Abu Bakr Effendi: Difference between revisions
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
|||
| (91 intermediate revisions by 41 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Ottoman-Cape Colony clergyman (1814–1880)}} |
|||
{{About|Abu Bakr Effendi (1814–1880)|Abu Bakr Effendi (1863–1942)|Mulla Effendi}} |
{{About|Abu Bakr Effendi (1814–1880)|Abu Bakr Effendi (1863–1942)|Mulla Effendi}} |
||
{{more footnotes|date=February 2018}} |
{{more footnotes|date=February 2018}} |
||
{{use dmy dates|date=February 2023}} |
|||
{{use South African English|date=February 2023}} |
|||
{{Infobox religious biography|religion=[[Islam]] |
{{Infobox religious biography|religion=[[Islam]] |
||
| honorific_prefix = Sheikh |
| honorific_prefix = Sheikh |
||
| name = Abu Bakr Effendi |
| name = Abu Bakr Effendi |
||
| image = File:Abu Bakr Effendi.jpg |
| image = File:Abu Bakr Effendi.jpg |
||
| alt = |
|||
| alt = ''Bayānu ddīn'' by Abu Bakr Effendi, published 1869 was one of the first books translated into [[Afrikaans]] |
|||
| caption = |
|||
| caption = ''Bayānu ddīn'' by Abu Bakr Effendi, published 1869 was one of the first books translated into [[Afrikaans]] |
|||
| title = |
| title = |
||
| birth_name = |
| birth_name = |
||
| birth_date = |
| birth_date = {{circa|1814}} |
||
| birth_place = |
| birth_place = |
||
| death_date = 1880 |
| death_date = 1880 |
||
| death_place = |
| death_place = |
||
| death_cause = |
| death_cause = |
||
| resting_place = |
| resting_place = |
||
| other_names = |
| other_names = |
||
| nationality = |
| nationality = |
||
| ethnicity = |
| ethnicity = |
||
| era = |
| era = |
||
| region = |
| region = |
||
| occupation = |
| occupation = |
||
| denomination = |
| denomination = |
||
| jurisprudence = |
| jurisprudence = [[Qadi]] |
||
| creed = |
| creed = |
||
| movement = |
| movement = |
||
| main_interests = |
| main_interests = |
||
| notable_ideas = |
| notable_ideas = |
||
| notable_works = |
| notable_works = ''Bayân al-Dîn'' (1877) |
||
| alma_mater = |
| alma_mater = |
||
| teachers = |
| teachers = |
||
| students = |
| students = |
||
| expand_students = |
| expand_students = |
||
| Sufi_order = |
| Sufi_order = |
||
| disciple_of = |
| disciple_of = |
||
| disciples = |
| disciples = |
||
| expand_disciples = |
| expand_disciples = |
||
| influences = |
| influences = |
||
| expand_influences = |
| expand_influences = |
||
| influenced = |
| influenced = |
||
| expand_influenced = |
| expand_influenced = |
||
| awards = |
| awards = |
||
| module = |
| module = |
||
| website = |
| website = |
||
| office1 = |
| office1 = |
||
| term1 = |
| term1 = |
||
| predecessor1 = |
| predecessor1 = |
||
| successor1 = |
| successor1 = |
||
| office2 = |
| office2 = |
||
| term2 = |
| term2 = |
||
| predecessor2 = |
| predecessor2 = |
||
| successor2 = |
| successor2 = |
||
| office3 = |
| office3 = |
||
| term3 = |
| term3 = |
||
| predecessor3 = |
| predecessor3 = |
||
| successor3 = |
| successor3 = |
||
| office4 = |
| office4 = |
||
| term4 = |
| term4 = |
||
| predecessor4 = |
| predecessor4 = |
||
| successor4 = |
| successor4 = |
||
| signature = |
| signature = |
||
| signature_alt = |
| signature_alt = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Sheikh '''Abu Bakr Effendi''' ({{circa|1814}} – 29 June 1880), also spelt '''Ebu Bekir Efendi''', was an [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] ''[[qadi]]'' sent in 1862 by Sultan [[Abdulaziz]] at the request of [[Queen Victoria]] to the [[Cape of Good Hope]], in order to teach and assist the [[Muslim]] community of the [[Cape Malays]]. He is known for having made several major contributions to [[Islam in South Africa]], including the translation of his 1877 work, ''Bayân al-Dîn'', into the [[Afrikaans language]], then in a very early stage of development. He is credited with introducing the [[fez (hat)|fez]] as headwear for male Muslims in the Cape, and his presence had a significant impact on the expansion and consolidation of [[Islam]] at the [[Dutch Cape Colony]]. |
|||
==Early life== |
|||
Effendi was from a Kurdish/Arab [[Sayyid]] family which originated from [[Mecca]] and migrated into Abbasid then Sejuk territory. Abubakr was born in the Ottoman Province of Shehrizur. He is a Sayyid, direct descendant of the Islamic prophet, [[Muhammad]] through [[Zayd ibn Ali]], son of Imam [[Zayn al-Abidin]]. Other [[imam]]s in the Cape were mostly teaching the [[Shafi`i]] school of [[Islamic jurisprudence]]; he was a follower and the first teacher of [[Hanafi]] school, for which he also established a [[madrassa]] in [[Cape Town]]. He gained notoriety in 1869 after ruling that [[rock lobster]] and [[Thyrsites atun|snoek]], two staple foods in the Cape, were sinful ([[haraam]]). He has often been mistaken for being a Shafi'i on the basis of him being a Scholar of the 4 schools of Sunni Islam, and being able to issue religious edicts according to each one. His ancestors and children practised the Hanafi school of thought. |
