is about {{convert|2.5|cm|0}} in length and {{convert|0.7|cm|1}} in diameter. |
||
== Structure== |
== Structure== |
||
The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of |
The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of auricle. The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal contains small hairs and specialized sweat glands, called [[Apocrine sweat gland|apocrine]] glands, which produce cerumen ([[Earwax|ear wax]]). The bony part forms the inner two thirds. The bony part is much shorter in children and is only a ring (''annulus tympanicus'') in the newborn. The layer of epithelium encompassing the bony portion of the ear canal is much thinner and therefore, more sensitive in comparison to the cartilaginous portion. |
||
Size and shape of the canal vary among individuals. The canal is approximately {{convert|2.5|cm|0}} long and {{convert|0.7|cm}} in diameter.<ref>Faddis, B. T. (2008). "Structural and functional anatomy of the outer and middle ear". In W. Clark & K. Ohlemiller (Eds.), ''Anatomy and physiology of hearing for audiologists'' (pp. 93–108). Thomson Delmar Learning.</ref> It has a [[wikt:sigmoid|sigmoid form]] and runs from behind and above downward and forward. On the cross-section, it is of oval shape. These are important factors to consider when fitting [[earplug]]s. |
Size and shape of the canal vary among individuals. The canal is approximately {{convert|2.5|cm|0}} long and {{convert|0.7|cm}} in diameter.<ref>Faddis, B. T. (2008). "Structural and functional anatomy of the outer and middle ear". In W. Clark & K. Ohlemiller (Eds.), ''Anatomy and physiology of hearing for audiologists'' (pp. 93–108). Thomson Delmar Learning.</ref> It has a [[wikt:sigmoid|sigmoid form]] and runs from behind and above downward and forward. On the cross-section, it is of oval shape. These are important factors to consider when fitting [[earplug]]s. |
||
| Line 47: | Line 48: | ||
File:Gray907.png|External and middle ear, opened from the front. Right side. |
File:Gray907.png|External and middle ear, opened from the front. Right side. |
||
File:Gray908.png|Horizontal section through left ear; upper half of section. |
File:Gray908.png|Horizontal section through left ear; upper half of section. |
||
File:Slide1CAC.JPG|Lateral head anatomy detail.Facial nerve dissection. |
File:Slide1CAC.JPG|Lateral head anatomy detail. Facial nerve dissection. |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
| Line 61: | Line 62: | ||
*[http://www.entusa.com/external_ear_canal.htm Continuing Medical Education Ear Photographs] |
*[http://www.entusa.com/external_ear_canal.htm Continuing Medical Education Ear Photographs] |
||
*[https://www.entbristol.co.uk/gp-education Otoscopy Tutorial w/ Images] |
*[https://www.entbristol.co.uk/gp-education Otoscopy Tutorial w/ Images] |
||
* {{cite web|url=http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s34257.000-1.html|title=Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1|work=Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator|publisher=Elsevier| |
* {{cite web|url=http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s34257.000-1.html|title=Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1|work=Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator|publisher=Elsevier|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120722052131/http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s34257.000-1.html|archive-date=2012-07-22|url-status=dead}} |
||
{{Auditory system}} |
{{Auditory system}} |
||
| Line 68: | Line 69: | ||
[[Category:Auditory system]] |
[[Category:Auditory system]] |
||
[[Category:Ear]] |
[[Category:Ear]] |
||
[[Category:Otology]] |
|||
[[Category:Audiology]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 21:52, 3 May 2024
| Ear canal | |
|---|---|
 Anatomy of the human ear. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Groove (cleft) of the first branchial arch[1] |
| Artery | Anterior part: superficial temporal artery posterior part: posterior auricular artery |
| Vein | Superficial temporal veins, external jugular vein, pterygoid plexus |
| Nerve | Auriculotemporal nerve, great auricular nerve, auricular branch of vagus nerve |
| Lymph | Superficial cervical lymph nodes, deep cervical lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | meatus acusticus externus |
| MeSH | D004424 |
| TA98 | A15.3.01.045 |
| TA2 | 6867 |
| FMA | 61734 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the auricle to the eardrum and is about 2.5 centimetres (1 in) in length and 0.7 centimetres (0.3 in) in diameter.
Structure
[edit]The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of auricle. The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal contains small hairs and specialized sweat glands, called apocrine glands, which produce cerumen (ear wax). The bony part forms the inner two thirds. The bony part is much shorter in children and is only a ring (annulus tympanicus) in the newborn. The layer of epithelium encompassing the bony portion of the ear canal is much thinner and therefore, more sensitive in comparison to the cartilaginous portion.
Size and shape of the canal vary among individuals. The canal is approximately 2.5 centimetres (1 in) long and 0.7 centimetres (0.28 in) in diameter.[2] It has a sigmoid form and runs from behind and above downward and forward. On the cross-section, it is of oval shape. These are important factors to consider when fitting earplugs.
Disorders
[edit]Due to its relative exposure to the outside world, the ear canal is susceptible to diseases and other disorders. Some disorders include:
- Atresia of the ear canal
- Cerumen impaction
- Bone exposure, caused by the wearing away of skin in the canal
- Auditory canal osteoma (bony outgrowths of the temporal bone)
- Cholesteatoma
- Contact dermatitis of the ear canal
- Fungal infection (otomycosis)
- Ear mites in animals
- Ear myiasis, an extremely rare infestation of maggots
- Foreign body in ear
- Granuloma, a scar usually caused by tympanostomy tubes
- Otitis externa (swimmer's ear), bacteria-caused inflammation of the ear canal
- Stenosis, a gradual closing of the canal
Earwax
[edit]Earwax, also known as cerumen, is a yellowish, waxy substance secreted in the ear canals. It plays an important role in the human ear canal, assisting in cleaning and lubrication, and also provides some protection from bacteria, fungi, and insects. Excess or impacted cerumen can press against the eardrum and/or occlude the external auditory canal and impair hearing, causing conductive hearing loss. If left untreated, cerumen impaction can also increase the risk of developing an infection within the ear canal.
Additional images
[edit]-
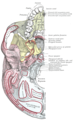
Base of skull. Inferior surface.
-
Left infratemporal fossa.
-
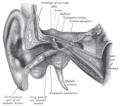
External and middle ear, opened from the front. Right side.
-
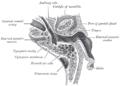
Horizontal section through left ear; upper half of section.
-
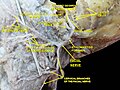
Lateral head anatomy detail. Facial nerve dissection.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ hednk-022—Embryo Images at University of North Carolina
- ^ Faddis, B. T. (2008). "Structural and functional anatomy of the outer and middle ear". In W. Clark & K. Ohlemiller (Eds.), Anatomy and physiology of hearing for audiologists (pp. 93–108). Thomson Delmar Learning.
External links
[edit]- Veterans Health Administration web site
- OSHA web site
- Continuing Medical Education Ear Photographs
- Otoscopy Tutorial w/ Images
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.