Brazil: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 984098865 by The Article Fixer (talk)-sock puppet. Pure vandalism |
Legofan3484 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{short description|Country in South America}} |
||
{{redirect|Brazilian Republic|other uses|Brazil (disambiguation)|and|Brazilian Republic (disambiguation)}} |
|||
{{pp|vandalism|small=yes}} |
|||
{{redirect|Brasil|the phantom island|Brasil (mythical island)}} |
|||
{{short description|Largest country in South America}} |
|||
{{pp-semi-indef|small=yes}} |
|||
{{Use American English|date=February 2017}} |
|||
{{Use |
{{Use American English|date=January 2022}} |
||
{{Use dmy dates|date=February 2024}} |
|||
{{Coord|10|S|52|W|display=title}} |
|||
{{Infobox country |
{{Infobox country |
||
|conventional_long_name = Federative Republic of Brazil |
| conventional_long_name = Federative Republic of Brazil |
||
|common_name = Brazil |
| common_name = Brazil |
||
|native_name = {{ |
| native_name = {{lang|pt|República Federativa do Brasil}} |
||
|image_flag = Flag of Brazil.svg |
| image_flag = Flag of Brazil.svg |
||
|alt_flag = |
| alt_flag = |
||
|image_coat = Coat of arms of Brazil.svg |
| image_coat = Coat of arms of Brazil.svg |
||
|alt_coat = |
| alt_coat = |
||
|symbol_type = Coat of arms |
| symbol_type = Coat of arms |
||
|other_symbol = {{vunblist | |
| other_symbol = {{vunblist |{{lang|pt|[[National Seal of Brazil|Selo Nacional do Brasil]]}}<br />National Seal of Brazil <br />[[File:National Seal of Brazil (color).svg|100px|link=National Seal of Brazil]]}} |
||
|other_symbol_type |
| other_symbol_type = National Seal |
||
|national_motto = {{ |
| national_motto = <br />{{lang|pt|Ordem e Progresso}}<br />"Order and Progress" |
||
|national_anthem = |
| national_anthem = <br />{{lang|pt|[[Brazilian National Anthem|Hino Nacional Brasileiro]]}}<br />"Brazilian National Anthem"<br /><div style="display:inline-block;margin-top:0.4em;">[[File:Hino-Nacional-Brasil-instrumental-mec.ogg]]</div> |
||
|flag_anthem= |
| flag_anthem = <br />{{lang|pt|[[Brazilian Flag Anthem|Hino à Bandeira Nacional]]}}<ref name="HinoBandeira">{{Cite web |last=Exército Brasileiro |title=Hino à Bandeira Nacional |url=http://www.eb.mil.br/web/midia-eletronica/hino-a-bandeira-nacional |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140222123948/http://www.eb.mil.br/web/midia-eletronica/hino-a-bandeira-nacional |archive-date=22 February 2014 |access-date=29 January 2014 |language=pt}}</ref><br />"National Flag Anthem"<br /><div style="display:inline-block;margin-top:0.4em;">[[File:Brazilian Flag Anthem (Ministry of Education).ogg]]</div> |
||
|image_map = BRA orthographic.svg |
| image_map = BRA orthographic.svg |
||
|alt_map = |
| alt_map = |
||
|capital = [[Brasília]] |
| capital = [[Brasília]] |
||
|coordinates = |
| coordinates = {{Coord|15|47|S|47|52|W|type:city}} |
||
|largest_city = [[São Paulo]]<br> |
| largest_city = [[São Paulo]]<br />{{coord|23|33|S|46|38|W|display=inline}} |
||
|languages_type = Official language<br />{{nobold|and national language}} |
| languages_type = Official language<br />{{nobold|and national language}} |
||
| languages = [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]] |
|||
|languages = [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Demographics |publisher=Brazilian Government |url=http://www.brasil.gov.br/sobre/brazil/brazil-in-numbers/demographics |accessdate=8 October 2011 |archivedate=17 November 2011 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20111117051415/http://www.brasil.gov.br/sobre/brazil/brazil-in-numbers/demographics}}</ref> |
|||
| languages2_type = Recognized regional languages |
|||
|ethnic_groups = |
|||
| languages2 = See [[Languages of Brazil#Language co-officialization|regional official languages]] |
|||
{{vunblist |
|||
| ethnic_groups = {{Tree list}} |
|||
|47.73% [[White Brazilians|White]] |
|||
*{{nowrap|45.3% [[Pardo Brazilians|Pardo]]}} |
|||
*43.5% [[White Brazilians|White]] |
|||
*10.2% [[Afro-Brazilians|Black]] |
|||
*0.6% [[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|Indigenous]] |
|||
*0.4% [[Asian Brazilians|East Asian]]{{efn|The Brazilian census uses the term ''amarela'' (or ''yellow'' in English) as a racial category to describe people of East Asian background. This category therefore excludes those of other Asian origins, such as West Asians/[[Arab Brazilian|Arabs]], who are included in the white category, and South Asians.}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Tree list/end}} |
|||
|ethnic_groups_year = 2010 |
|||
| ethnic_groups_year = 2022 |
|||
|ethnic_groups_ref = <ref name="raca2010">{{cite web |url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/censo2010/caracteristicas_da_populacao/tabelas_pdf/tab3.pdf |title=Caracteristicas da População e dos Domicílios do Censo Demográfico 2010 – Cor ou raça |accessdate=7 April 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120217041601/http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/censo2010/caracteristicas_da_populacao/tabelas_pdf/tab3.pdf |archive-date=17 February 2012 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
| ethnic_groups_ref = <ref name="census2022">{{cite web | url=https://g1.globo.com/google/amp/economia/censo/noticia/2023/12/22/censo-2022-cor-ou-raca.ghtml | title=Censo 2022: Pela 1ª vez, Brasil se declara mais pardo que branco; populações preta e indígena também crescem | date=22 December 2023 | access-date=22 December 2023 | archive-date=22 December 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231222234415/https://g1.globo.com/google/amp/economia/censo/noticia/2023/12/22/censo-2022-cor-ou-raca.ghtml | url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
|demonym = [[Brazilians|Brazilian]] |
|||
| demonym = [[Brazilians|Brazilian]] |
|||
|government_type = [[Federalism|Federal]] [[Presidential system|presidential]] {{nowrap|[[Constitutionalism|constitutional]] [[republic]]}} |
|||
| government_type = Federal [[presidential republic]] |
|||
|leader_title1 = [[President of Brazil|President]] |
|||
| leader_title1 = [[President of Brazil|President]] |
|||
|leader_name1 = [[Jair Bolsonaro]] |
|||
| leader_name1 = [[Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva]] |
|||
|leader_title2 = [[Vice President of Brazil|Vice President]] |
|||
| leader_title2 = [[Vice President of Brazil|Vice President]] |
|||
|leader_name2 = [[Hamilton Mourão]] |
|||
|leader_title3 = {{nowrap|[[President of the Chamber of Deputies (Brazil)|President of the<br />Chamber of Deputies]]}} |
| leader_name2 = [[Geraldo Alckmin]] |
||
| leader_title3 = {{nowrap|[[President of the Chamber of Deputies (Brazil)|President of the<br />Chamber of Deputies]]}} |
|||
|leader_name3 = [[ |
| leader_name3 = [[Arthur Lira]] |
||
|leader_title4 = [[President of the Federal Senate (Brazil)|President of the <br />Federal Senate]] |
| leader_title4 = [[President of the Federal Senate (Brazil)|President of the <br />Federal Senate]] |
||
|leader_name4 = {{nowrap|[[ |
| leader_name4 = {{nowrap|[[Rodrigo Pacheco (politician)|Rodrigo Pacheco]]}} |
||
|leader_title5 = {{nowrap|[[ |
| leader_title5 = {{nowrap|[[President of the Supreme Federal Court|President of the<br />Supreme Federal Court]]}} |
||
|leader_name5 = [[ |
| leader_name5 = [[Luís Roberto Barroso]] |
||
|legislature = [[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]] |
| legislature = {{nowrap|[[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]]}} |
||
|upper_house = [[ |
| upper_house = {{nowrap|[[Federal Senate (Brazil)|Federal Senate]]}} |
||
|lower_house = [[Chamber of Deputies (Brazil)|Chamber of Deputies]] |
| lower_house = {{nowrap|[[Chamber of Deputies (Brazil)|Chamber of Deputies]]}} |
||
|sovereignty_type = [[Independence of Brazil|Independence]] |
| sovereignty_type = [[Independence of Brazil|Independence]] |
||
|sovereignty_note = from |
| sovereignty_note = from [[United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves|Portugal]] |
||
|established_event1 = [[Independence of Brazil|Declared]] |
| established_event1 = [[Independence of Brazil|Declared]] |
||
|established_date1 = 7 September 1822 |
| established_date1 = 7 September 1822 |
||
|established_event2 = [[Treaty of Rio de Janeiro (1825)|Recognized]] |
| established_event2 = [[Treaty of Rio de Janeiro (1825)|Recognized]] |
||
|established_date2 = 29 August 1825 |
| established_date2 = 29 August 1825 |
||
|established_event3 = [[Proclamation of the Republic (Brazil)|Republic]] |
| established_event3 = [[Proclamation of the Republic (Brazil)|Republic]] |
||
|established_date3 = 15 November 1889 |
| established_date3 = 15 November 1889 |
||
|established_event4 = [[Constitution of Brazil|Current constitution]] |
| established_event4 = [[Constitution of Brazil|Current constitution]] |
||
|established_date4 = 5 October 1988 |
| established_date4 = 5 October 1988 |
||
|area_km2 = 8515767 |
| area_km2 = 8515767 |
||
|area_label = Total |
| area_label = Total |
||
|area_rank = 5th |
| area_rank = 5th |
||
|area_sq_mi = 3287597 |
| area_sq_mi = 3287597 |
||
|percent_water = 0.65 |
| percent_water = 0.65 |
||
| population_estimate = |
|||
|population_estimate = 210,147,125<ref name="IBGE Official Estimate">{{cite web |last1=Silva |first1=Antonio Carlos Coutinho Gouvea da |title=Projeções da População {{!}} Estatísticas {{!}} IBGE :: Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística |url=https://www.ibge.gov.br/estatisticas-novoportal/sociais/populacao/9109-projecao-da-populacao.html?=&t=resultados |website=ibge.gov.br |accessdate=30 August 2018 |language=pt-br}}</ref> |
|||
| population_census = {{IncreaseNeutral}} 203,080,756<ref>{{Cite news |last=Araujo |first=Gabriel |editor1-last=Grattan |editor1-first=Steven |editor2-last=Rumney |editor2-first=Emma |date=28 June 2023 |title=Brazil census shows population growth at its slowest since 1872 |work=[[Reuters]] |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/americas/brazil-census-shows-population-growth-its-slowest-since-1872-2023-06-28/ |archive-url=https://archive.today/20230629025834/https://www.reuters.com/world/americas/brazil-census-shows-population-growth-its-slowest-since-1872-2023-06-28/ |archive-date=29 June 2023}}</ref> |
|||
|population_estimate_year = 2019 |
|||
| population_census_year = [[2022 Brazilian census|2022]] |
|||
|population_estimate_rank = 6th |
|||
| population_estimate_year = 2024 |
|||
|population_density_km2 = 25 |
|||
| population_estimate_rank = 7th |
|||
|population_density_sq_mi = 63 |
|||
| population_census_rank = 7th |
|||
|population_density_rank = 200th |
|||
| population_density_km2 = 23.8<ref>{{Cite web |date=28 June 2023 |title=País tem 90 milhões de domicílios, 34% a mais que em 2010 {{!}} Agência de Notícias |url=https://agenciadenoticias.ibge.gov.br/agencia-noticias/2012-agencia-de-noticias/noticias/37238-pais-tem-90-milhoes-de-domicilios-34-a-mais-que-em-2010 |access-date=11 January 2024 |website=Agência de Notícias – IBGE |language=pt-BR |archive-date=5 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230705200605/https://agenciadenoticias.ibge.gov.br/agencia-noticias/2012-agencia-de-noticias/noticias/37238-pais-tem-90-milhoes-de-domicilios-34-a-mais-que-em-2010 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
|GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $3.596 trillion<ref name="IMFWEOBR">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2019/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=48&pr.y=18&sy=2017&ey=2021&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=223&s=NGDPD%2CPPPGDP%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPPC&grp=0&a= |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2019 |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |website=IMF.org |access-date=13 January 2020}}</ref> |
|||
| population_density_sq_mi = 64 |
|||
|GDP_PPP_year = 2020 |
|||
| population_density_rank = 193rd |
|||
|GDP_PPP_rank = 8th |
|||
| GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $4.702 trillion<ref name="IMFWEO.BR">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/October/weo-report?c=223,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2022&ey=2029&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Brazil) |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |website=www.imf.org |date=22 October 2024 |access-date=22 October 2024}}</ref> |
|||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $17,016<ref name="IMFWEOBR"/> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_year = 2024 |
|||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 80th |
|||
| GDP_PPP_rank = 8th |
|||
|GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $1.893 trillion<ref name="IMFWEOBR"/> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $22,122<ref name="IMFWEO.BR" /> |
|||
|GDP_nominal_year = 2020 |
|||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 78th |
|||
|GDP_nominal_rank = 9th |
|||
| |
| GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $2.188 trillion<ref name="IMFWEO.BR" /> |
||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2024 |
|||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 73rd |
|||
| GDP_nominal_rank = 8th |
|||
|Gini = 53.9<!--number only--> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $10,296<ref name="IMFWEO.BR" /> |
|||
|Gini_year = 2018 |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 78th |
|||
|Gini_change = increase <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| Gini = 52 <!--number only--> |
|||
|Gini_ref =<ref name="WBgini">{{cite web |url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=BR |title=GINI index (World Bank estimate) - Brazil |publisher= World Bank |accessdate=22 March 2020}}</ref> |
|||
| Gini_year = 2022 |
|||
|Gini_rank = 10th |
|||
| Gini_change = decrease <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
|HDI = 0.761 <!--number only--> |
|||
| Gini_ref = <ref name="WBgini">{{Cite web |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=BR |title=World Bank Open Data |access-date=14 April 2024 |archive-date=9 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191009111239/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI%3Flocations%3DBR |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
|HDI_year = 2018<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> |
|||
| HDI = 0.760<!--number only--> |
|||
|HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> |
|||
|HDI_ref = <ref name="HDI">{{cite web |url=http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr2019.pdf |title=2019 Human Development Report |year=2019 |accessdate=9 December 2019 |publisher=United Nations Development Programme }}</ref> |
|||
| HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
|HDI_rank = 79th |
|||
| HDI_ref = <ref name="UNHDR">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2023/24|language=en|publisher=[[United Nations Development Programme]]|date=13 March 2024|page=289|access-date=13 March 2024|archive-date=13 March 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240313164319/https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|currency = [[Brazilian real|Real]] (R$) |
|||
| HDI_rank = 89th |
|||
|currency_code = BRL |
|||
| currency = [[Brazilian real|Real]] (R$) |
|||
|time_zone = [[Time in Brazil|BRT]] |
|||
| currency_code = BRL |
|||
|utc_offset = −2 to −5 |
|||
| time_zone = [[Time in Brazil|BRT]] |
|||
|antipodes = |
|||
| utc_offset = −2 to −5 |
|||
|date_format = dd/mm/yyyy ([[Common Era|CE]]) |
|||
| DST_note = ''[[Daylight saving time|DST]] is not observed.'' |
|||
|drives_on = right |
|||
| |
| date_format = [[Date and time notation in Brazil|dd/mm/yyyy]] ([[Common Era|CE]]) |
||
| drives_on = right |
|||
|iso3166code = |
|||
| calling_code = [[Telephone numbers in Brazil|+55]] |
|||
|cctld = [[.br]] |
|||
| iso3166code = |
|||
| religion = 86.8% [[Christianity]]<br />—64.6% [[Catholic Church in Brazil|Roman Catholicism]]<br />—22.2% [[Protestantism in Brazil|Protestantism]]<br />8.0% [[Irreligion in Brazil|No religion]]<br />2.0% [[Spiritism]]<br />3.2% Other [[Religion in Brazil|religion]]s<br /> |
|||
| cctld = [[.br]] |
|||
| religion_ref = <ref name="census2010">[ftp://ftp.ibge.gov.br/Censos/Censo_Demografico_2010/Caracteristicas_Gerais_Religiao_Deficiencia/tab1_4.pdf IBGE – Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (Brazilian Institute for Geography and Statistics). 2010 Census]. Retrieved 7 August 2012.</ref><ref>{{cite web | title=2010 Population Census - General characteristics of population, religion and persons with disabilities (Portuguese) | website=ibge.gov.br | date=2012-11-16 | url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/presidencia/noticias/noticia_impressao.php?id_noticia=2170 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121116103249/http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/presidencia/noticias/noticia_impressao.php?id_noticia=2170 | archive-date=2012-11-16 | url-status=unfit | language=pt | access-date=2019-08-10}}</ref> |
|||
| |
| religion = {{Tree list}} |
||
*79% [[Christianity in Brazil|Christianity]] |
|||
**51% [[Catholic Church in Brazil|Catholicism]] |
|||
**28% [[Protestantism in Brazil|Protestantism]] |
|||
*12% [[Irreligion in Brazil|no religion]] |
|||
*5% other religions |
|||
**[[Kardecist spiritism|Spiritism]] |
|||
**[[Umbanda]] |
|||
**[[Candomblé]], etc.{{Tree list/end}} |
|||
| religion_ref = <ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/brazil/#:~:text=Religious%20Demography,-The%20U.S.%20government&text=Datafolha's%202022%20electoral%20polls%20also,do%20not%20specify%20a%20religion. |title=2022 Report on International Religious Freedom: Brazil |website=United States Department of State |access-date=12 March 2024 |archive-date=12 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240312161743/https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/brazil/#:~:text=Religious%20Demography,-The%20U.S.%20government&text=Datafolha's%202022%20electoral%20polls%20also,do%20not%20specify%20a%20religion. |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2022-06-30 |title=Datafolha: Brazilians Go to Church Less and Give Less Contributions |url=https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/internacional/en/brazil/2022/06/datafolha-brazilians-go-to-church-less-and-give-less-contributions.shtml |access-date=2024-06-02 |website=Folha de S.Paulo |language=en-US |archive-date=28 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240628014425/https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/internacional/en/brazil/2022/06/datafolha-brazilians-go-to-church-less-and-give-less-contributions.shtml |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| religion_year = 2022 |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Brazil''',{{efn|{{langx|pt|Brasil}}, {{IPA|pt-BR|bɾaˈziw|pron|Pt-br-brasil.ogg}}.}} officially the '''Federative Republic of Brazil''',{{efn|{{langx|pt|República Federativa do Brasil|links=no}},<ref name="Bello1966v">{{Cite book |last=José María Bello |url=<!--removed URL to Google Books as the content cannot be accessed from that source--> |title=A History of Modern Brazil: 1889–1964 |publisher=[[Stanford University Press]] |year=1966 |isbn=978-0-8047-0238-6 |page=[[iarchive:historyofmodernb0000bell/page/56/mode/1up|56]]}}</ref> {{IPA|pt-BR|ʁeˈpublikɐ fedeɾaˈtʃivɐ du bɾaˈziw|pron|Pt-br-República Federativa do Brasil.ogg}}.}} is the largest and easternmost country in [[South America]] and [[Latin America]]. It is the world's [[List of countries and dependencies by area|fifth-largest country by area]] and one of the [[List of countries and dependencies by population|most populated countries]]. Its capital is [[Brasília]], and [[List of cities in Brazil by population|its most populous city]] is [[São Paulo]]. Brazil is a [[federation]] composed of 26 [[States of Brazil|states]] and a [[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]]. It is the only country in the [[Americas]] where [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]] is an [[List of countries and territories where Portuguese is an official language|official language]].<ref name="Philander2012">{{Cite book |last=Philander |first=S. George |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=B8VE92tDqEEC&pg=PA148 |title=Encyclopedia of Global Warming and Climate Change, Second Edition |publisher=Princeton University |year=2012 |isbn=978-1-4129-9261-9 |edition=Second |volume=1 |location=Los Angeles |page=148 |oclc=970592418 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=25 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231025210536/https://books.google.com/books?id=B8VE92tDqEEC&pg=PA148#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="CrocittiVallance2011">{{Cite book |last=Vallance |first=Monique M. |title=Brazil Today: An Encyclopedia of Life in the Republic |publisher=ABC-CLIO |others=Contributing editor Monique M. Vallance |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-313-34672-9 |editor-last=Crocitti |editor-first=John J. |page=xxiii |chapter=Preface and Observations on Contemporary Brazil |oclc=787850982 |ref={{harvid|Crocitti|Vallance|2012}} |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vP9jHaoL_s4C&pg=PR23 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=25 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231025210603/https://books.google.com/books?id=vP9jHaoL_s4C&pg=PR23 |url-status=live }}</ref> Brazil is among the world's most [[Multiculturalism|multicultural]] and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass [[Immigration to Brazil|immigration from around the world]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Os migrantes de hoje |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/portuguese/especial/migrantes/migrantes.shtml |access-date=24 October 2018 |publisher=BBC Brasil |archive-date=27 September 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130927075051/http://www.bbc.co.uk/portuguese/especial/migrantes/migrantes.shtml |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Bounded by the [[Atlantic Ocean]] on the east, Brazil has a [[Coastline of Brazil|coastline]] of {{convert|7491|km|mi|0|sp=us}}.<ref name="CIA Geo" /> Covering roughly half of South America's land area, it borders all other countries and territories on the continent except [[Ecuador]] and [[Chile]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=<!--not specified--> |date=<!--not specified--> |title=Brazil – Land |url=http://www.un.int/brazil/brasil/brazil-land.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141023154830/http://www.un.int/brazil/brasil/brazil-land.htm |archive-date=23 October 2014 |access-date=<!--not specified--> |website=Permanent Missions |publisher=United Nations |at=Geography}}</ref> Brazil's [[Amazon basin]] includes a [[Amazon rainforest|vast tropical forest]] home to diverse [[Wildlife of Brazil|wildlife]], a variety of [[Environment of Brazil|ecological systems]], and extensive natural resources spanning numerous [[protected areas of Brazil|protected habitats]].<ref name="CIA Geo">{{Cite CIA World Factbook|country=Brazil|section=geography|access-date=4 May 2018|year=2018}}</ref> This unique environmental heritage positions Brazil at number one of 17 [[megadiverse countries]]. The country's natural richness is also the subject of significant global interest, as [[environmental degradation]] (through processes such as [[Deforestation in Brazil|deforestation]]) has direct impacts on global issues such as [[Climate change in Brazil|climate change]] and [[biodiversity loss]]. |
|||
'''Brazil''' ({{lang-pt|Brasil}}; {{IPA-pt|bɾaˈziw|br}}),<ref group="nt">{{IPA-pt|bɾɐˈziɫ|eu}}</ref> officially the '''Federative Republic of Brazil''' (Portuguese: {{Audio|Pt-br-República Federativa do Brasil.ogg|''República Federativa do Brasil''|help=no}}),<ref name="Bello1966v">{{cite book|url=<!--removed URL to Google Books as the content cannot be accessed from that source-->|title=A History of Modern Brazil: 1889–1964|author=José María Bello|publisher=Stanford University Press|year=1966|isbn=978-0-8047-0238-6|page=56}}</ref> is the largest country in both [[South America]] and [[Latin America]]. At 8.5 million square kilometers (3.2 million square miles)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/geociencias/cartografia/default_territ_area.shtm|title=Área Territorial Brasileira|last=<!--no byline-->|date=<!--no source date-->|publisher=Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística|language=Portuguese|trans-title=Brazilian Territorial Area|access-date=4 May 2018|quote=Para a superfície do Brasil foi obtido o valor de 8.515.759,090 km2, publicado no DOU nº 124 de 30/06/2017, conforme Resolução Nº 02, de 29 de junho de 2017.|archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/64i0P2Lb0?url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/geociencias/cartografia/default_territ_area.shtm|archive-date=15 January 2012|url-status=dead}}</ref> and with over 211 million people, Brazil is the world's [[List of countries and dependencies by area|fifth-largest country by area]] and the [[List of countries and dependencies by population|sixth most populous]]. Its capital is [[Brasília]], and [[List of cities in Brazil by population|its most populous city]] is [[São Paulo]]. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 [[States of Brazil|states]] and the [[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]]. It is the largest country to have [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]] as an [[List of territorial entities where Portuguese is an official language|official language]] and the only one in the [[Americas]];<ref name="Philander2012">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=B8VE92tDqEEC&pg=PA148|title=Encyclopedia of Global Warming and Climate Change, Second Edition|last=Philander|first=S. George|publisher=Princeton University|year=2012|isbn=978-1-4129-9261-9|edition=Second|volume=Vol. 1|location=Los Angeles|page=148|oclc=970592418}}</ref><ref name="CrocittiVallance2011">{{cite book|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vP9jHaoL_s4C&pg=PR23|title=Brazil Today: An Encyclopedia of Life in the Republic|last=Vallance|first=Monique M.|publisher=ABC-CLIO|others=Contributing editor Monique M. Vallance|year=2012|isbn=978-0-313-34672-9|editor-last=Crocitti|editor-first=John J.|page=xxiii|chapter=Preface and Observations on Contemporary Brazil|oclc=787850982|ref={{harvid|Crocitti|Vallance|2012}} }}</ref> it is also one of the most [[Multiculturalism|multicultural]] and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass [[Immigration to Brazil|immigration from around the world]];<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/portuguese/especial/migrantes/migrantes.shtml|title=Os migrantes de hoje|publisher=BBC Brasil |accessdate=24 October 2018}}</ref> as well as the most populous [[Catholic Church by country|Roman Catholic-majority country.]] |
|||
The territory of present-day Brazil was inhabited by [[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|numerous tribal nations]] prior to the landing of explorer [[Pedro Álvares Cabral]] in 1500. Subsequently claimed by the [[Portuguese Empire]], Brazil remained a [[Colonial Brazil|Portuguese colony]] until 1808, when the capital of the empire was [[Transfer of the Portuguese court to Brazil|transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro]]. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the [[United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves]]. [[Independence of Brazil|Independence]] was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the [[Empire of Brazil]], a [[unitary state]] governed under a [[Brazilian imperial family|constitutional monarchy]] and a [[Parliamentary sovereignty|parliamentary system]]. The ratification of the [[Brazilian Constitution of 1824|first constitution in 1824]] led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the [[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]]. [[Slavery in Brazil|Slavery]] was [[Lei Áurea|abolished]] in 1888. The country [[Proclamation of the Republic (Brazil)|became a presidential republic]] in 1889 following a military [[coup d'état]]. An authoritarian [[Military dictatorship in Brazil|military dictatorship]] emerged [[1964 Brazilian coup d'état|in 1964]] and ruled until 1985, after which civilian governance resumed. Brazil's current [[Constitution of Brazil|constitution]], formulated in 1988, defines it as a [[Democracy|democratic]] [[federal republic]].<ref name="Constituição">{{Cite web |year=1988 |title=Brazilian Federal Constitution |url=http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/Constituicao/Constituiçao.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071213194044/http://www.planalto.gov.br/CCIVIL_03/Constituicao/Constitui%C3%A7ao.htm |archive-date=13 December 2007 |access-date=3 June 2008 |publisher=Presidency of the Republic |language=pt}} {{cite web |title=Brazilian Federal Constitution |publisher=v-brazil.com |year=2007 |url=http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleI.html |quote=Unofficial translate |access-date=3 June 2008 |archive-date=28 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180928070506/http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleI.html }}</ref> Due to its rich culture and history, the country ranks [[List of World Heritage Sites in Brazil|thirteenth in the world]] by number of [[UNESCO]] [[World Heritage Site]]s.<ref>{{Cite web |title=UNESCO World Heritage Centre — World Heritage List |url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/list |access-date=25 May 2012 |publisher=UNESCO |archive-date=14 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210314170923/https://whc.unesco.org/en/list |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a [[Coastline of Brazil|coastline]] of {{convert|7491|km|mi|0|sp=us}}.<ref name="CIA Geo"/> It borders all other countries in South America except [[Ecuador]] and [[Chile]] and covers 47.3% of the continent's land area.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.un.int/brazil/brasil/brazil-land.htm|title=Brazil – Land|last=<!--not specified-->|date=<!--not specified-->|website=Permanent Missions|publisher=United Nations|at=Geography|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20141023154830/http://www.un.int/brazil/brasil/brazil-land.htm|archivedate=23 October 2014|access-date=<!--not specified-->}}</ref> Its [[Amazon basin]] includes a [[Amazon rainforest|vast tropical forest]], home to diverse [[Wildlife of Brazil|wildlife]], a variety of [[Environment of Brazil|ecological systems]], and extensive natural resources spanning numerous [[protected areas of Brazil|protected habitats]].<ref name="CIA Geo">{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/br.html|title=Geography of Brazil|last=<!--no byline-->|date=1 May 2018|website=The World Factbook|publisher=Central Intelligence Agency|at=Geography > Coastline|accessdate=4 May 2018}}</ref> This unique environmental heritage makes Brazil one of 17 [[megadiverse countries]], and is the subject of significant global interest and debate regarding deforestation and environmental protection. |
|||
Brazil is a [[regional power|regional]] and [[middle power]]<ref name="SchaeferPoffenbarger2014">{{Cite book |last1=M. Schaefer |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yXdaBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT32 |title=The Formation of the BRICS and its Implication for the United States: Emerging Together |last2=J. Poffenbarger |date=2014 |publisher=Springer |isbn=978-1-137-38794-3 |page=32 |access-date=17 November 2018 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183440/https://books.google.com/books?id=yXdaBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT32#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Burges2016">{{Cite book |last=Sean W. Burges |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=tolwCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA114 |title=Latin America and the Shifting Sands of Globalization |publisher=Routledge |year=2016 |isbn=978-1-317-69658-2 |pages=114–15 |access-date=2 May 2018 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183445/https://books.google.com/books?id=tolwCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA114#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Gina">{{Cite journal |last=Gardini |first=Gian Luca |year=2016 |title=Brazil: What Rise of What Power? |journal=Bulletin of Latin American Research |volume=35 |pages=5–19 |doi=10.1111/blar.12417 |doi-access=free |issn=0261-3050}}</ref> that is an [[emerging power]]<ref name="FRIDE">{{Cite web |last=Gratius |first=Susanne |date=April 2008 |title=The international arena and emerging powers: stabilising or destabilising forces? |url=http://fride.org/descarga/com_emerging_powers_eng_abr08.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160615194931/http://fride.org/descarga/com_emerging_powers_eng_abr08.pdf |archive-date=15 June 2016 |website=[[FRIDE]]}}</ref><ref name="Collecott">{{Cite web |last=Peter Collecott |date=29 October 2011 |title=Brazil's Quest for Superpower Status |url=http://www.diplomaticourier.com/2011/10/29/brazil-s-quest-for-superpower-status/ |access-date=10 August 2014 |publisher=The Diplomatic Courier |archive-date=2 April 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190402030604/https://www.diplomaticourier.com/2011/10/29/brazil-s-quest-for-superpower-status/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Clendenning |first=Alan |date=17 April 2008 |title=Booming Brazil could be world power soon |page=2 |work=USA Today |agency=The Associated Press |url=https://www.usatoday.com/money/economy/2008-04-17-310212789_x.htm |access-date=12 December 2008 |archive-date=20 August 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110820003302/http://www.usatoday.com/money/economy/2008-04-17-310212789_x.htm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="DominguezKim2013">{{Cite book |last1=Jorge Dominguez |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=c0I_4JmjFbwC&pg=PA98 |title=Between Compliance and Conflict: East Asia Latin America and the New Pax Americana |last2=Byung Kook Kim |publisher=Center for International Affairs, Harvard University |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-136-76983-2 |pages=98–99}}</ref> and a [[major non-NATO ally]] of the [[United States]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Vandiver |first=John |date=9 May 2019 |title=Trump bumps up Brazil to 'major non-NATO' ally |url=https://www.stripes.com/news/trump-bumps-up-brazil-to-major-non-nato-ally-1.580256 |access-date=2 April 2023 |website=Stars and Stripes |language=en |archive-date=13 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191013035014/https://www.stripes.com/news/trump-bumps-up-brazil-to-major-non-nato-ally-1.580256 |url-status=live }}</ref> Categorized as a [[developing country]], Brazil is considered an advanced [[Emerging market|emerging economy]],<ref>{{Cite web |date=September 2018 |title=FTSE Country Classification |url=https://www.ftse.com/products/downloads/FTSE-Country-Classification-Update-2018.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181121072632/https://www.ftse.com/products/downloads/FTSE-Country-Classification-Update-2018.pdf |archive-date=21 November 2018 |access-date=20 November 2018 |publisher=[[FTSE Group]]}}</ref> having the [[List of countries by GDP (nominal)|one of the-largest GDP]] in the world in both nominal and [[List of countries by GDP (PPP)|PPP]] terms—the largest in Latin America and the [[Southern Hemisphere]].<ref name="IMFWEO.BR" /><ref>{{Cite web |title=CIA – The World Factbook – Country Comparisons – GDP (purchasing power parity) |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2001rank.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110604195034/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2001rank.html |archive-date=4 June 2011 |access-date=25 January 2011 |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency]]}}</ref> Classified as an upper-middle income economy by the [[World Bank]],<ref name="wb-upper-middle">{{Cite web |title=Country and Lending Groups |url=http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-classifications/country-and-lending-groups#Upper_middle_income |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110318125456/http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-classifications/country-and-lending-groups |archive-date=18 March 2011 |access-date=5 March 2011 |publisher=World Bank |quote=Uppermiddle Income defined as a per capita income between $3,976 – $12,275}}</ref> and a [[newly industrialized country]] by the [[International Monetary Fund|IMF]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019 |url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2019/01/weodata/weoselco.aspx?g=2200&sg=All+countries+%2f+Emerging+market+and+developing+economies |access-date=29 September 2019 |website=IMF.org |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190617091704/https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2019/01/weodata/weoselco.aspx?g=2200&sg=All+countries+%2f+Emerging+market+and+developing+economies |archive-date=17 June 2019 }}</ref> Brazil has the [[List of countries by total wealth|largest share of wealth]] and the [[Economic Complexity Index|most complex economy]] in South America. It is also one of the world's major [[breadbasket]]s, being the largest [[Coffee production in Brazil|producer of coffee]] for the last 150 years.<ref name="Neilson102" /> Despite its growing economic and global profile, the country continues to face high levels of [[Corruption in Brazil|corruption]], [[Crime in Brazil|crime]] and [[Social issues in Brazil|social inequality]]. Brazil is a founding member of the [[United Nations]], the [[G20]], [[BRICS]], [[G4 nations|G4]], [[Mercosur|Mercosul]], [[Organization of American States]], [[Organization of Ibero-American States]] and the [[Community of Portuguese Language Countries]] and also an observer state of the [[Arab League]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=14 August 2019 |title=Brazil must be a 'facilitator' in the Middle East, says VP |url=https://anba.com.br/en/brazil-must-be-a-facilitator-in-the-middle-east-says-vp/ |access-date=26 May 2023 |archive-date=26 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230526041219/https://anba.com.br/en/brazil-must-be-a-facilitator-in-the-middle-east-says-vp/ |url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil was inhabited by [[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|numerous tribal nations]] prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer [[Pedro Álvares Cabral]], who claimed the area for the [[Portuguese Empire]]. Brazil remained a [[Colonial Brazil|Portuguese colony]] until 1808 when the capital of the empire was [[Transfer of the Portuguese court to Brazil|transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro]]. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the [[United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves]]. [[Independence of Brazil|Independence]] was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the [[Empire of Brazil]], a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the [[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]]. The country [[Proclamation of the Republic (Brazil)|became a presidential republic]] in 1889 following a military [[coup d'état]]. An authoritarian [[Military dictatorship in Brazil|military junta]] came to power [[1964 Brazilian coup d'état|in 1964]] and ruled until 1985, after which civilian governance resumed. Brazil's current [[Constitution of Brazil|constitution]], formulated in 1988, defines it as a [[Democracy|democratic]] [[federal republic]].<ref name="Constituição">{{cite web |title=Brazilian Federal Constitution |publisher=Presidency of the Republic |year=1988 |url=http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/Constituicao/Constituiçao.htm |language=Portuguese |accessdate=3 June 2008}} {{cite web |title=Brazilian Federal Constitution |publisher=v-brazil.com |year=2007 |url=http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleI.html |quote=Unofficial translate |accessdate=3 June 2008}}</ref> Due to its rich culture and history, the country ranks [[List of World Heritage Sites in Brazil|thirteenth in the world]] by number of [[UNESCO]] [[World Heritage Site]]s.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/list |title=UNESCO World Heritage Centre — World Heritage List |publisher=UNESCO |accessdate=25 May 2012}}</ref> |
|||
== Etymology == |
|||
Brazil is classified as an upper-middle income economy by the [[World Bank]]<ref name="wb-upper-middle">{{cite web|url=http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-classifications/country-and-lending-groups#Upper_middle_income |title=Country and Lending Groups |publisher=World Bank |accessdate=5 March 2011 |quote=Uppermiddle Income defined as a per capita income between $3,976 – $12,275 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110318125456/http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-classifications/country-and-lending-groups |archivedate=18 March 2011}}</ref> and a [[newly industrialized country]],<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2019/01/weodata/weoselco.aspx?g=2200&sg=All+countries+%2f+Emerging+market+and+developing+economies |title=World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019 |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |website=IMF.org |access-date=29 September 2019}}</ref> with [[List of countries by total wealth|the largest share of global wealth]] in Latin America. It is considered an advanced [[Emerging market|emerging economy]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ftse.com/products/downloads/FTSE-Country-Classification-Update-2018.pdf |title=FTSE Country Classification |publisher=[[FTSE Group]] |date= September 2018 |accessdate=20 November 2018}}</ref> It has the ninth largest GDP in the world by [[List of countries by GDP (nominal)|nominal]], and eighth by [[List of countries by GDP (PPP)|PPP]] measures.<ref name="IMF, October 2015">{{cite web|url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2018/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=44&pr.y=11&sy=2018&ey=2018&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=512%2C668%2C914%2C672%2C612%2C946%2C614%2C137%2C311%2C546%2C213%2C962%2C911%2C674%2C314%2C676%2C193%2C548%2C122%2C556%2C912%2C678%2C313%2C181%2C419%2C867%2C513%2C682%2C316%2C684%2C913%2C273%2C124%2C868%2C339%2C921%2C638%2C948%2C514%2C943%2C218%2C686%2C963%2C688%2C616%2C518%2C223%2C728%2C516%2C836%2C918%2C558%2C748%2C138%2C618%2C196%2C624%2C278%2C522%2C692%2C622%2C694%2C156%2C142%2C626%2C449%2C628%2C564%2C228%2C565%2C924%2C283%2C233%2C853%2C632%2C288%2C636%2C293%2C634%2C566%2C238%2C964%2C662%2C182%2C960%2C359%2C423%2C453%2C935%2C968%2C128%2C922%2C611%2C714%2C321%2C862%2C243%2C135%2C248%2C716%2C469%2C456%2C253%2C722%2C642%2C942%2C643%2C718%2C939%2C724%2C734%2C576%2C644%2C936%2C819%2C961%2C172%2C813%2C132%2C726%2C646%2C199%2C648%2C733%2C915%2C184%2C134%2C524%2C652%2C361%2C174%2C362%2C328%2C364%2C258%2C732%2C656%2C366%2C654%2C144%2C336%2C146%2C263%2C463%2C268%2C528%2C532%2C923%2C944%2C738%2C176%2C578%2C534%2C537%2C536%2C742%2C429%2C866%2C433%2C369%2C178%2C744%2C436%2C186%2C136%2C925%2C343%2C869%2C158%2C746%2C439%2C926%2C916%2C466%2C664%2C112%2C826%2C111%2C542%2C298%2C967%2C927%2C443%2C846%2C917%2C299%2C544%2C582%2C941%2C474%2C446%2C754%2C666%2C698&s=NGDPD&grp=0&a=#cs120|title=International Monetary Fund|author=|first=|date=|website=imf.org|access-date=}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2001rank.html |title=CIA – The World Factbook – Country Comparisons – GDP (purchasing power parity) |publisher=Cia.gov |accessdate=25 January 2011}}</ref> It is one of the world's major [[breadbasket]]s, being the largest [[Coffee production in Brazil|producer of coffee]] for the last 150 years.<ref name=Neilson102/> Brazil is a [[regional power]] and sometimes considered a [[Great power|great]]<ref name="SchaeferPoffenbarger2014">{{cite book|author1=M. Schaefer|author2=J. Poffenbarger|title=The Formation of the BRICS and its Implication for the United States: Emerging Together|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yXdaBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT32|date= 2014|publisher=Springer|isbn=978-1-137-38794-3|page=32}}</ref><ref name="Gina" /><ref name="Burges2016">{{cite book|author=Sean W. Burges|title=Latin America and the Shifting Sands of Globalization|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=tolwCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA114|year= 2016|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-317-69658-2|pages=114–15}}</ref> or a [[middle power]] in [[International relations|international affairs]].<ref name="Burges2016"/><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ibsanews.com/pt/eeuu-eespecialistas-reclamam-reconhecimento-do-brasil-como-potecircncia-mundial/ |title=Especialistas reclamam reconhecimento do Brasil como potência mundial|publisher=IBS News|date=15 June 2011 |accessdate=7 April 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.dci.com.br/pela-primeira-vez-brasil-emerge-como-potencia-internacional,-diz-patriota-id293466.html |title=Pela primeira vez Brasil emerge como potência internacional, diz Patriota |publisher= |date=10 May 2012 |accessdate=7 April 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304023906/http://www.dci.com.br/pela-primeira-vez-brasil-emerge-como-potencia-internacional,-diz-patriota-id293466.html |archive-date=4 March 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://allafrica.com/stories/201109150218.html |title=Brazil – Emerging Soft Power of the World|publisher=allAfrica.com |date=15 September 2011 |accessdate=7 April 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.sidneyrezende.com/noticia/143872+brasil+ganha+dos+estados+unidos+em+influencia+na+america+do+sul |title=Brasil ganha dos Estados Unidos em influência na América do Sul |newspaper=[[The Economist]] |date=2 September 2011 |accessdate=7 April 2017}}</ref><ref name="Gina">{{Cite journal |doi=10.1111/blar.12417|title = Brazil: What Rise of What Power?|journal = Bulletin of Latin American Research|volume = 35|pages = 5–19|year = 2016|last1 = Gardini|first1 = Gian Luca}}</ref> On account of its international recognition and influence, the country is subsequently classified as an [[emerging power]]<ref name="FRIDE">[http://fride.org/descarga/com_emerging_powers_eng_abr08.pdf FRIDE: The international arena and emerging powers: stabilising or destabilising forces?] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160615194931/http://fride.org/descarga/com_emerging_powers_eng_abr08.pdf |date=15 June 2016 }}, Susanne Gratius, April 2008</ref> and a [[Potential superpowers|potential superpower]] by several analysts.<ref name="Collecott">{{cite web|author=Peter Collecott|url=http://www.diplomaticourier.com/2011/10/29/brazil-s-quest-for-superpower-status/|title=Brazil's Quest for Superpower Status|publisher=The Diplomatic Courier|date=29 October 2011|accessdate=10 August 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Clendenning |first=Alan |title=Booming Brazil could be world power soon |page=2 |newspaper=USA Today |agency=The Associated Press |date=17 April 2008 |url=https://www.usatoday.com/money/economy/2008-04-17-310212789_x.htm |accessdate=12 December 2008}}</ref><ref name="DominguezKim2013">{{cite book|author1=Jorge Dominguez|author2=Byung Kook Kim|title=Between Compliance and Conflict: East Asia Latin America and the New Pax Americana|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=c0I_4JmjFbwC&pg=PA98|year=2013|publisher=Center for International Affairs, Harvard University|isbn=978-1-136-76983-2|pages=98–99}}</ref> Brazil is a founding member of the [[United Nations]], the [[G20]], [[BRICS]], [[Mercosur|Mercosul]], [[Organization of American States]], [[Organization of Ibero-American States]] and the [[Community of Portuguese Language Countries]]. |
|||
==Etymology== |
|||
{{Main|Name of Brazil}} |
{{Main|Name of Brazil}} |
||
The word |
The word ''Brazil'' probably comes from the Portuguese word for [[Caesalpinia echinata|brazilwood]], a tree that once grew plentifully along the Brazilian coast.<ref name="Fausto1999">{{Cite book |last=Fausto |first=Boris |url=https://archive.org/details/concisehistoryof00faus |title=A Concise History of Brazil |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-521-56526-4 |page=[https://archive.org/details/concisehistoryof00faus/page/9 9] |url-access=registration}}</ref> In Portuguese, brazilwood is called ''pau-brasil'', with the word ''brasil'' commonly given the etymology "red like an [[ember]]", formed from ''brasa'' ('ember') and the suffix ''-il'' (from ''-iculum'' or ''-ilium'').<ref name="Vincent2003">{{Cite book |last=Jon S. Vincent. |url=https://archive.org/details/culturecustomsof0000vinc |title=Culture and Customs of Brazil |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-313-30495-8 |page=[https://archive.org/details/culturecustomsof0000vinc/page/36 36] |url-access=registration}}</ref> It has alternatively been suggested that this is a folk etymology for a word for the plant related to an Arabic or Asian word for a red plant.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.etymonline.com/word/Brazil#etymonline_v_17075 |title=Brazil | Etymology of the name Brazil by etymonline |access-date=24 March 2024 |archive-date=24 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240324183937/https://www.etymonline.com/word/Brazil#etymonline_v_17075 |url-status=live }}</ref> As [[Paubrasilia|brazilwood]] produces a deep red dye, it was highly valued by the European textile industry and was the earliest commercially exploited product from Brazil.<ref name="Tucker2007">{{Cite book |last=Richard P. Tucker |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2V2q30BdEJ8C&pg=PA186 |title=Insatiable Appetite: The Ecological Degradation of the Tropical World |publisher=University of Michigan |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7425-5365-1 |page=186 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183601/https://books.google.com/books?id=2V2q30BdEJ8C&pg=PA186#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> Throughout the 16th century, massive amounts of brazilwood were harvested by [[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|indigenous peoples]] (mostly [[Tupi people|Tupi]]) along the Brazilian coast, who sold the timber to European traders (mostly Portuguese, but also French) in return for assorted European consumer goods.<ref name="Lee2011">{{Cite book |last=Wayne E. Lee |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xatMrooibacC&pg=PA196 |title=Empires and Indigenes: Intercultural Alliance, Imperial Expansion, and Warfare in the Early Modern World |publisher=NYU Press |year=2011 |isbn=978-0-8147-6527-2 |page=196 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215221303/https://books.google.com/books?id=xatMrooibacC&pg=PA196#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
The official Portuguese name of the land, in original Portuguese records, was the "Land of the Holy Cross" (''Terra da Santa Cruz''),<ref name="Corporation1880">{{ |
The official Portuguese name of the land, in original Portuguese records, was the "Land of the Holy Cross" (''Terra da Santa Cruz''),<ref name="Corporation1880">{{Cite magazine |last=Daly |first=Charles P. |year=1880 |title=Maps and Map-making Before Mercator |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hiQDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA493 |magazine=The Popular Science Monthly |publisher=Bonnier Corporation |at=473–495, see page 493 |issn=0161-7370 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215221315/https://books.google.com/books?id=hiQDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA493#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> but European sailors and merchants commonly called it the "Land of Brazil" (''Terra do Brasil'') because of the brazilwood trade.<ref name="Léry1990">{{Cite book |last=Jean de Léry |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=F8qqKoCSWVkC&pg=PA242 |title=History of a Voyage to the Land of Brazil, Otherwise Called America |publisher=University of California Press |year=1990 |isbn=978-0-520-91380-6 |page=242 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215221327/https://books.google.com/books?id=F8qqKoCSWVkC&pg=PA242#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> The popular appellation eclipsed and eventually supplanted the official Portuguese name. Some early sailors called it the "Land of Parrots".<ref name="Sokolow2003">{{Cite book |last=Jayme A. Sokolow. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ytghV9q6v3cC&pg=PA84 |title=The Great Encounter: Native Peoples and European Settlers in the Americas, 1492–1800 |publisher=M.E. Sharpe |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-7656-0982-3 |page=84 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215221351/https://books.google.com/books?id=ytghV9q6v3cC&pg=PA84#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
In the [[ |
In the [[Guaraní language]], an official language of [[Paraguay]], Brazil is called "Pindorama", meaning 'land of the palm trees'.<ref name="Herrera-Sobek2012">{{Cite book |last=Maria Herrera-Sobek |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lY-tY62V1FIC&pg=PA155 |title=Celebrating Latino Folklore |publisher=ABC-CLIO |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-313-34340-7 |page=155 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=15 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240215221353/https://books.google.com/books?id=lY-tY62V1FIC&pg=PA155 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
==History== |
== History == |
||
{{Main|History of Brazil|Timeline of Brazilian history}} |
{{Main|History of Brazil}} |
||
{{For timeline|Timeline of Brazilian history}} |
|||
===Pre-Cabraline era=== |
=== Pre-Cabraline era === |
||
{{Main|Pre-Columbian history of Brazil{{!}}Pre-Cabraline history of Brazil}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
{{See also|Indigenous peoples in Brazil|Marajoara culture}} |
|||
| align = left |
|||
[[File:Pinturas Rupestres - Serra da Capivara I.jpg|thumb|left|[[Rock art]] at [[Serra da Capivara National Park]], one of the largest and oldest concentrations of prehistoric sites in the [[Americas]]<ref>{{Cite news |last=Romero |first=Simon |date=27 March 2014 |title=Discoveries Challenge Beliefs on Humans' Arrival in the Americas |work=[[The New York Times]] |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2014/03/28/world/americas/discoveries-challenge-beliefs-on-humans-arrival-in-the-americas.html |url-access=limited |access-date=31 May 2014 |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220101/https://www.nytimes.com/2014/03/28/world/americas/discoveries-challenge-beliefs-on-humans-arrival-in-the-americas.html |archive-date=1 January 2022}}{{cbignore}}</ref>]] |
|||
| image1 = Parque Nacional da Serra da Capivara (31729373313).jpg |
|||
| width1 = 150 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = [[Cave painting]] at [[Serra da Capivara National Park]], one of the largest and oldest concentrations of prehistoric sites in the [[Americas]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Discoveries Challenge Beliefs on Humans' Arrival in the Americas|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2014/03/28/world/americas/discoveries-challenge-beliefs-on-humans-arrival-in-the-americas.html|website=New York Times|date=27 March 2014|accessdate=31 May 2014|first=Simon|last=Romero}}</ref> |
|||
| image2 = Burian urn, AD 1000-1250, Marajoara culture - AMNH - DSC06177 b.jpg |
|||
| width2 = 167 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = Burial urn, [[Marajoara culture]], [[American Museum of Natural History]]. That culture appeared to flourish between 400 AD and 1400 AD, based on archeological studies.<ref name=Mann/> |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
Some of the earliest human remains found in the [[Americas]], [[Luzia Woman]], were found in the area of [[Pedro Leopoldo]], [[Minas Gerais]] and provide evidence of human habitation going back at least 11,000 years.<ref> |
Some of the earliest human remains found in the [[Americas]], [[Luzia Woman]], were found in the area of [[Pedro Leopoldo]], [[Minas Gerais]] and provide evidence of human habitation going back at least 11,000 years.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Ribeiro |first=Patricia |date=27 March 2014 |title=Peter Lund Museum |url=http://gobrazil.about.com/od/ecotourismadventure/ss/Peter-Lund-Museum.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170812171650/http://gobrazil.about.com/od/ecotourismadventure/ss/Peter-Lund-Museum.htm |archive-date=12 August 2017 |website=[[About.com]]}}</ref><ref name="LevineCrocitti1999">{{Cite book |last1=Robert M. Levine |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=R28K2JA9PM8C&pg=PA11 |title=The Brazil Reader: History, Culture, Politics |last2=John J. Crocitti |publisher=Duke University Press |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-8223-2290-0 |pages=11– |access-date=12 December 2012 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129182919/https://books.google.com/books?id=R28K2JA9PM8C&pg=PA11#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
The earliest [[pottery]] ever found in the Western Hemisphere was excavated in the [[Amazon basin]] of Brazil and [[Radiocarbon dating|radiocarbon dated]] to 8,000 years ago (6000 BC). The pottery was found near [[Santarém, Pará|Santarém]] and provides evidence that the region supported a complex prehistoric culture.<ref name="Eighth Millennium Pottery from a Prehistoric Shell Midden in the Brazilian Amazon">{{Cite journal |last1=Roosevelt |first1=Anna Curtenius |author1-link=Anna Curtenius Roosevelt |last2=Housley |first2=Rupert A. |last3=Imazio da Silveira |first3=Maura |last4=Maranca |first4=Silvia |last5=Johnson |first5=Richard Irwin |name-list-style=vanc |date=13 December 1991 |title=Eighth Millennium Pottery from a Prehistoric Shell Midden [sic] in the Brazilian Amazon |url=https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.254.5038.1621 |journal=[[Science (journal)|Science]] |language=en |volume=254 |issue=5038 |pages=1621–1624 |doi=10.1126/science.254.5038.1621 |pmid=17782213 |bibcode=1991Sci...254.1621R |s2cid=34969614 |issn=0036-8075 |access-date=4 July 2023 |archive-date=16 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231016114734/https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.254.5038.1621 |url-status=live }}</ref> The [[Marajoara culture]] flourished on [[Marajó]] in the Amazon delta from AD 400 to 1400, developing sophisticated pottery, [[social stratification]], large populations, [[mound building]], and complex social formations such as [[chiefdom]]s.<ref name="Mann">{{Cite book |last=Mann |first=Charles C. |url=https://archive.org/details/149100char/page/326 |title=1491: New Revelations of the Americas Before Columbus |publisher=Vintage Books |year=2006 |isbn=978-1-4000-3205-1 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/149100char/page/326 326–33] |author-link=Charles C. Mann |orig-date=2005}}</ref> |
|||
Around the time of the Portuguese arrival, the territory of current day Brazil had an estimated indigenous population of 7 million people,<ref>{{Cite book |last=Levine |first=Robert M. |title=The History of Brazil |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year=2003 |isbn=978-1-4039-6255-3 |page=32}}</ref> mostly semi-nomadic, who subsisted on hunting, fishing, gathering, and migrant agriculture. The population comprised several large indigenous ethnic groups (e.g., the [[Tupí people|Tupis]], [[Guaraní people|Guaranis]], [[Gê peoples|Gês]], and [[Arawak peoples|Arawaks]]). The Tupi people were subdivided into the [[Tupiniquim|Tupiniquins]] and [[Tupinambá people|Tupinambás]].{{sfnp|Levine|2003|p=31}} |
|||
The earliest [[pottery]] ever found in the Western Hemisphere was excavated in the [[Amazon basin]] of Brazil and [[Radiocarbon dating|radiocarbon dated]] to 8,000 years ago (6000 BC). The pottery was found near [[Santarém, Pará|Santarém]] and provides evidence that the tropical forest region supported a complex prehistoric culture.<ref name="Eighth Millennium Pottery from a Prehistoric Shell Midden in the Brazilian Amazon">Science Magazine, 13 December 1991 http://www.sciencemag.org/content/254/5038/1621.abstract</ref> The [[Marajoara culture]] flourished on [[Marajó]] in the Amazon delta from 400 CE to 1400 CE, developing sophisticated pottery, [[social stratification]], large populations, [[mound building]], and complex social formations such as [[chiefdom]]s.<ref name=Mann>{{cite book |last=Mann |first=Charles C. |authorlink=Charles C. Mann |title=1491: New Revelations of the Americas Before Columbus |origyear=2005 |year=2006 |publisher=Vintage Books |pages=[https://archive.org/details/149100char/page/326 326–33] |isbn=978-1-4000-3205-1 |url=https://archive.org/details/149100char/page/326 }}</ref> |
|||
Before the arrival of the Europeans, the boundaries between these groups and their subgroups were marked by wars that arose from differences in culture, language and moral beliefs.<ref name="Fausto">{{Cite book |last=Fausto |first=Carlos |title=Os Índios antes do Brasil |year=2000 |isbn=978-85-7110-543-0 |editor-last=Zahar |editor-first=Jorge |pages=45–46, 55 |publisher=Jorge Zahar Editor |language=pt |trans-title=The Indians before Brazil}}</ref> These wars also involved large-scale military actions on land and water, with [[Human cannibalism|cannibalistic]] rituals on [[Prisoner of war|prisoners of war]].<ref>Gomes, Mercio P. ''The Indians and Brazil'' University Press of Florida 2000 {{ISBN|0-8130-1720-3}} pp. 28–29</ref>{{sfnp|Fausto|2000|pp=78–80}} While heredity had some weight, leadership was a status more won over time than assigned in succession ceremonies and conventions.<ref name="Fausto" /> [[Slavery]] among the indigenous groups had a different meaning than it had for Europeans, since it originated from a diverse socioeconomic organization, in which asymmetries were translated into [[kinship]] relations.{{sfnp|Fausto|2000|p=50}} |
|||
Around the time of the Portuguese arrival, the territory of current day Brazil had an estimated indigenous population of 7 million people,<ref>{{cite book |last=Levine |first=Robert M. |title=The History of Brazil |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year=2003 |isbn=978-1-4039-6255-3 |page=32 |ref=harv}}</ref> mostly semi-nomadic, who subsisted on hunting, fishing, gathering, and migrant agriculture. The indigenous population of Brazil comprised several large indigenous ethnic groups (e.g. the [[Tupí people|Tupis]], [[Guaraní people|Guaranis]], [[Gê peoples|Gês]] and [[Arawak peoples|Arawaks]]). The Tupí people were subdivided into the [[Tupiniquim people|Tupiniquins]] and [[Tupinambá people|Tupinambás]], and there were also many subdivisions of the other groups.{{sfnp|Levine|2003|p=31}} |
|||
=== Portuguese colonization === |
|||
Before the arrival of the Europeans, the boundaries between these groups and their subgroups were marked by wars that arose from differences in culture, language and moral beliefs.<ref name="Fausto">{{cite book |last=Fausto |first=Carlos |title=Os Índios antes do Brasil |trans-title=The Indians before Brazil |language=pt |editor-first=Jorge |editor-last=Zahar |year=2000 |isbn =978-85-7110-543-0 |pages=45–46, 55 |ref=harv}}</ref> These wars also involved large-scale military actions on land and water, with [[cannibalism|cannibalistic]] rituals on [[Prisoner of war|prisoners of war]].<ref>Gomes, Mercio P. ''The Indians and Brazil'' University Press of Florida 2000 {{ISBN|0-8130-1720-3}} pp. 28–29</ref>{{sfnp|Fausto|2000|pp=78–80}} While heredity had some weight, leadership status was more subdued over time, than allocated in succession ceremonies and conventions.<ref name="Fausto"/> [[Slavery]] among the Indians had a different meaning than it had for Europeans, since it originated from a diverse socioeconomic organization, in which asymmetries were translated into [[kinship]] relations.{{sfnp|Fausto|2000|p=50}} |
|||
{{Main|Colonial Brazil|Portuguese Empire}} |
|||
{{ |
{{See also|Slavery in Brazil|War of the Emboabas|Inconfidência Mineira{{!}}Minas Gerais Conspiracy}} |
||
{{multiple image |
|||
[[File:Desembarque de Pedro Álvares Cabral em Porto Seguro em 1500 by Oscar Pereira da Silva (1865–1939).jpg|thumb|Representation of the landing of [[Pedro Álvares Cabral]] in [[Porto Seguro]], 1500. Painting of 1922.]] |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| image1 = Desembarque de Pedro Álvares Cabral em Porto Seguro em 1500 by Oscar Pereira da Silva (1865–1939).jpg |
|||
| caption1 = [[Pedro Álvares Cabral]] landing in [[Porto Seguro]] in 1500, ushering in more than 300 years of [[Portuguese Empire|Portuguese rule]] |
|||
| image2 = Conjunto arquitetônico e urbanístico de Ouro Preto.JPG |
|||
| caption2 = [[Ouro Preto]], [[Minas Gerais]], was the center of the [[Brazilian Gold Rush]] and was designated a [[World Heritage Site]] by [[UNESCO]] due to its [[Portuguese colonial architecture|Baroque colonial architecture]]. |
|||
| image3 = L'Exécution de la Punition de Fouet by Jean-Baptiste Debret.jpg |
|||
| caption3 = ''Execution of the Punishment of the Whip'' by [[Jean-Baptiste Debret]]. Nearly 5 million enslaved Africans were [[Slavery in Brazil|imported to Brazil]] during the [[Atlantic slave trade]], more than any country.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Terrence McCoy |date=17 January 2022 |title=More enslaved Africans came to the Americas through this port than anywhere else. Why have so few heard of it? |newspaper=[[Washington Post]] |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2022/01/17/brazil-slavery-valongo-wharf/ |access-date=3 January 2023 |archive-date=10 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221010164227/https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2022/01/17/brazil-slavery-valongo-wharf/ |url-status=live }}<!-- auto-translated by Module:CS1 translator --></ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
Following the 1494 [[Treaty of Tordesillas]], the land now called Brazil was claimed for the [[Portuguese Empire]] on 22 April 1500, with [[Discovery of Brazil|the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral]].<ref name="Boxer, p. 98">Boxer, p. 98.</ref> The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several ethnic societies, most of whom spoke languages of the [[Tupi–Guaraní|Tupi–Guarani]] family and fought among themselves.<ref name="Boxer, p. 100">Boxer, p. 100.</ref> Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, [[colonization]] effectively began in 1534, when King [[John III of Portugal|John III of Portugal]] divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous [[Captaincies of Brazil|captaincies]].<ref>Boxer, pp. 100–101.</ref><ref name="Skidmore, p. 27">Skidmore, p. 27.</ref> |
|||
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the [[Governorate General of Brazil]] in the city of [[Salvador, Bahia|Salvador]], which became the capital of a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America.<ref name="Skidmore, p. 27" /><ref>Boxer, p. 101.</ref> In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other.<ref>Meuwese, Mark "Brothers in Arms, Partners in Trade: Dutch-Indigenous Alliances in the Atlantic World, 1595–1674" Koninklijke Brill NV 2012 {{ISBN|978-90-04-21083-7}} ''Chapter III''</ref><ref>Metcalf, Alida C. "Go-betweens And the Colonization of Brazil: 1500–1600" University of Texas Press 2005, pp. 70, 79, 202 [https://books.google.com/books?id=lWuNIISvBqIC&pg=PA202 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129182912/https://books.google.com/books?id=lWuNIISvBqIC&pg=PA202#v=onepage&q&f=false |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref>{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012}}<ref>Minahan, James B. "Ethnic Groups of the Americas" ABC-CLIO 2013 {{ISBN|978-1-61069-163-5}} p. 300, [https://books.google.com/books?id=8jVig0ysnu8C&pg=PA300 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129182912/https://books.google.com/books?id=8jVig0ysnu8C&pg=PA300 |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref> |
|||
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the [[Portuguese Empire]] on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by [[Pedro Álvares Cabral]].<ref name="Boxer, p. 98">Boxer, p. 98.</ref> The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the [[Tupi–Guarani]] family, and fought among themselves.<ref name="Boxer, p. 100">Boxer, p. 100.</ref> Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, [[colonization]] effectively began in 1534, when King [[John III of Portugal|John III of Portugal]] divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous [[Captaincies of Brazil|Captaincy Colonies of Brazil]].<ref>Boxer, pp. 100–101.</ref><ref name="Skidmore, p. 27">Skidmore, p. 27.</ref> |
|||
By the mid-16th century, [[Sugar#Sugarcane|cane sugar]] had become Brazil's most important export,<ref name="Boxer, p. 100" /><ref>Skidmore, p. 36.</ref> while slaves purchased in [[Sub-Saharan Africa]] in the [[Slavery in Africa#Atlantic slave trade|slave market of Western Africa]]<ref>Richard Middleton and Anne Lombard "Colonial America: A History to 1763" Wiley-Blackwell Publishing 1st edition 1992 {{ISBN|978-1-4443-9628-7}} Chapter 2, Section 4 (final, last page and half of previous one) [https://books.google.com/books?id=2hexv5SmqLgC&pg=PT54 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129182805/https://books.google.com/books?id=2hexv5SmqLgC&pg=PT54#v=onepage&q&f=false |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref> (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in [[Portuguese Angola|Angola]] and [[Portuguese Mozambique|Mozambique]]), had become its largest import,<ref>Boxer, p. 110</ref><ref>Skidmore, p. 34.</ref> to cope with [[Engenho|sugarcane plantations]], due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar.<ref name="Boxer, p. 102">Boxer, p. 102.</ref><ref>Skidmore, pp. 32–33.</ref> Brazil received more than 2.8 million slaves from Africa between the years 1500 and 1800.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Murray |first=Stuart A. P. |title=The Library An Illustrated History |date=2009 |publisher=Skyhorse Publishing |isbn=978-1-60239-706-4 |location=New York |page=101}}</ref> |
|||
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline<ref>Boxer, p. 164.</ref> and the discovery of gold by [[bandeirantes]] in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony's economy, fostering a [[Brazilian Gold Rush|gold rush]]<ref>Boxer, pp. 168, 170.</ref> which attracted thousands of new [[Settler colonialism|settlers]] to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world.<ref>Boxer, p. 169.</ref> This increased level of immigration in turn caused [[War of the Emboabas|some conflicts]] between newcomers and old settlers.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Kohn |first=George C. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OIzreCGlHxIC&pg=PT186 |title=Dictionary of Wars |publisher=Facts on File, Inc. |year=1986 |isbn=978-1-4381-2916-7 |edition=1st |page=174 |access-date=16 October 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183330/https://books.google.com/books?id=OIzreCGlHxIC&pg=PT186#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Antônio Parreiras - Prisão de Tiradentes, 1914.jpg|thumb|left|Painting showing the arrest of [[Tiradentes]]; he was sentenced to death for his involvement in the best known [[Inconfidência Mineira|movement for independence]] in Colonial Brazil. Painting of 1914.]] |
|||
Portuguese expeditions known as ''bandeiras'' gradually [[Uti possidetis#The Brazilian frontier movement into Spanish-claimed lands|expanded Brazil's original colonial frontiers]] in South America to its approximately current borders.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=George Richard Potter |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1BY9AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA498 |title=The New Cambridge Modern History |last2=Henry Clifford Darby |last3=Harold Fullard |publisher=CUP Archive |year=1957 |edition=1st |volume=3 |page=498 |access-date=16 October 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183451/https://books.google.com/books?id=1BY9AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA498#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>Corrado, Jacopo "The Creole Elite and the Rise of Angolan Protonationalism" [[Cambria Press]] 2008 {{ISBN|978-1-60497-529-1}} pp. 95 (Brazil) and 145, note 5 [https://books.google.com/books?id=BKKf4PYI-IIC&q=tordesilha+bandeira+portugal+brazil+advance&pg=PA145 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230502120801/https://books.google.com/books?id=BKKf4PYI-IIC&q=tordesilha+bandeira+portugal+brazil+advance&pg=PA145 |date=2 May 2023 }}</ref> In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French [[France Antarctique|in Rio during the 1560s]], [[Equinoctial France|in Maranhão during the 1610s]], and the [[Dutch invasions of Brazil|Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco]], during the [[Dutch–Portuguese War]], after the end of [[Iberian Union]].<ref>Bethell, Leslie "Colonial Brazil" Cambridge University Press 1987 pp. 19, 74, 86, 169–70</ref> |
|||
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline,<ref>Boxer, p. 164.</ref> and the discovery of gold by [[bandeirantes]] in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony's economy, fostering a [[Brazilian Gold Rush]]<ref>Boxer, pp. 168, 170.</ref> which attracted thousands of new [[Settler colonialism|settlers]] to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world.<ref>Boxer, p. 169.</ref> This increased level of immigration in turn caused [[War of the Emboabas|some conflicts]] between newcomers and old settlers.<ref>{{cite book|last=Kohn|first=George C.|title=Dictionary of Wars|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OIzreCGlHxIC&pg=PT186|edition=1st|year=1986|publisher=Facts on File, Inc.|isbn=978-1-4381-2916-7|page=174}}</ref> |
|||
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the [[monopoly]] of Portugal's wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of [[slave rebellion]] and resistance, such as the [[Palmares (quilombo)|Quilombo of Palmares]],<ref>Schwartz, Stuart B. "Slaves, Peasants, and Rebels" Board of Trustees of the University of Illinois 1992 {{ISBN|0-252-06549-2}} Chapter 4 [https://books.google.com/books?id=YTnY5h0NE3sC&pg=PA103 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183446/https://books.google.com/books?id=YTnY5h0NE3sC&pg=PA103#v=onepage&q&f=false |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref> and to repress all movements for autonomy or [[independence]], such as the [[Inconfidência Mineira|Minas Gerais Conspiracy]].<ref>MacLachlan, Colin M. "A History of Modern Brazil: The Past Against the Future"; Scholarly Resources Inc. 2003 p. 3 [https://books.google.com/books?id=8m3RcnkKwJgC&pg=PA3 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183443/https://books.google.com/books?id=8m3RcnkKwJgC&pg=PA3#v=onepage&q&f=false |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref> |
|||
Portuguese expeditions known as [[Bandeirantes|Bandeiras]] gradually advanced the Portugal colonial [[Treaty of Tordesillas|original frontiers]] in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders.<ref>{{cite book|author1=George Richard Potter|author2=Henry Clifford Darby|author3=Harold Fullard|title=The New Cambridge Modern History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1BY9AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA498|edition=1st|volume=3|year=1957|publisher=CUP Archive|page=498}}</ref><ref>Corrado, Jacopo "The Creole Elite and the Rise of Angolan Protonationalism" [[Cambria Press]] 2008 {{ISBN|978-1-60497-529-1}} pp. 95 (Brazil) and 145, note 5 [https://books.google.com/books?id=BKKf4PYI-IIC&pg=PA145#v=onepage&q=tordesilha%20bandeira%20portugal%20brazil%20advance View on Google Books]</ref> In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French [[France Antarctique|in Rio during the 1560s]], [[Equinoctial France|in Maranhão during the 1610s]], and the [[Dutch Brazil|Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco]], during the [[Dutch–Portuguese War]], after the end of [[Iberian Union]].<ref>Bethell, Leslie "Colonial Brazil" Cambridge University Press 1987 pp. 19, 74, 86, 169–70</ref> |
|||
=== Elevation to kingdom === |
|||
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the [[monopoly]] of Portugal's wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of [[slave rebellion]] and resistance, such as the [[Palmares (quilombo)|Quilombo of Palmares]],<ref>Schwartz, Stuart B. "Slaves, Peasants, and Rebels" Board of Trustees of the University of Illinois 1992 {{ISBN|0-252-06549-2}} Chapter 4 [https://books.google.com/books?id=YTnY5h0NE3sC&pg=PA103 View on Google Books]</ref> and to repress all movements for [[Autonomous administrative division|autonomy]] or [[independence]], such as the [[Inconfidência Mineira|Minas Conspiracy]].<ref>MacLachlan, Colin M. "A History of Modern Brazil: The Past Against the Future"; Scholarly Resources Inc. 2003 p. 3 [https://books.google.com/books?id=8m3RcnkKwJgC&pg=PA3 View on Google Books]</ref> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
===United Kingdom with Portugal=== |
|||
{{Main|United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves}} |
{{Main|United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves}} |
||
[[File:Aclamação do rei Dom João VI no Rio de Janeiro.jpg|thumb |
{{See also|Invasion of Portugal (1807)|Transfer of the Portuguese court to Brazil}} |
||
[[File:Aclamação do rei Dom João VI no Rio de Janeiro.jpg|thumb|The Acclamation of [[John VI of Portugal|King João VI]] of the [[United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves]] in [[Rio de Janeiro]], 6 February 1818]] |
|||
In late 1807, Spanish and Napoleonic forces threatened the security of [[continental Portugal]], causing [[John VI of Portugal|Prince Regent |
In late 1807, Spanish and Napoleonic forces threatened the security of [[continental Portugal]], causing [[John VI of Portugal|Prince Regent John]], in the name of [[Maria I of Portugal|Queen Maria I]], to [[Transfer of the Portuguese court to Brazil|move the royal court]] from [[Lisbon]] to [[Rio de Janeiro]].<ref name="Boxer, p. 213">Boxer, p. 213</ref> There they established some of Brazil's first financial institutions, such as its local [[stock exchange]]s<ref>Marta Barcellos & Simone Azevedo; ''Histórias do Mercado de Capitais no Brasil'' ("Financial Markets' Histories in Brazil") (Portuguese) Campus Elsevier 2011 {{ISBN|85-352-3994-4}} Introduction (by Ney Carvalho), Intro. p. xiv</ref> and its [[Banco do Brasil|National Bank]], additionally ending the Portuguese monopoly on Brazilian trade and opening Brazil's ports to other nations. In 1809, in retaliation for being forced into exile, the Prince Regent ordered the [[Portuguese conquest of French Guiana|conquest of French Guiana]].<ref>Bueno, p. 145.</ref> |
||
With the end of the [[Peninsular War]] in 1814, the courts of Europe demanded that Queen Maria I and Prince Regent |
With the end of the [[Peninsular War]] in 1814, the courts of Europe demanded that Queen Maria I and Prince Regent John return to Portugal, deeming it unfit for the head of an ancient European monarchy to reside in a [[colony]]. In 1815, to justify continuing to live in Brazil, where the royal court had thrived for six years, the Crown established the [[United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves]], thus creating a [[pluricontinental]] transatlantic monarchic state.<ref name="Mosher2008">{{Cite book |last=Jeffrey C. Mosher |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=T_yszWOZUCkC&pg=PA9 |title=Political Struggle, Ideology, and State Building: Pernambuco and the Construction of Brazil, 1817–1850 |publisher=U of Nebraska Press |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-8032-3247-1 |page=9 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183447/https://books.google.com/books?id=T_yszWOZUCkC&pg=PA9#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> However, the leadership in Portugal, resentful of the new status of its larger colony, continued to demand the return of the court to Lisbon (see [[Liberal Revolution of 1820]]). In 1821, acceding to the demands of revolutionaries who had taken the city of [[Porto]],<ref name="Adelman2006">{{Cite book |last=Jeremy Adelman |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nvFpURNsBRIC&pg=PA334 |title=Sovereignty and Revolution in the Iberian Atlantic |publisher=Princeton University Press |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-691-12664-7 |pages=334– |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183956/https://books.google.com/books?id=nvFpURNsBRIC&pg=PA334#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> John VI departed for Lisbon. There he swore an oath to the new constitution, leaving his son, [[Pedro I of Brazil|Prince Pedro de Alcântara]], as Regent of the [[Kingdom of Brazil]].<ref>Lustosa, pp. 109–110</ref> |
||
===Independent empire=== |
=== Independent empire === |
||
{{Main|Independence of Brazil|Empire of Brazil}} |
{{Main|Independence of Brazil|Empire of Brazil}} |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Pedro Américo - Independência ou Morte - cores ajustadas.jpg|thumb|Declaration of the [[War of Independence of Brazil|Brazilian independence]] by [[Pedro I of Brazil|Pedro I]] on [[Independence Day (Brazil)|7 September 1822]]]] |
||
Tensions between Portuguese and Brazilians increased |
Tensions between Portuguese and Brazilians increased and the [[Portuguese Cortes]], guided by the new political regime imposed by the [[Liberal Revolution of 1820|Liberal Revolution]], tried to re-establish Brazil as a colony.<ref>Lustosa, pp. 117–19</ref> The Brazilians refused to yield, and Prince Pedro decided to stand with them, [[Brazilian Declaration of Independence|declaring the country's independence from Portugal]] on 7 September 1822.<ref>Lustosa, pp. 150–153</ref> A month later, Prince Pedro was declared the first [[Emperor of Brazil]], with the royal title of Dom [[Pedro I of Brazil|Pedro I]], resulting in the founding of the [[Empire of Brazil]].<ref>Vianna, p. 418</ref> |
||
The [[Brazilian War of Independence]], which had already begun along this process, spread through the northern, northeastern regions and in [[Cisplatina]] province.<ref>Diégues 2004, pp. 168, 164, 178</ref> The last Portuguese soldiers surrendered on 8 March 1824;<ref>Diégues 2004, pp. 179–80</ref> Portugal officially recognized |
The [[Brazilian War of Independence]], which had already begun along this process, spread through the northern, northeastern regions and in the [[Cisplatina]] province.<ref>Diégues 2004, pp. 168, 164, 178</ref> The last Portuguese soldiers surrendered on 8 March 1824;<ref>Diégues 2004, pp. 179–80</ref> Portugal [[Treaty of Rio de Janeiro (1825)|officially recognized]] Brazilian independence on 29 August 1825.<ref>Lustosa, p. 208</ref> |
||
On 7 April 1831, worn down by years of administrative turmoil and political dissent with both liberal and conservative sides of politics, including an attempt of [[Confederation of the Equator|republican secession]] |
On 7 April 1831, worn down by years of administrative turmoil and political dissent with both liberal and conservative sides of politics, including an attempt of [[Confederation of the Equator|republican secession]]{{sfnp|Fausto|1999|pp=82–83}} and unreconciled to the way that absolutists in Portugal had given in the succession of King John VI, Pedro I departed for Portugal to [[Liberal Wars|reclaim his daughter's crown]] after [[Abdication of Pedro I of Brazil|abdicating the Brazilian throne]] in favor of his five-year-old son and heir (Dom [[Pedro II of Brazil|Pedro II]]).<ref>Lyra (v. 1), p. 17</ref> |
||
[[File:Pedro Américo - D. Pedro II na abertura da Assembléia Geral.jpg|thumb|upright|[[Pedro II of Brazil|Pedro II]], [[List of monarchs of Brazil|Emperor of Brazil]] between 1831 and 1889 |
[[File:Pedro Américo - D. Pedro II na abertura da Assembléia Geral.jpg|left|thumb|upright|[[Pedro II of Brazil|Pedro II]], [[List of monarchs of Brazil|Emperor of Brazil]] between 1831 and 1889]] |
||
As the new Emperor could not exert his constitutional powers until he came of age, a [[Regency ( |
As the new Emperor could not exert his constitutional powers until he came of age, a [[Regency period (Empire of Brazil)|regency]] was set up by the National Assembly.<ref>Carvalho 2007, p. 21</ref> In the absence of a charismatic figure who could represent a moderate face of power, during this period a series of localized rebellions took place, such as the [[Cabanagem]] in [[Grão-Pará Province|Grão-Pará]], the [[Malê Revolt]] in Salvador, the [[Balaiada]] ([[Maranhão]]), the [[Sabinada]] ([[Bahia]]), and the [[Ragamuffin War]], which began in [[Rio Grande do Sul]] and was supported by [[Giuseppe Garibaldi]]. These emerged from the provinces' dissatisfaction with the central power, coupled with old and latent social tensions peculiar to a vast, slaveholding and newly independent [[nation state]].{{sfnp|Fausto|1999|loc=Chapter 2, 2.1 to 2.3}} This period of internal political and social upheaval, which included the [[Praieira revolt]] in [[Pernambuco]], was overcome only at the end of the 1840s, years after the end of the regency, which occurred with the [[Dom Pedro II#Early coronation|premature coronation of Pedro II]] in 1841.{{sfnp|Fausto|1999}} |
||
During the last phase of the monarchy, internal political debate centered on the issue of slavery. The [[Atlantic slave trade]] was abandoned in 1850,<ref>[[Leslie Bethell|Bethell, Leslie]] "The Abolition of the Brazilian Slave Trade: Britain, Brazil and the Slave Trade" [[Cambridge University Press]] 1970, ''"Cambridge Latin American Studides"'', Chapters 9 to 12. [https://books.google.com/books?id=2LsNTUPI_6sC View on Google Books]</ref> as a result of the [[United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland|British]] [[Aberdeen Act]], but only in |
During the last phase of the monarchy, internal political debate centered on the issue of slavery. The [[Atlantic slave trade to Brazil|Atlantic slave trade]] was abandoned in 1850,<ref>[[Leslie Bethell|Bethell, Leslie]] "The Abolition of the Brazilian Slave Trade: Britain, Brazil and the Slave Trade" [[Cambridge University Press]] 1970, ''"Cambridge Latin American Studides"'', Chapters 9 to 12. [https://books.google.com/books?id=2LsNTUPI_6sC View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183843/https://books.google.com/books?id=2LsNTUPI_6sC |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref> as a result of the [[United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland|British]] [[Aberdeen Act]] and the [[Eusébio de Queirós Law]], but only in May 1888, after a long process of internal mobilization and debate for an ethical and legal dismantling of [[Slavery in Brazil|slavery in the country]], was the institution formally abolished with the approval of the [[Lei Áurea|Golden Law]].<ref>Scott, Rebecca and others, ''The Abolition of Slavery and the Aftermath of Emancipation in Brazil'', Duke University Press 1988 {{ISBN|0-8223-0888-6}} [[Seymour Drescher]], Chap. 2: "Brazilian Abolition in Comparative Perspective"</ref> |
||
The foreign-affairs policies of the monarchy dealt with issues with the countries of the [[Southern Cone]] with whom Brazil had borders. Long after the [[Cisplatine War]] that resulted in independence |
The foreign-affairs policies of the monarchy dealt with issues with the countries of the [[Southern Cone]] with whom Brazil had borders. Long after the [[Cisplatine War]] that resulted in the independence of [[Uruguay]],<ref>Levine, Robert M. "The history of Brazil" Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc. 1999, p. 62, [https://books.google.com/books?id=8RpIxe2utj8C&pg=PA62 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183943/https://books.google.com/books?id=8RpIxe2utj8C&pg=PA62 |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref> Brazil won three international wars during the 58-year reign of Pedro II: the [[Platine War]], the [[Uruguayan War]] and the devastating [[Paraguayan War]], the largest [[war effort]] in Brazilian history.<ref>Lyra (v.1), pp. 164, 225, 272</ref>{{sfnp|Fausto|1999|loc=Chapter 2, p. 83, and 2.6 "The Paraguayan War"}} |
||
Although there was no desire among the majority of Brazilians to change the country's [[form of government]],{{sfn|Ermakoff|2006|p=189}} on 15 November 1889, in disagreement with the majority of [[Imperial Brazilian Army|Army]] officers, as well as with rural and financial elites (for different reasons), the monarchy was overthrown by a military coup.<ref>{{ |
Although there was no desire among the majority of Brazilians to change the country's [[form of government]],{{sfn|Ermakoff|2006|p=189}} on 15 November 1889, in disagreement with the majority of the [[Imperial Brazilian Army|Imperial Army]] officers, as well as with rural and financial elites (for different reasons), the monarchy was overthrown by a military coup.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Smallman |first=Shawn C. |title=Fear in Memory in the Brazilian Army and Society |publisher=[[University of North Carolina]] Press |year=2002 |isbn=978-0-8078-5359-7 |pages=16–18 |chapter=The Overthrow of the Empire}}</ref> A few days later, the [[Flag of Brazil|national flag]] was replaced with a new design that included the national motto "''Ordem e Progresso''", influenced by [[positivism]]. 15 November is now [[Republic Day]], a national holiday.<ref>{{Cite news |date=15 November 2017 |title=Brazil's Proclamation of the Republic through the press |language=en-US |work=The Brazilian Report |url=https://brazilian.report/opinion/2017/11/15/brazils-press-republic-day/ |access-date=13 November 2018 |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193405/https://brazilian.report/opinion/2017/11/15/brazils-press-republic-day/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
===Early republic=== |
=== Early republic === |
||
{{Main|First Brazilian Republic|Vargas Era |
{{Main|First Brazilian Republic|Vargas Era|Second Brazilian Republic}} |
||
{{multiple image |
|||
[[File:Proclamação da República by Benedito Calixto 1893.jpg|thumb|upright=1.1|left|''[[Proclamation of the Republic (Brazil)|Proclamation of the Republic]]'', 1893, oil on canvas by [[Benedito Calixto]].]] |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| image1 = Proclamação da República by Benedito Calixto 1893.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = ''[[Proclamation of the Republic (Brazil)|Proclamation of the Republic]]'', 1893, oil on canvas by [[Benedito Calixto]] |
|||
| image2 = Revolução de 1930 (cropped).jpg |
|||
| caption2 = [[Getúlio Vargas]] (''center'') during the [[Revolution of 1930]] |
|||
| image3 = Massarosaw.jpg |
|||
| caption3 = [[Brazilian Expeditionary Force]] in [[Massarosa]], [[Italian Social Republic|Italy]], during [[World War II|WWII]] |
|||
}} |
|||
The early republican government was |
The early republican government was a military dictatorship, with the army dominating affairs both in Rio de Janeiro and in the states. Freedom of the press disappeared and elections were controlled by those in power.{{sfnp|Smallman|2002|loc=end of Chapter 1, from p. 18 "Military rule"}} Not until 1894, following an [[Encilhamento|economic crisis]] and [[Revolta da Armada|a military one]], did civilians take power, remaining there until October 1930.{{sfnp|Smallman|2002|pp=21–26}}<ref>Triner, Gail D. "Banking and Economic Development: Brazil, 1889–1930" Palgrave 2000, pp. 69–74 {{ISBN|0-312-23399-X}}</ref><ref>Needell, Jeffrey D. "A Tropical Belle Epoque: Elite Culture and Society in Turn-of-the-Century Rio de Janeiro" Cambridge University Press 2010, pp. 10, 12</ref> |
||
In relation to its foreign policy, the country in this first republican period maintained a relative balance characterized by a success in resolving border disputes with neighboring countries,<ref>David R. Mares; "Violent peace: militarized interstate bargaining in Latin America" [[Columbia University]] Press 2001 Chapter 5 p. 125</ref> only broken by the [[Acre War]] (1899–1902) and [[Brazil during World War I|its involvement]] in [[World War I]] (1914–1918),<ref>Bradford Burns 1993, p. 305</ref><ref>M.Sharp, I. Westwell & J.Westwood; "History of World War I, Volume 1" Marshall Cavendish Corporation 2002, p. 97</ref><ref>{{Citation |title=Uma história diplomática do Brasil, 1531–1945 |pages=265–69}}</ref> followed by a failed attempt to exert a prominent role in the [[League of Nations]];<ref>Charles Howard Ellis; "The origin, structure & working of the League of Nations" The LawBook Exchange Ltd 2003 pp. 105, 145</ref> Internally, from the crisis of ''Encilhamento''<ref>{{Citation |last=Viscount of Taunay |title=O encilhamento: scenas contemporaneas da bolsa em 1890, 1891 e 1892 |year=1893 |publisher=Melhoramentos}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last=Nassif |first=Luís |title=Os cabeças-de-planilha |pages=69–107 |year=2007 |publisher=Ediouro |isbn=978-85-00-02094-0}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last=de Carvalho |first=Ney O. Ribeiro |title=O Encilhamento: anatomia de uma bolha brasileira |year=2004 |publisher=Bovespa |isbn=978-85-904019-1-9}}</ref> and the [[Revolta da Armada|Navy Revolts]],<ref>{{Citation |last=Martins |first=Hélio L |title=A Revolta da Armada |year=1997 |publisher=BibliEx}}</ref> a prolonged cycle of financial, political and social instability began until the 1920s, keeping the country besieged by various rebellions, both civilian<ref>{{Citation |last=Moniz |first=Edmundo |title=Canudos: a luta pela terra |year=1984 |publisher=Global}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last=Sevcenko |first=Nicolau |title=A Revolta da Vacina |year=2010 |publisher=Cosac Naify |isbn=978-85-7503-868-0}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last=de Moura |first=Aureliano P |title=Contestado: a guerra cabocla |year=2003 |publisher=Biblioteca do Exército}}</ref> and military.<ref>{{Citation |last=Thompson |first=Arthur |title=Guerra civil do Brazil de 1893–1895 |year=1934 |publisher=Ravaro}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last=Roland |first=Maria Inês |title=A Revolta da Chibata |year=2000 |publisher=Saraiva |isbn=978-85-02-03095-4}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last=Forjaz |first=Maria CS |title=Tenentismo e politica |year=1977 |publisher=Paz e Terra}}</ref> |
|||
If in relation to its foreign policy, the country in this first republican period maintained a relative balance characterized by a success in resolving border disputes with neighboring countries,<ref> |
|||
David R. Mares; "Violent peace: militarized interstate bargaining in Latin America" [[Columbia University]] Press 2001 Chapter 5 p. 125 |
|||
</ref> only broken by the [[Acre War]] (1899–1902) and [[Brazil during World War I|its involvement]] in [[World War I]] (1914–1918),<ref> |
|||
Bradford Burns 1993, p. 305 |
|||
</ref><ref> |
|||
M.Sharp, I. Westwell & J.Westwood; "History of World War I, Volume 1" Marshall Cavendish Corporation 2002, p. 97 |
|||
</ref><ref> |
|||
{{Citation |title= Uma história diplomática do Brasil, 1531–1945 |pages= 265–69}}</ref> followed by a failed attempt to exert a prominent role in the [[League of Nations]];<ref>Charles Howard Ellis; "The origin, structure & working of the League of Nations" The LawBook Exchange Ltd 2003 pp. 105, 145</ref> Internally, from the ''crisis of Encilhamento''<ref>{{Citation |author= Viscount of Taunay |title= O encilhamento: scenas contemporaneas da bolsa em 1890, 1891 e 1892 |publisher= Melhoramentos |year=1893}}</ref><ref> |
|||
{{Citation |last = Nassif |first = Luís |title= Os cabeças-de-planilha |publisher= Ediouro |year= 2007 | isbn = 978-85-00-02094-0 |pages= 69–107}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |first= Ney O. Ribeiro |last= de Carvalho |title= O Encilhamento: anatomia de uma bolha brasileira |publisher= Bovespa |year= 2004 |isbn = 978-85-904019-1-9}}</ref> and the [[Revolta da Armada|Armada Revolts]],<ref>{{Citation |first = Hélio L |last = Martins |title= A Revolta da Armada |publisher= BibliEx |year= 1997}}</ref> a prolonged cycle of financial, political and social instability began until the 1920s, keeping the country besieged by various rebellions, both civilian<ref>{{Citation |first = Edmundo |last = Moniz |title= Canudos: a luta pela terra |publisher= Global |year= 1984}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last = Sevcenko |first = Nicolau |title= A Revolta da Vacina | publisher= Cosac Naify |year= 2010 | isbn = 978-85-7503-868-0}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |first = Aureliano P |last = de Moura |title= Contestado: a guerra cabocla |publisher= Biblioteca do Exército |year= 2003}}</ref> and military.<ref>{{Citation |first = Arthur |last = Thompson |title= Guerra civil do Brazil de 1893–1895 |publisher= Ravaro |year= 1934}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last = Roland |first = Maria Inês |title= A Revolta da Chibata |publisher= Saraiva |year= 2000 | isbn = 978-85-02-03095-4}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |first = Maria CS |last = Forjaz |title= Tenentismo e politica |publisher= Paz e Terra |year= 1977}}</ref> |
|||
{{Multiple image |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
Little by little, [[Rebellions and revolutions in Brazil#1st Republican period (1889–1930)|a cycle of general instability]] sparked by these crises undermined the regime to such an extent that in the wake of the murder of his running mate, the defeated opposition presidential candidate [[Getúlio Vargas]], supported by most of the military, successfully led the [[Brazilian Revolution of 1930|Revolution of 1930]].<ref>Levine; Robert M. & Crocitti; John J. ''The Brazil Reader: History, Culture, Politics'', Duke University Press 1999, IV – The Vargas Era</ref><ref>Keen, Benjamin / Haynes, Kate ''A History of Latin America; Volume 2'', Waldsworth Cengage Learning 2004, pp. 356–57</ref> Vargas and the military were supposed to assume power temporarily, but instead closed down Congress, extinguished the Constitution, ruled with emergency powers and replaced the states' governors with his own supporters.<ref>McCann; Frank D. ''Soldiers of the Patria: A History of the Brazilian Army, 1889–1937'', [[Stanford University]] Press 2004, p. 303 {{ISBN|0-8047-3222-1}}</ref><ref>Ibidem Williams 2001</ref> |
|||
| image1 = 50º Aniversário da República Brasileira.png |
|||
| caption1 = In half of the first 100 years of republic, the [[Brazilian Army|Army]] exercised power directly or through figures like [[Getúlio Vargas]] (center). |
|||
In the 1930s, three attempts to remove Vargas and his supporters from power failed. The first was the [[Constitutionalist Revolution]] in 1932, led by São Paulo's [[oligarchy]]. The second was a [[Brazilian uprising of 1935|Communist uprising]] in November 1935, and the last one a ''[[Integralist Uprising|putsch]]'' attempt by [[Brazilian Integralism|local fascists]] in May 1938.<ref>E. Bradford Burns; ''A History of Brazil'' Columbia University Press 1993 p. 352 {{ISBN|978-0-231-07955-6}}</ref><ref>Dulles, John W.F. ''Anarchists and Communists in Brazil, 1900–1935'' University of Texas Press 2012 {{ISBN|0-292-74076-X}}</ref><ref>Frank M. Colby, Allen L. Churchill, Herbert T. Wade & Frank H. Vizetelly; ''The New international year book'' Dodd, Mead & Co. 1989, p. 102 "The Fascist Revolt"</ref> The 1935 uprising created a security crisis in which Congress transferred more power to the executive branch. The [[1937 Brazilian coup d'état|1937 ''coup d'état'']] resulted in the cancellation of the 1938 election and formalized Vargas as dictator, beginning the [[Estado Novo (Brazil)|Estado Novo]] era. During this period, government brutality and censorship of the press increased.<ref>Bourne, Richard ''Getulio Vargas of Brazil, 1883–1954'' C. Knight 1974, p. 77</ref> |
|||
| image2 = Massarosaw.jpg |
|||
| caption2 = Soldiers of the [[Brazilian Expeditionary Force]] greet [[Italian people|Italian civilians]] in [[Massarosa]], during [[World War II]]. Brazil was the only independent Latin American country to send ground troops to fight in WWII. |
|||
}} |
|||
Little by little, [[Rebellions and revolutions in Brazil#1st Republican period (1889-1930)|a cycle of general instability]] sparked by these crises undermined the regime to such an extent that in the wake of the murder of his running mate, the defeated opposition presidential candidate [[Getúlio Vargas]], supported by most of the military, successfully led the [[Brazilian Revolution of 1930|October 1930 Coup]].<ref>Levine; Robert M. & Crocitti; John J. ''The Brazil Reader: History, Culture, Politics'', Duke University Press 1999, IV – The Vargas Era</ref><ref>Keen, Benjamin / Haynes, Kate ''A History of Latin America; Volume 2'', Waldsworth Cengage Learning 2004, pp. 356–57</ref> Vargas and the military were supposed to assume power temporarily, but instead closed the Congress, extinguished the Constitution, ruled with emergency powers and replaced the states' governors with their own supporters.<ref>McCann; Frank D. ''Soldiers of the Patria: A History of the Brazilian Army, 1889–1937'', [[Stanford University]] Press 2004, p. 303 {{ISBN|0-8047-3222-1}}</ref><ref>Ibidem Williams 2001</ref> |
|||
In the 1930s, three failed attempts to remove Vargas and his supporters from power occurred. The first was the [[Constitutionalist Revolution]] in 1932, led by the [[São Paulo (state)|Paulista]] [[oligarchy]]. The second was a [[Brazilian uprising of 1935|Communist uprising]] in November 1935, and the last one a ''putsch'' attempt by [[Brazilian Integralism|local fascists]] in May 1938.<ref>E. Bradford Burns; ''A History of Brazil'' Columbia University Press 1993 p. 352 {{ISBN|978-0-231-07955-6}}</ref><ref>Dulles, John W.F. ''Anarchists and Communists in Brazil, 1900–1935'' University of Texas Press 2012 {{ISBN|0-292-74076-X}}</ref><ref>Frank M. Colby, Allen L. Churchill, Herbert T. Wade & Frank H. Vizetelly; ''The New international year book'' Dodd, Mead & Co. 1989, p. 102 "The Fascist Revolt"</ref> The 1935 uprising created a security crisis in which the Congress transferred more power to the executive. The 1937 ''coup d'état'' resulted in the cancellation of the 1938 election, formalized Vargas as dictator, beginning the [[Estado Novo (Brazil)|Estado Novo]] era, which was noted for government brutality and censorship of the press.<ref>Bourne, Richard ''Getulio Vargas of Brazil, 1883–1954'' C. Knight 1974, p. 77</ref> |
|||
During [[World War II]], Brazil remained neutral until August 1942, when the country suffered [[Submarine warfare#Atlantic ocean|retaliation]] by [[Nazi Germany]] and [[Italy under fascism|Fascist Italy]] in a strategic dispute over the South Atlantic, and, therefore, [[Brazil in World War II|entered the war]] on the [[Allies of World War II|allied side]].<ref>Scheina, Robert L. ''Latin America's Wars Vol.II: The Age of the Professional Soldier, 1900–2001''. Potomac Books, 2003 {{ISBN|1-57488-452-2}} Part 9; Ch. 17 – World War II, Brazil, and Mexico, 1942–45</ref><ref>Thomas M. Leonard & John F. Bratzel; ''Latin America during World War II'' Rowman & Littlefield Publishers Inc. 2007 p. 150</ref><ref>Mónica Hirst & [[Andrew Hurrell]]; ''The United States and Brazil: A Long Road of Unmet Expectations'', Taylor & Francis Books 2005 {{ISBN|0-415-95066-X}} pp. 4–5</ref> In addition to [[Battle of the Atlantic#South Atlantic (May 1942 – September 1943)|its participation in the battle of the Atlantic]], Brazil also sent an [[Brazilian Expeditionary Force|expeditionary force]] to fight in the [[Italian Campaign (World War II)|Italian campaign]].<ref>{{Citation |last1=Castro |first1=Celso |title=Nova história militar brasileira |pages=13–14 |year=2004 |publisher=Fundação Getúlio Vargas |isbn=978-85-225-0496-1 |last2=Izecksohn |first2=Vitor |last3=Kraay |first3=Hendrik}}</ref> |
|||
With the Allied victory in 1945 and the end of the |
With the Allied victory in 1945 and the end of the fascist regimes in Europe, Vargas's position became unsustainable, and he was [[1945 Brazilian coup d'état|swiftly overthrown]] in another military coup, with democracy "reinstated" by the same army that had ended it 15 years earlier.<ref>McCann 2004, p. 441</ref> Vargas committed suicide in August 1954 amid a political crisis, after having returned to power by election in 1950.<ref>Roett; Riordan ''Brazil: Politics in a Patrimonial Society'', GreenWood Publishing Group 1999, pp. 106–08 {{ISBN|0-275-95899-X}}</ref><ref>Keen & Haynes 2004, pp. 361–62</ref> |
||
===Contemporary era=== |
=== Contemporary era === |
||
{{Main|Military dictatorship in Brazil|History of Brazil since 1985}} |
{{Main|Military dictatorship in Brazil|History of Brazil since 1985}} |
||
[[File:Construção do Congresso Nacional Esplanada dos Ministérios 1959-10 (cropped).jpg|thumb|Construction of the [[National Congress Palace|National Congress building]] in [[Brasília]], 1959, during the [[Juscelino Kubitschek#Presidency|JK administration]]]] |
|||
Several brief interim governments followed Vargas's suicide.<ref>Skidmore, p. 201</ref> [[Juscelino Kubitschek]] became president in 1956 and assumed a conciliatory posture towards the [[Opposition (politics)|political opposition]] that allowed him to govern without major crises.<ref>Skidmore, pp. 202–203</ref> The economy and industrial sector grew remarkably,<ref>Skidmore, p. 204</ref> but his greatest achievement was the construction of the new capital city of [[Brasília]], inaugurated in 1960.<ref>Skidmore, pp. 204–205</ref> |
Several brief interim governments followed Vargas's suicide.<ref>Skidmore, p. 201</ref> [[Juscelino Kubitschek]] became president in 1956 and assumed a conciliatory posture towards the [[Opposition (politics)|political opposition]] that allowed him to govern without major crises.<ref>Skidmore, pp. 202–203</ref> The economy and industrial sector grew remarkably,<ref>Skidmore, p. 204</ref> but his greatest achievement was the construction of the new capital city of [[Brasília]], inaugurated in 1960.<ref>Skidmore, pp. 204–205</ref> Kubitschek's successor, [[Jânio Quadros]], resigned in 1961 less than a year after taking office.<ref>Skidmore, pp. 209–210</ref> His vice-president, [[João Goulart]], assumed the presidency, but aroused strong political opposition<ref>Skidmore, p. 210</ref> and was [[1964 Brazilian coup d'état|deposed in April 1964]] by a coup that resulted in a [[Military dictatorship in Brazil|military dictatorship]].<ref>Fausto (2005), p. 397</ref> |
||
[[File:Tanques ocupam a Avenida Presidente Vargas, 1968-04-04.jpg|thumb|[[M41 Walker Bulldog|M41s]] along the [[Avenida Presidente Vargas]], [[Rio de Janeiro]], in April 1968, during the [[Military dictatorship in Brazil|military dictatorship]]]] |
|||
{{Multiple image |
|||
| align = left |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
The new regime was intended to be transitory<ref>Gaspari, ''A Ditadura Envergonhada'', pp. 141–42.</ref> but gradually closed in on itself and became a full dictatorship with the promulgation of the [[AI-5|Fifth Institutional Act]] in 1968.<ref name="Gaspari p.35">Gaspari, ''A Ditadura Envergonhada'', p. 35.</ref> Oppression was not limited to those who resorted to guerrilla tactics to fight the regime, but also reached institutional opponents, artists, journalists and other members of civil society,{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VhkvhllLooUC&pg=PA395 395], last paragraph}}<ref>Richard Young, Odile Cisneros "Historical Dictionary of Latin American Literature and Theater" Scare Crow Press 2011, p. 224, 2nd § [https://books.google.com/books?id=i0ZyleoLY5UC&pg=PA224 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183956/https://books.google.com/books?id=i0ZyleoLY5UC&pg=PA224#v=onepage&q&f=false |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref> inside and outside the country through the infamous "[[Operation Condor]]".<ref>Laurence Burgorgue-Larsen & Amaya Úbeda de Torres "The Inter-American Court of Human Rights: Case Law and Commentary" Oxford University Press 2011 {{ISBN|978-0-19-958878-7}} p. 299 [https://books.google.com/books?id=fQpnBsRWNlYC&pg=PA299 View on Google Books] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183958/https://books.google.com/books?id=fQpnBsRWNlYC&pg=PA299 |date=29 November 2023 }}</ref>{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VhkvhllLooUC&pg=PA396 396]}} Like other brutal [[authoritarianism|authoritarian regimes]], due to an economic boom, known as the "[[Brazilian Miracle|economic miracle]]", the regime reached a peak in popularity in the early 1970s.{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VhkvhllLooUC&pg=PA395 395–97]}} |
|||
| image1 = Construção do Congresso Nacional Esplanada dos Ministérios 1959-10.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = Construction of the building of [[National Congress of Brazil]] in [[Brasília]], the new capital, 1959. |
|||
Slowly, however, the wear and tear of years of dictatorial power had not slowed the repression, even after the defeat of the leftist guerrillas.<ref>Bradford Burns 1993, p. 457</ref> The inability to deal with the economic crises of the period and popular pressure made an opening policy inevitable, which from the regime side was led by Generals [[Ernesto Geisel]] and [[Golbery do Couto e Silva]].{{sfnp|Fausto|1999|loc=Chapter 6 "The military government and the transition to democracy (1964–1984)"}} With the enactment of the [[Amnesty law#Brazil|Amnesty Law]] in 1979, Brazil began a slow [[Political opening of Brazil|return to democracy]], which was completed during the 1980s.{{sfnp|Fausto|1999}} |
|||
|image2 = Tanques ocupam a Avenida Presidente Vargas, 1968-04-04.jpg |
|||
[[File:Ulyssesguimaraesconstituicao.jpg|thumb|[[Ulysses Guimarães]] holding the [[Constitution of Brazil|Constitution of 1988]]]] |
|||
|caption2 =[[M41 Walker Bulldog|M41s]] along the [[Avenida Presidente Vargas]] during the [[Brazilian military government|military government]]. |
|||
}} |
|||
Civilians returned to power in 1985 when [[José Sarney]] assumed the presidency. He became unpopular during his tenure through failure to control the economic crisis and [[hyperinflation]] he inherited from the military regime.<ref>Fausto (2005), pp. 464–65.</ref> Sarney's unsuccessful government led to the [[Brazilian presidential election, 1989|election in 1989]] of the almost-unknown [[Fernando Collor de Mello|Fernando Collor]], who was subsequently impeached by the National Congress in 1992.<ref>Fausto (2005), pp. 465, 475.</ref> Collor was succeeded by his vice-president, [[Itamar Franco]], who appointed [[Fernando Henrique Cardoso]] Minister of Finance. In 1994, Cardoso produced a highly successful [[Plano Real]],<ref>Skidmore, p. 311.</ref> that, after decades of failed economic plans made by previous governments attempting to curb hyperinflation, finally stabilized the Brazilian economy.{{sfnp|Fausto|1999|loc=Epilogue}}<ref>Fausto (2005), p. 482.</ref> Cardoso won the [[Brazilian presidential election, 1994|1994 election]], and [[Brazilian presidential election, 1998|again in 1998]].<ref>Fausto (2005), p. 474.</ref> |
|||
Kubitschek's successor, [[Jânio Quadros]], resigned in 1961 less than a year after taking office.<ref>Skidmore, pp. 209–210</ref> His vice-president, [[João Goulart]], assumed the presidency, but aroused strong political opposition<ref>Skidmore, p. 210</ref> and was [[1964 Brazilian coup d'état|deposed in April 1964]] by a coup that resulted in a [[Brazilian military government|military regime]].<ref>Fausto (2005), p. 397</ref> |
|||
The [[peaceful transition of power]] from Cardoso to his main opposition leader, [[Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva]] ([[Brazilian presidential election, 2002|elected in 2002]] and [[Brazilian presidential election, 2006|re-elected in 2006]]), was seen as proof that Brazil had achieved a long-sought political stability.<ref>Fausto (2005), p. 502.</ref><ref>Zirin, 2014. Chapter 3</ref> However, sparked by indignation and frustrations accumulated over decades from corruption, [[Police brutality by country#Brazil|police brutality]], inefficiencies of the political [[The Establishment|establishment]] and [[public service]], [[2013 protests in Brazil|numerous peaceful protests]] erupted in Brazil in the middle of the first term of [[Dilma Rousseff]], who had succeeded Lula after winning election [[Brazilian presidential election, 2010|in 2010]] and again [[Brazilian presidential election, 2014|in 2014]] by narrow margins.<ref>[https://www.theguardian.com/world/2013/jun/22/urban-protest-changing-global-social-network "Global protest grows as citizens lose faith in politics and the State"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210608173307/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2013/jun/22/urban-protest-changing-global-social-network |date=8 June 2021 }} article on "the Guardian"</ref><ref>Zirin, 2014. Chapter 7 & Conclusion.</ref> |
|||
The new regime was intended to be transitory<ref>Gaspari, ''A Ditadura Envergonhada'', pp. 141–42.</ref> but gradually closed in on itself and became a full dictatorship with the promulgation of the [[AI-5|Fifth Institutional Act]] in 1968.<ref name="Gaspari p.35">Gaspari, ''A Ditadura Envergonhada'', p. 35.</ref> Oppression was not limited to those who resorted to guerrilla tactics to fight the regime, but also reached institutional opponents, artists, journalists and other members of civil society,{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VhkvhllLooUC&pg=PA395 395], last paragraph}}<ref>Richard Young, Odile Cisneros "Historical Dictionary of Latin American Literature and Theater" Scare Crow Press 2011, p. 224, 2nd § [https://books.google.com/books?id=i0ZyleoLY5UC&pg=PA224 View on Google Books]</ref> inside and outside the country through the infamous "[[Operation Condor]]".<ref>Laurence Burgorgue-Larsen & Amaya Úbeda de Torres "The Inter-American Court of Human Rights: Case Law and Commentary" Oxford University Press 2011 {{ISBN|978-0-19-958878-7}} p. 299 [https://books.google.com/books?id=fQpnBsRWNlYC&pg=PA299 View on Google Books]</ref>{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VhkvhllLooUC&pg=PA396 396]}} Despite its brutality, like other [[authoritarianism|authoritarian regimes]], due to an economic boom, known as an "economic miracle", the regime reached a peak in popularity in the early 1970s.{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VhkvhllLooUC&pg=PA395 395–97]}} |
|||
Rousseff [[Impeachment of Dilma Rousseff|was impeached]] by the [[Brazilian Congress]] in 2016, halfway into her second term,<ref name="auto1">{{Cite news |last=Jonathan Watts & Donna Bowater |title=Dilma Rousseff impeached by Brazilian senate |work=The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/aug/31/dilma-rousseff-impeached-president-brazilian-senate-michel-temer |access-date=31 August 2016 |archive-date=31 August 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160831175437/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/aug/31/dilma-rousseff-impeached-president-brazilian-senate-michel-temer |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>[https://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/01/world/americas/brazil-impeachment-coup.html Article of] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210514001235/https://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/01/world/americas/brazil-impeachment-coup.html |date=14 May 2021 }} New York Times about the denouement of Rousseff's impeachment process.</ref> and replaced by her Vice-president [[Michel Temer]], who assumed full presidential powers after Rousseff's impeachment was accepted on 31 August. Large street [[2015–16 protests in Brazil|protests for and against her]] took place during the impeachment process.<ref>[http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/28879ada-0499-11e6-96e5-f85cb08b0730.html#axzz46ZJ07xgT Article] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160624140848/http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/28879ada-0499-11e6-96e5-f85cb08b0730.html#axzz46ZJ07xgT |date=24 June 2016 }} in ''[[Financial Times]]'' (18 April 2016) about the political ambiance in Brazil on the day vote for the Deputies chamber decision about open an impeachment procedure against President Dilma. 2nd to 4th paragraph.</ref> The charges against her were fueled by political and economic crises along with evidence of involvement with politicians from all the primary political parties. In 2017, the Supreme Court requested the investigation of 71 Brazilian lawmakers and nine ministers of President [[Michel Temer]]'s cabinet who were allegedly linked to the [[Operation Car Wash|Petrobras corruption scandal]].<ref>[https://www.reuters.com/article/brazil-politics-probes-idUSL1N1HJ1NO? "Brazil supreme court judge orders probe into nine ministers – paper"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170816074621/https://www.reuters.com/article/brazil-politics-probes-idUSL1N1HJ1NO |date=16 August 2017 }}. Reuters. 11 April 2017.</ref> President Temer himself was also accused of [[Corruption in Brazil|corruption]].<ref>[https://www.nytimes.com/2017/06/26/world/americas/brazil-temer-corruption-charge-joesley-batista.html "President Michel Temer of Brazil Is Charged With Corruption"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210414030047/https://www.nytimes.com/2017/06/26/world/americas/brazil-temer-corruption-charge-joesley-batista.html |date=14 April 2021 }}. ''The New York Times''. 26 June 2017.</ref> According to a 2018 poll, 62% of the population said that corruption was Brazil's biggest problem.<ref>{{Cite news |title=A scary election in Brazil |language=en |newspaper=The Economist |url=https://www.economist.com/briefing/2018/09/20/a-scary-election-in-brazil |access-date=1 October 2018 |archive-date=15 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210415033118/https://www.economist.com/briefing/2018/09/20/a-scary-election-in-brazil |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Slowly, however, the wear and tear of years of dictatorial power that had not slowed the repression, even after the defeat of the leftist guerrillas,<ref>Bradford Burns 1993, p. 457</ref> plus the inability to deal with the economic crises of the period and popular pressure, made an opening policy inevitable, which from the regime side was led by Generals [[Ernesto Geisel]] and [[Golbery do Couto e Silva]].{{sfnp|Fausto|1999|loc=Chapter 6 "The military government and the transition to democracy (1964–1984)"}} With the enactment of the [[Amnesty law#Brazil|Amnesty Law]] in 1979, Brazil began a slow return to democracy, which was completed during the 1980s.{{sfnp|Fausto|1999}} |
|||
In the fiercely disputed [[2018 Brazilian general election|2018 elections]], the controversial conservative candidate [[Jair Bolsonaro]] of the [[Social Liberal Party (Brazil)|Social Liberal Party]] (PSL) was elected president, winning in the second round against [[Fernando Haddad]], of the [[Workers' Party (Brazil)|Workers Party]] (PT), with the support of 55.13% of the valid votes.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Jair Bolsonaro é eleito presidente do Brasil |url=https://veja.abril.com.br/politica/jair-bolsonaro-e-eleito-presidente-do-brasil/ |website=veja.abril.com.br |access-date=11 November 2020 |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193324/https://veja.abril.com.br/politica/jair-bolsonaro-e-eleito-presidente-do-brasil/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In the early 2020s, Brazil became [[COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil|one of the hardest hit countries]] during the [[COVID-19 pandemic]], receiving the second-highest death toll worldwide after the United States.<ref name="BBCGuerin">{{Cite news |last=Guerin |first=Orla |date=9 July 2021 |title=Covid-19 pandemic: 'Everything you should not do, Brazil has done' |work=[[BBC News]] |publisher=BBC |location=[[Brasília]] |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-57733540 |access-date=2 August 2021 |archive-date=3 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210803062031/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-57733540 |url-status=live }}</ref> In May 2021, [[Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva]] stated that he would run for a third term in the [[2022 Brazilian general election]] against Bolsonaro.<ref name=Valor2021-05-20a>{{cite web|url=https://valorinveste.globo.com/mercados/brasil-e-politica/noticia/2021/05/20/lula-reitera-candidatura-presidencial-contra-bolsonaro-em-2022.ghtml|title=Lula reitera candidatura presidencial contra Bolsonaro em 2022|website=Valor|date=20 May 2021|access-date=5 August 2021|archive-date=5 August 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210805163619/https://valorinveste.globo.com/mercados/brasil-e-politica/noticia/2021/05/20/lula-reitera-candidatura-presidencial-contra-bolsonaro-em-2022.ghtml|url-status=live}}</ref> In October 2022, Lula was in first place in the first round, with 48.43% of the support from the electorate, and received 50.90% of the votes in the second round.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Análise das Eleições 2022: Veja Detalhes dos Resultados da Votação|url=https://noticias.uol.com.br/eleicoes/2022/analise/presidente-1-turno/ |access-date=31 October 2022|website=noticias.uol.com.br|language=pt |archive-date=30 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221030225737/https://noticias.uol.com.br/eleicoes/2022/analise/presidente-1-turno/ |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=Resultados – TSE|url=https://resultados.tse.jus.br/oficial/app/index.html#/eleicao/resultados |access-date=31 October 2022|website=resultados.tse.jus.br |archive-date=2 November 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221102121453/https://resultados.tse.jus.br/oficial/app/index.html#/eleicao/resultados }}</ref> On 8 January 2023, a week after Lula's inauguration, a mob of Bolsonaro's supporters [[2023 Brazilian Congress attack|attacked Brazil's federal government buildings]] in the capital, [[Brasília]], after several weeks of unrest.<ref>{{cite web |last=Phillips |first=Tom |date=8 January 2023 |title=Jair Bolsonaro supporters storm Brazil's presidential palace and supreme court |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/jan/08/jair-bolsonaro-supporters-storm-brazils-presidential-palace-and-supreme-court |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230108191923/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/jan/08/jair-bolsonaro-supporters-storm-brazils-presidential-palace-and-supreme-court |archive-date=8 January 2023 |work=The Guardian}}</ref><ref name="CNN">{{cite web |last=Rocha |first=Lucas |title=Manifestantes furam bloqueio, entram na Esplanada e invadem o Congresso Nacional |trans-title=Protesters break through the blockade, enter the Esplanade and invade the National Congress |url=https://www.cnnbrasil.com.br/politica/manifestantes-furam-bloqueio-e-entram-na-esplanada-em-brasilia/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230108184449/https://www.cnnbrasil.com.br/politica/manifestantes-furam-bloqueio-e-entram-na-esplanada-em-brasilia/ |archive-date=8 January 2023 |access-date=8 January 2023 |publisher=[[CNN Brazil]]}}</ref> |
|||
Civilians returned to power in 1985 when [[José Sarney]] assumed the presidency. He became unpopular during his tenure through failure to control the economic crisis and [[hyperinflation]] he inherited from the military regime.<ref>Fausto (2005), pp. 464–65.</ref> Sarney's unsuccessful government led to the [[Brazilian presidential election, 1989|election in 1989]] of the almost-unknown [[Fernando Collor de Mello|Fernando Collor]], subsequently impeached by the National Congress in 1992.<ref>Fausto (2005), pp. 465, 475.</ref> |
|||
== Geography == |
|||
Collor was succeeded by his vice-president, [[Itamar Franco]], who appointed [[Fernando Henrique Cardoso]] Minister of Finance. In 1994, Cardoso produced a highly successful [[Plano Real]],<ref>Skidmore, p. 311.</ref> that, after decades of failed economic plans made by previous governments attempting to curb hyperinflation, finally stabilized the Brazilian economy.{{sfnp|Fausto|1999|loc=Epilogue}}<ref>Fausto (2005), p. 482.</ref> Cardoso won the [[Brazilian presidential election, 1994|1994 election]], and [[Brazilian presidential election, 1998|again in 1998]].<ref>Fausto (2005), p. 474.</ref> |
|||
{{Multiple image |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| image1 = Ulyssesguimaraesconstituicao.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = [[Ulysses Guimarães]] holding the [[Constitution of Brazil|Constitution of 1988]] in his hands. |
|||
|image2 = Protesto no Congresso Nacional do Brasil, 17 de junho de 2013.jpg |
|||
|caption2 =Protesters climbed the [[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]] during the massive [[2013 protests in Brazil|2013 protests]]. |
|||
}} |
|||
The peaceful transition of power from Cardoso to his main opposition leader, [[Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva]] ([[Brazilian presidential election, 2002|elected in 2002]] and [[Brazilian presidential election, 2006|re-elected in 2006]]), was seen as proof that Brazil had achieved a long-sought political stability.<ref>Fausto (2005), p. 502.</ref><ref>Zirin, 2014. Chapter 3</ref> However, sparked by indignation and frustrations accumulated over decades from corruption, [[police brutality]], inefficiencies of the political [[The Establishment|establishment]] and [[public service]], [[2013 protests in Brazil|numerous peaceful protests]] erupted in Brazil from the middle of first term of [[Dilma Rousseff]], who had succeeded Lula after winning election [[Brazilian presidential election, 2010|in 2010]].<ref>[https://www.theguardian.com/world/2013/jun/22/urban-protest-changing-global-social-network "Global protest grows as citizens lose faith in politics and the State"] article on "the Guardian"</ref><ref>Zirin, 2014. Chapter 7 & Conclusion.</ref> |
|||
Enhanced by political and economic crises with evidence of involvement by politicians from all the primary political parties in several [[bribery]] and [[tax evasion]] schemes,<ref>[https://www.nytimes.com/2016/04/20/opinion/dilma-rousseffs-impeachment-isnt-a-coup-its-a-cover-up.html Article] at [[The New York Times]], 19 April 2016, On the Brazilian political context that led to the approval of impeachment proceedings against Dilma Rousseff.</ref><ref>[https://www.reuters.com/article/us-panama-tax-brazil-idUSKCN0X11C1 Article] at [[Reuters]] on the involvement of Brazilian politicians in tax evasion schemes unveiled by the [[Panama Papers]]. 4 April 2016.</ref> with [[2015–16 protests in Brazil|large street protests for and against her]],<ref>[http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/28879ada-0499-11e6-96e5-f85cb08b0730.html#axzz46ZJ07xgT Article] at [[Financial Times]] (18 April 2016) about the political ambiance in Brazil on the day vote for the Deputies chamber decision about open an impeachment procedure against President Dilma. 2nd to 4th paragraph.</ref> Rousseff [[Impeachment of Dilma Rousseff|was impeached]] by the [[Brazilian Congress]] in 2016.<ref name="auto1">{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/aug/31/dilma-rousseff-impeached-president-brazilian-senate-michel-temer |title=Dilma Rousseff impeached by Brazilian senate |author=Jonathan Watts & Donna Bowater |newspaper=The Guardian |accessdate=31 August 2016}}</ref><ref>[https://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/01/world/americas/brazil-impeachment-coup.html Article of] New York Times about the denouement of Roussef's impeachment process.</ref> In 2017, the Supreme Court asked for the investigation of 71 Brazilian lawmakers and nine ministers in President [[Michel Temer]]'s cabinet allegedly linked to the [[Operation Car Wash|Petrobras corruption scandal]].<ref>"[https://www.reuters.com/article/brazil-politics-probes-idUSL1N1HJ1NO? Brazil supreme court judge orders probe into nine ministers – paper]". Reuters. 11 April 2017.</ref> President Temer is himself accused of [[Corruption in Brazil|corruption]].<ref>"[https://www.nytimes.com/2017/06/26/world/americas/brazil-temer-corruption-charge-joesley-batista.html President Michel Temer of Brazil Is Charged With Corruption]". ''The New York Times.'' 26 June 2017.</ref> In 2018, 62% of the population on a poll claimed that corruption was Brazil's biggest problem.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.economist.com/briefing/2018/09/20/a-scary-election-in-brazil|title=A scary election in Brazil|work=The Economist|access-date=1 October 2018|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
Starting in 2013, there is a total change in Brazilian politics, with the overthrow of the [[Left-wing politics|left]] and the rise of conservatism in [[Right-wing politics|right]]. With the discovery that the [[Workers' Party (Brazil)|PT]] governments have practically gone bankrupt in [[Petrobras]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://g1.globo.com/economia/negocios/noticia/2015/04/prejuizo-da-petrobras-e-o-maior-desde-1986-entre-empresas-de-capital-aberto.html|title=Prejuízo da Petrobras é o maior desde 1986 entre empresas de capital aberto|first1=Do|last1=G1|first2=em São|last2=Paulo|date=23 April 2015|website=Negócios}}</ref> [[Correios]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://istoe.com.br/como-o-pt-quebrou-os-correios/|title=Como o PT quebrou os Correios|date=15 March 2019}}</ref> and many other state companies, through a great diversion of public funds and the use of their funds to bribe the [[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]], the [[Brazilian Senate]] and [[Judiciary]], in addition to the indiscriminate use of [[National Bank for Economic and Social Development|BNDES]] to finance socialist dictatorships in Cuba, Venezuela, Latin America, Africa and the Middle East<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.mises.org.br/Article.aspx?id=1985|title=20 obras que o BNDES financiou em outros países|website=Mises Brasil}}</ref> (with Lula and Dilma openly supporting controversial figures such as [[Hugo Chávez]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://veja.abril.com.br/mundo/telegrama-mostra-como-lula-atuou-na-reeleicao-de-hugo-chavez/|title=Documento mostra como Lula atuou na reeleição de Hugo Chávez|website=VEJA}}</ref> [[Nicolás Maduro]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.gazetadopovo.com.br/politica/republica/maduro-e-lula-ditador-da-venezuela-expressa-apoio-ao-lado-de-lider-do-mst-e8tuns9x475pam8hzsqlajo7e/|title=Maduro é Lula! Ditador da Venezuela expressa apoio ao lado de líder do MST|website=Gazeta do Povo}}</ref> [[Mahmoud Ahmadinejad]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://noticias.uol.com.br/politica/ultimas-noticias/2009/11/24/dialogo-de-lula-com-ditaduras-tem-auge-com-visita-de-ahmadinejad.htm|title=Diálogo de Lula com ditaduras tem auge com visita de Ahmadinejad|website=noticias.uol.com.br}}</ref> [[Evo Morales]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://veja.abril.com.br/politica/lula-classifica-renuncia-de-evo-na-bolivia-como-golpe-de-estado/|title=Lula classifica renúncia de Evo na Bolívia como 'golpe de estado'|website=VEJA}}</ref> [[Vladimir Putin]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://revistaforum.com.br/global/lula-exalta-putin-e-diz-que-brasil-pode-deter-a-loucura-de-trump/|title=Lula exalta Putin e diz que Brasil pode deter "a loucura" de Trump|date=3 October 2019|website=Revista Fórum}}</ref> [[Kim Jong-un]] and the [[Chinese Communist Party]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://gazetabrasil.com.br/politica/gleisi-fortalece-alianca-do-pt-com-partido-comunista-da-china/|title=Gleisi fortalece aliança do PT com partido comunista da China|first=Gazeta|last=Brasil|date=8 July 2020}}</ref> among others), also counting on the attempts of Dilma Roussef to install "Popular Councils" to replace the power of the federal deputies,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://g1.globo.com/politica/noticia/2014/06/dilma-defende-participacao-de-conselhos-em-decisoes-do-governo.html|title=Dilma defende consulta a conselhos populares nas decisões do governo|first1=Filipe MatosoDo|last1=G1|first2=em|last2=Brasília|date=5 June 2014|website=Política}}</ref> [[Jair Bolsonaro]], former military and candidate of the right, is freely elected.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.correiobraziliense.com.br/app/noticia/diversao-e-arte/2019/07/24/interna_diversao_arte,773374/filme-sobre-bolsonaro-tera-auxilio-da-ancine.shtml|title=Filme sobre ascensão de Bolsonaro e extrema-direita terá auxílio da Ancine|first='Bettina Novaes Ferraz/Diário de Pernambuco, Mariana Moraes/ Diário de|last=Pernambuco'|date=24 July 310|website=Acervo}}</ref> Through the [[Operation Car Wash]], the [[Federal Police of Brazil]] has since acted on the deviations and corruption of the PT and allied parties at that time. |
|||
==Geography== |
|||
{{Main|Geography of Brazil}} |
{{Main|Geography of Brazil}} |
||
[[File:Brazil topo.jpg|thumb|left|upright=1.3|Topographic map of Brazil]] |
|||
Brazil occupies a large area along the eastern coast of South America and includes much of the continent's interior,<ref name="Encarta 6">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Land and Resources |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html# |accessdate=11 June 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028044617/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |archivedate=28 October 2009 |url-status=dead}} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref> sharing land borders with [[Uruguay]] to the south; [[Argentina]] and [[Paraguay]] to the southwest; [[Bolivia]] and [[Peru]] to the west; [[Colombia]] to the northwest; and [[Venezuela]], [[Guyana]], [[Suriname]] and [[France]] (French overseas region of [[French Guiana]]) to the north. It shares a border with every South American country except [[Ecuador]] and [[Chile]].<ref name="CIA Geo"/> |
|||
It also encompasses a number of oceanic [[archipelago]]s, such as [[Fernando de Noronha]], [[Rocas Atoll]], [[Saint Peter and Saint Paul Archipelago|Saint Peter and Paul Rocks]], and [[Trindade and Martim Vaz]].<ref name="CIA Geo"/> Its size, relief, climate, and natural resources make Brazil geographically diverse.<ref name="Encarta 6"/> Including its [[Atlantic Ocean|Atlantic]] islands, Brazil lies between latitudes [[6th parallel north|6°N]] and [[34th parallel south|34°S]], and longitudes [[28th meridian west|28°]] and [[74th meridian west|74°W]].<ref name="CIA Geo"/> |
|||
Brazil is the [[List of countries and outlying territories by total area|fifth largest]] country in the world, and third largest in the Americas, with a total area of {{convert|8515767.049|km2|sqmi|0|abbr=on}},<ref name="Official Area">[http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/geociencias/cartografia/default_territ_area.shtm Official Area (In Portuguese)] {{Webarchive|url=https://www.webcitation.org/64i0P2Lb0?url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/geociencias/cartografia/default_territ_area.shtm |date=15 January 2012 }} IBGE: Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Retrieved 8 January 2010.</ref> including {{convert|55455|km2|sqmi|0|abbr=on}} of water.<ref name="CIA Geo"/> It spans four [[time zone]]s; from [[UTC-05|UTC−5]] comprising the state of [[Acre (state)|Acre]] and the westernmost portion of [[Amazonas (Brazilian state)|Amazonas]], to [[UTC−04|UTC−4]] in the western states, to [[UTC−03|UTC−3]] in the eastern states (the [[Time in Brazil|national time]]) and [[UTC−02|UTC−2]] in the [[List of islands of Brazil|Atlantic islands]].<ref name="timezones">{{cite web |title=Hora Legal Brasileira |publisher=Observatório Nacional |url=http://pcdsh01.on.br/Fusbr.htm |accessdate=28 December 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110722173247/http://pcdsh01.on.br/Fusbr.htm |archive-date=22 July 2011 |url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil is the only country in the world that has the [[equator]] and the [[Tropic of Capricorn]] running through it. Brazilian topography is also diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. Much of the terrain lies between {{convert|200|m}} and {{convert|800|m}} in elevation.<ref name="Encarta 7">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Natural Regions |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html# |accessdate=11 June 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028044617/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |archivedate=28 October 2009 |url-status=dead}} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref> The main upland area occupies most of the southern half of the country.<ref name="Encarta 7"/> The northwestern parts of the plateau consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, rounded hills.<ref name="Encarta 7"/> |
|||
{{multiple image |
{{multiple image |
||
| align = right |
| align = right |
||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| image1 = Amanhecer_no_Hercules_--.jpg |
|||
| |
| width = 220 |
||
| image1 = Amanhecer no Hercules --.jpg |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 |
| caption1 = [[Serra dos Órgãos National Park]], [[Teresópolis]], [[Rio de Janeiro state]] |
||
| image2 |
| image2 = Amazon River ESA387332.jpg |
||
| caption2 = Satellite image of the [[Amazon Delta]] |
|||
| width2 = 197 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = Canion of [[Canindé de São Francisco]], [[Sergipe]], a geological accident carved by the [[São Francisco River]]. |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
Brazil occupies a large area along the eastern coast of South America and includes much of the continent's interior,<ref name="Encarta 6">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Land and Resources |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |access-date=11 June 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028044617/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |archive-date=28 October 2009 }} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref> sharing land borders with [[Uruguay]] to the south; [[Argentina]] and [[Paraguay]] to the southwest; [[Bolivia]] and [[Peru]] to the west; [[Colombia]] to the northwest; and [[Venezuela]], [[Guyana]], [[Suriname]] and France (French overseas region of [[French Guiana]]) to the north. It shares a border with every South American country except [[Ecuador]] and [[Chile]].<ref name="CIA Geo" /> |
|||
The brazilian territory also encompasses a number of oceanic [[archipelago]]s, such as [[Fernando de Noronha]], [[Rocas Atoll]], [[Saint Peter and Saint Paul Archipelago|Saint Peter and Paul Rocks]], and [[Trindade and Martim Vaz]].<ref name="CIA Geo" /> Its size, relief, climate, and natural resources make Brazil geographically diverse.<ref name="Encarta 6" /> Including its [[Atlantic Ocean|Atlantic]] islands, Brazil lies between latitudes [[6th parallel north|6°N]] and [[34th parallel south|34°S]], and longitudes [[28th meridian west|28°]] and [[74th meridian west|74°W]].<ref name="CIA Geo" /> |
|||
The southeastern section is more rugged, with a complex mass of ridges and mountain ranges reaching elevations of up to {{convert|1200|m}}.<ref name="Encarta 7"/> These ranges include the [[Mantiqueira Mountains|Mantiqueira]] and [[Espinhaço Mountains|Espinhaço]] mountains and the [[Serra do Mar]].<ref name="Encarta 7"/> |
|||
Brazil is the [[List of countries and outlying territories by total area|fifth largest]] country in the world, and third largest in the Americas, with a total area of {{convert|8515767.049|km2|sqmi|0|abbr=on}},<ref name="Official Area">[http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/geociencias/cartografia/default_territ_area.shtm Official Area (In Portuguese)] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120106154550/http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/geociencias/cartografia/default_territ_area.shtm |date=6 January 2012 }} IBGE: Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Retrieved 8 January 2010.</ref> including {{convert|55455|km2|sqmi|0|abbr=on}} of water. North to South, Brazil is also the longest country in the world, spanning 4,395 km (2,731 mi) from north to south,<ref name="CIA Geo" /> and the only country in the world that has the [[equator]] and the [[Tropic of Capricorn]] running through it.<ref name="CIA Geo" /> It spans four [[time zone]]s; from [[UTC-05|UTC−5]] comprising the state of [[Acre (state)|Acre]] and the westernmost portion of [[Amazonas (Brazilian state)|Amazonas]], to [[UTC−04|UTC−4]] in the western states, to [[UTC−03|UTC−3]] in the eastern states (the [[Time in Brazil|national time]]) and [[UTC−02|UTC−2]] in the [[List of islands of Brazil|Atlantic islands]].<ref name="timezones">{{Cite web |title=Hora Legal Brasileira |url=http://pcdsh01.on.br/Fusbr.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110722173247/http://pcdsh01.on.br/Fusbr.htm |archive-date=22 July 2011 |access-date=28 December 2014 |publisher=Observatório Nacional}}</ref> |
|||
In the north, the [[Guiana Shield|Guiana Highlands]] form a major drainage divide, separating rivers that flow south into the [[Amazon Basin]] from rivers that empty into the [[Orinoco|Orinoco River]] system, in Venezuela, to the north. The highest point in Brazil is the [[Pico da Neblina]] at {{convert|2994|m}}, and the lowest is the Atlantic Ocean.<ref name="CIA Geo"/> |
|||
=== Climate === |
|||
Brazil has a dense and complex system of rivers, one of the world's most extensive, with eight major drainage basins, all of which drain into the Atlantic.<ref name="Encarta 8">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Rivers and Lakes |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |accessdate=11 June 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028044617/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |archivedate=28 October 2009 |url-status=dead}} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref> Major rivers include the [[Amazon River|Amazon]] (the world's second-longest river and the largest in terms of volume of water), the [[Paraná River|Paraná]] and its major tributary the [[Iguazu River|Iguaçu]] (which includes the [[Iguazu Falls]]), the [[Rio Negro (Amazon)|Negro]], [[São Francisco River|São Francisco]], [[Xingu River|Xingu]], [[Madeira River|Madeira]] and [[Tapajós]] rivers.<ref name="Encarta 8"/> |
|||
{{clr}} |
|||
{{wide image|Chapada_Diamantina_Panorama_(cropped).jpg|800px|align-cap=center|[[Chapada Diamantina]], in the [[Chapada Diamantina National Park]], [[Bahia]].}} |
|||
===Climate=== |
|||
{{Main|Climate of Brazil}} |
{{Main|Climate of Brazil}} |
||
[[File:Köppen climate types of Brazil.svg|thumb |
[[File:Köppen climate types of Brazil.svg|thumb|Brazil map of [[Köppen climate classification]] zones]] |
||
The climate of Brazil comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a large area and varied topography, but most of the country is tropical.<ref name="CIA Geo"/> According to the [[Köppen climate classification|Köppen system]], Brazil hosts six major climatic subtypes: [[Desert climate|desert]], [[Tropical rainforest climate|equatorial]], [[tropical climate|tropical]], [[Semi-arid climate|semiarid]], [[Oceanic climate|oceanic]] and [[Humid subtropical climate|subtropical]]. The different climatic conditions produce environments ranging from [[Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests|equatorial rainforests]] in the north and semiarid deserts in the northeast, to [[temperate coniferous forest]]s in the south and [[tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands|tropical savannas]] in central Brazil.<ref name="BBC Weather">{{ |
The climate of Brazil comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a large area and varied topography, but most of the country is tropical.<ref name="CIA Geo" /> According to the [[Köppen climate classification|Köppen system]], Brazil hosts six major climatic subtypes: [[Desert climate|desert]], [[Tropical rainforest climate|equatorial]], [[tropical climate|tropical]], [[Semi-arid climate|semiarid]], [[Oceanic climate|oceanic]] and [[Humid subtropical climate|subtropical]]. The different climatic conditions produce environments ranging from [[Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests|equatorial rainforests]] in the north and semiarid deserts in the northeast, to [[temperate coniferous forest]]s in the south and [[tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands|tropical savannas]] in central Brazil.<ref name="BBC Weather">{{Cite web |title=Brazil |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/world/country_guides/results.shtml?tt=TT005220 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110208034235/http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/world/country_guides/results.shtml?tt=TT005220 |archive-date=8 February 2011 |access-date=11 June 2008 |website=Country Guide |publisher=BBC Weather}}</ref> |
||
In Brazil, [[forest cover]] is around 59% of the total land area, equivalent to 496,619,600 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, down from 588,898,000 hectares (ha) in 1990. In 2020, naturally regenerating forest covered 485,396,000 hectares (ha) and planted forest covered 11,223,600 hectares (ha). Of the naturally regenerating forest, 44% was reported to be [[primary forest]] (consisting of native tree species with no clearly visible indications of human activity) and around 30% of the forest area was found within protected areas. For 2015, 56.% of the forest area was reported to be under [[State ownership|public ownership]] and 44% [[Private property|private ownership]].<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/enwiki/api/core/bitstreams/a6e225da-4a31-4e06-818d-ca3aeadfd635/content |title=Terms and Definitions FRA 2025 Forest Resources Assessment, Working Paper 194 |publisher=Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations |year=2023}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Brazil |url=https://fra-data.fao.org/assessments/fra/2020/BRA/home/overview |website=Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations}}</ref> |
|||
An equatorial climate characterizes much of northern Brazil. There is no real [[dry season]], but there are some variations in the period of the year when most rain falls.<ref name="BBC Weather"/> Temperatures average {{convert|25|°C}},<ref name="BT"/> with more significant temperature variation between night and day than between seasons.<ref name="Encarta 9"/> |
|||
Many regions have starkly different [[microclimate]]s.<ref name="Encarta 9">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Natural Regions |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_2/Brazil.html |access-date=11 June 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029034943/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_2/Brazil.html |archive-date=29 October 2009 }} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref><ref name="BT">{{Cite web |title=Temperature in Brazil |url=http://www.v-brazil.com/information/geography/temperature-graphs.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080612200827/http://www.v-brazil.com/information/geography/temperature-graphs.html |archive-date=12 June 2008 |access-date=11 June 2008 |publisher=Brazil Travel}}</ref> An equatorial climate characterizes much of northern Brazil. There is no real [[dry season]], but there are some variations in the period of the year when most rain falls.<ref name="BBC Weather" /> Temperatures average {{convert|25|°C}},<ref name="BT" /> with more significant temperature variation between night and day than between seasons.<ref name="Encarta 9" /> Over central Brazil, rainfall is more seasonal, characteristic of a savanna climate.<ref name="Encarta 9" /> This region is as extensive as the Amazon basin but has a very different climate as it lies farther south at a higher altitude.<ref name="BBC Weather" /> In the interior northeast, seasonal rainfall is even more extreme.<ref name="Rain" /> South of Bahia, near the coasts, and more southerly most of the state of São Paulo, the distribution of rainfall changes, with rain falling throughout the year.<ref name="BBC Weather" /> The south enjoys subtropical conditions, with cool winters and average annual temperatures not exceeding {{convert|18|°C|1}};<ref name="BT" /> winter frosts and [[Snow in Brazil|snowfall]] are not rare in the highest areas.<ref name="BBC Weather" /><ref name="Encarta 9" /> |
|||
Over central Brazil rainfall is more seasonal, characteristic of a savanna climate.<ref name="Encarta 9"/> This region is as extensive as the Amazon basin but has a very different climate as it lies farther south at a higher altitude.<ref name="BBC Weather"/> In the interior northeast, seasonal rainfall is even more extreme.<ref name="Rain"/> |
|||
The semiarid climatic region generally receives less than {{convert|800|mm|1}} of rain,<ref name="Rain">{{ |
The semiarid climatic region generally receives less than {{convert|800|mm|1|sp=us}} of rain,<ref name="Rain">{{Cite web |last=Embrapa |author-link=Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária |title=Annual averages of Mandacaru Agro-meteorological station |url=http://www.cpatsa.embrapa.br/servicos/dadosmet/cem-anual.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070820215606/http://www.cpatsa.embrapa.br/servicos/dadosmet/cem-anual.html |archive-date=20 August 2007 |access-date=21 October 2008 |language=pt}}</ref> most of which generally falls in a period of three to five months of the year<ref>{{Cite web |title=CPD: South America, Site SA19, Caatinga of North-eastern Brazil, Brazil |url=http://botany.si.edu/projects/cpd/sa/sa19.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090606055642/http://botany.si.edu/projects/cpd/sa/sa19.htm |archive-date=6 June 2009 |access-date=29 October 2009 |publisher=Botany.si.edu}}</ref> and occasionally less than this, creating long periods of drought.<ref name="Encarta 9" /> Brazil's 1877–78 ''[[Grande Seca]]'' (Great Drought), the worst in Brazil's history,<ref>[http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/15/6/07-1331_article.htm "Drought, Smallpox, and Emergence of Leishmania braziliensis in Northeastern Brazil"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131129144751/http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/15/6/07-1331_article.htm |date=29 November 2013 }}. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).</ref> caused approximately half a million deaths.<ref>[http://press.princeton.edu/chapters/s8857.html "Ó Gráda, C.: Famine: A Short History"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160112061115/http://press.princeton.edu/chapters/s8857.html |date=12 January 2016 }}. Princeton University Press.</ref> A similarly devastating drought occurred in 1915.<ref>[http://www.fao.org/DOCREP/005/W8514E/W8514E29.htm "Inland fishery enhancements"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140306225557/http://www.fao.org/DOCREP/005/W8514E/W8514E29.htm |date=6 March 2014 }}. FAO.</ref> In 2024, for the first time, "a drought has covered all the way from the North to the country’s Southeast". It is the strongest drought in Brazil since the beginning of measurement in the 1950s, covering almost 60% of the country's territory. The drought is linked to deforestation and climate change.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Maisonnave |first1=Fabiano |title=Brazil faces its worst drought as wildfires rage and Amazon River falls to record low |url=https://www.pbs.org/newshour/world/brazil-faces-its-worst-drought-as-wildfires-rage-and-amazon-river-falls-to-record-low |access-date=16 September 2024 |agency=PBS News |publisher=Associated Press |date=10 September 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last1=McCoy |first1=Terrence |title=More than half of Brazil is racked by drought. Blame deforestation. |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2024/09/12/brazil-drought/ |access-date=16 September 2024 |agency=Washington Post |date=12 September 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Brazil Endures Worst Drought on Record, Affecting 58% of the Country |url=https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/internacional/en/scienceandhealth/2024/09/brazil-endures-worst-drought-on-record-affecting-58-of-the-country.shtml |access-date=16 September 2024 |agency=Folha de S.Paulo |date=5 September 2024}}</ref> |
||
=== Topography and hydrography === |
|||
South of Bahia, near the coasts, and more southerly most of the state of São Paulo, the distribution of rainfall changes, with rain falling throughout the year.<ref name="BBC Weather"/> The south enjoys subtropical conditions, with cool winters and average annual temperatures not exceeding {{convert|18|°C|1}};<ref name="BT"/> winter frosts and [[Snow in Brazil|snowfall]] are not rare in the highest areas.<ref name="BBC Weather"/><ref name="Encarta 9"/> |
|||
{{See also|List of rivers of Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Brazil topo.jpg|thumb|Topographic map of Brazil]] |
|||
Brazilian topography is also diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. Much of the terrain lies between {{convert|200|m|sp=us}} and {{convert|800|m|sp=us}} in elevation.<ref name="Encarta 7">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Natural Regions |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |access-date=11 June 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028044617/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |archive-date=28 October 2009 }} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref> The main upland area occupies most of the southern half of the country.<ref name="Encarta 7" /> The northwestern parts of the plateau consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, rounded hills.<ref name="Encarta 7" /> |
|||
===Biodiversity and environment=== |
|||
{{Main|Wildlife of Brazil|Deforestation in Brazil|Conservation in Brazil}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| image1 = Jaguar_(Panthera_onca_palustris)_female_Piquiri_River_2.JPG |
|||
| width1 = 145 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = Female [[pantanal jaguar]] in [[Piquirí River (São Lourenço)|Piquirí River]], [[Pantanal]]. |
|||
| image2 = Golden_Lion_Tamarin_Poco_das_Antas.jpg |
|||
| width2 = 220 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = [[Golden lion tamarin]], an [[endemic]] animal of Brazil, in the [[Poço das Antas Biological Reserve]]. |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
The southeastern section is more rugged, with a complex mass of ridges and mountain ranges reaching elevations of up to {{convert|1200|m|sp=us}}.<ref name="Encarta 7" /> These ranges include the [[Mantiqueira Mountains|Mantiqueira]] and [[Espinhaço Mountains|Espinhaço]] mountains and the [[Serra do Mar]].<ref name="Encarta 7" /> In the north, the [[Guiana Shield|Guiana Highlands]] form a major drainage divide, separating rivers that flow south into the [[Amazon Basin]] from rivers that empty into the [[Orinoco]] River system, in Venezuela, to the north. The highest point in Brazil is the [[Pico da Neblina]] at {{convert|2994|m|sp=us}}, and the lowest is the Atlantic Ocean.<ref name="CIA Geo" /> |
|||
Brazil's large territory comprises different ecosystems, such as the [[Amazon rainforest]], recognized as having the greatest [[Biodiversity|biological diversity]] in the world,<ref name="WWF">{{cite web |title=One fifth of the world's freshwater |website=Amazon |publisher=World Wide Fund for Nature |date=6 August 2007 |url=http://wwf.panda.org/what_we_do/where_we_work/amazon/about_the_amazon/ecosystems_amazon/rivers/ |accessdate=12 June 2008}}</ref> with the [[Atlantic Forest]] and the [[Cerrado]], sustaining the greatest biodiversity.<ref name="Encarta 10">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Plant and Animal Life |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_2/Brazil.html |accessdate=12 June 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029034943/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_2/Brazil.html |archivedate=29 October 2009 |url-status=dead}}</ref> In the south, the [[Araucaria]] pine forest grows under temperate conditions.<ref name="Encarta 10"/> The rich wildlife of Brazil reflects the variety of natural habitats. Scientists estimate that the total number of [[Wildlife of Brazil|plant]] and [[Wildlife of Brazil|animal species]] in Brazil could approach four million, mostly invertebrates.<ref name="Encarta 10"/> |
|||
Brazil has a dense and complex system of rivers, one of the world's most extensive, with eight major drainage basins, all of which drain into the Atlantic.<ref name="Encarta 8">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Rivers and Lakes |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |access-date=11 June 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028044617/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342/Brazil.html |archive-date=28 October 2009 }} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref> Major rivers include the [[Amazon River|Amazon]] (the world's second-longest river and the largest in terms of volume of water), the [[Paraná River|Paraná]] and its major tributary the [[Iguazu River|Iguaçu]] (which includes the [[Iguazu Falls]]), the [[Rio Negro (Amazon)|Negro]], [[São Francisco River|São Francisco]], [[Xingu River|Xingu]], [[Madeira River|Madeira]] and [[Tapajós]] rivers.<ref name="Encarta 8" /> |
|||
Larger mammals include carnivores [[Cougar|pumas]], [[jaguar]]s, [[ocelot]]s, rare [[bush dog]]s, and [[fox]]es, and herbivores [[peccary|peccaries]], [[tapir]]s, [[anteater]]s, [[sloth]]s, [[opossum]]s, and [[armadillo]]s. [[Deer]] are plentiful in the south, and many species of [[New World monkey]]s are found in the northern [[Rainforest|rain forests]].<ref name="Encarta 10"/><ref>{{cite news |title=Atlantic Forest, Brazil |work=Map: Biodiversity hotspots |publisher=BBC News |date=1 October 2004 |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/3707888.stm#brazil |accessdate=12 June 2008}}</ref> Concern for the environment has grown in response to global interest in environmental issues.<ref name="Encarta 11">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Environmental Issues |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_2/Brazil.html |accessdate=12 June 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029034943/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_2/Brazil.html |archivedate=29 October 2009 |url-status=dead}}</ref> Brazil's Amazon Basin is home to an extremely diverse array of fish species, including the [[red-bellied piranha]]. |
|||
=== Biodiversity and conservation === |
|||
By 2013, Brazil's "dramatic policy-driven reduction in Amazon Basin deforestation" was a "global exception in terms of forest change", according to scientific journal ''[[Science (journal)|Science]]''.<ref name="sciencemag_Hansen_20131115">{{Cite journal| doi = 10.1126/science.1244693| pmid = 24233722 | volume = 342| issue = 6160| pages = 850–853| last1 = Hansen| first1 = M. C.| last2 = Potapov| first2 = P. V.| last3 = Moore| first3 = R.| last4 = Hancher| first4 = M.| last5 = Turubanova| first5 = S. A.| last6 = Tyukavina| first6 = A.| last7 = Thau| first7 = D.| last8 = Stehman| first8 = S. V.| last9 = Goetz| first9 = S. J.| last10 = Loveland| first10 = T. R.| last11 = Kommareddy| first11 = A.| last12 = Egorov| first12 = A.| last13 = Chini| first13 = L.| last14 = Justice| first14 = C. O.| last15 = Townshend| first15 = J. R. G.| title = High-Resolution Global Maps of 21st-Century Forest Cover Change| journal = Science| date = 15 November 2013| bibcode = 2013Sci...342..850H| s2cid = 23541992 | url = http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/d4e9/8078fbc0767ebc341f442f64ca7ce9e008db.pdf}}</ref>{{rp|852}} From 2003 to 2011, compared to all other countries in the world, Brazil had the "largest decline in annual forest loss", as indicated in the study using high-resolution satellite maps showing global forest cover changes.<ref name="sciencemag_Hansen_20131115"/>{{rp|850}} The annual loss of forest cover decreased from a 2003/2004 record high of more than {{convert|40,000|km2|e3ha e6acre mi2}} to a 2010/2011 low of under {{convert|20,000|km2|e3ha e6acre mi2}},<ref name="sciencemag_Hansen_20131115"/>{{rp|850}} reversing widespread deforestation<ref name="sciencemag_Hansen_20131115"/>{{rp|852}} from the 1970s to 2003. |
|||
{{Main|Environment of Brazil|Wildlife of Brazil|Conservation in Brazil}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
{{Further|Environmental issues in Brazil|Protected areas of Brazil}} |
|||
| align = left |
|||
[[File:Toco Toucan (Ramphastos toco) - 48153967707.jpg|thumb|The [[toco toucan]] is an animal typical of the [[Cerrado|Brazilian savannas]].]] |
|||
| image1 = Lear's Macaw Anodorhynchus leari (cropped).jpg |
|||
The [[wildlife of Brazil]] comprises all naturally occurring [[animal]]s, [[plant]]s, and [[fungus|fungi]] in the [[South America]]n country. Home to 60% of the [[Amazon Rainforest|Amazon rainforest]], which accounts for approximately one-tenth of all [[species]] in the world,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Amazon – World's largest tropical rain forest and river basin |url=http://www.worldwildlife.org/what/wherewework/amazon/index.html |access-date=3 June 2010 |publisher=[[World Wide Fund for Nature]] |archive-date=5 August 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120805092911/http://www.worldwildlife.org/what/wherewework/amazon/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Brazil is considered to have the greatest [[biodiversity]] of any country on the planet, containing over 70% of all animal and plant species catalogued.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Brazil |url=https://iucngreenlist.org/country/brazil/ |access-date=19 November 2022 |website=IUCN Green List |language=en-US |archive-date=19 November 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221119014359/https://iucngreenlist.org/country/brazil/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Brazil has the most known species of [[plant]]s (55,000), freshwater [[fish]] (3,000) and [[mammal]]s (over 689).<ref name="DannyP_2007_shoestring">{{Cite book |last=Palmerlee |first=Danny |title=South America on a Shoestring |publisher=[[Lonely Planet]] Publications |year=2007 |isbn=978-1-74104-443-0 |page=275 |oclc=76936293}}</ref> It also ranks third on the list of countries with the most [[bird]] species (1,832) and second with the most [[reptile]] species (744).<ref name="DannyP_2007_shoestring" /> The number of fungal species is unknown but is large.<ref name="Silva, M 1995">Da Silva, M. and D.W. Minter. 1995. ''Fungi from Brazil recorded by Batista and Co-workers''. Mycological Papers 169. CABI, Wallingford, UK. 585 pp.</ref> Brazil is second only to [[Indonesia]] as the country with the most [[endemic]] species.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Chapman |first=A.D |date=September 2005 |title=Numbers of Living Species in Australia and the World: A Report for the Department of the Environment and Heritage |work=Australian Biological Resources Study |publisher=Australian Biodiversity Information Services |url=http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/abrs/publications/other/species-numbers/05-comparisons.html |access-date=26 November 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071101090709/http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/abrs/publications/other/species-numbers/05-comparisons.html <!-- Bot retrieved archive --> |archive-date=1 November 2007}}</ref> |
|||
| width1 = 220 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
Brazil's large territory comprises different ecosystems, such as the Amazon rainforest, recognized as having the greatest [[Biodiversity|biological diversity]] in the world,<ref name="WWF">{{Cite web |date=6 August 2007 |title=One fifth of the world's freshwater |url=http://wwf.panda.org/what_we_do/where_we_work/amazon/about_the_amazon/ecosystems_amazon/rivers/ |access-date=12 June 2008 |website=Amazon |publisher=World Wide Fund for Nature |archive-date=1 March 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110301055230/http://wwf.panda.org/what_we_do/where_we_work/amazon/about_the_amazon/ecosystems_amazon/rivers/ |url-status=live }}</ref> with the [[Atlantic Forest]] and the [[Cerrado]] sustaining the greatest biodiversity.<ref name="Encarta 10">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Plant and Animal Life |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_2/Brazil.html |access-date=12 June 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029034943/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_2/Brazil.html |archive-date=29 October 2009 }}</ref> In the south, the [[Araucaria moist forests]] grow under temperate conditions.<ref name="Encarta 10" /> The rich wildlife of Brazil reflects the variety of natural habitats. Scientists estimate that the total number of [[Wildlife of Brazil|plant]] and [[Wildlife of Brazil|animal species]] in Brazil could approach four million, mostly invertebrates.<ref name="Encarta 10" /> Larger mammals include carnivores [[Cougar|pumas]], [[jaguar]]s, [[ocelot]]s, rare [[bush dog]]s, and [[fox]]es, and herbivores [[peccary|peccaries]], [[tapir]]s, [[anteater]]s, [[sloth]]s, [[opossum]]s and [[armadillo]]s. [[Deer]] are plentiful in the south, and many species of [[New World monkey]]s are found in the northern [[Rainforest|rain forests]].<ref name="Encarta 10" /><ref>{{Cite news |date=1 October 2004 |title=Atlantic Forest, Brazil |work=Map: Biodiversity hotspots |publisher=BBC News |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/3707888.stm#brazil |access-date=12 June 2008 |archive-date=19 July 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080719212941/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/3707888.stm#brazil |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
| caption1 = [[Lear's macaw]], [[endemic]] to [[Raso da Catarina]], [[Bahia]]. |
|||
| image2 = Amazon CIAT (5).jpg |
|||
[[File:20220910 Amazon deforestation and degradation, by country - Amazon Watch.svg|thumb|Cumulatively, Brazil has the highest percentage of deforested and degraded rainforest of any Amazonia nation.<ref name="AmazonWatch_202209">{{Cite web |date=September 2022 |title=Amazon Against the Clock: A Regional Assessment on Where and How to Protect 80% by 2025 |url=https://amazonwatch.org/assets/files/2022-amazonia-against-the-clock-executive-summary.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220910025229/https://amazonwatch.org/assets/files/2022-amazonia-against-the-clock-executive-summary.pdf |archive-date=10 September 2022 |website=Amazon Watch |page=8 |quote=Graphic 2: Current State of the Amazon by country, by percentage / Source: RAISG (Red Amazónica de Información Socioambiental Georreferenciada) Elaborated by authors.}}</ref>]] |
|||
| width2 = 220 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = The [[Amazon rainforest]], the most biodiverse [[rainforest]] in the world. |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
More than one-fifth of the Amazon rainforest in Brazil has been completely destroyed, and more than 70 mammals are endangered.<ref name="DannyP_2007_shoestring" /> The threat of extinction comes from several sources, including [[Deforestation in Brazil|deforestation]] and [[poaching]]. Extinction is even more problematic in the [[Atlantic Forest]], where nearly 93% of the forest has been cleared.<ref>{{Cite web |year=2007 |title=Places We Work: The Atlantic Forest of Brazil |url=http://www.nature.org/wherewework/southamerica/brazil/work/art5080.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100702223313/http://www.nature.org/wherewework/southamerica/brazil/work/art5080.html |archive-date=2 July 2010 |access-date=5 December 2007 |publisher=[[The Nature Conservancy]]}}</ref> Of the 202 endangered animals in Brazil, 171 are in the Atlantic Forest.<ref name="mre.gov">{{Cite web |last=Capobianco |first=João Paulo |title=Biodiversity in the Atlantic Forest |url=http://www.mre.gov.br/cdbrasil/itamaraty/web/ingles/meioamb/biodiv/matatlan/biodiv/index.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071215123917/http://www.mre.gov.br/cdbrasil/itamaraty/web/ingles/meioamb/biodiv/matatlan/biodiv/index.htm |archive-date=15 December 2007 |access-date=5 December 2007 |website=Brazil on CD-ROM and Internet |publisher=Ministry of External Relations}}</ref> The Amazon rainforest has been under direct threat of deforestation since the 1970s because of rapid [[economic]] and [[demographic]] expansion. Extensive legal and [[Illegal logging|illegal]] [[logging]] destroy [[forest]]s the size of a small country per year, and with it a diverse series of species through [[habitat destruction]] and [[habitat fragmentation]].<ref name="usda">[[United States Department of Agriculture|USDA]] Forest Service website, [http://www.fs.fed.us/global/globe/l_amer/brazil.htm Forest Service International Programs: Brazil] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200406090854/https://www.fs.usda.gov/about-agency/international-programs |date=6 April 2020 }}, retrieved February 2007.</ref> Since 1970, over {{convert|600,000|km2|sqmi|sp=us}} of the Amazon rainforest have been cleared by logging.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Butler |first=Rhett A. |date=28 March 2006 |title=Brazil to Protect Amazon Rainforest |publisher=MongaBay.com |url=http://news.mongabay.com/2006/0328-amazon.html |access-date=28 November 2007 |archive-date=5 April 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200405222718/http://news.mongabay.com/2006/0328-amazon.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
However, in 2019, when the [[Bolsonaro government]] came to power, the rate of [[deforestation of the Amazon rainforest]] increased sharply threatening to reach a tipping point after it the forest will collapse, having severe consequences for the world. (see [[Tipping points in the climate system]]) This can also complicate the trade agreement with the [[European Union]]<ref>{{cite news |last1=Watts |first1=Jonathan |title=Amazon deforestation accelerating towards unrecoverable 'tipping point' |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jul/25/amazonian-rainforest-near-unrecoverable-tipping-point |accessdate=28 July 2019 |agency=The Guardian |date=25 July 2019}}</ref> Speaking at the [[UN General Assembly]], Bolsonaro criticised what he described as sensational reporting in the international media. "It is a fallacy to say that the Amazon is the heritage of [[humankind]], and a misconception, as confirmed by scientists, to say that our Amazonian forests are the lungs of world. Using these fallacies, certain countries instead of helping, embarked on the media lies and behaved in a disrespectful manner and with a [[colonialist]] spirit." he said. President Jair Bolsonaro asserted Brazil's [[sovereignty]] over the [[Amazônia Legal|Amazon]].<ref>{{cite news|title= Brazilian President speaks out against 'media lies' surrounding Amazon fires|url= https://news.un.org/en/story/2019/09/1047192|accessdate=29 September 2019 |agency= news.un.org |date=24 September 2019}}</ref> |
|||
In 2017, preserved native vegetation occupied 61% of the Brazilian territory. Agriculture occupied only 8% of the national territory and pastures 19.7%.<ref>{{Cite web |date=27 January 2017 |title=Preserved native vegetation occupies 61% of Brazil's area, says Embrapa |url=https://g1.globo.com/mato-grosso-do-sul/noticia/2017/01/vegetacao-nativa-preservada-ocupa-61-da-area-do-brasil-diz-embrapa.html |access-date=14 August 2021 |archive-date=12 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201112015832/http://g1.globo.com/mato-grosso-do-sul/noticia/2017/01/vegetacao-nativa-preservada-ocupa-61-da-area-do-brasil-diz-embrapa.html |url-status=live }}</ref> For comparison, in 2019, although 43% of the entire European continent has forests, only 3% of the total forest area in Europe is of native forest.<ref>{{Cite news |title=How Europe has multiplied its forests and why this can be a problem |work=BBC News Brasil |url=https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/internacional-50162105 |access-date=14 August 2021 |archive-date=14 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210814031104/https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/internacional-50162105 |url-status=live }}</ref> Brazil has a strong interest in conservation, as its agriculture sector directly depends on its forests.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Ruiz |first=Sarah |date=12 November 2021 |title=Climate change is pushing Brazil's farmland out of agricultural suitability range |url=https://www.woodwellclimate.org/brazils-farms-losing-agricultural-suitability/ |access-date=22 September 2022 |website=Woodwell climate research center |publisher=Nature Climate Change |archive-date=22 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220922162632/https://www.woodwellclimate.org/brazils-farms-losing-agricultural-suitability/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2020, the government of Brazil pledged to reduce its annual [[greenhouse gas]] emissions by 43% by 2030. It also sets an indicative target of reaching [[carbon neutrality]] by 2060 if the country gets 10 billion dollars per year.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Felin |first=Bruno |date=10 December 2020 |title=STATEMENT: Brazil Sets Weak 2030 Emission Reduction Target |url=https://www.wri.org/news/2020/12/statement-brazil-sets-weak-2030-emission-reduction-target |access-date=3 January 2021 |website=World Resources Institute |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193227/https://www.wri.org/news/2020/12/statement-brazil-sets-weak-2030-emission-reduction-target |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
According to a 2008 GreenPeace article, the natural heritage of Brazil is severely threatened by cattle ranching and agriculture, logging, mining, resettlement, oil and gas extraction, over-fishing, wildlife trade, dams and infrastructure, water pollution, climate change, fire, and invasive species.<ref name="WWF"/> In many areas of the country, the natural environment is threatened by development.<ref>{{cite web |title=Under threat |publisher=Greenpeace |url=http://www.greenpeace.org/international/en/campaigns/forests/south-america/under-threat/ |accessdate=12 June 2008}}</ref> The construction of highways has opened up previously remote areas for agriculture and settlement; dams have flooded valleys and inundated wildlife habitats; and mines have scarred and polluted the landscape.<ref name="Encarta 11"/><ref>{{cite web |title=Amazon destruction: six football fields a minute |publisher=Greenpeace |url=http://www.greenpeace.org/international/news/amazon-destruction |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080405192352/http://www.greenpeace.org/international/news/amazon-destruction |archivedate=5 April 2008 |accessdate=12 June 2008}}</ref> At least 70 dams are said to be planned for the Amazon region, including the controversial [[Belo Monte Dam|Belo Monte]] hydroelectric dam.<ref>"[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/8492577.stm Brazil grants environmental licence for Belo Monte dam]." ''BBC News''. 2 February 2010.</ref> In summer 2019, 2 states in Brazil [[Paraná (state)|Paraná]] and [[Santa Catarina (state)|Santa Catarina]] banned [[fracking]], what will have positive effects on the climate and water quality, because the [[shale gas]] and [[shale oil]] reserves in the state of Parana are the larger in the southern hemisphere.<ref>{{cite web |title=The biggest shale reserve in the southern hemisphere will never be fracked |url=https://350.org/press-release/brazil-approves-its-first-law-against-fracking-in-parana-state/ |website=350 org |accessdate=28 July 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=7 million people in South Brazil are about to leave oil and shale gas on the ground |url=https://naofrackingbrasil.com.br/2019/07/17/7-million-people-in-south-brazil-are-about-to-leave-oil-and-shale-gas-on-the-ground/ |website=Não Fracking Brasil |accessdate=28 July 2019}}</ref> |
|||
==Government and politics== |
== Government and politics == |
||
{{Main|Politics of Brazil|Federal government of Brazil|Elections in Brazil}} |
{{Main|Politics of Brazil|Federal government of Brazil|Elections in Brazil}} |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Palácio Nereu Ramos - Brasília - 20150603172246.jpg|thumb|[[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]], seat of the [[legislative branch]]]] |
||
[[File:Palacio do Planalto (5348220087).jpg|thumb|[[Palácio do Planalto]], the official workplace of the [[President of Brazil]]]] |
|||
The form of government is a [[Democracy|democratic]] [[Federation|federative]] [[republic]], with a [[presidential system]].<ref name="Constituição"/> The president is both head of state and head of government of the Union and is elected for a four-year term,<ref name="Constituição"/> with the possibility of re-election for a second successive term. The current president is [[Jair Bolsonaro]]. The previous president, [[Michel Temer]], replaced [[Dilma Rousseff]] after her [[Impeachment of Dilma Rousseff|impeachment]].<ref name="auto">{{cite news|url=http://www.cnn.com/2016/08/31/americas/brazil-rousseff-impeachment-vote/index.html|title=Brazil's Senate ousts Rousseff in impeachment vote|first1=Catherine E. |last1=Shoichet |first2=Euan |last2=McKirdy|website=CNN|access-date=31 August 2016}}</ref> The President appoints the [[Minister of State|Ministers of State]], who assist in government.<ref name="Constituição"/> Legislative houses in each political entity are the main source of law in Brazil. The [[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]] is the Federation's bicameral legislature, consisting of the [[Chamber of Deputies of Brazil|Chamber of Deputies]] and the [[Senate of Brazil|Federal Senate]]. Judiciary authorities exercise jurisdictional duties almost exclusively. Brazil is a [[democracy]], according to the [[Democracy Index]] 2010.<ref>{{cite web |title=Democracy Index 2010 |url=http://graphics.eiu.com/PDF/Democracy_Index_2010_web.pdf|website=eiu.com|accessdate=12 February 2016}}</ref> |
|||
The form of government is a [[Democracy|democratic]] [[Federation|federative]] [[republic]], with a [[presidential system]].<ref name="Constituição" /> The president is both head of state and head of government of the Union and is elected for a four-year term,<ref name="Constituição" /> with the possibility of re-election for a second successive term. The current president is [[Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva]].<ref name="auto">{{Cite news |last=Pimentel |first=Mauro |title=Lula returns for third term as Brazil president |work=CNN |url=https://www.france24.com/en/live-news/20230101-lula-returns-for-third-term-as-brazil-president |access-date=1 January 2022 |archive-date=1 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230101031904/https://www.france24.com/en/live-news/20230101-lula-returns-for-third-term-as-brazil-president |url-status=live }}</ref> The President appoints the [[Minister of State|Ministers of State]], who assist in government.<ref name="Constituição" /> |
|||
The political-administrative organization of the Federative Republic of Brazil comprises the Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities.<ref name="Constituição"/> The Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities, are the "spheres of government". The [[federation]] is set on five fundamental principles:<ref name="Constituição"/> sovereignty, citizenship, dignity of human beings, the social values of labor and freedom of enterprise, and political [[pluralism (political theory)|pluralism]]. The classic tripartite branches of government (executive, legislative and judicial under a checks and balances system) are formally established by the Constitution.<ref name="Constituição"/> The executive and legislative are organized [[Separation of powers|independently in all three spheres of government]], while the judiciary is organized only at the federal and state and Federal District spheres. |
|||
[[File:Brasilia Congresso Nacional 05 2007 221.jpg|thumb|[[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]], seat of the [[legislative branch]].]] |
|||
[[File:Fotos produzidas pelo Senado (36736219051).jpg|thumb|Aerial view of the [[Monumental Axis]], [[Praça dos Três Poderes]] and surrounds, in [[Brasília]], where the government offices are located.]] |
|||
Legislative houses in each political entity are the main source of law in Brazil. The [[National Congress of Brazil|National Congress]] is the Federation's bicameral legislature, consisting of the [[Chamber of Deputies of Brazil|Chamber of Deputies]] and the [[Senate of Brazil|Federal Senate]]. Judiciary authorities exercise jurisdictional duties almost exclusively. In 2021, the [[Economist Intelligence Unit]]'s [[Democracy Index]] categorized Brazil as a "[[flawed democracy]]", ranking 46th in the report,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Democracy Index 2021: the China challenge |url=https://pages.eiu.com/rs/753-RIQ-438/images/eiu-democracy-index-2021.pdf?mkt_tok=NzUzLVJJUS00MzgAAAGDWhBlxfqM9cMZEewC0HoBG0xhm9PFkxb-_IqDsjlxRZgDssKgB0pHGt7yS48UFv94hU4ZW0C_jXaFfmK_5TbL23wtQarQv22nFbg8ZTnHQrrcPg |website=Economist Intelligence Unit |language=en-GB |access-date=18 December 2022 |archive-date=26 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220326122737/https://pages.eiu.com/rs/753-RIQ-438/images/eiu-democracy-index-2021.pdf?mkt_tok=NzUzLVJJUS00MzgAAAGDWhBlxfqM9cMZEewC0HoBG0xhm9PFkxb-_IqDsjlxRZgDssKgB0pHGt7yS48UFv94hU4ZW0C_jXaFfmK_5TbL23wtQarQv22nFbg8ZTnHQrrcPg |url-status=live }}</ref> and [[Freedom House]] classified it as a [[Free World|free country]] at ''[[Freedom in the World]]'' report.<ref name="FITW-TG-2021">{{Cite web |date=3 March 2021 |title=Freedom in the World 2021 |url=https://freedomhouse.org/sites/default/files/2021-02/FIW2021_World_02252021_FINAL-web-upload.pdf |access-date=3 March 2021 |publisher=Freedom House |archive-date=26 December 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211226172012/https://freedomhouse.org/sites/default/files/2021-02/FIW2021_World_02252021_FINAL-web-upload.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
All members of the executive and legislative branches are directly elected.<ref name=embassy>{{cite web |url=http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/brazil_in_brief/political_institution.html |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110725100724/http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/brazil_in_brief/political_institution.html |archivedate=25 July 2011 |title=Embassy of Brazil – Ottawa |quote=Political Institutions – The Executive |accessdate=19 July 2007}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.citymayors.com/government/brazil_government.html |title=City Mayors |quote=Brazil federal, state and local government |accessdate=19 July 2007}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |
|||
|title = Contributions to the Physical Geography of the Mississippi River, and Its Delta |
|||
|last = Fontaine |
|||
|first = Edward |
|||
|journal = Journal of the American Geographical Society of New York |
|||
|issn = 1536-0407 |
|||
|volume = 3 |
|||
|year = 1872 |
|||
|pages = 343–78 |
|||
|doi = 10.2307/196424 |
|||
|jstor = 196424 |
|||
}}</ref> Judges and other judicial officials are appointed after passing entry exams.<ref name=embassy/> For most of its democratic history, Brazil has had a multi-party system, proportional representation. Voting is compulsory for the literate between 18 and 70 years old and optional for illiterates and those between 16 and 18 or beyond 70.<ref name="Constituição"/> |
|||
The political-administrative organization of the Federative Republic of Brazil comprises the Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities.<ref name="Constituição" /> The Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities, are the "spheres of government". The federation is set on five fundamental principles: sovereignty, citizenship, dignity of human beings, the social values of labor and freedom of enterprise, and political [[pluralism (political theory)|pluralism]].<ref name="Constituição" /> |
|||
Together with several smaller parties, four political parties stand out: [[Workers' Party (Brazil)|Workers' Party]] (PT), [[Brazilian Social Democracy Party]] (PSDB), [[Brazilian Democratic Movement]] (MDB) and [[Democrats (Brazil)|Democrats]] (DEM). Fifteen political parties are represented in Congress. It is common for politicians to switch parties, and thus the proportion of congressional seats held by particular parties changes regularly.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.southtravels.com/america/brazil/government.html |title=Government – Brazil |publisher=Southtravels.com |date=5 October 1988 |accessdate=17 March 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111128075345/http://www.southtravels.com/america/brazil/government.html |archive-date=28 November 2011 |url-status=dead}}</ref> Almost all governmental and administrative functions are exercised by authorities and agencies affiliated to the Executive. |
|||