|||
Abu Bakr Effendi (Ebu Bekir Efendi<ref name=citizens>{{cite web | title=Ottoman descendants in South Africa get Turkish citizenship | website=[[Daily Sabah]] | date=17 September 2020 | url=https://www.dailysabah.com/arts/ottoman-descendants-in-south-africa-get-turkish-citizenship/news | access-date=26 February 2023}}</ref>) was born in 1814, although his year of birth has often been erroneously cited as 1835.<ref>{{cite web | title=The Shaykh of Knowledge Abu Bakr Effendi | website=abubakreffendi.net | date=28 July 2012 | url=http://www.abubakreffendi.net/errors.html | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130916012456/http://www.abubakreffendi.net/errors.html | archive-date=16 September 2013 | url-status=dead | access-date=21 February 2023}}</ref> He was from a [[Sayyid]] family which originated from [[Mecca]] and migrated into Abbasid then [[Seljuk Empire|Seljuk]] territory. Effendi was born in the Ottoman Province of Zor. He is a direct descendant of the Islamic prophet [[Muhammad]] through [[Zayd ibn Ali]], son of Imam [[Zayn al-Abidin]],{{cn|date=February 2023}} and was of Arab and Kurdish origin.<ref name=worden2004/> |
|||
| ⚫ | He was born in Ottoman province [[Shahrizor Eyalet]].<ref name=citizens/> His father, Molla Omar Al-Baghdadi, an Ottoman Governor, was killed in a local nationalist Kurdish uprising against the Ottoman authority. He studied at the [[madrassa]] originally set up by his ancestor Abu Nasr Al-Amiyr Sulaymaan Al-Qurashiy Al-Amjadiy (c. 1060 - c.1134) for any who wish to learn. He also studied in Makkah, and joined his family in Erzurum. His Cousin and future son in law was Seyyid Abdürrezzak ilmi Efendi. He is also the great uncle of [[%C3%96mer Nasuhi Bilmen]]. Not much is known of Emir Sulaymaan from Effendi's personal documents. He was however a contemporary of Suleyman Ghazi, the founder of the Ottoman Empire and Suleyman Sultan of Rum.{{cn|date=February 2023}} |
||
He died after contracting malaria from reportedly travelling to Dera [[Mozambique]], after having made several major contributions to [[Islam in South Africa]]. He introduced the [[fez (clothing)|fez]] for men,{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} as well as reinstating the [[hijab]] for women {{Citation needed|date=July 2013}}. More importantly, besides his role as teacher he also published the [[Arabic Afrikaans]] "Uiteensetting van die godsdiens" ("Bayan ad-Din", or "The Exposition of the Religion") in 1877. |
|||
He undertook further studies and in [[Erzurum]], and then went to [[Istanbul]] in 1862 to ask for help for the people of Erzurum, who were suffering the effects of [[famine]]. He was then asked by the government to give holy teachings in the [[Cape Colony]]. This came about after [[Queen Victoria]] had written to [[Sultan Abdulaziz]] to ask him to send someone, as discord had arisen among the [[Cape Malays]] between groups who had been isolated from their [[mother tongue]] and original religious traditions. On 3 September<ref name=citizens/> or October 1862, an Ottoman Imperial decree was issued for the dispatch of Abu Bakr and Omar Lutfi Effendi to the Cape. The two men travelled first to [[London]] via [[Paris]] on 1 December,<ref name=argun2000/> spending two months there<ref name=citizens/> before travelling to [[Liverpool]], their port of departure, whence their journey by sea took 44 days to reach the Cape.<ref name=argun2000>{{cite web|author=Argun, Selim| date=2000| url=http://ujdigispace.uj.ac.za:8080/dspace/bitstream/10210/1246/1/ARTICLE.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110831200806/http://ujdigispace.uj.ac.za:8080/dspace/bitstream/10210/1246/1/ARTICLE.pdf| archive-date=31 August 2011|title= Life and Contribution of Osmanli Scholar, Abu bakr Effendi, towards Islamic thought and Culture in South Africa| pages=7–8}} </ref> They arrived in the Cape on 17 January 1863.<ref name=citizens/> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
According to the '''Travelogue of Omar Lutfi Effendi''', while he and Abu Bakr traveled by sea. At a later age Omar Lutfi returned to Turkey where his descendants still reside. His Travelogue was translated into English from Ottoman Turkish by Turkish/American Islamic Scholar Yusuf Kavakci. |
|||
