Norbaeocystin: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Importing Wikidata short description: "Chemical compound" (Shortdesc helper) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
| melting_high = |
| melting_high = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
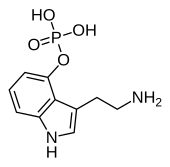
'''Norbaeocystin''' is a [[psilocybin mushroom]] [[alkaloid]] and [[analog (chemistry)|analog]] of [[psilocybin]]. It is found as a minor compound in most [[psilocybin mushroom]]s together with [[psilocin]], [[psilocybin]] and [[baeocystin]], from which it is a derivative.<ref name="Leung_1968">{{cite journal | vauthors = Leung AY, Paul AG | title = Baeocystin and norbaeocystin: new analogs of psilocybin from Psilocybe baeocystis | journal = Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences | volume = 57 | issue = 10 | pages = 1667–71 | date = October 1968 | pmid = 5684732 | doi = 10.1002/jps.2600571007 }}</ref> |
'''Norbaeocystin''' is a [[psilocybin mushroom]] [[alkaloid]] and [[analog (chemistry)|analog]] of [[psilocybin]]. It is found as a minor compound in most [[psilocybin mushroom]]s together with [[psilocin]], [[psilocybin]], [[aeruginascin]], and [[baeocystin]], from which it is a derivative.<ref name="Leung_1968">{{cite journal | vauthors = Leung AY, Paul AG | title = Baeocystin and norbaeocystin: new analogs of psilocybin from Psilocybe baeocystis | journal = Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences | volume = 57 | issue = 10 | pages = 1667–71 | date = October 1968 | pmid = 5684732 | doi = 10.1002/jps.2600571007 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Gotvaldova |first1=Klara |last2=Borovicka |first2=Jan |last3=Hajkova |first3=Katerina |last4=Cihlarova |first4=Petra |last5=Rockefeller |first5=Alan |last6=Kuchar |first6=Martin |year=2022 |title=Extensive Collection of Psychotropic Mushrooms with Determination of Their Tryptamine Alkaloids |journal=International Journal of Molecular Sciences |volume=23 |issue=22 |language=en |pages=14068 |doi=10.3390/ijms232214068 |issn=1422-0067}}</ref> |
||
Norbaeocystin is a N-demethylated derivative of baeocystin (itself a N-demethylated derivative of psilocybin), and a phosphorylated derivative of [[4-hydroxytryptamine]]. The latter is notable as a positional isomer of [[serotonin]], which is 5-hydroxytryptamine. |
Norbaeocystin is a N-demethylated derivative of baeocystin (itself a N-demethylated derivative of psilocybin), and a phosphorylated derivative of [[4-hydroxytryptamine]]. The latter is notable as a positional isomer of [[serotonin]], which is 5-hydroxytryptamine. |
||
Revision as of 13:07, 12 December 2022
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (June 2013) |
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H13N2O4P |
| Molar mass | 256.198 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Norbaeocystin is a psilocybin mushroom alkaloid and analog of psilocybin. It is found as a minor compound in most psilocybin mushrooms together with psilocin, psilocybin, aeruginascin, and baeocystin, from which it is a derivative.[1][2]
Norbaeocystin is a N-demethylated derivative of baeocystin (itself a N-demethylated derivative of psilocybin), and a phosphorylated derivative of 4-hydroxytryptamine. The latter is notable as a positional isomer of serotonin, which is 5-hydroxytryptamine.
See also
References
- ^ Leung AY, Paul AG (October 1968). "Baeocystin and norbaeocystin: new analogs of psilocybin from Psilocybe baeocystis". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 57 (10): 1667–71. doi:10.1002/jps.2600571007. PMID 5684732.
- ^ Gotvaldova, Klara; Borovicka, Jan; Hajkova, Katerina; Cihlarova, Petra; Rockefeller, Alan; Kuchar, Martin (2022). "Extensive Collection of Psychotropic Mushrooms with Determination of Their Tryptamine Alkaloids". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 23 (22): 14068. doi:10.3390/ijms232214068. ISSN 1422-0067.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