The classic tripartite branches of government (executive, legislative and judicial under a checks and balances system) are formally established by the Constitution.<ref name="Constituição" /> The executive and legislative are organized [[Separation of powers|independently in all three spheres of government]], while the judiciary is organized only at the federal and state and Federal District spheres. All members of the executive and legislative branches are directly elected.<ref name="embassy">{{Cite web |title=Embassy of Brazil – Ottawa |url=http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/brazil_in_brief/political_institution.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110725100724/http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/brazil_in_brief/political_institution.html |archive-date=25 July 2011 |access-date=19 July 2007 |quote=Political Institutions – The Executive}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=City Mayors |url=http://www.citymayors.com/government/brazil_government.html |access-date=19 July 2007 |quote=Brazil federal, state and local government |archive-date=1 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181001100905/http://citymayors.com/government/brazil_government.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Fontaine |first=Edward |year=1872 |title=Contributions to the Physical Geography of the Mississippi River, and Its Delta |journal=Journal of the American Geographical Society of New York |volume=3 |pages=343–78 |doi=10.2307/196424 |issn=1536-0407 |jstor=196424}}</ref> |
|||
The country has more than 40 active political parties, and only one of them defines itself as a right-wing party ([[Social Liberal Party (Brazil)|PSL]]), with a clear political imbalance. The country has several far-left parties like [[Socialism and Liberty Party|PSOL]], [[Workers' Cause Party|PCO]], [[United Socialist Workers' Party|PSTU]], [[Brazilian Communist Party|PCB]], [[Communist Party of Brazil|PC do B]], left parties like [[Workers' Party (Brazil)|PT]], [[Brazilian Socialist Party|PSB]], [[Democratic Labour Party (Brazil)|PDT]], [[Green Party (Brazil)|PV]], [[Sustainability Network|Rede]] and [[Solidariedade]] and center-left like [[Brazilian Social Democracy Party|PSDB]], [[Democrats (Brazil)|DEM]], [[Party of National Mobilization|PMN]] and [[Cidadania]]. Ten parties declare themselves as the center: [[Brazilian Democratic Movement|MDB]], [[Liberal Party (Brazil, 2006)|PL]], [[Social Democratic Party (Brazil, 2011)|PSD]], [[Christian Labour Party|PTC]], [[Christian Democracy (Brazil)|DC]], [[Republican Party of the Social Order|PROS]], [[Avante (political party)|Avante]], [[Patriota]], [[Podemos (Brazil)|Podemos]] and [[Party of the Brazilian Woman|PMB]]. Five parties declare themselves as center-right: [[Brazilian Labour Party (current)|PTB]], [[Progressistas]], [[Social Christian Party (Brazil)|PSC]], [[Brazilian Labour Renewal Party|PRTB]] and [[Republicans (Brazil)|Republicanos]]. The only party that claims to be purely liberal, without further consideration, is [[New Party (Brazil)|Novo]]. When asked about their ideological spectrum, Brazilian parties tend to give obtuse and non-conclusive answers on the subject.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.gazetadopovo.com.br/republica/apenas-um-partido-se-define-como-de-direita-no-brasil-esquerda-tem-sete/|title=Apenas um partido se define como de direita no Brasil; Esquerda tem sete|website=Gazeta do Povo}}</ref> |
|||
For most of its democratic history, Brazil has had a [[multi-party system]], with [[proportional representation]]. Voting is [[Compulsory voting|compulsory]] for the literate between 18 and 70 years old and optional for illiterates and those between 16 and 18 or beyond 70.<ref name="Constituição" /> The country has around [[List of political parties in Brazil|30 registered political parties]]. Twenty political parties are represented in Congress. It is common for politicians to switch parties, and thus the proportion of congressional seats held by particular parties changes regularly.<ref>{{Cite web |date=5 October 1988 |title=Government – Brazil |url=http://www.southtravels.com/america/brazil/government.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111128075345/http://www.southtravels.com/america/brazil/government.html |archive-date=28 November 2011 |access-date=17 March 2010 |publisher=Southtravels.com}}</ref> |
|||
===Law=== |
|||
{{Main|Law of Brazil|Law enforcement in Brazil|Crime in Brazil}} |
|||
=== Law === |
|||
[[File:Supremo Brasil.jpg|thumb|left|[[Supreme Federal Court of Brazil]] serves primarily as the Constitutional Court of the country]] |
|||
{{Main|Law of Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Supremo Tribunal de Justiça (4893152130).jpg|thumb|[[Supreme Federal Court of Brazil]] serves primarily as the Constitutional Court of the country.]] |
|||
Brazilian law is based on the [[Civil law (legal system)|civil law]] legal system<ref>[http://www.oas.org/juridico/mla/en/bra/en_bra-int-des-ordrjur.html "The Brazilian Legal System"], Organization of American States. Retrieved 17 May 2007.</ref> and [[civil law (legal system)|civil law]] concepts prevail over common law practice. Most of Brazilian law is codified, although non-codified statutes also represent a substantial part, playing a complementary role. Court decisions set out interpretive guidelines; however, they are seldom binding on other specific cases. Doctrinal works and the works of academic jurists have strong influence in law creation and in law cases. |
|||
Brazilian law is based on the [[Civil law (legal system)|civil law]] legal system<ref>[http://www.oas.org/juridico/mla/en/bra/en_bra-int-des-ordrjur.html "The Brazilian Legal System"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091008001827/http://www.oas.org/juridico/mla/en/bra/en_bra-int-des-ordrjur.html |date=8 October 2009 }}, Organization of American States. Retrieved 17 May 2007.</ref> and [[civil law (legal system)|civil law]] concepts prevail over common law practice. Most of Brazilian law is codified, although non-codified statutes also represent a substantial part, playing a complementary role. Court decisions set out interpretive guidelines; however, they are seldom binding on other specific cases. Doctrinal works and the works of academic jurists have strong influence in law creation and in law cases. Judges and other judicial officials are appointed after passing entry exams.<ref name="embassy" /> |
|||
The legal system is based on the [[Constitution of Brazil|Federal Constitution]], promulgated on 5 October 1988, and the fundamental law of Brazil. All other legislation and court decisions must conform to its rules.<ref>José Afonso da Silva, ''Curso de Direito Constitucional Positivo'' (Malheiros, 2004; {{ISBN|85-7420-559-1}}), p. 46.</ref> {{As of|2007|04}}, there have been 53 amendments. States have their own constitutions, which must not contradict the Federal Constitution.<ref>Silva, ''Curso de Direito Constitucional Positivo'', p. 592.</ref> Municipalities and the Federal District have "organic laws" ({{lang|pt|leis orgânicas}}), which act in a similar way to constitutions.<ref name="DeffentiBarral2011">{{cite book|author1=Fabiano Deffenti|author2=Welber Oliveira Barral|title=Introduction to Brazilian Law|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1Ba2J5eD8wYC&pg=PA20|accessdate=6 June 2013|year=2011|publisher=Kluwer Law International|isbn=978-90-411-2506-4|pages=20–}}</ref> Legislative entities are the main source of statutes, although in certain matters judiciary and executive bodies may enact legal norms.<ref name="Constituição"/> Jurisdiction is administered by the judiciary entities, although in rare situations the [[Constitution of Brazil|Federal Constitution]] allows the Federal Senate to pass on legal judgments.<ref name="Constituição"/> There are also specialized military, labor, and electoral courts.<ref name="Constituição"/> The highest court is the [[Supreme Federal Court]]. |
|||
The legal system is based on the [[Constitution of Brazil|Federal Constitution]], promulgated on 5 October 1988, and the fundamental law of Brazil. All other legislation and court decisions must conform to its rules.<ref>José Afonso da Silva, ''Curso de Direito Constitucional Positivo'' (Malheiros, 2004; {{ISBN|85-7420-559-1}}), p. 46.</ref> {{As of|2022|07}}, there have been 124 amendments.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Amendments to the Brazilian Constitution |url=http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/constituicao/Emendas/Emc/quadro_emc.htm |website=Brazilian Law Compiled |access-date=23 July 2022 |archive-date=22 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220722185649/http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/constituicao/emendas/emc/quadro_emc.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> The highest court is the [[Supreme Federal Court]]. States have their own constitutions, which must not contradict the Federal Constitution.<ref>Silva, ''Curso de Direito Constitucional Positivo'', p. 592.</ref> Municipalities and the Federal District have "organic laws" ({{lang|pt|leis orgânicas}}), which act in a similar way to constitutions.<ref name="DeffentiBarral2011">{{Cite book |last1=Fabiano Deffenti |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1Ba2J5eD8wYC&pg=PA20 |title=Introduction to Brazilian Law |last2=Welber Oliveira Barral |publisher=Kluwer Law International |year=2011 |isbn=978-90-411-2506-4 |pages=20– |access-date=6 June 2013}}</ref> Legislative entities are the main source of statutes, although in certain matters judiciary and executive bodies may enact legal norms.<ref name="Constituição" /> Jurisdiction is administered by the judiciary entities, although in rare situations the [[Constitution of Brazil|Federal Constitution]] allows the Federal Senate to pass on legal judgments.<ref name="Constituição" /> There are also specialized military, labor and electoral courts.<ref name="Constituição" /> |
|||
This system has been criticized over the last few decades for the slow pace of decision-making. Lawsuits on appeal may take several years to resolve, and in some cases more than a decade elapses before definitive rulings.<ref>Miguel Glugoski and Odete Medauar, "[http://www.usp.br/jorusp/arquivo/2003/jusp667/pag0304.htm Nossos direitos nas suas mãos]," [[University of São Paulo|USP]] Journal, 24–30 November 2003. Retrieved 17 May 2007.</ref> Nevertheless, the Supreme Federal Tribunal was the first court in the world to transmit its sessions on television, and also via [[YouTube]].<ref>Diego Abreu, "[http://g1.globo.com/Noticias/Brasil/0,,MUL1326475-5598,00.html Primeira Corte do mundo a ter canal de vídeo no YouTube é o STF]," [http://g1.globo.com/ G1]. {{in lang|pt}} Accessed 12 October 2009.</ref><ref>"[https://web.archive.org/web/20110706160609/http://esma.tjpb.jus.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=109%3Astf-primeira-corte-no-mundo-no-youtube&catid=1%3Anoticias&Itemid=20 STF: Primeira corte do mundo no YouTube]." [http://esma.tjpb.jus.br/ ESMA-PB]. {{in lang|pt}} Accessed 12 October 2009.</ref> More recently, in December 2009, the Supreme Court adopted [[Twitter]] to display items on the day planner of the ministers, to inform the daily actions of the Court and the most important decisions made by them.<ref>"[http://www.stf.jus.br/portal/cms/verNoticiaDetalhe.asp?idConteudo=117153 Página do STF no Twitter está no ar]" (12 January 2009). [http://www.stf.jus.br/ STF Official Website]. {{in lang|pt}} Consulted on 5 December 2009.</ref> |
|||
===Military=== |
=== Military === |
||
{{Main|Brazilian Armed Forces}} |
{{Main|Brazilian Armed Forces}} |
||
{{multiple image |
{{multiple image |
||
| Line 395: | Line 331: | ||
| align = right |
| align = right |
||
| width = 220 |
| width = 220 |
||
| footer = |
|||
| image1 = 200923ASO Anderson Soares 50.jpg |
| image1 = 200923ASO Anderson Soares 50.jpg |
||
| caption1 = [[Brazilian Air Force]] [[Saab JAS 39 Gripen#Brazil|Saab Gripen NG]] |
| caption1 = [[Brazilian Air Force]] [[Saab JAS 39 Gripen#Brazil|Saab Gripen NG]] |
||
| image2 = |
| image2 = Operação "Poseidon 2021" (51475998419).jpg |
||
| caption2 = [[Brazilian |
| caption2 = [[Brazilian Navy]]'s [[flagship]] [[PHM Atlântico|PHM ''Atlântico'']] and [[Brazilian frigate Liberal (F-43)|frigate ''Liberal'' (F-43)]] (background) |
||
| image3 = GLAM_MB_Chegada_do_PHM_"Atlântico"_(29323273127).jpg |
|||
| caption3 = [[Brazilian Navy]]'s [[flagship]] [[PHM Atlântico|PHM ''Atlântico'']] |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The armed forces of Brazil are the [[List of countries by number of military and paramilitary personnel|largest]] in Latin America by active personnel and the largest in terms of military equipment.<ref>[http://revistaepoca.globo.com/Revista/Epoca/0,,EMI14439-15273-2,00-UMA+NOVA+AGENDA+MILITAR.html Uma Nova Agenda Militar] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170325232014/http://revistaepoca.globo.com/Revista/Epoca/0%2C%2CEMI14439-15273-2%2C00-UMA%2BNOVA%2BAGENDA%2BMILITAR.html |date=25 March 2017 }} Revista Época. Retrieved on 19 February 2009.</ref> It consists of the [[Brazilian Army]] (including the [[Brazilian Army Aviation Command|Army Aviation Command]]), the [[Brazilian Navy]] (including the [[Brazilian Marine Corps|Marine Corps]] and [[Brazilian Naval Aviation|Naval Aviation]]) |
The armed forces of Brazil are the [[List of countries by number of military and paramilitary personnel|largest]] in Latin America by active personnel and the largest in terms of military equipment.<ref>[http://revistaepoca.globo.com/Revista/Epoca/0,,EMI14439-15273-2,00-UMA+NOVA+AGENDA+MILITAR.html Uma Nova Agenda Militar] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170325232014/http://revistaepoca.globo.com/Revista/Epoca/0%2C%2CEMI14439-15273-2%2C00-UMA%2BNOVA%2BAGENDA%2BMILITAR.html |date=25 March 2017 }} Revista Época. Retrieved on 19 February 2009.</ref> The country was considered the 9th largest military power on the planet in 2021.<ref>{{Cite web |title=2021 Military Strength Ranking |url=https://www.globalfirepower.com/countries-listing.php |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210305160211/https://www.globalfirepower.com/countries-listing.php |archive-date=5 March 2021 |access-date=11 January 2022 |publisher=Global Firepower}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Brazil is among the 10 largest military powers in the world |url=https://ocp.news/economia/brasil-esta-entre-dez-maiores-potencias-militares-diz-publicacao |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721204255/https://ocp.news/economia/brasil-esta-entre-dez-maiores-potencias-militares-diz-publicacao |archive-date=21 July 2021 |access-date=11 January 2022 |publisher=OCP News}}</ref> It consists of the [[Brazilian Army]] (including the [[Brazilian Army Aviation Command|Army Aviation Command]]), the [[Brazilian Navy]] (including the [[Brazilian Marine Corps|Marine Corps]] and [[Brazilian Naval Aviation|Naval Aviation]]) and the [[Brazilian Air Force]]. Brazil's [[conscription]] policy gives it one of the world's largest military forces, estimated at more than 1.6 million [[Military Reserve|reservists]] annually.<ref>{{Citation |title=The World Factbook |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/brazil/ |access-date=26 March 2010 |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency]] |archive-date=12 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210812124129/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/brazil/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The Air Force is the largest in Latin America and has about 700 crewed aircraft in service and effective about 67,000 personnel.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Sala de imprensa – FAB em números |url=http://www.fab.mil.br/portal/imprensa/fab_numeros.php |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080617153748/http://www.fab.mil.br/portal/imprensa/fab_numeros.php |archive-date=17 June 2008 |access-date=12 December 2007 |publisher=Força Aérea Brasileira |language=pt}}</ref> |
||
Numbering close to 236,000 active personnel,<ref>{{ |
Numbering close to 236,000 active personnel,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Decreto Nº 5.670 de 10 de Janeiro de 2006 |url=http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2004-2006/2006/Decreto/D5670.htm |access-date=2 October 2010 |publisher=Presidência da República |language=pt |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010151021/http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2004-2006/2006/Decreto/D5670.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> the Brazilian Army has the largest number of armored vehicles in South America, including armored transports and [[battle tank|tanks]].<ref name="militarypower1">{{Cite web |title=Military Power |url=http://www.militarypower.com.br/mundo.htm |access-date=27 June 2010 |place=Brasil |archive-date=11 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210211045946/http://www.militarypower.com.br/mundo.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> The states' [[Military Police (Brazil)|Military Police]] and the [[Military Firefighters Corps]] are described as an ancillary forces of the Army by the constitution, but are under the control of each state's governor.<ref name="Constituição" /> |
||
Brazil's navy |
Brazil's navy once operated some of the most powerful warships in the world with the two {{Sclass|Minas Geraes|battleship|0}} [[dreadnought]]s, sparking a [[South American dreadnought race|naval arms race between Argentina, Brazil, and Chile]].<ref>Scheina (1987), p. 81.</ref> Today, it is a [[green-water navy|green water]] force and has a group of specialized elite in retaking ships and naval facilities, [[GRUMEC]], unit specially trained to protect Brazilian oil platforms along its coast.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Grupamento de Mergulhadores de Combate – GruMeC |url=http://tropaselite.t35.com/BRASIL_GRUMEC.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100327162505/http://tropaselite.t35.com/BRASIL_GRUMEC.htm |archive-date=27 March 2010 |access-date=27 June 2010 |website=tropaselite.t35.com}}</ref> {{As of|2022}}, it is the only navy in Latin America that operates a [[helicopter carrier]], [[Brazilian aircraft carrier Atlântico|NAM ''Atlântico'']] and one of twelve <!--Popular Mechanics reference from April 2022 below lists thirteen navies, but South Korea is merely contemplating them.-->navies in the world to operate or have one under construction.<ref name="Poder Naval">{{Cite news |date=26 November 2020 |title=Porta-Helicópteros Atlântico agora é Navio-Aeródromo Multipropósito |language=pt-br |publisher=Poder Naval |url=https://www.naval.com.br/blog/2020/11/26/porta-helicopteros-atlantico-agora-e-navio-aerodromo-multiproposito/ |access-date=12 May 2022 |archive-date=26 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201126180831/https://www.naval.com.br/blog/2020/11/26/porta-helicopteros-atlantico-agora-e-navio-aerodromo-multiproposito/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
=== Foreign policy === |
|||
The Air Force is the largest in Latin America and has about 700 manned aircraft in service and effective about 67,000 personnel.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fab.mil.br/portal/imprensa/fab_numeros.php |title=Sala de imprensa – FAB em números |publisher=Força Aérea Brasileira |language=Portuguese |accessdate=12 December 2007 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080617153748/http://www.fab.mil.br/portal/imprensa/fab_numeros.php |archivedate=17 June 2008}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil has not been invaded since 1865 during the [[Paraguayan War]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://revistaepoca.globo.com/Revista/Epoca/0,,EMI14439-15273-3,00-UMA+NOVA+AGENDA+MILITAR.html |title=Especial – NOTÍCIAS – Uma nova agenda militar |publisher=Revistaepoca.globo.com |accessdate=19 June 2010}}</ref> Additionally, Brazil has no contested territorial disputes with any of its neighbors<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/br.html |title=CIA – The World Factbook |publisher=Cia.gov |accessdate=2 October 2013}}</ref> and neither does it have rivalries, like Chile and Bolivia have with each other.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://english.peopledaily.com.cn/200610/25/eng20061025_315049.html |title=People's Daily Online – Bolivia bans Argentina from reselling gas to Chile |publisher=English.peopledaily.com.cn |date=25 October 2006 |accessdate=19 June 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/3632235.stm |work=BBC News |title=Fresh anger over Bolivia gas plan |date=16 April 2004 |accessdate=1 April 2010}}</ref> The Brazilian military has also three times intervened militarily to overthrow the [[Government of Brazil|Brazilian government]].<ref name="revistaepoca.globo.com">{{cite web|url=http://revistaepoca.globo.com/Revista/Epoca/1,,EMI14440-15273,00.html |title=Especial – NOTÍCIAS – Os pés de barro de um gigante |publisher=Revistaepoca.globo.com |accessdate=19 June 2010 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20100825094407/http://revistaepoca.globo.com/Revista/Epoca/1%2C%2CEMI14440-15273%2C00.html |archivedate=25 August 2010 |df= }}</ref> It has built a tradition of participating in UN [[peacekeeping]] missions such as in [[Haiti]], [[East Timor]] and [[Central African Republic]].<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2004/08/01/world/brazil-is-leading-a-largely-south-american-mission-to-haiti.html |work=The New York Times |title=Brazil Is Leading a Largely South American Mission to Haiti |first=Larry |last=Rohter |date=1 August 2004 |accessdate=1 April 2010}}</ref> Brazil signed the UN [[treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&mtdsg_no=XXVI-9&chapter=26&clang=_en |title=Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons |publisher=United Nations Treaty Collection |date=7 July 2017}}</ref> |
|||
===Foreign policy=== |
|||
{{Main|Foreign relations of Brazil}} |
{{Main|Foreign relations of Brazil}} |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Itamaraty Palace at night, January 2010.jpg|thumb|[[Itamaraty Palace]], the seat of the [[Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Brazil)|Ministry of Foreign Affairs]]]] |
||
Brazil's international relations are based on Article 4 of the [[Constitution of Brazil|Federal Constitution]], which establishes [[Non-interventionism|non-intervention]], [[self-determination]], [[Internationalism (politics)|international cooperation]] and the [[Peacebuilding|peaceful settlement of conflicts]] as the guiding principles of Brazil's relationship with other countries and multilateral organizations.<ref>[http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleI.html Article 4 of the Federal Constitution of Brazil] V-Brazil. Retrieved on 20 September 2011.</ref> |
Brazil's international relations are based on Article 4 of the [[Constitution of Brazil|Federal Constitution]], which establishes [[Non-interventionism|non-intervention]], [[self-determination]], [[Internationalism (politics)|international cooperation]] and the [[Peacebuilding|peaceful settlement of conflicts]] as the guiding principles of Brazil's relationship with other countries and multilateral organizations.<ref>[http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleI.html Article 4 of the Federal Constitution of Brazil] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180928070506/http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleI.html |date=28 September 2018 }} V-Brazil. Retrieved on 20 September 2011.</ref> According to the Constitution, the [[President of Brazil|President]] has ultimate authority over foreign policy, while the [[National Congress of Brazil|Congress]] is tasked with reviewing and considering all diplomatic nominations and [[Treaty|international treaties]], as well as legislation relating to Brazilian foreign policy.<ref>[http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleIV.html Article 84 of the Federal Constitution of Brazil] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190919114914/http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleIV.html |date=19 September 2019 }} V-Brazil. Retrieved on 20 September 2011.</ref> |
||
Brazil's foreign policy is a by-product of the country's position as a [[regional power]] in [[Latin America]], a leader among [[developing countries]], and an emerging [[world power]].<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20090710013700/http://www.wilsoncenter.org/news/docs/RL33456.pdf U.S. Congressional Report on Brazil] [[United States Congress]]. Retrieved on 23 June 2009.</ref> Brazilian foreign policy has generally been based on the principles of [[multilateralism]], peaceful dispute settlement, and [[non-interventionism|non-intervention]] in the affairs of other countries.<ref>Georges D. Landau, "The Decision-making Process in Foreign Policy: The Case of Brazil", Center for Strategic and International Studies: Washington DC: March 2003</ref> Brazil is a founding member state of the [[Community of Portuguese Language Countries]] (CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth, an international organization and political association of [[Lusophone]] nations. |
|||
According to the Constitution, the [[President of Brazil|President]] has ultimate authority over foreign policy, while the [[National Congress of Brazil|Congress]] is tasked with reviewing and considering all diplomatic nominations and [[Treaty|international treaties]], as well as legislation relating to Brazilian foreign policy.<ref>[http://www.v-brazil.com/government/laws/titleIV.html Article 84 of the Federal Constitution of Brazil] V-Brazil. Retrieved on 20 September 2011.</ref> |
|||
An increasingly well-developed tool of Brazil's foreign policy is providing aid as a donor to other developing countries.<ref name="ODI1">Cabral and Weinstock 2010. [http://www.odi.org.uk/resources/details.asp?id=5120&title=brazil-election-emerging-donor-aid Brazil: an emerging aid player] ({{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110113185641/http://www.odi.org.uk/resources/details.asp?id=5120&title=brazil-election-emerging-donor-aid|date=13 January 2011}}). London: [[Overseas Development Institute]]</ref> Brazil does not just use its growing economic strength to provide financial aid, but it also provides high levels of expertise and most importantly of all, a quiet non-confrontational diplomacy to improve governance levels.<ref name="ODI1" /> Total aid is estimated to be around $1 billion per year, which includes.<ref name="ODI1" /> In addition, Brazil already managed a [[United Nations Stabilisation Mission in Haiti|peacekeeping mission in Haiti]] ($350 million) and makes in-kind contributions to the [[World Food Programme]] ($300 million).<ref name="ODI1" /> The scale of this aid places it on par with China and India.<ref name="ODI1" /> The Brazilian [[South-South]] aid has been described as a "global model in waiting".<ref>Cabral, Lidia 2010. [http://blogs.odi.org.uk/blogs/main/archive/2010/07/22/brazil_south_south_cooperation.aspx Brazil's development cooperation with the South: a global model in waiting] ({{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110430190841/http://blogs.odi.org.uk/blogs/main/archive/2010/07/22/brazil_south_south_cooperation.aspx|date=30 April 2011}}). London: [[Overseas Development Institute]]</ref> |
|||
Brazil's foreign policy is a by-product of the country's position as a [[regional power]] in [[Latin America]], a leader among [[developing countries]], and an emerging [[world power]].<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20090710013700/http://www.wilsoncenter.org/news/docs/RL33456.pdf U.S. Congressional Report on Brazil] [[United States Congress]]. Retrieved on 23 June 2009.</ref> Brazilian foreign policy has generally been based on the principles of [[multilateralism]], peaceful dispute settlement, and [[non-interventionism|non-intervention]] in the affairs of other countries.<ref>Georges D. Landau, "The Decision-making Process in Foreign Policy: The Case of Brazil," Center for Strategic and International Studies: Washington DC: March 2003</ref> |
|||
=== Law enforcement and crime === |
|||
Brazil is a founding member state of the [[Community of Portuguese Language Countries]] (CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth, an international organization and political association of [[Lusophone]] nations across four continents, where [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]] is an official language. |
|||
{{Main|Law enforcement in Brazil|Crime in Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Sede da Polícia Federal.jpg|thumb|Headquarters of the [[Federal Police of Brazil]] in [[Brasília]]]] |
|||
In Brazil, the [[Constitution of Brazil|Constitution]] establishes six different police agencies for law enforcement: [[Federal Police Department]], [[Federal Highway Police (Brazil)|Federal Highway Police]], [[Federal Railroad Police]], Federal, District and State Penal Police (included by the Constitutional Amendment No. 104, of 2019), [[Military Police (Brazil)|Military Police]] and [[Civil Police (Brazil)|Civil Police]]. Of these, the first three are affiliated with federal authorities, the last two are subordinate to state governments and the Penal Police can be subordinated to the federal or state/district government. All police forces are overseen by the executive branch of the federal or state government.<ref name="Constituição" /> The [[National Public Security Force]] also can act in public disorder situations arising anywhere in the country.<ref>{{Cite web |date=29 April 2012 |title=Ordem pública é prioridade da Força Nacional de Segurança |url=http://www.brasil.gov.br/defesa-e-seguranca/2012/05/ordem-publica-e-prioridade-da-forca-nacional-de-seguranca |access-date=8 February 2015 |publisher=Portal Brasil |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010152940/http://www.brasil.gov.br/defesa-e-seguranca/2012/05/ordem-publica-e-prioridade-da-forca-nacional-de-seguranca |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
An increasingly well-developed tool of Brazil's foreign policy is providing aid as a donor to other developing countries.<ref name="ODI1">Cabral and Weinstock 2010. [http://www.odi.org.uk/resources/details.asp?id=5120&title=brazil-election-emerging-donor-aid Brazil: an emerging aid player] ({{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110113185641/http://www.odi.org.uk/resources/details.asp?id=5120&title=brazil-election-emerging-donor-aid|date=13 January 2011}}). London: [[Overseas Development Institute]]</ref> Brazil does not just use its growing economic strength to provide financial aid, but it also provides high levels of expertise and most importantly of all, a quiet non-confrontational diplomacy to improve governance levels.<ref name="ODI1"/> Total aid is estimated to be around $1 billion per year, which includes:<ref name="ODI1"/> |
|||
[[File:Diplomatic missions in Brazil.PNG|thumb|upright=1.5|[[List of diplomatic missions in Brazil|Diplomatic missions of Brazil]]]] |
|||
* technical cooperation of around $480 million ($30 million in 2010 provided directly by the Brazilian Cooperation Agency (ABC)); |
|||
* estimated $450 million for in-kind expertise provided by Brazilian institutions specializing in technical cooperation. |
|||
The country has high levels of violent crime, such as gun violence and homicides. In 2012, the [[World Health Organization]] (WHO) estimated the number of 32 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, one of the [[List of countries by intentional homicide rate|highest rates of homicide of the world]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=10 December 2014 |title=Brasil tem maior número absoluto de homicídios do mundo |url=http://brasil.estadao.com.br/noticias/geral,brasil-tem-maior-numero-absoluto-de-homicidios-do-mundo,1604827 |publisher=[[O Estado de S. Paulo]] |access-date=4 February 2015 |archive-date=14 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210414194042/https://brasil.estadao.com.br/noticias/geral,brasil-tem-maior-numero-absoluto-de-homicidios-do-mundo,1604827 |url-status=live }}</ref> The number considered acceptable by the WHO is about 10 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants.<ref>{{Cite web |date=31 January 2011 |title=Taxa de delito por 100 mil habitantes |url=http://www.ssp.sp.gov.br/estatistica/dados.aspx?id=E |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110811121142/http://www.ssp.sp.gov.br/estatistica/dados.aspx?id=E |archive-date=11 August 2011 |access-date=14 February 2011 |publisher=Secretaria de Segurança Pública do Estado de São Paulo}}</ref> In 2018, Brazil had a record 63,880 murders.<ref>{{Cite news |date=10 August 2018 |title=A Year of Violence Sees Brazil's Murder Rate Hit Record High |work=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2018/08/10/world/americas/brazil-murder-rate-record.html |url-access=limited |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220101/https://www.nytimes.com/2018/08/10/world/americas/brazil-murder-rate-record.html |archive-date=1 January 2022}}{{cbignore}}</ref> However, there are differences between the crime rates in the [[States of Brazil|Brazilian states]]. While in [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]] the homicide rate registered in 2013 was 10.8 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, in [[Alagoas]] it was 64.7 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants.<ref>{{Cite magazine |date=11 November 2014 |title=Os estados com mais homicídios no Brasil |url=http://exame.abril.com.br/brasil/noticias/uma-pessoa-e-assassinada-a-cada-dez-minutos-no-brasil |magazine=[[Exame]] |access-date=5 February 2015 |archive-date=28 August 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160828212304/http://exame.abril.com.br/brasil/noticias/uma-pessoa-e-assassinada-a-cada-dez-minutos-no-brasil |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
In addition, Brazil manages a peacekeeping mission in [[2010 Haiti earthquake|Haiti]] ($350 million) and makes in-kind contributions to the [[World Food Programme]] ($300 million).<ref name="ODI1"/> This is in addition to humanitarian assistance and contributions to multilateral development agencies. The scale of this aid places it on par with China and India.<ref name=ODI1/> The Brazilian South-South aid has been described as a "global model in waiting."<ref>Cabral, Lidia 2010. [http://blogs.odi.org.uk/blogs/main/archive/2010/07/22/brazil_south_south_cooperation.aspx Brazil's development cooperation with the South: a global model in waiting] ({{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110430190841/http://blogs.odi.org.uk/blogs/main/archive/2010/07/22/brazil_south_south_cooperation.aspx|date=30 April 2011}}). London: [[Overseas Development Institute]]</ref> |
|||
Brazil also has high levels of incarceration. It had the third largest prison population in the world of approximately 700,000 prisoners as of June 2014, which put it only behind the United States (2,228,424) and China (1,701,344).<ref>{{Cite news |date=5 June 2014 |title=Brasil passa a Rússia e tem a terceira maior população carcerária do mundo |work=[[Folha de S.Paulo]] |url=http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/cotidiano/2014/06/1465527-brasil-passa-a-russia-e-tem-a-terceira-maior-populacao-carceraria-do-mundo.shtml |access-date=4 February 2015 |archive-date=14 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210414193136/https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/cotidiano/2014/06/1465527-brasil-passa-a-russia-e-tem-a-terceira-maior-populacao-carceraria-do-mundo.shtml |url-status=live }}</ref> The high number of prisoners eventually overloaded the Brazilian prison system, leading to a shortfall of about 200,000 accommodations.<ref>{{Cite web |date=15 January 2014 |title=Brasil tem hoje deficit de 200 mil vagas no sistema prisional |url=http://g1.globo.com/brasil/noticia/2014/01/brasil-tem-hoje-deficit-de-200-mil-vagas-no-sistema-prisional.html |access-date=21 March 2014 |publisher=G1 |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193044/http://g1.globo.com/brasil/noticia/2014/01/brasil-tem-hoje-deficit-de-200-mil-vagas-no-sistema-prisional.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
===Law enforcement and crime=== |
|||
=== Human rights === |
|||
{{Main|Law enforcement in Brazil|Crime in Brazil}} |
|||
{{See also|Human rights in Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:COT (6883689782).jpg|thumb|left|Field agents of the [[Federal Police of Brazil|Federal Police]]'s [[Comando de Operações Táticas|Tactical Operations Command]].]] |
|||
{{Excerpt|Human rights in Brazil|hat=no||only=paragraphs}}Same-sex couples in Brazil have held nationwide [[Same-sex marriage in Brazil|marriage rights]] since May 2013.<ref name="edition.cnn.com">{{cite web |last=Brocchetto |first=Marilia |date=May 15, 2013 |title=Brazilian judicial council orders notaries to recognize same-sex marriage |url=http://edition.cnn.com/2013/05/15/world/americas/brazil-same-sex-marriage/index.html?eref=edition |access-date=July 11, 2017 |work=CNN}}</ref> |
|||
In Brazil, the [[Constitution of Brazil|Constitution]] establishes five different police agencies for law enforcement: [[Federal Police Department]], [[Federal Highway Police (Brazil)|Federal Highway Police]], [[Federal Railroad Police]], [[Military Police (Brazil)|Military Police]] and [[Civil Police (Brazil)|Civil Police]]. Of these, the first three are affiliated with federal authorities and the last two are subordinate to state governments. All police forces are the responsibility of the executive branch of any of the federal or state powers.<ref name="Constituição" /> The [[National Public Security Force]] also can act in public disorder situations arising anywhere in the country.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.brasil.gov.br/defesa-e-seguranca/2012/05/ordem-publica-e-prioridade-da-forca-nacional-de-seguranca |title=Ordem pública é prioridade da Força Nacional de Segurança |publisher=Portal Brasil |date=29 April 2012 |accessdate=8 February 2015}}</ref> |
|||
=== Political subdivisions === |
|||
The country still has above-average levels of violent crime and particularly high levels of gun violence and homicide. In 2012, the [[World Health Organization]] (WHO) estimated the number of 32 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, one of the [[List of countries by intentional homicide rate|highest rates of homicide of the world]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://brasil.estadao.com.br/noticias/geral,brasil-tem-maior-numero-absoluto-de-homicidios-do-mundo,1604827|title=Brasil tem maior número absoluto de homicídios do mundo|publisher=[[O Estado de S. Paulo]]|date=10 December 2014}}</ref> The number considered tolerable by the WHO is about 10 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants.<ref>{{cite web |publisher=Secretaria de Segurança Pública do Estado de São Paulo |url=http://www.ssp.sp.gov.br/estatistica/dados.aspx?id=E |title=Taxa de delito por 100 mil habitantes |date=31 January 2011 |accessdate=14 February 2011 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110811121142/http://www.ssp.sp.gov.br/estatistica/dados.aspx?id=E |archivedate=11 August 2011 |url-status=dead}}</ref> In 2018, Brazil had a record 63,880 murders.<ref>{{cite news |title=A Year of Violence Sees Brazil's Murder Rate Hit Record High |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2018/08/10/world/americas/brazil-murder-rate-record.html |work=The New York Times |date=10 August 2018}}</ref> However, there are differences between the crime rates in the [[States of Brazil|Brazilian states]]. While in [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]] the homicide rate registered in 2013 was 10.8 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, in [[Alagoas]] it was 64.7 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants.<ref>{{cite magazine|url=http://exame.abril.com.br/brasil/noticias/uma-pessoa-e-assassinada-a-cada-dez-minutos-no-brasil|title=Os estados com mais homicídios no Brasil|magazine=[[Exame]]|date=11 November 2014|accessdate=5 February 2015}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Subdivisions of Brazil}} |
|||
{{Further|Municipalities of Brazil|States of Brazil|Regions of Brazil}} |
|||
Brazil is a federation composed of 26 [[Federated state|states]], one [[federal district]], and the 5,570 [[Municipality|municipalities]].<ref name="Constituição" /> States have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the Federal government. They have a governor and a unicameral legislative body elected directly by their voters. They also have independent [[Court of Justice (Brazil)|Courts of Law]] for common justice. Despite this, states have much less autonomy to create their own laws than in other federal states such as the United States. For example, criminal and civil laws can be voted by only the federal bicameral Congress and are uniform throughout the country.<ref name="Constituição" /> |
|||
{{Brazil Labelled Map|width=700|float=center}} |
|||
Brazil also has high levels of incarceration and the third largest prison population in the world (behind only [[China]] and the [[United States]]), with an estimated total of approximately 700,000 prisoners around the country (June 2014), an increase of about 300% compared to the index registered in 1992.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/cotidiano/2014/06/1465527-brasil-passa-a-russia-e-tem-a-terceira-maior-populacao-carceraria-do-mundo.shtml|title=Brasil passa a Rússia e tem a terceira maior população carcerária do mundo|newspaper=[[Folha de S.Paulo]]|date=5 June 2014}}</ref> The high number of prisoners eventually overloaded the Brazilian prison system, leading to a shortfall of about 200,000 accommodations.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://g1.globo.com/brasil/noticia/2014/01/brasil-tem-hoje-deficit-de-200-mil-vagas-no-sistema-prisional.html|title=Brasil tem hoje deficit de 200 mil vagas no sistema prisional|publisher=G1|date=15 January 2014|accessdate=21 March 2014}}</ref> |
|||
Municipalities, as the states, have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the federal and state government.<ref name="Constituição" /> Each has an elected mayor and legislative body, but no separate Court of Law. Indeed, a Court of Law organized by the state can encompass many municipalities in a single justice administrative division called ''[[comarca]]'' (county).<ref name="Constituição" /> |
|||
===Administrative divisions=== |
|||
{{Main|States of Brazil|Municipalities of Brazil}} |
|||
{{See also|Regions of Brazil}} |
|||
{| class="infobox" |
|||
|style="text-align: center;"|{{Brazil Labelled Map}}[[States of Brazil]] and [[Regions of Brazil]] |
|||
|} |
|||
Brazil is a federation composed of 26 [[Federated state|states]], one [[federal district]], and the 5570 [[Municipality|municipalities]].<ref name="Constituição" /> States have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the Federal government. They have a governor and a unicameral legislative body elected directly by their voters. They also have independent Courts of Law for common justice. Despite this, states have much less autonomy to create their own laws than in the United States. For example, criminal and civil laws can be voted by only the federal bicameral Congress and are uniform throughout the country.<ref name="Constituição" /> |
|||
Brazil's constitution also provides for the creation of [[Federal territories of Brazil|federal territories]], which are administrative divisions directly controlled by the federal government. However, there are currently no federal territories in the country, as the 1988 Constitution abolished the last three: Amapá and Roraima (which gained statehood status) and Fernando de Noronha, which became a state district of Pernambuco.<ref name=":4">{{Cite journal |last=da Cunha Melo |first=Leopoldo |date=January 1948 |title=Conceituação de "Território Federal" como unidade política |trans-title=Conceptualization of "Federal Territory" as a political unit |url=https://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/visualizacao/periodicos/19/bg_1948_v5_n58_jan.pdf |journal=Boletim Geográfico |language=pt-br |volume=5 |issue=58 |pages=1128–1133 |access-date=26 October 2023 |archive-date=20 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231020120613/https://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/visualizacao/periodicos/19/bg_1948_v5_n58_jan.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Porto |first=Jadson Luís Rebelo |date=March 1999 |title=Os territórios federais e a sua evolução no Brasil |trans-title=The federal territories and their evolution in Brazil |url=http://www.revistapresenca.unir.br/artigos_presenca/15jadsonluisrebeloporto_osterritoriosfederaiseasuaevolucao.pdf |journal=Revista de Educação, Cultura e meio ambiente |language=pt-br |volume=III |issue=15 |access-date=26 October 2023 |archive-date=17 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231117070657/http://www.revistapresenca.unir.br/artigos_presenca/15jadsonluisrebeloporto_osterritoriosfederaiseasuaevolucao.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The states and the federal district may be grouped into regions: [[Northern Region, Brazil|Northern]], [[Northeast Region, Brazil|Northeast]], [[Central-West Region, Brazil|Central-West]], [[Southeast Region, Brazil|Southeast]] and [[Southern Region, Brazil|Southern]]. The Brazilian regions are merely geographical, not political or administrative divisions, and they do not have any specific form of government. Although defined by law, Brazilian regions are useful mainly for statistical purposes, and also to define the distribution of federal funds in development projects. |
|||
== Economy == |
|||
Municipalities, as the states, have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the Union and state government.<ref name="Constituição" /> Each has a mayor and an elected legislative body, but no separate Court of Law. Indeed, a Court of Law organized by the state can encompass many municipalities in a single justice administrative division called ''[[comarca]]'' (county). |
|||
==Economy== |
|||
{{Main|Economy of Brazil}} |
{{Main|Economy of Brazil}} |
||
{{See also|Brazilian real|Agriculture in Brazil|Mining in Brazil|Industry in Brazil}} |
{{See also|Brazilian real|Agriculture in Brazil|Mining in Brazil|Industry in Brazil}} |
||
[[File:Avenida Paulista no pôr do sol.jpg|thumb|Paulista Avenue, in São Paulo, is considered the main financial center of Brazil]] |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
[[File:Sao Paulo Stock Exchange.jpg|thumb|[[B3 (stock exchange)|B3]], the [[List of stock exchanges|largest stock exchange of Latin America by market capitalization]]<ref>{{Cite web |title=21 Largest Stock Exchanges in the World |url=https://finance.yahoo.com/news/21-largest-stock-exchanges-world-154737743.html |access-date=20 June 2023 |website=Yahoo Finance |date=27 March 2023 |archive-date=13 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230913071913/https://finance.yahoo.com/news/21-largest-stock-exchanges-world-154737743.html |url-status=live }}</ref>]] |
|||
| align = left |
|||
[[File:Soja_Tangará.jpg|thumb|[[Soybean]] crop in [[Tangará da Serra]], [[Mato Grosso]]<ref name="exportaçãoagrícola">{{Cite news |date=1 July 2015 |title=Brasil será maior exportador agrícola mundial em 2024 |language=pt |publisher=EXAME |url=https://exame.abril.com.br/economia/brasil-sera-maior-exportador-agricola-mundial-em-2024/ |access-date=9 May 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180509220949/https://exame.abril.com.br/economia/brasil-sera-maior-exportador-agricola-mundial-em-2024/ |archive-date=9 May 2018}}</ref>]] |
|||
| image1 = Sao Paulo Stock Exchange.jpg |
|||
[[File:10 03 2022 Operação Repatriação - Chegada dos Brasileiros e Estrangeiros provenientes da Ucrânia (51931465965).jpg|thumb|The [[Embraer C-390 Millennium|C-390]], developed by [[Embraer]], the third largest producer of [[civil aircraft]], after [[Boeing]] and [[Airbus]]<ref>{{Cite web |date=10 October 2010 |title=Embraer vê clientes mais dispostos à compra de aviões |url=http://exame.abril.com.br/negocios/empresas/noticias/embraer-ve-clientes-mais-dispostos-compra-avioes-554715 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110728095448/http://exame.abril.com.br/negocios/empresas/noticias/embraer-ve-clientes-mais-dispostos-compra-avioes-554715 |archive-date=28 July 2011 |access-date=8 February 2014 |publisher=Exame Magazine}}</ref>]] |
|||
| width1 = 275 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = Quotes panel in the interior of [[B3 (stock exchange)|B3]], in [[São Paulo]], one of the [[List of stock exchanges|top 20 stock exchanges by market capitalization]]. |
|||
| image2 = Itaim Bibi (232990015).jpeg |
|||
| width2 = 195 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = [[São Paulo]], the country's main [[financial center]] |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
Brazil's [[List of countries by GNI (nominal) per capita#Upper-middle income group|upper-middle income]] [[mixed economy|mixed]] [[market economy]] is rich in natural resources.<ref>{{Cite web |title=6. Brazil |url=https://www.fao.org/3/w7560e/W7560E06.htm |access-date=3 October 2022 |publisher=[[Food and Agriculture Organization]] (FAO) |quote=Brazil is rich in a variety of natural resources and is the world's leading producer of tin, iron ore and phosphate. It has large deposits of diamonds, manganese, chromium, copper, bauxite and many other minerals. |archive-date=3 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221003111320/https://www.fao.org/3/w7560e/W7560E06.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> It has the largest national economy in [[Latin America]], the [[List of countries by GDP (nominal)|eighth-largest economy]] in the world by nominal GDP, and the [[List of countries by GDP (PPP)|eighth-largest]] by [[purchasing power parity|PPP]]. After rapid growth in preceding decades, the country [[2014–2016 Brazilian economic recession|entered an ongoing recession in 2014]] amid a political corruption scandal and nationwide protests. A [[developing country]], Brazil has a [[labor force]] of roughly 100 million,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Labor force, total – Brazil |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SL.TLF.TOTL.IN?locations=Br |access-date=3 October 2022 |website=[[World Bank]] |archive-date=3 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221003105226/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SL.TLF.TOTL.IN?locations=Br |url-status=live }}</ref> which is the world's [[List of countries by labour force|fifth-largest]]; with a high unemployment rate of 14.4% {{as of|2021|lc=y}}.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) (modeled ILO estimate) – Brazil |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SL.UEM.TOTL.ZS?locations=BR |access-date=3 October 2022 |website=[[World Bank]] |archive-date=13 August 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200813064142/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SL.UEM.TOTL.ZS?locations=BR |url-status=live }}</ref> Its [[foreign exchange reserves]] are the [[List of countries by foreign exchange reserves|tenth-highest]] in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Banco Central do Brasil – SDDS |url=https://www.bcb.gov.br/en/financialstability/internationalreserves |access-date=21 July 2022 |website=www.bcb.gov.br |publisher=[[Central Bank of Brazil]] |archive-date=21 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721234432/https://www.bcb.gov.br/en/financialstability/internationalreserves |url-status=live }}</ref> The [[B3 (stock exchange)|B3]] in São Paulo is the [[List of stock exchanges|largest stock exchange of Latin America by market capitalization]]. In regards to poverty, about 1.9% of the total population lives at $2.15 a day,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Poverty headcount ratio at $2.15 a day (2017 PPP) (% of population) – Brazil |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.DDAY?locations=BR |access-date=3 October 2022 |website=[[World Bank]] |archive-date=3 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221003111321/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.DDAY?locations=BR |url-status=live }}</ref> while about 19% live at $6.85 a day.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Poverty headcount ratio at $6.85 a day (2017 PPP) (% of population) – Brazil |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.UMIC?locations=BR |access-date=3 October 2022 |website=[[World Bank]] |archive-date=3 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221003111317/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.UMIC?locations=BR |url-status=live }}</ref> Brazil's economy suffers from [[Corruption in Brazil|endemic corruption]] and [[Income inequality in Brazil|high income inequality]].<ref>{{Cite web |last=France |first=Guilherme |date=29 January 2019 |title=Brazil: Overview of corruption and anti-corruption |url=https://knowledgehub.transparency.org/assets/uploads/helpdesk/Brazil-Country-Profile-2019_PR.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://knowledgehub.transparency.org/assets/uploads/helpdesk/Brazil-Country-Profile-2019_PR.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |access-date=3 October 2022 |publisher=[[Transparency International]] |quote=Corruption remains one of the biggest impediments to economic development in Brazil.}}</ref> The [[Brazilian real]] is the national currency. |
|||
Brazil is the largest national economy in [[Latin America]], the [[List of countries by GDP (nominal)|world's ninth largest economy]] and the [[List of countries by GDP (PPP)|eighth largest]] in [[purchasing power parity]] (PPP) according to 2018 estimates. Brazil has a [[mixed economy]] with abundant natural resources. After rapid growth in preceding decades, the country [[2014–2016 Brazilian economic recession|entered an ongoing recession in 2014]] amid a political corruption scandal and nationwide protests. |
|||
Brazil's diversified economy includes agriculture, industry and a wide range of services.<ref name="BansalPhatak2009">{{Cite book |last1=Alok Bansal |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Wm4IWvB4rEUC&pg=PA29 |title=Transcending Horizons Through Innovative Global Practices |last2=Yogeshwari Phatak |last3=I C Gupta |last4=Rajendra Jain |publisher=Excel Books |year=2009 |isbn=978-81-7446-708-9 |page=29 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183849/https://books.google.com/books?id=Wm4IWvB4rEUC&pg=PA29#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> The large service sector accounts for about 72.7% of total GDP, followed by the industrial sector (20.7%), while the [[Agriculture in Brazil|agriculture sector]] is by far the smallest, making up 6.6% of total GDP.<ref>{{Cite web |title=GDP – composition, by sector of origin |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/gdp-composition-by-sector-of-origin/ |access-date=3 October 2022 |website=[[The World Factbook]] |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency]] |archive-date=19 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230419042310/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/gdp-composition-by-sector-of-origin/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Its [[Gross domestic product]] (PPP) per capita was $15,919 in 2017<ref name="imf">{{cite web |url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2016/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2015&ey=2020&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&pr1.x=54&pr1.y=7&c=223&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC&grp=0&a= |title=Brazil |publisher=International Monetary Fund (IMF) |accessdate=1 April 2016}}</ref> putting Brazil in the 77th position according to IMF data. Active in [[agriculture|agricultural]], [[mining]], [[manufacturing]] and [[Tertiary sector of the economy|service sectors]] Brazil has a labor force of over 107 million (ranking 6th worldwide) and unemployment of 6.2% (ranking 64th worldwide).<ref name="CIA Econ">{{cite web |title=Economy of Brazil |website=The World Factbook |publisher=Central Intelligence Agency |year=2008 |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/br.html |accessdate=3 June 2008}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil is one of the [[List of largest producing countries of agricultural commodities|largest producers of various agricultural commodities]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=FAOSTAT |url=http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/ |website=www.fao.org |access-date=11 January 2021 |archive-date=12 November 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161112130804/http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and also has a large [[cooperative]] sector that provides 50% of the food in the country.<ref>{{Cite web |title=How are agricultural co-operatives making a difference in Brazil? {{pipe}} ICA |url=https://www.ica.coop/en/media/news/how-are-agricultural-co-operatives-making-difference-brazil |website=ica.coop |access-date=1 February 2019 |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193227/https://www.ica.coop/en/media/news/how-are-agricultural-co-operatives-making-difference-brazil |url-status=live }}</ref> It has been the world's largest [[Coffee production in Brazil|producer of coffee]] for the last 150 years.<ref name="Neilson102">{{Cite book |last1=Jeff Neilson |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wokuHhx1AOUC&pg=PA1834 |title=Value Chain Struggles |last2=Bill Pritchard |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-4443-5544-4 |page=102 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=25 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231025210521/https://books.google.com/books?id=wokuHhx1AOUC&pg=PA1834#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> Brazil is the world's largest producer of [[sugarcane]], [[soy]], [[coffee]] and [[Orange (fruit)|orange]]; is one of the top 5 producers of [[maize]], [[cotton]], [[lemon]], [[tobacco]], [[pineapple]], [[banana]], [[beans]], [[coconut]], [[watermelon]] and [[papaya]]; and is one of the top 10 world producers of [[Cocoa bean|cocoa]], [[cashew]], [[mango]], [[rice]], [[tomato]], [[sorghum]], [[tangerine]], [[avocado]], [[persimmon]], and [[guava]], among others. Regarding livestock, it is one of the 5 largest producers of [[chicken meat]], [[beef]], [[pork]] and [[cow's milk]] in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Production of Brazil, by FAO |url=http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/ |access-date=4 October 2022 |archive-date=12 November 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161112130804/http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In the [[Mining in Brazil|mining sector]], Brazil is among the largest producers of [[iron ore]], copper, gold,<ref>{{Cite web |date=29 June 2019 |title=Brasil extrai cerca de 2 gramas de ouro por habitante em 5 anos |url=https://noticias.r7.com/brasil/brasil-extrai-cerca-de-2-gramas-de-ouro-por-habitante-em-5-anos-29062019 |website=R7.com |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=12 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200712095924/https://noticias.r7.com/brasil/brasil-extrai-cerca-de-2-gramas-de-ouro-por-habitante-em-5-anos-29062019 |url-status=live }}</ref> [[bauxite]], [[manganese]], [[tin]], [[niobium]],<ref>{{Cite web |date=12 December 2019 |title=Nióbio: G1 visita em MG complexo industrial do maior produtor do mundo |url=https://g1.globo.com/economia/noticia/2019/12/12/niobio-g1-visita-em-mg-complexo-industrial-do-maior-produtor-do-mundo.ghtml |website=G1 |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=12 December 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191212144838/https://g1.globo.com/economia/noticia/2019/12/12/niobio-g1-visita-em-mg-complexo-industrial-do-maior-produtor-do-mundo.ghtml |url-status=live }}</ref> and [[nickel]]. In terms of precious stones, Brazil is the world's largest producer of [[amethyst]], [[topaz]], [[agate]] and one of the main producers of [[tourmaline]], [[emerald]], [[aquamarine (gemstone)|aquamarine]], [[garnet]] and [[opal]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Serviço Geológico do Brasil |url=http://www.cprm.gov.br/publique/Redes-Institucionais/Rede-de-Bibliotecas---Rede-Ametista/Algumas-Gemas-Classicas-1104.html |website=cprm.gov.br |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=6 September 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190906194936/http://www.cprm.gov.br/publique/Redes-Institucionais/Rede-de-Bibliotecas---Rede-Ametista/Algumas-Gemas-Classicas-1104.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Rio Grande do Sul: o maior exportador de pedras preciosas do Brasil |url=https://noticias.band.uol.com.br/noticias/100000911432/rio-grande-do-sul-o-maior-exportador-de-pedras-preciosas-do-brasil.html |website=Band.com.br |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=2 May 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180502153003/https://noticias.band.uol.com.br/noticias/100000911432/rio-grande-do-sul-o-maior-exportador-de-pedras-preciosas-do-brasil.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The country is a major exporter of soy, iron ore, pulp (cellulose), maize, beef, chicken meat, soybean meal, sugar, coffee, tobacco, cotton, orange juice, footwear, airplanes, cars, vehicle parts, gold, ethanol and semi-finished iron, among other products.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Fazcomex Tecnologia para Comércio Exterior – Soluções para Comex |url=https://www.fazcomex.com.br/ |website=Fazcomex | Tecnologia para Comércio Exterior |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=29 June 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210629234222/https://www.fazcomex.com.br/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Agronegócio tem oito entre os dez produtos líderes das exportações brasileiras em 2019 |url=https://www.aviculturaindustrial.com.br/imprensa/agronegocio-tem-oito-entre-dez-produtos-l%C3%ADderes-das-exportacoes-brasileiras/20200102-130051-c255 |website=Avicultura Industrial |date=2 January 2020 |access-date=11 January 2021 |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193049/https://www.aviculturaindustrial.com.br/imprensa/agronegocio-tem-oito-entre-dez-produtos-l%C3%ADderes-das-exportacoes-brasileiras/20200102-130051-c255 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The country has been expanding its presence in international financial and [[commodity market|commodities markets]], and is one of a group of four emerging economies called the [[BRIC|BRIC countries]].<ref>{{cite web |last=O'Neill |first=Jim |authorlink=Jim O'Neill (economist) |title=BRICs |publisher=Goldman Sachs |url=http://www.goldmansachs.com/our-thinking/ |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> Brazil has been the world's largest [[Coffee production in Brazil|producer of coffee]] for the last 150 years.<ref name="Neilson102">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wokuHhx1AOUC&pg=PA1834|page=102|title=Value Chain Struggles|author1=Jeff Neilson |author2=Bill Pritchard |publisher=John Wiley & Sons|year=2011|isbn=978-1-4443-5544-4}}</ref> |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| image1 = Ronodonópolis colheita soja (Roosevelt Pinheiro) 28mar09.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = [[Soybean]] crop in [[Rondonópolis]], [[Mato Grosso]]. Brazil is the second largest agricultural exporter in the world.<ref name="exportaçãoagrícola">{{cite news|title=Brasil será maior exportador agrícola mundial em 2024|publisher=EXAME|date=1 July 2015|url=https://exame.abril.com.br/economia/brasil-sera-maior-exportador-agricola-mundial-em-2024/|accessdate=9 May 2018|language=Portuguese}}</ref> |
|||
|image2 = KC-390 - RIAT 2018 (41847171670).jpg |
|||
| caption2 = The [[KC-390]], developed by [[Embraer]]. |
|||
|image3 = Oil platform P-51 (Brazil).jpg |
|||
| caption3 = P-51, an [[oil platform]] of [[Petrobras]] |
|||
|image4 = Itaipu_geral.jpg |
|||
| caption4 = The [[Itaipu Dam]] on the [[Paraná River]], located on the border between Brazil and Paraguay, is the second largest of the world (the first is the [[Three Gorges Dam]], in China). Approximately 75% of the [[Energy policy of Brazil|Brazilian energy matrix]], one of the [[Clean energy|cleanest]] in the world, comes from [[hydropower]]. |
|||
Brazil is the world's [[List of countries by exports|24th-largest exporter]] and [[List of countries by imports|26th-largest importer]] {{as of|2021|lc=y}}.<ref>{{Cite web |title=List of importing markets for the product exported by Brazil in 2021 |url=https://www.trademap.org/Country_SelProductCountry.aspx?nvpm=1%7c076%7c%7c%7c%7cTOTAL%7c%7c%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c1 |access-date=3 October 2022 |publisher=[[International Trade Centre]] |archive-date=12 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230412235829/https://www.trademap.org/Country_SelProductCountry.aspx?nvpm=1%7C076%7C%7C%7C%7CTOTAL%7C%7C%7C2%7C1%7C1%7C2%7C1%7C1%7C2%7C1%7C1%7C1 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=List of supplying markets for the product imported by Brazil in 2021 |url=https://www.trademap.org/Country_SelProductCountry.aspx?nvpm=1%7c076%7c%7c%7c%7cTOTAL%7c%7c%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c1%7c1%7c1%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c1 |access-date=3 October 2022 |publisher=[[International Trade Centre]] |archive-date=3 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221003114043/https://www.trademap.org/Country_SelProductCountry.aspx?nvpm=1%7C076%7C%7C%7C%7CTOTAL%7C%7C%7C2%7C1%7C1%7C1%7C1%7C1%7C2%7C1%7C1%7C1 |url-status=live }}</ref> [[China]] is its largest trading partner, accounting for 32% of the total trade. Other large trading partners include the [[United States]], [[Argentina]], the [[Netherlands]] and [[Canada]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Brazil Trade |url=https://wits.worldbank.org/CountrySnapshot/en/BRA |access-date=3 October 2022 |publisher=[[World Integrated Trade Solution]] (WITS) |archive-date=3 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221003114046/https://wits.worldbank.org/CountrySnapshot/en/BRA |url-status=live }}</ref> Its [[Automotive industry in Brazil|automotive industry]] is the [[List of countries by motor vehicle production|eighth-largest]] in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |date=23 January 2022 |title=Official History of Automobile Industry in Brazil |url=https://anfavea.com.br/site/timeline/?lang=en/ |publisher=National Association of Vehicles Industries |access-date=3 October 2022 |archive-date=3 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221003114043/https://anfavea.com.br/site/timeline/?lang=en/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In the [[food industry]], Brazil was the second-largest exporter of processed foods in the world in 2019.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Alimentos Processados {{pipe}} A indústria de alimentos e bebidas na sociedade brasileira atual |url=https://alimentosprocessados.com.br/industria-na-sociedade-brasileira.php |website=alimentosprocessados.com.br |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=25 March 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180325142658/https://alimentosprocessados.com.br/industria-na-sociedade-brasileira.php |url-status=live }}</ref> The country was the second-largest producer of [[Pulp (paper)|pulp]] in the world and the eighth-largest producer of paper in 2016.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Produção nacional de celulose cai 6,6% em 2019, aponta Ibá |url=https://valor.globo.com/empresas/noticia/2020/02/21/producao-nacional-de-celulose-cai-66percent-em-2019-aponta-iba.ghtml |website=Valor Econômico |date=21 February 2020 |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=21 February 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200221134709/https://valor.globo.com/empresas/noticia/2020/02/21/producao-nacional-de-celulose-cai-66percent-em-2019-aponta-iba.ghtml |url-status=live }}</ref> In the [[footwear industry]], Brazil was the fourth-largest producer in 2019.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Indústrias calçadistas em Franca, SP registram queda de 40% nas vagas de trabalho em 6 anos |url=https://g1.globo.com/sp/ribeirao-preto-franca/noticia/2019/07/14/industrias-calcadistas-em-franca-sp-registram-queda-de-40percent-nas-vagas-de-trabalho-em-6-anos.ghtml |website=G1 |date=14 July 2019 |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=14 July 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190714205803/https://g1.globo.com/sp/ribeirao-preto-franca/noticia/2019/07/14/industrias-calcadistas-em-franca-sp-registram-queda-de-40percent-nas-vagas-de-trabalho-em-6-anos.ghtml |url-status=live }}</ref> It was also the ninth-largest producer of steel in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Comércio |first=Diário do |date=24 January 2020 |title=Minas Gerais produz 32,3% do aço nacional em 2019 |url=https://diariodocomercio.com.br/livre/minas-gerais-produz-323-do-aco-nacional-em-2019/ |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=14 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200614182655/https://diariodocomercio.com.br/livre/minas-gerais-produz-323-do-aco-nacional-em-2019/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=8 March 2019 |title=O novo mapa das montadoras, que agora rumam para o interior do País |url=https://www.istoedinheiro.com.br/o-novo-mapa-das-montadoras/ |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=8 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190308152711/https://www.istoedinheiro.com.br/o-novo-mapa-das-montadoras/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Indústria automobilística do Sul do Rio impulsiona superavit na economia |url=https://g1.globo.com/rj/sul-do-rio-costa-verde/noticia/industria-automobilistica-do-sul-do-rio-impulsiona-superavit-na-economia.ghtml |website=G1 |date=12 July 2017 |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=19 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170719091817/https://g1.globo.com/rj/sul-do-rio-costa-verde/noticia/industria-automobilistica-do-sul-do-rio-impulsiona-superavit-na-economia.ghtml |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2018, the [[chemical industry]] of Brazil was the eighth-largest in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Indústria Química no Brasil |url=https://www.pwc.com.br/pt/publicacoes/setores-atividade/assets/quimico-petroquimico/2013/pwc-chemicals-port-13.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.pwc.com.br/pt/publicacoes/setores-atividade/assets/quimico-petroquimico/2013/pwc-chemicals-port-13.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Estudo de 2018 |url=https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/br/Documents/energy-resources/Deloitte-Abiquim-Setor-Quimico-Relatorio.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/br/Documents/energy-resources/Deloitte-Abiquim-Setor-Quimico-Relatorio.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Produção nacional da indústria de químicos cai 5,7% em 2019, diz Abiquim |url=https://economia.uol.com.br/noticias/estadao-conteudo/2020/02/03/producao-nacional-da-industria-de-quimicos-cai-57-em-2019-diz-abiquim.htm |website=economia.uol.com.br |access-date=15 August 2020 |archive-date=14 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200614230629/https://economia.uol.com.br/noticias/estadao-conteudo/2020/02/03/producao-nacional-da-industria-de-quimicos-cai-57-em-2019-diz-abiquim.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Although it was among the five largest world producers in 2013, Brazil's textile industry is very little integrated into world trade.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Industria Textil no Brasil |url=https://www.bnb.gov.br/documents/80223/2509338/textil_16_2017%28V2%29.pdf/063d7521-342f-e81e-232a-e251964fa1c3 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200619042050/https://www.bnb.gov.br/documents/80223/2509338/textil_16_2017%28V2%29.pdf/063d7521-342f-e81e-232a-e251964fa1c3 |archive-date=19 June 2020 |access-date=15 August 2020}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
The tertiary sector (trade and services) represented 75.8% of the country's GDP in 2018, according to the IBGE. The service sector was responsible for 60% of GDP and trade for 13%. It covers commerce, transport, education, social and health services, research and development, sports activities, etc.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Setor de serviços sustenta o crescimento do PIB de 2018 |url=https://veja.abril.com.br/economia/setor-de-servicos-sustenta-o-crescimento-do-pib-de-2018/ |website=VEJA |access-date=6 January 2021 |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193256/https://veja.abril.com.br/economia/setor-de-servicos-sustenta-o-crescimento-do-pib-de-2018/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Produtividade e Comércio Exterior |url=https://www.gov.br/produtividade-e-comercio-exterior/pt-br/index |website=SECINT e SEPEC |access-date=1 April 2021 |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193204/https://www.gov.br/produtividade-e-comercio-exterior/pt-br/index |url-status=live }}</ref> Micro and small businesses represent 30% of the country's GDP. In the commercial sector, for example, they represent 53% of the GDP within the activities of the sector.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Pequenos negócios já representam 30% do Produto Interno Bruto do país |date=7 November 2022 |url=https://revistapegn.globo.com/Negocios/noticia/2020/04/pequenos-negocios-ja-representam-30-do-produto-interno-bruto-do-pais.html |access-date=6 January 2021 |archive-date=13 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210413193345/https://revistapegn.globo.com/Negocios/noticia/2020/04/pequenos-negocios-ja-representam-30-do-produto-interno-bruto-do-pais.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Brazil's diversified economy includes agriculture, industry, and a wide range of services.<ref name="BansalPhatak2009">{{cite book|author1=Alok Bansal|author2=Yogeshwari Phatak|author3=I C Gupta|author4=Rajendra Jain|title=Transcending Horizons Through Innovative Global Practices|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Wm4IWvB4rEUC&pg=PA29|year= 2009|publisher=Excel Books |isbn=978-81-7446-708-9|page=29}}</ref> [[Agriculture in Brazil|Agriculture]] and allied sectors like [[forestry]], [[logging]] and [[fishing]] accounted for 5.1% of the [[gross domestic product|GDP]] in 2007.<ref name="CIA GDP">{{cite web |title=Field Listing – GDP – composition by sector |website=The World Factbook |publisher=Central Intelligence Agency |year=2008 |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2012.html |accessdate=9 June 2008}}</ref> Brazil is the [[List of largest producing countries of agricultural commodities|largest producer]] of [[sugar cane]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://revistagloborural.globo.com/Noticias/Agricultura/Cana/noticia/2020/05/producao-de-cana-deve-ser-19-menor-na-safra-20202021-aponta-conab.html|title=Produção de cana deve ser 1,9% menor na safra 2020/2021, aponta Conab|website=Revista Globo Rural}}</ref> [[soybeans]],<ref name="auto2">{{Cite web|url=https://revistagloborural.globo.com/Noticias/Agricultura/noticia/2020/06/brasil-deve-colher-131-milhoes-de-toneladas-de-soja-na-safra-202021-aponta-usda.html|title=Brasil deve colher 131 milhões de toneladas de soja na safra 2020/21, aponta USDA|website=Revista Globo Rural}}</ref> [[coffee]],<ref name="auto3">{{Cite web|url=https://agenciadenoticias.ibge.gov.br/agencia-sala-de-imprensa/2013-agencia-de-noticias/releases/26537-ibge-preve-safra-recorde-de-graos-em-2020|title=IBGE prevê safra recorde de grãos em 2020|website=agenciadenoticias.ibge.gov.br}}</ref> [[Orange (fruit)|orange]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cnpmf.embrapa.br/Base_de_Dados/index_pdf/dados/brasil/laranja/b1_laranja.pdf|title=Produção brasileira de laranja em 2018}}</ref><ref name="Luck1998">{{cite book|author=Steve Luck|title=The American Desk Encyclopedia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=o8MdoOd6pOcC&pg=PA121|year=1998|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-521465-9|page=121}}</ref> and is the 2nd largest producer in the world of [[papaya]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cnpmf.embrapa.br/Base_de_Dados/index_pdf/dados/brasil/mamao/b1_mamao.pdf|title=Produção brasileira de mamão em 2018}}</ref> 3rd largest of [[maize]],<ref name="auto2"/> [[tobacco]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.noticiasagricolas.com.br/noticias/agronegocio/209105-regiao-sul-e-responsavel-por-98-da-producao-de-tabaco-no-brasil.html|title=Região Sul é responsável por 98% da produção de tabaco no Brasil|website=noticiasagricolas.com.br}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.portaldoagronegocio.com.br/conteudo.php?id=25822|title=Notícia: Região Sul deverá produzir 760 mil toneladas de fumo em 2008/2009}}</ref> and [[pineapple]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cnpmf.embrapa.br/Base_de_Dados/index_pdf/dados/brasil/abacaxi/b1_abacaxi.pdf|title=Produção brasileira de abacaxi em 2018, Embrapa}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.adepara.pa.gov.br/artigos/abacaxi-faz-o-par%C3%A1-despontar-como-o-maior-produtor-nacional-do-fruto|title=Abacaxi faz o Pará despontar como o maior produtor nacional do fruto | ADEPARÁ|website=adepara.pa.gov.br}}</ref> 4th place in [[cotton]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/ba/bahia/noticia/2019/06/08/segundo-maior-produtor-de-algodao-do-pais-bahia-tem-previsao-de-15percent-de-crescimento-da-safra.ghtml|title=Segundo maior produtor de algodão do país, Bahia tem previsão de 15% de crescimento da safra|website=G1}}</ref><ref>[https://www.agroolhar.com.br/noticias/exibir.asp?id=25834¬icia=mt-segue-como-lider-isolado-na-producao-de-algodao-e-safra-sobe-para-65-em-201718 MT segue como líder isolado na produção de algodão e safra sobe para 65% em 2017/18]</ref> and [[cassava]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cnpmf.embrapa.br/Base_de_Dados/index_pdf/dados/brasil/mandioca/b1_mandioca.pdf|title=Produção brasileira de mandioca em 2018}}</ref> 5th place in [[coconut]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.bnb.gov.br/documents/80223/4296541/61_coco.pdf/c172dd8f-3044-f1db-5d0c-a94c5eb735e0|title=PRODUÇÃO DE COCO: O NORDESTE É DESTAQUE NACIONAL}}</ref> and [[lemon]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cnpmf.embrapa.br/Base_de_Dados/index_pdf/dados/brasil/limao/b1_limao.pdf|title=Produção brasileira de limão em 2018}}</ref> 6th in [[Cocoa bean|cocoa]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/economia/agronegocios/globo-rural/noticia/2019/11/03/lideranca-na-producao-brasileira-de-cacau-volta-para-casa-no-para-com-a-uniao-de-agricultores.ghtml|title=Pará retoma liderança na produção brasileira de cacau, com a união de agricultores|website=G1}}</ref> and [[avocado]], 9th in [[rice]],<ref name="auto3"/> 10th in [[tomato]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/economia/agronegocios/globo-rural/noticia/2020/06/07/safra-de-tomate-deve-vir-12percent-menor-este-ano-em-goias.ghtml|title=Safra de tomate deve vir 12% menor este ano em Goiás|website=G1}}</ref> and 11th in [[grape]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.jvanguarda.com.br/site2012/2018/07/27/regiao-sul-e-responsavel-por-mais-de-90-das-uvas-produzidas-para-processamento-no-brasil/|title=Região Sul é responsável por mais de 90% das uvas produzidas para processamento no Brasil}}</ref> and [[apple]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nsctotal.com.br/noticias/safra-da-maca-deve-render-600-mil-toneladas-em-santa-catarina|title=Safra da maçã deve render 600 mil toneladas em Santa Catarina|website=nsctotal.com.br}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://estado.rs.gov.br/governador-abre-oficialmente-a-colheita-da-maca-e-da-uva-no-rs|title=Qualidade da fruta marca abertura da colheita da maçã e da uva no RS|date=16 February 2019|website=Portal do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul}}</ref> The country is also one of the 3 largest [[banana]] producers in the world,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cnpmf.embrapa.br/Base_de_Dados/index_pdf/dados/brasil/banana/b1_banana.pdf|title=Produção brasileira de banana em 2018}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/403361/custo-de-producao-de-banana-no-sudeste-paraense|title=Custo de produção de banana no sudeste paraense. - Portal Embrapa|website=embrapa.br}}</ref> but almost all production is destined for national consumption. The country also produces large quantities of [[beans]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.agricultura.pr.gov.br/sites/default/arquivos_restritos/files/documento/2019-09/feijao_2019_v1.pdf|title=Feijão - Análise da Conjuntura Agropecuária}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.terra.com.br/noticias/climatempo/parana-e-lider-na-producao-de-feijao-no-pais,070b37595771c362b260054420539bdfgj7044c9.html|title=Paraná é líder na produção de feijão no País|website=Terra}}</ref> [[peanut]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-noticias/-/noticia/40697528/estudo-mapeia-areas-de-producao-de-amendoim-do-brasil-para-prevenir-doenca-do-carvao|title=Estudo mapeia áreas de produção de amendoim do Brasil para prevenir doença do carvão|website=embrapa.br}}</ref> [[potato]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://g1.globo.com/economia/agronegocios/globo-rural/noticia/2017/07/produtores-de-batata-vivem-realidades-distintas-em-minas-gerais.html|title=Produtores de batata vivem realidades distintas em Minas Gerais|date=23 July 2017|website=Globo Rural}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cnabrasil.org.br/noticias/aumento-da-demanda-elevara-a-colheita-de-batata-em-minas|title=Aumento da demanda elevará a colheita de batata em Minas|website=Confederação da Agricultura e Pecuária do Brasil (CNA)}}</ref> [[carrot]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.ceasa.pr.gov.br/arquivos/File/BOLETIM/Boletim_Tecnico_Cenoura.pdf|title=CENOURA:Produção, mercado e preços}}</ref> [[cashew nuts]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.bnb.gov.br/documents/80223/4141162/54_caju.pdf/95e65093-50e1-b48d-ab01-15f3a8f690b4|title=CAJUCULTURA NORDESTINA EM RECUPERAÇÃO}}</ref> [[tangerine]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cnpmf.embrapa.br/Base_de_Dados/index_pdf/dados/brasil/tangerina/b1_tangerina.pdf|title=Produção brasileira de tangerina em 2018}}</ref> [[persimmon]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://revistacampoenegocios.com.br/caqui-panorama-nacional-da-producao/|title=Caqui - Panorama nacional da produção|date=17 May 2019}}</ref> [[strawberry]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://revistacampoenegocios.com.br/qual-o-panorama-da-producao-de-morango-no-brasil/|title=Qual o panorama da produção de morango no Brasil?|date=18 December 2019}}</ref> [[guaraná]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://valor.globo.com/agronegocios/noticia/2018/01/29/incentivos-mantem-guarana-na-amazonia.ghtml|title=Incentivos mantêm guaraná na Amazônia|website=Valor Econômico}}</ref> [[guava]], [[açaí]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/pa/para/noticia/2019/03/15/caminhos-do-acai-para-produz-95-da-producao-do-brasil-fruto-movimenta-us-15-bi-e-sao-paulo-e-o-principal-destino-no-pais.ghtml|title=Caminhos do açaí: Pará produz 95% da produção do Brasil, fruto movimenta US$ 1,5 bi e São Paulo é o principal destino no país|website=G1}}</ref> [[Brazil nut]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/economia/agronegocios/globo-rural/noticia/2020/04/19/producao-comercial-de-castanhas-na-amazonia-ajuda-na-recuperacao-de-florestas-e-movimenta-economia-local.ghtml|title=Produção comercial de castanhas na Amazônia ajuda na recuperação de florestas e movimenta economia local|website=G1}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-noticias/-/noticia/26131296/pesquisa-aponta-queda-de-70-na-producao-de-castanha-da-amazonia|title=Pesquisa aponta queda de 70% na produção de castanha-da-amazônia|website=embrapa.br}}</ref> [[yerba mate]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.gazetadopovo.com.br/agronegocio/mercado-internacional-esta-sedento-por-erva-mate-brasileira/|title=Setor de erva-mate muda para conquistar novos consumidores|website=Gazeta do Povo}}</ref> [[wheat]], among others. Part of the production is exported, and another part goes to the domestic market. |
|||
=== Tourism === |
|||
In the production of animal proteins, Brazil is today one of the largest countries in the world. In 2019, the country was the world's largest exporter of [[chicken meat]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.aviculturaindustrial.com.br/imprensa/conheca-os-3-paises-que-desafiam-o-brasil-nas-exportacoes-de-frango/20200122-093443-o532|title=Conheça os 3 países que desafiam o Brasil nas exportações de frango|website=Avicultura Industrial}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.farmnews.com.br/mercado/maiores-exportadores-de-carne-de-frango/|title=Maiores exportadores de carne de frango entre 2015 e 2019|first=Ivan|last=Formigoni|date=30 May 2019}}</ref> It was also the second largest producer of [[beef]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.beefpoint.com.br/ibge-rebanho-de-bovinos-tinha-21823-milhoes-de-cabecas-em-2016/|title=IBGE: rebanho de bovinos tinha 218,23 milhões de cabeças em 2016 | BeefPoint|website=beefpoint.com.br}}</ref> the world's third largest producer of [[milk]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://agronewsbrazil.com.br/brasil-e-o-3o-maior-produtor-de-leite-do-mundo-superando-o-padrao-europeu-em-alguns-municipios/|title=Brasil é o 3º maior produtor de leite do mundo, superando o padrão Europeu em alguns municípios|date=8 February 2020}}</ref> the world's fourth largest producer of [[pork]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.farmnews.com.br/mercado/principais-paises-produtores-de-carne-suina/|title=Principais países produtores de carne suína entre 2017 e 2019|date=23 July 2019}}</ref> and the seventh largest producer of [[Egg as food|egg]]s in the world.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.aviculturaindustrial.com.br/imprensa/brasil-e-setimo-maior-produtor-mundial-de-ovos/20171113-144114-a215|title=Brasil é sétimo maior produtor mundial de ovos|website=Avicultura Industrial}}</ref> |
|||
In the mining sector, Brazil stands out in the extraction of [[iron ore]] (where it is the second world exporter), [[copper]], [[gold]], [[bauxite]] (one of the 5 largest producers in the world), [[manganese]] (one of the 5 largest producers in the world), [[tin]] (one of the largest producers in the world), [[niobium]] (concentrates 98% of reserves known to the world) and [[nickel]]. In terms of precious stones, Brazil is the world's largest producer of [[amethyst]], [[topaz]], [[agate]] and one of the main producers of [[tourmaline]], [[emerald]], [[aquamarine (gemstone)|aquamarine]] and [[garnet]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.gov.br/anm/pt-br/pagina-inicial|title=ANM|website=gov.br Agência Nacional de Mineração}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://noticias.r7.com/brasil/brasil-extrai-cerca-de-2-gramas-de-ouro-por-habitante-em-5-anos-29062019|title=Brasil extrai cerca de 2 gramas de ouro por habitante em 5 anos|date=29 June 2019|website=R7.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://g1.globo.com/Noticias/Economia_Negocios/0,,MUL190262-9356,00-VOTORANTIM+METAIS+ADQUIRE+RESERVAS+DE+ZINCO+DA+MASA.html|title=G1 > Economia e Negócios - NOTÍCIAS - Votorantim Metais adquire reservas de zinco da Masa|website=g1.globo.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/economia/noticia/2019/12/12/niobio-g1-visita-em-mg-complexo-industrial-do-maior-produtor-do-mundo.ghtml|title=Nióbio: G1 visita em MG complexo industrial do maior produtor do mundo|website=G1}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cprm.gov.br/publique/Redes-Institucionais/Rede-de-Bibliotecas---Rede-Ametista/Algumas-Gemas-Classicas-1104.html|title=Serviço Geológico do Brasil|website=cprm.gov.br}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://noticias.band.uol.com.br/noticias/100000911432/rio-grande-do-sul-o-maior-exportador-de-pedras-preciosas-do-brasil.html|title=Rio Grande do Sul: o maior exportador de pedras preciosas do Brasil|website=Band.com.br}}</ref> |
|||
[[Industry in Brazil]] – from [[automobile]]s, [[steel]] and [[petrochemical]]s to [[computer]]s, [[aircraft]] and [[durable good|consumer durables]] – accounted for 30.8% of the gross domestic product.<ref name="CIA GDP" /> Industry is highly concentrated in metropolitan São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, [[Campinas]], [[Porto Alegre]], and [[Belo Horizonte]].<ref name="GiordanoLanzafame2005">{{cite book|author1=Paolo Maria Giordano|author2=Francesco Lanzafame|author3=Jörg Meyer-Stamer|title=Asymmetries in Regional Integration And Local Development|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-HZoGDAc_y0C&pg=PA129|year=2005|publisher=IDB|isbn=978-1-59782-004-2|page=129}}</ref> Brazil has become the fourth largest car market in the world.<ref>{{cite web |last=Gasnier |first=Mat|date=15 January 2012|title=The 20 biggest car markets in the world: Russia on the up! |publisher=Best Selling Cars |url=http://bestsellingcarsblog.com/2012/01/15/the-20-biggest-car-markets-in-the-world-russia-on-the-up/ |accessdate=17 November 2014}}</ref> Major export products include [[Fixed-wing aircraft|aircraft]], [[electrical equipment]], [[automobile]]s, [[ethanol fuel|ethanol]], [[textile]]s, [[footwear]], [[iron ore]], [[steel]], [[coffee]], [[orange juice]], [[soybean]]s and [[corned beef]].<ref>{{cite news |title=The economy of heat |newspaper=The Economist |date=12 April 2007 |url=https://www.economist.com/node/8952496?story_id=8952496 |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> In total, Brazil ranks 23rd worldwide in [[List of countries by exports|value of exports]]. In the [[food industry]], in 2019, Brazil was the second largest exporter of processed foods in the world.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://alimentosprocessados.com.br/industria-na-sociedade-brasileira.php|title=Alimentos Processados | A indústria de alimentos e bebidas na sociedade brasileira atual|website=alimentosprocessados.com.br}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/economia/noticia/2020/02/18/faturamento-da-industria-de-alimentos-cresceu-67percent-em-2019.ghtml|title=Faturamento da indústria de alimentos cresceu 6,7% em 2019|website=G1}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://agenciabrasil.ebc.com.br/economia/noticia/2020-02/industria-de-alimentos-e-bebidas-faturaram-r-6999-bi-em-2019|title=Indústria de alimentos e bebidas faturou R$ 699,9 bi em 2019|date=18 February 2020|website=Agência Brasil}}</ref> In 2016, the country was the 2nd largest producer of [[Pulp (paper)|pulp]] in the world and the 8th producer of [[paper]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://valor.globo.com/empresas/noticia/2020/02/21/producao-nacional-de-celulose-cai-66percent-em-2019-aponta-iba.ghtml|title=Produção nacional de celulose cai 6,6% em 2019, aponta Ibá|website=Valor Econômico}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.celuloseonline.com.br/sabe-qual-e-o-estado-brasileiro-que-mais-produz-madeira-nao-e-sao-paulo/|title=Sabe qual é o estado brasileiro que mais produz Madeira?|date=9 October 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/espirito-santo/noticia/sao-mateus-e-o-6-maior-produtor-de-madeira-em-tora-para-papel-e-celulose-no-pais-diz-ibge.ghtml|title=São Mateus é o 6º maior produtor de madeira em tora para papel e celulose no país, diz IBGE|website=G1}}</ref> In the [[footwear industry]], in 2019, Brazil ranked 4th among world producers.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/sp/ribeirao-preto-franca/noticia/2019/07/14/industrias-calcadistas-em-franca-sp-registram-queda-de-40percent-nas-vagas-de-trabalho-em-6-anos.ghtml|title=Indústrias calçadistas em Franca, SP registram queda de 40% nas vagas de trabalho em 6 anos|website=G1}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.fenac.com.br/producao-de-calcados-deve-crescer-3-em-2019|title=Fenac - Centro de Eventos e Negócios | Produção de calçados deve crescer 3% em 2019|first=Agência Maya: Criação de Sites e Marketing|last=Digital|website=fenac.com.br}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.abicalcados.com.br/noticia/abicalcados-apresenta-relatorio-setorial-2019|title=Abicalçados apresenta Relatório Setorial 2019|website=abicalcados.com.br}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.fazcomex.com.br/blog/exportacao-de-calcados-saiba-mais/|title=Exportação de Calçados: Saiba mais|date=27 February 2020}}</ref> In 2019, the country was the 8th producer of [[vehicles]] and the 9th producer of [[steel]] in the world.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://diariodocomercio.com.br/livre/minas-gerais-produz-323-do-aco-nacional-em-2019/|title=Minas Gerais produz 32,3% do aço nacional em 2019|first=Diário do|last=Comércio|date=24 January 2020}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.istoedinheiro.com.br/o-novo-mapa-das-montadoras/|title=O novo mapa das montadoras, que agora rumam para o interior do País|date=8 March 2019}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/rj/sul-do-rio-costa-verde/noticia/industria-automobilistica-do-sul-do-rio-impulsiona-superavit-na-economia.ghtml|title=Indústria automobilística do Sul do Rio impulsiona superavit na economia|website=G1}}</ref> In 2018, the [[chemical industry]] of Brazil was the 8th in the world.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.pwc.com.br/pt/publicacoes/setores-atividade/assets/quimico-petroquimico/2013/pwc-chemicals-port-13.pdf|title=Indústria Química no Brasil}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/br/Documents/energy-resources/Deloitte-Abiquim-Setor-Quimico-Relatorio.pdf|title=Estudo de 2018}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://economia.uol.com.br/noticias/estadao-conteudo/2020/02/03/producao-nacional-da-industria-de-quimicos-cai-57-em-2019-diz-abiquim.htm|title=Produção nacional da indústria de químicos cai 5,7% em 2019, diz Abiquim|website=economia.uol.com.br}}</ref> In [[textile industry]], Brazil, although it was among the 5 largest world producers in 2013, is very little integrated in world trade.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.bnb.gov.br/documents/80223/2509338/textil_16_2017%28V2%29.pdf/063d7521-342f-e81e-232a-e251964fa1c3|title=Industria Textil no Brasil}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil pegged its currency, the [[Brazilian real|real]], to the U.S. dollar in 1994. However, after the [[1997 Asian financial crisis|East Asian financial crisis]], the [[1998 Russian financial crisis|Russian default]] in 1998<ref>{{cite conference |first1=Taimur |last1=Baig |first2=Ilan |last2=Goldfajn |title=The Russian default and the contagion to Brazil |booktitle=IMF Working Paper |publisher=International Monetary Fund |year=2000 |url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/wp/2000/wp00160.pdf |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> and the series of adverse financial events that followed it, the [[Central Bank of Brazil]] temporarily changed its [[monetary policy]] to a [[managed float regime]]<ref>{{cite conference |title=Os impasses da política econômica brasileira nos anos 90 |booktitle=Revista FAAP |year=2010 |url=http://www.faap.br/revista_faap/rel_internacionais/rel_04/garcia.htm |accessdate=4 February 2015}}</ref> scheme while undergoing a [[currency crisis]], until definitively changing the exchange regime to [[free-float]] in January 1999.<ref>{{cite conference |first=Arminio |last=Fraga |title=Monetary Policy During the Transition to a Floating Exchange Rate: Brazil's Recent Experience |publisher=International Monetary Fund |year=2000 |url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2000/03/fraga.htm |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil received an [[International Monetary Fund]] (IMF) rescue package in mid-2002 of $30.4 billion,<ref>{{cite magazine |last=Wheatley |first=Jonathan |title=Brazil: When an IMF Bailout Is Not Enough |magazine=Business Week |date=2 September 2002 |url=http://www.businessweek.com/magazine/content/02_35/b3797071.htm |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> a record sum at the time. Brazil's central bank repaid the IMF loan in 2005, although it was not due to be repaid until 2006.<ref>{{cite news |title=Brazil to pay off IMF debts early |work=BBC News |date=14 December 2005 |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/4527438.stm |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> One of the issues the [[Central Bank of Brazil]] recently dealt with was an excess of [[speculation|speculative]] short-term capital inflows to the country, which may have contributed to a fall in the value of the U.S. dollar against the real during that period.<ref>{{cite conference |title=Economic Quarterly |page=171 |publisher=Institute of Applied Economic Research |date=1 March 2007 |url=http://www.ipea.gov.br/sites/000/2/publicacoes/eqb/ieq11.pdf |accessdate=6 June 2008 |conference= |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080527193112/http://www.ipea.gov.br/sites/000/2/publicacoes/eqb/ieq11.pdf |archive-date=27 May 2008 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Nonetheless, [[foreign direct investment]] (FDI), related to long-term, less speculative investment in production, is estimated to be $193.8 billion for 2007.<ref>{{cite press release |title=Capital Flows to Emerging Markets Set at Close to Record Levels |publisher=The Institute of International Finance |date=31 May 2007 |url=http://www.iif.com/press/press+32.php |accessdate=6 June 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110713005259/http://www.iif.com/press/press+32.php |archive-date=13 July 2011 |url-status=dead}}</ref> [[Inflation]] monitoring and control currently plays a major part in the Central bank's role in setting short-term [[interest rate]]s as a [[monetary policy]] measure.<ref>{{cite conference |title=IPCA, IPC-FIPE and IPC-BR: Methodological and Empirical Differences |publisher=Central Bank of Brazil |year=2004 |url=http://www.bcb.gov.br/htms/relinf/ing/2004/06/ri200406b2i.pdf |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> |
|||
Between 1993 and 2010, 7012 [[mergers and acquisitions]] with a total known value of $707 billion with the involvement of Brazilian firms were announced.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.imaa-institute.org/statistics-mergers-acquisitions.html#MergersAcquisitions_Brazil |title=Statistics on Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) – M&A Courses | Company Valuation Courses | Mergers & Acquisitions Courses |publisher=Imaa-institute.org |accessdate=16 April 2011 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120106045040/http://www.imaa-institute.org/statistics-mergers-acquisitions.html |archivedate= 6 January 2012 |df= }}</ref> The year 2010 was a new record in terms of value with US$115 billion in transactions. The largest transaction with involvement of Brazilian companies was the [[Vale (mining company)|Cia. Vale do Rio Doce]] acquisition of [[Vale Inco|Inco]] in a [[tender offer]] valued at US$18.9 billion. |
|||
[[Corruption in Brazil|Corruption]] costs Brazil almost $41 billion a year alone in 2010, with 69.9% of the country's firms identifying the issue as a major constraint in successfully penetrating the global market.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.latinbusinesschronicle.com/app/article.aspx?id=4550 |title=Brazil: Corruption Costs $41 Billion |publisher=Latin Business Chronicle |accessdate=22 March 2013 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130321110632/http://www.latinbusinesschronicle.com/app/article.aspx?id=4550 |archivedate=21 March 2013}}</ref> Local government corruption is so prevalent that voters perceive it as a problem only if it surpasses certain levels, and only if a local media e.g. a radio station is present to divulge the findings of corruption charges.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://emlab.berkeley.edu/~ffinan/Finan_Audit.pdf |title=Exposing corrupt politicians? the effect of Brazil's publicly released audits on electoral outcomes|publisher=Quarterly Journal of Economics|date= May 2008 |accessdate=22 March 2013}}</ref> Initiatives, like this exposure, strengthen awareness which is indicated by the Transparency International's [[Corruption Perceptions Index]]; ranking Brazil 69th out of 178 countries in 2012.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://cpi.transparency.org/cpi2012/ |title=Corruption perceptions index |publisher=Transparency International |accessdate=22 March 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121207220737/http://cpi.transparency.org/cpi2012/ |archive-date=7 December 2012 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
The [[purchasing power]] in Brazil is eroded by the so-called [[Brazil cost]].<ref name="brcost">{{cite web|url=http://mobile.bloomberg.com/news/2011-09-27/rousseff-crisis-spurred-by-lula-debts-as-brazil-boom-diminishes |title=Rousseff Crisis Spurred by Lula Debts as Brazil Boom Diminishes|publisher=Mobile.bloomberg.com |date=27 September 2011 |accessdate=7 April 2012 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120508113727/http://mobile.bloomberg.com/news/2011-09-27/rousseff-crisis-spurred-by-lula-debts-as-brazil-boom-diminishes |archivedate=8 May 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil also has a large [[cooperative]] sector that provides 50% of the food in the country.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ica.coop/en/media/news/how-are-agricultural-co-operatives-making-difference-brazil|title=How are agricultural co-operatives making a difference in Brazil? | ICA|website=ica.coop}}</ref> The world's largest healthcare cooperative [[Unimed (organization)|Unimed]] is also located in Brazil, and accounts for 32% of the healthcare insurance market in the country.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.thenews.coop/97242/sector/health/20-million-brazilians-rely-co-operative-healthcare/|title=Why 20 million Brazilians rely on a co-operative for healthcare|date=20 August 2015}}</ref> |
|||
===Energy=== |
|||
{{Main|Energy in Brazil}} |
|||
Brazil is the world's [[List of countries by total primary energy consumption and production|tenth largest]] energy consumer with much of its energy coming from [[Renewable energy|renewable sources]], particularly [[hydroelectricity]] and [[ethanol]]; the [[Itaipu Dam]] is the world's largest [[hydroelectricity|hydroelectric plant]] by energy generation,<ref name="SchmidtOnyango2011">{{cite book|author1=Michael Schmidt|author2=Vincent Onyango|author3=Dmytro Palekhov|title=Implementing Environmental and Resource Management|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=67bRqegVVcwC&pg=PA42|year=2011|publisher=Springer|isbn=978-3-540-77568-3|page=42}}</ref> and the country has other large plants like [[Belo Monte Dam|Belo Monte]] and [[Tucuruí Dam|Tucuruí]]. The first car with an ethanol engine was produced in 1978 and the first airplane engine running on ethanol in 2005.<ref name="OECDDevelopment2001">{{cite book|author1=OECD|author2=Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development|author3=Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Staff|title=OECD Economic Surveys: Brazil 2001|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=T6U8AUm1ef4C&pg=PA193|year=2001|publisher=OECD Publishing|isbn=978-92-64-19141-9|page=193}}</ref> In total electricity generation, in 2019 Brazil reached 170,000 megawatts of installed capacity, more than 75% from renewable sources (the majority, hydroelectric plants).<ref>[https://www.aneel.gov.br/sala-de-imprensa-exibicao/-/asset_publisher/XGPXSqdMFHrE/content/brasil-alcanca-170-mil-megawatts-de-capacidade-instalada-em-2019/656877?inheritRedirect=false Brasil alcança 170 mil megawatts de capacidade instalada em 2019]</ref> |
|||
Recent oil discoveries in the [[Pre-salt layer]] have opened the door for a large increase in oil production.<ref name="BrainardMartinez-Diaz2009">{{cite book|author1=Lael Brainard|author2=Leonardo Martinez-Diaz|title=Brazil As an Economic Superpower?: Understanding Brazil's Changing Role in the Global Economy|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gG3EhGct-z0C&pg=PA45|year=2009|publisher=Brookings Institution Press|isbn=978-0-8157-0365-5|page=45}}</ref> The governmental agencies responsible for the energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy, the National Council for Energy Policy, the [[National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (Brazil)|National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels]], and the [[Brazilian Electricity Regulatory Agency|National Agency of Electricity]].<ref name="OECD2005">{{cite book|author=OECD|title=Economic Surveys: Brazil|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kdYCwdYoyX4C&pg=PA105|year=2005|publisher=OECD Publishing|isbn=978-92-64-00749-9|page=105}}</ref> In the beginning of 2020, in the production of [[Petroleum|oil]] and [[natural gas]], the country exceeded 4 million barrels of oil equivalent per day, for the first time. In January this year, 3.168 million barrels of oil per day and 138.753 million cubic meters of natural gas were extracted.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.anp.gov.br/noticias/5628-producao-de-petroleo-e-gas-no-brasil-ultrapassa-4-milhoes-de-boe-d-pela-primeira-vez|title=Produção de petróleo e gás no Brasil ultrapassa 4 milhões de boe/d pela primeira vez|website=anp.gov.br}}</ref> |
|||
===Tourism=== |
|||
{{Main|Tourism in Brazil}} |
{{Main|Tourism in Brazil}} |
||
[[File:Cataratas.jpg|thumb|[[Iguaçu National Park]] in [[Paraná (state)|Paraná]]]] |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
[[File:Lençóis Maranhenses 2018 (cropped).jpg|thumb|[[Lençóis Maranhenses National Park]] in [[Maranhão]]]] |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| align = left |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| image1 = Fernando de Noronha 11.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = Sancho Bay in [[Fernando de Noronha|Fernando de Noronha Archipelago]], [[Pernambuco]], voted the most beautiful beach in the world by [[TripAdvisor]].<ref name="praias">{{cite web|url=http://oglobo.globo.com/boa-viagem/praia-de-fernando-de-noronha-eleita-mais-bonita-do-mundo-11916584|title=Praia de Fernando de Noronha é eleita a mais bonita do mundo|author=O Globo|date=18 March 2014|accessdate=4 January 2018|author-link=O Globo}}</ref> |
|||
|image2 = Abismo_Anhumas,_Bonito,_MS.JPG |
|||
| caption2 = [[Bonito, Mato Grosso do Sul|Bonito]], [[Mato Grosso do Sul]]. The rivers in the region are known for their [[crystal]] clear waters. |
|||
}} |
|||
Tourism in Brazil is a growing sector and key to the economy of several regions of the country. The country had 6.36 million visitors in 2015, ranking in terms of the international tourist arrivals as the main destination in [[South America]] and second in [[Latin America]] after [[Mexico]].<ref>{{cite book |title=UNWTO Tourism Highlights |year=2016 |isbn=978-92-844-1814-5|doi = 10.18111/9789284418145}}</ref> Revenues from international tourists reached {{USD|6}} billion in 2010, showing a recovery from the [[Late-2000s recession|2008–2009 economic crisis]].<ref name="UNWTO2011">{{cite web|url=http://mkt.unwto.org/sites/all/files/docpdf/unwtohighlights11enhr_1.pdf|title=UNWTO Tourism Highlights – 2011 Edition|publisher=World Tourism Organization|date=June 2011|accessdate=29 September 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120105081502/http://mkt.unwto.org/sites/all/files/docpdf/unwtohighlights11enhr_1.pdf|archive-date=5 January 2012|url-status=dead}}</ref> Historical records of 5.4 million visitors and {{USD|6.8}} billion in receipts were reached in 2011.<ref name="MT1_2011">{{cite web|url=http://www.dadosefatos.turismo.gov.br/dadosefatos/home.html|title=Estatisticas e Indicadores: Receita Cambial|publisher=Ministério do Turismo|year=2012|accessdate=13 February 2012|language=Portuguese}}</ref><ref name="MT2_2011">{{cite web|url=http://www.nopatio.com.br/o-que-acontece/turismo-brasileiro-com-novo-recorde-em-2011/|title=Turismo Brasileiro com novo recorde em 2011|author=Ministério do Turismo|publisher=No Pátio|date=13 January 2012|accessdate=13 February 2012|language=Portuguese|url-status=dead|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130822074421/http://www.nopatio.com.br/o-que-acontece/turismo-brasileiro-com-novo-recorde-em-2011/|archivedate=22 August 2013}}</ref> |
|||
Tourism in Brazil is a growing sector and key to the economies of several regions of the country. The country had 6.36 million visitors in 2015, ranking in terms of the international tourist arrivals as the main destination in South America and second in [[Latin America]] after Mexico.<ref>{{Cite book |year=2016 |isbn=978-92-844-1814-5 |doi=10.18111/9789284418145 |title=UNWTO Tourism Highlights, 2016 Edition }}</ref> Revenues from international tourists reached {{USD|6}} billion in 2010, showing a recovery from the [[Late-2000s recession|2008–2009 economic crisis]].<ref name="UNWTO2011">{{Cite web |date=June 2011 |title=UNWTO Tourism Highlights – 2011 Edition |url=http://mkt.unwto.org/sites/all/files/docpdf/unwtohighlights11enhr_1.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120105081502/http://mkt.unwto.org/sites/all/files/docpdf/unwtohighlights11enhr_1.pdf |archive-date=5 January 2012 |access-date=29 September 2011 |publisher=World Tourism Organization}}</ref> Historical records of 5.4 million visitors and {{USD|6.8}} billion in receipts were reached in 2011.<ref name="MT1_2011">{{Cite web |year=2012 |title=Estatisticas e Indicadores: Receita Cambial |url=http://www.dadosefatos.turismo.gov.br/dadosefatos/home.html |access-date=13 February 2012 |publisher=Ministério do Turismo |language=pt |archive-date=24 September 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120924012902/http://www.dadosefatos.turismo.gov.br/dadosefatos/home.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="MT2_2011">{{Cite web |last=Ministério do Turismo |date=13 January 2012 |title=Turismo Brasileiro com novo recorde em 2011 |url=http://www.nopatio.com.br/o-que-acontece/turismo-brasileiro-com-novo-recorde-em-2011/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130822074421/http://www.nopatio.com.br/o-que-acontece/turismo-brasileiro-com-novo-recorde-em-2011/ |archive-date=22 August 2013 |access-date=13 February 2012 |publisher=No Pátio |language=pt}}</ref> In the list of world tourist destinations, in 2018, Brazil was the 48th most visited country, with 6.6 million tourists (and revenues of 5.9 billion dollars).<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://www.e-unwto.org/doi/pdf/10.18111/9789284421152 |year=2019 |isbn=978-92-844-2115-2 |doi=10.18111/9789284421152 |access-date=20 December 2021 |archive-url=http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20190830135934/https://www.e-unwto.org/doi/pdf/10.18111/9789284421152 |archive-date=30 August 2019 |s2cid=240665765 |title=International Tourism Highlights, 2019 Edition |publisher=World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) }}</ref> |
|||
Natural areas are its most popular tourism product, a combination of [[ecotourism]] with [[leisure]] and [[recreation]], mainly sun and beach, and [[adventure travel]], as well as [[cultural tourism]]. Among the most popular destinations are the [[Amazon Rainforest]], [[beach]]es and [[dune]]s in the [[Northeast Region, Brazil|Northeast Region]], the [[Pantanal]] in the [[Center-West Region, Brazil|Center-West Region]], beaches at [[Rio de Janeiro (state)|Rio de Janeiro]] and [[Santa Catarina (state)|Santa Catarina]], cultural tourism in [[Minas Gerais]] and business trips to [[São Paulo]].<ref name="Palhares2012">{{cite book|author=Guilherme Lohmann Palhares|title=Tourism in Brazil: Environment, Management and Segments|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=O91SVF9nH8gC&pg=PA126|year=2012|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-0-415-67432-4|page=126}}</ref> |
|||
Natural areas are its most popular tourism product, a combination of [[ecotourism]] with leisure and recreation, mainly sun and beach, and adventure travel, as well as cultural tourism. Among the most popular destinations are the [[Amazon Rainforest]], beaches and dunes in the [[Northeast Region, Brazil|Northeast Region]], the [[Pantanal]] in the [[Center-West Region, Brazil|Center-West Region]], beaches at [[Rio de Janeiro (state)|Rio de Janeiro]] and [[Santa Catarina (state)|Santa Catarina]], cultural tourism in [[Minas Gerais]] and business trips to [[São Paulo]].<ref name="Palhares2012">{{Cite book |last=Guilherme Lohmann Palhares |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=O91SVF9nH8gC&pg=PA126 |title=Tourism in Brazil: Environment, Management and Segments |publisher=Routledge |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-415-67432-4 |page=126 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129183955/https://books.google.com/books?id=O91SVF9nH8gC&pg=PA126#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
In terms of the 2015 [[Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report|Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index]] (TTCI), which is a measurement of the factors that make it attractive to develop business in the travel and tourism industry of individual countries, Brazil ranked in the 28st place at the world's level, third in the [[Americas]], after [[Canada]] and [[United States]].<ref>{{cite web |title=The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2015 |publisher=World Economic Forum |url=http://www3.weforum.org/docs/TT15/WEF_Global_Travel&Tourism_Report_2015.pdf |date=May 2015}}</ref><ref name="TTCI2013">{{cite web|url =http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TT_Competitiveness_Report_2013.pdf|editor1=Jennifer Blanke |editor2=Thea Chiesa |year = 2013 |title = Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2013 |publisher = [[World Economic Forum]], Geneva, Switzerland|accessdate=14 April 2013}} ''See Table 4, pp. 18–19 and Country/Economy Profile: Brazil, pp. 116–17.''</ref> |
|||
In terms of the 2015 [[Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report|Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index]] (TTCI), which is a measurement of the factors that make it attractive to develop business in the travel and tourism industry of individual countries, Brazil ranked in the 28th place at the world's level, third in the [[Americas]], after Canada and United States.<ref>{{Cite web |date=May 2015 |title=The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2015 |url=http://www3.weforum.org/docs/TT15/WEF_Global_Travel&Tourism_Report_2015.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www3.weforum.org/docs/TT15/WEF_Global_Travel&Tourism_Report_2015.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |publisher=World Economic Forum}}</ref><ref name="TTCI2013">{{Cite web |year=2013 |editor2-last=Thea Chiesa |title=Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2013 |url=http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TT_Competitiveness_Report_2013.pdf |access-date=14 April 2013 |publisher=[[World Economic Forum]], Geneva, Switzerland |editor1=Jennifer Blanke |archive-date=5 November 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191105024651/http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TT_Competitiveness_Report_2013.pdf |url-status=live }} ''See Table 4, pp. 18–19 and Country/Economy Profile: Brazil, pp. 116–17.''</ref> [[Domestic tourism]] is a key market segment for the tourism industry in Brazil. In 2005, 51 million Brazilian nationals made ten times more trips than foreign tourists and spent five times more money than their international counterparts.<ref name="FIPE007">{{cite web |author=Fundação Instituto de Pesquisas Econômicas |year=2007 |title=Caracterização e Dimensionamento do Turismo Domêstico no Brasil 2002 e 2006 |url=http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/demanda%20turistica/relatorio_executivo___turismo_domestico___2002_e_2006.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081003062341/http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/demanda%20turistica/relatorio_executivo___turismo_domestico___2002_e_2006.pdf |archive-date=3 October 2008 |access-date=21 June 2008 |publisher=Ministério do Turismo |language=pt}}</ref> The main destination states in 2023 were [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]], [[Rio de Janeiro (state)|Rio de Janeiro]], and [[Rio Grande do Sul]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Veja ranking dos Estados brasileiros que atraem mais turistas estrangeiros |url=https://www.estadao.com.br/web-stories/economia/brasil-qual-estado-brasileiro-atrai-mais-turistas-estrangeiros-ranking-2024-quais-estados-embratur-sao-paulo-sp-rio-de-janeiro-rj-nprei/ |access-date=2024-06-19 |website=Estadão |language=pt-br |archive-date=25 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240625212216/https://www.estadao.com.br/web-stories/economia/brasil-qual-estado-brasileiro-atrai-mais-turistas-estrangeiros-ranking-2024-quais-estados-embratur-sao-paulo-sp-rio-de-janeiro-rj-nprei/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Redação |first=Da |date=2024-01-18 |title=Brasil recebe 5,9 milhões de estrangeiros em 2023 |url=https://www.panrotas.com.br/mercado/pesquisas-e-estatisticas/2024/01/brasil-recebe-59-milhoes-de-estrangeiros-em-2023_202520.html |access-date=2024-06-19 |website=Portal PANROTAS |language=pt-br |archive-date=28 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240628014430/https://www.panrotas.com.br/mercado/pesquisas-e-estatisticas/2024/01/brasil-recebe-59-milhoes-de-estrangeiros-em-2023_202520.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The main source of tourists for the entire country is São Paulo state.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Cedeño |first=Karina |date=2024-06-12 |title=Turismo é grande negócio e São Paulo seguirá investindo nele, diz Lucena |url=https://www.panrotas.com.br/mercado/destinos/2024/06/turismo-e-grande-negocio-e-sao-paulo-seguira-investindo-nele-diz-lucena_206258.html |access-date=2024-06-19 |website=Portal PANROTAS |language=pt-br |archive-date=28 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240628014439/https://www.panrotas.com.br/mercado/destinos/2024/06/turismo-e-grande-negocio-e-sao-paulo-seguira-investindo-nele-diz-lucena_206258.html |url-status=live }}</ref> In terms of tourism revenues, the top earners by state were [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]] and [[Bahia]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Movimentação do turismo bate recorde em vários estados e aquece economia |url=https://agenciagov.ebc.com.br/noticias/202404/movimentacao-do-turismo-cresce-e-bate-recorde-em-varios-estados |access-date=2024-06-19 |website=Agência Gov |language=pt-br |archive-date=19 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240619181329/https://agenciagov.ebc.com.br/noticias/202404/movimentacao-do-turismo-cresce-e-bate-recorde-em-varios-estados |url-status=live }}</ref> For 2005, the three main trip purposes were visiting friends and family (53.1%), sun and beach (40.8%), and cultural tourism (12.5%).<ref name="FIPE006">{{cite web |url=http://www.braziltour.com/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/demanda%20turistica/demanda_turismo_domestico_setembro_2006.pdf |author=Fundação Instituto de Pesquisas Econômicas e EMBRATUR |year=2006 |title=Caracterização e Dimensionamento do Turismo Domêstico no Brasil 2002 e 2006: Metodologia e Desenvolvimento |publisher=Ministério do Turismo |access-date=22 June 2008 |language=pt |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061130164741/http://www.braziltour.com/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/demanda%20turistica/demanda_turismo_domestico_setembro_2006.pdf |archive-date=30 November 2006 }}</ref> |
|||
Brazil's main competitive advantages are its natural resources, which ranked 1st on this criteria out of all countries considered, and ranked 23rd for its cultural resources, due to its many [[World Heritage site]]s. The TTCI report notes Brazil's main weaknesses: its ground transport infrastructure remains underdeveloped (ranked 116th), with the quality of roads ranking in 105th place; and the country continues to suffer from a lack of price competitiveness (ranked 114th), due in part to high ticket taxes and airport charges, as well as high prices and high taxation. Safety and security have improved significantly: 75th in 2011, up from 128th in 2008.<ref name="TTCI2013" /> |
|||
=== Science and technology === |
|||
According to the [[World Tourism Organization]] (WTO), international travel to Brazil accelerated in 2000, particularly during 2004 and 2005. However, in 2006 a slow-down took place, and international arrivals had almost no growth in 2007–08.<ref name="WTO2007">{{cite web|url=http://www.unwto.org/facts/eng/pdf/highlights/highlights_07_eng_hr.pdf|title=UNWTO Tourism Highlights, Edition 2007|publisher=UNWTO|author=World Tourism Organization|accessdate=14 June 2008|year=2007|url-status=dead|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130409090548/http://www.unwto.org/facts/eng/pdf/highlights/highlights_07_eng_hr.pdf|archivedate=9 April 2013}}</ref><ref name="EMBRATUR09">{{cite web |year = 2009 |url=http://www.abav.com.br/info_indicadores_detalhe.aspx?id=24&id_area=20&id_doc=28|title = Anuário Estatístico de Turismo 2009|author = EMBRATUR|publisher= Ministério de Turismo |accessdate=5 September 2008|language=Portuguese}} ''See tables 1.1 and 3.8''</ref><ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.worldtourism.org/facts/eng/pdf/highlights/highlights_06_eng_lr.pdf |title = Tourism Highlights 2006 [pdf] |publisher = |author = The World Tourism Organization |accessdate = 6 January 2006 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20070628064808/http://www.worldtourism.org/facts/eng/pdf/highlights/highlights_06_eng_lr.pdf |archive-date = 28 June 2007 |url-status=dead |df = dmy-all }}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Science and technology in Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Vls1-mockup-test.jpg|thumb|[[VLS-1]] at the [[Alcântara Launch Center]] of the [[Brazilian Space Agency]], in [[Alcântara, Maranhão|Alcântara]], [[Maranhão]]]] |
|||
[[File:Ministro participa da inauguração do acelerador de partículas Sirius. (30970744907).jpg|thumb|[[Sirius (synchrotron light source)|Sirius]], a [[diffraction-limited storage ring]] [[synchrotron light source]] at the [[Laboratório Nacional de Luz Síncrotron]], in [[Campinas]], [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]]]] |
|||
Technological research in Brazil is largely carried out in public universities and research institutes, with the majority of funding for basic research coming from various government agencies.<ref name="DevelopmentStaff2006v">{{Cite book |last1=Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lI8pqyWIluYC&pg=PA94 |title=OECD Economic Surveys: Brazil 2006 |last2=Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Staff |publisher=OECD Publishing |year=2006 |isbn=978-92-64-02999-6 |page=94}}</ref> Brazil's most esteemed technological hubs are the [[Fundação Oswaldo Cruz|Oswaldo Cruz Institute]], the [[Instituto Butantan|Butantan Institute]], the Air Force's [[Brazilian General Command for Aerospace Technology|Aerospace Technical Center]], the [[Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária|Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation]] and the [[National Institute for Space Research]].<ref name="Scientific2010f">{{Cite book |last=United Nations Educational, Scientific |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2ZTLCOe_fqwC&pg=PA110 |title=UNESCO Science Report 2010: The Current Status of Science Around the World |publisher=UNESCO |year=2010 |isbn=978-92-3-104132-7 |pages=110–18 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129184347/https://books.google.com/books?id=2ZTLCOe_fqwC&pg=PA110#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="HarveySmid2010">{{Cite book |last1=Brian Harvey |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XD1ZaYbiWwMC&pg=PA324 |title=Emerging Space Powers: The New Space Programs of Asia, the Middle East and South-America |last2=Henk H.F. Smid |last3=Thâeo Pirard |publisher=Springer |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-4419-0874-2 |page=324 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129184349/https://books.google.com/books?id=XD1ZaYbiWwMC&pg=PA324#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
In spite of this trend, revenues from international tourism continued to rise, from [[USD]] 4 billion in 2005 to 5 billion in 2007, despite 330 000 fewer arrivals. This favorable trend is the result of the strong devaluation of the US dollar against the [[Brazilian Real]], which began in 2004, but which makes Brazil a more expensive international destination.<ref name="Boletim0207">{{cite web|year=2007 |url=http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/Boletimdedesempenho/boletim_13___fevereiro_de_2007.pdf |title=Boletim de Desempenho Econômico do Turismo |author=Facultade Getúlio Vargas |publisher=Ministério de Turismo |accessdate=21 June 2008 |language=Portuguese |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20081003062353/http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/Boletimdedesempenho/boletim_13___fevereiro_de_2007.pdf |archivedate=3 October 2008}} ''Fevereiro 2007, Ano IV, nº 13, p. 3''</ref> |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| image1 = Vista do Morro Dona Marta.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = The city of [[Rio de Janeiro]] is featured in [[tourism]] in Brazil. |
|||
|image2 = Cataratas.jpg |
|||
| caption2 = [[Iguazu Falls]], [[Paraná (state)|Paraná]], at the [[Argentina–Brazil relations|Brazil-Argentina border]]. The Garganta do Diabo Walkway allows a panoramic view of the falls from the Brazilian side. |
|||
}} |
|||
The [[Brazilian Space Agency]] has the most advanced space program in Latin America, with significant resources to launch vehicles, and manufacture of [[artificial satellite|satellites]].{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=vP9jHaoL_s4C&pg=PA628 628]}} The country develops [[submarine]]s and aircraft, as well as being involved in space research, having a Vehicle Launch Center Light and being the only country in the [[Southern Hemisphere]] to integrate a team building the well-known [[International Space Station]] (ISS).<ref name="NASA">[http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/news/releases/1996_1998/h97-233.html NASA Signs International Space Station Agreement With Brazil] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201127012829/http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/news/releases/1996_1998/h97-233.html |date=27 November 2020 }} [[NASA]].</ref> |
|||
This trend changed in 2009, when both visitors and revenues fell as a result of the [[Great Recession]] of 2008–09.<ref name="WTO2010">{{cite web|year=2010 |url=http://unwto.org/facts/menu.html |title=UNTWO Tourism Highlights 2010 Edition |publisher=[[World Tourism Organization]] |accessdate=31 October 2010 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130607130445/http://www.unwto.org/facts/menu.html |archivedate= 7 June 2013 |df= }} ''Click on the link "UNWTO Tourism Highlights" to access the pdf report.''</ref> By 2010, the industry had recovered, and arrivals grew above 2006 levels to 5.2 million international visitors, and receipts from these visitors reached US$6 billion.<ref name="UNWTO2011" /> In 2011 the historical record was reached with 5.4 million visitors and {{USD|6.8}} billion in receipts.<ref name="MT1_2011" /><ref name="MT2_2011" /> |
|||
The country is also a pioneer in the search for oil in deep water, from where it extracts 73% of its reserves. [[Uranium]] is enriched at the [[Resende Nuclear Fuel Factory]], mostly for research purposes (as Brazil obtains 88% of its electricity from [[hydroelectricity]]<ref>{{Cite web |last=O.C. Ferreira |title=O Sistema Elétrico Brasileiro |url=http://www.ecen.com/eee32/sistelet.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210225014002/http://www.ecen.com/eee32/sistelet.htm |archive-date=25 February 2021 |access-date=21 March 2013}}</ref>) and the country's [[Brazilian submarine Álvaro Alberto|first nuclear submarine]] is expected to be launched in 2029.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Previsão de lançamento |language=pt |work=Marinha do Brasil |url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/programas-estrategicos/prosub |access-date=25 January 2022 |archive-date=25 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220125114741/https://www.marinha.mil.br/programas-estrategicos/prosub |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Despite continuing record-breaking international tourism revenues, the number of Brazilian tourists travelling overseas has been growing steadily since 2003, resulting in a net negative [[Foreign exchange market|foreign exchange]] balance, as more money is spent abroad by Brazilians than comes in as receipts from international tourists visiting Brazil.<ref name="Boletim0308" /> |
|||
Brazil is one of the three countries in Latin America<ref>{{Cite web |date=18 August 2008 |title=Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität |url=http://www-elsa.physik.uni-bonn.de/accelerator_list.html |access-date=30 October 2010 |publisher=Elsa.physik.uni-bonn.de |archive-date=4 August 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080804121907/http://www-elsa.physik.uni-bonn.de/accelerator_list.html |url-status=live }}</ref> with an operational [[Synchrotron]] Laboratory, a research facility on physics, chemistry, material science and life sciences, and Brazil is the only Latin American country to have a [[semiconductor]] company with its own [[Semiconductor fabrication plant|fabrication plant]], the [[CEITEC]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=CEITEC |url=http://www.brasil.gov.br/sobre/science-and-technology/the-digital-electronics-industry/ceitec/br_model1?set_language=en |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111117055936/http://www.brasil.gov.br/sobre/science-and-technology/the-digital-electronics-industry/ceitec/br_model1?set_language=en |archive-date=17 November 2011 |access-date=8 August 2011 |website=Portal Brasil |publisher=Brasil.gov.br}}</ref> According to the Global Information Technology Report 2009–2010 of the World Economic Forum, Brazil is the world's 61st largest developer of information technology.<ref>{{Citation |title=Brasil cai duas posições em ranking mundial |date=26 March 2010 |url=http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/fsp/dinheiro/fi2603201010.htm |work=[[Folha de S.Paulo]] |access-date=26 March 2010 |archive-date=26 September 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130926123816/http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/fsp/dinheiro/fi2603201010.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Brazil was ranked 50th in the [[Global Innovation Index]] in 2024, up from 66th in 2019.<ref>{{Cite book |author=[[World Intellectual Property Organization]] |year=2024 |title=Global Innovation Index 2024: Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship |url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/ |access-date=2024-10-06 |website=www.wipo.int |page=18 |publisher=World Intellectual Property Organization |language=en |doi=10.34667/tind.50062 |isbn=978-92-805-3681-2}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Innovation Index 2019 |url=https://www.wipo.int/global_innovation_index/en/2019/index.html |access-date=2 September 2021 |website=www.wipo.int |language=en |archive-date=2 September 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210902101818/https://www.wipo.int/global_innovation_index/en/2019/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=28 October 2013 |title=Global Innovation Index |url=https://knowledge.insead.edu/entrepreneurship-innovation/global-innovation-index-2930 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210902101622/https://knowledge.insead.edu/entrepreneurship-innovation/global-innovation-index-2930 |archive-date=2 September 2021 |access-date=2 September 2021 |website=INSEAD Knowledge |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
Tourism expenditures abroad grew from US$5.8 billion in 2006, to US$8.2 billion in 2007, a 42% increase, representing a net deficit of US$3.3 billion in 2007, as compared to US$1.5 billion in 2006, a 125% increase from the previous year.<ref name="Boletim0308">{{cite web|year=2008 |url=http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/pesquisaanual/pacet4_12_mar.pdf |title=Pesquisa Anual de Conjuntura Econômica do Turismo |author=Facultade Getúlio Vargas |publisher=Ministério de Turismo |accessdate=22 June 2008 |language=Portuguese |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20081003062332/http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/pesquisaanual/pacet4_12_mar.pdf |archivedate=3 October 2008}} ''Março 2008, Ano IV, p. 11''</ref> This trend is caused by Brazilians taking advantage of the stronger [[Brazilian real|Real]] to travel and making relatively cheaper expenditures abroad.<ref name="Boletim0308" /> Brazilians traveling overseas in 2006 represented 4% of the country's population.<ref name="FIPE006">{{cite web|url=http://www.braziltour.com/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/demanda%20turistica/demanda_turismo_domestico_setembro_2006.pdf |author=Fundação Instituto de Pesquisas Econômicas e EMBRATUR |year=2006 |title=Caracterização e Dimensionamento do Turismo Domêstico no Brasil 2002 e 2006: Metodologia e Desenvolvimento |publisher=Ministério do Turismo |accessdate=22 June 2008 |language=Portuguese |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20061130164741/http://www.braziltour.com/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/demanda%20turistica/demanda_turismo_domestico_setembro_2006.pdf |archivedate=30 November 2006}}</ref> |
|||
Among the most renowned Brazilian inventors are priests [[Bartolomeu de Gusmão]], [[Landell de Moura]] and Francisco João de Azevedo, besides [[Alberto Santos-Dumont]],<ref>{{Cite news |date=20 October 1901 |title=M. Santos Dumont Rounds Eiffel Tower |work=The New York Times |url=https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1901/10/20/106920457.pdf |url-status=live |access-date=29 December 2010 |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1901/10/20/106920457.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022}}</ref> [[Evaristo Conrado Engelberg]],<ref name="patentbritish">{{Cite web |year=2011 |title=Engelberg, Inc |url=http://vintagemachinery.org/mfgindex/detail.aspx?id=294 |access-date=17 July 2011 |publisher=Vintage Machinery |archive-date=21 March 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120321054057/http://vintagemachinery.org/mfgindex/detail.aspx?id=294 |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Manuel Dias de Abreu]],<ref>Abreu, Manuel de, pag. 17 – Grande Enciclopédia Universal – edição de 1980 – Ed.Amazonas</ref> [[Andreas Pavel]]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Portable stereo's creator got his due, eventually |url=http://www.iht.com/articles/2005/12/16/news/profile.php |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090309065937/http://www.iht.com/articles/2005/12/16/news/profile.php |archive-date=9 March 2009 |access-date=16 December 2015}}</ref> and Nélio José Nicolai.<ref>[http://www.cefetmg.br/noticias/2010/11/noticia0014.html Exposição destaca centenário do CEFET-MG] Sítio do Cefet-MG, acessado em 13 de novembro de 2010 {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140813115503/http://www.cefetmg.br/noticias/2010/11/noticia0014.html |date=13 August 2014 }}</ref> Brazilian science is represented by the likes of [[César Lattes]] (Brazilian [[physicist]] Pathfinder of ''[[Pion|Pi Meson]]''),<ref name="Lattes">{{Cite web |last=Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação |title=50 anos do Méson-Pi |url=http://www.cbpf.br/meson/meson.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110526200502/http://www.cbpf.br/meson/meson.html |archive-date=26 May 2011 |access-date=29 December 2010}}</ref> [[Mário Schenberg]] (considered the greatest theoretical physicist of Brazil),<ref>{{Cite web |title=Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas – Coleção Galileo: Textos de Física |url=http://cbpfindex.cbpf.br/publication_pdfs/dh00186.2011_08_16_15_20_32.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130331194248/http://cbpfindex.cbpf.br/publication_pdfs/dh00186.2011_08_16_15_20_32.pdf |archive-date=31 March 2013 |access-date=21 October 2014}}</ref> [[José Leite Lopes]] (the only Brazilian physicist holder of the ''UNESCO Science Prize''),<ref>{{Cite web |title=Atta-Ur-Rahman, José Leite Lopes and Juan Martín Maldacena receive UNESCO science prizes |url=http://www.unesco.org/bpi/science/content/news/upress/99-147e.htm |access-date=21 October 2014 |publisher=UNESCOPRESS |archive-date=19 June 2002 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20020619150011/http://www.unesco.org/bpi/science/content/news/upress/99-147e.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Artur Ávila]] (the first Latin American winner of the [[Fields Medal]])<ref>[http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/ciencia/2014/08/1499290-brasileiro-ganha-a-medalha-fields-considerada-o-nobel-da-matematica.shtml Brasileiro ganha a Medalha Fields, considerada o "Nobel da Matemática"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210613202913/https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/ciencia/2014/08/1499290-brasileiro-ganha-a-medalha-fields-considerada-o-nobel-da-matematica.shtml |date=13 June 2021 }}.</ref> and [[Fritz Müller]] (pioneer in factual support of the theory of evolution by [[Charles Darwin]]).<ref name="West, David A 2003">West, David A. 2003. Fritz Müller: a naturalist in Brazil. Blacksburg: Pocahontas Press</ref> |
|||
In 2005, tourism contributed with 3.2% of the country's revenues from exports of goods and services, and represented 7% of direct and indirect employment in the Brazilian economy.<ref name="BID2006">{{cite web |author = Carmen Altés |year = 2006 |title = El Turismo en América Latina y el Caribe y la experiencia del BID|pages= 9, 47|publisher = Inter-American Development Bank; Sustainable Development Department, Technical Paper Series ENV-149, Washington, DC|language=Spanish|url=http://idbdocs.iadb.org/wsdocs/getdocument.aspx?docnum=984876|accessdate=14 June 2008}}</ref> In 2006 direct employment in the sector reached 1.9 million people.<ref name="IPEA08">{{cite web |url=http://www.ipea.gov.br/sites/000/2/publicacoes/tds/td_1320.pdf |author=Margerida Coelho |year=2008 |title=Distribução Espacial da Ocupação no Setor de Turismo: Brasil e Regiões |publisher=Instituto de Pesquisa Econômica Aplicada |accessdate=22 June 2008 |language=Portuguese |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081003062333/http://www.ipea.gov.br/sites/000/2/publicacoes/tds/td_1320.pdf |archive-date=3 October 2008 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
=== Energy === |
|||
Domestic tourism is a fundamental market segment for the industry, as 51 million people traveled throughout the country in 2005,<ref name="FIPE007">{{cite web|url=http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/demanda%20turistica/relatorio_executivo___turismo_domestico___2002_e_2006.pdf |author=Fundação Instituto de Pesquisas Econômicas |year=2007 |title=Caracterização e Dimensionamento do Turismo Domêstico no Brasil 2002 e 2006 |publisher=Ministério do Turismo |accessdate=21 June 2008 |language=Portuguese |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20081003062341/http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/demanda%20turistica/relatorio_executivo___turismo_domestico___2002_e_2006.pdf |archivedate=3 October 2008}}</ref> and direct revenues from Brazilian tourists reached US$22 billion,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cidadedesaopaulo.com/pesquisa/pdf/rel_boletim_anual_pesquisas_spturis_%202006.pdf |author=Diretoria de Turismo |year=2006 |title=Boletim Anual São Paulo Turismo |publisher=Prefeitura de São Paulo |accessdate=20 November 2008 |language=Portuguese}}{{dead link|date=June 2016|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}} see 2.1.3 "Receitas setor trurístico 2005".</ref> 5.6 times more receipts than international tourists in 2005. |
|||
{{Main|Energy in Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Itaipu geral.jpg|thumb|The [[Itaipu Dam]] on the [[Paraná River]], the second largest of the world. [[Energy policy of Brazil|Brazilian energy matrix]] is one of the [[Clean energy|cleanest]] in the world]] |
|||
[[File:Energia Eolica.jpg|thumb|[[Wind farm]] in [[Parnaíba]], [[Piauí]]. Brazil is one of the 5 largest producers of wind energy in the world]] |
|||
Brazil is the world's [[List of countries by total primary energy consumption and production|ninth-largest]] energy consumer.<ref>{{Cite web |title=International – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) |url=https://www.eia.gov/international/rankings/world?pa=44&u=2&f=A&v=none&y=01/01/2021&ev=false |access-date=23 October 2023 |website=www.eia.gov |archive-date=26 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231026222938/https://www.eia.gov/international/rankings/world?pa=44&u=2&f=A&v=none&y=1 |url-status=live }}</ref> Much of its energy comes from [[Renewable energy|renewable sources]], particularly [[hydroelectricity]] and [[ethanol]]; the [[Itaipu Dam]] is the world's largest [[hydroelectricity|hydroelectric plant]] by energy generation,<ref name="SchmidtOnyango2011">{{Cite book |last1=Michael Schmidt |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=67bRqegVVcwC&pg=PA42 |title=Implementing Environmental and Resource Management |last2=Vincent Onyango |last3=Dmytro Palekhov |publisher=Springer |year=2011 |isbn=978-3-540-77568-3 |page=42 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129184349/https://books.google.com/books?id=67bRqegVVcwC&pg=PA42#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> and the country has other large plants such as [[Belo Monte Dam|Belo Monte]] and [[Tucuruí Dam|Tucuruí]]. The first car with an ethanol engine was produced in 1978 and the first airplane engine running on ethanol in 2005.<ref name="OECDDevelopment2001">{{Cite book |last1=OECD |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=T6U8AUm1ef4C&pg=PA193 |title=OECD Economic Surveys: Brazil 2001 |last2=Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |last3=Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Staff |publisher=OECD Publishing |year=2001 |isbn=978-92-64-19141-9 |page=193 |access-date=16 June 2015 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129184453/https://books.google.com/books?id=T6U8AUm1ef4C&pg=PA193 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
In 2005, [[Rio de Janeiro]], [[Foz do Iguaçu]], [[São Paulo]], [[Florianópolis]] and [[Salvador, Bahia|Salvador]] were the most visited cities by international tourists for leisure trips. The most popular destinations for business trips were [[São Paulo]], [[Rio de Janeiro]] and [[Porto Alegre]].<ref name="EMBRATUR06">{{cite web|url=http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/Anuario/anuario_estatistico_2006_pdf.pdf |author=EMBRATUR |year=2006 |title=Anúario Estatístico Volume 33 2006 |publisher=Ministério do Turismo |accessdate=22 June 2008 |language=Portuguese |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080909235018/http://200.189.169.141/site/arquivos/dados_fatos/Anuario/anuario_estatistico_2006_pdf.pdf |archivedate=9 September 2008}} Tables 4.1 a 4.4: Summary Brasil by trip purpose 2004–2005</ref> In 2006 Rio de Janeiro and [[Fortaleza]] were the most popular destinations for business trips. |
|||
At the end of 2021 Brazil was the 2nd country in the world in terms of installed [[hydroelectric power]] (109.4 GW) and [[biomass]] (15.8 GW), the 7th country in the world in terms of installed [[wind power]] (21.1 GW) and the 14th country in the world in terms of installed [[solar power]] (13.0 GW)—on track to also become one of the top 10 in the world in solar energy.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Renewable Capacity Statistics 2022 |url=https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2022/Apr/IRENA_RE_Capacity_Statistics_2022.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2022/Apr/IRENA_RE_Capacity_Statistics_2022.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |access-date=19 May 2022 |website=IRENA}}</ref> At the end of 2021, Brazil was the 4th largest producer of wind energy in the world (72 TWh), behind only China, the United States and Germany, and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).<ref>[[Hannah Ritchie]] and [[Max Roser]], [https://ourworldindata.org/renewable-energy Solar Power Generation]</ref> |
|||
==Infrastructure== |
|||
The main characteristic of the Brazilian energy matrix is that it is much more renewable than that of the world. While in 2019, the world matrix was only 14% made up of renewable energy, Brazil's was at 45%. Petroleum and oil products made up 34.3% of the matrix; sugar cane derivatives, 18%; hydraulic energy, 12.4%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 8.8%; varied renewable energies, 7%; mineral coal, 5.3%; nuclear, 1.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.6%.<ref name="Matriz Energética e Elétrica">{{Cite web |url=https://www.epe.gov.br/pt/abcdenergia/matriz-energetica-e-eletrica |title=Matriz Energética e Elétrica |language=pt |website=Empresa de Pesquisa Energética }}</ref> |
|||
===Science and technology=== |
|||
{{Main|Science and technology in Brazil}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| align = left |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| image1 = Vls1-mockup-test.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = [[VLS-1]] at the [[Alcântara Launch Center]] of the [[Brazilian Space Agency]]. |
|||
In the electric energy matrix, the difference between Brazil and the world is even greater: while the world only had 25% of renewable electric energy in 2019, Brazil had 83%. The Brazilian electric matrix was composed of: hydraulic energy, 64.9%; biomass, 8.4%; wind energy, 8.6%; solar energy, 1%; natural gas, 9.3%; oil products, 2%; nuclear, 2.5%; coal and derivatives, 3.3%.<ref name="Matriz Energética e Elétrica" /> Brazil has the largest electricity sector in Latin America. Its capacity at the end of 2021 was 181,532 MW.<ref name="Ministério de Minas e Energia">[https://web.archive.org/web/20230411135506/https://antigo.aneel.gov.br/web/guest/sala-de-imprensa-exibicao-2/-/asset_publisher/zXQREz8EVlZ6/content/brasil-termina-2021-com-maior-acrescimo-em-potencia-instalada-desde-2016/656877?inheritRedirect=false&redirect=https://antigo.aneel.gov.br/web/guest/sala-de-imprensa-exibicao-2?p_p_id=101_INSTANCE_zXQREz8EVlZ6&p_p_lifecycle=0&p_p_state=normal&p_p_mode=view&p_p_col_id=column-2&p_p_col_pos=2&p_p_col_count=3&_101_INSTANCE_zXQREz8EVlZ6_advancedSearch=false&_101_INSTANCE_zXQREz8EVlZ6_keywords=&_101_INSTANCE_zXQREz8EVlZ6_delta=15&p_r_p_564233524_resetCur=false&_101_INSTANCE_zXQREz8EVlZ6_cur=5&_101_INSTANCE_zXQREz8EVlZ6_andOperator=true] National Agency of Energy</ref> |
|||
| image2 = Ministro participa da inauguração do acelerador de partículas Sirius. (45909188621).jpg |
|||
| caption2 = [[Sirius (synchrotron light source)|Sirius]], a [[diffraction-limited storage ring]] [[Synchrotron radiation|synchrotron light source]] at the [[Laboratório Nacional de Luz Síncrotron]], in the municipality of [[Campinas]], [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]]. |
|||
}} |
|||
As for [[Petroleum|oil]], the Brazilian government has embarked on a program over the decades to reduce dependence on imported oil, which previously accounted for more than 70% of the country's oil needs. Brazil became self-sufficient in oil in 2006–2007. In 2021, the country closed the year as the 7th oil producer in the world, with an average of close to three million barrels per day, becoming an exporter of the product.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cnnbrasil.com.br/economia/brasil-anuncia-aumento-da-producao-de-petroleo-em-10-para-ajudar-a-estabilizar-precos/|title=Brasil anuncia aumento da produção de petróleo em 10% para ajudar a estabilizar preços |first=Fernando |last=Nakagawa |date=23 March 2022 |website=CNN Brasil}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Produção de petróleo e gás no Brasil ultrapassa 4 milhões de boe/d pela primeira vez |url=http://www.anp.gov.br/noticias/5628-producao-de-petroleo-e-gas-no-brasil-ultrapassa-4-milhoes-de-boe-d-pela-primeira-vez |date=19 February 2020 |website=[[Agência Nacional do Petróleo, Gás Natural e Biocombustíveis]] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200220091405/http://www.anp.gov.br/noticias/5628-producao-de-petroleo-e-gas-no-brasil-ultrapassa-4-milhoes-de-boe-d-pela-primeira-vez |archive-date=20 February 2020 |access-date=16 August 2020}}</ref> |
|||
Technological research in Brazil is largely carried out in public universities and research institutes, with the majority of funding for basic research coming from various government agencies.<ref name="DevelopmentStaff2006v">{{cite book|author1=Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development|author2=Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Staff|title=OECD Economic Surveys: Brazil 2006|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lI8pqyWIluYC&pg=PA94|year=2006|publisher=OECD Publishing|isbn=978-92-64-02999-6|page=94}}</ref> Brazil's most esteemed technological hubs are the [[Fundação Oswaldo Cruz|Oswaldo Cruz Institute]], the [[Instituto Butantan|Butantan Institute]], the Air Force's [[Brazilian General Command for Aerospace Technology|Aerospace Technical Center]], the [[Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária|Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation]] and the [[National Institute for Space Research|INPE]].<ref name="Scientific2010f">{{cite book|author=United Nations Educational, Scientific|title=UNESCO Science Report 2010: The Current Status of Science Around the World|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2ZTLCOe_fqwC&pg=PA110|year=2010|publisher=UNESCO|isbn=978-92-3-104132-7|pages=110–18}}</ref><ref name="HarveySmid2010">{{cite book|author1=Brian Harvey|author2=Henk H.F. Smid|author3=Thâeo Pirard|title=Emerging Space Powers: The New Space Programs of Asia, the Middle East and South-America|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XD1ZaYbiWwMC&pg=PA324|year=2010|publisher=Springer|isbn=978-1-4419-0874-2|page=324}}</ref> |
|||
=== Transportation === |
|||
The [[Brazilian Space Agency]] has the most advanced space program in Latin America, with significant resources to launch vehicles, and manufacture of [[artificial satellite|satellites]].{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=vP9jHaoL_s4C&pg=PA628 628]}} Owner of relative technological sophistication, the country develops [[submarine]]s, aircraft, as well as being involved in space research, having a Vehicle Launch Center Light and being the only country in the [[Southern Hemisphere]] the integrate team building [[International Space Station]] (ISS).<ref name="NASA">[http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/news/releases/1996_1998/h97-233.html NASA Signs International Space Station Agreement With Brazil] [[NASA]].</ref> |
|||
The country is also a pioneer in the search for oil in deep water, from where it extracts 73% of its reserves. |
|||
[[Uranium]] is enriched at the [[Resende Nuclear Fuel Factory]], mostly for research purposes (as Brazil obtains 88% from its electricity from [[hydroelectricity]]<ref>{{cite web |title=O Sistema Elétrico Brasileiro |url=http://www.ecen.com/eee32/sistelet.htm |author=O.C. Ferreira |accessdate=21 March 2013}}</ref>) and the country's first nuclear submarine was delivered in 2015 (by France).<ref>{{cite news|title=Confirmed: Agreement with France Includes the Brazilian Nuclear Submarine |url=http://npsglobal.org/eng/news/139-peaceful-uses/490-confirmed-agreement-with-france-includes-the-brazilian-nuclear-submarine.html|work=[[Nonproliferation for Global Security Foundation]] |date=23 December 2008 |accessdate=23 December 2008}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil is one of the three countries in Latin America<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www-elsa.physik.uni-bonn.de/accelerator_list.html |title=Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität |publisher=Elsa.physik.uni-bonn.de |date=18 August 2008 |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> with an operational [[Synchrotron]] Laboratory, a research facility on physics, chemistry, material science and life sciences, and Brazil is the only Latin American country to have a [[semiconductor]] company with its own [[Semiconductor fabrication plant|fabrication plant]], the [[CEITEC]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.brasil.gov.br/sobre/science-and-technology/the-digital-electronics-industry/ceitec/br_model1?set_language=en |url-status=dead |title=CEITEC |website=Portal Brasil |publisher=Brasil.gov.br |accessdate=8 August 2011 |archivedate=17 November 2011 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20111117055936/http://www.brasil.gov.br/sobre/science-and-technology/the-digital-electronics-industry/ceitec/br_model1?set_language=en}}</ref> According to the Global Information Technology Report 2009-2010 of the World Economic Forum, Brazil is the world's 61st largest developer of information technology.<ref>{{Citation|url=http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/fsp/dinheiro/fi2603201010.htm|title=Brasil cai duas posições em ranking mundial|newspaper=[[Folha de S.Paulo]]|date=26 March 2010|access-date=26 March 2010}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil also has a large number of outstanding scientific personalities. Among the most renowned Brazilian inventors are priests [[Bartolomeu de Gusmão]], [[Landell de Moura]] and Francisco João de Azevedo, besides [[Alberto Santos-Dumont]],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1901/10/20/106920457.pdf |title=M. Santos Dumont Rounds Eiffel Tower." New York Times, 20 de outubro de 1901. Retrieved January 12, 2009|access-date=29 December 2010}}</ref> [[Evaristo Conrado Engelberg]],<ref name="patentbritish">{{cite web|url=http://vintagemachinery.org/mfgindex/detail.aspx?id=294 |title=Engelberg, Inc|access-date=17 July 2011|publisher=Vintage Machinery|year=2011}}</ref> [[Manuel Dias de Abreu]],<ref>Abreu, Manuel de, pag. 17 – Grande Enciclopédia Universal – edição de 1980 – Ed.Amazonas</ref> [[Andreas Pavel]]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iht.com/articles/2005/12/16/news/profile.php |accessdate=16 December 2015 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20090309065937/http://www.iht.com/articles/2005/12/16/news/profile.php |archivedate= 9 March 2009 |title=Portable stereo's creator got his due, eventually |df= }}</ref> and Nélio José Nicolai.<ref>[http://www.cefetmg.br/noticias/2010/11/noticia0014.html Exposição destaca centenário do CEFET-MG] Sítio do Cefet-MG, acessado em 13 de novembro de 2010 {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140813115503/http://www.cefetmg.br/noticias/2010/11/noticia0014.html |date=13 August 2014 }}</ref> |
|||
Brazilian science is represented by the likes of [[César Lattes]] (Brazilian [[physicist]] Pathfinder of ''[[Pion|Pi Meson]]''),<ref name="Lattes">{{cite web|url=http://www.cbpf.br/meson/meson.html|author=Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação|title=50 anos do Méson-Pi|access-date=29 December 2010|url-status=dead|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110526200502/http://www.cbpf.br/meson/meson.html|archivedate=26 May 2011}}</ref> [[Mário Schenberg]] (considered the greatest theoretical physicist of Brazil),<ref>{{cite web|url=http://cbpfindex.cbpf.br/publication_pdfs/dh00186.2011_08_16_15_20_32.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130331194248/http://cbpfindex.cbpf.br/publication_pdfs/dh00186.2011_08_16_15_20_32.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-date=31 March 2013|title=Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas – Coleção Galileo: Textos de Física|access-date=21 October 2014|date=}}</ref> [[José Leite Lopes]] (only Brazilian physicist holder of the ''UNESCO Science Prize''),<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.unesco.org/bpi/science/content/news/upress/99-147e.htm|title=Atta-Ur-Rahman, José Leite Lopes and Juan Martín Maldacena receive UNESCO science prizes|date=|publisher=UNESCOPRESS|access-date=21 October 2014}}</ref> [[Artur Ávila]] (the first Latin American winner of the [[Fields Medal]])<ref>[http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/ciencia/2014/08/1499290-brasileiro-ganha-a-medalha-fields-considerada-o-nobel-da-matematica.shtml Brasileiro ganha a Medalha Fields, considerada o "Nobel da Matemática"].</ref> and [[Fritz Müller]] (pioneer in factual support of the theory of evolution by Charles Darwin).<ref name="West, David A 2003">West, David A. 2003. Fritz Müller: a naturalist in Brazil. Blacksburg: Pocahontas Press</ref> |
|||
===Transport=== |
|||
{{Main|Transport in Brazil}} |
{{Main|Transport in Brazil}} |
||
[[File:Sao paulo airport terminal 3.jpg|thumb|Terminal 3 of the [[São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport]], the [[List of the busiest airports in South America|busiest airport in South America]]]] |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
[[File:Rodovia Dutra - panoramio.jpg|thumb|[[BR-116]] in [[São José dos Campos]], [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]], the longest [[Brazilian Highway System|highway]] in the country,<ref>{{Cite web |date=9 March 2022 |title=Qual é a maior rodovia do Brasil? |url=https://summitmobilidade.estadao.com.br/ir-e-vir-no-mundo/qual-e-a-maior-rodovia-do-brasil/ |access-date=22 November 2022 |publisher=[[O Estado de S.Paulo]] |language=pt-br}}</ref> with {{convert|4542|km|mi|abbr=on}} of extension<ref name="Extensão">{{Cite web |date=2018 |title=BR-116 |url=http://www2.transportes.gov.br/bit/02-rodo/3-loc-rodo/loc-rodo/116.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130127001608/http://www2.transportes.gov.br/bit/02-rodo/3-loc-rodo/loc-rodo/116.htm |archive-date=27 January 2013 |access-date=22 November 2022 |publisher=Banco de Informações e Mapas de Transportes/[[Ministry of Transport (Brazil)]] |language=pt-br}}</ref>]] |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| image1 = Saopaulo aerea aeroportocumbica.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = Aerial view of the [[São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport]], the [[List of the busiest airports in South America|busiest airport in South America]]. |
|||
|image2 = Rodovia Rio-Teresópolis (BR-116) - panoramio (cropped).jpg |
|||
| caption2 = [[BR-116]] in [[Guapimirim]], [[Rio de Janeiro (state)|Rio de Janeiro]], the longest [[Brazilian Highway System|highway]] in the country, with {{convert|4385|km|mi|abbr=on}} of extension.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://turismo.ig.com.br/destinos-nacionais/as-11-estradas-mais-incriveis-do-brasil/n1597216427845.html |title=As 11 estradas mais incríveis do Brasil |author=Fernanda Castello Branco |publisher=[[Internet Group|iG]] |accessdate=22 September 2014}}</ref> |
|||
|image3 = Seminário_da_TV_Tribuna_em_Santos._(42282761304).jpg |
|||
|caption3 = [[Port of Santos]], the busiest port in [[Latin America]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.gfmag.com/|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070512181621/http://www.gfmag.com/index.php?idPage=315|url-status=dead|title=Global Finance Magazine - Homepage|archivedate=12 May 2007|website=Global Finance Magazine}}</ref>}} |
|||
Brazilian roads are the primary carriers of freight and passenger traffic. The road system totaled 1.98 million km (1.23 million mi) in 2002. The total of paved roads increased from {{convert|35496|km|0|abbr=on}} in 1967 to {{convert|184140|km|0|abbr=on}} in 2002.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/Americas/Brazil-TRANSPORTATION.html|title=Road system in Brazil |publisher=Nationsencyclopedia.com |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> The country has about {{convert|14000|km|0|abbr=on}} of [[divided highways]], {{convert|5000|km|0|abbr=on}} only in the [[São Paulo (state)|State of São Paulo]]. Currently it's possible to travel from [[Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul|Rio Grande]], in the extreme south of the country, to [[Brasília]] ({{convert|2580|km|0|abbr=on}}) or [[Casimiro de Abreu, Rio de Janeiro|Casimiro de Abreu]], in the state of [[Rio de Janeiro (state)|Rio de Janeiro]] ({{convert|2045|km|0|abbr=on}}), only on divided highways. |
|||
Brazilian roads are the primary carriers of freight and passenger traffic. The [[Brazilian Highway System|road system]] totaled {{convert|1720000|km|0|abbr=on}} in 2019.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Brazilian road network in 2019 |url=https://anuariodotransporte.cnt.org.br/2021/Rodoviario/1-3-1-1-1-/Malha-rodovi%C3%A1ria-total |website=anuariodotransporte.cnt.org.br}}</ref> The total of paved roads increased from {{convert|35496|km|0|abbr=on}} in 1967 to {{convert|215000|km|0|abbr=on}} in 2018.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Road system in Brazil |url=http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/Americas/Brazil-TRANSPORTATION.html |access-date=30 October 2010 |publisher=Nationsencyclopedia.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Anuário CNT do Transporte |url=https://anuariodotransporte.cnt.org.br/2018/ |website=anuariodotransporte.cnt.org.br}}</ref> |
|||
The first investments in road infrastructure have given up in the 1920s, the government of [[Washington Luis]], being pursued in the governments of [[Getúlio Vargas]] and [[Eurico Gaspar Dutra]].<ref>{{Citation|last1=Pereira|first1=L.A.G|last2=Lessa|first2=S.N.|last3=Cardoso|first3=A.D.|title=Planejamento e Transporte Rodoviário no Brasil}}</ref> President [[Juscelino Kubitschek]] (1956–61), who designed and built the capital [[Brasília]], was another supporter of highways. Kubitschek was responsible for the installation of major car manufacturers in the country ([[Volkswagen]], [[Ford Motor Company|Ford]] and [[General Motors]] arrived in Brazil during his rule) and one of the points used to attract them was support for the construction of highways. With the implementation of [[Fiat]] in 1976 ending an automobile market closed loop, from the end of the 1990s the country has received large foreign direct investments installing in its territory other major car manufacturers and utilities, such as [[Iveco]], [[Renault]], [[Peugeot]], [[Citroen]], [[Honda]], [[Mitsubishi]], [[Mercedes-Benz]], [[BMW]], [[Hyundai Motor Company|Hyundai]], [[Toyota]] among others.<ref>Sydney Alberto Latini; "A Implantação da Indústria Automobilística no Brasil"; Editora Alaúde 2007 {{ISBN|978-85-98497-55-6}}</ref> Brazil is the seventh most important country in the [[auto industry]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://oica.net/wp-content/uploads/all-vehicles.pdf|title=Automotive industry in Brazil and the world|access-date=14 May 2010|publisher=International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil's [[Rail transport|railway]] |
Brazil's [[Rail transport in Brazil|railway system]] has been declining since 1945, when emphasis shifted to highway construction. The country's total railway track length was {{convert|30576|km|0|abbr=on}} in 2015,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Extensão da Malha Ferroviária – 2015 |url=http://anuario.antt.gov.br/index.php/content/view/4751/Ferroviaria.html |publisher=ANTT |access-date=23 October 2023 |archive-date=8 December 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231208195757/http://anuario.antt.gov.br/index.php/content/view/4751/Ferroviaria.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> as compared with {{convert|31848|km|0|abbr=on}} in 1970, making it the [[List of countries by rail transport network size|ninth largest network]] in the world. Most of the railway system belonged to the [[RFFSA|Federal Railroad Network Corporation]] (RFFSA), which was privatized in 2007.<ref>[http://www2.transportes.gov.br/bit/03-ferro/princ-ferro.html "OPrincipais ferrovias"]. Ministerio dos Transportes {{in lang|pt}} {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130329092636/http://www2.transportes.gov.br/bit/03-ferro/princ-ferro.html |date=29 March 2013 }}</ref> The [[São Paulo Metro]] began operating on 14 September 1974 as the first underground transit system in Brazil.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Arquitetura |first=INBEC Pós-Graduação- Engenharia |date=4 February 2020 |title=Conheça a história da construção do Metrô de São Paulo |url=https://inbec.com.br/blog/conheca-historia-construcao-metro-sao-paulo |access-date=23 October 2023 |website=INBEC Pós-Graduação |language=pt-BR}}</ref> |
||
There are about 2,500 airports in Brazil, including landing fields: the second-largest number in the world, after the United States.<ref>[http://g1.globo.com/Noticias/Brasil/0,,MUL86760-5598,00.html "Ociosidade atinge 70% dos principais aeroportos"]. ''O Globo'', 12 August 2007. {{in lang|pt}}</ref> [[São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport]], near São Paulo, is the largest and busiest airport with nearly 43 million passengers annually, while handling the vast majority of commercial traffic for the country.<ref name="Palhares2012x">{{Cite book |last=Guilherme Lohmann Palhares |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=O91SVF9nH8gC&pg=PA48 |title=Tourism in Brazil: Environment, Management and Segments |publisher=Routledge |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-415-67432-4 |page=48}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Relatorio Operacional 2018 |url=https://www.gru.com.br/pt/RelatorioOperacional/2018-12.pdf |access-date=June 19, 2024 |website=Aeroporto Internacional de São Paulo}}</ref> |
|||
The country has an extensive rail network of {{convert|28538|km|abbr=off}} in length, the tenth largest network in the world.<ref name="2012ciagini">[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2172.html Country Comparison to the World: Gini Index – Brazil] [[The World Factbook]]. Retrieved on 3 April 2012.</ref> Currently, the Brazilian government, unlike the past, seeks to encourage this mode of transport; an example of this incentive is the project of the [[Rio–São Paulo high-speed rail]], that will connect the two main cities of the country to carry passengers. |
|||
For freight transport, [[waterways]] are of importance. The [[Free Economic Zone of Manaus|industrial zones of Manaus]] can be reached only by means of the Solimões–Amazonas waterway ({{convert|3250|km|mi|disp=or|abbr=off|sp=us}} in length, with a minimum depth of {{convert|6|m|ft|0|disp=or|abbr=off|spell=in|sp=us}}). The country also has {{convert|50000|km|abbr=off|sp=us}} of waterways.<ref name="2012ciagini">[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2172.html Country Comparison to the World: Gini Index – Brazil] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070613005439/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2172.html |date=13 June 2007 }} [[The World Factbook]]. Retrieved on 3 April 2012.</ref> Coastal shipping links widely separated parts of the country. Bolivia and Paraguay have been given free ports at [[Santos, São Paulo|Santos]]. Of the 36 deep-water ports, Santos, Itajaí, Rio Grande, Paranaguá, Rio de Janeiro, Sepetiba, Vitória, Suape, Manaus and São Francisco do Sul are the most important.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20081227224101/http://www.mzweb.com.br/santosbrasil/web/conteudo_pt.asp?idioma=0&tipo=3958&conta=28 "Mercado Brasileiro Terminais de Contêineres"], Santos Brasil. {{in lang|pt}}</ref> Bulk carriers have to wait up to 18 days before being serviced; container ships take 36.3 hours on average.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=G1 |first1=Fábio AmatoDo |last2=Brasília |first2=em |date=24 March 2013 |title=Navios esperam até 16 dias para atracar em porto do país, diz MDIC |url=http://g1.globo.com/economia/noticia/2013/03/navios-esperam-ate-16-dias-para-atracar-em-porto-do-pais-diz-mdic.html |website=Economia}}</ref> |
|||
There are about 2,500 [[airport]]s in Brazil, including landing fields: the second largest number in the world, after the United States.<ref>"[http://g1.globo.com/Noticias/Brasil/0,,MUL86760-5598,00.html Ociosidade atinge 70% dos principais aeroportos]." globo.com, 12 August 2007. {{in lang|pt}}</ref> [[São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport]], near São Paulo, is the largest and busiest airport with nearly 20 million passengers annually, while handling the vast majority of commercial traffic for the country.<ref name="Palhares2012x">{{cite book|author=Guilherme Lohmann Palhares|title=Tourism in Brazil: Environment, Management and Segments|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=O91SVF9nH8gC&pg=PA48|year=2012|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-0-415-67432-4|page=48}}</ref> |
|||
== Demographics == |
|||
For freight transport [[waterways]] are of importance, e.g. the [[Free Economic Zone of Manaus|industrial zones of Manaus]] can be reached only by means of the Solimões–Amazonas waterway ({{convert|3250|km|abbr=off}} with {{convert|6|m|abbr=off}} minimum depth). The country also has {{convert|50000|km|abbr=off}} of waterways.<ref name="2012ciagini"/> |
|||
Coastal shipping links widely separated parts of the country. Bolivia and Paraguay have been given free [[port]]s at [[Santos, São Paulo|Santos]]. Of the 36 deep-water ports, Santos, Itajaí, Rio Grande, Paranaguá, Rio de Janeiro, Sepetiba, Vitória, Suape, Manaus and São Francisco do Sul are the most important.<ref>"[https://web.archive.org/web/20081227224101/http://www.mzweb.com.br/santosbrasil/web/conteudo_pt.asp?idioma=0&tipo=3958&conta=28 Mercado Brasileiro Terminais de Contêineres]," Santos Brasil. {{in lang|pt}}</ref> Bulk carriers have to wait up to 18 days before being serviced, container ships 36.3 hours on average.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://g1.globo.com/economia/noticia/2013/03/navios-esperam-ate-16-dias-para-atracar-em-porto-do-pais-diz-mdic.html |title=Navios esperam até 16 dias para atracar em porto do país, diz MDIC}}</ref> |
|||
===Health=== |
|||
{{Main|Health in Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Fotorreportagem do ICESP (42627443635).jpg|thumb|left|[[Institute of Cancer of São Paulo|Institute of Cancer]] of the [[Hospital das Clínicas da Universidade de São Paulo|University of São Paulo Clinics Hospital]], the largest [[academic health science centre|hospital complex]] in Latin America.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/cotidiano/2014/04/1440047-hc-faz-aniversario-em-meio-a-reformas-que-somam-r-350-milhoes.shtml|title=HC faz aniversário em meio a reformas que somam R$ 350 milhões|publisher=[[Folha de S.Paulo]]|date=13 April 2014|access-date=11 August 2014}}</ref>]] |
|||
The Brazilian [[public health]] system, the [[Sistema Único de Saúde|Unified Health System]] (SUS), is managed and provided by all levels of government,<ref name="ForgiaCouttolenc2008">{{cite book|author1=Gerard Martin La Forgia|author2=Bernard F. Couttolenc|title=Hospital Performance in Brazil: The Search for Excellence|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=i3R43xW5KqcC&pg=PA17|year=2008|publisher=World Bank Publications|isbn=978-0-8213-7359-0|page=17}}</ref> being the largest system of this type in the world.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://conselho.saude.gov.br/web_sus20anos/index.html|title=20 Anos do SUS|publisher=Conselho Nacional de Saúde|accessdate=13 April 2012}}</ref> On the other hand, private healthcare systems play a complementary role.<ref name="Wolper2004">{{cite book|author=Lawrence F. Wolper|title=Health Care Administration: Planning, Implementing, and Managing Organized Delivery Systems|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Zts-QdpDiWUC&pg=PA33|year=2004|publisher=Jones & Bartlett Learning|isbn=978-0-7637-3144-1|page=33}}</ref> |
|||
Public health services are universal and offered to all citizens of the country for free. However, the construction and maintenance of health centers and hospitals are financed by taxes, and the country spends about 9% of its GDP on expenditures in the area. In 2012, Brazil had 1.85 doctors and 2.3 hospital beds for every 1,000 inhabitants.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.MED.PHYS.ZS?locations=BR|title=Physicians (per 1,000 people)|last=|first=|date=|website=World Health Organization's Global Health Workforce Statistics|access-date=}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.MED.BEDS.ZS|title=Hospital beds (per 1,000 people)|last=|first=|date=|website=World Health Organization The World Bank|access-date=}}</ref> |
|||
Despite all the progress made since the creation of the [[universal health care]] system in 1988, there are still several public health problems in Brazil. In 2006, the main points to be solved were the high [[List of countries by infant mortality rate|infant]] (2.51%) and maternal mortality rates (73.1 deaths per 1000 births).<ref name="Radar social"/> |
|||
The number of deaths from noncommunicable diseases, such as [[cardiovascular diseases]] (151.7 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants) and [[cancer]] (72.7 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants), also has a considerable impact on the health of the Brazilian population. Finally, external but preventable factors such as car accidents, violence and suicide caused 14.9% of all deaths in the country.<ref name="Radar social">{{Cite web|title=Saúde|website=Radar social|publisher=Ministério do Planejamento|url=http://www.planejamento.gov.br/secretarias/upload/Arquivos/spi/programas_projeto/radar_social/2006_PRP_Radar_radarSocial.pdf|archive-url=https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20081216074831/http://www.planejamento.gov.br/secretarias/upload/Arquivos/spi/programas_projeto/radar_social/2006_PRP_Radar_radarSocial.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-date=16 December 2008|accessdate=10 June 2008}}</ref> The Brazilian health system was ranked 125th among the 191 countries evaluated by the [[World Health Organization]] (WHO) in 2000.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/paper30.pdf |title=Measuring overall health system performance for 191 countries|publisher=[[World Health Organization]]|date=2000|accessdate=30 April 2014}}</ref> |
|||
===Education=== |
|||
{{Main|Education in Brazil}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| width = 220 |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| image1 = Universidade Federal do Parana 4 Curitiba Parana.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = Historical building of the [[Federal University of Paraná]], one of the oldest universities in Brazil, located in [[Curitiba]] |
|||
|image2 = Sala_de_aula_CB_Unicamp.jpg |
|||
| caption2 = Classroom in the main campus of the [[University of Campinas]], [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]] |
|||
}} |
|||
The [[Constitution|Federal Constitution]] and the Law of Guidelines and Bases of National Education determine that the [[Federal government of Brazil|Union]], the [[States of Brazil|states]], the [[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]], and the [[Municipalities of Brazil|municipalities]] must manage and organize their respective education systems. Each of these public educational systems is responsible for its own maintenance, which manages funds as well as the mechanisms and funding sources. The constitution reserves 25% of the state budget and 18% of federal taxes and municipal taxes for education.<ref name="Usa2005">{{cite book|author=Usa Ibp Usa|title=Brazil: Tax Guide|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dzhWjfK8CswC&pg=PA42|year=2005|publisher=Int'l Business Publications|isbn=978-0-7397-3279-3|page=42}}</ref> |
|||
According to the [[Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics|IBGE]], in 2011, the literacy rate of the population was 90.4%, meaning that 13 million (9.6% of population) people are still illiterate in the country; functional illiteracy has reached 21.6% of the population.<ref name="Agency2010">{{cite book|author=The Central Intelligence Agency|title=The World Factbook 2010|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=m-9eSrZtYAAC&pg=PA143|year=2010|publisher=Potomac Books, Inc.|isbn=978-1-59797-541-4|page=143|edition=CIA 2009}}</ref> Illiteracy is highest in the Northeast, where 19.9% of the population is illiterate.<ref name="Bank2001">{{cite book|author=World Bank|title=Rural Poverty Alleviation in Brazil: Towards an Integrated Strategy|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YttV-Ggq90UC&pg=PA40|year=2001|publisher=World Bank Publications|isbn=978-0-8213-5206-9|page=40}}</ref> |
|||
Higher education starts with undergraduate or sequential [[course (education)|courses]], which may offer different options of specialization in academic or professional careers. Depending on the choice, students can improve their educational background with courses of post-graduate studies or broad sense. |
|||
Attending an institution of higher education is required by Law of Guidelines and Bases of Education. [[Kindergarten]], [[elementary school|elementary]] and medium education are required of all students, provided the student does not hold any disability, whether physical, [[Mind|mental]], [[visual]] or [[hearing (sense)|hearing]]. |
|||
The [[University of São Paulo]] is the second best [[university]] in [[Latin America]], according to recent 2019 [[QS World University Rankings]]. Of the top 20 Latin American universities, eight are Brazilian. Most of them are [[Public university|public]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.topuniversities.com/university-rankings/latin-american-university-rankings/2019|title=QS University Rankings Latin America|publisher=[[QS World University Rankings]]|accessdate=11 November 2018}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil's private institutions tend to be more exclusive and offer better quality education, so many high-income families send their children there. The result is a segregated educational system that reflects extreme income disparities and reinforces social inequality. However, efforts to change this are making impacts.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Laplane|first1=Mario|title=Efforts towards inclusion|url=https://www.dandc.eu/en/article/impact-public-and-private-education-social-inequality-brazil|website=D + C, Development and cooperation}}</ref> |
|||
===Media and communication{{anchor|Media}}=== |
|||
{{Main|Telecommunications in Brazil|Television in Brazil}} |
|||
{{see also|Concentration of media ownership#Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Jornal Nacional 3.jpg|thumb|left|Former President [[Dilma Rousseff]] at ''[[Jornal Nacional]]'' news program. [[Rede Globo]] is the world's second-largest commercial television network.<ref>{{cite web|title=Rede Globo se torna a 2ª maior emissora do mundo|url=http://ofuxico.terra.com.br/noticias-sobre-famosos/rede-globo-se-torna-a-2-maior-emissora-do-mundo/2012/05/11-139187.html|publisher=O Fuxico|accessdate=22 May 2012|language=Portuguese}}</ref>]] |
|||
The Brazilian press was officially born in [[Rio de Janeiro]] on 13 May 1808 with the creation of the Royal Printing National Press by the [[Prince Regent]] [[João VI of Portugal|Dom João]].<ref name="EchevarríaPupo-Walker1996">{{cite book|author1=Roberto Gonzalez Echevarría|author2=Enrique Pupo-Walker|title=The Cambridge History of Latin American Literature|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=97NoYRx96ZAC&pg=PA13|year=1996|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-41035-9|page=13}}</ref> |
|||
The ''Gazeta do Rio de Janeiro'', the first newspaper published in the country, began to circulate on 10 September 1808.<ref name="Johnston2003">{{cite book|author=Donald H. Johnston|title=Encyclopedia of international media and communications|volume=3|year=2003|publisher=Academic Press|isbn=978-0-12-387671-3|page=130}}</ref> The [[List of newspapers in the world by circulation|largest newspapers]] nowadays are ''[[Folha de S.Paulo]],'' ''Super Notícia'', ''[[O Globo]]'' and ''[[O Estado de S. Paulo]]''.<ref name="Vincent2003B">{{cite book|author=Jon S. Vincent|title=Culture and Customs of Brazil|url=https://archive.org/details/culturecustomsof0000vinc|url-access=registration|year=2003|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|isbn=978-0-313-30495-8|pages=[https://archive.org/details/culturecustomsof0000vinc/page/97 97]–100}}</ref> |
|||
Radio broadcasting began on 7 September 1922, with a speech by then President Pessoa, and was formalized on 20 April 1923 with the creation of "Radio Society of Rio de Janeiro."<ref name="McCann2004">{{cite book|author=Bryan McCann|title=Hello, Hello Brazil: Popular Music in the Making of Modern Brazil|url=https://archive.org/details/hellohellobrazil00mcca|url-access=registration|year=2004|publisher=Duke University Press|isbn=978-0-8223-3273-2|page=[https://archive.org/details/hellohellobrazil00mcca/page/22 22]}}</ref> |
|||
Television in Brazil began officially on 18 September 1950, with the founding of [[TV Tupi]] by [[Assis Chateaubriand]].<ref name="Ward2007">{{cite book|author=David Ward|title=Television and Public Policy: Change and Continuity in an Era of Global Liberalization|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zdEs1Av1CvAC&pg=PA28|year=2007|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-0-203-87728-9|page=28}}</ref> Since then television has grown in the country, creating large commercial broadcast networks such as [[Rede Globo|Globo]], [[Sistema Brasileiro de Televisão|SBT]], [[RecordTV]], [[Rede Bandeirantes|Bandeirantes]] and [[RedeTV!|RedeTV]]. Today it is the most important factor in popular culture of Brazilian society, indicated by research showing that as much as 67%<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.ibope.com.br/pt-br/relacionamento/duvidas-frequentes/Paginas/Audiencia-de-televisao.aspx |title=Um ponto de IBOPE equivale a quantas pessoas? E domicílios? |publisher=IBOPE |accessdate=23 March 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130522190248/http://www.ibope.com.br/pt-br/relacionamento/duvidas-frequentes/Paginas/Audiencia-de-televisao.aspx |archive-date=22 May 2013 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://entretenimento.br.msn.com/famosos/top-10-das-novelas?page=0px |title=Top 10 das novelas |publisher=MSN Brasil |accessdate=23 March 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130507101650/http://entretenimento.br.msn.com/famosos/top-10-das-novelas?page=0px |archive-date=7 May 2013 |url-status=dead }}</ref> of the general population follow the same daily [[soap opera]] broadcast. Digital Television, using the [[SBTVD]] standard (based on the Japanese standard [[ISDB-T]]), was adopted on 29 June 2006 and launched on 2 November 2007.<ref name="Alencar2009">{{cite book|author=Marcelo S. Alencar|title=Digital Television Systems|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=M96rKRAqHFgC&pg=PA179|year=2009|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-89602-3|pages=179–81}}</ref> In May 2010, the Brazilian government launched [[TV Brasil Internacional]], an international [[television station]], initially broadcasting to 49 countries.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/10152301 |title=Brazil launches international TV station for Africa |work=BBC News |date=25 May 2010 |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> Commercial television channels broadcast internationally include [[Globo Internacional]], [[RecordTV Internacional]] and [[Band Internacional]]. |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
{{Main|Demographics of Brazil|Brazilians}} |
{{Main|Demographics of Brazil|Brazilians}} |
||
{{See also|Immigration to Brazil|List of Brazilian states by population density}} |
{{See also|Immigration to Brazil|List of Brazilian states by population density}} |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Population density Brazil 2020.svg|thumb|Population density of Brazilian municipalities]] |
||