The Cape Malays had arrived in the [[Cape of Good Hope]] mainly as [[slavery in South Africa|slaves, brought there by Dutch settlers]] from 1653, from what is now [[Indonesia]]. The [[Dutch East India Company]], since an edict by [[Joan Maetsuycker]], [[Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies]], in 1657, had compelled the Malays to hide their religious practice, with death as the punishment for practising their faith in public or for attempting to convert anyone.<ref name=argun2000/><ref name=davids>{{cite journal | last=Davids | first=Achmat | title=Muslim-Christian relations in nineteenth century Cape Town (1825-1925) | journal=Kronos | publisher=[[University of Western Cape]] | issue=19 | year=1992 | issn=0259-0190 | jstor=41033772 | pages=84 | url=http://www.jstor.org/stable/41033772 | access-date=22 February 2023}}</ref> |
|||
Other [[imam]]s in the Cape were mostly trying to teach the [[Shafi`i]] school of [[Islamic jurisprudence]], but were influenced by cultural practices from their places of origin. Also being enslaved and away from their places of origin for so long meant that they had drifted from their original beliefs, hence their cry of assistance to the British Empire. Effendi was a follower and the first teacher of [[Hanafi]] school, for which he also established a [[madrassa]] in Cape Town.<ref name=worden2004/> Shortly after Effendi's arrival, Muslim men in the Cape started wearing the [[fez (clothing)|fez]] due to his influence;<ref name=argun2000/> they had formerly worn a conical style of hat.<ref name=worden2004/> It was easy for him to adapt considering he was a Mufi of all 4 schools of [[Madhhab]]. |
|||
Many of Abu Bakr Effendi's descendants originate from his marriage to Tohora Saban Cook whom he married after renouncing the "perfectly white" first wife, Rukea Maker. He had 5 sons, Ahmad Ataullah, Hisham Nimatullah, Omar Jalaluddin, Muhammad Alauddin, and Hussain Fowzy. Fahimah his daughter was Abu Bakr's eldest child from his marriage to Rukea. The family continues to reside in South Africa, with some returning to Turkey, and many migrating to Australia. Some of Abubakr's sons continued in his footsteps of serving far and wide, with one son, Ahmed, getting involved in Cape politics. He became a member of the Cemetery Committee because the cemetery where his father's grave was situated was threatened with closure by the Cape Administration. He stood for the legislature of the Cape but failed to get the required votes for a seat due to a change in the system for cumulative votes, amended especially to keep him out of the lCape legislature. Some also served in the Ottoman Army and fought in the Hejaz against the Anglo and Arab nationalist uprising against the Ottoman Empire. There currently exists in [[Singapore]] the grave of Abu Bakrs son, Ahmed, who served as the [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] [[Turkey|Turkish]] Ambassador to [[Singapore]]. |
|||
He gained notoriety in 1869 after ruling that [[rock lobster]] and [[Thyrsites atun|snoek]], two staple foods in the Cape, were sinful ([[haraam]]), and there was an unsuccessful petition run to have him removed.<ref name=worden2004/> He has often been mistaken for being a Shafi'i on the basis of him being a Scholar of the four schools of [[Sunni Islam]], and being able to issue religious edicts according to each one. Most of this opposite was due to Effendi's deep opposition to the Imam's of the Cape having a Succession system in the local mosques to maintain wealth and power instead of handing it over to the most learned. His ancestors and children practised the Hanafi school of thought, but some later converted under pressure and marriage to the local mathaab.{{cn|date=February 2023}} |
|||
==Struggle of acceptance by the Cape Malay populace== |
|||
==Death and legacy== |
|||
Abu Bakr's life in South Africa was not easy. It is clear that the [[Cape Malay]] Muslims had suffered and lost some of their religious identity {{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} as a result of their deportation by the Dutch from their home countries in [[Southern India]] and [[Maritime Southeast Asia]]. Historical documents talk of his influence of introducing the Islamic [[hijab]] and fez on the Cape Muslims {{Citation needed|date=July 2013}}, although many other Islamic scholars had come to South Africa. He also attempted to break the Cape Muslim 'Clerical Order' which existed.{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} Only those related to the previous imam were allowed to become the next in line,{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} holding knowledge to themselves and wielding power over the common people. This is further related in the 1866 Disputes; |
|||
Effendi died on 29 June 1880 at his home in Bree Street, Cape Town, and was buried in the [[Tana Baru Cemetery]].<ref name=argun2000/> He had contracted malaria from reportedly travelling to Dera in [[Mozambique]]. |
|||
