Common brown lemur: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Add: issue. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | Category:Use dmy dates from January 2013 | #UCB_Category 2287/4303 |
rearrange sections per WP:PRIM |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
The '''common brown lemur''' (''Eulemur fulvus'') is a species of [[lemur]] in the family [[Lemuridae]]. It is found in [[Madagascar]] and has been introduced to [[Mayotte]].<ref name=iucn/> |
The '''common brown lemur''' (''Eulemur fulvus'') is a species of [[lemur]] in the family [[Lemuridae]]. It is found in [[Madagascar]] and has been introduced to [[Mayotte]].<ref name=iucn/> |
||
== |
==Taxonomy== |
||
Five additional currently recognized species of lemur were until 2001 considered subspecies of ''E. fulvus''.<ref name=mitt3>{{cite book|title=Lemurs of Madagascar|edition=2nd|author=Russell Mittermeier|page=251|year=2006|isbn=1-881173-88-7|display-authors=etal}}</ref> These are: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==Physical description== |
==Physical description== |
||
| Line 35: | Line 43: | ||
Common brown lemur (Eulemur fulvus) juvenile head.jpg|juvenile |
Common brown lemur (Eulemur fulvus) juvenile head.jpg|juvenile |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The common brown lemur's diet consists primarily of fruits, young leaves, and flowers.<ref name=mitt/> In some locations it eats invertebrates, such as [[cicada]]s,<ref name=mad/> [[spider]]s<ref name=mad/> and [[millipede]]s.<ref name=pic>{{cite book|title=The Pictorial Guide to the Living Primates|url=https://archive.org/details/pictorialguideto0000rowe|url-access=registration|author=Noel Rowe|page=[https://archive.org/details/pictorialguideto0000rowe/page/40 40]|year=1996|isbn=0-9648825-0-7}}</ref> It also eats bark, sap, soil and red clay (see [[geophagy]]).<ref name=pic/> It can tolerate greater levels of toxic compounds from plants than other lemurs can.<ref name=mitt/><ref name=pic/> |
||
==Behavior== |
==Behavior== |
||
| Line 49: | Line 55: | ||
At Berenty (south Madagascar) there is a population of introduced ''E. fulvus rufus'' x ''collaris''.<ref>{{cite book|title=Ringtailed Lemur Biology: Lemur catta in Madagascar| chapter = Berenty Reserve: a research site in southern Madagascar |author1=Alison Jolly |author2=Naoki Koyama |author3=Hantanirina Rasamimanana |author4=Helen Crowley |author5=George Williams | editor = A. Jolly |editor2=R. W. Sussman |editor3=N. Koyama |editor4=H. Rasamimanana| year=2006|pages=32–42|isbn=0-387-32669-3}}</ref> These lemurs show linear hierarchy, adult female dominance, and the presence of conciliatory behavior after aggressions.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Norscia, I. |author2=Palagi, E. | title = Do wild brown lemurs reconcile? Not always |year= 2010| journal = Journal of Ethology| doi = 10.1007/s10164-010-0228-y | volume = 29 | pages = 181–185}}</ref> Additionally, stress levels (measured via self-directed behaviors) decrease at the increase of the hierarchical position of individuals within the social group and reconciliation is able to bring stress down to the baseline levels.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Palagi, E. |author2=Norscia, I. | title = Scratching around stress: hierarchy and reconciliation make the difference in wild brown lemurs ''Eulemur fulvus''|year= 2010| journal = Stress| doi = 10.3109/10253890.2010.505272 | pmid = 20666657 | volume = 14 |issue=1 | pages = 93–7}}</ref> |
At Berenty (south Madagascar) there is a population of introduced ''E. fulvus rufus'' x ''collaris''.<ref>{{cite book|title=Ringtailed Lemur Biology: Lemur catta in Madagascar| chapter = Berenty Reserve: a research site in southern Madagascar |author1=Alison Jolly |author2=Naoki Koyama |author3=Hantanirina Rasamimanana |author4=Helen Crowley |author5=George Williams | editor = A. Jolly |editor2=R. W. Sussman |editor3=N. Koyama |editor4=H. Rasamimanana| year=2006|pages=32–42|isbn=0-387-32669-3}}</ref> These lemurs show linear hierarchy, adult female dominance, and the presence of conciliatory behavior after aggressions.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Norscia, I. |author2=Palagi, E. | title = Do wild brown lemurs reconcile? Not always |year= 2010| journal = Journal of Ethology| doi = 10.1007/s10164-010-0228-y | volume = 29 | pages = 181–185}}</ref> Additionally, stress levels (measured via self-directed behaviors) decrease at the increase of the hierarchical position of individuals within the social group and reconciliation is able to bring stress down to the baseline levels.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Palagi, E. |author2=Norscia, I. | title = Scratching around stress: hierarchy and reconciliation make the difference in wild brown lemurs ''Eulemur fulvus''|year= 2010| journal = Stress| doi = 10.3109/10253890.2010.505272 | pmid = 20666657 | volume = 14 |issue=1 | pages = 93–7}}</ref> |
||
==Reproduction== |
===Reproduction=== |
||
The common brown lemur's mating season is May and June.<ref name=mad/> After a [[gestation|gestation period]] of about 120 days, the young are born in September and October.<ref name=mad/> Single births are most common, but twins have been reported.<ref name=mad/> The young are weaned after about 4 to 5 months.<ref name=mad/><ref name=pic/> Sexual maturity occurs at about 18 months,<ref name=mad/> and females give birth to their first young at 2 years old.<ref name=pic/> Life span can be as long as 30+ years.<ref name=pic/> |