According to the latest official projection, it is estimated that Brazil’s population was 210,862,983 on July 1, 2022—an adjustment of 3.9% from the initial figure of 203 million reported by the 2022 census.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-08-23 |title=Brazilian population likely to start shrinking in 2042 |url=https://agenciabrasil.ebc.com.br/en/geral/noticia/2024-08/brazilian-population-likely-start-shrinking-2042 |access-date=2024-08-24 |website=Agência Brasil |language=en}}</ref> The population of Brazil, as recorded by the 2008 PNAD, was approximately 190 million<ref>2008 PNAD, IBGE. [http://www.sidra.ibge.gov.br/bda/tabela/protabl.asp?c=261&i=P&nome=on¬arodape=on&tab=261&unit=0&pov=1&opc1=1&poc2=1&OpcTipoNivt=1&opn1=2&nivt=0&poc1=1&sec58=0&orp=6&qtu3=27&opv=1&sec1=0&opc2=1&pop=1&opn2=2&orv=2&orc2=4&opc58=1&qtu2=5&sev=93&sec2=0&opp=1&opn3=0&orc1=3&poc58=1&qtu1=1&cabec=on&orc58=5&opn7=0&decm=99&ascendente=on&sep=43343&orn=1&qtu7=9&pon=2&OpcCara=44&proc=1 "População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade"]</ref> ({{convert|22.31|PD/km2|disp=or|abbr=out|sp=us}}), with a ratio of men to women of 0.95:1<ref>2008 PNAD, IBGE. [http://www.sidra.ibge.gov.br/bda/tabela/protabl.asp?c=261&i=P&nome=on¬arodape=on&tab=261&unit=0&pov=1&opc1=1&poc2=3&OpcTipoNivt=1&opn1=2&nivt=0&poc1=1&sec58=0&orp=6&qtu3=27&opv=1&sec1=0&opc2=1&pop=1&opn2=2&orv=2&orc2=4&opc58=1&qtu2=5&sev=93&sec2=0&sec2=92956&sec2=92957&opp=1&opn3=0&orc1=3&poc58=1&qtu1=1&cabec=on&orc58=5&opn7=0&decm=99&ascendente=on&sep=43343&orn=1&qtu7=9&pon=2&OpcCara=44&proc=1 "População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade"]</ref> and 83.75% of the population defined as urban.<ref>2008 PNAD, IBGE. [http://www.sidra.ibge.gov.br/bda/tabela/protabl.asp?c=261&i=P&nome=on¬arodape=on&tab=261&unit=0&pov=3&opc1=1&poc2=1&OpcTipoNivt=1&opn1=2&nivt=0&poc1=2&sec58=0&orp=6&qtu3=27&opv=1&sec1=0&sec1=1&sec1=2&opc2=1&pop=1&opn2=2&orv=2&orc2=4&opc58=1&qtu2=5&sev=93&sev=1000093&sec2=0&opp=1&opn3=0&orc1=3&poc58=1&qtu1=1&cabec=on&orc58=5&opn7=0&decm=99&ascendente=on&sep=43343&orn=1&qtu7=9&pon=2&OpcCara=44&proc=1 "População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade"].</ref> The population is heavily concentrated in the Southeastern (79.8 million inhabitants) and Northeastern (53.5 million inhabitants) regions, while the two most extensive regions, the Center-West and the North, which together make up 64.12% of the Brazilian territory, have a total of only 29.1 million inhabitants. |
|||
{|class="wikitable" style="float: right; margin-left: 10px" |
|||
! colspan="4" style="text-align:center; background:#cfb;"|Population{{UN_Population|ref}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="background:#cfb;"|Year |
|||
! style="background:#cfb;"|Million |
|||
|- |
|||
|style="text-align:left;"|1950 ||style="text-align:right;"|54.0 |
|||
|- |
|||
|style="text-align:left;"|2000 ||style="text-align:right;"|175.3 |
|||
|- |
|||
|style="text-align:left;"|{{UN_Population|Year}} ||style="text-align:right;"|{{#expr:{{formatnum:{{UN_Population|Brazil}}|R}}/1e6 round 1}} |
|||
|} |
|||
The population of Brazil, as recorded by the 2008 PNAD, was approximately 190 million<ref>2008 PNAD, IBGE. "[http://www.sidra.ibge.gov.br/bda/tabela/protabl.asp?c=261&i=P&nome=on¬arodape=on&tab=261&unit=0&pov=1&opc1=1&poc2=1&OpcTipoNivt=1&opn1=2&nivt=0&poc1=1&sec58=0&orp=6&qtu3=27&opv=1&sec1=0&opc2=1&pop=1&opn2=2&orv=2&orc2=4&opc58=1&qtu2=5&sev=93&sec2=0&opp=1&opn3=0&orc1=3&poc58=1&qtu1=1&cabec=on&orc58=5&opn7=0&decm=99&ascendente=on&sep=43343&orn=1&qtu7=9&pon=2&OpcCara=44&proc=1 População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade]"</ref> ({{convert|22.31|PD/km2|disp=or|abbr=out}}), with a ratio of men to women of 0.95:1<ref>2008 PNAD, IBGE. "[http://www.sidra.ibge.gov.br/bda/tabela/protabl.asp?c=261&i=P&nome=on¬arodape=on&tab=261&unit=0&pov=1&opc1=1&poc2=3&OpcTipoNivt=1&opn1=2&nivt=0&poc1=1&sec58=0&orp=6&qtu3=27&opv=1&sec1=0&opc2=1&pop=1&opn2=2&orv=2&orc2=4&opc58=1&qtu2=5&sev=93&sec2=0&sec2=92956&sec2=92957&opp=1&opn3=0&orc1=3&poc58=1&qtu1=1&cabec=on&orc58=5&opn7=0&decm=99&ascendente=on&sep=43343&orn=1&qtu7=9&pon=2&OpcCara=44&proc=1 População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade]"</ref> and 83.75% of the population defined as urban.<ref>2008 PNAD, IBGE. "[http://www.sidra.ibge.gov.br/bda/tabela/protabl.asp?c=261&i=P&nome=on¬arodape=on&tab=261&unit=0&pov=3&opc1=1&poc2=1&OpcTipoNivt=1&opn1=2&nivt=0&poc1=2&sec58=0&orp=6&qtu3=27&opv=1&sec1=0&sec1=1&sec1=2&opc2=1&pop=1&opn2=2&orv=2&orc2=4&opc58=1&qtu2=5&sev=93&sev=1000093&sec2=0&opp=1&opn3=0&orc1=3&poc58=1&qtu1=1&cabec=on&orc58=5&opn7=0&decm=99&ascendente=on&sep=43343&orn=1&qtu7=9&pon=2&OpcCara=44&proc=1 População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade]."</ref> The population is heavily concentrated in the Southeastern (79.8 million inhabitants) and Northeastern (53.5 million inhabitants) regions, while the two most extensive regions, the Center-West and the North, which together make up 64.12% of the Brazilian territory, have a total of only 29.1 million inhabitants. |
|||
The first census in Brazil was carried out in 1872 and recorded a population of 9,930,478.<ref> |
The first census in Brazil was carried out in 1872 and recorded a population of 9,930,478.<ref>[http://www.brasil.gov.br/news/history/2011/04-1/29/brazil-population-reaches-190.8-million/newsitem_view?set_language=en "Brazil population reaches 190.8 million"] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130809205237/http://www.brasil.gov.br/news/history/2011/04-1/29/brazil-population-reaches-190.8-million/newsitem_view?set_language=en |date=9 August 2013 }}. Brasil.gov.br.</ref> From 1880 to 1930, 4 million Europeans arrived.<ref>[http://www.migrationinformation.org/profiles/display.cfm?id=311 "Shaping Brazil: The Role of International Migration"]. Migration Policy Institute.</ref> Brazil's population increased significantly between 1940 and 1970, because of a decline in the [[mortality rate]], even though the [[birth rate]] underwent a slight decline. In the 1940s the annual [[population growth]] rate was 2.4%, rising to 3.0% in the 1950s and remaining at 2.9% in the 1960s, as life expectancy rose from 44 to 54 years<ref>José Alberto Magno de Carvalho, [http://cedeplar.face.ufmg.br/pesquisas/td/TD%20227.pdf "Crescimento populacional e estrutura demográfica no Brasil"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161019004601/http://cedeplar.face.ufmg.br/pesquisas/td/TD%20227.pdf |date=19 October 2016 }} Belo Horizonte: UFMG/Cedeplar, 2004 (PDF file), p. 5.</ref> and to 72.6 years in 2007.<ref>{{Cite web |date=29 November 1999 |title=Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística |url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/presidencia/noticias/noticia_visualiza.php?id_noticia=1275&id_pagina=1 |access-date=25 January 2010 |publisher=IBGE}}</ref> It has been steadily falling since the 1960s, from 3.04% per year between 1950 and 1960 to 1.05% in 2008 and is expected to fall to a negative value of –0.29% by 2050<ref>{{Cite web |title=Projeção da População do Brasil – Brazil's populational projection |url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/presidencia/noticias/noticia_impressao.php?id_noticia=1272 |access-date=25 January 2010 |publisher=IBGE}}</ref> thus completing the [[demographic transition]].<ref>Magno de Carvalho, [http://www.observasaude.sp.gov.br/BibliotecaPortal/Acervo/Estrutura_Demogr%C3%A1fica_Brasil.pdf "Crescimento populacional e estrutura demográfica no Brasil"]{{dead link|date=May 2017|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}, pp. 7–8.</ref> |
||
It has been steadily falling since the 1960s, from 3.04% per year between 1950 and 1960 to 1.05% in 2008 and is expected to fall to a negative value of –0.29% by 2050<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/presidencia/noticias/noticia_impressao.php?id_noticia=1272 |title=Projeção da População do Brasil – Brazil's populational projection |publisher=IBGE |accessdate=25 January 2010}}</ref> thus completing the [[demographic transition]].<ref>Magno de Carvalho, "[http://www.observasaude.sp.gov.br/BibliotecaPortal/Acervo/Estrutura_Demogr%C3%A1fica_Brasil.pdf Crescimento populacional e estrutura demográfica no Brasil]{{dead link|date=May 2017|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}," pp. 7–8.</ref> |
|||
In 2008, the illiteracy rate was 11.48%<ref>PNAD 2008, IBGE. |
In 2008, the illiteracy rate was 11.48%.<ref>PNAD 2008, IBGE. [http://www.sidra.ibge.gov.br/bda/tabela/protabl.asp?c=271&i=P&sec59=93024&sec59=1023&sec59=1024&nome=on¬arodape=on&tab=271&unit=0&pov=3&opc1=1&poc2=1&orc59=5&OpcTipoNivt=1&opn1=2&nivt=0&poc1=1&sec58=0&orp=7&qtu3=27&opv=1&sec1=0&opc2=1&pop=1&opn2=0&orv=2&orc2=4&opc58=1&qtu2=5&sev=121&sev=1000121&sec2=0&poc59=2&opp=1&opn3=0&orc1=3&poc58=1&qtu1=1&cabec=on&opc59=1&ascendente=on&sep=43345&orn=1&qtu7=9&orc58=6&opn7=0&decm=99&pon=1&OpcCara=44&proc=1 "Pessoas de 5 anos ou mais de idade por situação, sexo, alfabetização e grupos de idade e grupos de idade"].</ref> |
||
===Race and ethnicity=== |
=== Race and ethnicity === |
||
{{ |
{{Main|Race and ethnicity in Brazil}} |
||
[[File:Fachada do Museu da Imigração de São Paulo.JPG|thumb|left|[[Immigration Museum of the State of São Paulo]] in the neighborhood of [[Mooca (district of São Paulo)|Mooca]], in [[São Paulo city]]. The [[Italian Brazilians]] are 15% of the population and the largest Italian community outside [[Italy]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.itamaraty.gov.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=5270&Itemid=478&cod_pais=ITA&tipo=ficha_pais&lang=pt-BR|title=República Italiana|author=|date=|website=itamaraty.gov.br}}</ref>]] |
|||
According to the [[Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics|National Research by Household Sample]] (PNAD) of 2008, 48.43% of the population (about 92 million) described themselves as [[White Brazilian|White]]; 43.80% (about 83 million) as [[Pardo Brazilians|Pardo]] ([[brown people|brown]]), 6.84% (about 13 million) as [[Black Brazilian|Black]]; 0.58% (about 1.1 million) as [[Asian Brazilian|Asian]]; and 0.28% (about 536 thousand) as [[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|Amerindian]] (officially called ''indígena'', Indigenous), while 0.07% (about 130 thousand) did not declare their race.<ref name="PNADIBGE">2008 PNAD, IBGE. "[https://web.archive.org/web/20110614225239/http://www.sidra.ibge.gov.br/bda/tabela/protabl.asp?c=262&i=P&nome=on¬arodape=on&tab=262&unit=0&pov=3&opc1=1&poc2=1&OpcTipoNivt=1&opn1=2&nivt=0&orc86=3&poc1=1&orp=6&qtu3=27&opv=1&poc86=2&sec1=0&opc2=1&pop=1&opn2=0&orv=2&orc2=5&qtu2=5&sev=93&sev=1000093&opc86=1&sec2=0&opp=1&opn3=0&sec86=0&sec86=2776&sec86=2777&sec86=2779&sec86=2778&sec86=2780&sec86=2781&ascendente=on&sep=43344&orn=1&qtu7=9&orc1=4&qtu1=1&cabec=on&pon=1&OpcCara=44&proc=1&opn7=0&decm=99 População residente por cor ou raça, situação e sexo]."</ref> |
|||
In 2007, the [[Fundação Nacional do Índio|National Indian Foundation]] estimated that Brazil has 67 different uncontacted tribes, up from their estimate of 40 in 2005. Brazil is believed to have the largest number of [[uncontacted peoples]] in the world.<ref>"[https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/07/07/AR2007070701312.html In Amazonia, Defending the Hidden Tribes]," ''The Washington Post'' (8 July 2007).</ref> |
|||
Since the arrival of the Portuguese in 1500, considerable genetic mixing between Amerindians, Europeans, and Africans has taken place in all regions of the country (with European ancestry being dominant nationwide according to the vast majority of all autosomal studies undertaken covering the entire population, accounting for between 65% to 77%).<ref name="alvaro.com.br">{{cite journal|url=http://www.alvaro.com.br/pdf/trabalhoCientifico/ARTIGO_BRASIL_LILIAN.pdf |title=Allele frequencies of 15 STRs in a representative sample of the Brazilian population |doi=10.1016/j.fsigen.2009.05.006 |year=2010 |last1=De Assis Poiares |first1=Lilian |last2=De Sá Osorio |first2=Paulo |last3=Spanhol |first3=Fábio Alexandre |last4=Coltre |first4=Sidnei César |last5=Rodenbusch |first5=Rodrigo |last6=Gusmão |first6=Leonor |last7=Largura |first7=Alvaro |last8=Sandrini |first8=Fabiano |last9=Da Silva |first9=Cláudia Maria Dornelles |journal=Forensic Science International: Genetics |volume=4 |issue=2 |pages=e61–63 |pmid=20129458 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://www.webcitation.org/5xmleMZgv?url=http://www.alvaro.com.br/pdf/trabalhoCientifico/ARTIGO_BRASIL_LILIAN.pdf |archivedate= 8 April 2011}}</ref><ref name="www1.folha.uol.com.br">[http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/folha/ciencia/ult306u633465.shtml Brazilian DNA is nearly 80% European, indicates study].</ref><ref name="bdtd.bce.unb.br">NMO Godinho [http://bdtd.bce.unb.br/tedesimplificado/tde_busca/arquivo.php?codArquivo=3873 O impacto das migrações na constituição genética de populações latino-americanas] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706162240/http://bdtd.bce.unb.br/tedesimplificado/tde_busca/arquivo.php?codArquivo=3873 |date=6 July 2011 }}. PhD Thesis, Universidade de Brasília (2008).</ref><ref name="plosone.org">{{cite journal|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0017063 |title=The Genomic Ancestry of Individuals from Different Geographical Regions of Brazil Is More Uniform Than Expected |year=2011 |last1=Pena |first1=Sérgio D. J. |last2=Di Pietro |first2=Giuliano |last3=Fuchshuber-Moraes |first3=Mateus |last4=Genro |first4=Julia Pasqualini |last5=Hutz |first5=Mara H. |last6=Kehdy Fde |first6=Fernanda de Souza Gomes |last7=Kohlrausch |first7=Fabiana |last8=Magno |first8=Luiz Alexandre Viana |last9=Montenegro |first9=Raquel Carvalho|journal=PLOS ONE |volume=6 |issue=2 |page=e17063 |pmid=21359226 |pmc=3040205|editor1-last=Harpending|editor1-first=Henry|last10=Moraes|first10=MO|last11=De Moraes|first11=ME|last12=De Moraes|first12=MR|last13=Ojopi|first13=EB|last14=Perini|first14=JA|last15=Racciopi|first15=C|last16=Ribeiro-Dos-Santos|first16=AK|last17=Rios-Santos|first17=F|last18=Romano-Silva|first18=MA|last19=Sortica|first19=VA|last20=Suarez-Kurtz|first20=G|display-authors=9|bibcode=2011PLoSO...617063P}}</ref> |
|||
{{Pie chart |
{{Pie chart |
||
|thumb = right |
|thumb = right |
||
|caption = [[Race and ethnicity in Brazil]] 2022 |
|||
|caption = [[Race and ethnicity in Brazil]]<ref name="IBGE Censo de 2000">{{cite web|url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/tendencia_demografica/analise_populacao/1940_2000/default.shtm |title=Tendências Demográficas: Uma análise da população com base nos resultados dos Censos Demográficos 1940 e 2000 |publisher=Ibge.gov.br |accessdate=7 April 2012}}</ref><ref name="Etnias Censo 2010">{{cite web|date=5 April 2011|url=http://port.pravda.ru/sociedade/curiosas/04-05-2011/31548-censo_demografico-0/ |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110607201813/http://port.pravda.ru/sociedade/curiosas/04-05-2011/31548-censo_demografico-0/ |archivedate=7 June 2011 |title=Demographical census reveals Brazil as older and less white |publisher=Port.pravda.ru |accessdate=7 April 2012|author=Antonio Carlos Lacerda}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.fatimanews.com.br/noticias/populacao-que-se-declara-branca-diminui-diz-ibge_116224/ |title=Self-declared White Brazilians decrease in number, says IBGE |publisher=Fatimanews.com.br |accessdate=7 April 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130116212707/http://www.fatimanews.com.br/noticias/populacao-que-se-declara-branca-diminui-diz-ibge_116224/ |archive-date=16 January 2013 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
|other = |
|other = |
||
|label1 =[[ |
|label1 =[[Pardo Brazilians|Mixed]] |
||
|value1 = |
|value1 =45.3 |
||
|color1 = |
|color1 =#9966CC |
||
|label2 =[[ |
|label2 =[[White Brazilians|White]] |
||
|value2 =43. |
|value2 =43.5 |
||
|color2 = |
|color2 =LightBlue |
||
|label3 =[[ |
|label3 =[[Afro-Brazilians|Black]] |
||
|value3 = |
|value3 =10.2 |
||
|color3 =MediumAquamarine |
|color3 =MediumAquamarine |
||
|label4 =[[ |
|label4 =[[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|Indigenous]] |
||
|value4 = |
|value4 =0.6 |
||
|color4 = |
|color4 =Red |
||
|label5 =[[ |
|label5 =[[Asian Brazilians|East Asian]] |
||
|value5 =0.4 |
|value5 =0.4 |
||
|color5 = |
|color5 =#FFE135 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
According to the [[2022 Brazilian census]], 45.3% of the population (92,1 million) described themselves as [[Pardo Brazilians|Pardo]] (meaning [[Brown (racial classification)|brown]] or mixed), 43.5% (88,2 million) as [[White Brazilians|White]], 10.2% (20,7 million) as [[Afro-Brazilians|Black]], 0.6% (1,2 million) as [[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|Indigenous]] and 0.4% (850 thousand) as [[Asian Brazilians|East Asian]] (officially called ''[[Mongoloid|yellow]]'' or ''amarela'').<ref name="PNADIBGE">2008 PNAD, IBGE. [https://g1.globo.com/google/amp/economia/censo/noticia/2023/12/22/censo-2022-cor-ou-raca.ghtml].</ref> |
|||
Brazilian society is more [[Social issues in Brazil|markedly divided by social class lines]], although a high [[Income inequality in Brazil|income disparity]] is found [[Social apartheid in Brazil|between race groups]], so [[racism]] and [[Class discrimination|classism]] can be conflated. Socially significant closeness to one racial group [[Race in Brazil|is taken in account]] more in the basis of appearance ([[phenotype]]s) rather than ancestry, to the extent that full [[sibling]]s can pertain to different "racial" groups.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Color and genomic ancestry in Brazilians|first1=Flavia C.|last1=Parra|first2=Roberto C.|last2=Amado|first3=José R.|last3=Lambertucci|first4=Jorge|last4=Rocha|first5=Carlos M.|last5=Antunes|first6=Sérgio D. J.|last6=Pena|date=7 January 2003|journal=Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A|volume=100|issue=1|pages=177–82|doi=10.1073/pnas.0126614100|pmc=140919|pmid=12509516|bibcode=2003PNAS..100..177P}}</ref> [[Socioeconomic status|Socioeconomic]] factors are also significant, because a minority of [[Pardo Brazilians|''pardos'']] are likely to start declaring themselves White or Black if socially upward.<ref>RIBEIRO, Darcy. O Povo Brasileiro, Companhia de Bolso, fourth reprint, 2008 (2008).</ref> Skin color and facial features do not line quite well with ancestry (usually, Afro-Brazilians are evenly mixed and European ancestry is dominant in Whites and ''pardos'' with a significant non-European contribution, but the individual variation is great).<ref name="plosone.org"/><ref name="afrobras">[https://web.archive.org/web/20101124105905/http://www.afrobras.org.br/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=2112&Itemid=2 Negros de origem européia]. afrobras.org.br</ref><ref>{{cite journal|title=Genetic signatures of parental contribution in black and white populations in Brazil |doi=10.1590/S1415-47572009005000001|year=2009|last1=Guerreiro-Junior|first1=Vanderlei|last2=Bisso-Machado|first2=Rafael|last3=Marrero|first3=Andrea|last4=Hünemeier|first4=Tábita|last5=Salzano|first5=Francisco M.|last6=Bortolini|first6=Maria Cátira|journal=Genetics and Molecular Biology|volume=32|pages=1–11|pmid=21637639|issue=1|pmc=3032968}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|title=Genetic heritage variability of Brazilians in even regional averages, 2009 study |doi=10.1590/S0100-879X2009005000026|year=2009|last1=Pena|first1=S.D.J.|last2=Bastos-Rodrigues|first2=L.|last3=Pimenta|first3=J.R.|last4=Bydlowski|first4=S.P.|journal=Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research|volume=42|issue=10|pages=870–76|pmid=19738982|doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
Since the arrival of the Portuguese in 1500, considerable genetic mixing between Amerindians, Europeans, and Africans has taken place in all regions of the country: European ancestry being dominant nationwide according to the vast majority of all autosomal studies undertaken covering the entire population, accounting for between 65% and 77%,<ref name="alvaro.com.br2">{{Cite journal |last1=De Assis Poiares |first1=Lilian |last2=De Sá Osorio |first2=Paulo |last3=Spanhol |first3=Fábio Alexandre |last4=Coltre |first4=Sidnei César |last5=Rodenbusch |first5=Rodrigo |last6=Gusmão |first6=Leonor |last7=Largura |first7=Alvaro |last8=Sandrini |first8=Fabiano |last9=Da Silva |first9=Cláudia Maria Dornelles |year=2010 |title=Allele frequencies of 15 STRs in a representative sample of the Brazilian population |url=http://www.alvaro.com.br/pdf/trabalhoCientifico/ARTIGO_BRASIL_LILIAN.pdf |journal=Forensic Science International: Genetics |volume=4 |issue=2 |pages=e61–63 |doi=10.1016/j.fsigen.2009.05.006 |pmid=20129458 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/5xmleMZgv?url=http://www.alvaro.com.br/pdf/trabalhoCientifico/ARTIGO_BRASIL_LILIAN.pdf |archive-date=8 April 2011}}</ref><ref name="www1.folha.uol.com.br2">[http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/folha/ciencia/ult306u633465.shtml Brazilian DNA is nearly 80% European, indicates study].</ref><ref name="bdtd.bce.unb.br2">NMO Godinho [http://bdtd.bce.unb.br/tedesimplificado/tde_busca/arquivo.php?codArquivo=3873 O impacto das migrações na constituição genética de populações latino-americanas] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706162240/http://bdtd.bce.unb.br/tedesimplificado/tde_busca/arquivo.php?codArquivo=3873|date=6 July 2011}}. PhD Thesis, Universidade de Brasília (2008).</ref><ref name="plosone.org2">{{Cite journal |last1=Pena |first1=Sérgio D. J. |last2=Di Pietro |first2=Giuliano |last3=Fuchshuber-Moraes |first3=Mateus |last4=Genro |first4=Julia Pasqualini |last5=Hutz |first5=Mara H. |last6=Kehdy Fde |first6=Fernanda de Souza Gomes |last7=Kohlrausch |first7=Fabiana |last8=Magno |first8=Luiz Alexandre Viana |last9=Montenegro |first9=Raquel Carvalho |last10=Moraes |first10=MO |last11=De Moraes |first11=ME |last12=De Moraes |first12=MR |last13=Ojopi |first13=EB |last14=Perini |first14=JA |last15=Racciopi |first15=C |display-authors=9 |year=2011 |editor-last=Harpending |editor-first=Henry |title=The Genomic Ancestry of Individuals from Different Geographical Regions of Brazil Is More Uniform Than Expected |journal=PLOS ONE |volume=6 |issue=2 |page=e17063 |bibcode=2011PLoSO...617063P |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0017063 |pmc=3040205 |pmid=21359226 |doi-access=free |last16=Ribeiro-Dos-Santos |first16=AK |last17=Rios-Santos |first17=F |last18=Romano-Silva |first18=MA |last19=Sortica |first19=VA |last20=Suarez-Kurtz |first20=G}}</ref> while the African ancestry among the Brazilians is estimated at 14.30% to 25%<ref name="bdtd.bce.unb.br2" /><ref name="wiley1">{{Cite journal |last1=Lins |first1=T. C. |last2=Vieira |first2=R. G. |last3=Abreu |first3=B. S. |last4=Grattapaglia |first4=D. |last5=Pereira |first5=R. W. |date=March–April 2009 |title=Genetic composition of Brazilian population samples based on a set of twenty-eight ancestry informative SNPs |url=https://repositorio.ucb.br:9443/jspui/handle/123456789/7489 |journal=[[American Journal of Human Biology]] |volume=22 |issue=2 |pages=187–192 |doi=10.1002/ajhb.20976 |pmid=19639555 |s2cid=205301927 |doi-access=free}}</ref> and more than 80% of Brazilians have over 10% African ancestry,<ref name="scielo.br2">{{cite journal |last1=Pena |first1=Sérgio D. J. |last2=Bortolini |first2=Maria Cátira |date=April 1, 2004 |title=Pode a genética definir quem deve se beneficiar das cotas universitárias e demais ações afirmativas? |journal=Estudos Avançados |volume=18 |issue=50 |pages=31–50 |doi=10.1590/S0103-40142004000100004 |doi-access=free |hdl-access=free |hdl=10183/19857}}</ref> and the Indigenous ancestry is significant and present in all regions of Brazil.<ref name="wiley12">{{Cite journal |last1=Lins |first1=T. C. |last2=Vieira |first2=R. G. |last3=Abreu |first3=B. S. |last4=Grattapaglia |first4=D. |last5=Pereira |first5=R. W. |date=March–April 2009 |title=Genetic composition of Brazilian population samples based on a set of twenty-eight ancestry informative SNPs |url=https://repositorio.ucb.br:9443/jspui/handle/123456789/7489 |journal=[[American Journal of Human Biology]] |volume=22 |issue=2 |pages=187–192 |doi=10.1002/ajhb.20976 |pmid=19639555 |s2cid=205301927 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name="alvaro.com.br3">{{cite web |title=Allele frequencies of 15 STRs in a representative sample of the Brazilian population |url=http://www.alvaro.com.br/pdf/trabalhoCientifico/ARTIGO_BRASIL_LILIAN.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/5xmleMZgv?url=http://www.alvaro.com.br/pdf/trabalhoCientifico/ARTIGO_BRASIL_LILIAN.pdf |archive-date=April 8, 2011 |access-date=2011-04-08 |df=mdy-all}}</ref><ref name="bdtd.bce.unb.br3">{{cite web |author=Godinho, Neide Maria de Oliveira |year=2008 |title=O impacto das migrações na constituição genética de populações latino-americanas |url=http://repositorio.unb.br/bitstream/10482/5542/1/2008_NeideMOGodinho.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706162240/http://bdtd.bce.unb.br/tedesimplificado/tde_busca/arquivo.php?codArquivo=3873 |archive-date=2011-07-06 |publisher=Universidade de Brasília}}</ref><ref name="plosone.org3">{{cite journal |last1=Pena |first1=Sérgio D. J. |last2=Pietro |first2=Giuliano Di |last3=Fuchshuber-Moraes |first3=Mateus |last4=Genro |first4=Julia Pasqualini |last5=Hutz |first5=Mara H. |last6=Kehdy |first6=Fernanda de Souza Gomes |last7=Kohlrausch |first7=Fabiana |last8=Magno |first8=Luiz Alexandre Viana |last9=Montenegro |first9=Raquel Carvalho |last10=Moraes |first10=Manoel Odorico |last11=Moraes |first11=Maria Elisabete Amaral de |last12=Moraes |first12=Milene Raiol de |last13=Ojopi |first13=Élida B. |last14=Perini |first14=Jamila A. |last15=Racciopi |first15=Clarice |date=February 16, 2011 |title=The Genomic Ancestry of Individuals from Different Geographical Regions of Brazil Is More Uniform Than Expected |journal=PLOS ONE |volume=6 |issue=2 |pages=e17063 |bibcode=2011PLoSO...617063P |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0017063 |pmc=3040205 |pmid=21359226 |doi-access=free |first16=Ândrea Kely Campos |last16=Ribeiro-dos-Santos |first17=Fabrício |last17=Rios-Santos |first18=Marco A. |last18=Romano-Silva |first19=Vinicius A. |last19=Sortica |first20=Guilherme |last20=Suarez-Kurtz}}</ref><ref name="hereditas.com.br2">{{cite web |title=SIDIA M. CALLEGARI-JACQUES et al., Historical Genetics: Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Formation |url=http://www.hereditas.com.br/pdfs/AJHB-Callegari-Jacquesetal2003.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706152708/http://www.hereditas.com.br/pdfs/AJHB-Callegari-Jacquesetal2003.pdf |archive-date=July 6, 2011 |access-date=August 21, 2017 |website=Hereditas.com.br |df=mdy-all}}</ref><ref name="pmid145958742">{{Cite journal |last1=Callegari-Jacques |first1=S. M. |last2=Grattapaglia |first2=D. |last3=Salzano |first3=F. M. |last4=Salamoni |first4=S. P. |last5=Crossetti |first5=S. G. |last6=Ferreira |first6=M. R. E. |last7=Hutz |first7=M. H. |date=November–December 2003 |title=Historical genetics: Spatiotemporal analysis of the formation of the Brazilian population |url=http://www.hereditas.com.br/pdfs/AJHB-Callegari-Jacquesetal2003.pdf |url-status=dead |journal=[[American Journal of Human Biology]] |volume=15 |issue=6 |pages=824–834 |doi=10.1002/ajhb.10217 |pmid=14595874 |s2cid=34610130 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706152708/http://www.hereditas.com.br/pdfs/AJHB-Callegari-Jacquesetal2003.pdf |archive-date=July 6, 2011 |df=mdy-all}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Retrato molecular do Brasil |url=http://publicacoes.gene.com.br/Imprensa_genealogia/Retrato%20molecular%20do%20Brasil@Folha%20de%20S%C3%A3o%20Paulo@26-03-2000.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080306064232/http://publicacoes.gene.com.br/Imprensa_genealogia/Retrato%20molecular%20do%20Brasil@Folha%20de%20S%C3%A3o%20Paulo@26-03-2000.htm |archive-date=March 6, 2008 |access-date=August 21, 2017 |website=Publicacoes.gene.com.br |df=mdy-all}}</ref> |
|||
From the 19th century, Brazil opened its borders to [[Immigration to Brazil|immigration]]. About five million people from over 60 countries migrated to Brazil between 1808 and 1972, most of them of [[Portuguese Brazilian|Portuguese]], [[Italian Brazilian|Italian]], [[Brazilians of Spanish descent|Spanish]], [[German Brazilian|German]], [[English Brazilian|English]], [[Ukrainian Brazilian|Ukrainian]], [[Polish Brazilian|Polish]], [[Jewish Brazilian|Jewish]], [[Afro-Brazilian|African]], [[Armenians|Armenian]], [[Russians in Brazil|Russian]], [[Chinese Brazilian|Chinese]], [[Japanese Brazilian|Japanese]], [[Korean Brazilian|Korean]] and [[Arab Brazilian|Arab]] origin.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Maria Stella Ferreira-Levy |year=1974 |title=O papel da migração internacional na evolução da população brasileira (1872 a 1972) |journal=Revista de Saúde Pública |volume=8 |issue=supl |pages=49–90 |doi=10.1590/S0034-89101974000500003 |doi-access=free}}, Table 2, p. 74. {{in lang|pt}}</ref><ref>Zirin, 2014. Chapter 2, Section ''"The Beginning of the 'Mosaic' ''".</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Grün |first=Roberto |date=July 1996 |title=The Armenian Renaissance in Brazil |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/americas/article/the-armenian-renaissance-in-brazil/759304E77521DF48F0C1F1DD95C0D3E2 |journal=The Americas |language=en |volume=53 |issue=1 |pages=113–151 |doi=10.2307/1007476 |issn=0003-1615 |jstor=1007476 |s2cid=143656550}}</ref> Brazil has the second-largest Jewish community in Latin America making up 0.06% of its population.<ref name="autogenerated2">{{Cite web |title=The Jewish Community in Brazil |url=https://www.bh.org.il/jewish-community-brazil/ |website=Beit Hatfutsot}}</ref> Outside in the [[Arab world]], Brazil also has the largest [[Arab diaspora|population]] of Arab ancestry in the world, with 15–20 million people.<ref name="Ferabolli2014">{{Cite book |last=Silvia Ferabolli |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=R5CbBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA151 |title=Arab Regionalism: A Post-Structural Perspective |date=25 September 2014 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-317-65803-0 |page=151 |quote=According to estimates by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), countersigned by the League of Arab States, Brazil has the largest Arab colony outside their countries of origin. There are estimated 15 million Arabs living in Brazil today, with some researchers suggesting numbers around 20 million.}}</ref><ref name="Amar2014">{{Cite book |last=Paul Amar |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XGKuCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA40 |title=The Middle East and Brazil: Perspectives on the New Global South |date=15 July 2014 |publisher=Indiana University Press |isbn=978-0-253-01496-2 |page=40 |quote=there are, according to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, more than sixteen million Arabs and descendants of Arabs in Brazil, constituting the largest community of Arabs descent outside the Middle East.}}</ref> According to Brazil's Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Brazil is home to a Lebanese diaspora of 7 million to 10 million, surpassing the population of Lebanese individuals residing in Lebanon.<ref>{{Cite web |last=cl1289 |date=8 June 2021 |title=From Beirut to Brazil |url=https://ccas.georgetown.edu/2021/06/08/from-beirut-to-brazil/ |access-date=7 November 2023 |website=CCAS |language=en-US}}</ref> |
|||
The brown population (officially called [[Pardo Brazilians|''pardo'']] in Portuguese, also colloquially ''[[wikt:moreno|moreno]]'')<ref name="Coelho 1996, p. |
Brazilian society is more [[Social issues in Brazil|markedly divided by social class lines]], although a high [[Income inequality in Brazil|income disparity]] is found [[Social apartheid in Brazil|between race groups]], so [[racism]] and [[Class discrimination|classism]] often overlap. The brown population (officially called [[Pardo Brazilians|''pardo'']] in Portuguese, also colloquially ''[[wikt:moreno|moreno]]'')<ref name="Coelho 1996, p. 268">Coelho (1996), p. 268.</ref><ref name="Vesentini 1988, p. 117">Vesentini (1988), p. 117.</ref> is a broad category that includes ''[[caboclo]]s'' (assimilated Amerindians in general, and descendants of Whites and Natives), ''[[Mulatto|mulatos]]'' (descendants of primarily Whites and Afro-Brazilians) and ''[[Zambo|cafuzos]]'' (descendants of Afro-Brazilians and Natives).<ref name="Coelho 1996, p. 268" /><ref name="Vesentini 1988, p. 117" /><ref>Adas, Melhem ''Panorama geográfico do Brasil'', 4th ed (São Paulo: Moderna, 2004), p. 268 {{ISBN|85-16-04336-3}}</ref><ref>Azevedo (1971), pp. 2–3.</ref><ref name="Moreira 1981, p. 108">Moreira (1981), p. 108.</ref> Higher percents of Blacks, mulattoes and tri-racials can be found in the eastern coast of the Northeastern region from Bahia to Paraíba<ref name="Moreira 1981, p. 108" /><ref>Azevedo (1971), pp. 74–75.</ref> and also in northern Maranhão,<ref>''Enciclopédia Barsa'', vol. 10 (Rio de Janeiro: Encyclopædia Britannica do Brasil, 1987), p. 355.</ref><ref>Azevedo (1971), p. 74.</ref> southern Minas Gerais<ref name="Azevedo 1971, p. 161">Azevedo (1971), p. 161.</ref> and eastern Rio de Janeiro.<ref name="Moreira 1981, p. 108" /><ref name="Azevedo 1971, p. 161" /> |
||
People of considerable Amerindian ancestry form the majority of the population in the Northern, Northeastern and Center-Western regions.<ref>''Enciclopédia Barsa'', vol. 4, pp. 254–55, 258, 265.</ref> In 2007, the [[Fundação Nacional do Índio|National Indian Foundation]] estimated that Brazil has 67 different uncontacted tribes, up from their estimate of 40 in 2005. Brazil is believed to have the largest number of [[uncontacted peoples]] in the world.<ref>[https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/07/07/AR2007070701312.html "In Amazonia, Defending the Hidden Tribes"], ''The Washington Post'' (8 July 2007).</ref> |
|||
Higher percents of Blacks, mulattoes and tri-racials can be found in the eastern coast of the Northeastern region from Bahia to Paraíba<ref name="Moreira 1981, p. 108"/><ref>Azevedo (1971), pp. 74–75.</ref> and also in northern Maranhão,<ref>''Enciclopédia Barsa'', vol. 10 (Rio de Janeiro: Encyclopædia Britannica do Brasil, 1987), p. 355.</ref><ref>Azevedo (1971), p. 74.</ref> southern Minas Gerais<ref name="Azevedo 1971, p. 161">Azevedo (1971), p. 161.</ref> and in eastern Rio de Janeiro.<ref name="Moreira 1981, p. 108"/><ref name="Azevedo 1971, p. 161"/> From the 19th century, Brazil opened its borders to [[Immigration to Brazil|immigration]]. About five million people from over 60 countries migrated to Brazil between 1808 and 1972, most of them of [[Portuguese Brazilian|Portuguese]], [[Italian Brazilian|Italian]], [[Brazilians of Spanish descent|Spanish]], [[German Brazilian|German]], [[Ukrainian Brazilian|Ukrainian]], [[Polish Brazilian|Polish]], [[Jewish Brazilian|Jewish]], [[Russians in Brazil|Russian]], [[Chinese Brazilian|Chinese]], [[Japanese Brazilian|Japanese]], and [[Arab Brazilian|Arab]] origin.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Maria Stella Ferreira-Levy|title=O papel da migração internacional na evolução da população brasileira (1872 a 1972)|journal=Revista de Saúde Pública|volume =8 (supl.)|pages=49–90|year= 1974|doi=10.1590/S0034-89101974000500003|doi-access=free}}, Table 2, p. 74. {{in lang|pt}}</ref><ref>Zirin, 2014. Chapter 2, Section ''"The Beginning of the 'Mosaic' ''".</ref> Brazil has the second largest Jewish community in Latin America making up 0.06% of its population.<ref name=autogenerated2>{{Cite web|url=https://www.bh.org.il/jewish-community-brazil/|title=The Jewish Community in Brazil|website=Beit Hatfutsot}}</ref> |
|||
===Religion=== |
=== Religion === |
||
{{Main|Religion in Brazil}} |
{{Main|Religion in Brazil}} |
||
{{Further|Catholic Church in Brazil|Protestantism in Brazil}} |
{{Further|Catholic Church in Brazil|Protestantism in Brazil}} |
||
{{Pie chart |
{{Pie chart |
||
|thumb = |
|thumb = right |
||
|caption = [[Religion in Brazil]] (2010 Census) |
|caption = [[Religion in Brazil]] (2010 Census) |
||
|label1 = [[Catholic Church in Brazil|Catholicism]] |
|label1 = [[Catholic Church in Brazil|Catholicism]] |
||
|value1 = 64.6 |
|value1 = 64.6 |
||
|color1 = |
|color1 = Purple |
||
|label2 = [[Protestantism in Brazil|Protestantism]] |
|label2 = [[Protestantism in Brazil|Protestantism]] |
||
|value2 = 22.2 |
|value2 = 22.2 |
||
|color2 = |
|color2 = Blue |
||
|label3 = [[Spiritism]] |
|label3 = [[Kardecist spiritism|Spiritism]] |
||
|value3 = 2.0 |
|value3 = 2.0 |
||
|color3 = Pink |
|color3 = Pink |
||
| Line 745: | Line 510: | ||
|value4 = 3.2 |
|value4 = 3.2 |
||
|color4 = Chartreuse |
|color4 = Chartreuse |
||
|label5 = No religion |
|label5 = [[Irreligion|No religion]] |
||
|value5 = 8.0 |
|value5 = 8.0 |
||
|color5 = WhiteSmoke |
|color5 = WhiteSmoke |
||
}} |
}} |
||
[[ |
[[Christianity]] is the country's predominant faith, with [[Roman Catholicism]] being its largest denomination. Brazil has the [[Catholic Church by country|world's largest Catholic population]].<ref name="PEWCATHOLIC">{{Cite web |date=13 February 2013 |title=The Global Catholic Population |url=https://www.pewforum.org/2013/02/13/the-global-catholic-population/ |access-date=10 June 2020 |publisher=[[Pew Research Center]]}}</ref><ref name="USDS">{{Cite conference |date=8 November 2005 |title=Brazil |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/2005/51629.htm |publisher=U.S. Department of State |access-date=8 June 2008 |book-title=International Religious Freedom Report}}</ref> According to the 2010 Demographic Census (the PNAD survey does not inquire about religion), 64.63% of the population followed [[Roman Catholicism in Brazil|Roman Catholicism]]; 22.2% [[Protestantism in Brazil|Protestantism]]; 2.0% Kardecist spiritism; 3.2% other religions, undeclared or undetermined; while 8.0% had no religion.<ref name="census2010">[ftp://ftp.ibge.gov.br/Censos/Censo_Demografico_2010/Caracteristicas_Gerais_Religiao_Deficiencia/tab1_4.pdf IBGE – Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (Brazilian Institute for Geography and Statistics). 2010 Census]. Retrieved 7 August 2012.</ref> |
||
Religion in Brazil was formed from the meeting of the Catholic Church with the religious traditions of enslaved African peoples and indigenous peoples.<ref name="BoyleSheen2013">{{ |
Religion in Brazil was formed from the meeting of the Catholic Church with the religious traditions of enslaved African peoples and indigenous peoples.<ref name="BoyleSheen2013">{{Cite book |last1=Kevin Boyle |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JxgFWwK8dXwC&pg=PT211 |title=Freedom of Religion and Belief: A World Report |last2=Juliet Sheen |publisher=Routledge |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-134-72229-7 |page=211}}</ref> This confluence of faiths during the Portuguese colonization of Brazil led to the development of a diverse array of syncretistic practices within the overarching umbrella of Brazilian Catholic Church, characterized by traditional Portuguese festivities.<ref name="georgetown1">{{Cite web |title=Brazil |url=http://berkleycenter.georgetown.edu/resources/countries/brazil |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110825203019/http://berkleycenter.georgetown.edu/resources/countries/brazil |archive-date=25 August 2011 |access-date=7 December 2011 |publisher=[[Berkley Center for Religion, Peace, and World Affairs]]}}</ref> |
||
Religious pluralism increased during the 20th century,<ref name="Morris2006a">{{Cite book |last=Brian Morris |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PguGB_uEQh4C&pg=PA223 |title=Religion and Anthropology: A Critical Introduction |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-521-85241-8 |page=223}}</ref> and the Protestant community has grown to include over 22% of the population.<ref name="JeynesRobinson2012">{{Cite book |last1=William Jeynes |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NIBlry_2oLQC&pg=PA405 |title=International Handbook of Protestant Education |last2=David W. Robinson |publisher=Springer |year=2012 |isbn=978-94-007-2386-3 |page=405}}</ref> The most common Protestant denominations are [[Evangelicalism|Evangelical]] [[Pentecostalism|Pentecostal]] ones. Other Protestant branches with a notable presence in the country include the [[Baptists]], [[Seventh-day Adventist Church|Seventh-day Adventists]], [[Lutheranism|Lutherans]] and the [[Calvinism|Reformed tradition]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=2010 census results |url=ftp://ftp.ibge.gov.br/Censos/Censo_Demografico_2010/Caracteristicas_Gerais_Religiao_Deficiencia/tab1_4.pdf}}</ref> |
|||
However, in the last ten years Protestantism, particularly in forms of Pentecostalism and Evangelicalism, has spread in Brazil, while the proportion of Catholics has dropped significantly.<ref name="georgetown2">{{cite web |url=http://berkleycenter.georgetown.edu/resources/countries/brazil |title=Brazil |website= |publisher=[[Berkley Center for Religion, Peace, and World Affairs]] |accessdate=7 December 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110825203019/http://berkleycenter.georgetown.edu/resources/countries/brazil |archive-date=25 August 2011 |url-status=dead}} See drop-down essay on "The Growth of Religious Pluralism"</ref> After Protestantism, individuals professing no religion are also a significant group, exceeding 8% of the population as of the 2010 census. The cities of [[Boa Vista, Roraima|Boa Vista]], [[Salvador, Bahia|Salvador]], and [[Porto Velho]] have the greatest proportion of [[Irreligion|Irreligious]] residents in Brazil. [[Teresina]], [[Fortaleza]], and [[Florianópolis]] were the most Roman Catholic in the country.<ref name="FGV no G1">{{cite web|author=Do G1, em São Paulo |url=http://g1.globo.com/brasil/noticia/2011/08/pais-tem-menor-nivel-de-adeptos-do-catolicismo-desde-1872-diz-estudo.html |title=G1 – País tem menor nível de adeptos do catolicismo desde 1872, diz estudo – notícias em Brasil |publisher=G1.globo.com |date=23 August 2011 |accessdate=7 April 2012}}</ref> [[Greater Rio de Janeiro]], not including the [[Rio de Janeiro|city proper]], is the most irreligious and least Roman Catholic Brazilian periphery, while [[Greater Porto Alegre]] and Greater [[Fortaleza]] are on the opposite sides of the lists, respectively.<ref name="FGV no G1"/> |
|||
In recent decades, [[Protestantism]], particularly in forms of Pentecostalism and Evangelicalism, has spread in Brazil, while the proportion of Catholics has dropped significantly.<ref name="georgetown2">{{Cite web |title=Brazil |url=http://berkleycenter.georgetown.edu/resources/countries/brazil |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110825203019/http://berkleycenter.georgetown.edu/resources/countries/brazil |archive-date=25 August 2011 |access-date=7 December 2011 |publisher=[[Berkley Center for Religion, Peace, and World Affairs]]}} See drop-down essay on "The Growth of Religious Pluralism"</ref> After Protestantism, individuals professing no religion are also a significant group, exceeding 8% of the population as of the 2010 census. The cities of [[Boa Vista, Roraima|Boa Vista]], [[Salvador, Bahia|Salvador]], and [[Porto Velho]] have the greatest proportion of [[Irreligion|Irreligious]] residents in Brazil. [[Teresina]], [[Fortaleza]], and [[Florianópolis]] were the most Roman Catholic in the country.<ref name="FGV no G1">{{Cite web |last=Do G1, em São Paulo |date=23 August 2011 |title=G1 – País tem menor nível de adeptos do catolicismo desde 1872, diz estudo |url=http://g1.globo.com/brasil/noticia/2011/08/pais-tem-menor-nivel-de-adeptos-do-catolicismo-desde-1872-diz-estudo.html |access-date=7 April 2012 |publisher=G1.globo.com}}</ref> [[Greater Rio de Janeiro]], not including the [[Rio de Janeiro|city proper]], is the most irreligious and least Roman Catholic Brazilian periphery, while [[Greater Porto Alegre]] and Greater [[Fortaleza]] are on the opposite sides of the lists, respectively.<ref name="FGV no G1" /> |
|||
In October 2009, the Brazilian Senate approved and enacted by the President of Brazil in February 2010, an agreement with the [[Holy See|Vatican]], in which the Legal Statute of the Catholic Church in Brazil is recognized.<ref>{{Cite web |year=2009 |title=Senado aprova acordo com o Vaticano |url=https://oglobo.globo.com/economia/senado-aprova-acordo-com-vaticano-3161783 |access-date=28 June 2020 |publisher=[[O Globo]]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Decreto nº 7.107, de 11 de fevereiro de 2010. |url=http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2007-2010/2010/Decreto/D7107.htm |access-date=28 June 2020 |publisher=Casa Civil da Presidência da República}}</ref> |
|||
=== Health === |
|||
{{Main|Health in Brazil|Sistema Único de Saúde}} |
|||
[[File:Hospital de Clínicas PMPA.jpg|thumb|The [[Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre|Clinical Hospital of Porto Alegre]] is academically linked to the [[Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul]] and is part of the [[Sistema Único de Saúde|SUS]], the Brazilian [[publicly funded health care]] system.]] |
|||
The Brazilian [[public health]] system, the [[Sistema Único de Saúde|Unified Health System]] (''Sistema Único de Saúde'' – SUS), is managed and provided by all levels of government,<ref name="ForgiaCouttolenc2008">{{Cite book |last1=Gerard Martin La Forgia |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=i3R43xW5KqcC&pg=PA17 |title=Hospital Performance in Brazil: The Search for Excellence |last2=Bernard F. Couttolenc |publisher=World Bank Publications |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-8213-7359-0 |page=17}}</ref> being the largest system of this type in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |title=20 Anos do SUS |url=http://conselho.saude.gov.br/web_sus20anos/index.html |access-date=13 April 2012 |publisher=Conselho Nacional de Saúde}}</ref> On the other hand, private healthcare systems play a complementary role.<ref name="Wolper2004">{{Cite book |last=Lawrence F. Wolper |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Zts-QdpDiWUC&pg=PA33 |title=Health Care Administration: Planning, Implementing, and Managing Organized Delivery Systems |publisher=Jones & Bartlett Learning |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-7637-3144-1 |page=33}}</ref> Public health services are universal and offered to all citizens of the country for free. However, the construction and maintenance of health centers and hospitals are financed by taxes, and the country spends about 9% of its GDP on expenditures in the area. In 2012, Brazil had 1.85 doctors and 2.3 hospital beds for every 1,000 inhabitants.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Physicians (per 1,000 people) |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.MED.PHYS.ZS?locations=BR |website=World Health Organization's Global Health Workforce Statistics}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Hospital beds (per 1,000 people) |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.MED.BEDS.ZS |website=World Health Organization The World Bank}}</ref> |
|||
Despite all the progress made since the creation of the [[universal health care]] system in 1988, there are still several public health problems in Brazil. In 2006, the main points to be solved were the high [[List of countries by infant mortality rate|infant]] (2.51%) and maternal mortality rates (73.1 deaths per 1000 births).<ref name="Radar social" /> |
|||
The number of deaths from noncommunicable diseases, such as [[cardiovascular diseases]] (151.7 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants) and [[cancer]] (72.7 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants), also has a considerable impact on the health of the Brazilian population. Finally, external but preventable factors such as car accidents, violence and suicide caused 14.9% of all deaths in the country.<ref name="Radar social">{{Cite web |title=Saúde |url=http://www.planejamento.gov.br/secretarias/upload/Arquivos/spi/programas_projeto/radar_social/2006_PRP_Radar_radarSocial.pdf |archive-url=https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20081216074831/http://www.planejamento.gov.br/secretarias/upload/Arquivos/spi/programas_projeto/radar_social/2006_PRP_Radar_radarSocial.pdf |archive-date=16 December 2008 |access-date=10 June 2008 |website=Radar social |publisher=Ministério do Planejamento}}</ref> The Brazilian health system was ranked 125th among the 191 countries evaluated by the [[World Health Organization]] (WHO) in 2000.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2000 |title=Measuring overall health system performance for 191 countries |url=https://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/paper30.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061118210828/http://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/paper30.pdf |archive-date=18 November 2006 |access-date=30 April 2014 |publisher=[[World Health Organization]]}}</ref> |
|||
=== Education === |
|||
{{Main|Education in Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Arquitetura Prédio Histórico da Universidade Federal do Paraná.jpg|thumb|Historical building of the [[Federal University of Paraná]], one of the oldest universities in Brazil, located in [[Curitiba]]]] |
|||
The [[Constitution|Federal Constitution]] and the Law of Guidelines and Bases of National Education determine that the [[Federal government of Brazil|Union]], the [[States of Brazil|states]], the [[Federal District (Brazil)|Federal District]] and the [[Municipalities of Brazil|municipalities]] must manage and organize their respective education systems. Each of these public educational systems is responsible for its own maintenance, which manages funds as well as the mechanisms and funding sources. The constitution reserves 25% of the state budget and 18% of federal taxes and municipal taxes for education.<ref name="Usa2005">{{Cite book |last=Usa Ibp Usa |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dzhWjfK8CswC&pg=PA42 |title=Brazil: Tax Guide |publisher=Int'l Business Publications |year=2005 |isbn=978-0-7397-3279-3 |page=42}}</ref> |
|||
According to the [[Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics|IBGE]], in 2019, the literacy rate of the population was 93.4%, meaning that 11.3 million (6.6% of population) people are still illiterate in the country, with some states such as [[Rio de Janeiro (state)|Rio de Janeiro]] and [[Santa Catarina (state)|Santa Catarina]] reaching around 97% of literacy rate;<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=IBGE: Analfabetismo cai no país, mas fica estagnado no Nordeste |url=https://valor.globo.com/brasil/noticia/2020/07/15/ibge-analfabetismo-cai-no-pas-mas-fica-estagnado-no-nordeste.ghtml |website=Globo.com |date=15 July 2020 |language=pt}}</ref> functional illiteracy has reached 21.6% of the population.<ref name="Agency2010">{{Cite book |last=The Central Intelligence Agency |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=m-9eSrZtYAAC&pg=PA143 |title=The World Factbook 2010 |publisher=Potomac Books, Inc. |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-59797-541-4 |edition=CIA 2009 |page=143}}</ref> Illiteracy is higher in the [[Northeast Region, Brazil|Northeast]], where 13.87% of the population is illiterate, while the [[South Region, Brazil|South]], has 3.3% of its population illiterate.<ref name="Bank2001">{{Cite book |last=World Bank |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YttV-Ggq90UC&pg=PA40 |title=Rural Poverty Alleviation in Brazil: Towards an Integrated Strategy |publisher=World Bank Publications |year=2001 |isbn=978-0-8213-5206-9 |page=40}}</ref><ref name=":0" /> |
|||
Brazil's private institutions tend to be more exclusive and offer better quality education, so many high-income families send their children there. The result is a segregated educational system that reflects extreme income disparities and reinforces social inequality. However, efforts to change this are making impacts.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Laplane |first=Mario |title=Efforts towards inclusion |url=https://www.dandc.eu/en/article/impact-public-and-private-education-social-inequality-brazil |website=D + C, Development and cooperation|date=14 May 2019 }}</ref> The [[University of São Paulo]] is often considered [[College and university rankings|the best in Brazil and Latin America]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=QS World University Rankings 2024 |url=https://www.topuniversities.com/world-university-rankings |access-date=2023-12-06 |website=Top Universities |language=en |archive-date=4 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240104115634/https://www.topuniversities.com/world-university-rankings |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=ShanghaiRanking's Academic Ranking of World Universities |url=https://www.shanghairanking.com/rankings/arwu/2023 |access-date=2023-12-06 |website=www.shanghairanking.com |archive-date=29 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230929224804/https://www.shanghairanking.com/rankings/arwu/2023 |url-status=live }}</ref> Of the top 20 Latin American universities, eight are Brazilian. Most of them are [[Public university|public]]. Attending an institution of higher education is required by Law of Guidelines and Bases of Education. [[Kindergarten]], [[elementary school|elementary]] and medium education are required of all students.<ref>{{Cite web |title=QS University Rankings Latin America |url=https://www.topuniversities.com/university-rankings/latin-american-university-rankings/2019 |access-date=11 November 2018 |publisher=[[QS World University Rankings]]}}</ref> |
|||
=== Language === |
|||
{{Main|Languages of Brazil|Portuguese language|Brazilian Portuguese|List of endangered languages in Brazil}} |
|||
<!--Galleries or clusters of images are generaly discouraged as they cause undue weight to one particular section of a summary article and may cause accessibility problems.--> |
|||
{{multiple image |
{{multiple image |
||
| |
| direction = vertical |
||
| align = right |
|||
| image1 = 1 cristor redentor 2014.jpg |
|||
| |
| width = 220px |
||
| image1 = Interior do Museu da Língua Portuguesa em São Paulo, Brasil.jpg |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = [[Museum of the Portuguese Language]] in [[São Paulo]] |
|||
| caption1 = The ''[[Christ the Redeemer (statue)|Christ the Redeemer]]'' statue in [[Rio de Janeiro]] is one of the most famous religious statues worldwide<ref>[https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/special/2014/newsspec_7141/index.html "Arms wide open" BBC], Retrieved 29 April 2017.</ref><ref>[http://edition.cnn.com/2014/12/08/travel/most-impressive-religious-statues/ "Religious statues: 10 of the world's most impressive" CNN], Retrieved 29 April 2017.</ref> |
|||
| image2 = AssuncaodoIcana.jpg |
|||
| image2 = Basilica of the National Shrine of Our Lady of Aparecida, 2007.jpg |
|||
| caption2 = [[Alto Rio Negro Indigenous Territory]], in [[São Gabriel da Cachoeira]], [[Amazonas (Brazilian state)|Amazonas]], |
|||
| width2 = 210 |
|||
where [[Nhengatu]], [[Tucano language|Tucano]] and [[Karu language|Baniwa]] are co-official languages |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
|image3 = Ruas de Pomerode (cropped).jpg |
|||
| caption2 = [[Basilica of the National Shrine of Our Lady of Aparecida]] in [[Aparecida]], [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]], is the second largest [[Roman Catholicism in Brazil|Catholic]] church in the world<ref>{{Cite book |author1=J. Gordon Melton |author2=Martin Baumann |title=Religions of the World, Second Edition: A Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Beliefs and Practices |publisher=ABC-Clio Inc |year=2010 |page=308}}</ref> |
|||
| caption3 = [[Pomerode]], [[Santa Catarina (state)|Santa Catarina]], where the [[East Pomeranian dialect|East Pomeranian]] is the [[second language]] (see [[Brazilian German]]) |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
In October 2009, the Brazilian Senate approved and enacted by the President of Brazil in February 2010, an agreement with the [[Holy See|Vatican]], in which the Legal Statute of the Catholic Church in Brazil is recognized. The agreement confirmed norms that were normally complied with regarding religious education in public elementary schools (which also ensures the teaching of other beliefs), marriage and spiritual assistance in prisons and hospitals. The project was criticized by parliamentarians who understood the end of the secular state with the approval of the agreement.<ref>{{cite web|publisher=[[O Globo]]|year=2009|title=Senado aprova acordo com o Vaticano|url=https://oglobo.globo.com/economia/senado-aprova-acordo-com-vaticano-3161783|access-date=June 28, 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|access-date=June 28, 2020|publisher=Casa Civil da Presidência da República|title=Decreto nº 7.107, de 11 de fevereiro de 2010.|url=http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2007-2010/2010/Decreto/D7107.htm}}</ref> |
|||
The official language of Brazil is [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]] (Article 13 of the [[Constitution of Brazil|Constitution of the Federal Republic of Brazil]]), which almost all of the population speaks and is virtually the only language used in newspapers, radio, television, and for business and administrative purposes. Brazil is the only Portuguese-speaking nation in the Americas, making the language an important part of Brazilian national identity and giving it a national culture distinct from those of its Spanish-speaking neighbors.<ref name="language2">{{Cite web |title=Brazil – Language |url=http://countrystudies.us/brazil/39.htm |website=countrystudies.us}}</ref> |
|||
===Urbanization=== |
|||
{{Main|List of largest cities in Brazil|Municipalities of Brazil}} |
|||
[[Brazilian Portuguese]] has had its own development, mostly similar to 16th-century Central and Southern dialects of European Portuguese<ref>{{Cite web |date=25 April 2009 |title=Learn About Portuguese Language |url=http://www.sibila.com.br/index.php/world-map-of-portuguese/424 |access-date=7 April 2012 |publisher=Sibila.com.br |archive-date=20 April 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120420010533/http://www.sibila.com.br/index.php/world-map-of-portuguese/424 }}</ref> (despite a very substantial number of Portuguese colonial settlers, and [[Portuguese Brazilian|more recent immigrants]], coming from [[Northern Portugal|Northern regions]], and in minor degree Portuguese [[Macaronesia]]), with a few influences from the [[Indigenous languages of the Americas|Amerindian]] and [[Languages of Africa|African languages]], especially [[West Africa]]n and [[Bantu languages|Bantu]] restricted to the vocabulary only.<ref name="Portuguese" /> As a result, the language is somewhat different, mostly in phonology, from the language of Portugal and other [[Portuguese-speaking countries]] (the dialects of the other countries, partly because of the more recent end of [[Portuguese Empire|Portuguese colonialism]] in these regions, have a closer connection to contemporary [[European Portuguese]]). These differences are comparable to those between [[American English|American]] and [[British English]].<ref name="Portuguese">{{Cite web |title=Languages of Brazil |url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=br |access-date=9 June 2008 |publisher=Ethnologue}}</ref> |
|||
According to IBGE (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics) urban areas already concentrate 84.35% of the population, while the Southeast region remains the most populated one, with over 80 million inhabitants.<ref>{{cite web|title=IDBGE|publisher=IBGE|year=2011|url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/censo2010/default.shtm|accessdate=8 October 2011|language=pt}}</ref> |
|||
The largest urban agglomerations in Brazil are [[São Paulo]], [[Rio de Janeiro]], and [[Belo Horizonte]] – all in the Southeastern Region – with 21.1, 12.3, and 5.1 million inhabitants respectively.<ref name="concentrações_urbanas"/><!-- defined by template:Largest urban agglomerations in Brazil --><ref>{{cite web|url=ftp://geoftp.ibge.gov.br/organizacao_do_territorio/divisao_regional/arranjos_populacionais/arranjos_populacionais.pdf|title=Arranjos Populacionais e Concentrações Urbanas do Brasil|page=148|language=portuguese|publisher=Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics|accessdate=16 March 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=ftp://ftp.ibge.gov.br/Estimativas_de_Populacao/Estimativas_2016/estimativa_dou_2016.pdf|title=Estimativas da população residente no Brasil e Unidades da Federação com data de referência em 1º de julho de 2016|language=portuguese|publisher=Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics|accessdate=16 March 2017}}</ref> The majority of state capitals are the largest cities in their states, except for [[Vitória, Brazil|Vitória]], the capital of [[Espírito Santo]], and [[Florianópolis]], the capital of Santa Catarina.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Principal Cities |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_3/Brazil.html |accessdate=10 June 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029034959/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_3/Brazil.html |archivedate=29 October 2009 |url-status=dead}} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref> |
|||
The 2002 [[recognition of sign languages|sign language law]]<ref name="Libras 2002">[https://web.archive.org/web/20100910070529/http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/LEIS/2002/L10436.htm LEI Nº 10.436, DE 24 DE ABRIL DE 2002]. Presidência da República, Casa Civil, Subchefia para Assuntos Jurídicos. Retrieved on 19 May 2012.</ref> requires government authorities and public agencies to accept and provide information in ''Língua Brasileira dos Sinais'' or "LIBRAS", the [[Brazilian Sign Language]], while a 2005 presidential edict<ref name="Libras 2005">[http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2004-2006/2005/decreto/d5626.htm Brazilian decree nº 5626, 22 December 2005]. Planalto.gov.br (23 December 2005). Retrieved on 19 May 2012.</ref> extends this to require teaching of the language as a part of the [[school of education|education]] and [[speech and language pathology]] curricula. LIBRAS teachers, instructors and translators are recognized professionals. Schools and health services must provide access ("[[inclusion (education)|inclusion]]") to [[Deaf community|deaf people]].<ref name="Russo2011">{{Cite book |last=Charles J. Russo |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JuV1cZ7NJHIC&pg=PA45 |title=The Legal Rights of Students with Disabilities: International Perspectives |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield Publishers |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-4422-1085-1 |page=45}}</ref> |
|||
Minority languages are spoken throughout the nation. One hundred and eighty [[Indigenous languages of the Americas|Amerindian languages]] are spoken in remote areas and a significant number of other languages are spoken by immigrants and their descendants.<ref name="Portuguese" /> In the municipality of [[São Gabriel da Cachoeira]], [[Nheengatu language|Nheengatu]] (a currently endangered South American [[creole language]]—or an 'anti-creole', according to some linguists—with mostly Indigenous Brazilian languages lexicon and Portuguese-based grammar that, together with its southern relative [[língua geral paulista]], once was a major [[lingua franca]] in Brazil,<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Campbell |first1=Lyle |title=The Indigenous Languages of South America: A Comprehensive Guide |last2=Grondona |first2=Verónica |last3=Muysken |first3=Peter |publisher=Walter de Gruyter |year=2012 |isbn=978-3-11-025803-5 |page=247 |chapter=Contacts between indigenous languages in South America |quote=Nheengatú (also called língua geral of Amazonia, or lingua Brasilica) originated in the 17th century in what are now the states of Pará Maranhão, as lingua franca on the basis of Tupinambá lexicon but with strong grammatical influence from Portuguese, also due to intervention by Jesuit missionaries [...] Around 1700 it was spoken in a large area in Brazil, as a contact language between whites and indians, but it lost some support with the expulsion of the Jesuits in 1758 [...] Its sister language in the colonial period was Língua Geral Paulista (in the state of São Paolo) a lingua franca which is now extinct.}}</ref> being replaced by Portuguese only after governmental prohibition led by [[Suppression of the Society of Jesus#Portugal|major political changes]]),{{overly detailed inline|date=July 2015}} [[Baniwa of Içana|Baniwa]] and Tucano languages had been granted co-official status with Portuguese.<ref name="nyt-language">{{Cite news |last=Rohter |first=Larry |date=28 August 2005 |title=Language Born of Colonialism Thrives Again in Amazon |work=[[The New York Times]] |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2005/08/28/international/americas/28amazon.html |access-date=14 July 2008}}</ref> |
|||
There are significant communities of German (mostly the [[Riograndenser Hunsrückisch|Brazilian Hunsrückisch]], a High German language dialect) and Italian (mostly the [[Talian dialect|Talian]], a [[Venetian language|Venetian]] dialect) origins in the Southern and Southeastern regions, whose ancestors' native languages were carried along to Brazil, and which, still alive there, are influenced by the Portuguese language.<ref>{{Cite web |title=O alemão lusitano do Sul do Brasil |url=http://www.dw.de/dw/article/0,,1174391,00.html |publisher=DW-World.de}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=ELB |url=https://www.labeurb.unicamp.br/elb/europeias/talian.htm |website=labeurb.unicamp.br}}</ref> Talian is officially a historic patrimony of [[Rio Grande do Sul]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Approvato il progetto che dichiara il 'Talian' come patrimonio del Rio Grande del Sud – Brasile |url=http://www.sitoveneto.org/talian_patrimonio_de_rio_grando_do_sul.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120304160633/http://www.sitoveneto.org/talian_patrimonio_de_rio_grando_do_sul.html |archive-date=4 March 2012 |access-date=9 March 2012 |publisher=Sitoveneto}}</ref> and two German dialects possess co-official status in a few municipalities.<ref name="Stevenson1997">{{Cite book |last=Patrick Stevenson |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AviTvt-cPaUC&pg=PA39 |title=The German Language and the Real World: Sociolinguistic, Cultural, and Pragmatic Perspectives on Contemporary German |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-19-823738-9 |page=39}}</ref> Italian is also recognized as ''ethnic language'' in the [[Microregions of Brazil|Santa Teresa]] microregion and [[Vila Velha]] (Espirito Santo state), and is taught as mandatory second language at school.<ref name="autogenerated1">{{Cite web |title=Constituição de 1988 da República Federativa do Brasil/Título II – Wikisource |url=https://pt.m.wikisource.org/wiki/Constitui%C3%A7%C3%A3o_de_1988_da_Rep%C3%BAblica_Federativa_do_Brasil/T%C3%ADtulo_II#Artigo_13 |website=pt.m.wikisource.org}}</ref> |
|||
=== Urbanization === |
|||
{{Main|List of cities in Brazil by population}} |
|||
According to IBGE (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics) urban areas already concentrate 84.35% of the population, while the Southeast region remains the most populated one, with over 80 million inhabitants.<ref>{{Cite web |year=2011 |title=IDBGE |url=http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/censo2010/default.shtm |access-date=8 October 2011 |publisher=IBGE |language=pt}}</ref> |
|||
The largest urban agglomerations in Brazil are [[São Paulo]], [[Rio de Janeiro]], and [[Belo Horizonte]]—all in the Southeastern Region—with 21.1, 12.3, and 5.1 million inhabitants respectively.<ref name="concentrações_urbanas" /><!-- defined by template:Largest urban agglomerations in Brazil --><ref>{{Cite web |title=Arranjos Populacionais e Concentrações Urbanas do Brasil |url=http://geoftp.ibge.gov.br/organizacao_do_territorio/divisao_regional/arranjos_populacionais/arranjos_populacionais.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://geoftp.ibge.gov.br/organizacao_do_territorio/divisao_regional/arranjos_populacionais/arranjos_populacionais.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |access-date=16 March 2017 |publisher=Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics |page=148 |language=pt}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Estimativas da população residente no Brasil e Unidades da Federação com data de referência em 1º de julho de 2016 |url=ftp://ftp.ibge.gov.br/Estimativas_de_Populacao/Estimativas_2016/estimativa_dou_2016.pdf |access-date=16 March 2017 |publisher=Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics |language=pt}}</ref> The majority of state capitals are the largest cities in their states, except for [[Vitória, Brazil|Vitória]], the capital of [[Espírito Santo]], and [[Florianópolis]], the capital of Santa Catarina.<ref>{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Principal Cities |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_3/Brazil.html |access-date=10 June 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029034959/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_3/Brazil.html |archive-date=29 October 2009 }} {{Dubious|date=January 2010}}<!-- tertiary source --></ref> |
|||
{{Largest urban agglomerations in Brazil}} |
{{Largest urban agglomerations in Brazil}} |
||
== |
== Culture == |
||
{{Main|Culture of Brazil}} |
|||
{{Main|Languages of Brazil|Portuguese language|Brazilian Portuguese|List of endangered languages in Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Desfile Portela 2014 (906185).jpg|thumb|Parade of [[Portela (samba school)|Portela]] [[samba school]] at the [[Rio Carnival]], the largest [[carnival]] in the world<ref name="Guiness">[http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/records-11000/largest-carnival/ Largest Carnival] ''Guinness World Records''.</ref>]] |
|||
[[File:Interior do Museu da Língua Portuguesa em São Paulo, Brasil.jpg|thumb|left|[[Museum of the Portuguese Language]] in [[São Paulo]] city, [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]].]] |
|||
The core culture of Brazil is derived from [[Culture of Portugal|Portuguese culture]], because of its strong colonial ties with the Portuguese Empire.<ref name="Meade2009">{{Cite book |author=Teresa A. Meade |author-link=Teresa Meade |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=e6Jw-KNq2QUC&pg=PA146 |title=A Brief History of Brazil |publisher=Infobase Publishing |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-8160-7788-5 |page=146}}</ref> Among other influences, the Portuguese introduced the [[Portuguese language]], [[Catholic Church|Roman Catholicism]] and [[Manueline|colonial architectural styles]]. The culture was also strongly influenced by [[Ethnic groups of Africa|African]], [[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|indigenous]] and non-Portuguese European cultures and traditions.<ref name="Levinson1998">{{Cite book |last=David Levinson |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uwi-rv3VV6cC&pg=PA325 |title=Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |year=1998 |isbn=978-1-57356-019-1 |page=325}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Parque Indígena do Xingu.jpg|thumb|left|[[Oca (structure)|Ocas]] of the [[Kuikuro people]], [[Xingu Indigenous Park]], [[Mato Grosso]]]] |
|||
Some aspects of Brazilian culture were influenced by the contributions of [[Italian Brazilian|Italian]], [[German Brazilian|German]] and other European as well as [[Japanese Brazilian|Japanese]], [[Jewish Brazilian|Jewish]] and [[Arab Brazilian|Arab]] immigrants who arrived in large numbers in the South and Southeast of Brazil during the 19th and 20th centuries.<ref name="Lesser2013a">{{Cite book |last=Jeffrey Lesser |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HJW029DYOZoC&pg=PA150 |title=Immigration, Ethnicity, and National Identity in Brazil, 1808 to the Present |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-521-19362-7 |pages=150–55}}</ref> The indigenous Amerindians influenced Brazil's language and [[Brazilian cuisine|cuisine]]; and the Africans influenced language, cuisine, [[Music of Brazil|music]], dance and religion.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Freyre |first=Gilberto |year=1986 |title=The Afro-Brazilian experiment: African influence on Brazilian culture |publisher=UNESCO |url=http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m1310/is_1986_May-June/ai_4375022 |access-date=8 June 2008 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120530050909/http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m1310/is_1986_May-June/ai_4375022 |archive-date=30 May 2012}}</ref> |
|||
The official language of Brazil is Portuguese<ref name="CIA People">{{cite web |title=People of Brazil |website=The World Factbook |publisher=Central Intelligence Agency |year=2008 |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/br.html |accessdate=3 June 2008}}</ref> (Article 13 of the [[Constitution of Brazil|Constitution of the Federal Republic of Brazil]]), which almost all of the population speaks and is virtually the only language used in newspapers, radio, television, and for business and administrative purposes. Brazil is the only Portuguese-speaking nation in the Americas, making the language an important part of Brazilian national identity and giving it a national culture distinct from those of its Spanish-speaking neighbors.<ref name="language2">{{Cite web|url=http://countrystudies.us/brazil/39.htm|title=Brazil - Language|website=countrystudies.us}}</ref> |
|||
[[Brazilian art]] has developed since the 16th century into different styles that range from [[Baroque in Brazil|Baroque]] (the dominant style in Brazil until the early 19th century)<ref>Leandro Karnal, ''Teatro da fé: Formas de representação religiosa no Brasil e no México do século XVI'', São Paulo, Editora Hucitec, 1998; available on [http://www.fflch.usp.br/dh/ceveh/public_html/biblioteca/livros/teatro_fe/index.htm fflch.usp.br] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130724010418/http://www.fflch.usp.br/dh/ceveh/public_html/biblioteca/livros/teatro_fe/index.htm |date=24 July 2013 }}</ref><ref name="itaucultural.org.br">[http://www.itaucultural.org.br/aplicExternas/enciclopedia_IC/index.cfm?fuseaction=termos_texto_ing&cd_verbete=3738&lst_palavras=&cd_idioma=28556&cd_item=8 "The Brazilian Baroque"], ''Encyclopaedia Itaú Cultural'' {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110430001754/http://www.itaucultural.org.br/aplicExternas/enciclopedia_IC/index.cfm?fuseaction=termos_texto_ing&cd_verbete=3738&lst_palavras=&cd_idioma=28556&cd_item=8 |date=30 April 2011 }}</ref> to [[Brazilian academic art|Romanticism]], [[Modern art|Modernism]], [[Expressionism]], [[Cubism]], [[Surrealism]] and [[Abstract art|Abstractionism]]. [[Cinema of Brazil|Brazilian cinema]] dates back to the birth of the medium in the late 19th century and has gained a new level of international acclaim since the 1960s.<ref name="Marsh2012">{{Cite book |last=Leslie Marsh |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=I5F7E6BQ5ukC&pg=PA3 |title=Brazilian Women's Filmmaking: From Dictatorship to Democracy |publisher=University of Illinois Press |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-252-09437-8 |page=3}}</ref> |
|||
[[Brazilian Portuguese]] has had its own development, mostly similar to 16th-century Central and Southern dialects of European Portuguese<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sibila.com.br/index.php/world-map-of-portuguese/424 |title=Learn About Portuguese Language |publisher=Sibila.com.br |accessdate=7 April 2012}}</ref> (despite a very substantial number of Portuguese colonial settlers, and [[Portuguese Brazilian|more recent immigrants]], coming from [[Northern Portugal|Northern regions]], and in minor degree Portuguese [[Macaronesia]]), with a few influences from the [[Indigenous languages of the Americas|Amerindian]] and [[Languages of Africa|African languages]], especially [[West Africa]]n and [[Bantu languages|Bantu]] restricted to the vocabulary only.<ref name="Portuguese"/> As a result,{{citation needed|date=April 2015}} the language is somewhat different, mostly in phonology, from the language of Portugal and other [[Portuguese-speaking countries]] (the dialects of the other countries, partly because of the more recent end of [[Portuguese Empire|Portuguese colonialism]] in these regions, have a closer connection to contemporary [[European Portuguese]]). These differences are comparable to those between [[American English|American]] and [[British English]].<ref name="Portuguese">{{cite web |title=Languages of Brazil |publisher=Ethnologue |url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=br |accessdate=9 June 2008}}</ref> |
|||
=== Architecture === |
|||
In 1990, the [[Community of Portuguese Language Countries]] (CPLP), which included representatives from all countries with Portuguese as the official language, reached an [[Portuguese Language Orthographic Agreement of 1990|agreement on the reform of the Portuguese orthography]] to unify the two standards then in use by Brazil on one side and the remaining lusophone countries on the other. This spelling reform went into effect in Brazil on 1 January 2009. In Portugal, the reform was signed into law by the President on 21 July 2008 allowing for a six-year adaptation period, during which both orthographies will co-exist. The remaining CPLP countries are free to establish their own transition timetables.<ref>{{cite news |last=Nash |first=Elizabeth |title=Portugal pays lip service to Brazil's supremacy |newspaper=The Independent |date=2 May 2008 |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/portugal-pays-lip-service-to-brazils-supremacy-819728.html |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110624131043/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/portugal-pays-lip-service-to-brazils-supremacy-819728.html |archivedate=24 June 2011 |accessdate=9 June 2008 |location=London}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Architecture of Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Catedral1 Rodrigo Marfan.jpg|thumb|The [[Cathedral of Brasília]], designed by Brazilian architect [[Oscar Niemeyer]] for the [[Brasília|federal capital]], an example of [[Modern architecture]]]] |
|||
The architecture of Brazil is influenced by Europe, especially Portugal. It has a history that goes back 500 years to the time, when [[Pedro Álvares Cabral]] landed in Brazil in 1500. [[Portuguese colonial architecture]] was the first wave of architecture to go to Brazil.<ref>Hue, Jorge de Souza (1999). Uma visão da arquitectura colonial no Brasil [A vision of Colonial Architecture in Brazil] (in Portuguese). Rio de Janeiro.</ref> It is the basis for all Brazilian architecture of later centuries.<ref>Boxer, Charles Ralph (1962). The Golden Age of Brazil, 1695–1750: Growing Pains of a Colonial Society. University of California Press.</ref> In the 19th century, during the time of the [[Empire of Brazil]], the country followed European trends and adopted [[Neoclassical architecture|Neoclassical]] and [[Gothic Revival architecture]]. Then, in the 20th century, especially in Brasília, Brazil experimented with [[modernist architecture]]. |
|||
The [[recognition of sign languages|sign language law]] legally recognized in 2002,<ref name="Libras 2002">[https://web.archive.org/web/20100910070529/http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/LEIS/2002/L10436.htm LEI Nº 10.436, DE 24 DE ABRIL DE 2002]. Presidência da República, Casa Civil, Subchefia para Assuntos Jurídicos. Retrieved on 19 May 2012.</ref> (the law was [[regulation|regulated]] in 2005)<ref name="Libras 2005">[http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2004-2006/2005/decreto/d5626.htm Brazilian decree nº 5626, 22 December 2005]. Planalto.gov.br (23 December 2005). Retrieved on 19 May 2012.</ref> the use of the [[Brazilian Sign Language]], more commonly known by its Portuguese [[acronym]] LIBRAS, in education and government services. The language must be taught as a part of the [[school of education|education]] and [[speech and language pathology]] curricula. LIBRAS teachers, instructors and translators are recognized professionals. Schools and health services must provide access ("[[inclusion (education)|inclusion]]") to [[Deaf community|deaf people]].<ref name="Russo2011">{{cite book|author=Charles J. Russo|title=The Legal Rights of Students with Disabilities: International Perspectives|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JuV1cZ7NJHIC&pg=PA45|year=2011|publisher=Rowman & Littlefield Publishers|isbn=978-1-4422-1085-1|page=45}}</ref> |
|||
The colonial architecture of Brazil dates to the early 16th century, when Brazil was first explored, conquered and settled by the Portuguese. The Portuguese built architecture familiar to them in Europe in their aim to colonize Brazil. They built Portuguese colonial architecture, which included churches and civic architecture, including houses and forts, in Brazilian cities and the countryside.<ref name="Guimaraens" /> |
|||
[[File:Festapomerana.jpg|thumb|[[Pomerode]], [[Santa Catarina (state)|Santa Catarina]], is one of the municipalities with a cooficial language. In this region, [[Hunsrückisch dialect|Hunsrückisch]] and [[East Pomeranian dialect|East Pomeranian]], German dialects, are two of the minor languages (see [[Brazilian German]]).]] |
|||
During the 19th century, Brazilian architecture saw the introduction of more European styles to Brazil, such as Neoclassical and Gothic Revival architecture. This was usually mixed with Brazilian influences from their own heritage.<ref name="Guimaraens">Guimaraens, Cêça de. [http://www.mre.gov.br/cdbrasil/itamaraty/web/port/artecult/arqurb/arquitet/index.htm ''Arquitetura''] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030908051315/http://www.mre.gov.br/CDBRASIL/ITAMARATY/WEB/port/artecult/arqurb/arquitet/index.htm |date=8 September 2003 }}. Portal do Ministério das Relações Exteriores.</ref> In the 1950s [[modernist architecture]] was introduced when [[Brasília]] was built as a new federal capital in the interior of Brazil to help develop the interior. The architect [[Oscar Niemeyer]] idealized and built government buildings, churches and civic buildings in the modernist style.<ref name="Claro">Claro, Mauro. [http://www.vitruvius.com.br/revistas/read/drops/09.025/1775 "Ambientes modernos. A casa modernista da Rua Santa Cruz, de Gregori Warchavchik, e outras casas da modernidade"]. In: ''Drops'', 2008; 09 (025.03)</ref> |
|||
Minority languages are spoken throughout the nation. One hundred and eighty [[Indigenous languages of the Americas|Amerindian languages]] are spoken in remote areas and a significant number of other languages are spoken by immigrants and their descendants.<ref name="Portuguese"/> In the municipality of [[São Gabriel da Cachoeira]], [[Nheengatu language|Nheengatu]] (a currently endangered South American [[creole language]] – or an 'anti-creole', according to some linguists – with mostly Indigenous Brazilian languages lexicon and Portuguese-based grammar that, together with its southern relative [[língua geral paulista]], once was a major [[lingua franca]] in Brazil,<ref>{{Cite book|last1=Campbell|first1=Lyle|title=The Indigenous Languages of South America: A Comprehensive Guide|last2=Grondona|first2=Verónica|last3=Muysken|first3=Peter|publisher=Walter de Gruyter|year=2012|isbn=978-3110258035|location=|pages=247|chapter=Contacts between indigenous languages in South America|quote=Nheengatú (also called língua geral of Amazonia, or lingua Brasilica) originated in the 17th century in what are now the states of Pará Maranhão, as lingua franca on the basis of Tupinambá lexicon but with strong grammatical influence from Portuguese, also due to intervention by Jesuit missionaries [...] Around 1700 it was spoken in a large area in Brazil, as a contact language between whites and indians, but it lost some support with the expulsion of the Jesuits in 1758 [...] Its sister language in the colonial period was Língua Geral Paulista (in the state of São Paolo) a lingua franca which is now extinct.}}</ref> being replaced by Portuguese only after governmental prohibition led by [[Suppression of the Society of Jesus#Portugal|major political changes]]){{overly detailed inline|date=July 2015}}, [[Baniwa of Içana|Baniwa]] and Tucano languages had been granted co-official status with Portuguese.<ref name="nyt-language">{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2005/08/28/international/americas/28amazon.html|title=Language Born of Colonialism Thrives Again in Amazon|newspaper=New York Times|accessdate=14 July 2008 |first=Larry |last=Rohter |date=28 August 2005}}</ref> |
|||
=== Music === |
|||
There are significant communities of German (mostly the [[Riograndenser Hunsrückisch|Brazilian Hunsrückisch]], a High German language dialect) and Italian (mostly the [[Talian dialect|Talian]], a [[Venetian language|Venetian]] dialect) origins in the Southern and Southeastern regions, whose ancestors' native languages were carried along to Brazil, and which, still alive there, are influenced by the Portuguese language.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dw.de/dw/article/0,,1174391,00.html|title=O alemão lusitano do Sul do Brasil|publisher=DW-World.de}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.labeurb.unicamp.br/elb/europeias/talian.htm|title=ELB|website=labeurb.unicamp.br}}</ref> Talian is officially a historic patrimony of [[Rio Grande do Sul]],<ref>{{cite web|title=Approvato il progetto che dichiara il 'Talian' come patrimonio del Rio Grande del Sud – Brasile|url=http://www.sitoveneto.org/talian_patrimonio_de_rio_grando_do_sul.html|publisher=Sitoveneto|accessdate=9 March 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120304160633/http://www.sitoveneto.org/talian_patrimonio_de_rio_grando_do_sul.html|archive-date=4 March 2012|url-status=dead}}</ref> and two German dialects possess co-official status in a few municipalities.<ref name="Stevenson1997">{{cite book|author=Patrick Stevenson|title=The German Language and the Real World: Sociolinguistic, Cultural, and Pragmatic Perspectives on Contemporary German|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AviTvt-cPaUC&pg=PA39|year=1997|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-823738-9|page=39}}</ref> Italian is also recognized as ''ethnic language'' in the [[Microregions of Brazil|Santa Teresa]] microregion and [[Vila Velha]] (Espirito Santo state), and is taught as mandatory second language at school.<ref name=autogenerated1>{{Cite web|url=https://pt.m.wikisource.org/wiki/Constitui%C3%A7%C3%A3o_de_1988_da_Rep%C3%BAblica_Federativa_do_Brasil/T%C3%ADtulo_II#Artigo_13|title=Constituição de 1988 da República Federativa do Brasil/Título II - Wikisource|website=pt.m.wikisource.org}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Music of Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Tom Jobim e Chico Buarque no Festival Internacional da Canção (FIC).tif|thumb|[[Tom Jobim]], one of the creators of ''[[bossa nova]]'', and [[Chico Buarque]], one of the leading names of [[Música popular brasileira|MPB]]]] |
|||
The music of Brazil was formed mainly from the fusion of European, Native Indigenous, and African elements.<ref name="FonsecaWeiner1991">{{Cite book |last1=Duduka Da Fonseca |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HuZQUm_hhygC&pg=PA7 |title=Brazilian Rhythms for Drumset |last2=Bob Weiner |publisher=Alfred Music Publishing |year=1991 |isbn=978-0-7692-0987-6 |page=7}}</ref> Until the nineteenth century, Portugal was the gateway to most of the influences that built Brazilian music, although many of these elements were not of Portuguese origin, but generally European. The first was [[José Maurício Nunes Garcia]], author of sacred pieces with an influence of Viennese classicism.<ref name="Grazia2013">{{Cite book |last=Donna M. Di Grazia |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qyPz1PUFxW8C&pg=PA457 |title=Nineteenth-Century Choral Music |publisher=Routledge |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-136-29409-9 |page=457 |author-link=Donna Di Grazia}}</ref> The major contribution of the African element was the rhythmic diversity and some dances and instruments.<ref name="FonsecaWeiner1991" /> |
|||
Learning at least one second language (generally English or Spanish) is mandatory for all the 12 grades of the mandatory [[Education in Brazil|education system]] ([[primary education|primary]] and [[secondary education]], there called ''ensino fundamental'' and ''ensino médio'' respectively). Brazil is the first country in South America to offer [[Esperanto]] to secondary students.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pagef30.com/2009/09/15-september-2009-esperanto-approved-by.html |title=Esperanto approved by Brazilian government as optional high school subject, mandatory if justified by demand |page= F30 |date=19 September 2009 |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> |
|||
Popular music since the late eighteenth century, [[Samba (music)|samba]] was considered the most typical and on the UNESCO cultural heritage list.<ref>{{Cite web |title=UNESCO Culture Sector – Intangible Heritage – 2003 Convention |url=http://www.unesco.org/culture/ich/index.php?RL=00101 |access-date=4 June 2013 |publisher=Unesco.org}}</ref> [[Samba-reggae]], [[Maracatu]], [[Frevo]] and [[Afoxê]] are four music traditions that have been popularized by their appearance in the annual [[Brazilian Carnival]]s.<ref name="Crook2009">{{Cite book |last=Larry Crook |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Skjwor64MXwC&pg=PA78 |title=Focus: Music of Northeast Brazil |publisher=Taylor & Francis |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-415-96066-3 |page=78}}</ref> [[Capoeira]] is usually played with its own music referred to as [[capoeira music]], which is usually considered to be a call-and-response type of folk music.<ref name="Fryer2000">{{Cite book |last=Peter Fryer |url=https://archive.org/details/rhythmsofresista0000frye |title=Rhythms of Resistance: African Musical Heritage in Brazil |publisher=Pluto Press |year=2000 |isbn=978-0-7453-0731-2 |page=[https://archive.org/details/rhythmsofresista0000frye/page/39 39] |url-access=registration}}</ref> [[Forró]] is a type of folk music prominent during the [[Festa Junina]] in [[Northeast Region, Brazil|northeastern Brazil]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=25 December 2015 |title=Brazil From A TO Z: FORRÓ |url=http://brazilianexperience.com/brazil-from-a-to-z-forro/ |website=Brazilian Experience}}</ref> Jack A. Draper III, a professor of Portuguese at the [[University of Missouri]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Jack A. Draper III |url=https://romancelanguages.missouri.edu/people/draper |website=Romance Languages and Literatures: University of Missouri}}</ref> argues that Forró was used as a way to subdue feelings of nostalgia for a rural lifestyle.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Draper |first=Jack A. III |title=Forró and redemptive regionalism from the Brazilian northeast: popular music in a culture of migration |title-link=Forró and Redemptive Regionalism from the Brazilian Northeast |publisher=Lang |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-4331-1076-4 |location=New York |oclc=643568832}}</ref> |
|||
==Culture== |
|||
{{Main|Culture of Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Puro ouro.jpg|thumb|Interior of the [[São Francisco Church and Convent]] in [[Salvador, Bahia]], one of the richest expressions of [[Baroque in Brazil|Brazilian baroque]].]] |
|||
The core culture of Brazil is derived from [[Culture of Portugal|Portuguese culture]], because of its strong colonial ties with the Portuguese Empire.<ref name="Meade2009">{{cite book|author=Teresa A. Meade|title=A Brief History of Brazil|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=e6Jw-KNq2QUC&pg=PA146|year=2009|publisher=Infobase Publishing|isbn=978-0-8160-7788-5|page=146}}</ref> Among other influences, the Portuguese introduced the [[Portuguese language]], [[Catholic Church|Roman Catholicism]] and [[Manueline|colonial architectural styles]]. The culture was, however, also strongly influenced by [[Ethnic groups of Africa|African]], [[Indigenous peoples in Brazil|indigenous]] and non-Portuguese European cultures and traditions.<ref name="Levinson1998">{{cite book|author=David Levinson|title=Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uwi-rv3VV6cC&pg=PA325|year=1998|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|isbn=978-1-57356-019-1|page=325}}</ref> |
|||
Some aspects of Brazilian culture were influenced by the contributions of [[Italian Brazilian|Italian]], [[German Brazilian|German]] and other European as well as [[Japanese Brazilian|Japanese]], [[Jewish Brazilian|Jewish]] and [[Arab Brazilian|Arab]] immigrants who arrived in large numbers in the South and Southeast of Brazil during the 19th and 20th centuries.<ref name="Lesser2013a">{{cite book|author=Jeffrey Lesser|title=Immigration, Ethnicity, and National Identity in Brazil, 1808 to the Present|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HJW029DYOZoC&pg=PA150|year=2013|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-19362-7|pages=150–55}}</ref> The indigenous Amerindians influenced Brazil's language and [[Brazilian cuisine|cuisine]]; and the Africans influenced language, cuisine, [[Music of Brazil|music]], dance and religion.<ref>{{cite news |last=Freyre |first=Gilberto |title=The Afro-Brazilian experiment: African influence on Brazilian culture |publisher=UNESCO |year=1986 |url=http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m1310/is_1986_May-June/ai_4375022 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120530050909/http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m1310/is_1986_May-June/ai_4375022 |url-status=dead |archive-date=30 May 2012 |accessdate=8 June 2008}}</ref> |
|||
[[Choro]] is a popular musical instrumental style. Its origins are in 19th-century Rio de Janeiro. The style often has a fast and happy rhythm, characterized by subtle [[Modulation (music)|modulations]] and full of [[syncopation]] and [[counterpoint]].<ref name="MacGowanPessanha1998">{{Cite book |last1=MacGowan |first1=Chris |url=https://archive.org/details/braziliansoundsa00mcgowa |title=The Brazilian Sound: Samba, Bossa Nova, and the Popular Music of Brazil |last2=Pessanha |first2=Ricardo |publisher=Temple University Press |year=1998 |isbn=978-1-56639-545-8 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/braziliansoundsa00mcgowa/page/159 159]–61 |url-access=registration}}</ref> [[Bossa nova]] is also a well-known style of Brazilian music developed and popularized in the 1950s and 1960s.{{sfnp|MacGowan|Pessanha|1998|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=7MFD-EoTR7MC&pg=PA6 6]}} The phrase "bossa nova" means literally 'new trend'.<ref name="Kassing2007">{{Cite book |last=Gayle Kassing |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofdancein00kass |title=History of Dance: An Interactive Arts Approach |publisher=Human Kinetics 10% |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7360-6035-6 |page=[https://archive.org/details/historyofdancein00kass/page/236 236] |url-access=registration}}</ref> A lyrical fusion of samba and [[jazz]], bossa nova acquired a large following starting in the 1960s.<ref name="Campbell2011b">{{Cite book |last=Michael Campbell |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rK5DMAZsuAgC&pg=PT299 |title=Popular Music in America: The Beat Goes on |publisher=Cengage Learning |year=2011 |isbn=978-0-8400-2976-8 |page=299}}</ref> Some international Brazilian music artists are, for example: [[Villa-Lobos]], [[Tom Jobim]], [[João Gilberto]], [[Sergio Mendes]], [[Eumir Deodato]], [[Kaoma]], [[Sepultura]], [[Olodum]] and [[CSS (band)|CSS]]. |
|||
[[Brazilian art]] has developed since the 16th century into different styles that range from [[Baroque in Brazil|Baroque]] (the dominant style in Brazil until the early 19th century)<ref>Leandro Karnal, ''Teatro da fé: Formas de representação religiosa no Brasil e no México do século XVI'', São Paulo, Editora Hucitec, 1998; available on [http://www.fflch.usp.br/dh/ceveh/public_html/biblioteca/livros/teatro_fe/index.htm fflch.usp.br] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130724010418/http://www.fflch.usp.br/dh/ceveh/public_html/biblioteca/livros/teatro_fe/index.htm |date=24 July 2013 }}</ref><ref name="itaucultural.org.br">"[http://www.itaucultural.org.br/aplicExternas/enciclopedia_IC/index.cfm?fuseaction=termos_texto_ing&cd_verbete=3738&lst_palavras=&cd_idioma=28556&cd_item=8 The Brazilian Baroque]," ''Encyclopaedia Itaú Cultural'' {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110430001754/http://www.itaucultural.org.br/aplicExternas/enciclopedia_IC/index.cfm?fuseaction=termos_texto_ing&cd_verbete=3738&lst_palavras=&cd_idioma=28556&cd_item=8 |date=30 April 2011 }}</ref> to [[Brazilian academic art|Romanticism]], [[Modern art|Modernism]], [[Expressionism]], [[Cubism]], [[Surrealism]] and [[Abstract art|Abstractionism]]. [[Cinema of Brazil|Brazilian cinema]] dates back to the birth of the medium in the late 19th century and has gained a new level of international acclaim since the 1960s.<ref name="Marsh2012">{{cite book|author=Leslie Marsh|title=Brazilian Women's Filmmaking: From Dictatorship to Democracy|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=I5F7E6BQ5ukC&pg=PA3|year=2012|publisher=University of Illinois Press|isbn=978-0-252-09437-8|page=3}}</ref> |
|||
=== |
=== Literature === |
||
{{Main|Brazilian literature}} |
|||
{{main|Architecture of Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Machado de Assis aos 57 anos (cropped).jpg|thumb|[[Machado de Assis]], poet and novelist, founder of the [[Academia Brasileira de Letras|Brazilian Academy of Letters]]]] |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = left |
|||
| image1 = Museudainconfidencia2006.jpg |
|||
| width1 = 200 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = The [[Museum of the Inconfidência]] in [[Minas Gerais]], an example of [[Portuguese colonial architecture]]. |
|||
| image2 = Catedral Metropolitana de Brasília 2.jpg |
|||
| width2 = 190 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = The [[Cathedral of Brasilia]], an example of [[Modern architecture]] |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
[[Brazilian literature]] dates back to the 16th century, to the writings of the first Portuguese explorers in Brazil, such as [[Pero Vaz de Caminha]], filled with descriptions of [[fauna]], [[flora]] and commentary about the indigenous population that fascinated European readers.{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VhkvhllLooUC&pg=PA360 360]}} |
|||
The architecture of Brazil is influenced by Europe, especially Portugal. It has a history that goes back 500 years to the time when [[Pedro Álvares Cabral|Pedro Cabral]] discovered Brazil in 1500. [[Portuguese colonial architecture]] was the first wave of architecture to go to Brazil.<ref>Hue, Jorge de Souza (1999). Uma visão da arquitectura colonial no Brasil [A vision of Colonial Architecture in Brazil] (in Portuguese). Rio de Janeiro.</ref> It is the basis for all Brazilian architecture of later centuries.<ref>Boxer, Charles Ralph (1962). The Golden Age of Brazil, 1695–1750: Growing Pains of a Colonial Society. University of California Press.</ref> In the 19th century during the time of the [[Empire of Brazil]], Brazil followed European trends and adopted [[Neoclassical architecture|Neoclassical]] and [[Gothic Revival architecture]]. Then in the 20th century especially in Brasilia, Brazil experimented with [[Modernist architecture]]. |
|||
Brazil produced significant works in [[Romanticism]]—novelists such as [[Joaquim Manuel de Macedo]] and [[José de Alencar]] wrote novels about love and pain. Alencar, in his long career, also treated indigenous people as heroes in the [[Indianism (arts)|Indigenist]] novels ''[[The Guarani|O Guarani]]'', ''[[Iracema]]'' and ''[[Ubirajara (novel)|Ubirajara]]''.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20110725100730/http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/culture_academic/literature.html "Brazilian Literature: An Introduction"]. [http://ottawa.itamaraty.gov.br/pt-br/ Embassy of Brasil – Ottawa]. Visited on 2 November 2009.</ref> [[Machado de Assis]], one of his contemporaries, wrote in virtually all genres and continues to gain international prestige from critics worldwide.<ref>[[Antonio Candido|Candido; Antonio]]. (1970) ''Vários escritos''. São Paulo: Duas Cidades. p. 18</ref><ref>Caldwell, Helen (1970) ''Machado de Assis: The Brazilian Master and his Novels''. Berkeley, Los Angeles and London, University of California Press.</ref><ref>Fernandez, Oscar Machado de Assis: The Brazilian Master and His Novels The ''Modern Language Journal'', Vol. 55, No. 4 (Apr. 1971), pp. 255–56</ref> |
|||
The colonial architecture of Brazil dates to the early 16th century when Brazil was first explored, conquered and settled by the Portuguese. The Portuguese built architecture familiar to them in Europe in their aim to colonize Brazil. They built Portuguese colonial architecture which included churches, civic architecture including houses and forts in Brazilian cities and the countryside. During 19th century Brazilian architecture saw the introduction of more European styles to Brazil such as Neoclassical and Gothic Revival architecture. This was usually mixed with Brazilian influences from their own heritage which produced a unique form of Brazilian architecture. In the 1950s the [[modernist architecture]] was introduced when [[Brasilia]] was built as new federal capital in the interior of Brazil to help develop the interior. The architect [[Oscar Niemeyer]] idealized and built government buildings, churches and civic buildings in the modernist style.<ref name="Guimaraens">Guimaraens, Cêça de. [http://www.mre.gov.br/cdbrasil/itamaraty/web/port/artecult/arqurb/arquitet/index.htm ''Arquitetura''] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081215103814/http://www2.mre.gov.br/cdbrasil/itamaraty/web/port/artecult/arqurb/arquitet/index.htm |date=15 December 2008 }}. Portal do Ministério das Relações Exteriores.</ref><ref name="Claro">Claro, Mauro. [http://www.vitruvius.com.br/revistas/read/drops/09.025/1775 "Ambientes modernos. A casa modernista da Rua Santa Cruz, de Gregori Warchavchik, e outras casas da modernidade"]. In: ''Drops'', 2008; 09 (025.03)</ref> |
|||
[[Brazilian literature#Modernism|Brazilian Modernism]], evidenced by the [[Modern Art Week]] in 1922, was concerned with a nationalist avant-garde literature,<ref>Beatriz Mugayar Kühl, ''Arquitetura do ferro e arquitetura ferroviária em São Paulo: reflexões sobre a sua preservação'', p. 202. Atelie Editorial, 1998.</ref> while [[Brazilian literature#Post-Modernism|Post-Modernism]] brought a generation of distinct poets such as [[João Cabral de Melo Neto]], [[Carlos Drummond de Andrade]], [[Vinicius de Moraes]], [[Cora Coralina]], [[Graciliano Ramos]], [[Cecília Meireles]], and internationally known writers dealing with universal and regional subjects such as [[Jorge Amado]], [[João Guimarães Rosa]], [[Clarice Lispector]] and [[Manuel Bandeira]].<ref>Daniel Balderston and Mike Gonzalez, ''Encyclopedia of Latin American and Caribbean Literature, 1900–2003'', p. 288. Routledge, 2004.</ref><ref>Sayers, ''Portugal and Brazil in Transitn'', "Literature". U of Minnesota Press, 1 January 1999.</ref><ref>Marshall C. Eakin and Paulo Roberto de Almeida, ''Envisioning Brazil: A Guide to Brazilian Studies in the United States'': "Literature, Culture and Civilization". University of Wisconsin Press, 31 October 2005.</ref> |
|||
===Music=== |
|||
{{main|Music of Brazil}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| image1 = Heitor Vila-Lobos (c. 1922)part.jpg |
|||
| width1 = 120 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = [[Heitor Villa-Lobos]], the most widely known South American composer.{{sfn|Wright|1992|loc=4}} |
|||
| image2 = Tom_Jobim_e_Chico_Buarque_no_Festival_Internacional_da_Canção_(FIC).tif |
|||
| width2 = 181 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = [[Tom Jobim]], one of the creators of ''[[bossa nova]]'', and [[Chico Buarque]], one of the leading names of [[Música popular brasileira|MPB]]. |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
Brazil's most significant literary award is the [[Camões Prize]], which it shares with the rest of the [[Lusophone|Portuguese-speaking world]]. As of 2016, Brazil has eleven recipients of the prize.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Prêmio Camões de Literatura | Biblioteca Nacional |url=https://www.bn.br/explore/premios-literarios/premio-camoes-literatura |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160316050256/http://www.bn.br/explore/premios-literarios/premio-camoes-literatura |archive-date=16 March 2016 |access-date=26 January 2017 |website=Bn.br |language=pt}}</ref> Brazil also holds its own literary academy, the [[Brazilian Academy of Letters]], a non-profit cultural organization aimed at perpetuating the care of the national language and literature.<ref>{{Cite web |date=3 August 2014 |title=Quem somos | Academia Brasileira de Letras |url=http://www.academia.org.br/academia/quem-somos |access-date=26 January 2017 |website=Academia.org.br |language=pt}}</ref> |
|||
The music of Brazil was formed mainly from the fusion of European and African elements.<ref name="FonsecaWeiner1991">{{cite book|author1=Duduka Da Fonseca|author2=Bob Weiner|title=Brazilian Rhythms for Drumset|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HuZQUm_hhygC&pg=PA7|year=1991|publisher=Alfred Music Publishing|isbn=978-0-7692-0987-6|page=7}}</ref> Until the nineteenth century, Portugal was the gateway to most of the influences that built Brazilian music, although many of these elements were not of Portuguese origin, but generally European. The first was José Maurício Nunes Garcia, author of sacred pieces with influence of Viennese classicism.<ref name="Grazia2013">{{cite book|author=Donna M. Di Grazia|title=Nineteenth-Century Choral Music|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qyPz1PUFxW8C&pg=PA457|year=2013|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-136-29409-9|page=457}}</ref> The major contribution of the African element was the rhythmic diversity and some dances and instruments that had a bigger role in the development of popular music and folk, flourishing especially in the twentieth century.<ref name="FonsecaWeiner1991"/> |
|||
=== Cinema === |
|||
Popular music since the late eighteenth century began to show signs of forming a characteristically Brazilian sound, with [[Samba (music)|samba]] considered the most typical and on the UNESCO cultural heritage list.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.unesco.org/culture/ich/index.php?RL=00101 |title=UNESCO Culture Sector – Intangible Heritage – 2003 Convention |publisher=Unesco.org |accessdate=4 June 2013}}</ref> [[Maracatu]] and [[Afoxê]] are two [[Afro-Brazilian]] music traditions that have been popularized by their appearance in the annual [[Brazilian Carnival]]s.<ref name="Crook2009">{{cite book|author=Larry Crook|title=Focus: Music of Northeast Brazil|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Skjwor64MXwC&pg=PA78|year=2009|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-0-415-96066-3|page=78}}</ref> The sport of [[capoeira]] is usually played with its own music referred to as [[capoeira music]], which is usually considered to be a call-and-response type of folk music.<ref name="Fryer2000">{{cite book|author=Peter Fryer|title=Rhythms of Resistance: African Musical Heritage in Brazil|url=https://archive.org/details/rhythmsofresista0000frye|url-access=registration|year=2000|publisher=Pluto Press|isbn=978-0-7453-0731-2|page=[https://archive.org/details/rhythmsofresista0000frye/page/39 39]}}</ref> [[Forró]] is a type of folk music prominent during the [[Festa Junina]] in [[Northeast Region, Brazil|northeastern Brazil]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://brazilianexperience.com/brazil-from-a-to-z-forro/|title=Brazil From A TO Z: FORRÓ|last=|first=|date=25 December 2015|website=Brazilian Experience|access-date=}}</ref> Jack A. Draper III, a professor of Portuguese at the [[University of Missouri]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://romancelanguages.missouri.edu/people/draper|title=Jack A. Draper III|last=|first=|date=|website=Romance Languages and Literatures: University of Missouri|access-date=}}</ref> argues that Forró was used as a way to subdue feelings of nostalgia for a rural lifestyle.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Forró and redemptive regionalism from the Brazilian northeast: popular music in a culture of migration|title-link=Forró and Redemptive Regionalism from the Brazilian Northeast |last=Draper |first=Jack A., III |year=2010 |publisher=Lang|isbn=978-1-4331-1076-4|location=New York|oclc=643568832}}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Cinema of Brazil}} |
|||
[[File:Palácio dos Festivais de Gramado.jpg|thumb|[[Festival de Gramado|Gramado Film Festival]], the biggest [[film festival]] in the country]] |
|||
The Brazilian film industry began in the late 19th century, during the early days of the [[Belle Époque]]. While there were national film productions during the early 20th century, American films such as ''Rio the Magnificent'' were made in [[Rio de Janeiro]] to promote tourism in the city.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Rio the Magnificent (1932) |url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7Q1kITY168 |url-status=bot: unknown |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151107002139/https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7Q1kITY168 |archive-date=7 November 2015 |access-date=19 October 2015 |website=[[YouTube]]| date=18 April 2008 }}</ref> The films ''[[Limite]]'' (1931) and ''[[Ganga Bruta]]'' (1933), the latter being produced by [[Adhemar Gonzaga]] through the prolific studio Cinédia, were poorly received at release and failed at the box office, but are acclaimed nowadays and placed among the finest Brazilian films of all time.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Larry |first=Rohter |date=9 November 2010 |title=Brazil's Best, Restored and Ready for a 21st-Century Audience |work=[[The New York Times]] |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/11/10/movies/10cinema.html |url-access=limited |access-date=3 November 2010 |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220101/https://www.nytimes.com/2010/11/10/movies/10cinema.html |archive-date=1 January 2022}}{{cbignore}}</ref> The 1941 unfinished film ''[[It's All True (film)|It's All True]]'' was divided into four segments, two of which were filmed in Brazil and directed by [[Orson Welles]]; it was originally produced as part of the United States' [[Good Neighbor Policy]] during Getúlio Vargas' Estado Novo government. |
|||
During the 1960s, the [[Cinema Novo]] movement rose to prominence with directors such as [[Glauber Rocha]], [[Nelson Pereira dos Santos]], [[Paulo Cesar Saraceni]] and [[Arnaldo Jabor]]. Rocha's films ''[[Deus e o Diabo na Terra do Sol]]'' (1964) and ''[[Terra em Transe]]'' (1967) are considered to be some of the greatest and most influential in Brazilian film history.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Tose |first=Juliano |title=Editorial |url=http://www.contracampo.com.br/27/frames.htm |access-date=19 October 2015 |website=Contracampo – revista de cinema |publisher=Revista Contracampo}}</ref> |
|||
[[Choro]] is a very popular music instrumental style. Its origins are in 19th-century Rio de Janeiro. In spite of the name, the style often has a fast and happy rhythm, characterized by virtuosity, improvisation, subtle [[Modulation (music)|modulations]] and full of [[syncopation]] and [[counterpoint]].<ref name="MacGowanPessanha1998">{{cite book|first1=Chris|last1=MacGowan|first2=Ricardo|last2=Pessanha|title=The Brazilian Sound: Samba, Bossa Nova, and the Popular Music of Brazil|url=https://archive.org/details/braziliansoundsa00mcgowa|url-access=registration|year=1998|publisher=Temple University Press|isbn=978-1-56639-545-8|pages=[https://archive.org/details/braziliansoundsa00mcgowa/page/159 159]–61|ref=harv}}</ref> [[Bossa nova]] is also a well-known style of Brazilian music developed and popularized in the 1950s and 1960s.{{sfnp|MacGowan|Pessanha|1998|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=7MFD-EoTR7MC&pg=PA6 6]}} The phrase "bossa nova" means literally "new trend".<ref name="Kassing2007">{{cite book|author=Gayle Kassing|title=History of Dance: An Interactive Arts Approach|url=https://archive.org/details/historyofdancein00kass|url-access=registration|year=2007|publisher=Human Kinetics 10%|isbn=978-0-7360-6035-6|page=[https://archive.org/details/historyofdancein00kass/page/236 236]}}</ref> A lyrical fusion of samba and [[jazz]], bossa nova acquired a large following starting in the 1960s.<ref name="Campbell2011b">{{cite book|author=Michael Campbell|title=Popular Music in America: The Beat Goes on|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rK5DMAZsuAgC&pg=PT299|year=2011|publisher=Cengage Learning|isbn=978-0-8400-2976-8|page=299}}</ref> |
|||
During the 1990s, Brazil saw a surge of critical and commercial success with films such as ''[[O Quatrilho]]'' ([[Fábio Barreto]], 1995), ''[[O Que É Isso, Companheiro?]]'' ([[Bruno Barreto]], 1997) and ''[[Central Station (film)|Central do Brasil]]'' ([[Walter Salles]], 1998), all of which were nominated for the [[Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film]], the latter receiving a [[Academy Award for Best Actress|Best Actress]] nomination for [[Fernanda Montenegro]]. The 2002 crime film ''[[City of God (2002 film)|City of God]]'', directed by [[Fernando Meirelles]], was critically acclaimed, scoring 90% on [[Rotten Tomatoes]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Cidade de Deus (City of God) (2003) – Rotten Tomatoes |url=https://www.rottentomatoes.com/m/city_of_god/#top-critics-numbers |access-date=19 October 2015 |website=[[Rotten Tomatoes]] |date=17 January 2003 |publisher=[[Flixster]]}}</ref> being placed in [[Roger Ebert]]'s Best Films of the Decade list<ref>{{Cite web |last=Ebert |first=Roger |title=The best films of the decade |url=https://www.rogerebert.com/rogers-journal/the-best-films-of-the-decade |access-date=19 October 2015 |website=RogerEbert.com|date=14 December 2012 }}</ref> and receiving four [[Academy Awards|Academy Award]] nominations in 2004, including [[Academy Award for Best Director|Best Director]]. Notable film festivals in Brazil include the [[São Paulo International Film Festival|São Paulo]] and [[Rio de Janeiro International Film Festival]]s and the [[Festival de Gramado|Gramado Festival]]. |
|||
===Literature=== |
|||
{{main|Brazilian literature}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| image1 = Machado de Assis aos 57 anos.jpg |
|||
| width1 = 135 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = [[Machado de Assis]], poet and novelist, founder of the [[Academia Brasileira de Letras|Brazilian Academy of Letters]]. |
|||
| image2 = Carlos Drummond de Andrade, 1970.tif |
|||
| width2 = 150 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = [[Carlos Drummond de Andrade]], considered by some as the greatest Brazilian poet.<ref>{{cite news|author=Garner, Dwight|title= Review:Multitudinous Heart:Newly translated poetry by Carlos Drummond de Andrade|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/07/03/books/review-multitudinous-heart-newly-translated-poetry-by-carlos-drummond-de-andrade.html|date=3 July 2015|newspaper=The New York Times|access-date=20 January 2016}}</ref> |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
[[Brazilian literature]] dates back to the 16th century, to the writings of the first Portuguese explorers in Brazil, such as [[Pêro Vaz de Caminha]], filled with descriptions of [[fauna]], [[flora]] and commentary about the indigenous population that fascinated European readers.{{sfnp|Crocitti|Vallance|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VhkvhllLooUC&pg=PA360 360]}} |
|||
=== Visual arts === |
|||
Brazil produced significant works in [[Romanticism]] – novelists like [[Joaquim Manuel de Macedo]] and [[José de Alencar]] wrote novels about love and pain. Alencar, in his long career, also treated indigenous people as heroes in the [[Indianism (arts)|Indigenist]] novels ''[[The Guarani|O Guarani]]'', ''[[Iracema]]'' and ''[[Ubirajara]]''.<ref>"[https://web.archive.org/web/20110725100730/http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/culture_academic/literature.html Brazilian Literature: An Introduction]." [http://ottawa.itamaraty.gov.br/pt-br/ Embassy of Brasil – Ottawa]. Visited on 2 November 2009.</ref> [[Machado de Assis]], one of his contemporaries, wrote in virtually all genres and continues to gain international prestige from critics worldwide.<ref>[[Antonio Candido|Candido; Antonio.]] (1970) ''Vários escritos''. São Paulo: Duas Cidades. p. 18</ref><ref>Caldwell, Helen (1970) ''Machado de Assis: The Brazilian Master and his Novels.'' Berkeley, Los Angeles and London, University of California Press.</ref><ref>Fernandez, Oscar Machado de Assis: The Brazilian Master and His Novels The ''Modern Language Journal'', Vol. 55, No. 4 (Apr. 1971), pp. 255–56</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Brazilian painting}} |
|||
[[File:Mural painting "Entry into the Forest" by Candido Portinari, on the vestibule wall of the Hispanic Reading room, Library of Congress, Thomas Jefferson Building, Washington, D.C LCCN2011631432.tif|thumb|''Entry in the Forest'' mural at the [[Thomas Jefferson Building]] by [[Candido Portinari]], one of the most important [[Brazilian painting|Brazilian painters]]]] |
|||
Brazilian painting emerged in the late 16th century,<ref>Louzada, Maria Alice & Louzada, Julio. [http://www.juliolouzada.com.br/primeirosmomentos.asp ''Os Primeiros Momentos da Arte Brasileira''] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706153216/http://www.juliolouzada.com.br/primeirosmomentos.asp |date=6 July 2011 }}. Júlio Louzada Artes Plásticas Brasil. Acesso 5 out 2010</ref> influenced by [[Baroque]], [[Rococo]], [[Neoclassicism]], [[Romanticism]], [[Realism (arts)|Realism]], [[Modernism]], [[Expressionism]], [[Surrealism]], [[Cubism]] and [[Abstract art|Abstracionism]] making it a major [[Style (visual arts)|art style]] called [[Brazilian academic art]].<ref>Leite, José Roberto Teixeira & Lemos, Carlos A.C. ''Os Primeiros Cem Anos'', in Civita, Victor. ''Arte no Brasil''. São Paulo: Abril Cultural, 1979</ref><ref name="Biscardi" /> |
|||
[[Brazilian literature#Modernism|Brazilian Modernism]], evidenced by the [[Week of Modern Art]] in 1922, was concerned with a nationalist avant-garde literature,<ref>Beatriz Mugayar Kühl, ''Arquitetura do ferro e arquitetura ferroviária em São Paulo: reflexões sobre a sua preservação'', p. 202. Atelie Editorial, 1998.</ref> while [[Brazilian literature#Post-Modernism|Post-Modernism]] brought a generation of distinct poets like [[João Cabral de Melo Neto]], [[Carlos Drummond de Andrade]], [[Vinicius de Moraes]], [[Cora Coralina]], [[Graciliano Ramos]], [[Cecília Meireles]], and internationally known writers dealing with universal and regional subjects like [[Jorge Amado]], [[João Guimarães Rosa]], [[Clarice Lispector]] and [[Manuel Bandeira]].<ref>Daniel Balderston and Mike Gonzalez, ''Encyclopedia of Latin American and Caribbean Literature, 1900–2003'', p. 288. Routledge, 2004.</ref><ref>Sayers, ''Portugal and Brazil in Transitn'', "Literature". U of Minnesota Press, 1 January 1999.</ref><ref>Marshall C. Eakin and Paulo Roberto de Almeida, ''Envisioning Brazil: A Guide to Brazilian Studies in the United States'': "Literature, Culture and Civilization". University of Wisconsin Press, 31 October 2005.</ref> |
|||
The [[Missão Artística Francesa|French Artistic Mission]] arrived in Brazil in 1816 proposing the creation of an art academy modeled after the respected Académie des Beaux-Arts, with graduation courses both for artists and craftsmen for activities such as modeling, decorating, carpentry and others and bringing artists such as [[Jean-Baptiste Debret]].<ref name="Biscardi">{{harvnb|Biscardi|Rocha|2006}}</ref> |
|||
===Cuisine=== |
|||
{{Main|Brazilian cuisine}} |
|||
{{See also|List of Brazilian dishes}} |
|||
Upon the creation of the [[Academia Imperial de Belas Artes|Imperial Academy of Fine Arts]], new artistic movements spread across the country during the 19th century and later the event called [[Modern Art Week]] broke with academic tradition in 1922 and started a nationalist trend which was influenced by modernist arts.<ref name="Amaral">{{Cite journal |last1=Amaral |first1=Aracy |last2=Kim Mrazek Hastings |year=1995 |title=Stages in the Formation of Brazil's Cultural Profile |journal=Journal of Decorative and Propaganda Arts |volume=21 |pages=9–25 |doi=10.2307/1504129 |jstor=1504129}}</ref> |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = left |
|||
| image1 = Brigadeiro.jpg |
|||
| width1 = 200 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = [[Brigadeiro]] is a national candy and one most and is recognized as one of the main dishes of [[Brazilian cuisine]]. |
|||
| image2 = Pao de queijo com cafe.jpg |
|||
| width2 = 200 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = [[Pão de queijo]] with [[Brazilian coffee|coffee]] and a small [[cachaça]] bottle, examples of the cuisine from the interior of Brazil. |
|||
| footer = |
|||
| direction = |
|||
| total_width = |
|||
}} |
|||
Among the best-known Brazilian painters are [[Ricardo do Pilar]] and [[Manuel da Costa Ataíde]] (baroque and rococo), [[Victor Meirelles]], [[Pedro Américo]] and [[José Ferraz de Almeida Júnior|Almeida Júnior]] (romanticism and realism), [[Anita Malfatti]], [[Ismael Nery]], [[Lasar Segall]], [[Emiliano di Cavalcanti]], [[Vicente do Rego Monteiro]], and [[Tarsila do Amaral]] (expressionism, surrealism and cubism), [[Aldo Bonadei]], [[José Pancetti]] and [[Cândido Portinari]] (modernism).<ref>Sevcenko, Nicolau. Pindorama revisitada: cultura e sociedade em tempos de virada. Série Brasil cidadão. Editora Peirópolis, 2000. pp. 39–47</ref> |
|||
Brazilian cuisine varies greatly by region, reflecting the country's varying mix of indigenous and immigrant populations. This has created a national cuisine marked by the preservation of regional differences.<ref name="Encarta 4">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Way of Life |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_4/Brazil.html |accessdate=8 June 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029035059/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_4/Brazil.html |archivedate=29 October 2009 |url-status=dead}}</ref> Examples are [[Feijoada]], considered the country's national dish;<ref>Roger, "[http://www.braziltravelguide.com/feijoada-the-brazilian-national-dish.html Feijoada: The Brazilian national dish] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091129154026/http://www.braziltravelguide.com/feijoada-the-brazilian-national-dish.html |date=29 November 2009 }}" braziltravelguide.com.</ref> and regional foods such as beiju, feijão tropeiro, [[vatapá]], [[moqueca]], [[polenta]] (from Italian cuisine) and [[acarajé]] (from African cuisine).<ref>Cascudo, Luis da Câmara. História da Alimentação no Brasil. São Paulo/Belo Horizonte: Editora USP/Itatiaia, 1983.</ref> |
|||
=== Theatre === |
|||
The national beverage is [[coffee]] and [[cachaça]] is Brazil's native [[Distilled beverage|liquor]]. Cachaça is distilled from [[Sugarcane|sugar cane]] and is the main ingredient in the national cocktail, [[Caipirinha]].<ref name="Bayor2011">{{cite book|first=Ronald H. |last=Bayor|title=Multicultural America: An Encyclopedia of the Newest Americans|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bJW79Rlu-igC&pg=PA181|year=2011|publisher=Georgia Institute of Technology|isbn=978-0-313-35786-2|page=181}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Augusto Boal nyc3.jpg|thumb|[[Augusto Boal]] presenting a workshop on the [[Theatre of the Oppressed]] at [[Riverside Church]] in [[New York City]] in 2008]] |
|||
The theatre in Brazil has its origins in the period of [[Jesuits|Jesuit]] expansion, when theater was used for the dissemination of Catholic doctrine in the 16th century. In the 17th and 18th centuries, dramatists on the scene of European derivation were for court or private performances.<ref>[http://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biografia/padre-anchieta.htm Padre Anchieta] ''Brasil Escola''.</ref> During the 19th century, the playwrights [[Gonçalves Dias|Antônio Gonçalves Dias]] and [[Martins Pena|Luís Carlos Martins Pena]] were known for their performance.<ref name=teatro>{{cite web|url=http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/culture_academic/theater.html |title=Brazilian Theatre: An Introduction |publisher=Ambasciata brasiliana a Ottawa |language=english |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120205061026/http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/culture_academic/theater.html |archive-date= 5 February 2012 }}</ref> There were also numerous operas and orchestras. The Brazilian conductor [[Antônio Carlos Gomes]] became internationally known with operas such as ''[[Il Guarany]]''. At the end of the 19th century, orchestrated dramaturgias were accompanied with songs of famous artists such as the conductress [[Chiquinha Gonzaga]].<ref>[http://www.arte.seed.pr.gov.br/modules/conteudo/conteudo.php?conteudo=196 O Teatro no Brasil] ''Secretaria da Educação do Paraná''.</ref> |
|||
A typical meal consists mostly of [[rice and beans]] with [[beef]], [[salad]], [[french fries]] and a [[fried egg]].<ref>{{cite journal|author=Barbosa, Lívia|title= Feijão com arroz e arroz com feijão: o Brasil no prato dos brasileiros|doi=10.1590/S0104-71832007000200005|year=2007|journal=Horizontes Antropológicos|volume=13|issue=28|pages= 87–116|doi-access=free}}</ref> Often, it is mixed with cassava flour ([[farofa]]). Fried potatoes, fried cassava, fried banana, fried meat and fried cheese are very often eaten in lunch and served in most typical restaurants.<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Ferraccioli, Patrícia |author2=Silveira, Eliane Augusta da |year=2010|title= Cultural feeding influence on palative memories in the usual brazilian cuisine|journal= Rev. Enferm. UERJ|volume=18|issue=2|pages=198–203|url=http://bases.bireme.br/cgi-bin/wxislind.exe/iah/online/?IsisScript=iah/iah.xis&base=BDENF&lang=p&nextAction=lnk&exprSearch=18716&indexSearch=ID}}</ref> Popular snacks are [[pastel (food)|pastel]] (a fried pastry); [[coxinha]] (a variation of chicken croquete); [[pão de queijo]] (cheese bread and cassava flour / [[tapioca]]); [[pamonha]] (corn and milk paste); [[sfiha|esfirra]] (a variation of Lebanese pastry); [[kibbeh]] (from Arabic cuisine); [[empanada]] (pastry) and [[empada]], little salt pies filled with shrimps or heart of palm. |
|||
Already in the early 20th century there was the presence of theaters, entrepreneurs and actor companies. In 1940, Paschoal Carlos Magno and his student's theater, the comedians group and the Italian actors [[Adolfo Celi]], Ruggero Jacobbi and Aldo Calvo, founders of the ''Teatro Brasileiro de Comédia'', renewed the Brazilian theater. From the 1960s, it was attended by a theater dedicated to social and religious issues. The most prominent authors at this stage were Jorge Andrade and [[Ariano Suassuna]].<ref name=teatro /> |
|||
Brazil has a variety of desserts such as [[brigadeiro]]s (chocolate fudge balls), [[bolo de rolo]] (roll cake with [[goiabada]]), [[cocada]] (a coconut sweet), [[beijinho]]s (coconut truffles and clove) and romeu e julieta (cheese with goiabada). Peanuts are used to make [[paçoca]], [[rapadura]] and [[pé-de-moleque]]. Local common fruits like [[açaí]], [[cupuaçu]], [[mango]], [[papaya]], [[cocoa bean|cocoa]], [[cashew]], [[guava]], [[orange (fruit)|orange]], [[Lime (fruit)|lime]], [[passionfruit]], [[pineapple]], and [[Spondias|hog plum]] are turned in [[juice]]s and used to make [[chocolate]]s, [[ice pop]]s and [[ice cream]].<ref>Freyre, Gilberto. Açúcar. Uma Sociologia do Doce, com Receitas de Bolos e Doces do Nordeste do Brasil. São Paulo, Companhia das Letras, 1997.</ref> |
|||
=== |
=== Cuisine === |
||
{{ |
{{Main|Brazilian cuisine}} |
||
{{See also|List of Brazilian dishes}} |
|||
{{Multiple image |
|||
|align = right |
|||
|direction = vertical |
|||
|width = 220 |
|||
[[File:Feijoada à brasileira -.jpg|thumb|[[Feijoada (Brazilian dish)|Feijoada]] is the [[national dish]] of [[Brazilian cuisine]].]] |
|||
|image1 = Palacio_festivais.jpg |
|||
|caption1 = [[Festival de Gramado]], the biggest [[film festival]] in the country |
|||
Brazilian cuisine varies greatly by region, reflecting the country's varying mix of indigenous and immigrant populations. This has created a national cuisine marked by the preservation of regional differences.<ref name="Encarta 4">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Way of Life |encyclopedia=Encarta |publisher=MSN |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_4/Brazil.html |access-date=8 June 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029035059/http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554342_4/Brazil.html |archive-date=29 October 2009 }}</ref> Examples are [[Feijoada]], considered the country's national dish;<ref>Roger, [http://www.braziltravelguide.com/feijoada-the-brazilian-national-dish.html "Feijoada: The Brazilian national dish"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091129154026/http://www.braziltravelguide.com/feijoada-the-brazilian-national-dish.html |date=29 November 2009 }} braziltravelguide.com.</ref> and regional foods such as beiju, feijão tropeiro, [[vatapá]], [[moqueca]], [[polenta]] (from Italian cuisine) and [[acarajé]] (from African cuisine).<ref>Cascudo, Luis da Câmara. História da Alimentação no Brasil. São Paulo/Belo Horizonte: Editora USP/Itatiaia, 1983.</ref> The national beverage is [[coffee]]; [[cachaça]] is Brazil's native [[Distilled beverage|liquor]]. Cachaça is distilled from [[Sugarcane|sugar cane]] and is the main ingredient in the national cocktail, [[Caipirinha]].<ref name="Bayor2011">{{Cite book |last=Bayor |first=Ronald H. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bJW79Rlu-igC&pg=PA181 |title=Multicultural America: An Encyclopedia of the Newest Americans |publisher=Georgia Institute of Technology |year=2011 |isbn=978-0-313-35786-2 |page=181}}</ref> |
|||
|image2 = Fernando_Meirelles_-_Österreichpremiere_360_Wiener_Volkstheater_01.jpg |
|||
|caption2 = [[Fernando Meirelles]], who was nominated for the [[Academy Award for Best Director]] for ''[[City of God (2002 film)|City of God]]'' |
|||
}} |
|||
The Brazilian film industry began in the late 19th century, during the early days of the [[Belle Époque]]. While there were national film productions during the early 20th century, American films such as ''Rio the Magnificent'' were made in [[Rio de Janeiro]] to promote tourism in the city.<ref>{{cite web|title=Rio the Magnificent (1932)|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7Q1kITY168|website=[[YouTube]]|accessdate=19 October 2015}}</ref> The films ''[[Limite]]'' (1931) and ''[[Ganga Bruta]]'' (1933), the latter being produced by [[Adhemar Gonzaga]] through the prolific studio Cinédia, were poorly received at release and failed at the box office, but are acclaimed nowadays and placed among the finest Brazilian films of all time.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/11/10/movies/10cinema.html |title=Brazil's Best, Restored and Ready for a 21st-Century Audience |last1=Larry |first1=Rohter |last2= |first2= |date=9 November 2010 |work=[[The New York Times]] |publisher= |accessdate=3 November 2010}}</ref> The 1941 unfinished film ''[[It's All True (film)|It's All True]]'' was divided in four segments, two of which were filmed in Brazil and directed by [[Orson Welles]]; it was originally produced as part of the United States' [[Good Neighbor Policy]] during Getúlio Vargas' Estado Novo government. |
|||
A typical meal consists mostly of [[rice and beans]] with [[beef]], [[salad]], [[french fries]] and a [[fried egg]].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Barbosa, Lívia |year=2007 |title=Feijão com arroz e arroz com feijão: o Brasil no prato dos brasileiros |journal=Horizontes Antropológicos |volume=13 |issue=28 |pages=87–116 |doi=10.1590/S0104-71832007000200005 |doi-access=free}}</ref> Often, it is mixed with cassava flour ([[farofa]]). Fried potatoes, fried cassava, fried banana, fried meat and fried cheese are very often eaten in lunch and served in most typical restaurants.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Ferraccioli, Patrícia |last2=Silveira, Eliane Augusta da |year=2010 |title=Cultural feeding influence on palative memories in the usual brazilian cuisine |url=http://bases.bireme.br/cgi-bin/wxislind.exe/iah/online/?IsisScript=iah/iah.xis&base=BDENF&lang=p&nextAction=lnk&exprSearch=18716&indexSearch=ID |journal=Rev. Enferm. UERJ |volume=18 |issue=2 |pages=198–203}}</ref> Popular snacks are [[pastel (food)|pastel]] (a fried pastry); [[coxinha]] (a variation of chicken croquete); [[pão de queijo]] (cheese bread and cassava flour / [[tapioca]]); [[pamonha]] (corn and milk paste); [[sfiha|esfirra]] (a variation of Lebanese pastry); [[kibbeh]] (from Arabic cuisine); [[empanada]] (pastry) and empada, little salt pies filled with shrimps or heart of palm. |
|||
During the 1960s, the [[Cinema Novo]] movement rose to prominence with directors such as [[Glauber Rocha]], [[Nelson Pereira dos Santos]], [[Paulo Cesar Saraceni]] and [[Arnaldo Jabor]]. Rocha's films ''[[Deus e o Diabo na Terra do Sol]]'' (1964) and ''[[Terra em Transe]]'' (1967) are considered to be some of the greatest and most influential in Brazilian film history.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Tose|first1=Juliano|title=Editorial|url=http://www.contracampo.com.br/27/frames.htm|website=Contracampo – revista de cinema|publisher=Revista Contracampo|accessdate=19 October 2015}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil has a variety of desserts such as [[brigadeiro]]s (chocolate fudge balls), [[bolo de rolo]] (roll cake with [[goiabada]]), [[cocada]] (a coconut sweet), [[beijinho]]s (coconut truffles and clove) and [[Romeu e Julieta]] (cheese with goiabada). Peanuts are used to make [[paçoca]], [[rapadura]] and [[pé-de-moleque]]. Local common fruits such as [[açaí]], [[cupuaçu]], [[mango]], [[papaya]], [[cocoa bean|cocoa]], [[cashew]], [[guava]], [[orange (fruit)|orange]], [[Lime (fruit)|lime]], [[passionfruit]], [[pineapple]], and [[Spondias|hog plum]] are turned in [[juice]]s and used to make [[chocolate]]s, [[ice pop]]s and [[ice cream]].<ref>Freyre, Gilberto. Açúcar. Uma Sociologia do Doce, com Receitas de Bolos e Doces do Nordeste do Brasil. São Paulo, Companhia das Letras, 1997.</ref> |
|||
During the 1990s, Brazil saw a surge of critical and commercial success with films such as ''[[O Quatrilho]]'' ([[Fábio Barreto]], 1995), ''[[O Que É Isso, Companheiro?]]'' ([[Bruno Barreto]], 1997) and ''[[Central Station (film)|Central do Brasil]]'' ([[Walter Salles]], 1998), all of which were nominated for the [[Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film]], the latter receiving a [[Academy Award for Best Actress|Best Actress]] nomination for [[Fernanda Montenegro]]. The 2002 crime film ''[[City of God (2002 film)|City of God]]'', directed by [[Fernando Meirelles]], was critically acclaimed, scoring 90% on [[Rotten Tomatoes]],<ref>{{cite web|title=Cidade de Deus (City of God) (2003) – Rotten Tomatoes|url=https://www.rottentomatoes.com/m/city_of_god/#top-critics-numbers|website=[[Rotten Tomatoes]]|publisher=[[Flixter]]|accessdate=19 October 2015}}</ref> being placed in [[Roger Ebert]]'s Best Films of the Decade list<ref>{{cite web|last1=Ebert|first1=Roger|title=The best films of the decade|url=https://www.rogerebert.com/rogers-journal/the-best-films-of-the-decade|website=RogerEbert.com|accessdate=19 October 2015}}</ref> and receiving four [[Academy Awards|Academy Award]] nominations in 2004, including [[Academy Award for Best Director|Best Director]]. Notable film festivals in Brazil include the [[São Paulo International Film Festival|São Paulo]] and [[Rio de Janeiro International Film Festival]]s and the [[Festival de Gramado|Gramado Festival]]. |
|||
=== |
=== Media === |
||
{{Main|Telecommunications in Brazil|Television in Brazil}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
{{See also|Concentration of media ownership#Brazil|Mass media regulation in Brazil}} |
|||
| align = left |
|||
[[File:Jornal Nacional 3.jpg|thumb|Former President [[Dilma Rousseff]] at ''[[Jornal Nacional]]'' news program. [[Rede Globo]] is the world's second-largest commercial television network.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Rede Globo se torna a 2ª maior emissora do mundo |url=http://ofuxico.terra.com.br/noticias-sobre-famosos/rede-globo-se-torna-a-2-maior-emissora-do-mundo/2012/05/11-139187.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120514045322/http://ofuxico.terra.com.br/noticias-sobre-famosos/rede-globo-se-torna-a-2-maior-emissora-do-mundo/2012/05/11-139187.html |archive-date=14 May 2012 |access-date=22 May 2012 |publisher=O Fuxico |language=pt}}</ref>]] |
|||
| image1 = Teatro Municipal de São Paulo 8.jpg |
|||
| width1 = 230 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = [[Theatro Municipal (São Paulo)|São Paulo Municipal Theater]], significant both for its architectural value as well as for its [[Modern Art Week|historical importance]]. |
|||
| image2 = 01 - teatro Amazonas.jpg |
|||
| width2 = 220 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = Interior of the [[Amazon Theatre|Teatro Amazonas]], in [[Manaus]]. |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
The theatre in Brazil has its origins in the period of Jesuit expansion when theater was used for the dissemination of Catholic doctrine in the 16th century. in the 17th and 18th centuries the first dramatists who appeared on the scene of European derivation was for court or private performances.<ref>[http://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biografia/padre-anchieta.htm Padre Anchieta] ''Brasil Escola''.</ref> During the 19th century, dramatic theater gained importance and thickness, whose first representative was [[Luis Carlos Martins Pena]] (1813–1848), capable of describing contemporary reality. Always in this period the comedy of costume and comic production was imposed. Significant, also in the nineteenth century, was also the playwright [[Antônio Gonçalves Dias]].<ref name=teatro>{{cite web|url=http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/culture_academic/theater.html |title=Brazilian Theatre: An Introduction |publisher=Ambasciata brasiliana a Ottawa |language=english |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120205061026/http://www.brasembottawa.org/en/culture_academic/theater.html |archivedate= 5 February 2012 }}</ref> There were also numerous operas and orchestras. The Brazilian conductor [[Antônio Carlos Gomes]] became internationally known with operas like ''[[Il Guarany]]''. At the end of the 19th century orchestrated dramaturgias became very popular and were accompanied with songs of famous artists like the conductress [[Chiquinha Gonzaga]].<ref>[http://www.arte.seed.pr.gov.br/modules/conteudo/conteudo.php?conteudo=196 O Teatro no Brasil] ''Secretaria da Educação do Paraná''.</ref> |
|||
The Brazilian press was officially born in [[Rio de Janeiro]] on 13 May 1808 with the creation of the Royal Printing National Press by the [[Prince Regent]] [[João VI of Portugal|Dom João]].<ref name="EchevarríaPupo-Walker1996">{{Cite book |last1=Roberto Gonzalez Echevarría |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=97NoYRx96ZAC&pg=PA13 |title=The Cambridge History of Latin American Literature |last2=Enrique Pupo-Walker |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-521-41035-9 |page=13}}</ref> The {{lang|pt|Gazeta do Rio de Janeiro}}, the first newspaper published in the country, began to circulate on 10 September 1808.<ref name="Johnston2003">{{Cite book |last=Donald H. Johnston |title=Encyclopedia of international media and communications |publisher=Academic Press |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-12-387671-3 |volume=3 |page=130}}</ref> The largest newspapers nowadays are {{lang|pt|[[Folha de S.Paulo]]}}, ''Super Notícia'', ''[[O Globo]]'' and ''[[O Estado de S. Paulo]]''.<ref name="Vincent2003B">{{Cite book |last=Jon S. Vincent |url=https://archive.org/details/culturecustomsof0000vinc |title=Culture and Customs of Brazil |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-313-30495-8 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/culturecustomsof0000vinc/page/97 97]–100 |url-access=registration}}</ref> |
|||
Already in the early 20th century there was the presence of theaters, entrepreneurs and actor companies, but paradoxically the quality of the products staggered, and only in 1940 the Brazilian theater received a boost of renewal thanks to the action of Paschoal Carlos Magno and his student's theater, the comedians group and the Italian actors [[Adolfo Celi]], Ruggero Jacobbi and Aldo Calvo, founders of the ''Teatro Brasileiro de Comedia''. From the 1960s it was attended by a theater dedicated to social and religious issues and to the flourishing of schools of dramatic art. The most prominent authors at this stage were [[Jorge Andrade]] and [[Ariano Suassuna]].<ref name=teatro/> |
|||
Radio broadcasting began on 7 September 1922, with a speech by then President Pessoa, and was formalized on 20 April 1923 with the creation of the "Radio Society of Rio de Janeiro".<ref name="McCann2004">{{Cite book |last=Bryan McCann |url=https://archive.org/details/hellohellobrazil00mcca |title=Hello, Hello Brazil: Popular Music in the Making of Modern Brazil |publisher=Duke University Press |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-8223-3273-2 |page=[https://archive.org/details/hellohellobrazil00mcca/page/22 22] |url-access=registration}}</ref> Television in Brazil began officially on 18 September 1950, with the founding of [[TV Tupi]] by [[Assis Chateaubriand]].<ref name="Ward2007">{{Cite book |last=David Ward |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zdEs1Av1CvAC&pg=PA28 |title=Television and Public Policy: Change and Continuity in an Era of Global Liberalization |publisher=Routledge |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-203-87728-9 |page=28}}</ref> Since then, television has grown in the country, creating large commercial broadcast networks such as [[Rede Globo|Globo]], [[Sistema Brasileiro de Televisão|SBT]], [[RecordTV]], [[Rede Bandeirantes|Bandeirantes]] and [[RedeTV!|RedeTV]]. Today it is the most important factor in the popular culture of Brazilian society, as indicated by research showing that as much as 67%<ref>{{Cite news |title=Um ponto de IBOPE equivale a quantas pessoas? E domicílios? |publisher=IBOPE |url=http://www.ibope.com.br/pt-br/relacionamento/duvidas-frequentes/Paginas/Audiencia-de-televisao.aspx |access-date=23 March 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130522190248/http://www.ibope.com.br/pt-br/relacionamento/duvidas-frequentes/Paginas/Audiencia-de-televisao.aspx |archive-date=22 May 2013}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |title=Top 10 das novelas |publisher=MSN Brasil |url=http://entretenimento.br.msn.com/famosos/top-10-das-novelas?page=0px |access-date=23 March 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130507101650/http://entretenimento.br.msn.com/famosos/top-10-das-novelas?page=0px |archive-date=7 May 2013}}</ref> of the general population follow the same daily [[telenovela]] broadcast. |
|||
===Visual arts=== |
|||
{{main|Brazilian painting}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| image1 = Americo-noite.jpg |
|||
| width1 = 150 |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = ''The Night escorted by the geniuses of Love and Study'', by [[Pedro Américo]] |
|||
| image2 = Discovery of the Land1.jpg |
|||
| width2 = 200 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = ''Discovery of the Land'' mural, by Brazilian painter [[Candido Portinari]], at the [[Library of Congress]] |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
|||
By the mid-1960s, [[List of universities in Brazil by state|Brazilian universities]] had installed [[mainframe computer]]s from [[IBM]] and [[Burroughs Large Systems]]. In the 1970s and 1980s, the Brazilian government restricted foreign [[import]]s to protect the local manufacturing of computers. In the 1980s, Brazil produced half of the computers sold in the country. By 2009, the [[mobile phone]] and [[Internet]] use in Brazil was the fifth largest in the world.<ref>{{Cite book|title= Computer: A History of the Information Machine | author1=Martin Campbell-Kelly | author2= William F. Aspray | author3= Jeffrey R. Yost | author4= Honghong Tinn | author5= Gerardo Con Díaz |publisher= Taylor & Francis |year=2023 |isbn= 978-1-00-087875-2 }}</ref> |
|||
Brazilian painting emerged in the late 16th century,<ref>Louzada, Maria Alice & Louzada, Julio. [http://www.juliolouzada.com.br/primeirosmomentos.asp ''Os Primeiros Momentos da Arte Brasileira''] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110706153216/http://www.juliolouzada.com.br/primeirosmomentos.asp |date=6 July 2011 }}. Júlio Louzada Artes Plásticas Brasil. Acesso 5 out 2010</ref> influenced by [[Baroque]], [[Rococo]], [[Neoclassicism]], [[Romanticism]], [[Realism (arts)|Realism]], [[Modernism]], [[Expressionism]], [[Surrealism]], [[Cubism]] and [[Abstract art|Abstracionism]] making it a major [[Style (visual arts)|art style]] called [[Brazilian academic art]].<ref>Leite, José Roberto Teixeira & Lemos, Carlos A.C. ''Os Primeiros Cem Anos'', in Civita, Victor. ''Arte no Brasil''. São Paulo: Abril Cultural, 1979</ref><ref name="Biscardi"/> The [[Missão Artística Francesa]] (French Artistic Mission) arrived in Brazil in 1816 proposing the creation of an art academy modeled after the respected Académie des Beaux-Arts, with graduation courses both for artists and craftsmen for activities such as modeling, decorating, carpentry and others and bringing artists like [[Jean-Baptiste Debret]].<ref name="Biscardi">{{harvnb|Biscardi|Rocha|2006}}</ref> |
|||
In May 2010, the Brazilian government launched [[TV Brasil Internacional]], an international [[television station]], initially broadcasting to 49 countries.<ref>{{Cite news |date=25 May 2010 |title=Brazil launches international TV station for Africa |work=BBC News |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/10152301 |access-date=30 October 2010}}</ref> Commercial television channels broadcast internationally include [[Globo Internacional]], [[RecordTV Internacional]] and [[Band Internacional]]. |
|||
Upon the creation of the [[Academia Imperial de Belas Artes|Imperial Academy of Fine Arts]], new artistic movements spread across the country during the 19th century and later the event called [[Week of Modern Art]] broke definitely with academic tradition in 1922 and started a nationalist trend which was influenced by modernist arts. Among the best-known Brazilian painters are [[Ricardo do Pilar]] and [[Manuel da Costa Ataíde]] (baroque and rococo), [[Victor Meirelles]], [[Pedro Américo]] and [[Almeida Junior]] (romanticism and realism), [[Anita Malfatti]], [[Ismael Nery]], [[Lasar Segall]], [[Emiliano di Cavalcanti]], [[Vicente do Rego Monteiro]], and [[Tarsila do Amaral]] (expressionism, surrealism and cubism), [[Aldo Bonadei]], [[José Pancetti]] and [[Cândido Portinari]] (modernism).<ref>Sevcenko, Nicolau. Pindorama revisitada: cultura e sociedade em tempos de virada. Série Brasil cidadão. Editora Peirópolis, 2000. pp. 39–47</ref> |
|||
===Sports=== |
=== Sports === |
||
{{ |
{{Main|Sport in Brazil}} |
||
{{See also|Brazil at the Olympics}} |
|||
{{ |
{{Multiple image |
||
| align = |
| align = right |
||
| direction = horizontal |
|||
| image1 = Brasil conquista primeiro ouro olímpico nos penaltis 1039264-20082016- mg 4348.jpg |
|||
| total_width = 300 |
|||
| width1 = 200 |
|||
| image1 = Pele con brasil (cropped).jpg |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = [[Pelé]], a [[footballer]] as well as sport figures of the 20th century<ref name=fifa>{{cite web |url=https://www.fifa.com/news/pele-the-greatest-them-all-1656982 |title=FIFA: Pele, the greatest of them all |date=28 June 2012 |publisher=FIFA |access-date=11 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210109195631/https://www.fifa.com/news/pele-the-greatest-them-all-1656982 |archive-date=9 January 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://newsvote.bbc.co.uk/sport2/hi/football/world_cup_2006/5051768.stm|title=Pele tops World Cup legends poll|work=BBC News|date=12 June 2006|access-date=21 January 2016|archive-date=26 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190326070105/http://newsvote.bbc.co.uk/sport2/hi/football/world_cup_2006/5051768.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
| caption1 = Players at the podium with the first [[Olympic medal|Olympic Gold]] of the [[Brazil national football team]], won in the [[Football at the 2016 Summer Olympics – Men's tournament|2016 Summer Olympics]]. [[Association football|Football]] is the most popular sport in the country. |
|||
| image2 = Ayrton Senna |
| image2 = Ayrton Senna Imola 1989 (cropped).jpg |
||
| caption2 = [[Ayrton Senna]], the driver with [[List of Formula One driver records#Most consecutive wins at the same Grand Prix|most consecutive wins]] and [[List of Formula One driver records#Most consecutive pole positions at the same Grand Prix|pole positions]] at the same [[List of Formula One Grands Prix|Grand Prix]] of [[Formula One]] |
|||
| width2 = 200 |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = [[Ayrton Senna]], who won the [[Formula One]] [[List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions|World Drivers' Championship]] in [[1988 Formula One season|1988]], [[1990 Formula One season|1990]] and [[1991 Formula One season|1991]], is widely regarded as one of the greatest Formula One drivers of all time.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://vimeo.com/89217406|title=Ayrton Senna Top Gear Tribute|website=Vimeo}}</ref> |
|||
| footer = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The most popular sport in Brazil is [[association football|football]].<ref>{{ |
The most popular sport in Brazil is [[association football|football]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Futebol, o esporte mais popular do Brasil, é destaque no Via Legal |url=http://justica-federal.jusbrasil.com.br/noticias/74894/futebol-o-esporte-mais-popular-do-brasil-e-destaque-no-via-legal |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120330164959/http://justica-federal.jusbrasil.com.br/noticias/74894/futebol-o-esporte-mais-popular-do-brasil-e-destaque-no-via-legal |archive-date=30 March 2012 |access-date=16 April 2011 |publisher=Jusbrasil.com.br}}</ref> The [[Brazil national football team|Brazilian men's national team]] is ranked among the best in the world according to the [[FIFA World Rankings]], and has won the [[FIFA World Cup|World Cup]] tournament a record five times.<ref>{{Cite web |date=15 April 2008 |title=Football in Brazil |url=https://www.fifa.com/associations/association=bra/goalprogramme/index.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070604173556/http://www.fifa.com/associations/association=bra/goalprogramme/index.html |archive-date=4 June 2007 |access-date=6 June 2008 |website=Goal Programme |publisher=International Federation of Association Football}}</ref><ref>Zirin, 2014. Chapter 4 ''"Futebol: The Journey from Daring to Fear"''</ref> |
||
[[Volleyball]], [[basketball]], [[auto racing]], and [[martial arts]] also attract large audiences. The [[Brazil men's national volleyball team]], for example, currently holds the titles of the [[FIVB Volleyball World League|World League]], [[FIVB Volleyball World Grand Champions Cup|World Grand Champions Cup]], [[FIVB Volleyball Men's World Championship|World Championship]] and the [[FIVB Volleyball Men's World Cup|World Cup]]. In auto racing, three Brazilian drivers have won the [[Formula One]] world championship eight times.<ref>{{cite web |last=Donaldson |first=Gerald |title=Emerson Fittipaldi |website=Hall of Fame |publisher=The Official Formula 1 Website |url=http://www.formula1.com/teams_and_drivers/hall_of_fame/282/ |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Donaldson |first=Gerald |title=Nelson Piquet |website=Hall of Fame |publisher=The Official Formula 1 Website |url=http://www.formula1.com/teams_and_drivers/hall_of_fame/181/ |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Donaldson |first=Gerald |title=Ayrton Senna |website=Hall of Fame |publisher=The Official Formula 1 Website |url=http://www.formula1.com/teams_and_drivers/hall_of_fame/45/ |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> |
|||
[[Volleyball]], [[basketball]], [[auto racing]] and [[martial arts]] also has large audiences. The [[Brazil men's national volleyball team]], for example, currently holds the titles of the [[FIVB Volleyball World League|World League]], [[FIVB Volleyball World Grand Champions Cup|World Grand Champions Cup]], [[FIVB Volleyball Men's World Championship|World Championship]] and the [[FIVB Volleyball Men's World Cup|World Cup]]. In auto racing, three Brazilian drivers have won the [[Formula One]] world championship eight times.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Donaldson |first=Gerald |title=Emerson Fittipaldi |url=http://www.formula1.com/teams_and_drivers/hall_of_fame/282/ |access-date=6 June 2008 |website=Hall of Fame |publisher=The Official Formula 1 Website}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Donaldson |first=Gerald |title=Nelson Piquet |url=http://www.formula1.com/teams_and_drivers/hall_of_fame/181/ |access-date=6 June 2008 |website=Hall of Fame |publisher=The Official Formula 1 Website}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Donaldson |first=Gerald |title=Ayrton Senna |url=http://www.formula1.com/teams_and_drivers/hall_of_fame/45/ |access-date=6 June 2008 |website=Hall of Fame |publisher=The Official Formula 1 Website}}</ref> The country has also produced significant achievements in other sports such as [[Sailing (sport)|sailing]], [[Swimming (sport)|swimming]], [[tennis]], [[surfing]], [[skateboarding]], [[MMA]], [[gymnastics]], [[boxing]], [[judo]], [[Track and field|athletics]] and [[table tennis]]. |
|||
Some sport variations have their origins in Brazil: [[beach soccer|beach football]],<ref>{{cite web |title=Beach Soccer |publisher=International Federation of Association Football |url=https://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/developing/beachsoccer/index.html |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> [[futsal]] (indoor football)<ref>{{cite web |title=Futsal |publisher=International Federation of Association Football |url=https://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/developing/futsal/index.html |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> and [[footvolley]] emerged in Brazil as variations of football. In martial arts, Brazilians developed [[Capoeira]],<ref>{{cite web |title=The art of capoeira |publisher=BBC |date=20 September 2006 |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/northyorkshire/content/articles/2005/09/13/capoeira_feature.shtml |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> [[Vale tudo]],<ref>{{cite web |title=Brazilian Vale Tudo |publisher=I.V.C |url=http://valetudo.com.br/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/19980530081959/http://www.valetudo.com.br/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=30 May 1998 |accessdate=6 June 2008 }}</ref> and [[Brazilian jiu-jitsu]].<ref>{{cite web |title=International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation |publisher=[[International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation]] |url=http://www.ibjjf.org/index.htm |url-status=dead |accessdate=6 June 2008 |archivedate=20 April 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080420155232/http://www.ibjjf.org/index.htm}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Terminam os Jogos Olímpicos Rio 2016 (29040726262).jpg|thumb|[[2016 Summer Olympics closing ceremony|Closing ceremony]] of the [[2016 Summer Olympics]] at the [[Maracanã Stadium]], [[Rio de Janeiro]].]] |
|||
Some sport variations have their origins in Brazil: [[beach soccer|beach football]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Beach Soccer |url=https://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/developing/beachsoccer/index.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070623115807/http://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/developing/beachsoccer/index.html |archive-date=23 June 2007 |access-date=6 June 2008 |publisher=International Federation of Association Football}}</ref> [[futsal]] (indoor football)<ref>{{Cite web |title=Futsal |url=https://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/developing/futsal/index.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070603161352/http://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/developing/futsal/index.html |archive-date=3 June 2007 |access-date=6 June 2008 |publisher=International Federation of Association Football}}</ref> and [[footvolley]] emerged in Brazil as variations of football. In martial arts, Brazilians developed [[Capoeira]],<ref>{{Cite web |date=20 September 2006 |title=The art of capoeira |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/northyorkshire/content/articles/2005/09/13/capoeira_feature.shtml |access-date=6 June 2008 |publisher=BBC}}</ref> [[Vale tudo]]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Brazilian Vale Tudo |url=http://valetudo.com.br/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/19980530081959/http://www.valetudo.com.br/ |archive-date=30 May 1998 |access-date=6 June 2008 |publisher=I.V.C}}</ref> and [[Brazilian jiu-jitsu]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation |url=http://www.ibjjf.org/index.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080420155232/http://www.ibjjf.org/index.htm |archive-date=20 April 2008 |access-date=6 June 2008 |publisher=[[International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation]]}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil has hosted several high-profile international sporting events, like the [[1950 FIFA World Cup]]<ref>{{cite web |title=1950 FIFA World Cup Brazil |website=Previous FIFA World Cups |publisher=International Federation of Association Football |url=https://www.fifa.com/worldcup/archive/edition=7/index.html |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> and recently has hosted the [[2014 FIFA World Cup]] and [[2019 Copa América]].<ref>{{cite web|title=2014 FIFA World Cup Brazil |publisher=International Federation of Association Football |url=https://www.fifa.com/worldcup/preliminarydraw/index.html |accessdate=6 June 2008 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080609044247/http://www.fifa.com/worldcup/preliminarydraw/index.html |archivedate=9 June 2008}}</ref> The [[São Paulo]] circuit, [[Autódromo José Carlos Pace]], hosts the annual [[Brazilian Grand Prix|Grand Prix of Brazil]].<ref>{{cite web |title=The Official Formula 1 Website |publisher=[[Formula One Administration]] |url=http://www.formula1.com/races/in_detail/brazil_804/circuit_diagram.html |url-status=dead |archivedate=4 June 2008 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080604141640/http://www.formula1.com/races/in_detail/brazil_804/circuit_diagram.html |accessdate=6 June 2008}}</ref> São Paulo organized the [[1963 Pan American Games|IV Pan American Games]] in 1963, and Rio de Janeiro hosted the [[2007 Pan American Games|XV Pan American Games]] in 2007.<ref name="LiMacIntosh2011">{{cite book|author1=Ming Li|author2=Eric W. MacIntosh|author3=Gonzalo A. Bravo|title=International Sport Management|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=udBgtzFSlBIC&pg=PA129|year=2011|publisher=Human Kinetics – College of Business at Ohio University|isbn=978-1-4504-2241-3|page=129}}</ref> On 2 October 2009, Rio de Janeiro was selected to host the [[2016 Summer Olympics|2016 Olympic Games]] and [[2016 Summer Paralympics|2016 Paralympic Games]], making it the first South American city to host the games<ref name="guardian_olympics">"[https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2009/oct/02/olympics-2016-games-rio-pele Olympics 2016: Tearful Pele and weeping Lula greet historic win for Rio]," ''[[The Guardian]]'', 2 October 2009.</ref> and second in Latin America, after [[Mexico City]]. Furthermore, the country hosted the [[FIBA Basketball World Cup]]s in [[1954 FIBA World Championship|1954]] and [[1963 FIBA World Championship|1963]]. At the 1963 event, the [[Brazil national basketball team]] won one of its two world championship titles.<ref name="FIBA History">{{cite web|url=http://www.fiba.com/downloads/v3_abouFiba/mp/FIBA_world_championships_history.pdf|title=FIBA World Championship History (pdf)|publisher=[[FIBA]]|date=1 January 2007 |accessdate=24 February 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Brazil has hosted several high-profile international sporting events, such as the [[1950 FIFA World Cup]],<ref>{{Cite web |title=1950 FIFA World Cup Brazil |url=https://www.fifa.com/worldcup/archive/edition=7/index.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070603185404/http://fifa.com/worldcup/archive/edition=7/index.html |archive-date=3 June 2007 |access-date=6 June 2008 |website=Previous FIFA World Cups |publisher=International Federation of Association Football}}</ref> and recently has hosted the [[2014 FIFA World Cup]], [[2019 Copa América]] and [[2021 Copa América]] .<ref>{{Cite web |title=2014 FIFA World Cup Brazil |url=https://www.fifa.com/worldcup/preliminarydraw/index.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080609044247/http://www.fifa.com/worldcup/preliminarydraw/index.html |archive-date=9 June 2008 |access-date=6 June 2008 |publisher=International Federation of Association Football}}</ref> The [[São Paulo]] circuit, [[Autódromo José Carlos Pace]], hosts the annual [[Brazilian Grand Prix|Grand Prix of Brazil]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Official Formula 1 Website |url=http://www.formula1.com/races/in_detail/brazil_804/circuit_diagram.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080604141640/http://www.formula1.com/races/in_detail/brazil_804/circuit_diagram.html |archive-date=4 June 2008 |access-date=6 June 2008 |publisher=[[Formula One Administration]]}}</ref> São Paulo organized the [[1963 Pan American Games|IV Pan American Games]] in 1963, and Rio de Janeiro hosted the [[2007 Pan American Games|XV Pan American Games]] in 2007.<ref name="LiMacIntosh2011">{{Cite book |last1=Ming Li |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=udBgtzFSlBIC&pg=PA129 |title=International Sport Management |last2=Eric W. MacIntosh |last3=Gonzalo A. Bravo |publisher=Human Kinetics – College of Business at Ohio University |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-4504-2241-3 |page=129}}</ref> On 2 October 2009, Rio de Janeiro was selected to host the [[2016 Summer Olympics|2016 Olympic Games]] and [[2016 Summer Paralympics|2016 Paralympic Games]], making it the first South American city to host the games<ref name="guardian_olympics">[https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2009/oct/02/olympics-2016-games-rio-pele "Olympics 2016: Tearful Pele and weeping Lula greet historic win for Rio"], ''[[The Guardian]]'', 2 October 2009.</ref> and second in Latin America, after [[Mexico City]]. Furthermore, the country hosted the [[FIBA Basketball World Cup]]s in [[1954 FIBA World Championship|1954]] and [[1963 FIBA World Championship|1963]]. At the 1963 event, the [[Brazil national basketball team]] won one of its two world championship titles.<ref name="FIBA History">{{Cite web |date=1 January 2007 |title=FIBA World Championship History (pdf) |url=http://www.fiba.com/downloads/v3_abouFiba/mp/FIBA_world_championships_history.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.fiba.com/downloads/v3_abouFiba/mp/FIBA_world_championships_history.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |access-date=24 February 2012 |publisher=[[FIBA]]}}</ref> |
|||
===National holidays=== |
|||
{|class="wikitable" |
|||
|- |
|||
! Date !! Local name !! Name !! Observation |
|||
|- |
|||
|1 January ||Confraternização Universal ||[[New Year's Day]] ||Beginning of the calendar year |
|||
|- |
|||
|21 April ||Tiradentes ||[[Tiradentes]] ||In honor of the martyr of the [[Minas Conspiracy]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|1 May ||Dia do Trabalhador ||[[Labour Day]] ||Tribute to all [[workers]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|7 September ||Independência ||[[Independence of Brazil]] ||Proclamation of Independence against Portugal |
|||
|- |
|||
|12 October ||Nossa Senhora Aparecida || [[Our Lady of Aparecida]] ||[[Patroness]] of Brazil |
|||
|- |
|||
|2 November ||Finados ||[[All Souls' Day]] ||Day of remembrance for the dead |
|||
|- |
|||
|15 November ||Proclamação da República ||Proclamation of the Republic ||Transformation of [[Empire of Brazil|Empire]] into [[First Brazilian Republic|Republic]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|25 December ||Natal ||Christmas ||Traditional Christmas celebration |
|||
|} |
|||
==See also== |
== See also == |
||
{{Portal|Brazil| |
{{Portal|Brazil|Latin America}} |
||
* [[Outline of Brazil]]{{clear right}} |
|||
{{Wikipedia books}}<!-- TURNED OFF https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Wikipedia_books --> |
|||
* [[Index of Brazil-related articles]] |
|||
* [[Outline of Brazil]] |
|||
==Notes== |
== Notes == |
||
{{Reflist|group=nt}} |
{{Reflist|group=nt}} |
||
{{Notelist}} |
|||
==References== |
== References == |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
==Bibliography== |
== Bibliography == |
||
{{Refbegin| |
{{Refbegin|indent=yes|2}} |
||
* Azevedo, Aroldo. ''O Brasil e suas regiões''. São Paulo: Companhia Editora Nacional, 1971 |
* Azevedo, Aroldo. ''O Brasil e suas regiões''. São Paulo: Companhia Editora Nacional, 1971 |
||
* Barman, Roderick J. ''Citizen Emperor: Pedro II and the Making of Brazil, 1825–1891 |
* Barman, Roderick J. ''Citizen Emperor: Pedro II and the Making of Brazil, 1825–1891''. Stanford: Stanford University Press, 1999. {{ISBN|0-8047-3510-7}} |
||
* {{ |
* {{Citation |last1=Biscardi |first1=Afrânio |title=O Mecenato Artístico de D. Pedro II e o Projeto Imperial |date=May 2006 |url=http://www.dezenovevinte.net/ensino_artistico/mecenato_dpedro.htm |work=19&20 – A revista eletrônica de DezenoveVinte |volume=I |issue=1 |last2=Rocha |first2=Frederico Almeida}} |
||
* [[C. R. Boxer|Boxer, Charles R.]] |
* [[C. R. Boxer|Boxer, Charles R.]] ''The Portuguese Seaborne Empire'' (1969) |
||
** ''O império marítimo português 1415–1825''. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 2002. {{ISBN|85-359-0292-9}} |
|||
* Bueno, Eduardo. ''Brasil: uma História''. São Paulo: Ática, 2003. {{ISBN|85-08-08213-4}} |
* Bueno, Eduardo. ''Brasil: uma História''. São Paulo: Ática, 2003. {{ISBN|85-08-08213-4}} |
||
* Calmon, Pedro. ''História da Civilização Brasileira''. Brasília: Senado Federal, 2002 |
* Calmon, Pedro. ''História da Civilização Brasileira''. Brasília: Senado Federal, 2002 |
||
| Line 1,016: | Line 716: | ||
* Diégues, Fernando. ''A revolução brasílica''. Rio de Janeiro: Objetiva, 2004 |
* Diégues, Fernando. ''A revolução brasílica''. Rio de Janeiro: Objetiva, 2004 |
||
* ''[[Barsa (encyclopedia)|Enciclopédia Barsa]]''. Volume 4: Batráquio – Camarão, Filipe. Rio de Janeiro: Encyclopædia Britannica do Brasil, 1987 |
* ''[[Barsa (encyclopedia)|Enciclopédia Barsa]]''. Volume 4: Batráquio – Camarão, Filipe. Rio de Janeiro: Encyclopædia Britannica do Brasil, 1987 |
||
* {{Cite book |last=Ermakoff |first=George |title=Rio de Janeiro – 1840–1900 – Uma crônica fotográfica |publisher=G. Ermakoff Casa Editorial |year=2006 |isbn=978-85-98815-05-3 |location=Rio de Janeiro |language=pt}} |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last1 = Ermakoff |
|||
| first1 = George |
|||
| year = 2006 |
|||
| language = Portuguese |
|||
| title = Rio de Janeiro – 1840–1900 – Uma crônica fotográfica |
|||
| publisher = G. Ermakoff Casa Editorial |
|||
| location = Rio de Janeiro |
|||
| isbn = 978-85-98815-05-3 |
|||
| ref = harv |
|||
}} |
|||
* Fausto, Boris and Devoto, Fernando J. ''Brasil e Argentina: Um ensaio de história comparada (1850–2002)'', 2nd ed. São Paulo: Editoria 34, 2005. {{ISBN|85-7326-308-3}} |
* Fausto, Boris and Devoto, Fernando J. ''Brasil e Argentina: Um ensaio de história comparada (1850–2002)'', 2nd ed. São Paulo: Editoria 34, 2005. {{ISBN|85-7326-308-3}} |
||
* [[Elio Gaspari|Gaspari, Elio]]. ''A ditadura envergonhada''. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 2002. {{ISBN|85-359-0277-5}} |
* [[Elio Gaspari|Gaspari, Elio]]. ''A ditadura envergonhada''. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 2002. {{ISBN|85-359-0277-5}} |
||
* Janotti, Aldo. ''O Marquês de Paraná: inícios de uma carreira política num momento crítico da história da nacionalidade''. Belo Horizonte: Itatiaia, 1990 |
* Janotti, Aldo. ''O Marquês de Paraná: inícios de uma carreira política num momento crítico da história da nacionalidade''. Belo Horizonte: Itatiaia, 1990 |
||
* Lyra, Heitor. ''História de Dom Pedro II (1825–1891): Ascenção (1825–1870). v. 1''. Belo Horizonte: Itatiaia, 1977 |
* Lyra, Heitor. ''História de Dom Pedro II (1825–1891): Ascenção (1825–1870). v. 1''. Belo Horizonte: Itatiaia, 1977 |
||
| Line 1,037: | Line 727: | ||
* Peres, Damião (1949) ''O Descobrimento do Brasil por Pedro Álvares Cabral: antecedentes e intencionalidade'' Porto: Portucalense. |
* Peres, Damião (1949) ''O Descobrimento do Brasil por Pedro Álvares Cabral: antecedentes e intencionalidade'' Porto: Portucalense. |
||
* Scheina, Robert L. ''Latin America: A Naval History, 1810–1987''. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press, 1987. {{ISBN|0-87021-295-8}} |
* Scheina, Robert L. ''Latin America: A Naval History, 1810–1987''. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press, 1987. {{ISBN|0-87021-295-8}} |
||
* {{Cite Q|Q18238040|ref={{harvid|Schwarcz|1998}}}} |
|||
* Schwarcz, Lilia Moritz. ''As barbas do Imperador: D. Pedro II, um monarca nos trópicos''. 2nd ed. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 1998. {{ISBN|85-7164-837-9}} |
|||
* [[Stuart B. Schwartz]] ''Sovereignty and Society in Colonial Brazil'' (1973) |
|||
* [[Thomas Skidmore|Skidmore, Thomas E]]. ''Uma História do Brasil''. 4th ed. São Paulo: Paz e Terra, 2003. {{ISBN|85-219-0313-8}} |
|||
** ''Early Latin America'' (1983) |
|||
** ''Sugar Plantations in the Formation of Brazilian Society'' (1985) |
|||
* [[Thomas Skidmore|Skidmore, Thomas E]]. ''Brazil: Five Centuries of Change'' (Oxford University Press, 1999) |
|||
** ''Uma História do Brasil''. 4th ed. São Paulo: Paz e Terra, 2003. {{ISBN|85-219-0313-8}} |
|||
* Souza, Adriana Barreto de. ''Duque de Caxias: o homem por trás do monumento''. Rio de Janeiro: Civilização Brasileira, 2008. {{ISBN|978-85-200-0864-5}}. |
* Souza, Adriana Barreto de. ''Duque de Caxias: o homem por trás do monumento''. Rio de Janeiro: Civilização Brasileira, 2008. {{ISBN|978-85-200-0864-5}}. |
||
* {{wikicite|ref={{harvid|Wright|1992}}|reference=Wright, Simon. 1992. ''Villa-Lobos''. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. {{ISBN|0-19-315475-7}}}} |
* {{wikicite|ref={{harvid|Wright|1992}}|reference=Wright, Simon. 1992. ''Villa-Lobos''. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. {{ISBN|0-19-315475-7}}}} |
||
* Vainfas, Ronaldo. ''Dicionário do Brasil Imperial''. Rio de Janeiro: Objetiva, 2002. {{ISBN|85-7302-441-0}} |
* Vainfas, Ronaldo. ''Dicionário do Brasil Imperial''. Rio de Janeiro: Objetiva, 2002. {{ISBN|85-7302-441-0}} |
||
* Vesentini, José William. ''Brasil, sociedade e espaço – Geografia do Brasil''. 7th Ed. São Paulo: Ática, 1988 |
* Vesentini, José William. ''Brasil, sociedade e espaço – Geografia do Brasil''. 7th Ed. São Paulo: Ática, 1988 |
||
* Vianna, Hélio. ''História do Brasil: período colonial, monarquia e república'', 15th ed. São Paulo: Melhoramentos, 1994 |
* Vianna, Hélio. ''História do Brasil: período colonial, monarquia e república'', 15th ed. São Paulo: Melhoramentos, 1994 |
||
* Zirin, Dave. ''Brazil's Dance with the Devil: The World Cup, The Olympics, and the Fight for Democracy'' Haymarket Books 2014. {{ISBN|978-1-60846-360-2}} |
* Zirin, Dave. ''Brazil's Dance with the Devil: The World Cup, The Olympics, and the Fight for Democracy'' Haymarket Books 2014. {{ISBN|978-1-60846-360-2}} |
||
{{Refend}} |
{{Refend}} |
||
==Further reading== |
== Further reading == |
||
{{Refbegin| |
{{Refbegin|indent=yes|2}} |
||
* Alencastro Felipe, Luiz Felipe de. ''The Trade in the Living: The Formation of Brazil in the South Atlantic, Sixteenth to Seventeenth Centuries'' (SUNY Press, 2019) |
|||
* {{cite book |author=Alves, Maria Helena Moreira |title=State and Opposition in Military Brazil |location=Austin, TX |publisher=University of Texas Press |year=1985}} |
|||
* {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Alves, Maria Helena Moreira |title=State and Opposition in Military Brazil |publisher=University of Texas Press |year=1985 |location=Austin, TX}} |
||
* {{Cite book |last=Amann, Edmund |title=The Illusion of Stability: The Brazilian Economy under Cardoso |publisher=World Development (pp. 1805–19) |year=1990}} |
|||
* {{cite web |title=Background Note: Brazil |publisher=US Department of State |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35640.htm |accessdate=16 June 2011}} |
|||
* {{ |
* {{Cite web |title=Background Note: Brazil |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35640.htm |access-date=16 June 2011 |publisher=US Department of State}} |
||
* {{Cite book |last=Bellos, Alex |url=https://archive.org/details/futebolbrazilian0000bell |title=Futebol: The Brazilian Way of Life |publisher=Bloomsbury Publishing plc |year=2003 |location=London |url-access=registration}} |
|||
* {{cite book |author=Bethell, Leslie |title=Colonial Brazil |location=Cambridge |publisher=CUP |year=1991}} |
|||
* {{Cite book |last=Bethell, Leslie |title=Colonial Brazil |publisher=CUP |year=1991 |location=Cambridge}} |
|||
* {{cite book |author=Costa, João Cruz |title=A History of Ideas in Brazil |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofideasin0000cost |url-access=registration |location=Los Angeles, CA |publisher=University of California Press |year=1964}} |
|||
* {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Costa, João Cruz |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofideasin0000cost |title=A History of Ideas in Brazil |publisher=University of California Press |year=1964 |location=Los Angeles, CA |url-access=registration}} |
||
* {{Cite book |last=Fausto, Boris |title=A Concise History of Brazil |publisher=CUP |year=1999 |location=Cambridge}} |
|||
* {{cite book |author=Furtado, Celso |title=The Economic Growth of Brazil: A Survey from Colonial to Modern Times |url=https://archive.org/details/economicgrowthof0000furt |url-access=registration |location=Berkeley, CA |publisher=University of California Press}} |
|||
* {{Cite book |last=Furtado, Celso |url=https://archive.org/details/economicgrowthof0000furt |title=The Economic Growth of Brazil: A Survey from Colonial to Modern Times |publisher=University of California Press |year=1963 |location=Berkeley, CA |url-access=registration}} |
|||
* {{cite book |author=Leal, Victor Nunes |title=Coronelismo: The Municipality and Representative Government in Brazil |location=Cambridge |publisher=CUP |year=1977}} |
|||
* {{Cite EB1911|wstitle= Brazil | volume= 4 |last1= Lamoureux |first1= Andrew Jackson |author1-link= |last2= and three others |first2= |author2-link= | pages = 438–463 |short= 1}} |
|||
* {{cite book |author=Malathronas, John |title=Brazil: Life, Blood, Soul |location=Chichester |publisher=Summersdale |year=2003}} |
|||
* {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Leal, Victor Nunes |title=Coronelismo: The Municipality and Representative Government in Brazil |publisher=CUP |year=1977 |location=Cambridge}} |
||
* Levine, Robert M. ''Historical Dictionary of Brazil'' (2019) |
|||
* {{cite book |author=Prado Júnior, Caio |title=The Colonial Background of Modern Brazil |location=Los Angeles, CA |publisher=University of California Press |year=1967}} |
|||
* {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Malathronas, John |title=Brazil: Life, Blood, Soul |publisher=Summersdale |year=2003 |location=Chichester}} |
||
* {{Cite book |last=Martinez-Lara, Javier |title=Building Democracy in Brazil: The Politics of Constitutional Change |publisher=Macmillan |year=1995}} |
|||
* {{cite book |author=Skidmore, Thomas E. |title=Black into White: Race and Nationality in Brazilian Thought |url=https://archive.org/details/blackintowhitera0000skid |url-access=registration |location=Oxford |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1974}} |
|||
* {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Prado Júnior, Caio |title=The Colonial Background of Modern Brazil |publisher=University of California Press |year=1967 |location=Los Angeles, CA}} |
||
* {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Schneider, Ronald |title=Brazil: Culture and Politics in a New Economic Powerhouse |publisher=Boulder Westview |year=1995}} |
||
* {{Cite book |last=Skidmore, Thomas E. |url=https://archive.org/details/blackintowhitera0000skid |title=Black into White: Race and Nationality in Brazilian Thought |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1974 |isbn=978-0-19-501776-2 |location=Oxford |url-access=registration}} |
|||
* {{Cite book |last=Wagley, Charles |title=An Introduction to Brazil |publisher=Columbia University Press |year=1963 |location=New York, New York}} |
|||
{{Refend}} |
{{Refend}} |
||
==External links== |
== External links == |
||
<!-- {{No more links}} |
|||
Please be cautious adding more external links. |
Please be cautious adding more external links. |
||
| Line 1,090: | Line 786: | ||
* {{Wikiatlas|Brazil}} |
* {{Wikiatlas|Brazil}} |
||
* {{osmrelation-inline|59470}} |
* {{osmrelation-inline|59470}} |
||
{{Anchor|Related information}}<!-- |
{{Anchor|Related information}}<!-- Target for Navbox link at See also section --> |
||
{{Brazil topics}} |
{{Brazil topics}} |
||
{{Navboxes |
{{Navboxes |
||
| Line 1,096: | Line 792: | ||
|list1= |
|list1= |
||
{{navboxes|title=[[File:Gnome-globe.svg|25px]]{{nbsp}}Geographic locale|list= |
{{navboxes|title=[[File:Gnome-globe.svg|25px]]{{nbsp}}Geographic locale|list= |
||
'''[[Geographic coordinate system|Lat. {{small|and}} Long.]] {{Coord|15|45|S|47|57|W|display=inline}} {{color|darkblue|( |
'''[[Geographic coordinate system|Lat. {{small|and}} Long.]] {{Coord|15|45|S|47|57|W|display=inline}} {{color|darkblue|(Brasília)}}''' |
||
{{Countries of South America}} |
{{Countries of South America}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 1,114: | Line 810: | ||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
{{Coord|10|S|52|W|display=title}} |
|||
[[Category:Brazil| ]]<!--leave the empty space as for standard--> |
|||
[[Category:Brazil| ]]<!--Leave the empty space as standard.--> |
|||
[[Category:Countries in South America]] |
[[Category:Countries in South America]] |
||
[[Category:Federal constitutional republics]] |
[[Category:Federal constitutional republics]] |
||
[[Category:Former Portuguese colonies]] |
[[Category:Former Portuguese colonies]] |
||
[[Category:Southern Cone countries]] |
|||
[[Category:G15 nations]] |
[[Category:G15 nations]] |
||
[[Category:G20 |
[[Category:G20 members]] |
||
[[Category:Member states of Mercosur]] |
[[Category:Member states of Mercosur]] |
||
[[Category:Member states of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries]] |
[[Category:Member states of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries]] |
||
[[Category:Member states of the United Nations]] |
[[Category:Member states of the United Nations]] |
||
[[Category:Newly industrializing countries]] |
[[Category:Newly industrializing countries]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Countries and territories where Portuguese is an official language]] |
||
[[Category:States and territories established in 1822]] |
[[Category:States and territories established in 1822]] |
||
[[Category:BRICS nations]] |
[[Category:BRICS nations]] |
||
[[Category:E7 nations]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 14:24, 24 November 2024
Federative Republic of Brazil República Federativa do Brasil | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Ordem e Progresso "Order and Progress" | |
| Anthem: Hino Nacional Brasileiro "Brazilian National Anthem" | |
National Seal
| |
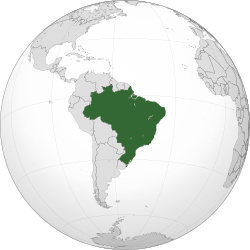 | |
| Capital | Brasília 15°47′S 47°52′W / 15.783°S 47.867°W |
| Largest city | São Paulo 23°33′S 46°38′W / 23.550°S 46.633°W |
| Official language and national language | Portuguese |
| Recognized regional languages | See regional official languages |
| Ethnic groups (2022)[2] |
|
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Brazilian |
| Government | Federal presidential republic |
| Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva | |
| Geraldo Alckmin | |
| Arthur Lira | |
| Rodrigo Pacheco | |
| Luís Roberto Barroso | |
| Legislature | National Congress |
| Federal Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Independence from Portugal | |
• Declared | 7 September 1822 |
| 29 August 1825 | |
• Republic | 15 November 1889 |
| 5 October 1988 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 8,515,767 km2 (3,287,956 sq mi) (5th) |
• Water (%) | 0.65 |
| Population | |
• 2022 census | |
• Density | 23.8[6]/km2 (61.6/sq mi) (193rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2022) | high inequality |
| HDI (2022) | high (89th) |
| Currency | Real (R$) (BRL) |
| Time zone | UTC−2 to −5 (BRT) |
| DST is not observed. | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (CE) |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +55 |
| ISO 3166 code | BR |
| Internet TLD | .br |
Brazil,[b] officially the Federative Republic of Brazil,[c] is the largest and easternmost country in South America and Latin America. It is the world's fifth-largest country by area and one of the most populated countries. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. Brazil is a federation composed of 26 states and a Federal District. It is the only country in the Americas where Portuguese is an official language.[11][12] Brazil is among the world's most multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass immigration from around the world.[13]
Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of 7,491 kilometers (4,655 mi).[14] Covering roughly half of South America's land area, it borders all other countries and territories on the continent except Ecuador and Chile.[15] Brazil's Amazon basin includes a vast tropical forest home to diverse wildlife, a variety of ecological systems, and extensive natural resources spanning numerous protected habitats.[14] This unique environmental heritage positions Brazil at number one of 17 megadiverse countries. The country's natural richness is also the subject of significant global interest, as environmental degradation (through processes such as deforestation) has direct impacts on global issues such as climate change and biodiversity loss.
The territory of present-day Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral in 1500. Subsequently claimed by the Portuguese Empire, Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. Slavery was abolished in 1888. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d'état. An authoritarian military dictatorship emerged in 1964 and ruled until 1985, after which civilian governance resumed. Brazil's current constitution, formulated in 1988, defines it as a democratic federal republic.[16] Due to its rich culture and history, the country ranks thirteenth in the world by number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.[17]
Brazil is a regional and middle power[18][19][20] that is an emerging power[21][22][23][24] and a major non-NATO ally of the United States.[25] Categorized as a developing country, Brazil is considered an advanced emerging economy,[26] having the one of the-largest GDP in the world in both nominal and PPP terms—the largest in Latin America and the Southern Hemisphere.[7][27] Classified as an upper-middle income economy by the World Bank,[28] and a newly industrialized country by the IMF,[29] Brazil has the largest share of wealth and the most complex economy in South America. It is also one of the world's major breadbaskets, being the largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years.[30] Despite its growing economic and global profile, the country continues to face high levels of corruption, crime and social inequality. Brazil is a founding member of the United Nations, the G20, BRICS, G4, Mercosul, Organization of American States, Organization of Ibero-American States and the Community of Portuguese Language Countries and also an observer state of the Arab League.[31]
Etymology
The word Brazil probably comes from the Portuguese word for brazilwood, a tree that once grew plentifully along the Brazilian coast.[32] In Portuguese, brazilwood is called pau-brasil, with the word brasil commonly given the etymology "red like an ember", formed from brasa ('ember') and the suffix -il (from -iculum or -ilium).[33] It has alternatively been suggested that this is a folk etymology for a word for the plant related to an Arabic or Asian word for a red plant.[34] As brazilwood produces a deep red dye, it was highly valued by the European textile industry and was the earliest commercially exploited product from Brazil.[35] Throughout the 16th century, massive amounts of brazilwood were harvested by indigenous peoples (mostly Tupi) along the Brazilian coast, who sold the timber to European traders (mostly Portuguese, but also French) in return for assorted European consumer goods.[36]
The official Portuguese name of the land, in original Portuguese records, was the "Land of the Holy Cross" (Terra da Santa Cruz),[37] but European sailors and merchants commonly called it the "Land of Brazil" (Terra do Brasil) because of the brazilwood trade.[38] The popular appellation eclipsed and eventually supplanted the official Portuguese name. Some early sailors called it the "Land of Parrots".[39]
In the Guaraní language, an official language of Paraguay, Brazil is called "Pindorama", meaning 'land of the palm trees'.[40]
History
Pre-Cabraline era