His most visible impact was the wearing of the fez by Malay men,<ref name=worden2004/><ref name=argun2000/> but his presence also had a significant impact on the growth and self-identity of the Cape Malay Muslims at the Cape. The expansion of Islamic schools drew children from Christian [[mission school]]s, and conversion to [[Christianity]] drew to a halt. Attendance at [[mosque]]s and other Islamic religious observances grew.<ref name=worden2004/> |
|||
''Over the years the Cape Muslim `clerical' order developed with the imams wielding appreciable power. The status of the imams, together with economic security and in many cases prosperity was due to the generous monetary donations and gifts by the congregation. Between 1866 and 1900, over twenty cases pertaining to masjid in the Cape peninsula were heard in the Supreme Court with regard to the positions of imams and their succession. Practically every masjid at the Cape in the 19th century faced this problem.''<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sahistory.org.za/pages/library-resources/online+books/history-muslims/1800s.htm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090609152419/http://www.sahistory.org.za/pages/library-resources/online%20books/history-muslims/1800s.htm|url-status=dead|archive-date=9 June 2009|title=Wayback Machine|date=9 June 2009}}</ref> |
|||
===Publication=== |
|||
This would have thrown him into further dispute with the Cape Malay population. It is also related in the Travelogue of Omar Lutfi, that the Malay people although they had held onto their Islamic heritage where not able to correctly pronounce the Arabic words and text, and it had been "corrupted" (as Abu Bakr would have seen it) with some Malay words.{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} Their practices also involved non Islamic traditional and tribal Malay practices which originated from their ancestral homes on the Indonesian and Malay islands. These practices still exist in Indonesia where some of the population generally practice [[Islam]] but also practice spirit worship. |
|||
He published the [[Arabic Afrikaans]] ''Uiteensetting van die godsdiens'' (''Bayân al-Dîn'' (meaning "the exposition of the religion") in 1877, printed by the Turkish Ministry of Education in [[Istanbul]].<!----This was not the first text in Afrikaans, according to the SA History Online article---> The book is of particular significance as one of the most extensive publications when the Afrikaans language was still in its infancy. The ''Bayân al-Dîn'' described topics of [[Islamic law]], including [[Islamic hygienical jurisprudence|ritual ablution]], prayer, [[pilgrimage]] and [[dietary laws]].<ref name=argun2000/> |
|||
Also, written in a modified [[Arabic script]] with [[phonetic]] spelling, it gives a good indication of the pronunciation of the new language in the Cape at the time<ref name=worden2004/> as used in the Islamic neighbourhoods (colloquially known as "Slams") of Cape Town, giving insight into the use of the new language in these communities. It was written in a modified Arabic script in which [[diacritic]] signs are used to indicate the pronunciation of Afrikaans, and bears testimony to the [[slavery in South Africa|slave origins of the language]], which was not later accredited by the White [[Afrikaners]], especially during the era of [[apartheid]] in the mid-20th century. (The Cape Malays did not have [[Dutch language|Dutch]] as [[mother tongue]], and were therefore mostly unaffected by its [[orthography]].){{cn|date=February 2023}} |
|||
One of the main reasons for Abu Bakr's unpopularity was his declaration that crayfish, a staple item of the diet of the Muslims of the Cape, was "khabahith" or "evil food". The matter was taken to court by the "kreef (crayfish) party" in 1863. Magistrate Hill found in favour of the "kreef party" and against Abu Bakr. After this and his evidence in the 1869 imam succession trial, a petition was drawn up by some Muslims to have him removed from the Cape. He left his residence in Cape Town and moved 12 km away to Newlands to a spacious house, "Stony Place". |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Abu Bakr also seemingly followed and practiced according to the [[Hanafi]] school of thought.{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} He swore in the Supreme Court in 1869, when he was the prime witness in the abovementioned affair relating to the succession of the imam of the Buitengracht St mosque, that he had always been a Shafi'i.{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} But because he used hanafi texts, many doubted his word. He also taught and wrote the book the 'Bayan-al-din' which is written on Abu Bakrs own rulings since he was a fiqh scholar, but has many similarities to the Multaqa.{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} Abu Bakr's statements made in court meant it was difficult to associate him with one school or the other. His title was 'Mufti of the 4 Schools' so one could argue he was of the Hanafi, Shafi'i, Malaki or Hanbali School.{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} |