The common brown lemur's mating season is May and June.<ref name=mad/> After a [[gestation|gestation period]] of about 120 days, the young are born in September and October.<ref name=mad/> Single births are most common, but twins have been reported.<ref name=mad/> The young are weaned after about 4 to 5 months.<ref name=mad/><ref name=pic/> Sexual maturity occurs at about 18 months,<ref name=mad/> and females give birth to their first young at 2 years old.<ref name=pic/> Life span can be as long as 30+ years.<ref name=pic/> |
||
== |
==Ecology== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Five additional currently recognized species of lemur were until 2001 considered subspecies of ''E. fulvus''.<ref name=mitt3>{{cite book|title=Lemurs of Madagascar|edition=2nd|author=Russell Mittermeier|page=251|year=2006|isbn=1-881173-88-7|display-authors=etal}}</ref> These are: |
|||
| ⚫ | The common brown lemur's diet consists primarily of fruits, young leaves, and flowers.<ref name=mitt/> In some locations it eats invertebrates, such as [[cicada]]s,<ref name=mad/> [[spider]]s<ref name=mad/> and [[millipede]]s.<ref name=pic>{{cite book|title=The Pictorial Guide to the Living Primates|url=https://archive.org/details/pictorialguideto0000rowe|url-access=registration|author=Noel Rowe|page=[https://archive.org/details/pictorialguideto0000rowe/page/40 40]|year=1996|isbn=0-9648825-0-7}}</ref> It also eats bark, sap, soil and red clay (see [[geophagy]]).<ref name=pic/> It can tolerate greater levels of toxic compounds from plants than other lemurs can.<ref name=mitt/><ref name=pic/> |
||
==Distribution== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
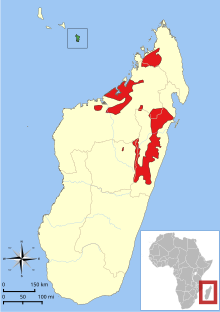
The common brown lemur lives in western Madagascar north of the [[Betsiboka River]] and eastern Madagascar between the [[Mangoro River]] and [[Tsaratanana]], as well as in inland Madagascar connecting the eastern and western ranges.<ref name=mitt>{{cite book|title=Lemurs of Madagascar|edition=2nd|author=Russell Mittermeier|pages=272–274|year=2006|isbn=1-881173-88-7|display-authors=etal}}</ref> They also live on the island of Mayotte, although this population has been [[introduced species|introduced]] there by man.<ref name=mitt/> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 07:54, 15 July 2021
| Common brown lemur | |
|---|---|

| |
| male | |

| |
| female with juvenile both in Peyrieras, Madagascar | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Strepsirrhini |
| Family: | Lemuridae |
| Genus: | Eulemur |
| Species: | E. fulvus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eulemur fulvus É. Geoffroy, 1796[3]
| |
| |
| Distribution of E. fulvus:[1]red = native, green = introduced | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The common brown lemur (Eulemur fulvus) is a species of lemur in the family Lemuridae. It is found in Madagascar and has been introduced to Mayotte.[1]
Taxonomy
Five additional currently recognized species of lemur were until 2001 considered subspecies of E. fulvus.[4] These are:
- White-fronted brown lemur, E. albifrons
- Gray-headed lemur, E. cinereiceps
- Collared brown lemur, E. collaris
- Red-fronted brown lemur, E. rufus
- Sanford's brown lemur, E. sanfordi
However, a number of zoologists believe that E. albifrons and E. rufus should continue to be considered subspecies of E. fulvus.[4]
Physical description
The common brown lemur has a total length of 84 to 101 cm (33 to 40 in), including 41 to 51 cm (16 to 20 in) of tail.[5] Weight ranges from 2 to 3 kg (4.4 to 6.6 lb).[5] The short, dense fur is primarily brown or grey-brown.[5] The face, muzzle and crown are dark grey or black with paler eyebrow patches, and the eyes are orange-red.[5]
Similar lemur species within their range include the mongoose lemur, E. mongoz, in the west and the red-bellied lemur, E. rubriventer, in the east.[5] They can be distinguished from these species by the fact that E. mongoz is more of a grey color and E. rubriventer is more reddish. There is also some overlap with the black lemur in northeast Madagascar in the Galoko, Manongarivo and Tsaratanana Massifs.[6] There is also overlap and hybridization with the white-fronted brown lemur, E. albifrons, in the northeast portion of the common brown lemur's range.[7]
-
female
-
juvenile
Behavior
Consistent with its large range, the common brown lemur occupies a variety of forest types, including lowland rainforests, montane rainforests, moist evergreen forests and dry deciduous forests.[5] They spend about 95% of their time in upper layers of the forest and less than 2% of their time on the ground.[8]
They normally live in groups of 5 to 12, but group size can be larger, especially on Mayotte.[5] Groups occupy home ranges of 1 to 9 hectares in the west, but more than 20 hectares in the east.[9] Groups include members of both sexes, including juveniles, and there are no discernible dominance hierarchies.[5]
They are primarily active during the day, but can exhibit cathemeral activity and continue into the night, especially during full moons[5] and during the dry season.[10][11]
In the western part of its range, the common brown lemur overlaps that of the mongoose lemur, and the two species sometimes travel together.[8] In the areas of overlap, the two species also adapt their activity patterns to avoid conflict.[11] For example, the mongoose lemur can become primarily nocturnal during the dry season in the areas of overlap.