Some of the earliest human remains found in the Americas, Luzia Woman, were found in the area of Pedro Leopoldo, Minas Gerais and provide evidence of human habitation going back at least 11,000 years.[42][43] The earliest pottery ever found in the Western Hemisphere was excavated in the Amazon basin of Brazil and radiocarbon dated to 8,000 years ago (6000 BC). The pottery was found near Santarém and provides evidence that the region supported a complex prehistoric culture.[44] The Marajoara culture flourished on Marajó in the Amazon delta from AD 400 to 1400, developing sophisticated pottery, social stratification, large populations, mound building, and complex social formations such as chiefdoms.[45]
Around the time of the Portuguese arrival, the territory of current day Brazil had an estimated indigenous population of 7 million people,[46] mostly semi-nomadic, who subsisted on hunting, fishing, gathering, and migrant agriculture. The population comprised several large indigenous ethnic groups (e.g., the Tupis, Guaranis, Gês, and Arawaks). The Tupi people were subdivided into the Tupiniquins and Tupinambás.[47]
Before the arrival of the Europeans, the boundaries between these groups and their subgroups were marked by wars that arose from differences in culture, language and moral beliefs.[48] These wars also involved large-scale military actions on land and water, with cannibalistic rituals on prisoners of war.[49][50] While heredity had some weight, leadership was a status more won over time than assigned in succession ceremonies and conventions.[48] Slavery among the indigenous groups had a different meaning than it had for Europeans, since it originated from a diverse socioeconomic organization, in which asymmetries were translated into kinship relations.[51]
Portuguese colonization
Following the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas, the land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral.[53] The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several ethnic societies, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family and fought among themselves.[54] Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King John III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous captaincies.[55][56]
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil in the city of Salvador, which became the capital of a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America.[56][57] In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other.[58][59][60][61]
By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil's most important export,[54][62] while slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa in the slave market of Western Africa[63] (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import,[64][65] to cope with sugarcane plantations, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar.[66][67] Brazil received more than 2.8 million slaves from Africa between the years 1500 and 1800.[68]
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline[69] and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony's economy, fostering a gold rush[70] which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world.[71] This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.[72]
Portuguese expeditions known as bandeiras gradually expanded Brazil's original colonial frontiers in South America to its approximately current borders.[73][74] In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.[75]
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal's wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares,[76] and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Gerais Conspiracy.[77]
Elevation to kingdom