|||
==Analysis of the religious and linguistic impact of Abubakr Effendi== |
|||
From 1862 to 1869 Effendi had studied the local language use and then proceeded to compile the book "Bayan-al-Din". Printed by the Turkish Ministry of Education in [[Istanbul]], it is an interesting and significant part of South Africa's history, and serves as a valuable reference of the Afrikaans usage during that era in the Islamic neighbourhoods of Cape Town. It gives an invaluable insight into the use of Afrikaans in the so-called "Slams" (slang for Islamic) neighbourhoods of Cape Town in that period. It is also significant, since this community did not have [[Dutch language|Dutch]] as [[mother tongue]] and were therefore mostly unaffected by its [[orthography]]. As such this was the first substantial book ever written and published in Afrikaans, although written in a modified Arabic script where the diacritic signs are used to indicate the pronunciation of Afrikaans. It bears testimony to the slave origins of the language which was not accredited by the White Afrikaners, especially during the Apartheid Era. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
# ritual cleansing (pp. 2–66) |
# ritual cleansing (pp. 2–66) |
||
# ritual prayer (pp. 66–219) |
# ritual prayer (pp. 66–219) |
||
| Line 100: | Line 101: | ||
# hunting (pp. 349–354) |
# hunting (pp. 349–354) |
||
{{ill|Adrianus van Selms|nl}}, a [[Dutch people|Dutch]] scholar and [[Semitic studies|Semitic]] researcher, published a transliteration in [[Latin script]] of Effendi's work in 1979. Since the original work presented spoken Afrikaans without using vowels, van Selms biggest task was to decipher which Afrikaans words were being referred to. Effendi had also innovated new Arabic characters for several Afrikaans letters not found in the Arabic alphabet, the letter 'P' for example. What is interesting is that these innovated letters had to be unique, yet still recognisable by the population who were already schooled in traditional Arabic. Since this was a local modification to the language, used only amongst the Cape Muslim Community, it may have proved illegible for those familiar with traditional Arabic.{{cn|date=February 2023}} |
|||
== |
==Family and descendants== |
||
Abu Bakr Effendi's first wife was from Erzurum with whom he had children but were left in the Ottoman Empire on his mission to South Africa. His first wife in South Africa was Rukea Maker, said to be the daughter of an English woman and a Cape Muslim man, but this marriage ended with divorce and his wife eloping.<ref name=worden2004/> He sent his 2 sons from this marriage to Istanbul under the patronage of the Ottoman Sultan. His daughter Fahimah was his eldest child from his marriage to Maker.{{cn|date=February 2023}}. This is however contested as Fahimah has no birth certificates in South Africa unlike his other children. |
|||
His second wife was the daughter of a [[shipbuilder]] from [[Yorkshire]], England,<ref name=worden2004>{{cite book | last1=Worden | first1=N. | last2=Van Heyningen | first2=E. | last3=Bickford-Smith | first3=V. | title=Cape Town: The Making of a City : an Illustrated Social History | publisher=David Philip | year=2004 | isbn=978-0-86486-656-1 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ysU2Ii9nxcUC | access-date=23 February 2023 | page=}}</ref> Jeremiah Cook, who was a relative of famous explorer [[James Cook]].<ref name=citizens/> Many of Effendi's descendants originate from his marriage to Tohora Saban Cook, with whom he had six children.<ref name=citizens/> His five sons were Ahmad Ataullah, Hisham Nimatullah, Omar Jalaluddin, Muhammad Alauddin, and Hussain Fowzy.{{cn|date=February 2023}} |
|||
Ahmad (also spelt Achmat<ref name=davids/>) became involved in Cape politics. He became a member of the Cemetery Committee because the cemetery where his father's grave was situated was threatened with closure by the Cape Administration. He stood for the legislature of the Cape but failed to get the required votes for a seat due to a change in the system for cumulative votes, amended especially to keep him out of the Cape legislature. In [[Singapore]] is the grave of Abu Bakr Effendi's son, Ahmed, who was the Ottoman Ambassador to Singapore.{{explain|Below says Ahmed buried in Singapore.|date=February 2023}} |
|||
Some of Effendi's sons served in the [[Ottoman Army]] and fought in the [[Hejaz]], against the Anglo and Arab nationalist uprising against the Ottoman Empire.{{cn|date=February 2023}} |
|||
Many of Abu Bakr Effendi's descendants continue to reside in South Africa,{{when|date=February 2023}} some under the surname Emjedi, while some returned to Turkey and others migrated to Australia.{{cn|date=February 2023}} |
