Cyanohydrin reaction: Difference between revisions
CrafterNova (talk | contribs) Adding short description: "Addition reaction of carbonyl compounds and cyanide" |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
* Cyanohydrin reaction of [[acetone]] with potassium cyanide [[Organic Syntheses]] Coll. Vol. 2, p. 7; Vol. 15, p. 1 [https://web.archive.org/web/20121022154058/http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/prep.asp?prep=cv2p0007 Article] |
* Cyanohydrin reaction of [[acetone]] with potassium cyanide [[Organic Syntheses]] Coll. Vol. 2, p. 7; Vol. 15, p. 1 [https://web.archive.org/web/20121022154058/http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/prep.asp?prep=cv2p0007 Article] |
||
* Cyanohydrin reaction of [[benzoquinone]] with trimethylsilylcyanide [[Organic Syntheses]] Coll. Vol. 7, p. 517; Vol. 60, p. 126 [https://web.archive.org/web/20120329051335/http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/prep.asp?prep=cv7p0517 Article] |
* Cyanohydrin reaction of [[benzoquinone]] with trimethylsilylcyanide [[Organic Syntheses]] Coll. Vol. 7, p. 517; Vol. 60, p. 126 [https://web.archive.org/web/20120329051335/http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/prep.asp?prep=cv7p0517 Article] |
||
{{Organic reactions}} |
|||
[[Category:Nucleophilic addition reactions]] |
[[Category:Nucleophilic addition reactions]] |
||
[[Category:Carbohydrate chemistry]] |
[[Category:Carbohydrate chemistry]] |
||
Revision as of 08:37, 9 July 2022
| Cyanohydrin reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Friedrich Urech |
| Reaction type | Addition reaction |
A cyanohydrin reaction is an organic chemical reaction in which an aldehyde or ketone reacts with a cyanide anion or a nitrile to form a cyanohydrin. This nucleophilic addition is a reversible reaction but with aliphatic carbonyl compounds equilibrium is in favor of the reaction products. The cyanide source can be potassium cyanide, sodium cyanide or trimethylsilyl cyanide. With aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde, the benzoin condensation is a competing reaction. The reaction is used in carbohydrate chemistry as a chain extension method for example that of D-xylose.
Examples


Reaction mechanism
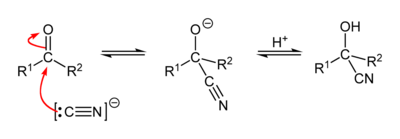
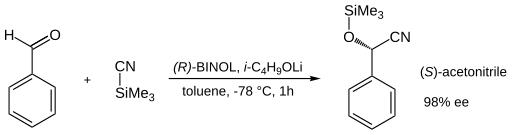
Asymmetric synthesis
The asymmetric cyanohydrin reaction of benzaldehyde with trimethylsilylcyanide is made possible by employment of (R)-Binol[1] at 1–10% catalyst loading. This ligand firsts reacts with a lithium alkoxy compound to form a lithium binaphtholate Complex.
The chemist Urech in 1872 was the first to synthesize cyanohydrins from ketones with alkali cyanides and acetic acid[2] and therefore this reaction also goes by the name of Urech cyanohydrin method. With HCN in acidic conditions – i.e. the cyanohydrin is the functional group CN–C–OH.
References
- ^ Hatano, Manabu; Ikeno, Takumi; Miyamoto, Takashi; Ishihara, Kazuaki (2005). "Chiral Lithium Binaphtholate Aqua Complex as a Highly Effective Asymmetric Catalyst for Cyanohydrin Synthesis". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 (31): 10776–77. doi:10.1021/ja051125c. PMID 16076152.
- ^ Urech, Friedrich (1872). "Ueber einige Cyanderivate des Acetons". Liebigs Ann. 164 (2): 255. doi:10.1002/jlac.18721640207.
External links
- Cyanohydrin reaction of formaldehyde to hydroxyacetonitrile or glycolonitrile with sodium cyanide in Organic Syntheses Coll. Vol. 2, p. 387; Vol. 13, p. 56 Article
- Cyanohydrin reaction of formaldehyde with potassium cyanide Organic Syntheses Coll. Vol. 3, p. 436; Vol. 27, p. 41 Article
- Cyanohydrin reaction of acetophenone with potassium cyanide Organic Syntheses Coll. Vol. 4, p. 58; Vol. 33, p. 7 Article
- Cyanohydrin reaction of D-xylose with potassium cyanide Organic Syntheses Coll. Vol. 4, p. 506; Vol. 36, p. 38 Article
- Cyanohydrin reaction of acetone with potassium cyanide Organic Syntheses Coll. Vol. 2, p. 7; Vol. 15, p. 1 Article
- Cyanohydrin reaction of benzoquinone with trimethylsilylcyanide Organic Syntheses Coll. Vol. 7, p. 517; Vol. 60, p. 126 Article