In late 1807, Spanish and Napoleonic forces threatened the security of continental Portugal, causing Prince Regent John, in the name of Queen Maria I, to move the royal court from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro.[78] There they established some of Brazil's first financial institutions, such as its local stock exchanges[79] and its National Bank, additionally ending the Portuguese monopoly on Brazilian trade and opening Brazil's ports to other nations. In 1809, in retaliation for being forced into exile, the Prince Regent ordered the conquest of French Guiana.[80]
With the end of the Peninsular War in 1814, the courts of Europe demanded that Queen Maria I and Prince Regent John return to Portugal, deeming it unfit for the head of an ancient European monarchy to reside in a colony. In 1815, to justify continuing to live in Brazil, where the royal court had thrived for six years, the Crown established the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves, thus creating a pluricontinental transatlantic monarchic state.[81] However, the leadership in Portugal, resentful of the new status of its larger colony, continued to demand the return of the court to Lisbon (see Liberal Revolution of 1820). In 1821, acceding to the demands of revolutionaries who had taken the city of Porto,[82] John VI departed for Lisbon. There he swore an oath to the new constitution, leaving his son, Prince Pedro de Alcântara, as Regent of the Kingdom of Brazil.[83]
Independent empire

Tensions between Portuguese and Brazilians increased and the Portuguese Cortes, guided by the new political regime imposed by the Liberal Revolution, tried to re-establish Brazil as a colony.[84] The Brazilians refused to yield, and Prince Pedro decided to stand with them, declaring the country's independence from Portugal on 7 September 1822.[85] A month later, Prince Pedro was declared the first Emperor of Brazil, with the royal title of Dom Pedro I, resulting in the founding of the Empire of Brazil.[86]
The Brazilian War of Independence, which had already begun along this process, spread through the northern, northeastern regions and in the Cisplatina province.[87] The last Portuguese soldiers surrendered on 8 March 1824;[88] Portugal officially recognized Brazilian independence on 29 August 1825.[89]
On 7 April 1831, worn down by years of administrative turmoil and political dissent with both liberal and conservative sides of politics, including an attempt of republican secession[90] and unreconciled to the way that absolutists in Portugal had given in the succession of King John VI, Pedro I departed for Portugal to reclaim his daughter's crown after abdicating the Brazilian throne in favor of his five-year-old son and heir (Dom Pedro II).[91]