|||
On 20 August 2020, 15 of Abu Bakr Effendi's South African descendants became Turkish citizens by [[presidential decree]].<ref name=citizens/> |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
| ⚫ | *{{citation|chapter=A nineteenth-century Kurdish scholar in South Africa|last=Van Bruineessen|first=Martin|authorlink=Martin van Bruinessen|title=Mullas, Sufis and heretics: the role of religion in Kurdish society. Collected articles.| |
||
===Sources=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*{{citation|last=Orakçı|first=Serhat|date=October 2007|title=A Historical Analysis of the Emerging Links between the Ottoman Empire and South Africa between 1861–1923.|url=http://ujdigispace.uj.ac.za:8080/dspace/bitstream/10210/3241/1/Orakci.pdf|access-date=2010-05-26|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110831201139/http://ujdigispace.uj.ac.za:8080/dspace/bitstream/10210/3241/1/Orakci.pdf|archive-date=2011-08-31|url-status=dead}} |
* {{citation|last=Orakçı|first=Serhat|date=October 2007|title=A Historical Analysis of the Emerging Links between the Ottoman Empire and South Africa between 1861–1923.|url=http://ujdigispace.uj.ac.za:8080/dspace/bitstream/10210/3241/1/Orakci.pdf|access-date=2010-05-26|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110831201139/http://ujdigispace.uj.ac.za:8080/dspace/bitstream/10210/3241/1/Orakci.pdf|archive-date=2011-08-31|url-status=dead}} |
||
| ⚫ | * {{citation|chapter=A nineteenth-century Kurdish scholar in South Africa|last=Van Bruineessen|first=Martin|authorlink=Martin van Bruinessen|title=Mullas, Sufis and heretics: the role of religion in Kurdish society. Collected articles.|location=Istanbul|publisher=The Isis Press|year=2000|pages=133–141|chapter-url=http://www.let.uu.nl/~martin.vanbruinessen/personal/publications/Abu%20Bakar%20Effendi.pdf|isbn=975-428-162-9|access-date=2009-12-04|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110605071405/http://www.let.uu.nl/~martin.vanbruinessen/personal/publications/Abu%20Bakar%20Effendi.pdf|archive-date=2011-06-05|url-status=dead}} |
||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20110831200806/http://ujdigispace.uj.ac.za:8080/dspace/bitstream/10210/1246/1/ARTICLE.pdf Ebrahim Mahomed Mahida – History of Muslims in South Africa: A Chronology] |
|||
*http://www.biyografya.com/biyografi/9179 "Seyyid Abdürrezzak ilmi efendi" |
|||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20090609152419/http://www.sahistory.org.za/pages/library-resources/online%20books/history-muslims/1800s.htm Selim Argun, Life and Contribution of Osmanli Scholar, Abu bakr Effendi, towards Islamic thought and Culture in South Africa, 2000] |
|||
*https://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C3%96mer_Nasuhi_Bilmen "Omer Nasuhi Bilmen" |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20130917012314/http://www.abubakreffendi.net/dethnnt2.html Death Certificate of Abu Bakr Effendi] |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
*{{cite web | title=History of Muslims in South Africa: A Chronology | website=SA History Online | date=30 October 2007 | url=http://www.sahistory.org.za/pages/library-resources/online%20books/history-muslims/1800s.htm | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090609152419/http://www.sahistory.org.za/pages/library-resources/online%20books/history-muslims/1800s.htm | archive-date=9 June 2009 | url-status=dead }} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
| Line 119: | Line 139: | ||
[[Category:1880 deaths]] |
[[Category:1880 deaths]] |
||
[[Category:South African Muslims]] |
[[Category:South African Muslims]] |
||
[[Category:Expatriates |
[[Category:Expatriates from the Ottoman Empire in South Africa]] |
||
Latest revision as of 13:58, 3 November 2024
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (February 2018) |
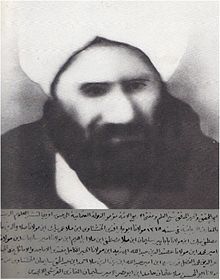
Sheikh Abu Bakr Effendi | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Personal life | |
| Born | c. 1814 |
| Died | 1880 |
| Notable work(s) | Bayân al-Dîn (1877) |
| Religious life | |
| Religion | Islam |
| Jurisprudence | Qadi |
Sheikh Abu Bakr Effendi (c. 1814 – 29 June 1880), also spelt Ebu Bekir Efendi, was an Ottoman qadi sent in 1862 by Sultan Abdulaziz at the request of Queen Victoria to the Cape of Good Hope, in order to teach and assist the Muslim community of the Cape Malays. He is known for having made several major contributions to Islam in South Africa, including the translation of his 1877 work, Bayân al-Dîn, into the Afrikaans language, then in a very early stage of development. He is credited with introducing the fez as headwear for male Muslims in the Cape, and his presence had a significant impact on the expansion and consolidation of Islam at the Dutch Cape Colony.