At Berenty (south Madagascar) there is a population of introduced E. fulvus rufus x collaris.[12] These lemurs show linear hierarchy, adult female dominance, and the presence of conciliatory behavior after aggressions.[13] Additionally, stress levels (measured via self-directed behaviors) decrease at the increase of the hierarchical position of individuals within the social group and reconciliation is able to bring stress down to the baseline levels.[14]
Reproduction
The common brown lemur's mating season is May and June.[5] After a gestation period of about 120 days, the young are born in September and October.[5] Single births are most common, but twins have been reported.[5] The young are weaned after about 4 to 5 months.[5][8] Sexual maturity occurs at about 18 months,[5] and females give birth to their first young at 2 years old.[8] Life span can be as long as 30+ years.[8]
Ecology
Diet
The common brown lemur's diet consists primarily of fruits, young leaves, and flowers.[10] In some locations it eats invertebrates, such as cicadas,[5] spiders[5] and millipedes.[8] It also eats bark, sap, soil and red clay (see geophagy).[8] It can tolerate greater levels of toxic compounds from plants than other lemurs can.[10][8]
Distribution
The common brown lemur lives in western Madagascar north of the Betsiboka River and eastern Madagascar between the Mangoro River and Tsaratanana, as well as in inland Madagascar connecting the eastern and western ranges.[10] They also live on the island of Mayotte, although this population has been introduced there by man.[10]
References
- ^ a b c "Eulemur fulvus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T8207A115562499. 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ "Checklist of CITES Species". CITES. UNEP-WCMC. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 115. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b Russell Mittermeier; et al. (2006). Lemurs of Madagascar (2nd ed.). p. 251. ISBN 1-881173-88-7.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Nick Garbutt (2007). Mammals of Madagascar. pp. 155–156. ISBN 978-0-300-12550-4.
- ^ Russell Mittermeier; et al. (2006). Lemurs of Madagascar (2nd ed.). p. 288. ISBN 1-881173-88-7.
- ^ Russell Mittermeier; et al. (2006). Lemurs of Madagascar (2nd ed.). p. 282. ISBN 1-881173-88-7.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Noel Rowe (1996). The Pictorial Guide to the Living Primates. p. 40. ISBN 0-9648825-0-7.
- ^ name=perspective>Lisa Gould; Michelle Sauther (2007). "Lemuriformes". In Christina J. Campbell; Agustin Fuentes; Katherine C. MacKinnon; Melissa Panger; Simon K. Bearder (eds.). Primates in Perspective. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-19-517133-4.
- ^ a b c d e Russell Mittermeier; et al. (2006). Lemurs of Madagascar (2nd ed.). pp. 272–274. ISBN 1-881173-88-7.
- ^ a b Robert W. Sussman (1999). Primate Ecology and Social Structure Volume 1: Lorises, Lemurs and Tarsiers. pp. 186–187. ISBN 0-536-02256-9.
- ^ Alison Jolly; Naoki Koyama; Hantanirina Rasamimanana; Helen Crowley; George Williams (2006). "Berenty Reserve: a research site in southern Madagascar". In A. Jolly; R. W. Sussman; N. Koyama; H. Rasamimanana (eds.). Ringtailed Lemur Biology: Lemur catta in Madagascar. pp. 32–42. ISBN 0-387-32669-3.
- ^ Norscia, I.; Palagi, E. (2010). "Do wild brown lemurs reconcile? Not always". Journal of Ethology. 29: 181–185. doi:10.1007/s10164-010-0228-y.
- ^ Palagi, E.; Norscia, I. (2010). "Scratching around stress: hierarchy and reconciliation make the difference in wild brown lemurs Eulemur fulvus". Stress. 14 (1): 93–7. doi:10.3109/10253890.2010.505272. PMID 20666657.