As the new Emperor could not exert his constitutional powers until he came of age, a regency was set up by the National Assembly.[92] In the absence of a charismatic figure who could represent a moderate face of power, during this period a series of localized rebellions took place, such as the Cabanagem in Grão-Pará, the Malê Revolt in Salvador, the Balaiada (Maranhão), the Sabinada (Bahia), and the Ragamuffin War, which began in Rio Grande do Sul and was supported by Giuseppe Garibaldi. These emerged from the provinces' dissatisfaction with the central power, coupled with old and latent social tensions peculiar to a vast, slaveholding and newly independent nation state.[93] This period of internal political and social upheaval, which included the Praieira revolt in Pernambuco, was overcome only at the end of the 1840s, years after the end of the regency, which occurred with the premature coronation of Pedro II in 1841.[94]
During the last phase of the monarchy, internal political debate centered on the issue of slavery. The Atlantic slave trade was abandoned in 1850,[95] as a result of the British Aberdeen Act and the Eusébio de Queirós Law, but only in May 1888, after a long process of internal mobilization and debate for an ethical and legal dismantling of slavery in the country, was the institution formally abolished with the approval of the Golden Law.[96]
The foreign-affairs policies of the monarchy dealt with issues with the countries of the Southern Cone with whom Brazil had borders. Long after the Cisplatine War that resulted in the independence of Uruguay,[97] Brazil won three international wars during the 58-year reign of Pedro II: the Platine War, the Uruguayan War and the devastating Paraguayan War, the largest war effort in Brazilian history.[98][99]
Although there was no desire among the majority of Brazilians to change the country's form of government,[100] on 15 November 1889, in disagreement with the majority of the Imperial Army officers, as well as with rural and financial elites (for different reasons), the monarchy was overthrown by a military coup.[101] A few days later, the national flag was replaced with a new design that included the national motto "Ordem e Progresso", influenced by positivism. 15 November is now Republic Day, a national holiday.[102]
Early republic
The early republican government was a military dictatorship, with the army dominating affairs both in Rio de Janeiro and in the states. Freedom of the press disappeared and elections were controlled by those in power.[103] Not until 1894, following an economic crisis and a military one, did civilians take power, remaining there until October 1930.[104][105][106]
In relation to its foreign policy, the country in this first republican period maintained a relative balance characterized by a success in resolving border disputes with neighboring countries,[107] only broken by the Acre War (1899–1902) and its involvement in World War I (1914–1918),[108][109][110] followed by a failed attempt to exert a prominent role in the League of Nations;[111] Internally, from the crisis of Encilhamento[112][113][114] and the Navy Revolts,[115] a prolonged cycle of financial, political and social instability began until the 1920s, keeping the country besieged by various rebellions, both civilian[116][117][118] and military.[119][120][121]
Little by little, a cycle of general instability sparked by these crises undermined the regime to such an extent that in the wake of the murder of his running mate, the defeated opposition presidential candidate Getúlio Vargas, supported by most of the military, successfully led the Revolution of 1930.[122][123] Vargas and the military were supposed to assume power temporarily, but instead closed down Congress, extinguished the Constitution, ruled with emergency powers and replaced the states' governors with his own supporters.[124][125]
In the 1930s, three attempts to remove Vargas and his supporters from power failed. The first was the Constitutionalist Revolution in 1932, led by São Paulo's oligarchy. The second was a Communist uprising in November 1935, and the last one a putsch attempt by local fascists in May 1938.[126][127][128] The 1935 uprising created a security crisis in which Congress transferred more power to the executive branch. The 1937 coup d'état resulted in the cancellation of the 1938 election and formalized Vargas as dictator, beginning the Estado Novo era. During this period, government brutality and censorship of the press increased.[129]
During World War II, Brazil remained neutral until August 1942, when the country suffered retaliation by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy in a strategic dispute over the South Atlantic, and, therefore, entered the war on the allied side.[130][131][132] In addition to its participation in the battle of the Atlantic, Brazil also sent an expeditionary force to fight in the Italian campaign.[133]
With the Allied victory in 1945 and the end of the fascist regimes in Europe, Vargas's position became unsustainable, and he was swiftly overthrown in another military coup, with democracy "reinstated" by the same army that had ended it 15 years earlier.[134] Vargas committed suicide in August 1954 amid a political crisis, after having returned to power by election in 1950.[135][136]
Contemporary era