Early life
[edit]Abu Bakr Effendi (Ebu Bekir Efendi[1]) was born in 1814, although his year of birth has often been erroneously cited as 1835.[2] He was from a Sayyid family which originated from Mecca and migrated into Abbasid then Seljuk territory. Effendi was born in the Ottoman Province of Zor. He is a direct descendant of the Islamic prophet Muhammad through Zayd ibn Ali, son of Imam Zayn al-Abidin,[citation needed] and was of Arab and Kurdish origin.[3]
He was born in Ottoman province Shahrizor Eyalet.[1] His father, Molla Omar Al-Baghdadi, an Ottoman Governor, was killed in a local nationalist Kurdish uprising against the Ottoman authority. He studied at the madrassa originally set up by his ancestor Abu Nasr Al-Amiyr Sulaymaan Al-Qurashiy Al-Amjadiy (c. 1060 - c.1134) for any who wish to learn. He also studied in Makkah, and joined his family in Erzurum. His Cousin and future son in law was Seyyid Abdürrezzak ilmi Efendi. He is also the great uncle of Ömer Nasuhi Bilmen. Not much is known of Emir Sulaymaan from Effendi's personal documents. He was however a contemporary of Suleyman Ghazi, the founder of the Ottoman Empire and Suleyman Sultan of Rum.[citation needed]
He undertook further studies and in Erzurum, and then went to Istanbul in 1862 to ask for help for the people of Erzurum, who were suffering the effects of famine. He was then asked by the government to give holy teachings in the Cape Colony. This came about after Queen Victoria had written to Sultan Abdulaziz to ask him to send someone, as discord had arisen among the Cape Malays between groups who had been isolated from their mother tongue and original religious traditions. On 3 September[1] or October 1862, an Ottoman Imperial decree was issued for the dispatch of Abu Bakr and Omar Lutfi Effendi to the Cape. The two men travelled first to London via Paris on 1 December,[4] spending two months there[1] before travelling to Liverpool, their port of departure, whence their journey by sea took 44 days to reach the Cape.[4] They arrived in the Cape on 17 January 1863.[1]
Life and work in South Africa
[edit]The Cape Malays had arrived in the Cape of Good Hope mainly as slaves, brought there by Dutch settlers from 1653, from what is now Indonesia. The Dutch East India Company, since an edict by Joan Maetsuycker, Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies, in 1657, had compelled the Malays to hide their religious practice, with death as the punishment for practising their faith in public or for attempting to convert anyone.[4][5]
Other imams in the Cape were mostly trying to teach the Shafi`i school of Islamic jurisprudence, but were influenced by cultural practices from their places of origin. Also being enslaved and away from their places of origin for so long meant that they had drifted from their original beliefs, hence their cry of assistance to the British Empire. Effendi was a follower and the first teacher of Hanafi school, for which he also established a madrassa in Cape Town.[3] Shortly after Effendi's arrival, Muslim men in the Cape started wearing the fez due to his influence;[4] they had formerly worn a conical style of hat.[3] It was easy for him to adapt considering he was a Mufi of all 4 schools of Madhhab.
He gained notoriety in 1869 after ruling that rock lobster and snoek, two staple foods in the Cape, were sinful (haraam), and there was an unsuccessful petition run to have him removed.[3] He has often been mistaken for being a Shafi'i on the basis of him being a Scholar of the four schools of Sunni Islam, and being able to issue religious edicts according to each one. Most of this opposite was due to Effendi's deep opposition to the Imam's of the Cape having a Succession system in the local mosques to maintain wealth and power instead of handing it over to the most learned. His ancestors and children practised the Hanafi school of thought, but some later converted under pressure and marriage to the local mathaab.[citation needed]
Death and legacy
[edit]Effendi died on 29 June 1880 at his home in Bree Street, Cape Town, and was buried in the Tana Baru Cemetery.[4] He had contracted malaria from reportedly travelling to Dera in Mozambique.
His most visible impact was the wearing of the fez by Malay men,[3][4] but his presence also had a significant impact on the growth and self-identity of the Cape Malay Muslims at the Cape. The expansion of Islamic schools drew children from Christian mission schools, and conversion to Christianity drew to a halt. Attendance at mosques and other Islamic religious observances grew.[3]
Publication
[edit]He published the Arabic Afrikaans Uiteensetting van die godsdiens (Bayân al-Dîn (meaning "the exposition of the religion") in 1877, printed by the Turkish Ministry of Education in Istanbul. The book is of particular significance as one of the most extensive publications when the Afrikaans language was still in its infancy. The Bayân al-Dîn described topics of Islamic law, including ritual ablution, prayer, pilgrimage and dietary laws.[4]
Also, written in a modified Arabic script with phonetic spelling, it gives a good indication of the pronunciation of the new language in the Cape at the time[3] as used in the Islamic neighbourhoods (colloquially known as "Slams") of Cape Town, giving insight into the use of the new language in these communities. It was written in a modified Arabic script in which diacritic signs are used to indicate the pronunciation of Afrikaans, and bears testimony to the slave origins of the language, which was not later accredited by the White Afrikaners, especially during the era of apartheid in the mid-20th century. (The Cape Malays did not have Dutch as mother tongue, and were therefore mostly unaffected by its orthography.)[citation needed]
The book, totalling 254 pages, appears to follow the Hanafite law-school. It was divided into eight parts, each dealing with a specific part of Islamic law:
- ritual cleansing (pp. 2–66)
- ritual prayer (pp. 66–219)
- religious tax (pp. 219–258)
- fasting (pp. 258–284)
- slaughtering of livestock (pp. 284–302)
- religious prohibitions (pp. 302–344)
- drink (pp. 344–349)
- hunting (pp. 349–354)
Adrianus van Selms, a Dutch scholar and Semitic researcher, published a transliteration in Latin script of Effendi's work in 1979. Since the original work presented spoken Afrikaans without using vowels, van Selms biggest task was to decipher which Afrikaans words were being referred to. Effendi had also innovated new Arabic characters for several Afrikaans letters not found in the Arabic alphabet, the letter 'P' for example. What is interesting is that these innovated letters had to be unique, yet still recognisable by the population who were already schooled in traditional Arabic. Since this was a local modification to the language, used only amongst the Cape Muslim Community, it may have proved illegible for those familiar with traditional Arabic.[citation needed]
Family and descendants
[edit]Abu Bakr Effendi's first wife was from Erzurum with whom he had children but were left in the Ottoman Empire on his mission to South Africa. His first wife in South Africa was Rukea Maker, said to be the daughter of an English woman and a Cape Muslim man, but this marriage ended with divorce and his wife eloping.[3] He sent his 2 sons from this marriage to Istanbul under the patronage of the Ottoman Sultan. His daughter Fahimah was his eldest child from his marriage to Maker.[citation needed]. This is however contested as Fahimah has no birth certificates in South Africa unlike his other children.
His second wife was the daughter of a shipbuilder from Yorkshire, England,[3] Jeremiah Cook, who was a relative of famous explorer James Cook.[1] Many of Effendi's descendants originate from his marriage to Tohora Saban Cook, with whom he had six children.[1] His five sons were Ahmad Ataullah, Hisham Nimatullah, Omar Jalaluddin, Muhammad Alauddin, and Hussain Fowzy.[citation needed]
Ahmad (also spelt Achmat[5]) became involved in Cape politics. He became a member of the Cemetery Committee because the cemetery where his father's grave was situated was threatened with closure by the Cape Administration. He stood for the legislature of the Cape but failed to get the required votes for a seat due to a change in the system for cumulative votes, amended especially to keep him out of the Cape legislature. In Singapore is the grave of Abu Bakr Effendi's son, Ahmed, who was the Ottoman Ambassador to Singapore.[further explanation needed]
Some of Effendi's sons served in the Ottoman Army and fought in the Hejaz, against the Anglo and Arab nationalist uprising against the Ottoman Empire.[citation needed]
Many of Abu Bakr Effendi's descendants continue to reside in South Africa,[when?] some under the surname Emjedi, while some returned to Turkey and others migrated to Australia.[citation needed]
On 20 August 2020, 15 of Abu Bakr Effendi's South African descendants became Turkish citizens by presidential decree.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h "Ottoman descendants in South Africa get Turkish citizenship". Daily Sabah. 17 September 2020. Retrieved 26 February 2023.
- ^ "The Shaykh of Knowledge Abu Bakr Effendi". abubakreffendi.net. 28 July 2012. Archived from the original on 16 September 2013. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Worden, N.; Van Heyningen, E.; Bickford-Smith, V. (2004). Cape Town: The Making of a City : an Illustrated Social History. David Philip. ISBN 978-0-86486-656-1. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g Argun, Selim (2000). "Life and Contribution of Osmanli Scholar, Abu bakr Effendi, towards Islamic thought and Culture in South Africa" (PDF). pp. 7–8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 August 2011.
- ^ a b Davids, Achmat (1992). "Muslim-Christian relations in nineteenth century Cape Town (1825-1925)". Kronos (19). University of Western Cape: 84. ISSN 0259-0190. JSTOR 41033772. Retrieved 22 February 2023.
Sources
[edit]- Orakçı, Serhat (October 2007), A Historical Analysis of the Emerging Links between the Ottoman Empire and South Africa between 1861–1923. (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on 31 August 2011, retrieved 26 May 2010
- Van Bruineessen, Martin (2000), "A nineteenth-century Kurdish scholar in South Africa" (PDF), Mullas, Sufis and heretics: the role of religion in Kurdish society. Collected articles., Istanbul: The Isis Press, pp. 133–141, ISBN 975-428-162-9, archived from the original (PDF) on 5 June 2011, retrieved 4 December 2009
- http://www.biyografya.com/biyografi/9179 "Seyyid Abdürrezzak ilmi efendi"
- https://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C3%96mer_Nasuhi_Bilmen "Omer Nasuhi Bilmen"
Further reading
[edit]- Babb, Glenn (2010), "Abubakr Effendi – A Young Turk among the Afrikaners", A Young Turk among the Afrikaners, Cape Town: National Library Quarterly Review Vol. 62 No 1 Jan-Mar 2010
- Babb, Glenn (2020). "Ons Taal se begin in die Bo-Kaap", Rapport Weekliks, 5 January 2020
- "History of Muslims in South Africa: A Chronology". SA History Online. 30 October 2007. Archived from the original on 9 June 2009.