Several brief interim governments followed Vargas's suicide.[137] Juscelino Kubitschek became president in 1956 and assumed a conciliatory posture towards the political opposition that allowed him to govern without major crises.[138] The economy and industrial sector grew remarkably,[139] but his greatest achievement was the construction of the new capital city of Brasília, inaugurated in 1960.[140] Kubitschek's successor, Jânio Quadros, resigned in 1961 less than a year after taking office.[141] His vice-president, João Goulart, assumed the presidency, but aroused strong political opposition[142] and was deposed in April 1964 by a coup that resulted in a military dictatorship.[143]

The new regime was intended to be transitory[144] but gradually closed in on itself and became a full dictatorship with the promulgation of the Fifth Institutional Act in 1968.[145] Oppression was not limited to those who resorted to guerrilla tactics to fight the regime, but also reached institutional opponents, artists, journalists and other members of civil society,[146][147] inside and outside the country through the infamous "Operation Condor".[148][149] Like other brutal authoritarian regimes, due to an economic boom, known as the "economic miracle", the regime reached a peak in popularity in the early 1970s.[150]
Slowly, however, the wear and tear of years of dictatorial power had not slowed the repression, even after the defeat of the leftist guerrillas.[151] The inability to deal with the economic crises of the period and popular pressure made an opening policy inevitable, which from the regime side was led by Generals Ernesto Geisel and Golbery do Couto e Silva.[152] With the enactment of the Amnesty Law in 1979, Brazil began a slow return to democracy, which was completed during the 1980s.[94]

Civilians returned to power in 1985 when José Sarney assumed the presidency. He became unpopular during his tenure through failure to control the economic crisis and hyperinflation he inherited from the military regime.[153] Sarney's unsuccessful government led to the election in 1989 of the almost-unknown Fernando Collor, who was subsequently impeached by the National Congress in 1992.[154] Collor was succeeded by his vice-president, Itamar Franco, who appointed Fernando Henrique Cardoso Minister of Finance. In 1994, Cardoso produced a highly successful Plano Real,[155] that, after decades of failed economic plans made by previous governments attempting to curb hyperinflation, finally stabilized the Brazilian economy.[156][157] Cardoso won the 1994 election, and again in 1998.[158]
The peaceful transition of power from Cardoso to his main opposition leader, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva (elected in 2002 and re-elected in 2006), was seen as proof that Brazil had achieved a long-sought political stability.[159][160] However, sparked by indignation and frustrations accumulated over decades from corruption, police brutality, inefficiencies of the political establishment and public service, numerous peaceful protests erupted in Brazil in the middle of the first term of Dilma Rousseff, who had succeeded Lula after winning election in 2010 and again in 2014 by narrow margins.[161][162]
Rousseff was impeached by the Brazilian Congress in 2016, halfway into her second term,[163][164] and replaced by her Vice-president Michel Temer, who assumed full presidential powers after Rousseff's impeachment was accepted on 31 August. Large street protests for and against her took place during the impeachment process.[165] The charges against her were fueled by political and economic crises along with evidence of involvement with politicians from all the primary political parties. In 2017, the Supreme Court requested the investigation of 71 Brazilian lawmakers and nine ministers of President Michel Temer's cabinet who were allegedly linked to the Petrobras corruption scandal.[166] President Temer himself was also accused of corruption.[167] According to a 2018 poll, 62% of the population said that corruption was Brazil's biggest problem.[168]
In the fiercely disputed 2018 elections, the controversial conservative candidate Jair Bolsonaro of the Social Liberal Party (PSL) was elected president, winning in the second round against Fernando Haddad, of the Workers Party (PT), with the support of 55.13% of the valid votes.[169] In the early 2020s, Brazil became one of the hardest hit countries during the COVID-19 pandemic, receiving the second-highest death toll worldwide after the United States.[170] In May 2021, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva stated that he would run for a third term in the 2022 Brazilian general election against Bolsonaro.[171] In October 2022, Lula was in first place in the first round, with 48.43% of the support from the electorate, and received 50.90% of the votes in the second round.[172][173] On 8 January 2023, a week after Lula's inauguration, a mob of Bolsonaro's supporters attacked Brazil's federal government buildings in the capital, Brasília, after several weeks of unrest.[174][175]
Geography
Brazil occupies a large area along the eastern coast of South America and includes much of the continent's interior,[176] sharing land borders with Uruguay to the south; Argentina and Paraguay to the southwest; Bolivia and Peru to the west; Colombia to the northwest; and Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname and France (French overseas region of French Guiana) to the north. It shares a border with every South American country except Ecuador and Chile.[14]
The brazilian territory also encompasses a number of oceanic archipelagos, such as Fernando de Noronha, Rocas Atoll, Saint Peter and Paul Rocks, and Trindade and Martim Vaz.[14] Its size, relief, climate, and natural resources make Brazil geographically diverse.[176] Including its Atlantic islands, Brazil lies between latitudes 6°N and 34°S, and longitudes 28° and 74°W.[14]
Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world, and third largest in the Americas, with a total area of 8,515,767.049 km2 (3,287,956 sq mi),[177] including 55,455 km2 (21,411 sq mi) of water. North to South, Brazil is also the longest country in the world, spanning 4,395 km (2,731 mi) from north to south,[14] and the only country in the world that has the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn running through it.[14] It spans four time zones; from UTC−5 comprising the state of Acre and the westernmost portion of Amazonas, to UTC−4 in the western states, to UTC−3 in the eastern states (the national time) and UTC−2 in the Atlantic islands.[178]
Climate

The climate of Brazil comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a large area and varied topography, but most of the country is tropical.[14] According to the Köppen system, Brazil hosts six major climatic subtypes: desert, equatorial, tropical, semiarid, oceanic and subtropical. The different climatic conditions produce environments ranging from equatorial rainforests in the north and semiarid deserts in the northeast, to temperate coniferous forests in the south and tropical savannas in central Brazil.[179]
In Brazil, forest cover is around 59% of the total land area, equivalent to 496,619,600 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, down from 588,898,000 hectares (ha) in 1990. In 2020, naturally regenerating forest covered 485,396,000 hectares (ha) and planted forest covered 11,223,600 hectares (ha). Of the naturally regenerating forest, 44% was reported to be primary forest (consisting of native tree species with no clearly visible indications of human activity) and around 30% of the forest area was found within protected areas. For 2015, 56.% of the forest area was reported to be under public ownership and 44% private ownership.[180][181]
Many regions have starkly different microclimates.[182][183] An equatorial climate characterizes much of northern Brazil. There is no real dry season, but there are some variations in the period of the year when most rain falls.[179] Temperatures average 25 °C (77 °F),[183] with more significant temperature variation between night and day than between seasons.[182] Over central Brazil, rainfall is more seasonal, characteristic of a savanna climate.[182] This region is as extensive as the Amazon basin but has a very different climate as it lies farther south at a higher altitude.[179] In the interior northeast, seasonal rainfall is even more extreme.[184] South of Bahia, near the coasts, and more southerly most of the state of São Paulo, the distribution of rainfall changes, with rain falling throughout the year.[179] The south enjoys subtropical conditions, with cool winters and average annual temperatures not exceeding 18 °C (64.4 °F);[183] winter frosts and snowfall are not rare in the highest areas.[179][182]
The semiarid climatic region generally receives less than 800 millimeters (31.5 in) of rain,[184] most of which generally falls in a period of three to five months of the year[185] and occasionally less than this, creating long periods of drought.[182] Brazil's 1877–78 Grande Seca (Great Drought), the worst in Brazil's history,[186] caused approximately half a million deaths.[187] A similarly devastating drought occurred in 1915.[188] In 2024, for the first time, "a drought has covered all the way from the North to the country’s Southeast". It is the strongest drought in Brazil since the beginning of measurement in the 1950s, covering almost 60% of the country's territory. The drought is linked to deforestation and climate change.[189][190][191]
Topography and hydrography

Brazilian topography is also diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. Much of the terrain lies between 200 meters (660 ft) and 800 meters (2,600 ft) in elevation.[192] The main upland area occupies most of the southern half of the country.[192] The northwestern parts of the plateau consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, rounded hills.[192]
The southeastern section is more rugged, with a complex mass of ridges and mountain ranges reaching elevations of up to 1,200 meters (3,900 ft).[192] These ranges include the Mantiqueira and Espinhaço mountains and the Serra do Mar.[192] In the north, the Guiana Highlands form a major drainage divide, separating rivers that flow south into the Amazon Basin from rivers that empty into the Orinoco River system, in Venezuela, to the north. The highest point in Brazil is the Pico da Neblina at 2,994 meters (9,823 ft), and the lowest is the Atlantic Ocean.[14]
Brazil has a dense and complex system of rivers, one of the world's most extensive, with eight major drainage basins, all of which drain into the Atlantic.[193] Major rivers include the Amazon (the world's second-longest river and the largest in terms of volume of water), the Paraná and its major tributary the Iguaçu (which includes the Iguazu Falls), the Negro, São Francisco, Xingu, Madeira and Tapajós rivers.[193]
Biodiversity and conservation

The wildlife of Brazil comprises all naturally occurring animals, plants, and fungi in the South American country. Home to 60% of the Amazon rainforest, which accounts for approximately one-tenth of all species in the world,[194] Brazil is considered to have the greatest biodiversity of any country on the planet, containing over 70% of all animal and plant species catalogued.[195] Brazil has the most known species of plants (55,000), freshwater fish (3,000) and mammals (over 689).[196] It also ranks third on the list of countries with the most bird species (1,832) and second with the most reptile species (744).[196] The number of fungal species is unknown but is large.[197] Brazil is second only to Indonesia as the country with the most endemic species.[198]
Brazil's large territory comprises different ecosystems, such as the Amazon rainforest, recognized as having the greatest biological diversity in the world,[199] with the Atlantic Forest and the Cerrado sustaining the greatest biodiversity.[200] In the south, the Araucaria moist forests grow under temperate conditions.[200] The rich wildlife of Brazil reflects the variety of natural habitats. Scientists estimate that the total number of plant and animal species in Brazil could approach four million, mostly invertebrates.[200] Larger mammals include carnivores pumas, jaguars, ocelots, rare bush dogs, and foxes, and herbivores peccaries, tapirs, anteaters, sloths, opossums and armadillos. Deer are plentiful in the south, and many species of New World monkeys are found in the northern rain forests.[200][201]

More than one-fifth of the Amazon rainforest in Brazil has been completely destroyed, and more than 70 mammals are endangered.[196] The threat of extinction comes from several sources, including deforestation and poaching. Extinction is even more problematic in the Atlantic Forest, where nearly 93% of the forest has been cleared.[203] Of the 202 endangered animals in Brazil, 171 are in the Atlantic Forest.[204] The Amazon rainforest has been under direct threat of deforestation since the 1970s because of rapid economic and demographic expansion. Extensive legal and illegal logging destroy forests the size of a small country per year, and with it a diverse series of species through habitat destruction and habitat fragmentation.[205] Since 1970, over 600,000 square kilometers (230,000 sq mi) of the Amazon rainforest have been cleared by logging.[206]
In 2017, preserved native vegetation occupied 61% of the Brazilian territory. Agriculture occupied only 8% of the national territory and pastures 19.7%.[207] For comparison, in 2019, although 43% of the entire European continent has forests, only 3% of the total forest area in Europe is of native forest.[208] Brazil has a strong interest in conservation, as its agriculture sector directly depends on its forests.[209] In 2020, the government of Brazil pledged to reduce its annual greenhouse gas emissions by 43% by 2030. It also sets an indicative target of reaching carbon neutrality by 2060 if the country gets 10 billion dollars per year.[210]
Government and politics


The form of government is a democratic federative republic, with a presidential system.[16] The president is both head of state and head of government of the Union and is elected for a four-year term,[16] with the possibility of re-election for a second successive term. The current president is Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva.[211] The President appoints the Ministers of State, who assist in government.[16]
Legislative houses in each political entity are the main source of law in Brazil. The National Congress is the Federation's bicameral legislature, consisting of the Chamber of Deputies and the Federal Senate. Judiciary authorities exercise jurisdictional duties almost exclusively. In 2021, the Economist Intelligence Unit's Democracy Index categorized Brazil as a "flawed democracy", ranking 46th in the report,[212] and Freedom House classified it as a free country at Freedom in the World report.[213]
The political-administrative organization of the Federative Republic of Brazil comprises the Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities.[16] The Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities, are the "spheres of government". The federation is set on five fundamental principles: sovereignty, citizenship, dignity of human beings, the social values of labor and freedom of enterprise, and political pluralism.[16]
The classic tripartite branches of government (executive, legislative and judicial under a checks and balances system) are formally established by the Constitution.[16] The executive and legislative are organized independently in all three spheres of government, while the judiciary is organized only at the federal and state and Federal District spheres. All members of the executive and legislative branches are directly elected.[214][215][216]
For most of its democratic history, Brazil has had a multi-party system, with proportional representation. Voting is compulsory for the literate between 18 and 70 years old and optional for illiterates and those between 16 and 18 or beyond 70.[16] The country has around 30 registered political parties. Twenty political parties are represented in Congress. It is common for politicians to switch parties, and thus the proportion of congressional seats held by particular parties changes regularly.[217]
Law

Brazilian law is based on the civil law legal system[218] and civil law concepts prevail over common law practice. Most of Brazilian law is codified, although non-codified statutes also represent a substantial part, playing a complementary role. Court decisions set out interpretive guidelines; however, they are seldom binding on other specific cases. Doctrinal works and the works of academic jurists have strong influence in law creation and in law cases. Judges and other judicial officials are appointed after passing entry exams.[214]
The legal system is based on the Federal Constitution, promulgated on 5 October 1988, and the fundamental law of Brazil. All other legislation and court decisions must conform to its rules.[219] As of July 2022[update], there have been 124 amendments.[220] The highest court is the Supreme Federal Court. States have their own constitutions, which must not contradict the Federal Constitution.[221] Municipalities and the Federal District have "organic laws" (leis orgânicas), which act in a similar way to constitutions.[222] Legislative entities are the main source of statutes, although in certain matters judiciary and executive bodies may enact legal norms.[16] Jurisdiction is administered by the judiciary entities, although in rare situations the Federal Constitution allows the Federal Senate to pass on legal judgments.[16] There are also specialized military, labor and electoral courts.[16]
Military
The armed forces of Brazil are the largest in Latin America by active personnel and the largest in terms of military equipment.[223] The country was considered the 9th largest military power on the planet in 2021.[224][225] It consists of the Brazilian Army (including the Army Aviation Command), the Brazilian Navy (including the Marine Corps and Naval Aviation) and the Brazilian Air Force. Brazil's conscription policy gives it one of the world's largest military forces, estimated at more than 1.6 million reservists annually.[226] The Air Force is the largest in Latin America and has about 700 crewed aircraft in service and effective about 67,000 personnel.[227]
Numbering close to 236,000 active personnel,[228] the Brazilian Army has the largest number of armored vehicles in South America, including armored transports and tanks.[229] The states' Military Police and the Military Firefighters Corps are described as an ancillary forces of the Army by the constitution, but are under the control of each state's governor.[16]
Brazil's navy once operated some of the most powerful warships in the world with the two Minas Geraes-class dreadnoughts, sparking a naval arms race between Argentina, Brazil, and Chile.[230] Today, it is a green water force and has a group of specialized elite in retaking ships and naval facilities, GRUMEC, unit specially trained to protect Brazilian oil platforms along its coast.[231] As of 2022[update], it is the only navy in Latin America that operates a helicopter carrier, NAM Atlântico and one of twelve navies in the world to operate or have one under construction.[232]
Foreign policy

Brazil's international relations are based on Article 4 of the Federal Constitution, which establishes non-intervention, self-determination, international cooperation and the peaceful settlement of conflicts as the guiding principles of Brazil's relationship with other countries and multilateral organizations.[233] According to the Constitution, the President has ultimate authority over foreign policy, while the Congress is tasked with reviewing and considering all diplomatic nominations and international treaties, as well as legislation relating to Brazilian foreign policy.[234]
Brazil's foreign policy is a by-product of the country's position as a regional power in Latin America, a leader among developing countries, and an emerging world power.[235] Brazilian foreign policy has generally been based on the principles of multilateralism, peaceful dispute settlement, and non-intervention in the affairs of other countries.[236] Brazil is a founding member state of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth, an international organization and political association of Lusophone nations.
An increasingly well-developed tool of Brazil's foreign policy is providing aid as a donor to other developing countries.[237] Brazil does not just use its growing economic strength to provide financial aid, but it also provides high levels of expertise and most importantly of all, a quiet non-confrontational diplomacy to improve governance levels.[237] Total aid is estimated to be around $1 billion per year, which includes.[237] In addition, Brazil already managed a peacekeeping mission in Haiti ($350 million) and makes in-kind contributions to the World Food Programme ($300 million).[237] The scale of this aid places it on par with China and India.[237] The Brazilian South-South aid has been described as a "global model in waiting".[238]
Law enforcement and crime

In Brazil, the Constitution establishes six different police agencies for law enforcement: Federal Police Department, Federal Highway Police, Federal Railroad Police, Federal, District and State Penal Police (included by the Constitutional Amendment No. 104, of 2019), Military Police and Civil Police. Of these, the first three are affiliated with federal authorities, the last two are subordinate to state governments and the Penal Police can be subordinated to the federal or state/district government. All police forces are overseen by the executive branch of the federal or state government.[16] The National Public Security Force also can act in public disorder situations arising anywhere in the country.[239]
The country has high levels of violent crime, such as gun violence and homicides. In 2012, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated the number of 32 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, one of the highest rates of homicide of the world.[240] The number considered acceptable by the WHO is about 10 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants.[241] In 2018, Brazil had a record 63,880 murders.[242] However, there are differences between the crime rates in the Brazilian states. While in São Paulo the homicide rate registered in 2013 was 10.8 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, in Alagoas it was 64.7 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants.[243]
Brazil also has high levels of incarceration. It had the third largest prison population in the world of approximately 700,000 prisoners as of June 2014, which put it only behind the United States (2,228,424) and China (1,701,344).[244] The high number of prisoners eventually overloaded the Brazilian prison system, leading to a shortfall of about 200,000 accommodations.[245]
Human rights
Human rights in Brazil include the right to life and freedom of speech; and condemnation of slavery and torture. The nation ratified the American Convention on Human Rights.[246] The 2017 Freedom in the World report by Freedom House gives Brazil a score of "2" for both political rights and civil liberties; "1" represents the most free, and "7", the least.[247]
However, the following human rights problems have been reported: torture of detainees and inmates by police and prison security forces; inability to protect witnesses involved in criminal cases; harsh conditions; prolonged pretrial detention and inordinate delays of trials; reluctance to prosecute as well as inefficiency in prosecuting government officials for corruption; violence and discrimination against women;[248] violence against children, including sexual abuse; human trafficking; police brutality;[249] discrimination against black and indigenous people;[250] failure to enforce labour laws; and child labour in the informal sector. Human rights violators often enjoy impunity.[251] According to UNESCO, "Brazil promotes a vast array of actions for the advancement and defense of human rights, even though it faces enormous social and economic inequalities".[252]Same-sex couples in Brazil have held nationwide marriage rights since May 2013.[253]
Political subdivisions
Brazil is a federation composed of 26 states, one federal district, and the 5,570 municipalities.[16] States have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the Federal government. They have a governor and a unicameral legislative body elected directly by their voters. They also have independent Courts of Law for common justice. Despite this, states have much less autonomy to create their own laws than in other federal states such as the United States. For example, criminal and civil laws can be voted by only the federal bicameral Congress and are uniform throughout the country.[16]
Municipalities, as the states, have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the federal and state government.[16] Each has an elected mayor and legislative body, but no separate Court of Law. Indeed, a Court of Law organized by the state can encompass many municipalities in a single justice administrative division called comarca (county).[16]
Brazil's constitution also provides for the creation of federal territories, which are administrative divisions directly controlled by the federal government. However, there are currently no federal territories in the country, as the 1988 Constitution abolished the last three: Amapá and Roraima (which gained statehood status) and Fernando de Noronha, which became a state district of Pernambuco.[254][255]
Economy




Brazil's upper-middle income mixed market economy is rich in natural resources.[259] It has the largest national economy in Latin America, the eighth-largest economy in the world by nominal GDP, and the eighth-largest by PPP. After rapid growth in preceding decades, the country entered an ongoing recession in 2014 amid a political corruption scandal and nationwide protests. A developing country, Brazil has a labor force of roughly 100 million,[260] which is the world's fifth-largest; with a high unemployment rate of 14.4% as of 2021[update].[261] Its foreign exchange reserves are the tenth-highest in the world.[262] The B3 in São Paulo is the largest stock exchange of Latin America by market capitalization. In regards to poverty, about 1.9% of the total population lives at $2.15 a day,[263] while about 19% live at $6.85 a day.[264] Brazil's economy suffers from endemic corruption and high income inequality.[265] The Brazilian real is the national currency.
Brazil's diversified economy includes agriculture, industry and a wide range of services.[266] The large service sector accounts for about 72.7% of total GDP, followed by the industrial sector (20.7%), while the agriculture sector is by far the smallest, making up 6.6% of total GDP.[267]
Brazil is one of the largest producers of various agricultural commodities,[268] and also has a large cooperative sector that provides 50% of the food in the country.[269] It has been the world's largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years.[30] Brazil is the world's largest producer of sugarcane, soy, coffee and orange; is one of the top 5 producers of maize, cotton, lemon, tobacco, pineapple, banana, beans, coconut, watermelon and papaya; and is one of the top 10 world producers of cocoa, cashew, mango, rice, tomato, sorghum, tangerine, avocado, persimmon, and guava, among others. Regarding livestock, it is one of the 5 largest producers of chicken meat, beef, pork and cow's milk in the world.[270] In the mining sector, Brazil is among the largest producers of iron ore, copper, gold,[271] bauxite, manganese, tin, niobium,[272] and nickel. In terms of precious stones, Brazil is the world's largest producer of amethyst, topaz, agate and one of the main producers of tourmaline, emerald, aquamarine, garnet and opal.[273][274] The country is a major exporter of soy, iron ore, pulp (cellulose), maize, beef, chicken meat, soybean meal, sugar, coffee, tobacco, cotton, orange juice, footwear, airplanes, cars, vehicle parts, gold, ethanol and semi-finished iron, among other products.[275][276]
Brazil is the world's 24th-largest exporter and 26th-largest importer as of 2021[update].[277][278] China is its largest trading partner, accounting for 32% of the total trade. Other large trading partners include the United States, Argentina, the Netherlands and Canada.[279] Its automotive industry is the eighth-largest in the world.[280] In the food industry, Brazil was the second-largest exporter of processed foods in the world in 2019.[281] The country was the second-largest producer of pulp in the world and the eighth-largest producer of paper in 2016.[282] In the footwear industry, Brazil was the fourth-largest producer in 2019.[283] It was also the ninth-largest producer of steel in the world.[284][285][286] In 2018, the chemical industry of Brazil was the eighth-largest in the world.[287][288][289] Although it was among the five largest world producers in 2013, Brazil's textile industry is very little integrated into world trade.[290]
The tertiary sector (trade and services) represented 75.8% of the country's GDP in 2018, according to the IBGE. The service sector was responsible for 60% of GDP and trade for 13%. It covers commerce, transport, education, social and health services, research and development, sports activities, etc.[291][292] Micro and small businesses represent 30% of the country's GDP. In the commercial sector, for example, they represent 53% of the GDP within the activities of the sector.[293]
Tourism


Tourism in Brazil is a growing sector and key to the economies of several regions of the country. The country had 6.36 million visitors in 2015, ranking in terms of the international tourist arrivals as the main destination in South America and second in Latin America after Mexico.[294] Revenues from international tourists reached US$6 billion in 2010, showing a recovery from the 2008–2009 economic crisis.[295] Historical records of 5.4 million visitors and US$6.8 billion in receipts were reached in 2011.[296][297] In the list of world tourist destinations, in 2018, Brazil was the 48th most visited country, with 6.6 million tourists (and revenues of 5.9 billion dollars).[298]
Natural areas are its most popular tourism product, a combination of ecotourism with leisure and recreation, mainly sun and beach, and adventure travel, as well as cultural tourism. Among the most popular destinations are the Amazon Rainforest, beaches and dunes in the Northeast Region, the Pantanal in the Center-West Region, beaches at Rio de Janeiro and Santa Catarina, cultural tourism in Minas Gerais and business trips to São Paulo.[299]
In terms of the 2015 Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index (TTCI), which is a measurement of the factors that make it attractive to develop business in the travel and tourism industry of individual countries, Brazil ranked in the 28th place at the world's level, third in the Americas, after Canada and United States.[300][301] Domestic tourism is a key market segment for the tourism industry in Brazil. In 2005, 51 million Brazilian nationals made ten times more trips than foreign tourists and spent five times more money than their international counterparts.[302] The main destination states in 2023 were São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Rio Grande do Sul.[303][304] The main source of tourists for the entire country is São Paulo state.[305] In terms of tourism revenues, the top earners by state were São Paulo and Bahia.[306] For 2005, the three main trip purposes were visiting friends and family (53.1%), sun and beach (40.8%), and cultural tourism (12.5%).[307]
Science and technology


Technological research in Brazil is largely carried out in public universities and research institutes, with the majority of funding for basic research coming from various government agencies.[308] Brazil's most esteemed technological hubs are the Oswaldo Cruz Institute, the Butantan Institute, the Air Force's Aerospace Technical Center, the Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation and the National Institute for Space Research.[309][310]
The Brazilian Space Agency has the most advanced space program in Latin America, with significant resources to launch vehicles, and manufacture of satellites.[311] The country develops submarines and aircraft, as well as being involved in space research, having a Vehicle Launch Center Light and being the only country in the Southern Hemisphere to integrate a team building the well-known International Space Station (ISS).[312]
The country is also a pioneer in the search for oil in deep water, from where it extracts 73% of its reserves. Uranium is enriched at the Resende Nuclear Fuel Factory, mostly for research purposes (as Brazil obtains 88% of its electricity from hydroelectricity[313]) and the country's first nuclear submarine is expected to be launched in 2029.[314]
Brazil is one of the three countries in Latin America[315] with an operational Synchrotron Laboratory, a research facility on physics, chemistry, material science and life sciences, and Brazil is the only Latin American country to have a semiconductor company with its own fabrication plant, the CEITEC.[316] According to the Global Information Technology Report 2009–2010 of the World Economic Forum, Brazil is the world's 61st largest developer of information technology.[317] Brazil was ranked 50th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024, up from 66th in 2019.[318][319][320]
Among the most renowned Brazilian inventors are priests Bartolomeu de Gusmão, Landell de Moura and Francisco João de Azevedo, besides Alberto Santos-Dumont,[321] Evaristo Conrado Engelberg,[322] Manuel Dias de Abreu,[323] Andreas Pavel[324] and Nélio José Nicolai.[325] Brazilian science is represented by the likes of César Lattes (Brazilian physicist Pathfinder of Pi Meson),[326] Mário Schenberg (considered the greatest theoretical physicist of Brazil),[327] José Leite Lopes (the only Brazilian physicist holder of the UNESCO Science Prize),[328] Artur Ávila (the first Latin American winner of the Fields Medal)[329] and Fritz Müller (pioneer in factual support of the theory of evolution by Charles Darwin).[330]
Energy


Brazil is the world's ninth-largest energy consumer.[331] Much of its energy comes from renewable sources, particularly hydroelectricity and ethanol; the Itaipu Dam is the world's largest hydroelectric plant by energy generation,[332] and the country has other large plants such as Belo Monte and Tucuruí. The first car with an ethanol engine was produced in 1978 and the first airplane engine running on ethanol in 2005.[333]
At the end of 2021 Brazil was the 2nd country in the world in terms of installed hydroelectric power (109.4 GW) and biomass (15.8 GW), the 7th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (21.1 GW) and the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13.0 GW)—on track to also become one of the top 10 in the world in solar energy.[334] At the end of 2021, Brazil was the 4th largest producer of wind energy in the world (72 TWh), behind only China, the United States and Germany, and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).[335]
The main characteristic of the Brazilian energy matrix is that it is much more renewable than that of the world. While in 2019, the world matrix was only 14% made up of renewable energy, Brazil's was at 45%. Petroleum and oil products made up 34.3% of the matrix; sugar cane derivatives, 18%; hydraulic energy, 12.4%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 8.8%; varied renewable energies, 7%; mineral coal, 5.3%; nuclear, 1.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.6%.[336]
In the electric energy matrix, the difference between Brazil and the world is even greater: while the world only had 25% of renewable electric energy in 2019, Brazil had 83%. The Brazilian electric matrix was composed of: hydraulic energy, 64.9%; biomass, 8.4%; wind energy, 8.6%; solar energy, 1%; natural gas, 9.3%; oil products, 2%; nuclear, 2.5%; coal and derivatives, 3.3%.[336] Brazil has the largest electricity sector in Latin America. Its capacity at the end of 2021 was 181,532 MW.[337]
As for oil, the Brazilian government has embarked on a program over the decades to reduce dependence on imported oil, which previously accounted for more than 70% of the country's oil needs. Brazil became self-sufficient in oil in 2006–2007. In 2021, the country closed the year as the 7th oil producer in the world, with an average of close to three million barrels per day, becoming an exporter of the product.[338][339]
Transportation


Brazilian roads are the primary carriers of freight and passenger traffic. The road system totaled 1,720,000 km (1,068,758 mi) in 2019.[342] The total of paved roads increased from 35,496 km (22,056 mi) in 1967 to 215,000 km (133,595 mi) in 2018.[343][344]
Brazil's railway system has been declining since 1945, when emphasis shifted to highway construction. The country's total railway track length was 30,576 km (18,999 mi) in 2015,[345] as compared with 31,848 km (19,789 mi) in 1970, making it the ninth largest network in the world. Most of the railway system belonged to the Federal Railroad Network Corporation (RFFSA), which was privatized in 2007.[346] The São Paulo Metro began operating on 14 September 1974 as the first underground transit system in Brazil.[347]
There are about 2,500 airports in Brazil, including landing fields: the second-largest number in the world, after the United States.[348] São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport, near São Paulo, is the largest and busiest airport with nearly 43 million passengers annually, while handling the vast majority of commercial traffic for the country.[349][350]
For freight transport, waterways are of importance. The industrial zones of Manaus can be reached only by means of the Solimões–Amazonas waterway (3,250 kilometers or 2,020 miles in length, with a minimum depth of six meters or 20 feet). The country also has 50,000 kilometers (31,000 miles) of waterways.[351] Coastal shipping links widely separated parts of the country. Bolivia and Paraguay have been given free ports at Santos. Of the 36 deep-water ports, Santos, Itajaí, Rio Grande, Paranaguá, Rio de Janeiro, Sepetiba, Vitória, Suape, Manaus and São Francisco do Sul are the most important.[352] Bulk carriers have to wait up to 18 days before being serviced; container ships take 36.3 hours on average.[353]
Demographics

According to the latest official projection, it is estimated that Brazil’s population was 210,862,983 on July 1, 2022—an adjustment of 3.9% from the initial figure of 203 million reported by the 2022 census.[354] The population of Brazil, as recorded by the 2008 PNAD, was approximately 190 million[355] (22.31 inhabitants per square kilometer or 57.8/sq mi), with a ratio of men to women of 0.95:1[356] and 83.75% of the population defined as urban.[357] The population is heavily concentrated in the Southeastern (79.8 million inhabitants) and Northeastern (53.5 million inhabitants) regions, while the two most extensive regions, the Center-West and the North, which together make up 64.12% of the Brazilian territory, have a total of only 29.1 million inhabitants.
The first census in Brazil was carried out in 1872 and recorded a population of 9,930,478.[358] From 1880 to 1930, 4 million Europeans arrived.[359] Brazil's population increased significantly between 1940 and 1970, because of a decline in the mortality rate, even though the birth rate underwent a slight decline. In the 1940s the annual population growth rate was 2.4%, rising to 3.0% in the 1950s and remaining at 2.9% in the 1960s, as life expectancy rose from 44 to 54 years[360] and to 72.6 years in 2007.[361] It has been steadily falling since the 1960s, from 3.04% per year between 1950 and 1960 to 1.05% in 2008 and is expected to fall to a negative value of –0.29% by 2050[362] thus completing the demographic transition.[363]
In 2008, the illiteracy rate was 11.48%.[364]
Race and ethnicity
Race and ethnicity in Brazil 2022
According to the 2022 Brazilian census, 45.3% of the population (92,1 million) described themselves as Pardo (meaning brown or mixed), 43.5% (88,2 million) as White, 10.2% (20,7 million) as Black, 0.6% (1,2 million) as Indigenous and 0.4% (850 thousand) as East Asian (officially called yellow or amarela).[365]
Since the arrival of the Portuguese in 1500, considerable genetic mixing between Amerindians, Europeans, and Africans has taken place in all regions of the country: European ancestry being dominant nationwide according to the vast majority of all autosomal studies undertaken covering the entire population, accounting for between 65% and 77%,[366][367][368][369] while the African ancestry among the Brazilians is estimated at 14.30% to 25%[368][370] and more than 80% of Brazilians have over 10% African ancestry,[371] and the Indigenous ancestry is significant and present in all regions of Brazil.[372][373][374][375][376][377][378]
From the 19th century, Brazil opened its borders to immigration. About five million people from over 60 countries migrated to Brazil between 1808 and 1972, most of them of Portuguese, Italian, Spanish, German, English, Ukrainian, Polish, Jewish, African, Armenian, Russian, Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Arab origin.[379][380][381] Brazil has the second-largest Jewish community in Latin America making up 0.06% of its population.[382] Outside in the Arab world, Brazil also has the largest population of Arab ancestry in the world, with 15–20 million people.[383][384] According to Brazil's Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Brazil is home to a Lebanese diaspora of 7 million to 10 million, surpassing the population of Lebanese individuals residing in Lebanon.[385]
Brazilian society is more markedly divided by social class lines, although a high income disparity is found between race groups, so racism and classism often overlap. The brown population (officially called pardo in Portuguese, also colloquially moreno)[386][387] is a broad category that includes caboclos (assimilated Amerindians in general, and descendants of Whites and Natives), mulatos (descendants of primarily Whites and Afro-Brazilians) and cafuzos (descendants of Afro-Brazilians and Natives).[386][387][388][389][390] Higher percents of Blacks, mulattoes and tri-racials can be found in the eastern coast of the Northeastern region from Bahia to Paraíba[390][391] and also in northern Maranhão,[392][393] southern Minas Gerais[394] and eastern Rio de Janeiro.[390][394]
People of considerable Amerindian ancestry form the majority of the population in the Northern, Northeastern and Center-Western regions.[395] In 2007, the National Indian Foundation estimated that Brazil has 67 different uncontacted tribes, up from their estimate of 40 in 2005. Brazil is believed to have the largest number of uncontacted peoples in the world.[396]
Religion
Religion in Brazil (2010 Census)
Christianity is the country's predominant faith, with Roman Catholicism being its largest denomination. Brazil has the world's largest Catholic population.[397][398] According to the 2010 Demographic Census (the PNAD survey does not inquire about religion), 64.63% of the population followed Roman Catholicism; 22.2% Protestantism; 2.0% Kardecist spiritism; 3.2% other religions, undeclared or undetermined; while 8.0% had no religion.[399]
Religion in Brazil was formed from the meeting of the Catholic Church with the religious traditions of enslaved African peoples and indigenous peoples.[400] This confluence of faiths during the Portuguese colonization of Brazil led to the development of a diverse array of syncretistic practices within the overarching umbrella of Brazilian Catholic Church, characterized by traditional Portuguese festivities.[401]
Religious pluralism increased during the 20th century,[402] and the Protestant community has grown to include over 22% of the population.[403] The most common Protestant denominations are Evangelical Pentecostal ones. Other Protestant branches with a notable presence in the country include the Baptists, Seventh-day Adventists, Lutherans and the Reformed tradition.[404]
In recent decades, Protestantism, particularly in forms of Pentecostalism and Evangelicalism, has spread in Brazil, while the proportion of Catholics has dropped significantly.[405] After Protestantism, individuals professing no religion are also a significant group, exceeding 8% of the population as of the 2010 census. The cities of Boa Vista, Salvador, and Porto Velho have the greatest proportion of Irreligious residents in Brazil. Teresina, Fortaleza, and Florianópolis were the most Roman Catholic in the country.[406] Greater Rio de Janeiro, not including the city proper, is the most irreligious and least Roman Catholic Brazilian periphery, while Greater Porto Alegre and Greater Fortaleza are on the opposite sides of the lists, respectively.[406]
In October 2009, the Brazilian Senate approved and enacted by the President of Brazil in February 2010, an agreement with the Vatican, in which the Legal Statute of the Catholic Church in Brazil is recognized.[407][408]
Health

The Brazilian public health system, the Unified Health System (Sistema Único de Saúde – SUS), is managed and provided by all levels of government,[409] being the largest system of this type in the world.[410] On the other hand, private healthcare systems play a complementary role.[411] Public health services are universal and offered to all citizens of the country for free. However, the construction and maintenance of health centers and hospitals are financed by taxes, and the country spends about 9% of its GDP on expenditures in the area. In 2012, Brazil had 1.85 doctors and 2.3 hospital beds for every 1,000 inhabitants.[412][413]
Despite all the progress made since the creation of the universal health care system in 1988, there are still several public health problems in Brazil. In 2006, the main points to be solved were the high infant (2.51%) and maternal mortality rates (73.1 deaths per 1000 births).[414]
The number of deaths from noncommunicable diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases (151.7 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants) and cancer (72.7 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants), also has a considerable impact on the health of the Brazilian population. Finally, external but preventable factors such as car accidents, violence and suicide caused 14.9% of all deaths in the country.[414] The Brazilian health system was ranked 125th among the 191 countries evaluated by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2000.[415]
Education

The Federal Constitution and the Law of Guidelines and Bases of National Education determine that the Union, the states, the Federal District and the municipalities must manage and organize their respective education systems. Each of these public educational systems is responsible for its own maintenance, which manages funds as well as the mechanisms and funding sources. The constitution reserves 25% of the state budget and 18% of federal taxes and municipal taxes for education.[416]
According to the IBGE, in 2019, the literacy rate of the population was 93.4%, meaning that 11.3 million (6.6% of population) people are still illiterate in the country, with some states such as Rio de Janeiro and Santa Catarina reaching around 97% of literacy rate;[417] functional illiteracy has reached 21.6% of the population.[418] Illiteracy is higher in the Northeast, where 13.87% of the population is illiterate, while the South, has 3.3% of its population illiterate.[419][417]
Brazil's private institutions tend to be more exclusive and offer better quality education, so many high-income families send their children there. The result is a segregated educational system that reflects extreme income disparities and reinforces social inequality. However, efforts to change this are making impacts.[420] The University of São Paulo is often considered the best in Brazil and Latin America.[421][422] Of the top 20 Latin American universities, eight are Brazilian. Most of them are public. Attending an institution of higher education is required by Law of Guidelines and Bases of Education. Kindergarten, elementary and medium education are required of all students.[423]
Language
The official language of Brazil is Portuguese (Article 13 of the Constitution of the Federal Republic of Brazil), which almost all of the population speaks and is virtually the only language used in newspapers, radio, television, and for business and administrative purposes. Brazil is the only Portuguese-speaking nation in the Americas, making the language an important part of Brazilian national identity and giving it a national culture distinct from those of its Spanish-speaking neighbors.[424]
Brazilian Portuguese has had its own development, mostly similar to 16th-century Central and Southern dialects of European Portuguese[425] (despite a very substantial number of Portuguese colonial settlers, and more recent immigrants, coming from Northern regions, and in minor degree Portuguese Macaronesia), with a few influences from the Amerindian and African languages, especially West African and Bantu restricted to the vocabulary only.[426] As a result, the language is somewhat different, mostly in phonology, from the language of Portugal and other Portuguese-speaking countries (the dialects of the other countries, partly because of the more recent end of Portuguese colonialism in these regions, have a closer connection to contemporary European Portuguese). These differences are comparable to those between American and British English.[426]
The 2002 sign language law[427] requires government authorities and public agencies to accept and provide information in Língua Brasileira dos Sinais or "LIBRAS", the Brazilian Sign Language, while a 2005 presidential edict[428] extends this to require teaching of the language as a part of the education and speech and language pathology curricula. LIBRAS teachers, instructors and translators are recognized professionals. Schools and health services must provide access ("inclusion") to deaf people.[429]
Minority languages are spoken throughout the nation. One hundred and eighty Amerindian languages are spoken in remote areas and a significant number of other languages are spoken by immigrants and their descendants.[426] In the municipality of São Gabriel da Cachoeira, Nheengatu (a currently endangered South American creole language—or an 'anti-creole', according to some linguists—with mostly Indigenous Brazilian languages lexicon and Portuguese-based grammar that, together with its southern relative língua geral paulista, once was a major lingua franca in Brazil,[430] being replaced by Portuguese only after governmental prohibition led by major political changes),[excessive detail?] Baniwa and Tucano languages had been granted co-official status with Portuguese.[431]
There are significant communities of German (mostly the Brazilian Hunsrückisch, a High German language dialect) and Italian (mostly the Talian, a Venetian dialect) origins in the Southern and Southeastern regions, whose ancestors' native languages were carried along to Brazil, and which, still alive there, are influenced by the Portuguese language.[432][433] Talian is officially a historic patrimony of Rio Grande do Sul,[434] and two German dialects possess co-official status in a few municipalities.[435] Italian is also recognized as ethnic language in the Santa Teresa microregion and Vila Velha (Espirito Santo state), and is taught as mandatory second language at school.[436]
Urbanization
According to IBGE (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics) urban areas already concentrate 84.35% of the population, while the Southeast region remains the most populated one, with over 80 million inhabitants.[437] The largest urban agglomerations in Brazil are São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Belo Horizonte—all in the Southeastern Region—with 21.1, 12.3, and 5.1 million inhabitants respectively.[438][439][440] The majority of state capitals are the largest cities in their states, except for Vitória, the capital of Espírito Santo, and Florianópolis, the capital of Santa Catarina.[441]
Largest urban agglomerations in Brazil
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | State | Pop. | Rank | Name | State | Pop. | ||
 São Paulo  Rio de Janeiro |
1 | São Paulo | São Paulo | 21,314,716 | 11 | Belém | Pará | 2,157,180 | |
| 2 | Rio de Janeiro | Rio de Janeiro | 12,389,775 | 12 | Manaus | Amazonas | 2,130,264 | ||
| 3 | Belo Horizonte | Minas Gerais | 5,142,260 | 13 | Campinas | São Paulo | 2,105,600 | ||
| 4 | Recife | Pernambuco | 4,021,641 | 14 | Vitória | Espírito Santo | 1,837,047 | ||
| 5 | Brasília | Federal District | 3,986,425 | 15 | Baixada Santista | São Paulo | 1,702,343 | ||
| 6 | Porto Alegre | Rio Grande do Sul | 3,894,232 | 16 | São José dos Campos | São Paulo | 1,572,943 | ||
| 7 | Salvador | Bahia | 3,863,154 | 17 | São Luís | Maranhão | 1,421,569 | ||
| 8 | Fortaleza | Ceará | 3,594,924 | 18 | Natal | Rio Grande do Norte | 1,349,743 | ||
| 9 | Curitiba | Paraná | 3,387,985 | 19 | Maceió | Alagoas | 1,231,965 | ||
| 10 | Goiânia | Goiás | 2,347,557 | 20 | João Pessoa | Paraíba | 1,168,941 | ||
Culture

The core culture of Brazil is derived from Portuguese culture, because of its strong colonial ties with the Portuguese Empire.[445] Among other influences, the Portuguese introduced the Portuguese language, Roman Catholicism and colonial architectural styles. The culture was also strongly influenced by African, indigenous and non-Portuguese European cultures and traditions.[446]
Some aspects of Brazilian culture were influenced by the contributions of Italian, German and other European as well as Japanese, Jewish and Arab immigrants who arrived in large numbers in the South and Southeast of Brazil during the 19th and 20th centuries.[447] The indigenous Amerindians influenced Brazil's language and cuisine; and the Africans influenced language, cuisine, music, dance and religion.[448]
Brazilian art has developed since the 16th century into different styles that range from Baroque (the dominant style in Brazil until the early 19th century)[449][450] to Romanticism, Modernism, Expressionism, Cubism, Surrealism and Abstractionism. Brazilian cinema dates back to the birth of the medium in the late 19th century and has gained a new level of international acclaim since the 1960s.[451]
Architecture

The architecture of Brazil is influenced by Europe, especially Portugal. It has a history that goes back 500 years to the time, when Pedro Álvares Cabral landed in Brazil in 1500. Portuguese colonial architecture was the first wave of architecture to go to Brazil.[452] It is the basis for all Brazilian architecture of later centuries.[453] In the 19th century, during the time of the Empire of Brazil, the country followed European trends and adopted Neoclassical and Gothic Revival architecture. Then, in the 20th century, especially in Brasília, Brazil experimented with modernist architecture.
The colonial architecture of Brazil dates to the early 16th century, when Brazil was first explored, conquered and settled by the Portuguese. The Portuguese built architecture familiar to them in Europe in their aim to colonize Brazil. They built Portuguese colonial architecture, which included churches and civic architecture, including houses and forts, in Brazilian cities and the countryside.[454]
During the 19th century, Brazilian architecture saw the introduction of more European styles to Brazil, such as Neoclassical and Gothic Revival architecture. This was usually mixed with Brazilian influences from their own heritage.[454] In the 1950s modernist architecture was introduced when Brasília was built as a new federal capital in the interior of Brazil to help develop the interior. The architect Oscar Niemeyer idealized and built government buildings, churches and civic buildings in the modernist style.[455]
Music

The music of Brazil was formed mainly from the fusion of European, Native Indigenous, and African elements.[456] Until the nineteenth century, Portugal was the gateway to most of the influences that built Brazilian music, although many of these elements were not of Portuguese origin, but generally European. The first was José Maurício Nunes Garcia, author of sacred pieces with an influence of Viennese classicism.[457] The major contribution of the African element was the rhythmic diversity and some dances and instruments.[456]
Popular music since the late eighteenth century, samba was considered the most typical and on the UNESCO cultural heritage list.[458] Samba-reggae, Maracatu, Frevo and Afoxê are four music traditions that have been popularized by their appearance in the annual Brazilian Carnivals.[459] Capoeira is usually played with its own music referred to as capoeira music, which is usually considered to be a call-and-response type of folk music.[460] Forró is a type of folk music prominent during the Festa Junina in northeastern Brazil.[461] Jack A. Draper III, a professor of Portuguese at the University of Missouri,[462] argues that Forró was used as a way to subdue feelings of nostalgia for a rural lifestyle.[463]
Choro is a popular musical instrumental style. Its origins are in 19th-century Rio de Janeiro. The style often has a fast and happy rhythm, characterized by subtle modulations and full of syncopation and counterpoint.[464] Bossa nova is also a well-known style of Brazilian music developed and popularized in the 1950s and 1960s.[465] The phrase "bossa nova" means literally 'new trend'.[466] A lyrical fusion of samba and jazz, bossa nova acquired a large following starting in the 1960s.[467] Some international Brazilian music artists are, for example: Villa-Lobos, Tom Jobim, João Gilberto, Sergio Mendes, Eumir Deodato, Kaoma, Sepultura, Olodum and CSS.
Literature

Brazilian literature dates back to the 16th century, to the writings of the first Portuguese explorers in Brazil, such as Pero Vaz de Caminha, filled with descriptions of fauna, flora and commentary about the indigenous population that fascinated European readers.[468]
Brazil produced significant works in Romanticism—novelists such as Joaquim Manuel de Macedo and José de Alencar wrote novels about love and pain. Alencar, in his long career, also treated indigenous people as heroes in the Indigenist novels O Guarani, Iracema and Ubirajara.[469] Machado de Assis, one of his contemporaries, wrote in virtually all genres and continues to gain international prestige from critics worldwide.[470][471][472]
Brazilian Modernism, evidenced by the Modern Art Week in 1922, was concerned with a nationalist avant-garde literature,[473] while Post-Modernism brought a generation of distinct poets such as João Cabral de Melo Neto, Carlos Drummond de Andrade, Vinicius de Moraes, Cora Coralina, Graciliano Ramos, Cecília Meireles, and internationally known writers dealing with universal and regional subjects such as Jorge Amado, João Guimarães Rosa, Clarice Lispector and Manuel Bandeira.[474][475][476]
Brazil's most significant literary award is the Camões Prize, which it shares with the rest of the Portuguese-speaking world. As of 2016, Brazil has eleven recipients of the prize.[477] Brazil also holds its own literary academy, the Brazilian Academy of Letters, a non-profit cultural organization aimed at perpetuating the care of the national language and literature.[478]
Cinema

The Brazilian film industry began in the late 19th century, during the early days of the Belle Époque. While there were national film productions during the early 20th century, American films such as Rio the Magnificent were made in Rio de Janeiro to promote tourism in the city.[479] The films Limite (1931) and Ganga Bruta (1933), the latter being produced by Adhemar Gonzaga through the prolific studio Cinédia, were poorly received at release and failed at the box office, but are acclaimed nowadays and placed among the finest Brazilian films of all time.[480] The 1941 unfinished film It's All True was divided into four segments, two of which were filmed in Brazil and directed by Orson Welles; it was originally produced as part of the United States' Good Neighbor Policy during Getúlio Vargas' Estado Novo government.
During the 1960s, the Cinema Novo movement rose to prominence with directors such as Glauber Rocha, Nelson Pereira dos Santos, Paulo Cesar Saraceni and Arnaldo Jabor. Rocha's films Deus e o Diabo na Terra do Sol (1964) and Terra em Transe (1967) are considered to be some of the greatest and most influential in Brazilian film history.[481]
During the 1990s, Brazil saw a surge of critical and commercial success with films such as O Quatrilho (Fábio Barreto, 1995), O Que É Isso, Companheiro? (Bruno Barreto, 1997) and Central do Brasil (Walter Salles, 1998), all of which were nominated for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film, the latter receiving a Best Actress nomination for Fernanda Montenegro. The 2002 crime film City of God, directed by Fernando Meirelles, was critically acclaimed, scoring 90% on Rotten Tomatoes,[482] being placed in Roger Ebert's Best Films of the Decade list[483] and receiving four Academy Award nominations in 2004, including Best Director. Notable film festivals in Brazil include the São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro International Film Festivals and the Gramado Festival.
Visual arts

Brazilian painting emerged in the late 16th century,[484] influenced by Baroque, Rococo, Neoclassicism, Romanticism, Realism, Modernism, Expressionism, Surrealism, Cubism and Abstracionism making it a major art style called Brazilian academic art.[485][486]
The French Artistic Mission arrived in Brazil in 1816 proposing the creation of an art academy modeled after the respected Académie des Beaux-Arts, with graduation courses both for artists and craftsmen for activities such as modeling, decorating, carpentry and others and bringing artists such as Jean-Baptiste Debret.[486]
Upon the creation of the Imperial Academy of Fine Arts, new artistic movements spread across the country during the 19th century and later the event called Modern Art Week broke with academic tradition in 1922 and started a nationalist trend which was influenced by modernist arts.[487]
Among the best-known Brazilian painters are Ricardo do Pilar and Manuel da Costa Ataíde (baroque and rococo), Victor Meirelles, Pedro Américo and Almeida Júnior (romanticism and realism), Anita Malfatti, Ismael Nery, Lasar Segall, Emiliano di Cavalcanti, Vicente do Rego Monteiro, and Tarsila do Amaral (expressionism, surrealism and cubism), Aldo Bonadei, José Pancetti and Cândido Portinari (modernism).[488]
Theatre

The theatre in Brazil has its origins in the period of Jesuit expansion, when theater was used for the dissemination of Catholic doctrine in the 16th century. In the 17th and 18th centuries, dramatists on the scene of European derivation were for court or private performances.[489] During the 19th century, the playwrights Antônio Gonçalves Dias and Luís Carlos Martins Pena were known for their performance.[490] There were also numerous operas and orchestras. The Brazilian conductor Antônio Carlos Gomes became internationally known with operas such as Il Guarany. At the end of the 19th century, orchestrated dramaturgias were accompanied with songs of famous artists such as the conductress Chiquinha Gonzaga.[491]
Already in the early 20th century there was the presence of theaters, entrepreneurs and actor companies. In 1940, Paschoal Carlos Magno and his student's theater, the comedians group and the Italian actors Adolfo Celi, Ruggero Jacobbi and Aldo Calvo, founders of the Teatro Brasileiro de Comédia, renewed the Brazilian theater. From the 1960s, it was attended by a theater dedicated to social and religious issues. The most prominent authors at this stage were Jorge Andrade and Ariano Suassuna.[490]
Cuisine

Brazilian cuisine varies greatly by region, reflecting the country's varying mix of indigenous and immigrant populations. This has created a national cuisine marked by the preservation of regional differences.[492] Examples are Feijoada, considered the country's national dish;[493] and regional foods such as beiju, feijão tropeiro, vatapá, moqueca, polenta (from Italian cuisine) and acarajé (from African cuisine).[494] The national beverage is coffee; cachaça is Brazil's native liquor. Cachaça is distilled from sugar cane and is the main ingredient in the national cocktail, Caipirinha.[495]
A typical meal consists mostly of rice and beans with beef, salad, french fries and a fried egg.[496] Often, it is mixed with cassava flour (farofa). Fried potatoes, fried cassava, fried banana, fried meat and fried cheese are very often eaten in lunch and served in most typical restaurants.[497] Popular snacks are pastel (a fried pastry); coxinha (a variation of chicken croquete); pão de queijo (cheese bread and cassava flour / tapioca); pamonha (corn and milk paste); esfirra (a variation of Lebanese pastry); kibbeh (from Arabic cuisine); empanada (pastry) and empada, little salt pies filled with shrimps or heart of palm.
Brazil has a variety of desserts such as brigadeiros (chocolate fudge balls), bolo de rolo (roll cake with goiabada), cocada (a coconut sweet), beijinhos (coconut truffles and clove) and Romeu e Julieta (cheese with goiabada). Peanuts are used to make paçoca, rapadura and pé-de-moleque. Local common fruits such as açaí, cupuaçu, mango, papaya, cocoa, cashew, guava, orange, lime, passionfruit, pineapple, and hog plum are turned in juices and used to make chocolates, ice pops and ice cream.[498]
Media

The Brazilian press was officially born in Rio de Janeiro on 13 May 1808 with the creation of the Royal Printing National Press by the Prince Regent Dom João.[500] The Gazeta do Rio de Janeiro, the first newspaper published in the country, began to circulate on 10 September 1808.[501] The largest newspapers nowadays are Folha de S.Paulo, Super Notícia, O Globo and O Estado de S. Paulo.[502]
Radio broadcasting began on 7 September 1922, with a speech by then President Pessoa, and was formalized on 20 April 1923 with the creation of the "Radio Society of Rio de Janeiro".[503] Television in Brazil began officially on 18 September 1950, with the founding of TV Tupi by Assis Chateaubriand.[504] Since then, television has grown in the country, creating large commercial broadcast networks such as Globo, SBT, RecordTV, Bandeirantes and RedeTV. Today it is the most important factor in the popular culture of Brazilian society, as indicated by research showing that as much as 67%[505][506] of the general population follow the same daily telenovela broadcast.
By the mid-1960s, Brazilian universities had installed mainframe computers from IBM and Burroughs Large Systems. In the 1970s and 1980s, the Brazilian government restricted foreign imports to protect the local manufacturing of computers. In the 1980s, Brazil produced half of the computers sold in the country. By 2009, the mobile phone and Internet use in Brazil was the fifth largest in the world.[507]
In May 2010, the Brazilian government launched TV Brasil Internacional, an international television station, initially broadcasting to 49 countries.[508] Commercial television channels broadcast internationally include Globo Internacional, RecordTV Internacional and Band Internacional.
Sports
The most popular sport in Brazil is football.[511] The Brazilian men's national team is ranked among the best in the world according to the FIFA World Rankings, and has won the World Cup tournament a record five times.[512][513]
Volleyball, basketball, auto racing and martial arts also has large audiences. The Brazil men's national volleyball team, for example, currently holds the titles of the World League, World Grand Champions Cup, World Championship and the World Cup. In auto racing, three Brazilian drivers have won the Formula One world championship eight times.[514][515][516] The country has also produced significant achievements in other sports such as sailing, swimming, tennis, surfing, skateboarding, MMA, gymnastics, boxing, judo, athletics and table tennis.
Some sport variations have their origins in Brazil: beach football,[517] futsal (indoor football)[518] and footvolley emerged in Brazil as variations of football. In martial arts, Brazilians developed Capoeira,[519] Vale tudo[520] and Brazilian jiu-jitsu.[521]
Brazil has hosted several high-profile international sporting events, such as the 1950 FIFA World Cup,[522] and recently has hosted the 2014 FIFA World Cup, 2019 Copa América and 2021 Copa América .[523] The São Paulo circuit, Autódromo José Carlos Pace, hosts the annual Grand Prix of Brazil.[524] São Paulo organized the IV Pan American Games in 1963, and Rio de Janeiro hosted the XV Pan American Games in 2007.[525] On 2 October 2009, Rio de Janeiro was selected to host the 2016 Olympic Games and 2016 Paralympic Games, making it the first South American city to host the games[526] and second in Latin America, after Mexico City. Furthermore, the country hosted the FIBA Basketball World Cups in 1954 and 1963. At the 1963 event, the Brazil national basketball team won one of its two world championship titles.[527]
See also
Notes
- ^ The Brazilian census uses the term amarela (or yellow in English) as a racial category to describe people of East Asian background. This category therefore excludes those of other Asian origins, such as West Asians/Arabs, who are included in the white category, and South Asians.
- ^ Portuguese: Brasil, pronounced [bɾaˈziw] .
- ^ Portuguese: República Federativa do Brasil,[10] pronounced [ʁeˈpublikɐ fedeɾaˈtʃivɐ du bɾaˈziw] .
References
- ^ Exército Brasileiro. "Hino à Bandeira Nacional" (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 29 January 2014.
- ^ "Censo 2022: Pela 1ª vez, Brasil se declara mais pardo que branco; populações preta e indígena também crescem". 22 December 2023. Archived from the original on 22 December 2023. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- ^ "2022 Report on International Religious Freedom: Brazil". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 12 March 2024. Retrieved 12 March 2024.
- ^ "Datafolha: Brazilians Go to Church Less and Give Less Contributions". Folha de S.Paulo. 30 June 2022. Archived from the original on 28 June 2024. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- ^ Araujo, Gabriel (28 June 2023). Grattan, Steven; Rumney, Emma (eds.). "Brazil census shows population growth at its slowest since 1872". Reuters. Archived from the original on 29 June 2023.
- ^ "País tem 90 milhões de domicílios, 34% a mais que em 2010 | Agência de Notícias". Agência de Notícias – IBGE (in Brazilian Portuguese). 28 June 2023. Archived from the original on 5 July 2023. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Brazil)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. 22 October 2024. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ "World Bank Open Data". Archived from the original on 9 October 2019. Retrieved 14 April 2024.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. p. 289. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ José María Bello (1966). A History of Modern Brazil: 1889–1964. Stanford University Press. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-8047-0238-6.
- ^ Philander, S. George (2012). Encyclopedia of Global Warming and Climate Change, Second Edition. Vol. 1 (Second ed.). Los Angeles: Princeton University. p. 148. ISBN 978-1-4129-9261-9. OCLC 970592418. Archived from the original on 25 October 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Vallance, Monique M. (2012). "Preface and Observations on Contemporary Brazil". In Crocitti, John J. (ed.). Brazil Today: An Encyclopedia of Life in the Republic. Contributing editor Monique M. Vallance. ABC-CLIO. p. xxiii. ISBN 978-0-313-34672-9. OCLC 787850982. Archived from the original on 25 October 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ "Os migrantes de hoje". BBC Brasil. Archived from the original on 27 September 2013. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Brazil § geography". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 4 May 2018. (Archived 2018 edition.)
- ^ "Brazil – Land". Permanent Missions. United Nations. Geography. Archived from the original on 23 October 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Brazilian Federal Constitution" (in Portuguese). Presidency of the Republic. 1988. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 3 June 2008. "Brazilian Federal Constitution". v-brazil.com. 2007. Archived from the original on 28 September 2018. Retrieved 3 June 2008.
Unofficial translate
- ^ "UNESCO World Heritage Centre — World Heritage List". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 14 March 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- ^ M. Schaefer; J. Poffenbarger (2014). The Formation of the BRICS and its Implication for the United States: Emerging Together. Springer. p. 32. ISBN 978-1-137-38794-3. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2018.
- ^ Sean W. Burges (2016). Latin America and the Shifting Sands of Globalization. Routledge. pp. 114–15. ISBN 978-1-317-69658-2. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- ^ Gardini, Gian Luca (2016). "Brazil: What Rise of What Power?". Bulletin of Latin American Research. 35: 5–19. doi:10.1111/blar.12417. ISSN 0261-3050.
- ^ Gratius, Susanne (April 2008). "The international arena and emerging powers: stabilising or destabilising forces?" (PDF). FRIDE. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2016.
- ^ Peter Collecott (29 October 2011). "Brazil's Quest for Superpower Status". The Diplomatic Courier. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ Clendenning, Alan (17 April 2008). "Booming Brazil could be world power soon". USA Today. The Associated Press. p. 2. Archived from the original on 20 August 2011. Retrieved 12 December 2008.
- ^ Jorge Dominguez; Byung Kook Kim (2013). Between Compliance and Conflict: East Asia Latin America and the New Pax Americana. Center for International Affairs, Harvard University. pp. 98–99. ISBN 978-1-136-76983-2.
- ^ Vandiver, John (9 May 2019). "Trump bumps up Brazil to 'major non-NATO' ally". Stars and Stripes. Archived from the original on 13 October 2019. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ "FTSE Country Classification" (PDF). FTSE Group. September 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "CIA – The World Factbook – Country Comparisons – GDP (purchasing power parity)". Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 25 January 2011.
- ^ "Country and Lending Groups". World Bank. Archived from the original on 18 March 2011. Retrieved 5 March 2011.
Uppermiddle Income defined as a per capita income between $3,976 – $12,275
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 17 June 2019. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- ^ a b Jeff Neilson; Bill Pritchard (2011). Value Chain Struggles. John Wiley & Sons. p. 102. ISBN 978-1-4443-5544-4. Archived from the original on 25 October 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ "Brazil must be a 'facilitator' in the Middle East, says VP". 14 August 2019. Archived from the original on 26 May 2023. Retrieved 26 May 2023.
- ^ Fausto, Boris (1999). A Concise History of Brazil. Cambridge University Press. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-521-56526-4.
- ^ Jon S. Vincent. (2003). Culture and Customs of Brazil. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 36. ISBN 978-0-313-30495-8.
- ^ "Brazil | Etymology of the name Brazil by etymonline". Archived from the original on 24 March 2024. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ Richard P. Tucker (2007). Insatiable Appetite: The Ecological Degradation of the Tropical World. University of Michigan. p. 186. ISBN 978-0-7425-5365-1. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Wayne E. Lee (2011). Empires and Indigenes: Intercultural Alliance, Imperial Expansion, and Warfare in the Early Modern World. NYU Press. p. 196. ISBN 978-0-8147-6527-2. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Daly, Charles P. (1880). "Maps and Map-making Before Mercator". The Popular Science Monthly. Bonnier Corporation. 473–495, see page 493. ISSN 0161-7370. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Jean de Léry (1990). History of a Voyage to the Land of Brazil, Otherwise Called America. University of California Press. p. 242. ISBN 978-0-520-91380-6. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Jayme A. Sokolow. (2003). The Great Encounter: Native Peoples and European Settlers in the Americas, 1492–1800. M.E. Sharpe. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-7656-0982-3. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Maria Herrera-Sobek (2012). Celebrating Latino Folklore. ABC-CLIO. p. 155. ISBN 978-0-313-34340-7. Archived from the original on 15 February 2024. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Romero, Simon (27 March 2014). "Discoveries Challenge Beliefs on Humans' Arrival in the Americas". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 1 January 2022. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ^ Ribeiro, Patricia (27 March 2014). "Peter Lund Museum". About.com. Archived from the original on 12 August 2017.
- ^ Robert M. Levine; John J. Crocitti (1999). The Brazil Reader: History, Culture, Politics. Duke University Press. pp. 11–. ISBN 978-0-8223-2290-0. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 12 December 2012.
- ^ Roosevelt AC, Housley RA, Imazio da Silveira M, Maranca S, Johnson RI (13 December 1991). "Eighth Millennium Pottery from a Prehistoric Shell Midden [sic] in the Brazilian Amazon". Science. 254 (5038): 1621–1624. Bibcode:1991Sci...254.1621R. doi:10.1126/science.254.5038.1621. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17782213. S2CID 34969614. Archived from the original on 16 October 2023. Retrieved 4 July 2023.
- ^ Mann, Charles C. (2006) [2005]. 1491: New Revelations of the Americas Before Columbus. Vintage Books. pp. 326–33. ISBN 978-1-4000-3205-1.
- ^ Levine, Robert M. (2003). The History of Brazil. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 32. ISBN 978-1-4039-6255-3.
- ^ Levine (2003), p. 31.
- ^ a b Fausto, Carlos (2000). Zahar, Jorge (ed.). Os Índios antes do Brasil [The Indians before Brazil] (in Portuguese). Jorge Zahar Editor. pp. 45–46, 55. ISBN 978-85-7110-543-0.
- ^ Gomes, Mercio P. The Indians and Brazil University Press of Florida 2000 ISBN 0-8130-1720-3 pp. 28–29
- ^ Fausto (2000), pp. 78–80.
- ^ Fausto (2000), p. 50.
- ^ Terrence McCoy (17 January 2022). "More enslaved Africans came to the Americas through this port than anywhere else. Why have so few heard of it?". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 10 October 2022. Retrieved 3 January 2023.
- ^ Boxer, p. 98.
- ^ a b Boxer, p. 100.
- ^ Boxer, pp. 100–101.
- ^ a b Skidmore, p. 27.
- ^ Boxer, p. 101.
- ^ Meuwese, Mark "Brothers in Arms, Partners in Trade: Dutch-Indigenous Alliances in the Atlantic World, 1595–1674" Koninklijke Brill NV 2012 ISBN 978-90-04-21083-7 Chapter III
- ^ Metcalf, Alida C. "Go-betweens And the Colonization of Brazil: 1500–1600" University of Texas Press 2005, pp. 70, 79, 202 View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Crocitti & Vallance (2012).
- ^ Minahan, James B. "Ethnic Groups of the Americas" ABC-CLIO 2013 ISBN 978-1-61069-163-5 p. 300, View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Skidmore, p. 36.
- ^ Richard Middleton and Anne Lombard "Colonial America: A History to 1763" Wiley-Blackwell Publishing 1st edition 1992 ISBN 978-1-4443-9628-7 Chapter 2, Section 4 (final, last page and half of previous one) View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Boxer, p. 110
- ^ Skidmore, p. 34.
- ^ Boxer, p. 102.
- ^ Skidmore, pp. 32–33.
- ^ Murray, Stuart A. P. (2009). The Library An Illustrated History. New York: Skyhorse Publishing. p. 101. ISBN 978-1-60239-706-4.
- ^ Boxer, p. 164.
- ^ Boxer, pp. 168, 170.
- ^ Boxer, p. 169.
- ^ Kohn, George C. (1986). Dictionary of Wars (1st ed.). Facts on File, Inc. p. 174. ISBN 978-1-4381-2916-7. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- ^ George Richard Potter; Henry Clifford Darby; Harold Fullard (1957). The New Cambridge Modern History. Vol. 3 (1st ed.). CUP Archive. p. 498. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- ^ Corrado, Jacopo "The Creole Elite and the Rise of Angolan Protonationalism" Cambria Press 2008 ISBN 978-1-60497-529-1 pp. 95 (Brazil) and 145, note 5 View on Google Books Archived 2 May 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bethell, Leslie "Colonial Brazil" Cambridge University Press 1987 pp. 19, 74, 86, 169–70
- ^ Schwartz, Stuart B. "Slaves, Peasants, and Rebels" Board of Trustees of the University of Illinois 1992 ISBN 0-252-06549-2 Chapter 4 View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ MacLachlan, Colin M. "A History of Modern Brazil: The Past Against the Future"; Scholarly Resources Inc. 2003 p. 3 View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Boxer, p. 213
- ^ Marta Barcellos & Simone Azevedo; Histórias do Mercado de Capitais no Brasil ("Financial Markets' Histories in Brazil") (Portuguese) Campus Elsevier 2011 ISBN 85-352-3994-4 Introduction (by Ney Carvalho), Intro. p. xiv
- ^ Bueno, p. 145.
- ^ Jeffrey C. Mosher (2008). Political Struggle, Ideology, and State Building: Pernambuco and the Construction of Brazil, 1817–1850. U of Nebraska Press. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-8032-3247-1. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Jeremy Adelman (2006). Sovereignty and Revolution in the Iberian Atlantic. Princeton University Press. pp. 334–. ISBN 978-0-691-12664-7. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Lustosa, pp. 109–110
- ^ Lustosa, pp. 117–19
- ^ Lustosa, pp. 150–153
- ^ Vianna, p. 418
- ^ Diégues 2004, pp. 168, 164, 178
- ^ Diégues 2004, pp. 179–80
- ^ Lustosa, p. 208
- ^ Fausto (1999), pp. 82–83.
- ^ Lyra (v. 1), p. 17
- ^ Carvalho 2007, p. 21
- ^ Fausto (1999), Chapter 2, 2.1 to 2.3.
- ^ a b Fausto (1999).
- ^ Bethell, Leslie "The Abolition of the Brazilian Slave Trade: Britain, Brazil and the Slave Trade" Cambridge University Press 1970, "Cambridge Latin American Studides", Chapters 9 to 12. View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Scott, Rebecca and others, The Abolition of Slavery and the Aftermath of Emancipation in Brazil, Duke University Press 1988 ISBN 0-8223-0888-6 Seymour Drescher, Chap. 2: "Brazilian Abolition in Comparative Perspective"
- ^ Levine, Robert M. "The history of Brazil" Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc. 1999, p. 62, View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lyra (v.1), pp. 164, 225, 272
- ^ Fausto (1999), Chapter 2, p. 83, and 2.6 "The Paraguayan War".
- ^ Ermakoff 2006, p. 189.
- ^ Smallman, Shawn C. (2002). "The Overthrow of the Empire". Fear in Memory in the Brazilian Army and Society. University of North Carolina Press. pp. 16–18. ISBN 978-0-8078-5359-7.
- ^ "Brazil's Proclamation of the Republic through the press". The Brazilian Report. 15 November 2017. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2018.
- ^ Smallman (2002), end of Chapter 1, from p. 18 "Military rule".
- ^ Smallman (2002), pp. 21–26.
- ^ Triner, Gail D. "Banking and Economic Development: Brazil, 1889–1930" Palgrave 2000, pp. 69–74 ISBN 0-312-23399-X
- ^ Needell, Jeffrey D. "A Tropical Belle Epoque: Elite Culture and Society in Turn-of-the-Century Rio de Janeiro" Cambridge University Press 2010, pp. 10, 12
- ^ David R. Mares; "Violent peace: militarized interstate bargaining in Latin America" Columbia University Press 2001 Chapter 5 p. 125
- ^ Bradford Burns 1993, p. 305
- ^ M.Sharp, I. Westwell & J.Westwood; "History of World War I, Volume 1" Marshall Cavendish Corporation 2002, p. 97
- ^ Uma história diplomática do Brasil, 1531–1945, pp. 265–69
- ^ Charles Howard Ellis; "The origin, structure & working of the League of Nations" The LawBook Exchange Ltd 2003 pp. 105, 145
- ^ Viscount of Taunay (1893), O encilhamento: scenas contemporaneas da bolsa em 1890, 1891 e 1892, Melhoramentos
- ^ Nassif, Luís (2007), Os cabeças-de-planilha, Ediouro, pp. 69–107, ISBN 978-85-00-02094-0
- ^ de Carvalho, Ney O. Ribeiro (2004), O Encilhamento: anatomia de uma bolha brasileira, Bovespa, ISBN 978-85-904019-1-9
- ^ Martins, Hélio L (1997), A Revolta da Armada, BibliEx
- ^ Moniz, Edmundo (1984), Canudos: a luta pela terra, Global
- ^ Sevcenko, Nicolau (2010), A Revolta da Vacina, Cosac Naify, ISBN 978-85-7503-868-0
- ^ de Moura, Aureliano P (2003), Contestado: a guerra cabocla, Biblioteca do Exército
- ^ Thompson, Arthur (1934), Guerra civil do Brazil de 1893–1895, Ravaro
- ^ Roland, Maria Inês (2000), A Revolta da Chibata, Saraiva, ISBN 978-85-02-03095-4
- ^ Forjaz, Maria CS (1977), Tenentismo e politica, Paz e Terra
- ^ Levine; Robert M. & Crocitti; John J. The Brazil Reader: History, Culture, Politics, Duke University Press 1999, IV – The Vargas Era
- ^ Keen, Benjamin / Haynes, Kate A History of Latin America; Volume 2, Waldsworth Cengage Learning 2004, pp. 356–57
- ^ McCann; Frank D. Soldiers of the Patria: A History of the Brazilian Army, 1889–1937, Stanford University Press 2004, p. 303 ISBN 0-8047-3222-1
- ^ Ibidem Williams 2001
- ^ E. Bradford Burns; A History of Brazil Columbia University Press 1993 p. 352 ISBN 978-0-231-07955-6
- ^ Dulles, John W.F. Anarchists and Communists in Brazil, 1900–1935 University of Texas Press 2012 ISBN 0-292-74076-X
- ^ Frank M. Colby, Allen L. Churchill, Herbert T. Wade & Frank H. Vizetelly; The New international year book Dodd, Mead & Co. 1989, p. 102 "The Fascist Revolt"
- ^ Bourne, Richard Getulio Vargas of Brazil, 1883–1954 C. Knight 1974, p. 77
- ^ Scheina, Robert L. Latin America's Wars Vol.II: The Age of the Professional Soldier, 1900–2001. Potomac Books, 2003 ISBN 1-57488-452-2 Part 9; Ch. 17 – World War II, Brazil, and Mexico, 1942–45
- ^ Thomas M. Leonard & John F. Bratzel; Latin America during World War II Rowman & Littlefield Publishers Inc. 2007 p. 150
- ^ Mónica Hirst & Andrew Hurrell; The United States and Brazil: A Long Road of Unmet Expectations, Taylor & Francis Books 2005 ISBN 0-415-95066-X pp. 4–5
- ^ Castro, Celso; Izecksohn, Vitor; Kraay, Hendrik (2004), Nova história militar brasileira, Fundação Getúlio Vargas, pp. 13–14, ISBN 978-85-225-0496-1
- ^ McCann 2004, p. 441
- ^ Roett; Riordan Brazil: Politics in a Patrimonial Society, GreenWood Publishing Group 1999, pp. 106–08 ISBN 0-275-95899-X
- ^ Keen & Haynes 2004, pp. 361–62
- ^ Skidmore, p. 201
- ^ Skidmore, pp. 202–203
- ^ Skidmore, p. 204
- ^ Skidmore, pp. 204–205
- ^ Skidmore, pp. 209–210
- ^ Skidmore, p. 210
- ^ Fausto (2005), p. 397
- ^ Gaspari, A Ditadura Envergonhada, pp. 141–42.
- ^ Gaspari, A Ditadura Envergonhada, p. 35.
- ^ Crocitti & Vallance (2012), p. 395, last paragraph.
- ^ Richard Young, Odile Cisneros "Historical Dictionary of Latin American Literature and Theater" Scare Crow Press 2011, p. 224, 2nd § View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Laurence Burgorgue-Larsen & Amaya Úbeda de Torres "The Inter-American Court of Human Rights: Case Law and Commentary" Oxford University Press 2011 ISBN 978-0-19-958878-7 p. 299 View on Google Books Archived 29 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Crocitti & Vallance (2012), p. 396.
- ^ Crocitti & Vallance (2012), p. 395–97.
- ^ Bradford Burns 1993, p. 457
- ^ Fausto (1999), Chapter 6 "The military government and the transition to democracy (1964–1984)".
- ^ Fausto (2005), pp. 464–65.
- ^ Fausto (2005), pp. 465, 475.
- ^ Skidmore, p. 311.
- ^ Fausto (1999), Epilogue.
- ^ Fausto (2005), p. 482.
- ^ Fausto (2005), p. 474.
- ^ Fausto (2005), p. 502.
- ^ Zirin, 2014. Chapter 3
- ^ "Global protest grows as citizens lose faith in politics and the State" Archived 8 June 2021 at the Wayback Machine article on "the Guardian"
- ^ Zirin, 2014. Chapter 7 & Conclusion.
- ^ Jonathan Watts & Donna Bowater. "Dilma Rousseff impeached by Brazilian senate". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 31 August 2016. Retrieved 31 August 2016.
- ^ Article of Archived 14 May 2021 at the Wayback Machine New York Times about the denouement of Rousseff's impeachment process.
- ^ Article Archived 24 June 2016 at the Wayback Machine in Financial Times (18 April 2016) about the political ambiance in Brazil on the day vote for the Deputies chamber decision about open an impeachment procedure against President Dilma. 2nd to 4th paragraph.
- ^ "Brazil supreme court judge orders probe into nine ministers – paper" Archived 16 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Reuters. 11 April 2017.
- ^ "President Michel Temer of Brazil Is Charged With Corruption" Archived 14 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine. The New York Times. 26 June 2017.
- ^ "A scary election in Brazil". The Economist. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ^ "Jair Bolsonaro é eleito presidente do Brasil". veja.abril.com.br. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ Guerin, Orla (9 July 2021). "Covid-19 pandemic: 'Everything you should not do, Brazil has done'". BBC News. Brasília: BBC. Archived from the original on 3 August 2021. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ "Lula reitera candidatura presidencial contra Bolsonaro em 2022". Valor. 20 May 2021. Archived from the original on 5 August 2021. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ "Análise das Eleições 2022: Veja Detalhes dos Resultados da Votação". noticias.uol.com.br (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 30 October 2022. Retrieved 31 October 2022.
- ^ "Resultados – TSE". resultados.tse.jus.br. Archived from the original on 2 November 2022. Retrieved 31 October 2022.
- ^ Phillips, Tom (8 January 2023). "Jair Bolsonaro supporters storm Brazil's presidential palace and supreme court". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023.
- ^ Rocha, Lucas. "Manifestantes furam bloqueio, entram na Esplanada e invadem o Congresso Nacional" [Protesters break through the blockade, enter the Esplanade and invade the National Congress]. CNN Brazil. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- ^ a b "Land and Resources". Encarta. MSN. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 11 June 2008. [dubious – discuss]
- ^ Official Area (In Portuguese) Archived 6 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine IBGE: Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ^ "Hora Legal Brasileira". Observatório Nacional. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- ^ a b c d e "Brazil". Country Guide. BBC Weather. Archived from the original on 8 February 2011. Retrieved 11 June 2008.
- ^ Terms and Definitions FRA 2025 Forest Resources Assessment, Working Paper 194. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023.
- ^ "Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Brazil". Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- ^ a b c d e "Natural Regions". Encarta. MSN. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 11 June 2008. [dubious – discuss]
- ^ a b c "Temperature in Brazil". Brazil Travel. Archived from the original on 12 June 2008. Retrieved 11 June 2008.
- ^ a b Embrapa. "Annual averages of Mandacaru Agro-meteorological station" (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 20 August 2007. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ "CPD: South America, Site SA19, Caatinga of North-eastern Brazil, Brazil". Botany.si.edu. Archived from the original on 6 June 2009. Retrieved 29 October 2009.
- ^ "Drought, Smallpox, and Emergence of Leishmania braziliensis in Northeastern Brazil" Archived 29 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- ^ "Ó Gráda, C.: Famine: A Short History" Archived 12 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Princeton University Press.
- ^ "Inland fishery enhancements" Archived 6 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine. FAO.
- ^ Maisonnave, Fabiano (10 September 2024). "Brazil faces its worst drought as wildfires rage and Amazon River falls to record low". Associated Press. PBS News. Retrieved 16 September 2024.
- ^ McCoy, Terrence (12 September 2024). "More than half of Brazil is racked by drought. Blame deforestation". Washington Post. Retrieved 16 September 2024.
- ^ "Brazil Endures Worst Drought on Record, Affecting 58% of the Country". Folha de S.Paulo. 5 September 2024. Retrieved 16 September 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "Natural Regions". Encarta. MSN. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 11 June 2008. [dubious – discuss]
- ^ a b "Rivers and Lakes". Encarta. MSN. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 11 June 2008. [dubious – discuss]
- ^ "Amazon – World's largest tropical rain forest and river basin". World Wide Fund for Nature. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 3 June 2010.
- ^ "Brazil". IUCN Green List. Archived from the original on 19 November 2022. Retrieved 19 November 2022.
- ^ a b c Palmerlee, Danny (2007). South America on a Shoestring. Lonely Planet Publications. p. 275. ISBN 978-1-74104-443-0. OCLC 76936293.
- ^ Da Silva, M. and D.W. Minter. 1995. Fungi from Brazil recorded by Batista and Co-workers. Mycological Papers 169. CABI, Wallingford, UK. 585 pp.
- ^ Chapman, A.D (September 2005). "Numbers of Living Species in Australia and the World: A Report for the Department of the Environment and Heritage". Australian Biological Resources Study. Australian Biodiversity Information Services. Archived from the original on 1 November 2007. Retrieved 26 November 2007.
- ^ "One fifth of the world's freshwater". Amazon. World Wide Fund for Nature. 6 August 2007. Archived from the original on 1 March 2011. Retrieved 12 June 2008.
- ^ a b c d "Plant and Animal Life". Encarta. MSN. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2008.
- ^ "Atlantic Forest, Brazil". Map: Biodiversity hotspots. BBC News. 1 October 2004. Archived from the original on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 12 June 2008.
- ^ "Amazon Against the Clock: A Regional Assessment on Where and How to Protect 80% by 2025" (PDF). Amazon Watch. September 2022. p. 8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 September 2022.
Graphic 2: Current State of the Amazon by country, by percentage / Source: RAISG (Red Amazónica de Información Socioambiental Georreferenciada) Elaborated by authors.
- ^ "Places We Work: The Atlantic Forest of Brazil". The Nature Conservancy. 2007. Archived from the original on 2 July 2010. Retrieved 5 December 2007.
- ^ Capobianco, João Paulo. "Biodiversity in the Atlantic Forest". Brazil on CD-ROM and Internet. Ministry of External Relations. Archived from the original on 15 December 2007. Retrieved 5 December 2007.
- ^ USDA Forest Service website, Forest Service International Programs: Brazil Archived 6 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved February 2007.
- ^ Butler, Rhett A. (28 March 2006). "Brazil to Protect Amazon Rainforest". MongaBay.com. Archived from the original on 5 April 2020. Retrieved 28 November 2007.
- ^ "Preserved native vegetation occupies 61% of Brazil's area, says Embrapa". 27 January 2017. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 14 August 2021.
- ^ "How Europe has multiplied its forests and why this can be a problem". BBC News Brasil. Archived from the original on 14 August 2021. Retrieved 14 August 2021.
- ^ Ruiz, Sarah (12 November 2021). "Climate change is pushing Brazil's farmland out of agricultural suitability range". Woodwell climate research center. Nature Climate Change. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Felin, Bruno (10 December 2020). "STATEMENT: Brazil Sets Weak 2030 Emission Reduction Target". World Resources Institute. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 3 January 2021.
- ^ Pimentel, Mauro. "Lula returns for third term as Brazil president". CNN. Archived from the original on 1 January 2023. Retrieved 1 January 2022.
- ^ "Democracy Index 2021: the China challenge" (PDF). Economist Intelligence Unit. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 March 2022. Retrieved 18 December 2022.
- ^ "Freedom in the World 2021" (PDF). Freedom House. 3 March 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 December 2021. Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ a b "Embassy of Brazil – Ottawa". Archived from the original on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 19 July 2007.
Political Institutions – The Executive
- ^ "City Mayors". Archived from the original on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 19 July 2007.
Brazil federal, state and local government
- ^ Fontaine, Edward (1872). "Contributions to the Physical Geography of the Mississippi River, and Its Delta". Journal of the American Geographical Society of New York. 3: 343–78. doi:10.2307/196424. ISSN 1536-0407. JSTOR 196424.
- ^ "Government – Brazil". Southtravels.com. 5 October 1988. Archived from the original on 28 November 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2010.
- ^ "The Brazilian Legal System" Archived 8 October 2009 at the Wayback Machine, Organization of American States. Retrieved 17 May 2007.
- ^ José Afonso da Silva, Curso de Direito Constitucional Positivo (Malheiros, 2004; ISBN 85-7420-559-1), p. 46.
- ^ "Amendments to the Brazilian Constitution". Brazilian Law Compiled. Archived from the original on 22 July 2022. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ Silva, Curso de Direito Constitucional Positivo, p. 592.
- ^ Fabiano Deffenti; Welber Oliveira Barral (2011). Introduction to Brazilian Law. Kluwer Law International. pp. 20–. ISBN 978-90-411-2506-4. Retrieved 6 June 2013.
- ^ Uma Nova Agenda Militar Archived 25 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine Revista Época. Retrieved on 19 February 2009.
- ^ "2021 Military Strength Ranking". Global Firepower. Archived from the original on 5 March 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ^ "Brazil is among the 10 largest military powers in the world". OCP News. Archived from the original on 21 July 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ^ The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, archived from the original on 12 August 2021, retrieved 26 March 2010
- ^ "Sala de imprensa – FAB em números" (in Portuguese). Força Aérea Brasileira. Archived from the original on 17 June 2008. Retrieved 12 December 2007.
- ^ "Decreto Nº 5.670 de 10 de Janeiro de 2006" (in Portuguese). Presidência da República. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 2 October 2010.
- ^ "Military Power". Brasil. Archived from the original on 11 February 2021. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Scheina (1987), p. 81.
- ^ "Grupamento de Mergulhadores de Combate – GruMeC". tropaselite.t35.com. Archived from the original on 27 March 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Article 4 of the Federal Constitution of Brazil Archived 28 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine V-Brazil. Retrieved on 20 September 2011.
- ^ Article 84 of the Federal Constitution of Brazil Archived 19 September 2019 at the Wayback Machine V-Brazil. Retrieved on 20 September 2011.
- ^ U.S. Congressional Report on Brazil United States Congress. Retrieved on 23 June 2009.
- ^ Georges D. Landau, "The Decision-making Process in Foreign Policy: The Case of Brazil", Center for Strategic and International Studies: Washington DC: March 2003
- ^ a b c d e Cabral and Weinstock 2010. Brazil: an emerging aid player (Archived 13 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine). London: Overseas Development Institute
- ^ Cabral, Lidia 2010. Brazil's development cooperation with the South: a global model in waiting (Archived 30 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine). London: Overseas Development Institute
- ^ "Ordem pública é prioridade da Força Nacional de Segurança". Portal Brasil. 29 April 2012. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Brasil tem maior número absoluto de homicídios do mundo". O Estado de S. Paulo. 10 December 2014. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Taxa de delito por 100 mil habitantes". Secretaria de Segurança Pública do Estado de São Paulo. 31 January 2011. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 14 February 2011.
- ^ "A Year of Violence Sees Brazil's Murder Rate Hit Record High". The New York Times. 10 August 2018. Archived from the original on 1 January 2022.
- ^ "Os estados com mais homicídios no Brasil". Exame. 11 November 2014. Archived from the original on 28 August 2016. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Brasil passa a Rússia e tem a terceira maior população carcerária do mundo". Folha de S.Paulo. 5 June 2014. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Brasil tem hoje deficit de 200 mil vagas no sistema prisional". G1. 15 January 2014. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
- ^ "Multilateral Treaties - AMERICAN CONVENTION ON HUMAN RIGHTS "PACT OF SAN JOSE, COSTA RICA" (B-32)". Organization of American States. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ^ "Brazil - Freedom in the World 2017". Freedom House. Archived from the original on 8 July 2019. Retrieved 4 May 2021.
- ^ "Brazil - World - Americas". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ^ "Brazil 2016/2017". Amnesty International. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ^ "ENGLISH VERSION of Human Rights Complaint Document submitted to the United Nations OHCHR by the National Indigenous Peoples Organization from Brazil (APIB)". EARTH PEOPLES. 13 November 2012. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 19 November 2012.
- ^ "Human rights in Brazil". State.gov. 25 February 2009. Archived from the original on 26 February 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ^ "Human Rights in Brazil". UNESCO. United Nations. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ^ Brocchetto, Marilia (15 May 2013). "Brazilian judicial council orders notaries to recognize same-sex marriage". CNN. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ^ da Cunha Melo, Leopoldo (January 1948). "Conceituação de "Território Federal" como unidade política" [Conceptualization of "Federal Territory" as a political unit] (PDF). Boletim Geográfico (in Brazilian Portuguese). 5 (58): 1128–1133. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 October 2023. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ Porto, Jadson Luís Rebelo (March 1999). "Os territórios federais e a sua evolução no Brasil" [The federal territories and their evolution in Brazil] (PDF). Revista de Educação, Cultura e meio ambiente (in Brazilian Portuguese). III (15). Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 November 2023. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ "21 Largest Stock Exchanges in the World". Yahoo Finance. 27 March 2023. Archived from the original on 13 September 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ^ "Brasil será maior exportador agrícola mundial em 2024" (in Portuguese). EXAME. 1 July 2015. Archived from the original on 9 May 2018. Retrieved 9 May 2018.
- ^ "Embraer vê clientes mais dispostos à compra de aviões". Exame Magazine. 10 October 2010. Archived from the original on 28 July 2011. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ "6. Brazil". Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
Brazil is rich in a variety of natural resources and is the world's leading producer of tin, iron ore and phosphate. It has large deposits of diamonds, manganese, chromium, copper, bauxite and many other minerals.
- ^ "Labor force, total – Brazil". World Bank. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) (modeled ILO estimate) – Brazil". World Bank. Archived from the original on 13 August 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Banco Central do Brasil – SDDS". www.bcb.gov.br. Central Bank of Brazil. Archived from the original on 21 July 2021. Retrieved 21 July 2022.
- ^ "Poverty headcount ratio at $2.15 a day (2017 PPP) (% of population) – Brazil". World Bank. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Poverty headcount ratio at $6.85 a day (2017 PPP) (% of population) – Brazil". World Bank. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ France, Guilherme (29 January 2019). "Brazil: Overview of corruption and anti-corruption" (PDF). Transparency International. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
Corruption remains one of the biggest impediments to economic development in Brazil.
- ^ Alok Bansal; Yogeshwari Phatak; I C Gupta; Rajendra Jain (2009). Transcending Horizons Through Innovative Global Practices. Excel Books. p. 29. ISBN 978-81-7446-708-9. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ "GDP – composition, by sector of origin". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 19 April 2023. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "FAOSTAT". www.fao.org. Archived from the original on 12 November 2016. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ "How are agricultural co-operatives making a difference in Brazil? | ICA". ica.coop. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- ^ "Production of Brazil, by FAO". Archived from the original on 12 November 2016. Retrieved 4 October 2022.
- ^ "Brasil extrai cerca de 2 gramas de ouro por habitante em 5 anos". R7.com. 29 June 2019. Archived from the original on 12 July 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Nióbio: G1 visita em MG complexo industrial do maior produtor do mundo". G1. 12 December 2019. Archived from the original on 12 December 2019. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Serviço Geológico do Brasil". cprm.gov.br. Archived from the original on 6 September 2019. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Rio Grande do Sul: o maior exportador de pedras preciosas do Brasil". Band.com.br. Archived from the original on 2 May 2018. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Fazcomex Tecnologia para Comércio Exterior – Soluções para Comex". Fazcomex | Tecnologia para Comércio Exterior. Archived from the original on 29 June 2021. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Agronegócio tem oito entre os dez produtos líderes das exportações brasileiras em 2019". Avicultura Industrial. 2 January 2020. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ "List of importing markets for the product exported by Brazil in 2021". International Trade Centre. Archived from the original on 12 April 2023. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "List of supplying markets for the product imported by Brazil in 2021". International Trade Centre. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Brazil Trade". World Integrated Trade Solution (WITS). Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Official History of Automobile Industry in Brazil". National Association of Vehicles Industries. 23 January 2022. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Alimentos Processados | A indústria de alimentos e bebidas na sociedade brasileira atual". alimentosprocessados.com.br. Archived from the original on 25 March 2018. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Produção nacional de celulose cai 6,6% em 2019, aponta Ibá". Valor Econômico. 21 February 2020. Archived from the original on 21 February 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Indústrias calçadistas em Franca, SP registram queda de 40% nas vagas de trabalho em 6 anos". G1. 14 July 2019. Archived from the original on 14 July 2019. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ Comércio, Diário do (24 January 2020). "Minas Gerais produz 32,3% do aço nacional em 2019". Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "O novo mapa das montadoras, que agora rumam para o interior do País". 8 March 2019. Archived from the original on 8 March 2019. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Indústria automobilística do Sul do Rio impulsiona superavit na economia". G1. 12 July 2017. Archived from the original on 19 July 2017. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Indústria Química no Brasil" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- ^ "Estudo de 2018" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- ^ "Produção nacional da indústria de químicos cai 5,7% em 2019, diz Abiquim". economia.uol.com.br. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Industria Textil no Brasil". Archived from the original on 19 June 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Setor de serviços sustenta o crescimento do PIB de 2018". VEJA. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- ^ "Produtividade e Comércio Exterior". SECINT e SEPEC. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Pequenos negócios já representam 30% do Produto Interno Bruto do país". 7 November 2022. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- ^ UNWTO Tourism Highlights, 2016 Edition. 2016. doi:10.18111/9789284418145. ISBN 978-92-844-1814-5.
- ^ "UNWTO Tourism Highlights – 2011 Edition" (PDF). World Tourism Organization. June 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2012. Retrieved 29 September 2011.
- ^ "Estatisticas e Indicadores: Receita Cambial" (in Portuguese). Ministério do Turismo. 2012. Archived from the original on 24 September 2012. Retrieved 13 February 2012.
- ^ Ministério do Turismo (13 January 2012). "Turismo Brasileiro com novo recorde em 2011" (in Portuguese). No Pátio. Archived from the original on 22 August 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2012.
- ^ International Tourism Highlights, 2019 Edition. World Tourism Organization (UNWTO). 2019. doi:10.18111/9789284421152. ISBN 978-92-844-2115-2. S2CID 240665765. Archived from the original on 30 August 2019. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ Guilherme Lohmann Palhares (2012). Tourism in Brazil: Environment, Management and Segments. Routledge. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-415-67432-4. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ "The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2015" (PDF). World Economic Forum. May 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- ^ Jennifer Blanke; Thea Chiesa, eds. (2013). "Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2013" (PDF). World Economic Forum, Geneva, Switzerland. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 November 2019. Retrieved 14 April 2013. See Table 4, pp. 18–19 and Country/Economy Profile: Brazil, pp. 116–17.
- ^ Fundação Instituto de Pesquisas Econômicas (2007). "Caracterização e Dimensionamento do Turismo Domêstico no Brasil 2002 e 2006" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Ministério do Turismo. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 October 2008. Retrieved 21 June 2008.
- ^ "Veja ranking dos Estados brasileiros que atraem mais turistas estrangeiros". Estadão (in Brazilian Portuguese). Archived from the original on 25 June 2024. Retrieved 19 June 2024.
- ^ Redação, Da (18 January 2024). "Brasil recebe 5,9 milhões de estrangeiros em 2023". Portal PANROTAS (in Brazilian Portuguese). Archived from the original on 28 June 2024. Retrieved 19 June 2024.
- ^ Cedeño, Karina (12 June 2024). "Turismo é grande negócio e São Paulo seguirá investindo nele, diz Lucena". Portal PANROTAS (in Brazilian Portuguese). Archived from the original on 28 June 2024. Retrieved 19 June 2024.
- ^ "Movimentação do turismo bate recorde em vários estados e aquece economia". Agência Gov (in Brazilian Portuguese). Archived from the original on 19 June 2024. Retrieved 19 June 2024.
- ^ Fundação Instituto de Pesquisas Econômicas e EMBRATUR (2006). "Caracterização e Dimensionamento do Turismo Domêstico no Brasil 2002 e 2006: Metodologia e Desenvolvimento" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Ministério do Turismo. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 November 2006. Retrieved 22 June 2008.
- ^ Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Staff (2006). OECD Economic Surveys: Brazil 2006. OECD Publishing. p. 94. ISBN 978-92-64-02999-6.
- ^ United Nations Educational, Scientific (2010). UNESCO Science Report 2010: The Current Status of Science Around the World. UNESCO. pp. 110–18. ISBN 978-92-3-104132-7. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Brian Harvey; Henk H.F. Smid; Thâeo Pirard (2010). Emerging Space Powers: The New Space Programs of Asia, the Middle East and South-America. Springer. p. 324. ISBN 978-1-4419-0874-2. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ Crocitti & Vallance (2012), p. 628.
- ^ NASA Signs International Space Station Agreement With Brazil Archived 27 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine NASA.
- ^ O.C. Ferreira. "O Sistema Elétrico Brasileiro". Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 21 March 2013.
- ^ "Previsão de lançamento". Marinha do Brasil (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 25 January 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität". Elsa.physik.uni-bonn.de. 18 August 2008. Archived from the original on 4 August 2008. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- ^ "CEITEC". Portal Brasil. Brasil.gov.br. Archived from the original on 17 November 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ "Brasil cai duas posições em ranking mundial", Folha de S.Paulo, 26 March 2010, archived from the original on 26 September 2013, retrieved 26 March 2010
- ^ World Intellectual Property Organization (2024). Global Innovation Index 2024: Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship. World Intellectual Property Organization. p. 18. doi:10.34667/tind.50062. ISBN 978-92-805-3681-2. Retrieved 6 October 2024.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ "Global Innovation Index 2019". www.wipo.int. Archived from the original on 2 September 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index". INSEAD Knowledge. 28 October 2013. Archived from the original on 2 September 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "M. Santos Dumont Rounds Eiffel Tower" (PDF). The New York Times. 20 October 1901. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ "Engelberg, Inc". Vintage Machinery. 2011. Archived from the original on 21 March 2012. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ^ Abreu, Manuel de, pag. 17 – Grande Enciclopédia Universal – edição de 1980 – Ed.Amazonas
- ^ "Portable stereo's creator got his due, eventually". Archived from the original on 9 March 2009. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ Exposição destaca centenário do CEFET-MG Sítio do Cefet-MG, acessado em 13 de novembro de 2010 Archived 13 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação. "50 anos do Méson-Pi". Archived from the original on 26 May 2011. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ "Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas – Coleção Galileo: Textos de Física" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 March 2013. Retrieved 21 October 2014.
- ^ "Atta-Ur-Rahman, José Leite Lopes and Juan Martín Maldacena receive UNESCO science prizes". UNESCOPRESS. Archived from the original on 19 June 2002. Retrieved 21 October 2014.
- ^ Brasileiro ganha a Medalha Fields, considerada o "Nobel da Matemática" Archived 13 June 2021 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ West, David A. 2003. Fritz Müller: a naturalist in Brazil. Blacksburg: Pocahontas Press
- ^ "International – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)". www.eia.gov. Archived from the original on 26 October 2023. Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ Michael Schmidt; Vincent Onyango; Dmytro Palekhov (2011). Implementing Environmental and Resource Management. Springer. p. 42. ISBN 978-3-540-77568-3. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ OECD; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Staff (2001). OECD Economic Surveys: Brazil 2001. OECD Publishing. p. 193. ISBN 978-92-64-19141-9. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2015.
- ^ "Renewable Capacity Statistics 2022" (PDF). IRENA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 19 May 2022.
- ^ Hannah Ritchie and Max Roser, Solar Power Generation
- ^ a b "Matriz Energética e Elétrica". Empresa de Pesquisa Energética (in Portuguese).
- ^ [1] National Agency of Energy
- ^ Nakagawa, Fernando (23 March 2022). "Brasil anuncia aumento da produção de petróleo em 10% para ajudar a estabilizar preços". CNN Brasil.
- ^ "Produção de petróleo e gás no Brasil ultrapassa 4 milhões de boe/d pela primeira vez". Agência Nacional do Petróleo, Gás Natural e Biocombustíveis. 19 February 2020. Archived from the original on 20 February 2020. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- ^ "Qual é a maior rodovia do Brasil?" (in Brazilian Portuguese). O Estado de S.Paulo. 9 March 2022. Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ "BR-116" (in Brazilian Portuguese). Banco de Informações e Mapas de Transportes/Ministry of Transport (Brazil). 2018. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ "Brazilian road network in 2019". anuariodotransporte.cnt.org.br.
- ^ "Road system in Brazil". Nationsencyclopedia.com. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- ^ "Anuário CNT do Transporte". anuariodotransporte.cnt.org.br.
- ^ "Extensão da Malha Ferroviária – 2015". ANTT. Archived from the original on 8 December 2023. Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ "OPrincipais ferrovias". Ministerio dos Transportes (in Portuguese) Archived 29 March 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Arquitetura, INBEC Pós-Graduação- Engenharia (4 February 2020). "Conheça a história da construção do Metrô de São Paulo". INBEC Pós-Graduação (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ "Ociosidade atinge 70% dos principais aeroportos". O Globo, 12 August 2007. (in Portuguese)
- ^ Guilherme Lohmann Palhares (2012). Tourism in Brazil: Environment, Management and Segments. Routledge. p. 48. ISBN 978-0-415-67432-4.
- ^ "Relatorio Operacional 2018" (PDF). Aeroporto Internacional de São Paulo. Retrieved 19 June 2024.
- ^ Country Comparison to the World: Gini Index – Brazil Archived 13 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine The World Factbook. Retrieved on 3 April 2012.
- ^ "Mercado Brasileiro Terminais de Contêineres", Santos Brasil. (in Portuguese)
- ^ G1, Fábio AmatoDo; Brasília, em (24 March 2013). "Navios esperam até 16 dias para atracar em porto do país, diz MDIC". Economia.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Brazilian population likely to start shrinking in 2042". Agência Brasil. 23 August 2024. Retrieved 24 August 2024.
- ^ 2008 PNAD, IBGE. "População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade"
- ^ 2008 PNAD, IBGE. "População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade"
- ^ 2008 PNAD, IBGE. "População residente por situação, sexo e grupos de idade".
- ^ "Brazil population reaches 190.8 million" Archived 9 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Brasil.gov.br.
- ^ "Shaping Brazil: The Role of International Migration". Migration Policy Institute.
- ^ José Alberto Magno de Carvalho, "Crescimento populacional e estrutura demográfica no Brasil" Archived 19 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine Belo Horizonte: UFMG/Cedeplar, 2004 (PDF file), p. 5.
- ^ "Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística". IBGE. 29 November 1999. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- ^ "Projeção da População do Brasil – Brazil's populational projection". IBGE. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- ^ Magno de Carvalho, "Crescimento populacional e estrutura demográfica no Brasil"[dead link], pp. 7–8.
- ^ PNAD 2008, IBGE. "Pessoas de 5 anos ou mais de idade por situação, sexo, alfabetização e grupos de idade e grupos de idade".
- ^ 2008 PNAD, IBGE. [2].
- ^ De Assis Poiares, Lilian; De Sá Osorio, Paulo; Spanhol, Fábio Alexandre; Coltre, Sidnei César; Rodenbusch, Rodrigo; Gusmão, Leonor; Largura, Alvaro; Sandrini, Fabiano; Da Silva, Cláudia Maria Dornelles (2010). "Allele frequencies of 15 STRs in a representative sample of the Brazilian population" (PDF). Forensic Science International: Genetics. 4 (2): e61–63. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2009.05.006. PMID 20129458. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2011.
- ^ Brazilian DNA is nearly 80% European, indicates study.
- ^ a b NMO Godinho O impacto das migrações na constituição genética de populações latino-americanas Archived 6 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine. PhD Thesis, Universidade de Brasília (2008).
- ^ Pena, Sérgio D. J.; Di Pietro, Giuliano; Fuchshuber-Moraes, Mateus; Genro, Julia Pasqualini; Hutz, Mara H.; Kehdy Fde, Fernanda de Souza Gomes; Kohlrausch, Fabiana; Magno, Luiz Alexandre Viana; Montenegro, Raquel Carvalho; et al. (2011). Harpending, Henry (ed.). "The Genomic Ancestry of Individuals from Different Geographical Regions of Brazil Is More Uniform Than Expected". PLOS ONE. 6 (2): e17063. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...617063P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017063. PMC 3040205. PMID 21359226.
- ^ Lins, T. C.; Vieira, R. G.; Abreu, B. S.; Grattapaglia, D.; Pereira, R. W. (March–April 2009). "Genetic composition of Brazilian population samples based on a set of twenty-eight ancestry informative SNPs". American Journal of Human Biology. 22 (2): 187–192. doi:10.1002/ajhb.20976. PMID 19639555. S2CID 205301927.
- ^ Pena, Sérgio D. J.; Bortolini, Maria Cátira (1 April 2004). "Pode a genética definir quem deve se beneficiar das cotas universitárias e demais ações afirmativas?". Estudos Avançados. 18 (50): 31–50. doi:10.1590/S0103-40142004000100004. hdl:10183/19857.
- ^ Lins, T. C.; Vieira, R. G.; Abreu, B. S.; Grattapaglia, D.; Pereira, R. W. (March–April 2009). "Genetic composition of Brazilian population samples based on a set of twenty-eight ancestry informative SNPs". American Journal of Human Biology. 22 (2): 187–192. doi:10.1002/ajhb.20976. PMID 19639555. S2CID 205301927.
- ^ "Allele frequencies of 15 STRs in a representative sample of the Brazilian population" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on April 8, 2011. Retrieved April 8, 2011.
- ^ Godinho, Neide Maria de Oliveira (2008). "O impacto das migrações na constituição genética de populações latino-americanas". Universidade de Brasília. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011.
- ^ Pena, Sérgio D. J.; Pietro, Giuliano Di; Fuchshuber-Moraes, Mateus; Genro, Julia Pasqualini; Hutz, Mara H.; Kehdy, Fernanda de Souza Gomes; Kohlrausch, Fabiana; Magno, Luiz Alexandre Viana; Montenegro, Raquel Carvalho; Moraes, Manoel Odorico; Moraes, Maria Elisabete Amaral de; Moraes, Milene Raiol de; Ojopi, Élida B.; Perini, Jamila A.; Racciopi, Clarice; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Ândrea Kely Campos; Rios-Santos, Fabrício; Romano-Silva, Marco A.; Sortica, Vinicius A.; Suarez-Kurtz, Guilherme (16 February 2011). "The Genomic Ancestry of Individuals from Different Geographical Regions of Brazil Is More Uniform Than Expected". PLOS ONE. 6 (2): e17063. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...617063P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017063. PMC 3040205. PMID 21359226.
- ^ "SIDIA M. CALLEGARI-JACQUES et al., Historical Genetics: Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Formation" (PDF). Hereditas.com.br. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 6, 2011. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- ^ Callegari-Jacques, S. M.; Grattapaglia, D.; Salzano, F. M.; Salamoni, S. P.; Crossetti, S. G.; Ferreira, M. R. E.; Hutz, M. H. (November–December 2003). "Historical genetics: Spatiotemporal analysis of the formation of the Brazilian population" (PDF). American Journal of Human Biology. 15 (6): 824–834. doi:10.1002/ajhb.10217. PMID 14595874. S2CID 34610130. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 6, 2011.
- ^ "Retrato molecular do Brasil". Publicacoes.gene.com.br. Archived from the original on March 6, 2008. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- ^ Maria Stella Ferreira-Levy (1974). "O papel da migração internacional na evolução da população brasileira (1872 a 1972)". Revista de Saúde Pública. 8 (supl): 49–90. doi:10.1590/S0034-89101974000500003., Table 2, p. 74. (in Portuguese)
- ^ Zirin, 2014. Chapter 2, Section "The Beginning of the 'Mosaic' ".
- ^ Grün, Roberto (July 1996). "The Armenian Renaissance in Brazil". The Americas. 53 (1): 113–151. doi:10.2307/1007476. ISSN 0003-1615. JSTOR 1007476. S2CID 143656550.
- ^ "The Jewish Community in Brazil". Beit Hatfutsot.
- ^ Silvia Ferabolli (25 September 2014). Arab Regionalism: A Post-Structural Perspective. Routledge. p. 151. ISBN 978-1-317-65803-0.
According to estimates by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), countersigned by the League of Arab States, Brazil has the largest Arab colony outside their countries of origin. There are estimated 15 million Arabs living in Brazil today, with some researchers suggesting numbers around 20 million.
- ^ Paul Amar (15 July 2014). The Middle East and Brazil: Perspectives on the New Global South. Indiana University Press. p. 40. ISBN 978-0-253-01496-2.
there are, according to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, more than sixteen million Arabs and descendants of Arabs in Brazil, constituting the largest community of Arabs descent outside the Middle East.
- ^ cl1289 (8 June 2021). "From Beirut to Brazil". CCAS. Retrieved 7 November 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Coelho (1996), p. 268.
- ^ a b Vesentini (1988), p. 117.
- ^ Adas, Melhem Panorama geográfico do Brasil, 4th ed (São Paulo: Moderna, 2004), p. 268 ISBN 85-16-04336-3
- ^ Azevedo (1971), pp. 2–3.
- ^ a b c Moreira (1981), p. 108.
- ^ Azevedo (1971), pp. 74–75.
- ^ Enciclopédia Barsa, vol. 10 (Rio de Janeiro: Encyclopædia Britannica do Brasil, 1987), p. 355.
- ^ Azevedo (1971), p. 74.
- ^ a b Azevedo (1971), p. 161.
- ^ Enciclopédia Barsa, vol. 4, pp. 254–55, 258, 265.
- ^ "In Amazonia, Defending the Hidden Tribes", The Washington Post (8 July 2007).
- ^ "The Global Catholic Population". Pew Research Center. 13 February 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ "Brazil". International Religious Freedom Report. U.S. Department of State. 8 November 2005. Retrieved 8 June 2008.
- ^ IBGE – Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (Brazilian Institute for Geography and Statistics). 2010 Census. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ Kevin Boyle; Juliet Sheen (2013). Freedom of Religion and Belief: A World Report. Routledge. p. 211. ISBN 978-1-134-72229-7.
- ^ "Brazil". Berkley Center for Religion, Peace, and World Affairs. Archived from the original on 25 August 2011. Retrieved 7 December 2011.
- ^ Brian Morris (2006). Religion and Anthropology: A Critical Introduction. Cambridge University Press. p. 223. ISBN 978-0-521-85241-8.
- ^ William Jeynes; David W. Robinson (2012). International Handbook of Protestant Education. Springer. p. 405. ISBN 978-94-007-2386-3.
- ^ "2010 census results" (PDF).
- ^ "Brazil". Berkley Center for Religion, Peace, and World Affairs. Archived from the original on 25 August 2011. Retrieved 7 December 2011. See drop-down essay on "The Growth of Religious Pluralism"
- ^ a b Do G1, em São Paulo (23 August 2011). "G1 – País tem menor nível de adeptos do catolicismo desde 1872, diz estudo". G1.globo.com. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Senado aprova acordo com o Vaticano". O Globo. 2009. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ "Decreto nº 7.107, de 11 de fevereiro de 2010". Casa Civil da Presidência da República. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ Gerard Martin La Forgia; Bernard F. Couttolenc (2008). Hospital Performance in Brazil: The Search for Excellence. World Bank Publications. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-8213-7359-0.
- ^ "20 Anos do SUS". Conselho Nacional de Saúde. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- ^ Lawrence F. Wolper (2004). Health Care Administration: Planning, Implementing, and Managing Organized Delivery Systems. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-7637-3144-1.
- ^ "Physicians (per 1,000 people)". World Health Organization's Global Health Workforce Statistics.
- ^ "Hospital beds (per 1,000 people)". World Health Organization The World Bank.
- ^ "Measuring overall health system performance for 191 countries" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2000. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 November 2006. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- ^ Usa Ibp Usa (2005). Brazil: Tax Guide. Int'l Business Publications. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-7397-3279-3.
- ^ a b "IBGE: Analfabetismo cai no país, mas fica estagnado no Nordeste". Globo.com (in Portuguese). 15 July 2020.
- ^ The Central Intelligence Agency (2010). The World Factbook 2010 (CIA 2009 ed.). Potomac Books, Inc. p. 143. ISBN 978-1-59797-541-4.
- ^ World Bank (2001). Rural Poverty Alleviation in Brazil: Towards an Integrated Strategy. World Bank Publications. p. 40. ISBN 978-0-8213-5206-9.
- ^ Laplane, Mario (14 May 2019). "Efforts towards inclusion". D + C, Development and cooperation.
- ^ "QS World University Rankings 2024". Top Universities. Archived from the original on 4 January 2024. Retrieved 6 December 2023.
- ^ "ShanghaiRanking's Academic Ranking of World Universities". www.shanghairanking.com. Archived from the original on 29 September 2023. Retrieved 6 December 2023.
- ^ "QS University Rankings Latin America". QS World University Rankings. Retrieved 11 November 2018.
- ^ "Brazil – Language". countrystudies.us.
- ^ "Learn About Portuguese Language". Sibila.com.br. 25 April 2009. Archived from the original on 20 April 2012. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- ^ a b c "Languages of Brazil". Ethnologue. Retrieved 9 June 2008.
- ^ LEI Nº 10.436, DE 24 DE ABRIL DE 2002. Presidência da República, Casa Civil, Subchefia para Assuntos Jurídicos. Retrieved on 19 May 2012.
- ^ Brazilian decree nº 5626, 22 December 2005. Planalto.gov.br (23 December 2005). Retrieved on 19 May 2012.
- ^ Charles J. Russo (2011). The Legal Rights of Students with Disabilities: International Perspectives. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-4422-1085-1.
- ^ Campbell, Lyle; Grondona, Verónica; Muysken, Peter (2012). "Contacts between indigenous languages in South America". The Indigenous Languages of South America: A Comprehensive Guide. Walter de Gruyter. p. 247. ISBN 978-3-11-025803-5.
Nheengatú (also called língua geral of Amazonia, or lingua Brasilica) originated in the 17th century in what are now the states of Pará Maranhão, as lingua franca on the basis of Tupinambá lexicon but with strong grammatical influence from Portuguese, also due to intervention by Jesuit missionaries [...] Around 1700 it was spoken in a large area in Brazil, as a contact language between whites and indians, but it lost some support with the expulsion of the Jesuits in 1758 [...] Its sister language in the colonial period was Língua Geral Paulista (in the state of São Paolo) a lingua franca which is now extinct.
- ^ Rohter, Larry (28 August 2005). "Language Born of Colonialism Thrives Again in Amazon". The New York Times. Retrieved 14 July 2008.
- ^ "O alemão lusitano do Sul do Brasil". DW-World.de.
- ^ "ELB". labeurb.unicamp.br.
- ^ "Approvato il progetto che dichiara il 'Talian' come patrimonio del Rio Grande del Sud – Brasile". Sitoveneto. Archived from the original on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
- ^ Patrick Stevenson (1997). The German Language and the Real World: Sociolinguistic, Cultural, and Pragmatic Perspectives on Contemporary German. Oxford University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-19-823738-9.
- ^ "Constituição de 1988 da República Federativa do Brasil/Título II – Wikisource". pt.m.wikisource.org.
- ^ "IDBGE" (in Portuguese). IBGE. 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ a b "Mais da metade da população vive em 294 arranjos formados por contiguidade urbana e por deslocamentos para trabalho e estudo" (in Portuguese). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Retrieved 16 March 2017.
- ^ "Arranjos Populacionais e Concentrações Urbanas do Brasil" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. p. 148. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 16 March 2017.
- ^ "Estimativas da população residente no Brasil e Unidades da Federação com data de referência em 1º de julho de 2016" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Retrieved 16 March 2017.
- ^ "Principal Cities". Encarta. MSN. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 10 June 2008. [dubious – discuss]
- ^ "Arranjos Populacionais e Concentrações Urbanas do Brasil" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. p. 148. Retrieved 16 March 2017.
- ^ "Estimativas da população residente no Brasil e Unidades da Federação com data de referência em 1º de julho de 2017" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Retrieved 14 May 2018.
- ^ Largest Carnival Guinness World Records.
- ^ Teresa A. Meade (2009). A Brief History of Brazil. Infobase Publishing. p. 146. ISBN 978-0-8160-7788-5.
- ^ David Levinson (1998). Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 325. ISBN 978-1-57356-019-1.
- ^ Jeffrey Lesser (2013). Immigration, Ethnicity, and National Identity in Brazil, 1808 to the Present. Cambridge University Press. pp. 150–55. ISBN 978-0-521-19362-7.
- ^ Freyre, Gilberto (1986). "The Afro-Brazilian experiment: African influence on Brazilian culture". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 30 May 2012. Retrieved 8 June 2008.
- ^ Leandro Karnal, Teatro da fé: Formas de representação religiosa no Brasil e no México do século XVI, São Paulo, Editora Hucitec, 1998; available on fflch.usp.br Archived 24 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The Brazilian Baroque", Encyclopaedia Itaú Cultural Archived 30 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Leslie Marsh (2012). Brazilian Women's Filmmaking: From Dictatorship to Democracy. University of Illinois Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-252-09437-8.
- ^ Hue, Jorge de Souza (1999). Uma visão da arquitectura colonial no Brasil [A vision of Colonial Architecture in Brazil] (in Portuguese). Rio de Janeiro.
- ^ Boxer, Charles Ralph (1962). The Golden Age of Brazil, 1695–1750: Growing Pains of a Colonial Society. University of California Press.
- ^ a b Guimaraens, Cêça de. Arquitetura Archived 8 September 2003 at the Wayback Machine. Portal do Ministério das Relações Exteriores.
- ^ Claro, Mauro. "Ambientes modernos. A casa modernista da Rua Santa Cruz, de Gregori Warchavchik, e outras casas da modernidade". In: Drops, 2008; 09 (025.03)
- ^ a b Duduka Da Fonseca; Bob Weiner (1991). Brazilian Rhythms for Drumset. Alfred Music Publishing. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-7692-0987-6.
- ^ Donna M. Di Grazia (2013). Nineteenth-Century Choral Music. Routledge. p. 457. ISBN 978-1-136-29409-9.
- ^ "UNESCO Culture Sector – Intangible Heritage – 2003 Convention". Unesco.org. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ^ Larry Crook (2009). Focus: Music of Northeast Brazil. Taylor & Francis. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-415-96066-3.
- ^ Peter Fryer (2000). Rhythms of Resistance: African Musical Heritage in Brazil. Pluto Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-7453-0731-2.
- ^ "Brazil From A TO Z: FORRÓ". Brazilian Experience. 25 December 2015.
- ^ "Jack A. Draper III". Romance Languages and Literatures: University of Missouri.
- ^ Draper, Jack A. III (2010). Forró and redemptive regionalism from the Brazilian northeast: popular music in a culture of migration. New York: Lang. ISBN 978-1-4331-1076-4. OCLC 643568832.
- ^ MacGowan, Chris; Pessanha, Ricardo (1998). The Brazilian Sound: Samba, Bossa Nova, and the Popular Music of Brazil. Temple University Press. pp. 159–61. ISBN 978-1-56639-545-8.
- ^ MacGowan & Pessanha (1998), p. 6.
- ^ Gayle Kassing (2007). History of Dance: An Interactive Arts Approach. Human Kinetics 10%. p. 236. ISBN 978-0-7360-6035-6.
- ^ Michael Campbell (2011). Popular Music in America: The Beat Goes on. Cengage Learning. p. 299. ISBN 978-0-8400-2976-8.
- ^ Crocitti & Vallance (2012), p. 360.
- ^ "Brazilian Literature: An Introduction". Embassy of Brasil – Ottawa. Visited on 2 November 2009.
- ^ Candido; Antonio. (1970) Vários escritos. São Paulo: Duas Cidades. p. 18
- ^ Caldwell, Helen (1970) Machado de Assis: The Brazilian Master and his Novels. Berkeley, Los Angeles and London, University of California Press.
- ^ Fernandez, Oscar Machado de Assis: The Brazilian Master and His Novels The Modern Language Journal, Vol. 55, No. 4 (Apr. 1971), pp. 255–56
- ^ Beatriz Mugayar Kühl, Arquitetura do ferro e arquitetura ferroviária em São Paulo: reflexões sobre a sua preservação, p. 202. Atelie Editorial, 1998.
- ^ Daniel Balderston and Mike Gonzalez, Encyclopedia of Latin American and Caribbean Literature, 1900–2003, p. 288. Routledge, 2004.
- ^ Sayers, Portugal and Brazil in Transitn, "Literature". U of Minnesota Press, 1 January 1999.
- ^ Marshall C. Eakin and Paulo Roberto de Almeida, Envisioning Brazil: A Guide to Brazilian Studies in the United States: "Literature, Culture and Civilization". University of Wisconsin Press, 31 October 2005.
- ^ "Prêmio Camões de Literatura | Biblioteca Nacional". Bn.br (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 16 March 2016. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ^ "Quem somos | Academia Brasileira de Letras". Academia.org.br (in Portuguese). 3 August 2014. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ^ "Rio the Magnificent (1932)". YouTube. 18 April 2008. Archived from the original on 7 November 2015. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Larry, Rohter (9 November 2010). "Brazil's Best, Restored and Ready for a 21st-Century Audience". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 1 January 2022. Retrieved 3 November 2010.
- ^ Tose, Juliano. "Editorial". Contracampo – revista de cinema. Revista Contracampo. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ "Cidade de Deus (City of God) (2003) – Rotten Tomatoes". Rotten Tomatoes. Flixster. 17 January 2003. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ Ebert, Roger (14 December 2012). "The best films of the decade". RogerEbert.com. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ Louzada, Maria Alice & Louzada, Julio. Os Primeiros Momentos da Arte Brasileira Archived 6 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Júlio Louzada Artes Plásticas Brasil. Acesso 5 out 2010
- ^ Leite, José Roberto Teixeira & Lemos, Carlos A.C. Os Primeiros Cem Anos, in Civita, Victor. Arte no Brasil. São Paulo: Abril Cultural, 1979
- ^ a b Biscardi & Rocha 2006
- ^ Amaral, Aracy; Kim Mrazek Hastings (1995). "Stages in the Formation of Brazil's Cultural Profile". Journal of Decorative and Propaganda Arts. 21: 9–25. doi:10.2307/1504129. JSTOR 1504129.
- ^ Sevcenko, Nicolau. Pindorama revisitada: cultura e sociedade em tempos de virada. Série Brasil cidadão. Editora Peirópolis, 2000. pp. 39–47
- ^ Padre Anchieta Brasil Escola.
- ^ a b "Brazilian Theatre: An Introduction". Ambasciata brasiliana a Ottawa. Archived from the original on 5 February 2012.
- ^ O Teatro no Brasil Secretaria da Educação do Paraná.
- ^ "Way of Life". Encarta. MSN. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 8 June 2008.
- ^ Roger, "Feijoada: The Brazilian national dish" Archived 29 November 2009 at the Wayback Machine braziltravelguide.com.
- ^ Cascudo, Luis da Câmara. História da Alimentação no Brasil. São Paulo/Belo Horizonte: Editora USP/Itatiaia, 1983.
- ^ Bayor, Ronald H. (2011). Multicultural America: An Encyclopedia of the Newest Americans. Georgia Institute of Technology. p. 181. ISBN 978-0-313-35786-2.
- ^ Barbosa, Lívia (2007). "Feijão com arroz e arroz com feijão: o Brasil no prato dos brasileiros". Horizontes Antropológicos. 13 (28): 87–116. doi:10.1590/S0104-71832007000200005.
- ^ Ferraccioli, Patrícia; Silveira, Eliane Augusta da (2010). "Cultural feeding influence on palative memories in the usual brazilian cuisine". Rev. Enferm. UERJ. 18 (2): 198–203.
- ^ Freyre, Gilberto. Açúcar. Uma Sociologia do Doce, com Receitas de Bolos e Doces do Nordeste do Brasil. São Paulo, Companhia das Letras, 1997.
- ^ "Rede Globo se torna a 2ª maior emissora do mundo" (in Portuguese). O Fuxico. Archived from the original on 14 May 2012. Retrieved 22 May 2012.
- ^ Roberto Gonzalez Echevarría; Enrique Pupo-Walker (1996). The Cambridge History of Latin American Literature. Cambridge University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-521-41035-9.
- ^ Donald H. Johnston (2003). Encyclopedia of international media and communications. Vol. 3. Academic Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-0-12-387671-3.
- ^ Jon S. Vincent (2003). Culture and Customs of Brazil. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 97–100. ISBN 978-0-313-30495-8.
- ^ Bryan McCann (2004). Hello, Hello Brazil: Popular Music in the Making of Modern Brazil. Duke University Press. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-8223-3273-2.
- ^ David Ward (2007). Television and Public Policy: Change and Continuity in an Era of Global Liberalization. Routledge. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-203-87728-9.
- ^ "Um ponto de IBOPE equivale a quantas pessoas? E domicílios?". IBOPE. Archived from the original on 22 May 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- ^ "Top 10 das novelas". MSN Brasil. Archived from the original on 7 May 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- ^ Martin Campbell-Kelly; William F. Aspray; Jeffrey R. Yost; Honghong Tinn; Gerardo Con Díaz (2023). Computer: A History of the Information Machine. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-00-087875-2.
- ^ "Brazil launches international TV station for Africa". BBC News. 25 May 2010. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- ^ "FIFA: Pele, the greatest of them all". FIFA. 28 June 2012. Archived from the original on 9 January 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ "Pele tops World Cup legends poll". BBC News. 12 June 2006. Archived from the original on 26 March 2019. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ^ "Futebol, o esporte mais popular do Brasil, é destaque no Via Legal". Jusbrasil.com.br. Archived from the original on 30 March 2012. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ^ "Football in Brazil". Goal Programme. International Federation of Association Football. 15 April 2008. Archived from the original on 4 June 2007. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ Zirin, 2014. Chapter 4 "Futebol: The Journey from Daring to Fear"
- ^ Donaldson, Gerald. "Emerson Fittipaldi". Hall of Fame. The Official Formula 1 Website. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ Donaldson, Gerald. "Nelson Piquet". Hall of Fame. The Official Formula 1 Website. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ Donaldson, Gerald. "Ayrton Senna". Hall of Fame. The Official Formula 1 Website. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "Beach Soccer". International Federation of Association Football. Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "Futsal". International Federation of Association Football. Archived from the original on 3 June 2007. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "The art of capoeira". BBC. 20 September 2006. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "Brazilian Vale Tudo". I.V.C. Archived from the original on 30 May 1998. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation". International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation. Archived from the original on 20 April 2008. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "1950 FIFA World Cup Brazil". Previous FIFA World Cups. International Federation of Association Football. Archived from the original on 3 June 2007. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "2014 FIFA World Cup Brazil". International Federation of Association Football. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "The Official Formula 1 Website". Formula One Administration. Archived from the original on 4 June 2008. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ Ming Li; Eric W. MacIntosh; Gonzalo A. Bravo (2011). International Sport Management. Human Kinetics – College of Business at Ohio University. p. 129. ISBN 978-1-4504-2241-3.
- ^ "Olympics 2016: Tearful Pele and weeping Lula greet historic win for Rio", The Guardian, 2 October 2009.
- ^ "FIBA World Championship History (pdf)" (PDF). FIBA. 1 January 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
Bibliography
- Azevedo, Aroldo. O Brasil e suas regiões. São Paulo: Companhia Editora Nacional, 1971
- Barman, Roderick J. Citizen Emperor: Pedro II and the Making of Brazil, 1825–1891. Stanford: Stanford University Press, 1999. ISBN 0-8047-3510-7
- Biscardi, Afrânio; Rocha, Frederico Almeida (May 2006), "O Mecenato Artístico de D. Pedro II e o Projeto Imperial", 19&20 – A revista eletrônica de DezenoveVinte, vol. I, no. 1
- Boxer, Charles R. The Portuguese Seaborne Empire (1969)
- O império marítimo português 1415–1825. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 2002. ISBN 85-359-0292-9
- Bueno, Eduardo. Brasil: uma História. São Paulo: Ática, 2003. ISBN 85-08-08213-4
- Calmon, Pedro. História da Civilização Brasileira. Brasília: Senado Federal, 2002
- Carvalho, José Murilo de. D. Pedro II. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 2007
- Coelho, Marcos Amorim. Geografia do Brasil. 4th ed. São Paulo: Moderna, 1996
- Diégues, Fernando. A revolução brasílica. Rio de Janeiro: Objetiva, 2004
- Enciclopédia Barsa. Volume 4: Batráquio – Camarão, Filipe. Rio de Janeiro: Encyclopædia Britannica do Brasil, 1987
- Ermakoff, George (2006). Rio de Janeiro – 1840–1900 – Uma crônica fotográfica (in Portuguese). Rio de Janeiro: G. Ermakoff Casa Editorial. ISBN 978-85-98815-05-3.
- Fausto, Boris and Devoto, Fernando J. Brasil e Argentina: Um ensaio de história comparada (1850–2002), 2nd ed. São Paulo: Editoria 34, 2005. ISBN 85-7326-308-3
- Gaspari, Elio. A ditadura envergonhada. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 2002. ISBN 85-359-0277-5
- Janotti, Aldo. O Marquês de Paraná: inícios de uma carreira política num momento crítico da história da nacionalidade. Belo Horizonte: Itatiaia, 1990
- Lyra, Heitor. História de Dom Pedro II (1825–1891): Ascenção (1825–1870). v. 1. Belo Horizonte: Itatiaia, 1977
- Lyra, Heitor. História de Dom Pedro II (1825–1891): Declínio (1880–1891). v. 3. Belo Horizonte: Itatiaia, 1977
- Lustosa, Isabel. D. Pedro I: um herói sem nenhum caráter. São Paulo: Companhia das letras, 2006. ISBN 85-359-0807-2
- Moreira, Igor A. G. O Espaço Geográfico, geografia geral e do Brasil. 18. Ed. São Paulo: Ática, 1981
- Munro, Dana Gardner. The Latin American Republics; A History. New York: D. Appleton, 1942.
- Peres, Damião (1949) O Descobrimento do Brasil por Pedro Álvares Cabral: antecedentes e intencionalidade Porto: Portucalense.
- Scheina, Robert L. Latin America: A Naval History, 1810–1987. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press, 1987. ISBN 0-87021-295-8
- Lilia Schwarcz (30 November 1998). As barbas do imperador: D. Pedro II, um monarca nos trópicos (in Portuguese). São Paulo: Companhia das Letras. ISBN 978-85-7164-837-1. OL 142027M. Wikidata Q18238040.
- Stuart B. Schwartz Sovereignty and Society in Colonial Brazil (1973)
- Early Latin America (1983)
- Sugar Plantations in the Formation of Brazilian Society (1985)
- Skidmore, Thomas E. Brazil: Five Centuries of Change (Oxford University Press, 1999)
- Uma História do Brasil. 4th ed. São Paulo: Paz e Terra, 2003. ISBN 85-219-0313-8
- Souza, Adriana Barreto de. Duque de Caxias: o homem por trás do monumento. Rio de Janeiro: Civilização Brasileira, 2008. ISBN 978-85-200-0864-5.
- Wright, Simon. 1992. Villa-Lobos. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-315475-7
- Vainfas, Ronaldo. Dicionário do Brasil Imperial. Rio de Janeiro: Objetiva, 2002. ISBN 85-7302-441-0
- Vesentini, José William. Brasil, sociedade e espaço – Geografia do Brasil. 7th Ed. São Paulo: Ática, 1988
- Vianna, Hélio. História do Brasil: período colonial, monarquia e república, 15th ed. São Paulo: Melhoramentos, 1994
- Zirin, Dave. Brazil's Dance with the Devil: The World Cup, The Olympics, and the Fight for Democracy Haymarket Books 2014. ISBN 978-1-60846-360-2
Further reading
- Alencastro Felipe, Luiz Felipe de. The Trade in the Living: The Formation of Brazil in the South Atlantic, Sixteenth to Seventeenth Centuries (SUNY Press, 2019)
- Alves, Maria Helena Moreira (1985). State and Opposition in Military Brazil. Austin, TX: University of Texas Press.
- Amann, Edmund (1990). The Illusion of Stability: The Brazilian Economy under Cardoso. World Development (pp. 1805–19).
- "Background Note: Brazil". US Department of State. Retrieved 16 June 2011.
- Bellos, Alex (2003). Futebol: The Brazilian Way of Life. London: Bloomsbury Publishing plc.
- Bethell, Leslie (1991). Colonial Brazil. Cambridge: CUP.
- Costa, João Cruz (1964). A History of Ideas in Brazil. Los Angeles, CA: University of California Press.
- Fausto, Boris (1999). A Concise History of Brazil. Cambridge: CUP.
- Furtado, Celso (1963). The Economic Growth of Brazil: A Survey from Colonial to Modern Times. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
- Lamoureux, Andrew Jackson; and three others (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). pp. 438–463.
- Leal, Victor Nunes (1977). Coronelismo: The Municipality and Representative Government in Brazil. Cambridge: CUP.
- Levine, Robert M. Historical Dictionary of Brazil (2019)
- Malathronas, John (2003). Brazil: Life, Blood, Soul. Chichester: Summersdale.
- Martinez-Lara, Javier (1995). Building Democracy in Brazil: The Politics of Constitutional Change. Macmillan.
- Prado Júnior, Caio (1967). The Colonial Background of Modern Brazil. Los Angeles, CA: University of California Press.
- Schneider, Ronald (1995). Brazil: Culture and Politics in a New Economic Powerhouse. Boulder Westview.
- Skidmore, Thomas E. (1974). Black into White: Race and Nationality in Brazilian Thought. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-501776-2.
- Wagley, Charles (1963). An Introduction to Brazil. New York, New York: Columbia University Press.
External links
Government
- Brazilian Federal Government
- Official Tourist Guide of Brazil
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics
 Wikimedia Atlas of Brazil
Wikimedia Atlas of Brazil Geographic data related to Brazil at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Brazil at OpenStreetMap
- Brazil
- Countries in South America
- Federal constitutional republics
- Former Portuguese colonies
- G15 nations
- G20 members
- Member states of Mercosur
- Member states of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries
- Member states of the United Nations
- Newly industrializing countries
- Countries and territories where Portuguese is an official language
- States and territories established in 1822
- BRICS nations






















